HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS MATH 1910 Sections 5.1, 5.2 Fall 2016
|
|
|
- Karen Cameron
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HOMEWORK SOLUTIOS MATH 9 Sections.,. Fall 6 Problem.. An ostrich runs with velocit km/h for minutes min), km/h for min, and km/h for another minute. Compute the total distance traveled and indicate with a graph how this quantit can be interpreted as an area. SOLUTIO. The total distance traveled b the ostrich is ) ) + 6 ) ) + 6 ) ) = = 9 km This distance is the area under the graph below which shows the ostrich s velocit as a function of time. Problem.. Compute R and L over [, ] using the following values: f) SOLUTIO. We have = =.. Hence we have L = ) =.) = 6 and R = ) =.) =...
2 Problem.. Use linearit and formulas )-) to rewrite and evaluate the sum m= + m ) SOLUTIO. m= + m ) = m= = + m + 9 m ) m= + = + m= m + 9 m m= + ) ) 6 = 7... Problem..86 Prove that for an function f on [a, b], R L = b a fb) fa)). SOLUTIO. Let = b a)/ and partition the interval [a, b] into equal-length subintervals with endpoints a = < < < < = b. We have L = f k ) and R = k= R L = = k= f k ), so k= ) f k ) f k ) f ) + k= f k ) f ) + k= = f ) f )) = b a k= f k ) )) fb) fa))...86
3 Problem..88 Use [the previous problem] to show that if f is positive and monotonic, then the area A under its graph over [a, b] satisfies R A b a fb) fa). SOLUTIO. Suppose f is positive and increasing. Then R is an over-approimation of the area under the graph of f, and L is an under-approimation. That is, we have L A R. Subtracting R from all three parts of that inequalit ields and negating all three parts gives From the previous problem we have L R A R, R A R L. R A b a and taking absolute values gives the desired result. fb) fa)), R A b a fb) fa)) Since R A and fb) fa) are positive, the are equal to their own absolute values.) The case in which f is decreasing is similar...88
4 SECTIO. The Definite Integral Problem..7.. Draw a graph of the signed area represented b the integral and compute it using geometr: 7. d d. solution The region bounded b the graph of = and the -ais over the interval [, ] is one-quarter of a circle of radius. Hence, SOLUTIO. The region below = over [, ] is a quarter of the circle of radius centered at the origin: d = π) = π SECTIO.. The Definite Integral The region bounded b the graph of = 8andthe-ais over the interval [, ] consists of a triangle below the ais with base and height and a triangle above the ais with base and height 8. Hence, 8)d = )) + 8. d Hence d = π) = π...7 solution The region bounded b the graph of = and the -ais over the interval [, ] consists of two right triangles, both above the ais. One triangle has area )) =, and the other has area )) = 9. Hence, InProblem Eercises.. and, refer to Figure. Let f) figure shown in the figure below. d = 9 + =. = f) )8) = )d FIGURE The two parts of the graph are semicircles. 6 Compute a) f) d b) f) d solution The region bounded b the graph 6 of = and the -ais over the interval [, ] is a. triangle Evaluate: above the a) ais f)d with base and b) height f)d. Consequentl, SOLUTIO. a) The region between the graph of f and -ais consists of a quarter of a circle of solution radius and Letaf)be quartergiven b Figure. )d = )) =. a) The definite integral of a circle of radius. Remembering that the definite integral computes signed area, we have f)dis the signed area of a semicircle of radius which lies below the -ais. Therefore, f) d = π) π) = π. f ) d = π ) = π b) For this integral, we compute the unsigned area between the. graph of f and the -ais, which consists of a quarter circle b) The definite integral or radius and a semicircles of radius. 6 f)dis the signed area of a semicircle of radius which lies below the -ais 6 and a semicircle of radius which lies f) above d = the -ais. Therefore, π) + π) = 9 π )d 6 f ) d = π ) π ) = π. solution The region bounded b the graph of = + and the -ais over the interval [, ] consists of a triangle below the ais with base and height, a triangle above the ais of base and height 6. and a Evaluate: triangle below a) the f)d ais of base b) and height f ). d Consequentl, solution Let f)be given b Figure.
5 Problem.. Determine the sign of the integral without calculating it. Draw a graph if necessar. d SOLUTIO. B smmetr, the positive area from the interval [, ] is cancelled b the negative area from [, ]. With the interval [, ] contributing more negative area, the definite integral must be negative... Problem..7 Calculate the integral: d. SOLUTIO. Since is negative on [, ] and positive on [, ], we have { ), =. Hence d = = ) d + [ ] = + ) d [ ] = =...7 Problem..78 Prove that.77 π/ cos d.6. SOLUTIO. cos is decreasing on the interval [, π/]. Hence, for π/, Since cosπ/) = /, Since cos).9,.77 π 8 π/ cos d cosπ/) cos cos). π/ = d π/ π/ cos d..9 d = π.9).6. 8 Therefore,.77 π cos
6 Problem..8 State whether true or false. If false, sketch the graph of a countereample. a) If f) >, then b f) d >. a b) If b f) d >, then f) >. a SOLUTIO. a) This is true in the case that b > a. If a > b, then b a f) d = a f) d and the integral b is negative. b) It is false that if b f) d >, then f) > for [a, b]. A countereample is f) = + a with a = and b =. We see that + )d = 7. >, et f ) = <. Here is the graph...8 6
6 = 1 2. The right endpoints of the subintervals are then 2 5, 3, 7 2, 4, 2 9, 5, while the left endpoints are 2, 5 2, 3, 7 2, 4, 9 2.
 5 THE ITEGRAL 5. Approimating and Computing Area Preliminar Questions. What are the right and left endpoints if [, 5] is divided into si subintervals? If the interval [, 5] is divided into si subintervals,
5 THE ITEGRAL 5. Approimating and Computing Area Preliminar Questions. What are the right and left endpoints if [, 5] is divided into si subintervals? If the interval [, 5] is divided into si subintervals,
Section 1.4 Circles. Objective #1: Writing the Equation of a Circle in Standard Form.
 1 Section 1. Circles Objective #1: Writing the Equation of a Circle in Standard Form. We begin by giving a definition of a circle: Definition: A Circle is the set of all points that are equidistant from
1 Section 1. Circles Objective #1: Writing the Equation of a Circle in Standard Form. We begin by giving a definition of a circle: Definition: A Circle is the set of all points that are equidistant from
A11.1 Areas under curves
 Applications 11.1 Areas under curves A11.1 Areas under curves Before ou start You should be able to: calculate the value of given the value of in algebraic equations of curves calculate the area of a trapezium.
Applications 11.1 Areas under curves A11.1 Areas under curves Before ou start You should be able to: calculate the value of given the value of in algebraic equations of curves calculate the area of a trapezium.
Review Exercises for Chapter 3. Review Exercises for Chapter r v 0 2. v ft sec. x 1 2 x dx f x x 99.4.
 Review Eercises for Chapter 6. r v 0 sin. Let f, 00, d 0.6. v 0 00 ftsec changes from 0 to dr 00 cos d 6 0 d 0 r dr 80 00 6 96 feet 80 cos 0 96 feet 8080 f f fd d f 99. 00 0.6 9.97 00 Using a calculator:
Review Eercises for Chapter 6. r v 0 sin. Let f, 00, d 0.6. v 0 00 ftsec changes from 0 to dr 00 cos d 6 0 d 0 r dr 80 00 6 96 feet 80 cos 0 96 feet 8080 f f fd d f 99. 00 0.6 9.97 00 Using a calculator:
Review Sheet for Exam 1 SOLUTIONS
 Math b Review Sheet for Eam SOLUTIONS The first Math b midterm will be Tuesday, February 8th, 7 9 p.m. Location: Schwartz Auditorium Room ) The eam will cover: Section 3.6: Inverse Trig Appendi F: Sigma
Math b Review Sheet for Eam SOLUTIONS The first Math b midterm will be Tuesday, February 8th, 7 9 p.m. Location: Schwartz Auditorium Room ) The eam will cover: Section 3.6: Inverse Trig Appendi F: Sigma
Name Period. Date: Topic: 9-2 Circles. Standard: G-GPE.1. Objective:
 Name Period Date: Topic: 9-2 Circles Essential Question: If the coefficients of the x 2 and y 2 terms in the equation for a circle were different, how would that change the shape of the graph of the equation?
Name Period Date: Topic: 9-2 Circles Essential Question: If the coefficients of the x 2 and y 2 terms in the equation for a circle were different, how would that change the shape of the graph of the equation?
AP Calculus BC : The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 AP Calculus BC 415 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Tuesday, November 5, 008 Homework Answers 6. (a) approimately 0.5 (b) approimately 1 (c) approimately 1.75 38. 4 40. 5 50. 17 Introduction In
AP Calculus BC 415 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Tuesday, November 5, 008 Homework Answers 6. (a) approimately 0.5 (b) approimately 1 (c) approimately 1.75 38. 4 40. 5 50. 17 Introduction In
UNCORRECTED. To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: y = x 1 y 2 = x
 5A galler of graphs Objectives To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: = = = (rectangular hperbola) + = (circle). To be able to sketch the graphs of these relations. To be able
5A galler of graphs Objectives To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: = = = (rectangular hperbola) + = (circle). To be able to sketch the graphs of these relations. To be able
10.4 Nonlinear Inequalities and Systems of Inequalities. OBJECTIVES 1 Graph a Nonlinear Inequality. 2 Graph a System of Nonlinear Inequalities.
 Section 0. Nonlinear Inequalities and Sstems of Inequalities 6 CONCEPT EXTENSIONS For the eercises below, see the Concept Check in this section.. Without graphing, how can ou tell that the graph of + =
Section 0. Nonlinear Inequalities and Sstems of Inequalities 6 CONCEPT EXTENSIONS For the eercises below, see the Concept Check in this section.. Without graphing, how can ou tell that the graph of + =
Math 030 Review for Final Exam Revised Fall 2010 RH/ DM 1
 Math 00 Review for Final Eam Revised Fall 010 RH/ DM 1 1. Solve the equations: (-1) (7) (-) (-1) () 1 1 1 1 f. 1 g. h. 1 11 i. 9. Solve the following equations for the given variable: 1 Solve for. D ab
Math 00 Review for Final Eam Revised Fall 010 RH/ DM 1 1. Solve the equations: (-1) (7) (-) (-1) () 1 1 1 1 f. 1 g. h. 1 11 i. 9. Solve the following equations for the given variable: 1 Solve for. D ab
Math 53 Spring 2018 Practice Midterm 2
 Math 53 Spring 218 Practice Midterm 2 Nikhil Srivastava 8 minutes, closed book, closed notes 1. alculate 1 y 2 (x 2 + y 2 ) 218 dxdy Solution. Since the type 2 region D = { y 1, x 1 y 2 } is a quarter
Math 53 Spring 218 Practice Midterm 2 Nikhil Srivastava 8 minutes, closed book, closed notes 1. alculate 1 y 2 (x 2 + y 2 ) 218 dxdy Solution. Since the type 2 region D = { y 1, x 1 y 2 } is a quarter
Math 107. Rumbos Fall Solutions to Review Problems for Exam 3
 Math 17. umbos Fall 29 1 Solutions to eview Problems for Eam 3 1. Consider a wheel of radius a which is rolling on the ais in the plane. Suppose that the center of the wheel moves in the positive direction
Math 17. umbos Fall 29 1 Solutions to eview Problems for Eam 3 1. Consider a wheel of radius a which is rolling on the ais in the plane. Suppose that the center of the wheel moves in the positive direction
6.6 General Form of the Equation for a Linear Relation
 6.6 General Form of the Equation for a Linear Relation FOCUS Relate the graph of a line to its equation in general form. We can write an equation in different forms. y 0 6 5 y 10 = 0 An equation for this
6.6 General Form of the Equation for a Linear Relation FOCUS Relate the graph of a line to its equation in general form. We can write an equation in different forms. y 0 6 5 y 10 = 0 An equation for this
FINAL EXAM REVIEW Math 200 Spring 2007
 FINL EXM REVIEW Math 00 Spring 007 The final eam will be on Monda, Ma 14 from 7:00-9:00 in room. The eam will cover all material covered in class this semester, all of chapters 1,, 3, and 7. ll of the
FINL EXM REVIEW Math 00 Spring 007 The final eam will be on Monda, Ma 14 from 7:00-9:00 in room. The eam will cover all material covered in class this semester, all of chapters 1,, 3, and 7. ll of the
Sections 5.1: Areas and Distances
 Sections.: Areas and Distances In this section we shall consider problems closely related to the problems we considered at the beginning of the semester (the tangent and velocity problems). Specifically,
Sections.: Areas and Distances In this section we shall consider problems closely related to the problems we considered at the beginning of the semester (the tangent and velocity problems). Specifically,
Integration. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 4 Integration Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 4.3 Riemann Sums and Definite Integrals Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Objectives Understand the definition of a Riemann
4 Integration Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 4.3 Riemann Sums and Definite Integrals Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Objectives Understand the definition of a Riemann
4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations
 The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem Graphs of Equations in Two Variables -intercepts and -intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the Pthagorean
The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem Graphs of Equations in Two Variables -intercepts and -intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the Pthagorean
The standard form of the equation of a circle is based on the distance formula. The distance formula, in turn, is based on the Pythagorean Theorem.
 Unit, Lesson. Deriving the Equation of a Circle The graph of an equation in and is the set of all points (, ) in a coordinate plane that satisf the equation. Some equations have graphs with precise geometric
Unit, Lesson. Deriving the Equation of a Circle The graph of an equation in and is the set of all points (, ) in a coordinate plane that satisf the equation. Some equations have graphs with precise geometric
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE. Functions & Graphs
 STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
Math 2300 Calculus II University of Colorado
 Math 3 Calculus II University of Colorado Spring Final eam review problems: ANSWER KEY. Find f (, ) for f(, y) = esin( y) ( + y ) 3/.. Consider the solid region W situated above the region apple apple,
Math 3 Calculus II University of Colorado Spring Final eam review problems: ANSWER KEY. Find f (, ) for f(, y) = esin( y) ( + y ) 3/.. Consider the solid region W situated above the region apple apple,
Math 0200 Final Exam Review Questions
 Math 000 Final Eam Review Questions 1. Simplif: 4 8i + 8 ( 7). Simplif: 11 ( 9) + 6(10 4) + 4. Simplif ( 5 + 7) ( ) 8 6 4. Simplif: (4 ) 9 i 5. Simplif: 4 7 6. Evaluate 4 + 5 when = and = Write each of
Math 000 Final Eam Review Questions 1. Simplif: 4 8i + 8 ( 7). Simplif: 11 ( 9) + 6(10 4) + 4. Simplif ( 5 + 7) ( ) 8 6 4. Simplif: (4 ) 9 i 5. Simplif: 4 7 6. Evaluate 4 + 5 when = and = Write each of
Vocabulary. The Pythagorean Identity. Lesson 4-3. Pythagorean Identity Theorem. Mental Math
 Lesson 4-3 Basic Basic Trigonometric Identities Identities Vocabular identit BIG IDEA If ou know cos, ou can easil fi nd cos( ), cos(90º - ), cos(180º - ), and cos(180º + ) without a calculator, and similarl
Lesson 4-3 Basic Basic Trigonometric Identities Identities Vocabular identit BIG IDEA If ou know cos, ou can easil fi nd cos( ), cos(90º - ), cos(180º - ), and cos(180º + ) without a calculator, and similarl
CALCULUS EXPLORATION OF THE SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS. Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (Chain Rule Version): f t dt
 CALCULUS EXPLORATION OF THE SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS d d d d t dt 6 cos t dt Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: d f tdt d a d d 4 t dt d d a f t dt d d 6 cos t dt Second Fundamental
CALCULUS EXPLORATION OF THE SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS d d d d t dt 6 cos t dt Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: d f tdt d a d d 4 t dt d d a f t dt d d 6 cos t dt Second Fundamental
17. f(x) = x 2 + 5x f(x) = x 2 + x f(x) = x 2 + 3x f(x) = x 2 + 3x f(x) = x 2 16x f(x) = x 2 + 4x 96
 Section.3 Zeros of the Quadratic 473.3 Eercises In Eercises 1-8, factor the given quadratic polnomial. 1. 2 + 9 + 14 2. 2 + 6 + 3. 2 + + 9 4. 2 + 4 21. 2 4 6. 2 + 7 8 7. 2 7 + 12 8. 2 + 24 In Eercises
Section.3 Zeros of the Quadratic 473.3 Eercises In Eercises 1-8, factor the given quadratic polnomial. 1. 2 + 9 + 14 2. 2 + 6 + 3. 2 + + 9 4. 2 + 4 21. 2 4 6. 2 + 7 8 7. 2 7 + 12 8. 2 + 24 In Eercises
MATH 60 Review Problems for Final Exam
 MATH 60 Review Problems for Final Eam Scientific Calculators Onl - Graphing Calculators Not Allowed NO CLASS NOTES PERMITTED Evaluate the epression for the given values. m 1) m + 3 for m = 3 2) m 2 - n2
MATH 60 Review Problems for Final Eam Scientific Calculators Onl - Graphing Calculators Not Allowed NO CLASS NOTES PERMITTED Evaluate the epression for the given values. m 1) m + 3 for m = 3 2) m 2 - n2
MATH 115: Final Exam Review. Can you find the distance between two points and the midpoint of a line segment? (1.1)
 MATH : Final Eam Review Can ou find the distance between two points and the midpoint of a line segment? (.) () Consider the points A (,) and ( 6, ) B. (a) Find the distance between A and B. (b) Find the
MATH : Final Eam Review Can ou find the distance between two points and the midpoint of a line segment? (.) () Consider the points A (,) and ( 6, ) B. (a) Find the distance between A and B. (b) Find the
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 07 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 07 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
MA 114 Worksheet #01: Integration by parts
 Fall 8 MA 4 Worksheet Thursday, 3 August 8 MA 4 Worksheet #: Integration by parts. For each of the following integrals, determine if it is best evaluated by integration by parts or by substitution. If
Fall 8 MA 4 Worksheet Thursday, 3 August 8 MA 4 Worksheet #: Integration by parts. For each of the following integrals, determine if it is best evaluated by integration by parts or by substitution. If
A constant is a value that is always the same. (This means that the value is constant / unchanging). o
 Math 8 Unit 7 Algebra and Graphing Relations Solving Equations Using Models We will be using algebra tiles to help us solve equations. We will practice showing work appropriately symbolically and pictorially
Math 8 Unit 7 Algebra and Graphing Relations Solving Equations Using Models We will be using algebra tiles to help us solve equations. We will practice showing work appropriately symbolically and pictorially
1998 AP Calculus AB: Section I, Part A
 55 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number.. What is the -coordinate of the point
55 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number.. What is the -coordinate of the point
Lesson 9.1 Using the Distance Formula
 Lesson. Using the Distance Formula. Find the eact distance between each pair of points. a. (0, 0) and (, ) b. (0, 0) and (7, ) c. (, 8) and (, ) d. (, ) and (, 7) e. (, 7) and (8, ) f. (8, ) and (, 0)
Lesson. Using the Distance Formula. Find the eact distance between each pair of points. a. (0, 0) and (, ) b. (0, 0) and (7, ) c. (, 8) and (, ) d. (, ) and (, 7) e. (, 7) and (8, ) f. (8, ) and (, 0)
10.2 The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine
 0. The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine 77 0. The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine In Section 0.., we introduced circular motion and derived a formula which describes the linear velocit of an object moving on
0. The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine 77 0. The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine In Section 0.., we introduced circular motion and derived a formula which describes the linear velocit of an object moving on
Chapter 18 Quadratic Function 2
 Chapter 18 Quadratic Function Completed Square Form 1 Consider this special set of numbers - the square numbers or the set of perfect squares. 4 = = 9 = 3 = 16 = 4 = 5 = 5 = Numbers like 5, 11, 15 are
Chapter 18 Quadratic Function Completed Square Form 1 Consider this special set of numbers - the square numbers or the set of perfect squares. 4 = = 9 = 3 = 16 = 4 = 5 = 5 = Numbers like 5, 11, 15 are
Appendices ( ) ( ) Appendix A: Equations and Inequalities 13. ( ) 1. Solve the equation 2x+ 7 = x + 8= x + 15.
 Appendices Appendi A: Equations and Inequalities. Solve the equation + = + = + = + = + = = 8 Moreover, replacing with 8 in + = yields a true statement. Therefore, the given statement is true.. The equations
Appendices Appendi A: Equations and Inequalities. Solve the equation + = + = + = + = + = = 8 Moreover, replacing with 8 in + = yields a true statement. Therefore, the given statement is true.. The equations
APPENDIX D Rotation and the General Second-Degree Equation
 APPENDIX D Rotation and the General Second-Degree Equation Rotation of Aes Invariants Under Rotation After rotation of the - and -aes counterclockwise through an angle, the rotated aes are denoted as the
APPENDIX D Rotation and the General Second-Degree Equation Rotation of Aes Invariants Under Rotation After rotation of the - and -aes counterclockwise through an angle, the rotated aes are denoted as the
SAMPLE. A Gallery of Graphs. To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relationships: y = x 1,
 Objectives C H A P T E R 5 A Galler of Graphs To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relationships: =, =, = / and + =. To be able to sketch the graphs and simple transformations of these
Objectives C H A P T E R 5 A Galler of Graphs To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relationships: =, =, = / and + =. To be able to sketch the graphs and simple transformations of these
y=5 y=1+x 2 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions
 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
P.4 Lines in the Plane
 28 CHAPTER P Prerequisites P.4 Lines in the Plane What ou ll learn about Slope of a Line Point-Slope Form Equation of a Line Slope-Intercept Form Equation of a Line Graphing Linear Equations in Two Variables
28 CHAPTER P Prerequisites P.4 Lines in the Plane What ou ll learn about Slope of a Line Point-Slope Form Equation of a Line Slope-Intercept Form Equation of a Line Graphing Linear Equations in Two Variables
review math0410 (1-174) and math 0320 ( ) aafinm mg
 Eam Name review math04 (1-174) and math 0320 (17-243) 03201700aafinm0424300 mg MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplif. 1) 7 2-3 A)
Eam Name review math04 (1-174) and math 0320 (17-243) 03201700aafinm0424300 mg MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplif. 1) 7 2-3 A)
Math 101 Chapter Four Practice Exam Questions SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Math 101 Chapter Four Practice Eam Questions SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. What is the domain of f()? What is its range? 1) f() = 1-1
Math 101 Chapter Four Practice Eam Questions SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. What is the domain of f()? What is its range? 1) f() = 1-1
Learning Goals. College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 101: College Algebra Final Exam Review Problems 1
 College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 0: College Algebra Final Eam Review Problems Learning Goals (AL-) Arithmetic of Real and Comple Numbers: I can classif numbers as natural, integer,
College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 0: College Algebra Final Eam Review Problems Learning Goals (AL-) Arithmetic of Real and Comple Numbers: I can classif numbers as natural, integer,
Math 101 chapter six practice exam MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Math 1 chapter si practice eam MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Which equation matches the given calculator-generated graph and description?
Math 1 chapter si practice eam MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Which equation matches the given calculator-generated graph and description?
cos 5x dx e dt dx 20. CALCULUS AB WORKSHEET ON SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM AND REVIEW Work the following on notebook paper. No calculator.
 WORKSHEET ON SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM AND REVIEW Work the following on notebook paper. No calculator. Find the derivative. Do not leave negative eponents or comple fractions in our answers. 4. 8 4 f
WORKSHEET ON SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM AND REVIEW Work the following on notebook paper. No calculator. Find the derivative. Do not leave negative eponents or comple fractions in our answers. 4. 8 4 f
Diagnostic Tests. (c) (sa sb )(sa sb ) Diagnostic Test: Algebra
 Diagnostic Tests Success in calculus depends to a large etent on knowledge of the mathematics that precedes calculus: algebra, analtic geometr, functions, and trigonometr. The following tests are intended
Diagnostic Tests Success in calculus depends to a large etent on knowledge of the mathematics that precedes calculus: algebra, analtic geometr, functions, and trigonometr. The following tests are intended
Solutions to the Exercises of Chapter 5
 Solutions to the Eercises of Chapter 5 5A. Lines and Their Equations. The slope is 5 5. Since (, is a point on the line, y ( ( is an ( 6 8 8 equation of the line in point-slope form. This simplifies to
Solutions to the Eercises of Chapter 5 5A. Lines and Their Equations. The slope is 5 5. Since (, is a point on the line, y ( ( is an ( 6 8 8 equation of the line in point-slope form. This simplifies to
Math098 Practice Final Test
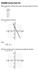 Math098 Practice Final Test Find an equation of the line that contains the points listed in the table. 1) 0-6 1-2 -4 3-3 4-2 Find an equation of the line. 2) 10-10 - 10 - -10 Solve. 3) 2 = 3 + 4 Find the
Math098 Practice Final Test Find an equation of the line that contains the points listed in the table. 1) 0-6 1-2 -4 3-3 4-2 Find an equation of the line. 2) 10-10 - 10 - -10 Solve. 3) 2 = 3 + 4 Find the
1998 AP Calculus AB: Section I, Part A
 998 AP Calculus AB: 55 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number.. What is the -coordinate
998 AP Calculus AB: 55 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number.. What is the -coordinate
Math 19, Homework-1 Solutions
 SSEA Summer 207 Math 9, Homework- Solutions. Consider the graph of function f shown below. Find the following its or eplain why they do not eist: (a) t 2 f(t). = 0. (b) t f(t). =. (c) t 0 f(t). (d) Does
SSEA Summer 207 Math 9, Homework- Solutions. Consider the graph of function f shown below. Find the following its or eplain why they do not eist: (a) t 2 f(t). = 0. (b) t f(t). =. (c) t 0 f(t). (d) Does
Geometry/Trig Name: Date: Lesson 1-11 Writing the Equation of a Perpendicular Bisector
 Name: Date: Lesson 1-11 Writing the Equation of a Perpendicular Bisector Learning Goals: #14: How do I write the equation of a perpendicular bisector? Warm-up What is the equation of a line that passes
Name: Date: Lesson 1-11 Writing the Equation of a Perpendicular Bisector Learning Goals: #14: How do I write the equation of a perpendicular bisector? Warm-up What is the equation of a line that passes
The Coordinate Plane. Circles and Polygons on the Coordinate Plane. LESSON 13.1 Skills Practice. Problem Set
 LESSON.1 Skills Practice Name Date The Coordinate Plane Circles and Polgons on the Coordinate Plane Problem Set Use the given information to show that each statement is true. Justif our answers b using
LESSON.1 Skills Practice Name Date The Coordinate Plane Circles and Polgons on the Coordinate Plane Problem Set Use the given information to show that each statement is true. Justif our answers b using
Lesson 8.2 Exercises, pages
 Lesson 8. Eercises, pages 38 A Students should verif the solutions to all equations.. Which values of are not roots of each equation? a) ƒ - 3 ƒ = 7 = 5 or =- Use mental math. 5: L.S. 7 R.S. 7 : L.S. 7
Lesson 8. Eercises, pages 38 A Students should verif the solutions to all equations.. Which values of are not roots of each equation? a) ƒ - 3 ƒ = 7 = 5 or =- Use mental math. 5: L.S. 7 R.S. 7 : L.S. 7
2 variables. is the same value as the solution of. 1 variable. You can use similar reasoning to solve quadratic equations. Work with a partner.
 9. b Graphing Essential Question How can ou use a graph to solve a quadratic equation in one variable? Based on what ou learned about the -intercepts of a graph in Section., it follows that the -intercept
9. b Graphing Essential Question How can ou use a graph to solve a quadratic equation in one variable? Based on what ou learned about the -intercepts of a graph in Section., it follows that the -intercept
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 Fundamental Theorem of Calculus MATH 6 Calculus I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 208 Remarks The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (FTC) will make the evaluation of definite integrals
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus MATH 6 Calculus I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 208 Remarks The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (FTC) will make the evaluation of definite integrals
3.1-Quadratic Functions & Inequalities
 3.1-Quadratic Functions & Inequalities Quadratic Functions: Quadratic functions are polnomial functions of the form also be written in the form f ( ) a( h) k. f ( ) a b c. A quadratic function ma Verte
3.1-Quadratic Functions & Inequalities Quadratic Functions: Quadratic functions are polnomial functions of the form also be written in the form f ( ) a( h) k. f ( ) a b c. A quadratic function ma Verte
Name: Block: Unit 2 Inequalities
 Name: Block: Unit 2 Inequalities 2.1 Graphing and Writing Inequalities 2.2 Solving by Adding and Subtracting 2.3 Solving by Multiplying and Dividing 2.4 Solving Two Step and Multi Step Inequalities 2.5
Name: Block: Unit 2 Inequalities 2.1 Graphing and Writing Inequalities 2.2 Solving by Adding and Subtracting 2.3 Solving by Multiplying and Dividing 2.4 Solving Two Step and Multi Step Inequalities 2.5
Introducing Instantaneous Rate of Change
 Introducing Instantaneous Rate of Change The diagram shows a door with an automatic closer. At time t = 0 seconds someone pushes the door. It swings open, slows down, stops, starts closing, then closes
Introducing Instantaneous Rate of Change The diagram shows a door with an automatic closer. At time t = 0 seconds someone pushes the door. It swings open, slows down, stops, starts closing, then closes
8/6/2010 Assignment Previewer
 Week 12 Tuesday Homework (1329184) Question 1234567891011121314151617181920 webassign.net/ /control.pl 1/9 1. Question DetailsSCalcET6 5.1.AE.01. [708910] EXAMPLE 1 Use rectangles to estimate the area
Week 12 Tuesday Homework (1329184) Question 1234567891011121314151617181920 webassign.net/ /control.pl 1/9 1. Question DetailsSCalcET6 5.1.AE.01. [708910] EXAMPLE 1 Use rectangles to estimate the area
University of Waterloo Final Examination MATH 116 Calculus 1 for Engineering
 Last name (Print): First name (Print): UW Student ID Number: University of Waterloo Final Eamination MATH 116 Calculus 1 for Engineering Instructor: Matthew Douglas Johnston Section: 001 Date: Monday,
Last name (Print): First name (Print): UW Student ID Number: University of Waterloo Final Eamination MATH 116 Calculus 1 for Engineering Instructor: Matthew Douglas Johnston Section: 001 Date: Monday,
Math Worksheet 1 SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK! f(x) = (x a) 2 + b. = x 2 + 6x + ( 6 2 )2 ( 6 2 )2 + 7 = (x 2 + 6x + 9) = (x + 3) 2 2
 Names Date. Consider the function Math 0550 Worksheet SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK! f() = + 6 + 7 (a) Complete the square and write the function in the form f() = ( a) + b. f() = + 6 + 7 = + 6 + ( 6 ) ( 6 ) +
Names Date. Consider the function Math 0550 Worksheet SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK! f() = + 6 + 7 (a) Complete the square and write the function in the form f() = ( a) + b. f() = + 6 + 7 = + 6 + ( 6 ) ( 6 ) +
math FALL developmental mathematics sullivan 1e
 TSIpractice eam review 1 131 180 plus 34 TSI questions for elementar and intermediate algebra m0300004301 aaa Name www.alvarezmathhelp.com math0300004301 FALL 01 100 interactmath developmental mathematics
TSIpractice eam review 1 131 180 plus 34 TSI questions for elementar and intermediate algebra m0300004301 aaa Name www.alvarezmathhelp.com math0300004301 FALL 01 100 interactmath developmental mathematics
Albert Einstein High School Summer Task Cover Sheet
 Albert Einstein High School Summer Task Cover Sheet Algebra 2 Teacher(s): Kenneth Alford, Lori Scherr Honors Algebra 2 Teacher(s): Michael Long, Tim Miamoto, Cnthia Reese Teacher(s) Contact Information:
Albert Einstein High School Summer Task Cover Sheet Algebra 2 Teacher(s): Kenneth Alford, Lori Scherr Honors Algebra 2 Teacher(s): Michael Long, Tim Miamoto, Cnthia Reese Teacher(s) Contact Information:
MATHEMATICS 200 December 2014 Final Exam Solutions
 MATHEMATICS 2 December 214 Final Eam Solutions 1. Suppose that f,, z) is a function of three variables and let u 1 6 1, 1, 2 and v 1 3 1, 1, 1 and w 1 3 1, 1, 1. Suppose that at a point a, b, c), Find
MATHEMATICS 2 December 214 Final Eam Solutions 1. Suppose that f,, z) is a function of three variables and let u 1 6 1, 1, 2 and v 1 3 1, 1, 1 and w 1 3 1, 1, 1. Suppose that at a point a, b, c), Find
Math 0210 Common Final Review Questions (2 5 i)(2 5 i )
 Math 0 Common Final Review Questions In problems 1 6, perform the indicated operations and simplif if necessar. 1. ( 8)(4) ( )(9) 4 7 4 6( ). 18 6 8. ( i) ( 1 4 i ) 4. (8 i ). ( 9 i)( 7 i) 6. ( i)( i )
Math 0 Common Final Review Questions In problems 1 6, perform the indicated operations and simplif if necessar. 1. ( 8)(4) ( )(9) 4 7 4 6( ). 18 6 8. ( i) ( 1 4 i ) 4. (8 i ). ( 9 i)( 7 i) 6. ( i)( i )
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS. (c) (sa sb )(sa sb )
 DIAGNOSTIC TESTS Success in calculus depends to a large etent on knowledge of the mathematics that precedes calculus: algebra, analtic geometr, functions, and trigonometr. The following tests are intended
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS Success in calculus depends to a large etent on knowledge of the mathematics that precedes calculus: algebra, analtic geometr, functions, and trigonometr. The following tests are intended
MATH 150/GRACEY PRACTICE FINAL. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MATH 0/GRACEY PRACTICE FINAL Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Choose the graph that represents the given function without using
MATH 0/GRACEY PRACTICE FINAL Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Choose the graph that represents the given function without using
3.1 Graph Quadratic Functions
 3. Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMA3b, MMA3c Goal p Use intervals of increase and decrease to understand average rates of change of quadratic functions. Your
3. Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMA3b, MMA3c Goal p Use intervals of increase and decrease to understand average rates of change of quadratic functions. Your
Examples of the Accumulation Function (ANSWERS) dy dx. This new function now passes through (0,2). Make a sketch of your new shifted graph.
 Eamples of the Accumulation Function (ANSWERS) Eample. Find a function y=f() whose derivative is that f()=. dy d tan that satisfies the condition We can use the Fundamental Theorem to write a function
Eamples of the Accumulation Function (ANSWERS) Eample. Find a function y=f() whose derivative is that f()=. dy d tan that satisfies the condition We can use the Fundamental Theorem to write a function
9.1 Circles and Parabolas. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 9.1 Circles and Parabolas Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Recognize a conic as the intersection of a plane and a double-napped cone. Write equations of circles in
9.1 Circles and Parabolas Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Recognize a conic as the intersection of a plane and a double-napped cone. Write equations of circles in
M151B Practice Problems for Final Exam
 M5B Practice Problems for Final Eam Calculators will not be allowed on the eam. Unjustified answers will not receive credit. On the eam you will be given the following identities: n k = n(n + ) ; n k =
M5B Practice Problems for Final Eam Calculators will not be allowed on the eam. Unjustified answers will not receive credit. On the eam you will be given the following identities: n k = n(n + ) ; n k =
F (x) is an antiderivative of f(x) if F (x) = f(x). Lets find an antiderivative of f(x) = x. We know that d. Any ideas?
 Math 24 - Calculus for Management and Social Science Antiderivatives and the Indefinite Integral: Notes So far we have studied the slope of a curve at a point and its applications. This is one of the fundamental
Math 24 - Calculus for Management and Social Science Antiderivatives and the Indefinite Integral: Notes So far we have studied the slope of a curve at a point and its applications. This is one of the fundamental
Mathematics Extension 2
 Student Number ABBOTSLEIGH AUGUST 007 YEAR ASSESSMENT 4 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE TRIAL EXAMINATION Mathematics Etension General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes. Working time 3 hours. Write using blue
Student Number ABBOTSLEIGH AUGUST 007 YEAR ASSESSMENT 4 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE TRIAL EXAMINATION Mathematics Etension General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes. Working time 3 hours. Write using blue
Homework Assignments Math /02 Spring 2015
 Homework Assignments Math 1-01/0 Spring 015 Assignment 1 Due date : Frida, Januar Section 5.1, Page 159: #1-, 10, 11, 1; Section 5., Page 16: Find the slope and -intercept, and then plot the line in problems:
Homework Assignments Math 1-01/0 Spring 015 Assignment 1 Due date : Frida, Januar Section 5.1, Page 159: #1-, 10, 11, 1; Section 5., Page 16: Find the slope and -intercept, and then plot the line in problems:
Math 141 Review for Midterm
 Math 141 Review for Midterm There will be two parts to this test. Part 1 will have graph sketching, and no calculator is allowed. Part will have everthing else, and a calculator and/or graphing calculator
Math 141 Review for Midterm There will be two parts to this test. Part 1 will have graph sketching, and no calculator is allowed. Part will have everthing else, and a calculator and/or graphing calculator
Math Analysis Chapter 2 Notes: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Math Analysis Chapter Notes: Polynomial and Rational Functions Day 13: Section -1 Comple Numbers; Sections - Quadratic Functions -1: Comple Numbers After completing section -1 you should be able to do
Math Analysis Chapter Notes: Polynomial and Rational Functions Day 13: Section -1 Comple Numbers; Sections - Quadratic Functions -1: Comple Numbers After completing section -1 you should be able to do
Reteaching (continued)
 Quadratic Functions and Transformations If a, the graph is a stretch or compression of the parent function b a factor of 0 a 0. 0 0 0 0 0 a a 7 The graph is a vertical The graph is a vertical compression
Quadratic Functions and Transformations If a, the graph is a stretch or compression of the parent function b a factor of 0 a 0. 0 0 0 0 0 a a 7 The graph is a vertical The graph is a vertical compression
Evaluate nth Roots and Use Rational Exponents. p Evaluate nth roots and study rational exponents. VOCABULARY. Index of a radical
 . Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMA2a, MMA2b, MMAd Your Notes Evaluate nth Roots and Use Rational Eponents Goal VOCABULARY nth root of a p Evaluate nth roots and stud rational eponents. Inde of a radical
. Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMA2a, MMA2b, MMAd Your Notes Evaluate nth Roots and Use Rational Eponents Goal VOCABULARY nth root of a p Evaluate nth roots and stud rational eponents. Inde of a radical
Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
 Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Completing the Square Learning Objectives: 1. Use the square root propert to solve quadratic equations.. Solve quadratic equations b completing the square.
Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Completing the Square Learning Objectives: 1. Use the square root propert to solve quadratic equations.. Solve quadratic equations b completing the square.
4.4 AREAS, INTEGRALS AND ANTIDERIVATIVES
 1 4.4 AREAS, INTEGRALS AND ANTIDERIVATIVES This section explores properties of functions defined as areas and examines some of the connections among areas, integrals and antiderivatives. In order to focus
1 4.4 AREAS, INTEGRALS AND ANTIDERIVATIVES This section explores properties of functions defined as areas and examines some of the connections among areas, integrals and antiderivatives. In order to focus
y=5 y=1+x 2 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions
 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval................... 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem...... 0 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval................... 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem...... 0 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and
ANOTHER FIVE QUESTIONS:
 No peaking!!!!! See if you can do the following: f 5 tan 6 sin 7 cos 8 sin 9 cos 5 e e ln ln @ @ Epress sin Power Series Epansion: d as a Power Series: Estimate sin Estimate MACLAURIN SERIES ANOTHER FIVE
No peaking!!!!! See if you can do the following: f 5 tan 6 sin 7 cos 8 sin 9 cos 5 e e ln ln @ @ Epress sin Power Series Epansion: d as a Power Series: Estimate sin Estimate MACLAURIN SERIES ANOTHER FIVE
Math 323 Exam 2 - Practice Problem Solutions. 2. Given the vectors a = 1,2,0, b = 1,0,2, and c = 0,1,1, compute the following:
 Math 323 Eam 2 - Practice Problem Solutions 1. Given the vectors a = 2,, 1, b = 3, 2,4, and c = 1, 4,, compute the following: (a) A unit vector in the direction of c. u = c c = 1, 4, 1 4 =,, 1+16+ 17 17
Math 323 Eam 2 - Practice Problem Solutions 1. Given the vectors a = 2,, 1, b = 3, 2,4, and c = 1, 4,, compute the following: (a) A unit vector in the direction of c. u = c c = 1, 4, 1 4 =,, 1+16+ 17 17
Solve Quadratic Equations by Graphing
 0.3 Solve Quadratic Equations b Graphing Before You solved quadratic equations b factoring. Now You will solve quadratic equations b graphing. Wh? So ou can solve a problem about sports, as in Eample 6.
0.3 Solve Quadratic Equations b Graphing Before You solved quadratic equations b factoring. Now You will solve quadratic equations b graphing. Wh? So ou can solve a problem about sports, as in Eample 6.
Sample Problems For Grade 9 Mathematics. Grade. 1. If x 3
 Sample roblems For 9 Mathematics DIRECTIONS: This section provides sample mathematics problems for the 9 test forms. These problems are based on material included in the New York Cit curriculum for 8.
Sample roblems For 9 Mathematics DIRECTIONS: This section provides sample mathematics problems for the 9 test forms. These problems are based on material included in the New York Cit curriculum for 8.
Essential Question How can you solve a nonlinear system of equations?
 .5 Solving Nonlinear Sstems Essential Question Essential Question How can ou solve a nonlinear sstem of equations? Solving Nonlinear Sstems of Equations Work with a partner. Match each sstem with its graph.
.5 Solving Nonlinear Sstems Essential Question Essential Question How can ou solve a nonlinear sstem of equations? Solving Nonlinear Sstems of Equations Work with a partner. Match each sstem with its graph.
UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS
 12 Introduction to differential calculus 12.1 Kick off with CAS 12.2 Rates of change 12.3 Gradients of secants 12.4 The derivative function 12.5 Differentiation of polnomials b rule 12.6 Review 12.1 Kick
12 Introduction to differential calculus 12.1 Kick off with CAS 12.2 Rates of change 12.3 Gradients of secants 12.4 The derivative function 12.5 Differentiation of polnomials b rule 12.6 Review 12.1 Kick
Trigonometric Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 4 Trigonometric Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 4.1 Radian and Degree Measure Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Describe angles. Use radian
4 Trigonometric Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 4.1 Radian and Degree Measure Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Describe angles. Use radian
15.4 Equation of a Circle
 Name Class Date 1.4 Equation of a Circle Essential Question: How can ou write the equation of a circle if ou know its radius and the coordinates of its center? Eplore G.1.E Show the equation of a circle
Name Class Date 1.4 Equation of a Circle Essential Question: How can ou write the equation of a circle if ou know its radius and the coordinates of its center? Eplore G.1.E Show the equation of a circle
4.3. Riemann Sums. Riemann Sums. Riemann Sums and Definite Integrals. Objectives
 4.3 Riemann Sums and Definite Integrals Objectives Understand the definition of a Riemann sum. Evaluate a definite integral using limits & Riemann Sums. Evaluate a definite integral using geometric formulas
4.3 Riemann Sums and Definite Integrals Objectives Understand the definition of a Riemann sum. Evaluate a definite integral using limits & Riemann Sums. Evaluate a definite integral using geometric formulas
on Œ0; 1, p p p q q p C q.p C q/ pcq :
 388 C HAPTER 4 APPLICATIONS OF THE DERIVATIVE 0 0 30 4 4 4 0 (A) (B) FIGURE Cubic polnomials Let f./ D 3 3 C a C b C c. UsingEercise9,wehaveg./ D f 0./ D C a C b>0for all provided b> 4 a, in which case
388 C HAPTER 4 APPLICATIONS OF THE DERIVATIVE 0 0 30 4 4 4 0 (A) (B) FIGURE Cubic polnomials Let f./ D 3 3 C a C b C c. UsingEercise9,wehaveg./ D f 0./ D C a C b>0for all provided b> 4 a, in which case
CHAPTER 3 Polynomial Functions
 CHAPTER Polnomial Functions Section. Quadratic Functions and Models............. 7 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree......... 7 Section. Polnomial and Snthetic Division............ Section.
CHAPTER Polnomial Functions Section. Quadratic Functions and Models............. 7 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree......... 7 Section. Polnomial and Snthetic Division............ Section.
Test 2 Review Math 1111 College Algebra
 Test 2 Review Math 1111 College Algebra 1. Begin by graphing the standard quadratic function f(x) = x 2. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. g(x) = x 2 + 2 *a. b. c. d.
Test 2 Review Math 1111 College Algebra 1. Begin by graphing the standard quadratic function f(x) = x 2. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. g(x) = x 2 + 2 *a. b. c. d.
CHAPTER 6 Applications of Integration
 PART II CHAPTER Applications of Integration Section. Area of a Region Between Two Curves.......... Section. Volume: The Disk Method................. 7 Section. Volume: The Shell Method................
PART II CHAPTER Applications of Integration Section. Area of a Region Between Two Curves.......... Section. Volume: The Disk Method................. 7 Section. Volume: The Shell Method................
Integration. Tuesday, December 3, 13
 4 Integration 4.3 Riemann Sums and Definite Integrals Objectives n Understand the definition of a Riemann sum. n Evaluate a definite integral using properties of definite integrals. 3 Riemann Sums 4 Riemann
4 Integration 4.3 Riemann Sums and Definite Integrals Objectives n Understand the definition of a Riemann sum. n Evaluate a definite integral using properties of definite integrals. 3 Riemann Sums 4 Riemann
Are You Ready? Find Area in the Coordinate Plane
 SKILL 38 Are You Read? Find Area in the Coordinate Plane Teaching Skill 38 Objective Find the areas of figures in the coordinate plane. Review with students the definition of area. Ask: Is the definition
SKILL 38 Are You Read? Find Area in the Coordinate Plane Teaching Skill 38 Objective Find the areas of figures in the coordinate plane. Review with students the definition of area. Ask: Is the definition
4 A Catalogue of Functions and Inequalities 8. SECTION E Modulus Function
 4 A Catalogue of Functions and Inequalities 8 SECTION E Modulus Function By the end of this section you will be able to visualize the geometric interpretation of the modulus function derive some inequalities
4 A Catalogue of Functions and Inequalities 8 SECTION E Modulus Function By the end of this section you will be able to visualize the geometric interpretation of the modulus function derive some inequalities
Conic Section: Circles
 Conic Section: Circles Circle, Center, Radius A circle is defined as the set of all points that are the same distance awa from a specific point called the center of the circle. Note that the circle consists
Conic Section: Circles Circle, Center, Radius A circle is defined as the set of all points that are the same distance awa from a specific point called the center of the circle. Note that the circle consists
y x can be solved using the quadratic equation Y1 ( x 5), then the other is
 Math 0 Precalculus Sstem of Equation Review Questions Multiple Choice. The sstem of equations A. 7 0 7 0 0 0 and can be solved using the quadratic equation. In solving the quadratic equation 0 ( ) intersection
Math 0 Precalculus Sstem of Equation Review Questions Multiple Choice. The sstem of equations A. 7 0 7 0 0 0 and can be solved using the quadratic equation. In solving the quadratic equation 0 ( ) intersection
TEST 1 FORM A (SOLUTIONS)
 TEST FORM A SOLUTIONS) MAT 68 Directions: Solve as many problems as well as you can in the blue eamination book, writing in pencil and showing all work. Put away any cell phones; the mere appearance will
TEST FORM A SOLUTIONS) MAT 68 Directions: Solve as many problems as well as you can in the blue eamination book, writing in pencil and showing all work. Put away any cell phones; the mere appearance will
c) domain {x R, x 3}, range {y R}
 Answers Chapter 1 Functions 1.1 Functions, Domain, and Range 1. a) Yes, no vertical line will pass through more than one point. b) No, an vertical line between = 6 and = 6 will pass through two points..
Answers Chapter 1 Functions 1.1 Functions, Domain, and Range 1. a) Yes, no vertical line will pass through more than one point. b) No, an vertical line between = 6 and = 6 will pass through two points..
