Intracluster Age Gradients And Disk Longevities In Numerous MYStIX And SFiNCs Young Stellar Clusters
|
|
|
- Jonah Wiggins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Intracluster Age Gradients And Disk Longevities In Numerous MYStIX And SFiNCs Young Stellar Clusters K. Getman, E. Feigelson, M. Kuhn, A. Richert, M. Bate, P. Broos, M. Povich, G. Garmire Pennsylvania State University, USA, Universidad de Valparaiso, Chile, University of Exeter, UK, California State Polytechnic University, Pomona, USA, Huntingdon Institute for X-ray Astronomy, USA
2 Data & Age JX estimator SURVEYS: MYStIX (Feigelson et al. 0 and references therein) and SFiNCs (Getman et al. 07). Based on re-analyses of archival data from the Chandra X-ray Observatory, Spitzer Space Telescope, UKIRT and/or MASS. Characterize >0 young, nearby star forming regions. Age JX is a PMS age estimator (Getman et al. 0a). Based on X-ray and near-ir photometry. Calibrated to the X-ray Luminosity Mass PMS relation (Telleschi et al. 007) and to theoretical evolutionary tracks of Siess et al. (000).
3 Age JX estimates are in good agreement with stellar ages derived from near-ir spectroscopy + photometry (Winston et al. 009). Age JX estimator
4 Intracluster Age Gradients (Getman et al. in prep) MYStIX+SFiNCs sub-sample of 9 clusters that: ) have simple core-halo morphology; ) are isolated; ) have relatively high numbers of Age JX stars. Example: Stellar surface density map of W0 (Age JX stars are black points): Many individual clusters show trends of increasing core->halo age. But statistical significance is generally low.
5 Intracluster Age Gradients (Getman et al. in prep) To reduce statistical uncertainties the clusters are merged together. Utilizing standardized age and radial distance variables: x i,stn = (x i - µ cluster )/σ cluster Now, the core-halo age gradient is statistically significant at over - sigma level. The gradients can be explained by the theoretical model of Vazquez- Semadeni et al. (07).
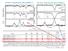
6 Disk Longevities (Richert et al. in prep) For each cluster:. NIR+IRAC SED-based disk classification;. YSO sub-samples with similar mass distributions for disky and diskless. The inferred disk fractions and median Age JX are consistent with an exponential IRAC disk half-life of t / Myr. The similarity between the MYStIX+SFiNCs IRAC half-lives and those of Mamajek (009; t /.7Myr), Fedele et al. (00; t /.Myr), and Ribas et al. (0; t /.6-.9Myr) is surprising considering numerous differing factors (YSO data, cluster samples, age methods, disk classifications, mass sensitivities, and so on). 69 MYStIX+SFiNCs young ( Myr) stellar clusters
7 pc pc pc W0 A Intracluster Age Gradients And Disk Longevities In Numerous MYStIX And SFiNCs Young Stellar Clusters K. Getman, E. Feigelson, M. Kuhn, A. Richert, M. Bate, P. Broos, M. Povich, G. Garmire Pennsylvania State University, USA, Universidad de Valparaiso, Chile, University of Exeter, UK, California State Polytechnic University, Pomona, USA, Huntingdon Institute for X-ray Astronomy, USA ABSTRACT. This study is based on YSO samples from the MYStIX and SFiNCs surveys, and a new estimator of pre-main sequence stellar ages (AgeJX), derived from X-ray and near-ir photometric data. We present two main results here. First, the discovery of core-halo age gradients (with younger cores and older halos) in numerous morphologically simple, isolated, and relatively rich stellar clusters. The observed spatio-age gradients can be explained within the framework of the global hierarchical collapse model. Second, the MYStIX+SFiNCs cluster surveys provide the largest cluster dataset to date to study circumstellar disk longevity in young ( Myr) clusters. By imposing similar stellar mass sensitivity limits for disky and diskless YSOs and assuming disk fraction of 00% at the zero age, we estimate an exponential disk half-life of Myr (based on AgeJX scale). This value agrees closely with the results of a few previous studies. SURVEYS. MYStIX (Feigelson et al. 0 and references therein) and SFiNCs (Getman et al. 07) projects characterize >0 young star forming regions at distances < kpc, based on re-analyses of archival data from the Chandra X-ray Observatory, Spitzer Space Telescope, UKIRT, and MASS. CONCEPT OF AGEJX. Our age method (Age JX; Getman et al. 0a) employs NIR and X-ray photometry. Stellar masses are derived from absorption-corrected X-ray luminosities using the Lx-Mass relation from young stars in Taurus. J-band magnitudes corrected for absorption and distance are compared to the mass-dependent PMS evolutionary models of Siess et al. (000) to estimate ages. Comparison of ages for indivdual stars in the nearby NGC and Serpens Main SFRs: individual AgeJX estimates are in good agreement with stellar ages derived from near-ir spectroscopy + photometry (Winston et al. 009). M J [mag] 0. Myr Age IR Winston et al. (009) [Myr] 6 Myr Mass [M O ] orion flame w0 rcw6 ngc6 rosette lagoon ngc6 dr rcw8 ngc6 ngc67 eagle m7 w carina ngc NGC and Serpens Main Unity Age JX [Myr] AGE GRADIENTS. To reduce statistical uncertainties on the age variations, the clusters are merged together. Since they span wide ranges of ages and spatial extends, the merger is performed using standardized age and radial distance variables: xi,stn = (x i - <x> cluster)/σ cluster. This analysis shows that the observed core-halo age gradient (with younger cores and older halos) is statistically significant at over -sigma level. Median spatio-age gradient among all the considered MYStIX+SFiNCs clusters is 0.9 Myr/pc. Standardized Age 0 - Merged MYStIX+SFiNCs; 87 YSOs with Age JX 7% quartile Small uncertainties on median ages 0% quartile % quartile Standardized Radial Distance The observed gradient can be explained by the model of Vazquez-Semadeni et al. (07): a large cloud globally gravitationally contracts, with multiple filaments (harboring non-coeval stellar groups) falling towards the center of gravitational potential, where the main cluster forms. Due to their higher velocity dispersions the in-falling older stars tend to appear further from the cluster center. AGE GRADIENTS (Getman et al. in prep). Getman et al. (0b) discovered core-halo age gradients in ONC and NGC 0. Here we consider a larger MYStIX+SFiNCs sub-sample of clusters that: ) have simple core-halo morphology; ) are isolated; ) have relatively high numbers of AgeJX stars (black points superimposed on the smoothed stellar surface densities of the clusters). Eagle B M7 L NGC67 F NGC89 B Flame A Orion Subcl. B+C Rosette D RCW6 B CepOBb A Be9 B GGD- A CepA A CepC A IC8 B IC6 B LkHa0 A Serpens Main B DISK LONGEVITIES (Richert et al. in prep). Separation of the MYStIX and SFiNCs YSOs into disky and diskless stars was done using two classification schemes: ) the original NIR+IRAC SED-based classifications of Povich et al. (0; MYStIX) and Getman et al. (07; SFiNCs); ) classification based on apparent IRAC SED slope, adopting a critical value of αirac=-.9 for separating disky and diskless. Stellar masses are estimated using near-ir photometry. For each cluster: ) the mass distributions of disky and diskless populations are compared; ) the lowest-mass YSOs are iteratively removed to achieve similar mass distributions and mass sensitivities for disky and diskless YSOs; ) disk fractions are then calculated. ECDF Disk-bearing YSOs Disk-free YSOs Mcut Stellar mass (M ) pc Age JX as a function of radial distance from the centers of the clusters shows that for many individual clusters, there are trends of increasing age from the cluster center toward the cluster periphery; however, the statistical significance of the observed age variations is generally low. Age JX [Myr] be9 cepb ggd_ SFiNCs Examples: : : : :9 :8 :8 :8 : : : : :9 cepa cepc ic8 R [pc] : : : :7 :0 :0 :0 :7 :0 :0 :0 :7 ic6 lkha0 serpens : : : : : : : :7 :6 :6 :6 : DISK LONGEVITIES. The inferred disk fractions and median AgeJX estimates for 69 MYStIX+SFiNCs clusters are consistent with an exponential disk half-life of ~ Myr (Richert et al. in prep.). Our cluster sample exceeds previous cluster samples by more than a factor of three. The similarity between the MYStIX+SFiNCs IRAC disk half-lives and those derived in Mamajek (009), Fedele et al. (00), and Ribas et al. (0) is surprising considering numerous differing factors (YSO data, cluster samples, age methods, disk classifications, mass sensitivities, and so on). With regards to the study of Bell et al. (0), the MYStIX+SFiNCs and Bell et al. cluster ages are farily consistent for out of 6 clusters in common. The age inconsistency for Cep OBb and IC 8 (~- Myr in SFiNCs versus ~6 Myr in Bell et al. ) can be partially explained by discrepant distance values MYStIX fit (t/ =.9 Myr) SFiNCs fit (t/ =.0 Myr) HLL0 fit (linear) M09 fit (t/ =.7 Myr) F0 fit (t/ =. Myr) REFERENCES. Bell et al., 0, MNRAS,, 806 Fedele et al., 00, A&A, 0, A7 Feigelson et al., 0, ApJS, 09, 6 Getman et al., 0a, ApJ, 787, 08 Getman et al., 0b, ApJ, 787, 09 Getman et al., 07, ApJS, 9, 8 Mamajek, 009, AIofPCS, Vol. 8 Povich et al., 0, ApJS, 09, Ribas et al., 0, A&A, 6, A Siess et al., 000, A&A, 8, 9 Vazquez-Semadeni et al., 07, MNRAS, 67, Winston et al., 009, AJ, 7, 777 Disk fraction AgeJX (Myr) Disk fraction MYStIX fit (t/ =.9 Myr) SFiNCs fit (t/ =.0 Myr) Age (Myr)
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Mar 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Mar 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Mar 2014](/thumbs/81/84054964.jpg) Age Gradients in the Stellar Populations of Massive Star Forming Regions Based on a New Stellar Chronometer arxiv:1403.2741v1 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Mar 2014 Konstantin V. Getman 1, Eric D. Feigelson 1,2, Michael
Age Gradients in the Stellar Populations of Massive Star Forming Regions Based on a New Stellar Chronometer arxiv:1403.2741v1 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Mar 2014 Konstantin V. Getman 1, Eric D. Feigelson 1,2, Michael
Core-Halo Age Gradients and Star Formation in the Orion Nebula and NGC 2024 Young Stellar Clusters
 Core-Halo Age Gradients and Star Formation in the Orion Nebula and NGC 2024 Young Stellar Clusters Konstantin V. Getman, Eric D. Feigelson, Michael A. Kuhn Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics, 525 Davey
Core-Halo Age Gradients and Star Formation in the Orion Nebula and NGC 2024 Young Stellar Clusters Konstantin V. Getman, Eric D. Feigelson, Michael A. Kuhn Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics, 525 Davey
The Spatial Structure of Young Stellar Clusters. III. Physical Properties and Evolutionary States
 Accepted for publication in ApJ, July 2015 The Spatial Structure of Young Stellar Clusters. III. Physical Properties and Evolutionary States Michael A. Kuhn 1,2,3, Eric D. Feigelson 1, Konstantin V. Getman
Accepted for publication in ApJ, July 2015 The Spatial Structure of Young Stellar Clusters. III. Physical Properties and Evolutionary States Michael A. Kuhn 1,2,3, Eric D. Feigelson 1, Konstantin V. Getman
The Spatial Structure of Young Stellar Clusters. II. Total Young Stellar Populations
 The Spatial Structure of Young Stellar Clusters. II. Total Young Stellar Populations Michael A. Kuhn 1,2, Konstantin V. Getman 1, Eric D. Feigelson 1 ABSTRACT We investigate the intrinsic stellar populations
The Spatial Structure of Young Stellar Clusters. II. Total Young Stellar Populations Michael A. Kuhn 1,2, Konstantin V. Getman 1, Eric D. Feigelson 1 ABSTRACT We investigate the intrinsic stellar populations
Recent developments on the formation and evolution of young low-mass stars
 Recent developments on the formation and evolution of young low-mass stars Rob Jeffries Keele University, UK Observations of young clusters that probe: The influence of magnetic activity and rotation on
Recent developments on the formation and evolution of young low-mass stars Rob Jeffries Keele University, UK Observations of young clusters that probe: The influence of magnetic activity and rotation on
Part III: Circumstellar Properties of Intermediate-Age PMS Stars
 160 Part III: Circumstellar Properties of Intermediate-Age PMS Stars 161 Chapter 7 Spitzer Observations of 5 Myr-old Brown Dwarfs in Upper Scorpius 7.1 Introduction Ground-based infrared studies have found
160 Part III: Circumstellar Properties of Intermediate-Age PMS Stars 161 Chapter 7 Spitzer Observations of 5 Myr-old Brown Dwarfs in Upper Scorpius 7.1 Introduction Ground-based infrared studies have found
A Massive Young Star-Forming Complex Study in Infrared and X-ray: Mid-Infrared Observations and Catalogs
 Accepted 12 September, 2013 A Massive Young Star-Forming Complex Study in Infrared and X-ray: Mid-Infrared Observations and Catalogs Michael A. Kuhn 1, Matthew S. Povich 1,2, Kevin L. Luhman 1,3, Konstantin
Accepted 12 September, 2013 A Massive Young Star-Forming Complex Study in Infrared and X-ray: Mid-Infrared Observations and Catalogs Michael A. Kuhn 1, Matthew S. Povich 1,2, Kevin L. Luhman 1,3, Konstantin
Star Formation. Spitzer Key Contributions to Date
 Star Formation Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase Lori Allen CfA John Carpenter, Caltech Lee Hartmann, University of Michigan Michael Liu, University of Hawaii Tom Megeath,
Star Formation Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase Lori Allen CfA John Carpenter, Caltech Lee Hartmann, University of Michigan Michael Liu, University of Hawaii Tom Megeath,
A Spitzer View of the Giant Molecular Cloud Mon OB1/NGC 2264
 University of Massachusetts Amherst From the SelectedWorks of Robert A. Gutermuth October 1, 2014 A Spitzer View of the Giant Molecular Cloud Mon OB1/NGC 2264 Valerie A. Rapson Judith L. Pipher R. A. Gutermuth,
University of Massachusetts Amherst From the SelectedWorks of Robert A. Gutermuth October 1, 2014 A Spitzer View of the Giant Molecular Cloud Mon OB1/NGC 2264 Valerie A. Rapson Judith L. Pipher R. A. Gutermuth,
Star formation in nearby young clusters! Catarina Alves de Oliveira!
 Star formation in nearby young clusters! Catarina Alves de Oliveira! What determines the mass of a star? Credits: Adapted from Bastian et al. 2010 & de Marchi et al. 2010. Introduction Bridging the gap
Star formation in nearby young clusters! Catarina Alves de Oliveira! What determines the mass of a star? Credits: Adapted from Bastian et al. 2010 & de Marchi et al. 2010. Introduction Bridging the gap
PMS OBJECTS IN THE STAR FORMATION REGION Cep OB3. II. YOUNG STELLAR OBJECTS IN THE Ha NEBULA Cep B
 Astrophysics, Vol. 56, No. 2, June, 2013 PMS OBJECTS IN THE STAR FORMATION REGION Cep OB3. II. YOUNG STELLAR OBJECTS IN THE Ha NEBULA Cep B E. H. Nikoghosyan Models for the spectral energy distributions
Astrophysics, Vol. 56, No. 2, June, 2013 PMS OBJECTS IN THE STAR FORMATION REGION Cep OB3. II. YOUNG STELLAR OBJECTS IN THE Ha NEBULA Cep B E. H. Nikoghosyan Models for the spectral energy distributions
Star Formation. Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase
 Star Formation Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase Lori Allen CfA John Carpenter, Caltech Lee Hartmann, University of Michigan Michael Liu, University of Hawaii Tom Megeath,
Star Formation Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase Lori Allen CfA John Carpenter, Caltech Lee Hartmann, University of Michigan Michael Liu, University of Hawaii Tom Megeath,
Age Distributions of Low Mass Stars in the Rho Ophiuchi and Upper Scorpius Associations
 Age Distributions of Low Mass Stars in the Rho Ophiuchi and Upper Scorpius Associations John Keller University of Missouri St. Louis Dr. Bruce Wilking Abstract The young star forming molecular cloud of
Age Distributions of Low Mass Stars in the Rho Ophiuchi and Upper Scorpius Associations John Keller University of Missouri St. Louis Dr. Bruce Wilking Abstract The young star forming molecular cloud of
Chapter 1 Multiwavelength Studies of Young OB Associations
 Chapter 1 Multiwavelength Studies of Young OB Associations Eric D. Feigelson Abstract We discuss how contemporary multiwavelength observations of young OB-dominated clusters address long-standing astrophysical
Chapter 1 Multiwavelength Studies of Young OB Associations Eric D. Feigelson Abstract We discuss how contemporary multiwavelength observations of young OB-dominated clusters address long-standing astrophysical
THE STAR FORMATION NEWSLETTER No. 266 (#36-40) 17 Apr. 2015
 THE STAR FORMATION NEWSLETTER No. 266 (#36-4) ( ) 17 Apr. 21 The Spatial Structure of Young Stellar Clousters. II. Total Young Stellar Populations M.I.A. Kuhn et al. MYStIX stellar population 2 MYStIX:
THE STAR FORMATION NEWSLETTER No. 266 (#36-4) ( ) 17 Apr. 21 The Spatial Structure of Young Stellar Clousters. II. Total Young Stellar Populations M.I.A. Kuhn et al. MYStIX stellar population 2 MYStIX:
THE SPITZER SPACE TELESCOPE SURVEY OF THE ORION A AND B MOLECULAR CLOUDS II: THE SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION AND DEMOGRAPHICS OF DUSTY YOUNG STELLAR OBJECTS
 Draft version November 2, 215 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 8/13/1 THE SPITZER SPACE TELESCOPE SURVEY OF THE ORION A AND B MOLECULAR CLOUDS II: THE SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION AND DEMOGRAPHICS
Draft version November 2, 215 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 8/13/1 THE SPITZER SPACE TELESCOPE SURVEY OF THE ORION A AND B MOLECULAR CLOUDS II: THE SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION AND DEMOGRAPHICS
High mass star formation in the Herschel era: highlights of the HOBYS key program
 Recent Advances in Star Formation ASI Conference Series, 2012, Vol. 4, pp 55 62 Edited by Annapurni Subramaniam & Sumedh Anathpindika High mass star formation in the Herschel era: highlights of the HOBYS
Recent Advances in Star Formation ASI Conference Series, 2012, Vol. 4, pp 55 62 Edited by Annapurni Subramaniam & Sumedh Anathpindika High mass star formation in the Herschel era: highlights of the HOBYS
AST 6336, Interstellar Medium, Spring 2015
 AST 6336, Interstellar Medium, Spring 2015 Young stellar clusters (lectures by Nicola Da Rio ndario@ufl.edu) January 2, 4, 2015 Star formation A molecular cloud may become unsupported gas pressure + magnetic
AST 6336, Interstellar Medium, Spring 2015 Young stellar clusters (lectures by Nicola Da Rio ndario@ufl.edu) January 2, 4, 2015 Star formation A molecular cloud may become unsupported gas pressure + magnetic
Chandra Detection of An Evolved Population of Young Stars in Serpens South.
 Chandra Detection of An Evolved Population of Young Stars in Serpens South. E. Winston 1, S. J. Wolk 1, R. Gutermuth 2, T.L. Bourke 3 arxiv:1804.05067v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Apr 2018 elaine.winston@cfa.harvard.edu
Chandra Detection of An Evolved Population of Young Stars in Serpens South. E. Winston 1, S. J. Wolk 1, R. Gutermuth 2, T.L. Bourke 3 arxiv:1804.05067v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Apr 2018 elaine.winston@cfa.harvard.edu
Protoplanetary discs of isolated VLMOs discovered in the IPHAS survey
 Protoplanetary discs of isolated VLMOs discovered in the IPHAS survey Luisa Valdivielso Casas Collaborators: E. Martín, H. Bouy, E. Solano,J. Drew,R. Greimel 1 IAC - ULL 14 de septiembre 2010 Outline Introduction
Protoplanetary discs of isolated VLMOs discovered in the IPHAS survey Luisa Valdivielso Casas Collaborators: E. Martín, H. Bouy, E. Solano,J. Drew,R. Greimel 1 IAC - ULL 14 de septiembre 2010 Outline Introduction
The Fate of Discs in Dense Star Clusters
 Hoher List, 2. December 2006 The Fate of Discs in Dense Star Clusters The Perspective Universität zu Köln, I. Physikalisches Institut UNIVERSITÄT Motivation protoplanetary discs: important for late stages
Hoher List, 2. December 2006 The Fate of Discs in Dense Star Clusters The Perspective Universität zu Köln, I. Physikalisches Institut UNIVERSITÄT Motivation protoplanetary discs: important for late stages
Astronomy 730. Evolution
 Astronomy 730 Evolution Outline } Evolution } Formation of structure } Processes on the galaxy scale } Gravitational collapse, merging, and infall } SF, feedback and chemical enrichment } Environment }
Astronomy 730 Evolution Outline } Evolution } Formation of structure } Processes on the galaxy scale } Gravitational collapse, merging, and infall } SF, feedback and chemical enrichment } Environment }
Multi-wavelength analysis of Hickson Compact Groups of Galaxies.
 Multi-wavelength analysis of Hickson Compact Groups of Galaxies. Thodoris Bitsakis Department of Physics, University of Crete Paper: Bitsakis T., Charmandaris V., da Cunha E., Diaz-Santos T., Le Floc h
Multi-wavelength analysis of Hickson Compact Groups of Galaxies. Thodoris Bitsakis Department of Physics, University of Crete Paper: Bitsakis T., Charmandaris V., da Cunha E., Diaz-Santos T., Le Floc h
Structure of Merger Remnants:
 Structure of Merger Remnants: Lessons from Spectral Line Observations John E. Hibbard NRAO-CV Merger Hypothesis: Two gas-rich Spirals Merge into One Elliptical Toomre Sequence of On-going Mergers (Toomre
Structure of Merger Remnants: Lessons from Spectral Line Observations John E. Hibbard NRAO-CV Merger Hypothesis: Two gas-rich Spirals Merge into One Elliptical Toomre Sequence of On-going Mergers (Toomre
The Protostellar Luminosity Function
 Design Reference Mission Case Study Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy Science Steering Committee Program contacts: Lynne Hillenbrand, Tom Greene, Paul Harvey Scientific category: STAR FORMATION
Design Reference Mission Case Study Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy Science Steering Committee Program contacts: Lynne Hillenbrand, Tom Greene, Paul Harvey Scientific category: STAR FORMATION
Observed Relationships between Filaments and Star Formation
 Observed Relationships between Filaments and Star Formation James Di Francesco (Ph. André, J. Pineda, R. Pudritz, D. Ward-Thompson, S.Inutsuka & the Herschel GBS, JCMT GBS and HOBYS Teams Herschel Gould
Observed Relationships between Filaments and Star Formation James Di Francesco (Ph. André, J. Pineda, R. Pudritz, D. Ward-Thompson, S.Inutsuka & the Herschel GBS, JCMT GBS and HOBYS Teams Herschel Gould
University of Naples Federico II, Academic Year Istituzioni di Astrofisica, read by prof. Massimo Capaccioli. Lecture 16
 University of Naples Federico II, Academic Year 2011-2012 Istituzioni di Astrofisica, read by prof. Massimo Capaccioli Lecture 16 Stellar populations Walter Baade (1893-1960) Learning outcomes The student
University of Naples Federico II, Academic Year 2011-2012 Istituzioni di Astrofisica, read by prof. Massimo Capaccioli Lecture 16 Stellar populations Walter Baade (1893-1960) Learning outcomes The student
The Milky Way Formation Timescale
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 13 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della The Milky Way Formation Timescale A. Aparicio 1,2, A. Rosenberg 2, G. Piotto 3, I. Saviane 4 and A. Recio-Blanco 3 1 Departamento de Astrofisica, Universidad
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 13 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della The Milky Way Formation Timescale A. Aparicio 1,2, A. Rosenberg 2, G. Piotto 3, I. Saviane 4 and A. Recio-Blanco 3 1 Departamento de Astrofisica, Universidad
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Feb 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Feb 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Feb 2015](/thumbs/94/118561873.jpg) Baltic Astronomy, vol. 23, 221 229, 2014 MODELS OF LATE-TYPE DISK GALAXIES: 1-D VERSUS 2-D arxiv:1502.00232v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Feb 2015 T. Mineikis 1,2 and V. Vansevičius 1,2 1 Vilnius University Observatory,
Baltic Astronomy, vol. 23, 221 229, 2014 MODELS OF LATE-TYPE DISK GALAXIES: 1-D VERSUS 2-D arxiv:1502.00232v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Feb 2015 T. Mineikis 1,2 and V. Vansevičius 1,2 1 Vilnius University Observatory,
Young stellar objects and their environment
 Recent Advances in Star Formation: Observations and Theory ASI Conference Series, 2012, Vol. 4, pp 107 111 Edited by Annapurni Subramaniam & Sumedh Anathpindika Young stellar objects and their environment
Recent Advances in Star Formation: Observations and Theory ASI Conference Series, 2012, Vol. 4, pp 107 111 Edited by Annapurni Subramaniam & Sumedh Anathpindika Young stellar objects and their environment
The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds
 The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
the Solar Neighborhood
 Click to edit Master title style Star Formation at High A V in the Solar Neighborhood Amanda Heiderman NSF Fellow UVa/NRAO (w/ Neal Evans, UT Austin) Filaments 2014, October, 11, 2014 10/13/2014 1 Click
Click to edit Master title style Star Formation at High A V in the Solar Neighborhood Amanda Heiderman NSF Fellow UVa/NRAO (w/ Neal Evans, UT Austin) Filaments 2014, October, 11, 2014 10/13/2014 1 Click
Are Low Surface Brightness Discs Young?
 Are Low Surface Brightness Discs Young? Paolo Padoan Theoretical Astrophysics Center, Juliane Maries Vej 30, DK-2100 Copenhagen, DK Raul Jimenez arxiv:astro-ph/9609091v1 12 Sep 1996 Royal Observatory,
Are Low Surface Brightness Discs Young? Paolo Padoan Theoretical Astrophysics Center, Juliane Maries Vej 30, DK-2100 Copenhagen, DK Raul Jimenez arxiv:astro-ph/9609091v1 12 Sep 1996 Royal Observatory,
II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies
 II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies Ferguson & Binggeli 1994, A&ARev 6, 67 1 1. Properties low mass : 10 6 10 10 M slow rotators : 10 100 km s -1 low luminosity : 10 6 10 10 L low surface brightness
II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies Ferguson & Binggeli 1994, A&ARev 6, 67 1 1. Properties low mass : 10 6 10 10 M slow rotators : 10 100 km s -1 low luminosity : 10 6 10 10 L low surface brightness
Star Formation in GMCs: Lessons from Herschel Observations of the Aquila Complex
 Herschel PACS/SPIRE map of Aquila (Gould Belt survey) ORISTARS erc project Lab. AIM, Paris-Saclay, France Ph. André, A. Men'shchikov, N. Schneider, S. Bontemps, D. Arzoumanian, N. Peretto, P. Didelon,
Herschel PACS/SPIRE map of Aquila (Gould Belt survey) ORISTARS erc project Lab. AIM, Paris-Saclay, France Ph. André, A. Men'shchikov, N. Schneider, S. Bontemps, D. Arzoumanian, N. Peretto, P. Didelon,
Measuring star formation in galaxies and its evolution. Andrew Hopkins Australian Astronomical Observatory
 Measuring star formation in galaxies and its evolution Andrew Hopkins Australian Astronomical Observatory Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of
Measuring star formation in galaxies and its evolution Andrew Hopkins Australian Astronomical Observatory Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of Star Formation Evolution of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1. Identification of classical Cepheids: We identified three classical Cepheids amongst the 45 short-period variables discovered. Our sample includes classical Cepheids, type II Cepheids, eclipsing binaries
1. Identification of classical Cepheids: We identified three classical Cepheids amongst the 45 short-period variables discovered. Our sample includes classical Cepheids, type II Cepheids, eclipsing binaries
This is an author produced version of Overview of the massive young star-forming complex study in infrared and X-ray (MYStIX) project.
 This is an author produced version of Overview of the massive young star-forming complex study in infrared and X-ray (MYStIX) project. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/84010/
This is an author produced version of Overview of the massive young star-forming complex study in infrared and X-ray (MYStIX) project. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/84010/
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 10 Jul 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 10 Jul 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 10 Jul 2015](/thumbs/90/103296331.jpg) A WISE Census of Young Stellar Objects in Perseus OB2 Association Mohaddesseh Azimlu 1 ; J. Rafael Martinez-Galarza 1 ; August A., Muench 1 ABSTRACT arxiv:1507.02966v1 [astro-ph.sr] 10 Jul 2015 We have
A WISE Census of Young Stellar Objects in Perseus OB2 Association Mohaddesseh Azimlu 1 ; J. Rafael Martinez-Galarza 1 ; August A., Muench 1 ABSTRACT arxiv:1507.02966v1 [astro-ph.sr] 10 Jul 2015 We have
Young Stellar Structures in the Magellanic Clouds as Revealed by the VMC Survey
 Young Stellar Structures in the Magellanic Clouds as Revealed by the VMC Survey SFDE17, Aug.11, 2017 Speaker: Ning-Chen Sun (KIAA-PKU) Advisor: Prof. Richard de Grijs in collaboration with the VMC team
Young Stellar Structures in the Magellanic Clouds as Revealed by the VMC Survey SFDE17, Aug.11, 2017 Speaker: Ning-Chen Sun (KIAA-PKU) Advisor: Prof. Richard de Grijs in collaboration with the VMC team
High Redshift Universe
 High Redshift Universe Finding high z galaxies Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) Photometric redshifts Deep fields Starburst galaxies Extremely red objects (EROs) Sub-mm galaxies Lyman α systems Finding high
High Redshift Universe Finding high z galaxies Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) Photometric redshifts Deep fields Starburst galaxies Extremely red objects (EROs) Sub-mm galaxies Lyman α systems Finding high
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Jul 2011
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Jul 2011 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Jul 2011](/thumbs/92/109407226.jpg) Stellar Clusters & Associations: A RIA Workshop on Gaia Granada, 23 rd - 27 th May 2011 Dissecting high-mass star-forming regions; tracing back their complex formation history arxiv:1107.0148v1 [astro-ph.ga]
Stellar Clusters & Associations: A RIA Workshop on Gaia Granada, 23 rd - 27 th May 2011 Dissecting high-mass star-forming regions; tracing back their complex formation history arxiv:1107.0148v1 [astro-ph.ga]
Lyα-Emitting Galaxies at z=3.1: L* Progenitors Experiencing Rapid Star Formation
 Lyα-Emitting Galaxies at z=3.1: L* Progenitors Experiencing Rapid Star Formation Gawiser et al., 2007 Presented on October 22, 2009 PHYS 689: Galaxy Formation Lyman-α Emitters (LAEs) Lyα line is easily
Lyα-Emitting Galaxies at z=3.1: L* Progenitors Experiencing Rapid Star Formation Gawiser et al., 2007 Presented on October 22, 2009 PHYS 689: Galaxy Formation Lyman-α Emitters (LAEs) Lyα line is easily
Star formation : circumstellar environment around Young Stellar Objects
 Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2005) 33, 327 331 Star formation : circumstellar environment around Young Stellar Objects Manoj Puravankara Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune - 411007,
Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2005) 33, 327 331 Star formation : circumstellar environment around Young Stellar Objects Manoj Puravankara Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune - 411007,
Philamentary Structure and Velocity Gradients in the Orion A Cloud
 Red: CO from Mini survey Orion B Philamentary Structure and Velocity Gradients in the Orion A Cloud Spitzer Orion Cloud Survey: 10 sq. degrees in Orion A and Orion B mapped between 2004-2009 Orion A Green
Red: CO from Mini survey Orion B Philamentary Structure and Velocity Gradients in the Orion A Cloud Spitzer Orion Cloud Survey: 10 sq. degrees in Orion A and Orion B mapped between 2004-2009 Orion A Green
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars
 Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs
 A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs Spavone Marilena (INAF-OAC) Iodice Enrica (INAF-OAC), Arnaboldi Magda (ESO-Garching), Longo Giuseppe (Università Federico II ), Gerhard Ortwin (MPE-Garching).
A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs Spavone Marilena (INAF-OAC) Iodice Enrica (INAF-OAC), Arnaboldi Magda (ESO-Garching), Longo Giuseppe (Università Federico II ), Gerhard Ortwin (MPE-Garching).
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 25. Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 25 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 25 Galaxies and Dark Matter Units of Chapter 25 25.1 Dark Matter in the Universe 25.2 Galaxy Collisions 25.3 Galaxy Formation
Lecture Outlines Chapter 25 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 25 Galaxies and Dark Matter Units of Chapter 25 25.1 Dark Matter in the Universe 25.2 Galaxy Collisions 25.3 Galaxy Formation
Gaia News:Counting down to launch A. Vallenari. INAF, Padova Astronomical Observatory on behalf of DPACE
 Gaia News:Counting down to launch A. Vallenari INAF, Padova Astronomical Observatory on behalf of DPACE Outline Gaia Spacecraft status The Gaia sky Gaia open and globular clusters From data to science:
Gaia News:Counting down to launch A. Vallenari INAF, Padova Astronomical Observatory on behalf of DPACE Outline Gaia Spacecraft status The Gaia sky Gaia open and globular clusters From data to science:
Enrique Vázquez-Semadeni. Centro de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica, UNAM, México
 Enrique Vázquez-Semadeni Centro de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica, UNAM, México 1 Collaborators: CRyA UNAM: Abroad: Javier Ballesteros-Paredes Pedro Colín Gilberto Gómez Recent PhDs: Alejandro González
Enrique Vázquez-Semadeni Centro de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica, UNAM, México 1 Collaborators: CRyA UNAM: Abroad: Javier Ballesteros-Paredes Pedro Colín Gilberto Gómez Recent PhDs: Alejandro González
Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
 ASTR 3830 Astrophysics 2 - Galactic and Extragalactic Phil Armitage office: JILA tower A909 email: pja@jilau1.colorado.edu Spitzer Space telescope image of M81 Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
ASTR 3830 Astrophysics 2 - Galactic and Extragalactic Phil Armitage office: JILA tower A909 email: pja@jilau1.colorado.edu Spitzer Space telescope image of M81 Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
SURVEYING THE SUBSTELLAR COMPONENT OF THE ORION DISPERSED POPULATIONS
 SURVEYING THE SUBSTELLAR COMPONENT OF THE ORION DISPERSED POPULATIONS Juan José Downes (1,2), César Briceño (1), Jesús Hernández (1), Nuria Calvet (3) & Lee Hartmann (3) WITH THE COLLABORATION OF: Cecilia
SURVEYING THE SUBSTELLAR COMPONENT OF THE ORION DISPERSED POPULATIONS Juan José Downes (1,2), César Briceño (1), Jesús Hernández (1), Nuria Calvet (3) & Lee Hartmann (3) WITH THE COLLABORATION OF: Cecilia
Radio Nebulae around Luminous Blue Variable Stars
 Radio Nebulae around Luminous Blue Variable Stars Claudia Agliozzo 1 G. Umana 2 C. Trigilio 2 C. Buemi 2 P. Leto 2 A. Ingallinera 1 A. Noriega-Crespo 3 J. Hora 4 1 University of Catania, Italy 2 INAF-Astrophysical
Radio Nebulae around Luminous Blue Variable Stars Claudia Agliozzo 1 G. Umana 2 C. Trigilio 2 C. Buemi 2 P. Leto 2 A. Ingallinera 1 A. Noriega-Crespo 3 J. Hora 4 1 University of Catania, Italy 2 INAF-Astrophysical
Galaxies. The majority of known galaxies fall into one of three major classes: spirals (78 %), ellipticals (18 %) and irregulars (4 %).
 Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Nuclear Star Formation, The Torus, & Gas Inflow in Seyfert Galaxies
 Nuclear Star Formation, The Torus, & Gas Inflow in Seyfert Galaxies Richard Davies 1, H. Engel 1, M. Schartmann 1, G. Orban de Xivry 1, E. Sani 2, E. Hicks 3, A. Sternberg 4, R. Genzel 1, L. Tacconi 1,
Nuclear Star Formation, The Torus, & Gas Inflow in Seyfert Galaxies Richard Davies 1, H. Engel 1, M. Schartmann 1, G. Orban de Xivry 1, E. Sani 2, E. Hicks 3, A. Sternberg 4, R. Genzel 1, L. Tacconi 1,
Near-Infrared properties of the X-ray emitting young stellar objects in the Carina Nebula
 Toappear intheapjsspecialissueonthe ChandraCarinaComplex Project, May 2011 Near-Infrared properties of the X-ray emitting young stellar objects in the Carina Nebula Thomas Preibisch Universitäts-Sternwarte
Toappear intheapjsspecialissueonthe ChandraCarinaComplex Project, May 2011 Near-Infrared properties of the X-ray emitting young stellar objects in the Carina Nebula Thomas Preibisch Universitäts-Sternwarte
XMM-Newton EPIC observations of stellar clusters and star forming regions
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 434 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della XMM-Newton EPIC observations of stellar clusters and star forming regions R. Pallavicini 1, E. Franciosini 1 and S. Randich 2 1 INAF/Osservatorio Astronomico
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 434 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della XMM-Newton EPIC observations of stellar clusters and star forming regions R. Pallavicini 1, E. Franciosini 1 and S. Randich 2 1 INAF/Osservatorio Astronomico
X-ray emission and variability of young, nearby stars
 Young Stars Near Earth: Progress and Prospects ASP Conference Series, Vol.???, 2001 Ray Jayawardhana and Thomas Greene, eds. X-ray emission and variability of young, nearby stars B. Stelzer, R. Neuhäuser
Young Stars Near Earth: Progress and Prospects ASP Conference Series, Vol.???, 2001 Ray Jayawardhana and Thomas Greene, eds. X-ray emission and variability of young, nearby stars B. Stelzer, R. Neuhäuser
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 13 Apr 2006
 **FULL TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Clusters of Galaxies at 1 < z < 2 : The Spitzer Adaptation of the Red-Sequence Cluster Survey arxiv:astro-ph/0604289
**FULL TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Clusters of Galaxies at 1 < z < 2 : The Spitzer Adaptation of the Red-Sequence Cluster Survey arxiv:astro-ph/0604289
The Statistical Analysis of stars with H emission in IC 348 Cluster.
 Submitted to Astrophysics (2015) The Statistical Analysis of stars with H emission in IC 348 Cluster. E. H. Nikoghosyan, A. V. Vardanyan, К. G. Khachatryan Byurakan Astrophysical observatory, Armenia,
Submitted to Astrophysics (2015) The Statistical Analysis of stars with H emission in IC 348 Cluster. E. H. Nikoghosyan, A. V. Vardanyan, К. G. Khachatryan Byurakan Astrophysical observatory, Armenia,
VISTA SV Orion Survey
 VISTA SV Orion Survey M. Petr-Gotzens, J. M. Alcalá, F. ComerÓn, T. Stanke, S. Ramsay, C. Briceño, M. McCaughrean, M. R. Zapatero Osorio, G. Hussain, H. Zinnecker, P. Teixeira, L. Spezzi, J. Oliviera,
VISTA SV Orion Survey M. Petr-Gotzens, J. M. Alcalá, F. ComerÓn, T. Stanke, S. Ramsay, C. Briceño, M. McCaughrean, M. R. Zapatero Osorio, G. Hussain, H. Zinnecker, P. Teixeira, L. Spezzi, J. Oliviera,
Fossil Galaxy Groups; Halo and all therein
 Fossil Galaxy Groups; Halo and all therein Habib Khosroshahi School of Astronomy, Thanks to Mojtaba Raouf, Amin Farhang, Halime Miraghaei School of Astronomy, Ghassem Gozali, Alexi Finoguenov University
Fossil Galaxy Groups; Halo and all therein Habib Khosroshahi School of Astronomy, Thanks to Mojtaba Raouf, Amin Farhang, Halime Miraghaei School of Astronomy, Ghassem Gozali, Alexi Finoguenov University
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 6 Nov 2002
 ACCEPTED IN APJL. TO BE APPEAR IN DEC. 10TH ISSUE Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 14/09/00 LITHIUM DEPLETION BOUNDARY IN A PRE-MAIN SEQUENCE BINARY SYSTEM INSEOK SONG 1,2, M. S. BESSELL
ACCEPTED IN APJL. TO BE APPEAR IN DEC. 10TH ISSUE Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 14/09/00 LITHIUM DEPLETION BOUNDARY IN A PRE-MAIN SEQUENCE BINARY SYSTEM INSEOK SONG 1,2, M. S. BESSELL
Ram Pressure Stripping in NGC 4330
 The Evolving ISM in the Milky Way & Nearby Galaxies Ram Pressure Stripping in NGC 4330 Anne Abramson 1 & Jeffrey D. P. Kenney 1 1 Astronomy Department, Yale University, P.O. Box 208101 New Haven, CT 06520-8101
The Evolving ISM in the Milky Way & Nearby Galaxies Ram Pressure Stripping in NGC 4330 Anne Abramson 1 & Jeffrey D. P. Kenney 1 1 Astronomy Department, Yale University, P.O. Box 208101 New Haven, CT 06520-8101
Exploring the structure and evolu4on of the Milky Way disk
 Exploring the structure and evolu4on of the Milky Way disk Results from the Gaia-ESO survey and plans for 4MOST Thomas Bensby Dept. of Astronomy and Theore3cal Physics Lund University Sweden Chemistry
Exploring the structure and evolu4on of the Milky Way disk Results from the Gaia-ESO survey and plans for 4MOST Thomas Bensby Dept. of Astronomy and Theore3cal Physics Lund University Sweden Chemistry
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 29 Dec 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 29 Dec 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 29 Dec 2018](/thumbs/92/110975761.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Damiani_NGC6530 c ESO 2019 January 1, 2019 A wide-area photometric and astrometric (Gaia DR2) study of the young cluster NGC 6530 F. Damiani 1, L. Prisinzano 1,
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Damiani_NGC6530 c ESO 2019 January 1, 2019 A wide-area photometric and astrometric (Gaia DR2) study of the young cluster NGC 6530 F. Damiani 1, L. Prisinzano 1,
Molecular clouds (see review in astro-ph/990382) (also CO [12.1,12.2])
![Molecular clouds (see review in astro-ph/990382) (also CO [12.1,12.2]) Molecular clouds (see review in astro-ph/990382) (also CO [12.1,12.2])](/thumbs/81/83160044.jpg) Molecular clouds (see review in astro-ph/990382) (also CO [12.1,12.2]) Massive interstellar gas clouds Up to ~10 5 M 100 s of LY in diameter. Giant Molecular Clouds (GMCs) defined to be M > 10 4 M High
Molecular clouds (see review in astro-ph/990382) (also CO [12.1,12.2]) Massive interstellar gas clouds Up to ~10 5 M 100 s of LY in diameter. Giant Molecular Clouds (GMCs) defined to be M > 10 4 M High
The origin of lopsidedness in galaxies
 The Galaxy Disk in Cosmological Context Proceedings IAU Symposium No. xxx, 2008 c 2008 International Astronomical Union J. Andersen (Chief Editor), J. Bland-Hawthorn & B. Nordström, eds. The origin of
The Galaxy Disk in Cosmological Context Proceedings IAU Symposium No. xxx, 2008 c 2008 International Astronomical Union J. Andersen (Chief Editor), J. Bland-Hawthorn & B. Nordström, eds. The origin of
The Spatial Structure of Young Stellar Clusters. I. Subclusters
 Accepted, 13 March, 2014 The Spatial Structure of Young Stellar Clusters. I. Subclusters Michael A. Kuhn 1, Eric D. Feigelson 1, Konstantin V. Getman 1, Adrian J. Baddeley 2, Patrick S. Broos 1, Alison
Accepted, 13 March, 2014 The Spatial Structure of Young Stellar Clusters. I. Subclusters Michael A. Kuhn 1, Eric D. Feigelson 1, Konstantin V. Getman 1, Adrian J. Baddeley 2, Patrick S. Broos 1, Alison
Revealing the Large Scale Distribution of Star Formation in the Milky Way with WISE
 Revealing the Large Scale Distribution of Star Formation in the Milky Way with WISE Xavier Koenig Yale University WISE @ 5 Conference Feb 11 2015 Collaborators: David Leisawitz Debbie Padgett Luisa Rebull
Revealing the Large Scale Distribution of Star Formation in the Milky Way with WISE Xavier Koenig Yale University WISE @ 5 Conference Feb 11 2015 Collaborators: David Leisawitz Debbie Padgett Luisa Rebull
The Giant Branches of Open and Globular Clusters in the Infrared as Metallicity Indicators: A Comparison with Theory
 Accepted for publicaton in The Astronomical Journal The Giant Branches of Open and Globular Clusters in the Infrared as Metallicity Indicators: A Comparison with Theory GlennP.Tiede,PaulMartini,&JayA.Frogel
Accepted for publicaton in The Astronomical Journal The Giant Branches of Open and Globular Clusters in the Infrared as Metallicity Indicators: A Comparison with Theory GlennP.Tiede,PaulMartini,&JayA.Frogel
11. Virial Theorem Distances of Spiral and Elliptical Galaxies
 Virial Theorem 11. Virial Theorem Distances of Spiral and Elliptical Galaxies v 2 rot = s G M(R 0) R 0 2 = e G M(R eff ) R eff (s1) spiral galaxies (e1) elliptical galaxies v rot rotational velocity of
Virial Theorem 11. Virial Theorem Distances of Spiral and Elliptical Galaxies v 2 rot = s G M(R 0) R 0 2 = e G M(R eff ) R eff (s1) spiral galaxies (e1) elliptical galaxies v rot rotational velocity of
Using Globular Clusters to. Study Elliptical Galaxies. The View Isn t Bad... Omega Centauri. Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office M13
 Using Globular Clusters to Omega Centauri Study Elliptical Galaxies Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office 10,000 1,000,000 stars up to 1000 stars/pc3 typical sizes ~10 parsec Mike Beasley (IAC, Tenerife)
Using Globular Clusters to Omega Centauri Study Elliptical Galaxies Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office 10,000 1,000,000 stars up to 1000 stars/pc3 typical sizes ~10 parsec Mike Beasley (IAC, Tenerife)
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 15 Nov 2004
 Submitted to The Astrophysical Journal Letters Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 6/22/04 ARE SUPERNOVA KICKS RESPONSIBLE FOR X-RAY BINARY EJECTION FROM YOUNG CLUSTERS? J. Sepinsky 1, V.
Submitted to The Astrophysical Journal Letters Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 6/22/04 ARE SUPERNOVA KICKS RESPONSIBLE FOR X-RAY BINARY EJECTION FROM YOUNG CLUSTERS? J. Sepinsky 1, V.
Star Formation in Disk Galaxies: From Kiloparsec to Giant Molecular Cloud Scales
 Star Formation in Disk Galaxies: From Kiloparsec to Giant Molecular Cloud Scales Suzanne N. Shaske1 and Dr. Jonathan C. Tan2 1 2 Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Florida Departments of
Star Formation in Disk Galaxies: From Kiloparsec to Giant Molecular Cloud Scales Suzanne N. Shaske1 and Dr. Jonathan C. Tan2 1 2 Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Florida Departments of
Major Review: A very dense article" Dawes Review 4: Spiral Structures in Disc Galaxies; C. Dobbs and J Baba arxiv "
 The Components of a Spiral Galaxy-a Bit of a Review- See MBW chap 11! we have discussed this in the context of the Milky Way" Disks:" Rotationally supported, lots of gas, dust, star formation occurs in
The Components of a Spiral Galaxy-a Bit of a Review- See MBW chap 11! we have discussed this in the context of the Milky Way" Disks:" Rotationally supported, lots of gas, dust, star formation occurs in
1. The AGB dust budget in nearby galaxies
 **Volume Title** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **Volume Number** **Author** c **Copyright Year** Astronomical Society of the Pacific Identifying the chemistry of the dust around AGB stars in nearby galaxies
**Volume Title** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **Volume Number** **Author** c **Copyright Year** Astronomical Society of the Pacific Identifying the chemistry of the dust around AGB stars in nearby galaxies
High Energy Processes in Young Stellar Objects
 High Energy Processes in Young Stellar Objects Ji Wang Department of Astronomy, University of Florida, Gainesville, Fl 32601 jwang@astro.ufl.edu Received ; accepted 2 ABSTRACT In this paper, I present
High Energy Processes in Young Stellar Objects Ji Wang Department of Astronomy, University of Florida, Gainesville, Fl 32601 jwang@astro.ufl.edu Received ; accepted 2 ABSTRACT In this paper, I present
Studying the Milky Way with pulsating stars
 Studying the Milky Way with pulsating stars ( 東京大学 ) Noriyuki Matsunaga (The University of Tokyo) The first C-rich Miras found in the bulge All the AGB stars confirmed in the bulge were O-rich. C-rich
Studying the Milky Way with pulsating stars ( 東京大学 ) Noriyuki Matsunaga (The University of Tokyo) The first C-rich Miras found in the bulge All the AGB stars confirmed in the bulge were O-rich. C-rich
NUCLEAR STAR CLUSTERS IN 228 SPIRAL GALAXIES WITH HUBBLE
 Inter-Departmental Science Workshop Aranjuez, Spain, 20 October 2013 NUCLEAR STAR CLUSTERS IN 228 SPIRAL GALAXIES WITH HUBBLE Iskren Georgiev International Research Fellow ESTEC, Noordwijk, Netherlands
Inter-Departmental Science Workshop Aranjuez, Spain, 20 October 2013 NUCLEAR STAR CLUSTERS IN 228 SPIRAL GALAXIES WITH HUBBLE Iskren Georgiev International Research Fellow ESTEC, Noordwijk, Netherlands
Lecture Five: The Milky Way: Structure
 Lecture Five: The Milky Way: Structure The Celestial Sphere http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/pog14 We use equatorial coordinates to determine the positions of stars in the sky. A stars declination (like
Lecture Five: The Milky Way: Structure The Celestial Sphere http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/pog14 We use equatorial coordinates to determine the positions of stars in the sky. A stars declination (like
Lecture 26 Low-Mass Young Stellar Objects
 Lecture 26 Low-Mass Young Stellar Objects 1. Nearby Star Formation 2. General Properties of Young Stars 3. T Tauri Stars 4. Herbig Ae/Be Stars References Adams, Lizano & Shu ARAA 25 231987 Lada OSPS 1999
Lecture 26 Low-Mass Young Stellar Objects 1. Nearby Star Formation 2. General Properties of Young Stars 3. T Tauri Stars 4. Herbig Ae/Be Stars References Adams, Lizano & Shu ARAA 25 231987 Lada OSPS 1999
The Stellar Population And Origin Of The Mysterious High-Latitude Star Forming Cloud CG 12
 Submitted to the Astrophysical Journal 05/08/07 The Stellar Population And Origin Of The Mysterious High-Latitude Star Forming Cloud CG 12 Konstantin V. Getman 1, Eric D. Feigelson 1, Warrick A. Lawson
Submitted to the Astrophysical Journal 05/08/07 The Stellar Population And Origin Of The Mysterious High-Latitude Star Forming Cloud CG 12 Konstantin V. Getman 1, Eric D. Feigelson 1, Warrick A. Lawson
Anomalous Spectral Types and Intrinsic Colors of Young Stars
 Young Stars & Planets Near the Sun Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 314, 2015 J. H. Kastner, B. Stelzer, & S. A. Metchev, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2016 doi:10.1017/s1743921315006079 Anomalous
Young Stars & Planets Near the Sun Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 314, 2015 J. H. Kastner, B. Stelzer, & S. A. Metchev, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2016 doi:10.1017/s1743921315006079 Anomalous
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability. Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida
 Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
Open clusters and stellar associations: recent results of the Italian community
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 78, 616 c SAIt 2007 Memorie della Open clusters and stellar associations: recent results of the Italian community S. Sciortino 1,2 1 INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Palermo Giuseppe
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 78, 616 c SAIt 2007 Memorie della Open clusters and stellar associations: recent results of the Italian community S. Sciortino 1,2 1 INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Palermo Giuseppe
Thom et al. (2008), ApJ
 Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
Galactic Supershells and GSH Vanessa A. Moss Parkes 50th Symposium 3rd November
 Galactic Supershells and GSH 006-15+7 Vanessa A. Moss Parkes 50th Symposium 3rd November 2011 1 Contents Early history of supershells Discovery Early interpretation Surveys of supershells Northern hemisphere
Galactic Supershells and GSH 006-15+7 Vanessa A. Moss Parkes 50th Symposium 3rd November 2011 1 Contents Early history of supershells Discovery Early interpretation Surveys of supershells Northern hemisphere
Optical studies of an ultraluminous X-ray source: NGC1313 X-2
 Optical studies of an ultraluminous X-ray source: NGC1313 X-2 Jifeng Liu Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in collaboration with Joel Bregman, Jon Miller, Philip Kaaret outline background: ultraluminous
Optical studies of an ultraluminous X-ray source: NGC1313 X-2 Jifeng Liu Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in collaboration with Joel Bregman, Jon Miller, Philip Kaaret outline background: ultraluminous
Measuring Black Hole Masses in Nearby Galaxies with Laser Guide Star Adaptive Optics
 Measuring Black Hole Masses in Nearby Galaxies with Laser Guide Star Adaptive Optics Claire Max Anne Medling Mark Ammons UC Santa Cruz Ric Davies Hauke Engel MPE-Garching Image of NGC 6240: Bush et al.
Measuring Black Hole Masses in Nearby Galaxies with Laser Guide Star Adaptive Optics Claire Max Anne Medling Mark Ammons UC Santa Cruz Ric Davies Hauke Engel MPE-Garching Image of NGC 6240: Bush et al.
The star formation history of Virgo spiral galaxies
 The star formation history of Virgo spiral galaxies Combined spectral and photometric inversion Ciro Pappalardo INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri Cluster galaxies Abell 1689 Physical effects acting
The star formation history of Virgo spiral galaxies Combined spectral and photometric inversion Ciro Pappalardo INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri Cluster galaxies Abell 1689 Physical effects acting
SPITZER-MIPS OBSERVATIONS OF THE CHAMAELEONTIS YOUNG ASSOCIATION
 The Astrophysical Journal, 683:813Y821, 2008 August 20 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. SPITZER-MIPS OBSERVATIONS OF THE CHAMAELEONTIS YOUNG ASSOCIATION
The Astrophysical Journal, 683:813Y821, 2008 August 20 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. SPITZER-MIPS OBSERVATIONS OF THE CHAMAELEONTIS YOUNG ASSOCIATION
Zoccali et al. 2003, A&A, 399, 931. Overview of (old) Galactic components. bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo. metallicity & age distribution
 Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
Monte Carlo Modelling of Globular Clusters
 Monte Carlo Modelling of Globular Clusters Douglas Heggie University of Edinburgh d.c.heggie@ed.ac.uk Collaboration with Mirek Giersz (Warsaw) The globular cluster M4 Distance from sun Mass Core radius
Monte Carlo Modelling of Globular Clusters Douglas Heggie University of Edinburgh d.c.heggie@ed.ac.uk Collaboration with Mirek Giersz (Warsaw) The globular cluster M4 Distance from sun Mass Core radius
Cosmic Hide and Seek: Tracking Missing and Invisible Matter in the Universe. Sheila Kannappan Physics & Astronomy Department UNC Chapel Hill
 Cosmic Hide and Seek: Tracking Missing and Invisible Matter in the Universe Sheila Kannappan Physics & Astronomy Department UNC Chapel Hill narrow meaning of visible : λ=400-700nm Light = Electromagnetic
Cosmic Hide and Seek: Tracking Missing and Invisible Matter in the Universe Sheila Kannappan Physics & Astronomy Department UNC Chapel Hill narrow meaning of visible : λ=400-700nm Light = Electromagnetic
TRACING STAR FORMATION IN THE ROSETTE MOLECULAR CLOUD
 TRACING STAR FORMATION IN THE ROSETTE MOLECULAR CLOUD By JASON ERIC YBARRA A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE
TRACING STAR FORMATION IN THE ROSETTE MOLECULAR CLOUD By JASON ERIC YBARRA A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE
Multi-wavelength observations and variability of Young Stellar Objects
 X-ray to radio Multi-wavelength observations and variability of Young Stellar Objects Jan Forbrich Harvard-Smithsonian CfA Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/CfA/J.Forbrich et al.; Infrared: NASA/SSC/CfA/IRAC GTO
X-ray to radio Multi-wavelength observations and variability of Young Stellar Objects Jan Forbrich Harvard-Smithsonian CfA Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/CfA/J.Forbrich et al.; Infrared: NASA/SSC/CfA/IRAC GTO
The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters
 IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
ASTRO 310: Galactic & Extragalactic Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney
 ASTRO 310: Galactic & Extragalactic Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 3 January 23, 2017 The Milky Way Galaxy: Vertical Distributions of Stars & the Stellar Disk disks exist in many astrophysical systems
ASTRO 310: Galactic & Extragalactic Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 3 January 23, 2017 The Milky Way Galaxy: Vertical Distributions of Stars & the Stellar Disk disks exist in many astrophysical systems
Physical parameter determinations of young Ms
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 85, 773 c SAIt 2014 Memorie della Physical parameter determinations of young Ms Taking advantage of the Virtual Observatory to compare methodologies A. Bayo 1,2, C. Rodrigo 3,4, D. Barrado
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 85, 773 c SAIt 2014 Memorie della Physical parameter determinations of young Ms Taking advantage of the Virtual Observatory to compare methodologies A. Bayo 1,2, C. Rodrigo 3,4, D. Barrado
