Field Validation of Algebraic Equations for Stack and Wind Driven Air Infiltration Calculations
|
|
|
- Alisha Ryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LBNL 4361 Field Validati f Algebraic Equatis fr Stack ad Wid Drive Air Ifiltrati Calculatis Published i ASHRAE HVAC&R Research Jural, Vl. 4, N., April Iai S. Walker* ad David J. Wils** * Eergy Perfrmace f Buildigs Grup Eergy ad Evirmet Divisi Lawrece Berkeley Natial Labratry Berkeley, CA, USA ** Departmet f Mechaical Egieerig Uiversity f Alberta Edmt, AB, Caada ABSTRACT Explicit algebraic equatis fr calculati f wid ad stack drive vetilati were develped by parametrically matchig exact slutis t the flw equatis fr buildig evelpes. These separate wid ad stack effect flw calculati prcedures were icrprated i a simple atural vetilati mdel, AIM-, with empirical fuctis fr superpsiti f wid ad stack effect ad fr estimatig wid shelter. The majr imprvemets ver previus simplified vetilati calculatis are: a pwer law pressureflw relatiship is used t develp the flw equatis frm first priciples, the furace r fireplace flue is icluded as a separate leakage site ad the mdel differetiates betwee huses with basemets (r slab--grade) ad crawlspaces. Over 3400 hurs f measured vetilati rates frm the test huses at the Alberta Hme Heatig Research Facility were used t validate the predictis f vetilati rates ad t cmpare the AIM- predictis t thse f ther vetilati mdels. The AIM- mdel had bias ad scatter errrs f less tha 15% fr wid-dmiated vetilati, ad less tha 7% fr buyacy ("stack-effect") dmiated cases. KEYWORDS Vetilati, ifiltrati, mdelig, pwer-law, wid shelter, furace flue. 1
2 INTRODUCTION This paper is iteded t derive the techical basis fr the relatiships used i the AIM- air ifiltrati mdel, ad t describe the validati prcedure used t evaluate its predictive skill. Sme f the algebraic equatis used i AIM- were preseted i Walker ad Wils (1990a). A simplified versi f AIM- has als bee used fr calculatig attic vetilati rates by Walker, Frest ad Wils (1995). Hwever, derivati r physical explaati f the relatiships were give. AIM- cmbies ideas frm previus vetilati mdels (particularly the LBL mdel f Sherma ad Grimsrud (1980)) with ew ccepts (rigially develped by Walker (1989)) that accut fr pwer law evelpe leakage, separate flue/fireplace leaks ad the differeces betwee huses with basemets (r slab--grade) ad crawlspaces. Additial refiemets regardig wid shelter calculatis ad adjustig widspeeds frm the measuremet site t the buildig have als bee added.. Althugh AIM- has t bee published i cmplete frm the algrithms have bee used sice they were listed by Walker ad Wils (1990a). AIM- is used i the HOT000/AUDIT000 series f eergy aalysis prgrams prduced by Natural Resurces Caada (CHBA (1994)). AIM- has bee used by ther researchers i studies t mdel ifiltrati rates i residetial buildigs. The predictis f AIM- were evaluated by cmparig t measured data by Palmiter ad Bd (1994) ad Palmiter, Bd ad Sherma (1991), ad i the develpmet f a simple methd fr cmbiig atural ad mechaical vetilati by Palmiter ad Bd (1991). I ather study by Hamli ad Pushka (1994), the AIM- algrithms were used t predict ifiltrati rates fr a idr air quality mdel. I the preset study, ver 3400 hurs f measured vetilati rates i tw huses were used t test AIM-. This is part f the data base f vetilati measuremets frm six huses f the Alberta Hme Heatig Research Facility that iclude huses with ther magitudes ad distributis f leakage. The large set f measured data prvided a wide rage f weather cditis ad huse leakage distributis, i rder t exercise all parts f the mdel. Large quatities f measured data were required fr validati because f the substatial hurly variati f atural vetilati rates. The measured data were t used t tue cefficiets i the AIM- mdel equatis. Istead, the measuremets were used t determie typical errrs that might ccur i calculatig vetilati rates based parameters that are easily determied fr mst huses. I.e., rather tha specifyig the size ad lcati f every leak (which is t pssible i mst practical situatis) the parameters used i the mdel are the evelpe leakage characteristics (usually determied usig a fa pressurizati test, e.g., ASTM (1995) r CGSB (1986)) ad simple estimates f the evelpe leakage distributi. The evaluati als icluded cmparis f the measuremets with ther simple vetilati mdels. The ther mdels icluded fr cmparis are: the LBL (USA) mdel Sherma ad Grimsrud (1980), the VFE (Caada) the variable extesis f the LBL mdel by Yuill (1985) ad by Reard (1989), the NRC (Caada) mdel f Shaw (1985), ad the BRE (U.K.) mdel f Warre ad Webb (1980). MODEL DEVELOPMENT The develpmet f the AIM- mdel bega with derivig a exact umerical sluti t the -liear cmbied wid pressure ad buyacy-drive mass flw balace it ad ut f the buildig. This exact sluti is preseted i the Appedix. The algebraic 1
3 relatiships used i AIM- were the develped by trial ad errr as clsed frm apprximatis t this exact sluti. Fr AIM- wid ad stack effect flws are determied separately, the superpsed as a sum f effective pressures, with a crrecti term that accuts fr the iteracti f wid ad stack iduced pressure. This wid ad stack effect iteracti term is the ly empirical cstat determied by cmparig the AIM- equatis t measured data. The AIM- mdel imprves estimates f air ifiltrati rates by icrpratig a pwer law pressure-flw relatiship, Q = C P, it the mdel frm first priciples, by treatig the furace r fireplace flue as a separate leakage site with its w wid shelter, ad by lcatig the flue utlet abve the huse (depedig the actual flue height), rather tha grupig the flue leakage with the ther buildig leaks as i ther mdels. The fllwig simplifyig assumptis were used i the develpmet f the exact vetilati calculatis: The buildig is a sigle, well mixed ze, wall leaks are evely distributed ver fur walls, evely distributed with height, the flue is filled with air at idr rm temperature, ad the flw thrugh all buildig leaks are characterised by the same pwer law expet f pressure,. I rder t simplify the calculati f wid factr, the fllwig assumptis were made abut the pressure cefficiets i crawl spaces ad attics: The pressure cefficiet the exterir flr f the buildig i a crawl space ca be apprximated by averagig the pressure cefficiets the fur exteral surfaces f the crawl space; the pressures crawl space surfaces were the same as the walls abve them each side f the buildig; ad the pressure cefficiet fr the ceilig (i.e. fr the attic) was assumed t be the average f the expsed attic rf ad sffit surfaces. Determiig Algebraic Apprximatis t Exact Numerical Slutis A key part f AIM- was the develpmet f the algebraic apprximatis t the exact umerical slutis f the flw equatis. The chice f algebraic fuctis was made by lkig at plts f the depedece f the wid ad stack factrs (f s ad f w ) the leakage lcati ad pressure expet parameters. A list f cadidate algebraic fuctis that had the same shape ad asympttic limits was the made. The algebraic fuctis fr each parameter were the chse sequetially, with the mst sigificat parameters selected first. Less sigificat parameters were the cmbied i such a way that they did t mdify the existig fuctis. The fuctis fr the mst sigificat parameters were chse t capture mst f the variability (e.g., the depedece wall leakage) ad the additi r multiplicati f ther fuctis are fr secdary effects (e.g., the separate furace flue leakage). Thus a cmpsite fucti was built up that has several primary fuctis embedded withi it. The algebraic equatis i this mdel were develped based several guidig pricipals: The fuctis had t retai dimesial csistecy. The fuctis had t be as simple as pssible (e.g., hyperblic tagets) s that they culd be used i egieerig desig (spreadsheet) calculatis. The fuctis had be rbust (i.e. t blw up fr ay pssible iput parameter, e.g., limits f impermeable walls cmbied with leaky ceiligs) ad smth s as t t give uusual values fr specific cases. The cstats ad expets were chse t be itegers, prper fractis r the leakage parameters themselves.
4 Pwer Law Flw Relatiship Fa pressurizati tests f huses perfrmed by the authrs ad thers, icludig Beach (1979), Sulatisky (1984) ad Warre ad Webb (1980), as well as theretical csideratis frm Walker, Wils ad Sherma (1996), have shw that the rifice flw assumpti used i the may ifiltrati mdels is urealistic, ad that it is better t use a pwer law pressureflw relatiship: Q = C P (1) The parameters C ad are usually fud frm fa pressurizati tests f the buildig. Fr a typical residetial buildig ~ 0.67, abut midway i its rage frm = 0.50 fr rifice flw t = 1.0 fr fully develped lamiar flw. Leakage Distributi Pieerig wrk by Sherma ad Grimsrud (1980) itrduced the idea f usig a set f quatitative parameters t describe the leakage distributi f a buildig evelpe, ad t determie the idepedet stack-drive ad wid-drive flw rates i terms f stack ad wid factrs, f s ad f w. Sherma ad Grimsrud characterised the leakage distributi i terms f R, the fracti f the 4 Pa fa pressurizati leakage area (A 4 ) i the flr plus the ceilig, ad X, the differece i leakage betwee the flr ad ceilig as fractis f the ttal leakage. They defied the "flr" leakage as thse leakage sites that are lcated at (r ear) the level f the buildig flr that rests the basemet walls, slab--grade r crawlspace. The "ceilig" leakage are the leakage sites that are at (r ear) the ceilig level f the upper strey f the buildig. I AIM-, the furace/fireplace flue is treated separately frm the ther leaks. ad additial parameters are itrduced t accut fr this separate leak: the flue leakage fracti, Y, ad a flue height parameter, Z f. The leakage distributi is specified i terms f the rati parameters R, X ad Y, that are calculated frm the leakage cefficiets C flue, C c, C f, ad C w, i Equati (1) rather tha frm the A 4 leakage areas. Explicit slutis require the assumpti that the expet i Equati (1) is the same fr all leakage sites. I this case, the ttal leakage cefficiet, C, is simply the algebraic sum C = C + C + C + C () c f w flue Leakage distributi parameters are defied usig the frmat suggested by Sherma (1980), but usig C istead f leakage area A 4, ad with the additi f a separate flue fracti, Y. C Cf R = C ceilig - flr sum (3) Cc Cf X = C ceilig - flr differece (4) Cflue Y = C flue fracti (5) c + I additi t the distributed leakage f the buildig evelpe expressed i terms f R, X ad Y, the rmalized height Z f f the flue is give by 3
5 Hf Zf = (6) H Stack Effect Ifiltrati The flw iduced by stack effect, Q s, is give by Q s s s = Cf P (7) where P s is the drivig pressure fr buyacy-drive stack-effect flw. Ti - Tut Ps = ρ gh ut (8) Ti The stack factr, f s, was determied usig the umerical sluti f the exact flw equatis t calculate the stack drive vetilati rate flwrate, Q s i Equati (7) ver a wide rage f R, X, Y, Z f ad flw expet,. The explicit algebraic apprximati fr stack factr was develped (as discussed earlier) t give the same geeral depedece f f s these parameters as the umerical sluti f the liear flw balace equatis. The resultig apprximati fr f s is give by Equati (9). The fuctial frm f this apprximati was selected t prduce the crrect limits fr f s whe all leakage is ccetrated i the walls (R = 0), r i the flr ad ceilig (R = 1), fr the ceilig-flr differece rati limits f X = +1.0, -1.0 ad at the X = 0 midpit. 1 + R 1 1 = - M +1 5 f 4 s where (X + ( +1)Y ) M = - R with a limitig value f M = 1.0 fr +1 + F (X + ( +1)Y ) - R (X + ( +1)Y ) fr - R > 1 The additive flue fucti, F, is give by F = Y(Z where f -1) (Xc X ) R 1- (Zf +1) 1- (9) 1 (10) (11) (1) (1- R - Y) Xc = R + - Y(Zf -1) (13) +1 The flue factr F i Equati (9) is always additive because the flue utlet is the highest leakage site ad will always act t icrease the vetilati flws. With very strg flue exfiltrati, eve the ceilig ca becme a ifiltrati site, thrugh which attic air is draw it the buildig. The variable X c is the critical value f the 4
6 ceilig-flr leakage differece X at which the eutral level (zer idr t utdr pressure differece) is lcated at the ceilig i the exact umerical sluti. Fr X > X c the eutral level will be abve the ceilig, ad air will flw i thrugh the ceilig. Fr X < X c rm air will exfiltrate thrugh the ceilig. (These flw directis assume T i > T ut, ad will be reversed if T ut > T i.) The rle f the flue i reducig ceilig exfiltrati is evidet frm the ctributi f the Y factr i Equati (13). The stack factr f s frm Equati (9) is shw i Figure 1a fr typical values f = 0.67, Z f = 1.5 ad Y = 0., ad fr flue, Y=0. Figure 1a shws that treatig the flue as a separate leakage site with a stack height abve the ceilig has a sigificat effect the stack factr f s. I additi, Figure 1a shws the reducti i f s as leakage becmes ccetrated at sigle lcatis, i.e. whe X = R. Whe R = 0 the X = 0 ad ly a sigle pit ca be determied. I Figure 1a, the value f f s fr R = 0 is give by a crss fr the flue case ad by a star fr Y = 0.. Because the AIM- relatiships fr calculatig f s are apprximatis, they d t match the exact umerical sluti perfectly. Differeces betwee the stack factr estimated by Equati (9) ad the exact umerical sluti are abut ±0.005 fr a huse with Y = 0 ( flue) t ±0.01 fr Y=0.. With f s typically abut 0.3, these differeces represet errrs f abut ±1.5% i f s. The maximum differece betwee exact ad apprximate stack factrs ca be as high as 0.03, abut 10% i f s ad i Q s. Wid Effect Ifiltrati Fr AIM- we prpse tw differet mdels, e fr huses with basemets r slab grade cstructi, ad ather fr huses with crawl spaces. The differece betwee the tw is the pressure cefficiet applied t the flr level leaks. Fr basemet r slab grade cstructi the flr level leaks are split it fur equal parts belw each wall, each assumed t have the same pressure cefficiet as the walls abve them. Fr crawlspaces the pressure cefficiets the fur walls were averaged ad used as the pressure cefficiet i the crawlspace actig the flr level leakage betwee the huse ad the crawlspace. Fr bth cases the wid pressure cefficiets measured by Akis et al. (1979) wid tuel simulatis were used fr the walls f the buildig. The attic pressure cefficiet i AIM- is assumed t be a eave-legth weighted average f the pressure cefficiets the eave ad ed wall vets, ad the rf surface vets. The eave vets are assumed t have the same pressure as the adjacet wall. The attic rf vets were assumed t have a size equal t the sum f the eave vets. These algebraically averaged wid pressure cefficiets imply a liear relatiship betwee pressure ad flw, which is clearly t true if 1 i Equati (1). The errrs caused by algebraically averagig pressure cefficiets were determied by applyig the exact -liear flw balacig equatis t fid the actual pressure cefficiets the flr ad ceilig required t balace the flw i ad ut f attics r crawlspaces. The algebraic average pressure cefficiet fr the fur walls f a square buildig with the wid rmal t the upwid wall (the mst extreme case) was -0.5, usig pressure cefficiets frm Akis et al. (1979). The exact equatis shwed that the actual pressure cefficiet required t balace the flws was -0.3, with =0.67. This result shwed that a simple algebraic average f wall pressure cefficiets was sufficietly accurate t defie crawl space r attic pressures. 5
7 Wid Shelter Effect Wid Pressures The wid iduced ifiltrati rate Q w is give by Q = Cf P (14) w w w where P w is give by ( S U) ρut w Pw = (15) Lcal shieldig by earby buildigs, trees ad bstructis is difficult t estimate by ispectig the buildig site, ad ucertaity i estimatig the lcal shelter cefficiet S w is fte the majr surce f errr i estimatig wid drive ifiltrati flw rates. Previus vetilati studies have icluded shelter ly i brad classes, with sharp chages frm class t class. Fr example, Sherma ad Grimsrud (1980) used a lk-up table with five descriptive classes f shelter such as "Light lcal shieldig with few bstructis". T allw fr chages i wid shelter with wid directi, AIM- uses the shelter iterplati fucti suggested by Walker ad Wils (1991) t determie the shelter fr the buildig, S w. This fucti takes estimates f wid shelter fr wids perpedicular t each side f the buildig ad calculates wid shelter fr ay itermediate agle. S w is cmbied i AIM- with a differet cefficiet (S wflue ) fr the tp f the flue stack t give a imprved estimate f the ttal shieldig. These wid shelter factrs are cmbied liearly: S = S (1 Y) S (1.5Y) (16) w w + wflue where the factr 1.5 is a empirical adjustmet fud by cmparig the AIM- mdel predictis t the exact umerical sluti where each leakage site has its w pressure cefficiet ad shelter. S wflue = 1.0 fr a usheltered flue, which prtrudes abve surrudig bstacles, ad S wflue = S w fr a flue tp which has the same wid shelter as the buildig walls. With flue, Y = 0 ad S w = S w. Table 1 gives the AIM- wid shelter factr estimates fr wids perpedicular t the sides f the buildig. This table uses the same shieldig class descripti suggested by Sherma ad Grimsrud (1980), with the additi f a ew class f "cmplete shieldig". Hwever, it is imprtat t te that althugh the terrai classes are the same, the shelter values i Table 1 are t the same as Sherma ad Grimsrud s geeralized shieldig cefficiet. Adjustig Widspeed fr Lcal Terrai The pressure cefficiets used t fid f w were take frm wid tuel tests. Fr mst wid tuel tests the wid pressure cefficiet, Cp, was calculated usig a referece wid speed at eaves height, H. Mst meterlgical data is measured at greater heights ad must be cverted t the eave height t accut fr the chage i widspeed with height i the atmspheric budary layer. Walker ad Wils (1990b) shwed hw meterlgical widspeeds measured remtely frm the buildig site ca be cverted t a eaves height widspeed at the buildig assumig a pwer law budary layer wid velcity prfile. Wieriga (1980) recmmeded usig the wid speed at the tp f the cstat shear stress surface layer whe cvertig wid speeds frm e lcati t ather. Wieriga estimated this height t be abut 80m plus the area-averaged height δz, f the rughess elemets betwee the tw lcatis. 6
8 Usig this referece height, the relatiship fr cvertig airprt widspeeds t lcal cditis is p p met 80 + δz H U = Umet H met 80 (17) + δz p ad p met deped widspeed, grud rughess, slar islati ad atmspheric stability. Irwi (1979) gives values f p frm 0.1 t 0.47 fr a wide rage f cditis. Fr typical urba husig p ~ 0.3, ad fr meterlgical statis lcated at airprts r ther expsed sites p ~ Huses with Basemets r Slab--Grade Cstructi The wid factr, f w, was fud by usig the exact flw balace equatis t determie Q w umerically. f w was the determied by rearragig Equati (14) ad substitutig this value f Q w ad the apprpriate value f P w. The apprximatig fucti fr f w was geerated usig the methds discussed earlier, by calculatig f w ver a wide rage f leakage parameters ad fidig fuctial frms that wuld reprduce the same characteristic depedece the leakage lcati ad pressure expet. The exact umerical sluti fr f w, ad its apprximatig fucti deped the set f wid pressure cefficiets used. I AIM-, the wid pressure cefficiets frm Akis et al. (1979) ad the flue cap pressure cefficiet frm Haysm ad Swit (1987) were used. Usig these pressure cefficiets, f w was fud t be apprximated by 3 ( -Y) X + R Y f = 0.19( - ) 4 w 1- - (J - YJ ) (18) 4 where X + R + Y J = (19) The fuctial frm fr f w was chse t prduce the crrect behaviur fr the limitig values f all leakage ccetrated i either walls, flr r ceilig, ad fr X = 0 where the flr ad ceilig leakage are equal. The flue height, Z f, des t appear i Equati (18) because flue height is ly felt very weakly thrugh the chage i widspeed at the flue/fireplace utlet. The wid factr calculated usig Equati (18) is shw i Figure 1b fr = /3, Y = 0., ad fr flue (Y=0). This figure shws that there is little effect wid factr f w f csiderig the flue leakage as a hle i the ceilig (equivalet t Y=0), vetig it the attic, r as a separate leakage site with its w flue cap pressure cefficiet abve the rf (Y=0.). I the same way as fr the stack factr, whe R = 0 the X = 0 ad ly a sigle pit ca be determied. I Figure 1b, the value f f w fr R = 0 is give by a crss fr the flue case ad by a star fr Y = 0.. It will be shw later that the majr advatage f the separate flue leakage site fr wid effect is t allw it t have differet wid shelter tha the rest f the buildig. As with the stack factr, fr the wid effect there are differeces betwee the exact umerical sluti ad the apprximatig equatis. A typical differece i wid factrs is abut ±0.005, r with f w typically 0., a errr f ±.5%. The maximum errr i f w is abut ±0.0 r abut ±10%. 7
9 Huses With Crawl Spaces Fr a huse with a crawl space, the pressure iside the crawl space was apprximated i AIM- by the average f the fur walls which chaged the depedece f f w X ad R. Usig this assumpti chaged bth the exact umerical sluti (see Appedix) ad the required apprximatig fucti. Therefre a differet wid factr was required fr huses with crawl spaces, f wc. The algebraic apprximati fr f wc was develped usig the same methds as f s ad f w ad is give by: * * * f = 0.19( ) X R Y (0) wc where R * = 1 R + 0. (1) Y Y * = 1 4 () X * 3 4 X X s 1 = (3) R ad 1 R X s = 1.5Y (4) 5 The critical value f the flr-ceilig differece fracti, X crit, abve which f wc des t chage with X is give by = 1 Y (5) X crit I the AIM- apprximati, if X > X crit the X is set equal t X crit. Fr the case where all the leaks are i the walls (R = 0) the wid factr fr huses with crawl spaces shuld be the same as huses withut crawl spaces. Usig Equati (1) fr this case is f wc = 0.76, which is 3% less tha fr a huse with crawl space. The small differece represets the errr caused by usig apprximatig fuctis fr f w ad f wc. Three ther wid tuel data sets, ASHRAE (1989), Liddamet (1986) ad Wire (1984), fr wall ad rf pressure cefficiets were als used t fid umerical slutis fr f w. These ther sets f pressure cefficiets prduce wid factrs that are fuctially the same, but with a differece i the magitude f the leadig cefficiet 0.19 i Equatis (16) ad (18). The tw extreme results are frm Wire's ad ASHRAE's data sets, ad these prduce values f f w that are respectively 10-0% larger ad 10-0% smaller cmpared t the values f f w fud usig the data set frm Akis et al. The exact umerical flw balace equatis were used t estimate the variability f Q s with wid directi. These exact calculatis f the vetilati rate fr each wid directi usig pressure cefficiets frm Akis et al. itrduced a variability i f w f abut ±10% with wid directi. The AIM- mdel eglects these wid directi effects. Cmbiig Wid ad Stack Effect Flws 8
10 The superpsiti techique used i AIM- adds the stack ad wid drive flws -liearly, as if their pressure differeces added, ad itrduces a extra term t accut fr the iteracti f the wid ad stack effects i prducig the iteral pressure that acts t balace the flws i ad ut f the buildig. The AIM- mdel uses a simple first-rder eutral pressure level shift that prduces the superpsiti ( Q Q ) 1 Q = Q s Qw B1 s w (6) where Q is the ttal flw due t cmbied wid ad stack effects [m 3 /s], ad B 1 is the stack ad wid effect iteracti cefficiet, assumed cstat. A study f superpsiti effects i air ifiltrati mdels was perfrmed by Walker ad Wils (1993) t shw that simple pressure additi superpsiti with B 1 = 0 ca prduce as little bias as the superpsiti techique used here. Hwever further parametric studies have shw that the iteracti term with B 1 0 is ecessary whe applied ver a wider rage f leakage distributis. The cstat B 1 was determied empirically usig direct measuremets f air ifiltrati. Aalysis f data frm the six test huses i several differet leakage cfiguratis fr perids where Q s ad Q w were apprximately equal suggested that a reasable estimate fr B 1 is As discussed further i Walker ad Wils (1993), this aalysis methd ivlved least squares fittig t data at lw temperature differeces t determie the relatiship betwee widspeed ad measured vetilati rate ad similarly, usig lw widspeed data t determie a empirical relatiship betwee the temperature differece ad the measured vetilati rate. These empirical relatiships were the used t calculate Q s ad Q w fr ay wid speed r temperature differece. Equati 6 was the used t estimate the ttal vetilati rate ad cmpare it t the measured vetilati rate fr differet values f B 1. The value f B 1 used here prved t be the mst apprpriate ver a wide rage f leakage distributis. Hwever, differet values f B 1 wuld give better results fr sme specific leakage distributis, s this value f B 1 is t uiversal, it just represets the best cmprmise fr the widest rage f cditis. Frtuately, the agreemet betwee measured ad predicted vetilati rates was t very sesitive t the value f B 1 because it is a secd rder effect (cmpared t the sesitivity t f s ad f w, fr example). Give the scatter i measured data, selecti f ther values fr B 1 did t make much differece t the cmparis f measured ad predicted values. Because B 1 is egative it reduces the ttal ifiltrati rate frm the level predicted by a simple sum f pressures superpsiti. It is imprtat t keep i mid that the iteracti cefficiet B 1 is the ly cstat that was determied by fits t measured ifiltrati data. Mdel evaluati, described i the fllwig secti used data sets chse t be dmiated by wid r stack effects, s that iteracti term i Equati (4) ivlvig the empirical cefficiet B 1 was egligible. I this way, the mdel culd be tested agaist idepedet ifiltrati measuremets that played part i its develpmet. Cmparis f AIM- With Other Vetilati Mdels The ther mdels icluded fr cmparis t AIM- ad measured data were: the LBL (USA) mdel Sherma ad Grimsrud (1980), the VFE (Caada) the variable extesis f the LBL mdel by Yuill (1985) ad by Reard (1989), the NRC (Caada) mdel f Shaw (1985), ad the BRE (U.K.) mdel f Warre ad Webb (1980). 9
11 The tw mdels that mst clsely resemble AIM- use variable leakage distributi. They are Sherma's rifice flw mdel frm Sherma ad Grimsrud (1980) (fte referred t as the LBL mdel), ad a variable flw expet mdel, adapted by Reard (1989) frm Yuill's (1985) extesi f Sherma's mdel that used a pwer law fr evelpe leakage. The sigificat differeces betwee AIM- ad Sherma's ad Yuill's mdels are: AIM- des t assume a zer pressure cefficiet fr the attic r flr level leaks. AIM- differetiates betwee huses with crawl spaces ad thse with basemets r slab--grade cstructi. I AIM- the furace flue is icrprated as a separate leakage site, at a rmalized height Z f abve the flr. AIM- uses a pwer law pressure-flw relatiship. AIM- icludes a wid-stack pressure iteracti term which accuts empirically fr the buildig iteral pressure. The tw ther vetilati mdels icluded i this paper fr cmparis d t allw fr variable leakage distributi. A mdel develped i the U.K. by Warre ad Webb (1980) gives three differet stack ad wid factrs based the buildig cfigurati: detached, semi-detached ad terraced (rw huses). The mdel develped by Shaw (1985) calculates stack ad wid flw rates usig cefficiets fitted t measured data at a sigle test huse. Evaluati f Mdels with Measured Air Ifiltrati AIM- ad the ther mdels were evaluated by cmparig predictis t air ifiltrati measuremets i tw huses at the Alberta Hme Heatig Research Facility. Ctiuus hurly ifiltrati measuremets were carried ut i the test huses usig a cstat ccetrati SF 6 tracer gas ijecti system i each huse described i detail by Wils ad Dale (1985) ad Wils ad Walker (199). The test huses were sigle strey wd frame cstructi with full pured ccrete basemets. ad were umbered 4 ad 5 at the test facility. A imprtat aspect f the test facility is that the huses were situated i rural terrai. Because the huses were i a East - West rw they were usheltered fr wids frm Nrth ad Suth ad prvide strg shelter fr each ther fr East ad West wids. Evelpe leakage characteristics were measured i the tw huses usig a fa pressurizati test ver the rage frm 1 Pa t 75 Pa, frm which C, ad the 4 Pa leakage area A 4 were determied, see Table. T remve the effect f buildig size the predictis the vetilati rates were cverted frm m 3 /s t Air Chages per Hur (ACH) by dividig by the buildig vlume (apprximately 0 m 3 fr the test huses used i this study). The leakage distributi was estimated by visual ispecti at the test facility. Fr huse 4 with the flue blcked it was estimated that R=0.5, X=0, Y=0. Fr huse 4 with a 7.5 cm diameter rifice i a 15 cm diameter flue it was estimated that R=0.3, X=0, Y=0.4. Fr huse 5 with a 15 cm diameter flue R=0.1, X=0, Y=0.6. Later, the variability i R ad X prduced by havig differet peple make these estimates will be discussed. The mdels were cmpared by testig their ability t predict wid ad stack dmiated vetilati rates separately. The effects f differet superpsiti methds fr cmbiig wid ad stack effect were discussed elsewhere by Walker ad Wils (1993). The ability f the mdels t predict average hurly vetilati rates fr give ambiet weather cditis is shw by their bias ad scatter cmpared t the measured data. 10
12 The measured data was srted it bis cverig 5 C idr t utdr temperature differece fr stack dmiated vetilati ad 1 m/s wid speed rages fr wid dmiated vetilati. The criteria fr wid dmiated vetilati were U > 1.5 m/s ad T < 10 C. Fr stack dmiated vetilati the criteria were U < 1.5 m/s ad T > 10 C. T be able t srt fr high ad lw wid speeds ad temperature differeces, ad still prvide eugh data fr biig, a large umber f hurs f vetilati mitrig were required. Fr this study 01 hurs were measured i huse 4 ad 154 i huse 5. Large quatities f data were required due t the substatial hurly variati i vetilati rates. The average weather cditis fr each bi were used as the iput values t the mdels ad the mdel predictis fr a give bi are cmpared t the average measured vetilati rate i the bi. Bias idicates the average errr that wuld be btaied ver a lg time perid if each bi f widspeed r temperature differece were equally likely t ccur. Scatter is the variati betwee the predicted ad measured averages frm bi t bi, ad is a idicatr f hw well the mdels fllw treds i the data if the bias is remved. The bias ca be thught f as the errr i prprtiality cstats, ad the scatter as the errr i the fuctial frm f the mdels. The predictis f AIM- ad the ther fur mdels, are cmpared t measured data i Table 3 fr usheltered cditis (Nrth ad Suth wids) fr huse 5 with a 15 cm diameter flue, ad fr huse 4 with the flue blcked. These results shw that AIM- has the best verall perfrmace fr huses with ad withut furace flues. Fr huses with a flue AIM- is clearly superir because the furace flue is treated as a separate leakage site with its w wid pressure ad wid shelter cefficiets. Fr the VFE ad LBL mdels the furace flue leakage is assumed t be i the ceilig. The ther tw mdels d t separate the leakage by lcati the buildig evelpe s that the flue leakage is simply icluded i the ttal leakage fr the buildig, ad t ccetrated at a sigle lcati. The same data used t calculate bias ad scatter i Table 3 are shw i Figures a ad b with bied data where the mea is shw by a square symbl ad e stadard deviati by errr bars. Figure 4a cmpares the widspeed depedece f the mdels fr huse 5 with a pe 15 cm diameter flue where the huse is heavily sheltered (East ad West wids). All the mdels except AIM- sigificatly uderpredict the wid effect ifiltrati rate Q w because they cat have a usheltered flue utlet with a sheltered buildig. The same data pits that were bied fr Figure 4a are shw idividually i Figure 3. This shws the amut f variati preset i the measured data ad the eed fr data biig fr mdel cmpariss. The measured variati was maily due t the wid speed ad directi variability durig the e hur averagig perid fr the measured data where e stadard deviati fr a sigle bi (a rage f widspeeds f 1 m/s) is abut 0.04 ACH. The ucertaity f the ifiltrati measuremets themselves was abut ±5% r ±0.004 ACH (frm Wils ad Dale (1985)). Table 4 presets a summary f the bias ad scatter fr each mdel fr wid dmiated sheltered buildigs, alg with mdel predictis fr a huse withut a flue. The mdels f Shaw ad Warre ad Webb verpredict i part because they are icapable f accutig fr the variati i leakage distributi. Figure 4b illustrates the temperature differece depedece f the mdels fr huse 4 with a 7.5 cm diameter restricti rifice i the flue, ad Table 5 presets a summary f the bias ad scatter fr stack dmiated vetilati. AIM- gave the best verall agreemet because it allwed the flue leakage t be abve the ceilig height fr stack effect. Table 5 als icludes the mdel errrs fr stack dmiated vetilati i huse 5 with flue. As 11
13 with wid dmiated vetilati the assumptis abut leakage distributi, ad mdel cefficiets frm limited data sets itrduced large errrs it the mdel predictis f Shaw ad Warre ad Webb. I mst cases the LBL mdel had the greatest scatter. This was because its assumpti f rifice flw fr the buildig evelpe prduces a icrrect variati i vetilati rate with widspeed ad temperature differece. Sesitivity t Leakage Distributi Oe f the mst difficult iput parameters t estimate is the distributi f leakage betwee the flr, walls ad ceilig. T estimate the magitude f variati likely t ccur i vetilati rates predicted usig differet leakage distributis, a ifrmal survey f the staff wrkig at Alberta Hme Heatig Research Facility was cducted. The survey resulted i eight differet estimates f leakage distributi fr huse 4. The estimated leakage distributis cvered a rage f 10% t 45% fr flrs, 35% t 60% fr walls ad 0% t 40% fr the ceilig. These were sigificat chages i leakage distributi ad idicated the ucertaity with which these values may be estimated, eve by peple familiar with the structure i questi. This rage f leakage distributi parameters resulted i predicted vetilati rates frm 0.91 t ACH, r abut ±7% f the average. Hwever, due t the liear ature f vetilati flws this relatively small ucertaity ccurs ly if the leakage distributi is varied ver a reasable rage. Puttig all f the leakage i a sigle lcati ca cause large chages i calculated vetilati rate. e.g. puttig all f the leakage i the ceilig wuld result i zer vetilati because all f the leakage wuld experiece the same pressure differece. Errrs due t leakage distributi estimates were reduced fr huses with furace ad fireplace flues because a sigificat prprti f the leakage has a specific, well kw, size ad lcati. This aalysis shwed that estimates f leakage distributi are t critical uless extreme values are used. Cclusis A simple algebraic mdel, AIM-, has bee develped t calculate vetilati rates frm weather cditis ad buildig leakage parameters. The explicit relatiships i AIM- were develped t reprduce the results f umerical slutis f the exact flw balace equatis. Over 3400 hurs f measured vetilati rates were used t validate the AIM- predictis. By cmparig the perfrmace f AIM- t bth measured data ad ther simple vetilati mdels the fllwig cclusis ca be made. The pwer law flw relatiship ad the separate treatmet f the furace flue were sigificat imprvemets, reducig errrs by up t a factr f five. Icludig the furace flue (r fireplace) as a separate leakage site allws AIM- t accut fr the effect f the flue atural vetilati rates better tha the ther simple mdels tested i the paper. This is because the furace flue is lcated at a differet height fr stack effect ad has its w wid pressure cefficiet ad wid shelter factr. Usig a pwer law pressure-flw relatiship esures that AIM- has the apprpriate fuctial frm fr the depedece f vetilati rate the wid ad stack pressures. Typical differeces betwee measured vetilati rates ad AIM- mdel predictis were abut ±10% APPENDIX: EXACT NUMERICAL SOLUTION TO FLOW EQUATIONS 1
14 AIM- ad this umerical sluti use the same methd f separatig leak lcati ad geeratig stack ad wid effect pressures. The umerical vetilati mdel explicitly states the flw thrugh each leak lcati as a fucti f the amut f leakage at that lcati ad the effective wid ad stack pressures actig at that lcati. The effective pressure acrss the leak icludes the chage i iterir pressure f the buildig required t balace the flws i ad ut thrugh the evelpe. The chage i iterir pressure is cmm t the flws fr all the leaks ad is determied umerically s that the iflw thrugh the evelpe is equal t the utflw. Oce this iteral pressure is kw, the the flws thrugh all the leaks ad the ttal vetilati flw are als kw. Cmbiig this ttal flw with the ttal evelpe leakage ad the wid ad stack effect pressures allws the calculati f wid ad stack factrs (f w ad f s ) determied frm a exact umerical sluti. Stack Effect The fllwig example calculati shws hw the exact equatis were develped. I this case, T i > T ut ad the eutral pressure plae lies belw the ceilig. The same apprach was used fr ther cases, but t give here fr brevity. The height f each leak was give i -dimesialized frm (Z). It was -dimesialized by dividig by the height f the ceilig abve grade. At the eutral pressure plae: Z = Z. Ceilig leaks have utflw. Q ceilig s = C P (1 Z ) (A1) c Flr leaks have iflw. Qflr = Cf Ps (Z ) (A) The furace/fireplace flue(s) have utflw. Qflue = Cflue Ps ( Zf - Z) (A3) The walls have iflw belw the eutral level ad utflw abve it. Als, the flw geerated by the pressure differece prfile must be itegrated ver the wall due t the liearity f flw with pressure. Fr this itegrati, a elemet f the wall was determied by its fracti f the ttal wall height ad is give by: CwdZ dcw = (A4) H This fractial wall height wasexpressed i dimesial height dz dz = (A5) H Assumig that the leaks are evely distributed with height ver the wall, the the icremetal flw dq w t be itegrated becmes dq = C ( P ( Z Z) ) dz (A6) wall w s Belw the eutral level the ifiltrati flw is 13
15 Z ( Z Z) Q = C P dz (A7) walli w Perfrmig the itegrati gives + 1 Z Qwalli = Cw Ps + 1 s 0 Similarly, fr flw ut abve the eutral level + 1 ( 1 Z ) Qwallut = Cw Ps + 1 (A8) (A9) Equatis (A1), (A), (A3), (A8) ad (A9) ca be writte i terms f R, X ad Y, ad all the iflw terms gruped tgether t give ( R X) ( 1 R Y) +1 Q stacki = C Ps Z + Z (A10) + 1 Similarly fr the utflws (R + X) (1- R - Y) +1 Q = C Ps (1- Z ) + (1- Z ) + Y(Zf Z ) +1 Settig the iflws ad utflws equal gives a sigle equati, with a sigle ukw Z stackut (A11) R Z X = + (1- Z (1- R - Y) ( - (1- Z ) ) + ( Z - (1- Z ) ) +1 Z ) - Y(Z The wid iduced flw at each leakage site was the determied by the flw cefficiet fr each site ad the pressure differece calculated usig Equati (A14). Settig the iflw ad utflw t be equal resulted i a sigle equati that is slved fr the iterir pressure 14 f Z ) (A1) Z was fud usig a Newt-Raphs techique. The et ifiltrati rate was fud by averagig the iflw ad utflw tgether ad substitutig Equati (A1) fr X. After csiderable algebraic maipulati, the stack factr was give by f s Z = 1+ R - Y + Y(Z +1 Z + (1- Z ) (1- Z ) f Z ) Z (A13) The eutral level determied frm the sluti t Equati (A1) was substituted i Equati (A13) t btai a umerical value f the stack factr. Wid Effect Fr wid effect, the pressure acrss each leak was determied by the pressure cefficiet the exterir surface, Cp i, ad the iterir pressure cefficiet, Cp i, that acts t balace the iflws ad utflws. Fr leak i 1 Pi = ρutu ( Cpi Cpi ) (A14)
16 cefficiet. The Cp's were take frm measured wid tuel data. The ceilig ad flr Cp's were discussed i the mai text. The flue pressure cefficiet f -0.5 was take frm measured data by Haysm ad Swit (1987) ad was crrected fr the icreased widspeed at the flue tp cmpared t the referece widspeed at eaves height. Usig the expet, p frm the budary layer wid prfile p flue = -0.5Z f Cp (A15) A value f p = 0.17 was used here. Assumig we have a slab grade r basemet huse the flw fr the walls ad flrs is give by Equati (A16). Q wall, i = C 1- R X + Ai 1 - Y ρ A i ut U ( Cp - Cp ) wall,i i (A16) The prcedure fr a crawlspace is the same except that the flr level leaks were expressed separately. The flw fr the ceilig was give by Q ceilig ( Cpceilig Cpi R + X 1 = C ρutu ) (A17) ad the flw thrugh the flue(s) was Q flue p ( 0.5Zf Cpi 1 = CY ρutu ) (A18) Cp i is the fud by grupig the iflws ad utflws tgether (by lkig at the sig f the pressure differece acrss each leak) ad equatig them. The resultig equati was the slved usig a Newt-Raphs umerical techique. The resultig flws were the used t determie the wid factr, f w. NOMENCLATURE A 4 effective leakage area fr 4.0 Pa pressure differece, m A i area f wall i, m B 1 wid ad stack effect pressure iteracti cefficiet C flw cefficiet, m 3 /spa C c leakage flw cefficiet, C, f ceilig, m 3 /spa at H [m] C f leakage flw cefficiet, C, f flr level leaks, m 3 /spa C flue leakage flw cefficiet, C, f flue ad fireplaces, m 3 /spa at H f C w leakage f walls, m 3 /spa Cp wid pressure cefficiet Cp ceilig wid pressure cefficiet fr ceilig leaks Cp flue wid pressure cefficiet fr flue/fireplace tp Cp i wid pressure cefficiet fr leak i Cp i wid pressure cefficiet fr iside buildig Cp wall,i wid pressure cefficiet fr wall if s stack factr wid factr f w 15
17 f wc wid factr fr a huse with a crawlspace F flue fucti g gravitatial accelerati, m/s H ceilig height f tp strey abve flr (same as eaves height), m H f height f flue utlet abve flr, m H met height at which U met is measured, m J wid factr parameter M stack factr parameter pressure flw expet p met pwer law expet f the wid speed prfile at the meterlgical stati p pwer law expet f the wid speed prfile at the buildig site Q flw rate, m 3 /s Q ceilig ceilig flw, m 3 /s Q flr flr flw, m 3 /sq flue flue/fireplace flw, m 3 /s Q s stack effect flw, m 3 /s Q stacki stack effect iflw, m 3 /s Q stackut stack effect utflw, m 3 /s Q w wid effect flw, m 3 /s Q wall wall flw, m 3 /s Q wall,i wall flw thrugh wall i, m 3 /s Q walli iflw thrugh wall, m 3 /s Q wallut utflw thrugh wall, m 3 /sr cmbied fracti f leakage i the flr plus ceilig R * crawlspace wid factr parameter fr R S w ttal wid shelter factr S w wid shelter factr fr buildig walls S wflue wid shelter factr fr flues ad fireplaces T i idr temperature, K T ut utdr temperature, K U wid speed at eaves height at the buildig site, m/s U met wid speed at the meterlgical site, m/s X differece i leakage fracti betwee the flr ad ceilig X c critical value f X fr which eutral level is at ceilig fr stack effect X crit critical value f X fr which eutral level is at ceilig fr wid effect X s shifted value f X fr crawlspace wid factr X * crawlspace wid factr parameter fr X Y flue leakage fracti Y * crawlspace wid factr parameter fr Y Z rmalized height abve flr Z f rmalized flue height Z rmalized eutral pressure plae height δz area averaged height f terrai rughess elemets P buildig evelpe pressure differece, Pa P i pressure acrss leak i, Pa P s stack effect referece pressure, Pa P w referece wid pressure, Pa T idr-utdr temperature differece, K 16
18 ρut utdr air desity, Kg/m 3 REFERENCES Akis, R.E., J.A. Peterka ad J.E. Cermak Averaged Pressure Cefficiets fr Rectagular Buildigs. Wid Egieerig Vl. 1, Prc. 5th It. Wid Egieerig Cferece. pp ASHRAE ASHRAE Hadbk - Fudametals. Air Flw Arud Buildigs (Chapter 14). Atlata: ASHRAE. ASTM ASTM Stadard E Determiig Air Leakage by Fa Pressurizati. Aual bk f ASTM Stadards. Vl , pp Philadelphia. America Sciety fr Testig ad Materials. Beach, R.K Relative Airtightess f New Husig i the Ottawa Area. Buildig Research Nte N Ottawa: Natial Research Cucil Caada. CGSB CGSB Stadard M86. Determiati f Airtightess f Buildig Evelpes by the Fa Depressurizati Methd. Ottawa. Caada. Caadia Geeral Stadards Bard. CHBA HOT000 Techical Maual. Ottawa. Caada. Caadia Hme Builders Assciati. Hamli, T. ad W. Pushka Predicted ad Measured Air Chage Rates i Huses with Predictis f Occupat IAQ Cmfrt. Prc. 15th AIVC Cferece, Buxt, UK, pp Haysm, J.C. ad M.C. Swit The Ifluece f Termiati Cfigurati the Flw Perfrmace f Flues. Caada Mrtgage ad Husig Crprati Research Reprt. Ottawa: Caada Mrtgage ad Husig Crprati. Irwi, J.S A Theretical Variati f the Wid Prfile Pwer Law Expet as a Fucti f Surface Rughess ad Stability. Atmspheric Evirmet (13): pp
19 Liddamet, M.W Air Ifiltrati Calculati Techiques - A Applicatis Guide. Air Ifiltrati ad Vetilati Cetre, Brackell, U.K. Palmiter, L. ad T. Bd Mdeled ad Measured Ifiltrati II - A Detailed Case Study f Three Hmes. Electric Pwer Research Istitute Reprt TR Pal Alt, Califria: Electric Pwer Research Istitute. Palmiter, L. ad T. Bd Iteracti f Mechaical Systems ad Natural Ifiltrati, Prc. 1th AIVC Cferece, Ottawa, Caada, pp Palmiter, L., T. Bd ad M. Sherma Mdeled ad Measured Ifiltrati - A Detailed Case Study f Fur Electrically Heated Hmes. Electric Pwer Research Istitute Reprt CU 737. Pal Alt, Califria: Electric Pwer Research Istitute. Reard, J.T Air Ifiltrati Mdellig Study. Reprt #CR fr Eergy Mies ad Resurces Caada. Ottawa: Natial Research Cucil Caada. Shaw, C.Y Methds fr Estimatig Air Chage Rates ad Sizig Mechaical Vetilati Systems fr Huses. Buildig Research Nte 37. Ottawa: Natial Research Cucil Caada. Sherma, M.H. ad D.T. Grimsrud Measuremet f Ifiltrati Usig Fa Pressurizati ad Weather Data. Reprt #LBL Lawrece Berkeley Labratry, Berkeley, Califria. Sulatisky, M Airtightess Tests 00 New Huses Acrss Caada: Summary f Results. Buildigs Eergy Techlgy Trasfer Prgram, Publicati N Ottawa, Caada: Eergy Mies ad Resurces Caada. Walker, I.S Sigle Ze Air Ifiltrati Mdellig. M.Sc. Thesis, Departmet f Mechaical Egieerig, Uiversity f Alberta, Edmt, Caada. Walker, I.S. ad D.J. Wils. 1990a. Icludig furace flue leakage i a simple air ifiltrati mdel. Air Ifiltrati Review, Vl.11, N.4, September 1990, AIVC, Cvetry, U.K. Walker, I.S. ad D.J. Wils. 1990b. The Alberta Ifiltrati Mdel: AIM-. Techical reprt N. 71. Edmt: Uiversity f Alberta, Dept. f Mechaical Egieerig. Walker, I.S. ad D.J. Wils Evaluatig Mdels fr Superpsiti f Wid ad Stack Effect i Air Ifiltrati. Buildig ad Evirmet, Vl. 8, N., pp , 1993, Oxfrd, U.K., Pergam Press. 18
20 Walker, I.S. ad D.J. Wils Simple Methds fr Imprvig Estimates f Natural Vetilati Rates. Prc. 15th AIVC Cferece, Buxt, UK. September Walker, I.S., T.W. Frest ad D.J. Wils A Simple Mdel fr Calculatig Attic Vetilati Rates, Prc. 16th AIVC Cferece, Palm Sprigs, USA. September Walker, I.S., D.J. Wils ad M.H. Sherma Des the Pwer Law Rule fr Lw Pressure Buildig Evelpe Leakage? Prc. 17th AIVC Cferece. Gtebrg. Swede. September Warre, P.R., ad B.C. Webb The Relatiship Betwee Tracer Gas ad Pressurizati Techiques i Dwelligs, Prc. First Air Ifiltrati Ceter Cferece. pp , Widsr, U.K., Wieriga, J., Represetativeess f wid bservatis at airprts. Bulleti Am. Met. Sc., N. 61, pp Wils, D.J. ad I.S. Walker Feasibility f Passive Vetilati by Cstat Area Vets t Maitai Idr Air Quality. Prc. Idr Air Quality '9. ASHRAE/ACGIH/AIHA Cf., Sa Fracisc, Octber 199. Wils, D.J., ad J.D. Dale Measuremet f Wid Shelter Effects Air Ifiltrati. Prceedigs f Cferece Thermal Perfrmace f the Exterir Evelpes f Buildigs, Clearwater Beach, Flrida, Dec Wils, D.J. ad I.S. Walker Wid Shelter Effects fr a Rw f Huses. Prc. 1th AIVC Cf., Ottawa, Caada. Wire, B.G Wid Pressure Distributis ad Vetilati Lsses fr a Sigle- Family Huse as Iflueced by Surrudig Buildigs - A Wid Tuel Study, Prc. Air Ifiltrati Cetre Wid Pressure Wrkshp, pp , Brussels, Belgium, Yuill, G.K Ivestigati f Surces f Errr ad Their Effects the Accuracy f the Miimum Natural Ifiltrati Prcedure. Reprt fr Saskatchewa Research Cucil. Saskat, Caada : Saskatchewa Research Cucil. 19
21 Table 1. Estimates f Shelter Cefficiet Shelter Cefficiet, S w Descripti 1.00 N bstructis r lcal shieldig 0.90 Light lcal shieldig with few bstructis withi tw buildig heights 0.70 Lcal shieldig with may large bstructis withi tw buildig heights 0.50 Heavily shielded, may large bstructis withi e buildig height 0.30 Cmplete shieldig with large buildigs immediately adjacet Huse Number Flue Cfigurati Table. Huse Leakage Characteristics Flw cefficiet, C [m 3 /spa ] Flw expet, Leakage area at 4 Pa, A 4 [cm ] 4 clsed pe with 7.5 cm diameter rifice 5 pe with 15 cm diameter flue
22 Table 3. Differeces Betwee Mdel Predictis ad Measured Data fr Bied Averages Wid Dmiated Vetilati fr Usheltered Buildigs at AHHRF Huse 4: flue (85 hurs) Huse 5: 15 cm flue (79 hurs) Mdel Bias Scatter Bias Scatter AIM- 10% (0.008 ACH) LBL (Sherma) 34% (0.018 ACH) VFE (Yuill/Reard) 5% (0.0 ACH) Shaw 45% (0.038 ACH) Warre ad Webb 4% (0.005 ACH) 3% (0.00 ACH) 18% (0.016 ACH) 4% (0.003 ACH) % (0.00 ACH) 5% (0.003 ACH) -8% (-0.0 ACH) -0% ( ACH) -% ( ACH) -1% ( ACH) -19% ( ACH) 4% (0.011 ACH) 6% (0.016 ACH) 3% (0.009 ACH) 8% (0.017 ACH) % (0.009 ACH) Table 4. Mdel Errrs fr Bied Averages f Wid Dmiated Vetilati fr a Sheltered Buildig at AHHRF Huse 4: flue (464 Hurs) Huse 5: 15 cm flue (461 Hurs) Mdel Bias scatter Bias Scatter AIM- % (0.003 ACH) LBL (Sherma) 11% (0.00 ACH) VFE (Yuill/Reard) -7% ( ACH) Shaw 65% (0.030 ACH) Warre ad Webb 43% (0.07 ACH) 14% (0.006 ACH) 14% (0.008 ACH) 7% (0.004 ACH) 13% (0.007 ACH) 4% (0.011 ACH) -1% ( ACH) -60% ( ACH) -66% (-0.15 ACH) -9% (-0.1 ACH) -35% (-0.11 ACH) 4% (0.011 ACH) 8% (0.078 ACH) 3% (0.063 ACH) 30% (0.084 ACH) 6% (0.014 ACH) 1
23 Table 5. Mdel Errrs fr Bied Averages f Stack Dmiated Vetilati Huse 4: 7.5 cm flue rifice (10 Hurs) Huse 5: N flue (74 Hurs) Mdel Bias Scatter Bias Scatter AIM- -3% ( ACH) % (0.00 ACH) 1% (0.001 ACH) 7% (0.005 ACH) LBL (Sherma) -14% ( ACH) 7% (0.008 ACH) 4% (0.015 ACH) 1% (0.009 ACH) VFE (Yuill/Reard) -6% (-0.03 ACH) % (0.00 ACH) 4% (0.00 ACH) 7% (0.005 ACH) Shaw 4.6% (0.051 ACH) % (0.00 ACH) 45% (0.03 ACH) 7% (0.005 ACH) Warre ad Webb -44% ( ACH) 5% (0.006 ACH) -% ( ACH) 9% (0.007 ACH)
ENGI 4421 Central Limit Theorem Page Central Limit Theorem [Navidi, section 4.11; Devore sections ]
![ENGI 4421 Central Limit Theorem Page Central Limit Theorem [Navidi, section 4.11; Devore sections ] ENGI 4421 Central Limit Theorem Page Central Limit Theorem [Navidi, section 4.11; Devore sections ]](/thumbs/80/82121747.jpg) ENGI 441 Cetral Limit Therem Page 11-01 Cetral Limit Therem [Navidi, secti 4.11; Devre sectis 5.3-5.4] If X i is t rmally distributed, but E X i, V X i ad is large (apprximately 30 r mre), the, t a gd
ENGI 441 Cetral Limit Therem Page 11-01 Cetral Limit Therem [Navidi, secti 4.11; Devre sectis 5.3-5.4] If X i is t rmally distributed, but E X i, V X i ad is large (apprximately 30 r mre), the, t a gd
Chapter 3.1: Polynomial Functions
 Ntes 3.1: Ply Fucs Chapter 3.1: Plymial Fuctis I Algebra I ad Algebra II, yu ecutered sme very famus plymial fuctis. I this secti, yu will meet may ther members f the plymial family, what sets them apart
Ntes 3.1: Ply Fucs Chapter 3.1: Plymial Fuctis I Algebra I ad Algebra II, yu ecutered sme very famus plymial fuctis. I this secti, yu will meet may ther members f the plymial family, what sets them apart
Axial Temperature Distribution in W-Tailored Optical Fibers
 Axial Temperature Distributi i W-Tailred Optical ibers Mhamed I. Shehata (m.ismail34@yah.cm), Mustafa H. Aly(drmsaly@gmail.cm) OSA Member, ad M. B. Saleh (Basheer@aast.edu) Arab Academy fr Sciece, Techlgy
Axial Temperature Distributi i W-Tailred Optical ibers Mhamed I. Shehata (m.ismail34@yah.cm), Mustafa H. Aly(drmsaly@gmail.cm) OSA Member, ad M. B. Saleh (Basheer@aast.edu) Arab Academy fr Sciece, Techlgy
MATH Midterm Examination Victor Matveev October 26, 2016
 MATH 33- Midterm Examiati Victr Matveev Octber 6, 6. (5pts, mi) Suppse f(x) equals si x the iterval < x < (=), ad is a eve peridic extesi f this fucti t the rest f the real lie. Fid the csie series fr
MATH 33- Midterm Examiati Victr Matveev Octber 6, 6. (5pts, mi) Suppse f(x) equals si x the iterval < x < (=), ad is a eve peridic extesi f this fucti t the rest f the real lie. Fid the csie series fr
[1 & α(t & T 1. ' ρ 1
 NAME 89.304 - IGNEOUS & METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY DENSITY & VISCOSITY OF MAGMAS I. Desity The desity (mass/vlume) f a magma is a imprtat parameter which plays a rle i a umber f aspects f magma behavir ad evluti.
NAME 89.304 - IGNEOUS & METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY DENSITY & VISCOSITY OF MAGMAS I. Desity The desity (mass/vlume) f a magma is a imprtat parameter which plays a rle i a umber f aspects f magma behavir ad evluti.
Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers. David Miller
 Quatum Mechaics fr Scietists ad Egieers David Miller Time-depedet perturbati thery Time-depedet perturbati thery Time-depedet perturbati basics Time-depedet perturbati thery Fr time-depedet prblems csider
Quatum Mechaics fr Scietists ad Egieers David Miller Time-depedet perturbati thery Time-depedet perturbati thery Time-depedet perturbati basics Time-depedet perturbati thery Fr time-depedet prblems csider
Grade 3 Mathematics Course Syllabus Prince George s County Public Schools
 Ctet Grade 3 Mathematics Curse Syllabus Price Gerge s Cuty Public Schls Prerequisites: Ne Curse Descripti: I Grade 3, istructial time shuld fcus fur critical areas: (1) develpig uderstadig f multiplicati
Ctet Grade 3 Mathematics Curse Syllabus Price Gerge s Cuty Public Schls Prerequisites: Ne Curse Descripti: I Grade 3, istructial time shuld fcus fur critical areas: (1) develpig uderstadig f multiplicati
5.1 Two-Step Conditional Density Estimator
 5.1 Tw-Step Cditial Desity Estimatr We ca write y = g(x) + e where g(x) is the cditial mea fucti ad e is the regressi errr. Let f e (e j x) be the cditial desity f e give X = x: The the cditial desity
5.1 Tw-Step Cditial Desity Estimatr We ca write y = g(x) + e where g(x) is the cditial mea fucti ad e is the regressi errr. Let f e (e j x) be the cditial desity f e give X = x: The the cditial desity
Physical Chemistry Laboratory I CHEM 445 Experiment 2 Partial Molar Volume (Revised, 01/13/03)
 Physical Chemistry Labratry I CHEM 445 Experimet Partial Mlar lume (Revised, 0/3/03) lume is, t a gd apprximati, a additive prperty. Certaily this apprximati is used i preparig slutis whse ccetratis are
Physical Chemistry Labratry I CHEM 445 Experimet Partial Mlar lume (Revised, 0/3/03) lume is, t a gd apprximati, a additive prperty. Certaily this apprximati is used i preparig slutis whse ccetratis are
A Study on Estimation of Lifetime Distribution with Covariates Under Misspecification
 Prceedigs f the Wrld Cgress Egieerig ad Cmputer Sciece 2015 Vl II, Octber 21-23, 2015, Sa Fracisc, USA A Study Estimati f Lifetime Distributi with Cvariates Uder Misspecificati Masahir Ykyama, Member,
Prceedigs f the Wrld Cgress Egieerig ad Cmputer Sciece 2015 Vl II, Octber 21-23, 2015, Sa Fracisc, USA A Study Estimati f Lifetime Distributi with Cvariates Uder Misspecificati Masahir Ykyama, Member,
Solutions. Definitions pertaining to solutions
 Slutis Defiitis pertaiig t slutis Slute is the substace that is disslved. It is usually preset i the smaller amut. Slvet is the substace that des the disslvig. It is usually preset i the larger amut. Slubility
Slutis Defiitis pertaiig t slutis Slute is the substace that is disslved. It is usually preset i the smaller amut. Slvet is the substace that des the disslvig. It is usually preset i the larger amut. Slubility
BIO752: Advanced Methods in Biostatistics, II TERM 2, 2010 T. A. Louis. BIO 752: MIDTERM EXAMINATION: ANSWERS 30 November 2010
 BIO752: Advaced Methds i Bistatistics, II TERM 2, 2010 T. A. Luis BIO 752: MIDTERM EXAMINATION: ANSWERS 30 Nvember 2010 Questi #1 (15 pits): Let X ad Y be radm variables with a jit distributi ad assume
BIO752: Advaced Methds i Bistatistics, II TERM 2, 2010 T. A. Luis BIO 752: MIDTERM EXAMINATION: ANSWERS 30 Nvember 2010 Questi #1 (15 pits): Let X ad Y be radm variables with a jit distributi ad assume
Intermediate Division Solutions
 Itermediate Divisi Slutis 1. Cmpute the largest 4-digit umber f the frm ABBA which is exactly divisible by 7. Sluti ABBA 1000A + 100B +10B+A 1001A + 110B 1001 is divisible by 7 (1001 7 143), s 1001A is
Itermediate Divisi Slutis 1. Cmpute the largest 4-digit umber f the frm ABBA which is exactly divisible by 7. Sluti ABBA 1000A + 100B +10B+A 1001A + 110B 1001 is divisible by 7 (1001 7 143), s 1001A is
ENGI 4421 Central Limit Theorem Page Central Limit Theorem [Navidi, section 4.11; Devore sections ]
![ENGI 4421 Central Limit Theorem Page Central Limit Theorem [Navidi, section 4.11; Devore sections ] ENGI 4421 Central Limit Theorem Page Central Limit Theorem [Navidi, section 4.11; Devore sections ]](/thumbs/89/100002025.jpg) ENGI 441 Cetral Limit Therem Page 11-01 Cetral Limit Therem [Navidi, secti 4.11; Devre sectis 5.3-5.4] If X i is t rmally distributed, but E X i, V X i ad is large (apprximately 30 r mre), the, t a gd
ENGI 441 Cetral Limit Therem Page 11-01 Cetral Limit Therem [Navidi, secti 4.11; Devre sectis 5.3-5.4] If X i is t rmally distributed, but E X i, V X i ad is large (apprximately 30 r mre), the, t a gd
Ch. 1 Introduction to Estimation 1/15
 Ch. Itrducti t stimati /5 ample stimati Prblem: DSB R S f M f s f f f ; f, φ m tcsπf t + φ t f lectrics dds ise wt usually white BPF & mp t s t + w t st. lg. f & φ X udi mp cs π f + φ t Oscillatr w/ f
Ch. Itrducti t stimati /5 ample stimati Prblem: DSB R S f M f s f f f ; f, φ m tcsπf t + φ t f lectrics dds ise wt usually white BPF & mp t s t + w t st. lg. f & φ X udi mp cs π f + φ t Oscillatr w/ f
Multi-objective Programming Approach for. Fuzzy Linear Programming Problems
 Applied Mathematical Scieces Vl. 7 03. 37 8-87 HIKARI Ltd www.m-hikari.cm Multi-bective Prgrammig Apprach fr Fuzzy Liear Prgrammig Prblems P. Padia Departmet f Mathematics Schl f Advaced Scieces VIT Uiversity
Applied Mathematical Scieces Vl. 7 03. 37 8-87 HIKARI Ltd www.m-hikari.cm Multi-bective Prgrammig Apprach fr Fuzzy Liear Prgrammig Prblems P. Padia Departmet f Mathematics Schl f Advaced Scieces VIT Uiversity
ALE 26. Equilibria for Cell Reactions. What happens to the cell potential as the reaction proceeds over time?
 Name Chem 163 Secti: Team Number: AL 26. quilibria fr Cell Reactis (Referece: 21.4 Silberberg 5 th editi) What happes t the ptetial as the reacti prceeds ver time? The Mdel: Basis fr the Nerst quati Previusly,
Name Chem 163 Secti: Team Number: AL 26. quilibria fr Cell Reactis (Referece: 21.4 Silberberg 5 th editi) What happes t the ptetial as the reacti prceeds ver time? The Mdel: Basis fr the Nerst quati Previusly,
D.S.G. POLLOCK: TOPICS IN TIME-SERIES ANALYSIS STATISTICAL FOURIER ANALYSIS
 STATISTICAL FOURIER ANALYSIS The Furier Represetati f a Sequece Accrdig t the basic result f Furier aalysis, it is always pssible t apprximate a arbitrary aalytic fucti defied ver a fiite iterval f the
STATISTICAL FOURIER ANALYSIS The Furier Represetati f a Sequece Accrdig t the basic result f Furier aalysis, it is always pssible t apprximate a arbitrary aalytic fucti defied ver a fiite iterval f the
Sound Absorption Characteristics of Membrane- Based Sound Absorbers
 Purdue e-pubs Publicatis f the Ray W. Schl f Mechaical Egieerig 8-28-2003 Sud Absrpti Characteristics f Membrae- Based Sud Absrbers J Stuart Blt, blt@purdue.edu Jih Sg Fllw this ad additial wrks at: http://dcs.lib.purdue.edu/herrick
Purdue e-pubs Publicatis f the Ray W. Schl f Mechaical Egieerig 8-28-2003 Sud Absrpti Characteristics f Membrae- Based Sud Absrbers J Stuart Blt, blt@purdue.edu Jih Sg Fllw this ad additial wrks at: http://dcs.lib.purdue.edu/herrick
Study in Cylindrical Coordinates of the Heat Transfer Through a Tow Material-Thermal Impedance
 Research ural f Applied Scieces, Egieerig ad echlgy (): 9-63, 3 ISSN: 4-749; e-issn: 4-7467 Maxwell Scietific Orgaiati, 3 Submitted: uly 4, Accepted: September 8, Published: May, 3 Study i Cylidrical Crdiates
Research ural f Applied Scieces, Egieerig ad echlgy (): 9-63, 3 ISSN: 4-749; e-issn: 4-7467 Maxwell Scietific Orgaiati, 3 Submitted: uly 4, Accepted: September 8, Published: May, 3 Study i Cylidrical Crdiates
The Excel FFT Function v1.1 P. T. Debevec February 12, The discrete Fourier transform may be used to identify periodic structures in time ht.
 The Excel FFT Fucti v P T Debevec February 2, 26 The discrete Furier trasfrm may be used t idetify peridic structures i time ht series data Suppse that a physical prcess is represeted by the fucti f time,
The Excel FFT Fucti v P T Debevec February 2, 26 The discrete Furier trasfrm may be used t idetify peridic structures i time ht series data Suppse that a physical prcess is represeted by the fucti f time,
5.80 Small-Molecule Spectroscopy and Dynamics
 MIT OpeCurseWare http://cw.mit.edu 5.8 Small-Mlecule Spectrscpy ad Dyamics Fall 8 Fr ifrmati abut citig these materials r ur Terms f Use, visit: http://cw.mit.edu/terms. 5.8 Lecture #33 Fall, 8 Page f
MIT OpeCurseWare http://cw.mit.edu 5.8 Small-Mlecule Spectrscpy ad Dyamics Fall 8 Fr ifrmati abut citig these materials r ur Terms f Use, visit: http://cw.mit.edu/terms. 5.8 Lecture #33 Fall, 8 Page f
, the random variable. and a sample size over the y-values 0:1:10.
 Lecture 3 (4//9) 000 HW PROBLEM 3(5pts) The estimatr i (c) f PROBLEM, p 000, where { } ~ iid bimial(,, is 000 e f the mst ppular statistics It is the estimatr f the ppulati prprti I PROBLEM we used simulatis
Lecture 3 (4//9) 000 HW PROBLEM 3(5pts) The estimatr i (c) f PROBLEM, p 000, where { } ~ iid bimial(,, is 000 e f the mst ppular statistics It is the estimatr f the ppulati prprti I PROBLEM we used simulatis
WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY
 WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY PLASMA PHYSICS GROUP INTERNAL REPORT PL - 045 Mea Optical epth ad Optical Escape Factr fr Helium Trasitis i Helic Plasmas R.F. Bivi Nvember 000 Revised March 00 TABLE OF CONTENT.0
WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY PLASMA PHYSICS GROUP INTERNAL REPORT PL - 045 Mea Optical epth ad Optical Escape Factr fr Helium Trasitis i Helic Plasmas R.F. Bivi Nvember 000 Revised March 00 TABLE OF CONTENT.0
Study of Energy Eigenvalues of Three Dimensional. Quantum Wires with Variable Cross Section
 Adv. Studies Ther. Phys. Vl. 3 009. 5 3-0 Study f Eergy Eigevalues f Three Dimesial Quatum Wires with Variale Crss Secti M.. Sltai Erde Msa Departmet f physics Islamic Aad Uiversity Share-ey rach Ira alrevahidi@yah.cm
Adv. Studies Ther. Phys. Vl. 3 009. 5 3-0 Study f Eergy Eigevalues f Three Dimesial Quatum Wires with Variale Crss Secti M.. Sltai Erde Msa Departmet f physics Islamic Aad Uiversity Share-ey rach Ira alrevahidi@yah.cm
E o and the equilibrium constant, K
 lectrchemical measuremets (Ch -5 t 6). T state the relati betwee ad K. (D x -b, -). Frm galvaic cell vltage measuremet (a) K sp (D xercise -8, -) (b) K sp ad γ (D xercise -9) (c) K a (D xercise -G, -6)
lectrchemical measuremets (Ch -5 t 6). T state the relati betwee ad K. (D x -b, -). Frm galvaic cell vltage measuremet (a) K sp (D xercise -8, -) (b) K sp ad γ (D xercise -9) (c) K a (D xercise -G, -6)
Author. Introduction. Author. o Asmir Tobudic. ISE 599 Computational Modeling of Expressive Performance
 ISE 599 Cmputatial Mdelig f Expressive Perfrmace Playig Mzart by Aalgy: Learig Multi-level Timig ad Dyamics Strategies by Gerhard Widmer ad Asmir Tbudic Preseted by Tsug-Ha (Rbert) Chiag April 5, 2006
ISE 599 Cmputatial Mdelig f Expressive Perfrmace Playig Mzart by Aalgy: Learig Multi-level Timig ad Dyamics Strategies by Gerhard Widmer ad Asmir Tbudic Preseted by Tsug-Ha (Rbert) Chiag April 5, 2006
MATHEMATICS 9740/01 Paper 1 14 Sep hours
 Cadidate Name: Class: JC PRELIMINARY EXAM Higher MATHEMATICS 9740/0 Paper 4 Sep 06 3 hurs Additial Materials: Cver page Aswer papers List f Frmulae (MF5) READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST Write yur full ame
Cadidate Name: Class: JC PRELIMINARY EXAM Higher MATHEMATICS 9740/0 Paper 4 Sep 06 3 hurs Additial Materials: Cver page Aswer papers List f Frmulae (MF5) READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST Write yur full ame
NOT FOR A400. Urbia 103 DUNDAS CORPORATION 103 DUNDAS STREET W OAKVILLE, ONTARIO NORTH ELEVATIONS LEGEND NORTH ELEVATION 1 : 125
 TES: ALL GUDS T MEET REQUIREMETS F THE BC 202 MAUFACTURER/SUPPLIER T PRVIDE EGIEERED, STAMPED SHP DRIGS CMPLETE WITH MUTIG DETAILS GUDS SHALL CMPLY WITH BC 337, 3465 AD 40 GUDS SHALL CMPLY WITH BC 436
TES: ALL GUDS T MEET REQUIREMETS F THE BC 202 MAUFACTURER/SUPPLIER T PRVIDE EGIEERED, STAMPED SHP DRIGS CMPLETE WITH MUTIG DETAILS GUDS SHALL CMPLY WITH BC 337, 3465 AD 40 GUDS SHALL CMPLY WITH BC 436
Chapter 4. Problem Solutions
 Chapter 4. Prblem Slutis. The great majrity f alpha particles pass thrugh gases ad thi metal fils with deflectis. T what cclusi abut atmic structure des this bservati lead? The fact that mst particles
Chapter 4. Prblem Slutis. The great majrity f alpha particles pass thrugh gases ad thi metal fils with deflectis. T what cclusi abut atmic structure des this bservati lead? The fact that mst particles
A New Method for Finding an Optimal Solution. of Fully Interval Integer Transportation Problems
 Applied Matheatical Scieces, Vl. 4, 200,. 37, 89-830 A New Methd fr Fidig a Optial Sluti f Fully Iterval Iteger Trasprtati Prbles P. Padia ad G. Nataraja Departet f Matheatics, Schl f Advaced Scieces,
Applied Matheatical Scieces, Vl. 4, 200,. 37, 89-830 A New Methd fr Fidig a Optial Sluti f Fully Iterval Iteger Trasprtati Prbles P. Padia ad G. Nataraja Departet f Matheatics, Schl f Advaced Scieces,
x 2 x 3 x b 0, then a, b, c log x 1 log z log x log y 1 logb log a dy 4. dx As tangent is perpendicular to the x axis, slope
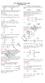 The agle betwee the tagets draw t the parabla y = frm the pit (-,) 5 9 6 Here give pit lies the directri, hece the agle betwee the tagets frm that pit right agle Ratig :EASY The umber f values f c such
The agle betwee the tagets draw t the parabla y = frm the pit (-,) 5 9 6 Here give pit lies the directri, hece the agle betwee the tagets frm that pit right agle Ratig :EASY The umber f values f c such
A Hartree-Fock Calculation of the Water Molecule
 Chemistry 460 Fall 2017 Dr. Jea M. Stadard Nvember 29, 2017 A Hartree-Fck Calculati f the Water Mlecule Itrducti A example Hartree-Fck calculati f the water mlecule will be preseted. I this case, the water
Chemistry 460 Fall 2017 Dr. Jea M. Stadard Nvember 29, 2017 A Hartree-Fck Calculati f the Water Mlecule Itrducti A example Hartree-Fck calculati f the water mlecule will be preseted. I this case, the water
Electrostatics. . where,.(1.1) Maxwell Eqn. Total Charge. Two point charges r 12 distance apart in space
 Maxwell Eq. E ρ Electrstatics e. where,.(.) first term is the permittivity i vacuum 8.854x0 C /Nm secd term is electrical field stregth, frce/charge, v/m r N/C third term is the charge desity, C/m 3 E
Maxwell Eq. E ρ Electrstatics e. where,.(.) first term is the permittivity i vacuum 8.854x0 C /Nm secd term is electrical field stregth, frce/charge, v/m r N/C third term is the charge desity, C/m 3 E
APPLICATION OF FEM ANALYSIS METHODS TO A CYLINDER-CYLINDER INTERSECTION STRUCTURE
 18th Iteratial Cferece Structural Mechaics i Reactr echlgy (SMiR 18) Beijig, Chia, August 7-12, 25 SMiR18-F7-4 APPLICAION OF FEM ANALYSIS MEHODS O A CYLINDER-CYLINDER INERSECION SRUCURE Lipig XUE G.E.O.
18th Iteratial Cferece Structural Mechaics i Reactr echlgy (SMiR 18) Beijig, Chia, August 7-12, 25 SMiR18-F7-4 APPLICAION OF FEM ANALYSIS MEHODS O A CYLINDER-CYLINDER INERSECION SRUCURE Lipig XUE G.E.O.
Examination No. 3 - Tuesday, Nov. 15
 NAME (lease rit) SOLUTIONS ECE 35 - DEVICE ELECTRONICS Fall Semester 005 Examiati N 3 - Tuesday, Nv 5 3 4 5 The time fr examiati is hr 5 mi Studets are allwed t use 3 sheets f tes Please shw yur wrk, artial
NAME (lease rit) SOLUTIONS ECE 35 - DEVICE ELECTRONICS Fall Semester 005 Examiati N 3 - Tuesday, Nv 5 3 4 5 The time fr examiati is hr 5 mi Studets are allwed t use 3 sheets f tes Please shw yur wrk, artial
are specified , are linearly independent Otherwise, they are linearly dependent, and one is expressed by a linear combination of the others
 Chater 3. Higher Order Liear ODEs Kreyszig by YHLee;4; 3-3. Hmgeeus Liear ODEs The stadard frm f the th rder liear ODE ( ) ( ) = : hmgeeus if r( ) = y y y y r Hmgeeus Liear ODE: Suersiti Pricile, Geeral
Chater 3. Higher Order Liear ODEs Kreyszig by YHLee;4; 3-3. Hmgeeus Liear ODEs The stadard frm f the th rder liear ODE ( ) ( ) = : hmgeeus if r( ) = y y y y r Hmgeeus Liear ODE: Suersiti Pricile, Geeral
K [f(t)] 2 [ (st) /2 K A GENERALIZED MEIJER TRANSFORMATION. Ku(z) ()x) t -)-I e. K(z) r( + ) () (t 2 I) -1/2 e -zt dt, G. L. N. RAO L.
![K [f(t)] 2 [ (st) /2 K A GENERALIZED MEIJER TRANSFORMATION. Ku(z) ()x) t -)-I e. K(z) r( + ) () (t 2 I) -1/2 e -zt dt, G. L. N. RAO L. K [f(t)] 2 [ (st) /2 K A GENERALIZED MEIJER TRANSFORMATION. Ku(z) ()x) t -)-I e. K(z) r( + ) () (t 2 I) -1/2 e -zt dt, G. L. N. RAO L.](/thumbs/74/70813931.jpg) Iterat. J. Math. & Math. Scl. Vl. 8 N. 2 (1985) 359-365 359 A GENERALIZED MEIJER TRANSFORMATION G. L. N. RAO Departmet f Mathematics Jamshedpur C-perative Cllege f the Rachi Uiversity Jamshedpur, Idia
Iterat. J. Math. & Math. Scl. Vl. 8 N. 2 (1985) 359-365 359 A GENERALIZED MEIJER TRANSFORMATION G. L. N. RAO Departmet f Mathematics Jamshedpur C-perative Cllege f the Rachi Uiversity Jamshedpur, Idia
Fourier Series & Fourier Transforms
 Experimet 1 Furier Series & Furier Trasfrms MATLAB Simulati Objectives Furier aalysis plays a imprtat rle i cmmuicati thery. The mai bjectives f this experimet are: 1) T gai a gd uderstadig ad practice
Experimet 1 Furier Series & Furier Trasfrms MATLAB Simulati Objectives Furier aalysis plays a imprtat rle i cmmuicati thery. The mai bjectives f this experimet are: 1) T gai a gd uderstadig ad practice
Fourier Method for Solving Transportation. Problems with Mixed Constraints
 It. J. Ctemp. Math. Scieces, Vl. 5, 200,. 28, 385-395 Furier Methd fr Slvig Trasprtati Prblems with Mixed Cstraits P. Padia ad G. Nataraja Departmet f Mathematics, Schl f Advaced Scieces V I T Uiversity,
It. J. Ctemp. Math. Scieces, Vl. 5, 200,. 28, 385-395 Furier Methd fr Slvig Trasprtati Prblems with Mixed Cstraits P. Padia ad G. Nataraja Departmet f Mathematics, Schl f Advaced Scieces V I T Uiversity,
ESWW-2. Israeli semi-underground great plastic scintillation multidirectional muon telescope (ISRAMUTE) for space weather monitoring and forecasting
 ESWW-2 Israeli semi-udergrud great plastic scitillati multidirectial mu telescpe (ISRAMUTE) fr space weather mitrig ad frecastig L.I. Drma a,b, L.A. Pustil'ik a, A. Sterlieb a, I.G. Zukerma a (a) Israel
ESWW-2 Israeli semi-udergrud great plastic scitillati multidirectial mu telescpe (ISRAMUTE) fr space weather mitrig ad frecastig L.I. Drma a,b, L.A. Pustil'ik a, A. Sterlieb a, I.G. Zukerma a (a) Israel
Comparative analysis of bayesian control chart estimation and conventional multivariate control chart
 America Jural f Theretical ad Applied Statistics 3; ( : 7- ublished lie Jauary, 3 (http://www.sciecepublishiggrup.cm//atas di:.648/.atas.3. Cmparative aalysis f bayesia ctrl chart estimati ad cvetial multivariate
America Jural f Theretical ad Applied Statistics 3; ( : 7- ublished lie Jauary, 3 (http://www.sciecepublishiggrup.cm//atas di:.648/.atas.3. Cmparative aalysis f bayesia ctrl chart estimati ad cvetial multivariate
Unifying the Derivations for. the Akaike and Corrected Akaike. Information Criteria. from Statistics & Probability Letters,
 Uifyig the Derivatis fr the Akaike ad Crrected Akaike Ifrmati Criteria frm Statistics & Prbability Letters, Vlume 33, 1997, pages 201{208. by Jseph E. Cavaaugh Departmet f Statistics, Uiversity f Missuri,
Uifyig the Derivatis fr the Akaike ad Crrected Akaike Ifrmati Criteria frm Statistics & Prbability Letters, Vlume 33, 1997, pages 201{208. by Jseph E. Cavaaugh Departmet f Statistics, Uiversity f Missuri,
Pipe Networks - Hardy Cross Method Page 1. Pipe Networks
 Pie Netwrks - Hardy Crss etd Page Pie Netwrks Itrducti A ie etwrk is a itercected set f ies likig e r mre surces t e r mre demad (delivery) its, ad ca ivlve ay umber f ies i series, bracig ies, ad arallel
Pie Netwrks - Hardy Crss etd Page Pie Netwrks Itrducti A ie etwrk is a itercected set f ies likig e r mre surces t e r mre demad (delivery) its, ad ca ivlve ay umber f ies i series, bracig ies, ad arallel
Review for cumulative test
 Hrs Math 3 review prblems Jauary, 01 cumulative: Chapters 1- page 1 Review fr cumulative test O Mday, Jauary 7, Hrs Math 3 will have a curse-wide cumulative test cverig Chapters 1-. Yu ca expect the test
Hrs Math 3 review prblems Jauary, 01 cumulative: Chapters 1- page 1 Review fr cumulative test O Mday, Jauary 7, Hrs Math 3 will have a curse-wide cumulative test cverig Chapters 1-. Yu ca expect the test
Design and Implementation of Cosine Transforms Employing a CORDIC Processor
 C16 1 Desig ad Implemetati f Csie Trasfrms Emplyig a CORDIC Prcessr Sharaf El-Di El-Nahas, Ammar Mttie Al Hsaiy, Magdy M. Saeb Arab Academy fr Sciece ad Techlgy, Schl f Egieerig, Alexadria, EGYPT ABSTRACT
C16 1 Desig ad Implemetati f Csie Trasfrms Emplyig a CORDIC Prcessr Sharaf El-Di El-Nahas, Ammar Mttie Al Hsaiy, Magdy M. Saeb Arab Academy fr Sciece ad Techlgy, Schl f Egieerig, Alexadria, EGYPT ABSTRACT
The Molecular Diffusion of Heat and Mass from Two Spheres
 Iteratial Jural f Mder Studies i Mechaical Egieerig (IJMSME) Vlume 4, Issue 1, 018, PP 4-8 ISSN 454-9711 (Olie) DOI: http://dx.di.rg/10.0431/454-9711.0401004 www.arcjurals.rg The Mlecular Diffusi f Heat
Iteratial Jural f Mder Studies i Mechaical Egieerig (IJMSME) Vlume 4, Issue 1, 018, PP 4-8 ISSN 454-9711 (Olie) DOI: http://dx.di.rg/10.0431/454-9711.0401004 www.arcjurals.rg The Mlecular Diffusi f Heat
Analysis of pressure wave dynamics in fuel rail system
 It. Jl. f Multiphysics Vlume Number 3 8 3 Aalysis f pressure wave dyamics i fuel rail system Basem Alzahabi ad Keith Schulz Ketterig Uiversity Siemes Autmtive ABSTRACT A mdel f a amplified cmm rail fuel
It. Jl. f Multiphysics Vlume Number 3 8 3 Aalysis f pressure wave dyamics i fuel rail system Basem Alzahabi ad Keith Schulz Ketterig Uiversity Siemes Autmtive ABSTRACT A mdel f a amplified cmm rail fuel
AP Statistics Notes Unit Eight: Introduction to Inference
 AP Statistics Ntes Uit Eight: Itrducti t Iferece Syllabus Objectives: 4.1 The studet will estimate ppulati parameters ad margis f errrs fr meas. 4.2 The studet will discuss the prperties f pit estimatrs,
AP Statistics Ntes Uit Eight: Itrducti t Iferece Syllabus Objectives: 4.1 The studet will estimate ppulati parameters ad margis f errrs fr meas. 4.2 The studet will discuss the prperties f pit estimatrs,
MODIFIED LEAKY DELAYED LMS ALGORITHM FOR IMPERFECT ESTIMATE SYSTEM DELAY
 5th Eurpea Sigal Prcessig Cferece (EUSIPCO 7), Pza, Plad, September 3-7, 7, cpyright by EURASIP MOIFIE LEAKY ELAYE LMS ALGORIHM FOR IMPERFEC ESIMAE SYSEM ELAY Jua R. V. López, Orlad J. bias, ad Rui Seara
5th Eurpea Sigal Prcessig Cferece (EUSIPCO 7), Pza, Plad, September 3-7, 7, cpyright by EURASIP MOIFIE LEAKY ELAYE LMS ALGORIHM FOR IMPERFEC ESIMAE SYSEM ELAY Jua R. V. López, Orlad J. bias, ad Rui Seara
Introduction Purpose of study
 VERTICAL WATER INJECTION IN A HETEREOGENEOU AND COLUMN; EXPERIMENT AND ANALYI vei H Midtlyg, Jstei Alvestad, tatil, Gerge Virvsky, Rgalad Research Itrducti Partly gravity dmiated ater flds take place i
VERTICAL WATER INJECTION IN A HETEREOGENEOU AND COLUMN; EXPERIMENT AND ANALYI vei H Midtlyg, Jstei Alvestad, tatil, Gerge Virvsky, Rgalad Research Itrducti Partly gravity dmiated ater flds take place i
Thermodynamic study of CdCl 2 in 2-propanol (5 mass %) + water mixture using potentiometry
 Thermdyamic study f CdCl 2 i 2-prpal (5 mass %) + water mixture usig ptetimetry Reat Tmaš, Ađelka Vrdljak UDC: 544.632.4 Uiversity f Split, Faculty f Chemistry ad Techlgy, Teslia 10/V, HR-21000 Split,
Thermdyamic study f CdCl 2 i 2-prpal (5 mass %) + water mixture usig ptetimetry Reat Tmaš, Ađelka Vrdljak UDC: 544.632.4 Uiversity f Split, Faculty f Chemistry ad Techlgy, Teslia 10/V, HR-21000 Split,
M~R \2 una t3eac" linscott, law &
 March 27,212 Mr. Edward Lhrbach LM PCH, LLC 31742 Cast Highway Lagua Beach, Califria 92651 Subject: Dear Mr. Lhrbach: RECEEO Egieers & Plaers Traffic Trasprtati Parkig MR 2 8 2\2 ua t3eac" lisctt, law
March 27,212 Mr. Edward Lhrbach LM PCH, LLC 31742 Cast Highway Lagua Beach, Califria 92651 Subject: Dear Mr. Lhrbach: RECEEO Egieers & Plaers Traffic Trasprtati Parkig MR 2 8 2\2 ua t3eac" lisctt, law
Frequency-Domain Study of Lock Range of Injection-Locked Non- Harmonic Oscillators
 0 teratial Cferece mage Visi ad Cmputig CVC 0 PCST vl. 50 0 0 ACST Press Sigapre DO: 0.776/PCST.0.V50.6 Frequecy-Dmai Study f Lck Rage f jecti-lcked N- armic Oscillatrs Yushi Zhu ad Fei Yua Departmet f
0 teratial Cferece mage Visi ad Cmputig CVC 0 PCST vl. 50 0 0 ACST Press Sigapre DO: 0.776/PCST.0.V50.6 Frequecy-Dmai Study f Lck Rage f jecti-lcked N- armic Oscillatrs Yushi Zhu ad Fei Yua Departmet f
ANALOG FILTERS. C. Sauriol. Algonquin College Ottawa, Ontario
 LOG ILT By. auril lgqui llege Ottawa, Otari ev. March 4, 003 TBL O OTT alg ilters TIO PI ILT. irst-rder lw-pass filter- -4. irst-rder high-pass filter- 4-6 3. ecd-rder lw-pass filter- 6-4. ecd-rder bad-pass
LOG ILT By. auril lgqui llege Ottawa, Otari ev. March 4, 003 TBL O OTT alg ilters TIO PI ILT. irst-rder lw-pass filter- -4. irst-rder high-pass filter- 4-6 3. ecd-rder lw-pass filter- 6-4. ecd-rder bad-pass
Matching a Distribution by Matching Quantiles Estimation
 Jural f the America Statistical Assciati ISSN: 0162-1459 (Prit) 1537-274X (Olie) Jural hmepage: http://www.tadflie.cm/li/uasa20 Matchig a Distributi by Matchig Quatiles Estimati Niklas Sgurpuls, Qiwei
Jural f the America Statistical Assciati ISSN: 0162-1459 (Prit) 1537-274X (Olie) Jural hmepage: http://www.tadflie.cm/li/uasa20 Matchig a Distributi by Matchig Quatiles Estimati Niklas Sgurpuls, Qiwei
The Acoustical Physics of a Standing Wave Tube
 UIUC Physics 93POM/Physics 406POM The Physics f Music/Physics f Musical Istrumets The Acustical Physics f a Stadig Wave Tube A typical cylidrical-shaped stadig wave tube (SWT) {aa impedace tube} f legth
UIUC Physics 93POM/Physics 406POM The Physics f Music/Physics f Musical Istrumets The Acustical Physics f a Stadig Wave Tube A typical cylidrical-shaped stadig wave tube (SWT) {aa impedace tube} f legth
On the affine nonlinearity in circuit theory
 O the affie liearity i circuit thery Emauel Gluski The Kieret Cllege the Sea f Galilee; ad Ort Braude Cllege (Carmiel), Israel. gluski@ee.bgu.ac.il; http://www.ee.bgu.ac.il/~gluski/ E. Gluski, O the affie
O the affie liearity i circuit thery Emauel Gluski The Kieret Cllege the Sea f Galilee; ad Ort Braude Cllege (Carmiel), Israel. gluski@ee.bgu.ac.il; http://www.ee.bgu.ac.il/~gluski/ E. Gluski, O the affie
Unit -2 THEORY OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS
 Uit - THEORY OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS 1) hat is sluti? : It is a hmgeus mixture f tw r mre cmpuds. ) hat is dilute sluti? : It is a sluti i which slute ccetrati is very less. 3) Give a example fr slid- slid
Uit - THEORY OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS 1) hat is sluti? : It is a hmgeus mixture f tw r mre cmpuds. ) hat is dilute sluti? : It is a sluti i which slute ccetrati is very less. 3) Give a example fr slid- slid
Lecture 18. MSMPR Crystallization Model
 ecture 18. MSMPR Crystalliati Mdel MSMPR Crystalliati Mdel Crystal-Ppulati alace - Number f crystals - Cumulative umber f crystals - Predmiat crystal sie - Grwth rate MSMPR Crystalliati Mdel Mixed-suspesi,
ecture 18. MSMPR Crystalliati Mdel MSMPR Crystalliati Mdel Crystal-Ppulati alace - Number f crystals - Cumulative umber f crystals - Predmiat crystal sie - Grwth rate MSMPR Crystalliati Mdel Mixed-suspesi,
Mean residual life of coherent systems consisting of multiple types of dependent components
 Mea residual life f cheret systems csistig f multiple types f depedet cmpets Serka Eryilmaz, Frak P.A. Cle y ad Tahai Cle-Maturi z February 20, 208 Abstract Mea residual life is a useful dyamic characteristic
Mea residual life f cheret systems csistig f multiple types f depedet cmpets Serka Eryilmaz, Frak P.A. Cle y ad Tahai Cle-Maturi z February 20, 208 Abstract Mea residual life is a useful dyamic characteristic
Every gas consists of a large number of small particles called molecules moving with very high velocities in all possible directions.
 Kietic thery f gases ( Kietic thery was develped by Berlli, Jle, Clasis, axwell ad Bltzma etc. ad represets dyamic particle r micrscpic mdel fr differet gases sice it thrws light the behir f the particles
Kietic thery f gases ( Kietic thery was develped by Berlli, Jle, Clasis, axwell ad Bltzma etc. ad represets dyamic particle r micrscpic mdel fr differet gases sice it thrws light the behir f the particles
Anisotropic discs loaded by parabolically distributed pressure
 Available lie at www.sciecedirect.cm Draft ScieceDirect Draft Draft Structural Itegrity Prcedia 00 (016) 000 000 www.elsevier.cm/lcate/prcedia 1st Eurpea Cferece Fracture, ECF1, 0-4 Jue 016, Cataia, Italy
Available lie at www.sciecedirect.cm Draft ScieceDirect Draft Draft Structural Itegrity Prcedia 00 (016) 000 000 www.elsevier.cm/lcate/prcedia 1st Eurpea Cferece Fracture, ECF1, 0-4 Jue 016, Cataia, Italy
Chapter 5. Root Locus Techniques
 Chapter 5 Rt Lcu Techique Itrducti Sytem perfrmace ad tability dt determied dby cled-lp l ple Typical cled-lp feedback ctrl ytem G Ope-lp TF KG H Zer -, - Ple 0, -, - K Lcati f ple eaily fud Variati f
Chapter 5 Rt Lcu Techique Itrducti Sytem perfrmace ad tability dt determied dby cled-lp l ple Typical cled-lp feedback ctrl ytem G Ope-lp TF KG H Zer -, - Ple 0, -, - K Lcati f ple eaily fud Variati f
Energy 43 (2012) 19e29. Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Energy. journal homepage:
 Eergy 43 (2012) 19e29 tets lists available at civerse ciecedirect Eergy jural hmepage: www.elsevier.cm/lcate/eergy Validati ad aalysis f detailed kietic mdels fr ethylee cmbusti haqi Xu a,b, Alexader A.
Eergy 43 (2012) 19e29 tets lists available at civerse ciecedirect Eergy jural hmepage: www.elsevier.cm/lcate/eergy Validati ad aalysis f detailed kietic mdels fr ethylee cmbusti haqi Xu a,b, Alexader A.
Markov processes and the Kolmogorov equations
 Chapter 6 Markv prcesses ad the Klmgrv equatis 6. Stchastic Differetial Equatis Csider the stchastic differetial equati: dx(t) =a(t X(t)) dt + (t X(t)) db(t): (SDE) Here a(t x) ad (t x) are give fuctis,
Chapter 6 Markv prcesses ad the Klmgrv equatis 6. Stchastic Differetial Equatis Csider the stchastic differetial equati: dx(t) =a(t X(t)) dt + (t X(t)) db(t): (SDE) Here a(t x) ad (t x) are give fuctis,
A Simplified Nonlinear Generalized Maxwell Model for Predicting the Time Dependent Behavior of Viscoelastic Materials
 Wrld Jural f Mechaics, 20,, 58-67 di:0.4236/wj.20.302 Published Olie Jue 20 (http://www.scirp.rg/jural/wj) A Siplified Nliear Geeralized Maxwell Mdel fr Predictig the Tie Depedet Behavir f Viscelastic
Wrld Jural f Mechaics, 20,, 58-67 di:0.4236/wj.20.302 Published Olie Jue 20 (http://www.scirp.rg/jural/wj) A Siplified Nliear Geeralized Maxwell Mdel fr Predictig the Tie Depedet Behavir f Viscelastic
Modern Physics. Unit 15: Nuclear Structure and Decay Lecture 15.2: The Strong Force. Ron Reifenberger Professor of Physics Purdue University
 Mder Physics Uit 15: Nuclear Structure ad Decay Lecture 15.: The Strg Frce R Reifeberger Prfessr f Physics Purdue Uiversity 1 Bidig eergy er ucle - the deuter Eergy (MeV) ~0.4fm B.E. A =.MeV/ = 1.1 MeV/ucle.
Mder Physics Uit 15: Nuclear Structure ad Decay Lecture 15.: The Strg Frce R Reifeberger Prfessr f Physics Purdue Uiversity 1 Bidig eergy er ucle - the deuter Eergy (MeV) ~0.4fm B.E. A =.MeV/ = 1.1 MeV/ucle.
Chapter 1: Fundamentals
 Chapter 1: Fudametals 1.1 Real Numbers Irratial umbers are real umbers that cat be expressed as ratis f itegers. That such umbers exist was a prfud embarrassmet t the Pythagrea brtherhd, ad they are said
Chapter 1: Fudametals 1.1 Real Numbers Irratial umbers are real umbers that cat be expressed as ratis f itegers. That such umbers exist was a prfud embarrassmet t the Pythagrea brtherhd, ad they are said
.-. ;::;> -,-~ ~ ~..--~-~=~-~ ;~~~ ~ -= ~ -l (. ~.~ _~~J&fiH~l_ L._.
 :z:...~':j..li~j.t~.. ~~_._._._'...._.u.lf:tdt OA~..M~~. -.--.-.~,.~... ~~~t(.-. ;::;> -,-~ ~---- --..-- _.~~.~ _ _. mu _ ~~)rt/.~~'!.... --P l~;---~_~~:'~~i~"fuk -- --_.- lv~vf4-t J'tt',.. 5-- - --.-~..--~-~=~-~
:z:...~':j..li~j.t~.. ~~_._._._'...._.u.lf:tdt OA~..M~~. -.--.-.~,.~... ~~~t(.-. ;::;> -,-~ ~---- --..-- _.~~.~ _ _. mu _ ~~)rt/.~~'!.... --P l~;---~_~~:'~~i~"fuk -- --_.- lv~vf4-t J'tt',.. 5-- - --.-~..--~-~=~-~
Seismic Performance of Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Buildings with Heavy Loads
 Seismic Perfrmace f Symmetrical ad al Buildigs with Heavy Lads Md. Jaweed Jilai Kha, Seshadri Sekhar ad Bellam Sivarama Krisha Prasad esearch Schlar, Departmet f Civil gieerig esearch, Gitam Uiversity,
Seismic Perfrmace f Symmetrical ad al Buildigs with Heavy Lads Md. Jaweed Jilai Kha, Seshadri Sekhar ad Bellam Sivarama Krisha Prasad esearch Schlar, Departmet f Civil gieerig esearch, Gitam Uiversity,
Preliminary Test Single Stage Shrinkage Estimator for the Scale Parameter of Gamma Distribution
 America Jural f Mathematics ad Statistics, (3): 3-3 DOI:.593/j.ajms.3. Prelimiary Test Sigle Stage Shrikage Estimatr fr the Scale Parameter f Gamma Distributi Abbas Najim Salma,*, Aseel Hussei Ali, Mua
America Jural f Mathematics ad Statistics, (3): 3-3 DOI:.593/j.ajms.3. Prelimiary Test Sigle Stage Shrikage Estimatr fr the Scale Parameter f Gamma Distributi Abbas Najim Salma,*, Aseel Hussei Ali, Mua
General Chemistry 1 (CHEM1141) Shawnee State University Fall 2016
 Geeral Chemistry 1 (CHEM1141) Shawee State Uiversity Fall 2016 September 23, 2016 Name E x a m # I C Please write yur full ame, ad the exam versi (IC) that yu have the scatr sheet! Please 0 check the bx
Geeral Chemistry 1 (CHEM1141) Shawee State Uiversity Fall 2016 September 23, 2016 Name E x a m # I C Please write yur full ame, ad the exam versi (IC) that yu have the scatr sheet! Please 0 check the bx
A unified brittle fracture criterion for structures with sharp V-notches under mixed mode loading
 Jural f Mechaical Sciece ad Techlgy Jural f Mechaical Sciece ad Techlgy 22 (2008) 269~278 www.sprigerlik.cm/ctet/738-494x A uified brittle fracture criteri fr structures with sharp V-tches uder mixed mde
Jural f Mechaical Sciece ad Techlgy Jural f Mechaical Sciece ad Techlgy 22 (2008) 269~278 www.sprigerlik.cm/ctet/738-494x A uified brittle fracture criteri fr structures with sharp V-tches uder mixed mde
Journal of Applied and Computational Mechanics, Vol. 3, No. 1, (2017), DOI: /jacm
 Jural f Applied ad Cmputatial echaics, Vl., N., (7), -79 DOI:.55/jacm.7. Therm-mechaical liear vibrati aalysis f fluidcveyig structures subjected t differet budary cditis usig Galerki-Newt-Harmic balacig
Jural f Applied ad Cmputatial echaics, Vl., N., (7), -79 DOI:.55/jacm.7. Therm-mechaical liear vibrati aalysis f fluidcveyig structures subjected t differet budary cditis usig Galerki-Newt-Harmic balacig
Copyright 1978, by the author(s). All rights reserved.
 Cpyright 1978, by the authr(s). All rights reserved. Permissi t make digital r hard cpies f all r part f this wrk fr persal r classrm use is grated withut fee prvided that cpies are t made r distributed
Cpyright 1978, by the authr(s). All rights reserved. Permissi t make digital r hard cpies f all r part f this wrk fr persal r classrm use is grated withut fee prvided that cpies are t made r distributed
Experimental and Theoretical Investigations of PAN Molecular Weight Increase in Precipitation Polymerization as a Function of H 2 O/DMSO Ratio
 Carb Letters Vl., N. March 00 pp. -7 Experimetal ad Theretical Ivestigatis f PAN Mlecular Weight Icrease i Precipitati Plymerizati as a ucti f H O/DMSO Rati Jig Zhag, egjig Bu, Ygqiag Dai, Liwei Xue, Zhixia
Carb Letters Vl., N. March 00 pp. -7 Experimetal ad Theretical Ivestigatis f PAN Mlecular Weight Icrease i Precipitati Plymerizati as a ucti f H O/DMSO Rati Jig Zhag, egjig Bu, Ygqiag Dai, Liwei Xue, Zhixia
Directional Duality Theory
 Suther Illiis Uiversity Carbdale OpeSIUC Discussi Papers Departmet f Ecmics 2004 Directial Duality Thery Daiel Primt Suther Illiis Uiversity Carbdale Rlf Fare Oreg State Uiversity Fllw this ad additial
Suther Illiis Uiversity Carbdale OpeSIUC Discussi Papers Departmet f Ecmics 2004 Directial Duality Thery Daiel Primt Suther Illiis Uiversity Carbdale Rlf Fare Oreg State Uiversity Fllw this ad additial
Identical Particles. We would like to move from the quantum theory of hydrogen to that for the rest of the periodic table
 We wuld like t ve fr the quatu thery f hydrge t that fr the rest f the peridic table Oe electr at t ultielectr ats This is cplicated by the iteracti f the electrs with each ther ad by the fact that the
We wuld like t ve fr the quatu thery f hydrge t that fr the rest f the peridic table Oe electr at t ultielectr ats This is cplicated by the iteracti f the electrs with each ther ad by the fact that the
(b) y(t) is not periodic although sin t and 4 cos 2πt are independently periodic.
 Chapter 7, Sluti. (a) his is peridic with ω which leads t /ω. (b) y(t) is t peridic althugh si t ad cs t are idepedetly peridic. (c) Sice si A cs B.5[si(A B) si(a B)], g(t) si t cs t.5[si 7t si( t)].5
Chapter 7, Sluti. (a) his is peridic with ω which leads t /ω. (b) y(t) is t peridic althugh si t ad cs t are idepedetly peridic. (c) Sice si A cs B.5[si(A B) si(a B)], g(t) si t cs t.5[si 7t si( t)].5
Spatio-temporal Modeling of Environmental Data for Epidemiologic Health Effects Analyses
 Spati-tempral Mdelig f Evirmetal Data fr Epidemilgic Health Effects Aalyses Paul D. Samps Uiversity f Washigt Air Quality ad Health: a glbal issue with lcal challeges 8 Aug 2017 -- Mexic City 1 The MESA
Spati-tempral Mdelig f Evirmetal Data fr Epidemilgic Health Effects Aalyses Paul D. Samps Uiversity f Washigt Air Quality ad Health: a glbal issue with lcal challeges 8 Aug 2017 -- Mexic City 1 The MESA
Differentiation Applications 1: Related Rates
 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
Electrochemistry Redox Half-Reactions
 Electrchemistry Electrchemistry deals with the relatiship betwee chemical chage ad electricity Electrchemical s (tw types) Galvaic s use a sptaeus ( G < 0) reacti t prduce electricity (batteries) Electrlytic
Electrchemistry Electrchemistry deals with the relatiship betwee chemical chage ad electricity Electrchemical s (tw types) Galvaic s use a sptaeus ( G < 0) reacti t prduce electricity (batteries) Electrlytic
REGRESSION (Physics 1210 Notes, Partial Modified Appendix A)
 REGRESSION (Physics 0 Notes, Partial Modified Appedix A) HOW TO PERFORM A LINEAR REGRESSION Cosider the followig data poits ad their graph (Table I ad Figure ): X Y 0 3 5 3 7 4 9 5 Table : Example Data
REGRESSION (Physics 0 Notes, Partial Modified Appedix A) HOW TO PERFORM A LINEAR REGRESSION Cosider the followig data poits ad their graph (Table I ad Figure ): X Y 0 3 5 3 7 4 9 5 Table : Example Data
Motor Stability. Plateau and Mesa Burning
 Mtr Stability Recall mass cservati fr steady erati ( =cstat) m eit m b b r b s r m icr m eit Is this cditi (it) stable? ly if rmally use.3
Mtr Stability Recall mass cservati fr steady erati ( =cstat) m eit m b b r b s r m icr m eit Is this cditi (it) stable? ly if rmally use.3
First-Principles Modelling of Electrospraying, and the Effects of Dissipation in Electrospray Thrusters
 First-Priciples Mdellig f Electrsprayig, ad the Effects f Dissipati i Electrspray Thrusters IEPC-7-49 Preseted at the 35th Iteratial Electric Prpulsi Cferece Gergia Istitute f Techlgy Atlata, Gergia USA
First-Priciples Mdellig f Electrsprayig, ad the Effects f Dissipati i Electrspray Thrusters IEPC-7-49 Preseted at the 35th Iteratial Electric Prpulsi Cferece Gergia Istitute f Techlgy Atlata, Gergia USA
Solutions to Midterm II. of the following equation consistent with the boundary condition stated u. y u x y
 Sltis t Midterm II Prblem : (pts) Fid the mst geeral slti ( f the fllwig eqati csistet with the bdary cditi stated y 3 y the lie y () Slti : Sice the system () is liear the slti is give as a sperpsiti
Sltis t Midterm II Prblem : (pts) Fid the mst geeral slti ( f the fllwig eqati csistet with the bdary cditi stated y 3 y the lie y () Slti : Sice the system () is liear the slti is give as a sperpsiti
, which yields. where z1. and z2
 The Gaussian r Nrmal PDF, Page 1 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin Authr: Jhn M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revisin: 11 September 13 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin
The Gaussian r Nrmal PDF, Page 1 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin Authr: Jhn M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revisin: 11 September 13 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin
Fluctuating Groundwater Flow in Homogeneous Finite Porous Domain
 The SIJ Trasactis Cmputer Sciece Egieerig & its Applicatis (CSEA), Vl. 4, N. 3, July 6 Fluctuatig rudwater Flw i Hmgeeus Fiite Prus Dmai Nyambae Zachary Nyakudi*, Mathew Kiyaui** & Jhaa K Sigey*** *Departmet
The SIJ Trasactis Cmputer Sciece Egieerig & its Applicatis (CSEA), Vl. 4, N. 3, July 6 Fluctuatig rudwater Flw i Hmgeeus Fiite Prus Dmai Nyambae Zachary Nyakudi*, Mathew Kiyaui** & Jhaa K Sigey*** *Departmet
Characteristics of helical flow in slim holes and calculation of hydraulics for ultra-deep wells
 6 Pet.Sci.(00)7:6-3 DOI 0.007/s8-00-006-8 Characteristics f helical flw i slim hles ad calculati f hydraulics fr ultra-deep wells Fu Jiahg, Yag Yu, Che Pig ad Zha Jihai 3 State Key Labratry f Oil ad Gas
6 Pet.Sci.(00)7:6-3 DOI 0.007/s8-00-006-8 Characteristics f helical flw i slim hles ad calculati f hydraulics fr ultra-deep wells Fu Jiahg, Yag Yu, Che Pig ad Zha Jihai 3 State Key Labratry f Oil ad Gas
Cold mirror based on High-Low-High refractive index dielectric materials
 Cld mirrr based High-Lw-High refractive idex dielectric materials V.V. Elyuti.A. Butt S.N. Khia Samara Natial Research Uiversity 34 skvske Shsse 443086 Samara Russia Image Prcessig Systems Istitute Brach
Cld mirrr based High-Lw-High refractive idex dielectric materials V.V. Elyuti.A. Butt S.N. Khia Samara Natial Research Uiversity 34 skvske Shsse 443086 Samara Russia Image Prcessig Systems Istitute Brach
An Investigation of Stratified Jackknife Estimators Using Simulated Establishment Data Under an Unequal Probability Sample Design
 Secti Survey Research Methds SM 9 A Ivestigati f Stratified ackkife Estimatrs Usig Simulated Establishmet Data Uder a Uequal Prbability Sample Desig Abstract Plip Steel, Victria McNerey, h Slata Csiderig
Secti Survey Research Methds SM 9 A Ivestigati f Stratified ackkife Estimatrs Usig Simulated Establishmet Data Uder a Uequal Prbability Sample Desig Abstract Plip Steel, Victria McNerey, h Slata Csiderig
How do scientists measure trees? What is DBH?
 Hw d scientists measure trees? What is DBH? Purpse Students develp an understanding f tree size and hw scientists measure trees. Students bserve and measure tree ckies and explre the relatinship between
Hw d scientists measure trees? What is DBH? Purpse Students develp an understanding f tree size and hw scientists measure trees. Students bserve and measure tree ckies and explre the relatinship between
Super-efficiency Models, Part II
 Super-efficiec Mdels, Part II Emilia Niskae The 4th f Nvember S steemiaalsi Ctets. Etesis t Variable Returs-t-Scale (0.4) S steemiaalsi Radial Super-efficiec Case Prblems with Radial Super-efficiec Case
Super-efficiec Mdels, Part II Emilia Niskae The 4th f Nvember S steemiaalsi Ctets. Etesis t Variable Returs-t-Scale (0.4) S steemiaalsi Radial Super-efficiec Case Prblems with Radial Super-efficiec Case
OBJECTIVES. Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO INSTRUMENTATION FUNCTION AND ADVANTAGES INTRODUCTION. At the end of this chapter, students should be able to:
 OBJECTIVES Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO INSTRUMENTATION At the ed of this chapter, studets should be able to: 1. Explai the static ad dyamic characteristics of a istrumet. 2. Calculate ad aalyze the measuremet
OBJECTIVES Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO INSTRUMENTATION At the ed of this chapter, studets should be able to: 1. Explai the static ad dyamic characteristics of a istrumet. 2. Calculate ad aalyze the measuremet
STRUCTURES IN MIKE 21. Flow over sluice gates A-1
 A-1 STRUCTURES IN MIKE 1 Fl ver luice gate Fr a give gemetry f the luice gate ad k ater level uptream ad dtream f the tructure, the fl rate, ca be determied thrugh the equati f eergy ad mmetum - ee B Pedere,
A-1 STRUCTURES IN MIKE 1 Fl ver luice gate Fr a give gemetry f the luice gate ad k ater level uptream ad dtream f the tructure, the fl rate, ca be determied thrugh the equati f eergy ad mmetum - ee B Pedere,
Activity 3: Length Measurements with the Four-Sided Meter Stick
 Activity 3: Legth Measuremets with the Four-Sided Meter Stick OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this experimet is to study errors ad the propagatio of errors whe experimetal data derived usig a four-sided meter
Activity 3: Legth Measuremets with the Four-Sided Meter Stick OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this experimet is to study errors ad the propagatio of errors whe experimetal data derived usig a four-sided meter
8.0 Negative Bias Temperature Instability (NBTI)
 EE650R: Reliability Physics f Naelectric Devices Lecture 8: Negative Bias Temerature Istability Date: Se 27 2006 Class Ntes: Vijay Rawat Reviewed by: Saakshi Gagwal 8.0 Negative Bias Temerature Istability
EE650R: Reliability Physics f Naelectric Devices Lecture 8: Negative Bias Temerature Istability Date: Se 27 2006 Class Ntes: Vijay Rawat Reviewed by: Saakshi Gagwal 8.0 Negative Bias Temerature Istability
Internal vs. external validity. External validity. Internal validity
 Secti 7 Mdel Assessmet Iteral vs. exteral validity Iteral validity refers t whether the aalysis is valid fr the pplati ad sample beig stdied. Exteral validity refers t whether these reslts ca be geeralized
Secti 7 Mdel Assessmet Iteral vs. exteral validity Iteral validity refers t whether the aalysis is valid fr the pplati ad sample beig stdied. Exteral validity refers t whether these reslts ca be geeralized
A NEW METHOD OF THRUSTER CONTROL IN POSITIONING OF SHIPS BASED ON POWER CONTROL
 A NEW METHOD O THRUSTER CONTROL IN POSITIONING O SHIPS BASED ON POWER CONTROL Asgeir J. Sørese*, Alf Kåre Ådaes*, Thr I. sse** ad Ja-Peter Strad** *ABB Idustri AS, Hasleveie 50, P. O. Bx 6540 Rdeløkka,
A NEW METHOD O THRUSTER CONTROL IN POSITIONING O SHIPS BASED ON POWER CONTROL Asgeir J. Sørese*, Alf Kåre Ådaes*, Thr I. sse** ad Ja-Peter Strad** *ABB Idustri AS, Hasleveie 50, P. O. Bx 6540 Rdeløkka,
