Precision measurements with atomic co-magnetometer at the South Pole. Michael Romalis Princeton University
|
|
|
- Eustace Gilmore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Precision measurements with atomic co-magnetometer at the South Pole Michael Romalis Princeton University
2 Outline Alkali metal - noble gas co-magnetometer Rotating co-magnetometer at the South Pole New Physics Constraints Lorentz violation Long-range spin-dependent forces Slowly oscillating fields Current experiments Search for spin-mass interaction on 20 cm scale Search for spin-spin interactions
3 Operation of Atomic Co-Magnetometer Alkali metal vapor in a glass cell Magnetic Field Linearly Polarized Probe light Cell contents [K] ~ 1014 cm-3 3 He buffer gas, N2 quenching z y x Magnetization Circularly Polarized Pumping light Polarization angle rotation Physics signal
4 Elimination of spin-exchange broadening at zero field Ground state Zeeman and hyperfine levels in K Zeeman transitions + F=2 High field: Spin exchange collisions F=1 Zeeman transitions mf Linewidth at finite field: 3 khz Low field: Linewidth at zero field: 1 Hz Spin-Exchange Relaxation Free (SERF) regime W. Happer and H. Tang, PRL 31, 273 (1973); J. C. Allred, R. N. Lyman, T. W. Kornack, and MVR, PRL. 89, (2002)
5 K-3He Co-magnetometer 1. Optically pump potassium atoms at high density ( /cm3) 2. 3He nuclear spins are polarized by spin-exchange collisions with K vapor 3. Polarized 3He creates a magnetic field felt by K atoms 8 B K = 3 0 M He 4. Apply external magnetic field Bz to cancel field BK K magnetometer operates near zero magnetic field 5. At zero field and high alkali density K-K spinexchange relaxation is suppressed 6. Obtain high sensitivity of K to magnetic fields in spin-exchange relaxation free (SERF) regime Turn most-sensitive atomic magnetometer into a co-magnetometer J. C. Allred, R. N. Lyman, T. W. Kornack, and MVR, PRL 89, (2002) I. K. Kominis, T. W. Kornack, J. C. Allred and MVR, Nature 422, 596 (2003) T.W. Kornack and MVR, PRL 89, (2002) T. W. Kornack, R. K. Ghosh and MVR, PRL 95, (2005)
6 Magnetic field self-compensation
7 Response to transient signals Fast transient response 3He has T2 of 1000s of seconds Transient signals decay in 0.3 seconds Due to spin-damping coupling to K atoms Integral of the signal is proportional to spin rotation angle for arbitrary pulse shape
8 Co-magnetometer Setup Simple pump-probe arrangement Measure Faraday rotation of fardetuned probe beam Sensitive to spin coupling orthogonal to pump and probe Details: Ferrite inner-most shield 3 layers of -metal Cell and beams in mtorr vacuum Polarization modulation of probe beam for polarimetry at 10-7rad/Hz1/2 Whole apparatus in vacuum at 1 Torr
9 Magnetic field sensitivity Best operating region Sensitivity of ~1 ft/hz1/2 for both electron and nuclear interactions Frequency uncertainty of 20 phz/month1/2 = ev for 3He 20 nhz/month1/2 = ev for electrons So search for preferred spatial direction, reverse co-magnetometer orientation every 20 sec to operate in the region of best sensitivity
10 Rotating K-3He co-magnetometer Rotate stop measure rotate Fast transient response crucial Record signal as a function of magnetometer orientation b eff S Pz e y 1 1 R e n
11 South Pole Most systematic errors are due to two preferred directions in the lab: gravity vector and Earth rotation vector If the two vectors are aligned, rotation about that axis will eliminate most systematic errors Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station Lab location within 200 meters of geographic South Pole Experiment Geographic South Pole
12 South Pole Setup Use 21Ne with I=3/2 to look for tensor CPT-even Lorentz-violating effects Reliable operation with minimal human intervention: Simple optical setup with DBR diode lasers Whole apparatus in vacuum at 1 Torr Automatic fine-tuning and calibration procedures Remote-controlled mirrors, lasers, etc M2K Laser polarizer 894 nm DBR tapered amplifier pump laser for Cs D1 photodiode PEM λ/4 WP λ/4 WP μ-metal shields vapor cell ferrite shield vacuum chamber polarizers 795 nm DBR probe laser for Rb D1 mirrors 10 mm
13 Apparatus Orientations Dipole and quadrupole Lorentz violating coefficients are constrained by operating with the quantization axis in two orthogonal configurations Bz Bz
14 South pole data sample 2=1.7 2=1.1
15 Summary of Lorentz-violation data Two years of data taking About 60% duty factor
16 Room Temperature ( C) Temperature Difference( C) Challenges at the Pole The building s tilt on ice is slowly drifting Requires regular automatic leveling Aggressive temperature cycling Temperature gradient across apparatus Other challenges: Isolation platform damping failed, probe laser burned out, air-bearing rotation stage got stuck, etc Need spares for everything. First atomic physics experiment operated at the South Pole First experiment to take advantage of geographic pole location
17 Tests of Lorentz symmetry Lorentz symmetry is at the foundation of two very successful but mutually incompatible theories: General Relativity Quantum Field Theory One approach for resolving this problem is to modify Lorentz symmetry Quantum Field Theory General General Relativity Relativity Lorentz Symmetry
18 Is the space really isotropic? Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Map The universe appears warmer on one side! Well, we are actually moving relative to CMB rest frame v = 369 km/sec ~ 10 c Space and time vector components mix by Lorentz transformation A test of spatial isotropy becomes a true test of Lorentz invariance (i.e. equivalence of space and time)
19 Local Lorentz Invariance Is the speed of light (photons) rotationally invariant in our moving frame? First established by Michelson-Morley experiment as a foundation of Special Relativity Is the speed of light as it enters into particle Lorentz transformation rotationally invariant in the moving frame? Princeton Best constrained by Hughes-Drever experiments due to finite kinetic energy of nucleons From Clifford M. Will, Living Rev. Relativity 9, (2006)
20 Parametrization of Lorentz violation = (m + a + b ) + L 5 i ( + c + d ) 5 2 a,b - CPT-odd c,d - CPT-even Alan Kostelecky a,b,c,d are vector fields in space with non-zero expectation value Vector and tensor analogues to the scalar Higgs vacuum expectation value Maximum attainable particle velocity v MAX c (1 c00 c0 j vˆ j c jk vˆ j vˆk ) Implications for ultra-high energy cosmic rays, Cherenkov radiation, etc Many laboratory limits (optical cavities, cold atoms, etc) Something special needs to happen when particle momentum reaches Planck scale Doubly-special relativity Horava-Lifshitz gravity Your favorite recent theory
21 Search for CPT-even Lorentz violation with nuclear spin Need nuclei with orbital angular momentum and total spin >1/2 Quadrupole energy shift due to angular momentum of the valence nucleon: EQ ~ (c11 c22 2c33 ) p x2 p y2 2 p z2 p x2 p y2 2 p z2 0 I,L pn Previously has been searched for in experiments using 201Hg and 21Ne with sensitivity of about 0.5 Hz Suppressed by vearth
22 Preliminary Results Vary frequency of the fit around sidereal period to independently estimate errors
23 Constrains on SME coefficients
24 Long-range spin-spin interactions with Geo-electrons
25 Slowly-modulated signals: light axions, dark photons Careful: Look-elsewhere effects Interference with sidereal frequency giving rise to slow drifts General sensitivity to E on the order of GeV in the frequency range Hz ft ft Sidereal frequency
26 Searches for spin-dependent forces Frequency shift Sˆ1 rˆ B Sˆ1 Sˆ2 S Acceleration or S Induced magnetization SQUID S S or Magnetic shield
27 Search for nuclear spin-dependent forces Spin Source: He spins at 20 atm. Spin direction reversed every 3 sec with Adiabatic Fast Passage b e b n 0.05aT 0.56 at K-3He comagnetometer Sensitivity: 0.7 ft/hz1/2 G. Vasilakis, J. M. Brown, T. W. Kornack, MVR, Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, (2009) Uncertainty (1 ) = 18 phz or GeV 3He energy after 1 month Smallest energy shift ever measured
28 Spin-mass searches with co-magnetometer Will be more sensitive than astrophysical limits Existing experiments Current experimental goal Astrophysical gravitational limits from G. Raffelt Phys. Rev. D 86, (2012)
29 Movable mass constructed and tested Probe beam Apparatus is suspended from ceiling to reduce mechanical coupling to optical table Pb Masses (~ 210 kg each) z Probe Beam Optics y x Glass cell (within vacuum chamber) Pump Beam Optics Magnetic correlation ~ 2 G Pump beam A Yaskawa 4kW servo motor smoothly raise/lower the two 210 kg Pb weights through a distance of 0.5m in 1s. Optical table tilt correlation ~2 nrad Gravitational effect on Tiltmeter 19.4 ± 0.5 nrad
30 Spin-spin long-range force B, G Use a permanent magnet spin source with 1024 polarized electrons (Eöt-Wash approach) Use co-magnetometer as spin sensor Limits both e-e and e-n interactions Expect gp~10, better than current laboratory limits but not quite reaching astrophysics limits Currently testing magnetic field leakage with 3 shields Measured field leakage as shields are added R, cm
31 Conclusions Atomic co-magnetometers set the most stringent limits on both CPT-odd and CPTeven Lorentz violation coefficients Set limits on spin-dependent forces at 20 phz level, the most sensitive energy shift measurements Can place limits on oscillating spin couplings in the Hz-Hz range Search for spin-mass coupling under way, should exceed astrophysical limits. Junyi Lee Himawan Winarto David Hoyos Ahmed Akhtar Marc Smiciklas Morgan Hedges Neal Schiebe Andrew Vernaza Funding:NSF
Atomic magnetometers: new twists to the old story. Michael Romalis Princeton University
 Atomic magnetometers: new twists to the old story Michael Romalis Princeton University Outline K magnetometer Elimination of spin-exchange relaxation Experimental setup Magnetometer performance Theoretical
Atomic magnetometers: new twists to the old story Michael Romalis Princeton University Outline K magnetometer Elimination of spin-exchange relaxation Experimental setup Magnetometer performance Theoretical
Tests of Lorentz Invariance with alkalimetal noble-gas co-magnetometer. (+ other application) Michael Romalis Princeton University
 Tests of Lorentz Invariance with alkalimetal noble-gas co-magnetometer (+ other application) Michael Romalis Princeton University Tests of Fundamental Symmetries Parity violation weak interactions CP violation
Tests of Lorentz Invariance with alkalimetal noble-gas co-magnetometer (+ other application) Michael Romalis Princeton University Tests of Fundamental Symmetries Parity violation weak interactions CP violation
Nuclear spin maser with a novel masing mechanism and its application to the search for an atomic EDM in 129 Xe
 Nuclear spin maser with a novel masing mechanism and its application to the search for an atomic EDM in 129 Xe A. Yoshimi RIKEN K. Asahi, S. Emori, M. Tsukui, RIKEN, Tokyo Institute of Technology Nuclear
Nuclear spin maser with a novel masing mechanism and its application to the search for an atomic EDM in 129 Xe A. Yoshimi RIKEN K. Asahi, S. Emori, M. Tsukui, RIKEN, Tokyo Institute of Technology Nuclear
Clock based on nuclear spin precession spin-clock
 Clock based on nuclear spin precession spin-clock signal (a.u.) detector t exp - T (G. D. Cates, et al., Phys. Rev. A 37, 877) T T T, field T, field 4 4R 75D B, z B, y B, x R 4 p B (ms ) T 00h Long T :
Clock based on nuclear spin precession spin-clock signal (a.u.) detector t exp - T (G. D. Cates, et al., Phys. Rev. A 37, 877) T T T, field T, field 4 4R 75D B, z B, y B, x R 4 p B (ms ) T 00h Long T :
Suppression Method of AC-Stark Shift in SERF Atomic. Magnetometer
 Suppression Method of AC-Stark Shift in SERF Atomic Magnetometer YANG LI, MING DING*, XUEJING LIU, HONGWEI CAI, JUNPENG ZHAO, AND JIANCHENG FANG School of Instrument Science and Opto-Electronics Engineering,
Suppression Method of AC-Stark Shift in SERF Atomic Magnetometer YANG LI, MING DING*, XUEJING LIU, HONGWEI CAI, JUNPENG ZHAO, AND JIANCHENG FANG School of Instrument Science and Opto-Electronics Engineering,
arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 16 Aug 2012
![arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 16 Aug 2012 arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 16 Aug 2012](/thumbs/93/114260424.jpg) Low Energy Tests of Lorentz and CPT Violation Don Colladay 5800 Bay Shore Road, New College of Florida arxiv:1208.3474v1 [hep-ph] 16 Aug 2012 Abstract. An overview of the theoretical framework of the Standard
Low Energy Tests of Lorentz and CPT Violation Don Colladay 5800 Bay Shore Road, New College of Florida arxiv:1208.3474v1 [hep-ph] 16 Aug 2012 Abstract. An overview of the theoretical framework of the Standard
A MODERN MICHELSON-MORLEY EXPERIMENT USING ACTIVELY ROTATED OPTICAL RESONATORS
 A MODERN MICHELSON-MORLEY EXPERIMENT USING ACTIVELY ROTATED OPTICAL RESONATORS S. HERRMANN, A. SENGER, K. MÖHLE, E. V. KOVALCHUK, A. PETERS Institut für Physik, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin Hausvogteiplatz
A MODERN MICHELSON-MORLEY EXPERIMENT USING ACTIVELY ROTATED OPTICAL RESONATORS S. HERRMANN, A. SENGER, K. MÖHLE, E. V. KOVALCHUK, A. PETERS Institut für Physik, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin Hausvogteiplatz
Ultrasensitive Atomic Magnetometers
 Ultrasensitive Atomic Magnetometers Faculty Thad Walker Ron Wakai Grad Students Bob Wyllie Zhimin Li (University of Texas Houston Health Science Center) University of Wisconsin-Madison Principles and Sensitivity
Ultrasensitive Atomic Magnetometers Faculty Thad Walker Ron Wakai Grad Students Bob Wyllie Zhimin Li (University of Texas Houston Health Science Center) University of Wisconsin-Madison Principles and Sensitivity
Citation IEEE Transactions on Magnetics (201.
 Effect of Spatial Homogeneity of Sp TitleMagnetic Field Response of an Optic Magnetometer Using a Hybrid Cell of Author(s) Ito, Yosuke; Ohnishi, Hiroyuki; Kam Tetsuo Citation IEEE Transactions on Magnetics
Effect of Spatial Homogeneity of Sp TitleMagnetic Field Response of an Optic Magnetometer Using a Hybrid Cell of Author(s) Ito, Yosuke; Ohnishi, Hiroyuki; Kam Tetsuo Citation IEEE Transactions on Magnetics
Lorentz-violating energy shift for hydrogen in the presence of a weak magnetic field
 Lorentz-violating energy shift for hydrogen in the presence of a weak magnetic field δε = j A j0 (nfjl) Fm F j0 Fm F Clebsch-Gordan coefficients n principal quantum number n F hydrogen total angular momentum
Lorentz-violating energy shift for hydrogen in the presence of a weak magnetic field δε = j A j0 (nfjl) Fm F j0 Fm F Clebsch-Gordan coefficients n principal quantum number n F hydrogen total angular momentum
Part I. Principles and techniques
 Part I Principles and techniques 1 General principles and characteristics of optical magnetometers D. F. Jackson Kimball, E. B. Alexandrov, and D. Budker 1.1 Introduction Optical magnetometry encompasses
Part I Principles and techniques 1 General principles and characteristics of optical magnetometers D. F. Jackson Kimball, E. B. Alexandrov, and D. Budker 1.1 Introduction Optical magnetometry encompasses
Investigations of optical pumping for magnetometry using an autolocking
 Investigations of optical pumping for magnetometry using an autolocking laser system A. Pouliot a, H.C. Beica a, A. Carew a, A. Vorozcovs a, G. Carlse a, B. Barrett b and A. Kumarakrishnan a, a Dept. of
Investigations of optical pumping for magnetometry using an autolocking laser system A. Pouliot a, H.C. Beica a, A. Carew a, A. Vorozcovs a, G. Carlse a, B. Barrett b and A. Kumarakrishnan a, a Dept. of
Optical Cavity Tests of Lorentz Invariance
 Light driven Nuclear-Particle physics and Cosmology 2017 (Pacifico Yokohama) April 20, 2017 Optical Cavity Tests of Lorentz Invariance Yuta Michimura Department of Physics, University of Tokyo H. Takeda,
Light driven Nuclear-Particle physics and Cosmology 2017 (Pacifico Yokohama) April 20, 2017 Optical Cavity Tests of Lorentz Invariance Yuta Michimura Department of Physics, University of Tokyo H. Takeda,
High Accuracy Strontium Ion Optical Clock
 High Accuracy Strontium Ion Optical Clock Helen Margolis, Geoff Barwood, Hugh Klein, Guilong Huang, Stephen Lea, Krzysztof Szymaniec and Patrick Gill T&F Club 15 th April 2005 Outline Optical frequency
High Accuracy Strontium Ion Optical Clock Helen Margolis, Geoff Barwood, Hugh Klein, Guilong Huang, Stephen Lea, Krzysztof Szymaniec and Patrick Gill T&F Club 15 th April 2005 Outline Optical frequency
Nuclear spin maser and experimental search for 129 Xe atomic EDM
 Hyperfine Interact DOI 10.1007/s10751-012-0751-z Nuclear spin maser and experimental search for 129 Xe atomic EDM T. Inoue T. Furukawa A. Yoshimi Y. Ichikawa M. Chikamori Y. Ohtomo M. Tsuchiya N. Yoshida
Hyperfine Interact DOI 10.1007/s10751-012-0751-z Nuclear spin maser and experimental search for 129 Xe atomic EDM T. Inoue T. Furukawa A. Yoshimi Y. Ichikawa M. Chikamori Y. Ohtomo M. Tsuchiya N. Yoshida
Rb-Xe spin relaxation in dilute Xe mixtures
 PHYSICAL REVIEW A, VOLUME 65, 012712 Rb-Xe spin relaxation in dilute Xe mixtures I. A. Nelson and T. G. Walker Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Madison, Madison, Wisconsin 53706 Received
PHYSICAL REVIEW A, VOLUME 65, 012712 Rb-Xe spin relaxation in dilute Xe mixtures I. A. Nelson and T. G. Walker Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Madison, Madison, Wisconsin 53706 Received
Fundamentals of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing. Course Outline 2009
 Fundamentals of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing Course Outline 2009 Part I. Fundamentals of Quantum Mechanics Chapter 1. Concepts of Quantum and Experimental Facts 1.1. Blackbody Radiation and
Fundamentals of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing Course Outline 2009 Part I. Fundamentals of Quantum Mechanics Chapter 1. Concepts of Quantum and Experimental Facts 1.1. Blackbody Radiation and
Collaborator ==============================
 RI Collaborator ============================== 20 CKM : 100 GeV (Plank scale): 10 19 GeV EDM + + + - - - Time: t -t Spin: s -s EDM: d d + + + - - - d 0 T-violation CP-violation CPT theorem Standard Model
RI Collaborator ============================== 20 CKM : 100 GeV (Plank scale): 10 19 GeV EDM + + + - - - Time: t -t Spin: s -s EDM: d d + + + - - - d 0 T-violation CP-violation CPT theorem Standard Model
Saturation Absorption Spectroscopy of Rubidium Atom
 Saturation Absorption Spectroscopy of Rubidium Atom Jayash Panigrahi August 17, 2013 Abstract Saturated absorption spectroscopy has various application in laser cooling which have many relevant uses in
Saturation Absorption Spectroscopy of Rubidium Atom Jayash Panigrahi August 17, 2013 Abstract Saturated absorption spectroscopy has various application in laser cooling which have many relevant uses in
EDM measurement in 129 Xe atom using dual active feedback nuclear spin maser
 Hyperfine Interact DOI 10.1007/s10751-014-1113-9 EDM measurement in 129 Xe atom using dual active feedback nuclear spin maser T. Sato Y. Ichikawa Y. Ohtomo Y. Sakamoto S. Kojima C. Funayama T. Suzuki M.
Hyperfine Interact DOI 10.1007/s10751-014-1113-9 EDM measurement in 129 Xe atom using dual active feedback nuclear spin maser T. Sato Y. Ichikawa Y. Ohtomo Y. Sakamoto S. Kojima C. Funayama T. Suzuki M.
Spin-exchange-relaxation-free magnetometry with Cs vapor
 Spin-exchange-relaxation-free magnetometry with Cs vapor M. P. Ledbetter,* I. M. Savukov, V. M. Acosta, and D. Budker Department of Physics, University of California at Berkeley, Berkeley, California 9470-7300,
Spin-exchange-relaxation-free magnetometry with Cs vapor M. P. Ledbetter,* I. M. Savukov, V. M. Acosta, and D. Budker Department of Physics, University of California at Berkeley, Berkeley, California 9470-7300,
Low Field MRI of Laser Polarized Noble Gases. Yuan Zheng, 4 th year seminar, Feb, 2013
 Low Field MRI of Laser Polarized Noble Gases Yuan Zheng, 4 th year seminar, Feb, 2013 Outline Introduction to conventional MRI Low field MRI of Laser Polarized (LP) noble gases Spin Exchange Optical Pumping
Low Field MRI of Laser Polarized Noble Gases Yuan Zheng, 4 th year seminar, Feb, 2013 Outline Introduction to conventional MRI Low field MRI of Laser Polarized (LP) noble gases Spin Exchange Optical Pumping
Spectroscopy of lithium ions at 34% of the speed of light with sub-doppler linewidth
 Towards a test of time dilation: Spectroscopy of lithium ions at 34% of the speed of light with sub-doppler linewidth.07.008 /3 Outline Introduction: test theories for SRT Tools for modern test of time
Towards a test of time dilation: Spectroscopy of lithium ions at 34% of the speed of light with sub-doppler linewidth.07.008 /3 Outline Introduction: test theories for SRT Tools for modern test of time
Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment of 199 Hg
 Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment of 199 Hg NIST, Boulder: University of Washington: Princeton University: W. Clark Griffith M. David Swallows David Meyer Blayne Heckel E. Norval Fortson Michael
Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment of 199 Hg NIST, Boulder: University of Washington: Princeton University: W. Clark Griffith M. David Swallows David Meyer Blayne Heckel E. Norval Fortson Michael
Parity Violation in Diatomic Molecules
 Parity Violation in Diatomic Molecules Jeff Ammon, E. Altuntas, S.B. Cahn, R. Paolino*, D. DeMille Physics Department, Yale University *Physics Department, US Coast Guard Academy DeMille Group Funding:
Parity Violation in Diatomic Molecules Jeff Ammon, E. Altuntas, S.B. Cahn, R. Paolino*, D. DeMille Physics Department, Yale University *Physics Department, US Coast Guard Academy DeMille Group Funding:
ATOMIC AND LASER SPECTROSCOPY
 ALAN CORNEY ATOMIC AND LASER SPECTROSCOPY CLARENDON PRESS OXFORD 1977 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Planck's radiation law. 1 1.2. The photoelectric effect 4 1.3. Early atomic spectroscopy 5 1.4. The postulates
ALAN CORNEY ATOMIC AND LASER SPECTROSCOPY CLARENDON PRESS OXFORD 1977 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Planck's radiation law. 1 1.2. The photoelectric effect 4 1.3. Early atomic spectroscopy 5 1.4. The postulates
Xe nuclear spin maser and search for atomic EDM
 Xe nuclear spin maser and search for atomic EDM T. Inoue, A. Yoshimi *, M. Uchida, T. Furukawa, N. Hatakeyama, M. Tsuchiya, H. Hayashi, and K. Asahi Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology
Xe nuclear spin maser and search for atomic EDM T. Inoue, A. Yoshimi *, M. Uchida, T. Furukawa, N. Hatakeyama, M. Tsuchiya, H. Hayashi, and K. Asahi Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology
OPTI 511L Fall Objectives:
 RJ Jones OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Optical Sciences Experiment: Saturated Absorption Spectroscopy (2 weeks) In this experiment we explore the use of a single mode tunable external cavity diode laser (ECDL) to
RJ Jones OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Optical Sciences Experiment: Saturated Absorption Spectroscopy (2 weeks) In this experiment we explore the use of a single mode tunable external cavity diode laser (ECDL) to
Axion Detection With NMR
 PRD 84 (2011) arxiv:1101.2691 + to appear Axion Detection With NMR Peter Graham Stanford with Dmitry Budker Micah Ledbetter Surjeet Rajendran Alex Sushkov Dark Matter Motivation two of the best candidates:
PRD 84 (2011) arxiv:1101.2691 + to appear Axion Detection With NMR Peter Graham Stanford with Dmitry Budker Micah Ledbetter Surjeet Rajendran Alex Sushkov Dark Matter Motivation two of the best candidates:
Two-Dimensional Nuclear Magnetic. Resonance at Zero-Field
 13 C-Decoupled J-coupling Spectroscopy Using Two-Dimensional Nuclear Magnetic Resonance at Zero-Field Tobias F. Sjolander,, Michael C. D. Tayler,, Arne Kentner,, Dmitry Budker,,, and Alexander Pines,,
13 C-Decoupled J-coupling Spectroscopy Using Two-Dimensional Nuclear Magnetic Resonance at Zero-Field Tobias F. Sjolander,, Michael C. D. Tayler,, Arne Kentner,, Dmitry Budker,,, and Alexander Pines,,
Laser Searches for New Particles at Fermilab. William Wester Fermilab
 Laser Searches for New Particles at Fermilab William Wester Fermilab Motivation Outline Experimental evidence Theoretical interest Experimental Implementation GammeV and GammeV-CHASE Results Outline x
Laser Searches for New Particles at Fermilab William Wester Fermilab Motivation Outline Experimental evidence Theoretical interest Experimental Implementation GammeV and GammeV-CHASE Results Outline x
Tests of Lorentz invariance using spinning fermions and laser-ranging ranging to the moon. Eric G. Adelberger University of Washington
 Tests of Lorentz invariance using spinning fermions and laser-ranging ranging to the moon Eric G. Adelberger University of Washington cosmic preferred frames? We all were taught that there are no preferred
Tests of Lorentz invariance using spinning fermions and laser-ranging ranging to the moon Eric G. Adelberger University of Washington cosmic preferred frames? We all were taught that there are no preferred
High Sensitivity Optically Pumped Quantum Magnetometer
 Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications 2013 2013 High Sensitivity Optically Pumped Quantum Magnetometer Valentina Tiporlini Edith Cowan University, vtiporl0@our.ecu.edu.au Kamal Alameh
Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications 2013 2013 High Sensitivity Optically Pumped Quantum Magnetometer Valentina Tiporlini Edith Cowan University, vtiporl0@our.ecu.edu.au Kamal Alameh
Precision measurements and fundamental physics: some recent results and new approaches
 Precision measurements and fundamental physics: some recent results and new approaches (at Harvard-Smithsonian Maser Lab) Ronald Walsworth Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Harvard University,
Precision measurements and fundamental physics: some recent results and new approaches (at Harvard-Smithsonian Maser Lab) Ronald Walsworth Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Harvard University,
Optical Pumping in 85 Rb and 87 Rb
 Optical Pumping in 85 Rb and 87 Rb John Prior III*, Quinn Pratt, Brennan Campbell, Kjell Hiniker University of San Diego, Department of Physics (Dated: December 14, 2015) Our experiment aimed to determine
Optical Pumping in 85 Rb and 87 Rb John Prior III*, Quinn Pratt, Brennan Campbell, Kjell Hiniker University of San Diego, Department of Physics (Dated: December 14, 2015) Our experiment aimed to determine
Shuichiro Kojima, Chikako Funayama, Shunya Tanaka, Yu Sakamoto, Yuichi Ohtomo, Chika Hirao, Masatoshi Chikamori, Eri Hikota
 Development Of 131 Xe Co-magnetometry For Xe Atomic EDM Search, Yuichi Ichikawa, Koichiro Asahi Department of Physics, Tokyo Tech./RIKEN Nishina Center E-mail: tomoya.sato@riken.jp Shuichiro Kojima, Chikako
Development Of 131 Xe Co-magnetometry For Xe Atomic EDM Search, Yuichi Ichikawa, Koichiro Asahi Department of Physics, Tokyo Tech./RIKEN Nishina Center E-mail: tomoya.sato@riken.jp Shuichiro Kojima, Chikako
The null result of the celebrated 1887 Michelson Morley
 Lorentz Invariance on Trial Precision experiments and astrophysical observations provide complementary tests of Lorentz invariance and may soon open a window onto new physics. They have already constrained
Lorentz Invariance on Trial Precision experiments and astrophysical observations provide complementary tests of Lorentz invariance and may soon open a window onto new physics. They have already constrained
Internal magnetic field measurement in tokamak plasmas using a Zeeman polarimeter
 PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 55, Nos 5 & 6 journal of Nov. & Dec. 2000 physics pp. 751 756 Internal magnetic field measurement in tokamak plasmas using a Zeeman polarimeter M JAGADEESHWARI
PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 55, Nos 5 & 6 journal of Nov. & Dec. 2000 physics pp. 751 756 Internal magnetic field measurement in tokamak plasmas using a Zeeman polarimeter M JAGADEESHWARI
Transverse measurements of polarization in optically pumped Rb vapor cells
 PHYSICAL REVIEW A 86, 053416 (2012) Transverse measurements of polarization in optically pumped Rb vapor cells J. M. Dreiling, 1 E. B. Norrgard, 1,* D. Tupa, 2 and T. J. Gay 1 1 Department of Physics and
PHYSICAL REVIEW A 86, 053416 (2012) Transverse measurements of polarization in optically pumped Rb vapor cells J. M. Dreiling, 1 E. B. Norrgard, 1,* D. Tupa, 2 and T. J. Gay 1 1 Department of Physics and
Excitation of high angular momentum Rydberg states
 J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Phys. 19 (1986) L461-L465. Printed in Great Britain LE ITER TO THE EDITOR Excitation of high angular momentum Rydberg states W A Molanderi, C R Stroud Jr and John A Yeazell The Institute
J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Phys. 19 (1986) L461-L465. Printed in Great Britain LE ITER TO THE EDITOR Excitation of high angular momentum Rydberg states W A Molanderi, C R Stroud Jr and John A Yeazell The Institute
Magnetic Field measurements with Csmagnetometers
 Magnetic Field measurements with Csmagnetometers in nedm project at PSI A.Pazgalev *, M.Cvijovic, P.Knowles, and A.Weis FRAP, Fribourg University, CH-1700 FRIOURG * on leave from IOFFE Phys.-Tech. Instit.,
Magnetic Field measurements with Csmagnetometers in nedm project at PSI A.Pazgalev *, M.Cvijovic, P.Knowles, and A.Weis FRAP, Fribourg University, CH-1700 FRIOURG * on leave from IOFFE Phys.-Tech. Instit.,
Accurate 3 He polarimetry using the Rb Zeeman frequency shift due to the Rb- 3 He spin-exchange collisions
 PHYSICAL REVIEW A VOLUME 58, NUMBER 4 OCTOBER 1998 Accurate 3 He polarimetry using the Rb Zeeman frequency shift due to the Rb- 3 He spin-exchange collisions M. V. Romalis* and G. D. Cates Department of
PHYSICAL REVIEW A VOLUME 58, NUMBER 4 OCTOBER 1998 Accurate 3 He polarimetry using the Rb Zeeman frequency shift due to the Rb- 3 He spin-exchange collisions M. V. Romalis* and G. D. Cates Department of
Optical Lattice Clock with Neutral Mercury
 Optical Lattice Clock with Neutral Mercury R. Tyumenev, Z. Xu, J.J. McFerran, Y. Le Coq and S. Bize SYRTE, Observatoire de Paris 61 avenue de l Observatoire, 75014 Paris, France rinat.tyumenev@obspm.fr
Optical Lattice Clock with Neutral Mercury R. Tyumenev, Z. Xu, J.J. McFerran, Y. Le Coq and S. Bize SYRTE, Observatoire de Paris 61 avenue de l Observatoire, 75014 Paris, France rinat.tyumenev@obspm.fr
Outline of my talk 1) Axion BEC: a model beyond CDM. 2) Production and Detection of Axion-like Particles by Interferometry.
 Outline of my talk 1) Axion BEC: a model beyond CDM. 2) Production and Detection of Axion-like Particles by Interferometry. Axion BEC: a model beyond CDM Based on: Bose-Einstein Condensation of Dark Matter
Outline of my talk 1) Axion BEC: a model beyond CDM. 2) Production and Detection of Axion-like Particles by Interferometry. Axion BEC: a model beyond CDM Based on: Bose-Einstein Condensation of Dark Matter
Polarized 3 He Target For Future Experiments
 Polarized 3 He Target For Future Experiments Kai Jin, University of Virginia, on behalf of JLab polarized 3 He group Hall C Winter Collaboration Meeting, January 20, 2017 Introduction to polarized 3 He
Polarized 3 He Target For Future Experiments Kai Jin, University of Virginia, on behalf of JLab polarized 3 He group Hall C Winter Collaboration Meeting, January 20, 2017 Introduction to polarized 3 He
Experiment 3 1. The Michelson Interferometer and the He- Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado
 Experiment 3 1 Introduction The Michelson Interferometer and the He- Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado The Michelson interferometer is one example of an optical interferometer.
Experiment 3 1 Introduction The Michelson Interferometer and the He- Ne Laser Physics 2150 Experiment No. 3 University of Colorado The Michelson interferometer is one example of an optical interferometer.
In-beam measurement of the hydrogen hyperfine splitting: towards antihydrogen spectroscopy. Martin Diermaier LEAP 2016 Kanazawa Japan
 In-beam measurement of the hydrogen hyperfine splitting: towards antihydrogen spectroscopy Martin Diermaier LEAP 2016 Kanazawa Japan Martin Diermaier Stefan-Meyer-Institute March th 2016 MOTIVATION Charge
In-beam measurement of the hydrogen hyperfine splitting: towards antihydrogen spectroscopy Martin Diermaier LEAP 2016 Kanazawa Japan Martin Diermaier Stefan-Meyer-Institute March th 2016 MOTIVATION Charge
Characterization and stabilization of fiber-coupled laser diode arrays
 REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS VOLUME 70, NUMBER 7 JULY 1999 Characterization and stabilization of fiber-coupled laser diode arrays D. F. Phillips, a) G. P. Wong, D. Bear, R. E. Stoner, and R. L. Walsworth
REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS VOLUME 70, NUMBER 7 JULY 1999 Characterization and stabilization of fiber-coupled laser diode arrays D. F. Phillips, a) G. P. Wong, D. Bear, R. E. Stoner, and R. L. Walsworth
Axion dark matter search using the storage ring EDM method
 Axion dark matter search using the storage ring EDM method Seung Pyo Chang, a,b Selcuk Haciomeroglu, a On Kim, a,b Soohyung Lee, a Seongtae Park, a Yannis K. Semertzidis a,b a Center for Axion and Precision
Axion dark matter search using the storage ring EDM method Seung Pyo Chang, a,b Selcuk Haciomeroglu, a On Kim, a,b Soohyung Lee, a Seongtae Park, a Yannis K. Semertzidis a,b a Center for Axion and Precision
Midterm Solutions. 1 1 = 0.999c (0.2)
 Midterm Solutions 1. (0) The detected muon is seen km away from the beam dump. It carries a kinetic energy of 4 GeV. Here we neglect the energy loss and angular scattering of the muon for simplicity. a.
Midterm Solutions 1. (0) The detected muon is seen km away from the beam dump. It carries a kinetic energy of 4 GeV. Here we neglect the energy loss and angular scattering of the muon for simplicity. a.
CONTENTS. 2 CLASSICAL DESCRIPTION 2.1 The resonance phenomenon 2.2 The vector picture for pulse EPR experiments 2.3 Relaxation and the Bloch equations
 CONTENTS Preface Acknowledgements Symbols Abbreviations 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Scope of pulse EPR 1.2 A short history of pulse EPR 1.3 Examples of Applications 2 CLASSICAL DESCRIPTION 2.1 The resonance phenomenon
CONTENTS Preface Acknowledgements Symbols Abbreviations 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Scope of pulse EPR 1.2 A short history of pulse EPR 1.3 Examples of Applications 2 CLASSICAL DESCRIPTION 2.1 The resonance phenomenon
An optically modulated zero-field atomic magnetometer with suppressed spinexchange
 An optically modulated zero-field atomic magnetometer with suppressed spinexchange broadening R. Jiménez-Martínez 1,2,a), S. Knappe 1, and J. Kitching 1 1 Time and Frequency Division, National Institute
An optically modulated zero-field atomic magnetometer with suppressed spinexchange broadening R. Jiménez-Martínez 1,2,a), S. Knappe 1, and J. Kitching 1 1 Time and Frequency Division, National Institute
Cavity Control in a Single-Electron Quantum Cyclotron
 Cavity Control in a Single-Electron Quantum Cyclotron An Improved Measurement of the Electron Magnetic Moment David Hanneke Michelson Postdoctoral Prize Lectures 13 May 2010 The Quantum Cyclotron Single
Cavity Control in a Single-Electron Quantum Cyclotron An Improved Measurement of the Electron Magnetic Moment David Hanneke Michelson Postdoctoral Prize Lectures 13 May 2010 The Quantum Cyclotron Single
Experimental Atomic Physics Research in the Budker Group
 Experimental Atomic Physics Research in the Budker Group Tests of fundamental symmetries using atomic physics: Parity Time-reversal invariance Permutation Postulate/Spin-Statistics Connection Temporal
Experimental Atomic Physics Research in the Budker Group Tests of fundamental symmetries using atomic physics: Parity Time-reversal invariance Permutation Postulate/Spin-Statistics Connection Temporal
Different ion-qubit choises. - One electron in the valence shell; Alkali like 2 S 1/2 ground state.
 Different ion-qubit choises - One electron in the valence shell; Alkali like 2 S 1/2 ground state. Electronic levels Structure n 2 P 3/2 n 2 P n 2 P 1/2 w/o D Be + Mg + Zn + Cd + 313 nm 280 nm 206 nm 226
Different ion-qubit choises - One electron in the valence shell; Alkali like 2 S 1/2 ground state. Electronic levels Structure n 2 P 3/2 n 2 P n 2 P 1/2 w/o D Be + Mg + Zn + Cd + 313 nm 280 nm 206 nm 226
LASER SPECTROSCOPIC STUDIES OF NEUTRON-DEFICIENT EUROPIUM AND GADOLINIUM ISOTOPES
 LASER SPECTROSCOPIC STUDIES OF NEUTRON-DEFICIENT EUROPIUM AND GADOLINIUM ISOTOPES A.E. Barzakh, D.V. Fedorov, A.M. Ionan, V.S. Ivanov, F.V. Moroz, K.A. Mezilev, S.Yu. Orlov, V.N. Panteleev, Yu.M. Volkov
LASER SPECTROSCOPIC STUDIES OF NEUTRON-DEFICIENT EUROPIUM AND GADOLINIUM ISOTOPES A.E. Barzakh, D.V. Fedorov, A.M. Ionan, V.S. Ivanov, F.V. Moroz, K.A. Mezilev, S.Yu. Orlov, V.N. Panteleev, Yu.M. Volkov
Suppressing the Lorentz violations in the matter sector A class of extended Hořava gravity
 Suppressing the Lorentz violations in the matter sector A class of extended Hořava gravity A. Emir Gümrükçüoğlu University of Nottingham [Based on arxiv:1410.6360; 1503.07544] with Mattia Colombo and Thomas
Suppressing the Lorentz violations in the matter sector A class of extended Hořava gravity A. Emir Gümrükçüoğlu University of Nottingham [Based on arxiv:1410.6360; 1503.07544] with Mattia Colombo and Thomas
Fundamental Physics with Atomic Interferometry
 Fundamental Physics with Atomic Interferometry Peter Graham Stanford with Savas Dimopoulos Jason Hogan Mark Kasevich Surjeet Rajendran PRL 98 (2007) PRD 78 (2008) PRD 78 (2008) PLB 678 (2009) arxiv:1009.2702
Fundamental Physics with Atomic Interferometry Peter Graham Stanford with Savas Dimopoulos Jason Hogan Mark Kasevich Surjeet Rajendran PRL 98 (2007) PRD 78 (2008) PRD 78 (2008) PLB 678 (2009) arxiv:1009.2702
Electron Beam Polarimetry at JLab Hall C Dave Gaskell PST 2009 September 7, 2009
 Electron Beam Polarimetry at JLab Hall C Dave Gaskell PST 2009 September 7, 2009 1. Møller Polarimeter 2. Compton Polarimeter 3. Summary JLab Polarimetry Techniques Three different processes used to measure
Electron Beam Polarimetry at JLab Hall C Dave Gaskell PST 2009 September 7, 2009 1. Møller Polarimeter 2. Compton Polarimeter 3. Summary JLab Polarimetry Techniques Three different processes used to measure
Electron EDM Searches
 Electron EDM Searches Paul Hamilton Yale University INT Workshop Seattle, October 2008 Outline Theoretical Motivation General detection method Past and current eedm searches Molecular eedm searches and
Electron EDM Searches Paul Hamilton Yale University INT Workshop Seattle, October 2008 Outline Theoretical Motivation General detection method Past and current eedm searches Molecular eedm searches and
Three Dimensional Compensation Spherical Coils for Compact Atomic Magnetometer
 Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, Vol. 17, No. 3, pp. 215 222 (2014) DOI: 10.6180/jase.2014.17.3.01 Three Dimensional Compensation Spherical Coils for Compact Atomic Magnetometer C. Zhuo*, H.
Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, Vol. 17, No. 3, pp. 215 222 (2014) DOI: 10.6180/jase.2014.17.3.01 Three Dimensional Compensation Spherical Coils for Compact Atomic Magnetometer C. Zhuo*, H.
Measurement of transverse spin-relaxation rates in a rubidium vapor by use of spin-noise spectroscopy
 Measurement of transverse spin-relaxation rates in a rubidium vapor by use of spin-noise spectroscopy G. E. Katsoprinakis, A. T. Dellis, and I. K. Kominis* 1 Department of Physics, University of Crete,
Measurement of transverse spin-relaxation rates in a rubidium vapor by use of spin-noise spectroscopy G. E. Katsoprinakis, A. T. Dellis, and I. K. Kominis* 1 Department of Physics, University of Crete,
CESIUM ATOMIC FOUNTAIN CLOCKS AT NMIJ
 CESIUM ATOMIC FOUNTAIN CLOCKS AT NMIJ A. Takamizawa 1, S. Yanagimachi 1, Y. Shirakawa 2, K. Watabe 1, K. Hagimoto 1, and T. Ikegami 1 1 National Metrology Institute of Japan (NMIJ), AIST 2 Tokyo University
CESIUM ATOMIC FOUNTAIN CLOCKS AT NMIJ A. Takamizawa 1, S. Yanagimachi 1, Y. Shirakawa 2, K. Watabe 1, K. Hagimoto 1, and T. Ikegami 1 1 National Metrology Institute of Japan (NMIJ), AIST 2 Tokyo University
Primary Frequency Standards at NIST. S.R. Jefferts NIST Time and Frequency Division
 Primary Frequency Standards at NIST S.R. Jefferts NIST Time and Frequency Division Outline Atomic Clocks - general Primary Frequency Standard Beam Standards Laser-Cooled Primary Standards Systematic Frequency
Primary Frequency Standards at NIST S.R. Jefferts NIST Time and Frequency Division Outline Atomic Clocks - general Primary Frequency Standard Beam Standards Laser-Cooled Primary Standards Systematic Frequency
What We Really Know About Neutrino Speeds
 What We Really Know About Neutrino Speeds Brett Altschul University of South Carolina March 22, 2013 In particle physics, the standard model has been incredibly successful. If the Higgs boson discovered
What We Really Know About Neutrino Speeds Brett Altschul University of South Carolina March 22, 2013 In particle physics, the standard model has been incredibly successful. If the Higgs boson discovered
Gravitational tests using simultaneous atom interferometers
 Gravitational tests using simultaneous atom interferometers Gabriele Rosi Quantum gases, fundamental interactions and cosmology conference 5-7 October 017, Pisa Outline Introduction to atom interferometry
Gravitational tests using simultaneous atom interferometers Gabriele Rosi Quantum gases, fundamental interactions and cosmology conference 5-7 October 017, Pisa Outline Introduction to atom interferometry
Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment in Ra EDM Spin EDM Spin EDM. Spin. Pseudo-scalar. s d
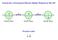 Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment in Ra-225 + T + P - - - + EDM Spin EDM Spin EDM Spin Pseudo-scalar s d C. S. Wu 1912-1997 Parity (space reversal) x, y, z -x, -y, -z z y Parity z x x y Pseudo-scalar
Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment in Ra-225 + T + P - - - + EDM Spin EDM Spin EDM Spin Pseudo-scalar s d C. S. Wu 1912-1997 Parity (space reversal) x, y, z -x, -y, -z z y Parity z x x y Pseudo-scalar
HYPERFINE STRUCTURE CONSTANTS IN THE 102D3/2 AND 112D 3/2 STATES OF 85Rb M. GLOW
 Vol. 83 (1993) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 HYPERFINE STRUCTURE CONSTANTS IN THE 102D3/2 AND 112D 3/2 STATES OF 85Rb M. GLOW Institute of Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences Al. Lotników 32/46, 02-668
Vol. 83 (1993) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 HYPERFINE STRUCTURE CONSTANTS IN THE 102D3/2 AND 112D 3/2 STATES OF 85Rb M. GLOW Institute of Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences Al. Lotników 32/46, 02-668
Angular Correlation Experiments
 Angular Correlation Experiments John M. LoSecco April 2, 2007 Angular Correlation Experiments J. LoSecco Notre Dame du Lac Nuclear Spin In atoms one can use the Zeeman Effect to determine the spin state.
Angular Correlation Experiments John M. LoSecco April 2, 2007 Angular Correlation Experiments J. LoSecco Notre Dame du Lac Nuclear Spin In atoms one can use the Zeeman Effect to determine the spin state.
Micromechanical Instruments for Ferromagnetic Measurements
 Micromechanical Instruments for Ferromagnetic Measurements John Moreland NIST 325 Broadway, Boulder, CO, 80305 Phone:+1-303-497-3641 FAX: +1-303-497-3725 E-mail: moreland@boulder.nist.gov Presented at
Micromechanical Instruments for Ferromagnetic Measurements John Moreland NIST 325 Broadway, Boulder, CO, 80305 Phone:+1-303-497-3641 FAX: +1-303-497-3725 E-mail: moreland@boulder.nist.gov Presented at
Precision Polarimetry of Polarized 3 He
 Precision Polarimetry of Polarized 3 He Nick Penthorn Mentor Todd Averett March 2014 Abstract This work presents the progress of an experimental procedure designed to do precision polarimetry on polarized
Precision Polarimetry of Polarized 3 He Nick Penthorn Mentor Todd Averett March 2014 Abstract This work presents the progress of an experimental procedure designed to do precision polarimetry on polarized
F.G. Major. The Quantum Beat. The Physical Principles of Atomic Clocks. With 230 Illustrations. Springer
 F.G. Major The Quantum Beat The Physical Principles of Atomic Clocks With 230 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface Chapter 1. Celestial and Mechanical Clocks 1 1.1 Cyclic Events in Nature 1 1.2 The
F.G. Major The Quantum Beat The Physical Principles of Atomic Clocks With 230 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface Chapter 1. Celestial and Mechanical Clocks 1 1.1 Cyclic Events in Nature 1 1.2 The
Unsolved Mysteries of the Universe: Looking for Clues in Surprising Places
 The 64 th Compton Lecture Series Unsolved Mysteries of the Universe: Looking for Clues in Surprising Places http://kicp.uchicago.edu/~odom/compton.htm Lecture 5: Using the Fine Structure Constant to Push
The 64 th Compton Lecture Series Unsolved Mysteries of the Universe: Looking for Clues in Surprising Places http://kicp.uchicago.edu/~odom/compton.htm Lecture 5: Using the Fine Structure Constant to Push
LASERS. Amplifiers: Broad-band communications (avoid down-conversion)
 L- LASERS Representative applications: Amplifiers: Broad-band communications (avoid down-conversion) Oscillators: Blasting: Energy States: Hydrogen atom Frequency/distance reference, local oscillators,
L- LASERS Representative applications: Amplifiers: Broad-band communications (avoid down-conversion) Oscillators: Blasting: Energy States: Hydrogen atom Frequency/distance reference, local oscillators,
The Minimal Lorentz-Violating Standard Model Extension
 The Minimal Lorentz-Violating Standard Model Extension Brett Altschul University of South Carolina June 17, 2018 We have been testing relativity experimentally for a long time. The first good test was
The Minimal Lorentz-Violating Standard Model Extension Brett Altschul University of South Carolina June 17, 2018 We have been testing relativity experimentally for a long time. The first good test was
Improvements to the Mercury Electric Dipole Moment Experiment
 Improvements to the Mercury Electric Dipole Moment Experiment Kyle Matsuda Advisor: Blayne Heckel INT REU, University of Washington August 2015 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 2 Experimental Setup 3 Current
Improvements to the Mercury Electric Dipole Moment Experiment Kyle Matsuda Advisor: Blayne Heckel INT REU, University of Washington August 2015 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 2 Experimental Setup 3 Current
General classifications:
 General classifications: Physics is perceived as fundamental basis for study of the universe Chemistry is perceived as fundamental basis for study of life Physics consists of concepts, principles and notions,
General classifications: Physics is perceived as fundamental basis for study of the universe Chemistry is perceived as fundamental basis for study of life Physics consists of concepts, principles and notions,
High-precision studies in fundamental physics with slow neutrons. Oliver Zimmer Institut Laue Langevin
 High-precision studies in fundamental physics with slow neutrons Oliver Zimmer Institut Laue Langevin ILL, 20 September 2016 Topics The impossible particle and its properties Search for an electric dipole
High-precision studies in fundamental physics with slow neutrons Oliver Zimmer Institut Laue Langevin ILL, 20 September 2016 Topics The impossible particle and its properties Search for an electric dipole
Experiment objectives: measure the ratio of Planck s constant to the electron charge h/e using the photoelectric effect.
 Chapter 1 Photoelectric Effect Experiment objectives: measure the ratio of Planck s constant to the electron charge h/e using the photoelectric effect. History The photoelectric effect and its understanding
Chapter 1 Photoelectric Effect Experiment objectives: measure the ratio of Planck s constant to the electron charge h/e using the photoelectric effect. History The photoelectric effect and its understanding
Modern Physics for Scientists and Engineers International Edition, 4th Edition
 Modern Physics for Scientists and Engineers International Edition, 4th Edition http://optics.hanyang.ac.kr/~shsong Review: 1. THE BIRTH OF MODERN PHYSICS 2. SPECIAL THEORY OF RELATIVITY 3. THE EXPERIMENTAL
Modern Physics for Scientists and Engineers International Edition, 4th Edition http://optics.hanyang.ac.kr/~shsong Review: 1. THE BIRTH OF MODERN PHYSICS 2. SPECIAL THEORY OF RELATIVITY 3. THE EXPERIMENTAL
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom
 Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Units of Chapter 37 37-7 Wave Nature of Matter 37-8 Electron Microscopes 37-9 Early Models of the Atom 37-10 Atomic Spectra: Key to the Structure
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Units of Chapter 37 37-7 Wave Nature of Matter 37-8 Electron Microscopes 37-9 Early Models of the Atom 37-10 Atomic Spectra: Key to the Structure
EDM. Spin. ν e. β - Li + Supported by DOE, Office of Nuclear Physics
 T + - + - He Ra EDM Spin EDM Spin β - θ ν e He Kr 6 He 6 Li + Supported by DOE, Office of Nuclear Physics Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment in Ra-225 + T + P - - - + EDM Spin EDM Spin EDM Spin
T + - + - He Ra EDM Spin EDM Spin β - θ ν e He Kr 6 He 6 Li + Supported by DOE, Office of Nuclear Physics Search for a Permanent Electric Dipole Moment in Ra-225 + T + P - - - + EDM Spin EDM Spin EDM Spin
Zeeman Effect. Alex Povilus Physics 441- Fall 2003 December 20, 2003
 Zeeman Effect Alex Povilus Physics 441- Fall 2003 December 20, 2003 Abstract The Zeeman Effect is observed by application of a strong magnetic field to a mercury vapor cell and exciting transitions by
Zeeman Effect Alex Povilus Physics 441- Fall 2003 December 20, 2003 Abstract The Zeeman Effect is observed by application of a strong magnetic field to a mercury vapor cell and exciting transitions by
Polarized 3 He Target Updates
 Polarized 3 He Target Updates Kai Jin, University of Virginia, on behalf of JLab polarized 3 He group Hall A Winter Collaboration Meeting, January 19, 2017 Introduction to polarized 3He target Target upgrade
Polarized 3 He Target Updates Kai Jin, University of Virginia, on behalf of JLab polarized 3 He group Hall A Winter Collaboration Meeting, January 19, 2017 Introduction to polarized 3He target Target upgrade
CW-Lyman- Source for Laser Cooling of Antihydrogen in a Magnetic Trap
 CW-Lyman- Source for Laser Cooling of Antihydrogen in a Magnetic Trap F. Markert, M. Scheid, D. Kolbe, A. Müllers, T. Weber, V. Neises, R. Steinborn and J. Walz Institut für Physik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität
CW-Lyman- Source for Laser Cooling of Antihydrogen in a Magnetic Trap F. Markert, M. Scheid, D. Kolbe, A. Müllers, T. Weber, V. Neises, R. Steinborn and J. Walz Institut für Physik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität
SUB-NATURAL-WIDTH N-RESONANCES OBSERVED IN LARGE FREQUENCY INTERVAL
 SUB-NATURAL-WIDTH N-RESONANCES OBSERVED IN LARGE FREQUENCY INTERVAL A. KRASTEVA 1, S. GATEVA 1, A. SARGSYAN 2, D. SARKISYAN 2 AND S. CARTALEVA 1 1 Institute of Electronics, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences,
SUB-NATURAL-WIDTH N-RESONANCES OBSERVED IN LARGE FREQUENCY INTERVAL A. KRASTEVA 1, S. GATEVA 1, A. SARGSYAN 2, D. SARKISYAN 2 AND S. CARTALEVA 1 1 Institute of Electronics, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences,
PHYS 4 CONCEPT PACKET Complete
 PHYS 4 CONCEPT PACKET Complete Written by Jeremy Robinson, Head Instructor Find Out More +Private Instruction +Review Sessions WWW.GRADEPEAK.COM Need Help? Online Private Instruction Anytime, Anywhere
PHYS 4 CONCEPT PACKET Complete Written by Jeremy Robinson, Head Instructor Find Out More +Private Instruction +Review Sessions WWW.GRADEPEAK.COM Need Help? Online Private Instruction Anytime, Anywhere
Supplementary Figure 1: Spin noise spectra of 55 Mn in bulk sample at BL =10.5 mt, before subtraction of the zero-frequency line. a, Contour plot of
 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Spin noise spectra of 55 Mn in bulk sample at BL =10.5 mt, before subtraction of the zero-frequency line. a, Contour plot of the spin noise spectra calculated with Eq. (2) for
1 Supplementary Figure 1: Spin noise spectra of 55 Mn in bulk sample at BL =10.5 mt, before subtraction of the zero-frequency line. a, Contour plot of the spin noise spectra calculated with Eq. (2) for
Spin resonance. Basic idea. PSC 3151, (301)
 Spin Resonance Phys623 Spring 2018 Prof. Ted Jacobson PSC 3151, (301)405-6020 jacobson@physics.umd.edu Spin resonance Spin resonance refers to the enhancement of a spin flipping probability in a magnetic
Spin Resonance Phys623 Spring 2018 Prof. Ted Jacobson PSC 3151, (301)405-6020 jacobson@physics.umd.edu Spin resonance Spin resonance refers to the enhancement of a spin flipping probability in a magnetic
Squeezed Light Techniques for Gravitational Wave Detection
 Squeezed Light Techniques for Gravitational Wave Detection July 6, 2012 Daniel Sigg LIGO Hanford Observatory Seminar at TIFR, Mumbai, India G1200688-v1 Squeezed Light Interferometry 1 Abstract Several
Squeezed Light Techniques for Gravitational Wave Detection July 6, 2012 Daniel Sigg LIGO Hanford Observatory Seminar at TIFR, Mumbai, India G1200688-v1 Squeezed Light Interferometry 1 Abstract Several
Students are required to pass a minimum of 15 AU of PAP courses including the following courses:
 School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences Division of Physics and Applied Physics Minor in Physics Curriculum - Minor in Physics Requirements for the Minor: Students are required to pass a minimum of
School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences Division of Physics and Applied Physics Minor in Physics Curriculum - Minor in Physics Requirements for the Minor: Students are required to pass a minimum of
Dynamics of star clusters containing stellar mass black holes: 1. Introduction to Gravitational Waves
 Dynamics of star clusters containing stellar mass black holes: 1. Introduction to Gravitational Waves July 25, 2017 Bonn Seoul National University Outline What are the gravitational waves? Generation of
Dynamics of star clusters containing stellar mass black holes: 1. Introduction to Gravitational Waves July 25, 2017 Bonn Seoul National University Outline What are the gravitational waves? Generation of
Electron spins in nonmagnetic semiconductors
 Electron spins in nonmagnetic semiconductors Yuichiro K. Kato Institute of Engineering Innovation, The University of Tokyo Physics of non-interacting spins Optical spin injection and detection Spin manipulation
Electron spins in nonmagnetic semiconductors Yuichiro K. Kato Institute of Engineering Innovation, The University of Tokyo Physics of non-interacting spins Optical spin injection and detection Spin manipulation
1. Introduction. 2. New approaches
 New Approaches To An Indium Ion Optical Frequency Standard Kazuhiro HAYASAKA National Institute of Information and Communications Technology(NICT) e-mail:hayasaka@nict.go.jp ECTI200 . Introduction Outline
New Approaches To An Indium Ion Optical Frequency Standard Kazuhiro HAYASAKA National Institute of Information and Communications Technology(NICT) e-mail:hayasaka@nict.go.jp ECTI200 . Introduction Outline
Characterization and Stabilization of Opto Power Fiber-Coupled Laser Diode Arrays. Abstract
 Characterization and Stabilization of Opto Power Fiber-Coupled Laser Diode Arrays D. F. Phillips, G. P. Wong, D. Bear, R. E. Stoner and R. L. Walsworth Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge,
Characterization and Stabilization of Opto Power Fiber-Coupled Laser Diode Arrays D. F. Phillips, G. P. Wong, D. Bear, R. E. Stoner and R. L. Walsworth Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge,
MIDTERM 3 REVIEW SESSION. Dr. Flera Rizatdinova
 MIDTERM 3 REVIEW SESSION Dr. Flera Rizatdinova Summary of Chapter 23 Index of refraction: Angle of reflection equals angle of incidence Plane mirror: image is virtual, upright, and the same size as the
MIDTERM 3 REVIEW SESSION Dr. Flera Rizatdinova Summary of Chapter 23 Index of refraction: Angle of reflection equals angle of incidence Plane mirror: image is virtual, upright, and the same size as the
CAST: "Blind" telescope looks at the Sun. Marin Karuza, University of Rijeka Imperial College, London,
 CAST: "Blind" telescope looks at the Sun CAST: "Blind" telescope looks at the Sun Introduction Looking for axions and not only Outlook Introduction CAST Cern Axion Solar Telescope Why blind? Not sensitive
CAST: "Blind" telescope looks at the Sun CAST: "Blind" telescope looks at the Sun Introduction Looking for axions and not only Outlook Introduction CAST Cern Axion Solar Telescope Why blind? Not sensitive
SYRTE - IACI. AtoM Interferometry dual Gravi- GradiOmeter AMIGGO. from capability demonstrations in laboratory to space missions
 SYRTE - IACI AtoM Interferometry dual Gravi- GradiOmeter AMIGGO from capability demonstrations in laboratory to space missions A. Trimeche, R. Caldani, M. Langlois, S. Merlet, C. Garrido Alzar and F. Pereira
SYRTE - IACI AtoM Interferometry dual Gravi- GradiOmeter AMIGGO from capability demonstrations in laboratory to space missions A. Trimeche, R. Caldani, M. Langlois, S. Merlet, C. Garrido Alzar and F. Pereira
Vacuum Energy and. Cosmological constant puzzle:
 Vacuum Energy and the cosmological constant puzzle Steven Bass Cosmological constant puzzle: (arxiv:1503.05483 [hep-ph], MPLA in press) Accelerating Universe: believed to be driven by energy of nothing
Vacuum Energy and the cosmological constant puzzle Steven Bass Cosmological constant puzzle: (arxiv:1503.05483 [hep-ph], MPLA in press) Accelerating Universe: believed to be driven by energy of nothing
Lorentz violation in cosmology why, how and where
 Lorentz violation in cosmology why, how and where Diego Blas w/ B. Audren, E. Barausse, M. Ivanov, J. Lesgourgues, O. Pujolàs, H. Sanctuary, S. Sibiryakov, K. Yagi, N. Yunes Diego Blas, COSMO 12 Beijing
Lorentz violation in cosmology why, how and where Diego Blas w/ B. Audren, E. Barausse, M. Ivanov, J. Lesgourgues, O. Pujolàs, H. Sanctuary, S. Sibiryakov, K. Yagi, N. Yunes Diego Blas, COSMO 12 Beijing
