Zone 258, Master Map Normal View
|
|
|
- Austen Johnson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Zone Master, Normal View, 10 deg FOV Zone 258, Master Map Normal View Hydra Vela κ ε δ γ Pyxis α ζ β η ρ ξ ο M ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ζ Puppis 09h 28m 09h 20m 09h 12m 08h 56m 08h 48m 08h 40m 08h 32m 08h 16m 08h 08m 08h 00m 07h 44m 07h 36m 07h 28m
2 , Map 1 Normal Image Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software isque Inc. h2449 h4088 Collinder 187 IC 2311 NGC 2566 Howe 22 NGC 2559 Ruprecht 53 os 756 Haffner 21 Stone 18 Dunlop 61 ur 202 h4037 NGC 2527 os 1086 Innes ' ' ' ' ' Ruprecht 50 NGC 2587 Olivier 30 h4024 NGC 2571 NGC 2533 Innes h 30m 08h 25m 08h 20m 08h 15m 08h 10m 08h 05m 08h 00m
3 , Map 1 Mirror Image Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software isque Inc. Haffner 21 ur 202 h4037 NGC 2527 os 1086 Innes 784 Dunlop 61 os 756 Ruprecht 53 Stone 18 IC 2311 NGC 2566 Howe 22 NGC 2559 Collinder 187 h4088 h ' ' ' ' ' Olivier 30 h4024 Ruprecht 50 NGC 2533 NGC 2571 NGC 2587 Innes h 00m 08h 05m 08h 10m 08h 15m 08h 20m 08h 25m 08h 30m
4 , Map 2 Normal Image Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software isque Inc. NGC 2580 NGC 2567 ur 454 NGC 2533 Harvard 201 Ruprecht 55 h4046 Innes 788 LDS 201 h ' ' ' ' ' 08h 30m Gilliss 96 08h 25m 08h 20m 08h 15m 08h 10m 08h 05m 08h 00m
5 , Map 2 Mirror Image Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software isque Inc. h4035 LDS 201 Innes 788 h4046 Ruprecht 55 ur 454 Harvard 201 NGC 2580 NGC ' ' ' ' ' Gilliss 96 08h 00m 08h 05m 08h 10m 08h 15m 08h 20m 08h 25m 08h 30m
6 , Map 3 Normal Image Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software isque Inc. h4106 Pyxis Vela Gilliss 96 h4093 Dunlop 67 h4063 NGC ' ' ' ' ' ζ 08h 30m 08h 25m 08h 20m 08h 15m 08h 10m 08h 05m 08h 00m
7 , Map 3 Mirror Image Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software isque Inc. NGC 2546 Dunlop 67 h4063 Gilliss 96 Pyxis Vela h ' ' ' ' ' ζ 08h 00m 08h 05m 08h 10m 08h 15m 08h 20m 08h 25m 08h 30m
8 , Map 4 Normal Image Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software isque Inc. h2481 Innes 1128 δ h2475 γ Gamma Pyx USNO 3 Harvard 119 os 161 η ur 206 South ' ' ' ' ' ζ Zeta Pyx Cordoba 77 NGC h 00m 08h 55m 08h 50m 08h 45m 08h 40m 08h 35m 08h 30m
9 , Map 4 Mirror Image Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software isque Inc. South 569 ur 206 η os 161 Harvard 119 γ USNO 3 Gamma Pyx h2475 δ Innes 1128 h ' ' ' ' ' ζ Zeta Pyx NGC 2627 Cordoba 77 08h 30m 08h 35m 08h 40m 08h 45m 08h 50m 08h 55m 09h 00m
10 , Map 5 Normal Image Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software isque Inc. Cordoba 77 α NGC 2658 NGC 2627 Stone ' ' ' ' ' Gilliss h 00m 08h 55m 08h 50m 08h 45m 08h 40m 08h 35m 08h 30m
11 , Map 5 Mirror Image Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software isque Inc. NGC 2627 Stone 61 α NGC 2658 Cordoba ' ' ' ' ' Gilliss 101 Gilliss 96 08h 30m 08h 35m 08h 40m 08h 45m 08h 50m 08h 55m 09h 00m
12 , Map 6 Normal Image Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software isque Inc. β eta Pyx h4106 Pyxis Vela ' ' ' ' ' 09h 00m 08h 55m 08h 50m 08h 45m 08h 40m 08h 35m 08h 30m
13 , Map 6 Mirror Image Sky charts generated by TheSky Software; used by permission of Software isque Inc. Vela h4093 h4106 β eta Pyx ' ' ' ' ' 08h 30m 08h 35m 08h 40m 08h 45m 08h 50m 08h 55m 09h 00m
14 2 Reference Stars, 31 Double Stars, 14 Open Clusters, 3 Galaxies eta Pyx os os ur ur ur C Collinder Cordoba D Dunlop Dunlop G Gamma Pyx Gilliss Gilliss H h h h h h h h h h h h Haffner Harvard Harvard Howe I IC Innes L LDS N NGC NGC NGC NGC NGC NGC NGC NGC NGC NGC NGC R Ruprecht
15 Ruprecht S South Stone Stone U USNO Z Zeta Pyx
16 Zone 258, Map 1 Double Stars Easy h4037 ur 203; DS 6544; HD Rating: 1 E Position: K1 IV Y No C W 1835: measurements. May be optical because Hipparcos gives different distances (1,050 and 680 light years). C 1874: measurements. C8 at 104x. h4024 DS 6515; HD 65945; SO Rating: 3 E Position: G5 III Y = : measurements. C8 at 104x. Moderate field
17 ur 202 DS 6535; HD 66306; SO Rating: 4 E Position: II W ? C ! ? 1874: measurements. C 1874: measurements. C8 at 206x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 10.2 inches. Separation: = 65.6 miles; C = 258 miles. Distance (LY): 5,530 Total luminosity (Suns): 5,980 Dunlop 61 os 148; DS 6601; HD 67409; SO Rating: 4 E Position: III W K0 do! 1896: measurements. C8 at 83x
18 Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 10.8 inches; = 25.8 inches. Separation: = 1,184 miles. Distance (LY): 10,900 Total luminosity (Suns): h2449 Position: Rating: 4 E G0 W W 1831: measurements. C11 at 98x. Moderate os 756 HD 67884; SO Rating: 5 M Position: K1 III Y! = 1960 O 1927: measurements. C11 at 98x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 2.40 inches. Separation: = 3,432 feet
19 Distance (LY): 100 Total luminosity (Suns): 0.30 Stone 18 DS 6636 Rating: 5 M Position: V W = W 1876: measurements. C8 at 280x. Very, very faint. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 9.00 inches. Separation: = 1.02 miles. Distance (LY): 194 Total luminosity (Suns): 1.7 Howe 22 Rossiter 1386 (); DS 6729 Rating: 5 M Position: F5 V W ? 1991 W 1877: measurements. Quadrant reversal? C11 at 98x
20 Difficult h4088 DS 6794; HD 70963; SO Rating: 5 D Position: IV W W? C W? 1837: measurements. C 1 measurement. C11 at 98x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 12.0 inches. Separation: = 29.0 miles; C = 10.7 miles. Distance (LY): 690 Total luminosity (Suns):
21 Deep Sky Objects Easy NGC 2527 Rating: 3 E Other Names: Collinder 174, H VIII 30 stronomical League Program: Herschel 400 Club, inocular Deep Sky Club Position: Type: Oc Class: II 2m Magnitude: 6.5 Dimensions: 22' Cluster population: 60 It is 1 billion years old and lies 28,500 light years from the galactic center and 60 light years above the galactic plane. The brightest star is 8.6m (200 times brighter than the Sun). C8 at 104x. Note the two parallel doglegs, and three 9m stars on the SE side, in a straight line. The cluster is round, bright and loose. Very rich field. Model (where the Sun is a baseball): Its diameter would be 4,120 miles with stars 525 miles apart. Distance (LY): 1,960 Luminosity (suns): 750 Ruprecht 53 Position: Rating: 5 E Type: Oc Class: IV 2 p Magnitude: 10.0 Dimensions: 18' Cluster population: 40 The cluster is 389 million years old. C11 at 98x. Very loose and poor group with not much of a center. I counted 14 stars on a hazy night with 12-day old moonlight. Distance (LY): 5,540 Total luminosity (Suns):
22 Moderate Ruprecht 50 Position: Rating: 4 M Type: OC Class: II2mb Dimensions: 3.5' Cluster population: 12 C11 at 98x. Small, triangular group of eight stars with a wide spread in magnitude. Very poor object. NGC 2571 Rating: 4 M Other Names: Collinder 181, H VI 39 stronomical League Program: Herschel 400 Club, inocular Deep Sky Club Position: Type: Oc Class: II 3m Magnitude: 7.0 Dimensions: 13' Cluster population: 30 It is 31 million years old and lies 32,000 light years from the galactic center and 250 light years above the galactic plane. The youngest stars are 8 types. The brightest star is 8.8m (1,100 times brighter than the Sun). C8 at 104x. This cluster is faint, rich and round, and has many doubles. Note the wide arc of faint stars about min N. Rich field. Model (where the Sun is a baseball): Its diameter would be 8,400 miles with stars 1,350 miles apart. Distance (LY): 4,370 Luminosity (suns): 2,
23 NGC 2533 Other Names: Collinder 175 Rating: 5 M Position: Type: Oc Class: II 2r Magnitude: 7.6 Dimensions: 3.5' Cluster population: 60 It is 752 million years old and lies 29,600 light years from the galactic center and 100 light years above the galactic plane. The brightest star is 9m (600 times brighter than the Sun). C8 at 104x. Very faint and round. Note the 7m pair 15 min NW. Model (where the Sun is a baseball): Its diameter would be 1,820 miles with stars 230 miles apart. Distance (LY): 11,000 Luminosity (suns): 8,600 Collinder 187 Position: Rating: 5 M Type: Oc Class: III 1 p Magnitude: 9.6 Dimensions: 7' Cluster population: 20 C11 at 193x. I counted only six stars in a double chevron on a hazy night with 12-day old moonlight. NGC 2587 Other Names: Collinder 184 Rating: 5 M Position: Type: Oc Class: III 2m Magnitude: 9.2 Dimensions: 9' Cluster population:
24 C8 at 104x. It looks nebulous, even with averted vision. Difficult Haffner 21 Position: Rating: 4 D Type: Oc Class: II 1p Magnitude: 10.3 Dimensions: 1.1' Cluster population: 20 The brightest star is 12.1m. C8 at 280x. Six extremely faint stars in a tight knot around an 9m star. Distance (LY): 9,620 Total luminosity (Suns): 550 NGC 2559 Other Names: UGC 4458, H III 234 Rating: 4 D Position: Type: Gal Class: S(s)bc pec: Magnitude: 10.9 Surface brightness: 12.8 Dimensions: 3.7' x 1.7' P: 6 This galaxy produced supernova 2002hc (type II). C11 at 193x. In hazy skies lit by a 12 day old moon, it showed up as a fairly bright fuzzy nucleus but no halo. n 11m star is 3 min E. Distance (LY): 59,000,000 Total luminosity (Suns): 11,900,000,000 Radial velocity (km/sec): +1,
25 NGC 2566 Other Names: PGC 23303, H III 288 Rating: 5 D Position: Type: Gal Class: (R')S(r)ab Magnitude: 11.0 Surface brightness: 13.1 Dimensions: 3.4' x 2.3' P: 110 C11 at 193x. Very faint with either a starlike nucleus or a 13m foreground star over it. Distance (LY): 62,000,000 Total luminosity (Suns): 12,000,000,000 Radial velocity (km/sec): +1,637 IC 2311 Other Names: ESO 495-G002 Rating: 5 D Position: Type: Gal Class: E0 Magnitude: 11.5 Surface brightness: 13.0 Dimensions: 2.1' x 1.9' C11 at 98x. Fuzzy star with a moderately bright center. There were five 13m-14m stars in the field. Distance (LY): 98,000,000 Total luminosity (Suns): 18,900,000,
26 Zone 258, Map 2 Double Stars Easy h4035 HD 66598; SO Rating: 3 E Position: K2 III Y : measurements. The primary is an infra-red source. Hipparcos/Tycho mission data show different distances for these stars (520 and 86 light years); they may be optical. The stars have a small difference in proper motion. C8 at 65x. h4046 Innes 189; HD 67243; SO Rating: 3 E Position: G5 Ib W III V C = 1919? 1837: measurements. The stars show similar proper motions. C 1903: measurements
27 C8 at 104x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 3.00 inches; = 13.2 inches. Separation: = 116 miles; C = 148 miles. Distance (LY): 3,400 Total luminosity (Suns): 3,436 LDS 201 os 2164 (C); HD 66791; SO Rating: 5 E Position: G3 V Y = 1991 W C ? D No CD : measurements. C 1 measurement. CD 1913: measurements. The stars show similar proper motions. C8 at 104x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 3.39 inches. Separation: = 19.2 miles; C = 24.1 miles; CD = 1.64 miles. Distance (LY): 257 Total luminosity (Suns):
28 Moderate ur 454 HD 69445; SO Rating: 4 M Position: G5 III O C No 1877: measurements. C 1 measurement. C8 at 280x. Very rich field. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 39 inches. Separation: = 1.03 miles; C = 10.4 miles. Distance (LY): 349 Total luminosity (Suns): 32 Difficult Harvard 201 HD 68978; SO Rating: 5 D Position: G2 V yw ? C W 1900: measurements. C 1 measurement
29 C8 at 206x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 3.30 inches. Separation: = 2.03 miles; C = 2.47 miles. Distance (LY): 88 Total luminosity (Suns): 1.3 Deep Sky Objects Moderate NGC 2567 Other Names: Melotte 86; Collinder 180; Raab 73, H VII 64 stronomical League Program: Herschel 400 Club Rating: 4 M Position: Type: Oc Class: II 2m Magnitude: 7.4 Dimensions: 10' Cluster population: 50 It is 68 million years old and lies 30,000 light years from the galactic center and 280 light years above the galactic plane. Over 115 stars are members of this group. The brightest star is 10m (240 times brighter than the Sun). C8 at 104x. This cluster is delicate and requires averted vision. nearby 9m star is bothersome. It almost gets lost in the rich field. chain of 9m stars (5 in number) runs N-S and nearly cuts the group in half. Model (where the Sun is a baseball): Its diameter would be 5,240 miles with stars 700 miles apart. Distance (LY): 5,470 Luminosity (suns): 2,
30 NGC 2580 Position: Rating: 5 M Type: Oc Class: II 2m Magnitude: 9.7 Dimensions: 9' Cluster population: 50 Its age may be 158 million years. C8 at 104x. It is small and faint, with a trapezoidal center. Distance (LY): 13,000 Total luminosity (Suns): 1,750 Difficult Ruprecht 55 Position: Rating: 5 D Type: Oc Class: IV 2p Magnitude: 7.8 Dimensions: 17.0' Cluster population: 12 sterism? If not, its age may be 7 million years. The brightest star is 8.6m. C8 at 83x. very poor group; without a list, you'd not know it was an open cluster! Distance (LY): 16,000 Total luminosity (Suns): 15,
31 Zone 258, Map 3 Double Stars Easy Dunlop 67 OS Pup; HD 69081; SO Rating: 3 E Position: IV W IV W 1837: measurements. The primary rotates at 213 km/sec. The secondary is a spectroscopic binary. oth stars are part of the Puppis O3 ssociation. May be optical because Hipparcos gives different distances (1,180 and 1,480 light years). C8 at 104x. h4063 HD 69402; SO Rating: 3 E Position: V W po 1835: measurements. Star is a spectroscopic binary. The stars have different proper motions
32 C8 at 104x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 12.0 inches. Separation: = 21.7 miles. Distance (LY): 860 Total luminosity (Suns): 68 h4093 NO Pup; ur 1605; HD 71488; SO Rating: 3 E Position: IV W W 1835: measurements. The stars have different proper motions. The primary is an lgol system. C8 at 104x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 11.7 inches; = 5.66 inches. Separation: = 7.71 miles. Distance (LY): 610 Total luminosity (Suns): 140 Gilliss 96 HD 71801; SO Rating: 4 E Position: V W ?
33 1851: measurements. Star is a spectroscopic binary and rotates at 158 kps. C8 at 104x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 12.6 inches. Separation: = 38.7 miles. Distance (LY): 1,000 Total luminosity (Suns): 408 Deep Sky Objects Difficult NGC 2546 Other Names: Collinder 178 Rating: 5 D Position: Type: Oc Class: III 2m Magnitude: 6.3 Dimensions: 41' Cluster population: 50 It is 75 million years old and the youngest stars are 0 types. The brightest star is 8.2m (440 times brighter than the Sun). This cluster lies 28,700 light years from the galactic center and 110 light years below the galactic plane. C8 at 83x. It's low latitude makes it a difficult object to see. It is large, coarse, and triangular. bright blue star lies at the N end. Model (where the Sun is a baseball): Its diameter would be 12,670 miles with stars 1,750 miles apart. Distance (LY): 3,300 Luminosity (suns): 2,
34 Zone 258, Map 4 Reference Star Gamma Pyx (HD 75691; SO ) Position: Mag : 4.01 Spectrum : K3 III Color : Y ssumed distance: 209 light years ssumed luminosity (suns): 86 This star is an infra-red source. Double Stars Easy South 569 os 158; DS 6847; HD 72136; SO Rating: 3 E Position: G0 Y O C8 at 83x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 16.5 inches. Separation: = 6.40 miles. Distance (LY): 171 Total luminosity (Suns):
35 Zeta Pyx h4120; DS 6923; HD 73898; SO Rating: 3 E Position: G5 III yw ! 61 +! 1980 G0? 1836: measurements. The primary is an infra-red source. The stars share common proper motion. C8 at 104x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 39 inches; = 18.0 inches. Separation: = 19.3 miles. Distance (LY): 236 Total luminosity (Suns): 49 USNO 3 HD 75198; SO Rating: 3 E Position: F5 V W F5 W 1877: measurements. The stars share common proper motion. C8 at 83x
36 Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 4.35 inches; = 13.8 inches. Separation: = 5.01 miles. Distance (LY): 127 Total luminosity (Suns): 0.8 os 161 DS 6904 Rating: 4 E Position: F6 IV/V W W 1927: measurements. May be optical because Hipparcos gives different distances (10,870 and 170 light years). C11 at 98x. This pair is the middle star of a five-star chain. Cordoba 77 DS 7108; HD 76740; SO Rating: 4 E Position: F5 yw bw 1920: measurements. C8 at 104x. It is the E vertex of a triangle, with 8.7m SO (NW) and 8.3m SO (SW). C11 at 98x
37 Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 13.1 inches. Separation: = 2.00 miles. Distance (LY): 126 Total luminosity (Suns): 1.60 Moderate Harvard 119 DS 6966 Rating: 5 M Position: m7- W ! 1965 W 1870: measurements. C11 at 98x. h2475 HD 76178; SO Rating: 5 M Position: K1 III Y = 1932 W? 1831: measurements. The Tycho-2 Catalogue indicates a single star entry. C11 at 98x
38 Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 2.40 inches. Separation: = 1.87 miles. Distance (LY): 59 Total luminosity (Suns): 0.09 h2481 DS 7122; HD 76997; SO Rating: 5 M Position: K2/3 III Y W 1831: measurements. C11 at 98x. Difficult ur 206 DS 6887 Rating: 3 D Position: G0 III Y yo 1877: measurements. C8 at 280x
39 Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 32.4 inches. Separation: = a few feet. Distance (LY): Total luminosity (Suns): 160 Innes 1128 DS 7101; HD Rating: 4 D Position: V W = 1991 W 1917: measurements. C11 at 634x. Deep Sky Objects Difficult NGC 2627 Other Names: Melotte 87; Collinder 188; Raab 74, H VII 63 stronomical League Program: Herschel 400 Club Rating: 5 D Position: Type: Oc Class: II 2r Magnitude: 8.4 Dimensions: 11' Cluster population: 70 The brightest star is 11m. The cluster is 368 million years old
40 C8 at 104x. It is faint, delicate, and does not magnify well. It is round and, under high powers, displays a void stripe down the center. Moderate field. Distance (LY): Total luminosity (Suns): 1,500 Zone 258, Map 5 Double Stars Easy Gilliss 101 HD 75199; SO Rating: 2 E Position: K5 III D! IV 1852: measurements. The stars show similar proper motions, although Hipparcos gives different distances (550 and 136 light years). has an 11.7m companion at 272 (199). C8 at 104x. Stone 61 HD 74005; SO Rating: 4 E Position: V W = W
41 1877: measurements. C8 at 206x. n 8.5m star lies 8 min SSW. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 9.00 inches. Separation: = 11.5 miles. Distance (LY): 1,600 Total luminosity (Suns): 135 Deep Sky Objects Difficult NGC 2658 Other Names: Melotte 90; Collinder 195; Raab 77 Rating: 5 D Position: Type: Oc Class: I 2r Magnitude: 9.2 Dimensions: 12' Cluster population: 80 The brightest star is 12m. The cluster is 1.4 billion years old. C8 at 104x. It is very, very faint and takes high power to resolve. Distance (LY): 6,590 Total luminosity (Suns):
42 Zone 258, Map 6 Reference Star eta Pyx (HD 74006; SO ) Position: Mag : 3.97 Spectrum : G5 III Color : Y Star is a spectroscopic binary. It is also a member of the Sco-Cen ssociation. Double Stars Difficult h4106 Luyten 223; HD 72435; SO Rating: 5 D Position: K0 IV Y ! 305 +! 1997 No C ? 1835: measurements. C 1913: measurements. C8 at 104x. Scale model (in which the Sun is the size of a baseball): Diameter: = 12.0 inches. Separation: = 1.36 miles; C = 15.2 miles. Distance (LY): 203 Total luminosity (Suns):
43 Zone 258 Mini-Catalog Double Stars Designation Position Rating Map Component Mag Separation P h E 1 C Gilliss E h E = 5.83 h E 2 h E 2 Dunlop E 3 h E 3 h E 3 South E 4 Zeta Pyx E 4 USNO E 4 ur E 1 Dunlop E 1 h E 1 Gilliss E 3 os E 4 Stone E 5 Cordoba E 4 LDS E 2 ur M 2 C C C D CD C ! ! = ! ! =
44 Designation Position Rating Map Component Mag Separation P os M = Stone M = Howe M ? Harvard M ! h M = h M ur D Innes D = Harvard D 2 C h D 1 h D 6 C C ! ! Deep Space Objects Specifications Surface Object Position Rating Map Type Mag r Population NGC E 1 Oc (II 2m) Ruprecht E 1 Oc (IV 2 p) Ruprecht M 1 Oc (II2mb) 12 NGC M 2 Oc (II 2m) NGC M 1 Oc (II 3m) NGC M 1 Oc (II 2r) NGC M 2 Oc (II 2m) NGC M 1 Oc (III 2m) Collinder M 1 Oc (III 1 p) Haffner D 1 Oc (II 1p) NGC D 1 Gal (S(s)bc pec:) Ruprecht D 2 Oc (IV 2p) NGC D 3 Oc (III 2m) NGC D 1 Gal ((R')S(r)ab) IC D 1 Gal (E0) NGC D 4 Oc (II 2r) NGC D 5 Oc (I 2r)
Zone 252, Master Map Normal View
 Zone Master, Normal View, 10 deg FOV, Master Map Normal View χ1 α ζ ε γ1 γ2 β η1 η3 η2 ψ Fornax ι2 ι1 λ2 ω λ1 φ µ No Map ν π ε π Cetus Sculptor τ -38 00' -36 00' -34 00' -32 00' -30 00' -28 00' -26 00'
Zone Master, Normal View, 10 deg FOV, Master Map Normal View χ1 α ζ ε γ1 γ2 β η1 η3 η2 ψ Fornax ι2 ι1 λ2 ω λ1 φ µ No Map ν π ε π Cetus Sculptor τ -38 00' -36 00' -34 00' -32 00' -30 00' -28 00' -26 00'
Zone 257, Master Map Normal View
 Zone Master, Normal View, 10 deg FOV, Master Map Normal View ρ ξ ο Puppis τ η ludra π ω Canis Major δ Wezen σ ε ο1 dhara κ Colum -38 00' -36 00' -34 00' -32 00' -30 00' -28 00' -26 00' -24 00' ζ 08h 32m
Zone Master, Normal View, 10 deg FOV, Master Map Normal View ρ ξ ο Puppis τ η ludra π ω Canis Major δ Wezen σ ε ο1 dhara κ Colum -38 00' -36 00' -34 00' -32 00' -30 00' -28 00' -26 00' -24 00' ζ 08h 32m
Zone 102, Master Map Normal View
 Zone Master, Normal View, 10 deg FOV Zone 102, Master Map Normal View α Deneb δ North merican Nebula ξ ν λ Pelican Nebula Cygnus γ M29 Sadr Crescent Nebula +36 00' +38 00' +40 00' +42 00' +44 00' η 21h
Zone Master, Normal View, 10 deg FOV Zone 102, Master Map Normal View α Deneb δ North merican Nebula ξ ν λ Pelican Nebula Cygnus γ M29 Sadr Crescent Nebula +36 00' +38 00' +40 00' +42 00' +44 00' η 21h
Zone 136, Master Map Normal View
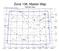 Zone Master, Normal View, 10 deg FOV Zone 136, Master Map Normal View ε Mebsuta ζ ω Mekbuda γ lhena ν µ Orion η Propus M35 Gemini χ2 Taurus χ1 +16 00' +18 00' +20 00' +22 00' +24 00' ν ξ 07h 04m 06h 56m
Zone Master, Normal View, 10 deg FOV Zone 136, Master Map Normal View ε Mebsuta ζ ω Mekbuda γ lhena ν µ Orion η Propus M35 Gemini χ2 Taurus χ1 +16 00' +18 00' +20 00' +22 00' +24 00' ν ξ 07h 04m 06h 56m
obtuse triangle close N with the nearest star 1.8' NW.
 Abell 262 - Observing Notes I observed the cluster on eight occasions and identified a total of 47 cluster members down to photographic magnitude 15.7, the majority of which are so-called anonymous galaxies
Abell 262 - Observing Notes I observed the cluster on eight occasions and identified a total of 47 cluster members down to photographic magnitude 15.7, the majority of which are so-called anonymous galaxies
A Tour of the Messier Catalog. ~~ in ~~ Eight Spellbinding and Enlightening Episodes. ~~ This Being Episode Three ~~
 A Tour of the Messier Catalog ~~ in ~~ Eight Spellbinding and Enlightening Episodes ~~ This Being Episode Three ~~ Globulars and Galaxies Warm-up for The Realm M83 Spiral Galaxy Constellation Hydra
A Tour of the Messier Catalog ~~ in ~~ Eight Spellbinding and Enlightening Episodes ~~ This Being Episode Three ~~ Globulars and Galaxies Warm-up for The Realm M83 Spiral Galaxy Constellation Hydra
A Tour of the Messier Catalog. ~~ in ~~ Eight Spellbinding and Enlightening Episodes. ~~ This Being Episode Seven ~~ One Last Slice of Summer Pie
 A Tour of the Messier Catalog ~~ in ~~ Eight Spellbinding and Enlightening Episodes ~~ This Being Episode Seven ~~ One Last Slice of Summer Pie M75 Globular Cluster Constellation Sagittarius 20 : 06.1
A Tour of the Messier Catalog ~~ in ~~ Eight Spellbinding and Enlightening Episodes ~~ This Being Episode Seven ~~ One Last Slice of Summer Pie M75 Globular Cluster Constellation Sagittarius 20 : 06.1
A Tour of the Messier Catalog. ~~ in ~~ Eight Spellbinding and Enlightening Episodes. ~~ This Being Episode Six ~~ Voyage to the Center of the Galaxy
 A Tour of the Messier Catalog ~~ in ~~ Eight Spellbinding and Enlightening Episodes ~~ This Being Episode Six ~~ Voyage to the Center of the Galaxy M11 Open Cluster Constellation Scutum 18 : 51.1 (h:m)
A Tour of the Messier Catalog ~~ in ~~ Eight Spellbinding and Enlightening Episodes ~~ This Being Episode Six ~~ Voyage to the Center of the Galaxy M11 Open Cluster Constellation Scutum 18 : 51.1 (h:m)
Basic Properties of the Stars
 Basic Properties of the Stars The Sun-centered model of the solar system laid out by Copernicus in De Revolutionibus (1543) made a very specific prediction: that the nearby stars should exhibit parallax
Basic Properties of the Stars The Sun-centered model of the solar system laid out by Copernicus in De Revolutionibus (1543) made a very specific prediction: that the nearby stars should exhibit parallax
University of Naples Federico II, Academic Year Istituzioni di Astrofisica, read by prof. Massimo Capaccioli. Lecture 16
 University of Naples Federico II, Academic Year 2011-2012 Istituzioni di Astrofisica, read by prof. Massimo Capaccioli Lecture 16 Stellar populations Walter Baade (1893-1960) Learning outcomes The student
University of Naples Federico II, Academic Year 2011-2012 Istituzioni di Astrofisica, read by prof. Massimo Capaccioli Lecture 16 Stellar populations Walter Baade (1893-1960) Learning outcomes The student
Sheet1. Page 1. Object R.A. DEC Mag Type NGC SMC NGC NGC
 Object R.A. DEC Mag Type Const NGC 104 0 24.1-72 5 4.5 GbCl Tuc SMC 0 52.8-72 50 2.7 Glxy Tuc NGC 362 1 3.2-70 51 6.6 GbCl Tuc NGC 1261 3 12.3-55 13 8.4 GbCl Hor NGC 1851 5 14.1-40 3 7.2 GbCl Col LMC 5
Object R.A. DEC Mag Type Const NGC 104 0 24.1-72 5 4.5 GbCl Tuc SMC 0 52.8-72 50 2.7 Glxy Tuc NGC 362 1 3.2-70 51 6.6 GbCl Tuc NGC 1261 3 12.3-55 13 8.4 GbCl Hor NGC 1851 5 14.1-40 3 7.2 GbCl Col LMC 5
Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy
 Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy Guidepost This chapter plays three parts in our cosmic drama. First, it introduces the concept of a galaxy. Second, it discusses our home, the Milky Way Galaxy, a natural
Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy Guidepost This chapter plays three parts in our cosmic drama. First, it introduces the concept of a galaxy. Second, it discusses our home, the Milky Way Galaxy, a natural
BAS - Monthly Sky Guide
 BAS - Monthly Sky Guide April 2018 The Sun sets earlier now and so we can get some extra observing hours each evening. The outer arms of our Milky Way Galaxy now lie across the low southern sky and looking
BAS - Monthly Sky Guide April 2018 The Sun sets earlier now and so we can get some extra observing hours each evening. The outer arms of our Milky Way Galaxy now lie across the low southern sky and looking
Binocular Universe: Here s the Poop
 Binocular Universe: Here s the Poop March 2012 Phil Harrington If you look at an old star map of the late winter sky created 250 or more years ago, you'll find a huge, unfamiliar constellation dominating
Binocular Universe: Here s the Poop March 2012 Phil Harrington If you look at an old star map of the late winter sky created 250 or more years ago, you'll find a huge, unfamiliar constellation dominating
Binocular Universe: The Table of Scorpius. July Phil Harrington
 Binocular Universe: The Table of Scorpius July 2011 Phil Harrington Last July, this column visited M6 and M7, two of the finest open star clusters visible through binoculars in the summer or for that matter,
Binocular Universe: The Table of Scorpius July 2011 Phil Harrington Last July, this column visited M6 and M7, two of the finest open star clusters visible through binoculars in the summer or for that matter,
JEWELS of the COSMIC DEEP Messier's first guide to the night sky
 JEWELS of the COSMIC DEEP Messier's first guide to the night sky Shane L. Larson USU Physics & Cache Valley Stargazers s.larson@usu.edu Cache Valley Stargazers 12 March 2010 M78 IN ORION 1 Storyline What
JEWELS of the COSMIC DEEP Messier's first guide to the night sky Shane L. Larson USU Physics & Cache Valley Stargazers s.larson@usu.edu Cache Valley Stargazers 12 March 2010 M78 IN ORION 1 Storyline What
M3 Globular Cluster Chart 6 Canes Venatici RA 13h 42.2m Dec m. Size 18 Mag 6.3 Difficulty Medium. Equipment Requires binoculars
 M3 Globular Cluster Chart 6 Canes Venatici RA 13h 42.2m Dec +28 23m Size 18 Mag 6.3 Difficulty Medium Requires binoculars Locate Arcturus the brightest star in Bootes Locate Cor Caroli the brightest star
M3 Globular Cluster Chart 6 Canes Venatici RA 13h 42.2m Dec +28 23m Size 18 Mag 6.3 Difficulty Medium Requires binoculars Locate Arcturus the brightest star in Bootes Locate Cor Caroli the brightest star
Gaia News:Counting down to launch A. Vallenari. INAF, Padova Astronomical Observatory on behalf of DPACE
 Gaia News:Counting down to launch A. Vallenari INAF, Padova Astronomical Observatory on behalf of DPACE Outline Gaia Spacecraft status The Gaia sky Gaia open and globular clusters From data to science:
Gaia News:Counting down to launch A. Vallenari INAF, Padova Astronomical Observatory on behalf of DPACE Outline Gaia Spacecraft status The Gaia sky Gaia open and globular clusters From data to science:
The Great Debate: The Size of the Universe (1920)
 The Great Debate: The Size of the Universe (1920) Heber Curtis Our Galaxy is rather small, with Sun near the center. 30,000 LY diameter. Universe composed of many separate galaxies Spiral nebulae = island
The Great Debate: The Size of the Universe (1920) Heber Curtis Our Galaxy is rather small, with Sun near the center. 30,000 LY diameter. Universe composed of many separate galaxies Spiral nebulae = island
The Milky Way. Overview: Number of Stars Mass Shape Size Age Sun s location. First ideas about MW structure. Wide-angle photo of the Milky Way
 Figure 70.01 The Milky Way Wide-angle photo of the Milky Way Overview: Number of Stars Mass Shape Size Age Sun s location First ideas about MW structure Figure 70.03 Shapely (~1900): The system of globular
Figure 70.01 The Milky Way Wide-angle photo of the Milky Way Overview: Number of Stars Mass Shape Size Age Sun s location First ideas about MW structure Figure 70.03 Shapely (~1900): The system of globular
The stars Delta Velorum and Kappa Velorum in Vela, and Iota Carinae and Epsilon Carinae in Carina.
 Asterism False Cross The False Cross lies between the constellations Carina and Vela. The stars Delta Velorum and Kappa Velorum in Vela, and Iota Carinae and Epsilon Carinae in Carina. Left the border
Asterism False Cross The False Cross lies between the constellations Carina and Vela. The stars Delta Velorum and Kappa Velorum in Vela, and Iota Carinae and Epsilon Carinae in Carina. Left the border
Lecture 16 The Measuring the Stars 3/26/2018
 Lecture 16 The Measuring the Stars 3/26/2018 Test 2 Results D C B A Questions that I thought were unfair: 13, 18, 25, 76, 77, 80 Curved from 85 to 79 Measuring stars How far away are they? How bright are
Lecture 16 The Measuring the Stars 3/26/2018 Test 2 Results D C B A Questions that I thought were unfair: 13, 18, 25, 76, 77, 80 Curved from 85 to 79 Measuring stars How far away are they? How bright are
MONTHLY OBSERVER S CHALLENGE Las Vegas Astronomical Society
 MONTHLY OBSERVER S CHALLENGE Las Vegas Astronomical Society Compiled by: Roger Ivester, Boiling Springs, North Carolina & Fred Rayworth, Las Vegas, Nevada Introduction March 2009 NGC-2403 (Caldwell 7)
MONTHLY OBSERVER S CHALLENGE Las Vegas Astronomical Society Compiled by: Roger Ivester, Boiling Springs, North Carolina & Fred Rayworth, Las Vegas, Nevada Introduction March 2009 NGC-2403 (Caldwell 7)
National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Glos. Glossary. of Astronomy. Terms. Related to Galaxies
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Glos of Astronomy Glossary Terms Related to Galaxies Asterism: A pattern formed by stars not recognized as one of the official 88 constellations. Examples
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Glos of Astronomy Glossary Terms Related to Galaxies Asterism: A pattern formed by stars not recognized as one of the official 88 constellations. Examples
Star clusters (and other neat stuff) in Ophiuchus
 Star clusters (and other neat stuff) in Ophiuchus Michael L Allen mlfa.astro@gmail.com Palouse Divide Lodge Star Party 2016 Michael L Allen Ophiuchus PDLSP 16 1 / 19 Quick facts 11th-largest constellation
Star clusters (and other neat stuff) in Ophiuchus Michael L Allen mlfa.astro@gmail.com Palouse Divide Lodge Star Party 2016 Michael L Allen Ophiuchus PDLSP 16 1 / 19 Quick facts 11th-largest constellation
Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way
 Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way Almost everything we see in the night sky belongs to the Milky Way We see most of the Milky Way as a faint band of light across the sky From the outside, our
Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way Almost everything we see in the night sky belongs to the Milky Way We see most of the Milky Way as a faint band of light across the sky From the outside, our
Binocular Universe: February 2011
 Binocular Universe: February 2011 Phil Harrington G ood evening, Mr. Barbee. On February 1, 1786 William Herschel, discovered a rift of emission nebulosity due south of the star Alnitak (Zeta [ζ] Orionis)
Binocular Universe: February 2011 Phil Harrington G ood evening, Mr. Barbee. On February 1, 1786 William Herschel, discovered a rift of emission nebulosity due south of the star Alnitak (Zeta [ζ] Orionis)
The Milky Way. Mass of the Galaxy, Part 2. Mass of the Galaxy, Part 1. Phys1403 Stars and Galaxies Instructor: Dr. Goderya
 Foundations Chapter of Astronomy 15 13e Our Milky Way Seeds Phys1403 Stars and Galaxies Instructor: Dr. Goderya Selected Topics in Chapter 15 A view our Milky Way? The Size of our Milky Way The Mass of
Foundations Chapter of Astronomy 15 13e Our Milky Way Seeds Phys1403 Stars and Galaxies Instructor: Dr. Goderya Selected Topics in Chapter 15 A view our Milky Way? The Size of our Milky Way The Mass of
National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Student Reading ABOUT GALAXIES
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Student Reading ABOUT GALAXIES OUR HOME PLANET, Earth, resides in a glittering city of stars called the Milky Way galaxy. Our Milky Way is one of billions
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Student Reading ABOUT GALAXIES OUR HOME PLANET, Earth, resides in a glittering city of stars called the Milky Way galaxy. Our Milky Way is one of billions
telescopes resolve it into many faint (i.e. distant) stars What does it tell us?
 The Milky Way From a dark site the Milky Way can be seen as a broad band across the sky What is it? telescopes resolve it into many faint (i.e. distant) stars What does it tell us? that we live in a spiral
The Milky Way From a dark site the Milky Way can be seen as a broad band across the sky What is it? telescopes resolve it into many faint (i.e. distant) stars What does it tell us? that we live in a spiral
Arvind Borde / AST 10, Week 8: Galaxies I
 Arvind Borde / AST 10, Week 8: Galaxies I It s been known by us, from the dawn of us, that there are stars in the sky. There are also hazy patches called nebulae: objects outside the solar system that
Arvind Borde / AST 10, Week 8: Galaxies I It s been known by us, from the dawn of us, that there are stars in the sky. There are also hazy patches called nebulae: objects outside the solar system that
Chandra: Revolution through Resolution. Martin Elvis, Chandra X-ray Center
 Chandra: Revolution through Resolution Martin Elvis, Chandra X-ray Center The Chandra X-ray Observatory Launched 5 years ago revolutionized X-ray astronomy, and all of astronomy. What is X-ray Astronomy?
Chandra: Revolution through Resolution Martin Elvis, Chandra X-ray Center The Chandra X-ray Observatory Launched 5 years ago revolutionized X-ray astronomy, and all of astronomy. What is X-ray Astronomy?
Constellations of the Month Andromeda
 Small Scope Objects: g And (Almach) 02hr 04m +42 20 R And 00hr 24m +38 34 M31! (NGC 224) M32 (NGC 221) M110 (NGC 205) 00hr 42.7m 00hr 42.7m 00hr 40.4m +41 16 +40 52 +41 41 NGC 752 01hr 58m +37 51 Big Scope
Small Scope Objects: g And (Almach) 02hr 04m +42 20 R And 00hr 24m +38 34 M31! (NGC 224) M32 (NGC 221) M110 (NGC 205) 00hr 42.7m 00hr 42.7m 00hr 40.4m +41 16 +40 52 +41 41 NGC 752 01hr 58m +37 51 Big Scope
The Discovery of Other Galaxies. 24. Normal Galaxies
 24. Normal Galaxies The discovery of other galaxies Edwin Hubble proved galaxies are very distant Edwin Hubble classified galaxies by shape Methods for determining distances to galaxies The Hubble Law
24. Normal Galaxies The discovery of other galaxies Edwin Hubble proved galaxies are very distant Edwin Hubble classified galaxies by shape Methods for determining distances to galaxies The Hubble Law
Figure 69.01a. Formation of Stars
 1. One cloud many clumps 2. Up to 1000 cores can form within 1 clump 3. Core: begins to build a star by attracting material from the cloud 4. Protostar, MS star 5. Up to 1000 stars 6. Stars usually form
1. One cloud many clumps 2. Up to 1000 cores can form within 1 clump 3. Core: begins to build a star by attracting material from the cloud 4. Protostar, MS star 5. Up to 1000 stars 6. Stars usually form
Constellations of the Month Cepheus
 Naked Eye Objects: Constellations of the Month Cepheus δ Cepheus.. Variable star, period of 5.366 days. Varies from magnitude 3.5 to 4.4 µ Cepheus.. The Garnet star Long term irregular variable red giant.
Naked Eye Objects: Constellations of the Month Cepheus δ Cepheus.. Variable star, period of 5.366 days. Varies from magnitude 3.5 to 4.4 µ Cepheus.. The Garnet star Long term irregular variable red giant.
AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy. Lecture 3: Galaxy Fundamentals
 AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy Lecture 3: Galaxy Fundamentals Galaxy Fundamentals How many stars are in a galaxy? How did galaxies form? How many galaxies are there? How far apart are they? How are they
AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy Lecture 3: Galaxy Fundamentals Galaxy Fundamentals How many stars are in a galaxy? How did galaxies form? How many galaxies are there? How far apart are they? How are they
The Milky Way Galaxy. Some thoughts. How big is it? What does it look like? How did it end up this way? What is it made up of?
 Some thoughts The Milky Way Galaxy How big is it? What does it look like? How did it end up this way? What is it made up of? Does it change 2 3 4 5 This is not a constant zoom The Milky Way Almost everything
Some thoughts The Milky Way Galaxy How big is it? What does it look like? How did it end up this way? What is it made up of? Does it change 2 3 4 5 This is not a constant zoom The Milky Way Almost everything
5. A particular star has an angle of parallax of 0.2 arcsecond. What is the distance to this star? A) 50 pc B) 2 pc C) 5 pc D) 0.
 Name: Date: 1. How far away is the nearest star beyond the Sun, in parsecs? A) between 1 and 2 pc B) about 12 pc C) about 4 pc D) between 1/2 and 1 pc 2. Parallax of a nearby star is used to estimate its
Name: Date: 1. How far away is the nearest star beyond the Sun, in parsecs? A) between 1 and 2 pc B) about 12 pc C) about 4 pc D) between 1/2 and 1 pc 2. Parallax of a nearby star is used to estimate its
FINEST SIGHTS for LX200
 FINEST SIGHTS for LX200 1. M81 UMa M81 (8) Spiral galaxy 09:56 +69.1 2. M82 UMa M82 (9) Irregular galaxy 09:56 +69.7 3. Gamma Leo *296 (3, 4)[4.5"] Double star 10:20 +19.9 4. NGC3242 Hya NGC3242 (9) Planetary
FINEST SIGHTS for LX200 1. M81 UMa M81 (8) Spiral galaxy 09:56 +69.1 2. M82 UMa M82 (9) Irregular galaxy 09:56 +69.7 3. Gamma Leo *296 (3, 4)[4.5"] Double star 10:20 +19.9 4. NGC3242 Hya NGC3242 (9) Planetary
Galaxies. The majority of known galaxies fall into one of three major classes: spirals (78 %), ellipticals (18 %) and irregulars (4 %).
 Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Friday, March 21, 2014 Reading for Exam 3: End of Section 6.6 (Type Ia binary evolution), 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A), NOT Chapter
 Friday, March 21, 2014 Reading for Exam 3: End of Section 6.6 (Type Ia binary evolution), 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A), NOT Chapter 8 (Neutron Stars), keep for Exam 4. Background: Sections
Friday, March 21, 2014 Reading for Exam 3: End of Section 6.6 (Type Ia binary evolution), 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A), NOT Chapter 8 (Neutron Stars), keep for Exam 4. Background: Sections
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. M42 The
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. M42 The
Lecture 25: The Cosmic Distance Scale Sections 25-1, 26-4 and Box 26-1
 Lecture 25: The Cosmic Distance Scale Sections 25-1, 26-4 and Box 26-1 Key Ideas The Distance Problem Geometric Distances Trigonometric Parallaxes Luminosity Distances Standard Candles Spectroscopic Parallaxes
Lecture 25: The Cosmic Distance Scale Sections 25-1, 26-4 and Box 26-1 Key Ideas The Distance Problem Geometric Distances Trigonometric Parallaxes Luminosity Distances Standard Candles Spectroscopic Parallaxes
IO March The Newsletter of the Eugene Astronomical Society EAS. Next Meeting: Thursday, March 16. PO Box 7264 Springfield, OR 97475
 IO March 2017 The Newsletter of the Eugene Astronomical Society PO Box 7264 Springfield, OR 97475 Next Meeting: Thursday, March 16 Optics workshop At this month's EAS meeting, John Walley will discuss
IO March 2017 The Newsletter of the Eugene Astronomical Society PO Box 7264 Springfield, OR 97475 Next Meeting: Thursday, March 16 Optics workshop At this month's EAS meeting, John Walley will discuss
MONTHLY OBSERVER S CHALLENGE Las Vegas Astronomical Society
 Introduction MONTHLY OBSERVER S CHALLENGE Las Vegas Astronomical Society Compiled by: Roger Ivester, Boiling Springs, North Carolina & Fred Rayworth, Las Vegas, Nevada With special assistance from: Rob
Introduction MONTHLY OBSERVER S CHALLENGE Las Vegas Astronomical Society Compiled by: Roger Ivester, Boiling Springs, North Carolina & Fred Rayworth, Las Vegas, Nevada With special assistance from: Rob
SEQUENCING THE STARS
 SEQUENCING THE STARS ROBERT J. VANDERBEI Using images acquired with modern CCD cameras, amateur astronomers can make Hertzsprung-Russell diagrams from their own images of clusters. In this way, we can
SEQUENCING THE STARS ROBERT J. VANDERBEI Using images acquired with modern CCD cameras, amateur astronomers can make Hertzsprung-Russell diagrams from their own images of clusters. In this way, we can
Astronomy 25. Astronomy 25. Anything back then that could not be seen clearly was called a nebulae. detect fuzzy light objects.
 Astronomy 25 Astronomy 25 Before the 1920 s s telescopes would detect fuzzy light objects. Anything back then that could not be seen clearly was called a nebulae. Immanuel Kant (1724-1804) 1804) Kant had
Astronomy 25 Astronomy 25 Before the 1920 s s telescopes would detect fuzzy light objects. Anything back then that could not be seen clearly was called a nebulae. Immanuel Kant (1724-1804) 1804) Kant had
Showpiece regions in the LMC
 Showpiece regions in the LMC 1) Tarantula Nebula region NGC 2070 = Tarantula Nebula (24"): at 200x unfiltered, I examined the 30 Doradus cluster = R136 cluster at the heart of the Tarantula Nebula. The
Showpiece regions in the LMC 1) Tarantula Nebula region NGC 2070 = Tarantula Nebula (24"): at 200x unfiltered, I examined the 30 Doradus cluster = R136 cluster at the heart of the Tarantula Nebula. The
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. M17 Swan
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. M17 Swan
Taurus stars membership in the Pleiades open cluster
 Taurus stars membership in the Pleiades open cluster Tadross, A. L., Hanna, M. A., Awadalla, N. S. National Research Institute of Astronomy & Geophysics, NRIAG, 11421 Helwan, Cairo, Egypt ABSTRACT In this
Taurus stars membership in the Pleiades open cluster Tadross, A. L., Hanna, M. A., Awadalla, N. S. National Research Institute of Astronomy & Geophysics, NRIAG, 11421 Helwan, Cairo, Egypt ABSTRACT In this
An Introduction to Summer & Spring Deep Sky Objects
 An Introduction to Summer & Spring Deep Sky Objects - 1 - The purpose of this program is to provide a starting point for new astronomers to begin their exploration of the sky. On a nice summer evening
An Introduction to Summer & Spring Deep Sky Objects - 1 - The purpose of this program is to provide a starting point for new astronomers to begin their exploration of the sky. On a nice summer evening
JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future
 JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future Timothy C. Beers Department of Physics & Astronomy Michigan State University & JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics Examples SDSS-I, II, and III
JINA Observations, Now and in the Near Future Timothy C. Beers Department of Physics & Astronomy Michigan State University & JINA: Joint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics Examples SDSS-I, II, and III
Galaxies: The Nature of Galaxies
 Galaxies: The Nature of Galaxies The Milky Way The Milky Way is visible to the unaided eye at most place on Earth Galileo in 1610 used his telescope to resolve the faint band into numerous stars In the
Galaxies: The Nature of Galaxies The Milky Way The Milky Way is visible to the unaided eye at most place on Earth Galileo in 1610 used his telescope to resolve the faint band into numerous stars In the
Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 14, 2017
 Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 14, 2017 Today: Ch. 19: Our Galaxy, the Milky Way Reading in Bennett: Ch 12 this week, Ch. 13 for next week 1 2 Chapter 12 The Milky Way Galaxy Band of light running around sky in
Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 14, 2017 Today: Ch. 19: Our Galaxy, the Milky Way Reading in Bennett: Ch 12 this week, Ch. 13 for next week 1 2 Chapter 12 The Milky Way Galaxy Band of light running around sky in
The Milky Way Galaxy (ch. 23)
 The Milky Way Galaxy (ch. 23) [Exceptions: We won t discuss sec. 23.7 (Galactic Center) much in class, but read it there will probably be a question or a few on it. In following lecture outline, numbers
The Milky Way Galaxy (ch. 23) [Exceptions: We won t discuss sec. 23.7 (Galactic Center) much in class, but read it there will probably be a question or a few on it. In following lecture outline, numbers
How to Understand Stars Chapter 17 How do stars differ? Is the Sun typical? Location in space. Gaia. How parallax relates to distance
 How to Understand Stars Chapter 7 How do stars differ? Is the Sun typical? Image of Orion illustrates: The huge number of stars Colors Interstellar gas Location in space Two dimensions are easy measure
How to Understand Stars Chapter 7 How do stars differ? Is the Sun typical? Image of Orion illustrates: The huge number of stars Colors Interstellar gas Location in space Two dimensions are easy measure
Star Clusters. Culpeper Astronomy Club (CAC) Meeting May 21, 2018
 Star Clusters Culpeper Astronomy Club (CAC) Meeting May 21, 2018 Overview Introductions Main Topic: Star Clusters - Open and Globular Constellations: Bootes, Canes Venatici, Coma Berenices Observing Session
Star Clusters Culpeper Astronomy Club (CAC) Meeting May 21, 2018 Overview Introductions Main Topic: Star Clusters - Open and Globular Constellations: Bootes, Canes Venatici, Coma Berenices Observing Session
A 103 Notes, Week 14, Kaufmann-Comins Chapter 15
 NEARBY GALAXIES I. Brief History A 103 Notes, Week 14, Kaufmann-Comins Chapter 15 A. Kant B. Curtis-Shapley debate C. Distance to Andromeda II. Classification of nearby galaxies: Spirals, Ellipticals,
NEARBY GALAXIES I. Brief History A 103 Notes, Week 14, Kaufmann-Comins Chapter 15 A. Kant B. Curtis-Shapley debate C. Distance to Andromeda II. Classification of nearby galaxies: Spirals, Ellipticals,
Astronomy 422! Lecture 7: The Milky Way Galaxy III!
 Astronomy 422 Lecture 7: The Milky Way Galaxy III Key concepts: The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way Radio and X-ray sources Announcements: Test next Tuesday, February 16 Chapters
Astronomy 422 Lecture 7: The Milky Way Galaxy III Key concepts: The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way Radio and X-ray sources Announcements: Test next Tuesday, February 16 Chapters
Chapter 19: The Milky Way A Classic Spiral Galaxy
 Chapter 19: The Milky Way A Classic Spiral Galaxy Here s the mystery story we ll unfold Fuzzy blobs in the sky new solar systems, or galaxies? Observational tests Herschel s map of the universe (what we
Chapter 19: The Milky Way A Classic Spiral Galaxy Here s the mystery story we ll unfold Fuzzy blobs in the sky new solar systems, or galaxies? Observational tests Herschel s map of the universe (what we
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program
 Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. M35: An
Kitt Peak Nightly Observing Program Splendors of the Universe on YOUR Night! Many pictures are links to larger versions. Click here for the Best images of the OTOP Gallery and more information. M35: An
The cosmic distance scale
 The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
Jason Kalirai (STScI)
 Jason Kalirai (STScI) Outline An Introduction: The First Hints on How Stars Evolve. Our Current Picture of Stellar Evolution A Surprise in our Backyard: The First Discovered White Dwarf Why Search for
Jason Kalirai (STScI) Outline An Introduction: The First Hints on How Stars Evolve. Our Current Picture of Stellar Evolution A Surprise in our Backyard: The First Discovered White Dwarf Why Search for
BHS Astronomy: Galaxy Classification and Evolution
 Name Pd Date BHS Astronomy: Galaxy Classification and Evolution This lab comes from http://cosmos.phy.tufts.edu/~zirbel/ast21/homework/hw-8.pdf (Tufts University) The word galaxy, having been used in English
Name Pd Date BHS Astronomy: Galaxy Classification and Evolution This lab comes from http://cosmos.phy.tufts.edu/~zirbel/ast21/homework/hw-8.pdf (Tufts University) The word galaxy, having been used in English
Binocular Targets: Omega Centauri is also a good object to view in binoculars.
 Eridanus Optics CC April 2006 Targets in Centaurus The following three targets are selected from the Constellation 'Centaurus' to present a naked eye challenge, as well as telescopic challenges. Binoculars
Eridanus Optics CC April 2006 Targets in Centaurus The following three targets are selected from the Constellation 'Centaurus' to present a naked eye challenge, as well as telescopic challenges. Binoculars
Our View of the Milky Way. 23. The Milky Way Galaxy
 23. The Milky Way Galaxy The Sun s location in the Milky Way galaxy Nonvisible Milky Way galaxy observations The Milky Way has spiral arms Dark matter in the Milky Way galaxy Density waves produce spiral
23. The Milky Way Galaxy The Sun s location in the Milky Way galaxy Nonvisible Milky Way galaxy observations The Milky Way has spiral arms Dark matter in the Milky Way galaxy Density waves produce spiral
Stellar Fossils: Globular clusters as probes of the galaxy
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Public Talks Astrophysics 7-1-2011 Stellar Fossils: Globular clusters as probes of the galaxy Shane L. Larson Utah State University Follow this and additional works
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Public Talks Astrophysics 7-1-2011 Stellar Fossils: Globular clusters as probes of the galaxy Shane L. Larson Utah State University Follow this and additional works
Stars: Stars and their Properties
 Stars: Stars and their Properties Astronomy 110 Class 10 WHEN I heard the learn d astronomer; When the proofs, the figures, were ranged in columns before me; When I was shown the charts and the diagrams,
Stars: Stars and their Properties Astronomy 110 Class 10 WHEN I heard the learn d astronomer; When the proofs, the figures, were ranged in columns before me; When I was shown the charts and the diagrams,
Properties of Stars. N. Sharp (REU/NOAO/AURA/NSF)
 Properties of Stars N. Sharp (REU/NOAO/AURA/NSF) What properties of the stars can we determine just from this image? Measuring Stars Measuring Stars Information you can get from 1 image: Position on the
Properties of Stars N. Sharp (REU/NOAO/AURA/NSF) What properties of the stars can we determine just from this image? Measuring Stars Measuring Stars Information you can get from 1 image: Position on the
PHY2083 ASTRONOMY. Dr. Rubina Kotak Office F016. Dr. Chris Watson Office S036
 PHY2083 ASTRONOMY Dr. Rubina Kotak r.kotak@qub.ac.uk Office F016 Dr. Chris Watson c.a.watson@qub.ac.uk Office S036 PHY2083 ASTRONOMY Weeks 1-6: Monday 10:00 DBB 0G.005 Wednesday 9:00 PFC 02/018 Friday
PHY2083 ASTRONOMY Dr. Rubina Kotak r.kotak@qub.ac.uk Office F016 Dr. Chris Watson c.a.watson@qub.ac.uk Office S036 PHY2083 ASTRONOMY Weeks 1-6: Monday 10:00 DBB 0G.005 Wednesday 9:00 PFC 02/018 Friday
MONTHLY OBSERVER S CHALLENGE Las Vegas Astronomical Society
 MONTHLY OBSERVER S CHALLENGE Las Vegas Astronomical Society Compiled by: Roger Ivester, Boiling Springs, North Carolina & Fred Rayworth, Las Vegas, Nevada With special assistance from: Rob Lambert, Las
MONTHLY OBSERVER S CHALLENGE Las Vegas Astronomical Society Compiled by: Roger Ivester, Boiling Springs, North Carolina & Fred Rayworth, Las Vegas, Nevada With special assistance from: Rob Lambert, Las
Goal - to understand what makes supernovae shine (Section 6.7).
 Wednesday, March 11, 2015 (Class Friday) Reading for Exam 3: Chapter 6, end of Section 6 (binary evolution), Section 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A) Background in Chapters 3, 4, 5. Background:
Wednesday, March 11, 2015 (Class Friday) Reading for Exam 3: Chapter 6, end of Section 6 (binary evolution), Section 6.7 (radioactive decay), Chapter 7 (SN 1987A) Background in Chapters 3, 4, 5. Background:
Astronomy 102 Lab: Distances to Galaxies
 Name: Astronomy 102 Lab: Distances to Galaxies You will access your textbook for this lab. Pre-Lab Assignment: As we began to talk about stars beyond the Sun, one of the most important pieces of information
Name: Astronomy 102 Lab: Distances to Galaxies You will access your textbook for this lab. Pre-Lab Assignment: As we began to talk about stars beyond the Sun, one of the most important pieces of information
The Universe o. Galaxies. The Universe of. Galaxies. Ajit Kembhavi IUCAA
 Hello! The Universe of Galaxies The Universe o Galaxies Ajit Kembhavi IUCAA Galaxies: Stars: ~10 11 Mass: ~10 11 M Sun Contain stars, gas and dust, possibly a supermassive black hole at the centre. Much
Hello! The Universe of Galaxies The Universe o Galaxies Ajit Kembhavi IUCAA Galaxies: Stars: ~10 11 Mass: ~10 11 M Sun Contain stars, gas and dust, possibly a supermassive black hole at the centre. Much
GALAXIES: BRIGHTEST AND NEAREST
 330 Brightest and Nearest Galaxies GALAXIES: BRIGHTEST AND NEAREST BY BARRY F. MADORE AND IAN STEER External galaxies are generally of such low surface brightness that they often prove disappointing objects
330 Brightest and Nearest Galaxies GALAXIES: BRIGHTEST AND NEAREST BY BARRY F. MADORE AND IAN STEER External galaxies are generally of such low surface brightness that they often prove disappointing objects
Galaxy Classification and the Hubble Deep Field
 Galaxy Classification and the Hubble Deep Field A. The Hubble Galaxy Classification Scheme Adapted from the UW Astronomy Dept., 1999 Introduction A galaxy is an assembly of between a billion (10 9 ) and
Galaxy Classification and the Hubble Deep Field A. The Hubble Galaxy Classification Scheme Adapted from the UW Astronomy Dept., 1999 Introduction A galaxy is an assembly of between a billion (10 9 ) and
Tour of the Universe!
 Tour of the Universe! Andromeda: M31 (NGC 224, the famous Andromeda Galaxy) is the nearest large galaxy to our own Milky Way galaxy. It is so bright that it is easily seen by naked eye as a faint fuzzy
Tour of the Universe! Andromeda: M31 (NGC 224, the famous Andromeda Galaxy) is the nearest large galaxy to our own Milky Way galaxy. It is so bright that it is easily seen by naked eye as a faint fuzzy
Rømer Science Mission Plan
 Institute of Physics and Astronomy, University of Aarhus Rømer Science Mission Plan Danish Small Satellite Programme Document No.(issue): MONS/IFA/MAN/PLN/0001(1) Date: 2001-05-29 Prepared by: Jørgen Christensen-Dalsgaard,
Institute of Physics and Astronomy, University of Aarhus Rømer Science Mission Plan Danish Small Satellite Programme Document No.(issue): MONS/IFA/MAN/PLN/0001(1) Date: 2001-05-29 Prepared by: Jørgen Christensen-Dalsgaard,
Catalog Information and Recommendations
 Catalog Information and Recommendations U.S. Naval Observatory, December, 2000 P.O.C. Sean Urban (seu@pyxis.usno.navy.mil) 1 Introduction The following is a list of widely used or well known catalogs for
Catalog Information and Recommendations U.S. Naval Observatory, December, 2000 P.O.C. Sean Urban (seu@pyxis.usno.navy.mil) 1 Introduction The following is a list of widely used or well known catalogs for
S part in the measurement of distances to the star clouds
 IV THE MILKY WAY INCE the star that varies in light plays a considerable S part in the measurement of distances to the star clouds of the h4ilky Way and to external galaxies I shall describe in this section
IV THE MILKY WAY INCE the star that varies in light plays a considerable S part in the measurement of distances to the star clouds of the h4ilky Way and to external galaxies I shall describe in this section
The Gaia Mission. Coryn Bailer-Jones Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany. ISYA 2016, Tehran
 The Gaia Mission Coryn Bailer-Jones Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany ISYA 2016, Tehran What Gaia should ultimately achieve high accuracy positions, parallaxes, proper motions e.g.
The Gaia Mission Coryn Bailer-Jones Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany ISYA 2016, Tehran What Gaia should ultimately achieve high accuracy positions, parallaxes, proper motions e.g.
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes Section III
 ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes Section III Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 4.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and students
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes Section III Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 4.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and students
Active Galaxies & Quasars
 Active Galaxies & Quasars Normal Galaxy Active Galaxy Galactic Nuclei Bright Active Galaxy NGC 5548 Galaxy Nucleus: Exact center of a galaxy and its immediate surroundings. If a spiral galaxy, it is the
Active Galaxies & Quasars Normal Galaxy Active Galaxy Galactic Nuclei Bright Active Galaxy NGC 5548 Galaxy Nucleus: Exact center of a galaxy and its immediate surroundings. If a spiral galaxy, it is the
Laboratory: Milky Way
 Department of Physics and Geology Laboratory: Milky Way Astronomy 1402 Equipment Needed Quantity Equipment Needed Quantity Milky Way galaxy Model 1 Ruler 1 1.1 Our Milky Way Part 1: Background Milky Way
Department of Physics and Geology Laboratory: Milky Way Astronomy 1402 Equipment Needed Quantity Equipment Needed Quantity Milky Way galaxy Model 1 Ruler 1 1.1 Our Milky Way Part 1: Background Milky Way
Neutron Stars. Neutron Stars and Black Holes. The Crab Pulsar. Discovery of Pulsars. The Crab Pulsar. Light curves of the Crab Pulsar.
 Chapter 11: Neutron Stars and Black Holes A supernova explosion of an M > 8 M sun star blows away its outer layers. Neutron Stars The central core will collapse into a compact object of ~ a few M sun.
Chapter 11: Neutron Stars and Black Holes A supernova explosion of an M > 8 M sun star blows away its outer layers. Neutron Stars The central core will collapse into a compact object of ~ a few M sun.
Galaxies. Galaxy Diversity. Galaxies, AGN and Quasars. Physics 113 Goderya
 Galaxies, AGN and Quasars Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 16 and 17 Learning Outcomes: Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars. Large variety of shapes
Galaxies, AGN and Quasars Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 16 and 17 Learning Outcomes: Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars. Large variety of shapes
MONTHLY OBSERVER S CHALLENGE Las Vegas Astronomical Society
 MONTHLY OBSERVER S CHALLENGE Las Vegas Astronomical Society Compiled by: Roger Ivester, Boiling Springs, North Carolina & Fred Rayworth, Las Vegas, Nevada With special assistance from: Rob Lambert, Las
MONTHLY OBSERVER S CHALLENGE Las Vegas Astronomical Society Compiled by: Roger Ivester, Boiling Springs, North Carolina & Fred Rayworth, Las Vegas, Nevada With special assistance from: Rob Lambert, Las
Chapter 10 Measuring the Stars
 Chapter 10 Measuring the Stars Some of the topics included in this chapter Stellar parallax Distance to the stars Stellar motion Luminosity and apparent brightness of stars The magnitude scale Stellar
Chapter 10 Measuring the Stars Some of the topics included in this chapter Stellar parallax Distance to the stars Stellar motion Luminosity and apparent brightness of stars The magnitude scale Stellar
This Week in Astronomy
 Homework #8 Due Wednesday, April 18, 11:59PM Covers Chapters 15 and 16 Estimated time to complete: 40 minutes Read chapters, review notes before starting This Week in Astronomy Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Homework #8 Due Wednesday, April 18, 11:59PM Covers Chapters 15 and 16 Estimated time to complete: 40 minutes Read chapters, review notes before starting This Week in Astronomy Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The Sun sets earlier now and so we can get some extra observing hours each evening. The outer arms of our Milky Way Galaxy now lie across the low
 The Sun sets earlier now and so we can get some extra observing hours each evening. The outer arms of our Milky Way Galaxy now lie across the low southern sky and looking towards the north and Leo we will
The Sun sets earlier now and so we can get some extra observing hours each evening. The outer arms of our Milky Way Galaxy now lie across the low southern sky and looking towards the north and Leo we will
MONTHLY OBSERVER S CHALLENGE Las Vegas Astronomical Society
 Introduction MONTHLY OBSERVER S CHALLENGE Las Vegas Astronomical Society Compiled by: Roger Ivester, Boiling Springs, North Carolina & Fred Rayworth, Las Vegas, Nevada With special assistance from: Rob
Introduction MONTHLY OBSERVER S CHALLENGE Las Vegas Astronomical Society Compiled by: Roger Ivester, Boiling Springs, North Carolina & Fred Rayworth, Las Vegas, Nevada With special assistance from: Rob
Stars & Galaxies. Chapter 27, Section 1. Composition & Temperature. Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Characteristics of Stars
 Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars Composition & Temperature Scientists use the following tools to study stars Telescope Observation Spectral
Stars & Galaxies Chapter 27 Modern Earth Science Chapter 27, Section 1 27.1 Characteristics of Stars Composition & Temperature Scientists use the following tools to study stars Telescope Observation Spectral
Winter Messier List Observing Club
 Winter Messier List Observing Club Raleigh Astronomy Club Version 1.1 24 November 2012 Introduction Welcome to the Winter Messier List Observing Club. The objects on this list represent many of the most
Winter Messier List Observing Club Raleigh Astronomy Club Version 1.1 24 November 2012 Introduction Welcome to the Winter Messier List Observing Club. The objects on this list represent many of the most
AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 QUIZ #3 - ISUSSION Ginger and Fred are two stars. Ginger s parallax is ½ of Fred s. Ginger s apparent brightness is 5 Magnitudes, Fred s is 10 Magnitudes. a) If Ginger is 1ly year away from us, how far
QUIZ #3 - ISUSSION Ginger and Fred are two stars. Ginger s parallax is ½ of Fred s. Ginger s apparent brightness is 5 Magnitudes, Fred s is 10 Magnitudes. a) If Ginger is 1ly year away from us, how far
Trumpler classification system
 Tonight s Novice topic is: An overview of the Trumpler classification system il d b i l Compiled by Jim Wessel Johnson Space Center Astronomical Society Shapley s Classification scheme a. Field Irregularities
Tonight s Novice topic is: An overview of the Trumpler classification system il d b i l Compiled by Jim Wessel Johnson Space Center Astronomical Society Shapley s Classification scheme a. Field Irregularities
Part 1. Estimates of the Sun s motion in the Milky Way Galaxy
 Homework 6: The Milky Way Astro 201 Prof. Bechtold Due: Thursday, October 21, 2010 This homework is patterned after lab assignments from the University of Michigan, and University of Washington Astronomy
Homework 6: The Milky Way Astro 201 Prof. Bechtold Due: Thursday, October 21, 2010 This homework is patterned after lab assignments from the University of Michigan, and University of Washington Astronomy
Measuring the Milky Way
 Printed: Mar/01/2013 Milky Way Lab Page MW- 13 NAME Name Group NAME Name Date Measuring the Milky Way References B Carroll and D. Ostlie, An Introduction to Modern Astrophysics (Addison-Wesley, 1996),
Printed: Mar/01/2013 Milky Way Lab Page MW- 13 NAME Name Group NAME Name Date Measuring the Milky Way References B Carroll and D. Ostlie, An Introduction to Modern Astrophysics (Addison-Wesley, 1996),
National Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event 19 May 2012 University of Central Florida Orlando, FL
 National Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event 19 May 2012 University of Central Florida Orlando, FL Artist Illustration of Red Giant, White Dwarf and Accretion Disk (Wikimedia) TEAM NUMBER: TEAM
National Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event 19 May 2012 University of Central Florida Orlando, FL Artist Illustration of Red Giant, White Dwarf and Accretion Disk (Wikimedia) TEAM NUMBER: TEAM
Imaging with SPIRIT Exposure Guide
 Imaging with SPIRIT Exposure Guide SPIRIT optical telescopes utilise extremely sensitive cameras to record the light from distant astronomical objects. Even so, exposures of several seconds up to a few
Imaging with SPIRIT Exposure Guide SPIRIT optical telescopes utilise extremely sensitive cameras to record the light from distant astronomical objects. Even so, exposures of several seconds up to a few
