Singularities of Asymptotic Lines on Surfaces in R 4
|
|
|
- Simon Sutton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Contemporary Mathematical Sciences Vol. 11, 2016, no. 7, HIKARI Ltd, Singularities of Asymptotic Lines on Surfaces in R 4 Yasuhiro Kurokawa Liberal Arts, Mathematics, Shibaura Institute of Technology, 307 Fukasaku, Minuma-ku, Saitama-shi, Saitama , Japan Copyright c 2016 Yasuhiro Kurokawa. This article is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract We give the local topological classification of configurations of asymptotic lines of generic locally convex surfaces around isolated inflection points in R 4. Mathematics Subject Classification: 53A05, 53C12, 37C10 Keywords: surfaces, singularities, asymptotic lines 1 Introduction In this paper we give the local topological classification of configurations of asymptotic lines defined around isolated inflection points of generic locally convex surfaces in R 4. Such local configurations are given by solution curves of differential equations of asymptotic lines (DEAL) which is a certain class of binary differential equation of the form a(x, y)dy 2 + b(x, y)dxdy + c(x, y)dx 2 = 0 (1) with b 2 4ac 0, where a, b, c are smooth functions which vanish at a point taking b 2 4ac = 0. If a point in the surface in R 4 is an isolated inflection point, it takes b 2 4ac = 0 ( hence a = b = c = 0) and otherwise satisfies b 2 4ac > 0. The local topological classification of integral curves of binary differential equation of this type is well-known ([6], [1], [2], [10]). Especially such differential equations also appear as differential equations of principal
2 302 Yasuhiro Kurokawa curvature lines around umbilic points of surfaces in R 3 ([4], [10], [1]), and the stable configurations of its integral curves are well-known as Darbouxian which are determined by the 1-jet of this differential equation. Moreover Gutierrez, Sotomayor and Garcia ([11], [16]) established umbilic bifurcations. In [3] Bruce and Tari pointed out the 1-jet of DEAL is precisely the 1-jet of (1) giving the principal curvature lines of a surface in R 3 at the umbilic point. Hence its configuration follows the same pattern. While Guíñez and Gutierrez([6],[7],[8],[9]) studied singularities of positive quadratic differential forms which are the left-hand side of (1), and these classification were established. Applying results of Guíñez and Gutierrez([6],[7],[8],[9]), we first investigate singularities depending on the 1-jet of DEAL. Then we give the local topological classification and conditions of possible rank-2 singular point (Theorem 3.1). In the classification, Darbouxian (D 1, D 2, D 3 ), D 12 and D 1 appear, which is actually the same as the case of the principal curvature line of a surface in R 3 at the umbilic point. Next we investigate a singularity depending on the 2-jet of DEAL and describes a condition for type D 23 (Theorem 4.2) which is rank-1 codimension one singularities studied in [9]. In a particular case, the condition for D 23 corresponds to that for type D 1 23 which describes a codimension one umbilic bifurcation studied in [11]. Recently the configurations near umbilic points for surfaces in R 4 were studied in [15], and it was shown that the same configurations as our classification of DEAL appears. The configurations of the integral curves of DEAL at each singular point above are illustrated in Figure 1. D D D D Figure 1: Asymptotic lines near the inflection points D i, D 12, D 23, and their separatrices. We shall suppose that all mappings, map germs and manifolds are of class C, unless otherwise stated. D
3 Singularities of asymptotic lines on surfaces in R Singularities of positive quadratic differential forms and geometry of surfaces in R 4 According to Guíñez ([6],[7]), we first review elements of the singularities of quadratic differential form ω = a(x, y)dy 2 + b(x, y)dxdy + c(x, y)dx 2 on R 2 = {(x, y)}. Let ω = b 2 4ac : R 2 R, and let g ω = (a, b, c) : R 2 R 3. Then ω is called positive if ω 0 and 1 ω (0) = gω 1 (0). Hereafter ω is assumed to be positive quadratic differential forms (PQD). A point in R 2 is said to be singular point of ω if ω vanishes (so is g ω ). Two PQDs ω 1, ω 2 are called equivalent if there exists homeomorphism h on R 2 such that h maps the singular set of ω 1 to that of ω 2, and maps the integral curves of ω 1 = 0 to that of ω 2 = 0. A singular point p is said to be of rank-k (k = 0, 1, 2) if rankdg ω (p) = k, where Dg ω (p) is the Jacobian matrix of g ω at p. Among rank-2 singular points, a point is said to be simple if ω is non-degenerate minimum, and a non-simple point is said to be semi-simple. We remark that a singular point is isolated if it is of rank-2. Let S(ω, p)(x, y) := da p (x, y)y 2 +db p (x, y)xy+dc p (x, y)x 2, where da p, db p, dc p are the linear parts of a, b, c at p respectively. This polynomial is called the separatrix polynomial. Then among rank-2 simple singular points, a point p is said to be (a) hyperbolic if S(ω, p) has only simple roots, (b) of type D 12 if S(ω, p) has one simple and one double roots, (c) of type D 1 if S(ω, p) has a triple root. Moreover the hyperbolic singular points has the three cases (so-called Darbouxian) D 1, D 2, D 3 in Proposition 2.1 below. Semi-simple singularities are also classified in [7]. We now assume that the origin is a rank-2 simple singular point of ω. Let a 1 = a(0), a x 2 = a(0), and also denote by b y i, c i (i = 1, 2) the differential of b, c at 0 respectively. Then by a linear change of coordinate we may suppose that 0 1 Dg ω (0) = b 1 b 2 (2) 0 1 with b 1 0. Then the separatrix polynomial is given by S(ω, 0) = y(y 2 + b 2 xy + (b 1 1)x 2 ). Proposition 2.1. ([6],[7]) Let ω be a PQD having the linear part (2) above. Suppose that the origin is a rank-2 simple singular point. Then the singular point is one of the following cases:
4 304 Yasuhiro Kurokawa D 1 : b b 1 < 0, D 2 : b b 1 > 0, b 1 > 0 and b 1 1, D 3 : b 1 < 0, D 12 : b 2 0 and either b b 1 = 0 or b 1 = 1, D 1 : b 1 = 1 and b 2 = 0. Remark 2.2. The configuration of D 1 is homeomorphic to that of D 1 ([8], [16]). Next we recall previous results of geometry of surfaces in R 4 (see [5], [13], [14]). Let f : M 2 R 4 be an embedding, where M is a compact surface. For a given point p M, the curvature ellipse is defined as a mapping η : S 1 N f(p) f(m), where S 1 is the unit circle in T f(p) f(m) parametrized by the angle θ [0, 2π], and N f(p) f(m) is the normal plane. The image of the curvature ellipse η is an ellipse in N f(p) f(m). This ellipse may degenerate on to a radial segment of a straight line, in which case f(p) is called an inflection point of the surface. This inflection point is of real type if f(p) belongs to the curvature ellipse, and of imaginary type if it doesn t. A direction θ in T f(p) f(m) is said to be an asymptotic direction if η and η(θ) are parallel. θ There are the following cases for asymptotic directions at f(p) : exactly two directions (f(p) is called a hyperbolic point), just one direction (f(p) is called a parabolic point) and all directions (this case occurs at any inflection point). If no direction is asymptotic, then the point is called elliptic. In [14] it is shown that for a generically embedded surface f(m) the set of hyperbolic points is a non empty open region. The line field of asymptotic directions at hyperbolic points collapse at the set of parabolic points and inflection points which are made of the union of curves and isolated points. Their integral lines are called asymptotic lines and their singular points coincide with the inflection points. In particular if f(m) is locally convex (i.e. has a locally support hyperplane at each point), then f(m) has no elliptic points, and can only have inflection points of imaginary type. Moreover these inflection points of imaginary type are isolated. Let f be an embedding of a compact surface M to R 4 such that f(m) is locally convex, and let f(p) be an isolated inflection point of imaginary type. In [12] it is shown that there exist local coordinates at p and f(p), f around p is given by f : (R 2, 0) (R 4, 0) which is defined by f(x, y) = (x, y, 1 2 (x2 + y 2 ) + F (x, y), G(x, y)), where F and G are function germs such that j 2 F (0) = j 2 G(0) = 0. Conversely for any F, G with j 2 F (0) = j 2 G(0) = 0 the embedding f defined by the above gives a local parametrization around an isolated inflection point of imaginary type.
5 Singularities of asymptotic lines on surfaces in R Moreover in [12] the differential equation of the asymptotic lines (DEAL) of f is obtained as the following form dy 2 dxdy dx F xx F xy 1 + F yy G xx G xy G yy = 0. Then DEAL is rewritten as ( G xy + 23 )dy 2 + (G yy G xx + 13 )dxdy + (G xy + 12 )dx 2 = 0 (3) where 23 = F xy G xy F yy G yy, 13 = F xx G xx F yy G yy, 12 = F xx G xx F xy G xy. We remark that the quadratic differential form giving the left-hand side of DEAL (3) is positive around the origin, the isolated singular point. For DEAL (3) we have G xxy (0) G xyy (0) Dg ω (0) = G xyy (0) G xxx (0) G yyy (0) G xxy (0). G xxy (0) G xyy (0) By a rotation in (x, y)-plane we may suppose that G xxy (0) = 0. In a particular case that the linear part of ω is such a form, we need the following lemma. Lemm.3. Let ω be a PQD with a 1 = c 1 = 0 and = c 2. Then (i) All rank-2 singular points are simple, that is, there is no semi-simple singular point. (ii) The origin is a simple singular point if and only if 0 and b 1 0. (iii) The singular point of rank-2 is one of the following cases: D 1 : ( b 2 2 ) b 1 < 0, D 2 : ( b 2 2 ) b 1 > 0, b 1 > 0 and b 1 D 3 : b 1 < 0, 1, D 12 : b 2 0 and either ( b 2 2 ) b 1 = 0 or b 1 D 1 : b 2 = 0 and b 1 = 1. Proof. (i), (ii) By direct calculations we have 2 ω x 2 = 1, (0) = b 2 1, 2 ω y 2 (0) = b , the determinant of Hess ω (0) = 4 2b 2 1, where Hess ω (0) is the Hessian matrix of ω at 0. Hence it is easily shown that the origin is a singular point of rank-2 if and only if the determinant of Hess ω (0) 0, that is, 0 and b 1 0. Therefore we conclude (i), (ii). (iii) The separatrix polynomial is given by S(ω, 0)(x, y) = y( y 2 + b 2 xy + (b 1 )x 2 ). The equation S(ω, 0)(x, y) = 0 has always a solution y = 0.
6 306 Yasuhiro Kurokawa Consider the equation ( y x )2 + b 2 ( y ) + (b x 1 ) = 0, and its discriminant D/4 = (b 2 /2) b 1. The case b 1 = : If b 2 = 0 (resp. 0), then S(ω, 0)(x, y) = 0 has the triple root y = 0 (resp. the simple root y = mx(m 0) and the double root y = 0). The case b 1 : If D/4 = 0 (resp. 0), then S(ω, 0)(x, y) = 0 has the simple root y = 0 and the double root y = mx(m 0) (resp. only simple root). Therefore by the definitions of D 1, D 12 we get the conditions for these singularities. For the hyperbolic cases D 1, D 2, D 3 we find the conditions as follows. Let ϕ : R 2 R 2 be a linear change of coordinates such that x = αu + βv, y = γu + δv. Let ω be the pull-back of ω by ϕ. Denote by ã 1 ã 2 ω = ϕ ω = ã dv 2 + b dudv + c du 2, Dg ω (0) = b 1 b2. c 1 c 2 Then we have the following formula ã = a(ϕ)δ 2 + b(ϕ)βδ + c(ϕ)β 2, b = 2a(ϕ)γδ + b(ϕ)(αδ + βγ) + 2c(ϕ)αβ, c = a(ϕ)γ 2 + b(ϕ)αγ + c(ϕ)α 2. Now set β = 0, γ = 0. Then we have 0 0 δ 3 Dg ω (0) = b 1 b 2, Dg ω (0) = α δb 1 αδ 2 b α 2 δ By taking α, δ such that ã 2 = δ 3 = 1, c 2 = α 2 δ = 1, we have 0 1 Dg ω (0) = b 1 b Then applying Proposition 2.1 we get the conditions for D 1, D 2, D 3. 3 Rank-2 singularities Hereafter the left-hand side of DEAL (3) is denoted by ω = Ldy 2 + Mdxdy + Ndx 2.
7 Singularities of asymptotic lines on surfaces in R Since we may suppose that G xxy (0) = 0, write G(x, y) = a 6 x3 + b 2 xy2 + c 6 y3 + h.o.t. 0 b Then the linear parts of L, M, N, namely Dg ω (0) = b a c is rank- 0 b 2 if and only if b(b a) 0. Applying Lemm.3 we have the following classification for rank-2 singularities depending on the 1-jet of DEAL. Theorem 3.1. The rank-2 singular points of PQD ω for DEAL (3) at the origin is one of the following types: D 1 : ( c 2b )2 a b + 2 < 0, D 2 : ( c 2b )2 a b + 2 > 0 and 1 < a b 2, D 3 : a b < 1, D 12 : bc(a b) 0 and either ( c 2b )2 a b + 2 = 0 or a b = 2, D 1 : c = 0 and a b = 2. Remark 3.2. Type D 12 corresponds to type D 1 2 with codimension 1 for umbilic points of surfaces in R 3 studied in [11], also type D 1 corresponds to type D 2 1 with codimension 2 studied in [16]. 4 D 23 -singular point In [9] the following type of a singular point of PQD is defined to study a generic 1-parameter bifurcation. Definition 4.1. Let ω = Ldy 2 + Mdxdy + Ndx 2 be a PQD. Suppose that the origin is rank-1 singular point of ω. Then the origin is called D 23 -singular point if 0 1 Dg ω (0) = and 2 M (0) 0. x2 We need the 2-jet to give a condition that a singular point of ω for DEAL (3) is of type D 23. Now write G in DEAL (3) as G(x, y) = a 6 x3 + b 2 xy2 + c 6 y3 + A 24 x4 + B 6 x3 y + C 4 x2 y 2 + D 6 xy3 + E 24 y4 + h.o.t.
8 308 Yasuhiro Kurokawa By direct calculations, we have L = by 1 2 (B 2bF xxy(0))x 2 (C cf xxy (0))xy 1 2 (D 2cF xyy(0) + 2bF yyy (0))y 2 + h.o.t. M = (b a)x + cy (C A + 2bF xxx(0) 2aF xyy (0))x 2 + (D B + cf xxx (0) af yyy (0) + bf xxy (0))xy (E C + 2cF xxy(0))y 2 + h.o.t. N = by (B 2aF xxy(0))x 2 + (C + bf xxx (0) af xyy (0))xy (D + 2bF xxy(0))y 2 + h.o.t. Theorem 4.2. Suppose that the origin is rank-1 singular point, that is, + b 2 + c 2 0 and b(b a) = 0. Then the origin is D 23 singular point if and only if G, F in DEAL (3) satisfy either (i) or (ii) below: (i) a = b 0 and cb b(c A) 2acF xxy (0) 2 (F xyy (0) F xxx (0)) (ii) b = 0 and ac 0 and c 2 B + 2acC + D 2ac(cF xxy (0) + af xyy (0)) Proof. (i) Suppose that a = b 0. Calculations give L = ay 1 2 (B 2aF xxy(0))x 2 (C cf xxy (0))xy 1 2 (D 2cF xyy(0) + 2aF yyy (0))y 2 + h.o.t. M = cy (C A + 2aF xxx(0) 2aF xyy (0))x 2 + (D B + cf xxx (0) af yyy (0) + af xxy (0))xy (E C + 2cF xxy(0))y 2 + h.o.t. N = ay (B 2aF xxy(0))x 2 + (C + af xxx (0) af xyy (0))xy (D + 2aF xxy(0))y 2 + h.o.t. Let ω = ϕ ω = Ldv 2 + Mdudv + Ñdu2 be the pull-back of ω by a linear change of coordinates ϕ defined by x = αu + βv, y = γu + δv. We have L = L(ϕ)δ 2 + M(ϕ)βδ + N(ϕ)β 2, M = 2L(ϕ)γδ + M(ϕ)(αδ + βγ) + 2N(ϕ)αβ, Ñ = L(ϕ)γ 2 + M(ϕ)αγ + N(ϕ)α 2.
9 Singularities of asymptotic lines on surfaces in R Set α = [(4 + c 2 )/(4a 4 )] 1/6, β = c/(2 α 2 ), γ = 0, δ = 1/(aα 2 ). Then it follows that Dg ω (0) satisfies the required condition of type D 23 in Definition 4.1. Moreover, by direct calculations, we have 2 M u 2 (0) = a 2 α ( a(a C) + cb 2acF xxy (0) + 2 (F xyy (0) F xxx (0)) ). Therefore by Definition 4.1 the singular point satisfying the condition (i) is of type D 23. (ii) Suppose that b = 0 and ac 0. Calculations give L = 1 2 Bx2 (C cf xxy (0))xy 1 2 (D 2cF xyy(0))y 2 + h.o.t. M = ax + cy (C A 2aF xyy(0))x 2 + (D B + cf xxx (0) af yyy (0))xy (E C + 2cF xxy(0))y 2 + h.o.t. N = 1 2 (B 2aF xxy(0))x 2 + (C af xyy (0))xy Dy2 + h.o.t. By the same argument as (i), setting α = β = ( c 2a ) 1 2 3, γ = ( a 2c ) 1 2 3, δ = γ, Dg ω (0) satisfies the required condition of type D 23 in Definition 4.1. Calculations give 2 M 1 (0) = 2 3 u2 ( + c 2 )(ac) 8 3 (c 2 B + 2acC + D 2ac 2 F xxy (0) 2 cf xyy (0)). Therefore the singular point satisfying the condition (ii) is of type D 23. Conversely if the conditions (i) or (ii) is not satisfied, then we see that Dg ω (0) does not satisfies the required condition in Definition 4.1 by Remark 14 in [9]. Remark 4.3. If the 3-jet of F at the origin vanishes, a condition (i) for type D 23 corresponds to the condition for type D 1 23 with codimension 1 studied in [11]. The classification in the case not satisfying the condition (i) or (ii) (this case corresponds to a case with codimension 2 studied in [16]) shall be studied in a forthcoming paper. Acknowledgements. Part of this work was developed during the author visits to ICMC, Universidade de São Paulo, in São Carlos. The author would like to thank its hospitality and express his gratitude to Professor M.A.S.Ruas for her valuable comments. This work was partially supported by a FAPESP grant.
10 310 Yasuhiro Kurokawa References [1] J.W. Bruce and D.L. Fidal, On binary differential equations and umbilics, Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 111A (1989), [2] J.W. Bruce and F. Tari, On binary differential equations, Nonlinearity, 8 (1995), [3] J.W. Bruce and F. Tari, Families of surfaces in R 4, Proceedings of the Edinburgh Math. Soci., 45 (2002), [4] G. Darboux, Sur la forme des lignes de courbure dans la voisingage d un ombilic, Leçons sur la théorie générale des surfaces IV, Note VII, Gauthiers-Villars, [5] R.A. Garcia, D.K.H. Mochida, M.D.C. Romero-Fuster and M.A.S. Ruas, Inflection points and topology of surfaces in 4-space, Trans. Amer. Math. Soc., 352 (2000), [6] V. Guíñez, Positive quadratic differential forms and foliations with singularities on surfaces, Trans. Amer. Math. Soc., 309 (1988), [7] V. Guíñez, Local stable singularities for positive quadratic differential forms, J. Differential Equations, 110 (1994), [8] C. Gutierrez and V. Guíñez Positive quadratic differential forms: linearization, finite determinacy and versal unfolding, Annales de la Faculté des Sciences de Toulouse Mathmatiques, 5 (1996), [9] V. Guíñez and C.Gutierrez, Rank-1 codimension one singularities of positive quadratic differential forms, J. Differential Equations, 206 (2004), [10] C. Gutierrez and J. Sotomayor, Structurally stable configurations of lines of principal curvature, Astérisque, (1982), [11] C. Gutierrez, J. Sotomayor and R. Garcia, Bifurcations of umbilic points and related principal cycles, J. Dynamics and Differential Equations, 16 (2004), no. 2,
11 Singularities of asymptotic lines on surfaces in R [12] C. Gutierrez and M. A. S. Ruas, Indices of Newton non-degenerate vector fields and a conjecture of Loewner for surfaces in R 4, Chapter in Real and Complex Singularities, Lecture Notes in Pure and Appl. Math., 232 Dekker, 2003, [13] J.A. Little, On singularities of submanifolds of higher dimensional Euclidean space, Annal. Mat. Pura et Appl., 83 (1969), [14] D.K.H. Mochida, M.D.C. Romero-Fuster and M.A.S. Ruas, The geometry of surfaces in 4-space from a contact viewpoint, Geometriae Dedicata, 54 (1995), [15] M. Navarro and A. Serrano, Codimension one bifurcations of non simple umbilical points for surfaces immersed in R 4, Abstraction & Applications, 13 (2015), [16] J. Sotomayor and R. Garcia, Codimension two umbilic points on surfaces immersed in R 3, Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems, 17 (2007), no. 2, Received: May 30, 2016; Published: July 10, 2016
Indices of Newton non-degenerate vector fields and a conjecture of Loewner for surfaces in R 4.
 CADERNOS DE MATEMÁTICA 02, 345 353 October (2001) ARTIGO NÚMERO SMA# 124 Indices of Newton non-degenerate vector fields and a conjecture of Loewner for surfaces in R 4. C. Gutierrez * Departamento de Matemática,
CADERNOS DE MATEMÁTICA 02, 345 353 October (2001) ARTIGO NÚMERO SMA# 124 Indices of Newton non-degenerate vector fields and a conjecture of Loewner for surfaces in R 4. C. Gutierrez * Departamento de Matemática,
ASYMPTOTIC CURVES ON SURFACES IN R 5
 ASYMPTOTIC CURVES ON SURFACES IN R 5 M. C. ROMERO-FUSTER, M. A. S. RUAS AND F. TARI Abstract. We study asymptotic curves on generically immersed surfaces in R 5. We characterise asymptotic directions via
ASYMPTOTIC CURVES ON SURFACES IN R 5 M. C. ROMERO-FUSTER, M. A. S. RUAS AND F. TARI Abstract. We study asymptotic curves on generically immersed surfaces in R 5. We characterise asymptotic directions via
Singularities and Duality in the Flat Geometry of Submanifolds of Euclidean Spaces
 Beiträge zur Algebra und Geometrie Contributions to Algebra and Geometry Volume 42 (2001), No. 1, 137-148. Singularities and Duality in the Flat Geometry of Submanifolds of Euclidean Spaces D. K. H. Mochida
Beiträge zur Algebra und Geometrie Contributions to Algebra and Geometry Volume 42 (2001), No. 1, 137-148. Singularities and Duality in the Flat Geometry of Submanifolds of Euclidean Spaces D. K. H. Mochida
Darbouxian Umbilic Points on Smooth Surfaces in R 3
 Darbouxian Umbilic Points on Smooth Surfaces in R 3 Luis Fernando Mello Universidade Federal de Itajubá UNIFEI E-mail: lfmelo@unifei.edu.br Texas Christian University, Fort Worth GaGA Seminar September
Darbouxian Umbilic Points on Smooth Surfaces in R 3 Luis Fernando Mello Universidade Federal de Itajubá UNIFEI E-mail: lfmelo@unifei.edu.br Texas Christian University, Fort Worth GaGA Seminar September
On the flat geometry of the cuspidal edge
 On the flat geometry of the cuspidal edge Raúl Oset Sinha and Farid Tari December 20, 2016 Abstract We study the geometry of the cuspidal edge M in R 3 derived from its contact with planes and lines (referred
On the flat geometry of the cuspidal edge Raúl Oset Sinha and Farid Tari December 20, 2016 Abstract We study the geometry of the cuspidal edge M in R 3 derived from its contact with planes and lines (referred
Self-adjoint operators on surfaces in R n
 Self-adjoint operators on surfaces in R n Farid Tari Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Durham, Science Laboratories South Rd, Durham DH1 3LE, UK. E-mail: farid.tari@durham.ac.uk Abstract
Self-adjoint operators on surfaces in R n Farid Tari Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Durham, Science Laboratories South Rd, Durham DH1 3LE, UK. E-mail: farid.tari@durham.ac.uk Abstract
Lines of axial curvature at critical points on surfaces mapped into R 4
 São Paulo Journal of Mathematical Sciences 6, 2 (2012), 277 300 Lines of axial curvature at critical points on surfaces mapped into R 4 Ronaldo Garcia Instituto de Matemática e Estatística Universidade
São Paulo Journal of Mathematical Sciences 6, 2 (2012), 277 300 Lines of axial curvature at critical points on surfaces mapped into R 4 Ronaldo Garcia Instituto de Matemática e Estatística Universidade
Codimension 2 submanifolds with flat normal bundle in euclidean space
 Codimension 2 submanifolds with flat normal bundle in euclidean space J.J. Nuño-Ballesteros and M.C. Romero-Fuster Abstract Given an immersed submanifold M n R n+2, we characterize the vanishing of the
Codimension 2 submanifolds with flat normal bundle in euclidean space J.J. Nuño-Ballesteros and M.C. Romero-Fuster Abstract Given an immersed submanifold M n R n+2, we characterize the vanishing of the
On the classification of certain curves up to projective tranformations
 On the classification of certain curves up to projective tranformations Mehdi Nadjafikhah Abstract The purpose of this paper is to classify the curves in the form y 3 = c 3 x 3 +c 2 x 2 + c 1x + c 0, with
On the classification of certain curves up to projective tranformations Mehdi Nadjafikhah Abstract The purpose of this paper is to classify the curves in the form y 3 = c 3 x 3 +c 2 x 2 + c 1x + c 0, with
SECOND ORDER GEOMETRY OF SPACELIKE SURFACES IN DE SITTER 5-SPACE. Masaki Kasedou, Ana Claudia Nabarro, and Maria Aparecida Soares Ruas
 Publ. Mat. 59 (215), 449 477 DOI: 1.5565/PUBLMAT 59215 7 SECOND ORDER GEOMETRY OF SPACELIKE SURFACES IN DE SITTER 5-SPACE Masaki Kasedou, Ana Claudia Nabarro, and Maria Aparecida Soares Ruas Abstract:
Publ. Mat. 59 (215), 449 477 DOI: 1.5565/PUBLMAT 59215 7 SECOND ORDER GEOMETRY OF SPACELIKE SURFACES IN DE SITTER 5-SPACE Masaki Kasedou, Ana Claudia Nabarro, and Maria Aparecida Soares Ruas Abstract:
1. Introduction INDEX OF AN IMPLICIT DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION. L. S. Challapa and M. A. S. Ruas
 Publ. Mat. 54 (2010), 173 186 INDEX OF AN IMPLICIT DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION L. S. Challapa and M. A. S. Ruas Abstract In this paper we introduce the concept of the index of an implicit differential equation
Publ. Mat. 54 (2010), 173 186 INDEX OF AN IMPLICIT DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION L. S. Challapa and M. A. S. Ruas Abstract In this paper we introduce the concept of the index of an implicit differential equation
arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 30 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 30 Jul 2018 arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 30 Jul 2018](/thumbs/89/99049956.jpg) CR-INVARIANTS FOR SURFACES IN 4-SPACE JORGE LUIZ DEOLINDO SILVA arxiv:1807.11133v1 [math.dg] 30 Jul 2018 Abstract. We establish cross-ratio invariants for surfaces in 4-space in an analogous way to Uribe-Vargas
CR-INVARIANTS FOR SURFACES IN 4-SPACE JORGE LUIZ DEOLINDO SILVA arxiv:1807.11133v1 [math.dg] 30 Jul 2018 Abstract. We establish cross-ratio invariants for surfaces in 4-space in an analogous way to Uribe-Vargas
Fronts of Whitney umbrella a differential geometric approach via blowing up
 Journal of Singularities Volume 4 (202), 35-67 received 3 October 20 in revised form 9 January 202 DOI: 0.5427/jsing.202.4c Fronts of Whitney umbrella a differential geometric approach via blowing up Toshizumi
Journal of Singularities Volume 4 (202), 35-67 received 3 October 20 in revised form 9 January 202 DOI: 0.5427/jsing.202.4c Fronts of Whitney umbrella a differential geometric approach via blowing up Toshizumi
Horo-tight immersions of S 1
 CADERNOS DE MATEMÁTICA 06, 129 134 May (2005) ARTIGO NÚMERO SMA#226 Horo-tight immersions of S 1 Marcelo Buosi * Faculdades Federais Integradas de Diamantina, Rua da Glória 187, 39100-000, Diamantina,
CADERNOS DE MATEMÁTICA 06, 129 134 May (2005) ARTIGO NÚMERO SMA#226 Horo-tight immersions of S 1 Marcelo Buosi * Faculdades Federais Integradas de Diamantina, Rua da Glória 187, 39100-000, Diamantina,
KKM-Type Theorems for Best Proximal Points in Normed Linear Space
 International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 12, 2018, no. 12, 603-609 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2018.81069 KKM-Type Theorems for Best Proximal Points in Normed
International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 12, 2018, no. 12, 603-609 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2018.81069 KKM-Type Theorems for Best Proximal Points in Normed
Vector fields in R 2 with maximal index *
 CADERNOS DE MATEMÁTICA 01, 169 181 October (2006) ARTIGO NÚMERO SMA#254 Vector fields in R 2 with maximal index * A. C. Nabarro Departamento de Matemática, Instituto de Ciências Matemáticas e de Computação,
CADERNOS DE MATEMÁTICA 01, 169 181 October (2006) ARTIGO NÚMERO SMA#254 Vector fields in R 2 with maximal index * A. C. Nabarro Departamento de Matemática, Instituto de Ciências Matemáticas e de Computação,
Center of Gravity and a Characterization of Parabolas
 KYUNGPOOK Math. J. 55(2015), 473-484 http://dx.doi.org/10.5666/kmj.2015.55.2.473 pissn 1225-6951 eissn 0454-8124 c Kyungpook Mathematical Journal Center of Gravity and a Characterization of Parabolas Dong-Soo
KYUNGPOOK Math. J. 55(2015), 473-484 http://dx.doi.org/10.5666/kmj.2015.55.2.473 pissn 1225-6951 eissn 0454-8124 c Kyungpook Mathematical Journal Center of Gravity and a Characterization of Parabolas Dong-Soo
Chapter 3 Second Order Linear Equations
 Partial Differential Equations (Math 3303) A Ë@ Õæ Aë áöß @. X. @ 2015-2014 ú GA JË@ É Ë@ Chapter 3 Second Order Linear Equations Second-order partial differential equations for an known function u(x,
Partial Differential Equations (Math 3303) A Ë@ Õæ Aë áöß @. X. @ 2015-2014 ú GA JË@ É Ë@ Chapter 3 Second Order Linear Equations Second-order partial differential equations for an known function u(x,
ON THE DEFORMATION WITH CONSTANT MILNOR NUMBER AND NEWTON POLYHEDRON
 ON THE DEFORMATION WITH CONSTANT MILNOR NUMBER AND NEWTON POLYHEDRON OULD M ABDERRAHMANE Abstract- We show that every µ-constant family of isolated hypersurface singularities satisfying a nondegeneracy
ON THE DEFORMATION WITH CONSTANT MILNOR NUMBER AND NEWTON POLYHEDRON OULD M ABDERRAHMANE Abstract- We show that every µ-constant family of isolated hypersurface singularities satisfying a nondegeneracy
MATH H53 : Final exam
 MATH H53 : Final exam 11 May, 18 Name: You have 18 minutes to answer the questions. Use of calculators or any electronic items is not permitted. Answer the questions in the space provided. If you run out
MATH H53 : Final exam 11 May, 18 Name: You have 18 minutes to answer the questions. Use of calculators or any electronic items is not permitted. Answer the questions in the space provided. If you run out
A Note on Cohomology of a Riemannian Manifold
 Int. J. Contemp. ath. Sciences, Vol. 9, 2014, no. 2, 51-56 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijcms.2014.311131 A Note on Cohomology of a Riemannian anifold Tahsin Ghazal King Saud
Int. J. Contemp. ath. Sciences, Vol. 9, 2014, no. 2, 51-56 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijcms.2014.311131 A Note on Cohomology of a Riemannian anifold Tahsin Ghazal King Saud
ON THE SYMMETRY OF ANNULAR BRYANT SURFACE WITH CONSTANT CONTACT ANGLE. Sung-Ho Park
 Korean J. Math. 22 (201), No. 1, pp. 133 138 http://dx.doi.org/10.11568/kjm.201.22.1.133 ON THE SYMMETRY OF ANNULAR BRYANT SURFACE WITH CONSTANT CONTACT ANGLE Sung-Ho Park Abstract. We show that a compact
Korean J. Math. 22 (201), No. 1, pp. 133 138 http://dx.doi.org/10.11568/kjm.201.22.1.133 ON THE SYMMETRY OF ANNULAR BRYANT SURFACE WITH CONSTANT CONTACT ANGLE Sung-Ho Park Abstract. We show that a compact
A Note of the Strong Convergence of the Mann Iteration for Demicontractive Mappings
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 10, 2016, no. 6, 255-261 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2016.511700 A Note of the Strong Convergence of the Mann Iteration for Demicontractive
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 10, 2016, no. 6, 255-261 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2016.511700 A Note of the Strong Convergence of the Mann Iteration for Demicontractive
International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 9, 2014, no. 36, HIKARI Ltd,
 International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 9, 2014, no. 36, 1751-1756 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/imf.2014.411187 Generalized Filters S. Palaniammal Department of Mathematics Thiruvalluvar
International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 9, 2014, no. 36, 1751-1756 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/imf.2014.411187 Generalized Filters S. Palaniammal Department of Mathematics Thiruvalluvar
Quadratic Optimization over a Polyhedral Set
 International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 9, 2014, no. 13, 621-629 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/imf.2014.4234 Quadratic Optimization over a Polyhedral Set T. Bayartugs, Ch. Battuvshin
International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 9, 2014, no. 13, 621-629 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/imf.2014.4234 Quadratic Optimization over a Polyhedral Set T. Bayartugs, Ch. Battuvshin
Centre for Mathematics and Its Applications The Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200 Australia. 1. Introduction
 ON LOCALLY CONVEX HYPERSURFACES WITH BOUNDARY Neil S. Trudinger Xu-Jia Wang Centre for Mathematics and Its Applications The Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200 Australia Abstract. In this
ON LOCALLY CONVEX HYPERSURFACES WITH BOUNDARY Neil S. Trudinger Xu-Jia Wang Centre for Mathematics and Its Applications The Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200 Australia Abstract. In this
THE IMPLICIT FUNCTION THEOREM FOR CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS. Carlos Biasi Carlos Gutierrez Edivaldo L. dos Santos. 1. Introduction
 Topological Methods in Nonlinear Analysis Journal of the Juliusz Schauder Center Volume 32, 2008, 177 185 THE IMPLICIT FUNCTION THEOREM FOR CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS Carlos Biasi Carlos Gutierrez Edivaldo L.
Topological Methods in Nonlinear Analysis Journal of the Juliusz Schauder Center Volume 32, 2008, 177 185 THE IMPLICIT FUNCTION THEOREM FOR CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS Carlos Biasi Carlos Gutierrez Edivaldo L.
Buffon-Laplace Type Problem for an Irregular Lattice
 Applied Mathematical Sciences Vol. 11 17 no. 15 731-737 HIKARI Ltd www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/1.1988/ams.17.783 Buffon-Laplace Type Problem for an Irregular Lattice Ersilia Saitta Department of Economics
Applied Mathematical Sciences Vol. 11 17 no. 15 731-737 HIKARI Ltd www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/1.1988/ams.17.783 Buffon-Laplace Type Problem for an Irregular Lattice Ersilia Saitta Department of Economics
Complete Surfaces of Constant Gaussian Curvature in Euclidean Space R 3.
 Summary of the Thesis in Mathematics by Valentina Monaco Complete Surfaces of Constant Gaussian Curvature in Euclidean Space R 3. Thesis Supervisor Prof. Massimiliano Pontecorvo 19 May, 2011 SUMMARY The
Summary of the Thesis in Mathematics by Valentina Monaco Complete Surfaces of Constant Gaussian Curvature in Euclidean Space R 3. Thesis Supervisor Prof. Massimiliano Pontecorvo 19 May, 2011 SUMMARY The
Lecture 5 - Fundamental Theorem for Line Integrals and Green s Theorem
 Lecture 5 - Fundamental Theorem for Line Integrals and Green s Theorem Math 392, section C September 14, 2016 392, section C Lect 5 September 14, 2016 1 / 22 Last Time: Fundamental Theorem for Line Integrals:
Lecture 5 - Fundamental Theorem for Line Integrals and Green s Theorem Math 392, section C September 14, 2016 392, section C Lect 5 September 14, 2016 1 / 22 Last Time: Fundamental Theorem for Line Integrals:
SINGULARITIES AND NORMAL FORMS OF SMOOTH DISTRIBUTIONS
 GEOMETRY IN NONLINEAR CONTROL AND DIFFERENTIAL INCLUSIONS BANACH CENTER PUBLICATIONS, VOLUME 32 INSTITUTE OF MATHEMATICS POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES WARSZAWA 1995 SINGULARITIES AND NORMAL FORMS OF SMOOTH
GEOMETRY IN NONLINEAR CONTROL AND DIFFERENTIAL INCLUSIONS BANACH CENTER PUBLICATIONS, VOLUME 32 INSTITUTE OF MATHEMATICS POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES WARSZAWA 1995 SINGULARITIES AND NORMAL FORMS OF SMOOTH
Math 215B: Solutions 3
 Math 215B: Solutions 3 (1) For this problem you may assume the classification of smooth one-dimensional manifolds: Any compact smooth one-dimensional manifold is diffeomorphic to a finite disjoint union
Math 215B: Solutions 3 (1) For this problem you may assume the classification of smooth one-dimensional manifolds: Any compact smooth one-dimensional manifold is diffeomorphic to a finite disjoint union
Qualitative Theory of Differential Equations and Dynamics of Quadratic Rational Functions
 Nonl. Analysis and Differential Equations, Vol. 2, 2014, no. 1, 45-59 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/nade.2014.3819 Qualitative Theory of Differential Equations and Dynamics of
Nonl. Analysis and Differential Equations, Vol. 2, 2014, no. 1, 45-59 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/nade.2014.3819 Qualitative Theory of Differential Equations and Dynamics of
INTRODUCTION TO SINGULARITY THEORY Michail Zhitomirskii Department of Math, Technion, Haifa, Israel
 INTRODUCTION TO SINGULARITY THEORY Michail Zhitomirskii Department of Math, Technion, 32000 Haifa, Israel Lecture 1 Ideology, main notions and definitions Lecture 2 Singularities of plane curves Lecture
INTRODUCTION TO SINGULARITY THEORY Michail Zhitomirskii Department of Math, Technion, 32000 Haifa, Israel Lecture 1 Ideology, main notions and definitions Lecture 2 Singularities of plane curves Lecture
Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 11, 2018, no. 48, HIKARI Ltd,
 Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 11, 2018, no. 48, 2349-2356 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ces.2018.85243 Radially Symmetric Solutions of a Non-Linear Problem with Neumann
Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 11, 2018, no. 48, 2349-2356 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ces.2018.85243 Radially Symmetric Solutions of a Non-Linear Problem with Neumann
Stable tangential families and singularities of their envelopes
 Stable tangential families and singularities of their envelopes arxiv:math/0406584v1 [math.dg] 28 Jun 2004 Gianmarco Capitanio Abstract We study tangential families, i.e. systems of rays emanating tangentially
Stable tangential families and singularities of their envelopes arxiv:math/0406584v1 [math.dg] 28 Jun 2004 Gianmarco Capitanio Abstract We study tangential families, i.e. systems of rays emanating tangentially
Invariants for Bifurcations
 CADERNOS DE MATEMÁTICA 03, 305 314 October (2002) ARTIGO NÚMERO SMA#153 Invariants for Bifurcations Isabel Salgado Labouriau Centro de Matemática Aplicada, Universidade do Porto R do Campo Alegre, 687
CADERNOS DE MATEMÁTICA 03, 305 314 October (2002) ARTIGO NÚMERO SMA#153 Invariants for Bifurcations Isabel Salgado Labouriau Centro de Matemática Aplicada, Universidade do Porto R do Campo Alegre, 687
Non-Degenerate Quadric Surfaces in Euclidean 3-Space
 Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 6, 2012, no. 52, 2555-2562 Non-Degenerate Quadric Surfaces in Euclidean 3-Space Dae Won Yoon and Ji Soon Jun Department of Mathematics Education and RINS Gyeongsang
Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 6, 2012, no. 52, 2555-2562 Non-Degenerate Quadric Surfaces in Euclidean 3-Space Dae Won Yoon and Ji Soon Jun Department of Mathematics Education and RINS Gyeongsang
Contra θ-c-continuous Functions
 International Journal of Contemporary Mathematical Sciences Vol. 12, 2017, no. 1, 43-50 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ijcms.2017.714 Contra θ-c-continuous Functions C. W. Baker
International Journal of Contemporary Mathematical Sciences Vol. 12, 2017, no. 1, 43-50 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ijcms.2017.714 Contra θ-c-continuous Functions C. W. Baker
ENGI 4430 PDEs - d Alembert Solutions Page 11.01
 ENGI 4430 PDEs - d Alembert Solutions Page 11.01 11. Partial Differential Equations Partial differential equations (PDEs) are equations involving functions of more than one variable and their partial derivatives
ENGI 4430 PDEs - d Alembert Solutions Page 11.01 11. Partial Differential Equations Partial differential equations (PDEs) are equations involving functions of more than one variable and their partial derivatives
International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 3, HIKARI Ltd, On KUS-Algebras. and Areej T.
 International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 3, 131-144 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com On KUS-Algebras Samy M. Mostafa a, Mokhtar A. Abdel Naby a, Fayza Abdel Halim b and Areej T. Hameed b a Department
International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 3, 131-144 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com On KUS-Algebras Samy M. Mostafa a, Mokhtar A. Abdel Naby a, Fayza Abdel Halim b and Areej T. Hameed b a Department
Superconformal ruled surfaces in E 4
 MATHEMATICAL COMMUNICATIONS 235 Math. Commun., Vol. 14, No. 2, pp. 235-244 (2009) Superconformal ruled surfaces in E 4 Bengü (Kılıç) Bayram 1, Betül Bulca 2, Kadri Arslan 2, and Günay Öztürk 3 1 Department
MATHEMATICAL COMMUNICATIONS 235 Math. Commun., Vol. 14, No. 2, pp. 235-244 (2009) Superconformal ruled surfaces in E 4 Bengü (Kılıç) Bayram 1, Betül Bulca 2, Kadri Arslan 2, and Günay Öztürk 3 1 Department
REGULARITY OF SUBELLIPTIC MONGE-AMPÈRE EQUATIONS IN THE PLANE
 REGULARITY OF SUBELLIPTIC MONGE-AMPÈRE EQUATIONS IN THE PLANE PENGFEI GUAN AND ERIC SAWYER (.). Introduction There is a vast body of elliptic regularity results for the Monge-Ampère equation det D u (x)
REGULARITY OF SUBELLIPTIC MONGE-AMPÈRE EQUATIONS IN THE PLANE PENGFEI GUAN AND ERIC SAWYER (.). Introduction There is a vast body of elliptic regularity results for the Monge-Ampère equation det D u (x)
A Direct Proof of Caristi s Fixed Point Theorem
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 10, 2016, no. 46, 2289-2294 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2016.66190 A Direct Proof of Caristi s Fixed Point Theorem Wei-Shih Du Department
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 10, 2016, no. 46, 2289-2294 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2016.66190 A Direct Proof of Caristi s Fixed Point Theorem Wei-Shih Du Department
i=1 α i. Given an m-times continuously
 1 Fundamentals 1.1 Classification and characteristics Let Ω R d, d N, d 2, be an open set and α = (α 1,, α d ) T N d 0, N 0 := N {0}, a multiindex with α := d i=1 α i. Given an m-times continuously differentiable
1 Fundamentals 1.1 Classification and characteristics Let Ω R d, d N, d 2, be an open set and α = (α 1,, α d ) T N d 0, N 0 := N {0}, a multiindex with α := d i=1 α i. Given an m-times continuously differentiable
Symmetry Reduction of Chazy Equation
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol 8, 2014, no 70, 3449-3459 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaricom http://dxdoiorg/1012988/ams201443208 Symmetry Reduction of Chazy Equation Figen AÇIL KİRAZ Department of Mathematics,
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol 8, 2014, no 70, 3449-3459 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaricom http://dxdoiorg/1012988/ams201443208 Symmetry Reduction of Chazy Equation Figen AÇIL KİRAZ Department of Mathematics,
PSEUDO-SPHERICAL EVOLUTES OF CURVES ON A TIMELIKE SURFACE IN THREE DIMENSIONAL LORENTZ-MINKOWSKI SPACE
 PSEUDO-SPHERICAL EVOLUTES OF CURVES ON A TIMELIKE SURFACE IN THREE DIMENSIONAL LORENTZ-MINKOWSKI SPACE S. IZUMIYA, A. C. NABARRO AND A. J. SACRAMENTO Abstract. In this paper we introduce the notion of
PSEUDO-SPHERICAL EVOLUTES OF CURVES ON A TIMELIKE SURFACE IN THREE DIMENSIONAL LORENTZ-MINKOWSKI SPACE S. IZUMIYA, A. C. NABARRO AND A. J. SACRAMENTO Abstract. In this paper we introduce the notion of
Areas associated with a Strictly Locally Convex Curve
 KYUNGPOOK Math. J. 56(206), 583-595 http://dx.doi.org/0.5666/kmj.206.56.2.583 pissn 225-695 eissn 0454-824 c Kyungpook Mathematical Journal Areas associated with a Strictly Locally Convex Curve Dong-Soo
KYUNGPOOK Math. J. 56(206), 583-595 http://dx.doi.org/0.5666/kmj.206.56.2.583 pissn 225-695 eissn 0454-824 c Kyungpook Mathematical Journal Areas associated with a Strictly Locally Convex Curve Dong-Soo
Stieltjes Transformation as the Iterated Laplace Transformation
 International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 11, 2017, no. 17, 833-838 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2017.7796 Stieltjes Transformation as the Iterated Laplace Transformation
International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 11, 2017, no. 17, 833-838 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2017.7796 Stieltjes Transformation as the Iterated Laplace Transformation
Generalized Derivation on TM Algebras
 International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 6, 251-258 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com Generalized Derivation on TM Algebras T. Ganeshkumar Department of Mathematics M.S.S. Wakf Board College Madurai-625020,
International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 6, 251-258 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com Generalized Derivation on TM Algebras T. Ganeshkumar Department of Mathematics M.S.S. Wakf Board College Madurai-625020,
CLASSIFICATION AND PRINCIPLE OF SUPERPOSITION FOR SECOND ORDER LINEAR PDE
 CLASSIFICATION AND PRINCIPLE OF SUPERPOSITION FOR SECOND ORDER LINEAR PDE 1. Linear Partial Differential Equations A partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation, for an unknown function u, that
CLASSIFICATION AND PRINCIPLE OF SUPERPOSITION FOR SECOND ORDER LINEAR PDE 1. Linear Partial Differential Equations A partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation, for an unknown function u, that
B 1 = {B(x, r) x = (x 1, x 2 ) H, 0 < r < x 2 }. (a) Show that B = B 1 B 2 is a basis for a topology on X.
 Math 6342/7350: Topology and Geometry Sample Preliminary Exam Questions 1. For each of the following topological spaces X i, determine whether X i and X i X i are homeomorphic. (a) X 1 = [0, 1] (b) X 2
Math 6342/7350: Topology and Geometry Sample Preliminary Exam Questions 1. For each of the following topological spaces X i, determine whether X i and X i X i are homeomorphic. (a) X 1 = [0, 1] (b) X 2
Devaney's Chaos of One Parameter Family. of Semi-triangular Maps
 International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 8, 2013, no. 29, 1439-1444 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/imf.2013.36114 Devaney's Chaos of One Parameter Family of Semi-triangular Maps
International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 8, 2013, no. 29, 1439-1444 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/imf.2013.36114 Devaney's Chaos of One Parameter Family of Semi-triangular Maps
SINGULAR CURVES OF AFFINE MAXIMAL MAPS
 Fundamental Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Vol. 1, Issue 1, 014, Pages 57-68 This paper is available online at http://www.frdint.com/ Published online November 9, 014 SINGULAR CURVES
Fundamental Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Vol. 1, Issue 1, 014, Pages 57-68 This paper is available online at http://www.frdint.com/ Published online November 9, 014 SINGULAR CURVES
On Bornological Divisors of Zero and Permanently Singular Elements in Multiplicative Convex Bornological Jordan Algebras
 Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 32, 1575-1586 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2013.3359 On Bornological Divisors of Zero and Permanently Singular Elements
Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 32, 1575-1586 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2013.3359 On Bornological Divisors of Zero and Permanently Singular Elements
Chapter 4: First-order differential equations. Similarity and Transport Phenomena in Fluid Dynamics Christophe Ancey
 Chapter 4: First-order differential equations Similarity and Transport Phenomena in Fluid Dynamics Christophe Ancey Chapter 4: First-order differential equations Phase portrait Singular point Separatrix
Chapter 4: First-order differential equations Similarity and Transport Phenomena in Fluid Dynamics Christophe Ancey Chapter 4: First-order differential equations Phase portrait Singular point Separatrix
Pólya-Szegö s Principle for Nonlocal Functionals
 International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 12, 218, no. 5, 245-25 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/1.12988/ijma.218.8327 Pólya-Szegö s Principle for Nonlocal Functionals Tiziano Granucci
International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 12, 218, no. 5, 245-25 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/1.12988/ijma.218.8327 Pólya-Szegö s Principle for Nonlocal Functionals Tiziano Granucci
Fixed Point Theorem of Uniformly Locally Geraghty Contractive Mappings on Connected Complete Metric Spaces
 International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 11, 2017, no. 9, 445-456 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2017.7457 Fixed Point Theorem of Uniformly Locally Geraghty Contractive
International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 11, 2017, no. 9, 445-456 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2017.7457 Fixed Point Theorem of Uniformly Locally Geraghty Contractive
On the Deformed Theory of Special Relativity
 Advanced Studies in Theoretical Physics Vol. 11, 2017, no. 6, 275-282 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/astp.2017.61140 On the Deformed Theory of Special Relativity Won Sang Chung 1
Advanced Studies in Theoretical Physics Vol. 11, 2017, no. 6, 275-282 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/astp.2017.61140 On the Deformed Theory of Special Relativity Won Sang Chung 1
On Permutation Polynomials over Local Finite Commutative Rings
 International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 12, 2018, no. 7, 285-295 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ija.2018.8935 On Permutation Polynomials over Local Finite Commutative Rings Javier
International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 12, 2018, no. 7, 285-295 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ija.2018.8935 On Permutation Polynomials over Local Finite Commutative Rings Javier
3.5 Quadratic Approximation and Convexity/Concavity
 3.5 Quadratic Approximation and Convexity/Concavity 55 3.5 Quadratic Approximation and Convexity/Concavity Overview: Second derivatives are useful for understanding how the linear approximation varies
3.5 Quadratic Approximation and Convexity/Concavity 55 3.5 Quadratic Approximation and Convexity/Concavity Overview: Second derivatives are useful for understanding how the linear approximation varies
Morera s Theorem for Functions of a Hyperbolic Variable
 Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 32, 1595-1600 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2013.212354 Morera s Theorem for Functions of a Hyperbolic Variable Kristin
Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 32, 1595-1600 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2013.212354 Morera s Theorem for Functions of a Hyperbolic Variable Kristin
TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 2010 SYLLABUS
 TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 200 SYLLABUS Algebra Permutations and combinations. Binomial theorem. Theory of equations. Inequalities. Complex numbers and De Moivre s theorem. Elementary set theory.
TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 200 SYLLABUS Algebra Permutations and combinations. Binomial theorem. Theory of equations. Inequalities. Complex numbers and De Moivre s theorem. Elementary set theory.
Antibound State for Klein-Gordon Equation
 International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 8, 2014, no. 59, 2945-2949 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2014.411374 Antibound State for Klein-Gordon Equation Ana-Magnolia
International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 8, 2014, no. 59, 2945-2949 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2014.411374 Antibound State for Klein-Gordon Equation Ana-Magnolia
Legendrian graphs generated by tangential families
 Legendrian graphs generated by tangential families arxiv:math/49577v1 [math.dg] 29 Sep 24 Gianmarco Capitanio Université D. Diderot Paris VII, Equipe de Géométrie et Dynamique Case 712 2, place Jussieu,
Legendrian graphs generated by tangential families arxiv:math/49577v1 [math.dg] 29 Sep 24 Gianmarco Capitanio Université D. Diderot Paris VII, Equipe de Géométrie et Dynamique Case 712 2, place Jussieu,
The Stable Types and Minimal Whitney Stratifications of Discriminants and Euler Obstruction.
 The Stable Types and Minimal Whitney Stratifications of Discriminants and Euler Obstruction. Grazielle F. Barbosa Nivaldo G. Grulha Jr. Marcelo J. Saia Support: Fapesp August 4th, 2010. Página 1 de 33
The Stable Types and Minimal Whitney Stratifications of Discriminants and Euler Obstruction. Grazielle F. Barbosa Nivaldo G. Grulha Jr. Marcelo J. Saia Support: Fapesp August 4th, 2010. Página 1 de 33
RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES RIMS On self-intersection of singularity sets of fold maps. Tatsuro SHIMIZU.
 RIMS-1895 On self-intersection of singularity sets of fold maps By Tatsuro SHIMIZU November 2018 RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES KYOTO UNIVERSITY, Kyoto, Japan On self-intersection of singularity
RIMS-1895 On self-intersection of singularity sets of fold maps By Tatsuro SHIMIZU November 2018 RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES KYOTO UNIVERSITY, Kyoto, Japan On self-intersection of singularity
Pre-Hilbert Absolute-Valued Algebras Satisfying (x, x 2, x) = (x 2, y, x 2 ) = 0
 International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 10, 2016, no. 9, 437-450 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ija.2016.6743 Pre-Hilbert Absolute-Valued Algebras Satisfying (x, x 2, x = (x 2,
International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 10, 2016, no. 9, 437-450 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ija.2016.6743 Pre-Hilbert Absolute-Valued Algebras Satisfying (x, x 2, x = (x 2,
Geometric approximation of curves and singularities of secant maps Ghosh, Sunayana
 University of Groningen Geometric approximation of curves and singularities of secant maps Ghosh, Sunayana IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Geometric approximation of curves and singularities of secant maps Ghosh, Sunayana IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
The Derivative. Appendix B. B.1 The Derivative of f. Mappings from IR to IR
 Appendix B The Derivative B.1 The Derivative of f In this chapter, we give a short summary of the derivative. Specifically, we want to compare/contrast how the derivative appears for functions whose domain
Appendix B The Derivative B.1 The Derivative of f In this chapter, we give a short summary of the derivative. Specifically, we want to compare/contrast how the derivative appears for functions whose domain
AM 205: lecture 14. Last time: Boundary value problems Today: Numerical solution of PDEs
 AM 205: lecture 14 Last time: Boundary value problems Today: Numerical solution of PDEs ODE BVPs A more general approach is to formulate a coupled system of equations for the BVP based on a finite difference
AM 205: lecture 14 Last time: Boundary value problems Today: Numerical solution of PDEs ODE BVPs A more general approach is to formulate a coupled system of equations for the BVP based on a finite difference
On a Certain Representation in the Pairs of Normed Spaces
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 12, 2018, no. 3, 115-119 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ams.2018.712362 On a Certain Representation in the Pairs of ormed Spaces Ahiro Hoshida
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 12, 2018, no. 3, 115-119 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ams.2018.712362 On a Certain Representation in the Pairs of ormed Spaces Ahiro Hoshida
Fuzzy Sequences in Metric Spaces
 Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 8, 2014, no. 15, 699-706 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2014.4262 Fuzzy Sequences in Metric Spaces M. Muthukumari Research scholar, V.O.C.
Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 8, 2014, no. 15, 699-706 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2014.4262 Fuzzy Sequences in Metric Spaces M. Muthukumari Research scholar, V.O.C.
Hyers-Ulam-Rassias Stability of a Quadratic-Additive Type Functional Equation on a Restricted Domain
 Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 7, 013, no. 55, 745-75 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.1988/ijma.013.394 Hyers-Ulam-Rassias Stability of a Quadratic-Additive Type Functional Equation
Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 7, 013, no. 55, 745-75 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.1988/ijma.013.394 Hyers-Ulam-Rassias Stability of a Quadratic-Additive Type Functional Equation
Calculus 2502A - Advanced Calculus I Fall : Local minima and maxima
 Calculus 50A - Advanced Calculus I Fall 014 14.7: Local minima and maxima Martin Frankland November 17, 014 In these notes, we discuss the problem of finding the local minima and maxima of a function.
Calculus 50A - Advanced Calculus I Fall 014 14.7: Local minima and maxima Martin Frankland November 17, 014 In these notes, we discuss the problem of finding the local minima and maxima of a function.
2. A die is rolled 3 times, the probability of getting a number larger than the previous number each time is
 . If P(A) = x, P = 2x, P(A B) = 2, P ( A B) = 2 3, then the value of x is (A) 5 8 5 36 6 36 36 2. A die is rolled 3 times, the probability of getting a number larger than the previous number each time
. If P(A) = x, P = 2x, P(A B) = 2, P ( A B) = 2 3, then the value of x is (A) 5 8 5 36 6 36 36 2. A die is rolled 3 times, the probability of getting a number larger than the previous number each time
On Strong Alt-Induced Codes
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 12, 2018, no. 7, 327-336 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ams.2018.8113 On Strong Alt-Induced Codes Ngo Thi Hien Hanoi University of Science and
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 12, 2018, no. 7, 327-336 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ams.2018.8113 On Strong Alt-Induced Codes Ngo Thi Hien Hanoi University of Science and
Topological K-equivalence of analytic function-germs
 Cent. Eur. J. Math. 8(2) 2010 338-345 DOI: 10.2478/s11533-010-0013-8 Central European Journal of Mathematics Topological K-equivalence of analytic function-germs Research Article Sérgio Alvarez 1, Lev
Cent. Eur. J. Math. 8(2) 2010 338-345 DOI: 10.2478/s11533-010-0013-8 Central European Journal of Mathematics Topological K-equivalence of analytic function-germs Research Article Sérgio Alvarez 1, Lev
Minimization problems on the Hardy-Sobolev inequality
 manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Minimization problems on the Hardy-Sobolev inequality Masato Hashizume Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract We study minimization problems on Hardy-Sobolev
manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Minimization problems on the Hardy-Sobolev inequality Masato Hashizume Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract We study minimization problems on Hardy-Sobolev
Caristi-type Fixed Point Theorem of Set-Valued Maps in Metric Spaces
 International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 11, 2017, no. 6, 267-275 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2017.717 Caristi-type Fixed Point Theorem of Set-Valued Maps in Metric
International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 11, 2017, no. 6, 267-275 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2017.717 Caristi-type Fixed Point Theorem of Set-Valued Maps in Metric
Exercise The solution of
 Exercise 8.51 The solution of dx dy = sin φ cos θdr + r cos φ cos θdφ r sin φ sin θdθ sin φ sin θdr + r cos φ sin θdφ r sin φ cos θdθ is dr dφ = dz cos φdr r sin φdφ dθ sin φ cos θdx + sin φ sin θdy +
Exercise 8.51 The solution of dx dy = sin φ cos θdr + r cos φ cos θdφ r sin φ sin θdθ sin φ sin θdr + r cos φ sin θdφ r sin φ cos θdθ is dr dφ = dz cos φdr r sin φdφ dθ sin φ cos θdx + sin φ sin θdy +
Weak Solutions to Nonlinear Parabolic Problems with Variable Exponent
 International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 1, 216, no. 12, 553-564 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.12988/ijma.216.6223 Weak Solutions to Nonlinear Parabolic Problems with Variable
International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 1, 216, no. 12, 553-564 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.12988/ijma.216.6223 Weak Solutions to Nonlinear Parabolic Problems with Variable
Generalized Boolean and Boolean-Like Rings
 International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 9, 429-438 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ija.2013.2894 Generalized Boolean and Boolean-Like Rings Hazar Abu Khuzam Department
International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 9, 429-438 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ija.2013.2894 Generalized Boolean and Boolean-Like Rings Hazar Abu Khuzam Department
ABSOLUTE CONTINUITY OF FOLIATIONS
 ABSOLUTE CONTINUITY OF FOLIATIONS C. PUGH, M. VIANA, A. WILKINSON 1. Introduction In what follows, U is an open neighborhood in a compact Riemannian manifold M, and F is a local foliation of U. By this
ABSOLUTE CONTINUITY OF FOLIATIONS C. PUGH, M. VIANA, A. WILKINSON 1. Introduction In what follows, U is an open neighborhood in a compact Riemannian manifold M, and F is a local foliation of U. By this
Spacelike surfaces with positive definite second fundamental form in 3-dimensional Lorentzian manifolds
 Spacelike surfaces with positive definite second fundamental form in 3-dimensional Lorentzian manifolds Alfonso Romero Departamento de Geometría y Topología Universidad de Granada 18071-Granada Web: http://www.ugr.es/
Spacelike surfaces with positive definite second fundamental form in 3-dimensional Lorentzian manifolds Alfonso Romero Departamento de Geometría y Topología Universidad de Granada 18071-Granada Web: http://www.ugr.es/
On projective classification of plane curves
 Global and Stochastic Analysis Vol. 1, No. 2, December 2011 Copyright c Mind Reader Publications On projective classification of plane curves Nadiia Konovenko a and Valentin Lychagin b a Odessa National
Global and Stochastic Analysis Vol. 1, No. 2, December 2011 Copyright c Mind Reader Publications On projective classification of plane curves Nadiia Konovenko a and Valentin Lychagin b a Odessa National
Laplace Type Problem with Non-uniform Distribution
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 1, 16, no. 3, 1595-16 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.1988/ams.16.66 Laplace Type Problem with Non-uniform Distribution Giuseppe Caristi Department
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 1, 16, no. 3, 1595-16 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.1988/ams.16.66 Laplace Type Problem with Non-uniform Distribution Giuseppe Caristi Department
A three terms Arithmetic-Geometric mean
 A three terms Arithmetic-Geometric mean Kenji Koike Faculty of Education University of Yamanashi Takeda 4-4-7,Kofu Yamanashi 400-850, Japan kkoike@yamanashi.ac.jp Hironori Shiga Inst. of Math. Physics
A three terms Arithmetic-Geometric mean Kenji Koike Faculty of Education University of Yamanashi Takeda 4-4-7,Kofu Yamanashi 400-850, Japan kkoike@yamanashi.ac.jp Hironori Shiga Inst. of Math. Physics
On the Power of Standard Polynomial to M a,b (E)
 International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 10, 2016, no. 4, 171-177 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ija.2016.6214 On the Power of Standard Polynomial to M a,b (E) Fernanda G. de Paula
International Journal of Algebra, Vol. 10, 2016, no. 4, 171-177 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ija.2016.6214 On the Power of Standard Polynomial to M a,b (E) Fernanda G. de Paula
Totally Marked Rational Maps. John Milnor. Stony Brook University. ICERM, April 20, 2012 [ ANNOTATED VERSION]
![Totally Marked Rational Maps. John Milnor. Stony Brook University. ICERM, April 20, 2012 [ ANNOTATED VERSION] Totally Marked Rational Maps. John Milnor. Stony Brook University. ICERM, April 20, 2012 [ ANNOTATED VERSION]](/thumbs/88/116967948.jpg) Totally Marked Rational Maps John Milnor Stony Brook University ICERM, April 20, 2012 [ ANNOTATED VERSION] Rational maps of degree d 2. (Mostly d = 2.) Let K be an algebraically closed field of characteristic
Totally Marked Rational Maps John Milnor Stony Brook University ICERM, April 20, 2012 [ ANNOTATED VERSION] Rational maps of degree d 2. (Mostly d = 2.) Let K be an algebraically closed field of characteristic
Common Fixed Point Theorems for Compatible Mappings in Dislocated Metric Space
 International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 9, 2015, no. 45, 2235-2242 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2015.57177 Common Fixed Point Theorems for Compatible Mappings
International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 9, 2015, no. 45, 2235-2242 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2015.57177 Common Fixed Point Theorems for Compatible Mappings
TEST CODE: MMA (Objective type) 2015 SYLLABUS
 TEST CODE: MMA (Objective type) 2015 SYLLABUS Analytical Reasoning Algebra Arithmetic, geometric and harmonic progression. Continued fractions. Elementary combinatorics: Permutations and combinations,
TEST CODE: MMA (Objective type) 2015 SYLLABUS Analytical Reasoning Algebra Arithmetic, geometric and harmonic progression. Continued fractions. Elementary combinatorics: Permutations and combinations,
A Cardinal Function on the Category of Metric Spaces
 International Journal of Contemporary Mathematical Sciences Vol. 9, 2014, no. 15, 703-713 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijcms.2014.4442 A Cardinal Function on the Category of
International Journal of Contemporary Mathematical Sciences Vol. 9, 2014, no. 15, 703-713 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijcms.2014.4442 A Cardinal Function on the Category of
A Note on Multiplicity Weight of Nodes of Two Point Taylor Expansion
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol, 207, no 6, 307-3032 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaricom https://doiorg/02988/ams2077302 A Note on Multiplicity Weight of Nodes of Two Point Taylor Expansion Koichiro Shimada
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol, 207, no 6, 307-3032 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaricom https://doiorg/02988/ams2077302 A Note on Multiplicity Weight of Nodes of Two Point Taylor Expansion Koichiro Shimada
Solving Homogeneous Systems with Sub-matrices
 Pure Mathematical Sciences, Vol 7, 218, no 1, 11-18 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaricom https://doiorg/112988/pms218843 Solving Homogeneous Systems with Sub-matrices Massoud Malek Mathematics, California State
Pure Mathematical Sciences, Vol 7, 218, no 1, 11-18 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaricom https://doiorg/112988/pms218843 Solving Homogeneous Systems with Sub-matrices Massoud Malek Mathematics, California State
Orthogonal Derivations on Semirings
 International Journal of Contemporary Mathematical Sciences Vol. 9, 2014, no. 13, 645-651 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijcms.2014.49100 Orthogonal Derivations on Semirings N.
International Journal of Contemporary Mathematical Sciences Vol. 9, 2014, no. 13, 645-651 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijcms.2014.49100 Orthogonal Derivations on Semirings N.
Math 115 ( ) Yum-Tong Siu 1. Euler-Lagrange Equations for Many Functions and Variables and High-Order Derivatives
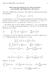 Math 115 006-007 Yum-Tong Siu 1 Euler-Lagrange Equations for Many Functions and Variables and High-Order Derivatives The Case of High-Order Derivatives. The context is to find the extremal for the functional
Math 115 006-007 Yum-Tong Siu 1 Euler-Lagrange Equations for Many Functions and Variables and High-Order Derivatives The Case of High-Order Derivatives. The context is to find the extremal for the functional
24. x 2 y xy y sec(ln x); 1 e x y 1 cos(ln x), y 2 sin(ln x) 25. y y tan x 26. y 4y sec 2x 28.
 16 CHAPTER 4 HIGHER-ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 11. y 3y y 1 4. x yxyy sec(ln x); 1 e x y 1 cos(ln x), y sin(ln x) ex 1. y y y 1 x 13. y3yy sin e x 14. yyy e t arctan t 15. yyy e t ln t 16. y y y 41x
16 CHAPTER 4 HIGHER-ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 11. y 3y y 1 4. x yxyy sec(ln x); 1 e x y 1 cos(ln x), y sin(ln x) ex 1. y y y 1 x 13. y3yy sin e x 14. yyy e t arctan t 15. yyy e t ln t 16. y y y 41x
PHASE PORTRAITS OF PLANAR SEMI HOMOGENEOUS VECTOR FIELDS (III)
 This is a preprint of: Phase portraits of planar semi-homogeneous systems III, Laurent Cairó, Jaume Llibre, Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst., vol. 10, 203 246, 2011. DOI: [10.1007/s12346-011-0052-y] PHASE PORTRAITS
This is a preprint of: Phase portraits of planar semi-homogeneous systems III, Laurent Cairó, Jaume Llibre, Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst., vol. 10, 203 246, 2011. DOI: [10.1007/s12346-011-0052-y] PHASE PORTRAITS
A Laplace Type Problems for a Lattice with Cell Composed by Three Quadrilaterals and with Maximum Probability
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 8, 1, no. 165, 879-886 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.1988/ams.1.11915 A Laplace Type Problems for a Lattice with Cell Composed by Three Quadrilaterals
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 8, 1, no. 165, 879-886 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.1988/ams.1.11915 A Laplace Type Problems for a Lattice with Cell Composed by Three Quadrilaterals
