Magne&c fields in HVCs
|
|
|
- Lee Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Magne&c fields in HVCs Alex S Hill Naomi McClure- Griffiths, Bob Benjamin, Ann Mao, Jay Lockman, Bryan Gaensler, Greg Madsen CSIRO ASTRONOMY & SPACE SCEINCE
2 ARI 19 July :54 Cloud life&me N HI (10 18 cm 2 ) Velocity (km s 1 ) (GSR) N HI and velocity Declination (J2000) h 58 m 56 m 54 m Galactic latitude ( ) Figure h 00 m 6 h 58 m 56 m 54 m Right ascension (J2000) Galactic longitude ( ) Left: Head-tail HI halo clouds with the outer contour at N HI = cm 2 (15.5-arcmin resolution; Putman, Saul & Putman, Mets 2011). Right: Peek, A HI high& velocity Joung cloud that (2012 shows signatures ARA&A) of interaction with the halo medium from the edge features (4-arcmin resolution; Peek et al. 2007). Putman, Saul, & Mets (2011 MNRAS) Peek et al (2007 ApJ) cloud (the fraction escaping normal to the disk is f esc 6% in this model) (Bland-Hawthorn et al. 1998; Bland-Hawthorn & Maloney 1999, 2002; Bland-Hawthorn & Putman 2001; Putman et al. 2003a). Most of the distances derived from Hα observations of HVCs have been consistent with their direct distance constraints using halo stars. Clouds without direct distance constraints (in particular 2 Magne(c the CHVCs) fields in HVCs are also Alex usually S Hilldetected in Hα emission, which is consistent with them being within 40 kpc of the Galactic disk (Tufte et al. 2002, Putman et al. 2003a). The striking Figure 5. Distance D 0 and timescale τ 0 within which a cloud of given mass will lose its total H i content. Each track represents the time sequence of one model, with each point indicating D 0 or τ 0 of the largest fragment (see Equations (3) and (4) and text). Thus, the disruption rate dm/dt increases over time. Colors denote the cloud velocities, showing that faster clouds are shorter-lived. Symbol sizes indicate model times, with large symbols for early times and small ones for late times. Note that D 0 is not a distance above the plane, but a disruption length scale. Heitsch & Putman (2009 ApJ)
3 Magne&c fields Hydrodynamics: HVCs should lose much of their neutral H before reaching the disk MagnePc fields could stabilise clouds Few numerical simulapons (Konz et al 2002, SanPllan et al 2004) or observapons to date Measure rotapon measure using Faraday rotapon RM n e B ds 3 Magne(c fields in HVCs Alex S Hill
4 o. 2, 2009 Rota&on measure ROTATION MEASURE IMAGE OF THE SKY Figure 3. Plot of 37,543 RM values over the sky north of δ = 40. Red circles are positive rotation measure and blue circles are negative. The size of the circle scales linearly with magnitude of rotation measure. Faraday rotapon towards extragalacpc point sources from NVSS, p > 0.4 mjy Taylor et al (2009 ApJ) Magne(c fields in HVCs Alex S Hill
5 HVC HVC in Leading Arm of Magellanic System Head- tail morphology H I RM > +σ RM < - σ RM < σ McClure- Griffiths et al (2010 ApJ) 5 Magne(c fields in HVCs Alex S Hill
6 HVC EsPmate magnepc field WHAM Hα: EM < 0.09 pc cm with assumppons, N(H + ) cm N(H I) > cm - 2 RM n e B L implies B +6 μg (towards observer) N(H I) (10 19 cm - 2 ) H I RM HVC > +σ RM HVC < - σ RM HVC < σ McClure- Griffiths et al (2010 ApJ) 6 Magne(c fields in HVCs Alex S Hill
7 Smith Cloud H I v GSR = +247 km/s (v LSR = +100 km/s at head) 7 Magne(c fields in HVCs Alex S Hill
8 Smith Cloud H I v GSR = +247 km/s (v LSR = +100 km/s at head) RM > 0 RM < 0 8 Magne(c fields in HVCs Alex S Hill
9 Decelerated gas v LSR +100 km/s +40 km/s 9 Magne(c fields in HVCs Alex S Hill
10 Decelerated gas v LSR +100 km/s +40 km/s 10 Magne(c fields in HVCs Alex S Hill
11 Decelerated gas v LSR +100 km/s +40 km/s 11 Magne(c fields in HVCs Alex S Hill
12 Hα, H I, and RMs +40 km/s H I +100 km/s H I +40 km/s WHAM- NSS Hα (grayscale) 12 Magne(c fields in HVCs Alex S Hill
13 Hα, H I, and RMs +40 km/s H I +100 km/s H I +40 km/s WHAM- NSS Hα (grayscale) RM HVC > 0 RM HVC < 0 13 Magne(c fields in HVCs Alex S Hill
14 Hα, H I, and RMs +40 km/s H I +100 km/s H I +40 km/s WHAM- NSS Hα (grayscale) RM HVC > 0 RM HVC < 0 n e s EM L H + B = RM 0.81n e L H + RM 0.81(L H +EM) 1/2 14 Magne(c fields in HVCs Alex S Hill
15 Hα, H I, and RMs +40 km/s H I +100 km/s H I +40 km/s WHAM- NSS Hα (grayscale) RM HVC > 0 RM HVC < 0 n e s EM L H + B = RM 0.81n e L H + RM 0.81(L H +EM) 1/2 RM = 95 rad m - 2 (σ =23 rad m - 2 ) EM = 1.1 pc cm - 6 (σ=0.7 pc cm - 6 ) B +6 μg (towards observer) 15 Magne(c fields in HVCs Alex S Hill
16 Conclusions RM signature evident in two HVCs Correlated with H I emission from HVC in Leading Arm - non- detecpon of Hα Correlated with decelerated H I and Hα in Smith Cloud - not correlated with (smooth) Hα at Smith Cloud velocity lower limit on B of 6 μg in each case - B ~ 4 μg sufficient to balance ram pressure for Leading Arm HVC These head- tail HVCs are in very different environments Real data for MHD simulapons? 16 Magne(c fields in HVCs Alex S Hill
17 Thank you Alex S Hill OCE Postdoctoral Fellow p e alex.hill@csiro.au CSIRO ASTRONOMY & SPACE SCIENCE
50 Years of Understanding Galactic Atomic Hydrogen with Parkes. Naomi McClure-Griffiths CSIRO Astronomy & Space Science
 50 Years of Understanding Galactic Atomic Hydrogen with Parkes Naomi McClure-Griffiths CSIRO Astronomy & Space Science Outline Parkes surveys of Galactic HI Large-scale distribution of HI in the Milky
50 Years of Understanding Galactic Atomic Hydrogen with Parkes Naomi McClure-Griffiths CSIRO Astronomy & Space Science Outline Parkes surveys of Galactic HI Large-scale distribution of HI in the Milky
Physical Conditions of Plasma in the Milky Way Halo. Results from the Wisconsin H-Alpha Mapper L. Matthew Haffner U.
 Physical Conditions of Plasma in the Milky Way Halo Results from the Wisconsin H-Alpha Mapper L. Matthew Haffner U. Wisconsin Madison v 2 5/28/2007 The WHAM Team! Ron Reynolds Alex Hill! Kurt Jaehnig!
Physical Conditions of Plasma in the Milky Way Halo Results from the Wisconsin H-Alpha Mapper L. Matthew Haffner U. Wisconsin Madison v 2 5/28/2007 The WHAM Team! Ron Reynolds Alex Hill! Kurt Jaehnig!
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Feb 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Feb 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Feb 2017](/thumbs/88/115123205.jpg) Draft version November 12, 218 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 THE EFFECT OF MIXING ON THE OBSERVED METALLICITY OF THE SMITH CLOUD David B. Henley, Jeffrey A. Gritton, and Robin
Draft version November 12, 218 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 THE EFFECT OF MIXING ON THE OBSERVED METALLICITY OF THE SMITH CLOUD David B. Henley, Jeffrey A. Gritton, and Robin
HI clouds near the Galactic Center:
 PHISCC 217 February 7th, Pune HI clouds near the Galactic Center: Possible tracers for a Milky-Way nuclear wind? Enrico Di Teodoro Research School of Astronomy and Astrophysics Australian National University
PHISCC 217 February 7th, Pune HI clouds near the Galactic Center: Possible tracers for a Milky-Way nuclear wind? Enrico Di Teodoro Research School of Astronomy and Astrophysics Australian National University
The Global Magneto-Ionic Medium Survey
 The Global Magneto-Ionic Medium Survey The Global Magneto-Ionic Medium Survey studying the polarized emission from the Galaxy The Global Magneto-Ionic Medium Survey GMIMS studying the polarized emission
The Global Magneto-Ionic Medium Survey The Global Magneto-Ionic Medium Survey studying the polarized emission from the Galaxy The Global Magneto-Ionic Medium Survey GMIMS studying the polarized emission
Head-Tail Clouds: Drops to Probe the Diffuse Galactic Halo
 Accepted by MNRAS Head-Tail Clouds: Drops to Probe the Diffuse Galactic Halo M. E. Putman, D. R. Saul & E. Mets arxiv:1110.0013v1 [astro-ph.ga] 30 Sep 2011 Department of Astronomy, Columbia University,
Accepted by MNRAS Head-Tail Clouds: Drops to Probe the Diffuse Galactic Halo M. E. Putman, D. R. Saul & E. Mets arxiv:1110.0013v1 [astro-ph.ga] 30 Sep 2011 Department of Astronomy, Columbia University,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Jul 2006
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper c ESO 217 June 5, 217 Physical properties of two compact high-velocity clouds possibly associated with the Leading Arm of the Magellanic System arxiv:astro-ph/67383v1
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper c ESO 217 June 5, 217 Physical properties of two compact high-velocity clouds possibly associated with the Leading Arm of the Magellanic System arxiv:astro-ph/67383v1
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 23 Jul 2008
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 23 Jul 2008 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 23 Jul 2008](/thumbs/93/118039872.jpg) APJ LETTERS, ACCEPTED 7/9/8 Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 8/22/9 A NEW SPIRAL ARM OF THE GALAXY: THE FAR 3-KPC ARM T. M. DAME AND P. THADDEUS Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics,
APJ LETTERS, ACCEPTED 7/9/8 Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 8/22/9 A NEW SPIRAL ARM OF THE GALAXY: THE FAR 3-KPC ARM T. M. DAME AND P. THADDEUS Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics,
Blas;ng Away a Dwarf Galaxy: The Tail of ESO 324- G024
 Blas;ng Away a Dwarf Galaxy: The Tail of ESO 324- G024 Megan Johnson PHISCC Workshop 16-18 March 2015 CSIRO ASTRONOMY AND SPACE SCIENCE, ATNF Collaborators Bärbel Koribalski Peter Kamphuis Jing Wang Sebas9an
Blas;ng Away a Dwarf Galaxy: The Tail of ESO 324- G024 Megan Johnson PHISCC Workshop 16-18 March 2015 CSIRO ASTRONOMY AND SPACE SCIENCE, ATNF Collaborators Bärbel Koribalski Peter Kamphuis Jing Wang Sebas9an
Thom et al. (2008), ApJ
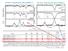 Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
Star S674 along the same LOS as Complex C Star S441 along the same LOS as Complex C Thom et al. (2008), ApJ Distances to HVCs From spectroscopy of high Galactic latitude stars at small angular separations
The Turbulent WIM: Distribution and MHD Simulations
 The Turbulent WIM: Distribution and MHD Simulations Alex S. Hill University of Wisconsin-Madison Collaborators: Robert A. Benjamin, Grzegorz Kowal, Ronald J. Reynolds, L. Matthew Haffner, Alex Lazarian
The Turbulent WIM: Distribution and MHD Simulations Alex S. Hill University of Wisconsin-Madison Collaborators: Robert A. Benjamin, Grzegorz Kowal, Ronald J. Reynolds, L. Matthew Haffner, Alex Lazarian
The Magellanic Stream Tim Connors Dr. D. Kawata Prof. B. Gibson
 High-resolution N-body Simulations of Galactic Cannibalism The Magellanic Stream Tim Connors Dr. D. Kawata Prof. B. Gibson tconnors@astro.swin.edu.au Swinburne University of Technology Page 1 of 31 July
High-resolution N-body Simulations of Galactic Cannibalism The Magellanic Stream Tim Connors Dr. D. Kawata Prof. B. Gibson tconnors@astro.swin.edu.au Swinburne University of Technology Page 1 of 31 July
Galactic Supershells and GSH Vanessa A. Moss Parkes 50th Symposium 3rd November
 Galactic Supershells and GSH 006-15+7 Vanessa A. Moss Parkes 50th Symposium 3rd November 2011 1 Contents Early history of supershells Discovery Early interpretation Surveys of supershells Northern hemisphere
Galactic Supershells and GSH 006-15+7 Vanessa A. Moss Parkes 50th Symposium 3rd November 2011 1 Contents Early history of supershells Discovery Early interpretation Surveys of supershells Northern hemisphere
S-PASS and Giant Magnetised outflows from the Centre of the Milky Way
 S-PASS and Giant Magnetised outflows from the Centre of the Milky Way Ettore Carretti The Universe as seen by Planck Noordwijk - 4 April 2013 CSIRO ASTRONOMY AND SPACE SCIENCE Outline S-PASS: S-band Polarization
S-PASS and Giant Magnetised outflows from the Centre of the Milky Way Ettore Carretti The Universe as seen by Planck Noordwijk - 4 April 2013 CSIRO ASTRONOMY AND SPACE SCIENCE Outline S-PASS: S-band Polarization
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 19 Jul 2004
 Draft version February 2, 2008 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 6/22/04 3D MHD MODELING OF THE GASEOUS STRUCTURE OF THE GALAXY: SYNTHETIC OBSERVATIONS. Gilberto C. Gómez 1 Department
Draft version February 2, 2008 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 6/22/04 3D MHD MODELING OF THE GASEOUS STRUCTURE OF THE GALAXY: SYNTHETIC OBSERVATIONS. Gilberto C. Gómez 1 Department
Mapping the Galactic halo with main-sequence and RR Lyrae stars
 EPJ Web of Conferences 19, 02002 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/20121902002 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2012 Mapping the Galactic halo with main-sequence and RR Lyrae stars B. Sesar
EPJ Web of Conferences 19, 02002 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/20121902002 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2012 Mapping the Galactic halo with main-sequence and RR Lyrae stars B. Sesar
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 21 Jan 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 21 Jan 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 21 Jan 2017](/thumbs/96/128507674.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 5 September 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Detection of a Coherent Magnetic Field in the Magellanic Bridge through Faraday Rotation J. F. Kaczmarek,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 5 September 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Detection of a Coherent Magnetic Field in the Magellanic Bridge through Faraday Rotation J. F. Kaczmarek,
6: Observing Warm Phases: Dispersion ( n e dl ) & Emission ( n
 6: Observing Warm Phases: Dispersion ( n e dl ) & Emission ( n 2 e dl ) Measure James R. Graham University of California Berkeley NGC 891 NGC 891 AY 216 2 Techniques & Components The Warm Ionized Medium
6: Observing Warm Phases: Dispersion ( n e dl ) & Emission ( n 2 e dl ) Measure James R. Graham University of California Berkeley NGC 891 NGC 891 AY 216 2 Techniques & Components The Warm Ionized Medium
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars
 Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
High Velocity Clouds: Dark Matter Dominated Failed Galaxies?
 High Velocity Clouds: Dark Matter Dominated Failed Galaxies? Leo Blitz UC Berkeley 1. HVCs and the Local Group Hypothesis 2. Four tests of the Hypothesis and why it has fallen from favor. 3. New observations
High Velocity Clouds: Dark Matter Dominated Failed Galaxies? Leo Blitz UC Berkeley 1. HVCs and the Local Group Hypothesis 2. Four tests of the Hypothesis and why it has fallen from favor. 3. New observations
ON THE ORIGIN OF ANOMALOUS VELOCITY CLOUDS IN THE MILKY WAY.
 Draft version June 12, 2006 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/26/04 ON THE ORIGIN OF ANOMALOUS VELOCITY CLOUDS IN THE MILKY WAY. Tim W. Connors 1, Daisuke Kawata 1,2, Jeremy Bailin
Draft version June 12, 2006 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/26/04 ON THE ORIGIN OF ANOMALOUS VELOCITY CLOUDS IN THE MILKY WAY. Tim W. Connors 1, Daisuke Kawata 1,2, Jeremy Bailin
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 13 Jul 2012
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 13 Jul 2012 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 13 Jul 2012](/thumbs/74/70127793.jpg) Magnetic field transport from disk to halo via the galactic chimney process in NGC 6946 George H. Heald 1 ASTRON, Postbus 2, 7990 AA Dwingeloo, The Netherlands arxiv:1206.6569v2 [astro-ph.co] 13 Jul 2012
Magnetic field transport from disk to halo via the galactic chimney process in NGC 6946 George H. Heald 1 ASTRON, Postbus 2, 7990 AA Dwingeloo, The Netherlands arxiv:1206.6569v2 [astro-ph.co] 13 Jul 2012
When it Rains, it Pours: An Abundance of New Small HI Clouds from the GALFA-HI Survey
 When it Rains, it Pours: An Aundance of New Small Clouds from the GALFA- Survey Destry R. Saul, J. E. G. Peek, J. Grcevich, M.E. Putman, et al. Columia University The Galactic Arecio L-Band Feed Array
When it Rains, it Pours: An Aundance of New Small Clouds from the GALFA- Survey Destry R. Saul, J. E. G. Peek, J. Grcevich, M.E. Putman, et al. Columia University The Galactic Arecio L-Band Feed Array
Rotation Measure Synthesis of the Local Magnetized ISM
 Rotation Measure Synthesis of the Local Magnetized ISM Maik Wolleben Covington Fellow, DRAO Outline Polarization, Faraday Rotation, and Rotation Measure Synthesis The Data: GMIMS The Global Magneto Ionic
Rotation Measure Synthesis of the Local Magnetized ISM Maik Wolleben Covington Fellow, DRAO Outline Polarization, Faraday Rotation, and Rotation Measure Synthesis The Data: GMIMS The Global Magneto Ionic
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA
 Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
Parkes MHz Rotation Measure Survey
 Parkes 300-900 MHz Rotation Measure Survey Maik Wolleben E. Carretti, J. Dickey, A. Fletcher, B. Gaensler, J. L. Han, M. Haverkorn, T. Landecker, J. Leahy, N. McClure-Griffiths, D. McConnell, W. Reich,
Parkes 300-900 MHz Rotation Measure Survey Maik Wolleben E. Carretti, J. Dickey, A. Fletcher, B. Gaensler, J. L. Han, M. Haverkorn, T. Landecker, J. Leahy, N. McClure-Griffiths, D. McConnell, W. Reich,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 10 Nov 1999
 Pulsar Astronomy 2000 and Beyond ASP Conference Series, Vol. e iπ + 1, 2000 M. Kramer, N. Wex, and R. Wielebinski, eds. The Parkes Multibeam Pulsar Survey arxiv:astro-ph/9911185v1 10 Nov 1999 F. Camilo
Pulsar Astronomy 2000 and Beyond ASP Conference Series, Vol. e iπ + 1, 2000 M. Kramer, N. Wex, and R. Wielebinski, eds. The Parkes Multibeam Pulsar Survey arxiv:astro-ph/9911185v1 10 Nov 1999 F. Camilo
Milky Way structure with Parkes
 R. Hurt: NASA/JPL- Caltech/SSC Milky Way structure with Parkes ATNF User Commi.ee Science Day: Science Drivers for Parkes Receivers Jimi Green Bolton Postdoctoral Fellow 29 October 2012 CSIRO ASTRONOMY
R. Hurt: NASA/JPL- Caltech/SSC Milky Way structure with Parkes ATNF User Commi.ee Science Day: Science Drivers for Parkes Receivers Jimi Green Bolton Postdoctoral Fellow 29 October 2012 CSIRO ASTRONOMY
Magnetic Fields in the Milky Way
 Magnetic Fields in the Milky Way Wolfgang Reich Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie Bonn Why is the Galactic B-field of interest? highest spatial resolution of B-fields clarify its role in spiral galaxies
Magnetic Fields in the Milky Way Wolfgang Reich Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie Bonn Why is the Galactic B-field of interest? highest spatial resolution of B-fields clarify its role in spiral galaxies
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Dec 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Dec 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Dec 2016](/thumbs/78/77895408.jpg) Neutral Gas Accretion onto Nearby Galaxies Felix J. Lockman arxiv:1612.00774v1 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Dec 2016 Abstract While there is no lack of evidence for the accretion of stellar systems onto nearby galaxies,
Neutral Gas Accretion onto Nearby Galaxies Felix J. Lockman arxiv:1612.00774v1 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Dec 2016 Abstract While there is no lack of evidence for the accretion of stellar systems onto nearby galaxies,
The Circulation of Ionized Gas in the Milky Way Galaxy. Andrew Eagon University of Wisconsin-Whitewater September 15, 2015
 The Circulation of Ionized Gas in the Milky Way Galaxy Andrew Eagon University of Wisconsin-Whitewater September 15, 2015 Abstract We use the Wisconsin H-alpha Mapper (WHAM) all sky survey to observe kinematic
The Circulation of Ionized Gas in the Milky Way Galaxy Andrew Eagon University of Wisconsin-Whitewater September 15, 2015 Abstract We use the Wisconsin H-alpha Mapper (WHAM) all sky survey to observe kinematic
A CATALOG OF FIELD HORIZONTAL BRANCH STARS ALIGNED WITH HIGH-VELOCITY CLOUDS
 The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 161:147 153, 2005 November # 2005. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A A CATALOG OF FIELD HORIZONTAL BRANCH STARS ALIGNED
The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 161:147 153, 2005 November # 2005. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A A CATALOG OF FIELD HORIZONTAL BRANCH STARS ALIGNED
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 20 Dec 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 20 Dec 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 20 Dec 2008](/thumbs/92/110433336.jpg) The Magellanic System: What have we learnt from FUSE? N. Lehner arxiv:0812.3977v1 [astro-ph] 20 Dec 2008 University of Notre Dame, 225 Nieuwland Science Hall Notre Dame, IN 46556 Abstract. I review some
The Magellanic System: What have we learnt from FUSE? N. Lehner arxiv:0812.3977v1 [astro-ph] 20 Dec 2008 University of Notre Dame, 225 Nieuwland Science Hall Notre Dame, IN 46556 Abstract. I review some
Testing the magnetic field models of disk galaxies with the SKA
 Testing the magnetic field models of disk galaxies with the SKA, a R. Stepanov b, R. Beck a, P. Frick b and M. Krause a a Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Auf dem Hügel 69, 3121 Bonn, Germany b
Testing the magnetic field models of disk galaxies with the SKA, a R. Stepanov b, R. Beck a, P. Frick b and M. Krause a a Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Auf dem Hügel 69, 3121 Bonn, Germany b
The Magnetic Field of the Large Magellanic Cloud Revealed Through Faraday Rotation
 The Magnetic Field of the Large Magellanic Cloud Revealed Through Faraday Rotation arxiv:astro-ph/0503226v1 9 Mar 2005 B. M. Gaensler, 1,2, M. Haverkorn, 1 L. Staveley-Smith, 3 J. M. Dickey, 4 N. M. McClure-Griffiths,
The Magnetic Field of the Large Magellanic Cloud Revealed Through Faraday Rotation arxiv:astro-ph/0503226v1 9 Mar 2005 B. M. Gaensler, 1,2, M. Haverkorn, 1 L. Staveley-Smith, 3 J. M. Dickey, 4 N. M. McClure-Griffiths,
Laboratory: Milky Way
 Department of Physics and Geology Laboratory: Milky Way Astronomy 1402 Equipment Needed Quantity Equipment Needed Quantity Milky Way galaxy Model 1 Ruler 1 1.1 Our Milky Way Part 1: Background Milky Way
Department of Physics and Geology Laboratory: Milky Way Astronomy 1402 Equipment Needed Quantity Equipment Needed Quantity Milky Way galaxy Model 1 Ruler 1 1.1 Our Milky Way Part 1: Background Milky Way
Re-fuelling the Milky Way
 Re-fuelling the Milky Way From single clouds to the full sky Daniel Lenz Supervisor: PD Dr. Jürgen Kerp Argelander-Institut für Astronomie September 30th, 2013 Daniel Lenz (AIfA) Re-fuelling the Milky
Re-fuelling the Milky Way From single clouds to the full sky Daniel Lenz Supervisor: PD Dr. Jürgen Kerp Argelander-Institut für Astronomie September 30th, 2013 Daniel Lenz (AIfA) Re-fuelling the Milky
Our Milky Way (MW) Galaxy L*, M* but not SFR*
 Our Milky Way (MW) Galaxy L*, M* but not SFR* (Our galaxy is revered as Galaxy and others are merely galaxy ;-).) (SFR is less than 5 solar mass per year) MW Structure Diagram Midplane molecular layer
Our Milky Way (MW) Galaxy L*, M* but not SFR* (Our galaxy is revered as Galaxy and others are merely galaxy ;-).) (SFR is less than 5 solar mass per year) MW Structure Diagram Midplane molecular layer
Abundance distribution in the Galactic thick disk
 Abundance distribution in the Galactic thick disk omas Bensby Lund Observatory, Department of Astronomy and eoretical Physics Discovery of thick disks (Burstein 1979, ApJ, 234, 829) Discovery of the Galactic
Abundance distribution in the Galactic thick disk omas Bensby Lund Observatory, Department of Astronomy and eoretical Physics Discovery of thick disks (Burstein 1979, ApJ, 234, 829) Discovery of the Galactic
The motions of stars in the Galaxy
 The motions of stars in the Galaxy The stars in the Galaxy define various components, that do not only differ in their spatial distribution but also in their kinematics. The dominant motion of stars (and
The motions of stars in the Galaxy The stars in the Galaxy define various components, that do not only differ in their spatial distribution but also in their kinematics. The dominant motion of stars (and
S- PASS: a new view of the polarized Sky Polarized Foregrounds for CMB Garching
 S- PASS: a new view of the polarized Sky Polarized Foregrounds for CMB Garching EJore CarreK CSIRO ASTRONOMY AND SPACE SCIENCE S- PASS: S- band PolarizaMon All Sky Survey To survey the polarized emission
S- PASS: a new view of the polarized Sky Polarized Foregrounds for CMB Garching EJore CarreK CSIRO ASTRONOMY AND SPACE SCIENCE S- PASS: S- band PolarizaMon All Sky Survey To survey the polarized emission
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies
 Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Dust-to-gas ratios of the GALFA-H I Compact Cloud Catalog
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stu498 Dust-to-gas ratios of the GALFA-H I Compact Cloud Catalog Destry R. Saul, J. E. G. Peek and M. E. Putman Department of Astronomy, Columbia University, New York, NY 10027, USA Accepted
doi:10.1093/mnras/stu498 Dust-to-gas ratios of the GALFA-H I Compact Cloud Catalog Destry R. Saul, J. E. G. Peek and M. E. Putman Department of Astronomy, Columbia University, New York, NY 10027, USA Accepted
Wanted: The best model for the distribution of electrons in the Milky Way. Dominic Schnitzeler (MPIfR), 12/7/2012
 Wanted: The best model for the distribution of electrons in the Milky Way Dominic Schnitzeler (MPIfR), 12/7/2012 schnitzeler@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de Abstract NE2001 is not the most accurate n_e model Most n_e
Wanted: The best model for the distribution of electrons in the Milky Way Dominic Schnitzeler (MPIfR), 12/7/2012 schnitzeler@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de Abstract NE2001 is not the most accurate n_e model Most n_e
Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields
 Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields 1. Introduction. Synchrotron radiation 3. Faraday rotation 4. Zeeman effect 5. Polarization of starlight 6. Summary of results References Zweibel & Heiles, Nature
Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields 1. Introduction. Synchrotron radiation 3. Faraday rotation 4. Zeeman effect 5. Polarization of starlight 6. Summary of results References Zweibel & Heiles, Nature
Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines!
 Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines Idealized 21cm spectra Example observed 21cm spectra HI densities
Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines Idealized 21cm spectra Example observed 21cm spectra HI densities
Galactic cosmic rays propagation
 Galactic cosmic rays propagation Side view of the Galaxy The Solar system is 8.5 kpc away from the galactic center. One pc is 3.10 18 cm, so we are at a distance of 2.55 10 17 km and the light from it
Galactic cosmic rays propagation Side view of the Galaxy The Solar system is 8.5 kpc away from the galactic center. One pc is 3.10 18 cm, so we are at a distance of 2.55 10 17 km and the light from it
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Dec 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Dec 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Dec 2015](/thumbs/92/108218052.jpg) Draft version April 14, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 arxiv:1512.04957v1 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Dec 2015 ON THE METALLICITY AND ORIGIN OF THE SMITH HIGH-VELOCITY CLOUD 1 Andrew
Draft version April 14, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 arxiv:1512.04957v1 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Dec 2015 ON THE METALLICITY AND ORIGIN OF THE SMITH HIGH-VELOCITY CLOUD 1 Andrew
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 13 Nov 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 13 Nov 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 13 Nov 2009](/thumbs/75/72777318.jpg) Submitted to the ApJ letters Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/01/06 ORIGIN(S) OF THE HIGHLY IONIZED HIGH-VELOCITY CLOUDS BASED ON THEIR DISTANCES 1 N. Lehner and J.C. Howk Department
Submitted to the ApJ letters Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/01/06 ORIGIN(S) OF THE HIGHLY IONIZED HIGH-VELOCITY CLOUDS BASED ON THEIR DISTANCES 1 N. Lehner and J.C. Howk Department
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 5 Sep 2006
 Draft version January 3, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/12/01 FIRST RESULTS FROM THE ARECIBO GALACTIC HI SURVEY: THE DISK/HALO INTERFACE REGION IN THE OUTER GALAXY Snežana Stanimirović
Draft version January 3, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/12/01 FIRST RESULTS FROM THE ARECIBO GALACTIC HI SURVEY: THE DISK/HALO INTERFACE REGION IN THE OUTER GALAXY Snežana Stanimirović
Large-Scale Structure of the Galactic Magnetic Field. Marijke Haverkorn & Jo-Anne Brown NRAO/UC-Berkeley University of Calgary
 Large-Scale Structure of the Galactic Magnetic Field Marijke Haverkorn & Jo-Anne Brown NRAO/UC-Berkeley University of Calgary Outline On the Large-Scale Structure of the GMF... Why do we care? What do
Large-Scale Structure of the Galactic Magnetic Field Marijke Haverkorn & Jo-Anne Brown NRAO/UC-Berkeley University of Calgary Outline On the Large-Scale Structure of the GMF... Why do we care? What do
HIGH-VELOCITY CLOUD EDGES AND MINI HIGH-VELOCITY CLOUDS G. Lyle Hoffman. E. E. Salpeter. and Michael G. Pocceschi
 The Astrophysical Journal, 576:232 240, 2002 September 1 # 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. HIGH-VELOCITY CLOUD EDGES AND MINI HIGH-VELOCITY CLOUDS G. Lyle
The Astrophysical Journal, 576:232 240, 2002 September 1 # 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. HIGH-VELOCITY CLOUD EDGES AND MINI HIGH-VELOCITY CLOUDS G. Lyle
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Apr 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Apr 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Apr 2017](/thumbs/93/112179587.jpg) The Galaxy s Veil of Excited Hydrogen Huanian Zhang 1* & Dennis Zaritsky 1 1 Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA arxiv:1704.02005v1 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Apr 2017 Abstract Many of the
The Galaxy s Veil of Excited Hydrogen Huanian Zhang 1* & Dennis Zaritsky 1 1 Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA arxiv:1704.02005v1 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Apr 2017 Abstract Many of the
Citation for published version (APA): Boomsma, R. (2007). The disk-halo connection in NGC 6946 and NGC 253 s.n.
 University of Groningen The disk-halo connection in NGC 6946 and NGC 253 Boomsma, Rense IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen The disk-halo connection in NGC 6946 and NGC 253 Boomsma, Rense IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
Felix J. Lockman ABSTRACT
 Discovery of a Population of H I Clouds in the Galactic Halo (Accepted for Publication in the Astrophysical Journal Letters) (Preprint October 14, 2002) Felix J. Lockman National Radio Astronomy Observatory
Discovery of a Population of H I Clouds in the Galactic Halo (Accepted for Publication in the Astrophysical Journal Letters) (Preprint October 14, 2002) Felix J. Lockman National Radio Astronomy Observatory
The Magellanic Stream: Circumnavigating the Galaxy
 arxiv:1511.05853v1 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Nov 2015 This article s doi: 10.1146/((please add article doi)) The Magellanic Stream: Circumnavigating the Galaxy Elena D Onghia, 1 and Andrew J. Fox, 2 1 Astronomy
arxiv:1511.05853v1 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Nov 2015 This article s doi: 10.1146/((please add article doi)) The Magellanic Stream: Circumnavigating the Galaxy Elena D Onghia, 1 and Andrew J. Fox, 2 1 Astronomy
Milky Way SKA: the ISM, star formation and stellar evolution with the SKA
 Milky Way SKA: the ISM, star formation and stellar evolution with the SKA Mark Thompson, Grazia Umana, Naomi McClure-Griffiths, Laurent Loinard, Gary Fuller, Guillem Anglada, Sergio Molinari, Raymond Oonk
Milky Way SKA: the ISM, star formation and stellar evolution with the SKA Mark Thompson, Grazia Umana, Naomi McClure-Griffiths, Laurent Loinard, Gary Fuller, Guillem Anglada, Sergio Molinari, Raymond Oonk
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 26 Jul 2005
 A High Resolution HI Study of Selected Virgo Galaxies - Preliminary Results on Gas Morphology & Extra-Planar Gas arxiv:astro-ph/0507592v1 26 Jul 2005 Aeree Chung and J. H. van Gorkom Department of Astronomy,
A High Resolution HI Study of Selected Virgo Galaxies - Preliminary Results on Gas Morphology & Extra-Planar Gas arxiv:astro-ph/0507592v1 26 Jul 2005 Aeree Chung and J. H. van Gorkom Department of Astronomy,
The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds
 The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 25 Aug 1998
 DETECTING PLANETS IN PLANETARY NEBULAE Noam Soker soker@physics.technion.ac.il arxiv:astro-ph/9808290v1 25 Aug 1998 Department of Physics, University of Haifa at Oranim Tivon 36006, Israel 2 ABSTRACT We
DETECTING PLANETS IN PLANETARY NEBULAE Noam Soker soker@physics.technion.ac.il arxiv:astro-ph/9808290v1 25 Aug 1998 Department of Physics, University of Haifa at Oranim Tivon 36006, Israel 2 ABSTRACT We
University of Groningen. The Galactic fountain as an origin for the Smith Cloud Marasco, Antonino; Fraternali, Filippo
 University of Groningen The Galactic fountain as an origin for the Smith Cloud Marasco, Antonino; Fraternali, Filippo Published in: Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters DOI: 10.1093/mnrasl/slw195
University of Groningen The Galactic fountain as an origin for the Smith Cloud Marasco, Antonino; Fraternali, Filippo Published in: Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters DOI: 10.1093/mnrasl/slw195
UNRESOLVED H ENHANCEMENTS AT HIGH GALACTIC LATITUDE IN THE WHAM SKY SURVEY MAPS
 The Astronomical Journal, 129:927 934, 2005 February # 2005. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. UNRESOLVED H ENHANCEMENTS AT HIGH GALACTIC LATITUDE IN THE WHAM SKY
The Astronomical Journal, 129:927 934, 2005 February # 2005. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. UNRESOLVED H ENHANCEMENTS AT HIGH GALACTIC LATITUDE IN THE WHAM SKY
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 2 Aug 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 2 Aug 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 2 Aug 2007](/thumbs/96/127765820.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 5 (2006) Printed 1 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Neutral hydrogen in galactic fountains C. M. Booth 1, Tom Theuns 1,2 1 Institute for Computational Cosmology,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 5 (2006) Printed 1 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Neutral hydrogen in galactic fountains C. M. Booth 1, Tom Theuns 1,2 1 Institute for Computational Cosmology,
The origin of lopsidedness in galaxies
 The Galaxy Disk in Cosmological Context Proceedings IAU Symposium No. xxx, 2008 c 2008 International Astronomical Union J. Andersen (Chief Editor), J. Bland-Hawthorn & B. Nordström, eds. The origin of
The Galaxy Disk in Cosmological Context Proceedings IAU Symposium No. xxx, 2008 c 2008 International Astronomical Union J. Andersen (Chief Editor), J. Bland-Hawthorn & B. Nordström, eds. The origin of
T. A. Oosterloo. and M. E. Putman 2
 The Astronomical Journal, 123:1953 1970, 2002 April # 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. H i FINE STRUCTURE IN MAGELLANIC TIDAL DEBRIS 1 B. P. Wakker Department
The Astronomical Journal, 123:1953 1970, 2002 April # 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. H i FINE STRUCTURE IN MAGELLANIC TIDAL DEBRIS 1 B. P. Wakker Department
FAINT, LARGE-SCALE Ha FILAMENTS IN THE MILKY WAY L. M. Haffner, R. J. Reynolds, and S. L. Tufte
 The Astrophysical Journal, 501:L83 L87, 1998 July 1 1998. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. FAINT, LARGE-SCALE Ha FILAMENTS IN THE MILKY WAY L. M. Haffner, R. J.
The Astrophysical Journal, 501:L83 L87, 1998 July 1 1998. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. FAINT, LARGE-SCALE Ha FILAMENTS IN THE MILKY WAY L. M. Haffner, R. J.
Ram Pressure Stripping in NGC 4330
 The Evolving ISM in the Milky Way & Nearby Galaxies Ram Pressure Stripping in NGC 4330 Anne Abramson 1 & Jeffrey D. P. Kenney 1 1 Astronomy Department, Yale University, P.O. Box 208101 New Haven, CT 06520-8101
The Evolving ISM in the Milky Way & Nearby Galaxies Ram Pressure Stripping in NGC 4330 Anne Abramson 1 & Jeffrey D. P. Kenney 1 1 Astronomy Department, Yale University, P.O. Box 208101 New Haven, CT 06520-8101
Using Pulsars to study the Magnetic Field in The Milky way
 Using Pulsars to study the Magnetic Field in The Milky way Dipanjan Mitra ( MPIFR Bonn) R. Wielebinski ( MPIFR Bonn) M. Kramer ( Jodrell Bank) A. Jessner ( MPIFR Bonn) MPIFR, Bonn (24 th April 2003) To
Using Pulsars to study the Magnetic Field in The Milky way Dipanjan Mitra ( MPIFR Bonn) R. Wielebinski ( MPIFR Bonn) M. Kramer ( Jodrell Bank) A. Jessner ( MPIFR Bonn) MPIFR, Bonn (24 th April 2003) To
The Vertical Structure of Warm Ionised Gas in the Milky Way
 Open Access Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia, 2008, 25, 184 200 CSIRO PUBLISHING www.publish.csiro.au/journals/pasa The Vertical Structure of Warm Ionised Gas in the Milky Way B. M.
Open Access Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia, 2008, 25, 184 200 CSIRO PUBLISHING www.publish.csiro.au/journals/pasa The Vertical Structure of Warm Ionised Gas in the Milky Way B. M.
Characterizing the Shape of the Large Magellanic Cloud's Bowshock
 Characterizing the Shape of the Large Magellanic Cloud's Bowshock Item Type text; Electronic Thesis Authors Setton, David Jonathan; Besla, Gurtina Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright
Characterizing the Shape of the Large Magellanic Cloud's Bowshock Item Type text; Electronic Thesis Authors Setton, David Jonathan; Besla, Gurtina Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright
Figure Grayscale images of IC 418. The gray levels have been selected in each image to show the nebular structure, saturating the central star.
 313 Figure 2.21. Grayscale images of IC 418. The gray levels have been selected in each image to show the nebular structure, saturating the central star. 2.21a. IC 418 J grayscale image. The main lobe
313 Figure 2.21. Grayscale images of IC 418. The gray levels have been selected in each image to show the nebular structure, saturating the central star. 2.21a. IC 418 J grayscale image. The main lobe
PROBLEM SET #1. Galactic Structure 37 pts total. due Tuesday, 2/19/2019
 PROBLEM SET #1 Galactic Structure 37 pts total due Tuesday, 2/19/2019 1. Stellar cluster problem [26 pts] The following refers to a star cluster observed on Aug 15, 2010 at about 4am UT. The cluster is
PROBLEM SET #1 Galactic Structure 37 pts total due Tuesday, 2/19/2019 1. Stellar cluster problem [26 pts] The following refers to a star cluster observed on Aug 15, 2010 at about 4am UT. The cluster is
Unusual orbits in the Andromeda galaxy Post-16
 Unusual orbits in the Andromeda galaxy Post-16 Topics covered: spectra, Doppler effect, Newton s law of gravitation, galaxy rotation curves, arc lengths, cosmological units, dark matter Teacher s Notes
Unusual orbits in the Andromeda galaxy Post-16 Topics covered: spectra, Doppler effect, Newton s law of gravitation, galaxy rotation curves, arc lengths, cosmological units, dark matter Teacher s Notes
Giant HI Hole inside the 3-kpc Ring and the North Polar Spur The Galactic Crater arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 27 Jun 2017
![Giant HI Hole inside the 3-kpc Ring and the North Polar Spur The Galactic Crater arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 27 Jun 2017 Giant HI Hole inside the 3-kpc Ring and the North Polar Spur The Galactic Crater arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 27 Jun 2017](/thumbs/88/115999804.jpg) Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan (2014) 00(0), 1 6 doi: 10.1093/pasj/xxx000 1 Giant HI Hole inside the 3-kpc Ring and the North Polar Spur The Galactic Crater arxiv:1706.08771v1 [astro-ph.ga] 27 Jun 2017 Yoshiaki
Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan (2014) 00(0), 1 6 doi: 10.1093/pasj/xxx000 1 Giant HI Hole inside the 3-kpc Ring and the North Polar Spur The Galactic Crater arxiv:1706.08771v1 [astro-ph.ga] 27 Jun 2017 Yoshiaki
The first stars and primordial IMBHs
 The first stars and primordial IMBHs Ab initio predictions of black hole merger rates by the time LISA flies? Tom Abel Penn State Initial Conditions Time Evolution z=100 z=24 z=20.4 10 comoving kpc Cosmological
The first stars and primordial IMBHs Ab initio predictions of black hole merger rates by the time LISA flies? Tom Abel Penn State Initial Conditions Time Evolution z=100 z=24 z=20.4 10 comoving kpc Cosmological
Dynamos on galactic scales, or Dynamos around us.
 Dynamos on galactic scales, or Dynamos around us. Part IV. Cluster dynamos Anvar Shukurov School of Mathematics and Statistics, Newcastle University, U.K. Outline 1. Evidence for intracluster magnetic
Dynamos on galactic scales, or Dynamos around us. Part IV. Cluster dynamos Anvar Shukurov School of Mathematics and Statistics, Newcastle University, U.K. Outline 1. Evidence for intracluster magnetic
Star Formation Law in the Milky Way
 Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 2014 000, 1 7 doi: 10.1093/pasj/xxx000 1 Star Formation Law in the Milky Way Yoshiaki SOFUE 1 and Hiroyuki NAKANISHI 2 1 Insitute of Astronomy, The University of Tokyo, Mitaka,
Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 2014 000, 1 7 doi: 10.1093/pasj/xxx000 1 Star Formation Law in the Milky Way Yoshiaki SOFUE 1 and Hiroyuki NAKANISHI 2 1 Insitute of Astronomy, The University of Tokyo, Mitaka,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 13 Oct 2006
 Accepted to ApJ: October 11, 2006 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 6/22/04 RECONSTRUCTING DECONSTRUCTION: HIGH-VELOCITY CLOUD DISTANCE THROUGH DISRUPTION MORPHOLOGY J. E. G. Peek 1, M.
Accepted to ApJ: October 11, 2006 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 6/22/04 RECONSTRUCTING DECONSTRUCTION: HIGH-VELOCITY CLOUD DISTANCE THROUGH DISRUPTION MORPHOLOGY J. E. G. Peek 1, M.
Galaxy Gas Halos and What They Can Tell Us About Galaxy Formation
 Galaxy Gas Halos and What They Can Tell Us About Galaxy Formation Ariyeh Maller CUNY Z Why Gas Halos? Gas Accretion Star Formation Stellar Populations Feedback dt Dust dm dt Gas Accretion Feedback Gas
Galaxy Gas Halos and What They Can Tell Us About Galaxy Formation Ariyeh Maller CUNY Z Why Gas Halos? Gas Accretion Star Formation Stellar Populations Feedback dt Dust dm dt Gas Accretion Feedback Gas
evident through early results from the Wisconsin Ha Mapper (WHAM) all-sky survey (Reynolds et al. 1998; Ha ner, Reynolds, & Tufte 1998).
 THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 525:799È807, 1999 November 10 ( 1999. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A MODEL FOR THE SCATTERED LIGHT CONTRIBUTION AND POLARIZATION
THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL, 525:799È807, 1999 November 10 ( 1999. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A MODEL FOR THE SCATTERED LIGHT CONTRIBUTION AND POLARIZATION
The International Galactic Plane Survey (IGPS)
 The International Galactic Plane Survey (IGPS) A Comprehensive View of the Galactic Interstellar Medium Charles Kerton - NRC Canada - HIA - DRAO The structure and evolution of a galaxy is controlled by
The International Galactic Plane Survey (IGPS) A Comprehensive View of the Galactic Interstellar Medium Charles Kerton - NRC Canada - HIA - DRAO The structure and evolution of a galaxy is controlled by
A pulsar wind nebula associated with PSR J as the powering source of TeV J
 A pulsar wind nebula associated with PSR J2032+4127 as the powering source of TeV J2032+4130 Javier Moldón Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy Extreme Astrophysics in an Ever-Changing Universe Crete,
A pulsar wind nebula associated with PSR J2032+4127 as the powering source of TeV J2032+4130 Javier Moldón Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy Extreme Astrophysics in an Ever-Changing Universe Crete,
Molecular clouds (see review in astro-ph/990382) (also CO [12.1,12.2])
![Molecular clouds (see review in astro-ph/990382) (also CO [12.1,12.2]) Molecular clouds (see review in astro-ph/990382) (also CO [12.1,12.2])](/thumbs/81/83160044.jpg) Molecular clouds (see review in astro-ph/990382) (also CO [12.1,12.2]) Massive interstellar gas clouds Up to ~10 5 M 100 s of LY in diameter. Giant Molecular Clouds (GMCs) defined to be M > 10 4 M High
Molecular clouds (see review in astro-ph/990382) (also CO [12.1,12.2]) Massive interstellar gas clouds Up to ~10 5 M 100 s of LY in diameter. Giant Molecular Clouds (GMCs) defined to be M > 10 4 M High
Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33
 Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33 Hinz, Reike et al., ApJ 154: S259 265 (2004). Presented by James Ledoux 24 µm 70 µm 160 µm Slide 1 M33 Properties Distance 840kpc = 2.7 Mlyr (1'' ~ 4 pc) Also
Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33 Hinz, Reike et al., ApJ 154: S259 265 (2004). Presented by James Ledoux 24 µm 70 µm 160 µm Slide 1 M33 Properties Distance 840kpc = 2.7 Mlyr (1'' ~ 4 pc) Also
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies
 Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES
 STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES 23. Piet van der Kruit Kapteyn Astronomical Institute University of Groningen, the Netherlands www.astro.rug.nl/ vdkruit Beijing, September 2011 Outline The local Mass
STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES 23. Piet van der Kruit Kapteyn Astronomical Institute University of Groningen, the Netherlands www.astro.rug.nl/ vdkruit Beijing, September 2011 Outline The local Mass
Knut Olsen DECam Community Workshop August 2011
 Knut Olsen DECam Community Workshop August 2011 Motivation The Magellanic Clouds are rich laboratories of astrophysical phenomena Their structure and stellar populations allow us to explore their evolution
Knut Olsen DECam Community Workshop August 2011 Motivation The Magellanic Clouds are rich laboratories of astrophysical phenomena Their structure and stellar populations allow us to explore their evolution
Halo Gas Velocities Using Multi-slit Spectroscopy
 Halo Gas Velocities Using Multi-slit Spectroscopy Cat Wu Thesis Proposal, Fall 2009 Astronomy Department New Mexico State University Outline Diffuse ionized gas; galaxy halos Origin of halo galactic fountain
Halo Gas Velocities Using Multi-slit Spectroscopy Cat Wu Thesis Proposal, Fall 2009 Astronomy Department New Mexico State University Outline Diffuse ionized gas; galaxy halos Origin of halo galactic fountain
Multiwavelength observations of the M15 intermediate-velocity cloud
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 337, 385 4 (22) Multiwavelength observations of the M15 intermediate-velocity cloud J. V. Smoker, 1 L. M. Haffner, 2 F. P. Keenan, 1 R. D. Davies 3 and D. Pollacco 1 1 Astrophysics
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 337, 385 4 (22) Multiwavelength observations of the M15 intermediate-velocity cloud J. V. Smoker, 1 L. M. Haffner, 2 F. P. Keenan, 1 R. D. Davies 3 and D. Pollacco 1 1 Astrophysics
Structure of Our Galaxy The Milkyway. More background Stars and Gas in our Galaxy
 Structure of Our Galaxy The Milkyway More background Stars and Gas in our Galaxy "What good are Mercator's North Poles and Equators Tropics, Zones, and Meridian Lines?" So the Bellman would cry, and the
Structure of Our Galaxy The Milkyway More background Stars and Gas in our Galaxy "What good are Mercator's North Poles and Equators Tropics, Zones, and Meridian Lines?" So the Bellman would cry, and the
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Jan 2002
 The Central kpc of Starbursts and AGN ASP Conference Series, Vol. xxx, 2001 J. H. Knapen, J. E. Beckman, I. Shlosman, and T. J. Mahoney Molecular Gas in The Central Kpc of Starbursts and AGN Shardha Jogee
The Central kpc of Starbursts and AGN ASP Conference Series, Vol. xxx, 2001 J. H. Knapen, J. E. Beckman, I. Shlosman, and T. J. Mahoney Molecular Gas in The Central Kpc of Starbursts and AGN Shardha Jogee
Simulating Gas Inflow at the Disk-Halo Interface
 Draft version January 18, 2019 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX62 Simulating Gas Inflow at the Disk-Halo Interface Nicole Melso, 1 Greg L. Bryan, 1, 2 and Miao Li ( 李邈 ) 2 1 Department of
Draft version January 18, 2019 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX62 Simulating Gas Inflow at the Disk-Halo Interface Nicole Melso, 1 Greg L. Bryan, 1, 2 and Miao Li ( 李邈 ) 2 1 Department of
Astrophysical Quantities
 Astr 8300 Resources Web page: http://www.astro.gsu.edu/~crenshaw/astr8300.html Electronic papers: http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abstract_service.html (ApJ, AJ, MNRAS, A&A, PASP, ARAA, etc.) General astronomy-type
Astr 8300 Resources Web page: http://www.astro.gsu.edu/~crenshaw/astr8300.html Electronic papers: http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abstract_service.html (ApJ, AJ, MNRAS, A&A, PASP, ARAA, etc.) General astronomy-type
7. THE ROTATION CURVE AND MASS OF THE GALAXY: DARK MATTER
 7. THE ROTATION CURVE AND MASS OF THE GALAXY: DARK MATTER GOALS In this lab, you will learn: 1. How to measure the speeds at which matter orbits our galaxy. 2. How to measure the rotation curve of our
7. THE ROTATION CURVE AND MASS OF THE GALAXY: DARK MATTER GOALS In this lab, you will learn: 1. How to measure the speeds at which matter orbits our galaxy. 2. How to measure the rotation curve of our
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 19 Dec 2014
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 19 Dec 2014 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 19 Dec 2014](/thumbs/93/113151948.jpg) Draft version October 10, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 PROBING THE FERMI BUBBLES IN ULTRAVIOLET ABSORPTION: A SPECTROSCOPIC SIGNATURE OF THE MILKY WAY S BICONICAL NUCLEAR
Draft version October 10, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 PROBING THE FERMI BUBBLES IN ULTRAVIOLET ABSORPTION: A SPECTROSCOPIC SIGNATURE OF THE MILKY WAY S BICONICAL NUCLEAR
The Case of the 300 kpc Long X-ray Jet in PKS at z=1.18
 SLAC-PUB-12762 astro-ph/78.1312 Extragalactic Jets: Theory and Observation from Radio to Gamma Ray ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** T. A. Rector and D. S. De Young (eds.)
SLAC-PUB-12762 astro-ph/78.1312 Extragalactic Jets: Theory and Observation from Radio to Gamma Ray ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** T. A. Rector and D. S. De Young (eds.)
galaxies: individual: NGC 6946 galaxies: spiral galaxies:
 Baltic Astronomy, vol. 25, 369 376, 2016 UNUSUAL OBJECTS IN THE SPIRAL GALAXY NGC 6946 Yu. N. Efremov Sternberg Astronomical Institute, M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Universitetskij pr. 13,
Baltic Astronomy, vol. 25, 369 376, 2016 UNUSUAL OBJECTS IN THE SPIRAL GALAXY NGC 6946 Yu. N. Efremov Sternberg Astronomical Institute, M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Universitetskij pr. 13,
STRUCTURE IN THE ROTATION MEASURE SKY
 Accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/26/04 STRUCTURE IN THE ROTATION MEASURE SKY J. M. Stil, A. R. Taylor, and C. Sunstrum Institute
Accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/26/04 STRUCTURE IN THE ROTATION MEASURE SKY J. M. Stil, A. R. Taylor, and C. Sunstrum Institute
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 28 Oct 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 28 Oct 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 28 Oct 2008](/thumbs/93/114216111.jpg) Accepted by the Astrophysical Journal Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 03/07/07 HIGH-VELOCITY CLOUDS IN THE NEARBY SPIRAL GALAXY M 83 Eric D. Miller 1, Joel N. Bregman 2, and Bart P.
Accepted by the Astrophysical Journal Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 03/07/07 HIGH-VELOCITY CLOUDS IN THE NEARBY SPIRAL GALAXY M 83 Eric D. Miller 1, Joel N. Bregman 2, and Bart P.
The Extragalactic Radio Background
 The Extragalactic Radio Background Challenges and Opportunities Al Kogut Goddard Space Flight Center Extragalactic Backgrounds Early Background Estimates T ex From Spectral Index Variations T ex = 30 80
The Extragalactic Radio Background Challenges and Opportunities Al Kogut Goddard Space Flight Center Extragalactic Backgrounds Early Background Estimates T ex From Spectral Index Variations T ex = 30 80
