The Two-Slit Interference of Vector Optical Fields with Both Radially and Azimuthally Variant States of Polarization
|
|
|
- Deborah Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
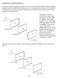
1 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 5, 75 8, 7 The Two-Slit Interference of Vector Optical Fields with Both Radially and Azimuthally Variant States of Polarization Tengyue Gao, Chaoyang Qian, Xiaoyu Zhang, and Rui-Pin Chen * Abstract The interference behaviors of a vector optical field with both radially and azimuthally variant states of polarization (SoP) through the Young s two-slits are theoretically studied. The optical field distribution with periodic stripes in the far field results from the interference of the vector optical field through the Young s two-slits with different initial SoP distributions. It is found that the far-field distribution can be manipulated by the incident vector optical field with the initial phase and SoP distributions. Particularly, the distribution of radially-variant SoP in the cross-section of the incident optical field provides an additional freedom to control the interference patterns of the x-component, y-component and total intensity distribution in far field. This approach provides a new method to further expand the functionality of an optical system by considering the distribution of SoP in field cross-section.. INTRODUCTION Recently, the studies about the vector optical field have attracted great interest due to its novel properties and potential applications [ ]. Compared to a scalar optical field with the uniform distribution of states of polarization (SoP), the vector optical field with nonuniform distribution of SoP in the field cross-section has many unique properties and potential applications on corresponding fields such as optical devices, optical trapping and micro-particle manipulation [5 7]. The current studies about the vector optical field are mainly focused on the manipulation of an optical field, characteristics of the focusing and propagation of a vector optical field, and their corresponding applications [8 ]. In particular, the generation of a vector optical field, focusing characteristics of a vector optical field and its propagation dynamics were demonstrated theoretically and experimentally [ 7]. The nonlinear dynamics of a vector optical field with different SoP distributions have been demonstrated [8, 9]. The evanescent wave part and near-field characteristics of a vector optical field have been studied []. As a fundamental experiment in an optics context, the double-slit experiment was performed originally by Thomas Young in 8 and played a vital part in the acceptance of the wave theory of light. Generally, the Young s double-slit interference experiment is performed with a scalar beam (i.e., with a uniform polarization in the cross-section of an optical field) []. More recently, the interference behaviors of a vector optical field with azimuthally variant SoP through the young s double-slits were explored []. The interference patterns in far field were analyzed in relation with the topological charge and initial phase of a vector optical field. However, a vector optical field can combine both radially and azimuthally variant SoP distributions. In particular, the radially variant SoP distributions will also contribute to interference patterns of the different components in far field. Therefore, the distribution of radiallyvariant SoP provides an additional freedom to control the interference pattern in far field including intensity, phase and polarization. The modern double-slit experiment is a demonstration that light and matter can display characteristics of both classically defined waves and particles; moreover, it displays Received 7 November, Accepted 7 January 7, Scheduled 9 February 7 * Corresponding author: Rui-Pin Chen (chenrp@zstu.edu.cn). The authors are with the Department of Physics, Zhejiang Sci.-Tech. University, Hangzhou 8, China.
2 7 Gao et al. the fundamentally probabilistic nature of quantum mechanical phenomena []. Obviously, exploring the interference behavior of a vector optical field with hybrid SoP can benefit deeper understanding of the nature of light [, ]. The vectorial effect of an optical field with hybrid SoP in the field crosssection leads to different interference behaviors [5] and may find potential applications in corresponding field. In this work, we study the novel interference behaviors of a vector optical field with both radially and azimuthally variant SoP distributions through the two-slits. Compared to the double-slit interference of a scalar optical field [] and a vector optical field with azimuthally variant polarization, the doubleslit interference phenomena with both radially and azimuthally variant polarizations provide a deeper understanding about the characteristics of the vector field and their interference characteristics. With different distributions of the initial SoP, the interference fringes in far field appear in different shapes. In particular, with the modulation of radially variant polarization, the interference patterns in far field have more complex interference fringes of the x and y components. These results provide a new method to further expand the functionality of an optical system and thus can find potential applications in the manipulation of an optical field [ ], nonlinear optics [8, 9], imaging [], and quantum optics [7,, ].. THEORETICAL FORMULATION In the polar coordinate system, the z-axis is taken to be the direction of light propagation. A cylindrical optical vector field with both radially and azimuthally variant SoP distributions can be expressed as [5, ] E(r, θ) =A [cos(mθ +πl(r/r )+θ ) e x +sin(mθ +πl(r/r )+θ ) e y ], () where r =(x + y ) / and θ =arctan(y/x) are the polar radius and azimuthal angle in the polar coordinate system, respectively. m is the topological charge, and θ is the initial phase. e x and e y are the unit vectors in x-andy-directions, respectively. l is an integer associated with the radially variant SoP distribution. A is the amplitude and thereafter setting A = for simplicity. The schematic diagram and demonstration of the two-slit interference are shown in Fig.. y x (a) (b) Figure. (Color online). (a) Double-slit device schematic diagram; (b) Vector beam cross section before and after passage through the double slit. There are two slits A and B in the x-y plane, and the distance between the two slits is b. Slits A and B are perpendicular to x axis, and the width of the two slits is a. The distance between the observation plane which is parallel to the x-y plane and the plane where the two slits are located is d. According to Eq. (), the vector optical field can be decomposed into x and y direction components: E x (r, θ) =cos[mθ +πl(r/r )+θ ], () E y (r, θ) =sin[mθ +πl(r/r )+θ ]. () When light beam is incident on the two slits, A and B, the x and y components interfer independently. According to the double-beam interference intensity formula [7]: I = EA + EB +E A E B cos δ, ()
3 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 5, 7 77 where E A and E B are the optical fields at the two slits positions, respectively. δ =πbx/(λd) isthe phase difference between E A and E B. As recognized from Fig., any two relative points at two slits are symmetrical about y axis. Their azimuthal angles θ A and θ B are supplementary, namely θ A = π θ B, and their polar radius r A = r B = b/( cos θ B ). The x components of E A and E B can be written as: E A =cosϕ A, E B =cosϕ B where ϕ A = mθ A +πl(r A /r )+θ, ϕ B = mθ B +πl(r B /r )+θ. On the other hand, y components of E A and E B are: E A =sinϕ A, E B =sinϕ B. According to Eq. (), the interference intensity distributions of x and y components in the observation plane therefore can be expressed as: I x (x, y) =cos ϕ A +cos ϕ B +cosϕ A cos ϕ B cos δ, (5) I y (x, y) =sin ϕ A +sin ϕ B +sinϕ A sin ϕ B cos δ. () And the total light intensity distribution is: I(x, y) =I x (x, y)+i y (x, y) = cos(mθ B )cosδ. (7). NUMERICAL RESULTS AND ANALYSIS In order to further explore the interference patterns of the vector optical field with radially and azimuthally variant polarization distributions through the double slits, the numerical calculations are.5 l = l = l = l = x component y component Total field Figure. (Color online). Patterns of the Young s two-slit interference of the vector optical fields after passage through the double slit for m =withθ =andl =,,,5.
4 78 Gao et al. performed according to Eqs. (5) (7) with λ =.nm, r = 5 mm, d = 5 mm and b = mm. The corresponding results of x, y components and the total intensity distributions are shown in Figs. for different parameters m, θ and l. The novel properties of the interference patterns are found with different initial SoPs, especially in the center parts of the interference patterns. Different from the well-known Young s two-slit interference of the scalar light field, the interference patterns of the vector optical fields exhibit the spatial structure in the y (slit) direction besides in the x direction as shown in Figs.. The interference patterns of the x component and y component are sensitively relative to parameters l, m and θ. However, the interference pattern of the total field depends only on parameter m but independent of parameters l and θ. In particular, the interference fringes in the central parts in the observation plane are modulated by both x and y components. Note that when m =,l =and θ =, the interference patterns are for a conventional scalar optical field as shown in the first row of Fig.. Figures show the different interference patterns of the vector optical fields for m =,and with θ =andl =,, and 5, respectively. If m =andl =, the light intensity distribution of x- component and the total field in far-field are the same, and the intensity of y-component is zero as shown in Fig.. This is because the incident optical field with m =,θ =andl = degenerate the uniform distribution of the polarization (i.e., a scalar optical field). When l, the optical field possesses a radially variant polarization distribution in the field cross section, the bright stripes and dark stripes appear alternately in the central parts of the interference patterns of x and y components. Away from the center of the interference patterns, the intensity distributions of x and y components is becoming more and more similar. With increasing values of l, the stripes are becoming more narrow. However, the total field distributions are always the same despite the variant values of l. These phenomena can be recognized from Eqs. (5) (7) that the values of ϕ A and ϕ B in the middle region of the optical field will change more quickly with the increasing values of l which leads to the intensity distributions of x component and y component in the central region changing more quickly. The interference patterns for the vector fields m =,,5withl =andθ =areshownin l = l = l = x component y component Total field Figure. (Color online). Patterns of the Young s two-slit interference of the vector optical fields after passage through the double slit for m =withθ =andl =,,5.
5 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 5, 7 79 l = l = l = x component y component Total field Figure. (Color online). Patterns of the Young s two-slit interference of the vector optical fields after passage through the double slit for m =withθ =andl =,,5. m = m = m = x component y component Total field Figure 5. (Color online). Patterns of the Young s two-slit interference of the vector optical fields after passage through the double slit with l =,θ =andm =,,5.
6 8 Gao et al. θ = θ = π/ θ = π/ θ = π/ x component y component Total field Figure. (Color online). Patterns of the Young s two-slit interference of the vector optical fields after passage through the double slit with l =,m =andθ =,π/, π/, π/. Fig. 5. It can be found that the interference fringes of x component, y component and the total field exhibit a chessboard structure in the middle region, and the number of squares in the checkerboard will increase with the increasing values of m. The total number of bright and dark regions is m. In this case for l =andθ =, the vector field is degenerated as an optical field with azimuthally variant SoP distribution in the field cross-section, but no variant in radial direction. The interference pattern is the same as the experimental results as shown in []. Fig. shows interference patterns for the vector fields θ =,π/, π/, π/ withl =andm =. One can find that the intensity distributions of y component with θ =andx component with θ = π/ are the same. In a similar way, the intensity distributions of y component with θ = π/ andx component with θ =π/ arethe same. This phenomenon can be explained by the initial vector optical field as described in Eqs. () (). As recognized from Eqs. () (), the x components of initial vector optical field with θ = π/ and θ =π/ are equal to that of the y components of initial vector optical field with θ =andθ = π/.. CONCLUSION The interference behaviors of the vector fields with both radially and azimuthally variant polarizations in two slits have been demonstrated. The results reveal that the interference pattern of the total intensity is determined by the topological charge of the initial vector field m. However, the interference patterns of x and y components are related to the initial phase θ and radially variant polarization parameter l
7 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 5, 7 8 of the initial vector field. In particular, with the modulation of radially variant SoP in the cross-section of the incident optical field, the interference patterns in far field indicate complex interference fringes of x and y components. The interference patterns of x-component, y-component and the total intensity distributions can be manipulated by the initial distributions of SoP in the field cross-section. These results provide a new method to further expand the functionality of an optical system and thus can find potential applications in the corresponding fields. ACKNOWLEDGMENT This work is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 577, the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation under Grant No. LQA the Science Research Foundation of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University (ZSTU) under Grant No. 78-Y. REFERENCES. Litchinitser, N. M., Structured light meets structured matter, Science, Vol. 7, 5 55,.. Chen, R. P., Z. Chen, K. H. Chew, P. G. Li, Z. Yu, J. Ding, and S. He, Structured caustic vector vortex optical field: Manipulating optical angular momentum flux and polarization rotation, Scientific Reports, Vol. 5, 8, 5.. Waller, E. H. and G. Freymann, Independent spatial intensity, phase and polarization distribution, Optics Express, Vol., 87 87,.. Chen, R. P., K. H. Chew, B. Gu, and G. Zhou, Effect of a spiral phase on a vector beam with hybrid polarization states, Journal of Optics, Vol. 7, 55, Bomzon, Z., V. Kleiner, and E. Hasman, Computer-generated space-variant polarization elements with subwavelength metal stripes, Optics Letters, Vol., 5,.. Chen, R., K. Agarwal, J. R. Colin, Sheppard, and X. D. Chen, Imaging using cylindrical vector beams in a high numerical-aperture microscopy system, Optics Letters, Vol. 8,,. 7. Visser, J., E. R. Elier, and G. Nierhuis, Polarization entanglement in a crystal with three fold symmetry, Physical Review A, Vol., 8,. 8. Dorn, R., S. Quabis, and G. Leuchs, Sharper focus for a radially polarized beam, Physical Review Letters, Vol. 9, 9,. 9. Tian, B. and J. Pu, Tight focusing of a double-ring-shaped azimuthally polarized beam, Optics Letters, Vol.,,.. Gu, B., Y. Pan, L. J. Wu, and Y. P. Cui, Tight focusing properties of spatial-variant linearlypolarized vector beams, Journal of Optics, Vol., 8 7,.. Hu, K. L., Z. Y. Chen, and J. X. Pu, Tight focusing properties of hybridly polarized vector beams, Journal of Optical Society of America A, Vol. 9, 99,.. Deng, D., Q. Guo, L. Wu, and X. Yang, Propagation of radially polarized elegant light beams, Journal of Optical Society of America B, Vol.,, 7.. Wang, X. L., J. P. Ding, W. J. Ni, C. S. Guo, and H. T. Wang, Generation of arbitrary vector beams with a spatial light modulator and a common path interferometric arrangement, Optics Letters, Vol., 59 55, 7.. Wang, X. L., Y. N. Li, J. Chen, C. S. Guo, J. P. Ding, and H. T. Wang, A new type of vector fields with hybrid states of polarization, Optics Express, Vol. 8, ,. 5. Chen, H., J. J. Hao, B. F. Zhang, J. Xu, J. P. Ding, and H. T. Wang, Generation of vector beam with space-variant distribution of both polarization and phase, Optics Letters, Vol., 79 8,.. Han, W., Y. F. Yang, W. Cheng, and Q. W. Zhan, Vectorial optical field generator for the creation of arbitrarily complex fields, Optics Express, Vol., 9 79,. 7. Lerman, G. M., L. Stern, and U. Levy, Generation and tight focusing of hybridly polarized vector beams, Optics Express, Vol. 8, ,.
8 8 Gao et al. 8. Li, S. M., Y. Li, X. L. Wang, L. J. Kong, K. Lou, C. Tu, Y. Tian, and H. T. Wang, Taming the collapse of optical fields, Scientific Reports, Vol., 7,. 9. Chen, R. P., L. X. Zhong, K. H. Chew, T. Y. Zhao, and X. Zhang, Collapse dynamics of a vector vortex optical field with inhomogeneous states of polarization, Laser Physics, Vol. 5, 75, 5.. Chen, R. P. and G. Li, The evanescent wavefield part of a cylindrical vector beam, Optics Express, Vol., 5,.. Setala, T., J. Tervo, and A. T. Frberg, Stokes parameters and polarization contrasts in Young s interference experiment, Optics Letters, Vol., 8,.. Li, Y. N., X. L. Wang, H. Zhao, L. J. Kong, K. Lou, B. Gu, C. G. Tu, and H. T. Wang, Young s two-slit interference of vector light fields, Optics Letters, Vol. 7, 79 79,.. Wootters, W. W. and W. H. Zurek, Complementarity in the double-slit experiment: Quantum nonseparability and quantitative statement of Bohr s principle, Phys. Rev. D, Vol. 9, 7 8, Svensson, B. E. Y., Pedagogical review of quantum measurement theory with an emphasis on weak measurements, Quanta, Vol., 8 9,. 5. Cai, F., J. Yu, and S. He, Vectorial electric field Monte Caro simulations for focused laser beams (8 nm nm) in a biological sample, Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol., 7 8,.. Imran, A. and Q. A. Naqvi, Diffraction of plane wave by two parallel slits in an infinitely long impedance plane using the method of Kobayashi potential, Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol., 7,. 7. Born, M. and E. Wolf, Principles of Optics, 7th Edition, Cambridge U. Press, 999.
Vectorial structure and beam quality of vector-vortex Bessel Gauss beams in the far field
 COL (Suppl., S6( CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS June 3, Vectorial structure and beam quality of vector-vortex Bessel Gauss beams in the far field Lina Guo (, and Zhilie Tang ( School of Physics and Telecommunication
COL (Suppl., S6( CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS June 3, Vectorial structure and beam quality of vector-vortex Bessel Gauss beams in the far field Lina Guo (, and Zhilie Tang ( School of Physics and Telecommunication
Generation and tight focusing of hybridly polarized vector beams
 Generation and tight focusing of hybridly polarized vector beams Gilad M. Lerman, 1, * Liron Stern, 1 and Uriel Levy 1,2 1 Department of Applied Physics, The Benin School of Engineering and Computer Science,
Generation and tight focusing of hybridly polarized vector beams Gilad M. Lerman, 1, * Liron Stern, 1 and Uriel Levy 1,2 1 Department of Applied Physics, The Benin School of Engineering and Computer Science,
Focusing of elliptically polarized Gaussian beams through an annular high numerical aperture
 Focusing of elliptically polarized Gaussian beams through an annular high numerical aperture Chen Bao-Suan( 陈宝算 ) and Pu Ji-Xiong( 蒲继雄 ) Department of Information Science & Engineering, Huaqiao University,
Focusing of elliptically polarized Gaussian beams through an annular high numerical aperture Chen Bao-Suan( 陈宝算 ) and Pu Ji-Xiong( 蒲继雄 ) Department of Information Science & Engineering, Huaqiao University,
arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 30 Mar 2010
![arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 30 Mar 2010 arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 30 Mar 2010](/thumbs/83/87689638.jpg) Analytical vectorial structure of non-paraxial four-petal Gaussian beams in the far field Xuewen Long a,b, Keqing Lu a, Yuhong Zhang a,b, Jianbang Guo a,b, and Kehao Li a,b a State Key Laboratory of Transient
Analytical vectorial structure of non-paraxial four-petal Gaussian beams in the far field Xuewen Long a,b, Keqing Lu a, Yuhong Zhang a,b, Jianbang Guo a,b, and Kehao Li a,b a State Key Laboratory of Transient
Analysis of second-harmonic generation microscopy under refractive index mismatch
 Vol 16 No 11, November 27 c 27 Chin. Phys. Soc. 19-1963/27/16(11/3285-5 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd Analysis of second-harmonic generation microscopy under refractive index mismatch Wang Xiang-Hui(
Vol 16 No 11, November 27 c 27 Chin. Phys. Soc. 19-1963/27/16(11/3285-5 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd Analysis of second-harmonic generation microscopy under refractive index mismatch Wang Xiang-Hui(
Analytical Study of Electromagnetic Wave Diffraction Through a Circular Aperture with Fringes on a Perfect Conducting Screen
 International Journal of High Energy Physics 016; 3(5): 33-40 http://wwwsciencepublishinggroupcom/j/ijhep doi: 1011648/jijhep016030511 ISSN: 376-7405 (Print); ISSN: 376-7448 (Online) Analytical Study of
International Journal of High Energy Physics 016; 3(5): 33-40 http://wwwsciencepublishinggroupcom/j/ijhep doi: 1011648/jijhep016030511 ISSN: 376-7405 (Print); ISSN: 376-7448 (Online) Analytical Study of
3D SUPER-RESOLUTION FLUORESCENCE MICROSC- OPY USING CYLINDRICAL VECTOR BEAMS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 43, 73 81, 2013 3D SUPER-RESOLUTION FLUORESCENCE MICROSC- OPY USING CYLINDRICAL VECTOR BEAMS Taikei Suyama 1 and Yaoju Zhang 2, * 1 Department of Electrical
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 43, 73 81, 2013 3D SUPER-RESOLUTION FLUORESCENCE MICROSC- OPY USING CYLINDRICAL VECTOR BEAMS Taikei Suyama 1 and Yaoju Zhang 2, * 1 Department of Electrical
Design of a Multi-Mode Interference Crossing Structure for Three Periodic Dielectric Waveguides
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 75, 47 52, 2018 Design of a Multi-Mode Interference Crossing Structure for Three Periodic Dielectric Waveguides Haibin Chen 1, Zhongjiao He 2,andWeiWang
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 75, 47 52, 2018 Design of a Multi-Mode Interference Crossing Structure for Three Periodic Dielectric Waveguides Haibin Chen 1, Zhongjiao He 2,andWeiWang
CREATION OF SUPER-RESOLUTION NON-DIFFRACT- ION BEAM BY MODULATING CIRCULARLY POLAR- IZED LIGHT WITH TERNARY OPTICAL ELEMENT
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 140, 589 598, 2013 CREATION OF SUPER-RESOLUTION NON-DIFFRACT- ION BEAM BY MODULATING CIRCULARLY POLAR- IZED LIGHT WITH TERNARY OPTICAL ELEMENT Jingsong Wei 1,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 140, 589 598, 2013 CREATION OF SUPER-RESOLUTION NON-DIFFRACT- ION BEAM BY MODULATING CIRCULARLY POLAR- IZED LIGHT WITH TERNARY OPTICAL ELEMENT Jingsong Wei 1,
Gravitational field around blackhole induces photonic spin-orbit interaction that twists. light
 Gravitational field around blackhole induces photonic spin-orbit interaction that twists light Deng Pan, Hong-Xing Xu ǂ School of Physics and Technology, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China Corresponding
Gravitational field around blackhole induces photonic spin-orbit interaction that twists light Deng Pan, Hong-Xing Xu ǂ School of Physics and Technology, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China Corresponding
Double-distance propagation of Gaussian beams passing through a tilted cat-eye optical lens in a turbulent atmosphere
 Double-distance propagation of Gaussian beams passing through a tilted cat-eye optical lens in a turbulent atmosphere Zhao Yan-Zhong( ), Sun Hua-Yan( ), and Song Feng-Hua( ) Department of Photoelectric
Double-distance propagation of Gaussian beams passing through a tilted cat-eye optical lens in a turbulent atmosphere Zhao Yan-Zhong( ), Sun Hua-Yan( ), and Song Feng-Hua( ) Department of Photoelectric
Propagation dynamics of abruptly autofocusing Airy beams with optical vortices
 Propagation dynamics of abruptly autofocusing Airy beams with optical vortices Yunfeng Jiang, 1 Kaikai Huang, 1,2 and Xuanhui Lu 1, * 1 Institute of Optics, Department of Physics, Zhejiang University,
Propagation dynamics of abruptly autofocusing Airy beams with optical vortices Yunfeng Jiang, 1 Kaikai Huang, 1,2 and Xuanhui Lu 1, * 1 Institute of Optics, Department of Physics, Zhejiang University,
Scattering of Poincaré beams: polarization speckles
 Research Article Vol. X, No. X / April 2016 / Optica 1 Scattering of Poincaré beams: polarization speckles SALLA GANGI REDDY 1, *, VIJAY KUMAR 2, YOKO MIYAMOTO 1, AND R. P. SINGH 2 arxiv:1705.04478v1 [physics.optics]
Research Article Vol. X, No. X / April 2016 / Optica 1 Scattering of Poincaré beams: polarization speckles SALLA GANGI REDDY 1, *, VIJAY KUMAR 2, YOKO MIYAMOTO 1, AND R. P. SINGH 2 arxiv:1705.04478v1 [physics.optics]
Transverse and longitudinal components of the propagating and evanescent waves associated to radially-polarized nonparaxial fields
 Transverse and longitudinal components of the propagating and evanescent waves associated to radially-polarized nonparaxial fields Rosario Martínez-Herrero, Pedro M. Mejías *, Ignasi Juvells, Artur Carnicer
Transverse and longitudinal components of the propagating and evanescent waves associated to radially-polarized nonparaxial fields Rosario Martínez-Herrero, Pedro M. Mejías *, Ignasi Juvells, Artur Carnicer
Dept. of Physics, MIT Manipal 1
 Chapter 1: Optics 1. In the phenomenon of interference, there is A Annihilation of light energy B Addition of energy C Redistribution energy D Creation of energy 2. Interference fringes are obtained using
Chapter 1: Optics 1. In the phenomenon of interference, there is A Annihilation of light energy B Addition of energy C Redistribution energy D Creation of energy 2. Interference fringes are obtained using
Probing the orbital angular momentum of light with a multipoint interferometer
 CHAPTER 2 Probing the orbital angular momentum of light with a multipoint interferometer We present an efficient method for probing the orbital angular momentum of optical vortices of arbitrary sizes.
CHAPTER 2 Probing the orbital angular momentum of light with a multipoint interferometer We present an efficient method for probing the orbital angular momentum of optical vortices of arbitrary sizes.
Vector Vortex Beam Generation with a Single Plasmonic Metasurface
 Vector Vortex Beam Generation with a Single Plasmonic Metasurface Fuyong Yue 1, Dandan Wen 1, Jingtao Xin, Brian D. Gerardot 1, Jensen Li 3, Xianzhong Chen 1* 1. SUPA, Institute of Photonics and Quantum
Vector Vortex Beam Generation with a Single Plasmonic Metasurface Fuyong Yue 1, Dandan Wen 1, Jingtao Xin, Brian D. Gerardot 1, Jensen Li 3, Xianzhong Chen 1* 1. SUPA, Institute of Photonics and Quantum
Directive Emission Obtained by Coordinate Transformation
 Directive Emission Obtained by Coordinate Transformation Jingjing Zhang 1, Yu Luo 1, Hongsheng Chen 1 2*, Lixin Ran 1, Bae-Ian Wu 2, and Jin Au Kong 1 2 1 The Electromagnetics Academy at Zhejiang University,
Directive Emission Obtained by Coordinate Transformation Jingjing Zhang 1, Yu Luo 1, Hongsheng Chen 1 2*, Lixin Ran 1, Bae-Ian Wu 2, and Jin Au Kong 1 2 1 The Electromagnetics Academy at Zhejiang University,
Efficient sorting of orbital angular momentum states of light
 CHAPTER 6 Efficient sorting of orbital angular momentum states of light We present a method to efficiently sort orbital angular momentum (OAM) states of light using two static optical elements. The optical
CHAPTER 6 Efficient sorting of orbital angular momentum states of light We present a method to efficiently sort orbital angular momentum (OAM) states of light using two static optical elements. The optical
Homogenous Optic-Null Medium Performs as Optical Surface Transformation
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 151, 169 173, 2015 Homogenous Optic-Null Medium Performs as Optical Surface Transformation Fei Sun 1 and Sailing He1, 2, * Abstract An optical surface transformation
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 151, 169 173, 2015 Homogenous Optic-Null Medium Performs as Optical Surface Transformation Fei Sun 1 and Sailing He1, 2, * Abstract An optical surface transformation
3.3 The Wave Nature of Light
 3.3 The Wave Nature of Light Much of the history of physics is concerned with the evolution of our ideas about the nature of light. The speed of light was first measured with some accuracy in 1675, by
3.3 The Wave Nature of Light Much of the history of physics is concerned with the evolution of our ideas about the nature of light. The speed of light was first measured with some accuracy in 1675, by
Interferences in Photodetachment of a Negative Molecular Ion Model
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 50 (2008) pp. 1401 1406 c Chinese Physical Society Vol. 50, No. 6, December 15, 2008 Interferences in Photodetachment of a Negative Molecular Ion Model A. Afaq 1,
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 50 (2008) pp. 1401 1406 c Chinese Physical Society Vol. 50, No. 6, December 15, 2008 Interferences in Photodetachment of a Negative Molecular Ion Model A. Afaq 1,
Transport properties through double-magnetic-barrier structures in graphene
 Chin. Phys. B Vol. 20, No. 7 (20) 077305 Transport properties through double-magnetic-barrier structures in graphene Wang Su-Xin( ) a)b), Li Zhi-Wen( ) a)b), Liu Jian-Jun( ) c), and Li Yu-Xian( ) c) a)
Chin. Phys. B Vol. 20, No. 7 (20) 077305 Transport properties through double-magnetic-barrier structures in graphene Wang Su-Xin( ) a)b), Li Zhi-Wen( ) a)b), Liu Jian-Jun( ) c), and Li Yu-Xian( ) c) a)
Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light
 Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light Lecture aims to explain: 1. Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications 2. Interference of two one dimensional electromagnetic waves 3. Typical
Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light Lecture aims to explain: 1. Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications 2. Interference of two one dimensional electromagnetic waves 3. Typical
Electricity & Optics
 Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 26 Chapter 33 sec. 1-4 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Interference of Light Interference phenomena are a consequence of the wave-like nature of light Electric
Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 26 Chapter 33 sec. 1-4 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Interference of Light Interference phenomena are a consequence of the wave-like nature of light Electric
Physics General Physics II. Electricity, Magnetism and Optics Lecture 20 Chapter Wave Optics. Fall 2015 Semester Prof.
 Physics 21900 General Physics II Electricity, Magnetism and Optics Lecture 20 Chapter 23.1-2 Wave Optics Fall 2015 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones Announcement Exam #2 will be on Thursday, November 5 th (tomorrow)
Physics 21900 General Physics II Electricity, Magnetism and Optics Lecture 20 Chapter 23.1-2 Wave Optics Fall 2015 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones Announcement Exam #2 will be on Thursday, November 5 th (tomorrow)
The Aharanov Bohm Effect
 Supplement 6-A The Aharanov Bohm Effect Let us return to the description of an electron of charge e and mass m e, in a timeindependent magnetic field. The system is described by the Hamiltonian and the
Supplement 6-A The Aharanov Bohm Effect Let us return to the description of an electron of charge e and mass m e, in a timeindependent magnetic field. The system is described by the Hamiltonian and the
Channel Optical Waveguides with Spatial Longitudinal Modulation of Their Parameters Induced in Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Samples
 Russian Forum of Young Scientists Volume 2018 Conference Paper Channel Optical Waveguides with Spatial Longitudinal Modulation of Their Parameters Induced in Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Samples A D
Russian Forum of Young Scientists Volume 2018 Conference Paper Channel Optical Waveguides with Spatial Longitudinal Modulation of Their Parameters Induced in Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Samples A D
Waveplate analyzer using binary magneto-optic rotators
 Waveplate analyzer using binary magneto-optic rotators Xiaojun Chen 1, Lianshan Yan 1, and X. Steve Yao 1, 1. General Photonics Corp. Chino, CA, 91710, USA Tel: 909-590-5473 Fax: 909-90-5535. Polarization
Waveplate analyzer using binary magneto-optic rotators Xiaojun Chen 1, Lianshan Yan 1, and X. Steve Yao 1, 1. General Photonics Corp. Chino, CA, 91710, USA Tel: 909-590-5473 Fax: 909-90-5535. Polarization
Lecture 11: Introduction to diffraction of light
 Lecture 11: Introduction to diffraction of light Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications Diffraction in everyday life Diffraction in applications Spectroscopy: physics, chemistry, medicine,
Lecture 11: Introduction to diffraction of light Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications Diffraction in everyday life Diffraction in applications Spectroscopy: physics, chemistry, medicine,
Scattering of light from quasi-homogeneous sources by quasi-homogeneous media
 Visser et al. Vol. 23, No. 7/July 2006/J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1631 Scattering of light from quasi-homogeneous sources by quasi-homogeneous media Taco D. Visser* Department of Physics and Astronomy, University
Visser et al. Vol. 23, No. 7/July 2006/J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1631 Scattering of light from quasi-homogeneous sources by quasi-homogeneous media Taco D. Visser* Department of Physics and Astronomy, University
Orbital Angular Momentum Density of a Hollow Vortex Gaussian Beam
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 38, 15 24, 214 Orbital Angular Momentum Density of a Hollow Vortex Gaussian Beam Yimin Zhou and Guoquan Zhou * Abstract Here the hollow vortex Gaussian beam
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 38, 15 24, 214 Orbital Angular Momentum Density of a Hollow Vortex Gaussian Beam Yimin Zhou and Guoquan Zhou * Abstract Here the hollow vortex Gaussian beam
Hanbury Brown Twiss effect and thermal light ghost imaging: A unified approach
 PHYSICAL REVIEW A 79, 033835 009 Hanbury Brown Twiss effect and thermal light ghost imaging: A unified approach Li-Gang Wang, 1, Sajid Qamar, 3 Shi-Yao Zhu, 1, and M. Suhail Zubairy 3,4 1 Department of
PHYSICAL REVIEW A 79, 033835 009 Hanbury Brown Twiss effect and thermal light ghost imaging: A unified approach Li-Gang Wang, 1, Sajid Qamar, 3 Shi-Yao Zhu, 1, and M. Suhail Zubairy 3,4 1 Department of
New Concept Conformal Antennas Utilizing Metamaterial and Transformation Optics
 New Concept Conformal Antennas Utilizing Metamaterial and Transformation Optics The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
New Concept Conformal Antennas Utilizing Metamaterial and Transformation Optics The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Rezonanse typu spin-orbit w meta-materiałowych elementach nanofotoniki Spin-orbit resonances in meta-material elements of nanophotonics
 Rezonanse typu spin-orbit w meta-materiałowych elementach nanofotoniki Spin-orbit resonances in meta-material elements of nanophotonics Wojciech Nasalski Zespół Badawczy Nanofotoniki Instytut Podstawowych
Rezonanse typu spin-orbit w meta-materiałowych elementach nanofotoniki Spin-orbit resonances in meta-material elements of nanophotonics Wojciech Nasalski Zespół Badawczy Nanofotoniki Instytut Podstawowych
Geometric interpretation of the Pancharatnam connection and non-cyclic polarization changes
 1972 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A/ Vol. 27, No. 9/ September 2010 van Dijk et al. Geometric interpretation of the Pancharatnam connection and non-cyclic polarization changes Thomas van Dijk, 1 Hugo F. Schouten,
1972 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A/ Vol. 27, No. 9/ September 2010 van Dijk et al. Geometric interpretation of the Pancharatnam connection and non-cyclic polarization changes Thomas van Dijk, 1 Hugo F. Schouten,
Vector diffraction theory of refraction of light by a spherical surface
 S. Guha and G. D. Gillen Vol. 4, No. 1/January 007/J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1 Vector diffraction theory of refraction of light by a spherical surface Shekhar Guha and Glen D. Gillen* Materials and Manufacturing
S. Guha and G. D. Gillen Vol. 4, No. 1/January 007/J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1 Vector diffraction theory of refraction of light by a spherical surface Shekhar Guha and Glen D. Gillen* Materials and Manufacturing
A GENERALIZED COUPLED-LINE DUAL-BAND WILKINSON POWER DIVIDER WITH EXTENDED PORTS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 19, 197 14, 1 A GENERALIZED COUPLED-LINE DUAL-BAND WILKINSON POWER DIVIDER WITH EXTENDED PORTS J. C. Li *, Y. L. Wu, Y. A. Liu, J. Y. Shen, S. L. Li, and C.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 19, 197 14, 1 A GENERALIZED COUPLED-LINE DUAL-BAND WILKINSON POWER DIVIDER WITH EXTENDED PORTS J. C. Li *, Y. L. Wu, Y. A. Liu, J. Y. Shen, S. L. Li, and C.
arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 21 Nov 2011
![arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 21 Nov 2011 arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 21 Nov 2011](/thumbs/85/92542022.jpg) Polarization manipulation holographic lithography by single refracting prism Yi Xu, Man Wu, Xiuming Lan, Xiaoxu Lu,Sheng Lan and Lijun Wu arxiv:1111.4860v1 [physics.optics] 21 Nov 2011 Laboratory of Photonic
Polarization manipulation holographic lithography by single refracting prism Yi Xu, Man Wu, Xiuming Lan, Xiaoxu Lu,Sheng Lan and Lijun Wu arxiv:1111.4860v1 [physics.optics] 21 Nov 2011 Laboratory of Photonic
Visualization of polarization state and its application in Optics classroom teaching
 Visualization of polarization state and its application in Optics classroom teaching Bing Lei 1, *, Wei Liu 1, Jianhua Shi 1, Wei Wang 1, Tianfu Yao 1 and Shugang Liu 2 1 College of Optoelectronic Science
Visualization of polarization state and its application in Optics classroom teaching Bing Lei 1, *, Wei Liu 1, Jianhua Shi 1, Wei Wang 1, Tianfu Yao 1 and Shugang Liu 2 1 College of Optoelectronic Science
Chapter 10. Interference of Light
 Chapter 10. Interference of Light Last Lecture Wave equations Maxwell equations and EM waves Superposition of waves This Lecture Two-Beam Interference Young s Double Slit Experiment Virtual Sources Newton
Chapter 10. Interference of Light Last Lecture Wave equations Maxwell equations and EM waves Superposition of waves This Lecture Two-Beam Interference Young s Double Slit Experiment Virtual Sources Newton
Bessel & Laguerre-Gauss Beam Generation using SLM as a Reconfigurable Diffractive Optical Element
 Bessel & Laguerre-Gauss Beam Generation using SLM as a Reconfigurable Diffractive Optical Element Sendhil Raja S., Rijuparna Chakraborty*, L.N.Hazra*, A.G.Bhujle Laser Instrumentation Section, Instrumentation
Bessel & Laguerre-Gauss Beam Generation using SLM as a Reconfigurable Diffractive Optical Element Sendhil Raja S., Rijuparna Chakraborty*, L.N.Hazra*, A.G.Bhujle Laser Instrumentation Section, Instrumentation
Max-Planck-Institut für Mathematik in den Naturwissenschaften Leipzig
 Max-Planck-Institut für Mathematik in den Naturwissenschaften Leipzig Coherence of Assistance and Regularized Coherence of Assistance by Ming-Jing Zhao, Teng Ma, and Shao-Ming Fei Preprint no.: 14 2018
Max-Planck-Institut für Mathematik in den Naturwissenschaften Leipzig Coherence of Assistance and Regularized Coherence of Assistance by Ming-Jing Zhao, Teng Ma, and Shao-Ming Fei Preprint no.: 14 2018
Infrared carpet cloak designed with uniform silicon grating structure
 Infrared carpet cloak designed with uniform silicon grating structure Xiaofei Xu, Yijun Feng, Yu Hao, Juming Zhao, Tian Jiang Department of Electronic Science and Engineering, Nanjing Univerisity, Nanjing,
Infrared carpet cloak designed with uniform silicon grating structure Xiaofei Xu, Yijun Feng, Yu Hao, Juming Zhao, Tian Jiang Department of Electronic Science and Engineering, Nanjing Univerisity, Nanjing,
Part 1: Fano resonances Part 2: Airy beams Part 3: Parity-time symmetric systems
 Lecture 3 Part 1: Fano resonances Part 2: Airy beams Part 3: Parity-time symmetric systems Yuri S. Kivshar Nonlinear Physics Centre, Australian National University, Canberra, Australia http://wwwrsphysse.anu.edu.au/nonlinear/
Lecture 3 Part 1: Fano resonances Part 2: Airy beams Part 3: Parity-time symmetric systems Yuri S. Kivshar Nonlinear Physics Centre, Australian National University, Canberra, Australia http://wwwrsphysse.anu.edu.au/nonlinear/
Holography and Optical Vortices
 WJP, PHY381 (2011) Wabash Journal of Physics v3.3, p.1 Holography and Optical Vortices Z. J. Rohrbach, J. M. Soller, and M. J. Madsen Department of Physics, Wabash College, Crawfordsville, IN 47933 (Dated:
WJP, PHY381 (2011) Wabash Journal of Physics v3.3, p.1 Holography and Optical Vortices Z. J. Rohrbach, J. M. Soller, and M. J. Madsen Department of Physics, Wabash College, Crawfordsville, IN 47933 (Dated:
Focusing of light. Colin Sheppard Division of Bioengineering and Department of Biological Sciences National University of Singapore
 Focusing of light Colin Sheppard Division of Bioengineering and Department of Biological Sciences National University of Singapore E-mail: colin@nus.edu.sg Tight focusing of light Microscopy Laser micromachining
Focusing of light Colin Sheppard Division of Bioengineering and Department of Biological Sciences National University of Singapore E-mail: colin@nus.edu.sg Tight focusing of light Microscopy Laser micromachining
New Feedback Control Model in the Lattice Hydrodynamic Model Considering the Historic Optimal Velocity Difference Effect
 Commun. Theor. Phys. 70 (2018) 803 807 Vol. 70, No. 6, December 1, 2018 New Feedback Control Model in the Lattice Hydrodynamic Model Considering the Historic Optimal Velocity Difference Effect Guang-Han
Commun. Theor. Phys. 70 (2018) 803 807 Vol. 70, No. 6, December 1, 2018 New Feedback Control Model in the Lattice Hydrodynamic Model Considering the Historic Optimal Velocity Difference Effect Guang-Han
Acoustic coupling between cascade sub-chambers and its influence on overall transmission loss
 Acoustic coupling between cascade sub-chambers and its influence on overall transmission loss Yuhui Tong School of Mechanical and Chemical Engineering, The University of Western Australia, Crawley WA 6009,
Acoustic coupling between cascade sub-chambers and its influence on overall transmission loss Yuhui Tong School of Mechanical and Chemical Engineering, The University of Western Australia, Crawley WA 6009,
Experimental observation of optical vortex evolution in a Gaussian beam. with an embedded fractional phase step
 Experimental observation of optical vortex evolution in a Gaussian beam with an embedded fractional phase step W.M. Lee 1, X.-C. Yuan 1 * and K.Dholakia 1 Photonics Research Center, School of Electrical
Experimental observation of optical vortex evolution in a Gaussian beam with an embedded fractional phase step W.M. Lee 1, X.-C. Yuan 1 * and K.Dholakia 1 Photonics Research Center, School of Electrical
CHAPTER I Review of Modern Physics. A. Review of Important Experiments
 CHAPTER I Review of Modern Physics A. Review of Important Experiments Quantum Mechanics is analogous to Newtonian Mechanics in that it is basically a system of rules which describe what happens at the
CHAPTER I Review of Modern Physics A. Review of Important Experiments Quantum Mechanics is analogous to Newtonian Mechanics in that it is basically a system of rules which describe what happens at the
Interference by Wavefront Division
 nterference by Wavefront Division One of the seminal experiments in physics was conducted in 1801 by Thomas Young, an English physicist who cut a small hole in an opaque screen, set a second screen in
nterference by Wavefront Division One of the seminal experiments in physics was conducted in 1801 by Thomas Young, an English physicist who cut a small hole in an opaque screen, set a second screen in
Optics Communications
 Optics Communications 294 (2013) 36 42 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Optics Communications journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Propagation properties and self-reconstruction
Optics Communications 294 (2013) 36 42 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Optics Communications journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Propagation properties and self-reconstruction
BISTABLE twisted nematic (BTN) liquid crystal displays
 JOURNAL OF DISPLAY TECHNOLOGY, VOL 1, NO 2, DECEMBER 2005 217 Analytic Solution of Film Compensated Bistable Twisted Nematic Liquid Crystal Displays Fushan Zhou and Deng-Ke Yang Abstract In this paper,
JOURNAL OF DISPLAY TECHNOLOGY, VOL 1, NO 2, DECEMBER 2005 217 Analytic Solution of Film Compensated Bistable Twisted Nematic Liquid Crystal Displays Fushan Zhou and Deng-Ke Yang Abstract In this paper,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Perovskite light-emitting diodes based on solution-processed self-organized multiple quantum wells Nana Wang 1*, Lu Cheng 1*, Rui Ge 1*, Shuting Zhang 1, Yanfeng Miao 1, Wei Zou 1, Chang Yi 1, Yan Sun
Perovskite light-emitting diodes based on solution-processed self-organized multiple quantum wells Nana Wang 1*, Lu Cheng 1*, Rui Ge 1*, Shuting Zhang 1, Yanfeng Miao 1, Wei Zou 1, Chang Yi 1, Yan Sun
Waves Part III Electromagnetic waves
 Waves Part III Electromagnetic waves Electromagnetic (light) waves Transverse waves Transport energy (and momentum) Can travel through vacuum (!) and certain solids, liquids and gases Do not transport
Waves Part III Electromagnetic waves Electromagnetic (light) waves Transverse waves Transport energy (and momentum) Can travel through vacuum (!) and certain solids, liquids and gases Do not transport
Propagation of Lorentz Gaussian Beams in Strongly Nonlocal Nonlinear Media
 Commun. Theor. Phys. 6 04 4 45 Vol. 6, No., February, 04 Propagation of Lorentz Gaussian Beams in Strongly Nonlocal Nonlinear Media A. Keshavarz and G. Honarasa Department of Physics, Faculty of Science,
Commun. Theor. Phys. 6 04 4 45 Vol. 6, No., February, 04 Propagation of Lorentz Gaussian Beams in Strongly Nonlocal Nonlinear Media A. Keshavarz and G. Honarasa Department of Physics, Faculty of Science,
Phase-Shift Estimation from Interferograms by Histogram of Phase Difference
 Copyright 2011 Tech Science Press SL, vol.5, no.2, pp.77-82, 2011 Phase-Shift Estimation from Interferograms by Histogram of Phase Difference Jiancheng Xu 1 and Yong Li 1 Abstract: We propose a non-iterative
Copyright 2011 Tech Science Press SL, vol.5, no.2, pp.77-82, 2011 Phase-Shift Estimation from Interferograms by Histogram of Phase Difference Jiancheng Xu 1 and Yong Li 1 Abstract: We propose a non-iterative
CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I
 CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I 5.1 X-Ray Scattering 5.2 De Broglie Waves 5.3 Electron Scattering 5.4 Wave Motion 5.5 Waves or Particles? 5.6 Uncertainty Principle 5.7 Probability,
CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I 5.1 X-Ray Scattering 5.2 De Broglie Waves 5.3 Electron Scattering 5.4 Wave Motion 5.5 Waves or Particles? 5.6 Uncertainty Principle 5.7 Probability,
Experiment and Simulation Study on A New Structure of Full Optical Fiber Current Sensor
 2017 2nd International Conference on Computational Modeling, Simulation and Applied Mathematics (CMSAM 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-499-8 Experiment and Simulation Study on A New Structure of Full Optical Fiber
2017 2nd International Conference on Computational Modeling, Simulation and Applied Mathematics (CMSAM 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-499-8 Experiment and Simulation Study on A New Structure of Full Optical Fiber
is the minimum stopping potential for which the current between the plates reduces to zero.
 Module 1 :Quantum Mechanics Chapter 2 : Introduction to Quantum ideas Introduction to Quantum ideas We will now consider some experiments and their implications, which introduce us to quantum ideas. The
Module 1 :Quantum Mechanics Chapter 2 : Introduction to Quantum ideas Introduction to Quantum ideas We will now consider some experiments and their implications, which introduce us to quantum ideas. The
Unbalanced lensless ghost imaging with thermal light
 886 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A / Vol. 3, No. 4 / April 04 Gao et al. Unbalanced lensless ghost imaging with thermal light Lu Gao,,3 Xiao-long Liu, hiyuan heng, and Kaige Wang, * School of Science, China University
886 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A / Vol. 3, No. 4 / April 04 Gao et al. Unbalanced lensless ghost imaging with thermal light Lu Gao,,3 Xiao-long Liu, hiyuan heng, and Kaige Wang, * School of Science, China University
Critical entanglement and geometric phase of a two-qubit model with Dzyaloshinski Moriya anisotropic interaction
 Chin. Phys. B Vol. 19, No. 1 010) 010305 Critical entanglement and geometric phase of a two-qubit model with Dzyaloshinski Moriya anisotropic interaction Li Zhi-Jian 李志坚 ), Cheng Lu 程璐 ), and Wen Jiao-Jin
Chin. Phys. B Vol. 19, No. 1 010) 010305 Critical entanglement and geometric phase of a two-qubit model with Dzyaloshinski Moriya anisotropic interaction Li Zhi-Jian 李志坚 ), Cheng Lu 程璐 ), and Wen Jiao-Jin
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics In order to understand the current-voltage characteristics, we need some knowledge of electron behavior in semiconductor when the electron is subjected to various potential
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics In order to understand the current-voltage characteristics, we need some knowledge of electron behavior in semiconductor when the electron is subjected to various potential
2108. Free vibration properties of rotate vector reducer
 2108. Free vibration properties of rotate vector reducer Chuan Chen 1, Yuhu Yang 2 School of Mechanical Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072, P. R. China 1 Corresponding author E-mail: 1 chenchuan1985728@126.com,
2108. Free vibration properties of rotate vector reducer Chuan Chen 1, Yuhu Yang 2 School of Mechanical Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072, P. R. China 1 Corresponding author E-mail: 1 chenchuan1985728@126.com,
Wigner function for nonparaxial wave fields
 486 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A/ Vol. 18, No. 10/ October 001 C. J. R. Sheppard and K. G. Larin Wigner function for nonparaxial wave fields Colin J. R. Sheppard* and Kieran G. Larin Department of Physical Optics,
486 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A/ Vol. 18, No. 10/ October 001 C. J. R. Sheppard and K. G. Larin Wigner function for nonparaxial wave fields Colin J. R. Sheppard* and Kieran G. Larin Department of Physical Optics,
Enhancing and suppressing radiation with some permeability-near-zero structures
 Enhancing and suppressing radiation with some permeability-near-zero structures Yi Jin 1,2 and Sailing He 1,2,3,* 1 Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical
Enhancing and suppressing radiation with some permeability-near-zero structures Yi Jin 1,2 and Sailing He 1,2,3,* 1 Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical
Light was recognised as a wave phenomenon well before its electromagnetic character became known.
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE MODULE 7 NATURE OF LIGHT WAVE or PARTICLE??? Light was recognised as a wave phenomenon well before its electromagnetic character became known. The problem of the nature of light is
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE MODULE 7 NATURE OF LIGHT WAVE or PARTICLE??? Light was recognised as a wave phenomenon well before its electromagnetic character became known. The problem of the nature of light is
Experimental observation of optical vortex evolution in a Gaussian beam. with an embedded fractional phase step
 Experimental observation of optical vortex evolution in a Gaussian beam with an embedded fractional phase step W.M. Lee 1, X.-C. Yuan 1 * and K.Dholakia 1 Photonics Research Center, School of Electrical
Experimental observation of optical vortex evolution in a Gaussian beam with an embedded fractional phase step W.M. Lee 1, X.-C. Yuan 1 * and K.Dholakia 1 Photonics Research Center, School of Electrical
Generation of helical modes of light by spin-to-orbital angular momentum conversion in inhomogeneous liquid crystals
 electronic-liquid Crystal Crystal Generation of helical modes of light by spin-to-orbital angular momentum conversion in inhomogeneous liquid crystals Lorenzo Marrucci Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche Università
electronic-liquid Crystal Crystal Generation of helical modes of light by spin-to-orbital angular momentum conversion in inhomogeneous liquid crystals Lorenzo Marrucci Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche Università
Conical diffraction and Bessel beam formation with a high optical quality biaxial crystal
 Conical diffraction and Bessel beam formation with a high optical quality biaxial crystal C. F. Phelan, D. P. O Dwyer, Y. P. Rakovich, J. F. Donegan and J. G. Lunney School of Physics, Trinity College
Conical diffraction and Bessel beam formation with a high optical quality biaxial crystal C. F. Phelan, D. P. O Dwyer, Y. P. Rakovich, J. F. Donegan and J. G. Lunney School of Physics, Trinity College
From optical graphene to topological insulator
 From optical graphene to topological insulator Xiangdong Zhang Beijing Institute of Technology (BIT), China zhangxd@bit.edu.cn Collaborator: Wei Zhong (PhD student, BNU) Outline Background: From solid
From optical graphene to topological insulator Xiangdong Zhang Beijing Institute of Technology (BIT), China zhangxd@bit.edu.cn Collaborator: Wei Zhong (PhD student, BNU) Outline Background: From solid
An Example of Telescope Resolution
 An Example of Telescope Resolution J. Kielkopf September 23, 2012 1 Principles Light leaves a distant source with the properties of a spherical wave. That is, the phase of the wave is constant on the surface
An Example of Telescope Resolution J. Kielkopf September 23, 2012 1 Principles Light leaves a distant source with the properties of a spherical wave. That is, the phase of the wave is constant on the surface
Two-dimensional Cross Embedded Metamaterials
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 3, NO. 3, 7 4 Two-dimensional Cross Embedded Metamaterials J. Zhang,, H. Chen,, L. Ran,, Y. Luo,, and J. A. Kong,3 The Electromagentics Academy at Zhejiang University, Zhejiang University
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 3, NO. 3, 7 4 Two-dimensional Cross Embedded Metamaterials J. Zhang,, H. Chen,, L. Ran,, Y. Luo,, and J. A. Kong,3 The Electromagentics Academy at Zhejiang University, Zhejiang University
Modeling microlenses by use of vectorial field rays and diffraction integrals
 Modeling microlenses by use of vectorial field rays and diffraction integrals Miguel A. Alvarez-Cabanillas, Fang Xu, and Yeshaiahu Fainman A nonparaxial vector-field method is used to describe the behavior
Modeling microlenses by use of vectorial field rays and diffraction integrals Miguel A. Alvarez-Cabanillas, Fang Xu, and Yeshaiahu Fainman A nonparaxial vector-field method is used to describe the behavior
Lecture 6 Scattering theory Partial Wave Analysis. SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2
 Lecture 6 Scattering theory Partial Wave Analysis SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2 1 The Born approximation for the differential cross section is valid if the interaction
Lecture 6 Scattering theory Partial Wave Analysis SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2 1 The Born approximation for the differential cross section is valid if the interaction
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 97, , 2009
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 97, 407 416, 2009 PRACTICAL LIMITATIONS OF AN INVISIBILITY CLOAK B. L. Zhang Research Laboratory of Electronics Massachusetts Institute of Technology MA 02139,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 97, 407 416, 2009 PRACTICAL LIMITATIONS OF AN INVISIBILITY CLOAK B. L. Zhang Research Laboratory of Electronics Massachusetts Institute of Technology MA 02139,
Matter Waves. Chapter 5
 Matter Waves Chapter 5 De Broglie pilot waves Electromagnetic waves are associated with quanta - particles called photons. Turning this fact on its head, Louis de Broglie guessed : Matter particles have
Matter Waves Chapter 5 De Broglie pilot waves Electromagnetic waves are associated with quanta - particles called photons. Turning this fact on its head, Louis de Broglie guessed : Matter particles have
INTERFERENCE 1.1 NATURE OF LIGHT
 1 INTERFERENCE 1.1 NATURE OF LIGHT In the year 1678, Christian Huygens proposed the wave theory of light. According to this, a Luminous body is a source of disturbance in hypothetical medium called ether
1 INTERFERENCE 1.1 NATURE OF LIGHT In the year 1678, Christian Huygens proposed the wave theory of light. According to this, a Luminous body is a source of disturbance in hypothetical medium called ether
A LOW-FREQUENCY METASURFACE ABSORBER BASED ON HELMHOLTZ RESONATORS
 A LOW-FREQUENCY METASURFACE ABSORBER BASED ON HELMHOLTZ RESONATORS Honggang Zhao )), Yang Wang ), Dan Zhao ), and Jihong Wen ) email: zhhg963@sina.com Yiu Wai Lam ), Olga Umnova ) ) Vibration and Acoustics
A LOW-FREQUENCY METASURFACE ABSORBER BASED ON HELMHOLTZ RESONATORS Honggang Zhao )), Yang Wang ), Dan Zhao ), and Jihong Wen ) email: zhhg963@sina.com Yiu Wai Lam ), Olga Umnova ) ) Vibration and Acoustics
The Monte Carlo Simulation of Secondary Electrons Excitation in the Resist PMMA
 Applied Physics Research; Vol. 6, No. 3; 204 ISSN 96-9639 E-ISSN 96-9647 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education The Monte Carlo Simulation of Secondary Electrons Excitation in the Resist
Applied Physics Research; Vol. 6, No. 3; 204 ISSN 96-9639 E-ISSN 96-9647 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education The Monte Carlo Simulation of Secondary Electrons Excitation in the Resist
Chapter 35. Interference
 Chapter 35 Interference The concept of optical interference is critical to understanding many natural phenomena, ranging from color shifting in butterfly wings to intensity patterns formed by small apertures.
Chapter 35 Interference The concept of optical interference is critical to understanding many natural phenomena, ranging from color shifting in butterfly wings to intensity patterns formed by small apertures.
Chapter 4. Development of a New Model
 Chapter 4 Development of a New Model Electrons behave like particles in some experiments, and like waves in others. The electron's 'wave/particle duality' has no real analogy in the everyday world. The
Chapter 4 Development of a New Model Electrons behave like particles in some experiments, and like waves in others. The electron's 'wave/particle duality' has no real analogy in the everyday world. The
Nonlinear Metamaterial Composite Structure with Tunable Tunneling Frequency
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 71, 91 96, 2017 Nonlinear Metamaterial Composite Structure with Tunable Tunneling Frequency Tuanhui Feng *,HongpeiHan,LiminWang,andFeiYang Abstract A
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 71, 91 96, 2017 Nonlinear Metamaterial Composite Structure with Tunable Tunneling Frequency Tuanhui Feng *,HongpeiHan,LiminWang,andFeiYang Abstract A
Using the Spectrometer
 Using the Spectrometer Introduction When an atom is stimulated it can respond by emitting a spectrum of light. The spectrum comprises discrete wavelengths whose values are characteristic of the particular
Using the Spectrometer Introduction When an atom is stimulated it can respond by emitting a spectrum of light. The spectrum comprises discrete wavelengths whose values are characteristic of the particular
Vector dark domain wall solitons in a fiber ring laser
 Vector dark domain wall solitons in a fiber ring laser H. Zhang, D. Y. Tang*, L. M. Zhao and R. J. Knize 1 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798
Vector dark domain wall solitons in a fiber ring laser H. Zhang, D. Y. Tang*, L. M. Zhao and R. J. Knize 1 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798
Generating Bessel beams by use of localized modes
 992 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A/ Vol. 22, No. 5/ May 2005 W. B. Williams and J. B. Pendry Generating Bessel beams by use of localized modes W. B. Williams and J. B. Pendry Condensed Matter Theory Group, The Blackett
992 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A/ Vol. 22, No. 5/ May 2005 W. B. Williams and J. B. Pendry Generating Bessel beams by use of localized modes W. B. Williams and J. B. Pendry Condensed Matter Theory Group, The Blackett
1/d o +1/d i =1/f. Chapter 24 Wave Optics. The Lens Equation. Diffraction Interference Polarization. The Nature of Light
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Interference Polarization 2F h o The Lens Equation 1/d o +1/d i =1/f F F O d o f d i h i Geometrical and Physical Optics Geometrical Optics: The study of optical phenomena
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Interference Polarization 2F h o The Lens Equation 1/d o +1/d i =1/f F F O d o f d i h i Geometrical and Physical Optics Geometrical Optics: The study of optical phenomena
Wave properties of matter & Quantum mechanics I. Chapter 5
 Wave properties of matter & Quantum mechanics I Chapter 5 X-ray diffraction Max von Laue suggested that if x-rays were a form of electromagnetic radiation, interference effects should be observed. Crystals
Wave properties of matter & Quantum mechanics I Chapter 5 X-ray diffraction Max von Laue suggested that if x-rays were a form of electromagnetic radiation, interference effects should be observed. Crystals
PH 222-3A Spring 2010
 PH -3A Spring 010 Interference Lecture 6-7 Chapter 35 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 35 Interference The concept of optical interference is critical to understanding
PH -3A Spring 010 Interference Lecture 6-7 Chapter 35 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 35 Interference The concept of optical interference is critical to understanding
Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers
 Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers I. FOCAL LENGTH OF LENSES The behavior of simplest optical devices can be described by the method of geometrical optics. For convex or converging and concave
Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers I. FOCAL LENGTH OF LENSES The behavior of simplest optical devices can be described by the method of geometrical optics. For convex or converging and concave
Periodic microstructures fabricated by multiplex interfering femtosecond laser beams on graphene sheet
 Int. J. Nanomanufacturing, Vol. 8, No. 3, 2012 221 Periodic microstructures fabricated by multiplex interfering femtosecond laser beams on graphene sheet Yan Li TEDA Applied Physics School, Nankai University,
Int. J. Nanomanufacturing, Vol. 8, No. 3, 2012 221 Periodic microstructures fabricated by multiplex interfering femtosecond laser beams on graphene sheet Yan Li TEDA Applied Physics School, Nankai University,
Perovskite Solar Cells Powered Electrochromic Batteries for Smart. Windows
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Materials Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information for Perovskite Solar Cells Powered Electrochromic Batteries for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Materials Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information for Perovskite Solar Cells Powered Electrochromic Batteries for
THE SCATTERING FROM AN ELLIPTIC CYLINDER IRRADIATED BY AN ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE WITH ARBITRARY DIRECTION AND POLARIZATION
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 5, 137 149, 2008 THE SCATTERING FROM AN ELLIPTIC CYLINDER IRRADIATED BY AN ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE WITH ARBITRARY DIRECTION AND POLARIZATION Y.-L. Li, M.-J.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 5, 137 149, 2008 THE SCATTERING FROM AN ELLIPTIC CYLINDER IRRADIATED BY AN ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE WITH ARBITRARY DIRECTION AND POLARIZATION Y.-L. Li, M.-J.
Chapter 7. Interference of Light
 Chapter 7. Interference of Light Last Lecture Superposition of waves Laser This Lecture Two-Beam Interference Young s Double Slit Experiment Virtual Sources Newton s Rings Film Thickness Measurement by
Chapter 7. Interference of Light Last Lecture Superposition of waves Laser This Lecture Two-Beam Interference Young s Double Slit Experiment Virtual Sources Newton s Rings Film Thickness Measurement by
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Light emission near a gradient metasurface Leonard C. Kogos and Roberto Paiella Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Photonics Center, Boston University, Boston,
Supporting Information Light emission near a gradient metasurface Leonard C. Kogos and Roberto Paiella Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Photonics Center, Boston University, Boston,
Supplementary information for Quantum delayed-choice experiment with a beam splitter in a quantum superposition
 Supplementary information for Quantum delayed-choice experiment with a beam splitter in a quantum superposition Shi-Biao Zheng 1, You-Peng Zhong 2, Kai Xu 2, Qi-Jue Wang 2, H. Wang 2, Li-Tuo Shen 1, Chui-Ping
Supplementary information for Quantum delayed-choice experiment with a beam splitter in a quantum superposition Shi-Biao Zheng 1, You-Peng Zhong 2, Kai Xu 2, Qi-Jue Wang 2, H. Wang 2, Li-Tuo Shen 1, Chui-Ping
Flute-Model Acoustic Metamaterials with Simultaneously. Negative Bulk Modulus and Mass Density
 Flute-Model Acoustic Metamaterials with Simultaneously Negative Bulk Modulus and Mass Density H. C. Zeng, C. R. Luo, H. J. Chen, S. L. Zhai and X. P. Zhao * Smart Materials Laboratory, Department of Applied
Flute-Model Acoustic Metamaterials with Simultaneously Negative Bulk Modulus and Mass Density H. C. Zeng, C. R. Luo, H. J. Chen, S. L. Zhai and X. P. Zhao * Smart Materials Laboratory, Department of Applied
VIC Effect and Phase-Dependent Optical Properties of Five-Level K-Type Atoms Interacting with Coherent Laser Fields
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing China) 50 (2008) pp. 741 748 c Chinese Physical Society Vol. 50 No. 3 September 15 2008 VIC Effect and Phase-Dependent Optical Properties of Five-Level K-Type Atoms Interacting
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing China) 50 (2008) pp. 741 748 c Chinese Physical Society Vol. 50 No. 3 September 15 2008 VIC Effect and Phase-Dependent Optical Properties of Five-Level K-Type Atoms Interacting
WAVE NATURE OF LIGHT
 WAVE NATURE OF LIGHT Light is electromagnetic radiation, a type of energy composed of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. The fields oscillate perpendicular to each other. In vacuum, these waves
WAVE NATURE OF LIGHT Light is electromagnetic radiation, a type of energy composed of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. The fields oscillate perpendicular to each other. In vacuum, these waves
