THE NEGATIVE BINOMIAL DISTRIBUTION
|
|
|
- Winfred Francis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE NEGATIVE BINOMIAL DISTRIBUTION BY R. A. FISHER, F.R.S. Although the algebra of the two cases is equivalent, the positive and negative binomial expansions play very different parts as statistical distributions. The positive binomial ((I + PIn occurs normally with n a known integer, but the fractions p and q = 1 -p, unknown. The case in which n also is unknown is conceivable, but rather artificial for the following reasons: If n is not integral the expansion after a certain stage develops negative coefficients; these cannot be interpreted as negative frequencies, so that the expansion does not correspond with any distribution. There remains the case in which n is necessarily integral, although unknown. A variety of problems may be constructed of this sort, all entirely academic. With a sufficiently large sample n is necessarily one less than the number of frequency classes, and is thus determined without reference to the actual frequencies. The negative binomial, on the other hand, which, following Haldane (11)) we may write gives on expansion the term (q-~)-~, q = 1 +p, k positive, which is positive for all positive values of x, whether k is integral or not. Consequently, in this case, there is a practical problem in the simultaneous estimation of p and k to which the positive binomial offers no analogy. In experimental sampling the negative binomial with unknown exponent arises in a simple extension of the conditions which give rise to the Poisson Series. The Poisson Series arises when equal samples are taken from perfectly homogeneous material. It is completely determined by the average or expected number, m, of occurrences per sample. If unequal samples were taken, or if the material were not perfectly homogeneous, the value of ~ra would vary from sample to sample. Since m is necessarily positive, the simplest frequency distribution which allows some variation of m is the Eulerian distribution, familiar as that of x, in which the frequency element is df= ~, p-kmk-le-mlp dm. (k- 1). For x the parameter k is always the half of a positive integer; in general it may be any number exceeding zero. When m varies in this way the frequency of occurrence of x units in the sample is
2 R. A. FISHER 1 This integral also is of the Eulerian type having the value (k+x-l)! p z!(k- l)! (l+p)k+z and this is identical.with the standmd form for the negative binomial. The variance of m always increases the variance of x for a given mean value, so that a positive binomial distribution cannot be obtained in this way, for it would correspond with m having a negative variance.. THE EFFICIENCY OF FITTING THE FIRST TWO MOMENTS The binomial with known exponent is efficiently fitted by the observed mean; it is therefore rational, and not inconvenient, to fit the negative binomial, using the first two moments. Jeffreys (1) has pointed out that this process is not efficient. The expression for the moments of the negative binomial are equivalent to those for the positive binomial, changing the sign of p, and remembering that k corresponds to -n, and q = 1+p. = pk, PS = Pdq+p)k, Pz=Mk, P--Paa=Pq(l+61)k* Consequently, for large samples, for which case alone the method of moments need be investigated, we may use the equations of estimation m,- P p=-, k=- E m,-e where Z is the mean, and m, the variance as estimated from the sample. To examine the efficiency of the method we shall need the determinant of the covariance matrix of p and k so estimated; this may be found as follows without determining the covariance matrix itself. The covariance matrix of P and m, for large samples of N is in general ( B N P P-P% P 1. substituting for p and k, this gives the determinant Pq(q + P) k N Pdq + P) k: = F,pqk(k + 1). PP( 1 + 6Pq) k + pq k To derive from this the determinant of the covariance matrix for the estimates of p and k, we need only multiply by the square of the Jacobian writing for P and ma their expected values. The Jacobian is -- a( m, - Z) m,-z (ma - Z) (m, - P),
3 1 THE NEGATIVE BINOMIAL DISTRIBUTION or - 1 /pk on substitution. The determinant of the covariance matrix of p and k estimated by the first two moments is, therefore, We may compare this with the corresponding determinant for any method of efficient estimation. The most convenient way of doing this is to calculate the information matrix, which will be the reciprocal of the covariance matrix for efficient estimation. Taking the general term of the negative binomial, it appears that C= (k+x-i)! p" x! (k - 1)! (1 +p)k+x' whence, substituting its mean value pk for x, we have in accordance with the well-known fact that if k were given, p would be efficiently estimated from the observed mean. Next a loge=-, or %pk =- ap ak q- a Finally, -- logc=f(k-1)-f(k+x-l) = ak k (k+ I) (k+x- 1)' and this expression averaged for varying x gives ikk in the form It is a curious fact that this awkward looking expression can be transformed into one suitable for the. comparison we have in view. If and ikk= (l-r)k ( kr (i) r =p/q, l/q = 1-r, - +- '(k+l)r r r r -k - -+ k(k+1)+6k(k+l)(k+)+..' EX- F (- l)! (k- I)! x=1x (k+x-l)! * In this form it is easily seen that the determinant of the information matrix is simply - N ipp ipk (ipk ikj lpx (x-i)!k! pq,=sxqx(k+z-l)!'
4 @(k R. A. FISHER 1 If the determinant of the covariance matrix corresponding with any method of estimation is multiplied by this expression, we have the reciprocal of the efficiency. For the method of moments - 1 = I Pa +... E t *(& ) + ) (k + ) + In accordance with the general theory E is always less than unity. The expression shows that it is near to unity when P f q W ) = (k+z)(k+) is small. When the mean is small, e.g. f =.1, high efficiencies occur even when k is as low as unity, for which value the expression above is 1/, low efficiencies are confined to the region where k-t. At this extreme if k > the value is less than 1/. When the mean is 1., k must be as high as for the value to fall to 1/. When the mean is 1, k must be for the value to fall to 1/.. However high f may be, values of k above 1 will bring this down below 1/. Thus if p is less than 1/ for any value of k, or if k exceeds 1 for any value of p, high efficiency is assured; for intermediate values, if the product (1 + 1/1) (k + ) exceeds, the efficiency is satisfactorily high.. NUMERICAL EXAMPLES Example 1. Table 1 gives a sample of sheep classified according to the number of ticks found on each. (Data due to A. Milne, King s College, Newcaatle-on-Tyne.) Table 1 Number of ticks ( I I Total Number of sheep f I 6 6, +IS Fitting by the first two moments we have z =, ma = = *6+ =.11, 1 Vol. 11
5 ~ 1 16 THE NEGATIVE BINOMIAL DISTRIBUTION giving the estimates p =.1, l/p = 1.176, k =.676, and (l+:)(k+) = 1.1. From this we may guess the efficiency to be about %. The actual terms in 1/E are ~ E =.7. With efficiency below yo many workers would think a more accurate fitting desirable. For this purpose the method of Haldane's note in this number may be recommended. Example. As an example with a somewhat heavier rate of infestation we may take the series Table I 6 7 ~- I1 I I1 I I.. --~ Total Here X = + = 6.676, s = Tlie moment estimates are p =.1, k = 1.66 il nd (1 +;) (k+ ) = -. In this case no further calculation is needed to show that the method of moments is decidedly inefficient. The result of fitting this example by maximal likelihood gives, of course, somewhat differelit estimates 1st and nd 1 Likelihood ~ I I I I
6 ~ R. A. FISHER 17 but such merences would scarcely mislead one as to the level of efficiency. The efficient values obtained by likelihood merely give a value of (1 + lip) (k + ) of. in place of -. The efficient solution does not give a bad fit, in spite of the abrupt changes in frequency, e.g. between 1 and ticks, or again between and 6, which the observed series shows. Grouping in eleven classes we have Number of ticks Expected number of sheep (m) Observed a Difference a-m (a m I I 1-1 I 6- Total -~.6 7'. 7. 7' ' 7' 6.1. I1 I XI ' +'1 - ' ~1.7' '7 " ~.6 Since, in addition to the total frequency, two parameters have been efficiently fitted, x has eight degrees of freedom. The value of x is thus very near to its expected value. In spite of their apparent regularity the deviations are no larger than might often be due to chance.. SUMMARY The cases of the positive and negative binomial distributions, in spite of their algebraic similarity, are very different in their applications, and in the statistical problems to which they give rise. With the negative binomial we ordinarily require to estimate the exponent in addition to the mean of the distribution. This can be done from the first two moments, but the process has been recognized as inefficient, and in the present note the theoretical efficiency is calculated so aa to make it easy to judge in practical cases whether a more exact fitting by maximal likelihood is required. REFERENCES J. B. S. HALDANE (11). 'The fitting of binomial distributions.' Ann. Eugen., Lond., ii, 17. H. JEFFREYS (1). Theory of Probability, p. 6. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
The Annals of Human Genetics has an archive of material originally published in print format by the Annals of Eugenics ( ).
 The Annals of Human Genetics has an archive of material originally published in print format by the Annals of Eugenics (11). This material is available in specialised libraries and archives. e believe
The Annals of Human Genetics has an archive of material originally published in print format by the Annals of Eugenics (11). This material is available in specialised libraries and archives. e believe
Factoring and Algebraic Fractions
 Worksheet. Algebraic Fractions Section Factoring and Algebraic Fractions As pointed out in worksheet., we can use factoring to simplify algebraic expressions, and in particular we can use it to simplify
Worksheet. Algebraic Fractions Section Factoring and Algebraic Fractions As pointed out in worksheet., we can use factoring to simplify algebraic expressions, and in particular we can use it to simplify
SOME RESULTS ON THE MULTIPLE GROUP DISCRIMINANT PROBLEM. Peter A. Lachenbruch
 .; SOME RESULTS ON THE MULTIPLE GROUP DISCRIMINANT PROBLEM By Peter A. Lachenbruch Department of Biostatistics University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, N.C. Institute of Statistics Mimeo Series No. 829
.; SOME RESULTS ON THE MULTIPLE GROUP DISCRIMINANT PROBLEM By Peter A. Lachenbruch Department of Biostatistics University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, N.C. Institute of Statistics Mimeo Series No. 829
2 Discrete Dynamical Systems (DDS)
 2 Discrete Dynamical Systems (DDS) 2.1 Basics A Discrete Dynamical System (DDS) models the change (or dynamics) of single or multiple populations or quantities in which the change occurs deterministically
2 Discrete Dynamical Systems (DDS) 2.1 Basics A Discrete Dynamical System (DDS) models the change (or dynamics) of single or multiple populations or quantities in which the change occurs deterministically
Review for Mastery. Integer Exponents. Zero Exponents Negative Exponents Negative Exponents in the Denominator. Definition.
 LESSON 6- Review for Mastery Integer Exponents Remember that means 8. The base is, the exponent is positive. Exponents can also be 0 or negative. Zero Exponents Negative Exponents Negative Exponents in
LESSON 6- Review for Mastery Integer Exponents Remember that means 8. The base is, the exponent is positive. Exponents can also be 0 or negative. Zero Exponents Negative Exponents Negative Exponents in
A quadratic expression is a mathematical expression that can be written in the form 2
 118 CHAPTER Algebra.6 FACTORING AND THE QUADRATIC EQUATION Textbook Reference Section 5. CLAST OBJECTIVES Factor a quadratic expression Find the roots of a quadratic equation A quadratic expression is
118 CHAPTER Algebra.6 FACTORING AND THE QUADRATIC EQUATION Textbook Reference Section 5. CLAST OBJECTIVES Factor a quadratic expression Find the roots of a quadratic equation A quadratic expression is
Discrete Distributions Chapter 6
 Discrete Distributions Chapter 6 Negative Binomial Distribution section 6.3 Consider k r, r +,... independent Bernoulli trials with probability of success in one trial being p. Let the random variable
Discrete Distributions Chapter 6 Negative Binomial Distribution section 6.3 Consider k r, r +,... independent Bernoulli trials with probability of success in one trial being p. Let the random variable
Chapter 7 Rational Expressions, Equations, and Functions
 Chapter 7 Rational Expressions, Equations, and Functions Section 7.1: Simplifying, Multiplying, and Dividing Rational Expressions and Functions Section 7.2: Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
Chapter 7 Rational Expressions, Equations, and Functions Section 7.1: Simplifying, Multiplying, and Dividing Rational Expressions and Functions Section 7.2: Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
Unit 2-1: Factoring and Solving Quadratics. 0. I can add, subtract and multiply polynomial expressions
 CP Algebra Unit -1: Factoring and Solving Quadratics NOTE PACKET Name: Period Learning Targets: 0. I can add, subtract and multiply polynomial expressions 1. I can factor using GCF.. I can factor by grouping.
CP Algebra Unit -1: Factoring and Solving Quadratics NOTE PACKET Name: Period Learning Targets: 0. I can add, subtract and multiply polynomial expressions 1. I can factor using GCF.. I can factor by grouping.
EXERCISES. a b = a + b l aq b = ab - (a + b) + 2. a b = a + b + 1 n0i) = oii + ii + fi. A. Examples of Rings. C. Ring of 2 x 2 Matrices
 / rings definitions and elementary properties 171 EXERCISES A. Examples of Rings In each of the following, a set A with operations of addition and multiplication is given. Prove that A satisfies all the
/ rings definitions and elementary properties 171 EXERCISES A. Examples of Rings In each of the following, a set A with operations of addition and multiplication is given. Prove that A satisfies all the
f(x θ)dx with respect to θ. Assuming certain smoothness conditions concern differentiating under the integral the integral sign, we first obtain
 0.1. INTRODUCTION 1 0.1 Introduction R. A. Fisher, a pioneer in the development of mathematical statistics, introduced a measure of the amount of information contained in an observaton from f(x θ). Fisher
0.1. INTRODUCTION 1 0.1 Introduction R. A. Fisher, a pioneer in the development of mathematical statistics, introduced a measure of the amount of information contained in an observaton from f(x θ). Fisher
Never leave a NEGATIVE EXPONENT or a ZERO EXPONENT in an answer in simplest form!!!!!
 1 ICM Unit 0 Algebra Rules Lesson 1 Rules of Exponents RULE EXAMPLE EXPLANANTION a m a n = a m+n A) x x 6 = B) x 4 y 8 x 3 yz = When multiplying with like bases, keep the base and add the exponents. a
1 ICM Unit 0 Algebra Rules Lesson 1 Rules of Exponents RULE EXAMPLE EXPLANANTION a m a n = a m+n A) x x 6 = B) x 4 y 8 x 3 yz = When multiplying with like bases, keep the base and add the exponents. a
SOME AMAZING PROPERTIES OF THE FUNCTION f(x) = x 2 * David M. Goldschmidt University of California, Berkeley U.S.A.
 SOME AMAZING PROPERTIES OF THE FUNCTION f(x) = x 2 * David M. Goldschmidt University of California, Berkeley U.S.A. 1. Introduction Today we are going to have a look at one of the simplest functions in
SOME AMAZING PROPERTIES OF THE FUNCTION f(x) = x 2 * David M. Goldschmidt University of California, Berkeley U.S.A. 1. Introduction Today we are going to have a look at one of the simplest functions in
ACTEX CAS EXAM 3 STUDY GUIDE FOR MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS
 ACTEX CAS EXAM 3 STUDY GUIDE FOR MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTORY NOTE NOTES AND PROBLEM SETS Section 1 - Point Estimation 1 Problem Set 1 15 Section 2 - Confidence Intervals and
ACTEX CAS EXAM 3 STUDY GUIDE FOR MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTORY NOTE NOTES AND PROBLEM SETS Section 1 - Point Estimation 1 Problem Set 1 15 Section 2 - Confidence Intervals and
Analysis of Variance and Co-variance. By Manza Ramesh
 Analysis of Variance and Co-variance By Manza Ramesh Contents Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) What is ANOVA? The Basic Principle of ANOVA ANOVA Technique Setting up Analysis of Variance Table Short-cut Method
Analysis of Variance and Co-variance By Manza Ramesh Contents Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) What is ANOVA? The Basic Principle of ANOVA ANOVA Technique Setting up Analysis of Variance Table Short-cut Method
P-adic numbers. Rich Schwartz. October 24, 2014
 P-adic numbers Rich Schwartz October 24, 2014 1 The Arithmetic of Remainders In class we have talked a fair amount about doing arithmetic with remainders and now I m going to explain what it means in a
P-adic numbers Rich Schwartz October 24, 2014 1 The Arithmetic of Remainders In class we have talked a fair amount about doing arithmetic with remainders and now I m going to explain what it means in a
Advanced Herd Management Probabilities and distributions
 Advanced Herd Management Probabilities and distributions Anders Ringgaard Kristensen Slide 1 Outline Probabilities Conditional probabilities Bayes theorem Distributions Discrete Continuous Distribution
Advanced Herd Management Probabilities and distributions Anders Ringgaard Kristensen Slide 1 Outline Probabilities Conditional probabilities Bayes theorem Distributions Discrete Continuous Distribution
SOLUTIONS FOR PROBLEMS 1-30
 . Answer: 5 Evaluate x x + 9 for x SOLUTIONS FOR PROBLEMS - 0 When substituting x in x be sure to do the exponent before the multiplication by to get (). + 9 5 + When multiplying ( ) so that ( 7) ( ).
. Answer: 5 Evaluate x x + 9 for x SOLUTIONS FOR PROBLEMS - 0 When substituting x in x be sure to do the exponent before the multiplication by to get (). + 9 5 + When multiplying ( ) so that ( 7) ( ).
MATCHING. Match the correct vocabulary word with its definition
 Name Algebra I Block UNIT 2 STUDY GUIDE Ms. Metzger MATCHING. Match the correct vocabulary word with its definition 1. Whole Numbers 2. Integers A. A value for a variable that makes an equation true B.
Name Algebra I Block UNIT 2 STUDY GUIDE Ms. Metzger MATCHING. Match the correct vocabulary word with its definition 1. Whole Numbers 2. Integers A. A value for a variable that makes an equation true B.
The Distributions of Sums, Products and Ratios of Inverted Bivariate Beta Distribution 1
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 2, 28, no. 48, 2377-2391 The Distributions of Sums, Products and Ratios of Inverted Bivariate Beta Distribution 1 A. S. Al-Ruzaiza and Awad El-Gohary 2 Department of
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 2, 28, no. 48, 2377-2391 The Distributions of Sums, Products and Ratios of Inverted Bivariate Beta Distribution 1 A. S. Al-Ruzaiza and Awad El-Gohary 2 Department of
27 Wyner Math 2 Spring 2019
 27 Wyner Math 2 Spring 2019 CHAPTER SIX: POLYNOMIALS Review January 25 Test February 8 Thorough understanding and fluency of the concepts and methods in this chapter is a cornerstone to success in the
27 Wyner Math 2 Spring 2019 CHAPTER SIX: POLYNOMIALS Review January 25 Test February 8 Thorough understanding and fluency of the concepts and methods in this chapter is a cornerstone to success in the
Your use of the JSTOR archive indicates your acceptance of the Terms & Conditions of Use, available at
 A Note on the Efficiency of Least-Squares Estimates Author(s): D. R. Cox and D. V. Hinkley Source: Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological), Vol. 30, No. 2 (1968), pp. 284-289
A Note on the Efficiency of Least-Squares Estimates Author(s): D. R. Cox and D. V. Hinkley Source: Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological), Vol. 30, No. 2 (1968), pp. 284-289
1.2 The Role of Variables
 1.2 The Role of Variables variables sentences come in several flavors true false conditional In this section, a name is given to mathematical sentences that are sometimes true, sometimes false they are
1.2 The Role of Variables variables sentences come in several flavors true false conditional In this section, a name is given to mathematical sentences that are sometimes true, sometimes false they are
Simplifying Radical Expressions
 Simplifying Radical Expressions Product Property of Radicals For any real numbers a and b, and any integer n, n>1, 1. If n is even, then When a and b are both nonnegative. n ab n a n b 2. If n is odd,
Simplifying Radical Expressions Product Property of Radicals For any real numbers a and b, and any integer n, n>1, 1. If n is even, then When a and b are both nonnegative. n ab n a n b 2. If n is odd,
Preliminary statistics
 1 Preliminary statistics The solution of a geophysical inverse problem can be obtained by a combination of information from observed data, the theoretical relation between data and earth parameters (models),
1 Preliminary statistics The solution of a geophysical inverse problem can be obtained by a combination of information from observed data, the theoretical relation between data and earth parameters (models),
CHAPTER 4 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE SAMPLE. From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum
 CHAPTER 4 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE SAMPLE From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum 1997 65 CHAPTER 4 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE SAMPLE 4.0. Introduction In Chapter
CHAPTER 4 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE SAMPLE From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum 1997 65 CHAPTER 4 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE SAMPLE 4.0. Introduction In Chapter
5.1. EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS
 5.1. EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS 1 What You Should Learn Recognize and evaluate exponential functions with base a. Graph exponential functions and use the One-to-One Property. Recognize, evaluate,
5.1. EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS 1 What You Should Learn Recognize and evaluate exponential functions with base a. Graph exponential functions and use the One-to-One Property. Recognize, evaluate,
A field trips costs $800 for the charter bus plus $10 per student for x students. The cost per student is represented by: 10x x
 LEARNING STRATEGIES: Activate Prior Knowledge, Shared Reading, Think/Pair/Share, Note Taking, Group Presentation, Interactive Word Wall A field trips costs $800 for the charter bus plus $10 per student
LEARNING STRATEGIES: Activate Prior Knowledge, Shared Reading, Think/Pair/Share, Note Taking, Group Presentation, Interactive Word Wall A field trips costs $800 for the charter bus plus $10 per student
Math 1302 Notes 2. How many solutions? What type of solution in the real number system? What kind of equation is it?
 Math 1302 Notes 2 We know that x 2 + 4 = 0 has How many solutions? What type of solution in the real number system? What kind of equation is it? What happens if we enlarge our current system? Remember
Math 1302 Notes 2 We know that x 2 + 4 = 0 has How many solutions? What type of solution in the real number system? What kind of equation is it? What happens if we enlarge our current system? Remember
Recall the Basics of Hypothesis Testing
 Recall the Basics of Hypothesis Testing The level of significance α, (size of test) is defined as the probability of X falling in w (rejecting H 0 ) when H 0 is true: P(X w H 0 ) = α. H 0 TRUE H 1 TRUE
Recall the Basics of Hypothesis Testing The level of significance α, (size of test) is defined as the probability of X falling in w (rejecting H 0 ) when H 0 is true: P(X w H 0 ) = α. H 0 TRUE H 1 TRUE
EE4601 Communication Systems
 EE4601 Communication Systems Week 2 Review of Probability, Important Distributions 0 c 2011, Georgia Institute of Technology (lect2 1) Conditional Probability Consider a sample space that consists of two
EE4601 Communication Systems Week 2 Review of Probability, Important Distributions 0 c 2011, Georgia Institute of Technology (lect2 1) Conditional Probability Consider a sample space that consists of two
Eco517 Fall 2004 C. Sims MIDTERM EXAM
 Eco517 Fall 2004 C. Sims MIDTERM EXAM Answer all four questions. Each is worth 23 points. Do not devote disproportionate time to any one question unless you have answered all the others. (1) We are considering
Eco517 Fall 2004 C. Sims MIDTERM EXAM Answer all four questions. Each is worth 23 points. Do not devote disproportionate time to any one question unless you have answered all the others. (1) We are considering
Confidence intervals and the Feldman-Cousins construction. Edoardo Milotti Advanced Statistics for Data Analysis A.Y
 Confidence intervals and the Feldman-Cousins construction Edoardo Milotti Advanced Statistics for Data Analysis A.Y. 2015-16 Review of the Neyman construction of the confidence intervals X-Outline of a
Confidence intervals and the Feldman-Cousins construction Edoardo Milotti Advanced Statistics for Data Analysis A.Y. 2015-16 Review of the Neyman construction of the confidence intervals X-Outline of a
On the Theoretical Foundations of Mathematical Statistics. RA Fisher
 On the Theoretical Foundations of Mathematical Statistics RA Fisher presented by Blair Christian 10 February 2003 1 Ronald Aylmer Fisher 1890-1962 (Born in England, Died in Australia) 1911- helped found
On the Theoretical Foundations of Mathematical Statistics RA Fisher presented by Blair Christian 10 February 2003 1 Ronald Aylmer Fisher 1890-1962 (Born in England, Died in Australia) 1911- helped found
The Matrix Algebra of Sample Statistics
 The Matrix Algebra of Sample Statistics James H. Steiger Department of Psychology and Human Development Vanderbilt University James H. Steiger (Vanderbilt University) The Matrix Algebra of Sample Statistics
The Matrix Algebra of Sample Statistics James H. Steiger Department of Psychology and Human Development Vanderbilt University James H. Steiger (Vanderbilt University) The Matrix Algebra of Sample Statistics
Chapter 1. The Noble Eightfold Path to Linear Regression
 Chapter 1 The Noble Eightfold Path to Linear Regression In this chapter, I show several di erent ways of solving the linear regression problem. The di erent approaches are interesting in their own way.
Chapter 1 The Noble Eightfold Path to Linear Regression In this chapter, I show several di erent ways of solving the linear regression problem. The di erent approaches are interesting in their own way.
Accuplacer Elementary Algebra Review
 Accuplacer Elementary Algebra Review Hennepin Technical College Placement Testing for Success Page 1 Overview The Elementary Algebra section of ACCUPLACER contains 1 multiple choice Algebra questions that
Accuplacer Elementary Algebra Review Hennepin Technical College Placement Testing for Success Page 1 Overview The Elementary Algebra section of ACCUPLACER contains 1 multiple choice Algebra questions that
Statistical techniques for data analysis in Cosmology
 Statistical techniques for data analysis in Cosmology arxiv:0712.3028; arxiv:0911.3105 Numerical recipes (the bible ) Licia Verde ICREA & ICC UB-IEEC http://icc.ub.edu/~liciaverde outline Lecture 1: Introduction
Statistical techniques for data analysis in Cosmology arxiv:0712.3028; arxiv:0911.3105 Numerical recipes (the bible ) Licia Verde ICREA & ICC UB-IEEC http://icc.ub.edu/~liciaverde outline Lecture 1: Introduction
6-1. Canonical Correlation Analysis
 6-1. Canonical Correlation Analysis Canonical Correlatin analysis focuses on the correlation between a linear combination of the variable in one set and a linear combination of the variables in another
6-1. Canonical Correlation Analysis Canonical Correlatin analysis focuses on the correlation between a linear combination of the variable in one set and a linear combination of the variables in another
P.1 Prerequisite skills Basic Algebra Skills
 P.1 Prerequisite skills Basic Algebra Skills Topics: Evaluate an algebraic expression for given values of variables Combine like terms/simplify algebraic expressions Solve equations for a specified variable
P.1 Prerequisite skills Basic Algebra Skills Topics: Evaluate an algebraic expression for given values of variables Combine like terms/simplify algebraic expressions Solve equations for a specified variable
LIE RING METHODS IN THE THEORY OF FINITE NILPOTENT GROUPS
 307 LIE RING METHODS IN THE THEORY OF FINITE NILPOTENT GROUPS By GRAHAM HIGMAN 1. Introduction There are, of course, many connections between Group Theory and the theory of Lie rings, and my title is,
307 LIE RING METHODS IN THE THEORY OF FINITE NILPOTENT GROUPS By GRAHAM HIGMAN 1. Introduction There are, of course, many connections between Group Theory and the theory of Lie rings, and my title is,
HS Algebra IIB Mathematics CC
 Scope And Sequence Timeframe Unit Instructional Topics 1 Week(s) 1 Week(s) 1 Week(s) 1 Week(s) 2 Week(s) 1 Week(s) 2 Week(s) 1 Week(s) Unit 1: Linear and Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities Unit
Scope And Sequence Timeframe Unit Instructional Topics 1 Week(s) 1 Week(s) 1 Week(s) 1 Week(s) 2 Week(s) 1 Week(s) 2 Week(s) 1 Week(s) Unit 1: Linear and Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities Unit
Geometry Summer Assignment 2018
 Geometry Summer Assignment 2018 The following packet contains topics and definitions that you will be required to know in order to succeed in Geometry this year. You are advised to be familiar with each
Geometry Summer Assignment 2018 The following packet contains topics and definitions that you will be required to know in order to succeed in Geometry this year. You are advised to be familiar with each
Algebra I. Book 2. Powered by...
 Algebra I Book 2 Powered by... ALGEBRA I Units 4-7 by The Algebra I Development Team ALGEBRA I UNIT 4 POWERS AND POLYNOMIALS......... 1 4.0 Review................ 2 4.1 Properties of Exponents..........
Algebra I Book 2 Powered by... ALGEBRA I Units 4-7 by The Algebra I Development Team ALGEBRA I UNIT 4 POWERS AND POLYNOMIALS......... 1 4.0 Review................ 2 4.1 Properties of Exponents..........
Unit 1 Notes. Polynomials
 Unit 1 Notes 1 Day Number Date Topic Problem Set 1 Wed. Sept. Operations with Signed Numbers and Order of Operations Pre-Unit Review PS (1 ) Thurs. Sept. Working with Exponents Start Exponent Laws P.S.
Unit 1 Notes 1 Day Number Date Topic Problem Set 1 Wed. Sept. Operations with Signed Numbers and Order of Operations Pre-Unit Review PS (1 ) Thurs. Sept. Working with Exponents Start Exponent Laws P.S.
Model Estimation Example
 Ronald H. Heck 1 EDEP 606: Multivariate Methods (S2013) April 7, 2013 Model Estimation Example As we have moved through the course this semester, we have encountered the concept of model estimation. Discussions
Ronald H. Heck 1 EDEP 606: Multivariate Methods (S2013) April 7, 2013 Model Estimation Example As we have moved through the course this semester, we have encountered the concept of model estimation. Discussions
Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 2 Powers & Roots PROPERTIES OF EXPONENTS:
 Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 2 Powers & Roots PROPERTIES OF EXPONENTS: 1 EXPONENT REVIEW PROBLEMS: 2 1. 2x + x x + x + 5 =? 2. (x 2 + x) (x + 2) =?. The expression 8x (7x 6 x 5 ) is equivalent to?.
Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 2 Powers & Roots PROPERTIES OF EXPONENTS: 1 EXPONENT REVIEW PROBLEMS: 2 1. 2x + x x + x + 5 =? 2. (x 2 + x) (x + 2) =?. The expression 8x (7x 6 x 5 ) is equivalent to?.
Lesson 21 Not So Dramatic Quadratics
 STUDENT MANUAL ALGEBRA II / LESSON 21 Lesson 21 Not So Dramatic Quadratics Quadratic equations are probably one of the most popular types of equations that you ll see in algebra. A quadratic equation has
STUDENT MANUAL ALGEBRA II / LESSON 21 Lesson 21 Not So Dramatic Quadratics Quadratic equations are probably one of the most popular types of equations that you ll see in algebra. A quadratic equation has
2. AXIOMATIC PROBABILITY
 IA Probability Lent Term 2. AXIOMATIC PROBABILITY 2. The axioms The formulation for classical probability in which all outcomes or points in the sample space are equally likely is too restrictive to develop
IA Probability Lent Term 2. AXIOMATIC PROBABILITY 2. The axioms The formulation for classical probability in which all outcomes or points in the sample space are equally likely is too restrictive to develop
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Chapter 7 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Simplify the expression. 1. 5x 6 + 3x. 3t + 7 3t 4 3. 8s 4 + 4s 6 5s 4. 9m + 3 + m 3 + 5m 5. 4 3p 7 3p 4 1 z 1 + 4 6. ( ) 7. 6( x + ) 4 8. 3( h + 4) 3( h
Chapter 7 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Simplify the expression. 1. 5x 6 + 3x. 3t + 7 3t 4 3. 8s 4 + 4s 6 5s 4. 9m + 3 + m 3 + 5m 5. 4 3p 7 3p 4 1 z 1 + 4 6. ( ) 7. 6( x + ) 4 8. 3( h + 4) 3( h
1.3 Algebraic Expressions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 1.3 Algebraic Expressions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Multiplying Algebraic Expressions Special Product Formulas Factoring Common Factors
1.3 Algebraic Expressions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Multiplying Algebraic Expressions Special Product Formulas Factoring Common Factors
Algebra Summer Review Packet
 Name: Algebra Summer Review Packet About Algebra 1: Algebra 1 teaches students to think, reason, and communicate mathematically. Students use variables to determine solutions to real world problems. Skills
Name: Algebra Summer Review Packet About Algebra 1: Algebra 1 teaches students to think, reason, and communicate mathematically. Students use variables to determine solutions to real world problems. Skills
Sect Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Division Properties of Equality
 Sect.1 - Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Division Properties of Equality Concept #1 Definition of a Linear Equation in One Variable An equation is a statement that two quantities are equal.
Sect.1 - Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Division Properties of Equality Concept #1 Definition of a Linear Equation in One Variable An equation is a statement that two quantities are equal.
DIFFERENTIATION RULES
 3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES We have: Seen how to interpret derivatives as slopes and rates of change Seen how to estimate derivatives of functions given by tables of values Learned how
3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES We have: Seen how to interpret derivatives as slopes and rates of change Seen how to estimate derivatives of functions given by tables of values Learned how
20A. Build. Build and add. Build a rectangle and find the area (product). l e s s o n p r a c t i c e 1. X X X 2 + 6X X
 l e s s o n p r a c t i c e 0A Build.. X X. X 6X 8 3. X 8 Build and add. 4. X 6X 3 3X 7X 9 5. X 8 X 6X 7 6. X 0X 7 X 8X 9 Build a rectangle and find the area (product). 7. (X )(X ) = 8. (X 4)(X 3) = 9.
l e s s o n p r a c t i c e 0A Build.. X X. X 6X 8 3. X 8 Build and add. 4. X 6X 3 3X 7X 9 5. X 8 X 6X 7 6. X 0X 7 X 8X 9 Build a rectangle and find the area (product). 7. (X )(X ) = 8. (X 4)(X 3) = 9.
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 1.4. ALGEBRA 4 (Logarithms) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 1.4 ALGEBRA 4 (Logarithms) by A.J.Hobson 1.4.1 Common logarithms 1.4.2 Logarithms in general 1.4.3 Useful Results 1.4.4 Properties of logarithms 1.4.5 Natural logarithms 1.4.6
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 1.4 ALGEBRA 4 (Logarithms) by A.J.Hobson 1.4.1 Common logarithms 1.4.2 Logarithms in general 1.4.3 Useful Results 1.4.4 Properties of logarithms 1.4.5 Natural logarithms 1.4.6
Lesson 3: Polynomials and Exponents, Part 1
 Lesson 2: Introduction to Variables Assessment Lesson 3: Polynomials and Exponents, Part 1 When working with algebraic expressions, variables raised to a power play a major role. In this lesson, we look
Lesson 2: Introduction to Variables Assessment Lesson 3: Polynomials and Exponents, Part 1 When working with algebraic expressions, variables raised to a power play a major role. In this lesson, we look
FLC Ch 6. Simplify. State any restrictions (if necessary). a) b) Simplify each. List all restrictions on the domain. Next, graph the function f.
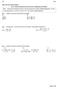 Math 0 Intermediate Algebra Defn Sec 6.: Rational Expressions and Functions: Multiplying and Dividing A polynomial divided by another nonzero polynomial is called a rational expression. If P and Q are
Math 0 Intermediate Algebra Defn Sec 6.: Rational Expressions and Functions: Multiplying and Dividing A polynomial divided by another nonzero polynomial is called a rational expression. If P and Q are
Something that can have different values at different times. A variable is usually represented by a letter in algebraic expressions.
 Lesson Objectives: Students will be able to define, recognize and use the following terms in the context of polynomials: o Constant o Variable o Monomial o Binomial o Trinomial o Polynomial o Numerical
Lesson Objectives: Students will be able to define, recognize and use the following terms in the context of polynomials: o Constant o Variable o Monomial o Binomial o Trinomial o Polynomial o Numerical
Chapter 4. Repeated Trials. 4.1 Introduction. 4.2 Bernoulli Trials
 Chapter 4 Repeated Trials 4.1 Introduction Repeated indepentent trials in which there can be only two outcomes are called Bernoulli trials in honor of James Bernoulli (1654-1705). As we shall see, Bernoulli
Chapter 4 Repeated Trials 4.1 Introduction Repeated indepentent trials in which there can be only two outcomes are called Bernoulli trials in honor of James Bernoulli (1654-1705). As we shall see, Bernoulli
Critical Values for the Test of Flatness of a Histogram Using the Bhattacharyya Measure.
 Tina Memo No. 24-1 To Appear in; Towards a Quantitative mehtodology for the Quantitative Assessment of Cerebral Blood Flow in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. PhD Thesis, M.L.J.Scott, Manchester, 24. Critical
Tina Memo No. 24-1 To Appear in; Towards a Quantitative mehtodology for the Quantitative Assessment of Cerebral Blood Flow in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. PhD Thesis, M.L.J.Scott, Manchester, 24. Critical
The number of distributions used in this book is small, basically the binomial and Poisson distributions, and some variations on them.
 Chapter 2 Statistics In the present chapter, I will briefly review some statistical distributions that are used often in this book. I will also discuss some statistical techniques that are important in
Chapter 2 Statistics In the present chapter, I will briefly review some statistical distributions that are used often in this book. I will also discuss some statistical techniques that are important in
Do not copy, post, or distribute
 14 CORRELATION ANALYSIS AND LINEAR REGRESSION Assessing the Covariability of Two Quantitative Properties 14.0 LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this chapter, we discuss two related techniques for assessing a possible
14 CORRELATION ANALYSIS AND LINEAR REGRESSION Assessing the Covariability of Two Quantitative Properties 14.0 LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this chapter, we discuss two related techniques for assessing a possible
Algebra 2 Secondary Mathematics Instructional Guide
 Algebra 2 Secondary Mathematics Instructional Guide 2009-2010 ALGEBRA 2AB (Grade 9, 10 or 11) Prerequisite: Algebra 1AB or Geometry AB 310303 Algebra 2A 310304 Algebra 2B COURSE DESCRIPTION Los Angeles
Algebra 2 Secondary Mathematics Instructional Guide 2009-2010 ALGEBRA 2AB (Grade 9, 10 or 11) Prerequisite: Algebra 1AB or Geometry AB 310303 Algebra 2A 310304 Algebra 2B COURSE DESCRIPTION Los Angeles
Regression Estimation - Least Squares and Maximum Likelihood. Dr. Frank Wood
 Regression Estimation - Least Squares and Maximum Likelihood Dr. Frank Wood Least Squares Max(min)imization Function to minimize w.r.t. β 0, β 1 Q = n (Y i (β 0 + β 1 X i )) 2 i=1 Minimize this by maximizing
Regression Estimation - Least Squares and Maximum Likelihood Dr. Frank Wood Least Squares Max(min)imization Function to minimize w.r.t. β 0, β 1 Q = n (Y i (β 0 + β 1 X i )) 2 i=1 Minimize this by maximizing
2015 SUMMER MATH PACKET
 Name: Date: 05 SUMMER MATH PACKET College Algebra Trig. - I understand that the purpose of the summer packet is for my child to review the topics they have already mastered in previous math classes and
Name: Date: 05 SUMMER MATH PACKET College Algebra Trig. - I understand that the purpose of the summer packet is for my child to review the topics they have already mastered in previous math classes and
Stat 134 Fall 2011: Notes on generating functions
 Stat 3 Fall 0: Notes on generating functions Michael Lugo October, 0 Definitions Given a random variable X which always takes on a positive integer value, we define the probability generating function
Stat 3 Fall 0: Notes on generating functions Michael Lugo October, 0 Definitions Given a random variable X which always takes on a positive integer value, we define the probability generating function
SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Linear Algebra
 1.1. Introduction SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Linear algebra is a specific branch of mathematics dealing with the study of vectors, vector spaces with functions that
1.1. Introduction SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Linear algebra is a specific branch of mathematics dealing with the study of vectors, vector spaces with functions that
Unit 2: Polynomials Guided Notes
 Unit 2: Polynomials Guided Notes Name Period **If found, please return to Mrs. Brandley s room, M 8.** Self Assessment The following are the concepts you should know by the end of Unit 1. Periodically
Unit 2: Polynomials Guided Notes Name Period **If found, please return to Mrs. Brandley s room, M 8.** Self Assessment The following are the concepts you should know by the end of Unit 1. Periodically
Clustering K-means. Clustering images. Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington. November 4, 2014.
 Clustering K-means Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington November 4, 2014 1 Clustering images Set of Images [Goldberger et al.] 2 1 K-means Randomly initialize k centers µ (0)
Clustering K-means Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington November 4, 2014 1 Clustering images Set of Images [Goldberger et al.] 2 1 K-means Randomly initialize k centers µ (0)
Parameter estimation and forecasting. Cristiano Porciani AIfA, Uni-Bonn
 Parameter estimation and forecasting Cristiano Porciani AIfA, Uni-Bonn Questions? C. Porciani Estimation & forecasting 2 Temperature fluctuations Variance at multipole l (angle ~180o/l) C. Porciani Estimation
Parameter estimation and forecasting Cristiano Porciani AIfA, Uni-Bonn Questions? C. Porciani Estimation & forecasting 2 Temperature fluctuations Variance at multipole l (angle ~180o/l) C. Porciani Estimation
Polynomials. This booklet belongs to: Period
 HW Mark: 10 9 8 7 6 RE-Submit Polynomials This booklet belongs to: Period LESSON # DATE QUESTIONS FROM NOTES Questions that I find difficult Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. REVIEW TEST Your teacher
HW Mark: 10 9 8 7 6 RE-Submit Polynomials This booklet belongs to: Period LESSON # DATE QUESTIONS FROM NOTES Questions that I find difficult Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. REVIEW TEST Your teacher
Probability and Distributions
 Probability and Distributions What is a statistical model? A statistical model is a set of assumptions by which the hypothetical population distribution of data is inferred. It is typically postulated
Probability and Distributions What is a statistical model? A statistical model is a set of assumptions by which the hypothetical population distribution of data is inferred. It is typically postulated
Chapter 5 Joint Probability Distributions
 Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers Sixth Edition Douglas C. Montgomery George C. Runger Chapter 5 Joint Probability Distributions 5 Joint Probability Distributions CHAPTER OUTLINE 5-1 Two
Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers Sixth Edition Douglas C. Montgomery George C. Runger Chapter 5 Joint Probability Distributions 5 Joint Probability Distributions CHAPTER OUTLINE 5-1 Two
Polynomial Functions
 Polynomial Functions Polynomials A Polynomial in one variable, x, is an expression of the form a n x 0 a 1 x n 1... a n 2 x 2 a n 1 x a n The coefficients represent complex numbers (real or imaginary),
Polynomial Functions Polynomials A Polynomial in one variable, x, is an expression of the form a n x 0 a 1 x n 1... a n 2 x 2 a n 1 x a n The coefficients represent complex numbers (real or imaginary),
SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Linear Algebra
 SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to 1.1. Introduction Linear algebra is a specific branch of mathematics dealing with the study of vectors, vector spaces with functions that
SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to 1.1. Introduction Linear algebra is a specific branch of mathematics dealing with the study of vectors, vector spaces with functions that
STA2603/205/1/2014 /2014. ry II. Tutorial letter 205/1/
 STA263/25//24 Tutorial letter 25// /24 Distribution Theor ry II STA263 Semester Department of Statistics CONTENTS: Examination preparation tutorial letterr Solutions to Assignment 6 2 Dear Student, This
STA263/25//24 Tutorial letter 25// /24 Distribution Theor ry II STA263 Semester Department of Statistics CONTENTS: Examination preparation tutorial letterr Solutions to Assignment 6 2 Dear Student, This
CHAPTER 2 Review of Algebra
 CHAPTER 2 Review of Algebra 2.1 Real Numbers The text assumes that you know these sets of numbers. You are asked to characterize each set in Problem 1 of Chapter 1 review. Name Symbol Set Examples Counting
CHAPTER 2 Review of Algebra 2.1 Real Numbers The text assumes that you know these sets of numbers. You are asked to characterize each set in Problem 1 of Chapter 1 review. Name Symbol Set Examples Counting
Exponents. Reteach. Write each expression in exponential form (0.4)
 9-1 Exponents You can write a number in exponential form to show repeated multiplication. A number written in exponential form has a base and an exponent. The exponent tells you how many times a number,
9-1 Exponents You can write a number in exponential form to show repeated multiplication. A number written in exponential form has a base and an exponent. The exponent tells you how many times a number,
Discrete Distributions
 Discrete Distributions STA 281 Fall 2011 1 Introduction Previously we defined a random variable to be an experiment with numerical outcomes. Often different random variables are related in that they have
Discrete Distributions STA 281 Fall 2011 1 Introduction Previously we defined a random variable to be an experiment with numerical outcomes. Often different random variables are related in that they have
4. Distributions of Functions of Random Variables
 4. Distributions of Functions of Random Variables Setup: Consider as given the joint distribution of X 1,..., X n (i.e. consider as given f X1,...,X n and F X1,...,X n ) Consider k functions g 1 : R n
4. Distributions of Functions of Random Variables Setup: Consider as given the joint distribution of X 1,..., X n (i.e. consider as given f X1,...,X n and F X1,...,X n ) Consider k functions g 1 : R n
STATISTICS SYLLABUS UNIT I
 STATISTICS SYLLABUS UNIT I (Probability Theory) Definition Classical and axiomatic approaches.laws of total and compound probability, conditional probability, Bayes Theorem. Random variable and its distribution
STATISTICS SYLLABUS UNIT I (Probability Theory) Definition Classical and axiomatic approaches.laws of total and compound probability, conditional probability, Bayes Theorem. Random variable and its distribution
(i) 2-5 (ii) (3 + 23) - 23 (v) 2π
 Number System - Worksheet Question 1: Express the following in the form p/q, where p and q are integers and q 0. Question 2: Express 0.99999... in the form p/q. Are you surprised by your answer? With your
Number System - Worksheet Question 1: Express the following in the form p/q, where p and q are integers and q 0. Question 2: Express 0.99999... in the form p/q. Are you surprised by your answer? With your
Stat 159/259: Linear Algebra Notes
 Stat 159/259: Linear Algebra Notes Jarrod Millman November 16, 2015 Abstract These notes assume you ve taken a semester of undergraduate linear algebra. In particular, I assume you are familiar with the
Stat 159/259: Linear Algebra Notes Jarrod Millman November 16, 2015 Abstract These notes assume you ve taken a semester of undergraduate linear algebra. In particular, I assume you are familiar with the
Estimators for the binomial distribution that dominate the MLE in terms of Kullback Leibler risk
 Ann Inst Stat Math (0) 64:359 37 DOI 0.007/s0463-00-036-3 Estimators for the binomial distribution that dominate the MLE in terms of Kullback Leibler risk Paul Vos Qiang Wu Received: 3 June 009 / Revised:
Ann Inst Stat Math (0) 64:359 37 DOI 0.007/s0463-00-036-3 Estimators for the binomial distribution that dominate the MLE in terms of Kullback Leibler risk Paul Vos Qiang Wu Received: 3 June 009 / Revised:
ESSAI sur la maniére de trouver le terme général des séries recurrentes.
 ESSAI sur la maniére de trouver le terme général des séries recurrentes. JEAN TREMBLEY Mémoires de l Académie royale des sciences et belles-lettres... Berlin, 1797 pp. -105 One knows that the general term
ESSAI sur la maniére de trouver le terme général des séries recurrentes. JEAN TREMBLEY Mémoires de l Académie royale des sciences et belles-lettres... Berlin, 1797 pp. -105 One knows that the general term
Lesson 2. When the exponent is a positive integer, exponential notation is a concise way of writing the product of repeated factors.
 Review of Exponential Notation: Lesson 2 - read to the power of, where is the base and is the exponent - if no exponent is denoted, it is understood to be a power of 1 - if no coefficient is denoted, it
Review of Exponential Notation: Lesson 2 - read to the power of, where is the base and is the exponent - if no exponent is denoted, it is understood to be a power of 1 - if no coefficient is denoted, it
Standard forms for writing numbers
 Standard forms for writing numbers In order to relate the abstract mathematical descriptions of familiar number systems to the everyday descriptions of numbers by decimal expansions and similar means,
Standard forms for writing numbers In order to relate the abstract mathematical descriptions of familiar number systems to the everyday descriptions of numbers by decimal expansions and similar means,
Regression Analysis. Ordinary Least Squares. The Linear Model
 Regression Analysis Linear regression is one of the most widely used tools in statistics. Suppose we were jobless college students interested in finding out how big (or small) our salaries would be 20
Regression Analysis Linear regression is one of the most widely used tools in statistics. Suppose we were jobless college students interested in finding out how big (or small) our salaries would be 20
Lesson 3 Algebraic expression: - the result obtained by applying operations (+, -,, ) to a collection of numbers and/or variables o
 Lesson 3 Algebraic expression: - the result obtained by applying operations (+, -,, ) to a collection of numbers and/or variables o o ( 1)(9) 3 ( 1) 3 9 1 Evaluate the second expression at the left, if
Lesson 3 Algebraic expression: - the result obtained by applying operations (+, -,, ) to a collection of numbers and/or variables o o ( 1)(9) 3 ( 1) 3 9 1 Evaluate the second expression at the left, if
Q 2.0.2: If it s 5:30pm now, what time will it be in 4753 hours? Q 2.0.3: Today is Wednesday. What day of the week will it be in one year from today?
 2 Mod math Modular arithmetic is the math you do when you talk about time on a clock. For example, if it s 9 o clock right now, then it ll be 1 o clock in 4 hours. Clearly, 9 + 4 1 in general. But on a
2 Mod math Modular arithmetic is the math you do when you talk about time on a clock. For example, if it s 9 o clock right now, then it ll be 1 o clock in 4 hours. Clearly, 9 + 4 1 in general. But on a
MAIDSTONE GRAMMAR SCHOOL FOR GIRLS
 MAIDSTONE GRAMMAR SCHOOL FOR GIRLS King Edward VI High School DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS Introduction to A level Maths INDUCTION BOOKLET CONTENTS Reading List... 3 Section 1: FRACTIONS... 4 Section : EXPANDING...
MAIDSTONE GRAMMAR SCHOOL FOR GIRLS King Edward VI High School DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS Introduction to A level Maths INDUCTION BOOKLET CONTENTS Reading List... 3 Section 1: FRACTIONS... 4 Section : EXPANDING...
Stat 5102 Final Exam May 14, 2015
 Stat 5102 Final Exam May 14, 2015 Name Student ID The exam is closed book and closed notes. You may use three 8 1 11 2 sheets of paper with formulas, etc. You may also use the handouts on brand name distributions
Stat 5102 Final Exam May 14, 2015 Name Student ID The exam is closed book and closed notes. You may use three 8 1 11 2 sheets of paper with formulas, etc. You may also use the handouts on brand name distributions
Poisson approximations
 Chapter 9 Poisson approximations 9.1 Overview The Binn, p) can be thought of as the distribution of a sum of independent indicator random variables X 1 + + X n, with {X i = 1} denoting a head on the ith
Chapter 9 Poisson approximations 9.1 Overview The Binn, p) can be thought of as the distribution of a sum of independent indicator random variables X 1 + + X n, with {X i = 1} denoting a head on the ith
A NEW NORMAL FORM FOR QUARTIC EQUATIONS*
 310 RAYMOND GARVER (May-June, A NEW NORMAL FORM FOR QUARTIC EQUATIONS* BY RAYMOND GARVER 1. Introduction. There are a number of well known normal forms to which the general quartic equation may be reduced
310 RAYMOND GARVER (May-June, A NEW NORMAL FORM FOR QUARTIC EQUATIONS* BY RAYMOND GARVER 1. Introduction. There are a number of well known normal forms to which the general quartic equation may be reduced
On monotonicity of expected values of some run-related distributions
 Ann Inst Stat Math (2016) 68:1055 1072 DOI 10.1007/s10463-015-0525-x On monotonicity of expected values of some run-related distributions Sigeo Aki 1 Katuomi Hirano 2 Received: 9 May 2014 / Revised: 11
Ann Inst Stat Math (2016) 68:1055 1072 DOI 10.1007/s10463-015-0525-x On monotonicity of expected values of some run-related distributions Sigeo Aki 1 Katuomi Hirano 2 Received: 9 May 2014 / Revised: 11
Algebra II/ Advanced Algebra II (2016)
 Algebra II/ Advanced Algebra II (2016) Course This course is intended to strengthen Algebra I skills and to develop the basic concepts of Algebra II. The course includes solving equations and inequalities
Algebra II/ Advanced Algebra II (2016) Course This course is intended to strengthen Algebra I skills and to develop the basic concepts of Algebra II. The course includes solving equations and inequalities
SISD Unit Bundles of TEKS/SEs and Pacing Guide Algebra 2
 SISD Unit Bundles of TEKS/SEs and Pacing Guide Algebra 2 UNIT 0 - Preparing for Advanced Algebra Estimated 6 Days TEKS Identify the domain and range of functions. Use the FOIL (First, Outside, Inside,
SISD Unit Bundles of TEKS/SEs and Pacing Guide Algebra 2 UNIT 0 - Preparing for Advanced Algebra Estimated 6 Days TEKS Identify the domain and range of functions. Use the FOIL (First, Outside, Inside,
REGRESSION WITH CORRELATED ERRORS C.A. GLASBEY
 41 REGRESSION WITH CORRELATED ERRORS C.A. GLASBEY SYSTEMATIC RESIDUALS When data exhibit systematic departures from a fitted regression line (see for example Figs 1 and 2), either the regression function
41 REGRESSION WITH CORRELATED ERRORS C.A. GLASBEY SYSTEMATIC RESIDUALS When data exhibit systematic departures from a fitted regression line (see for example Figs 1 and 2), either the regression function
REVIEW Chapter 1 The Real Number System
 REVIEW Chapter The Real Number System In class work: Complete all statements. Solve all exercises. (Section.4) A set is a collection of objects (elements). The Set of Natural Numbers N N = {,,, 4, 5, }
REVIEW Chapter The Real Number System In class work: Complete all statements. Solve all exercises. (Section.4) A set is a collection of objects (elements). The Set of Natural Numbers N N = {,,, 4, 5, }
