Supplementary information for: Frequency stabilization in nonlinear micro-mechanical oscillators
|
|
|
- Chester Payne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary information for: Frequency stabilization in nonlinear micro-mechanical oscillators Dario Antonio Center for Nanoscale Materials, Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL, USA Damián H. Zanette Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas, Centro Atómico Bariloche and Instituto Balseiro 8400 Bariloche, Río Negro, Argentina Daniel López Center for Nanoscale Materials, Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL, USA (Dated: April 10, 2012)
2 2 Oscillation frequency! Oscillation amplitude 1/2 A 1 / Driving force amplitude Driving force amplitude F 0 /m 1 Supplementary Figure S1. Oscillation frequency ν of the two coupled modes as a function of the driving force amplitude F 0, for ɛ 1/ω 2 = ɛ 2/ω 2 = 10 4 and j 1/ω2 2 = j 2/ω2 2 = The frequency ratio between the two modes is ω 2/ω 1 = Axes have been rescaled to make the plot independent of the specific values of ω 2 and β. In the horizontal axis, α = ω 3 2 β/(ɛ1/ω 2). Arrows show the hysteresis cycle in an experiment where F 0 is first increased, in such a way that ν overcomes ω 2 and jumps to the upper branch after the stabilization interval, and then decreased. The insert shows the oscillation amplitude A 1 of the first mode as a function of the driving force amplitude.
3 3 a b c A m p litu d e (m V ) F re q u e n c y (k H z ) Supplementary Figure S2. Internal resonance in different resonators. We have detected the coupling between the first mode and higher frequency modes at the internal resonance condition in a variety of micromechanical resonators. Depending on the frequency of the higher modes relative to the first mode, and the detuning reached with the maximum driving strength, one or more internal resonance conditions were detected (indicated by arrows in Supplementary Figure S2). In all cases the lower frequency mode was the first in-plane flexural mode, but the high frequency modes were both in-plane and out of plane, primary and secondary flexural modes, and also torsional modes. Therefore, the possibility of coupling with different types of modes gives great flexibility for the design of oscillators using this stabilization mechanism. All the devices are c-c resonators, actuated and detected using comb-drive electrodes, but differ in their dimensions and in the number of their parallel interconnected beams. The vertical arrows indicate the presence of an internal resonance condition a, Resonator 1, beam length l = 500µm, thickness t = 10µm, wih w = 2µm, number of beams n = 6. b, Resonator 2, same nominal dimensions as resonator 1 but with a coating of 20 nm of chrome and 500 nm of gold. c, Resonator 3, l = 1000µm, thickness t = 25µm, wih w = 2µm, number of beams n = 1.
4 4 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Analytical model for frequency stabilization by internal resonance Frequency stabilization by internal resonance in the clamped-clamped micro-oscillator considered in this paper is due to the transfer of energy from the first oscillation mode to the principal torsional mode. In the self-sustaining configuration, increasing the driving force causes a growth of both the amplitude and, due to nonlinear effects, the frequency f 1 of the first mode. When f 1 reaches one third of the frequency f 3 of the principal torsional mode, internal resonance takes place, and energy is transferred from the former to the latter. The coupling between the two modes is mediated by the 3f 1 -component of the first mode oscillations (1:3 internal resonance). As a result of this energy transfer, the growth rate of the amplitude and the frequency of the first mode decreases abruptly and, hence, both become stabilized. To demonstrate this mechanism by means of an exactly solvable analytical model, we study the analogous case of a 1:1 internal resonance, which simplifies the analysis without affecting the nature of the problem, and consider the coupled dynamics of two oscillators, each of them representing one of the participating modes. The first mode is represented by a nonlinear self-sustaining oscillator described by the equation d 2 x 1 m c dx m 1ω1x k 3 x 3 1 = F 0 cos(φ 1 (t) ψ 0 ) + J(x 2 x 1 ). (1) The first term in the right-hand-side is the driving force, with φ 1 (t) the oscillation phase of x 1 (t) and ψ 0 the phase shift of the force. The second term stands for the coupling with the higher frequency mode, with coupling strength J, and derives from a harmonic interaction potential V int = J 2 (x 2 x 1 ) 2. The higher frequency mode, in turn, is represented by a linear oscillator coupled to the first: d 2 x 2 m c dx m 2ω2x 2 2 = J(x 1 x 2 ). (2) We assume that ω 2 > ω 1, in such a way that increasing the driving force amplitude F 0 makes the frequency of the first oscillator approach ω 2, thus producing the resonance. In view of the dependence of the driving force of the first oscillator on its phase, it is convenient to introduce a phase-amplitude representation for the two oscillators, replacing the position x i (t) and the velocity v i (t) = dxi (i = 1, 2) by the phase φ i (t) and the amplitude A i (t). The new variables are defined by x i (t) = A i (t) cos φ i (t), v i (t) = νa i (t) sin φ i (t), (3) where ν is, in principle, an arbitrary constant. Seeking for solutions with time-independent A 1 and A 2, as expected to be the case in the long-time asymptotic oscillations, we get dφ1 = dφ2 = ν, which shows that the two oscillators move synchronously with frequency ν. We take φ 1 (t) = νt and φ 2 (t) = νt ψ 2, with ψ 2 the phase shift between the two oscillators. Separating terms in sin νt and cos νt and neglecting higher-harmonic contributions proportional to cos 3νt, the equations of motion become algebraic equations for the four unknowns ν, A 1, A 2, and ψ 2. For a driving phase shift ψ 0 = π/2, which corresponds to operating the nonlinear oscillator in its resonance peak, the oscillation frequency ν is given by the equation ( ) 2 ν 2 = ω1 2 + j 1 + j 1j 2 (ν 2 ω2 2 j 2 ) ν 2 ɛ (ν2 ω2 2 j 2) 2 + β F 0 /m 1 ν 2, (4) ɛ 1 + ɛ 2j 1j 2 ν 2 ɛ 2 2 +(ν2 ω 2 2 j2)2 with ɛ i = c i /m i, j i = J/m i (i = 1, 2), and β = 4k 3 /3m 1. This is equivalent to a polynomial third-degree equation for ν 2, whose exact solutions can be found analytically. Once it has been solved, the remaining unknowns are given by the relations and A 1 = νɛ 1 + F 0 /m 1 νɛ 2j 1j 2 (5) ν 2 ɛ 2 2 +(ν2 ω2 2 j2)2 j 2 A 1 A 2 exp iψ 2 = ν 2 ω2 2 j. (6) 2 + iνɛ 2
5 Supplementary Figure S1 illustrates the results for ν and A 1 as functions of the driving force amplitude F 0. The stabilization of the oscillation frequency and amplitude, as ν approaches ω 2, is apparent. Arrows show the path of an experiment in which, first, the driving force is increased in such a way that ν becomes stabilized, until it overcomes ω 2 and suddenly jumps to the upper branch. Then, upon decreasing F 0, the oscillation frequency decreases along the upper branch, completing the hysteresis cycle. 5
Frequency stabilization by synchronization of Duffing oscillators
 Frequency stabilization by synchronization of Duffing oscillators Damián H. Zanette arxiv:1608.00416v1 [nlin.ao] 1 Aug 2016 Centro Atómico Bariloche and Instituto Balseiro (Comisión Nacional de Energía
Frequency stabilization by synchronization of Duffing oscillators Damián H. Zanette arxiv:1608.00416v1 [nlin.ao] 1 Aug 2016 Centro Atómico Bariloche and Instituto Balseiro (Comisión Nacional de Energía
2.4 Nonlinear oscillations of cantilever
 4 Nonlinear oscillations of cantilever 41 Cantilever nonlinear oscillations (qualitative consideration) Consider cantilever oscillations, when in addition to driving force (see chapter 33) an external
4 Nonlinear oscillations of cantilever 41 Cantilever nonlinear oscillations (qualitative consideration) Consider cantilever oscillations, when in addition to driving force (see chapter 33) an external
arxiv: v3 [physics.class-ph] 7 Dec 2016
![arxiv: v3 [physics.class-ph] 7 Dec 2016 arxiv: v3 [physics.class-ph] 7 Dec 2016](/thumbs/85/91380776.jpg) Direct observation of coherent energy transfer in nonlinear micro-mechanical oscillators Changyao Chen 1, Damián H. Zanette 2, David Czaplewski 1, Steven Shaw 3, and Daniel López 1 arxiv:1612.49v3 [physics.class-ph]
Direct observation of coherent energy transfer in nonlinear micro-mechanical oscillators Changyao Chen 1, Damián H. Zanette 2, David Czaplewski 1, Steven Shaw 3, and Daniel López 1 arxiv:1612.49v3 [physics.class-ph]
arxiv:nlin/ v1 [nlin.cd] 25 Apr 2001
![arxiv:nlin/ v1 [nlin.cd] 25 Apr 2001 arxiv:nlin/ v1 [nlin.cd] 25 Apr 2001](/thumbs/84/91208485.jpg) Anticipated synchronization in coupled chaotic maps with delays arxiv:nlin/0104061v1 [nlin.cd] 25 Apr 2001 Cristina Masoller a, Damián H. Zanette b a Instituto de Física, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad
Anticipated synchronization in coupled chaotic maps with delays arxiv:nlin/0104061v1 [nlin.cd] 25 Apr 2001 Cristina Masoller a, Damián H. Zanette b a Instituto de Física, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad
Theory of bifurcation amplifiers utilizing the nonlinear dynamical response of an optically damped mechanical oscillator
 Theory of bifurcation amplifiers utilizing the nonlinear dynamical response of an optically damped mechanical oscillator Research on optomechanical systems is of relevance to gravitational wave detection
Theory of bifurcation amplifiers utilizing the nonlinear dynamical response of an optically damped mechanical oscillator Research on optomechanical systems is of relevance to gravitational wave detection
NANOSCALE SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
 . NANOSCALE SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY V Two-Level Quantum Systems (Qubits) Lecture notes 5 5. Qubit description Quantum bit (qubit) is an elementary unit of a quantum computer. Similar to classical computers,
. NANOSCALE SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY V Two-Level Quantum Systems (Qubits) Lecture notes 5 5. Qubit description Quantum bit (qubit) is an elementary unit of a quantum computer. Similar to classical computers,
arxiv:nlin/ v1 [nlin.ao] 25 Sep 2000
![arxiv:nlin/ v1 [nlin.ao] 25 Sep 2000 arxiv:nlin/ v1 [nlin.ao] 25 Sep 2000](/thumbs/94/119457436.jpg) Vertical transmission of culture and the distribution of family names arxiv:nlin/0009046v1 [nlin.ao] 25 Sep 2000 Damián H. Zanette a, Susanna C. Manrubia b a Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas
Vertical transmission of culture and the distribution of family names arxiv:nlin/0009046v1 [nlin.ao] 25 Sep 2000 Damián H. Zanette a, Susanna C. Manrubia b a Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas
Synchronizationinanarray of globally coupled maps with delayed interactions
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physica A 325 (2003) 186 191 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Synchronizationinanarray of globally coupled maps with delayed interactions Cristina Masoller a;, Arturo
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physica A 325 (2003) 186 191 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Synchronizationinanarray of globally coupled maps with delayed interactions Cristina Masoller a;, Arturo
Suppression of the primary resonance vibrations of a forced nonlinear system using a dynamic vibration absorber
 Suppression of the primary resonance vibrations of a forced nonlinear system using a dynamic vibration absorber J.C. Ji, N. Zhang Faculty of Engineering, University of Technology, Sydney PO Box, Broadway,
Suppression of the primary resonance vibrations of a forced nonlinear system using a dynamic vibration absorber J.C. Ji, N. Zhang Faculty of Engineering, University of Technology, Sydney PO Box, Broadway,
8 Quantized Interaction of Light and Matter
 8 Quantized Interaction of Light and Matter 8.1 Dressed States Before we start with a fully quantized description of matter and light we would like to discuss the evolution of a two-level atom interacting
8 Quantized Interaction of Light and Matter 8.1 Dressed States Before we start with a fully quantized description of matter and light we would like to discuss the evolution of a two-level atom interacting
The Sommerfeld Polynomial Method: Harmonic Oscillator Example
 Chemistry 460 Fall 2017 Dr. Jean M. Standard October 2, 2017 The Sommerfeld Polynomial Method: Harmonic Oscillator Example Scaling the Harmonic Oscillator Equation Recall the basic definitions of the harmonic
Chemistry 460 Fall 2017 Dr. Jean M. Standard October 2, 2017 The Sommerfeld Polynomial Method: Harmonic Oscillator Example Scaling the Harmonic Oscillator Equation Recall the basic definitions of the harmonic
Simulation of alpha particle current drive and heating in spherical tokamaks
 Simulation of alpha particle current drive and heating in spherical tokamaks R. Farengo 1, M. Zarco 1, H. E. Ferrari 1, 1 Centro Atómico Bariloche and Instituto Balseiro, Argentina. Consejo Nacional de
Simulation of alpha particle current drive and heating in spherical tokamaks R. Farengo 1, M. Zarco 1, H. E. Ferrari 1, 1 Centro Atómico Bariloche and Instituto Balseiro, Argentina. Consejo Nacional de
Linear and Nonlinear Oscillators (Lecture 2)
 Linear and Nonlinear Oscillators (Lecture 2) January 25, 2016 7/441 Lecture outline A simple model of a linear oscillator lies in the foundation of many physical phenomena in accelerator dynamics. A typical
Linear and Nonlinear Oscillators (Lecture 2) January 25, 2016 7/441 Lecture outline A simple model of a linear oscillator lies in the foundation of many physical phenomena in accelerator dynamics. A typical
Numerical Study on the Quasi-periodic Behavior in Coupled. MEMS Resonators
 THE INSTITUTE OF ELECTRONICS, INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERS TECHNICAL REPORT OF IEICE. Numerical Study on the Quasi-periodic Behavior in Coupled Abstract MEMS Resonators Suketu NAIK and Takashi
THE INSTITUTE OF ELECTRONICS, INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERS TECHNICAL REPORT OF IEICE. Numerical Study on the Quasi-periodic Behavior in Coupled Abstract MEMS Resonators Suketu NAIK and Takashi
STUDY OF ECOLOGICAL COMPETITION AMONG FOUR SPECIES. E. Marchi and R. Velasco. IMA Preprint Series #2469. (March 2016)
 STUDY OF ECOLOGICAL COMPETITION AMONG FOUR SPECIES By E. Marchi and R. Velasco IMA Preprint Series #2469 (March 2016) INSTITUTE FOR MATHEMATICS AND ITS APPLICATIONS UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA 400 Lind Hall
STUDY OF ECOLOGICAL COMPETITION AMONG FOUR SPECIES By E. Marchi and R. Velasco IMA Preprint Series #2469 (March 2016) INSTITUTE FOR MATHEMATICS AND ITS APPLICATIONS UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA 400 Lind Hall
Differential Equations 2280 Sample Midterm Exam 3 with Solutions Exam Date: 24 April 2015 at 12:50pm
 Differential Equations 228 Sample Midterm Exam 3 with Solutions Exam Date: 24 April 25 at 2:5pm Instructions: This in-class exam is 5 minutes. No calculators, notes, tables or books. No answer check is
Differential Equations 228 Sample Midterm Exam 3 with Solutions Exam Date: 24 April 25 at 2:5pm Instructions: This in-class exam is 5 minutes. No calculators, notes, tables or books. No answer check is
Optical Lattices. Chapter Polarization
 Chapter Optical Lattices Abstract In this chapter we give details of the atomic physics that underlies the Bose- Hubbard model used to describe ultracold atoms in optical lattices. We show how the AC-Stark
Chapter Optical Lattices Abstract In this chapter we give details of the atomic physics that underlies the Bose- Hubbard model used to describe ultracold atoms in optical lattices. We show how the AC-Stark
EE C245 / ME C218 INTRODUCTION TO MEMS DESIGN FALL 2011 C. Nguyen PROBLEM SET #7. Table 1: Gyroscope Modeling Parameters
 Issued: Wednesday, Nov. 23, 2011. PROBLEM SET #7 Due (at 7 p.m.): Thursday, Dec. 8, 2011, in the EE C245 HW box in 240 Cory. 1. Gyroscopes are inertial sensors that measure rotation rate, which is an extremely
Issued: Wednesday, Nov. 23, 2011. PROBLEM SET #7 Due (at 7 p.m.): Thursday, Dec. 8, 2011, in the EE C245 HW box in 240 Cory. 1. Gyroscopes are inertial sensors that measure rotation rate, which is an extremely
Hamilton-Jacobi theory
 Hamilton-Jacobi theory November 9, 04 We conclude with the crowning theorem of Hamiltonian dynamics: a proof that for any Hamiltonian dynamical system there exists a canonical transformation to a set of
Hamilton-Jacobi theory November 9, 04 We conclude with the crowning theorem of Hamiltonian dynamics: a proof that for any Hamiltonian dynamical system there exists a canonical transformation to a set of
Hopf Bifurcation Analysis and Approximation of Limit Cycle in Coupled Van Der Pol and Duffing Oscillators
 The Open Acoustics Journal 8 9-3 9 Open Access Hopf ifurcation Analysis and Approximation of Limit Cycle in Coupled Van Der Pol and Duffing Oscillators Jianping Cai *a and Jianhe Shen b a Department of
The Open Acoustics Journal 8 9-3 9 Open Access Hopf ifurcation Analysis and Approximation of Limit Cycle in Coupled Van Der Pol and Duffing Oscillators Jianping Cai *a and Jianhe Shen b a Department of
CHAPTER 4 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF CANTILEVER BEAM ELECTROSTATIC ACTUATORS
 61 CHAPTER 4 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF CANTILEVER BEAM ELECTROSTATIC ACTUATORS 4.1 INTRODUCTION The analysis of cantilever beams of small dimensions taking into the effect of fringing fields is studied and
61 CHAPTER 4 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF CANTILEVER BEAM ELECTROSTATIC ACTUATORS 4.1 INTRODUCTION The analysis of cantilever beams of small dimensions taking into the effect of fringing fields is studied and
A note on the numerical treatment of the k-epsilon turbulence model Λ
 A note on the numerical treatment of the k-epsilon turbulence model Λ Adrián J. Lew y, Gustavo C. Buscaglia z and Pablo M. Carrica Centro Atómico Bariloche and Instituto Balseiro, 8400 Bariloche, Argentina.
A note on the numerical treatment of the k-epsilon turbulence model Λ Adrián J. Lew y, Gustavo C. Buscaglia z and Pablo M. Carrica Centro Atómico Bariloche and Instituto Balseiro, 8400 Bariloche, Argentina.
433. New linear piezoelectric actuator based on traveling wave
 433. New linear piezoelectric actuator based on traveling wave D. Mažeika 1, P. Vasiljev 2, G. Kulvietis 3, S. Vaičiulien 4 1,3 Vilnius Gediminas Technical University, Saul tekio al. 11, Vilnius, LT-10223,
433. New linear piezoelectric actuator based on traveling wave D. Mažeika 1, P. Vasiljev 2, G. Kulvietis 3, S. Vaičiulien 4 1,3 Vilnius Gediminas Technical University, Saul tekio al. 11, Vilnius, LT-10223,
Transduction Based on Changes in the Energy Stored in an Electrical Field
 Lecture 6- Transduction Based on Changes in the Energy Stored in an Electrical Field Actuator Examples Microgrippers Normal force driving In-plane force driving» Comb-drive device F = εav d 1 ε oε F rwv
Lecture 6- Transduction Based on Changes in the Energy Stored in an Electrical Field Actuator Examples Microgrippers Normal force driving In-plane force driving» Comb-drive device F = εav d 1 ε oε F rwv
Nonlinear and Collective Effects in Mesoscopic Mechanical Oscillators
 Dynamics Days Asia-Pacific: Singapore, 2004 1 Nonlinear and Collective Effects in Mesoscopic Mechanical Oscillators Alexander Zumdieck (Max Planck, Dresden), Ron Lifshitz (Tel Aviv), Jeff Rogers (HRL,
Dynamics Days Asia-Pacific: Singapore, 2004 1 Nonlinear and Collective Effects in Mesoscopic Mechanical Oscillators Alexander Zumdieck (Max Planck, Dresden), Ron Lifshitz (Tel Aviv), Jeff Rogers (HRL,
QUANTUM MECHANICS I PHYS 516. Solutions to Problem Set # 5
 QUANTUM MECHANICS I PHYS 56 Solutions to Problem Set # 5. Crossed E and B fields: A hydrogen atom in the N 2 level is subject to crossed electric and magnetic fields. Choose your coordinate axes to make
QUANTUM MECHANICS I PHYS 56 Solutions to Problem Set # 5. Crossed E and B fields: A hydrogen atom in the N 2 level is subject to crossed electric and magnetic fields. Choose your coordinate axes to make
Midterm Exam Solutions
 SIMG-455 Midterm Exam Solutions 1. We used the Argand diagram (also called the phasor diagram) to represent temporal oscillatory motion. (a) Use the Argand diagram to demonstrate that the superposition
SIMG-455 Midterm Exam Solutions 1. We used the Argand diagram (also called the phasor diagram) to represent temporal oscillatory motion. (a) Use the Argand diagram to demonstrate that the superposition
S12 PHY321: Practice Final
 S12 PHY321: Practice Final Contextual information Damped harmonic oscillator equation: ẍ + 2βẋ + ω0x 2 = 0 ( ) ( General solution: x(t) = e [A βt 1 exp β2 ω0t 2 + A 2 exp )] β 2 ω0t 2 Driven harmonic oscillator
S12 PHY321: Practice Final Contextual information Damped harmonic oscillator equation: ẍ + 2βẋ + ω0x 2 = 0 ( ) ( General solution: x(t) = e [A βt 1 exp β2 ω0t 2 + A 2 exp )] β 2 ω0t 2 Driven harmonic oscillator
5 Applying the Fokker-Planck equation
 5 Applying the Fokker-Planck equation We begin with one-dimensional examples, keeping g = constant. Recall: the FPE for the Langevin equation with η(t 1 )η(t ) = κδ(t 1 t ) is = f(x) + g(x)η(t) t = x [f(x)p
5 Applying the Fokker-Planck equation We begin with one-dimensional examples, keeping g = constant. Recall: the FPE for the Langevin equation with η(t 1 )η(t ) = κδ(t 1 t ) is = f(x) + g(x)η(t) t = x [f(x)p
EE C245 ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design
 EE C245 ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design Fall 2007 Prof. Clark T.-C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Berkeley, CA 94720 Lecture 23: Electrical
EE C245 ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design Fall 2007 Prof. Clark T.-C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Berkeley, CA 94720 Lecture 23: Electrical
Vertical transmission of culture and the distribution of family names
 Physica A 295 (2001) 1 8 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Vertical transmission of culture and the distribution of family names Damian H. Zanette a;, Susanna C. Manrubia b a Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones
Physica A 295 (2001) 1 8 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Vertical transmission of culture and the distribution of family names Damian H. Zanette a;, Susanna C. Manrubia b a Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones
The New Boundary Condition Effect on The Free Vibration Analysis of Micro-beams Based on The Modified Couple Stress Theory
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 2015 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X / Vol, 9 (3): 274-279 Science Explorer Publications The New Boundary Condition Effect
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 2015 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X / Vol, 9 (3): 274-279 Science Explorer Publications The New Boundary Condition Effect
EE C245 ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design
 EE C245 ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design Fall 2007 Prof. Clark T.-C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Berkeley, CA 94720 Lecture 19: Resonance
EE C245 ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design Fall 2007 Prof. Clark T.-C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Berkeley, CA 94720 Lecture 19: Resonance
Written Test A. [Solve three out of the following five problems.] ψ = B(x + y + 2z)e x 2 +y 2 +z 2
![Written Test A. [Solve three out of the following five problems.] ψ = B(x + y + 2z)e x 2 +y 2 +z 2 Written Test A. [Solve three out of the following five problems.] ψ = B(x + y + 2z)e x 2 +y 2 +z 2](/thumbs/94/119597522.jpg) Written Test A Solve three out of the following five problems.] Problem 1. A spinless particle is described by the wave function where B is a constant. ψ = B(x + y + z)e x +y +z 1. Determine the total
Written Test A Solve three out of the following five problems.] Problem 1. A spinless particle is described by the wave function where B is a constant. ψ = B(x + y + z)e x +y +z 1. Determine the total
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7)
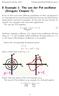 8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
One Dimensional Dynamical Systems
 16 CHAPTER 2 One Dimensional Dynamical Systems We begin by analyzing some dynamical systems with one-dimensional phase spaces, and in particular their bifurcations. All equations in this Chapter are scalar
16 CHAPTER 2 One Dimensional Dynamical Systems We begin by analyzing some dynamical systems with one-dimensional phase spaces, and in particular their bifurcations. All equations in this Chapter are scalar
An introduction to Birkhoff normal form
 An introduction to Birkhoff normal form Dario Bambusi Dipartimento di Matematica, Universitá di Milano via Saldini 50, 0133 Milano (Italy) 19.11.14 1 Introduction The aim of this note is to present an
An introduction to Birkhoff normal form Dario Bambusi Dipartimento di Matematica, Universitá di Milano via Saldini 50, 0133 Milano (Italy) 19.11.14 1 Introduction The aim of this note is to present an
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2016.254 Measurement of non-monotonic Casimir forces between silicon nanostructures Supplementary information L. Tang 1, M. Wang
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2016.254 Measurement of non-monotonic Casimir forces between silicon nanostructures Supplementary information L. Tang 1, M. Wang
221A Lecture Notes Convergence of Perturbation Theory
 A Lecture Notes Convergence of Perturbation Theory Asymptotic Series An asymptotic series in a parameter ɛ of a function is given in a power series f(ɛ) = f n ɛ n () n=0 where the series actually does
A Lecture Notes Convergence of Perturbation Theory Asymptotic Series An asymptotic series in a parameter ɛ of a function is given in a power series f(ɛ) = f n ɛ n () n=0 where the series actually does
Solutions 2: Simple Harmonic Oscillator and General Oscillations
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology MITES 2017 Physics III Solutions 2: Simple Harmonic Oscillator and General Oscillations Due Wednesday June 21, at 9AM under Rene García s door Preface: This problem
Massachusetts Institute of Technology MITES 2017 Physics III Solutions 2: Simple Harmonic Oscillator and General Oscillations Due Wednesday June 21, at 9AM under Rene García s door Preface: This problem
α Cubic nonlinearity coefficient. ISSN: x DOI: : /JOEMS
 Journal of the Egyptian Mathematical Society Volume (6) - Issue (1) - 018 ISSN: 1110-65x DOI: : 10.1608/JOEMS.018.9468 ENHANCING PD-CONTROLLER EFFICIENCY VIA TIME- DELAYS TO SUPPRESS NONLINEAR SYSTEM OSCILLATIONS
Journal of the Egyptian Mathematical Society Volume (6) - Issue (1) - 018 ISSN: 1110-65x DOI: : 10.1608/JOEMS.018.9468 ENHANCING PD-CONTROLLER EFFICIENCY VIA TIME- DELAYS TO SUPPRESS NONLINEAR SYSTEM OSCILLATIONS
Nonlinear Single-Particle Dynamics in High Energy Accelerators
 Nonlinear Single-Particle Dynamics in High Energy Accelerators Part 4: Canonical Perturbation Theory Nonlinear Single-Particle Dynamics in High Energy Accelerators There are six lectures in this course
Nonlinear Single-Particle Dynamics in High Energy Accelerators Part 4: Canonical Perturbation Theory Nonlinear Single-Particle Dynamics in High Energy Accelerators There are six lectures in this course
THE CHALLENGE OF MONTE CARLO METHOD IN TWO SIDED MULTIPACTOR
 Proceedings of SRF29, Berlin, Germany TUPPO58 THE CHALLENGE OF MONTE CARLO METHOD IN TWO SIDED MULTIPACTOR M. Mostajeran*, M. Lamehi Rachti Institute for Studies in Theoretical Physics and Mathematics
Proceedings of SRF29, Berlin, Germany TUPPO58 THE CHALLENGE OF MONTE CARLO METHOD IN TWO SIDED MULTIPACTOR M. Mostajeran*, M. Lamehi Rachti Institute for Studies in Theoretical Physics and Mathematics
Engineering Tripos Part IIB Nonlinear Systems and Control. Handout 3: Describing Functions
 Engineering Tripos Part IIB Module 4F2 Nonlinear Systems and Control Handout 3: Describing Functions 1 Harmonic balance The describing function method (also called the method of harmonic balance) uses
Engineering Tripos Part IIB Module 4F2 Nonlinear Systems and Control Handout 3: Describing Functions 1 Harmonic balance The describing function method (also called the method of harmonic balance) uses
Experimental analysis of spring hardening and softening nonlinearities in. microelectromechanical oscillators. Sarah Johnson
 Experimental analysis of spring hardening and softening nonlinearities in microelectromechanical oscillators. Sarah Johnson Department of Physics, University of Florida Mentored by Dr. Yoonseok Lee Abstract
Experimental analysis of spring hardening and softening nonlinearities in microelectromechanical oscillators. Sarah Johnson Department of Physics, University of Florida Mentored by Dr. Yoonseok Lee Abstract
Problem Set 5 Solutions
 Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 5 Solutions ow many vibrational modes do the following molecules or ions possess? [int: Drawing Lewis structures may be useful in some cases] In all of the
Chemistry 362 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 5 Solutions ow many vibrational modes do the following molecules or ions possess? [int: Drawing Lewis structures may be useful in some cases] In all of the
A new cantilever beam-rigid-body MEMS gyroscope: mathematical model and linear dynamics
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Mechatronics Toronto, Ontario, Canada, August 8-10 2013 Paper No. XXX (The number assigned by the OpenConf System) A new cantilever
Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Mechatronics Toronto, Ontario, Canada, August 8-10 2013 Paper No. XXX (The number assigned by the OpenConf System) A new cantilever
INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS
 IC/94/195 INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS A PHASE-TRANSITION INDUCED BY THE STRUGGLE FOR LIFE IN A COMPETITIVE COEXISTENCE MODEL IN ECOLOGY Horacio S. Wio and M.N. Kuperman INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC
IC/94/195 INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS A PHASE-TRANSITION INDUCED BY THE STRUGGLE FOR LIFE IN A COMPETITIVE COEXISTENCE MODEL IN ECOLOGY Horacio S. Wio and M.N. Kuperman INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC
d mx kx dt ( t) Note first that imposed variation in the mass term is easily dealt with, by simply redefining the time dt mt ( ).
 . Parametric Resonance Michael Fowler Introduction (Following Landau para 7 A one-dimensional simple harmonic oscillator, a mass on a spring, d mx kx ( = has two parameters, m and k. For some systems,
. Parametric Resonance Michael Fowler Introduction (Following Landau para 7 A one-dimensional simple harmonic oscillator, a mass on a spring, d mx kx ( = has two parameters, m and k. For some systems,
Coherent control and TLS-mediated damping of SiN nanoresonators. Eva Weig
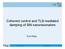 Coherent control and TLS-mediated damping of SiN nanoresonators Eva Weig Doubly-clamped pre-stressed silicon nitride string as Megahertz nanomechanical resonator fundamental flexural mode (in-plane) ~
Coherent control and TLS-mediated damping of SiN nanoresonators Eva Weig Doubly-clamped pre-stressed silicon nitride string as Megahertz nanomechanical resonator fundamental flexural mode (in-plane) ~
Prof. Krishna Vasudevan, Prof. G. Sridhara Rao, Prof. P. Sasidhara Rao
 2 Basic Principles As mentioned earlier the transformer is a static device working on the principle of Faraday s law of induction. Faraday s law states that a voltage appears across the terminals of an
2 Basic Principles As mentioned earlier the transformer is a static device working on the principle of Faraday s law of induction. Faraday s law states that a voltage appears across the terminals of an
( ( )) + w ( ) 3 / 2
 K K DA!NE TECHNICAL NOTE INFN - LNF, Accelerator Division Frascati, March 4, 1 Note: G-7 SYNCHROTRON TUNE SHIFT AND TUNE SPREAD DUE TO BEAM-BEAM COLLISIONS WITH A CROSSING ANGLE M. Zobov and D. Shatilov
K K DA!NE TECHNICAL NOTE INFN - LNF, Accelerator Division Frascati, March 4, 1 Note: G-7 SYNCHROTRON TUNE SHIFT AND TUNE SPREAD DUE TO BEAM-BEAM COLLISIONS WITH A CROSSING ANGLE M. Zobov and D. Shatilov
Frequency locking in a forced Mathieu van der Pol Duffing system
 Nonlinear Dyn (008) 54:3 1 DOI 10.1007/s11071-007-938-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE requency locking in a forced Mathieu van der Pol Duffing system Manoj Pandey Richard H. Rand Alan T. Zehnder Received: 4 August
Nonlinear Dyn (008) 54:3 1 DOI 10.1007/s11071-007-938-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE requency locking in a forced Mathieu van der Pol Duffing system Manoj Pandey Richard H. Rand Alan T. Zehnder Received: 4 August
MEMS Tuning-Fork Gyroscope Mid-Term Report Amanda Bristow Travis Barton Stephen Nary
 MEMS Tuning-Fork Gyroscope Mid-Term Report Amanda Bristow Travis Barton Stephen Nary Abstract MEMS based gyroscopes have gained in popularity for use as rotation rate sensors in commercial products like
MEMS Tuning-Fork Gyroscope Mid-Term Report Amanda Bristow Travis Barton Stephen Nary Abstract MEMS based gyroscopes have gained in popularity for use as rotation rate sensors in commercial products like
RECENTLY, microelectromechanical oscillators exploiting
 310 JOURNAL OF MICROELECTROMECHANICAL SYSTEMS, VOL. 16, NO. 2, APRIL 2007 Linear and Nonlinear Tuning of Parametrically Excited MEMS Oscillators Barry E. DeMartini, Student Member, IEEE, Jeffrey F. Rhoads,
310 JOURNAL OF MICROELECTROMECHANICAL SYSTEMS, VOL. 16, NO. 2, APRIL 2007 Linear and Nonlinear Tuning of Parametrically Excited MEMS Oscillators Barry E. DeMartini, Student Member, IEEE, Jeffrey F. Rhoads,
874. The squeeze film effect on micro-electromechanical resonators
 874. The squeeze film effect on micro-electromechanical resonators Shih-Chieh Sun 1, Chi-Wei Chung, Chao-Ming Hsu 3, Jao-Hwa Kuang 4 1,, 4 Department of Mechanical and Electromechanical Engineering National
874. The squeeze film effect on micro-electromechanical resonators Shih-Chieh Sun 1, Chi-Wei Chung, Chao-Ming Hsu 3, Jao-Hwa Kuang 4 1,, 4 Department of Mechanical and Electromechanical Engineering National
FIRST YEAR MATHS FOR PHYSICS STUDENTS NORMAL MODES AND WAVES. Hilary Term Prof. G.G.Ross. Question Sheet 1: Normal Modes
 FIRST YEAR MATHS FOR PHYSICS STUDENTS NORMAL MODES AND WAVES Hilary Term 008. Prof. G.G.Ross Question Sheet : Normal Modes [Questions marked with an asterisk (*) cover topics also covered by the unstarred
FIRST YEAR MATHS FOR PHYSICS STUDENTS NORMAL MODES AND WAVES Hilary Term 008. Prof. G.G.Ross Question Sheet : Normal Modes [Questions marked with an asterisk (*) cover topics also covered by the unstarred
Computational Physics (6810): Session 8
 Computational Physics (6810): Session 8 Dick Furnstahl Nuclear Theory Group OSU Physics Department February 24, 2014 Differential equation solving Session 7 Preview Session 8 Stuff Solving differential
Computational Physics (6810): Session 8 Dick Furnstahl Nuclear Theory Group OSU Physics Department February 24, 2014 Differential equation solving Session 7 Preview Session 8 Stuff Solving differential
Calculus I Exam 1 Review Fall 2016
 Problem 1: Decide whether the following statements are true or false: (a) If f, g are differentiable, then d d x (f g) = f g. (b) If a function is continuous, then it is differentiable. (c) If a function
Problem 1: Decide whether the following statements are true or false: (a) If f, g are differentiable, then d d x (f g) = f g. (b) If a function is continuous, then it is differentiable. (c) If a function
Oscillations. Simple Harmonic Motion of a Mass on a Spring The equation of motion for a mass m is attached to a spring of constant k is
 Dr. Alain Brizard College Physics I (PY 10) Oscillations Textbook Reference: Chapter 14 sections 1-8. Simple Harmonic Motion of a Mass on a Spring The equation of motion for a mass m is attached to a spring
Dr. Alain Brizard College Physics I (PY 10) Oscillations Textbook Reference: Chapter 14 sections 1-8. Simple Harmonic Motion of a Mass on a Spring The equation of motion for a mass m is attached to a spring
Phase Synchronization
 Phase Synchronization Lecture by: Zhibin Guo Notes by: Xiang Fan May 10, 2016 1 Introduction For any mode or fluctuation, we always have where S(x, t) is phase. If a mode amplitude satisfies ϕ k = ϕ k
Phase Synchronization Lecture by: Zhibin Guo Notes by: Xiang Fan May 10, 2016 1 Introduction For any mode or fluctuation, we always have where S(x, t) is phase. If a mode amplitude satisfies ϕ k = ϕ k
Additive resonances of a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator
 Additive resonances of a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator This paper has been published in Journal of Sound and Vibration vol. 5 issue - 8 pp.-. J.C. Ji N. Zhang Faculty of Engineering University
Additive resonances of a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator This paper has been published in Journal of Sound and Vibration vol. 5 issue - 8 pp.-. J.C. Ji N. Zhang Faculty of Engineering University
Physics 215 Quantum Mechanics 1 Assignment 5
 Physics 15 Quantum Mechanics 1 Assignment 5 Logan A. Morrison February 10, 016 Problem 1 A particle of mass m is confined to a one-dimensional region 0 x a. At t 0 its normalized wave function is 8 πx
Physics 15 Quantum Mechanics 1 Assignment 5 Logan A. Morrison February 10, 016 Problem 1 A particle of mass m is confined to a one-dimensional region 0 x a. At t 0 its normalized wave function is 8 πx
Qualifying Exam. Aug Part II. Please use blank paper for your work do not write on problems sheets!
 Qualifying Exam Aug. 2015 Part II Please use blank paper for your work do not write on problems sheets! Solve only one problem from each of the four sections Mechanics, Quantum Mechanics, Statistical Physics
Qualifying Exam Aug. 2015 Part II Please use blank paper for your work do not write on problems sheets! Solve only one problem from each of the four sections Mechanics, Quantum Mechanics, Statistical Physics
Energy Level Sets for the Morse Potential
 Energy Level Sets for the Morse Potential Fariel Shafee Department of Physics Princeton University Princeton, NJ 08540 Abstract: In continuation of our previous work investigating the possibility of the
Energy Level Sets for the Morse Potential Fariel Shafee Department of Physics Princeton University Princeton, NJ 08540 Abstract: In continuation of our previous work investigating the possibility of the
MATH 215/255 Solutions to Additional Practice Problems April dy dt
 . For the nonlinear system MATH 5/55 Solutions to Additional Practice Problems April 08 dx dt = x( x y, dy dt = y(.5 y x, x 0, y 0, (a Show that if x(0 > 0 and y(0 = 0, then the solution (x(t, y(t of the
. For the nonlinear system MATH 5/55 Solutions to Additional Practice Problems April 08 dx dt = x( x y, dy dt = y(.5 y x, x 0, y 0, (a Show that if x(0 > 0 and y(0 = 0, then the solution (x(t, y(t of the
DESIGN OF A NONLINEAR VIBRATION ABSORBER
 DESIGN OF A NONLINEAR VIBRATION ABSORBER Maxime Geeroms, Laurens Marijns, Mia Loccufier and Dirk Aeyels Ghent University, Department EESA, Belgium Abstract Linear vibration absorbers can only capture certain
DESIGN OF A NONLINEAR VIBRATION ABSORBER Maxime Geeroms, Laurens Marijns, Mia Loccufier and Dirk Aeyels Ghent University, Department EESA, Belgium Abstract Linear vibration absorbers can only capture certain
Yair Zarmi Physics Department & Jacob Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Midreshet Ben-Gurion, Israel
 PERTURBED NONLINEAR EVOLUTION EQUATIONS AND ASYMPTOTIC INTEGRABILITY Yair Zarmi Physics Department & Jacob Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Midreshet Ben-Gurion,
PERTURBED NONLINEAR EVOLUTION EQUATIONS AND ASYMPTOTIC INTEGRABILITY Yair Zarmi Physics Department & Jacob Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Midreshet Ben-Gurion,
Finite Element Analysis of Piezoelectric Cantilever
 Finite Element Analysis of Piezoelectric Cantilever Nitin N More Department of Mechanical Engineering K.L.E S College of Engineering and Technology, Belgaum, Karnataka, India. Abstract- Energy (or power)
Finite Element Analysis of Piezoelectric Cantilever Nitin N More Department of Mechanical Engineering K.L.E S College of Engineering and Technology, Belgaum, Karnataka, India. Abstract- Energy (or power)
Problem 1: Lagrangians and Conserved Quantities. Consider the following action for a particle of mass m moving in one dimension
 105A Practice Final Solutions March 13, 01 William Kelly Problem 1: Lagrangians and Conserved Quantities Consider the following action for a particle of mass m moving in one dimension S = dtl = mc dt 1
105A Practice Final Solutions March 13, 01 William Kelly Problem 1: Lagrangians and Conserved Quantities Consider the following action for a particle of mass m moving in one dimension S = dtl = mc dt 1
Robust Control For Variable-Speed Two-Bladed Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbines Via ChatteringControl
 Robust Control For Variable-Speed Two-Bladed Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbines Via ChatteringControl Leonardo Acho, Yolanda Vidal, Francesc Pozo CoDAlab, Escola Universitària d'enginyeria Tècnica Industrial
Robust Control For Variable-Speed Two-Bladed Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbines Via ChatteringControl Leonardo Acho, Yolanda Vidal, Francesc Pozo CoDAlab, Escola Universitària d'enginyeria Tècnica Industrial
ANALYSIS OF AN INJECTION-LOCKED BISTABLE SEMICONDUCTOR LASER WITH THE FREQUENCY CHIRPING
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 8, 121 133, 2009 ANALYSIS OF AN INJECTION-LOCKED BISTABLE SEMICONDUCTOR LASER WITH THE FREQUENCY CHIRPING M. Aleshams Department of Electrical and Computer
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 8, 121 133, 2009 ANALYSIS OF AN INJECTION-LOCKED BISTABLE SEMICONDUCTOR LASER WITH THE FREQUENCY CHIRPING M. Aleshams Department of Electrical and Computer
Tailoring the Nonlinear Response of MEMS Resonators Using Shape Optimization
 Tailoring the Nonlinear Response of MEMS Resonators Using Shape Optimization Lily L. Li, 1, a) Pavel M. Polunin, 2, 3 Suguang Dou, 4, 5 Oriel Shoshani, 2 B. Scott Strachan, 2, 6 Jakob S. Jensen, 4, 7 Steven
Tailoring the Nonlinear Response of MEMS Resonators Using Shape Optimization Lily L. Li, 1, a) Pavel M. Polunin, 2, 3 Suguang Dou, 4, 5 Oriel Shoshani, 2 B. Scott Strachan, 2, 6 Jakob S. Jensen, 4, 7 Steven
ON SPECTRAL FUNCTIONS SUM RULES
 IC/68/61 INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS ON SPECTRAL FUNCTIONS SUM RULES C. G. BOLLINI AND J. J. GIAMBIAGI 1968 MIRAMARE - TRIESTE IC/68/01 INTERNATIONAL
IC/68/61 INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS ON SPECTRAL FUNCTIONS SUM RULES C. G. BOLLINI AND J. J. GIAMBIAGI 1968 MIRAMARE - TRIESTE IC/68/01 INTERNATIONAL
2 = = 0 Thus, the number which is largest in magnitude is equal to the number which is smallest in magnitude.
 Limits at Infinity Two additional topics of interest with its are its as x ± and its where f(x) ±. Before we can properly discuss the notion of infinite its, we will need to begin with a discussion on
Limits at Infinity Two additional topics of interest with its are its as x ± and its where f(x) ±. Before we can properly discuss the notion of infinite its, we will need to begin with a discussion on
Harmonic Oscillator (9) use pib to think through 2012
 Harmonic Oscillator (9) use pib to think through 01 VI 9 Particle in box; Stubby box; Properties of going to finite potential w/f penetrate walls, w/f oscillate, # nodes increase with n, E n -levels less
Harmonic Oscillator (9) use pib to think through 01 VI 9 Particle in box; Stubby box; Properties of going to finite potential w/f penetrate walls, w/f oscillate, # nodes increase with n, E n -levels less
Nonlinear vibration of an electrostatically actuated microbeam
 11 (214) 534-544 Nonlinear vibration of an electrostatically actuated microbeam Abstract In this paper, we have considered a new class of critical technique that called the He s Variational Approach ()
11 (214) 534-544 Nonlinear vibration of an electrostatically actuated microbeam Abstract In this paper, we have considered a new class of critical technique that called the He s Variational Approach ()
A parametric amplification measurement scheme for MEMS in highly damped media. Cadee Hall. Department of Physics, University of Florida
 A parametric amplification measurement scheme for MEMS in highly damped media Cadee Hall Department of Physics, University of Florida Lee Research Group 1 ABSTRACT Micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS)
A parametric amplification measurement scheme for MEMS in highly damped media Cadee Hall Department of Physics, University of Florida Lee Research Group 1 ABSTRACT Micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS)
Problem Set Number 01, MIT (Winter-Spring 2018)
 Problem Set Number 01, 18.377 MIT (Winter-Spring 2018) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., room 2-337, Cambridge, MA 02139) February 28, 2018 Due Thursday, March 8, 2018. Turn it in (by 3PM) at the Math.
Problem Set Number 01, 18.377 MIT (Winter-Spring 2018) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., room 2-337, Cambridge, MA 02139) February 28, 2018 Due Thursday, March 8, 2018. Turn it in (by 3PM) at the Math.
accelerator physics and ion optics summary longitudinal optics
 accelerator physics and ion optics summary longitudinal optics Sytze Brandenburg sb/accphys007_5/1 coupling energy difference acceleration phase stability when accelerating on slope of sine low energy:
accelerator physics and ion optics summary longitudinal optics Sytze Brandenburg sb/accphys007_5/1 coupling energy difference acceleration phase stability when accelerating on slope of sine low energy:
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Nov 2012
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Nov 2012 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Nov 2012](/thumbs/76/73113920.jpg) Tailoring population inversion in Landau-Zener-Stückelberg interferometry of flux qubits Alejandro Ferrón Instituto de Modelado e Innovación Tecnológica (CONICET-UNNE), 34 Corrientes and Centro Atómico
Tailoring population inversion in Landau-Zener-Stückelberg interferometry of flux qubits Alejandro Ferrón Instituto de Modelado e Innovación Tecnológica (CONICET-UNNE), 34 Corrientes and Centro Atómico
1 (2n)! (-1)n (θ) 2n
 Complex Numbers and Algebra The real numbers are complete for the operations addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, or more suggestively, for the operations of addition and multiplication
Complex Numbers and Algebra The real numbers are complete for the operations addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, or more suggestively, for the operations of addition and multiplication
CHAPTER 5 FIXED GUIDED BEAM ANALYSIS
 77 CHAPTER 5 FIXED GUIDED BEAM ANALYSIS 5.1 INTRODUCTION Fixed guided clamped and cantilever beams have been designed and analyzed using ANSYS and their performance were calculated. Maximum deflection
77 CHAPTER 5 FIXED GUIDED BEAM ANALYSIS 5.1 INTRODUCTION Fixed guided clamped and cantilever beams have been designed and analyzed using ANSYS and their performance were calculated. Maximum deflection
Qualifying Exam for Ph.D. Candidacy Department of Physics October 11, 2014 Part I
 Qualifying Exam for Ph.D. Candidacy Department of Physics October 11, 214 Part I Instructions: The following problems are intended to probe your understanding of basic physical principles. When answering
Qualifying Exam for Ph.D. Candidacy Department of Physics October 11, 214 Part I Instructions: The following problems are intended to probe your understanding of basic physical principles. When answering
Transient Phenomena in Quantum Bound States Subjected to a Sudden Perturbation
 Symmetry, Integrability and Geometry: Methods and Applications Vol. (5), Paper 3, 9 pages Transient Phenomena in Quantum Bound States Subjected to a Sudden Perturbation Marcos MOSHINSKY and Emerson SADURNÍ
Symmetry, Integrability and Geometry: Methods and Applications Vol. (5), Paper 3, 9 pages Transient Phenomena in Quantum Bound States Subjected to a Sudden Perturbation Marcos MOSHINSKY and Emerson SADURNÍ
CHEM 301: Homework assignment #5
 CHEM 30: Homework assignment #5 Solutions. A point mass rotates in a circle with l =. Calculate the magnitude of its angular momentum and all possible projections of the angular momentum on the z-axis.
CHEM 30: Homework assignment #5 Solutions. A point mass rotates in a circle with l =. Calculate the magnitude of its angular momentum and all possible projections of the angular momentum on the z-axis.
Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701
 Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701 Z. E. Meziani 02/24//2017 Physics 5701 Lecture Commutation of Observables and First Consequences of the Postulates Outline 1 Commutation Relations 2 Uncertainty Relations
Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701 Z. E. Meziani 02/24//2017 Physics 5701 Lecture Commutation of Observables and First Consequences of the Postulates Outline 1 Commutation Relations 2 Uncertainty Relations
Sample Quantum Chemistry Exam 2 Solutions
 Chemistry 46 Fall 7 Dr. Jean M. Standard Name SAMPE EXAM Sample Quantum Chemistry Exam Solutions.) ( points) Answer the following questions by selecting the correct answer from the choices provided. a.)
Chemistry 46 Fall 7 Dr. Jean M. Standard Name SAMPE EXAM Sample Quantum Chemistry Exam Solutions.) ( points) Answer the following questions by selecting the correct answer from the choices provided. a.)
arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 13 May 2009
![arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 13 May 2009 arxiv: v1 [physics.pop-ph] 13 May 2009](/thumbs/81/83499284.jpg) A computer controlled pendulum with position readout H. Hauptfleisch, T. Gasenzer, K. Meier, O. Nachtmann, and J. Schemmel Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität Heidelberg, Philosophenweg 6, 69
A computer controlled pendulum with position readout H. Hauptfleisch, T. Gasenzer, K. Meier, O. Nachtmann, and J. Schemmel Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität Heidelberg, Philosophenweg 6, 69
Atomic cross sections
 Chapter 12 Atomic cross sections The probability that an absorber (atom of a given species in a given excitation state and ionziation level) will interact with an incident photon of wavelength λ is quantified
Chapter 12 Atomic cross sections The probability that an absorber (atom of a given species in a given excitation state and ionziation level) will interact with an incident photon of wavelength λ is quantified
A Quantum Mechanical Model for the Vibration and Rotation of Molecules. Rigid Rotor
 A Quantum Mechanical Model for the Vibration and Rotation of Molecules Harmonic Oscillator Rigid Rotor Degrees of Freedom Translation: quantum mechanical model is particle in box or free particle. A molecule
A Quantum Mechanical Model for the Vibration and Rotation of Molecules Harmonic Oscillator Rigid Rotor Degrees of Freedom Translation: quantum mechanical model is particle in box or free particle. A molecule
Physics 221A Fall 1996 Notes 12 Orbital Angular Momentum and Spherical Harmonics
 Physics 221A Fall 1996 Notes 12 Orbital Angular Momentum and Spherical Harmonics We now consider the spatial degrees of freedom of a particle moving in 3-dimensional space, which of course is an important
Physics 221A Fall 1996 Notes 12 Orbital Angular Momentum and Spherical Harmonics We now consider the spatial degrees of freedom of a particle moving in 3-dimensional space, which of course is an important
( ) = 9φ 1, ( ) = 4φ 2.
 Chemistry 46 Dr Jean M Standard Homework Problem Set 6 Solutions The Hermitian operator A ˆ is associated with the physical observable A Two of the eigenfunctions of A ˆ are and These eigenfunctions are
Chemistry 46 Dr Jean M Standard Homework Problem Set 6 Solutions The Hermitian operator A ˆ is associated with the physical observable A Two of the eigenfunctions of A ˆ are and These eigenfunctions are
Nonlinear Rolling Element Bearings in MADYN 2000 Version 4.3
 - 1 - Nonlinear Rolling Element Bearings in MADYN 2000 Version 4.3 In version 4.3 nonlinear rolling element bearings can be considered for transient analyses. The nonlinear forces are calculated with a
- 1 - Nonlinear Rolling Element Bearings in MADYN 2000 Version 4.3 In version 4.3 nonlinear rolling element bearings can be considered for transient analyses. The nonlinear forces are calculated with a
Structural Dynamics Lecture 2. Outline of Lecture 2. Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.)
 Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
Intermittent onset of turbulence and control of extreme events
 Intermittent onset of turbulence and control of extreme events Sergio Roberto Lopes, Paulo P. Galúzio Departamento de Física UFPR São Paulo 03 de Abril 2014 Lopes, S. R. (Física UFPR) Intermittent onset
Intermittent onset of turbulence and control of extreme events Sergio Roberto Lopes, Paulo P. Galúzio Departamento de Física UFPR São Paulo 03 de Abril 2014 Lopes, S. R. (Física UFPR) Intermittent onset
Gabriel Kron's biography here.
 Gabriel Kron, Electric Circuit Model of the Schrödinger Equation, 1945 - Component of :... Page 1 of 12 {This website: Please note: The following article is complete; it has been put into ASCII due to
Gabriel Kron, Electric Circuit Model of the Schrödinger Equation, 1945 - Component of :... Page 1 of 12 {This website: Please note: The following article is complete; it has been put into ASCII due to
The Effects of Machine Components on Bifurcation and Chaos as Applied to Multimachine System
 1 The Effects of Machine Components on Bifurcation and Chaos as Applied to Multimachine System M. M. Alomari and B. S. Rodanski University of Technology, Sydney (UTS) P.O. Box 123, Broadway NSW 2007, Australia
1 The Effects of Machine Components on Bifurcation and Chaos as Applied to Multimachine System M. M. Alomari and B. S. Rodanski University of Technology, Sydney (UTS) P.O. Box 123, Broadway NSW 2007, Australia
Equations of motion in an accelerator (Lecture 7)
 Equations of motion in an accelerator (Lecture 7) January 27, 2016 130/441 Lecture outline We consider several types of magnets used in accelerators and write down the vector potential of the magnetic
Equations of motion in an accelerator (Lecture 7) January 27, 2016 130/441 Lecture outline We consider several types of magnets used in accelerators and write down the vector potential of the magnetic
Introduction to Vibrational Spectroscopy
 Introduction to Vibrational Spectroscopy Harmonic oscillators The classical harmonic oscillator The uantum mechanical harmonic oscillator Harmonic approximations in molecular vibrations Vibrational spectroscopy
Introduction to Vibrational Spectroscopy Harmonic oscillators The classical harmonic oscillator The uantum mechanical harmonic oscillator Harmonic approximations in molecular vibrations Vibrational spectroscopy
