Scalar Hertz potentials for nonhomogeneous uniaxial dielectric magnetic mediums
|
|
|
- Wilfred Richard King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inernaional Journal of Applied Eleromagneis and Mehanis IOS Press Salar Herz poenials for nonhomogeneous uniaxial dieleri magnei mediums Werner S. Weiglhofer Deparmen of Mahemais, Universiy of Glasgow, Glasgow G 8QW, UK Absra. The salar Herz poenial ehnique is applied o he field analysis in uniaxial dieleri magnei mediums. These mediums may be eiher homogeneous or nonhomogeneous wih a nonhomogeneiy of a resried form. I is shown ha he omplee eleromagnei field in a uniaxial dieleri magnei medium an be derived from wo salar Herz poenials plus, for erain ypes of problems, a small number of soure speifi auxiliary funions. The orresponding salar Green funions are expliily given for he homogenous ase and appliaions for radiaion and propagaion problems are presened.. Inroduion The salar Herz poenial ehnique is an indire soluion mehod for he eleromagnei field. In i erain salar oupled or unoupled parial differenial equaions are solved for a small number of salar funions he salar Herz poenials from whih he aual field veors follow hrough simple manipulaions suh as differeniaions. For more bakground on Herz veors and Herz poenials, inluding many hisorially relevan referenes, he reader is referred o an exellen arile by Sein. The deailed mahemaial feaures of he salar Herz poenial ehnique may be delineaed for a simple, homogeneous isoropi dieleri magnei medium; see for a omprehensive analysis. However, where he mehod speifially proves is value is in is appliaion o mediums more omplex han isoropi: mediums ha are anisoropi or bianisoropi 3,4. Appliaion of he ehnique beyond isoropy were firs repored for soure free dieleri magnei gyroropi mediums 5,6. Those resuls were hen generalized o soures in dieleri magnei gyroropi mediums 7 9. Mediums ha inorporae magneoeleri oupling were invesigaed by applying he salar Herz poenial ehnique o homogeneous and nonhomogeneous isoropi hiral mediums in 0,, respeively. In more reen years, he ehnique was used o deail he soluion of he eleromagnei field problem for uniaxial bianisoropi mediums,3 and for so alled Faraday hiral mediums 4. There are also simply moving isoropi mediums 5,4, whih are bianisoropi in a frame of referene moving wih a relaive uniform veloiy wih respe o he medium. Is onsiuive relaions appear as speial ases of hose for he Faraday hiral mediums 4 and he salar Herz poenial ehnique an hus also be suessfully applied. I was observed in ha no explii reamen of he simples ype of anisoropi medium, he uniaxial dieleri magnei medium 5 wih he salar Herz poenial ehnique has ever appeared in prin. The purpose of he presen paper is hus hreefold: i o omprehensively delineae he salar Herz poenial ehnique for nonhomogeneous uniaxial dieleri magnei mediums for presribed, general eleri and magnei soures; ii o provide explii and losed form expressions for he assoiaed salar Green funions in he homogeneous ase; and iii o highligh he wo mos imporan /00/$ IOS Press. All righs reserved
2 3 W.S. Weiglhofer / Salar Herz poenials for nonhomogeneous uniaxial dieleri magnei mediums appliaions of he formalism o radiaion problems of soures parallel o he disinguished axis of he uniaxial mediums and o wave propagaion problems in soure free nonhomogeneous mediums. By doing so, a signifian gap in he researh lieraure on he opi of salar Herz poenials will be filled.. Field analysis.. Eleromagnei field represenaion The Maxwell equaions for a nonhomogeneous uniaxial dieleri magnei medium for frequeny dependen fields are given by iω ɛx Ex+ Hx =J e x, Ex iω µx Hx = J m x. In hese expressions, Ex is he eleri field and Hx is he magnei field; whereas J e x and J m x are he presribed eleri and magnei urren densiies. All hese quaniies are omplex valued field phasors and heir implii dependene on he irular frequeny ω is suppressed heneforh, as is he ime dependene of exp iω. The maerial properies of he uniaxial medium are speified by he permiiviy dyadi ɛx and he permeabiliy dyadi µx, respeively, whih are se up in he form ɛx =ɛ x I + ɛ x ɛ x, µx =µ x I + µ x µ x, where is a uni veor in he direion of he disinguished axis of he medium. The resried nonhomogeneiy is presen in he four salar onsiuive parameers of hrough heir dependene on x = x. To develop a field represenaion, a parial salarizaion of he differenial equaions wih respe o he direion speified by he uni veor is arried ou. The deomposiions E = E + E, H = H + H, 3 are inrodued, whereby E =0and H =0; E and H being alled he ransverse, E and H he longiudinal omponens of he field veors. Similarily, for he eleri and magnei urren densiy: J e = J e + J e, J m = J m + J m, 4 and also for he derivaive operaions: = + x, = + x, 5 The noaion in his paper is suh ha veors are in bold fae whereas dyadis are in normal fae and underlined wie. Conraion of indies is symbolized by a do; ha is, a b sands for aibi, whereas A = ab is a dyadi wih elemens i A ij = a i b j. The veor o he observaion poin is x and he uni dyadi is I. The supersrip indiaes inversion of dyadis and differenial operaors.
3 W.S. Weiglhofer / Salar Herz poenials for nonhomogeneous uniaxial dieleri magnei mediums 33 wherein is he Laplae operaor. The abbreviaions = / x and = / x are used subsequenly. Firs, manipulaion of he Maxwell equaions aking do produs wih leads o expressions for he omponens E and H in erms of E, H and he soure urren densiies in he form E = J e H, iωɛ H = iωµ J m + E. This leaves he following sysem of differenial equaions for he ransverse omponens as follows E iωµ H + H = J e J m, iωɛ iωɛ H + iωɛ E E = J m + J e. iωµ iωµ Insead of solving a sysem of equaions for E and H, he salarizaion proedure has lead o a siuaion whereby one needs o solve he sysem 7 for he ransverse omponens E and H only, wih E and H hen following from 6. The prie one has o pay for his reduion from he 6 omponen equaions of o he 4 omponen equaions of 7 is ha he former are parial differenial equaions of firs order while he laer are of seond order. Aing wih on 7 nex, permis he derivaion of he following sysem for E and H : + E = ɛ ɛ + k τ e + µ + k µ τ m iω J e iωµ J e + s e, ɛ H = iω µ J m iωɛ J m + s m, where he abbreviaions k = ω ɛ µ, τ e = ɛ /ɛ and τ m = µ /µ have been inrodued. 3 The soure erms s e and s m are given by s e = iω J e J m, ɛ s m = iω µ J m + J e. As for he isoropi ase, he differenial equaions for E and H are no oupled. The ruial sep in he formalism onsiss of he inroduion of salar poenials by using a wo dimensional version of he Helmholz heorem aording o E x = Φx+ Θx, H x = Πx+ Ψx Srily speaking, E, H and remain 3 veors wih null enries in heir respeive omponens for all erms in he relevan equaions o be properly defined. For all praial purposes, however, heir inerpreaion as veors is fully appropriae. 3 I should be emphasized ha beause of he dependene of he onsiuive parameers on x, he derivaive mus be viewed as an operaor in expressions suh as 8.
4 34 W.S. Weiglhofer / Salar Herz poenials for nonhomogeneous uniaxial dieleri magnei mediums In he firs insane, subsiuion of 0 ino 6 yields E = Je + Ψ, iωɛ H = Jm iωµ Θ. Nex, subsiuion of 0 ino 7 and appliaion of and gives four differenial equaions for he salar funions Φ, Θ, Π and Ψ. The four equaions ha are needed o oninue he analysis may be obained more onvenienly in an alernaive way. One akes of and hen deomposes easily o ge ɛ E = ɛ E + iω J e + J e, µ H = µ H + iω J m + J m. Using 0, hese equaions may be redued o Φ= Ψ+ iωɛ iωɛ J e, Π= Θ+ iωµ iωµ J m, 3 whih permi he omplee eliminaion of he funions Φ and Π from he field represenaion. Finally, use of in 8 yields he desired differenial equaions for E and H. They are + ɛ + k τ e Ψ= J e + iωɛ ɛ se, + µ + k τ m Θ=J m iωµ µ sm. In order o eliminae he inverse of he ransverse Laplae operaor from he preeding expressions, auxiliary funions are inrodued by virue of he definiions 4 J e = u e + v e, J m = u m + v m. 5 Consequenly, hese four auxiliary funions u e x, v e x, u m x and v m x are alulaed from he differenial equaions u p = J p, v p = J p, p = e, m. 6
5 W.S. Weiglhofer / Salar Herz poenials for nonhomogeneous uniaxial dieleri magnei mediums 35 One an hus summarize and represen he omplee eleromagnei field in he form E = iωɛ Ψ+ Θ + iωɛ u e, E = iωɛ Ψ+J e, H = iωµ Θ+ Ψ + iωµ u m, H = iωµ Θ J m. These formulas an be reas in ompa noaion as E = iω H = iω ɛ ɛ ɛ Ψ ɛ Ψ + Θ + J e + u e, iωɛ iωɛ µ µ µ Θ µ Θ + Ψ + iωµ J m + iωµ u m, he prime on ɛ and µ indiaing differeniaion wih respe o he argumen x. The expressions 8 show insruively how he orresponding formulas for he isoropi medium ge generalized due o i he uniaxial anisoropy and ii he nonhomogeneiy of he medium. For praial alulaions, however, 7 remain more suiable. Finally, he differenial equaions for he salar Herz poenials Ψ and Θ are given by L e Ψ= J e + ɛ u e iωɛ v m, ɛ L m Θ=J m µ u m iωµ v e, µ wih he Helmholz ype operaors L e, ; x = + ɛ + k ɛ τ e, L m, ; x = + µ + k τ m. µ I is noieable ha 9 for Ψ and Θ are no oupled. In more general ypes of mediums, for example gyroropi or uniaxial bianisoropi mediums, 9 are replaed by a sysem of differenial equaions ha ouple Ψ and Θ. Tha siuaion permis he inroduion of a so alled superpoenial, ha is a salar poenial ha fulfils a fourh order parial differenial equaion. The wo original salar Herz poenials and wih hem he eleromagnei field are hen derivable from ha one salar funion, he superpoenial; see 6,7 for more deails. Suh a possibiliy does no exis for he mediums under onsideraion here
6 36 W.S. Weiglhofer / Salar Herz poenials for nonhomogeneous uniaxial dieleri magnei mediums.. Salar Green funions Wih he eleromagnei field represenaion in plae and he problem fully salarized, he nex sep is he inroduion of salar Green funions. The definiion equaions are L p, ; x g p x, x = δx x, p = e, m. Therein, g e x, x is salar Green funion of he eleri ype, whereas g m x, x is a salar Green funion of he magnei ype and δx x is he Dira dela funion. Consequenly, from 9 and one obains { } Ψx = J e x ɛ x V ɛ x u ex + iωɛ x v m x g e x, x d 3 x, { } Θx = J m x +µ x µ x u mx + iωµ x v e x g m x, x d 3 x. V The salar Green funion equaions are no solvable unless a speifi profile for he onsiuive parameers ɛ x, ɛ x, µ x and µ x is speified. For he imporan homogeneous ase, however, when all four onsiuive parameers are onsan and do herefore no depend on x, simplifies o + τ p + k τ p gp x, x = δx x, p = e, m, 3 whih gives he losed form soluions g p x, x = exp ik D p 4πD p, p = e, m. 4 Therein, D e and D m are modified disanes aording o D e = ɛ x x ɛ x x, D m = µ x x µ x x. 5 While J e and J m, he omponens of J e x and J m x parallel o, appear expliily in he above field represenaion and differenial equaions, his is no he ase for he ransverse soures J e and J m. For hose he analysis an be pushed somewha furher. This is being done here by using aresian oordinaes x,x,x. Saring wih 6, some sraighforward manipulaions lead o u p x = hx,x,x x,x J px,x,x dx dx + hx,x,x x,x J px,x,x dx dx, v p x = 6 hx,x,x x,x J px,x,x dx dx hx,x,x x,x J px,x,x dx dx,
7 W.S. Weiglhofer / Salar Herz poenials for nonhomogeneous uniaxial dieleri magnei mediums 37 p = e, m. In hese expressions, J p and J p are he omponens of J p parallel o he direions speified by oordinaes x and x respeively. The funion hx,x,x,x is he salar Green funion of a sai line soure as defined by hx,x,x,x =δx x δx x, 7 whih has as is soluion hx,x,x,x = x 4π ln x + x x. 8 I is lear from heir defining equaions ha he auxiliary funions u e, u m, v e and v m are no medium speifi. They are generaed by he parial salarizaion approah in a naural way and are essenial o deal wih soures normal o. A deailed disussion of heir mahemaial properies an be found elsewhere 8,9. 3. Appliaions While he salar Herz poenial ehnique provides a self onsisen reamen of he field problem for general soures J e x and J m x, i is a is mos useful from an appliaional poin of view when J e x =J e x, J m x =J m x ; 9 i.e.; he soures have omponens parallel o he disinguished axis only. The resriion 9 also inludes he soure free ase. Then, as a onsequene u p x 0, v p x 0, p = e, m. 30 Therefore, 7 redue o E = Ψ+ Θ, iωɛ E = iωɛ Ψ+J e, H = Θ+ Ψ, iωµ H = iωµ Θ J m, wih Ψx = J e x g e x, x d 3 x, V Θx = J m x g m x, x d 3 x. V 3 3
8 38 W.S. Weiglhofer / Salar Herz poenials for nonhomogeneous uniaxial dieleri magnei mediums If boundaries are presen, he ehnique is one again very well adaped o geomeries whereby he boundaries oinide wih planes x = onsan. Then, he requiremen for oninuiy of he angenial omponens of E and H aross he boundary leads o Ψ+ Θ = Ψ+ Θ, iωɛ x + iωɛ x 33 Θ+ Ψ = Θ+ Ψ. iωµ iωµ x + While he salar Herz poenials are no oupled by heir differenial equaions, i is ineresing o noe ha in suh boundary value problems, a oupling beween he poenials is failiaed by he boundary ondiions. In he following, a brief exposiion is given of he wo mos imporan appliaions of he ehnique. 3.. Dipole radiaion For a homogeneous uniaxial dieleri magnei medium, le he urren densiy be speified as J e x =J 0 e δx x, J m x =0, 34 i.e., i is an eleri poin soure loaed a x = x wih J 0 e a onsan ampliude, in an infinie medium. From earlier expressions i an be found wihou diffiuly ha and hus Ψx =J 0 e g e x, x, Θx =0, 35 E = J 0 e iωɛ g e x, x, x E = J 0 e iωɛ + k H = J 0 e g e x, x, ge x, x, 36 H =0, where he remaining differeniaions an be performed easily as g e x, x is expliily given by Propagaion in nonhomogeneous mediums Consider finally a nonhomogeneous uniaxial dieleri magnei medium in he absene of soures, i.e., J e x =J m x =0. The salar Herz poenials an be speified in he form Ψx =Ψx expik s x, Θx =Θx expik s x, 37
9 W.S. Weiglhofer / Salar Herz poenials for nonhomogeneous uniaxial dieleri magnei mediums 39 where x = x x and s is a veor ha speifies he direion of propagaion in he plane normal o. Subsiuion of 37 ino 9 wih heir righ hand sides se o 0 as all soure erms vanish leads o Ψ ɛ Ψ + k s Ψ=0, ɛ τ e 38 Θ µ Θ + k s Θ=0, µ τ m where he prime again indiaes differeniaion wih respe o x and s = s s. Expressions 38 provide model ordinary differenial equaions ha an be solved when profiles i.e., x dependene of he onsiuive parameers are known. Two brief examples follow pursued here for Ψ only. Take ɛ ɛ 0 = ɛ ɛ 0 = ɛ 0 exp λx, µ = µ = µ 0, 39 where ɛ 0 and µ 0 are he vauum permiiviy and permeabiliy, respeively, and ɛ 0, ɛ 0, λ are onsans. The firs equaion of 38 hen beomes Ψ + a Ψ + b exp λx Ψ=0, 40 for some onsans a, b. If ɛ ɛ 0 = ɛ ɛ 0 n x = ɛ 0 x 0, µ = µ = µ 0, 4 where x 0 is some referene value. Now one has Ψ n Ψ + αx n Ψ=0, 4 x for some onsan α. Ineresingly, for n =, 4 is a Bernoulli equaion wih soluion Ψx =Ax η + Bx η, where A and B are inegraion onsans and η and η are he roos of he quadrai equaion η + η + α =0. 4. Conlusion A deailed derivaion of he salar Herz poenial ehnique for a nonhomogeneous uniaxial dieleri magnei medium has been delineaed. I was shown ha he omplee eleromagnei field an be represened by wo salar Herz poenials ha saisfy seond order parial differenial equaions ha are no oupled. Soure erms ha are based on eleri or magnei urren densiies normal o he disinguished axis of he uniaxial medium mus be aommodaed hrough four auxiliary funions. Salar Green funion represenaions were presened and explii soluions for a homogeneous medium were given. Radiaion from longiudinal soures was reaed and i was reognized ha he salar Herz poenial ehnique is well suied o suh problems. Also, he salar Herz poenial ehnique remains he only mehod ha an inorporae a resried form of nonhomogeneiy direly ino he formalism; an appliaion exemplified by he reamen of a wave propagaion problem.
10 40 W.S. Weiglhofer / Salar Herz poenials for nonhomogeneous uniaxial dieleri magnei mediums Aknowledgmen WSW is he holder of a RSE/SOEID Researh Suppor Fellowship of he Royal Soiey of Edinburgh Grea Briain. Referenes J.J. Sein, Soluions o ime harmoni Maxwell equaions wih a Herz veor, Am. J. Phys , 834. W.S. Weiglhofer, in: Eleromagnei Fields in Unonvenional Maerials and Sruures, O.N. Singh and A. Lakhakia, eds., Wiley, New York, 000,. 3 J.A. Kong, Theorems of bianisoropi media, Pro. IEEE 60 97, W.S. Weiglhofer, A perspeive of bianisoropy and Bianisoropis 97 in: speial issue Bianisoropis 97, W.S. Weiglhofer, gues ed., In. J. Appl. Eleromag. Meh , S. Przezdzieki and R.A. Hurd, A noe on salar Herz poenials for gyroropi media, Appl. Phys , S. Przezdzieki and W. Laprus, On he represenaion of eleromagnei fields in gyroropi media in erms of salar Herz poenials, J. Mah. Phys , W. Weiglhofer and W. Papousek, Skalare Herz she Poeniale für gyrorope Medien, Arh. Elekron. Überrag , W. Weiglhofer and W. Papousek, Salar Herz poenials for ransversally oriened urren densiy disribuions in gyroropi media, Arh. Elekron. Überrag , 4. 9 W. Weiglhofer, Reduion of dyadi Green s funions o salar Herz poenials for gyroropi media, Radio Si. 987, W.S. Weiglhofer, Isoropi hiral media and salar Herz poenials, J. Phys. A: Mah. Gen. 988, 49. W.S. Weiglhofer, Eleromagnei field represenaion in inhomogeneous isoropi hiral media, Eleromagneis 0 990, 7. W.S. Weiglhofer and I.V. Lindell, Fields and poenials in general uniaxial bianisoropi media I. Axial soures, In. J. Appl. Eleromagn. Maer ,. 3 W.S. Weiglhofer, Fields and poenials in general uniaxial bianisoropi media II. General soures and inhomogeneiies, In. J. Appl. Eleromagn. Meh ,. 4 W.S. Weiglhofer and S.O. Hansen, Faraday hiral media revisied I: Fields and soures, IEEE Trans. Anennas Propaga , H.C. Chen, Theory of Eleromagnei Waves, MGraw Hill, New York, W. Weiglhofer, Field represenaion in gyroropi media by one salar superpoenial, IEEE Trans. Anennas Propaga , W.S. Weiglhofer, Salar Green funions and superpoenials of a Faraday hiral medium, Arh. Elekron. Überrag , 09.
A New Formulation of Electrodynamics
 . Eleromagnei Analysis & Appliaions 1 457-461 doi:1.436/jemaa.1.86 Published Online Augus 1 hp://www.sirp.org/journal/jemaa A New Formulaion of Elerodynamis Arbab I. Arbab 1 Faisal A. Yassein 1 Deparmen
. Eleromagnei Analysis & Appliaions 1 457-461 doi:1.436/jemaa.1.86 Published Online Augus 1 hp://www.sirp.org/journal/jemaa A New Formulaion of Elerodynamis Arbab I. Arbab 1 Faisal A. Yassein 1 Deparmen
An Inventory Model for Weibull Time-Dependence. Demand Rate with Completely Backlogged. Shortages
 Inernaional Mahemaial Forum, 5, 00, no. 5, 675-687 An Invenory Model for Weibull Time-Dependene Demand Rae wih Compleely Baklogged Shorages C. K. Tripahy and U. Mishra Deparmen of Saisis, Sambalpur Universiy
Inernaional Mahemaial Forum, 5, 00, no. 5, 675-687 An Invenory Model for Weibull Time-Dependene Demand Rae wih Compleely Baklogged Shorages C. K. Tripahy and U. Mishra Deparmen of Saisis, Sambalpur Universiy
mywbut.com Lesson 11 Study of DC transients in R-L-C Circuits
 mywbu.om esson Sudy of DC ransiens in R--C Ciruis mywbu.om Objeives Be able o wrie differenial equaion for a d iruis onaining wo sorage elemens in presene of a resisane. To develop a horough undersanding
mywbu.om esson Sudy of DC ransiens in R--C Ciruis mywbu.om Objeives Be able o wrie differenial equaion for a d iruis onaining wo sorage elemens in presene of a resisane. To develop a horough undersanding
Boyce/DiPrima 9 th ed, Ch 6.1: Definition of. Laplace Transform. In this chapter we use the Laplace transform to convert a
 Boye/DiPrima 9 h ed, Ch 6.: Definiion of Laplae Transform Elemenary Differenial Equaions and Boundary Value Problems, 9 h ediion, by William E. Boye and Rihard C. DiPrima, 2009 by John Wiley & Sons, In.
Boye/DiPrima 9 h ed, Ch 6.: Definiion of Laplae Transform Elemenary Differenial Equaions and Boundary Value Problems, 9 h ediion, by William E. Boye and Rihard C. DiPrima, 2009 by John Wiley & Sons, In.
Lorentz Transformation Properties of Currents for the Particle-Antiparticle Pair Wave Functions
 Open Aess Library Journal 17, Volume 4, e373 ISSN Online: 333-971 ISSN Prin: 333-975 Lorenz Transformaion Properies of Currens for he Parile-Aniparile Pair Wave Funions Raja Roy Deparmen of Eleronis and
Open Aess Library Journal 17, Volume 4, e373 ISSN Online: 333-971 ISSN Prin: 333-975 Lorenz Transformaion Properies of Currens for he Parile-Aniparile Pair Wave Funions Raja Roy Deparmen of Eleronis and
Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR) - State Feedback Design
 Linear Quadrai Regulaor (LQR) - Sae Feedbak Design A sysem is expressed in sae variable form as x = Ax + Bu n m wih x( ) R, u( ) R and he iniial ondiion x() = x A he sabilizaion problem using sae variable
Linear Quadrai Regulaor (LQR) - Sae Feedbak Design A sysem is expressed in sae variable form as x = Ax + Bu n m wih x( ) R, u( ) R and he iniial ondiion x() = x A he sabilizaion problem using sae variable
Energy Momentum Tensor for Photonic System
 018 IJSST Volume 4 Issue 10 Prin ISSN : 395-6011 Online ISSN : 395-60X Themed Seion: Siene and Tehnology Energy Momenum Tensor for Phooni Sysem ampada Misra Ex-Gues-Teaher, Deparmens of Eleronis, Vidyasagar
018 IJSST Volume 4 Issue 10 Prin ISSN : 395-6011 Online ISSN : 395-60X Themed Seion: Siene and Tehnology Energy Momenum Tensor for Phooni Sysem ampada Misra Ex-Gues-Teaher, Deparmens of Eleronis, Vidyasagar
Mahgoub Transform Method for Solving Linear Fractional Differential Equations
 Mahgoub Transform Mehod for Solving Linear Fraional Differenial Equaions A. Emimal Kanaga Puhpam 1,* and S. Karin Lydia 2 1* Assoiae Professor&Deparmen of Mahemais, Bishop Heber College Tiruhirappalli,
Mahgoub Transform Mehod for Solving Linear Fraional Differenial Equaions A. Emimal Kanaga Puhpam 1,* and S. Karin Lydia 2 1* Assoiae Professor&Deparmen of Mahemais, Bishop Heber College Tiruhirappalli,
TRANSMISSION LINES AND WAVEGUIDES. Uniformity along the Direction of Propagation
 TRANSMISSION LINES AND WAVEGUIDES Uniformi along he Direion of Propagaion Definiion: Transmission Line TL is he erm o desribe ransmission ssems wih wo or more mealli onduors eleriall insulaed from eah
TRANSMISSION LINES AND WAVEGUIDES Uniformi along he Direion of Propagaion Definiion: Transmission Line TL is he erm o desribe ransmission ssems wih wo or more mealli onduors eleriall insulaed from eah
Amit Mehra. Indian School of Business, Hyderabad, INDIA Vijay Mookerjee
 RESEARCH ARTICLE HUMAN CAPITAL DEVELOPMENT FOR PROGRAMMERS USING OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE Ami Mehra Indian Shool of Business, Hyderabad, INDIA {Ami_Mehra@isb.edu} Vijay Mookerjee Shool of Managemen, Uniersiy
RESEARCH ARTICLE HUMAN CAPITAL DEVELOPMENT FOR PROGRAMMERS USING OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE Ami Mehra Indian Shool of Business, Hyderabad, INDIA {Ami_Mehra@isb.edu} Vijay Mookerjee Shool of Managemen, Uniersiy
Generalized electromagnetic energy-momentum tensor and scalar curvature of space at the location of charged particle
 Generalized eleromagnei energy-momenum ensor and salar urvaure of spae a he loaion of harged parile A.L. Kholmeskii 1, O.V. Missevih and T. Yarman 3 1 Belarus Sae Universiy, Nezavisimosi Avenue, 0030 Minsk,
Generalized eleromagnei energy-momenum ensor and salar urvaure of spae a he loaion of harged parile A.L. Kholmeskii 1, O.V. Missevih and T. Yarman 3 1 Belarus Sae Universiy, Nezavisimosi Avenue, 0030 Minsk,
EE40 Summer 2005: Lecture 2 Instructor: Octavian Florescu 1. Measuring Voltages and Currents
 Announemens HW # Due oday a 6pm. HW # posed online oday and due nex Tuesday a 6pm. Due o sheduling onflis wih some sudens, lasses will resume normally his week and nex. Miderm enaively 7/. EE4 Summer 5:
Announemens HW # Due oday a 6pm. HW # posed online oday and due nex Tuesday a 6pm. Due o sheduling onflis wih some sudens, lasses will resume normally his week and nex. Miderm enaively 7/. EE4 Summer 5:
Optimal Transform: The Karhunen-Loeve Transform (KLT)
 Opimal ransform: he Karhunen-Loeve ransform (KL) Reall: We are ineresed in uniary ransforms beause of heir nie properies: energy onservaion, energy ompaion, deorrelaion oivaion: τ (D ransform; assume separable)
Opimal ransform: he Karhunen-Loeve ransform (KL) Reall: We are ineresed in uniary ransforms beause of heir nie properies: energy onservaion, energy ompaion, deorrelaion oivaion: τ (D ransform; assume separable)
Analysis of Tubular Linear Permanent Magnet Motor for Drilling Application
 Analysis of Tubular Linear Permanen Magne Moor for Drilling Appliaion Shujun Zhang, Lars Norum, Rober Nilssen Deparmen of Eleri Power Engineering Norwegian Universiy of Siene and Tehnology, Trondheim 7491
Analysis of Tubular Linear Permanen Magne Moor for Drilling Appliaion Shujun Zhang, Lars Norum, Rober Nilssen Deparmen of Eleri Power Engineering Norwegian Universiy of Siene and Tehnology, Trondheim 7491
Generalized The General Relativity Using Generalized Lorentz Transformation
 P P P P IJISET - Inernaional Journal of Innoaie Siene, Engineering & Tehnology, Vol. 3 Issue 4, April 6. www.ijise.om ISSN 348 7968 Generalized The General Relaiiy Using Generalized Lorenz Transformaion
P P P P IJISET - Inernaional Journal of Innoaie Siene, Engineering & Tehnology, Vol. 3 Issue 4, April 6. www.ijise.om ISSN 348 7968 Generalized The General Relaiiy Using Generalized Lorenz Transformaion
B Signals and Systems I Solutions to Midterm Test 2. xt ()
 34-33B Signals and Sysems I Soluions o Miderm es 34-33B Signals and Sysems I Soluions o Miderm es ednesday Marh 7, 7:PM-9:PM Examiner: Prof. Benoi Boule Deparmen of Elerial and Compuer Engineering MGill
34-33B Signals and Sysems I Soluions o Miderm es 34-33B Signals and Sysems I Soluions o Miderm es ednesday Marh 7, 7:PM-9:PM Examiner: Prof. Benoi Boule Deparmen of Elerial and Compuer Engineering MGill
Derivation of longitudinal Doppler shift equation between two moving bodies in reference frame at rest
 Deriaion o longiudinal Doppler shi equaion beween wo moing bodies in reerene rame a res Masanori Sao Honda Eleronis Co., d., Oyamazuka, Oiwa-ho, Toyohashi, ihi 44-393, Japan E-mail: msao@honda-el.o.jp
Deriaion o longiudinal Doppler shi equaion beween wo moing bodies in reerene rame a res Masanori Sao Honda Eleronis Co., d., Oyamazuka, Oiwa-ho, Toyohashi, ihi 44-393, Japan E-mail: msao@honda-el.o.jp
Math 334 Fall 2011 Homework 11 Solutions
 Dec. 2, 2 Mah 334 Fall 2 Homework Soluions Basic Problem. Transform he following iniial value problem ino an iniial value problem for a sysem: u + p()u + q() u g(), u() u, u () v. () Soluion. Le v u. Then
Dec. 2, 2 Mah 334 Fall 2 Homework Soluions Basic Problem. Transform he following iniial value problem ino an iniial value problem for a sysem: u + p()u + q() u g(), u() u, u () v. () Soluion. Le v u. Then
The Asymptotical Behavior of Probability Measures for the Fluctuations of Stochastic Models
 The Asympoial Behavior of Probabiliy Measures for he Fluuaions of Sohasi Models JUN WANG CUINING WEI Deparmen of Mahemais College of Siene Beijing Jiaoong Universiy Beijing Jiaoong Universiy Beijing 44
The Asympoial Behavior of Probabiliy Measures for he Fluuaions of Sohasi Models JUN WANG CUINING WEI Deparmen of Mahemais College of Siene Beijing Jiaoong Universiy Beijing Jiaoong Universiy Beijing 44
AN INVENTORY MODEL FOR DETERIORATING ITEMS WITH EXPONENTIAL DECLINING DEMAND AND PARTIAL BACKLOGGING
 Yugoslav Journal of Operaions Researh 5 (005) Number 77-88 AN INVENTORY MODEL FOR DETERIORATING ITEMS WITH EXPONENTIAL DECLINING DEMAND AND PARTIAL BACKLOGGING Liang-Yuh OUYANG Deparmen of Managemen Sienes
Yugoslav Journal of Operaions Researh 5 (005) Number 77-88 AN INVENTORY MODEL FOR DETERIORATING ITEMS WITH EXPONENTIAL DECLINING DEMAND AND PARTIAL BACKLOGGING Liang-Yuh OUYANG Deparmen of Managemen Sienes
A state space approach to calculating the Beveridge Nelson decomposition
 Eonomis Leers 75 (00) 3 7 www.elsevier.om/ loae/ eonbase A sae spae approah o alulaing he Beveridge Nelson deomposiion James C. Morley* Deparmen of Eonomis, Washingon Universiy, Campus Box 08, Brookings
Eonomis Leers 75 (00) 3 7 www.elsevier.om/ loae/ eonbase A sae spae approah o alulaing he Beveridge Nelson deomposiion James C. Morley* Deparmen of Eonomis, Washingon Universiy, Campus Box 08, Brookings
Two Coupled Oscillators / Normal Modes
 Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
A New Formulation of Quantum Mechanics
 Journal of Modern Physis 3 63-69 hp://dxdoiorg/436/jmp3 Published Online February (hp://wwwsirporg/journal/jmp) A New Formulaion of Quanum Mehanis A I Arbab Faisal A Yassein Deparmen of Physis Fauly of
Journal of Modern Physis 3 63-69 hp://dxdoiorg/436/jmp3 Published Online February (hp://wwwsirporg/journal/jmp) A New Formulaion of Quanum Mehanis A I Arbab Faisal A Yassein Deparmen of Physis Fauly of
t is a basis for the solution space to this system, then the matrix having these solutions as columns, t x 1 t, x 2 t,... x n t x 2 t...
 Mah 228- Fri Mar 24 5.6 Marix exponenials and linear sysems: The analogy beween firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions (Chaper 5) and scalar linear differenial equaions (Chaper ) is much sronger
Mah 228- Fri Mar 24 5.6 Marix exponenials and linear sysems: The analogy beween firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions (Chaper 5) and scalar linear differenial equaions (Chaper ) is much sronger
New Oscillation Criteria For Second Order Nonlinear Differential Equations
 Researh Inveny: Inernaional Journal Of Engineering And Siene Issn: 78-47, Vol, Issue 4 (Feruary 03), Pp 36-4 WwwResearhinvenyCom New Osillaion Crieria For Seond Order Nonlinear Differenial Equaions Xhevair
Researh Inveny: Inernaional Journal Of Engineering And Siene Issn: 78-47, Vol, Issue 4 (Feruary 03), Pp 36-4 WwwResearhinvenyCom New Osillaion Crieria For Seond Order Nonlinear Differenial Equaions Xhevair
t 2 B F x,t n dsdt t u x,t dxdt
 Evoluion Equaions For 0, fixed, le U U0, where U denoes a bounded open se in R n.suppose ha U is filled wih a maerial in which a conaminan is being ranspored by various means including diffusion and convecion.
Evoluion Equaions For 0, fixed, le U U0, where U denoes a bounded open se in R n.suppose ha U is filled wih a maerial in which a conaminan is being ranspored by various means including diffusion and convecion.
EXPLICIT TIME INTEGRATORS FOR NONLINEAR DYNAMICS DERIVED FROM THE MIDPOINT RULE
 Version April 30, 2004.Submied o CTU Repors. EXPLICIT TIME INTEGRATORS FOR NONLINEAR DYNAMICS DERIVED FROM THE MIDPOINT RULE Per Krysl Universiy of California, San Diego La Jolla, California 92093-0085,
Version April 30, 2004.Submied o CTU Repors. EXPLICIT TIME INTEGRATORS FOR NONLINEAR DYNAMICS DERIVED FROM THE MIDPOINT RULE Per Krysl Universiy of California, San Diego La Jolla, California 92093-0085,
The Special Theory of Relativity Chapter II
 The Speial Theory of Relaiiy Chaper II 1. Relaiisi Kinemais. Time dilaion and spae rael 3. Lengh onraion 4. Lorenz ransformaions 5. Paradoes? Simulaneiy/Relaiiy If one obserer sees he eens as simulaneous,
The Speial Theory of Relaiiy Chaper II 1. Relaiisi Kinemais. Time dilaion and spae rael 3. Lengh onraion 4. Lorenz ransformaions 5. Paradoes? Simulaneiy/Relaiiy If one obserer sees he eens as simulaneous,
Physics 127b: Statistical Mechanics. Fokker-Planck Equation. Time Evolution
 Physics 7b: Saisical Mechanics Fokker-Planck Equaion The Langevin equaion approach o he evoluion of he velociy disribuion for he Brownian paricle migh leave you uncomforable. A more formal reamen of his
Physics 7b: Saisical Mechanics Fokker-Planck Equaion The Langevin equaion approach o he evoluion of he velociy disribuion for he Brownian paricle migh leave you uncomforable. A more formal reamen of his
Chapter 2. First Order Scalar Equations
 Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
6.2 Transforms of Derivatives and Integrals.
 SEC. 6.2 Transforms of Derivaives and Inegrals. ODEs 2 3 33 39 23. Change of scale. If l( f ()) F(s) and c is any 33 45 APPLICATION OF s-shifting posiive consan, show ha l( f (c)) F(s>c)>c (Hin: In Probs.
SEC. 6.2 Transforms of Derivaives and Inegrals. ODEs 2 3 33 39 23. Change of scale. If l( f ()) F(s) and c is any 33 45 APPLICATION OF s-shifting posiive consan, show ha l( f (c)) F(s>c)>c (Hin: In Probs.
GENERALIZATION OF THE FORMULA OF FAA DI BRUNO FOR A COMPOSITE FUNCTION WITH A VECTOR ARGUMENT
 Inerna J Mah & Mah Sci Vol 4, No 7 000) 48 49 S0670000970 Hindawi Publishing Corp GENERALIZATION OF THE FORMULA OF FAA DI BRUNO FOR A COMPOSITE FUNCTION WITH A VECTOR ARGUMENT RUMEN L MISHKOV Received
Inerna J Mah & Mah Sci Vol 4, No 7 000) 48 49 S0670000970 Hindawi Publishing Corp GENERALIZATION OF THE FORMULA OF FAA DI BRUNO FOR A COMPOSITE FUNCTION WITH A VECTOR ARGUMENT RUMEN L MISHKOV Received
A comparative Study of Contact Problems Solution Based on the Penalty and Lagrange Multiplier Approaches
 Journal of he Serbian Soiey for ompuaional Mehanis / Vol. / o., 2007 / pp. 74-83 A omparaive Sudy of ona Problems Soluion Based on he Penaly and Lagrange Muliplier Approahes S. Vulovi, M. Zivovi,. Grujovi,
Journal of he Serbian Soiey for ompuaional Mehanis / Vol. / o., 2007 / pp. 74-83 A omparaive Sudy of ona Problems Soluion Based on he Penaly and Lagrange Muliplier Approahes S. Vulovi, M. Zivovi,. Grujovi,
Some Basic Information about M-S-D Systems
 Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
The Special Theory of Relativity
 The Speial Theor of Relaii The Speial Theor of Relaii Chaper I. Conradiions in phsis?. Galilean Transformaions of lassial mehanis 3. The effe on Mawell s equaions ligh 4. Mihelson-Morle eperimen 5. insein
The Speial Theor of Relaii The Speial Theor of Relaii Chaper I. Conradiions in phsis?. Galilean Transformaions of lassial mehanis 3. The effe on Mawell s equaions ligh 4. Mihelson-Morle eperimen 5. insein
Finish reading Chapter 2 of Spivak, rereading earlier sections as necessary. handout and fill in some missing details!
 MAT 257, Handou 6: Ocober 7-2, 20. I. Assignmen. Finish reading Chaper 2 of Spiva, rereading earlier secions as necessary. handou and fill in some missing deails! II. Higher derivaives. Also, read his
MAT 257, Handou 6: Ocober 7-2, 20. I. Assignmen. Finish reading Chaper 2 of Spiva, rereading earlier secions as necessary. handou and fill in some missing deails! II. Higher derivaives. Also, read his
Peakon, pseudo-peakon, and cuspon solutions for two generalized Camassa-Holm equations
 JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS 54 13501 (013) Peakon pseudo-peakon and uspon soluions for wo generalized Camassa-Holm equaions Jibin Li 1a) and Zhijun Qiao 3a) 1 Deparmen of Mahemais Zhejiang Normal Universiy
JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS 54 13501 (013) Peakon pseudo-peakon and uspon soluions for wo generalized Camassa-Holm equaions Jibin Li 1a) and Zhijun Qiao 3a) 1 Deparmen of Mahemais Zhejiang Normal Universiy
Differential Equations
 Mah 21 (Fall 29) Differenial Equaions Soluion #3 1. Find he paricular soluion of he following differenial equaion by variaion of parameer (a) y + y = csc (b) 2 y + y y = ln, > Soluion: (a) The corresponding
Mah 21 (Fall 29) Differenial Equaions Soluion #3 1. Find he paricular soluion of he following differenial equaion by variaion of parameer (a) y + y = csc (b) 2 y + y y = ln, > Soluion: (a) The corresponding
Chapter 8 The Complete Response of RL and RC Circuits
 Chaper 8 The Complee Response of RL and RC Circuis Seoul Naional Universiy Deparmen of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Wha is Firs Order Circuis? Circuis ha conain only one inducor or only one capacior
Chaper 8 The Complee Response of RL and RC Circuis Seoul Naional Universiy Deparmen of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Wha is Firs Order Circuis? Circuis ha conain only one inducor or only one capacior
10. State Space Methods
 . Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
. Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
Mocanu Paradox of Different Types of Lorentz Transformations
 Page Moanu Parado of Differen Types of Lorenz Transformaions A R aizid and M S Alam * Deparmen of usiness Adminisraion Leading niersiy Sylhe 300 angladesh Deparmen of Physis Shahjalal niersiy of Siene
Page Moanu Parado of Differen Types of Lorenz Transformaions A R aizid and M S Alam * Deparmen of usiness Adminisraion Leading niersiy Sylhe 300 angladesh Deparmen of Physis Shahjalal niersiy of Siene
Physics 235 Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics Single Particle
 Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Problem Set 9 Due December, 7
 EE226: Random Proesses in Sysems Leurer: Jean C. Walrand Problem Se 9 Due Deember, 7 Fall 6 GSI: Assane Gueye his problem se essenially reviews Convergene and Renewal proesses. No all exerises are o be
EE226: Random Proesses in Sysems Leurer: Jean C. Walrand Problem Se 9 Due Deember, 7 Fall 6 GSI: Assane Gueye his problem se essenially reviews Convergene and Renewal proesses. No all exerises are o be
Capacitance and Inductance. The Capacitor
 apaiane and Induane OUTINE apaiors apaior volage, urren, power, energy Induors eure 9, 9/9/5 Reading Hambley haper 3 (A) EE4 Fall 5 eure 9, Slide The apaior Two onduors (a,b) separaed by an insulaor: differene
apaiane and Induane OUTINE apaiors apaior volage, urren, power, energy Induors eure 9, 9/9/5 Reading Hambley haper 3 (A) EE4 Fall 5 eure 9, Slide The apaior Two onduors (a,b) separaed by an insulaor: differene
MATH 128A, SUMMER 2009, FINAL EXAM SOLUTION
 MATH 28A, SUMME 2009, FINAL EXAM SOLUTION BENJAMIN JOHNSON () (8 poins) [Lagrange Inerpolaion] (a) (4 poins) Le f be a funcion defined a some real numbers x 0,..., x n. Give a defining equaion for he Lagrange
MATH 28A, SUMME 2009, FINAL EXAM SOLUTION BENJAMIN JOHNSON () (8 poins) [Lagrange Inerpolaion] (a) (4 poins) Le f be a funcion defined a some real numbers x 0,..., x n. Give a defining equaion for he Lagrange
Class Meeting # 10: Introduction to the Wave Equation
 MATH 8.5 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 0 8.5 Inroducion o PDEs, Fall 0 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeing # 0: Inroducion o he Wave Equaion. Wha is he wave equaion? The sandard wave equaion for a funcion
MATH 8.5 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 0 8.5 Inroducion o PDEs, Fall 0 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeing # 0: Inroducion o he Wave Equaion. Wha is he wave equaion? The sandard wave equaion for a funcion
Basic Circuit Elements Professor J R Lucas November 2001
 Basic Circui Elemens - J ucas An elecrical circui is an inerconnecion of circui elemens. These circui elemens can be caegorised ino wo ypes, namely acive and passive elemens. Some Definiions/explanaions
Basic Circui Elemens - J ucas An elecrical circui is an inerconnecion of circui elemens. These circui elemens can be caegorised ino wo ypes, namely acive and passive elemens. Some Definiions/explanaions
The Relativistic Field of a Rotating Body
 The Relaivisi Field of a Roaing Body Panelis M. Pehlivanides Alani IKE, Ahens 57, Greee ppexl@eemail.gr Absra Based on he pahs of signals emanaing from a roaing poin body, e find he equaions and properies
The Relaivisi Field of a Roaing Body Panelis M. Pehlivanides Alani IKE, Ahens 57, Greee ppexl@eemail.gr Absra Based on he pahs of signals emanaing from a roaing poin body, e find he equaions and properies
System of Linear Differential Equations
 Sysem of Linear Differenial Equaions In "Ordinary Differenial Equaions" we've learned how o solve a differenial equaion for a variable, such as: y'k5$e K2$x =0 solve DE yx = K 5 2 ek2 x C_C1 2$y''C7$y
Sysem of Linear Differenial Equaions In "Ordinary Differenial Equaions" we've learned how o solve a differenial equaion for a variable, such as: y'k5$e K2$x =0 solve DE yx = K 5 2 ek2 x C_C1 2$y''C7$y
1.054/1.541 Mechanics and Design of Concrete Structures (3-0-9) Outline 5 Creep and Shrinkage Deformation
 1.54/1.541 Mehanis and Design of Conree ruures pring 24 Prof. Oral Buyukozurk Massahuses Insiue of Tehnology Ouline 5 1.54/1.541 Mehanis and Design of Conree ruures (3--9 Ouline 5 and hrinkage Deformaion
1.54/1.541 Mehanis and Design of Conree ruures pring 24 Prof. Oral Buyukozurk Massahuses Insiue of Tehnology Ouline 5 1.54/1.541 Mehanis and Design of Conree ruures (3--9 Ouline 5 and hrinkage Deformaion
(Radiation Dominated) Last Update: 21 June 2006
 Chaper Rik s Cosmology uorial: he ime-emperaure Relaionship in he Early Universe Chaper he ime-emperaure Relaionship in he Early Universe (Radiaion Dominaed) Las Updae: 1 June 006 1. Inroduion n In Chaper
Chaper Rik s Cosmology uorial: he ime-emperaure Relaionship in he Early Universe Chaper he ime-emperaure Relaionship in he Early Universe (Radiaion Dominaed) Las Updae: 1 June 006 1. Inroduion n In Chaper
Solutions to Assignment 1
 MA 2326 Differenial Equaions Insrucor: Peronela Radu Friday, February 8, 203 Soluions o Assignmen. Find he general soluions of he following ODEs: (a) 2 x = an x Soluion: I is a separable equaion as we
MA 2326 Differenial Equaions Insrucor: Peronela Radu Friday, February 8, 203 Soluions o Assignmen. Find he general soluions of he following ODEs: (a) 2 x = an x Soluion: I is a separable equaion as we
κt π = (5) T surrface k BASELINE CASE
 II. BASELINE CASE PRACICAL CONSIDERAIONS FOR HERMAL SRESSES INDUCED BY SURFACE HEAING James P. Blanhard Universi of Wisonsin Madison 15 Engineering Dr. Madison, WI 5376-169 68-63-391 blanhard@engr.is.edu
II. BASELINE CASE PRACICAL CONSIDERAIONS FOR HERMAL SRESSES INDUCED BY SURFACE HEAING James P. Blanhard Universi of Wisonsin Madison 15 Engineering Dr. Madison, WI 5376-169 68-63-391 blanhard@engr.is.edu
Predator - Prey Model Trajectories and the nonlinear conservation law
 Predaor - Prey Model Trajecories and he nonlinear conservaion law James K. Peerson Deparmen of Biological Sciences and Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences Clemson Universiy Ocober 28, 213 Ouline Drawing Trajecories
Predaor - Prey Model Trajecories and he nonlinear conservaion law James K. Peerson Deparmen of Biological Sciences and Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences Clemson Universiy Ocober 28, 213 Ouline Drawing Trajecories
Number of modes per unit volume of the cavity per unit frequency interval is given by: Mode Density, N
 SMES404 - LASER PHYSCS (LECTURE 5 on /07/07) Number of modes per uni volume of he aviy per uni frequeny inerval is given by: 8 Mode Densiy, N (.) Therefore, energy densiy (per uni freq. inerval); U 8h
SMES404 - LASER PHYSCS (LECTURE 5 on /07/07) Number of modes per uni volume of he aviy per uni frequeny inerval is given by: 8 Mode Densiy, N (.) Therefore, energy densiy (per uni freq. inerval); U 8h
Stability and Bifurcation in a Neural Network Model with Two Delays
 Inernaional Mahemaical Forum, Vol. 6, 11, no. 35, 175-1731 Sabiliy and Bifurcaion in a Neural Nework Model wih Two Delays GuangPing Hu and XiaoLing Li School of Mahemaics and Physics, Nanjing Universiy
Inernaional Mahemaical Forum, Vol. 6, 11, no. 35, 175-1731 Sabiliy and Bifurcaion in a Neural Nework Model wih Two Delays GuangPing Hu and XiaoLing Li School of Mahemaics and Physics, Nanjing Universiy
Idealize Bioreactor CSTR vs. PFR... 3 Analysis of a simple continuous stirred tank bioreactor... 4 Residence time distribution... 4 F curve:...
 Idealize Bioreaor CSTR vs. PFR... 3 Analysis of a simple oninuous sirred ank bioreaor... 4 Residene ime disribuion... 4 F urve:... 4 C urve:... 4 Residene ime disribuion or age disribuion... 4 Residene
Idealize Bioreaor CSTR vs. PFR... 3 Analysis of a simple oninuous sirred ank bioreaor... 4 Residene ime disribuion... 4 F urve:... 4 C urve:... 4 Residene ime disribuion or age disribuion... 4 Residene
23.2. Representing Periodic Functions by Fourier Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
ODEs II, Lecture 1: Homogeneous Linear Systems - I. Mike Raugh 1. March 8, 2004
 ODEs II, Lecure : Homogeneous Linear Sysems - I Mike Raugh March 8, 4 Inroducion. In he firs lecure we discussed a sysem of linear ODEs for modeling he excreion of lead from he human body, saw how o ransform
ODEs II, Lecure : Homogeneous Linear Sysems - I Mike Raugh March 8, 4 Inroducion. In he firs lecure we discussed a sysem of linear ODEs for modeling he excreion of lead from he human body, saw how o ransform
CHAPTER 2 Signals And Spectra
 CHAPER Signals And Specra Properies of Signals and Noise In communicaion sysems he received waveform is usually caegorized ino he desired par conaining he informaion, and he undesired par. he desired par
CHAPER Signals And Specra Properies of Signals and Noise In communicaion sysems he received waveform is usually caegorized ino he desired par conaining he informaion, and he undesired par. he desired par
Relativistic Jets from Black Holes: A Unified Picture
 Relaivisi Jes from lak Holes: A Unified Piure C Sivaram and Kenah Arun Indian Insiue of Asrophysis, angalore Absra: The urren undersanding of he formaion of powerful bi-direional jes in sysems suh as radio
Relaivisi Jes from lak Holes: A Unified Piure C Sivaram and Kenah Arun Indian Insiue of Asrophysis, angalore Absra: The urren undersanding of he formaion of powerful bi-direional jes in sysems suh as radio
The Arcsine Distribution
 The Arcsine Disribuion Chris H. Rycrof Ocober 6, 006 A common heme of he class has been ha he saisics of single walker are ofen very differen from hose of an ensemble of walkers. On he firs homework, we
The Arcsine Disribuion Chris H. Rycrof Ocober 6, 006 A common heme of he class has been ha he saisics of single walker are ofen very differen from hose of an ensemble of walkers. On he firs homework, we
The expectation value of the field operator.
 The expecaion value of he field operaor. Dan Solomon Universiy of Illinois Chicago, IL dsolom@uic.edu June, 04 Absrac. Much of he mahemaical developmen of quanum field heory has been in suppor of deermining
The expecaion value of he field operaor. Dan Solomon Universiy of Illinois Chicago, IL dsolom@uic.edu June, 04 Absrac. Much of he mahemaical developmen of quanum field heory has been in suppor of deermining
Generalized Chebyshev polynomials
 Generalized Chebyshev polynomials Clemene Cesarano Faculy of Engineering, Inernaional Telemaic Universiy UNINETTUNO Corso Viorio Emanuele II, 39 86 Roma, Ialy email: c.cesarano@unineunouniversiy.ne ABSTRACT
Generalized Chebyshev polynomials Clemene Cesarano Faculy of Engineering, Inernaional Telemaic Universiy UNINETTUNO Corso Viorio Emanuele II, 39 86 Roma, Ialy email: c.cesarano@unineunouniversiy.ne ABSTRACT
Section 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equations; Method of Undetermined Coefficients
 Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
2. Nonlinear Conservation Law Equations
 . Nonlinear Conservaion Law Equaions One of he clear lessons learned over recen years in sudying nonlinear parial differenial equaions is ha i is generally no wise o ry o aack a general class of nonlinear
. Nonlinear Conservaion Law Equaions One of he clear lessons learned over recen years in sudying nonlinear parial differenial equaions is ha i is generally no wise o ry o aack a general class of nonlinear
An Introduction to Malliavin calculus and its applications
 An Inroducion o Malliavin calculus and is applicaions Lecure 5: Smoohness of he densiy and Hörmander s heorem David Nualar Deparmen of Mahemaics Kansas Universiy Universiy of Wyoming Summer School 214
An Inroducion o Malliavin calculus and is applicaions Lecure 5: Smoohness of he densiy and Hörmander s heorem David Nualar Deparmen of Mahemaics Kansas Universiy Universiy of Wyoming Summer School 214
dt = C exp (3 ln t 4 ). t 4 W = C exp ( ln(4 t) 3) = C(4 t) 3.
 Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
Mass Transfer Coefficients (MTC) and Correlations I
 Mass Transfer Mass Transfer Coeffiiens (MTC) and Correlaions I 7- Mass Transfer Coeffiiens and Correlaions I Diffusion an be desribed in wo ways:. Deailed physial desripion based on Fik s laws and he diffusion
Mass Transfer Mass Transfer Coeffiiens (MTC) and Correlaions I 7- Mass Transfer Coeffiiens and Correlaions I Diffusion an be desribed in wo ways:. Deailed physial desripion based on Fik s laws and he diffusion
Expert Advice for Amateurs
 Exper Advice for Amaeurs Ernes K. Lai Online Appendix - Exisence of Equilibria The analysis in his secion is performed under more general payoff funcions. Wihou aking an explici form, he payoffs of he
Exper Advice for Amaeurs Ernes K. Lai Online Appendix - Exisence of Equilibria The analysis in his secion is performed under more general payoff funcions. Wihou aking an explici form, he payoffs of he
3. Differential Equations
 3. Differenial Equaions 3.. inear Differenial Equaions of Firs rder A firs order differenial equaion is an equaion of he form d() d ( ) = F ( (),) (3.) As noed above, here will in general be a whole la
3. Differenial Equaions 3.. inear Differenial Equaions of Firs rder A firs order differenial equaion is an equaion of he form d() d ( ) = F ( (),) (3.) As noed above, here will in general be a whole la
Numerical simulation of damage in glass subjected to static indentation
 8 ème Congrès Français de Méanique Grenoble, 7- aoû 007 Numerial simulaion of damage in glass subjeed o sai indenaion Jewan Ismail, Fahmi Zaïri, Moussa Naï-Abdelaziz & Ziouni Azari Laboraoire de Méanique
8 ème Congrès Français de Méanique Grenoble, 7- aoû 007 Numerial simulaion of damage in glass subjeed o sai indenaion Jewan Ismail, Fahmi Zaïri, Moussa Naï-Abdelaziz & Ziouni Azari Laboraoire de Méanique
Concrete damaged plasticity model
 Conree damaged asiiy model Conree damaged asiiy model is a maerial model for he analysis of onree sruures mainly under dynami loads suh as earhquakes(only aes an be analyzed under he dynami loads like
Conree damaged asiiy model Conree damaged asiiy model is a maerial model for he analysis of onree sruures mainly under dynami loads suh as earhquakes(only aes an be analyzed under he dynami loads like
Theory of! Partial Differential Equations!
 hp://www.nd.edu/~gryggva/cfd-course/! Ouline! Theory o! Parial Dierenial Equaions! Gréar Tryggvason! Spring 011! Basic Properies o PDE!! Quasi-linear Firs Order Equaions! - Characerisics! - Linear and
hp://www.nd.edu/~gryggva/cfd-course/! Ouline! Theory o! Parial Dierenial Equaions! Gréar Tryggvason! Spring 011! Basic Properies o PDE!! Quasi-linear Firs Order Equaions! - Characerisics! - Linear and
Theory of! Partial Differential Equations-I!
 hp://users.wpi.edu/~grear/me61.hml! Ouline! Theory o! Parial Dierenial Equaions-I! Gréar Tryggvason! Spring 010! Basic Properies o PDE!! Quasi-linear Firs Order Equaions! - Characerisics! - Linear and
hp://users.wpi.edu/~grear/me61.hml! Ouline! Theory o! Parial Dierenial Equaions-I! Gréar Tryggvason! Spring 010! Basic Properies o PDE!! Quasi-linear Firs Order Equaions! - Characerisics! - Linear and
Some Ramsey results for the n-cube
 Some Ramsey resuls for he n-cube Ron Graham Universiy of California, San Diego Jozsef Solymosi Universiy of Briish Columbia, Vancouver, Canada Absrac In his noe we esablish a Ramsey-ype resul for cerain
Some Ramsey resuls for he n-cube Ron Graham Universiy of California, San Diego Jozsef Solymosi Universiy of Briish Columbia, Vancouver, Canada Absrac In his noe we esablish a Ramsey-ype resul for cerain
Chapter 8 The Complete Response of RL and RC Circuits
 Chaper 8 he Complee Response of R and RC Ciruis Exerises Ex 8.3-1 Before he swih loses: Afer he swih loses: 2 = = 8 Ω so = 8 0.05 = 0.4 s. 0.25 herefore R ( ) Finally, 2.5 ( ) = o + ( (0) o ) = 2 + V for
Chaper 8 he Complee Response of R and RC Ciruis Exerises Ex 8.3-1 Before he swih loses: Afer he swih loses: 2 = = 8 Ω so = 8 0.05 = 0.4 s. 0.25 herefore R ( ) Finally, 2.5 ( ) = o + ( (0) o ) = 2 + V for
( ) ( ) if t = t. It must satisfy the identity. So, bulkiness of the unit impulse (hyper)function is equal to 1. The defining characteristic is
 UNIT IMPULSE RESPONSE, UNIT STEP RESPONSE, STABILITY. Uni impulse funcion (Dirac dela funcion, dela funcion) rigorously defined is no sricly a funcion, bu disribuion (or measure), precise reamen requires
UNIT IMPULSE RESPONSE, UNIT STEP RESPONSE, STABILITY. Uni impulse funcion (Dirac dela funcion, dela funcion) rigorously defined is no sricly a funcion, bu disribuion (or measure), precise reamen requires
Guest Lectures for Dr. MacFarlane s EE3350 Part Deux
 Gues Lecures for Dr. MacFarlane s EE3350 Par Deux Michael Plane Mon., 08-30-2010 Wrie name in corner. Poin ou his is a review, so I will go faser. Remind hem o go lisen o online lecure abou geing an A
Gues Lecures for Dr. MacFarlane s EE3350 Par Deux Michael Plane Mon., 08-30-2010 Wrie name in corner. Poin ou his is a review, so I will go faser. Remind hem o go lisen o online lecure abou geing an A
A New Perturbative Approach in Nonlinear Singularity Analysis
 Journal of Mahemaics and Saisics 7 (: 49-54, ISSN 549-644 Science Publicaions A New Perurbaive Approach in Nonlinear Singulariy Analysis Ta-Leung Yee Deparmen of Mahemaics and Informaion Technology, The
Journal of Mahemaics and Saisics 7 (: 49-54, ISSN 549-644 Science Publicaions A New Perurbaive Approach in Nonlinear Singulariy Analysis Ta-Leung Yee Deparmen of Mahemaics and Informaion Technology, The
Second-Order Boundary Value Problems of Singular Type
 JOURNAL OF MATEMATICAL ANALYSIS AND APPLICATIONS 226, 4443 998 ARTICLE NO. AY98688 Seond-Order Boundary Value Probles of Singular Type Ravi P. Agarwal Deparen of Maheais, Naional Uniersiy of Singapore,
JOURNAL OF MATEMATICAL ANALYSIS AND APPLICATIONS 226, 4443 998 ARTICLE NO. AY98688 Seond-Order Boundary Value Probles of Singular Type Ravi P. Agarwal Deparen of Maheais, Naional Uniersiy of Singapore,
Problem Set #1. i z. the complex propagation constant. For the characteristic impedance:
 Problem Se # Problem : a) Using phasor noaion, calculae he volage and curren waves on a ransmission line by solving he wave equaion Assume ha R, L,, G are all non-zero and independen of frequency From
Problem Se # Problem : a) Using phasor noaion, calculae he volage and curren waves on a ransmission line by solving he wave equaion Assume ha R, L,, G are all non-zero and independen of frequency From
Hamilton- J acobi Equation: Explicit Formulas In this lecture we try to apply the method of characteristics to the Hamilton-Jacobi equation: u t
 M ah 5 2 7 Fall 2 0 0 9 L ecure 1 0 O c. 7, 2 0 0 9 Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Explici Formulas In his lecure we ry o apply he mehod of characerisics o he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: u + H D u, x = 0 in R n
M ah 5 2 7 Fall 2 0 0 9 L ecure 1 0 O c. 7, 2 0 0 9 Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Explici Formulas In his lecure we ry o apply he mehod of characerisics o he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: u + H D u, x = 0 in R n
New effective moduli of isotropic viscoelastic composites. Part I. Theoretical justification
 IOP Conference Series: Maerials Science and Engineering PAPE OPEN ACCESS New effecive moduli of isoropic viscoelasic composies. Par I. Theoreical jusificaion To cie his aricle: A A Sveashkov and A A akurov
IOP Conference Series: Maerials Science and Engineering PAPE OPEN ACCESS New effecive moduli of isoropic viscoelasic composies. Par I. Theoreical jusificaion To cie his aricle: A A Sveashkov and A A akurov
BEng (Hons) Telecommunications. Examinations for / Semester 2
 BEng (Hons) Telecommunicaions Cohor: BTEL/14/FT Examinaions for 2015-2016 / Semeser 2 MODULE: ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY MODULE CODE: ASE2103 Duraion: 2 ½ Hours Insrucions o Candidaes: 1. Answer ALL 4 (FOUR)
BEng (Hons) Telecommunicaions Cohor: BTEL/14/FT Examinaions for 2015-2016 / Semeser 2 MODULE: ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY MODULE CODE: ASE2103 Duraion: 2 ½ Hours Insrucions o Candidaes: 1. Answer ALL 4 (FOUR)
8. Basic RL and RC Circuits
 8. Basic L and C Circuis This chaper deals wih he soluions of he responses of L and C circuis The analysis of C and L circuis leads o a linear differenial equaion This chaper covers he following opics
8. Basic L and C Circuis This chaper deals wih he soluions of he responses of L and C circuis The analysis of C and L circuis leads o a linear differenial equaion This chaper covers he following opics
Chapter 6. Systems of First Order Linear Differential Equations
 Chaper 6 Sysems of Firs Order Linear Differenial Equaions We will only discuss firs order sysems However higher order sysems may be made ino firs order sysems by a rick shown below We will have a sligh
Chaper 6 Sysems of Firs Order Linear Differenial Equaions We will only discuss firs order sysems However higher order sysems may be made ino firs order sysems by a rick shown below We will have a sligh
KEY. Math 334 Midterm III Winter 2008 section 002 Instructor: Scott Glasgow
 KEY Mah 334 Miderm III Winer 008 secion 00 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his exam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably engineering
KEY Mah 334 Miderm III Winer 008 secion 00 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his exam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably engineering
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 3 Signals & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #2 Wha are Coninuous-Time Signals??? Reading Assignmen: Secion. of Kamen and Heck /22 Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show concepual flow beween ideas.
EECE 3 Signals & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #2 Wha are Coninuous-Time Signals??? Reading Assignmen: Secion. of Kamen and Heck /22 Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show concepual flow beween ideas.
Distance Between Two Ellipses in 3D
 Disance Beween Two Ellipses in 3D David Eberly Magic Sofware 6006 Meadow Run Cour Chapel Hill, NC 27516 eberly@magic-sofware.com 1 Inroducion An ellipse in 3D is represened by a cener C, uni lengh axes
Disance Beween Two Ellipses in 3D David Eberly Magic Sofware 6006 Meadow Run Cour Chapel Hill, NC 27516 eberly@magic-sofware.com 1 Inroducion An ellipse in 3D is represened by a cener C, uni lengh axes
Solutions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Math 246, Spring 2011, Professor David Levermore
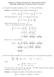 Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Lecture Outline. Introduction Transmission Line Equations Transmission Line Wave Equations 8/10/2018. EE 4347 Applied Electromagnetics.
 8/10/018 Course Insrucor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Office: A 337 Phone: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@uep.edu EE 4347 Applied Elecromagneics Topic 4a Transmission Line Equaions Transmission These Line noes
8/10/018 Course Insrucor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Office: A 337 Phone: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@uep.edu EE 4347 Applied Elecromagneics Topic 4a Transmission Line Equaions Transmission These Line noes
The Asymptotic Behavior of Nonoscillatory Solutions of Some Nonlinear Dynamic Equations on Time Scales
 Advances in Dynamical Sysems and Applicaions. ISSN 0973-5321 Volume 1 Number 1 (2006, pp. 103 112 c Research India Publicaions hp://www.ripublicaion.com/adsa.hm The Asympoic Behavior of Nonoscillaory Soluions
Advances in Dynamical Sysems and Applicaions. ISSN 0973-5321 Volume 1 Number 1 (2006, pp. 103 112 c Research India Publicaions hp://www.ripublicaion.com/adsa.hm The Asympoic Behavior of Nonoscillaory Soluions
PHYS-3301 Lecture 5. Chapter 2. Announcement. Sep. 12, Special Relativity. What about y and z coordinates? (x - direction of motion)
 Announemen Course webpage hp://www.phys.u.edu/~slee/33/ Tebook PHYS-33 Leure 5 HW (due 9/4) Chaper, 6, 36, 4, 45, 5, 5, 55, 58 Sep., 7 Chaper Speial Relaiiy. Basi Ideas. Consequenes of Einsein s Posulaes
Announemen Course webpage hp://www.phys.u.edu/~slee/33/ Tebook PHYS-33 Leure 5 HW (due 9/4) Chaper, 6, 36, 4, 45, 5, 5, 55, 58 Sep., 7 Chaper Speial Relaiiy. Basi Ideas. Consequenes of Einsein s Posulaes
Basic solution to Heat Diffusion In general, one-dimensional heat diffusion in a material is defined by the linear, parabolic PDE
 New Meio e yd 5 ydrology Program Quaniaie Meods in ydrology Basi soluion o ea iffusion In general one-dimensional ea diffusion in a maerial is defined by e linear paraboli PE or were we assume a is defined
New Meio e yd 5 ydrology Program Quaniaie Meods in ydrology Basi soluion o ea iffusion In general one-dimensional ea diffusion in a maerial is defined by e linear paraboli PE or were we assume a is defined
( ) = Q 0. ( ) R = R dq. ( t) = I t
 ircuis onceps The addiion of a simple capacior o a circui of resisors allows wo relaed phenomena o occur The observaion ha he ime-dependence of a complex waveform is alered by he circui is referred o as
ircuis onceps The addiion of a simple capacior o a circui of resisors allows wo relaed phenomena o occur The observaion ha he ime-dependence of a complex waveform is alered by he circui is referred o as
THE RECIPROCITY THEOREM APPLIED TO FIND THE BEST COUPLING INCIDENCE
 THE RECIPROCITY THEOREM APPLIED TO FIND THE BEST COUPLING INCIDENCE RECHERCHE DE LA DIRECTION D INCIDENCE DE PLUS FORT COUPLAGE A L AIDE DU THEOREME DE RECIPROCITE Jean-Pierre ADAM 1, Jean-Chrisophe JOLY
THE RECIPROCITY THEOREM APPLIED TO FIND THE BEST COUPLING INCIDENCE RECHERCHE DE LA DIRECTION D INCIDENCE DE PLUS FORT COUPLAGE A L AIDE DU THEOREME DE RECIPROCITE Jean-Pierre ADAM 1, Jean-Chrisophe JOLY
Matrix Versions of Some Refinements of the Arithmetic-Geometric Mean Inequality
 Marix Versions of Some Refinemens of he Arihmeic-Geomeric Mean Inequaliy Bao Qi Feng and Andrew Tonge Absrac. We esablish marix versions of refinemens due o Alzer ], Carwrigh and Field 4], and Mercer 5]
Marix Versions of Some Refinemens of he Arihmeic-Geomeric Mean Inequaliy Bao Qi Feng and Andrew Tonge Absrac. We esablish marix versions of refinemens due o Alzer ], Carwrigh and Field 4], and Mercer 5]
Hybrid probabilistic interval dynamic analysis of vehicle-bridge interaction system with uncertainties
 1 APCOM & SCM 11-14 h Deember, 13, Singapore Hybrid probabilisi inerval dynami analysis of vehile-bridge ineraion sysem wih unerainies Nengguang iu 1, * Wei Gao 1, Chongmin Song 1 and Nong Zhang 1 Shool
1 APCOM & SCM 11-14 h Deember, 13, Singapore Hybrid probabilisi inerval dynami analysis of vehile-bridge ineraion sysem wih unerainies Nengguang iu 1, * Wei Gao 1, Chongmin Song 1 and Nong Zhang 1 Shool
Problem 1 / 25 Problem 2 / 10 Problem 3 / 15 Problem 4 / 30 Problem 5 / 20 TOTAL / 100
 Deparmen of Applied Eonomis Johns Hopkins Universiy Eonomis 60 Maroeonomi Theory and Poliy Miderm Exam Suggesed Soluions Professor Sanjay Chugh Summer 0 NAME: The Exam has a oal of five (5) problems and
Deparmen of Applied Eonomis Johns Hopkins Universiy Eonomis 60 Maroeonomi Theory and Poliy Miderm Exam Suggesed Soluions Professor Sanjay Chugh Summer 0 NAME: The Exam has a oal of five (5) problems and
