A BURN MODEL BASED ON HEATING DUE TO SHEAR FLOW: PROOF OF PRINCIPLE CALCULATIONS. F. J. Zerilli, R. H. Guirguis, and C. S. Coffey
|
|
|
- Toby Hill
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A BURN MODEL BASED ON HEATING DUE TO SHEAR FLOW: PROOF OF PRINCIPLE CALCULATIONS F. J. Zerilli, R. H. Guirguis, and C. S. Coffey Indian Head Division Naval Surface Warfare Center Indian Head, MD Preliminary modeling calculations with the finite element material dynamics computer program EPIC using an ignition model incorporating heating due to shear show that this type of model can successfully predict ignition in a ballistic impact test in which a small wafer of energetic material is squeezed between an anvil and a striker. Both experiment and model indicate that ignition occurs at the periphery, in the region of large shear, rather than at the center, the region of high pressure. INTRODUCTION Preliminary modeling calculations for a ballistic impact test show that an ignition model incorporating heating due to shear successfully predicts the ignition pattern observed in the experiments, that is, ignition occurs in regions of high shear, and not necessarily high pressure. The reaction model addresses ignition due to combined compression and shear in plastic bonded explosives composed of energetic crystals interspersed in a back-bone of a polymeric binder. Both compression and shear dissipate plastic energy. Instead of uniformly heating the explosive, the resulting heat is localized in a number of discrete hot spots, the temperature of which is determined by the competition between energy dissipation and heat conduction to the cooler surrounding material. Both the elastic energy and the heat conducted from the hot spots are assumed to heat the material uniformly. A simple Arrhenius relation is then used to express the bulk rate of decomposition of the energetic material involved in the hot spot in terms of its temperature. The model also allows for liquefaction of the material once the buildup of decomposition products in the pore increases the pressure to the level of the macroscopic mean stress. Since the dissipation of plastic energy due to both compression and shear ceases after liquefaction, the model provides a natural way of limiting the extent of mechanically-induced ignition in the reaction process. In the ballistic impact test, a small wafer of energetic material is squeezed
2 between an anvil and a striker. When a friction-inducing material that prohibits sliding is introduced between the sample and the two surfaces squeezing it, the central region of the wafer is subjected to high pressures, but little shear, whereas the periphery undergoes large shear, but low pressures. The experimental result, as well as the model, show that ignition occurs at the periphery, in the region of high shear, not in the central high-pressure region. Several constitutive models have been implemented by Flis 1 in the 1997 version of EPIC 2, a Lagrangian material dynamics computer program. The models include the reaction model proposed by Guirguis 3. The original implementation of the Guirguis reaction model only allowed for a constant yield stress (reduced by the burn fraction) material so Flis also re-implemented the Guirguis model and included a variant of a constitutive model developed by Zerilli 4 for polytetra-fluoroethylene (PTFE) and also a modified Zerilli-Armstrong 5 model originally applied to PTFE and PTFE/Al mixtures. The implementation has not been completed, but it is at the stage at which some preliminary calculations, up to the point of ignition, can be performed. REACTION MODEL The reaction model addresses heterogeneous materials consisting of explosive grains interspersed with binder and pores filled with burned explosive. The model is described by the following three equations. The first equation says that the plastic energy is dissipated in hot spots and that heat conduction cools the hot spots: (1) The heat conduction is confined to a single element (cell) and is not a general heat conduction throughout the material. It is also an approximate expression. The second equation assumes that the elastic energy heats all the material uniformly: (2) The third equation is the Lee-Tarver rate equation with the ignition term replaced by an Arrhenius kinetics expression: (3) In Eq, (3), p is the pressure. The independent variables are, the microscopic hot spot temperature, T, the macroscopic average temperature, and f, the mass fraction of reaction products. In addition to the material parameters ( ) required for the Lee-Tarver growth term (right hand term in Eq. 3), four additional material parameters are required: f h, the mass fraction of material involved in hot spots; h, the heat conduction constant; and the Arrhenius constants, A and E. is the elastic energy per unit volume and is the rate of plastic work per unit volume. In practice, the average temperature
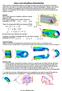
3 TABLE 1. CONSTITUTIVE EQUATION PARAMETERS USED IN BALLISTIC IMPACT TEST MODEL. c 0 (GPa) 0 Guide Schematic of Cross Section of BIC Test Striker c 1 (GPa) K 0 (MPa) 41.6 Pressure Gage and Optical Detector O Ring.177 Cal Barrel and Optical Detector K 1 (MPa) 0 n 0.07 $ 0 (K -1 ) $ 1 (K -1 ) ( 0 (K -1 ) 0 BIC Anvil Drawing not to scale Sample Material FIGURE 1. SCHEMATIC OF BALLISTIC IMPACT EXPERIMENT. Schematic of top view of modified BIC Test and the elastic energy can be assumed negligible. A simple model is used to describe the localization of plastic energy. The mass fraction of material involved in the hot spots is assumed constant, a single parameter that depends on the microstructure of the explosive. It is usually a small number of the order of 1 3%, the precise value of which is to be determined by fitting the model predictions to basic ignition experiments. Three additional parameters are required to characterize the thermo-chemical behavior of the explosive composite - the thermal conductivity coefficient, which theoretically may be obtained from the thermal conductivity of the unreacted material, but must be considered a fit parameter for practical purposes, and the Arrhenius constants, which can be determined by measuring the bulk rate of decomposition of the energetic crystals. A constitutive model is also required to calculate the material deformation resulting from the mechanical Pressure Gage Drawing not to scale.177 cal. Barrel Sample (60 to 100 mg) FIGURE 2. TOP VIEW OF BALLISTIC IMPACT EXPERIMENT. load applied, subject to the appropriate boundary conditions of the problem, from which the plastic energy dissipated can be calculated. The model allows for liquefaction (loss of shear strength) of the material when the pore pressure reaches the value of the surrounding medium ambient pressure. At this point M vanishes. This provides a natural way of limiting the reaction, but also adds a serious complication to implementation in a code which is not structured to handle multiphase materials. Specifically, the pore pressure, p i, must be tracked, as well as the
4 VELOCITY (m/s) BIC STRIKER VELOCITY TIME (µs) FIGURE 3. STRIKER VELOCITY VS. TIME. skeletal pressure, p, and the machinery to calculate the pore pressure must be included (volume of pores, mass of reaction products and binder, equations of state to calculate pore pressure from these quantities). The equation of state model also contains dissipative effects in the form of a bulk viscosity of the form (4) where is the equilibrium equation of state and 6 is a bulk viscosity. CONSTITUTIVE MODEL The plastic component of the deformation is described by the equation (5) and c 0, c 1, K 0, K 1, n, $ 0, $ 1, ( 0, ( 1 are constants. The values of the constants used in the ballistic impact experiment model are given in Table 1. BALLISTIC IMPACT EXPERIMENT Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of the ballistic impact experiment. In this experiment, a striker is dropped from a predetermined height on to a thin disk of test material placed on the anvil. The acceleration of the striker is monitored with an accelerometer and integrated to obtain its velocity and position. The sample height, radius and radial velocity at the edge of the cylindrical sample at the moment of initiation may be determined. Initiation is determined by four fast photo-diodes located on the interior walls of the Ballistic Impact Chamber as shown in Figure 2. It has been shown experimentally that initiation during impact always occurs at or near the edge of the impacted sample. This result applies to all crystalline explosives impacted with essentially undeformable anvils. The outer perimeter region of the sample is the region of maximum shear, shear deformation and minimum pressure. Initiation never has been observed in the center of the impacted sample where the pressure is highest. Figure 3 shows the velocity vs. time for the striker in an experiment performed by where (6)
5 FIGURE 4. SIMULATION OF BALLISTIC IMPACT EXPERIMENT. RADIAL CROSS SECTION OF DISC SHAPED SPECIMEN IS SHOWN AT 100 :S. AXIS OF SPECIMEN IS VERTICAL AT RIGHT OF FIGURE. ANVIL (NOT SHOWN) IS HORIZONTAL AT THE BOTTOM, STRIKER (NOT SHOWN) COMES IN FROM TOP. BURN FRACTION CONTOURS ARE SHOWN. Namkung and Coffey 6 on PBXN-109. The sample had an initial radius of 6.35 mm and thickness of 1.75 mm. Observation of light output from the sample indicates reaction starting at around 200 :s. BALLISTIC IMPACT EXPERIMENT MODELING Model calculations for the ballistic impact experiment were performed to determine the feasibility of doing such simulations with a Lagrangian code. The experimental velocity, depicted in Figure 3 was used as a boundary condition at the top surface of the sample in the calculation. The anvil is simulated as a rigid boundary at the bottom surface. The sample is squeezed to 1/20 th or less of its original thickness, not an easy model for a Lagrangian code. BURN FRACTION ELEMENT TIME (µs) FIGURE 5. BURN FRACTION VS. TIME FOR A CELL NEAR OUTER PERIPHERY OF SAMPLE. APPROXIMATE LOCATION OF CELL IS IN AREA OF LARGEST BURN FRACTION AS SHOWN IN FIG. 4. The results up to this point indicate that it is marginal, but feasible, to do such a simulation to obtain ignition parameters for energetic materials. Much more to the point, these calculations are able to model ignition in the ballistic impact test in which it is demonstrated that shear is the most important factor in the ignition of an energetic material. A generic explosive (that is, typical parameters not specific to any one explosive were used) was modeled for the feasibility study for a number of reasons, not the least of which was the lack of a complete set of data for any one explosive. In any case, the constants are good enough to enable a rough proof of principle calculation. The parameters A ( s -1 ) and E (220 kj/mole) were obtained from reaction data on pure HMX 7, h ( W/m 3 /K) was estimated by assuming a characteristic conduction time constant of 500 :s, and f h was
6 set arbitrarily to The bulk viscosity coefficient was set to zero for these calculations. The model was set up in EPIC using sample dimensions and striker velocity vs. time data for tests on PBXN-109 performed by Namkung and Coffey. The equation of state parameters for a Mie- Gruneisen equation were obtained from Hugoniot data for PBXW-110 provided by Sutherland 8. The Gruneisen parameter (0.8) was calculated from the specific heat, bulk modulus, and thermal expansion coefficient for PBXW-110. The constitutive equation used was that which was hardwired by Flis into the code. This was the modified Zerilli- Armstrong model, described above, for PTFE. The constants for the model are given in Table 1. Figure 4 shows a typical model at 100 :s. The beginnings of reaction are shown at the outer periphery of the sample at the position shown in typical experiments. The ignition reaction burn fraction becomes significant (0.01) at about 180 :s, about the time it is observed in the PBXN-109 experiment. After 180 :s it increases rapidly (see Fig. 5), but it is limited to the value of the fraction of hot spots, 0.01, by a parameter input to the model. Only the ignition term (that is, the Arrhenius term in Eq. (3)) is turned on in this model. The constants for the growth terms must be determined from separate experiments. CONCLUSIONS The simulation of the ballistic impact test for a generic explosive can be done up to the point of ignition. Pressures of kbar occur at the center of the sample. Current reaction models generally will show ignition at these pressures in spite of the fact that ignition does not occur in the actual experiment. The Guirguis model showed ignition occurred at the outer perimeter of the sample where it should have and no ignition in the high pressure region at the center where it should not have. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was supported in part by the Office of Naval Research and also internally by NSWC. REFERENCES 1. Flis, W. J., DE Technologies Technical Report DET-TR-A316-1 (Oct. 1999). 2. Johnson, G. R., and Cook, W. H., in Proceedings of the Seventh International Symposium on Ballistics, The Hague, The Netherlands, 1983, p. 541; Johnson, G. R., Stryk, R. A., and Beissel, S. R., User Instructions for the 1997 Version of the EPIC Code, Alliant Techsystems Inc., Technical Report MN55343, June Guirguis, R. H., in Proceedings of the 1996 JANNAF Propulsion Systems Hazards Subcommittee Meeting, Monterey, California, CPIA Publication 645, Vol. II, November 1996; Guirguis, R. H., in Shock Compression of Condensed Matter , edited by M. D. Furnish, L. C. Chhabildas, and R. S. Hixson, AIP Conference Proceedings CP 505, New York, 2000, p Zerilli, F. J., and Armstrong, R. W., J. Phys. IV France 10, 3 (2000).
7 5. Zerilli, F. J., and Armstrong, R. W., J. Appl. Phys. 61, 1816 (1 March 1987). 6. Namkung, J., and Coffey, C. S., in Shock Compression of Condensed Matter 2001, edited by M. D. Furnish, N. N. Thadani, and Y. Horie, AIP Conference Proceedings CP 620, New York, 2002, p Rogers, R. N., Thermochimica Acta 11, 131 (1975). 8.Sutherland, G. T., NSWC Indian Head, private communication.
An Analytic Investigation of Hot-Spot Formation in Compressible Energetic Materials
 Central European Journal of Energetic Materials ISSN 1733-7178; e-issn 2353-1843 Cent. Eur. J. Energ. Mater. 2017, 14(4): 806-820; DOI: 10.22211/cejem/78748 An Analytic Investigation of Hot-Spot Formation
Central European Journal of Energetic Materials ISSN 1733-7178; e-issn 2353-1843 Cent. Eur. J. Energ. Mater. 2017, 14(4): 806-820; DOI: 10.22211/cejem/78748 An Analytic Investigation of Hot-Spot Formation
Damage modeling for Taylor impact simulations
 J. Phys. IV France 134 (2006) 331 337 C EDP Sciences, Les Ulis DOI: 10.1051/jp4:2006134051 Damage modeling for Taylor impact simulations C.E. Anderson Jr. 1, I.S. Chocron 1 and A.E. Nicholls 1 1 Engineering
J. Phys. IV France 134 (2006) 331 337 C EDP Sciences, Les Ulis DOI: 10.1051/jp4:2006134051 Damage modeling for Taylor impact simulations C.E. Anderson Jr. 1, I.S. Chocron 1 and A.E. Nicholls 1 1 Engineering
ISENTROPIC COMPRESSION OF HIGH EXPLOSIVES WITH THE Z ACCELERATOR
 ISENTROPIC COMPRESSION OF HIGH EXPLOSIVES WITH THE Z ACCELERATOR David B. Reisman, Jerry W. Forbes, Craig M. Tarver, and Frank Garcia Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Livermore, CA 94551 Dennis B.
ISENTROPIC COMPRESSION OF HIGH EXPLOSIVES WITH THE Z ACCELERATOR David B. Reisman, Jerry W. Forbes, Craig M. Tarver, and Frank Garcia Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Livermore, CA 94551 Dennis B.
Simulation of sympathetic detonation by a CIP Eulerian code
 Computational Ballistics II 107 Simulation of sympathetic detonation by a CIP Eulerian code S. Kubota 1, Z. Liu 2, T. Saburi 1, Y. Ogata 1 & M. Yoshida 1 1 Research Center for Explosion Safety, National
Computational Ballistics II 107 Simulation of sympathetic detonation by a CIP Eulerian code S. Kubota 1, Z. Liu 2, T. Saburi 1, Y. Ogata 1 & M. Yoshida 1 1 Research Center for Explosion Safety, National
 LA-UR-01-3491 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Title: APPLYING MICRO-MECHANICS TO FINITE ELEMENT SIMULATIONS OF SPLIT HOPKINSON PRESSURE BAR EXPERIMENTS ON HIGH EXPLOSIVES Author(s):
LA-UR-01-3491 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Title: APPLYING MICRO-MECHANICS TO FINITE ELEMENT SIMULATIONS OF SPLIT HOPKINSON PRESSURE BAR EXPERIMENTS ON HIGH EXPLOSIVES Author(s):
Lecture #2: Split Hopkinson Bar Systems
 Lecture #2: Split Hopkinson Bar Systems by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing 2015 1 1 1 Uniaxial Compression
Lecture #2: Split Hopkinson Bar Systems by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing 2015 1 1 1 Uniaxial Compression
Los Alamos NATIONAL LABORATORY LA-UR Double Shock Initiation of the HMX Based Explosive EDC-37
 LA-UR- 01-3383 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Title: Double Shock Initiation of the HMX Based Explosive EDC-37 Author(s): R. L. Gustavsen, S. A. Sheffield, and R. R. Alcon Los
LA-UR- 01-3383 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Title: Double Shock Initiation of the HMX Based Explosive EDC-37 Author(s): R. L. Gustavsen, S. A. Sheffield, and R. R. Alcon Los
ISOCHORIC BURN, AN INTERNALLY CONSISTENT METHOD FOR THE REACTANT TO PRODUCT TRANSFORMATION IN REACTIVE FLOW
 Revised: 8/15/2002 ISOCHORIC BURN, AN INTERNALLY CONSISTENT METHOD FOR THE REACTANT TO PRODUCT TRANSFORMATION IN REACTIVE FLOW J. E. Reaugh, E. L. Lee, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore
Revised: 8/15/2002 ISOCHORIC BURN, AN INTERNALLY CONSISTENT METHOD FOR THE REACTANT TO PRODUCT TRANSFORMATION IN REACTIVE FLOW J. E. Reaugh, E. L. Lee, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore
Three Dimensional Analysis of Induced Detonation of Cased Explosive
 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Blast Three Dimensional Analysis of Induced Detonation of Cased Explosive Devon Downes 1, Amal Bouamoul 2 and Manouchehr Nejad Ensan 1 1 Aerospace
13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Blast Three Dimensional Analysis of Induced Detonation of Cased Explosive Devon Downes 1, Amal Bouamoul 2 and Manouchehr Nejad Ensan 1 1 Aerospace
NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF FAILURE IN STEEL BEAMS UNDER IMPACT CONDITIONS
 Blucher Mechanical Engineering Proceedings May 2014, vol. 1, num. 1 www.proceedings.blucher.com.br/evento/10wccm NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF FAILURE IN STEEL BEAMS UNDER IMPACT CONDITIONS E. D.
Blucher Mechanical Engineering Proceedings May 2014, vol. 1, num. 1 www.proceedings.blucher.com.br/evento/10wccm NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF FAILURE IN STEEL BEAMS UNDER IMPACT CONDITIONS E. D.
FFI RAPPORT GAP TEST EXPERIMENTS USED TO STUDY THE SENSITIVITY OF GRANULAR EXPLOSIVES. Eriksen Svein W, Moxnes John F, Strømgård Monica
 FFI RAPPORT GAP TEST EXPERIMENTS USED TO STUDY THE SENSITIVITY OF GRANULAR EXPLOSIVES Eriksen Svein W, Moxnes John F, Strømgård Monica FFI/RAPPORT-2004/01882 FFI-V/860/01 GAP TEST EXPERIMENTS USED TO
FFI RAPPORT GAP TEST EXPERIMENTS USED TO STUDY THE SENSITIVITY OF GRANULAR EXPLOSIVES Eriksen Svein W, Moxnes John F, Strømgård Monica FFI/RAPPORT-2004/01882 FFI-V/860/01 GAP TEST EXPERIMENTS USED TO
MODELLING OF DEFLAGRATION, ESTABLISHING MATERIAL DATA INTO ANSYS AUTODYN S POWDER BURN MODEL
 MODELLING OF DEFLAGRATION, ESTABLISHING MATERIAL DATA INTO ANSYS AUTODYN S POWDER BURN MODEL Eimund Smestad a, John F. Moxnes b,and Gard Ødegårdstuen a a Nammo Raufoss AS, P.O. Box 62, N-283 Raufoss, Norway
MODELLING OF DEFLAGRATION, ESTABLISHING MATERIAL DATA INTO ANSYS AUTODYN S POWDER BURN MODEL Eimund Smestad a, John F. Moxnes b,and Gard Ødegårdstuen a a Nammo Raufoss AS, P.O. Box 62, N-283 Raufoss, Norway
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
STANDARD SAMPLE. Reduced section " Diameter. Diameter. 2" Gauge length. Radius
 MATERIAL PROPERTIES TENSILE MEASUREMENT F l l 0 A 0 F STANDARD SAMPLE Reduced section 2 " 1 4 0.505" Diameter 3 4 " Diameter 2" Gauge length 3 8 " Radius TYPICAL APPARATUS Load cell Extensometer Specimen
MATERIAL PROPERTIES TENSILE MEASUREMENT F l l 0 A 0 F STANDARD SAMPLE Reduced section 2 " 1 4 0.505" Diameter 3 4 " Diameter 2" Gauge length 3 8 " Radius TYPICAL APPARATUS Load cell Extensometer Specimen
Crack propagation induced heating in crystalline energetic materials
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 110, NUMBER 7 15 FEBRUARY 1999 Crack propagation induced heating in crystalline energetic materials W. Holmes, a) R. S. Francis, and M. D. Fayer Department of Chemistry,
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 110, NUMBER 7 15 FEBRUARY 1999 Crack propagation induced heating in crystalline energetic materials W. Holmes, a) R. S. Francis, and M. D. Fayer Department of Chemistry,
The University of Melbourne Engineering Mechanics
 The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Four Poisson s Ratio and Axial Loading Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 9-22 from Hibbeler - Statics and Mechanics of Materials) A short
The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Four Poisson s Ratio and Axial Loading Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 9-22 from Hibbeler - Statics and Mechanics of Materials) A short
THEORETICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL MESOSCALE STUDIES OF IMPACT- LOADED GRANULAR EXPLOSIVE AND SIMULANT MATERIALS
 THEORETICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL MESOSCALE STUDIES OF IMPACT- LOADED GRANULAR EXPLOSIVE AND SIMULANT MATERIALS M. R. Baer and W. M. Trott Engineering Sciences Center Sandia National Laboratories *, Albuquerque,
THEORETICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL MESOSCALE STUDIES OF IMPACT- LOADED GRANULAR EXPLOSIVE AND SIMULANT MATERIALS M. R. Baer and W. M. Trott Engineering Sciences Center Sandia National Laboratories *, Albuquerque,
Optical Method for Micro Force Measurement. Yusaku FUJII Gunma University
 Optical Method for Micro Force Measurement Yusaku FUJII Gunma University Small Force (1mN to 1N ) It is difficult to generate and evaluate small force, properly. The causes of the Difficulties in measuring
Optical Method for Micro Force Measurement Yusaku FUJII Gunma University Small Force (1mN to 1N ) It is difficult to generate and evaluate small force, properly. The causes of the Difficulties in measuring
INFLUENCE OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES ON NON-SHOCK IGNITION
 INFLUENCE OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES ON NON-SHOCK IGNITION Richard V. Browning & Richard J. Scammon Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 87545 Modeling non-shock ignition as seen in safety related
INFLUENCE OF MECHANICAL PROPERTIES ON NON-SHOCK IGNITION Richard V. Browning & Richard J. Scammon Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 87545 Modeling non-shock ignition as seen in safety related
Mechanics of Materials and Structures
 Journal of Mechanics of Materials and Structures SHOCK-INDUCED DETONATION OF HIGH EXPLOSIVES BY HIGH VELOCITY IMPACT J. K. Chen, Hsu-Kuang Ching and Firooz A. Allahdadi Volume 2, Nº 9 November 2007 mathematical
Journal of Mechanics of Materials and Structures SHOCK-INDUCED DETONATION OF HIGH EXPLOSIVES BY HIGH VELOCITY IMPACT J. K. Chen, Hsu-Kuang Ching and Firooz A. Allahdadi Volume 2, Nº 9 November 2007 mathematical
An Approach to Simulate the Cook-off Response of Large Scale Munitions Using Small Scale Tests and Analysis
 An Approach to Simulate the Cook-off Response of Large Scale Munitions Using Small Scale Tests and Analysis By N. Albert Moussa* and Vijay V. Devarakonda BlazeTech Corp., Woburn MA, and Michael J. Kaneshige
An Approach to Simulate the Cook-off Response of Large Scale Munitions Using Small Scale Tests and Analysis By N. Albert Moussa* and Vijay V. Devarakonda BlazeTech Corp., Woburn MA, and Michael J. Kaneshige
Status of the target for the undulatorbased positron source
 Status of the target for the undulatorbased positron source POSIPOL 2018, Geneva Switzerland September 3 rd, 2018 Sabine Riemann, Felix Dietrich, DESY, Gudrid Moortgat-Pick, Andriy Ushakov (Hamburg U)
Status of the target for the undulatorbased positron source POSIPOL 2018, Geneva Switzerland September 3 rd, 2018 Sabine Riemann, Felix Dietrich, DESY, Gudrid Moortgat-Pick, Andriy Ushakov (Hamburg U)
4/14/11. Chapter 12 Static equilibrium and Elasticity Lecture 2. Condition for static equilibrium. Stability An object is in equilibrium:
 About Midterm Exam 3 When and where Thurs April 21 th, 5:45-7:00 pm Rooms: Same as Exam I and II, See course webpage. Your TA will give a brief review during the discussion session. Coverage: Chapts 9
About Midterm Exam 3 When and where Thurs April 21 th, 5:45-7:00 pm Rooms: Same as Exam I and II, See course webpage. Your TA will give a brief review during the discussion session. Coverage: Chapts 9
Finite element simulation of residual stresses in laser heating
 IAS-2008-66-546ST Finite element simulation of residual stresses in laser heating G. H. Farrahi 1, M. Sistaninia 2, H. Moeinoddini 3 1,2-School of Mechanical Engineering, Sharif University of Technology,
IAS-2008-66-546ST Finite element simulation of residual stresses in laser heating G. H. Farrahi 1, M. Sistaninia 2, H. Moeinoddini 3 1,2-School of Mechanical Engineering, Sharif University of Technology,
Chapter 5 Torsion STRUCTURAL MECHANICS: CE203. Notes are based on Mechanics of Materials: by R. C. Hibbeler, 7th Edition, Pearson
 STRUCTURAL MECHANICS: CE203 Chapter 5 Torsion Notes are based on Mechanics of Materials: by R. C. Hibbeler, 7th Edition, Pearson Dr B. Achour & Dr Eng. K. El-kashif Civil Engineering Department, University
STRUCTURAL MECHANICS: CE203 Chapter 5 Torsion Notes are based on Mechanics of Materials: by R. C. Hibbeler, 7th Edition, Pearson Dr B. Achour & Dr Eng. K. El-kashif Civil Engineering Department, University
SHOCK WAVE PRESSURE IN FREE WATER AS A FUNCTION OF EXPLOSIVE COMPOSITION
 SHOCK WAVE PRESSURE IN FREE WATER AS A FUNCTION OF EXPLOSIVE COMPOSITION G. W. Lawrence Indian Head Division Naval Surface Warfare Center Research and Technology Department Indian Head, MD 20640 Free field
SHOCK WAVE PRESSURE IN FREE WATER AS A FUNCTION OF EXPLOSIVE COMPOSITION G. W. Lawrence Indian Head Division Naval Surface Warfare Center Research and Technology Department Indian Head, MD 20640 Free field
MARKS DISTRIBUTION AS PER CHAPTER (QUESTION ASKED IN GTU EXAM) Name Of Chapter. Applications of. Friction. Centroid & Moment.
 Introduction Fundamentals of statics Applications of fundamentals of statics Friction Centroid & Moment of inertia Simple Stresses & Strain Stresses in Beam Torsion Principle Stresses DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL
Introduction Fundamentals of statics Applications of fundamentals of statics Friction Centroid & Moment of inertia Simple Stresses & Strain Stresses in Beam Torsion Principle Stresses DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL
Exercise: concepts from chapter 8
 Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 8 1) The following exercises explore elementary concepts associated with a linear elastic material that is isotropic and homogeneous with respect to elastic
Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 8 1) The following exercises explore elementary concepts associated with a linear elastic material that is isotropic and homogeneous with respect to elastic
EVIDENCE FOR THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM IN THE DETONATION OF HMX
 EVIDENCE FOR THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM IN THE DETONATION OF HMX B. F. Henson, L. Smilowitz, B. W Asay, P. M. Dickson and P. M. Howe Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 87545 The validity of modeling
EVIDENCE FOR THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM IN THE DETONATION OF HMX B. F. Henson, L. Smilowitz, B. W Asay, P. M. Dickson and P. M. Howe Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 87545 The validity of modeling
THE ROLE OF DAMAGE MODE IN DELAYED DETONATION OF COMPOSITE ENERGETIC MATERIALS
 THE ROLE OF DAMAGE MODE IN DELAYED DETONATION OF COMPOSITE ENERGETIC MATERIALS E. R. Matheson and J. T. Rosenberg Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company 1111 Lockheed Martin Way Sunnyvale, CA 94089 In addition
THE ROLE OF DAMAGE MODE IN DELAYED DETONATION OF COMPOSITE ENERGETIC MATERIALS E. R. Matheson and J. T. Rosenberg Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company 1111 Lockheed Martin Way Sunnyvale, CA 94089 In addition
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Computed radial stresses in a concrete target penetrated by a steel projectile G.R. Johnson*, S.R. Beissel", T.J. Holmquist* & D.J. Frew* "Alliant Techsystems, Incorporated, Hopkins, Minnesota, USA & U.S.
Computed radial stresses in a concrete target penetrated by a steel projectile G.R. Johnson*, S.R. Beissel", T.J. Holmquist* & D.J. Frew* "Alliant Techsystems, Incorporated, Hopkins, Minnesota, USA & U.S.
Investigation on Mie-Grüneisen type shock Hugoniot equation of state for concrete
 Int. Jnl. of Multiphysics Volume 11 Number 3 2017 255 Investigation on Mie-Grüneisen type shock Hugoniot equation of state for concrete M Katayama*, A Abe, A Takeba ITOCHU Techno-Solutions Corporation,
Int. Jnl. of Multiphysics Volume 11 Number 3 2017 255 Investigation on Mie-Grüneisen type shock Hugoniot equation of state for concrete M Katayama*, A Abe, A Takeba ITOCHU Techno-Solutions Corporation,
ROTATING RING. Volume of small element = Rdθbt if weight density of ring = ρ weight of small element = ρrbtdθ. Figure 1 Rotating ring
 ROTATIONAL STRESSES INTRODUCTION High centrifugal forces are developed in machine components rotating at a high angular speed of the order of 100 to 500 revolutions per second (rps). High centrifugal force
ROTATIONAL STRESSES INTRODUCTION High centrifugal forces are developed in machine components rotating at a high angular speed of the order of 100 to 500 revolutions per second (rps). High centrifugal force
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lectures & 3, 9/31 Aug 017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Discussion of Handin, JGR, 1969 and Chapter 1 Scholz, 00. Stress analysis and Mohr Circles Coulomb Failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lectures & 3, 9/31 Aug 017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Discussion of Handin, JGR, 1969 and Chapter 1 Scholz, 00. Stress analysis and Mohr Circles Coulomb Failure
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL UNCONFINED COMPRESSION TEST
 SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL DEFINITION The shear strength of the soil mass is the internal resistance per unit area that the soil mass can offer to resist failure and sliding along any plane inside it. INTRODUCTION
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL DEFINITION The shear strength of the soil mass is the internal resistance per unit area that the soil mass can offer to resist failure and sliding along any plane inside it. INTRODUCTION
Figure 43. Some common mechanical systems involving contact.
 33 Demonstration: experimental surface measurement ADE PhaseShift Whitelight Interferometer Surface measurement Surface characterization - Probability density function - Statistical analyses - Autocorrelation
33 Demonstration: experimental surface measurement ADE PhaseShift Whitelight Interferometer Surface measurement Surface characterization - Probability density function - Statistical analyses - Autocorrelation
Thermal properties of Engineering Materials
 Thermal properties of Engineering Materials Engineering materials are important in everyday life because of their versatile structural properties. Other than these properties, they do play an important
Thermal properties of Engineering Materials Engineering materials are important in everyday life because of their versatile structural properties. Other than these properties, they do play an important
Discrete Element Modelling of a Reinforced Concrete Structure
 Discrete Element Modelling of a Reinforced Concrete Structure S. Hentz, L. Daudeville, F.-V. Donzé Laboratoire Sols, Solides, Structures, Domaine Universitaire, BP 38041 Grenoble Cedex 9 France sebastian.hentz@inpg.fr
Discrete Element Modelling of a Reinforced Concrete Structure S. Hentz, L. Daudeville, F.-V. Donzé Laboratoire Sols, Solides, Structures, Domaine Universitaire, BP 38041 Grenoble Cedex 9 France sebastian.hentz@inpg.fr
N = Shear stress / Shear strain
 UNIT - I 1. What is meant by factor of safety? [A/M-15] It is the ratio between ultimate stress to the working stress. Factor of safety = Ultimate stress Permissible stress 2. Define Resilience. [A/M-15]
UNIT - I 1. What is meant by factor of safety? [A/M-15] It is the ratio between ultimate stress to the working stress. Factor of safety = Ultimate stress Permissible stress 2. Define Resilience. [A/M-15]
Mechanical characterization of single crystal BaTiO 3 film and insitu. XRD observation of microstructure change due to
 76 Chapter 4 Mechanical characterization of single crystal BaTiO 3 film and insitu XRD observation of microstructure change due to mechanical loading 4.1 Introduction Ferroelectric materials have many
76 Chapter 4 Mechanical characterization of single crystal BaTiO 3 film and insitu XRD observation of microstructure change due to mechanical loading 4.1 Introduction Ferroelectric materials have many
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF A THREE-DIMENSIONAL DISC-PAD MODEL WITH AND WITHOUT THERMAL EFFECTS
 THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 2015, Vol. 19, No. 6, pp. 2195-2204 2195 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF A THREE-DIMENSIONAL DISC-PAD MODEL WITH AND WITHOUT THERMAL EFFECTS by Ali BELHOCINE * Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 2015, Vol. 19, No. 6, pp. 2195-2204 2195 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF A THREE-DIMENSIONAL DISC-PAD MODEL WITH AND WITHOUT THERMAL EFFECTS by Ali BELHOCINE * Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
CRANFIELD UNIVERSITY DEFENCE COLLEGE OF MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY ENGINEERING SYSTEMS DEPARTMENT. PhD THESIS. Academic Year
 CRANFIELD UNIVERSITY DEFENCE COLLEGE OF MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY ENGINEERING SYSTEMS DEPARTMENT PhD THESIS Academic Year 2007-2008 Nicholas Whitworth Mathematical and Numerical Modelling of Shock Initiation
CRANFIELD UNIVERSITY DEFENCE COLLEGE OF MANAGEMENT AND TECHNOLOGY ENGINEERING SYSTEMS DEPARTMENT PhD THESIS Academic Year 2007-2008 Nicholas Whitworth Mathematical and Numerical Modelling of Shock Initiation
Exploiting pattern transformation to tune phononic band gaps in a two-dimensional granular crystal
 Exploiting pattern transformation to tune phononic band gaps in a two-dimensional granular crystal The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you.
Exploiting pattern transformation to tune phononic band gaps in a two-dimensional granular crystal The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you.
THERMAL PROPERTIES OF CRYSTALS AND POLYMERS AT STATIC HIGH PRESSURES
 THERMAL PROPERTIES OF CRYSTALS AND POLYMERS AT STATIC HIGH PRESSURES J. R. Carney, + H. D. Ladouceur,* T. P. Russell, + and G. I. Pangilinan + + Dynamics and Diagnostics Division Research and Technology
THERMAL PROPERTIES OF CRYSTALS AND POLYMERS AT STATIC HIGH PRESSURES J. R. Carney, + H. D. Ladouceur,* T. P. Russell, + and G. I. Pangilinan + + Dynamics and Diagnostics Division Research and Technology
1. Demonstrate that the minimum cation-to-anion radius ratio for a coordination number of 8 is
 1. Demonstrate that the minimum cation-to-anion radius ratio for a coordination number of 8 is 0.732. This problem asks us to show that the minimum cation-to-anion radius ratio for a coordination number
1. Demonstrate that the minimum cation-to-anion radius ratio for a coordination number of 8 is 0.732. This problem asks us to show that the minimum cation-to-anion radius ratio for a coordination number
Green Rocket Propellant Technologies Based on Energetic Thermoplastic Elastomers
 Green Rocket Propellant Technologies Based on Energetic Thermoplastic Elastomers Dewey M.A.*, Mancini V.E., Furfaro J.A., and Rose M.T. Thiokol Propulsion P. O. 707, M/S 200 Brigham City, Utah ABSTRACT
Green Rocket Propellant Technologies Based on Energetic Thermoplastic Elastomers Dewey M.A.*, Mancini V.E., Furfaro J.A., and Rose M.T. Thiokol Propulsion P. O. 707, M/S 200 Brigham City, Utah ABSTRACT
Solution: T, A1, A2, A3, L1, L2, L3, E1, E2, E3, P are known Five equations in five unknowns, F1, F2, F3, ua and va
 ME 323 Examination # 1 February 18, 2016 Name (Print) (Last) (First) Instructor PROBLEM #1 (20 points) A structure is constructed from members 1, 2 and 3, with these members made up of the same material
ME 323 Examination # 1 February 18, 2016 Name (Print) (Last) (First) Instructor PROBLEM #1 (20 points) A structure is constructed from members 1, 2 and 3, with these members made up of the same material
Members Subjected to Torsional Loads
 Members Subjected to Torsional Loads Torsion of circular shafts Definition of Torsion: Consider a shaft rigidly clamped at one end and twisted at the other end by a torque T = F.d applied in a plane perpendicular
Members Subjected to Torsional Loads Torsion of circular shafts Definition of Torsion: Consider a shaft rigidly clamped at one end and twisted at the other end by a torque T = F.d applied in a plane perpendicular
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF ARKANSAS TEST SERIES PILE #2 USING OPENSEES (WITH LPILE COMPARISON)
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF ARKANSAS TEST SERIES PILE #2 USING OPENSEES (WITH LPILE COMPARISON) Ahmed Elgamal and Jinchi Lu October 07 Introduction In this study, we conduct a finite element simulation
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF ARKANSAS TEST SERIES PILE #2 USING OPENSEES (WITH LPILE COMPARISON) Ahmed Elgamal and Jinchi Lu October 07 Introduction In this study, we conduct a finite element simulation
Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis
 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Internal shear force V & bending moment M must ensure equilibrium Fig. 3 2 Sign Conventions for Bending and Shear Fig. 3 3
Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Internal shear force V & bending moment M must ensure equilibrium Fig. 3 2 Sign Conventions for Bending and Shear Fig. 3 3
Simulation of Impact and Fragmentation with the Material Point Method
 Simulation of Impact and Fragmentation with the Material Point Method Biswajit Banerjee J. Guilkey, T. Harman, J. Schmidt, P. McMurtry Center for the Simulation of Accidental Fires and xplosions University
Simulation of Impact and Fragmentation with the Material Point Method Biswajit Banerjee J. Guilkey, T. Harman, J. Schmidt, P. McMurtry Center for the Simulation of Accidental Fires and xplosions University
Three-dimensional thermo-mechanical analysis of layered elasticlplastic solids
 Three-dimensional thermo-mechanical analysis of layered elasticlplastic solids W. Peng & Y.-T. Hsia Seagate Technology, U.S.A. Abstract At high temperature a layered solid undergoes intense thermal loading
Three-dimensional thermo-mechanical analysis of layered elasticlplastic solids W. Peng & Y.-T. Hsia Seagate Technology, U.S.A. Abstract At high temperature a layered solid undergoes intense thermal loading
BOUNDARY LAYER MODELLING OF THE HEAT TRANSFER PROCESSES FROM IGNITERS TO ENERGETIC MATERIALS Clive Woodley, Mike Taylor, Henrietta Wheal
 23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 BOUNDARY LAYER MODELLING OF THE HEAT TRANSFER PROCESSES FROM IGNITERS TO ENERGETIC MATERIALS Clive Woodley, Mike Taylor, Henrietta
23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 BOUNDARY LAYER MODELLING OF THE HEAT TRANSFER PROCESSES FROM IGNITERS TO ENERGETIC MATERIALS Clive Woodley, Mike Taylor, Henrietta
BENCHMARK LINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF LATERALLY LOADED SINGLE PILE USING OPENSEES & COMPARISON WITH ANALYTICAL SOLUTION
 BENCHMARK LINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF LATERALLY LOADED SINGLE PILE USING OPENSEES & COMPARISON WITH ANALYTICAL SOLUTION Ahmed Elgamal and Jinchi Lu October 07 Introduction In this study: I) The response
BENCHMARK LINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF LATERALLY LOADED SINGLE PILE USING OPENSEES & COMPARISON WITH ANALYTICAL SOLUTION Ahmed Elgamal and Jinchi Lu October 07 Introduction In this study: I) The response
FRICTION AND WEAR OF CARBON-CARBON COMPOSITE PART 2: TEMPERATURE AND STRESS FIELDS ANALYSIS
 FRICTION AND WEAR OF CARBON-CARBON COMPOSITE PART 2: TEMPERATURE AND STRESS FIELDS ANALYSIS Kia-Moh Teo and Khalid Lafdi NSF-University-Industry Center For Advanced Friction Studies, Southern Illinois
FRICTION AND WEAR OF CARBON-CARBON COMPOSITE PART 2: TEMPERATURE AND STRESS FIELDS ANALYSIS Kia-Moh Teo and Khalid Lafdi NSF-University-Industry Center For Advanced Friction Studies, Southern Illinois
Transient Analysis of Disk Brake By using Ansys Software
 Transient Analysis of Disk Brake By using Ansys Software G. Babukanth & M. Vimal Teja Department of Mechanical Engineering, Nimra College of Engineering & Technology, Ibrahimpatnam, Vijayawada E-mail :
Transient Analysis of Disk Brake By using Ansys Software G. Babukanth & M. Vimal Teja Department of Mechanical Engineering, Nimra College of Engineering & Technology, Ibrahimpatnam, Vijayawada E-mail :
C.J. Bennett, W. Sun Department of Mechanical, Materials and Manufacturing Engineering, University of Nottingham, Nottingham NG7 2RD, UK
 Optimisation of material properties for the modelling of large deformation manufacturing processes using a finite element model of the Gleeble compression test C.J. Bennett, W. Sun Department of Mechanical,
Optimisation of material properties for the modelling of large deformation manufacturing processes using a finite element model of the Gleeble compression test C.J. Bennett, W. Sun Department of Mechanical,
Expansion of circular tubes by rigid tubes as impact energy absorbers: experimental and theoretical investigation
 Expansion of circular tubes by rigid tubes as impact energy absorbers: experimental and theoretical investigation M Shakeri, S Salehghaffari and R. Mirzaeifar Department of Mechanical Engineering, Amirkabir
Expansion of circular tubes by rigid tubes as impact energy absorbers: experimental and theoretical investigation M Shakeri, S Salehghaffari and R. Mirzaeifar Department of Mechanical Engineering, Amirkabir
STRESS, STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS
 VELAMMAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, MADURAI 625009 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE8301 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS I -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VELAMMAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, MADURAI 625009 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE8301 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS I -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
LLNL-PRES W. M. Howard and S. Bastea Extreme Chemistry Group. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
 Titan s Interior :(I) A thermo-chemical assessment suggests N 2 is the dominate source of nitrogen near Titan s surface\\ and (II) future studies on the effects of comet impacts on organic and surface
Titan s Interior :(I) A thermo-chemical assessment suggests N 2 is the dominate source of nitrogen near Titan s surface\\ and (II) future studies on the effects of comet impacts on organic and surface
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy
 Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Material Constitutive Parameter Identification using an Electromagnetic Ring Expansion Experiment Coupled with LS-DYNA and LS-OPT
 10 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference pitmization (2) Material Constitutive Parameter Identification using an Electromagnetic ing Expansion Experiment Coupled with LS-DYNA and LS-PT Ismael Henchi*,
10 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference pitmization (2) Material Constitutive Parameter Identification using an Electromagnetic ing Expansion Experiment Coupled with LS-DYNA and LS-PT Ismael Henchi*,
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Fifth SI Edition CHAPTER 3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf David F. Mazurek Torsion Lecture Notes:
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Fifth SI Edition CHAPTER 3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf David F. Mazurek Torsion Lecture Notes:
OPTIMAL DESIGN OF COMPOSITE INSERTS FOR A HYBRID ULTRACENTRIFUGE ROTOR
 18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS OPTIMAL DESIGN OF COMPOSITE INSERTS Hak Gu Lee 1*, Jisang Park 1, Ji Hoon Kim 1 1 Composite Materials Group, KIMS, Changwon, Korea * Corresponding
18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS OPTIMAL DESIGN OF COMPOSITE INSERTS Hak Gu Lee 1*, Jisang Park 1, Ji Hoon Kim 1 1 Composite Materials Group, KIMS, Changwon, Korea * Corresponding
A multiscale framework for lubrication analysis of bearings with textured surface
 A multiscale framework for lubrication analysis of bearings with textured surface *Leiming Gao 1), Gregory de Boer 2) and Rob Hewson 3) 1), 3) Aeronautics Department, Imperial College London, London, SW7
A multiscale framework for lubrication analysis of bearings with textured surface *Leiming Gao 1), Gregory de Boer 2) and Rob Hewson 3) 1), 3) Aeronautics Department, Imperial College London, London, SW7
Modelling hypervelocity impact in DYNA3D J. Campbell, R. Vignjevic College of Aeronautics, Cranfield University, Cranfield,
 Modelling hypervelocity impact in DYNA3D J. Campbell, R. Vignjevic College of Aeronautics, Cranfield University, Cranfield, Abstract This paper presents part of the work on development of tools and modelling
Modelling hypervelocity impact in DYNA3D J. Campbell, R. Vignjevic College of Aeronautics, Cranfield University, Cranfield, Abstract This paper presents part of the work on development of tools and modelling
Dynamic Analysis Contents - 1
 Dynamic Analysis Contents - 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS 1.1 Overview... 1-1 1.2 Relation to Equivalent-Linear Methods... 1-2 1.2.1 Characteristics of the Equivalent-Linear Method... 1-2 1.2.2
Dynamic Analysis Contents - 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS 1.1 Overview... 1-1 1.2 Relation to Equivalent-Linear Methods... 1-2 1.2.1 Characteristics of the Equivalent-Linear Method... 1-2 1.2.2
Supplementary Figures
 Fracture Strength (GPa) Supplementary Figures a b 10 R=0.88 mm 1 0.1 Gordon et al Zhu et al Tang et al im et al 5 7 6 4 This work 5 50 500 Si Nanowire Diameter (nm) Supplementary Figure 1: (a) TEM image
Fracture Strength (GPa) Supplementary Figures a b 10 R=0.88 mm 1 0.1 Gordon et al Zhu et al Tang et al im et al 5 7 6 4 This work 5 50 500 Si Nanowire Diameter (nm) Supplementary Figure 1: (a) TEM image
An Analytical Model for Long Tube Hydroforming in a Square Cross-Section Die Considering Anisotropic Effects of the Material
 Journal of Stress Analysis Vol. 1, No. 2, Autumn Winter 2016-17 An Analytical Model for Long Tube Hydroforming in a Square Cross-Section Die Considering Anisotropic Effects of the Material H. Haghighat,
Journal of Stress Analysis Vol. 1, No. 2, Autumn Winter 2016-17 An Analytical Model for Long Tube Hydroforming in a Square Cross-Section Die Considering Anisotropic Effects of the Material H. Haghighat,
Mechanical Engineering Ph.D. Preliminary Qualifying Examination Solid Mechanics February 25, 2002
 student personal identification (ID) number on each sheet. Do not write your name on any sheet. #1. A homogeneous, isotropic, linear elastic bar has rectangular cross sectional area A, modulus of elasticity
student personal identification (ID) number on each sheet. Do not write your name on any sheet. #1. A homogeneous, isotropic, linear elastic bar has rectangular cross sectional area A, modulus of elasticity
Shock Wave Propagation due to Methane-Air Mixture Explosion and Effect on a Concrete Enclosure
 Shock Wave Propagation due to Methane-Air Mixture Explosion and Effect on a Concrete Enclosure Sharad Tripathi, T.C.Arun Murthy, Alain Hodin, K.Suresh, Anup Ghosh International Contents 1. Introduction
Shock Wave Propagation due to Methane-Air Mixture Explosion and Effect on a Concrete Enclosure Sharad Tripathi, T.C.Arun Murthy, Alain Hodin, K.Suresh, Anup Ghosh International Contents 1. Introduction
Szendrei's model follows the time history of the crater's radial growth, resulting in the following expression for the final crater radius (r f ):
 27T H INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTIC S F REIBURG, GERMANY, APRIL 22 26, 2013 ON THE CRATER DIAMETERS IN METALLIC PLATES IMPACTED B Y HIGH VELOCITY RODS Roman Kosits ki, Zvi Rosenberg and Erez Dekel
27T H INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTIC S F REIBURG, GERMANY, APRIL 22 26, 2013 ON THE CRATER DIAMETERS IN METALLIC PLATES IMPACTED B Y HIGH VELOCITY RODS Roman Kosits ki, Zvi Rosenberg and Erez Dekel
Chapter 2: Elasticity
 OHP 1 Mechanical Properties of Materials Chapter 2: lasticity Prof. Wenjea J. Tseng ( 曾文甲 ) Department of Materials ngineering National Chung Hsing University wenjea@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Reference: W.F.
OHP 1 Mechanical Properties of Materials Chapter 2: lasticity Prof. Wenjea J. Tseng ( 曾文甲 ) Department of Materials ngineering National Chung Hsing University wenjea@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Reference: W.F.
Elements of Rock Mechanics
 Elements of Rock Mechanics Stress and strain Creep Constitutive equation Hooke's law Empirical relations Effects of porosity and fluids Anelasticity and viscoelasticity Reading: Shearer, 3 Stress Consider
Elements of Rock Mechanics Stress and strain Creep Constitutive equation Hooke's law Empirical relations Effects of porosity and fluids Anelasticity and viscoelasticity Reading: Shearer, 3 Stress Consider
Compressibility & Consolidation
 CHAPTER Compressibility & Consolidation Settlement If a structure is placed on soil surface, then the soil will undergo an elastic and plastic deformation. In engineering practice, the deformation or reduction
CHAPTER Compressibility & Consolidation Settlement If a structure is placed on soil surface, then the soil will undergo an elastic and plastic deformation. In engineering practice, the deformation or reduction
Bending a slab of neural tissue
 arxiv:q-bio/0510034v1 [q-bio.to] 17 Oct 2005 Bending a slab of neural tissue Partha P. Mitra Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, NY 11724 March 2, 2008 Abstract In comparative and developmental neuroanatomy
arxiv:q-bio/0510034v1 [q-bio.to] 17 Oct 2005 Bending a slab of neural tissue Partha P. Mitra Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, NY 11724 March 2, 2008 Abstract In comparative and developmental neuroanatomy
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 84 (2014 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 84 (2014 ) 898 905 2014ISSST, 2014 International Symposium on Safety Science and Technology Study on dynamic numerical simulation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 84 (2014 ) 898 905 2014ISSST, 2014 International Symposium on Safety Science and Technology Study on dynamic numerical simulation
1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor.
 Elasticity Homework Problems 2014 Section 1. The Strain Tensor. 1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor. 2. Given a steel bar compressed with a deformation
Elasticity Homework Problems 2014 Section 1. The Strain Tensor. 1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor. 2. Given a steel bar compressed with a deformation
Fig. 1. Circular fiber and interphase between the fiber and the matrix.
 Finite element unit cell model based on ABAQUS for fiber reinforced composites Tian Tang Composites Manufacturing & Simulation Center, Purdue University West Lafayette, IN 47906 1. Problem Statement In
Finite element unit cell model based on ABAQUS for fiber reinforced composites Tian Tang Composites Manufacturing & Simulation Center, Purdue University West Lafayette, IN 47906 1. Problem Statement In
ANALYSIS OF YARN BENDING BEHAVIOUR
 ANALYSIS OF YARN BENDING BEHAVIOUR B. Cornelissen, R. Akkerman Faculty of Engineering Technology, University of Twente Drienerlolaan 5, P.O. Box 217; 7500 AE Enschede, the Netherlands b.cornelissen@utwente.nl
ANALYSIS OF YARN BENDING BEHAVIOUR B. Cornelissen, R. Akkerman Faculty of Engineering Technology, University of Twente Drienerlolaan 5, P.O. Box 217; 7500 AE Enschede, the Netherlands b.cornelissen@utwente.nl
Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics
 1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering First Assignment The first
1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering First Assignment The first
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
A Numerical Study on the Effect of Explosive Reactive Armour on a Lightweight Armoured Vehicle s Hull
 A Numerical Study on the Effect of Explosive Reactive Armour on a Lightweight Armoured Vehicle s Hull ADRIAN ROTARIU Military Technical Academy 81-83, George Coşbuc Avenue, District 5, Bucharest, 75275
A Numerical Study on the Effect of Explosive Reactive Armour on a Lightweight Armoured Vehicle s Hull ADRIAN ROTARIU Military Technical Academy 81-83, George Coşbuc Avenue, District 5, Bucharest, 75275
Module 5: Failure Criteria of Rock and Rock masses. Contents Hydrostatic compression Deviatoric compression
 FAILURE CRITERIA OF ROCK AND ROCK MASSES Contents 5.1 Failure in rocks 5.1.1 Hydrostatic compression 5.1.2 Deviatoric compression 5.1.3 Effect of confining pressure 5.2 Failure modes in rocks 5.3 Complete
FAILURE CRITERIA OF ROCK AND ROCK MASSES Contents 5.1 Failure in rocks 5.1.1 Hydrostatic compression 5.1.2 Deviatoric compression 5.1.3 Effect of confining pressure 5.2 Failure modes in rocks 5.3 Complete
WARHEAD FRAGMENTATION MODELING WITH PERIDYNAMICS
 23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 WARHEAD FRAGMENTATION MODELING WITH PERIDYNAMICS Paul N. Demmie 1, Dale S. Preece 1 and Stewart A. Silling 1 1 Sandia National
23 RD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON BALLISTICS TARRAGONA, SPAIN 16-20 APRIL 2007 WARHEAD FRAGMENTATION MODELING WITH PERIDYNAMICS Paul N. Demmie 1, Dale S. Preece 1 and Stewart A. Silling 1 1 Sandia National
Question Figure shows the strain-stress curve for a given material. What are (a) Young s modulus and (b) approximate yield strength for this material?
 Question. A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 x 10-5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 x 10-5 m 2 under a given load.
Question. A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 x 10-5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 x 10-5 m 2 under a given load.
Friction and Elongation of Al Electrodes due to Micro-Sliding between the Inner Mo Electrode and the Al Electrodes in High-Power Devices
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 43, No. 9 (2002) pp. 2326 to 2330 c 2002 The Japan Institute of Metals EXPRESS REGULAR ARTICLE Friction and Elongation of Al Electrodes due to Micro-Sliding between the Inner
Materials Transactions, Vol. 43, No. 9 (2002) pp. 2326 to 2330 c 2002 The Japan Institute of Metals EXPRESS REGULAR ARTICLE Friction and Elongation of Al Electrodes due to Micro-Sliding between the Inner
Lecture 6 Friction. Friction Phenomena Types of Friction
 Lecture 6 Friction Tangential forces generated between contacting surfaces are called friction forces and occur to some degree in the interaction between all real surfaces. whenever a tendency exists for
Lecture 6 Friction Tangential forces generated between contacting surfaces are called friction forces and occur to some degree in the interaction between all real surfaces. whenever a tendency exists for
Purpose of this Guide: To thoroughly prepare students for the exact types of problems that will be on Exam 3.
 ES230 STRENGTH OF MTERILS Exam 3 Study Guide Exam 3: Wednesday, March 8 th in-class Updated 3/3/17 Purpose of this Guide: To thoroughly prepare students for the exact types of problems that will be on
ES230 STRENGTH OF MTERILS Exam 3 Study Guide Exam 3: Wednesday, March 8 th in-class Updated 3/3/17 Purpose of this Guide: To thoroughly prepare students for the exact types of problems that will be on
EQUATION OF STATE FOR MODELING THE DETONATION REACTION ZONE
 EQUATION OF STATE FOR MODELING THE DETONATION REACTION ZONE D. Scott Stewart and Sunhee Yoo Department of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics University of Illinois, Urbana, IL 61801, USA William C. Davis
EQUATION OF STATE FOR MODELING THE DETONATION REACTION ZONE D. Scott Stewart and Sunhee Yoo Department of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics University of Illinois, Urbana, IL 61801, USA William C. Davis
Chapter 3: Stress and Equilibrium of Deformable Bodies
 Ch3-Stress-Equilibrium Page 1 Chapter 3: Stress and Equilibrium of Deformable Bodies When structures / deformable bodies are acted upon by loads, they build up internal forces (stresses) within them to
Ch3-Stress-Equilibrium Page 1 Chapter 3: Stress and Equilibrium of Deformable Bodies When structures / deformable bodies are acted upon by loads, they build up internal forces (stresses) within them to
 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 10 5 m 2 under a given load.
Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 10 5 m 2 under a given load.
PROBLEM #1.1 (4 + 4 points, no partial credit)
 PROBLEM #1.1 ( + points, no partial credit A thermal switch consists of a copper bar which under elevation of temperature closes a gap and closes an electrical circuit. The copper bar possesses a length
PROBLEM #1.1 ( + points, no partial credit A thermal switch consists of a copper bar which under elevation of temperature closes a gap and closes an electrical circuit. The copper bar possesses a length
Class XI Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Solids Physics
 Book Name: NCERT Solutions Question : A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 5 3.0 0 m stretches by the same 5 amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 0 m
Book Name: NCERT Solutions Question : A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 5 3.0 0 m stretches by the same 5 amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 0 m
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 51 Module 4: Lecture 2 on Stress-strain relationship and Shear strength of soils Contents Stress state, Mohr s circle analysis and Pole, Principal stressspace, Stress pathsin p-q space; Mohr-coulomb failure
51 Module 4: Lecture 2 on Stress-strain relationship and Shear strength of soils Contents Stress state, Mohr s circle analysis and Pole, Principal stressspace, Stress pathsin p-q space; Mohr-coulomb failure
4 Undrained Cylindrical Cavity Expansion in a Cam-Clay Medium
 Undrained Cylindrical Cavity Expansion in a Cam-Clay Medium 4-1 4 Undrained Cylindrical Cavity Expansion in a Cam-Clay Medium 4.1 Problem Statement The stress and pore pressure changes due to the expansion
Undrained Cylindrical Cavity Expansion in a Cam-Clay Medium 4-1 4 Undrained Cylindrical Cavity Expansion in a Cam-Clay Medium 4.1 Problem Statement The stress and pore pressure changes due to the expansion
Modified Symmetry Cell Approach for Simulation of Surface Enhancement Over Large Scale Structures
 Modified Symmetry Cell Approach for Simulation of Surface Enhancement Over Large Scale Structures T. Spradlin 1, R. Grandhi 2, and K. Langer 3 1 Doctoral Candidate, Wright State University, USA 2 Distinguished
Modified Symmetry Cell Approach for Simulation of Surface Enhancement Over Large Scale Structures T. Spradlin 1, R. Grandhi 2, and K. Langer 3 1 Doctoral Candidate, Wright State University, USA 2 Distinguished
Sliding Contact Bearings
 Sliding Contact Bearings Classification of Bearings 1. According to the direction of load to be supported. The bearings under this group are classified as: (a) Radial bearings (b) Thrust bearings. In radial
Sliding Contact Bearings Classification of Bearings 1. According to the direction of load to be supported. The bearings under this group are classified as: (a) Radial bearings (b) Thrust bearings. In radial
ENG1001 Engineering Design 1
 ENG1001 Engineering Design 1 Structure & Loads Determine forces that act on structures causing it to deform, bend, and stretch Forces push/pull on objects Structures are loaded by: > Dead loads permanent
ENG1001 Engineering Design 1 Structure & Loads Determine forces that act on structures causing it to deform, bend, and stretch Forces push/pull on objects Structures are loaded by: > Dead loads permanent
Name :. Roll No. :... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.TECH (CE-NEW)/SEM-3/CE-301/ SOLID MECHANICS
 Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. 2011 SOLID MECHANICS Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. 2011 SOLID MECHANICS Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
