Article 13. Ex-points and eight intersecting circles
|
|
|
- Hilary Lyons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Article 13 Ex-points and eight intersecting circles Christopher J Bradley H' F P3 W' L' A V' N E P2 M U O Q V P J H W M' B R C N' L To T S U' P1 D Figure 1. Introduction 1
2 In this article we use areal co-ordinates throughout. See Bradley [1, 2 ] for a review of how to use them. Incentres and ex-centres are well-known and if (a, b, c) are the co-ordinates of the incentre, then the three ex-centres I 1, I 2, I 3 have co-ordinates ( a, b, c), (a, b, c), (a, b, c) respectively. Less well-known, perhaps, are the ex-symmedian points D, E, F, which are the intersections of the tangents at the vertices of the circumcircle, D being the intersection of the tangents at B and C, with E, F similarly defined. These points can be seen in the Figure. Their co-ordinates are ( a 2, b 2, c 2 ), (a 2, b 2, c 2 ), (a 2, b 2 c 2 ) respectively. It is also true that if P (l, m, n) is any point internal to a triangle ABC, then there are three associated ex-points P 1 ( l, m, n), P 2 (l, m, n), P 3 (l, m, n). We show how these points may be constructed using compass and straight edge only. It turns out that the construction is a development of the construction of the Hagge circle [3] of the point P, so we are able to draw four Hagge circles, one for each of P, P 1, P 2, P 3, all of which, of course, pass through the orthocentre H of triangle ABC. As a bonus there are in addition four other circles and the CABRI II geometry computer software package indicates that these other four circles also have a common point, labelled H' in the Figure. The additional four circles have equations that are considerably more complicated than those of the four Hagge circles, so we have been unable to find the co-ordinates of H'. However, it may be proved by inversion that these four circles do indeed have a common point. This proof has been supplied by David Monk [4] and I am extremely grateful to him for providing the proof. We now describe the construction of the ex-points, starting from ABC and P. First draw the tangents at A, B, C to the circumcircle to provide D, E, F. Next draw the lines AP, BP, CP to meet the circumcircle at L, M, N respectively. Now draw DL, EM, FN to meet the circumcircle again at L', M', N' respectively. Note that these three lines are concurrent at a point Q, which we call the generating point. Now AL, BM', CN' are found to be concurrent at the point P 1, AL', BM, CN' are concurrent at P 2, and AL', BM', CN are concurrent at P 3. Section 2 provides the algebraic proof of these remarks. Q is called the generating point, because rather than start with P, one can start with Q, which must be internal to triangle DEF, and then reverse the construction, thus generating all 4 points P, P 1, P 2, P 3. We defer the description of the construction of the 8 circles until later in the text. 2. The ex-points P 1, P 2, P 3 and the generating point Q For those unfamiliar with areal co-ordinates for points on the circumcircle Γ we give a brief account of what is required. The co-ordinates of a general point on Γ are ( a 2 t(1 t), b 2 (1 t), c 2 t), where t is a parameter that can take any value (including infinity). Thus the points A(1, 0, 0), B(0, 1, 0), C(0, 0,1) have parameters, 0, 1 respectively and the equation of the circumcircle is. (2.1) For checking purposes it is useful to have the equation of the chord of Γ joining points with parameters t and s. This is 2
3 (2.2) Starting with P(l, m, n) we find the equation of AP to be ny = mz. This meets Γ, with Equation (2.1), at the point L with co-ordinates L( a 2 mn/(b 2 n + c 2 m), m, n). Similarly BP, CP meet Γ at M, N respectively with co-ordinates M(l, b 2 nl/(c 2 l + a 2 n), n) and N(l, m, c 2 lm/(a 2 m + b 2 l). The tangents to Γ with Equation (2.1) at A, B, C are respectively b 2 z + c 2 y = 0, c 2 x + a 2 y = 0, a 2 y + b 2 x = 0.The point D, that is the intersection of the tangents at B and C, therefore has coordinates D( a 2, b 2, c 2 ) and E, F respectively have co-ordinates E(a 2, b 2, c 2 ), F(a 2, b 2, c 2 ). It can now be seen that D, E, F are the ex-symmedians, as the symmedian point K has co-ordinates (a 2, b 2, c 2 ). The line DL has equation (2.3) This meets Γ again at the point L' with co-ordinates L'(a 2 mn/(b 2 n c 2 m), m, n) Note that this differs from L simply by a change of sign of m (or n). We can now write down, by cyclic change, the co-ordinates of M' and N', which are M'(l, b 2 nl/(c 2 l a 2 n), n) and N'( l, m, c 2 lm/(a 2 m b 2 l)). Now EM has equation that may be derived from that of DL by cyclic change and then the generating point Q is determined as DL^EM. The result is that Q has co-ordinates It may now be checked that Q also lies on the line FN. The equations of the lines AL', BM', CN' can now be determined and they are respectively (2.4) We now have enough to determine the co-ordinates of the points P 1 = AL^ BM'^CN', P 2 = AL'^BM^CN' and P 3 = AL'^BM'^CN, and, as you will have guessed, these are the ex-points of P with co-ordinates P 1 ( l, m, n), P 2 (l, m, n), P 3 (l, m, n). It may be checked that EP 2 and FP 3 intersect at a point R on BC, with S, T on CA, AB respectively defined similarly. In the Figure we have chosen P to be the isogonal conjugate of the nine-point centre. This point generates the Hagge circle with OH as diameter. 3. A 9 point hyperbola Using the standard 6 x 6 determinantal method to obtain the conic through P, its 3 ex-points and K the symmedian point we find the equation of a hyperbola (3.1) 3
4 Its form immediately indicates that not only does this hyperbola pass through the points just mentioned, but it also passes through D, E, F the ex-symmedians. It may be checked that it also passes through the generating point Q. Thus, it passes through 9 key points of the figure. As P may be any point, we have the result, for example, that a 9 point hyperbola passes through the incentre, the ex-centres, the symmedian point, the ex-symmedians and the point Q, which in this case is the circumcentre O. It is a rectangular hyperbola, since the incentre and ex-centres form an orthocentroidal quartet. If P lies at O, then the hyperbola is also rectangular, since the orthocentre of triangle O 1 O 2 O 3 lies on the hyperbola. 4. The reflected points The points in the Figure labelled U, V, W, U', V', W' are the reflections of the points L, M, N, L', M', N' in the sides BC, CA, AB, BC, CA, AB respectively. This is the same as in the construction of Hagge circles. The algebra for obtaining the co-ordinates of the reflected points is covered in detail in Bradley and Smith [3] and is not repeated here. We therefore state the coordinates of these points without proof and they are as follows: (4.1) (4.2) (4.3) (4.4) (4.5) (4.6) 5. The 8 circles There is, of course a circle through any 3 of these points, but there are 8 special circles found by choosing one of U, U', one of V, V' and one of W, W'. First we consider the circle UVW. This is the Hagge circle generated by P. The method is to write down the general equation of a circle, which is (5.1) Then we insert the co-ordinates of U, V, W in turn, to provide three equations for the real numbers u, v, w. Their values are then substituted back in Equation (5.1). The result is It may be checked that this circle passes through H, the orthocentre of ABC. The circle UV'W' has the equation derived from Equation (5.2) by changing the sign of l. It is therefore the Hagge circle generated by P 1. Similarly changes of sign of m, n in Equation (5.2) produce the Hagge circles of P 2, P 3 respectively. (5.2) 4
5 The other four circles U'V'W', U'VW, UV'W, UVW' have equations that are extremely lengthy and complicated, and the algebra computer package DERIVE was unable to solve the simultaneous quadratics of any pair of them to show that they have the common point, labelled H' in the figure. However, David Monk [4] has kindly provided the following proof: Invert the figure in H so that circles UVW, UV'W', U'VW', U'V'W become the lines uvw, uv'w', u'vw', u'v'w. The resulting figure is a complete quadrilateral, and thus the four triangles u'v'w', u'vw, uv'w, uvw' have circumcircles that possess a common point h'. Inverting back gives the result required. This proof does not tell us anything about the dependence of H' on the point P. All that we can say from drawings is that the locus of H' as P moves on a line is a curve that is not a conic. References 1. C.J.Bradley, Challenges in Geometry, Oxford (2005); 2. C.J.Bradley, The Algebra of Geometry, Highperception, Bath (2007); 3. Christopher Bradley and Geoff C. Smith, On a construction of Hagge, Forum Geometricorum p (2006). 4. D. Monk (private communication). Flat 4, Terrill Court, Apsley Road, Clifton, BRISTOL BS8 2SP 5
( 1 ) Show that P ( a, b + c ), Q ( b, c + a ) and R ( c, a + b ) are collinear.
 Problems 01 - POINT Page 1 ( 1 ) Show that P ( a, b + c ), Q ( b, c + a ) and R ( c, a + b ) are collinear. ( ) Prove that the two lines joining the mid-points of the pairs of opposite sides and the line
Problems 01 - POINT Page 1 ( 1 ) Show that P ( a, b + c ), Q ( b, c + a ) and R ( c, a + b ) are collinear. ( ) Prove that the two lines joining the mid-points of the pairs of opposite sides and the line
A Singular Miquel Configuration and the Miquel Direct Similarity
 Article: CJB/2010/8 A Singular Miquel Configuration and the Miquel Direct Similarity Christopher J Bradley Abstract: Let ABC be a triangle with P on AB, and let circle APC meet BC at Q and circle BPC meet
Article: CJB/2010/8 A Singular Miquel Configuration and the Miquel Direct Similarity Christopher J Bradley Abstract: Let ABC be a triangle with P on AB, and let circle APC meet BC at Q and circle BPC meet
Generalization of the Wallace-Simson line
 Generalization of the Wallace-Simson line Christopher J Bradley Article CJB/2010/7 Abstract: A Wallace-Simson line of a point J has the property that it passes through the midpoint Q of HJ, where H is
Generalization of the Wallace-Simson line Christopher J Bradley Article CJB/2010/7 Abstract: A Wallace-Simson line of a point J has the property that it passes through the midpoint Q of HJ, where H is
A Quadrilateral and resulting Conics Part 2 A Special Case showing the role of the New Points X and Y
 A Quadrilateral and resulting Conics Part 2 A Special Case showing the role of the New Points X and Y Christopher Bradley Article: CJB/231/2012 To 2 11 T G U To F To 7 X 24 41 P B A 13 1 34 14S D 5 6 E
A Quadrilateral and resulting Conics Part 2 A Special Case showing the role of the New Points X and Y Christopher Bradley Article: CJB/231/2012 To 2 11 T G U To F To 7 X 24 41 P B A 13 1 34 14S D 5 6 E
Mathematics. Single Correct Questions
 Mathematics Single Correct Questions +4 1.00 1. If and then 2. The number of solutions of, in the interval is : 3. If then equals : 4. A plane bisects the line segment joining the points and at right angles.
Mathematics Single Correct Questions +4 1.00 1. If and then 2. The number of solutions of, in the interval is : 3. If then equals : 4. A plane bisects the line segment joining the points and at right angles.
GAT-UGTP-2018 Page 1 of 5
 SECTION A: MATHEMATICS UNIT 1 SETS, RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS: Sets and their representation, Union, Intersection and compliment of sets, and their algebraic properties, power set, Relation, Types of relation,
SECTION A: MATHEMATICS UNIT 1 SETS, RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS: Sets and their representation, Union, Intersection and compliment of sets, and their algebraic properties, power set, Relation, Types of relation,
On a Construction of Hagge
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 7 (2007) 231 247. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 On a Construction of Hagge Christopher J. Bradley and Geoff C. Smith Abstract. In 1907 Hagge constructed a circle associated with
Forum Geometricorum Volume 7 (2007) 231 247. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 On a Construction of Hagge Christopher J. Bradley and Geoff C. Smith Abstract. In 1907 Hagge constructed a circle associated with
QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE
 QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; 4x + y + 4 = 0 and x + αy + β = 0, where α + β =, are concurrent then α =,
QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; 4x + y + 4 = 0 and x + αy + β = 0, where α + β =, are concurrent then α =,
(D) (A) Q.3 To which of the following circles, the line y x + 3 = 0 is normal at the point ? 2 (A) 2
 CIRCLE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. The line x y + = 0 is tangent to the circle at the point (, 5) and the centre of the circles lies on x y = 4. The radius of the circle is (A) 3 5 (B) 5 3 (C) 5 (D) 5
CIRCLE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. The line x y + = 0 is tangent to the circle at the point (, 5) and the centre of the circles lies on x y = 4. The radius of the circle is (A) 3 5 (B) 5 3 (C) 5 (D) 5
Two applications of the theorem of Carnot
 Two applications of the theorem of Carnot Zoltán Szilasi Abstract Using the theorem of Carnot we give elementary proofs of two statements of C Bradley We prove his conjecture concerning the tangents to
Two applications of the theorem of Carnot Zoltán Szilasi Abstract Using the theorem of Carnot we give elementary proofs of two statements of C Bradley We prove his conjecture concerning the tangents to
Recognise the Equation of a Circle. Solve Problems about Circles Centred at O. Co-Ordinate Geometry of the Circle - Outcomes
 1 Co-Ordinate Geometry of the Circle - Outcomes Recognise the equation of a circle. Solve problems about circles centred at the origin. Solve problems about circles not centred at the origin. Determine
1 Co-Ordinate Geometry of the Circle - Outcomes Recognise the equation of a circle. Solve problems about circles centred at the origin. Solve problems about circles not centred at the origin. Determine
Constructing a Triangle from Two Vertices and the Symmedian Point
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 18 (2018) 129 1. FORUM GEOM ISSN 154-1178 Constructing a Triangle from Two Vertices and the Symmedian Point Michel Bataille Abstract. Given three noncollinear points A, B, K,
Forum Geometricorum Volume 18 (2018) 129 1. FORUM GEOM ISSN 154-1178 Constructing a Triangle from Two Vertices and the Symmedian Point Michel Bataille Abstract. Given three noncollinear points A, B, K,
Calgary Math Circles: Triangles, Concurrency and Quadrilaterals 1
 Calgary Math Circles: Triangles, Concurrency and Quadrilaterals 1 1 Triangles: Basics This section will cover all the basic properties you need to know about triangles and the important points of a triangle.
Calgary Math Circles: Triangles, Concurrency and Quadrilaterals 1 1 Triangles: Basics This section will cover all the basic properties you need to know about triangles and the important points of a triangle.
TARGET : JEE 2013 SCORE. JEE (Advanced) Home Assignment # 03. Kota Chandigarh Ahmedabad
 TARGT : J 01 SCOR J (Advanced) Home Assignment # 0 Kota Chandigarh Ahmedabad J-Mathematics HOM ASSIGNMNT # 0 STRAIGHT OBJCTIV TYP 1. If x + y = 0 is a tangent at the vertex of a parabola and x + y 7 =
TARGT : J 01 SCOR J (Advanced) Home Assignment # 0 Kota Chandigarh Ahmedabad J-Mathematics HOM ASSIGNMNT # 0 STRAIGHT OBJCTIV TYP 1. If x + y = 0 is a tangent at the vertex of a parabola and x + y 7 =
Statics and the Moduli Space of Triangles
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 5 (2005) 181 10. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Statics and the Moduli Space of Triangles Geoff C. Smith Abstract. The variance of a weighted collection of points is used to prove
Forum Geometricorum Volume 5 (2005) 181 10. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Statics and the Moduli Space of Triangles Geoff C. Smith Abstract. The variance of a weighted collection of points is used to prove
QUESTION BANK ON. CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola)
 QUESTION BANK ON CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola) Question bank on Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. Two mutually perpendicular tangents
QUESTION BANK ON CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola) Question bank on Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. Two mutually perpendicular tangents
Chapter 4. Feuerbach s Theorem
 Chapter 4. Feuerbach s Theorem Let A be a point in the plane and k a positive number. Then in the previous chapter we proved that the inversion mapping with centre A and radius k is the mapping Inv : P\{A}
Chapter 4. Feuerbach s Theorem Let A be a point in the plane and k a positive number. Then in the previous chapter we proved that the inversion mapping with centre A and radius k is the mapping Inv : P\{A}
Q.2 A, B and C are points in the xy plane such that A(1, 2) ; B (5, 6) and AC = 3BC. Then. (C) 1 1 or
 STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. A variable rectangle PQRS has its sides parallel to fied directions. Q and S lie respectivel on the lines = a, = a and P lies on the ais. Then the locus of R
STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. A variable rectangle PQRS has its sides parallel to fied directions. Q and S lie respectivel on the lines = a, = a and P lies on the ais. Then the locus of R
Collinearity/Concurrence
 Collinearity/Concurrence Ray Li (rayyli@stanford.edu) June 29, 2017 1 Introduction/Facts you should know 1. (Cevian Triangle) Let ABC be a triangle and P be a point. Let lines AP, BP, CP meet lines BC,
Collinearity/Concurrence Ray Li (rayyli@stanford.edu) June 29, 2017 1 Introduction/Facts you should know 1. (Cevian Triangle) Let ABC be a triangle and P be a point. Let lines AP, BP, CP meet lines BC,
On a Porism Associated with the Euler and Droz-Farny Lines
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 7 (2007) 11 17. FRUM GEM ISS 1534-1178 n a Porism ssociated with the Euler and Droz-Farny Lines hristopher J. radley, David Monk, and Geoff. Smith bstract. The envelope of the
Forum Geometricorum Volume 7 (2007) 11 17. FRUM GEM ISS 1534-1178 n a Porism ssociated with the Euler and Droz-Farny Lines hristopher J. radley, David Monk, and Geoff. Smith bstract. The envelope of the
Two applications of the theorem of Carnot
 Annales Mathematicae et Informaticae 40 (2012) pp. 135 144 http://ami.ektf.hu Two applications of the theorem of Carnot Zoltán Szilasi Institute of Mathematics, MTA-DE Research Group Equations, Functions
Annales Mathematicae et Informaticae 40 (2012) pp. 135 144 http://ami.ektf.hu Two applications of the theorem of Carnot Zoltán Szilasi Institute of Mathematics, MTA-DE Research Group Equations, Functions
GEOMETRY OF KIEPERT AND GRINBERG MYAKISHEV HYPERBOLAS
 GEOMETRY OF KIEPERT ND GRINERG MYKISHEV HYPEROLS LEXEY. ZSLVSKY bstract. new synthetic proof of the following fact is given: if three points,, are the apices of isosceles directly-similar triangles,, erected
GEOMETRY OF KIEPERT ND GRINERG MYKISHEV HYPEROLS LEXEY. ZSLVSKY bstract. new synthetic proof of the following fact is given: if three points,, are the apices of isosceles directly-similar triangles,, erected
1 is equal to. 1 (B) a. (C) a (B) (D) 4. (C) P lies inside both C & E (D) P lies inside C but outside E. (B) 1 (D) 1
 Single Correct Q. Two mutuall perpendicular tangents of the parabola = a meet the ais in P and P. If S is the focus of the parabola then l a (SP ) is equal to (SP ) l (B) a (C) a Q. ABCD and EFGC are squares
Single Correct Q. Two mutuall perpendicular tangents of the parabola = a meet the ais in P and P. If S is the focus of the parabola then l a (SP ) is equal to (SP ) l (B) a (C) a Q. ABCD and EFGC are squares
Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Fall 2016 Solutions to the Quizzes
 Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Fall 2016 Solutions to the Quizzes Quiz #1. Wednesday, 13 September. [10 minutes] 1. Suppose you are given a line (segment) AB. Using
Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Fall 2016 Solutions to the Quizzes Quiz #1. Wednesday, 13 September. [10 minutes] 1. Suppose you are given a line (segment) AB. Using
Plane geometry Circles: Problems with some Solutions
 The University of Western ustralia SHL F MTHMTIS & STTISTIS UW MY FR YUNG MTHMTIINS Plane geometry ircles: Problems with some Solutions 1. Prove that for any triangle, the perpendicular bisectors of the
The University of Western ustralia SHL F MTHMTIS & STTISTIS UW MY FR YUNG MTHMTIINS Plane geometry ircles: Problems with some Solutions 1. Prove that for any triangle, the perpendicular bisectors of the
Mathematics Syllabus UNIT I ALGEBRA : 1. SETS, RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS
 Mathematics Syllabus UNIT I ALGEBRA : 1. SETS, RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS (i) Sets and their Representations: Finite and Infinite sets; Empty set; Equal sets; Subsets; Power set; Universal set; Venn Diagrams;
Mathematics Syllabus UNIT I ALGEBRA : 1. SETS, RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS (i) Sets and their Representations: Finite and Infinite sets; Empty set; Equal sets; Subsets; Power set; Universal set; Venn Diagrams;
Topic 2 [312 marks] The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle. Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths
![Topic 2 [312 marks] The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle. Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths Topic 2 [312 marks] The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle. Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths](/thumbs/86/93150791.jpg) Topic 2 [312 marks] 1 The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths [12 marks] 3 cm and (\9\) cm respectively E is a point on side [AB] such that AE is 3 cm Side [DE] is
Topic 2 [312 marks] 1 The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths [12 marks] 3 cm and (\9\) cm respectively E is a point on side [AB] such that AE is 3 cm Side [DE] is
On Tripolars and Parabolas
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 12 (2012) 287 300. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 On Tripolars and Parabolas Paris Pamfilos bstract. Starting with an analysis of the configuration of chords of contact points with
Forum Geometricorum Volume 12 (2012) 287 300. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 On Tripolars and Parabolas Paris Pamfilos bstract. Starting with an analysis of the configuration of chords of contact points with
 CONCURRENT LINES- PROPERTIES RELATED TO A TRIANGLE THEOREM The medians of a triangle are concurrent. Proof: Let A(x 1, y 1 ), B(x, y ), C(x 3, y 3 ) be the vertices of the triangle A(x 1, y 1 ) F E B(x,
CONCURRENT LINES- PROPERTIES RELATED TO A TRIANGLE THEOREM The medians of a triangle are concurrent. Proof: Let A(x 1, y 1 ), B(x, y ), C(x 3, y 3 ) be the vertices of the triangle A(x 1, y 1 ) F E B(x,
Roots and Coefficients of a Quadratic Equation Summary
 Roots and Coefficients of a Quadratic Equation Summary For a quadratic equation with roots α and β: Sum of roots = α + β = and Product of roots = αβ = Symmetrical functions of α and β include: x = and
Roots and Coefficients of a Quadratic Equation Summary For a quadratic equation with roots α and β: Sum of roots = α + β = and Product of roots = αβ = Symmetrical functions of α and β include: x = and
( 1 ) Find the co-ordinates of the focus, length of the latus-rectum and equation of the directrix of the parabola x 2 = - 8y.
 PROBLEMS 04 - PARABOLA Page 1 ( 1 ) Find the co-ordinates of the focus, length of the latus-rectum and equation of the directrix of the parabola x - 8. [ Ans: ( 0, - ), 8, ] ( ) If the line 3x 4 k 0 is
PROBLEMS 04 - PARABOLA Page 1 ( 1 ) Find the co-ordinates of the focus, length of the latus-rectum and equation of the directrix of the parabola x - 8. [ Ans: ( 0, - ), 8, ] ( ) If the line 3x 4 k 0 is
Q.1 If a, b, c are distinct positive real in H.P., then the value of the expression, (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4. (A) 2 (B) 5/2 (C) 3 (D) none of these
 Q. If a, b, c are distinct positive real in H.P., then the value of the expression, b a b c + is equal to b a b c () (C) (D) 4 Q. In a triangle BC, (b + c) = a bc where is the circumradius of the triangle.
Q. If a, b, c are distinct positive real in H.P., then the value of the expression, b a b c + is equal to b a b c () (C) (D) 4 Q. In a triangle BC, (b + c) = a bc where is the circumradius of the triangle.
Circle geometry investigation: Student worksheet
 Circle geometry investigation: Student worksheet http://topdrawer.aamt.edu.au/geometric-reasoning/good-teaching/exploringcircles/explore-predict-confirm/circle-geometry-investigations About these activities
Circle geometry investigation: Student worksheet http://topdrawer.aamt.edu.au/geometric-reasoning/good-teaching/exploringcircles/explore-predict-confirm/circle-geometry-investigations About these activities
1. In a triangle ABC altitude from C to AB is CF= 8 units and AB has length 6 units. If M and P are midpoints of AF and BC. Find the length of PM.
 1. In a triangle ABC altitude from C to AB is CF= 8 units and AB has length 6 units. If M and P are midpoints of AF and BC. Find the length of PM. 2. Let ABCD be a cyclic quadrilateral inscribed in a circle
1. In a triangle ABC altitude from C to AB is CF= 8 units and AB has length 6 units. If M and P are midpoints of AF and BC. Find the length of PM. 2. Let ABCD be a cyclic quadrilateral inscribed in a circle
Additional Mathematics Lines and circles
 Additional Mathematics Lines and circles Topic assessment 1 The points A and B have coordinates ( ) and (4 respectively. Calculate (i) The gradient of the line AB [1] The length of the line AB [] (iii)
Additional Mathematics Lines and circles Topic assessment 1 The points A and B have coordinates ( ) and (4 respectively. Calculate (i) The gradient of the line AB [1] The length of the line AB [] (iii)
Chapter (Circle) * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in
 Chapter - 10 (Circle) Key Concept * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in a plane. * Concentric circle - Circle having same centre called concentric circle.
Chapter - 10 (Circle) Key Concept * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in a plane. * Concentric circle - Circle having same centre called concentric circle.
= 0 1 (3 4 ) 1 (4 4) + 1 (4 3) = = + 1 = 0 = 1 = ± 1 ]
![= 0 1 (3 4 ) 1 (4 4) + 1 (4 3) = = + 1 = 0 = 1 = ± 1 ] = 0 1 (3 4 ) 1 (4 4) + 1 (4 3) = = + 1 = 0 = 1 = ± 1 ]](/thumbs/74/71228184.jpg) STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; x + y + = 0 and x + y + = 0, where + =, are concurrent then (A) =, = (B) =, = ± (C) =, = ± (D*) = ±, = [Sol. Lines are x + y + = 0
STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; x + y + = 0 and x + y + = 0, where + =, are concurrent then (A) =, = (B) =, = ± (C) =, = ± (D*) = ±, = [Sol. Lines are x + y + = 0
SYSTEM OF CIRCLES OBJECTIVES (a) Touch each other internally (b) Touch each other externally
 SYSTEM OF CIRCLES OBJECTIVES. A circle passes through (0, 0) and (, 0) and touches the circle x + y = 9, then the centre of circle is (a) (c) 3,, (b) (d) 3,, ±. The equation of the circle having its centre
SYSTEM OF CIRCLES OBJECTIVES. A circle passes through (0, 0) and (, 0) and touches the circle x + y = 9, then the centre of circle is (a) (c) 3,, (b) (d) 3,, ±. The equation of the circle having its centre
Bicevian Tucker Circles
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 7 (2007) 87 97. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 icevian Tucker ircles ernard Gibert bstract. We prove that there are exactly ten bicevian Tucker circles and show several curves containing
Forum Geometricorum Volume 7 (2007) 87 97. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 icevian Tucker ircles ernard Gibert bstract. We prove that there are exactly ten bicevian Tucker circles and show several curves containing
Maharashtra Board Class X Mathematics - Geometry Board Paper 2014 Solution. Time: 2 hours Total Marks: 40
 Maharashtra Board Class X Mathematics - Geometry Board Paper 04 Solution Time: hours Total Marks: 40 Note: - () All questions are compulsory. () Use of calculator is not allowed.. i. Ratio of the areas
Maharashtra Board Class X Mathematics - Geometry Board Paper 04 Solution Time: hours Total Marks: 40 Note: - () All questions are compulsory. () Use of calculator is not allowed.. i. Ratio of the areas
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS Duration : Two Hours Maximum Marks : 100. [ Q. 1 to 60 carry one mark each ] A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D.
![MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS Duration : Two Hours Maximum Marks : 100. [ Q. 1 to 60 carry one mark each ] A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS Duration : Two Hours Maximum Marks : 100. [ Q. 1 to 60 carry one mark each ] A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D.](/thumbs/95/125385791.jpg) M 68 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS Duration : Two Hours Maimum Marks : [ Q. to 6 carry one mark each ]. If sin sin sin y z, then the value of 9 y 9 z 9 9 y 9 z 9 A. B. C. D. is equal
M 68 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS Duration : Two Hours Maimum Marks : [ Q. to 6 carry one mark each ]. If sin sin sin y z, then the value of 9 y 9 z 9 9 y 9 z 9 A. B. C. D. is equal
Q1. If (1, 2) lies on the circle. x 2 + y 2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0. which is concentric with the circle x 2 + y 2 +4x + 2y 5 = 0 then c =
 Q1. If (1, 2) lies on the circle x 2 + y 2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 which is concentric with the circle x 2 + y 2 +4x + 2y 5 = 0 then c = a) 11 b) -13 c) 24 d) 100 Solution: Any circle concentric with x 2 +
Q1. If (1, 2) lies on the circle x 2 + y 2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 which is concentric with the circle x 2 + y 2 +4x + 2y 5 = 0 then c = a) 11 b) -13 c) 24 d) 100 Solution: Any circle concentric with x 2 +
Circle and Cyclic Quadrilaterals. MARIUS GHERGU School of Mathematics and Statistics University College Dublin
 Circle and Cyclic Quadrilaterals MARIUS GHERGU School of Mathematics and Statistics University College Dublin 3 Basic Facts About Circles A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of the
Circle and Cyclic Quadrilaterals MARIUS GHERGU School of Mathematics and Statistics University College Dublin 3 Basic Facts About Circles A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of the
Senior Math Circles February 18, 2009 Conics III
 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Senior Math Circles February 18, 2009 Conics III Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Eccentricity of Conics Fix a point F called the focus, a
University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Senior Math Circles February 18, 2009 Conics III Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Eccentricity of Conics Fix a point F called the focus, a
Harmonic Division and its Applications
 Harmonic ivision and its pplications osmin Pohoata Let d be a line and,,, and four points which lie in this order on it. he four-point () is called a harmonic division, or simply harmonic, if =. If is
Harmonic ivision and its pplications osmin Pohoata Let d be a line and,,, and four points which lie in this order on it. he four-point () is called a harmonic division, or simply harmonic, if =. If is
ON TWO SPECIAL POINTS IN TRIANGLE
 ON TWO SPEIL POINTS IN TRINGLE KPIL PUSE 1. Introduction Today we will learn about two intriguing special points in triangle that seem to have many interesting properties. You will see many examples where
ON TWO SPEIL POINTS IN TRINGLE KPIL PUSE 1. Introduction Today we will learn about two intriguing special points in triangle that seem to have many interesting properties. You will see many examples where
DEEPAWALI ASSIGNMENT CLASS 11 FOR TARGET IIT JEE 2012 SOLUTION
 DEEPAWALI ASSIGNMENT CLASS FOR TARGET IIT JEE 0 SOLUTION IMAGE OF SHRI GANESH LAXMI SARASWATI Director & H.O.D. IITJEE Mathematics SUHAG R. KARIYA (S.R.K. Sir) DOWNLOAD FREE STUDY PACKAGE, TEST SERIES
DEEPAWALI ASSIGNMENT CLASS FOR TARGET IIT JEE 0 SOLUTION IMAGE OF SHRI GANESH LAXMI SARASWATI Director & H.O.D. IITJEE Mathematics SUHAG R. KARIYA (S.R.K. Sir) DOWNLOAD FREE STUDY PACKAGE, TEST SERIES
Three Natural Homoteties of The Nine-Point Circle
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 13 (2013) 209 218. FRUM GEM ISS 1534-1178 Three atural omoteties of The ine-point ircle Mehmet Efe kengin, Zeyd Yusuf Köroğlu, and Yiğit Yargiç bstract. Given a triangle with
Forum Geometricorum Volume 13 (2013) 209 218. FRUM GEM ISS 1534-1178 Three atural omoteties of The ine-point ircle Mehmet Efe kengin, Zeyd Yusuf Köroğlu, and Yiğit Yargiç bstract. Given a triangle with
6 CHAPTER. Triangles. A plane figure bounded by three line segments is called a triangle.
 6 CHAPTER We are Starting from a Point but want to Make it a Circle of Infinite Radius A plane figure bounded by three line segments is called a triangle We denote a triangle by the symbol In fig ABC has
6 CHAPTER We are Starting from a Point but want to Make it a Circle of Infinite Radius A plane figure bounded by three line segments is called a triangle We denote a triangle by the symbol In fig ABC has
Some Collinearities in the Heptagonal Triangle
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 16 (2016) 249 256. FRUM GEM ISSN 1534-1178 Some ollinearities in the Heptagonal Triangle bdilkadir ltintaş bstract. With the methods of barycentric coordinates, we establish
Forum Geometricorum Volume 16 (2016) 249 256. FRUM GEM ISSN 1534-1178 Some ollinearities in the Heptagonal Triangle bdilkadir ltintaş bstract. With the methods of barycentric coordinates, we establish
Department of Mathematics
 Department of Mathematics TIME: 3 Hours Setter: DS DATE: 03 August 2015 GRADE 12 PRELIM EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS: PAPER II Total marks: 150 Moderator: AM Name of student: PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS
Department of Mathematics TIME: 3 Hours Setter: DS DATE: 03 August 2015 GRADE 12 PRELIM EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS: PAPER II Total marks: 150 Moderator: AM Name of student: PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS
International Mathematics TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS
 International Mathematics TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS Senior A-Level Paper Fall 2011 1 Pete has marked at least 3 points in the plane such that all distances between them are different A pair of marked points
International Mathematics TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS Senior A-Level Paper Fall 2011 1 Pete has marked at least 3 points in the plane such that all distances between them are different A pair of marked points
l (D) 36 (C) 9 x + a sin at which the tangent is parallel to x-axis lie on
 Dpp- to MATHEMATICS Dail Practice Problems Target IIT JEE 00 CLASS : XIII (VXYZ) DPP. NO.- to DPP- Q. If on a given base, a triangle be described such that the sum of the tangents of the base angles is
Dpp- to MATHEMATICS Dail Practice Problems Target IIT JEE 00 CLASS : XIII (VXYZ) DPP. NO.- to DPP- Q. If on a given base, a triangle be described such that the sum of the tangents of the base angles is
Isogonal Conjugates. Navneel Singhal October 9, Abstract
 Isogonal Conjugates Navneel Singhal navneel.singhal@ymail.com October 9, 2016 Abstract This is a short note on isogonality, intended to exhibit the uses of isogonality in mathematical olympiads. Contents
Isogonal Conjugates Navneel Singhal navneel.singhal@ymail.com October 9, 2016 Abstract This is a short note on isogonality, intended to exhibit the uses of isogonality in mathematical olympiads. Contents
INMO-2001 Problems and Solutions
 INMO-2001 Problems and Solutions 1. Let ABC be a triangle in which no angle is 90. For any point P in the plane of the triangle, let A 1,B 1,C 1 denote the reflections of P in the sides BC,CA,AB respectively.
INMO-2001 Problems and Solutions 1. Let ABC be a triangle in which no angle is 90. For any point P in the plane of the triangle, let A 1,B 1,C 1 denote the reflections of P in the sides BC,CA,AB respectively.
1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why. (a b)(a c)(a d)(b c)(b d)(c d) a 2 + ab b = 2018.
 New Zealand Mathematical Olympiad Committee Camp Selection Problems 2018 Solutions Due: 28th September 2018 1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why must be a multiple of
New Zealand Mathematical Olympiad Committee Camp Selection Problems 2018 Solutions Due: 28th September 2018 1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why must be a multiple of
The Distance Formula. The Midpoint Formula
 Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Distance Midpoint Formulas The Distance Formula The distance between two points P 1 = (x 1, y 1 ) P 2 = (x 1, y 1 ), denoted by d(p 1, P 2 ), is d(p 1, P 2 ) = (x
Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Distance Midpoint Formulas The Distance Formula The distance between two points P 1 = (x 1, y 1 ) P 2 = (x 1, y 1 ), denoted by d(p 1, P 2 ), is d(p 1, P 2 ) = (x
Objective Mathematics
 . In BC, if angles, B, C are in geometric seq- uence with common ratio, then is : b c a (a) (c) 0 (d) 6. If the angles of a triangle are in the ratio 4 : :, then the ratio of the longest side to the perimeter
. In BC, if angles, B, C are in geometric seq- uence with common ratio, then is : b c a (a) (c) 0 (d) 6. If the angles of a triangle are in the ratio 4 : :, then the ratio of the longest side to the perimeter
Classical Theorems in Plane Geometry 1
 BERKELEY MATH CIRCLE 1999 2000 Classical Theorems in Plane Geometry 1 Zvezdelina Stankova-Frenkel UC Berkeley and Mills College Note: All objects in this handout are planar - i.e. they lie in the usual
BERKELEY MATH CIRCLE 1999 2000 Classical Theorems in Plane Geometry 1 Zvezdelina Stankova-Frenkel UC Berkeley and Mills College Note: All objects in this handout are planar - i.e. they lie in the usual
Parabola. The fixed point is called the focus and it is denoted by S. A (0, 0), S (a, 0) and P (x 1, y 1 ) PM=NZ=NA+AZ= x 1 + a
 : Conic: The locus of a point moving on a plane such that its distance from a fixed point and a fixed straight line in the plane are in a constant ratio é, is called a conic. The fixed point is called
: Conic: The locus of a point moving on a plane such that its distance from a fixed point and a fixed straight line in the plane are in a constant ratio é, is called a conic. The fixed point is called
1 2n. i=1. 2m+1 i = m, while. 2m + 1 = 1. is the best possible for any odd n.
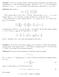 Problem 1. Let n be a positive integer. Find the largest nonnegative real number f(n) (depending on n) with the following property: whenever a 1, a,..., a n are real numbers such that a 1 + a + + a n is
Problem 1. Let n be a positive integer. Find the largest nonnegative real number f(n) (depending on n) with the following property: whenever a 1, a,..., a n are real numbers such that a 1 + a + + a n is
POINT. Preface. The concept of Point is very important for the study of coordinate
 POINT Preface The concept of Point is ver important for the stud of coordinate geometr. This chapter deals with various forms of representing a Point and several associated properties. The concept of coordinates
POINT Preface The concept of Point is ver important for the stud of coordinate geometr. This chapter deals with various forms of representing a Point and several associated properties. The concept of coordinates
21. Prove that If one side of the cyclic quadrilateral is produced then the exterior angle is equal to the interior opposite angle.
 21. Prove that If one side of the cyclic quadrilateral is produced then the exterior angle is equal to the interior opposite angle. 22. Prove that If two sides of a cyclic quadrilateral are parallel, then
21. Prove that If one side of the cyclic quadrilateral is produced then the exterior angle is equal to the interior opposite angle. 22. Prove that If two sides of a cyclic quadrilateral are parallel, then
Berkeley Math Circle, May
 Berkeley Math Circle, May 1-7 2000 COMPLEX NUMBERS IN GEOMETRY ZVEZDELINA STANKOVA FRENKEL, MILLS COLLEGE 1. Let O be a point in the plane of ABC. Points A 1, B 1, C 1 are the images of A, B, C under symmetry
Berkeley Math Circle, May 1-7 2000 COMPLEX NUMBERS IN GEOMETRY ZVEZDELINA STANKOVA FRENKEL, MILLS COLLEGE 1. Let O be a point in the plane of ABC. Points A 1, B 1, C 1 are the images of A, B, C under symmetry
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS
 DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AS level Mathematics Core mathematics 1 C1 2015-2016 Name: Page C1 workbook contents Indices and Surds Simultaneous equations Quadratics Inequalities Graphs Arithmetic series
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AS level Mathematics Core mathematics 1 C1 2015-2016 Name: Page C1 workbook contents Indices and Surds Simultaneous equations Quadratics Inequalities Graphs Arithmetic series
VKR Classes TIME BOUND TESTS 1-7 Target JEE ADVANCED For Class XI VKR Classes, C , Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No
 VKR Classes TIME BOUND TESTS -7 Target JEE ADVANCED For Class XI VKR Classes, C-9-0, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No. 9890605 Single Choice Question : PRACTICE TEST-. The smallest integer greater than log +
VKR Classes TIME BOUND TESTS -7 Target JEE ADVANCED For Class XI VKR Classes, C-9-0, Indra Vihar, Kota. Mob. No. 9890605 Single Choice Question : PRACTICE TEST-. The smallest integer greater than log +
Inversion Geometry on its head
 Inversion Geometry on its head Bibliography: Geometry revisited Coxeter & Greitzer MAA 1967 Introduction to Geometry Coxeter Wiley Classics 1961 Algebraic Projective Geometry Semple & Kneebone OUP 1952
Inversion Geometry on its head Bibliography: Geometry revisited Coxeter & Greitzer MAA 1967 Introduction to Geometry Coxeter Wiley Classics 1961 Algebraic Projective Geometry Semple & Kneebone OUP 1952
Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Winter 2012 Quiz Solutions
 Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Winter 2012 Quiz Solutions Quiz #1. Tuesday, 17 January, 2012. [10 minutes] 1. Given a line segment AB, use (some of) Postulates I V,
Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Winter 2012 Quiz Solutions Quiz #1. Tuesday, 17 January, 2012. [10 minutes] 1. Given a line segment AB, use (some of) Postulates I V,
Generalized Mandart Conics
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 4 (2004) 177 198. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Generalized Mandart onics ernard Gibert bstract. We consider interesting conics associated with the configuration of three points
Forum Geometricorum Volume 4 (2004) 177 198. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Generalized Mandart onics ernard Gibert bstract. We consider interesting conics associated with the configuration of three points
CBSE X Mathematics 2012 Solution (SET 1) Section B
 CBSE X Mathematics 01 Solution (SET 1) Section B Q11. Find the value(s) of k so that the quadratic equation x kx + k = 0 has equal roots. Given equation is x kx k 0 For the given equation to have equal
CBSE X Mathematics 01 Solution (SET 1) Section B Q11. Find the value(s) of k so that the quadratic equation x kx + k = 0 has equal roots. Given equation is x kx k 0 For the given equation to have equal
16 circles. what goes around...
 16 circles. what goes around... 2 lesson 16 this is the first of two lessons dealing with circles. this lesson gives some basic definitions and some elementary theorems, the most important of which is
16 circles. what goes around... 2 lesson 16 this is the first of two lessons dealing with circles. this lesson gives some basic definitions and some elementary theorems, the most important of which is
Practice Problems in Geometry
 Practice Problems in Geometry Navneel Singhal August 12, 2016 Abstract The problems here are not sorted in order of difficulty because sometimes after seeing the source of the problem, people get intimidated.
Practice Problems in Geometry Navneel Singhal August 12, 2016 Abstract The problems here are not sorted in order of difficulty because sometimes after seeing the source of the problem, people get intimidated.
VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER)
 BY:Prof. RAHUL MISHRA Class :- X QNo. VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER) CIRCLES Subject :- Maths General Instructions Questions M:9999907099,9818932244 1 In the adjoining figures, PQ
BY:Prof. RAHUL MISHRA Class :- X QNo. VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER) CIRCLES Subject :- Maths General Instructions Questions M:9999907099,9818932244 1 In the adjoining figures, PQ
CMO 2007 Solutions. 3. Suppose that f is a real-valued function for which. f(xy) + f(y x) f(y + x) for all real numbers x and y.
 CMO 2007 Solutions 1 What is the maximum number of non-overlapping 2 1 dominoes that can be placed on an 8 9 checkerboard if six of them are placed as shown? Each domino must be placed horizontally or
CMO 2007 Solutions 1 What is the maximum number of non-overlapping 2 1 dominoes that can be placed on an 8 9 checkerboard if six of them are placed as shown? Each domino must be placed horizontally or
PREPARED BY: ER. VINEET LOOMBA (B.TECH. IIT ROORKEE) 60 Best JEE Main and Advanced Level Problems (IIT-JEE). Prepared by IITians.
 www. Class XI TARGET : JEE Main/Adv PREPARED BY: ER. VINEET LOOMBA (B.TECH. IIT ROORKEE) ALP ADVANCED LEVEL PROBLEMS Straight Lines 60 Best JEE Main and Advanced Level Problems (IIT-JEE). Prepared b IITians.
www. Class XI TARGET : JEE Main/Adv PREPARED BY: ER. VINEET LOOMBA (B.TECH. IIT ROORKEE) ALP ADVANCED LEVEL PROBLEMS Straight Lines 60 Best JEE Main and Advanced Level Problems (IIT-JEE). Prepared b IITians.
Forum Geometricorum Volume 13 (2013) 1 6. FORUM GEOM ISSN Soddyian Triangles. Frank M. Jackson
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 3 (203) 6. FORUM GEOM ISSN 534-78 Soddyian Triangles Frank M. Jackson bstract. Soddyian triangle is a triangle whose outer Soddy circle has degenerated into a straight line.
Forum Geometricorum Volume 3 (203) 6. FORUM GEOM ISSN 534-78 Soddyian Triangles Frank M. Jackson bstract. Soddyian triangle is a triangle whose outer Soddy circle has degenerated into a straight line.
STRAIGHT LINES EXERCISE - 3
 STRAIGHT LINES EXERCISE - 3 Q. D C (3,4) E A(, ) Mid point of A, C is B 3 E, Point D rotation of point C(3, 4) by angle 90 o about E. 3 o 3 3 i4 cis90 i 5i 3 i i 5 i 5 D, point E mid point of B & D. So
STRAIGHT LINES EXERCISE - 3 Q. D C (3,4) E A(, ) Mid point of A, C is B 3 E, Point D rotation of point C(3, 4) by angle 90 o about E. 3 o 3 3 i4 cis90 i 5i 3 i i 5 i 5 D, point E mid point of B & D. So
MATH 680 : History of Mathematics
 1 MATH 680 : History of Mathematics Term: Spring 013 Instructor: S. Furino Assignment 5: Analytic Geometry Weight: 8% Due: 3:55 (11:55PM) Waterloo time on 18 June 013 When typesetting your solutions use
1 MATH 680 : History of Mathematics Term: Spring 013 Instructor: S. Furino Assignment 5: Analytic Geometry Weight: 8% Due: 3:55 (11:55PM) Waterloo time on 18 June 013 When typesetting your solutions use
The Lemoine Cubic and Its Generalizations
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 2 (2002) 47 63. FRUM GEM ISSN 1534-1178 The Lemoine ubic and Its Generalizations ernard Gibert bstract. For a given triangle, the Lemoine cubic is the locus of points whose cevian
Forum Geometricorum Volume 2 (2002) 47 63. FRUM GEM ISSN 1534-1178 The Lemoine ubic and Its Generalizations ernard Gibert bstract. For a given triangle, the Lemoine cubic is the locus of points whose cevian
SMT Power Round Solutions : Poles and Polars
 SMT Power Round Solutions : Poles and Polars February 18, 011 1 Definition and Basic Properties 1 Note that the unit circles are not necessary in the solutions. They just make the graphs look nicer. (1).0
SMT Power Round Solutions : Poles and Polars February 18, 011 1 Definition and Basic Properties 1 Note that the unit circles are not necessary in the solutions. They just make the graphs look nicer. (1).0
S56 (5.3) Recurrence Relations.notebook September 09, 2015
 Daily Practice 31.8.2015 Q1. Write down the equation of a circle with centre (-1, 4) and radius 5 Q2. Given the circle with equation (x 4) 2 + (y + 5) 2 = 40. Find the equation of the tangent to this circle
Daily Practice 31.8.2015 Q1. Write down the equation of a circle with centre (-1, 4) and radius 5 Q2. Given the circle with equation (x 4) 2 + (y + 5) 2 = 40. Find the equation of the tangent to this circle
GLOBAL TALENT SEARCH EXAMINATIONS (GTSE) CLASS -XI
 GLOBAL TALENT SEARCH EXAMINATIONS (GTSE) Date: rd November 008 CLASS -XI MATHEMATICS Max Marks: 80 Time: :0 to :5 a.m. General Instructions: (Read Instructions carefully). All questions are compulsory.
GLOBAL TALENT SEARCH EXAMINATIONS (GTSE) Date: rd November 008 CLASS -XI MATHEMATICS Max Marks: 80 Time: :0 to :5 a.m. General Instructions: (Read Instructions carefully). All questions are compulsory.
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR INTERMEDIATE PUBLIC EXAMINATIONS IN MATHS-IB
 ` KUKATPALLY CENTRE IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR INTERMEDIATE PUBLIC EXAMINATIONS IN MATHS-IB 017-18 FIITJEE KUKATPALLY CENTRE: # -97, Plot No1, Opp Patel Kunta Huda Park, Vijaynagar Colony, Hyderabad - 500
` KUKATPALLY CENTRE IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR INTERMEDIATE PUBLIC EXAMINATIONS IN MATHS-IB 017-18 FIITJEE KUKATPALLY CENTRE: # -97, Plot No1, Opp Patel Kunta Huda Park, Vijaynagar Colony, Hyderabad - 500
5. Polynomial Functions and Equations
 5. Polynomial Functions and Equations 1. Polynomial equations and roots. Solving polynomial equations in the chemical context 3. Solving equations of multiple unknowns 5.1. Polynomial equations and roots
5. Polynomial Functions and Equations 1. Polynomial equations and roots. Solving polynomial equations in the chemical context 3. Solving equations of multiple unknowns 5.1. Polynomial equations and roots
A Note on the Barycentric Square Roots of Kiepert Perspectors
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (2006) 263 268. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Note on the arycentric Square Roots of Kiepert erspectors Khoa Lu Nguyen bstract. Let be an interior point of a given triangle. We
Forum Geometricorum Volume 6 (2006) 263 268. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 Note on the arycentric Square Roots of Kiepert erspectors Khoa Lu Nguyen bstract. Let be an interior point of a given triangle. We
10.1 Tangents to Circles. Geometry Mrs. Spitz Spring 2005
 10.1 Tangents to Circles Geometry Mrs. Spitz Spring 2005 Objectives/Assignment Identify segments and lines related to circles. Use properties of a tangent to a circle. Assignment: Chapter 10 Definitions
10.1 Tangents to Circles Geometry Mrs. Spitz Spring 2005 Objectives/Assignment Identify segments and lines related to circles. Use properties of a tangent to a circle. Assignment: Chapter 10 Definitions
+ 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 if S
 CIRCLE DEFINITIONS A circle is the locus of a point which moves in such a way that its distance from a fixed point, called the centre, is always a constant. The distance r from the centre is called the
CIRCLE DEFINITIONS A circle is the locus of a point which moves in such a way that its distance from a fixed point, called the centre, is always a constant. The distance r from the centre is called the
IMO Training Camp Mock Olympiad #2
 IMO Training Camp Mock Olympiad #2 July 3, 2008 1. Given an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC. The midpoint of side BC is denoted by M. Let X be a variable point on the shorter arc MA of the circumcircle
IMO Training Camp Mock Olympiad #2 July 3, 2008 1. Given an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC. The midpoint of side BC is denoted by M. Let X be a variable point on the shorter arc MA of the circumcircle
1998 IMO Shortlist BM BN BA BC AB BC CD DE EF BC CA AE EF FD
 IMO Shortlist 1998 Geometry 1 A convex quadrilateral ABCD has perpendicular diagonals. The perpendicular bisectors of the sides AB and CD meet at a unique point P inside ABCD. the quadrilateral ABCD is
IMO Shortlist 1998 Geometry 1 A convex quadrilateral ABCD has perpendicular diagonals. The perpendicular bisectors of the sides AB and CD meet at a unique point P inside ABCD. the quadrilateral ABCD is
A NEW PROOF OF PTOLEMY S THEOREM
 A NEW PROOF OF PTOLEMY S THEOREM DASARI NAGA VIJAY KRISHNA Abstract In this article we give a new proof of well-known Ptolemy s Theorem of a Cyclic Quadrilaterals 1 Introduction In the Euclidean geometry,
A NEW PROOF OF PTOLEMY S THEOREM DASARI NAGA VIJAY KRISHNA Abstract In this article we give a new proof of well-known Ptolemy s Theorem of a Cyclic Quadrilaterals 1 Introduction In the Euclidean geometry,
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION
 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 02 F PERIODIC TEST III EXAM (2017-18) SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS(041) BLUE PRINT : CLASS IX Unit Chapter VSA (1 mark) SA I (2 marks) SA II (3 marks)
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 02 F PERIODIC TEST III EXAM (2017-18) SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS(041) BLUE PRINT : CLASS IX Unit Chapter VSA (1 mark) SA I (2 marks) SA II (3 marks)
2. (i) Find the equation of the circle which passes through ( 7, 1) and has centre ( 4, 3).
 Circle 1. (i) Find the equation of the circle with centre ( 7, 3) and of radius 10. (ii) Find the centre of the circle 2x 2 + 2y 2 + 6x + 8y 1 = 0 (iii) What is the radius of the circle 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 5x
Circle 1. (i) Find the equation of the circle with centre ( 7, 3) and of radius 10. (ii) Find the centre of the circle 2x 2 + 2y 2 + 6x + 8y 1 = 0 (iii) What is the radius of the circle 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 5x
Calculus With Analytic Geometry by SM. Yusaf & Prof.Muhammad Amin
 The Sphere Definition: The set of all points in space that are equidistant from a fixed point is called a sphere. The constant distance is called the radius of the sphere and the fixed point is called
The Sphere Definition: The set of all points in space that are equidistant from a fixed point is called a sphere. The constant distance is called the radius of the sphere and the fixed point is called
Olympiad Correspondence Problems. Set 3
 (solutions follow) 1998-1999 Olympiad Correspondence Problems Set 3 13. The following construction and proof was proposed for trisecting a given angle with ruler and Criticizecompasses the arguments. Construction.
(solutions follow) 1998-1999 Olympiad Correspondence Problems Set 3 13. The following construction and proof was proposed for trisecting a given angle with ruler and Criticizecompasses the arguments. Construction.
SOME NEW THEOREMS IN PLANE GEOMETRY II
 SOME NEW THEOREMS IN PLANE GEOMETRY II ALEXANDER SKUTIN 1. Introduction This work is an extension of [1]. In fact, I used the same ideas and sections as in [1], but introduced other examples of applications.
SOME NEW THEOREMS IN PLANE GEOMETRY II ALEXANDER SKUTIN 1. Introduction This work is an extension of [1]. In fact, I used the same ideas and sections as in [1], but introduced other examples of applications.
The Cevian Simson Transformation
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 14 (2014 191 200. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 The evian Simson Transformation Bernard Gibert Abstract. We study a transformation whose origin lies in the relation between concurrent
Forum Geometricorum Volume 14 (2014 191 200. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 The evian Simson Transformation Bernard Gibert Abstract. We study a transformation whose origin lies in the relation between concurrent
Math : Analytic Geometry
 7 EP-Program - Strisuksa School - Roi-et Math : Analytic Geometry Dr.Wattana Toutip - Department of Mathematics Khon Kaen University 00 :Wattana Toutip wattou@kku.ac.th http://home.kku.ac.th/wattou 7 Analytic
7 EP-Program - Strisuksa School - Roi-et Math : Analytic Geometry Dr.Wattana Toutip - Department of Mathematics Khon Kaen University 00 :Wattana Toutip wattou@kku.ac.th http://home.kku.ac.th/wattou 7 Analytic
Analytic Geometry MAT 1035
 Analytic Geometry MAT 035 5.09.04 WEEKLY PROGRAM - The first week of the semester, we will introduce the course and given a brief outline. We continue with vectors in R n and some operations including
Analytic Geometry MAT 035 5.09.04 WEEKLY PROGRAM - The first week of the semester, we will introduce the course and given a brief outline. We continue with vectors in R n and some operations including
A-Level Notes CORE 1
 A-Level Notes CORE 1 Basic algebra Glossary Coefficient For example, in the expression x³ 3x² x + 4, the coefficient of x³ is, the coefficient of x² is 3, and the coefficient of x is 1. (The final 4 is
A-Level Notes CORE 1 Basic algebra Glossary Coefficient For example, in the expression x³ 3x² x + 4, the coefficient of x³ is, the coefficient of x² is 3, and the coefficient of x is 1. (The final 4 is
P1 Chapter 6 :: Circles
 P1 Chapter 6 :: Circles jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 11 th August 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: www.drfrostmaths.com/homework
P1 Chapter 6 :: Circles jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 11 th August 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: www.drfrostmaths.com/homework
