Unit 2: Index Numbers
|
|
|
- Tamsin Flynn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 2: Index Numbers Index Number Index numbers are statistical devices designed to measrure the relative changes in the level of phenomenon with respect to time, geographical location or other characteristics such as income, profession etc Price Relative Price relative is the price in current year (p 1 ) expressed in the percentage of the price in the base year (p 0 ) Price Relative (P) = p 1 p 0 Quantity Relative It is the ratio of quantity of a commodity in the current year (q1) expressed as percentage of quantity in the base year (q0) and is given as Value Relative Quantity Relative (Q) = q 1 q 0 It is the ration of value of commodity in the current year (v1) as expressed as percentage of the value in base year (v0) and is given as: Characteristics of Index Numbers Value Relative (V) = v 1 v 0 = p 1q 1 p 0 q 0 1. Index numbers are specialized type of averages. 2. They are expressed in ratios but for comparison purposes are expressed as a percentage. 3. Index numbers study the effect of factors that cannot be measured directly. 4. Index numbers facilitate the comparison Uses of Index Numbers 1. Index numbers simplifies the data thus facilitates comparative study.] 2. Index numbers are used in studying trends and tendencies. 3. Index numbers help in measuring purchasing power of money and also used for deflation. 4. It measures change in cost of living of different groups of people. 5. Index numbers are used by the government to frame suitable policies regarding fixation of bank rates, allowances to employees, license to new firms, imports, exports, taxation.
2 Limitations of Index Numbers 1. Index numbers are based on sample data, it is only an approximate indicator. 2. There is a chance of error introduced at each stage of the construction of index numbers. 3. While constructing index numbers, quality of product is not taken into consideration. 4. Like other statistical techniques, index numbers can be misused to get desired conclusions. 5. As customs, tradition and habits fo people vary from time to time, it is difficult to assign proper weights to various items. 6. Many formulae are used in construction of index numbers and different formulae give different answers. Steps in Construction of Index Numbers 1. Purpose of the Index Number: Before constructing an index number, it should be decided the purpose for which it is needed. An index number constructed for one category or purpose cannot be used for others. A cost of living index of working classes cannot be used for farmers because the items entering into their consumption will be different. 2. Selection of the Base Period: The selection of the base period is the most important step in the construction of an index number. It is a period against which comparisons are made. The base period should be economically stable. The base period should not be too distant from the current period. a) If the period of comparison is kept fixed of current years, it is called fixed-base period. b) If the relative changes in the level of phenomenon for any period are compared with that of the immediate preceding period, it is called chain-base period. 3. Selection of Commodities: Commodities to be selected depend upon the purpose or objective of the index number to be constructed. But the number of commodities should neither be too large nor too small. Moreover, commodities to be selected must be broadly representative of the group of commodities. They should also be comparable in the sense that standard or graded items should be taken. 4. Selection of Prices: The next step is to select the prices of these commodities. For this purpose, care should be taken to select prices from representative persons, places or journals or other sources. But they must be reliable. 5. Selection of an Average: Since index numbers are averages, the problem is how to select an appropriate average. The two important and common averages are the arithmetic mean and geometric mean. The arithmetic mean is the simpler of the two. But geometric mean is more accurate. However, the average prices should be reduced to price relatives (percentages) either on the basis of the fixed base method or the chain base method. 6. Selection of Weights: While constructing an index number due weightage or importance should be given to the various commodities. Commodities which are more important in the consumption of consumers should be given higher weightage than other commodities. 7. Selection of Formula: A number of formulas have been devised to construct an index number. But the selection of an appropriate formula depends upon the availability of data and purpose of the index number. No single formula may be used for all types of index numbers.
3 Price Index Numbers (Unweighted) Simple Aggregative Method P 01 = p 1 p 0 Simple Unweighted Arithmetic Mean P 01 = P n Unweighted Simple Geometric Mean P 01 = Antilog ( logp ) n
4 Price Index Numbers (Weighted) Laspeyre s Price Index In Laspeyre s method base year quantities (q0) are used as weight. Paasche s Price Index P 01 L = p 1q 0 In Paasche s method, current year quantities (q1) are used as weight. P 01 P = p 1q 1 Marshall-Edgeworth Price Index In this method, base year and current year quantities are used to find the index numbers. Weights assigned are the average of the base year and current year quantities. Dorbish Bowley s Price Index P ME 01 = p 1q 0 + p 1 q 1 + It is the AM of Laspeyre s and Paasche s index numbers. It takes into account the base and current year quantities as weights. Fisher s Price Index P 01 DB = 1 2 ( p 1q 0 + p 1q 1 ) It is the GM of Laspeyre s and Paasche s index numbers. It takes into account the base and current year quantities as weights. P 01 F = p 1q 0 p 1 q 1
5 Why Fisher s Index Number is Ideal 1. It is based on geometric mean which considers appropriate average for averaging ratio. 2. It takes into account both current year as well as base year quantities. 3. It satisfies both Time Reversal Test and Factor Reversal Test, 4. It is free of bias. Kelly s Price Index / Fixed Weight Index P 01 K = p 1q p 0 q
6 Weighted Average of Price Relatives a) Weighted AM b) Weighted GM P 01 = WP W P 01 = Antilog ( WlogP W ) Quantity Index Numbers (Weighted) Laspeyre s Quantity Index Q L 01 = q 1p 0 q 0 p 0 Paasche s Quantity Index Q P 01 = q 1p 1 q 0 p 1 Marshall-Edgeworth Quantity Index Dorbish Bowley s Quantity Index Fisher s Quantity Index ME = q 1p 0 + q 1 p 1 q 0 p 0 + q 0 p 1 Q 01 Q DB 01 = 1 2 ( q 1p 0 + q 1p 1 ) q 0 p 0 q 0 p 1 It is the GM of Laspeyre s and Paasche s index numbers. It takes into account the base and current year quantities as weights. Q 01 F = q 1p 0 q 0 p 0 q 1p 1 q 0 p 1
7 Value Index Numbers V 01 = p 1q 1 Test for Adequacy of Index Number Unit Test This test requires index numbers must be independent of the units in which price or quantities of various commodities are quoted. It is satisfied by all index numbers discussed except Aggregative Price Index formula Time Reversal Test This was proposed by Irving Fisher. According to this, an index number P01 should be such that when base year and current year are interchanged (P10) the resulting inex number should be the reciprocal of the other. TRT requires that the index number computed backward should be reciprocal of the index number computed forward, except for constant proportionality. P 10 = 1 P 01 = P 01 P 10 = 1 Here P01 and P10 are ratios and must not be expressed as percentages. 1. Laspeyre s Method Accoridng to TRT P 01 L = p 1q 0 P 10 L = p 0q 1 p 1 q 1 Laspeyre s number does not satisfy TRT. P 01 L P 10 L = p 1q 0 p 0q 1 p 1 q 1 1
8 2. Paasche s Method P 01 P = p 1q 1 When reversed it is P 10 P = p 0q 0 p 1 q 0 Paasche s index number does not satisfy TRT. 3. Marshall-Edgeworth Method P 01 P P 10 P = p 1q 1 p 0q 0 p 1 q 0 1 When reversed it is: P 01 ME = ( p 1q 0 + p 1 q 1 ) ( p 0 q 0 + ) P 10 ME = ( p 0q 1 + ) ( p 1 q 1 + p 1 q 0 ) P 01 ME P 10 ME = ( p 1q 0 + p 1 q 1 ) ( + ) ( p 0q 1 + p 0 q 0 ) ( p 1 q 1 + p 1 q 0 ) = 1 Marshall-Edgeworth Index number satisfied TRT. 4. Dorbish Bowley s Index Number When reversed P 01 DB = 1 2 ( p 1 q 0 p 0 q 0 + p 1q 1 p 0 q 1 ) P 10 DB = 1 2 ( p 0q 1 p 1 q 1 + p 0q 0 p 1 q 0 ) P 01 DB P 10 DB = 1 2 ( p 1q 0 p 0 q 0 + p 1q 1 ) 1 2 ( p 0q 1 p 1 q 1 + p 0q 0 p 1 q 0 ) 1 Dorbish Bowley index number does not satisfy TRT.
9 5. Fisher s Method P 01 F = p 1q 0 p 1q 1 When reversed P 10 F = p 0q 1 p 1 q 1 p 0q 0 p 1 q 0 Fisher index number satisfies TRT 6. Kelly s Method When reversed P 01 F P 10 F = p 1q 0 p 1q 1 p 0q 1 p 1 q 1 p 0q 0 p 1 q 0 = 1 P 01 K = p 1q p 0 q P 10 K = p 0q p 1 q P 01 K P 10 K = p 1q p 0 q p 0q p 1 q = 1 Factor Reversal Test This was also made by Irving Fisher. It requires that the product of price index and quantity index number should be equal to corresponding value index number. According to this Only Fisher index number satisfies this test. P 01 Q 01 = V 01
10 Fisher Index Number: P 01 F = p 1q 0 p 1q 1 Q F 01 = q 1p 0 q 1p 1 q 0 p 0 q 0 p 1 According to FRT P 01 Q 01 = V 01 = p 1q 1 p 0 q 0 Consider P 01 Q 01 = p 1q 0 p 1q 1 p 0 q 1 q 1p 0 q 0 p 0 q 1p 1 q 0 p 1 P 01 Q 01 = ( p 1q 1 p 0 q 0 ) 2 P 01 Q 01 = p 1q 1 p 0 q 0 = V 01 Circular Test This was suggested by Westergaard, It is an extension of Time Reversal Test for more than two periods and is based on the ability to shift base period. This requires that the index number is to work in a circular manner and this property enables us to find the index numbers from period to period without referring back to original base each time. For 3 years; 0, 1, and 2 circular test is P 01 P 12 P 20 = 1
11 Bias in an Index Number Laspeyre s index which is based on base year quantities gives relatively more weightage for such commodities than needed and consequently the numerator is relatively larger. Hence Laspeyre s index number has Upward Bias Paasche s index number, which uses the current year quantities as weights is generally an underestimate. Because greater variations of price will be paid lesser importance needed and it shows Downward bias Cost of Living Index Number CPI is the index number of the cost met by a specified class of consumers in buying a basket of goods and services. Basket of goods and services means goods and services needed in day to day life of the specified class of consumers. Class of consumers means group of consumers who have almost identical pattern of consumption. Steps involved in Construction of CPI 1. The fixed basket of goods and services is defined. This requires figuring out where the typical consumer spends his or her money. The Bureau of Labor Statistics surveys consumers to gather this information. 2. The prices for every item in the fixed basket are found. Since the same basket of goods and services is used across a number of time periods to determine changes in the CPI, the price for every item in the fixed basket must be found for every point in time. 3. The cost of the fixed basket of goods and services must be calculated for each time period. Like computing GDP, the cost of the fixed basket of goods and services is found by multiplying the quantity of each item times its price. 4. A base year is chosen and the index is computed. The price of the fixed basket of goods and services for each comparison year is then divided by the price of the fixed basket of goods in the base year. The result is multiplied by 100 to give the relative level of the cost of living between the base year and the comparison years.
12 Computing CPI Aggregative Expenditure Method The base year quantities (q0) for various commodities consumed by a particular class of people are taken as weights. CPI or Cost of Living Index No = p 1q 0 p 0 q 0 Family Budget Method CPI is constructed by using weighted arithmetic mean of price relatives, the weight being values of the items consumed in base year. Weight (w) = p 0 q 0 CPI = WP W
ADDITIVE DECOMPOSITIONS FOR FISHER, TÖRNQVIST AND GEOMETRIC MEAN INDEXES
 ADDITIVE DECOMPOSITIONS FOR FISHER, TÖRNQVIST AND GEOMETRIC MEAN INDEXES by Marshall B. Reinsdorf, W. Erwin Diewert & Christian Ehemann DECEMBER 2000 Discussion Paper No.: 01-01 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS
ADDITIVE DECOMPOSITIONS FOR FISHER, TÖRNQVIST AND GEOMETRIC MEAN INDEXES by Marshall B. Reinsdorf, W. Erwin Diewert & Christian Ehemann DECEMBER 2000 Discussion Paper No.: 01-01 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS
Lecture 1 Introduction and Historical Notes
 Lecture and Historical Notes s 5415 Index Number Theory Winter 2019 Outline Test 2 3 4 5 6 Test 7 Required Readings Test Diewert, W.E. (1993) Early History of Price Index Research, in Diewert and Nakamura
Lecture and Historical Notes s 5415 Index Number Theory Winter 2019 Outline Test 2 3 4 5 6 Test 7 Required Readings Test Diewert, W.E. (1993) Early History of Price Index Research, in Diewert and Nakamura
EUROSTAT - OECD PPP PROGRAMME 1999 THE CALCULATION AND AGGREGATION OF PARITIES
 EUROSTAT - OECD PPP PROGRAMME 1999 THE CALCULATION AND AGGREGATION OF PARITIES INTRODUCTION The calculation and aggregation of parities requires from each country participating in a comparison, either
EUROSTAT - OECD PPP PROGRAMME 1999 THE CALCULATION AND AGGREGATION OF PARITIES INTRODUCTION The calculation and aggregation of parities requires from each country participating in a comparison, either
Lecture 2 Test Approach
 Economics 5415 Number Theory Winter 2017 Outline Required Readings Balk, Bert M. (1995) Price Theory: A Survey, International Statistical Review, 63(1), 69 93. Diewert, W.E. (1992) Fisher Ideal Output,
Economics 5415 Number Theory Winter 2017 Outline Required Readings Balk, Bert M. (1995) Price Theory: A Survey, International Statistical Review, 63(1), 69 93. Diewert, W.E. (1992) Fisher Ideal Output,
Grade 2 Social Studies
 Grade 2 Social Studies Social Studies Grade(s) 2nd Course Overview This course provides an opportunity for students to explore their community and how communities operate. Scope And Sequence Timeframe
Grade 2 Social Studies Social Studies Grade(s) 2nd Course Overview This course provides an opportunity for students to explore their community and how communities operate. Scope And Sequence Timeframe
INDEX NUMBER THEORY AND MEASUREMENT ECONOMICS. By W.E. Diewert. March 15, 2015.
 1 INDEX NUMBER THEORY AND MEASUREMENT ECONOMICS By W.E. Diewert. March 15, 2015. University of British Columbia and the University of New South Wales Email: erwin.diewert@ubc.ca Website: http://www.economics.ubc.ca/faculty-and-staff/w-erwin-diewert/
1 INDEX NUMBER THEORY AND MEASUREMENT ECONOMICS By W.E. Diewert. March 15, 2015. University of British Columbia and the University of New South Wales Email: erwin.diewert@ubc.ca Website: http://www.economics.ubc.ca/faculty-and-staff/w-erwin-diewert/
Chapter 3: An Introduction to Multilateral Index Number Theory
 1 Notes on Price Measurement 1 July 22, 2014. Chapter 3: An Introduction to Multilateral Index Number Theory W. Erwin Diewert University of British Columbia and the University of New South Wales Email:
1 Notes on Price Measurement 1 July 22, 2014. Chapter 3: An Introduction to Multilateral Index Number Theory W. Erwin Diewert University of British Columbia and the University of New South Wales Email:
Aggregation: A Brief Overview
 Aggregation: A Brief Overview January 2011 () Aggregation January 2011 1 / 20 Macroeconomic Aggregates Consumption, investment, real GDP, labour productivity, TFP, physical capital, human capital (quantity
Aggregation: A Brief Overview January 2011 () Aggregation January 2011 1 / 20 Macroeconomic Aggregates Consumption, investment, real GDP, labour productivity, TFP, physical capital, human capital (quantity
Mankiw Chapter 11. Aggregate Demand I. Building the IS-LM Model
 Mankiw Chapter 11 Building the IS-LM Model 0 IN THIS CHAPTER, WE WILL COVER: the IS curve and its relation to: the Keynesian cross the LM curve and its relation to: the theory of liquidity preference how
Mankiw Chapter 11 Building the IS-LM Model 0 IN THIS CHAPTER, WE WILL COVER: the IS curve and its relation to: the Keynesian cross the LM curve and its relation to: the theory of liquidity preference how
Assignment #5. 1 Keynesian Cross. Econ 302: Intermediate Macroeconomics. December 2, 2009
 Assignment #5 Econ 0: Intermediate Macroeconomics December, 009 Keynesian Cross Consider a closed economy. Consumption function: C = C + M C(Y T ) () In addition, suppose that planned investment expenditure
Assignment #5 Econ 0: Intermediate Macroeconomics December, 009 Keynesian Cross Consider a closed economy. Consumption function: C = C + M C(Y T ) () In addition, suppose that planned investment expenditure
Revealed Preference 2011
 Revealed Preference 2011 Motivation: 1. up until now we have started with preference and then described behaviour 2. revealed preference works backwards - start with behaviour and describe preferences
Revealed Preference 2011 Motivation: 1. up until now we have started with preference and then described behaviour 2. revealed preference works backwards - start with behaviour and describe preferences
Lowe and Cobb-Douglas CPIs and their Substitution Bias
 Lowe and Cobb-Douglas CPIs and their Substitution Bias Bert M. Balk Rotterdam School of Management Erasmus University Rotterdam E-mail bbalk@rsm.nl and Statistics Netherlands The Hague Draft, April 16,
Lowe and Cobb-Douglas CPIs and their Substitution Bias Bert M. Balk Rotterdam School of Management Erasmus University Rotterdam E-mail bbalk@rsm.nl and Statistics Netherlands The Hague Draft, April 16,
VIKAS PRE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, MANGALURU ANSWER KEY STATISTICS SECTION A SECTION B
 VIKAS PRE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, MANGALURU ANSWER KEY STATISTICS SECTION A 1. Fertility refers to the births occurring to women of child bearing age 2. Marshall Edgeworth s index number does not satisfy Factor
VIKAS PRE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, MANGALURU ANSWER KEY STATISTICS SECTION A 1. Fertility refers to the births occurring to women of child bearing age 2. Marshall Edgeworth s index number does not satisfy Factor
Answer key. Statistics March Section A
 Answer key Statistics March 2018 Section A One mark 1. Cohort is a group of individuals who are born at the same time and who experience the same mortality conditions 2. 100 3. Base year quantities 4.
Answer key Statistics March 2018 Section A One mark 1. Cohort is a group of individuals who are born at the same time and who experience the same mortality conditions 2. 100 3. Base year quantities 4.
Dr. G.R. Damodaran college of Science Coimbatore GRD School of Commerce and International Business II B Com(CS) ( ) Semester IV
 Dr. G.R. Damodaran college of Science Coimbatore 641 014 GRD School of Commerce and International Business II B Com(CS) (2016-2019) Semester IV Allied : Business Statistics - 405D Multiple Choice Question
Dr. G.R. Damodaran college of Science Coimbatore 641 014 GRD School of Commerce and International Business II B Com(CS) (2016-2019) Semester IV Allied : Business Statistics - 405D Multiple Choice Question
ECON501 - Vector Di erentiation Simon Grant
 ECON01 - Vector Di erentiation Simon Grant October 00 Abstract Notes on vector di erentiation and some simple economic applications and examples 1 Functions of One Variable g : R! R derivative (slope)
ECON01 - Vector Di erentiation Simon Grant October 00 Abstract Notes on vector di erentiation and some simple economic applications and examples 1 Functions of One Variable g : R! R derivative (slope)
W. Erwin Diewert From The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, Second Edition, 2008 Edited by Steven N. Durlauf and Lawrence E.
 index numbers W. Erwin Diewert From The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, Second Edition, 2008 Edited by Steven N. Durlauf and Lawrence E. Blume Abstract Index numbers are used to aggregate detailed
index numbers W. Erwin Diewert From The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, Second Edition, 2008 Edited by Steven N. Durlauf and Lawrence E. Blume Abstract Index numbers are used to aggregate detailed
Overview of Dispersion. Standard. Deviation
 15.30 STATISTICS UNIT II: DISPERSION After reading this chapter, students will be able to understand: LEARNING OBJECTIVES To understand different measures of Dispersion i.e Range, Quartile Deviation, Mean
15.30 STATISTICS UNIT II: DISPERSION After reading this chapter, students will be able to understand: LEARNING OBJECTIVES To understand different measures of Dispersion i.e Range, Quartile Deviation, Mean
Methods of Aggregation above the Basic Heading Level within Regions
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized International Comparison Program [06.01] Methods of Aggregation above the Basic Heading
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized International Comparison Program [06.01] Methods of Aggregation above the Basic Heading
Finansiell Statistik, GN, 15 hp, VT2008 Lecture 17-2: Index Numbers
 Finansiell Statistik, GN, 15 hp, VT2008 Lecture 17-2: Index Numbers Gebrenegus Ghilagaber, PhD, Associate Professor May 7, 2008 1 1 Introduction Index numbers are summary measures used to compare the general
Finansiell Statistik, GN, 15 hp, VT2008 Lecture 17-2: Index Numbers Gebrenegus Ghilagaber, PhD, Associate Professor May 7, 2008 1 1 Introduction Index numbers are summary measures used to compare the general
Holidays Homework(10+1) Economics. 1 Calculate arithmetic mean with the help of following data.use direct method.
 Holidays Homework(+1) Economics 1 Calculate arithmetic mean with the help of following data.use direct method. Wages : 0 0 Workers No. of : 1 Compute arithmetic mean by using short cut method. Salaries:
Holidays Homework(+1) Economics 1 Calculate arithmetic mean with the help of following data.use direct method. Wages : 0 0 Workers No. of : 1 Compute arithmetic mean by using short cut method. Salaries:
Economics th April 2011
 Economics 401 8th April 2011 Instructions: Answer 7 of the following 9 questions. All questions are of equal weight. Indicate clearly on the first page which questions you want marked. 1. Answer both parts.
Economics 401 8th April 2011 Instructions: Answer 7 of the following 9 questions. All questions are of equal weight. Indicate clearly on the first page which questions you want marked. 1. Answer both parts.
MA Macroeconomics 3. Introducing the IS-MP-PC Model
 MA Macroeconomics 3. Introducing the IS-MP-PC Model Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Autumn 2014 Karl Whelan (UCD) Introducing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn 2014 1 / 38 Beyond IS-LM We have reviewed the
MA Macroeconomics 3. Introducing the IS-MP-PC Model Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Autumn 2014 Karl Whelan (UCD) Introducing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn 2014 1 / 38 Beyond IS-LM We have reviewed the
The Measurement of Macroeconomic Price Level Changes. Ludwig von Auer. Research Papers in Economics No. 1/09
 The Measurement of Macroeconomic Price Level Changes Ludwig von Auer Research Papers in Economics No. /9 The Measurement of Macroeconomic Price Level Changes by Ludwig von Auer Universität Trier, Germany
The Measurement of Macroeconomic Price Level Changes Ludwig von Auer Research Papers in Economics No. /9 The Measurement of Macroeconomic Price Level Changes by Ludwig von Auer Universität Trier, Germany
Basic headings, representative products and quasi expenditure weights
 PPP methodological manual ANNEX V: CALCULATION AND AGGREGATION OF PPPS Introduction V.1. The calculation and aggregation of PPPs requires each country participating in a Eurostat-OECD comparison to provide
PPP methodological manual ANNEX V: CALCULATION AND AGGREGATION OF PPPS Introduction V.1. The calculation and aggregation of PPPs requires each country participating in a Eurostat-OECD comparison to provide
Diploma Part 2. Quantitative Methods. Examiners Suggested Answers
 Diploma Part 2 Quantitative Methods Examiners Suggested Answers Q1 (a) A frequency distribution is a table or graph (i.e. a histogram) that shows the total number of measurements that fall in each of a
Diploma Part 2 Quantitative Methods Examiners Suggested Answers Q1 (a) A frequency distribution is a table or graph (i.e. a histogram) that shows the total number of measurements that fall in each of a
Some considerations regarding the use of the fix and chained basis indices
 Theoretical and Applied Economics Volume XIX (22), No. 2(577), pp. 53-6 Some considerations regarding the use of the fix and chained basis indices Constantin ANGHELACHE Artifex University, Bucharest The
Theoretical and Applied Economics Volume XIX (22), No. 2(577), pp. 53-6 Some considerations regarding the use of the fix and chained basis indices Constantin ANGHELACHE Artifex University, Bucharest The
The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam?
 The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam? Jean Louis Brillet, France For presentation at the LINK 2014 Conference New York, 22nd 24th October, 2014 Advertisement!!! The model uses EViews The
The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam? Jean Louis Brillet, France For presentation at the LINK 2014 Conference New York, 22nd 24th October, 2014 Advertisement!!! The model uses EViews The
Weighting of Results. Sample weights
 Weighting of Results. Two inds of weights are used in processing the answers to qualitative questions. Here they are termed sample weights and size weights. Sample weights 2. Sample weights are the inverse
Weighting of Results. Two inds of weights are used in processing the answers to qualitative questions. Here they are termed sample weights and size weights. Sample weights 2. Sample weights are the inverse
The Lucas Imperfect Information Model
 The Lucas Imperfect Information Model Based on the work of Lucas (972) and Phelps (970), the imperfect information model represents an important milestone in modern economics. The essential idea of the
The Lucas Imperfect Information Model Based on the work of Lucas (972) and Phelps (970), the imperfect information model represents an important milestone in modern economics. The essential idea of the
Macroeconomics II. Dynamic AD-AS model
 Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Dynamic AD-AS model vs. AD-AS model Notes. Dynamic AD-AS model in a few words Notes. Notation to incorporate time-dimension Notes
 Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
The Making of Tests for Index Numbers
 Arthur Vogt Janos Barta The Making of Tests for Index Numbers Mathematical Methods of Descriptive Statistics Published in Honour of the 50th Anniversary of the Death of Irving Fisher With 8 Figures Physica-Verlag
Arthur Vogt Janos Barta The Making of Tests for Index Numbers Mathematical Methods of Descriptive Statistics Published in Honour of the 50th Anniversary of the Death of Irving Fisher With 8 Figures Physica-Verlag
Chapter 4. Explanation of the Model. Satoru Kumagai Inter-disciplinary Studies, IDE-JETRO, Japan
 Chapter 4 Explanation of the Model Satoru Kumagai Inter-disciplinary Studies, IDE-JETRO, Japan Toshitaka Gokan Inter-disciplinary Studies, IDE-JETRO, Japan Ikumo Isono Bangkok Research Center, IDE-JETRO,
Chapter 4 Explanation of the Model Satoru Kumagai Inter-disciplinary Studies, IDE-JETRO, Japan Toshitaka Gokan Inter-disciplinary Studies, IDE-JETRO, Japan Ikumo Isono Bangkok Research Center, IDE-JETRO,
Toulouse School of Economics, Macroeconomics II Franck Portier. Homework 1. Problem I An AD-AS Model
 Toulouse School of Economics, 2009-2010 Macroeconomics II Franck Portier Homework 1 Problem I An AD-AS Model Let us consider an economy with three agents (a firm, a household and a government) and four
Toulouse School of Economics, 2009-2010 Macroeconomics II Franck Portier Homework 1 Problem I An AD-AS Model Let us consider an economy with three agents (a firm, a household and a government) and four
Economic Impacts of Heritage Tourism in St. Johns County, Florida, by Tom Stevens, Alan Hodges and David Mulkey.
 Economic Impacts of Heritage Tourism in St. Johns County, Florida, 2001-02 by Tom Stevens, Alan Hodges and David Mulkey University of Florida, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, Food and Resource
Economic Impacts of Heritage Tourism in St. Johns County, Florida, 2001-02 by Tom Stevens, Alan Hodges and David Mulkey University of Florida, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, Food and Resource
problem. max Both k (0) and h (0) are given at time 0. (a) Write down the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) Equation in the dynamic programming
 1. Endogenous Growth with Human Capital Consider the following endogenous growth model with both physical capital (k (t)) and human capital (h (t)) in continuous time. The representative household solves
1. Endogenous Growth with Human Capital Consider the following endogenous growth model with both physical capital (k (t)) and human capital (h (t)) in continuous time. The representative household solves
POPULATION AND SAMPLE
 1 POPULATION AND SAMPLE Population. A population refers to any collection of specified group of human beings or of non-human entities such as objects, educational institutions, time units, geographical
1 POPULATION AND SAMPLE Population. A population refers to any collection of specified group of human beings or of non-human entities such as objects, educational institutions, time units, geographical
MARLBORO CENTRAL SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM MAP. Unit 1: Integers & Rational Numbers
 Timeframe September/ October (5 s) What is an integer? What are some real life situations where integers are used? represent negative and positive numbers on a vertical and horizontal number line? What
Timeframe September/ October (5 s) What is an integer? What are some real life situations where integers are used? represent negative and positive numbers on a vertical and horizontal number line? What
Test code: ME I/ME II, 2004 Syllabus for ME I. Matrix Algebra: Matrices and Vectors, Matrix Operations, Determinants,
 Test code: ME I/ME II, 004 Syllabus for ME I Matri Algebra: Matrices and Vectors, Matri Operations, Determinants, Nonsingularity, Inversion, Cramer s rule. Calculus: Limits, Continuity, Differentiation
Test code: ME I/ME II, 004 Syllabus for ME I Matri Algebra: Matrices and Vectors, Matri Operations, Determinants, Nonsingularity, Inversion, Cramer s rule. Calculus: Limits, Continuity, Differentiation
Section Summary. Sequences. Recurrence Relations. Summations. Examples: Geometric Progression, Arithmetic Progression. Example: Fibonacci Sequence
 Section 2.4 Section Summary Sequences. Examples: Geometric Progression, Arithmetic Progression Recurrence Relations Example: Fibonacci Sequence Summations Introduction Sequences are ordered lists of elements.
Section 2.4 Section Summary Sequences. Examples: Geometric Progression, Arithmetic Progression Recurrence Relations Example: Fibonacci Sequence Summations Introduction Sequences are ordered lists of elements.
Quality Adjustment and Hedonics: An Attempt at a Unified Approach
 Quality Adjustment and Hedonics: An Attempt at a Unified Approach by Erwin Diewert University of British Columbia and University of New South Wales EMG 2018 Workshop University of New South Wales Centre
Quality Adjustment and Hedonics: An Attempt at a Unified Approach by Erwin Diewert University of British Columbia and University of New South Wales EMG 2018 Workshop University of New South Wales Centre
By W.E. Diewert, January, CHAPTER 5: The Theory of the Cost of Living Index: The Many Consumer Case
 1 INDEX NUMBER THEORY AND MEASUREMENT ECONOMICS By W.E. Diewert, January, 2015. CHAPTER 5: The Theory of the Cost of Living Index: The Many Consumer Case 1. Introduction In previous chapters, we have considered
1 INDEX NUMBER THEORY AND MEASUREMENT ECONOMICS By W.E. Diewert, January, 2015. CHAPTER 5: The Theory of the Cost of Living Index: The Many Consumer Case 1. Introduction In previous chapters, we have considered
DATABASE AND METHODOLOGY
 CHAPTER 3 DATABASE AND METHODOLOGY In the present chapter, sources of database used and methodology applied for the empirical analysis has been presented The whole chapter has been divided into three sections
CHAPTER 3 DATABASE AND METHODOLOGY In the present chapter, sources of database used and methodology applied for the empirical analysis has been presented The whole chapter has been divided into three sections
Increasingly, economists are asked not just to study or explain or interpret markets, but to design them.
 What is market design? Increasingly, economists are asked not just to study or explain or interpret markets, but to design them. This requires different tools and ideas than neoclassical economics, which
What is market design? Increasingly, economists are asked not just to study or explain or interpret markets, but to design them. This requires different tools and ideas than neoclassical economics, which
Pacing 6th Advanced Math. 1st Nine Weeks. Integers
 Signed Numbers 7th Open Up Resources: Unit 5 Chapter 1 Chapter 2 7.NS.1 7.NS.2 7.NS.3 7.NS.1 7.NS.2 7.NS.3 1st Nine Weeks Integers Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to
Signed Numbers 7th Open Up Resources: Unit 5 Chapter 1 Chapter 2 7.NS.1 7.NS.2 7.NS.3 7.NS.1 7.NS.2 7.NS.3 1st Nine Weeks Integers Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to
Mathematics Grade 7. Solve problems involving scale drawings.
 Mathematics Grade 7 All West Virginia teachers are responsible for classroom instruction that integrates content standards and mathematical habits of mind. Students in the seventh grade will focus on four
Mathematics Grade 7 All West Virginia teachers are responsible for classroom instruction that integrates content standards and mathematical habits of mind. Students in the seventh grade will focus on four
10-1 Sequences as Functions. Determine whether each sequence is arithmetic. Write yes or no. 1. 8, 2, 12, 22
 Determine whether each sequence is arithmetic. Write yes or no. 1. 8, 2, 12, 22 Subtract each term from the term directly after it. The common difference is 10. 3. 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 Subtract each term from
Determine whether each sequence is arithmetic. Write yes or no. 1. 8, 2, 12, 22 Subtract each term from the term directly after it. The common difference is 10. 3. 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 Subtract each term from
NOWCASTING REPORT. Updated: April 15, 2016
 NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: April 15, 2016 GDP growth prospects remain moderate for the rst half of the year: the nowcasts stand at 0.8% for 2016:Q1 and 1.2% for 2016:Q2. News from this week's data releases
NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: April 15, 2016 GDP growth prospects remain moderate for the rst half of the year: the nowcasts stand at 0.8% for 2016:Q1 and 1.2% for 2016:Q2. News from this week's data releases
Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded areas indicate US recessions research.stlouisfed.org
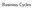 Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
7th Grade Mathematics
 Course Description In, instructional time should focus on four critical areas: (1) developing understanding of and applying proportional relationships; (2) developing understanding of operations with rational
Course Description In, instructional time should focus on four critical areas: (1) developing understanding of and applying proportional relationships; (2) developing understanding of operations with rational
Economic Theory of Spatial Costs. of Living Indices with. Application to Thailand
 Economic Theory of Spatial Costs of Living Indices with Application to Thailand spatial 5/10/97 ECONOMIC THEORY OF SPATIAL COSTS OF LIVING INDICES WITH APPLICATION TO THAILAND by N.Kakwani* School of Economics
Economic Theory of Spatial Costs of Living Indices with Application to Thailand spatial 5/10/97 ECONOMIC THEORY OF SPATIAL COSTS OF LIVING INDICES WITH APPLICATION TO THAILAND by N.Kakwani* School of Economics
VALIDATING A SURVEY ESTIMATE - A COMPARISON OF THE GUYANA RURAL FARM HOUSEHOLD SURVEY AND INDEPENDENT RICE DATA
 VALIDATING A SURVEY ESTIMATE - A COMPARISON OF THE GUYANA RURAL FARM HOUSEHOLD SURVEY AND INDEPENDENT RICE DATA David J. Megill, U.S. Bureau of the Census I. Background While attempting to validate survey
VALIDATING A SURVEY ESTIMATE - A COMPARISON OF THE GUYANA RURAL FARM HOUSEHOLD SURVEY AND INDEPENDENT RICE DATA David J. Megill, U.S. Bureau of the Census I. Background While attempting to validate survey
General Equilibrium and Welfare
 and Welfare Lectures 2 and 3, ECON 4240 Spring 2017 University of Oslo 24.01.2017 and 31.01.2017 1/37 Outline General equilibrium: look at many markets at the same time. Here all prices determined in the
and Welfare Lectures 2 and 3, ECON 4240 Spring 2017 University of Oslo 24.01.2017 and 31.01.2017 1/37 Outline General equilibrium: look at many markets at the same time. Here all prices determined in the
Centers at Malleshwaram Rajajinagar Yelahanka Mathikere
 1. x, y, z together start a business. If x invests 3 times as much as y invests and y invests two third of what z invests, then the ratio of capitals of x, y, z is : (a) 3 : 9 : 2 (b) 6 : 3 : 2 (c) 3 :
1. x, y, z together start a business. If x invests 3 times as much as y invests and y invests two third of what z invests, then the ratio of capitals of x, y, z is : (a) 3 : 9 : 2 (b) 6 : 3 : 2 (c) 3 :
The Central Bank of Iceland forecasting record
 Forecasting errors are inevitable. Some stem from errors in the models used for forecasting, others are due to inaccurate information on the economic variables on which the models are based measurement
Forecasting errors are inevitable. Some stem from errors in the models used for forecasting, others are due to inaccurate information on the economic variables on which the models are based measurement
Chapter 13 Fisher Ideal Output, Input and Productivity Indexes Revisited* W.E. Diewert. 1. Introduction
 Chapter 13 Fisher Ideal Output, Input and Productivity Indexes Revisited* W.E. Diewert 1. Introduction Essays in Index Number Theory, Volume I W.E. Diewert and A.O. Nakamura (Editors) c 1993 Elsevier Science
Chapter 13 Fisher Ideal Output, Input and Productivity Indexes Revisited* W.E. Diewert 1. Introduction Essays in Index Number Theory, Volume I W.E. Diewert and A.O. Nakamura (Editors) c 1993 Elsevier Science
APPLICATION OF THE COUNTRY PRODUCT DUMMY METHOD TO CONSTRUCT SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL PRICE INDICES FOR SRI LANKA
 APPLICATION OF THE COUNTRY PRODUCT DUMMY METHOD TO CONSTRUCT SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL PRICE INDICES FOR SRI LANKA Sri Lanka Journal of Economic Research Volume 2 (1) June 2014: 38-52 Sri Lanka Forum of University
APPLICATION OF THE COUNTRY PRODUCT DUMMY METHOD TO CONSTRUCT SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL PRICE INDICES FOR SRI LANKA Sri Lanka Journal of Economic Research Volume 2 (1) June 2014: 38-52 Sri Lanka Forum of University
The New Palgrave: Separability
 The New Palgrave: Separability Charles Blackorby Daniel Primont R. Robert Russell 1. Introduction July 29, 2006 Separability, as discussed here, refers to certain restrictions on functional representations
The New Palgrave: Separability Charles Blackorby Daniel Primont R. Robert Russell 1. Introduction July 29, 2006 Separability, as discussed here, refers to certain restrictions on functional representations
CHAPTER 5 FUNCTIONAL FORMS OF REGRESSION MODELS
 CHAPTER 5 FUNCTIONAL FORMS OF REGRESSION MODELS QUESTIONS 5.1. (a) In a log-log model the dependent and all explanatory variables are in the logarithmic form. (b) In the log-lin model the dependent variable
CHAPTER 5 FUNCTIONAL FORMS OF REGRESSION MODELS QUESTIONS 5.1. (a) In a log-log model the dependent and all explanatory variables are in the logarithmic form. (b) In the log-lin model the dependent variable
Measuring Real GDP and Changes in the Terms of Trade across space and time. WANG Yan, DUFE Presented at BNU
 Measuring Real GDP and Changes in the Terms of Trade across space and time WANG Yan, DUFE Presented at BNU 2018.10.29 Main Contents 1. Introduction 2. Literature Review 3. Measurement Framework 4. Conclusion
Measuring Real GDP and Changes in the Terms of Trade across space and time WANG Yan, DUFE Presented at BNU 2018.10.29 Main Contents 1. Introduction 2. Literature Review 3. Measurement Framework 4. Conclusion
Price Index Basics* (pg. 146 of Foundations of Economic Analysis)
 Price Index Basics* The fundamental problem upon which all the analysis rests is that of determining merely from price and quantity data which of two situations is higher up on an individual s preference
Price Index Basics* The fundamental problem upon which all the analysis rests is that of determining merely from price and quantity data which of two situations is higher up on an individual s preference
NOWCASTING REPORT. Updated: September 23, 2016
 NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: September 23, 216 The FRBNY Staff Nowcast stands at 2.3% and 1.2% for 216:Q3 and 216:Q4, respectively. Negative news since the report was last published two weeks ago pushed
NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: September 23, 216 The FRBNY Staff Nowcast stands at 2.3% and 1.2% for 216:Q3 and 216:Q4, respectively. Negative news since the report was last published two weeks ago pushed
NOWCASTING REPORT. Updated: May 20, 2016
 NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: May 20, 2016 The FRBNY Staff Nowcast for GDP growth in 2016:Q2 is 1.7%, half a percentage point higher than last week. Positive news came from manufacturing and housing data
NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: May 20, 2016 The FRBNY Staff Nowcast for GDP growth in 2016:Q2 is 1.7%, half a percentage point higher than last week. Positive news came from manufacturing and housing data
Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8
 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Problem 1: a: The average unemployment rate from 1959 to 2002 is 5.9136% 5.9%. b/c: 27 out of 43 years have a strictly negative sign for the product (π t π t 1 )(u
Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Problem 1: a: The average unemployment rate from 1959 to 2002 is 5.9136% 5.9%. b/c: 27 out of 43 years have a strictly negative sign for the product (π t π t 1 )(u
THE QUADRATIC APPROXIMATION LEMMA AND DECOMPOSITIONS OF SUPERLATIVE INDEXES. W. Erwin Diewert. October Discussion Paper No.
 1 THE QUADRATIC APPROXIMATION LEMMA AND DECOMPOSITIONS OF SUPERLATIVE INDEXES by W. Erwin Diewert October 2 Discussion Paper No.: -15 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA VANCOUVER,
1 THE QUADRATIC APPROXIMATION LEMMA AND DECOMPOSITIONS OF SUPERLATIVE INDEXES by W. Erwin Diewert October 2 Discussion Paper No.: -15 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA VANCOUVER,
Formelsammlung zu Wirtschaftstheorie IV
 Keynes and the Classics Notes on the Monetary Theory of Production Formelsammlung zu Wirtschaftstheorie IV Social production, value and distribution (436-445) The starting point is a Leontief price system:
Keynes and the Classics Notes on the Monetary Theory of Production Formelsammlung zu Wirtschaftstheorie IV Social production, value and distribution (436-445) The starting point is a Leontief price system:
Explaining Inflation During the Great Contraction
 Explaining Inflation During the Great Contraction Robert G. Murphy Department of Economics Boston College Chestnut Hill, MA 02467 murphyro@bc.edu January 4, 2013 ODE Advisor Session, American Economic
Explaining Inflation During the Great Contraction Robert G. Murphy Department of Economics Boston College Chestnut Hill, MA 02467 murphyro@bc.edu January 4, 2013 ODE Advisor Session, American Economic
Moral Hazard: Part 1. April 9, 2018
 Moral Hazard: Part 1 April 9, 2018 Introduction In a standard moral hazard problem, the agent A is characterized by only one type. As with adverse selection, the principal P wants to engage in an economic
Moral Hazard: Part 1 April 9, 2018 Introduction In a standard moral hazard problem, the agent A is characterized by only one type. As with adverse selection, the principal P wants to engage in an economic
Long-run Analysis of Production. Theory of Production
 ong-run Analysis of Production Theory of Production ong-run Production Analysis ong-run production analysis concerned about the producers behavior in the long-run. In the long-run, expansion of output
ong-run Analysis of Production Theory of Production ong-run Production Analysis ong-run production analysis concerned about the producers behavior in the long-run. In the long-run, expansion of output
Lars Svensson 10/2/05. Liquidity traps, the zero lower bound for interest rates, and deflation
 Eco 00, part, Fall 005 00L5_F05.tex Lars Svensson 0//05 Liquidity traps, the zero lower bound for interest rates, and deflation Japan: recession, low growth since early 90s, deflation in GDP deflator and
Eco 00, part, Fall 005 00L5_F05.tex Lars Svensson 0//05 Liquidity traps, the zero lower bound for interest rates, and deflation Japan: recession, low growth since early 90s, deflation in GDP deflator and
The Common-Scaling Social Cost-of-Living Index. Thomas F. Crossley and Krishna Pendakur
 The Common-Scaling Social Cost-of-Living Index. Thomas F. Crossley and Krishna Pendakur May 27, 2009 Abstract If preferences or budgets are heterogeneous across people (as they clearly are), then individual
The Common-Scaling Social Cost-of-Living Index. Thomas F. Crossley and Krishna Pendakur May 27, 2009 Abstract If preferences or budgets are heterogeneous across people (as they clearly are), then individual
CHOOSING THE RIGHT SAMPLING TECHNIQUE FOR YOUR RESEARCH. Awanis Ku Ishak, PhD SBM
 CHOOSING THE RIGHT SAMPLING TECHNIQUE FOR YOUR RESEARCH Awanis Ku Ishak, PhD SBM Sampling The process of selecting a number of individuals for a study in such a way that the individuals represent the larger
CHOOSING THE RIGHT SAMPLING TECHNIQUE FOR YOUR RESEARCH Awanis Ku Ishak, PhD SBM Sampling The process of selecting a number of individuals for a study in such a way that the individuals represent the larger
NOWCASTING REPORT. Updated: July 20, 2018
 NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: July 20, 2018 The New York Fed Staff Nowcast stands at 2.7% for 2018:Q2 and 2.4% for 2018:Q3. News from this week s data releases decreased the nowcast for 2018:Q2 by 0.1 percentage
NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: July 20, 2018 The New York Fed Staff Nowcast stands at 2.7% for 2018:Q2 and 2.4% for 2018:Q3. News from this week s data releases decreased the nowcast for 2018:Q2 by 0.1 percentage
NOWCASTING REPORT. Updated: October 21, 2016
 NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: October 21, 216 The FRBNY Staff Nowcast stands at 2.2% for 216:Q3 and 1.4% for 216:Q4. Overall this week s news had a negative effect on the nowcast. The most notable developments
NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: October 21, 216 The FRBNY Staff Nowcast stands at 2.2% for 216:Q3 and 1.4% for 216:Q4. Overall this week s news had a negative effect on the nowcast. The most notable developments
Pacing 7th Grade Advanced Math 1st Nine Weeks Introduction to Proportional Relationships. Proportional Relationships and Percentages
 7th: Illustrative Mathematics Unit 4 7th: Illustrative Mathematics Unit 2 7.RP.2 7.RP.2a 1st Nine Weeks Introduction to Proportional Relationships Recognize and represent proportional relationships between
7th: Illustrative Mathematics Unit 4 7th: Illustrative Mathematics Unit 2 7.RP.2 7.RP.2a 1st Nine Weeks Introduction to Proportional Relationships Recognize and represent proportional relationships between
Econ Review Set 2 - Answers
 Econ 4808 Review Set 2 - Answers EQUILIBRIUM ANALYSIS 1. De ne the concept of equilibrium within the con nes of an economic model. Provide an example of an economic equilibrium. Economic models contain
Econ 4808 Review Set 2 - Answers EQUILIBRIUM ANALYSIS 1. De ne the concept of equilibrium within the con nes of an economic model. Provide an example of an economic equilibrium. Economic models contain
KÖZGAZDASÁGI ALAPISMERETEK (ELMÉLETI GAZDASÁGTAN) ANGOL NYELVEN
 Közgazdasági alapismeretek (elméleti gazdaságtan) középszint angol nyelven Javítási-értékelésiútmutató 1212 ÉRETTSÉGI VIZSGA 2012. május 25. KÖZGAZDASÁGI ALAPISMERETEK (ELMÉLETI GAZDASÁGTAN) ANGOL NYELVEN
Közgazdasági alapismeretek (elméleti gazdaságtan) középszint angol nyelven Javítási-értékelésiútmutató 1212 ÉRETTSÉGI VIZSGA 2012. május 25. KÖZGAZDASÁGI ALAPISMERETEK (ELMÉLETI GAZDASÁGTAN) ANGOL NYELVEN
The B.E. Journal of Theoretical Economics
 The B.E. Journal of Theoretical Economics Topics Volume 9, Issue 1 2009 Article 43 Simple Economies with Multiple Equilibria Theodore C. Bergstrom Ken-Ichi Shimomura Takehiko Yamato University of California,
The B.E. Journal of Theoretical Economics Topics Volume 9, Issue 1 2009 Article 43 Simple Economies with Multiple Equilibria Theodore C. Bergstrom Ken-Ichi Shimomura Takehiko Yamato University of California,
NOWCASTING REPORT. Updated: August 17, 2018
 NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: August 17, 2018 The New York Fed Staff Nowcast for 2018:Q3 stands at 2.4%. News from this week s data releases decreased the nowcast for 2018:Q3 by 0.2 percentage point. Negative
NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: August 17, 2018 The New York Fed Staff Nowcast for 2018:Q3 stands at 2.4%. News from this week s data releases decreased the nowcast for 2018:Q3 by 0.2 percentage point. Negative
IS-LM Analysis. Math 202. Brian D. Fitzpatrick. Duke University. February 14, 2018 MATH
 IS-LM Analysis Math 202 Brian D. Fitzpatrick Duke University February 14, 2018 MATH Overview Background History Variables The GDP Equation Definition of GDP Assumptions The GDP Equation with Assumptions
IS-LM Analysis Math 202 Brian D. Fitzpatrick Duke University February 14, 2018 MATH Overview Background History Variables The GDP Equation Definition of GDP Assumptions The GDP Equation with Assumptions
NOWCASTING REPORT. Updated: May 5, 2017
 NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: May 5, 217 The FRBNY Staff Nowcast stands at 1.8% for 217:Q2. News from this week s data releases reduced the nowcast for Q2 by percentage point. Negative surprises from the
NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: May 5, 217 The FRBNY Staff Nowcast stands at 1.8% for 217:Q2. News from this week s data releases reduced the nowcast for Q2 by percentage point. Negative surprises from the
Chapter 10: Location effects, economic geography and regional policy
 Chapter 10: Location effects, economic geography and regional policy the Community shall aim at reducing disparities between the levels of development of the various regions and the backwardness of the
Chapter 10: Location effects, economic geography and regional policy the Community shall aim at reducing disparities between the levels of development of the various regions and the backwardness of the
STAT 212 Business Statistics II 1
 STAT 1 Business Statistics II 1 KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM & MINERALS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES DHAHRAN, SAUDI ARABIA STAT 1: BUSINESS STATISTICS II Semester 091 Final Exam Thursday Feb
STAT 1 Business Statistics II 1 KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM & MINERALS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES DHAHRAN, SAUDI ARABIA STAT 1: BUSINESS STATISTICS II Semester 091 Final Exam Thursday Feb
Dynamic Optimization: An Introduction
 Dynamic Optimization An Introduction M. C. Sunny Wong University of San Francisco University of Houston, June 20, 2014 Outline 1 Background What is Optimization? EITM: The Importance of Optimization 2
Dynamic Optimization An Introduction M. C. Sunny Wong University of San Francisco University of Houston, June 20, 2014 Outline 1 Background What is Optimization? EITM: The Importance of Optimization 2
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Page. Statistical Bulletin, June 2011 INTRODUCTORY NOTES SUMMARISED ACCOUNTS OF THE BANKING SYSTEM
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTORY NOTES... 3 1. SUMMARISED ACCOUNTS OF THE BANKING SYSTEM 1.1 CENTRAL BANK OF KENYA 1.1.1 Assets... 10 1.1.2 Liabilities... 11 1.2 OFFICIAL RESERVES 1.2.1 Foreign Assets...
TABLE OF CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTORY NOTES... 3 1. SUMMARISED ACCOUNTS OF THE BANKING SYSTEM 1.1 CENTRAL BANK OF KENYA 1.1.1 Assets... 10 1.1.2 Liabilities... 11 1.2 OFFICIAL RESERVES 1.2.1 Foreign Assets...
Published by the Stationery Office, Dublin, Ireland.
 An Phríomh-Oifig Staidrimh Central Statistics Office Published by the Stationery Office, Dublin, Ireland. Available from the: Central Statistics Office, Information Section, Skehard Road, Cork October
An Phríomh-Oifig Staidrimh Central Statistics Office Published by the Stationery Office, Dublin, Ireland. Available from the: Central Statistics Office, Information Section, Skehard Road, Cork October
Two Models of Macroeconomic Equilibrium
 Two Models of Macroeconomic Equilibrium 1 The Static IS-LM Model The model equations are given as C η +γ(y T) (1) T τy (2) I α r (3) G T (4) L φy θr (5) M µ (6) Y C +I +G (7) L M (8) where η,α,,φ,θ,µ >
Two Models of Macroeconomic Equilibrium 1 The Static IS-LM Model The model equations are given as C η +γ(y T) (1) T τy (2) I α r (3) G T (4) L φy θr (5) M µ (6) Y C +I +G (7) L M (8) where η,α,,φ,θ,µ >
UNIT 2: REASONING WITH LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES. Solving Equations and Inequalities in One Variable
 UNIT 2: REASONING WITH LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES This unit investigates linear equations and inequalities. Students create linear equations and inequalities and use them to solve problems. They
UNIT 2: REASONING WITH LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES This unit investigates linear equations and inequalities. Students create linear equations and inequalities and use them to solve problems. They
BRITISH VIRGIN ISLANDS SECTORAL GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT MARKET PRICES (current prices) (US$M)
 SECTORAL GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT MARKET PRICES (current prices) Sector 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000r 2001r 2002r 2003r 2004r 2005e Agriculture, Hunting & Forestry 1.36 1.50 1.63 1.77
SECTORAL GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT MARKET PRICES (current prices) Sector 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000r 2001r 2002r 2003r 2004r 2005e Agriculture, Hunting & Forestry 1.36 1.50 1.63 1.77
NOWCASTING REPORT. Updated: January 4, 2019
 NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: January 4, 2019 The New York Fed Staff Nowcast stands at 2.5% for 2018:Q4 and 2.1% for 2019:Q1. News from this week s data releases left the nowcast for both quarters broadly
NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: January 4, 2019 The New York Fed Staff Nowcast stands at 2.5% for 2018:Q4 and 2.1% for 2019:Q1. News from this week s data releases left the nowcast for both quarters broadly
2. Linear Programming Problem
 . Linear Programming Problem. Introduction to Linear Programming Problem (LPP). When to apply LPP or Requirement for a LPP.3 General form of LPP. Assumptions in LPP. Applications of Linear Programming.6
. Linear Programming Problem. Introduction to Linear Programming Problem (LPP). When to apply LPP or Requirement for a LPP.3 General form of LPP. Assumptions in LPP. Applications of Linear Programming.6
ALGEBRA 1 SEMESTER 1 INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS Courses: Algebra 1 S1 (#2201) and Foundations in Algebra 1 S1 (#7769)
 Multiple Choice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Ramal goes to the grocery store and buys pounds of apples and pounds of bananas. Apples cost dollars per
Multiple Choice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Ramal goes to the grocery store and buys pounds of apples and pounds of bananas. Apples cost dollars per
A Summary of Economic Methodology
 A Summary of Economic Methodology I. The Methodology of Theoretical Economics All economic analysis begins with theory, based in part on intuitive insights that naturally spring from certain stylized facts,
A Summary of Economic Methodology I. The Methodology of Theoretical Economics All economic analysis begins with theory, based in part on intuitive insights that naturally spring from certain stylized facts,
NOWCASTING REPORT. Updated: September 14, 2018
 NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: September 14, 2018 The New York Fed Staff Nowcast stands at 2.2% for 2018:Q3 and 2.8% for 2018:Q4. This week s data releases left the nowcast for both quarters broadly unchanged.
NOWCASTING REPORT Updated: September 14, 2018 The New York Fed Staff Nowcast stands at 2.2% for 2018:Q3 and 2.8% for 2018:Q4. This week s data releases left the nowcast for both quarters broadly unchanged.
PROPOSED TABLE OF CONTENTS FOR YEAR 11 GENERAL MATHEMATICS AND ESSENTIAL MATHEMATICS
 15 June 2015 PROPOSED TABLE OF CONTENTS FOR YEAR 11 GENERAL MATHEMATICS AND ESSENTIAL MATHEMATICS YEAR 11 GENERAL MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 1: A B C D E F G EQUATIONS AND FORMULAE Algebraic substitution Linear
15 June 2015 PROPOSED TABLE OF CONTENTS FOR YEAR 11 GENERAL MATHEMATICS AND ESSENTIAL MATHEMATICS YEAR 11 GENERAL MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 1: A B C D E F G EQUATIONS AND FORMULAE Algebraic substitution Linear
Grade 7 Math Spring 2017 Item Release
 Grade 7 Math Spring 2017 Item Release 1 Grade 7 Reporting Category: Ratio and Proportions Question 10 16689 20512 Content Cluster: Analyze proportional relationships and use them to solve real-world and
Grade 7 Math Spring 2017 Item Release 1 Grade 7 Reporting Category: Ratio and Proportions Question 10 16689 20512 Content Cluster: Analyze proportional relationships and use them to solve real-world and
Microeconomic Theory -1- Introduction
 Microeconomic Theory -- Introduction. Introduction. Profit maximizing firm with monopoly power 6 3. General results on maximizing with two variables 8 4. Model of a private ownership economy 5. Consumer
Microeconomic Theory -- Introduction. Introduction. Profit maximizing firm with monopoly power 6 3. General results on maximizing with two variables 8 4. Model of a private ownership economy 5. Consumer
Do not copy, post, or distribute
 14 CORRELATION ANALYSIS AND LINEAR REGRESSION Assessing the Covariability of Two Quantitative Properties 14.0 LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this chapter, we discuss two related techniques for assessing a possible
14 CORRELATION ANALYSIS AND LINEAR REGRESSION Assessing the Covariability of Two Quantitative Properties 14.0 LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this chapter, we discuss two related techniques for assessing a possible
Introduction to Forecasting
 Introduction to Forecasting Introduction to Forecasting Predicting the future Not an exact science but instead consists of a set of statistical tools and techniques that are supported by human judgment
Introduction to Forecasting Introduction to Forecasting Predicting the future Not an exact science but instead consists of a set of statistical tools and techniques that are supported by human judgment
