Deep Inelastic Neutron Scattering Studies of Atomic Momentum Distributions in Condensed Argon and Neon*
|
|
|
- Brenda Alexina Walker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Deep nelastc Neutron Scatterng Studes of Atomc Momentum Dstrbutons n Condensed Argon and Neon* M. A. Fradkn, S.-X. Zeng, and R. O. Smmons Physcs Department and Materals Research Laboratory, Unversty of llnos at Urbana-Champagn, USA Z. Naturforsch. 48a, (993); receved December 23, 99 Usng deep nelastc neutron scatterng, drect measurements have been made, ) of the dynamc structure factor of a seres of condensed argon samples over the temperature range 8 to 8 K, near meltng (for wave-vector transfers 2 to 26 Ä - ) and ) of lqud neon, near 27 K (for wave-vector transfers.4 to 27.6 Ä - ). Neutron tme-of-flght chopper spectrometers were employed. Snglepartcle knetc energes, < k >, can be obtaned from the analyss of the Doppler-broadened recol spectrum of the target partcles. For argon the temperature dependence of < k > can be compared to expectatons from theory, from thermodynamc data, and from prevous neutron scatterng measurements on collectve vbratonal modes. For lqud neon the wave-vector-transfer dependence of J{y), the longtudnal momentum dstrbuton functon, s beng analyzed for fnal-state effects. Key words: nelastc neutron scatterng; Momentum dstrbutons. PACS Scheme 6.2.Gz, 6.2.B, 63.2.Pw.. Purpose Usng epthermal neutrons, drect measurements of sngle-partcle momentum dstrbutons n condensed matter are possble through deep nelastc scatterng. uanttes drectly related to the sngle-partcle momentum dstrbuton, such as the average snglepartcle knetc energy, < k >, a part of the total energy htherto naccessble to drect measurement, can be determned. The condensed noble gases provde a prototype famly that exhbts ranges of behavor, such as quantum to classcal, ncreasng mportance of multbody nteratomc nteractons wth ncreasng atomc number, and ncreasng lattce vbratonal anharmoncty wth decreasng mass. Determnaton of the snglepartcle knetc energy provdes nformaton as to the mportance of these behavors. 2. Method Pulsed neutron spallaton facltes, such as the Argonne Natonal Laboratory ntense Pulsed Neutron Source (PNS), are capable of producng the large flux of epthermal neutrons necessary to carry out deep nelastc neutron scatterng studes. Chopper spectrometers, n whch the ncdent neutron energy selecton s performed by a phased Ferm chopper and the fnal neutron energy s determned va tme of flght, were employed n these measurements (Fgure ). The nstruments LRMECS and HRMECS were used to take the argon data and neon data, respectvely [], n the mpulse approxmaton for neutron scatterng, where the recol of the target partcle s assumed to be free, the dynamc structure factor S A (, E) s related to the atomc momentum dstrbuton n(p) smply by S A (ß, E) = \n(p)ö(e-e r -h-p/m) dp, () + Supported by U.S. Department of Energy BES-Materals Scences under contract No. DE-FG2-9ER4439. * Presented at the Sagamore X Conference on Charge, Spn and Momentum Denstes, Konstanz, Fed. Rep. of Germany, September -7, 99. Reprnt requests to Prof. R. O. Smmons, Physcs Department, Unversty of llnos, W. Green St., Urbana, L 68, USA. where s the wave-vector transfer, E the energy transfer, E T the recol energy of the target partcle, and M the atomc mass. The argument of the delta functon expresses conservaton of energy and momentum for the scatterng process. For an sotropc Gaussan n(p), n(p) = (na)~ 32 e\p{ p 2 /A), (2) / 93 / -438 $.3/. - Please order a reprnt rather than makng your own copy. Unauthentcated Download Date //8 :3 PM
2 M. A. Fracjkn et al. Neutron Studes of Atomc Momentum Dstrbutons Sample Poston 439 Hydrogenous Sheldng Beam Montor 2 Detectors (4) Sheld Tanks Fg.. Schematc horzontal secton of the LRMECS spectrometer at PNS-ANL [], Scattered neutrons can be detected over the broad angular range to 6. where A = 2MT* a n d T* s an effectve t e m p e r a t u r e, the d y n a m c structure factor assumes the G a u s s a n form, S A (, E) = C exp { - (E - E f M2/(A h2 2)}. (3) < k > can be o b t a n e d by ntegraton over all a t o m c m o m e n t a, weghted by the m o m e n t u m dstrbuton. < k > s related to S A (, E) by < k> = (3/4)(X/M). (4) Especally at large wave-vector transfers, nelastc neutron d a t a are c o m m o n l y presented n t e r m s of J(y), the longtudnal m o m e n t u m dstrbuton f u n c t o n, nstead of S((2, E). F o r an sotropc system, J(y) s related to S(,E) by J(y) = (h/m)s(,e), () where the scalng varable s y = (M/h2)(E-ET). (6) Varous agents, such as n s t r u m e n t resoluton, multple scatterng, a n d fnal-state effects (owng to the falure of the mpulse a p p r o x m a t o n ) can cause the observed S(, E) spectrum to be n o n - G a u s s a n. T h e effects of these agents m u s t be ether reduced to a neglgble level or accounted for n order to obtan accurate m o m e n t u m dstrbutons. F o r the d a t a t a k e n on condensed argon, multple scatterng a n d nstrument resoluton were accounted for by c o n v o l u t n g a G a u s s a n J ( y ) wth a fttng functon. T h e fttng functon was determned by fttng d a t a f r o m lqud a r g o n samples, for whch t s assumed t h a t < k > s gven by Unauthentcated Download Date //8 :3 PM
3 M. A. Fracjkn et al. Neutron Studes of Atomc Momentum Dstrbutons the expanson [2] < k > = (3/2) kbt { + (/2)(@/T) 2 - ( / 2 4 ) ( / 7 T +...}, (7) where &2 = (h2/3mkb) ( A Y }. (8) F r o m molecular-dynamcs calculatons for a LennardJ o n e s lqud one can obtan, usng the L e n n a r d - J o n e s parameters of Ross and D a n o n [3], a value of 6 K/Ä 2 for the average value of the Laplacan of the potental energy for lqud a r g o n at s a t u r a t e d v a p o r pressure at a t e m p e r a t u r e of.6 K [4], We have assumed n o u r present analyss that o u r expermental condtons have satsfed the mpulse a p p r o x m a t o n a n d hence t h a t fnal-state effects are neglgble. Justfcaton for neglectng fnal-state effects n the case of lqud a r g o n can be obtaned f r o m the theoretcal w o r k of Sears []. n Sears' treatment the m e a s u r e d J(y) of an sotropc system s related to J A (y) n the mpulse a p p r o x m a t o n by J{y) = y (nverse angstroms) Fg. 2. Calculated fnal-state effects n lqud argon at = 24 Ä~. The sold curve s J A (y) for lqud argon at.6 K, taken to be a Gaussan functon havng a wdth correspondng to a sngle-partcle knetc energy of 2.7 K. The dashed curve s the frst antsymmetrc term n the Sears expanson, enlarged by a factor of for vsblty. Owng to the small sze of the antsymmetrc term the expected measured J(y) s essentally the same as J, A (y). JM-A3[d3JlA{y)/dy3] + X4[d4JA(>/d/]-..., (9) where J(y) s the measured longtudnal m o m e n t u m dstrbuton functon, J A (y) s the longtudnal m o m e n t u m dstrbuton functon n the mpulse a p p r o x m a ton, a n d A3, A4,... are wave-vector-transfer dependent coeffcents. All odd coeffcents are antsymmetrc n a n d hence antsymmetrc n y\ all even coeffcents are symmetrc n a n d symmetrc n y. n partcular, A3 = M (AY} / 36 t2, where V s the par-potental energy a n d M s the mass of the scatterer. At <2 = 2 Ä - we calculate for lqud a r g o n at.6 K the frst ant-symmetrc term at ts m a x m u m to be a p p r o x m a t e l y.% of J A (y) at that value of y. A correcton of ths sze leaves the wdth, a n d hence < k >, essentally u n c h a n g e d f r o m that of JlA(y). Ths can be seen n Fg. 2, n whch we have plotted two curves, ) JlA(y), a G a u s s a n functon havng a wdth c o r r e s p o n d n g to an energy gven by (7), a n d ) the frst antsymmetrc term n the Sears expanson enlarged by a factor of to ad vsblty. O w n g to the small sze of the frst antsymmetrc term the expected m e a s u r e d J(y), consstng of A ( y ) a n d the antsymmetrc term, would not be vsbly dfferent from J A (y) s h o w n n Fgure 2. n solds, the m a g n t u d e of fnal-state effects s stll uncertan, n part owng to the absence of realstc par dstrbuton functons a n d a c c o m p a n y n g quanttatve o u c 2 u 2 7 Temperature (K) Fg. 3. Sngle-partcle knetc energy of condensed argon versus temperature. The sold lne represents the value of < k > predcted by equpartton, (3/2) kbt. Fnte nstrument resoluton and multple scatterng have been accounted for usng a fttng functon derved from data on lqud argon. Lqud data taken at.6k were used to determne the fttng functon for the three low-temperature sold-argon data sets (open crcles), lqud data taken at 87.4 K were used for the three hgh-temperature data sets (flled crcles). calculatons of such effects. F o r present p u r p o s e s of analyss we have a s s u m e d that fnal-state effects are neglgble n o u r d a t a on sold argon, whch were taken at smlar wave-vector transfers as o u r lqudargon data. Unauthentcated Download Date //8 :3 PM
4 44 M. A. Fracjkn et al. Neutron Studes of Atomc Momentum Dstrbutons.2 r.8.4 " : -.8 ** -.2 = 3. A" h «. >. } V «, - / «V = 2.9 A.4 - y (nverse angstroms) - y (nverse angstroms) «.8 Ml - / l -,' - r = 6.2 A" r l - y (nverse angstroms) : $. A" = y (nverse angstroms) Fg. 4. Longtudnal m o m e n t u m dstrbuton functon, J(y), for lqud neon at approxmately 27 K for four wave-vector transfers. These data were collected at a mean scatterng angle of 87, at ncdent neutron energes of 2, 9, 3, and mev, respectvely. They span a range of wave-vector transfers not prevously explored, and t can been seen that the shape of J(y) progressvely changes. The explct study of fnal-state effects n the scatterng process s now possble. 3. Results for Condensed Argon 4. Data on Lqud Neon The temperature dependence of < k > for condensed argon shows a devaton from equpartton behavor at low temperatures (Fgure 3). Several models, ncludng the self-consstent-average-phonon model (SCAP) [6], are currently beng nvestgated n order to account for the observed temperature dependence. ualtatvely the temperature dependence s that expected for a system of q u a n t u m oscllators. Wth an approprate model t should be possble to deduce a value for the ground-state knetc energy of sold argon. A Debye model employs the zero-temperature lmt of the heat capacty, yeldng < k ( T = )> = (9/6) C(T = ) = 2 K, from a heat capacty <9C value of Fnegold and Phllps [7]. t s of nterest to nvestgate more explctly the doman of applcablty of the mpulse approxmaton. We have therefore undertaken to do ths on flud neon, an sotropc scatterng system for whch the Sears analyss [] should apply. Pror to our study there was a wde gap n the avalable data. The measurements of Buyers et al. [8] had a maxmum wave-vector transfer of 2. Ä " whle those of Peek et al. [9] are for wavevector transfer greater than 2 Ä ~. We studed a wde range of wave-vector transfers,.4 to 27.6 Ä ~, usng the avalable range of scatterng angles (87 to 36 ) on the ANL spectrometer H R M E C S [] and dfferent ncdent neutron energes. Unauthentcated Download Date //8 :3 PM
5 442 M. A. Fracjkn et al. Neutron Studes of Atomc Momentum Dstrbutons 442 Neon brdges the gap between the quantum behavor of condensed helum and the classcal behavor of the heaver noble gas solds. t s therefore a good system for the study of fnal-state effects n the neutron-atom scatterng process. Shown n Fg. 4 s a subset of our data on flud neon. From estmaton of the value of A 3 (7) at near Ä - one expects to see a sgnfcant dfference between J(y) and J la {y). ndeed, by comparson wth the J(y) data at larger n Fg. 4, one sees, qualtatvely, the expected change of shape, ncreased ntensty at negatve y and reduced ntensty at postve y. The data shown nclude the effects of fnte nstrument resoluton and of multple scatterng, so further analyss s underway to refne ths qualtatve result. Acknowledgements Ths research has benefted from the use of the ntense Pulsed Neutron Source (PNS) at Argonne Laboratory. Ths faclty s funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, BES-Materals Scences under contract No. W-3-9-ENG-38. [] C. K. Loong, S. keda, and J. M. Carpenter, Nucl. nstrum. Methods A 26, 38 (987). [2] V. F. Sears, Can. J. Phys. 63, 68 (98). [3] J. C. Ross and F. Danon, Dscuss Faraday Soc. 4, 97 (96). [4] L. Verlet, Phys. Rev. 9, 98 (967). [] V. F. Sears, Phys. Rev. B 3, 44 (984). [6] K. Shukla, A. Paskn, D. O. Welch, and G. J. Denes, Phys. Rev. B 24, 724 (98). [7] L. Fnegold and N. E. Phllps, Phys. Rev. 77, 383 (969). [8] W. J. L. Buyers, V. F. Sears, P. A. Lonng, and D. A. Lonng, Phys. Rev. A, 697 (97). [9] D. A. Peek, M. C. Schmdt,. Fujta, and R. O. Smmons, Phys. Rev. B 4, 967 (992). Unauthentcated Download Date //8 :3 PM
Robert Eisberg Second edition CH 09 Multielectron atoms ground states and x-ray excitations
 Quantum Physcs 量 理 Robert Esberg Second edton CH 09 Multelectron atoms ground states and x-ray exctatons 9-01 By gong through the procedure ndcated n the text, develop the tme-ndependent Schroednger equaton
Quantum Physcs 量 理 Robert Esberg Second edton CH 09 Multelectron atoms ground states and x-ray exctatons 9-01 By gong through the procedure ndcated n the text, develop the tme-ndependent Schroednger equaton
RECEIVED. Negative Transverse Impedance
 RECEVED SEP 2 3 996 OSTt > LS- 4 O C a f L W. Chou March 2, 989 (Rev. June 2, 9S9) Negatve Transverse mpedance ntroducton n Ref. ( we report an observaton that the horzontal and the vertcal loss factors
RECEVED SEP 2 3 996 OSTt > LS- 4 O C a f L W. Chou March 2, 989 (Rev. June 2, 9S9) Negatve Transverse mpedance ntroducton n Ref. ( we report an observaton that the horzontal and the vertcal loss factors
Chapter 13: Multiple Regression
 Chapter 13: Multple Regresson 13.1 Developng the multple-regresson Model The general model can be descrbed as: It smplfes for two ndependent varables: The sample ft parameter b 0, b 1, and b are used to
Chapter 13: Multple Regresson 13.1 Developng the multple-regresson Model The general model can be descrbed as: It smplfes for two ndependent varables: The sample ft parameter b 0, b 1, and b are used to
Electrical double layer: revisit based on boundary conditions
 Electrcal double layer: revst based on boundary condtons Jong U. Km Department of Electrcal and Computer Engneerng, Texas A&M Unversty College Staton, TX 77843-318, USA Abstract The electrcal double layer
Electrcal double layer: revst based on boundary condtons Jong U. Km Department of Electrcal and Computer Engneerng, Texas A&M Unversty College Staton, TX 77843-318, USA Abstract The electrcal double layer
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 do: 0.08/nature09 I. Resonant absorpton of XUV pulses n Kr + usng the reduced densty matrx approach The quantum beats nvestgated n ths paper are the result of nterference between two exctaton paths of
do: 0.08/nature09 I. Resonant absorpton of XUV pulses n Kr + usng the reduced densty matrx approach The quantum beats nvestgated n ths paper are the result of nterference between two exctaton paths of
Chapter 9: Statistical Inference and the Relationship between Two Variables
 Chapter 9: Statstcal Inference and the Relatonshp between Two Varables Key Words The Regresson Model The Sample Regresson Equaton The Pearson Correlaton Coeffcent Learnng Outcomes After studyng ths chapter,
Chapter 9: Statstcal Inference and the Relatonshp between Two Varables Key Words The Regresson Model The Sample Regresson Equaton The Pearson Correlaton Coeffcent Learnng Outcomes After studyng ths chapter,
One-sided finite-difference approximations suitable for use with Richardson extrapolation
 Journal of Computatonal Physcs 219 (2006) 13 20 Short note One-sded fnte-dfference approxmatons sutable for use wth Rchardson extrapolaton Kumar Rahul, S.N. Bhattacharyya * Department of Mechancal Engneerng,
Journal of Computatonal Physcs 219 (2006) 13 20 Short note One-sded fnte-dfference approxmatons sutable for use wth Rchardson extrapolaton Kumar Rahul, S.N. Bhattacharyya * Department of Mechancal Engneerng,
Moderator & Moderator System
 NPTL Chemcal ngneerng Nuclear Reactor Technology Moderator & Moderator System K.S. Rajan Professor, School of Chemcal & Botechnology SASTRA Unversty Jont Intatve of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page of
NPTL Chemcal ngneerng Nuclear Reactor Technology Moderator & Moderator System K.S. Rajan Professor, School of Chemcal & Botechnology SASTRA Unversty Jont Intatve of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page of
Negative Binomial Regression
 STATGRAPHICS Rev. 9/16/2013 Negatve Bnomal Regresson Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Statstcal Model... 3 Analyss Summary... 4 Analyss Optons... 7 Plot of Ftted Model... 8 Observed Versus Predcted... 10 Predctons...
STATGRAPHICS Rev. 9/16/2013 Negatve Bnomal Regresson Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Statstcal Model... 3 Analyss Summary... 4 Analyss Optons... 7 Plot of Ftted Model... 8 Observed Versus Predcted... 10 Predctons...
Susceptibility and Inverted Hysteresis Loop of Prussian Blue Analogs with Orthorhombic Structure
 Commun. Theor. Phys. 58 (202) 772 776 Vol. 58, No. 5, November 5, 202 Susceptblty and Inverted Hysteress Loop of Prussan Blue Analogs wth Orthorhombc Structure GUO An-Bang (ÁËǑ) and JIANG We ( å) School
Commun. Theor. Phys. 58 (202) 772 776 Vol. 58, No. 5, November 5, 202 Susceptblty and Inverted Hysteress Loop of Prussan Blue Analogs wth Orthorhombc Structure GUO An-Bang (ÁËǑ) and JIANG We ( å) School
CHAPTER 5 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE
 CHAPTER 5 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE Analytcal soluton s usually not possble when exctaton vares arbtrarly wth tme or f the system s nonlnear. Such problems can be solved by numercal tmesteppng
CHAPTER 5 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE Analytcal soluton s usually not possble when exctaton vares arbtrarly wth tme or f the system s nonlnear. Such problems can be solved by numercal tmesteppng
Numerical Heat and Mass Transfer
 Master degree n Mechancal Engneerng Numercal Heat and Mass Transfer 06-Fnte-Dfference Method (One-dmensonal, steady state heat conducton) Fausto Arpno f.arpno@uncas.t Introducton Why we use models and
Master degree n Mechancal Engneerng Numercal Heat and Mass Transfer 06-Fnte-Dfference Method (One-dmensonal, steady state heat conducton) Fausto Arpno f.arpno@uncas.t Introducton Why we use models and
Investigation of a New Monte Carlo Method for the Transitional Gas Flow
 Investgaton of a New Monte Carlo Method for the Transtonal Gas Flow X. Luo and Chr. Day Karlsruhe Insttute of Technology(KIT) Insttute for Techncal Physcs 7602 Karlsruhe Germany Abstract. The Drect Smulaton
Investgaton of a New Monte Carlo Method for the Transtonal Gas Flow X. Luo and Chr. Day Karlsruhe Insttute of Technology(KIT) Insttute for Techncal Physcs 7602 Karlsruhe Germany Abstract. The Drect Smulaton
Simulated Power of the Discrete Cramér-von Mises Goodness-of-Fit Tests
 Smulated of the Cramér-von Mses Goodness-of-Ft Tests Steele, M., Chaselng, J. and 3 Hurst, C. School of Mathematcal and Physcal Scences, James Cook Unversty, Australan School of Envronmental Studes, Grffth
Smulated of the Cramér-von Mses Goodness-of-Ft Tests Steele, M., Chaselng, J. and 3 Hurst, C. School of Mathematcal and Physcal Scences, James Cook Unversty, Australan School of Envronmental Studes, Grffth
PHY688, Statistical Mechanics
 Department of Physcs & Astronomy 449 ESS Bldg. Stony Brook Unversty January 31, 2017 Nuclear Astrophyscs James.Lattmer@Stonybrook.edu Thermodynamcs Internal Energy Densty and Frst Law: ε = E V = Ts P +
Department of Physcs & Astronomy 449 ESS Bldg. Stony Brook Unversty January 31, 2017 Nuclear Astrophyscs James.Lattmer@Stonybrook.edu Thermodynamcs Internal Energy Densty and Frst Law: ε = E V = Ts P +
Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2004) Lecture 23 (12/3/04) Nuclear Reactions: Energetics and Compound Nucleus
 .101 Appled Nuclear Physcs (Fall 004) Lecture 3 (1/3/04) Nuclear Reactons: Energetcs and Compound Nucleus References: W. E. Meyerhof, Elements of Nuclear Physcs (McGraw-Hll, New York, 1967), Chap 5. Among
.101 Appled Nuclear Physcs (Fall 004) Lecture 3 (1/3/04) Nuclear Reactons: Energetcs and Compound Nucleus References: W. E. Meyerhof, Elements of Nuclear Physcs (McGraw-Hll, New York, 1967), Chap 5. Among
Experimental Studies of Quasi-fission Reactions. B.B.Back, B.G.Glagola, D.Henderson, S.B.Kaufman, J.G.Keller, S.J.Sanders, F.Videbaek, and B.D.
 Expermental Studes of Quas-fsson Reactons The submtted manuscrpt hs been authored by a contractor o the U. S. Government under contract No. W-31 19-ENG-3B. Accordmglv. the U. S- Government retans a nonexclusve,
Expermental Studes of Quas-fsson Reactons The submtted manuscrpt hs been authored by a contractor o the U. S. Government under contract No. W-31 19-ENG-3B. Accordmglv. the U. S- Government retans a nonexclusve,
Supplementary Notes for Chapter 9 Mixture Thermodynamics
 Supplementary Notes for Chapter 9 Mxture Thermodynamcs Key ponts Nne major topcs of Chapter 9 are revewed below: 1. Notaton and operatonal equatons for mxtures 2. PVTN EOSs for mxtures 3. General effects
Supplementary Notes for Chapter 9 Mxture Thermodynamcs Key ponts Nne major topcs of Chapter 9 are revewed below: 1. Notaton and operatonal equatons for mxtures 2. PVTN EOSs for mxtures 3. General effects
Psychology 282 Lecture #24 Outline Regression Diagnostics: Outliers
 Psychology 282 Lecture #24 Outlne Regresson Dagnostcs: Outlers In an earler lecture we studed the statstcal assumptons underlyng the regresson model, ncludng the followng ponts: Formal statement of assumptons.
Psychology 282 Lecture #24 Outlne Regresson Dagnostcs: Outlers In an earler lecture we studed the statstcal assumptons underlyng the regresson model, ncludng the followng ponts: Formal statement of assumptons.
Electron-Impact Double Ionization of the H 2
 I R A P 6(), Dec. 5, pp. 9- Electron-Impact Double Ionzaton of the H olecule Internatonal Scence Press ISSN: 9-59 Electron-Impact Double Ionzaton of the H olecule. S. PINDZOLA AND J. COLGAN Department
I R A P 6(), Dec. 5, pp. 9- Electron-Impact Double Ionzaton of the H olecule Internatonal Scence Press ISSN: 9-59 Electron-Impact Double Ionzaton of the H olecule. S. PINDZOLA AND J. COLGAN Department
Uncertainty as the Overlap of Alternate Conditional Distributions
 Uncertanty as the Overlap of Alternate Condtonal Dstrbutons Olena Babak and Clayton V. Deutsch Centre for Computatonal Geostatstcs Department of Cvl & Envronmental Engneerng Unversty of Alberta An mportant
Uncertanty as the Overlap of Alternate Condtonal Dstrbutons Olena Babak and Clayton V. Deutsch Centre for Computatonal Geostatstcs Department of Cvl & Envronmental Engneerng Unversty of Alberta An mportant
Physics 607 Exam 1. ( ) = 1, Γ( z +1) = zγ( z) x n e x2 dx = 1. e x2
 Physcs 607 Exam 1 Please be well-organzed, and show all sgnfcant steps clearly n all problems. You are graded on your wor, so please do not just wrte down answers wth no explanaton! Do all your wor on
Physcs 607 Exam 1 Please be well-organzed, and show all sgnfcant steps clearly n all problems. You are graded on your wor, so please do not just wrte down answers wth no explanaton! Do all your wor on
STATISTICAL MECHANICS
 STATISTICAL MECHANICS Thermal Energy Recall that KE can always be separated nto 2 terms: KE system = 1 2 M 2 total v CM KE nternal Rgd-body rotaton and elastc / sound waves Use smplfyng assumptons KE of
STATISTICAL MECHANICS Thermal Energy Recall that KE can always be separated nto 2 terms: KE system = 1 2 M 2 total v CM KE nternal Rgd-body rotaton and elastc / sound waves Use smplfyng assumptons KE of
/ n ) are compared. The logic is: if the two
 STAT C141, Sprng 2005 Lecture 13 Two sample tests One sample tests: examples of goodness of ft tests, where we are testng whether our data supports predctons. Two sample tests: called as tests of ndependence
STAT C141, Sprng 2005 Lecture 13 Two sample tests One sample tests: examples of goodness of ft tests, where we are testng whether our data supports predctons. Two sample tests: called as tests of ndependence
Chapter 4. Velocity analysis
 1 Chapter 4 Velocty analyss Introducton The objectve of velocty analyss s to determne the sesmc veloctes of layers n the subsurface. Sesmc veloctes are used n many processng and nterpretaton stages such
1 Chapter 4 Velocty analyss Introducton The objectve of velocty analyss s to determne the sesmc veloctes of layers n the subsurface. Sesmc veloctes are used n many processng and nterpretaton stages such
Georgia Tech PHYS 6124 Mathematical Methods of Physics I
 Georga Tech PHYS 624 Mathematcal Methods of Physcs I Instructor: Predrag Cvtanovć Fall semester 202 Homework Set #7 due October 30 202 == show all your work for maxmum credt == put labels ttle legends
Georga Tech PHYS 624 Mathematcal Methods of Physcs I Instructor: Predrag Cvtanovć Fall semester 202 Homework Set #7 due October 30 202 == show all your work for maxmum credt == put labels ttle legends
Uncertainty in measurements of power and energy on power networks
 Uncertanty n measurements of power and energy on power networks E. Manov, N. Kolev Department of Measurement and Instrumentaton, Techncal Unversty Sofa, bul. Klment Ohrdsk No8, bl., 000 Sofa, Bulgara Tel./fax:
Uncertanty n measurements of power and energy on power networks E. Manov, N. Kolev Department of Measurement and Instrumentaton, Techncal Unversty Sofa, bul. Klment Ohrdsk No8, bl., 000 Sofa, Bulgara Tel./fax:
Wilbur and Ague 4 WILBUR AND AGUE; APPENDIX DR1. Two-dimensional chemical maps as well as chemical profiles were done at 15 kv using
 DR2006139 Wlbur and Ague 4 WILBUR AND AGUE; APPENDIX DR1 MINERAL ANALYSES Two-dmensonal chemcal maps as well as chemcal profles were done at 15 kv usng the JEOL JXA-8600 electron mcroprobe at Yale Unversty
DR2006139 Wlbur and Ague 4 WILBUR AND AGUE; APPENDIX DR1 MINERAL ANALYSES Two-dmensonal chemcal maps as well as chemcal profles were done at 15 kv usng the JEOL JXA-8600 electron mcroprobe at Yale Unversty
The Exact Formulation of the Inverse of the Tridiagonal Matrix for Solving the 1D Poisson Equation with the Finite Difference Method
 Journal of Electromagnetc Analyss and Applcatons, 04, 6, 0-08 Publshed Onlne September 04 n ScRes. http://www.scrp.org/journal/jemaa http://dx.do.org/0.46/jemaa.04.6000 The Exact Formulaton of the Inverse
Journal of Electromagnetc Analyss and Applcatons, 04, 6, 0-08 Publshed Onlne September 04 n ScRes. http://www.scrp.org/journal/jemaa http://dx.do.org/0.46/jemaa.04.6000 The Exact Formulaton of the Inverse
DETERMINATION OF UNCERTAINTY ASSOCIATED WITH QUANTIZATION ERRORS USING THE BAYESIAN APPROACH
 Proceedngs, XVII IMEKO World Congress, June 7, 3, Dubrovn, Croata Proceedngs, XVII IMEKO World Congress, June 7, 3, Dubrovn, Croata TC XVII IMEKO World Congress Metrology n the 3rd Mllennum June 7, 3,
Proceedngs, XVII IMEKO World Congress, June 7, 3, Dubrovn, Croata Proceedngs, XVII IMEKO World Congress, June 7, 3, Dubrovn, Croata TC XVII IMEKO World Congress Metrology n the 3rd Mllennum June 7, 3,
Physics 181. Particle Systems
 Physcs 181 Partcle Systems Overvew In these notes we dscuss the varables approprate to the descrpton of systems of partcles, ther defntons, ther relatons, and ther conservatons laws. We consder a system
Physcs 181 Partcle Systems Overvew In these notes we dscuss the varables approprate to the descrpton of systems of partcles, ther defntons, ther relatons, and ther conservatons laws. We consder a system
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION
 NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION 1 Introducton Dfferentaton s a method to compute the rate at whch a dependent output y changes wth respect to the change n the ndependent nput x. Ths rate of change s called the
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION 1 Introducton Dfferentaton s a method to compute the rate at whch a dependent output y changes wth respect to the change n the ndependent nput x. Ths rate of change s called the
Neutral-Current Neutrino-Nucleus Inelastic Reactions for Core Collapse Supernovae
 Neutral-Current Neutrno-Nucleus Inelastc Reactons for Core Collapse Supernovae A. Juodagalvs Teornės Fzkos r Astronomjos Insttutas, Lthuana E-mal: andrusj@tpa.lt J. M. Sampao Centro de Físca Nuclear da
Neutral-Current Neutrno-Nucleus Inelastc Reactons for Core Collapse Supernovae A. Juodagalvs Teornės Fzkos r Astronomjos Insttutas, Lthuana E-mal: andrusj@tpa.lt J. M. Sampao Centro de Físca Nuclear da
More metrics on cartesian products
 More metrcs on cartesan products If (X, d ) are metrc spaces for 1 n, then n Secton II4 of the lecture notes we defned three metrcs on X whose underlyng topologes are the product topology The purpose of
More metrcs on cartesan products If (X, d ) are metrc spaces for 1 n, then n Secton II4 of the lecture notes we defned three metrcs on X whose underlyng topologes are the product topology The purpose of
ITTC - Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 Page of 9 able of Contents UCERAIY AALYSIS - EXAMPLE FOR WAERJE PROPULSIO ES... 2. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. EXAMPLE FOR WAERJE PROPULSIO ES... 2 2. est Desgn... 2 2.2 Measurement Systems and Procedure...
Page of 9 able of Contents UCERAIY AALYSIS - EXAMPLE FOR WAERJE PROPULSIO ES... 2. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. EXAMPLE FOR WAERJE PROPULSIO ES... 2 2. est Desgn... 2 2.2 Measurement Systems and Procedure...
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.scencemag.org/cg/content/full/2/7/e1600304/dc1 Supplementary Materals for Interface-drven topologcal Hall effect n SrRuO3-SrIrO3 blayer Jobu Matsuno, Naok Ogawa, Kenj Yasuda, Fumtaka Kagawa, Wataru
advances.scencemag.org/cg/content/full/2/7/e1600304/dc1 Supplementary Materals for Interface-drven topologcal Hall effect n SrRuO3-SrIrO3 blayer Jobu Matsuno, Naok Ogawa, Kenj Yasuda, Fumtaka Kagawa, Wataru
Temperature. Chapter Heat Engine
 Chapter 3 Temperature In prevous chapters of these notes we ntroduced the Prncple of Maxmum ntropy as a technque for estmatng probablty dstrbutons consstent wth constrants. In Chapter 9 we dscussed the
Chapter 3 Temperature In prevous chapters of these notes we ntroduced the Prncple of Maxmum ntropy as a technque for estmatng probablty dstrbutons consstent wth constrants. In Chapter 9 we dscussed the
Amplification and Relaxation of Electron Spin Polarization in Semiconductor Devices
 Amplfcaton and Relaxaton of Electron Spn Polarzaton n Semconductor Devces Yury V. Pershn and Vladmr Prvman Center for Quantum Devce Technology, Clarkson Unversty, Potsdam, New York 13699-570, USA Spn Relaxaton
Amplfcaton and Relaxaton of Electron Spn Polarzaton n Semconductor Devces Yury V. Pershn and Vladmr Prvman Center for Quantum Devce Technology, Clarkson Unversty, Potsdam, New York 13699-570, USA Spn Relaxaton
This column is a continuation of our previous column
 Comparson of Goodness of Ft Statstcs for Lnear Regresson, Part II The authors contnue ther dscusson of the correlaton coeffcent n developng a calbraton for quanttatve analyss. Jerome Workman Jr. and Howard
Comparson of Goodness of Ft Statstcs for Lnear Regresson, Part II The authors contnue ther dscusson of the correlaton coeffcent n developng a calbraton for quanttatve analyss. Jerome Workman Jr. and Howard
= z 20 z n. (k 20) + 4 z k = 4
 Problem Set #7 solutons 7.2.. (a Fnd the coeffcent of z k n (z + z 5 + z 6 + z 7 + 5, k 20. We use the known seres expanson ( n+l ( z l l z n below: (z + z 5 + z 6 + z 7 + 5 (z 5 ( + z + z 2 + z + 5 5
Problem Set #7 solutons 7.2.. (a Fnd the coeffcent of z k n (z + z 5 + z 6 + z 7 + 5, k 20. We use the known seres expanson ( n+l ( z l l z n below: (z + z 5 + z 6 + z 7 + 5 (z 5 ( + z + z 2 + z + 5 5
ONE-DIMENSIONAL COLLISIONS
 Purpose Theory ONE-DIMENSIONAL COLLISIONS a. To very the law o conservaton o lnear momentum n one-dmensonal collsons. b. To study conservaton o energy and lnear momentum n both elastc and nelastc onedmensonal
Purpose Theory ONE-DIMENSIONAL COLLISIONS a. To very the law o conservaton o lnear momentum n one-dmensonal collsons. b. To study conservaton o energy and lnear momentum n both elastc and nelastc onedmensonal
PART I: MULTIPLE CHOICE (32 questions, each multiple choice question has a 2-point value, 64 points total).
 CHEMISTRY 123-07 Mdterm #2 answer key November 04, 2010 Statstcs: Average: 68 p (68%); Hghest: 91 p (91%); Lowest: 37 p (37%) Number of students performng at or above average: 58 (53%) Number of students
CHEMISTRY 123-07 Mdterm #2 answer key November 04, 2010 Statstcs: Average: 68 p (68%); Hghest: 91 p (91%); Lowest: 37 p (37%) Number of students performng at or above average: 58 (53%) Number of students
x = , so that calculated
 Stat 4, secton Sngle Factor ANOVA notes by Tm Plachowsk n chapter 8 we conducted hypothess tests n whch we compared a sngle sample s mean or proporton to some hypotheszed value Chapter 9 expanded ths to
Stat 4, secton Sngle Factor ANOVA notes by Tm Plachowsk n chapter 8 we conducted hypothess tests n whch we compared a sngle sample s mean or proporton to some hypotheszed value Chapter 9 expanded ths to
Linear Regression Analysis: Terminology and Notation
 ECON 35* -- Secton : Basc Concepts of Regresson Analyss (Page ) Lnear Regresson Analyss: Termnology and Notaton Consder the generc verson of the smple (two-varable) lnear regresson model. It s represented
ECON 35* -- Secton : Basc Concepts of Regresson Analyss (Page ) Lnear Regresson Analyss: Termnology and Notaton Consder the generc verson of the smple (two-varable) lnear regresson model. It s represented
PROPERTIES OF FRACTIONAL EXCLUSION STATISTICS IN INTERACTING PARTICLE SYSTEMS
 PROPERTIES OF FRACTIONAL EXCLUSION STATISTICS IN INTERACTING PARTICLE SYSTEMS DRAGOŞ-VICTOR ANGHEL Department of Theoretcal Physcs, Hora Hulube Natonal Insttute for Physcs and Nuclear Engneerng (IFIN-HH),
PROPERTIES OF FRACTIONAL EXCLUSION STATISTICS IN INTERACTING PARTICLE SYSTEMS DRAGOŞ-VICTOR ANGHEL Department of Theoretcal Physcs, Hora Hulube Natonal Insttute for Physcs and Nuclear Engneerng (IFIN-HH),
Introduction to Vapor/Liquid Equilibrium, part 2. Raoult s Law:
 CE304, Sprng 2004 Lecture 4 Introducton to Vapor/Lqud Equlbrum, part 2 Raoult s Law: The smplest model that allows us do VLE calculatons s obtaned when we assume that the vapor phase s an deal gas, and
CE304, Sprng 2004 Lecture 4 Introducton to Vapor/Lqud Equlbrum, part 2 Raoult s Law: The smplest model that allows us do VLE calculatons s obtaned when we assume that the vapor phase s an deal gas, and
STAT 511 FINAL EXAM NAME Spring 2001
 STAT 5 FINAL EXAM NAME Sprng Instructons: Ths s a closed book exam. No notes or books are allowed. ou may use a calculator but you are not allowed to store notes or formulas n the calculator. Please wrte
STAT 5 FINAL EXAM NAME Sprng Instructons: Ths s a closed book exam. No notes or books are allowed. ou may use a calculator but you are not allowed to store notes or formulas n the calculator. Please wrte
Non-interacting Spin-1/2 Particles in Non-commuting External Magnetic Fields
 EJTP 6, No. 0 009) 43 56 Electronc Journal of Theoretcal Physcs Non-nteractng Spn-1/ Partcles n Non-commutng External Magnetc Felds Kunle Adegoke Physcs Department, Obafem Awolowo Unversty, Ile-Ife, Ngera
EJTP 6, No. 0 009) 43 56 Electronc Journal of Theoretcal Physcs Non-nteractng Spn-1/ Partcles n Non-commutng External Magnetc Felds Kunle Adegoke Physcs Department, Obafem Awolowo Unversty, Ile-Ife, Ngera
Average Matrix Relative Sensitivity Factors (AMRSFs) for Auger Electron Spectroscopy (AES)
 erage Matrx Relatve Senstvty Factors (AMRSFs) for Auger Electron Spectroscopy (AES) These tables and plots contan AMRSFs for AES calculated for the total peak area for the K, L, M and N shells for both
erage Matrx Relatve Senstvty Factors (AMRSFs) for Auger Electron Spectroscopy (AES) These tables and plots contan AMRSFs for AES calculated for the total peak area for the K, L, M and N shells for both
Comparison of Regression Lines
 STATGRAPHICS Rev. 9/13/2013 Comparson of Regresson Lnes Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Analyss Summary... 4 Plot of Ftted Model... 6 Condtonal Sums of Squares... 6 Analyss Optons... 7 Forecasts... 8 Confdence
STATGRAPHICS Rev. 9/13/2013 Comparson of Regresson Lnes Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Analyss Summary... 4 Plot of Ftted Model... 6 Condtonal Sums of Squares... 6 Analyss Optons... 7 Forecasts... 8 Confdence
A Robust Method for Calculating the Correlation Coefficient
 A Robust Method for Calculatng the Correlaton Coeffcent E.B. Nven and C. V. Deutsch Relatonshps between prmary and secondary data are frequently quantfed usng the correlaton coeffcent; however, the tradtonal
A Robust Method for Calculatng the Correlaton Coeffcent E.B. Nven and C. V. Deutsch Relatonshps between prmary and secondary data are frequently quantfed usng the correlaton coeffcent; however, the tradtonal
COMPARISON OF SOME RELIABILITY CHARACTERISTICS BETWEEN REDUNDANT SYSTEMS REQUIRING SUPPORTING UNITS FOR THEIR OPERATIONS
 Avalable onlne at http://sck.org J. Math. Comput. Sc. 3 (3), No., 6-3 ISSN: 97-537 COMPARISON OF SOME RELIABILITY CHARACTERISTICS BETWEEN REDUNDANT SYSTEMS REQUIRING SUPPORTING UNITS FOR THEIR OPERATIONS
Avalable onlne at http://sck.org J. Math. Comput. Sc. 3 (3), No., 6-3 ISSN: 97-537 COMPARISON OF SOME RELIABILITY CHARACTERISTICS BETWEEN REDUNDANT SYSTEMS REQUIRING SUPPORTING UNITS FOR THEIR OPERATIONS
Copyright 2017 by Taylor Enterprises, Inc., All Rights Reserved. Adjusted Control Limits for P Charts. Dr. Wayne A. Taylor
 Taylor Enterprses, Inc. Control Lmts for P Charts Copyrght 2017 by Taylor Enterprses, Inc., All Rghts Reserved. Control Lmts for P Charts Dr. Wayne A. Taylor Abstract: P charts are used for count data
Taylor Enterprses, Inc. Control Lmts for P Charts Copyrght 2017 by Taylor Enterprses, Inc., All Rghts Reserved. Control Lmts for P Charts Dr. Wayne A. Taylor Abstract: P charts are used for count data
EPR Paradox and the Physical Meaning of an Experiment in Quantum Mechanics. Vesselin C. Noninski
 EPR Paradox and the Physcal Meanng of an Experment n Quantum Mechancs Vesseln C Nonnsk vesselnnonnsk@verzonnet Abstract It s shown that there s one purely determnstc outcome when measurement s made on
EPR Paradox and the Physcal Meanng of an Experment n Quantum Mechancs Vesseln C Nonnsk vesselnnonnsk@verzonnet Abstract It s shown that there s one purely determnstc outcome when measurement s made on
This chapter illustrates the idea that all properties of the homogeneous electron gas (HEG) can be calculated from electron density.
 1 Unform Electron Gas Ths chapter llustrates the dea that all propertes of the homogeneous electron gas (HEG) can be calculated from electron densty. Intutve Representaton of Densty Electron densty n s
1 Unform Electron Gas Ths chapter llustrates the dea that all propertes of the homogeneous electron gas (HEG) can be calculated from electron densty. Intutve Representaton of Densty Electron densty n s
Week3, Chapter 4. Position and Displacement. Motion in Two Dimensions. Instantaneous Velocity. Average Velocity
 Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
829. An adaptive method for inertia force identification in cantilever under moving mass
 89. An adaptve method for nerta force dentfcaton n cantlever under movng mass Qang Chen 1, Mnzhuo Wang, Hao Yan 3, Haonan Ye 4, Guola Yang 5 1,, 3, 4 Department of Control and System Engneerng, Nanng Unversty,
89. An adaptve method for nerta force dentfcaton n cantlever under movng mass Qang Chen 1, Mnzhuo Wang, Hao Yan 3, Haonan Ye 4, Guola Yang 5 1,, 3, 4 Department of Control and System Engneerng, Nanng Unversty,
Bayesian Analysis for 4 7 Be + p 5 8 B + γ Based on Effective Field Theory
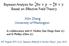 Bayesan Analyss for 4 7 Be + p 5 8 B + γ Based on Effectve Feld Theory Xln Zhang Unversty of Washngton In collaboraton wth K. Nollett (San Dego State U.) and D. Phllps (Oho U.) INT Program INT-16-a, Bayesan
Bayesan Analyss for 4 7 Be + p 5 8 B + γ Based on Effectve Feld Theory Xln Zhang Unversty of Washngton In collaboraton wth K. Nollett (San Dego State U.) and D. Phllps (Oho U.) INT Program INT-16-a, Bayesan
If two volatile and miscible liquids are combined to form a solution, Raoult s law is not obeyed. Use the experimental data in Table 9.
 9.9 Real Solutons Exhbt Devatons from Raoult s Law If two volatle and mscble lquds are combned to form a soluton, Raoult s law s not obeyed. Use the expermental data n Table 9.3: Physcal Chemstry 00 Pearson
9.9 Real Solutons Exhbt Devatons from Raoult s Law If two volatle and mscble lquds are combned to form a soluton, Raoult s law s not obeyed. Use the expermental data n Table 9.3: Physcal Chemstry 00 Pearson
A how to guide to second quantization method.
 Phys. 67 (Graduate Quantum Mechancs Sprng 2009 Prof. Pu K. Lam. Verson 3 (4/3/2009 A how to gude to second quantzaton method. -> Second quantzaton s a mathematcal notaton desgned to handle dentcal partcle
Phys. 67 (Graduate Quantum Mechancs Sprng 2009 Prof. Pu K. Lam. Verson 3 (4/3/2009 A how to gude to second quantzaton method. -> Second quantzaton s a mathematcal notaton desgned to handle dentcal partcle
Chapter 5 Multilevel Models
 Chapter 5 Multlevel Models 5.1 Cross-sectonal multlevel models 5.1.1 Two-level models 5.1.2 Multple level models 5.1.3 Multple level modelng n other felds 5.2 Longtudnal multlevel models 5.2.1 Two-level
Chapter 5 Multlevel Models 5.1 Cross-sectonal multlevel models 5.1.1 Two-level models 5.1.2 Multple level models 5.1.3 Multple level modelng n other felds 5.2 Longtudnal multlevel models 5.2.1 Two-level
Chapter 1. Probability
 Chapter. Probablty Mcroscopc propertes of matter: quantum mechancs, atomc and molecular propertes Macroscopc propertes of matter: thermodynamcs, E, H, C V, C p, S, A, G How do we relate these two propertes?
Chapter. Probablty Mcroscopc propertes of matter: quantum mechancs, atomc and molecular propertes Macroscopc propertes of matter: thermodynamcs, E, H, C V, C p, S, A, G How do we relate these two propertes?
Lecture 14: Forces and Stresses
 The Nuts and Bolts of Frst-Prncples Smulaton Lecture 14: Forces and Stresses Durham, 6th-13th December 2001 CASTEP Developers Group wth support from the ESF ψ k Network Overvew of Lecture Why bother? Theoretcal
The Nuts and Bolts of Frst-Prncples Smulaton Lecture 14: Forces and Stresses Durham, 6th-13th December 2001 CASTEP Developers Group wth support from the ESF ψ k Network Overvew of Lecture Why bother? Theoretcal
Adiabatic Sorption of Ammonia-Water System and Depicting in p-t-x Diagram
 Adabatc Sorpton of Ammona-Water System and Depctng n p-t-x Dagram J. POSPISIL, Z. SKALA Faculty of Mechancal Engneerng Brno Unversty of Technology Techncka 2, Brno 61669 CZECH REPUBLIC Abstract: - Absorpton
Adabatc Sorpton of Ammona-Water System and Depctng n p-t-x Dagram J. POSPISIL, Z. SKALA Faculty of Mechancal Engneerng Brno Unversty of Technology Techncka 2, Brno 61669 CZECH REPUBLIC Abstract: - Absorpton
Introduction to Statistical Methods
 Introducton to Statstcal Methods Physcs 4362, Lecture #3 hermodynamcs Classcal Statstcal Knetc heory Classcal hermodynamcs Macroscopc approach General propertes of the system Macroscopc varables 1 hermodynamc
Introducton to Statstcal Methods Physcs 4362, Lecture #3 hermodynamcs Classcal Statstcal Knetc heory Classcal hermodynamcs Macroscopc approach General propertes of the system Macroscopc varables 1 hermodynamc
Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson 6 Theory of Quantzaton Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:
Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson 6 Theory of Quantzaton Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:
Deterministic and Monte Carlo Codes for Multiple Scattering Photon Transport
 Determnstc and Monte Carlo Codes for Multple Scatterng Photon Transport Jorge E. Fernández 1 1 Laboratory of Montecuccolno DIENCA Alma Mater Studorum Unversty of Bologna Italy Isttuto Nazonale d Fsca Nucleare
Determnstc and Monte Carlo Codes for Multple Scatterng Photon Transport Jorge E. Fernández 1 1 Laboratory of Montecuccolno DIENCA Alma Mater Studorum Unversty of Bologna Italy Isttuto Nazonale d Fsca Nucleare
Uncertainty and auto-correlation in. Measurement
 Uncertanty and auto-correlaton n arxv:1707.03276v2 [physcs.data-an] 30 Dec 2017 Measurement Markus Schebl Federal Offce of Metrology and Surveyng (BEV), 1160 Venna, Austra E-mal: markus.schebl@bev.gv.at
Uncertanty and auto-correlaton n arxv:1707.03276v2 [physcs.data-an] 30 Dec 2017 Measurement Markus Schebl Federal Offce of Metrology and Surveyng (BEV), 1160 Venna, Austra E-mal: markus.schebl@bev.gv.at
Open Systems: Chemical Potential and Partial Molar Quantities Chemical Potential
 Open Systems: Chemcal Potental and Partal Molar Quanttes Chemcal Potental For closed systems, we have derved the followng relatonshps: du = TdS pdv dh = TdS + Vdp da = SdT pdv dg = VdP SdT For open systems,
Open Systems: Chemcal Potental and Partal Molar Quanttes Chemcal Potental For closed systems, we have derved the followng relatonshps: du = TdS pdv dh = TdS + Vdp da = SdT pdv dg = VdP SdT For open systems,
Maximizing the number of nonnegative subsets
 Maxmzng the number of nonnegatve subsets Noga Alon Hao Huang December 1, 213 Abstract Gven a set of n real numbers, f the sum of elements of every subset of sze larger than k s negatve, what s the maxmum
Maxmzng the number of nonnegatve subsets Noga Alon Hao Huang December 1, 213 Abstract Gven a set of n real numbers, f the sum of elements of every subset of sze larger than k s negatve, what s the maxmum
The equation of motion of a dynamical system is given by a set of differential equations. That is (1)
 Dynamcal Systems Many engneerng and natural systems are dynamcal systems. For example a pendulum s a dynamcal system. State l The state of the dynamcal system specfes t condtons. For a pendulum n the absence
Dynamcal Systems Many engneerng and natural systems are dynamcal systems. For example a pendulum s a dynamcal system. State l The state of the dynamcal system specfes t condtons. For a pendulum n the absence
At zero K: All atoms frozen at fixed positions on a periodic lattice.
 September, 00 Readng: Chapter Four Homework: None Entropy and The Degree of Dsorder: Consder a sold crystallne materal: At zero K: All atoms frozen at fxed postons on a perodc lattce. Add heat to a fnte
September, 00 Readng: Chapter Four Homework: None Entropy and The Degree of Dsorder: Consder a sold crystallne materal: At zero K: All atoms frozen at fxed postons on a perodc lattce. Add heat to a fnte
ECEN 5005 Crystals, Nanocrystals and Device Applications Class 19 Group Theory For Crystals
 ECEN 5005 Crystals, Nanocrystals and Devce Applcatons Class 9 Group Theory For Crystals Dee Dagram Radatve Transton Probablty Wgner-Ecart Theorem Selecton Rule Dee Dagram Expermentally determned energy
ECEN 5005 Crystals, Nanocrystals and Devce Applcatons Class 9 Group Theory For Crystals Dee Dagram Radatve Transton Probablty Wgner-Ecart Theorem Selecton Rule Dee Dagram Expermentally determned energy
Problem Set 9 Solutions
 Desgn and Analyss of Algorthms May 4, 2015 Massachusetts Insttute of Technology 6.046J/18.410J Profs. Erk Demane, Srn Devadas, and Nancy Lynch Problem Set 9 Solutons Problem Set 9 Solutons Ths problem
Desgn and Analyss of Algorthms May 4, 2015 Massachusetts Insttute of Technology 6.046J/18.410J Profs. Erk Demane, Srn Devadas, and Nancy Lynch Problem Set 9 Solutons Problem Set 9 Solutons Ths problem
Supporting Information
 Supportng Informaton The neural network f n Eq. 1 s gven by: f x l = ReLU W atom x l + b atom, 2 where ReLU s the element-wse rectfed lnear unt, 21.e., ReLUx = max0, x, W atom R d d s the weght matrx to
Supportng Informaton The neural network f n Eq. 1 s gven by: f x l = ReLU W atom x l + b atom, 2 where ReLU s the element-wse rectfed lnear unt, 21.e., ReLUx = max0, x, W atom R d d s the weght matrx to
and Statistical Mechanics Material Properties
 Statstcal Mechancs and Materal Propertes By Kuno TAKAHASHI Tokyo Insttute of Technology, Tokyo 15-855, JAPA Phone/Fax +81-3-5734-3915 takahak@de.ttech.ac.jp http://www.de.ttech.ac.jp/~kt-lab/ Only for
Statstcal Mechancs and Materal Propertes By Kuno TAKAHASHI Tokyo Insttute of Technology, Tokyo 15-855, JAPA Phone/Fax +81-3-5734-3915 takahak@de.ttech.ac.jp http://www.de.ttech.ac.jp/~kt-lab/ Only for
Feature Selection: Part 1
 CSE 546: Machne Learnng Lecture 5 Feature Selecton: Part 1 Instructor: Sham Kakade 1 Regresson n the hgh dmensonal settng How do we learn when the number of features d s greater than the sample sze n?
CSE 546: Machne Learnng Lecture 5 Feature Selecton: Part 1 Instructor: Sham Kakade 1 Regresson n the hgh dmensonal settng How do we learn when the number of features d s greater than the sample sze n?
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. D Alembert s Principle and The Lagrangian-1
 P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
THERMAL DISTRIBUTION IN THE HCL SPECTRUM OBJECTIVE
 ame: THERMAL DISTRIBUTIO I THE HCL SPECTRUM OBJECTIVE To nvestgate a system s thermal dstrbuton n dscrete states; specfcally, determne HCl gas temperature from the relatve occupatons of ts rotatonal states.
ame: THERMAL DISTRIBUTIO I THE HCL SPECTRUM OBJECTIVE To nvestgate a system s thermal dstrbuton n dscrete states; specfcally, determne HCl gas temperature from the relatve occupatons of ts rotatonal states.
3.1 Expectation of Functions of Several Random Variables. )' be a k-dimensional discrete or continuous random vector, with joint PMF p (, E X E X1 E X
 Statstcs 1: Probablty Theory II 37 3 EPECTATION OF SEVERAL RANDOM VARIABLES As n Probablty Theory I, the nterest n most stuatons les not on the actual dstrbuton of a random vector, but rather on a number
Statstcs 1: Probablty Theory II 37 3 EPECTATION OF SEVERAL RANDOM VARIABLES As n Probablty Theory I, the nterest n most stuatons les not on the actual dstrbuton of a random vector, but rather on a number
Energy, Entropy, and Availability Balances Phase Equilibria. Nonideal Thermodynamic Property Models. Selecting an Appropriate Model
 Lecture 4. Thermodynamcs [Ch. 2] Energy, Entropy, and Avalablty Balances Phase Equlbra - Fugactes and actvty coeffcents -K-values Nondeal Thermodynamc Property Models - P-v-T equaton-of-state models -
Lecture 4. Thermodynamcs [Ch. 2] Energy, Entropy, and Avalablty Balances Phase Equlbra - Fugactes and actvty coeffcents -K-values Nondeal Thermodynamc Property Models - P-v-T equaton-of-state models -
ANSWERS. Problem 1. and the moment generating function (mgf) by. defined for any real t. Use this to show that E( U) var( U)
 Econ 413 Exam 13 H ANSWERS Settet er nndelt 9 deloppgaver, A,B,C, som alle anbefales å telle lkt for å gøre det ltt lettere å stå. Svar er gtt . Unfortunately, there s a prntng error n the hnt of
Econ 413 Exam 13 H ANSWERS Settet er nndelt 9 deloppgaver, A,B,C, som alle anbefales å telle lkt for å gøre det ltt lettere å stå. Svar er gtt . Unfortunately, there s a prntng error n the hnt of
Effect of loading frequency on the settlement of granular layer
 Effect of loadng frequency on the settlement of granular layer Akko KONO Ralway Techncal Research Insttute, Japan Takash Matsushma Tsukuba Unversty, Japan ABSTRACT: Cyclc loadng tests were performed both
Effect of loadng frequency on the settlement of granular layer Akko KONO Ralway Techncal Research Insttute, Japan Takash Matsushma Tsukuba Unversty, Japan ABSTRACT: Cyclc loadng tests were performed both
12. The Hamilton-Jacobi Equation Michael Fowler
 1. The Hamlton-Jacob Equaton Mchael Fowler Back to Confguraton Space We ve establshed that the acton, regarded as a functon of ts coordnate endponts and tme, satsfes ( ) ( ) S q, t / t+ H qpt,, = 0, and
1. The Hamlton-Jacob Equaton Mchael Fowler Back to Confguraton Space We ve establshed that the acton, regarded as a functon of ts coordnate endponts and tme, satsfes ( ) ( ) S q, t / t+ H qpt,, = 0, and
Week 8: Chapter 9. Linear Momentum. Newton Law and Momentum. Linear Momentum, cont. Conservation of Linear Momentum. Conservation of Momentum, 2
 Lnear omentum Week 8: Chapter 9 Lnear omentum and Collsons The lnear momentum of a partcle, or an object that can be modeled as a partcle, of mass m movng wth a velocty v s defned to be the product of
Lnear omentum Week 8: Chapter 9 Lnear omentum and Collsons The lnear momentum of a partcle, or an object that can be modeled as a partcle, of mass m movng wth a velocty v s defned to be the product of
Snce h( q^; q) = hq ~ and h( p^ ; p) = hp, one can wrte ~ h hq hp = hq ~hp ~ (7) the uncertanty relaton for an arbtrary state. The states that mnmze t
 8.5: Many-body phenomena n condensed matter and atomc physcs Last moded: September, 003 Lecture. Squeezed States In ths lecture we shall contnue the dscusson of coherent states, focusng on ther propertes
8.5: Many-body phenomena n condensed matter and atomc physcs Last moded: September, 003 Lecture. Squeezed States In ths lecture we shall contnue the dscusson of coherent states, focusng on ther propertes
Army Ants Tunneling for Classical Simulations
 Electronc Supplementary Materal (ESI) for Chemcal Scence. Ths journal s The Royal Socety of Chemstry 2014 electronc supplementary nformaton (ESI) for Chemcal Scence Army Ants Tunnelng for Classcal Smulatons
Electronc Supplementary Materal (ESI) for Chemcal Scence. Ths journal s The Royal Socety of Chemstry 2014 electronc supplementary nformaton (ESI) for Chemcal Scence Army Ants Tunnelng for Classcal Smulatons
Transverse-velocity scaling of femtoscopy in proton proton collisions
 Journal of Physcs G: Nuclear and Partcle Physcs PAPER Transverse-velocty scalng of femtoscopy n proton proton collsons To cte ths artcle: T J Humanc 018 J. Phys. G: Nucl. Part. Phys. 45 055101 Vew the
Journal of Physcs G: Nuclear and Partcle Physcs PAPER Transverse-velocty scalng of femtoscopy n proton proton collsons To cte ths artcle: T J Humanc 018 J. Phys. G: Nucl. Part. Phys. 45 055101 Vew the
5.15 MICRO GAMMA SCANNING ON THE HIGH BURNUP PWR FUEL SAMPLES
 5.15 MICRO GAMMA SCANNING ON THE HIGH BURNUP PWR FUEL SAMPLES Hyoung-Mun Kwon, Hang-Seog Seo, Hyung-Kwon Lee, Duck-Kee Mn, Yong-Bum Chun Post Irradaton Examnaton Faclty, Korea Atomc Energy Research Insttute
5.15 MICRO GAMMA SCANNING ON THE HIGH BURNUP PWR FUEL SAMPLES Hyoung-Mun Kwon, Hang-Seog Seo, Hyung-Kwon Lee, Duck-Kee Mn, Yong-Bum Chun Post Irradaton Examnaton Faclty, Korea Atomc Energy Research Insttute
A NUMERICAL COMPARISON OF LANGRANGE AND KANE S METHODS OF AN ARM SEGMENT
 Internatonal Conference Mathematcal and Computatonal ology 0 Internatonal Journal of Modern Physcs: Conference Seres Vol. 9 0 68 75 World Scentfc Publshng Company DOI: 0.4/S009450059 A NUMERICAL COMPARISON
Internatonal Conference Mathematcal and Computatonal ology 0 Internatonal Journal of Modern Physcs: Conference Seres Vol. 9 0 68 75 World Scentfc Publshng Company DOI: 0.4/S009450059 A NUMERICAL COMPARISON
Panel transmission measurements: the influence of the non plane wave nature of the incident field
 Acoustcs 8 Pars Panel transmsson measurements: the nfluence of the non plane wave nature of the ncdent feld V. F Humphrey a J. Smth b a Insttute of Sound Vbraton, Unv. of Southampton, Unversty Road, Hghfeld,
Acoustcs 8 Pars Panel transmsson measurements: the nfluence of the non plane wave nature of the ncdent feld V. F Humphrey a J. Smth b a Insttute of Sound Vbraton, Unv. of Southampton, Unversty Road, Hghfeld,
Supporting information
 Supportng nformaton S1. Sample characterzaton S1.1. Hall coeffcent and resstvty measurements Hall and resstvty measurements on sample B have been performed wth a PPMS (Physcal Property Measurement System)
Supportng nformaton S1. Sample characterzaton S1.1. Hall coeffcent and resstvty measurements Hall and resstvty measurements on sample B have been performed wth a PPMS (Physcal Property Measurement System)
The internal structure of natural numbers and one method for the definition of large prime numbers
 The nternal structure of natural numbers and one method for the defnton of large prme numbers Emmanul Manousos APM Insttute for the Advancement of Physcs and Mathematcs 3 Poulou str. 53 Athens Greece Abstract
The nternal structure of natural numbers and one method for the defnton of large prme numbers Emmanul Manousos APM Insttute for the Advancement of Physcs and Mathematcs 3 Poulou str. 53 Athens Greece Abstract
A NEW EXPRESSION FOR RADIAL DISTRIBUTION FUNCTION OF NUCLEAR MATTER.
 Mathematcal and Computatonal Applcatons, Vol. 16, No., pp. 414-44, 011. Assocaton for Scentfc Research A NEW EXPRESSION FOR RADIAL DISTRIBUTION FUNCTION OF NUCLEAR MATTER Fatma Mansa 1, Atalay Küçükbursa
Mathematcal and Computatonal Applcatons, Vol. 16, No., pp. 414-44, 011. Assocaton for Scentfc Research A NEW EXPRESSION FOR RADIAL DISTRIBUTION FUNCTION OF NUCLEAR MATTER Fatma Mansa 1, Atalay Küçükbursa
Determination of Mass Attenuation Coefficients, Effective atomic number and Electron Density of Lumefantrine in the Energy Range 1 kev 100 GeV
 http://jopaar.com; 217 Vol. 4(1); pp. 42-5, ISSN: 2455-474X Determnaton of Mass Attenuaton Coeffcents, Effectve atomc number and Electron Densty of Lumefantrne n the Energy Range 1 kev 1 GeV Ingalagond.
http://jopaar.com; 217 Vol. 4(1); pp. 42-5, ISSN: 2455-474X Determnaton of Mass Attenuaton Coeffcents, Effectve atomc number and Electron Densty of Lumefantrne n the Energy Range 1 kev 1 GeV Ingalagond.
Binding energy of a Cooper pairs with non-zero center of mass momentum in d-wave superconductors
 Bndng energ of a Cooper pars wth non-zero center of mass momentum n d-wave superconductors M.V. remn and I.. Lubn Kazan State Unverst Kremlevsaa 8 Kazan 420008 Russan Federaton -mal: gor606@rambler.ru
Bndng energ of a Cooper pars wth non-zero center of mass momentum n d-wave superconductors M.V. remn and I.. Lubn Kazan State Unverst Kremlevsaa 8 Kazan 420008 Russan Federaton -mal: gor606@rambler.ru
Kernel Methods and SVMs Extension
 Kernel Methods and SVMs Extenson The purpose of ths document s to revew materal covered n Machne Learnng 1 Supervsed Learnng regardng support vector machnes (SVMs). Ths document also provdes a general
Kernel Methods and SVMs Extenson The purpose of ths document s to revew materal covered n Machne Learnng 1 Supervsed Learnng regardng support vector machnes (SVMs). Ths document also provdes a general
Transfer Functions. Convenient representation of a linear, dynamic model. A transfer function (TF) relates one input and one output: ( ) system
 Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
is the calculated value of the dependent variable at point i. The best parameters have values that minimize the squares of the errors
 Multple Lnear and Polynomal Regresson wth Statstcal Analyss Gven a set of data of measured (or observed) values of a dependent varable: y versus n ndependent varables x 1, x, x n, multple lnear regresson
Multple Lnear and Polynomal Regresson wth Statstcal Analyss Gven a set of data of measured (or observed) values of a dependent varable: y versus n ndependent varables x 1, x, x n, multple lnear regresson
Conjugacy and the Exponential Family
 CS281B/Stat241B: Advanced Topcs n Learnng & Decson Makng Conjugacy and the Exponental Famly Lecturer: Mchael I. Jordan Scrbes: Bran Mlch 1 Conjugacy In the prevous lecture, we saw conjugate prors for the
CS281B/Stat241B: Advanced Topcs n Learnng & Decson Makng Conjugacy and the Exponental Famly Lecturer: Mchael I. Jordan Scrbes: Bran Mlch 1 Conjugacy In the prevous lecture, we saw conjugate prors for the
