CONFORMAL MAPPING. Some examples where this method can be used is: the electrostatic potential; heat conduction; flow of fluids.
|
|
|
- Belinda Stevenson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CONFORMAL MAPPING In a limited group of problems one can use a short cut to the solution of the Laplace's equation, conformal mapping. The problem has to be D (two dimensional), i.e., the boundaries, boundary conditions and sources contain only two variables, and y say. Some eamples where this method can be used is: the electrostatic potential; heat conduction; flow of fluids. We will of course focus on the electrostatic potential. The idea is that the problem at hand with a certain geometry may be mapped into a problem with simpler geometry or with a geometry that we have already solved. For polygonal boundaries a general method of constructing the mapping is offered by Schwartz-Cristoffel transformations. For non-polygonal boundaries one must rely on "dictionaries" of mappings. One such dictionary with 30 different mappings is found in a student tet book by R. V. Churchill 1. Another dictionary is found in a book by K. J. Binns and P. J. Lawrenson. For further reading about conformal mapping see W. R. Smythe 3. 1 R. V. Churchill: Comple variables and applications, nd Edition, McGraw- Hill, New York K. J. Binns and P. J. Lawrenson, Analysis and Computation of Electric and Magnetic Field Problems, nd Edition, Pergamon Press, New York W. R. Smythe, Static and Dynamic Electricity, 3rd Edition, Taylor&Frances 1989.
2 Bo E. Sernelius 5: The conformal mapping relies on the properties of analytic functions. Thus we need to refresh our knowledge of these. The derivative of a comple valued function of comple variables ( ) = f' z0 lim z 0 ( ) ( ) f z0 + z f z0 z ( ) = ( ) + ( ) = ( ) + ( ) Let z = + iy, and f z u z iv z u y, ivy,. and y real valued. u and v are real valued functions of the real valued variables and y. One can show that: 1) If the derivative of f(z) eists at a point z then the partial derivatives of u and v eist at that point and obey the following conditions: u v u v = and = The Cauchy-Riemann conditions ) Let u and v be real and single valued functions of and y which, together with their partial derivatives of the first order, are continuous at a point. If those partial derivatives satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann conditions at that point, then the derivative of f eists at that point. Analytic Functions A function f(z) is analytic at a point z 0 if its derivative f'(z) eists not only at z 0 but at every point z in a neighborhood of z 0. One can show that if f(z) is analytic the partial derivatives of u and v of all orders eist and are continuous functions of and y. Thus we have
3 Bo E. Sernelius 5:3 u v v v u u = = = y y = = or u u + = 0 and in an analogous way we get v v + = 0 Thus both u(,y) and v(,y) satisfy Laplace's equation. Harmonic functions Any function that has continuous partial derivatives of the second order and that satisfies the Laplace's equation is called a Harmonic function. Thus both the real part, u, and imaginary part, v, of f are harmonic functions. If the function f = u+iv is analytic, u and v are conjugate harmonic functions. Given one of two harmonic functions, the Cauchy-Riemann equations can be used to find the other. That u and v are harmonic functions can be used to find the potential. Both u and v are candidates for the potential since they satisfy Laplace's equation. Alternatively the function f can be viewed as a change of variables, a transformation from the comple z-plane to the comple ω-plane. z = + iy ω = u + iv ;
4 Bo E. Sernelius 5:4 iy z-plane iv ω-plane u One can show that if the function f is analytic at a point z=z 0, where f'(z 0 ) 0, there eists a neighborhood of the point ω 0 in the ω-plane in which the function ω = f ( z ) has a unique inverse z = F( ω ) The functions f and F defines a change of variables from (,y) to (u,v) and from (u,v) to (,y), respectively. y y-plane v uv-plane u When this change of basis is defined through an analytic function all curves in the y-plane that cross each other at an angle are mapped into curves in the uv-plane that cross each other at eactly the same angle. This is why the mapping is called conformal. The curves can be the boundaries or equipotential curves, electric field lines or any curves. In particular since the set of curves that are horizontal in the y-plane are
5 Bo E. Sernelius 5:5 perpendicular to the set of curves that are vertical the two sets will be mapped into perpendicular sets in the uv-plane. Of course the opposite is also true. To be noted is that in points where f or its inverse is not analytical the transformation is not conformal. Transformation of boundary conditions. Two types of boundary conditions remain unchanged by the transformation and problems with these boundary conditions are best suited for conformal mapping. The types are: 1) The value of a harmonic function is constant on the boundary. (one type of Dirichlet problem) ) The normal derivative of a harmonic function is zero on the boundary. (one type of Neumann problem) (The conditions are that f and its inverse are analytical)
6 Bo E. Sernelius 5:6 Further properties Let the real part of the function f(,y) be the actual potential of our problem. Then the imaginary part is called the stream function. Its level curves are called stream lines. The name comes from the analogy in fluid flow. ( ) = ( ) + ( ) = ( ) + ( ) f, y u, y iv y, Φ y, iψ y, In electrostatic problems these stream lines are parallel to the electric field. We furthermore have ( ) = ( ) + ( ) = E z E, y iey, y * df ( z) dz or ( ) uy, E (, y) = uy, Ey (, y) = ( ) Eample 1: The potential from a line charge, of charge density σ l, along the z-ais is Φ( r) = σl ln( r) = σl Re[ ln ( z) ]. The electric field calculated in the two different ways is: * d [ ( ) ] = 1 = z = y σl ln z σl σl σl + i dz * z z + y + y and y E = σl ; Ey = σ l + y + y ( ) = + uy, E (, y) = l ln y σ l = σ + y ( ) = + uy, y Ey(, y) = l ln y σ y l y = σ + y
7 Bo E. Sernelius 5:7 Eample : The capacitance between two conductors If Q is the electrical charge on either conductor and V is the difference in potential between one conductor and the other, then the capacitance C is defined to be C Q = V In two-dimensional problems we calculate the capacitance per unit length, c, whose cross section is typically displayed in the comple plane. Let in this case Q L be the charge per unit length of one of the conductors. Then we have QL c = V Theorem: The electrical charge per unit length on a conductor that belongs to a charged two-dimensional configuration of conductors is QL = ε Ψ ( z ) 4π where ε is the permittivity, or dielectric constant, of the surrounding material and Ψ( z) is the decrement (initial value minus final value) of the stream function as we proceed in the positive direction once around the boundary of the cross section of the conductor in the comple plane. Usually Ψ(z) will be a multivalued function defined by means of a branch cut. Thus Ψ (z) does not return to its original value when we encircle the conductor, and thus Ψ 0. We get: c = ε π 4 Ψ V Theorem: The capacitance of a two-dimensional system of conductors is unaffected by a conformal transformation of its cross section.
8 Bo E. Sernelius 5:8 EXAMPLES We will just give a few eamples of conformal mapping. The Linear Fractional Transformation (Möbius transformation) az + b ω = cz + d, ( ad bc 0) ; ω z = d + b cω a where a, b, c and d are comple constants. Each point in the z-plane, ecept z = -d/c, has a unique image point in the ω-plane. And each point in the ω-plane, ecept ω = a/c, has a unique image point in the z-plane. We may include the points z = and ω = and then have a one to one correspondence between all points in the z- and ω-planes. This transformation always transforms circles and lines into circles and lines. There is just one bilinear transformation that maps three given distinct points z 1, z, z 3 into three specified distinct points ω 1, ω, ω 3, respectively. Find one transformation that maps the unit circle and its interior on the real ais and the whole upper half plane. iy iv u We let
9 Bo E. Sernelius 5:9 z = i be mapped into ω =, z = - i be mapped into ω = 0, and z = 0 be mapped into a point with v > 0 The first point guarantees that the circle transforms into a straight line, the second that the line passes through the origin and the third that it maps the interior of the circle to the upper half-plane and not the lower. The following transformation has the wanted properties: ( z + i) ω = i ( z i) The inverse transformation is ω i z = i ω + i It is useful to introduce the cross ratio of four points: ( ) = z1, z, z3, z4 ( )( ) ( )( ) z1 z z3 z4 z1 z4 z3 z Theorem: The cross ratio is invariant under the möbius transformation : ( ω ω )( ω ω ) ( ω ω )( ω ω ) = ( )( ) ( )( ) z1 z z3 z4 z1 z4 z3 z This is very useful when we want to find the transformation that maps three specific points, z 1, z, z 3 onto three specific images, ω 1, ω, ω 3. Let the forth point be taken as the general point: ( ω1 ω )( ω3 ω) ( ω ω) ( ω ω ) = ( )( ) ( )( ) 1 3 z1 z z3 z z1 z z3 z
26.2. Cauchy-Riemann Equations and Conformal Mapping. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Cauchy-Riemann Equations and Conformal Mapping 26.2 Introduction In this Section we consider two important features of complex functions. The Cauchy-Riemann equations provide a necessary and sufficient
Cauchy-Riemann Equations and Conformal Mapping 26.2 Introduction In this Section we consider two important features of complex functions. The Cauchy-Riemann equations provide a necessary and sufficient
MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 4
 MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 4 Harmonic conjugates 4.1 Check that each of the functions u(x, y) below is harmonic at every (x, y) R 2, and find the unique harmonic conjugate, v(x, y), satisfying v(0,
MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 4 Harmonic conjugates 4.1 Check that each of the functions u(x, y) below is harmonic at every (x, y) R 2, and find the unique harmonic conjugate, v(x, y), satisfying v(0,
The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and engineering.
 Lecture 16 Applications of Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 451.001 Complex Variables The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and
Lecture 16 Applications of Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 451.001 Complex Variables The purpose of this lecture is to present a few applications of conformal mappings in problems which arise in physics and
Math 185 Homework Exercises II
 Math 185 Homework Exercises II Instructor: Andrés E. Caicedo Due: July 10, 2002 1. Verify that if f H(Ω) C 2 (Ω) is never zero, then ln f is harmonic in Ω. 2. Let f = u+iv H(Ω) C 2 (Ω). Let p 2 be an integer.
Math 185 Homework Exercises II Instructor: Andrés E. Caicedo Due: July 10, 2002 1. Verify that if f H(Ω) C 2 (Ω) is never zero, then ln f is harmonic in Ω. 2. Let f = u+iv H(Ω) C 2 (Ω). Let p 2 be an integer.
MTH3101 Spring 2017 HW Assignment 4: Sec. 26: #6,7; Sec. 33: #5,7; Sec. 38: #8; Sec. 40: #2 The due date for this assignment is 2/23/17.
 MTH0 Spring 07 HW Assignment : Sec. 6: #6,7; Sec. : #5,7; Sec. 8: #8; Sec. 0: # The due date for this assignment is //7. Sec. 6: #6. Use results in Sec. to verify that the function g z = ln r + iθ r >
MTH0 Spring 07 HW Assignment : Sec. 6: #6,7; Sec. : #5,7; Sec. 8: #8; Sec. 0: # The due date for this assignment is //7. Sec. 6: #6. Use results in Sec. to verify that the function g z = ln r + iθ r >
Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping
 Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping View complex function as a mapping Unlike a real function, a complex function w = f(z) cannot be represented by a curve. Instead it is useful to view it as a mapping. Write
Aero III/IV Conformal Mapping View complex function as a mapping Unlike a real function, a complex function w = f(z) cannot be represented by a curve. Instead it is useful to view it as a mapping. Write
x y x 2 2 x y x x y x U x y x y
 Lecture 7 Appendi B: Some sample problems from Boas Here are some solutions to the sample problems assigned for hapter 4 4: 8 Solution: We want to learn about the analyticity properties of the function
Lecture 7 Appendi B: Some sample problems from Boas Here are some solutions to the sample problems assigned for hapter 4 4: 8 Solution: We want to learn about the analyticity properties of the function
(7) Suppose α, β, γ are nonzero complex numbers such that α = β = γ.
 January 22, 2011 COMPLEX ANALYSIS: PROBLEMS SHEET -1 M.THAMBAN NAIR (1) Show that C is a field under the addition and multiplication defined for complex numbers. (2) Show that the map f : R C defined by
January 22, 2011 COMPLEX ANALYSIS: PROBLEMS SHEET -1 M.THAMBAN NAIR (1) Show that C is a field under the addition and multiplication defined for complex numbers. (2) Show that the map f : R C defined by
D, domain or region. Chapter 2. Analytic Functions. Sec. 9. (1) w. function of a complex variable. Note: Domain of f may not be a domain.
 Chapter. Analytic Functions Sec. 9. D, domain or region f : D w (1) w f function of a comple variable. Note: Domain of f may not be a domain. (set theory ) (topology ) Let w = u + iv and = + iy u + iv
Chapter. Analytic Functions Sec. 9. D, domain or region f : D w (1) w f function of a comple variable. Note: Domain of f may not be a domain. (set theory ) (topology ) Let w = u + iv and = + iy u + iv
1. The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions.
 Complex Analysis Qualifying Examination 1 The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions 2 ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS:
Complex Analysis Qualifying Examination 1 The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions 2 ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS:
u = (u, v) = y The velocity field described by ψ automatically satisfies the incompressibility condition, and it should be noted that
 18.354J Nonlinear Dynamics II: Continuum Systems Lecture 1 9 Spring 2015 19 Stream functions and conformal maps There is a useful device for thinking about two dimensional flows, called the stream function
18.354J Nonlinear Dynamics II: Continuum Systems Lecture 1 9 Spring 2015 19 Stream functions and conformal maps There is a useful device for thinking about two dimensional flows, called the stream function
NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis. A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India. and. V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India
 NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India and V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India A.Swaminathan and V.K.Katiyar (NPTEL) Complex Analysis 1 / 36 Complex Analysis Module: 7:
NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India and V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India A.Swaminathan and V.K.Katiyar (NPTEL) Complex Analysis 1 / 36 Complex Analysis Module: 7:
Lecture 14 Conformal Mapping. 1 Conformality. 1.1 Preservation of angle. 1.2 Length and area. MATH-GA Complex Variables
 Lecture 14 Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 2451.001 Complex Variables 1 Conformality 1.1 Preservation of angle The open mapping theorem tells us that an analytic function such that f (z 0 ) 0 maps a small neighborhood
Lecture 14 Conformal Mapping MATH-GA 2451.001 Complex Variables 1 Conformality 1.1 Preservation of angle The open mapping theorem tells us that an analytic function such that f (z 0 ) 0 maps a small neighborhood
Complex Variables, Summer 2016 Homework Assignments
 Complex Variables, Summer 2016 Homework Assignments Homeworks 1-4, due Thursday July 14th Do twenty-four of the following problems. Question 1 Let a = 2 + i and b = 1 i. Sketch the complex numbers a, b,
Complex Variables, Summer 2016 Homework Assignments Homeworks 1-4, due Thursday July 14th Do twenty-four of the following problems. Question 1 Let a = 2 + i and b = 1 i. Sketch the complex numbers a, b,
Complex Functions (1A) Young Won Lim 2/22/14
 Complex Functions (1A) Copyright (c) 2011-2014 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or
Complex Functions (1A) Copyright (c) 2011-2014 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or
III.3. Analytic Functions as Mapping, Möbius Transformations
 III.3. Analytic Functions as Mapping, Möbius Transformations 1 III.3. Analytic Functions as Mapping, Möbius Transformations Note. To graph y = f(x) where x,y R, we can simply plot points (x,y) in R 2 (that
III.3. Analytic Functions as Mapping, Möbius Transformations 1 III.3. Analytic Functions as Mapping, Möbius Transformations Note. To graph y = f(x) where x,y R, we can simply plot points (x,y) in R 2 (that
EEE 203 COMPLEX CALCULUS JANUARY 02, α 1. a t b
 Comple Analysis Parametric interval Curve 0 t z(t) ) 0 t α 0 t ( t α z α ( ) t a a t a+α 0 t a α z α 0 t a α z = z(t) γ a t b z = z( t) γ b t a = (γ, γ,..., γ n, γ n ) a t b = ( γ n, γ n,..., γ, γ ) b
Comple Analysis Parametric interval Curve 0 t z(t) ) 0 t α 0 t ( t α z α ( ) t a a t a+α 0 t a α z α 0 t a α z = z(t) γ a t b z = z( t) γ b t a = (γ, γ,..., γ n, γ n ) a t b = ( γ n, γ n,..., γ, γ ) b
Möbius transformations and its applications
 Möbius transformation and its applications Every Möbius transformation is the composition of translations, dilations and the inversion. Proof. Let w = S(z) = az + b, ad bc 0 be a Möbius cz + d transformation.
Möbius transformation and its applications Every Möbius transformation is the composition of translations, dilations and the inversion. Proof. Let w = S(z) = az + b, ad bc 0 be a Möbius cz + d transformation.
Lecture 1 Functions of a Complex Variable
 Lecture 1 Functions of a Comple Variable 1 Comple Numbers and Functions The set of real numbers is not a sufficient basis 1 for the representation of the complete set of roots of algebraic equations. However,
Lecture 1 Functions of a Comple Variable 1 Comple Numbers and Functions The set of real numbers is not a sufficient basis 1 for the representation of the complete set of roots of algebraic equations. However,
MATH COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # Introduction to PDEs, Spring 2018 Professor: Jared Speck
 MATH 8.52 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 6 8.52 Introduction to PDEs, Spring 208 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeting # 6: Laplace s and Poisson s Equations We will now study the Laplace and Poisson equations
MATH 8.52 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 6 8.52 Introduction to PDEs, Spring 208 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeting # 6: Laplace s and Poisson s Equations We will now study the Laplace and Poisson equations
MATH COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # Introduction to PDEs, Fall 2011 Professor: Jared Speck
 MATH 8.52 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 6 8.52 Introduction to PDEs, Fall 20 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeting # 6: Laplace s and Poisson s Equations We will now study the Laplace and Poisson equations
MATH 8.52 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 6 8.52 Introduction to PDEs, Fall 20 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeting # 6: Laplace s and Poisson s Equations We will now study the Laplace and Poisson equations
IV. Conformal Maps. 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability. 2. Automorphisms of the Riemann sphere: Möbius transformations
 MTH6111 Complex Analysis 2009-10 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 IV. Conformal Maps 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability We saw from the definition of complex differentiability that if f
MTH6111 Complex Analysis 2009-10 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 IV. Conformal Maps 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability We saw from the definition of complex differentiability that if f
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2003 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES
 INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 23 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES DOUGLAS ULMER 1. Meromorphic functions on the Riemann sphere It s often useful to allow functions to take the value. This exercise outlines one way to
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 23 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES DOUGLAS ULMER 1. Meromorphic functions on the Riemann sphere It s often useful to allow functions to take the value. This exercise outlines one way to
Exercise 9: Model of a Submarine
 Fluid Mechanics, SG4, HT3 October 4, 3 Eample : Submarine Eercise 9: Model of a Submarine The flow around a submarine moving at a velocity V can be described by the flow caused by a source and a sink with
Fluid Mechanics, SG4, HT3 October 4, 3 Eample : Submarine Eercise 9: Model of a Submarine The flow around a submarine moving at a velocity V can be described by the flow caused by a source and a sink with
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2004 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES
 INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2004 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES PHILIP FOTH 1. Cauchy s Formula and Cauchy s Theorem 1. Suppose that γ is a piecewise smooth positively ( counterclockwise ) oriented simple closed
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2004 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES PHILIP FOTH 1. Cauchy s Formula and Cauchy s Theorem 1. Suppose that γ is a piecewise smooth positively ( counterclockwise ) oriented simple closed
= 2 x y 2. (1)
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS PART 5: HARMONIC FUNCTIONS A Let me start by asking you a question. Suppose that f is an analytic function so that the CR-equation f/ z = 0 is satisfied. Let us write u and v for the real
COMPLEX ANALYSIS PART 5: HARMONIC FUNCTIONS A Let me start by asking you a question. Suppose that f is an analytic function so that the CR-equation f/ z = 0 is satisfied. Let us write u and v for the real
Conformal Mapping Lecture 20 Conformal Mapping
 Let γ : [a, b] C be a smooth curve in a domain D. Let f (z) be a function defined at all points z on γ. Let C denotes the image of γ under the transformation w = f (z). The parametric equation of C is
Let γ : [a, b] C be a smooth curve in a domain D. Let f (z) be a function defined at all points z on γ. Let C denotes the image of γ under the transformation w = f (z). The parametric equation of C is
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58
 CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012 September 5, 2012 Mapping Properties Lecture 13 We shall once again return to the study of general behaviour of holomorphic functions
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012 September 5, 2012 Mapping Properties Lecture 13 We shall once again return to the study of general behaviour of holomorphic functions
65 Fluid Flows (6/1/2018)
 65 Fluid Flows 6//08 Consider a two dimensional fluid flow which we describe by its velocity field, V x, y = p x, y, q x, y = p + iq R. We are only going to consider flows which are incompressible, i.e.
65 Fluid Flows 6//08 Consider a two dimensional fluid flow which we describe by its velocity field, V x, y = p x, y, q x, y = p + iq R. We are only going to consider flows which are incompressible, i.e.
7.2 Conformal mappings
 7.2 Conformal mappings Let f be an analytic function. At points where f (z) 0 such a map has the remarkable property that it is conformal. This means that angle is preserved (in the sense that any 2 smooth
7.2 Conformal mappings Let f be an analytic function. At points where f (z) 0 such a map has the remarkable property that it is conformal. This means that angle is preserved (in the sense that any 2 smooth
CHAPTER 9. Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation. Dr. Pulak Sahoo
 CHAPTER 9 Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation BY Dr. Pulak Sahoo Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics University of Kalyani West Bengal, India E-mail : sahoopulak@gmail.com Module-3:
CHAPTER 9 Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation BY Dr. Pulak Sahoo Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics University of Kalyani West Bengal, India E-mail : sahoopulak@gmail.com Module-3:
. In particular if a b then N(
 Gaussian Integers II Let us summarise what we now about Gaussian integers so far: If a, b Z[ i], then N( ab) N( a) N( b). In particular if a b then N( a ) N( b). Let z Z[i]. If N( z ) is an integer prime,
Gaussian Integers II Let us summarise what we now about Gaussian integers so far: If a, b Z[ i], then N( ab) N( a) N( b). In particular if a b then N( a ) N( b). Let z Z[i]. If N( z ) is an integer prime,
Singularity structure of the electric field near the limiter of the tokamak
 Singularity structure of the electric field near the limiter of the tokamak Steinbrecher György, Pometescu Nicolae Department of Physics, University of Craiova, Str. A. I. Cuza, No., 200585 - Craiova,
Singularity structure of the electric field near the limiter of the tokamak Steinbrecher György, Pometescu Nicolae Department of Physics, University of Craiova, Str. A. I. Cuza, No., 200585 - Craiova,
2. Complex Analytic Functions
 2. Complex Analytic Functions John Douglas Moore July 6, 2011 Recall that if A and B are sets, a function f : A B is a rule which assigns to each element a A a unique element f(a) B. In this course, we
2. Complex Analytic Functions John Douglas Moore July 6, 2011 Recall that if A and B are sets, a function f : A B is a rule which assigns to each element a A a unique element f(a) B. In this course, we
Solutions to Exercises 6.1
 34 Chapter 6 Conformal Mappings Solutions to Exercises 6.. An analytic function fz is conformal where f z. If fz = z + e z, then f z =e z z + z. We have f z = z z += z =. Thus f is conformal at all z.
34 Chapter 6 Conformal Mappings Solutions to Exercises 6.. An analytic function fz is conformal where f z. If fz = z + e z, then f z =e z z + z. We have f z = z z += z =. Thus f is conformal at all z.
The result above is known as the Riemann mapping theorem. We will prove it using basic theory of normal families. We start this lecture with that.
 Lecture 15 The Riemann mapping theorem Variables MATH-GA 2451.1 Complex The point of this lecture is to prove that the unit disk can be mapped conformally onto any simply connected open set in the plane,
Lecture 15 The Riemann mapping theorem Variables MATH-GA 2451.1 Complex The point of this lecture is to prove that the unit disk can be mapped conformally onto any simply connected open set in the plane,
MAT665:ANALYTIC FUNCTION THEORY
 MAT665:ANALYTIC FUNCTION THEORY DR. RITU AGARWAL MALAVIYA NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY JAIPUR Contents 1. About 2 2. Complex Numbers 2 3. Fundamental inequalities 2 4. Continuously differentiable functions
MAT665:ANALYTIC FUNCTION THEORY DR. RITU AGARWAL MALAVIYA NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY JAIPUR Contents 1. About 2 2. Complex Numbers 2 3. Fundamental inequalities 2 4. Continuously differentiable functions
MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONFORMAL MAPPINGS LECTURE
 MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONFORMAL MAPPINGS LECTURE 1. Introduction Let D denote the unit disk and let D denote its boundary circle. Consider a piecewise continuous function on the boundary circle, {
MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONFORMAL MAPPINGS LECTURE 1. Introduction Let D denote the unit disk and let D denote its boundary circle. Consider a piecewise continuous function on the boundary circle, {
Electro-Static Potential Between Two Conducting Cylinders via the Group Method Approach
 Proceedings of Institute of Mathematics of NAS of Ukraine 2000, Vol. 30, Part 1, 60 67. Electro-Static Potential Between Two Conducting Cylinders via the Group Method Approach M.B. ABD-EL-MALEK, I.A. EL-AWADI
Proceedings of Institute of Mathematics of NAS of Ukraine 2000, Vol. 30, Part 1, 60 67. Electro-Static Potential Between Two Conducting Cylinders via the Group Method Approach M.B. ABD-EL-MALEK, I.A. EL-AWADI
1. (3) Write Gauss Law in differential form. Explain the physical meaning.
 Electrodynamics I Midterm Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 204/0/23 Name Electro Dynamic Instructions: Use SI units. Where appropriate, define all variables or symbols you use, in words. Try to tell about
Electrodynamics I Midterm Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 204/0/23 Name Electro Dynamic Instructions: Use SI units. Where appropriate, define all variables or symbols you use, in words. Try to tell about
Worked examples Conformal mappings and bilinear transformations
 Worked examples Conformal mappings and bilinear transformations Example 1 Suppose we wish to find a bilinear transformation which maps the circle z i = 1 to the circle w =. Since w/ = 1, the linear transformation
Worked examples Conformal mappings and bilinear transformations Example 1 Suppose we wish to find a bilinear transformation which maps the circle z i = 1 to the circle w =. Since w/ = 1, the linear transformation
Math 4263 Homework Set 1
 Homework Set 1 1. Solve the following PDE/BVP 2. Solve the following PDE/BVP 2u t + 3u x = 0 u (x, 0) = sin (x) u x + e x u y = 0 u (0, y) = y 2 3. (a) Find the curves γ : t (x (t), y (t)) such that that
Homework Set 1 1. Solve the following PDE/BVP 2. Solve the following PDE/BVP 2u t + 3u x = 0 u (x, 0) = sin (x) u x + e x u y = 0 u (0, y) = y 2 3. (a) Find the curves γ : t (x (t), y (t)) such that that
Theorem III.3.4. If f : G C is analytic then f preserves angles at each point z 0 of G where f (z 0 ) 0.
 Möbius Transformations; Supplemented by Hitchman 1 Supplemental Notes on III.3. Analytic Functions as Mappings: Möbius Transformations with Supplemental Material from Hitchman s Geometry with an Introduction
Möbius Transformations; Supplemented by Hitchman 1 Supplemental Notes on III.3. Analytic Functions as Mappings: Möbius Transformations with Supplemental Material from Hitchman s Geometry with an Introduction
CHAPTER 9. Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation. Dr. Pulak Sahoo
 CHAPTER 9 Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation BY Dr. Pulak Sahoo Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics University of Kalyani West Bengal, India E-mail : sahoopulak1@gmail.com 1 Module-4:
CHAPTER 9 Conformal Mapping and Bilinear Transformation BY Dr. Pulak Sahoo Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics University of Kalyani West Bengal, India E-mail : sahoopulak1@gmail.com 1 Module-4:
B.Tech. Theory Examination (Semester IV) Engineering Mathematics III
 Solved Question Paper 5-6 B.Tech. Theory Eamination (Semester IV) 5-6 Engineering Mathematics III Time : hours] [Maimum Marks : Section-A. Attempt all questions of this section. Each question carry equal
Solved Question Paper 5-6 B.Tech. Theory Eamination (Semester IV) 5-6 Engineering Mathematics III Time : hours] [Maimum Marks : Section-A. Attempt all questions of this section. Each question carry equal
Quasi-conformal maps and Beltrami equation
 Chapter 7 Quasi-conformal maps and Beltrami equation 7. Linear distortion Assume that f(x + iy) =u(x + iy)+iv(x + iy) be a (real) linear map from C C that is orientation preserving. Let z = x + iy and
Chapter 7 Quasi-conformal maps and Beltrami equation 7. Linear distortion Assume that f(x + iy) =u(x + iy)+iv(x + iy) be a (real) linear map from C C that is orientation preserving. Let z = x + iy and
Möbius Transformation
 Möbius Transformation 1 1 June 15th, 2010 Mathematics Science Center Tsinghua University Philosophy Rigidity Conformal mappings have rigidity. The diffeomorphism group is of infinite dimension in general.
Möbius Transformation 1 1 June 15th, 2010 Mathematics Science Center Tsinghua University Philosophy Rigidity Conformal mappings have rigidity. The diffeomorphism group is of infinite dimension in general.
Conformal maps. Lent 2019 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor. A star means optional and not necessarily harder.
 Lent 29 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor A star means optional and not necessarily harder. Conformal maps. (i) Let f(z) = az + b, with ad bc. Where in C is f conformal? cz + d (ii) Let f(z) = z +. What are the
Lent 29 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor A star means optional and not necessarily harder. Conformal maps. (i) Let f(z) = az + b, with ad bc. Where in C is f conformal? cz + d (ii) Let f(z) = z +. What are the
Riemann sphere and rational maps
 Chapter 3 Riemann sphere and rational maps 3.1 Riemann sphere It is sometimes convenient, and fruitful, to work with holomorphic (or in general continuous) functions on a compact space. However, we wish
Chapter 3 Riemann sphere and rational maps 3.1 Riemann sphere It is sometimes convenient, and fruitful, to work with holomorphic (or in general continuous) functions on a compact space. However, we wish
Complex Analysis MATH 6300 Fall 2013 Homework 4
 Complex Analysis MATH 6300 Fall 2013 Homework 4 Due Wednesday, December 11 at 5 PM Note that to get full credit on any problem in this class, you must solve the problems in an efficient and elegant manner,
Complex Analysis MATH 6300 Fall 2013 Homework 4 Due Wednesday, December 11 at 5 PM Note that to get full credit on any problem in this class, you must solve the problems in an efficient and elegant manner,
F (z) =f(z). f(z) = a n (z z 0 ) n. F (z) = a n (z z 0 ) n
 6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
Leplace s Equations. Analyzing the Analyticity of Analytic Analysis DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING. Engineering Math EECE
 Leplace s Analyzing the Analyticity of Analytic Analysis Engineering Math EECE 3640 1 The Laplace equations are built on the Cauchy- Riemann equations. They are used in many branches of physics such as
Leplace s Analyzing the Analyticity of Analytic Analysis Engineering Math EECE 3640 1 The Laplace equations are built on the Cauchy- Riemann equations. They are used in many branches of physics such as
Spring 2010 Exam 2. You may not use your books, notes, or any calculator on this exam.
 MTH 282 final Spring 2010 Exam 2 Time Limit: 110 Minutes Name (Print): Instructor: Prof. Houhong Fan This exam contains 6 pages (including this cover page) and 5 problems. Check to see if any pages are
MTH 282 final Spring 2010 Exam 2 Time Limit: 110 Minutes Name (Print): Instructor: Prof. Houhong Fan This exam contains 6 pages (including this cover page) and 5 problems. Check to see if any pages are
Mapping problems and harmonic univalent mappings
 Mapping problems and harmonic univalent mappings Antti Rasila Helsinki University of Technology antti.rasila@tkk.fi (Mainly based on P. Duren s book Harmonic mappings in the plane) Helsinki Analysis Seminar,
Mapping problems and harmonic univalent mappings Antti Rasila Helsinki University of Technology antti.rasila@tkk.fi (Mainly based on P. Duren s book Harmonic mappings in the plane) Helsinki Analysis Seminar,
Conformal Mapping, Möbius Transformations. Slides-13
 , Möbius Transformations Slides-13 Let γ : [a, b] C be a smooth curve in a domain D. Let f be a function defined at all points z on γ. Let C denotes the image of γ under the transformation w = f (z).
, Möbius Transformations Slides-13 Let γ : [a, b] C be a smooth curve in a domain D. Let f be a function defined at all points z on γ. Let C denotes the image of γ under the transformation w = f (z).
carries the circle w 1 onto the circle z R and sends w = 0 to z = a. The function u(s(w)) is harmonic in the unit circle w 1 and we obtain
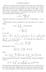 4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
Here are brief notes about topics covered in class on complex numbers, focusing on what is not covered in the textbook.
 Phys374, Spring 2008, Prof. Ted Jacobson Department of Physics, University of Maryland Complex numbers version 5/21/08 Here are brief notes about topics covered in class on complex numbers, focusing on
Phys374, Spring 2008, Prof. Ted Jacobson Department of Physics, University of Maryland Complex numbers version 5/21/08 Here are brief notes about topics covered in class on complex numbers, focusing on
RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM
 RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM VED V. DATAR Recall that two domains are called conformally equivalent if there exists a holomorphic bijection from one to the other. This automatically implies that there is an
RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM VED V. DATAR Recall that two domains are called conformally equivalent if there exists a holomorphic bijection from one to the other. This automatically implies that there is an
Math Subject GRE Questions
 Math Subject GRE Questions Calculus and Differential Equations 1. If f() = e e, then [f ()] 2 [f()] 2 equals (a) 4 (b) 4e 2 (c) 2e (d) 2 (e) 2e 2. An integrating factor for the ordinary differential equation
Math Subject GRE Questions Calculus and Differential Equations 1. If f() = e e, then [f ()] 2 [f()] 2 equals (a) 4 (b) 4e 2 (c) 2e (d) 2 (e) 2e 2. An integrating factor for the ordinary differential equation
Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions
 Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions Nikhil Srivastava December 12, 2015 1. True or false: (a) If f is analytic in the annulus A = {z : 1 < z < 2} then there exist functions g and h such that
Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions Nikhil Srivastava December 12, 2015 1. True or false: (a) If f is analytic in the annulus A = {z : 1 < z < 2} then there exist functions g and h such that
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm
 Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Introduction to Complex Analysis by Hilary Priestley Unofficial Solutions Manual
 Introduction to Complex Analysis by Hilary Priestley Unofficial Solutions Manual MOHAMMAD EHTISHAM AKHTAR IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON http://akhtarmath.wordpress.com Dedicated to my Parents ii Preface This
Introduction to Complex Analysis by Hilary Priestley Unofficial Solutions Manual MOHAMMAD EHTISHAM AKHTAR IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON http://akhtarmath.wordpress.com Dedicated to my Parents ii Preface This
MATH 566: FINAL PROJECT
 MATH 566: FINAL PROJECT December, 010 JAN E.M. FEYS Complex analysis is a standard part of any math curriculum. Less known is the intense connection between the pure complex analysis and fluid dynamics.
MATH 566: FINAL PROJECT December, 010 JAN E.M. FEYS Complex analysis is a standard part of any math curriculum. Less known is the intense connection between the pure complex analysis and fluid dynamics.
Linear Functions (I)
 4. MAPPING BY ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS There are many practical situations where we try to simplify a problem by transforming it. We investigate how various regions in the plane are transformed by elementary
4. MAPPING BY ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS There are many practical situations where we try to simplify a problem by transforming it. We investigate how various regions in the plane are transformed by elementary
Zero Gravity of Free-Surface Jet Flow
 International Mathematical Forum, 2, 2007, no. 66, 3273-3277 Zero Gravity of Free-Surface Jet Flow B. Bouderah, A. Gasmi and H. Serguine Laboratory of Pure and Applied Mathematics LPAM University of M
International Mathematical Forum, 2, 2007, no. 66, 3273-3277 Zero Gravity of Free-Surface Jet Flow B. Bouderah, A. Gasmi and H. Serguine Laboratory of Pure and Applied Mathematics LPAM University of M
Chapter 13: Complex Numbers
 Sections 13.3 & 13.4 1. A (single-valued) function f of a complex variable z is such that for every z in the domain of definition D of f, there is a unique complex number w such that w = f (z). The real
Sections 13.3 & 13.4 1. A (single-valued) function f of a complex variable z is such that for every z in the domain of definition D of f, there is a unique complex number w such that w = f (z). The real
Chapter II. Complex Variables
 hapter II. omplex Variables Dates: October 2, 4, 7, 2002. These three lectures will cover the following sections of the text book by Keener. 6.1. omplex valued functions and branch cuts; 6.2.1. Differentiation
hapter II. omplex Variables Dates: October 2, 4, 7, 2002. These three lectures will cover the following sections of the text book by Keener. 6.1. omplex valued functions and branch cuts; 6.2.1. Differentiation
From the definition of a surface, each point has a neighbourhood U and a homeomorphism. U : ϕ U(U U ) ϕ U (U U )
 3 Riemann surfaces 3.1 Definitions and examples From the definition of a surface, each point has a neighbourhood U and a homeomorphism ϕ U from U to an open set V in R 2. If two such neighbourhoods U,
3 Riemann surfaces 3.1 Definitions and examples From the definition of a surface, each point has a neighbourhood U and a homeomorphism ϕ U from U to an open set V in R 2. If two such neighbourhoods U,
Functions of a Complex Variable and Integral Transforms
 Functions of a Complex Variable and Integral Transforms Department of Mathematics Zhou Lingjun Textbook Functions of Complex Analysis with Applications to Engineering and Science, 3rd Edition. A. D. Snider
Functions of a Complex Variable and Integral Transforms Department of Mathematics Zhou Lingjun Textbook Functions of Complex Analysis with Applications to Engineering and Science, 3rd Edition. A. D. Snider
Physics 3211: Electromagnetic Theory (Tutorial)
 Question 1 a) The capacitor shown in Figure 1 consists of two parallel dielectric layers and a voltage source, V. Derive an equation for capacitance. b) Find the capacitance for the configuration of Figure
Question 1 a) The capacitor shown in Figure 1 consists of two parallel dielectric layers and a voltage source, V. Derive an equation for capacitance. b) Find the capacitance for the configuration of Figure
Math 423/823 Exam 1 Topics Covered
 Math 423/823 Exam 1 Topics Covered Complex numbers: C: z = x+yi, where i 2 = 1; addition and multiplication behaves like reals. Formally, x + yi (x,y), with (x,y) + (a,b) = (x + a,y + b) and (x,y)(a,b)
Math 423/823 Exam 1 Topics Covered Complex numbers: C: z = x+yi, where i 2 = 1; addition and multiplication behaves like reals. Formally, x + yi (x,y), with (x,y) + (a,b) = (x + a,y + b) and (x,y)(a,b)
Riemann Mapping Theorem (4/10-4/15)
 Math 752 Spring 2015 Riemann Mapping Theorem (4/10-4/15) Definition 1. A class F of continuous functions defined on an open set G is called a normal family if every sequence of elements in F contains a
Math 752 Spring 2015 Riemann Mapping Theorem (4/10-4/15) Definition 1. A class F of continuous functions defined on an open set G is called a normal family if every sequence of elements in F contains a
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 530) January 2019
 Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Complex varibles:contour integration examples
 omple varibles:ontour integration eamples 1 Problem 1 onsider the problem d 2 + 1 If we take the substitution = tan θ then d = sec 2 θdθ, which leads to dθ = π sec 2 θ tan 2 θ + 1 dθ Net we consider the
omple varibles:ontour integration eamples 1 Problem 1 onsider the problem d 2 + 1 If we take the substitution = tan θ then d = sec 2 θdθ, which leads to dθ = π sec 2 θ tan 2 θ + 1 dθ Net we consider the
Definition We say that a topological manifold X is C p if there is an atlas such that the transition functions are C p.
 13. Riemann surfaces Definition 13.1. Let X be a topological space. We say that X is a topological manifold, if (1) X is Hausdorff, (2) X is 2nd countable (that is, there is a base for the topology which
13. Riemann surfaces Definition 13.1. Let X be a topological space. We say that X is a topological manifold, if (1) X is Hausdorff, (2) X is 2nd countable (that is, there is a base for the topology which
Bilinear Transformations via a Computer Algebra System
 Bilinear Transformations via a Computer Algebra System Tilak de Alwis talwis@selu.edu Department of Mathematics Southeastern Louisiana University Hammond, LA 70403 USA Abstract: In this paper, we will
Bilinear Transformations via a Computer Algebra System Tilak de Alwis talwis@selu.edu Department of Mathematics Southeastern Louisiana University Hammond, LA 70403 USA Abstract: In this paper, we will
Schwarz-Christoffel Transformation and Applications in Applied Probability
 Schwarz-Christoffel Transformation and Applications in Applied Probability Yvik C. Swan and F. Thomas Bruss Université Libre de Bruxelles Summary Problems involving stochastic processes frequently involve
Schwarz-Christoffel Transformation and Applications in Applied Probability Yvik C. Swan and F. Thomas Bruss Université Libre de Bruxelles Summary Problems involving stochastic processes frequently involve
Considering our result for the sum and product of analytic functions, this means that for (a 0, a 1,..., a N ) C N+1, the polynomial.
 Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
Geometric Complex Analysis. Davoud Cheraghi Imperial College London
 Geometric Complex Analysis Davoud Cheraghi Imperial College London May 9, 2017 Introduction The subject of complex variables appears in many areas of mathematics as it has been truly the ancestor of many
Geometric Complex Analysis Davoud Cheraghi Imperial College London May 9, 2017 Introduction The subject of complex variables appears in many areas of mathematics as it has been truly the ancestor of many
MATH MIDTERM 1 SOLUTION. 1. (5 points) Determine whether the following statements are true of false, no justification is required.
 MATH 185-4 MIDTERM 1 SOLUTION 1. (5 points Determine whether the following statements are true of false, no justification is required. (1 (1pointTheprincipalbranchoflogarithmfunctionf(z = Logz iscontinuous
MATH 185-4 MIDTERM 1 SOLUTION 1. (5 points Determine whether the following statements are true of false, no justification is required. (1 (1pointTheprincipalbranchoflogarithmfunctionf(z = Logz iscontinuous
MATH 434 Fall 2016 Homework 1, due on Wednesday August 31
 Homework 1, due on Wednesday August 31 Problem 1. Let z = 2 i and z = 3 + 4i. Write the product zz and the quotient z z in the form a + ib, with a, b R. Problem 2. Let z C be a complex number, and let
Homework 1, due on Wednesday August 31 Problem 1. Let z = 2 i and z = 3 + 4i. Write the product zz and the quotient z z in the form a + ib, with a, b R. Problem 2. Let z C be a complex number, and let
Chapter 10: Rational Functions and the Riemann Sphere. By a rational function we mean a function f which can be expressed in the form
 Chapter 10: Rational Functions and the Riemann Sphere By a rational function we mean a function f which can be expressed in the form f(z) = p(z) q(z) = a nz n +a n 1 z n 1 + +a 1 z +a 0 b m z m +b m 1
Chapter 10: Rational Functions and the Riemann Sphere By a rational function we mean a function f which can be expressed in the form f(z) = p(z) q(z) = a nz n +a n 1 z n 1 + +a 1 z +a 0 b m z m +b m 1
1. (3) Write Gauss Law in differential form. Explain the physical meaning.
 Electrodynamics I Midterm Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 204/0/23 Name Instructions: Use SI units. Where appropriate, define all variables or symbols you use, in words. Try to tell about the physics involved,
Electrodynamics I Midterm Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 204/0/23 Name Instructions: Use SI units. Where appropriate, define all variables or symbols you use, in words. Try to tell about the physics involved,
COMPLEX ANALYSIS-I. DR. P.K. SRIVASTAVA Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics Galgotia s College of Engg. & Technology, Gr.
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS-I DR. P.K. SRIVASTAVA Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics Galgotia s College of Engg. & Technology, Gr. Noida An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Company Vayu Education of India 2/25,
COMPLEX ANALYSIS-I DR. P.K. SRIVASTAVA Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics Galgotia s College of Engg. & Technology, Gr. Noida An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Company Vayu Education of India 2/25,
Complex Analysis Homework 3
 Complex Analysis Homework 3 Steve Clanton David Holz March 3, 009 Problem 3 Solution. Let z = re iθ. Then, we see the mapping leaves the modulus unchanged while multiplying the argument by -3: Ω z = z
Complex Analysis Homework 3 Steve Clanton David Holz March 3, 009 Problem 3 Solution. Let z = re iθ. Then, we see the mapping leaves the modulus unchanged while multiplying the argument by -3: Ω z = z
ERRATA MATHEMATICS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL STUDENT MATHEMATICS HL (CORE) (2nd edition)
 ERRATA MATHEMATICS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL STUDENT MATHEMATICS HL (CORE) (nd edition) Second edition - 010 reprint page 95 TEXT last paragraph on the page should read: e is a special number in mathematics.
ERRATA MATHEMATICS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL STUDENT MATHEMATICS HL (CORE) (nd edition) Second edition - 010 reprint page 95 TEXT last paragraph on the page should read: e is a special number in mathematics.
COMPLEX VARIABLES. Principles and Problem Sessions YJ? A K KAPOOR. University of Hyderabad, India. World Scientific NEW JERSEY LONDON
 COMPLEX VARIABLES Principles and Problem Sessions A K KAPOOR University of Hyderabad, India NEW JERSEY LONDON YJ? World Scientific SINGAPORE BEIJING SHANGHAI HONG KONG TAIPEI CHENNAI CONTENTS Preface vii
COMPLEX VARIABLES Principles and Problem Sessions A K KAPOOR University of Hyderabad, India NEW JERSEY LONDON YJ? World Scientific SINGAPORE BEIJING SHANGHAI HONG KONG TAIPEI CHENNAI CONTENTS Preface vii
Some commonly encountered sets and their notations
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS (This notes are based on the book Introductory Mathematics by Ng Wee Seng ) LECTURE SETS & FUNCTIONS Some commonly encountered sets and their
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS (This notes are based on the book Introductory Mathematics by Ng Wee Seng ) LECTURE SETS & FUNCTIONS Some commonly encountered sets and their
Solution to Homework 4, Math 7651, Tanveer 1. Show that the function w(z) = 1 2
 Solution to Homework 4, Math 7651, Tanveer 1. Show that the function w(z) = 1 (z + 1/z) maps the exterior of a unit circle centered around the origin in the z-plane to the exterior of a straight line cut
Solution to Homework 4, Math 7651, Tanveer 1. Show that the function w(z) = 1 (z + 1/z) maps the exterior of a unit circle centered around the origin in the z-plane to the exterior of a straight line cut
Why airplanes fly, and ships sail
 Why airplanes fly, and ships sail A. Eremenko April 23, 2013 And windmills rotate and propellers pull, etc.... Denote z = x + iy and let v(z) = v 1 (z) + iv 2 (z) be the velocity field of a stationary
Why airplanes fly, and ships sail A. Eremenko April 23, 2013 And windmills rotate and propellers pull, etc.... Denote z = x + iy and let v(z) = v 1 (z) + iv 2 (z) be the velocity field of a stationary
Lecture 1 The complex plane. z ± w z + w.
 Lecture 1 The complex plane Exercise 1.1. Show that the modulus obeys the triangle inequality z ± w z + w. This allows us to make the complex plane into a metric space, and thus to introduce topological
Lecture 1 The complex plane Exercise 1.1. Show that the modulus obeys the triangle inequality z ± w z + w. This allows us to make the complex plane into a metric space, and thus to introduce topological
Mid Term-1 : Solutions to practice problems
 Mid Term- : Solutions to practice problems 0 October, 06. Is the function fz = e z x iy holomorphic at z = 0? Give proper justification. Here we are using the notation z = x + iy. Solution: Method-. Use
Mid Term- : Solutions to practice problems 0 October, 06. Is the function fz = e z x iy holomorphic at z = 0? Give proper justification. Here we are using the notation z = x + iy. Solution: Method-. Use
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser
 Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 2
 MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 2 Circles in the Riemann sphere Recall that the Riemann sphere is defined as the set Let P be the plane defined b Σ = { (a, b, c) R 3 a 2 + b 2 + c 2 = 1 } P = { (a, b, c)
MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 2 Circles in the Riemann sphere Recall that the Riemann sphere is defined as the set Let P be the plane defined b Σ = { (a, b, c) R 3 a 2 + b 2 + c 2 = 1 } P = { (a, b, c)
EE243 Advanced Electromagnetic Theory Lec #3: Electrostatics (Apps., Form),
 EE4 Advanced Electromagnetic Theory Lec #: Electrostatics Apps., Form, Electrostatic Boundary Conditions Energy, Force and Capacitance Electrostatic Boundary Conditions on Φ Image Solutions Eample Green
EE4 Advanced Electromagnetic Theory Lec #: Electrostatics Apps., Form, Electrostatic Boundary Conditions Energy, Force and Capacitance Electrostatic Boundary Conditions on Φ Image Solutions Eample Green
Lecture 13: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay. Poisson s and Laplace s Equations
 Poisson s and Laplace s Equations Lecture 13: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay We will spend some time in looking at the mathematical foundations of electrostatics.
Poisson s and Laplace s Equations Lecture 13: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay We will spend some time in looking at the mathematical foundations of electrostatics.
Exact V
 Problems 301 6 7 8 9 10 Exact V 1 2.4975 2.4993 2.4998 2.4999 2.5000 2.5000 V 2 1.9982 1.9995 1.9999 2.0000 2.0000 1.9771 V 3 2.4987 2.4996 2.4999 2.5000 2.5000 2.5000 V 4 2.9991 2.9997 2.9999 3.0000 3.0000
Problems 301 6 7 8 9 10 Exact V 1 2.4975 2.4993 2.4998 2.4999 2.5000 2.5000 V 2 1.9982 1.9995 1.9999 2.0000 2.0000 1.9771 V 3 2.4987 2.4996 2.4999 2.5000 2.5000 2.5000 V 4 2.9991 2.9997 2.9999 3.0000 3.0000
Homotopy Perturbation Method for Solving Systems of Nonlinear Coupled Equations
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol 6, 2012, no 96, 4787-4800 Homotopy Perturbation Method for Solving Systems of Nonlinear Coupled Equations A A Hemeda Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science Tanta
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol 6, 2012, no 96, 4787-4800 Homotopy Perturbation Method for Solving Systems of Nonlinear Coupled Equations A A Hemeda Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science Tanta
The Aharonov-Bohm Effect: Mathematical Aspects of the Quantum Flow
 Applied athematical Sciences, Vol. 1, 2007, no. 8, 383-394 The Aharonov-Bohm Effect: athematical Aspects of the Quantum Flow Luis Fernando ello Instituto de Ciências Exatas, Universidade Federal de Itajubá
Applied athematical Sciences, Vol. 1, 2007, no. 8, 383-394 The Aharonov-Bohm Effect: athematical Aspects of the Quantum Flow Luis Fernando ello Instituto de Ciências Exatas, Universidade Federal de Itajubá
