Geometry. Chapter 7 Resource Masters
|
|
|
- Posy Harper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Geometr hapter 7 Resource Masters
2 7 Reading to Learn Mathematics Vocabular uilder This is an alphabetical list of the ke vocabular terms ou will learn in hapter 7. s ou stud the chapter, complete each term s definition or description. Remember to add the page number where ou found the term. dd these pages to our Geometr Stud Notebook to review vocabular at the end of the chapter. Vocabular Term ambiguous case Found on Page Definition/Description/Eample Vocabular uilder angle of depression angle of elevation cosine geometric mean Law of osines Law of Sines Pthagorean identit puh thag uh REE ahn (continued on the net page) Glencoe/McGraw-Hill vii Glencoe Geometr
3 7 Reading to Learn Mathematics Vocabular uilder (continued) Vocabular Term Pthagorean triple Found on Page Definition/Description/Eample reciprocal identit ri SIP ruh kuhl sine solve a triangle tangent trigonometric identit trig uh nuh MET rik trigonometric ratio trigonometr Glencoe/McGraw-Hill viii Glencoe Geometr
4 7 Learning to Read Mathematics Proof uilder This is a list of ke theorems and postulates ou will learn in hapter 7. s ou stud the chapter, write each theorem or postulate in our own words. Include illustrations as appropriate. Remember to include the page number where ou found the theorem or postulate. dd this page to our Geometr Stud Notebook so ou can review the theorems and postulates at the end of the chapter. Theorem or Postulate Theorem 7.1 Found on Page Description/Illustration/bbreviation Proof uilder Theorem 7.2 Theorem 7.3 Theorem 7.4 Pthagorean Theorem Theorem 7.5 onverse of the Pthagorean Theorem Theorem 7.6 Theorem 7.7 Glencoe/McGraw-Hill i Glencoe Geometr
5 7-1 Stud Guide and Intervention Geometric Mean Geometric Mean The geometric mean between two numbers is the square root of their product. For two positive numbers a and b, the geometric mean of a and b is the positive number in the proportion a. ross multipling gives b 2 ab, so ab. Eample a. 12 and 3 Find the geometric mean between each pair of numbers. Let represent the geometric mean or 6 Definition of geometric mean ross multipl. Take the square root of each side. b. 8 and 4 Let represent the geometric mean Lesson 7-1 Eercises Find the geometric mean between each pair of numbers and and and and and and and and and and and and 24 The geometric mean and one etreme are given. Find the other etreme is the geometric mean between a and b. Find b if a is the geometric mean between a and b. Find b if a 3. Determine whether each statement is alwas, sometimes, or never true. 15. The geometric mean of two positive numbers is greater than the average of the two numbers. 16. If the geometric mean of two positive numbers is less than 1, then both of the numbers are less than 1. Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 351 Glencoe Geometr
6 7-1 Stud Guide and Intervention (continued) Geometric Mean ltitude of a Triangle In the diagram, D D. n altitude to the hpotenuse of a right triangle forms two right triangles. The two triangles are similar and each is similar to the original triangle. D Eample 1 Eample 2 Use right with D. Describe two geometric means. D a. D D so D D D. In, the altitude is the geometric mean between the two segments of the hpotenuse. b. D and D, so and. D D In, each leg is the geometric mean between the hpotenuse and the segment of the hpotenuse adjacent to that leg. Find,, and z. R PR PQ P Q PS z 5 PR 25, PQ 15, PS 15 Q ross multipl. 9 Divide each side b 25. Then PR SP PR Q R Q R RS 2 5 z PR 25, QR z, RS z 2 5 z 16 z 1 6 z ross multipl. z 20 Take the square root of each side. 25 S P 15 Eercises Find,, and z to the nearest tenth z 1 z z z Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 352 Glencoe Geometr
7 7-1 Skills Practice Geometric Mean Find the geometric mean between each pair of numbers. State eact answers and answers to the nearest tenth and and and and and and 5 5 Find the measure of each altitude. State eact answers and answers to the nearest tenth. Lesson D 8. P 2 M 7 12 L N 9. E 2 H 10. S 9 G F R 4.5 U 8 T Find and Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 353 Glencoe Geometr
8 7-1 Practice Geometric Mean Find the geometric mean between each pair of numbers to the nearest tenth and and and 2 5 Find the measure of each altitude. State eact answers and answers to the nearest tenth. 4. U 5. J 6 M 17 T 5 12 V L K Find,, and z z z z 10 2 z IVIL ENGINEERING n airport, a factor, and a shopping center are at the vertices of a right triangle formed b three highwas. The airport and factor are 6.0 miles apart. Their distances from the shopping center are 3.6 miles and 4.8 miles, respectivel. service road will be constructed from the shopping center to the highwa that connects the airport and factor. What is the shortest possible length for the service road? Round to the nearest hundredth. Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 354 Glencoe Geometr
9 7-1 Reading to Learn Mathematics Geometric Mean Pre-ctivit How can the geometric mean be used to view paintings? Read the introduction to Lesson 7-1 at the top of page 342 in our tetbook. What is a disadvantage of standing too close to a painting? What is a disadvantage of standing too far from a painting? Reading the Lesson 1. In the past, when ou have seen the word mean in mathematics, it referred to the average or arithmetic mean of the two numbers. a. omplete the following b writing an algebraic epression in each blank. If a and b are two positive numbers, then the geometric mean between a and b is Lesson 7-1 and their arithmetic mean is. b. Eplain in words, without using an mathematical smbols, the difference between the geometric mean and the algebraic mean. 2. Let r and s be two positive numbers. In which of the following equations is z equal to the geometric mean between r and s? s z. z r. r s r z z z. s: z z: r D. z s E. z r z s F. z s r z 3. Suppl the missing words or phrases to complete the statement of each theorem. a. The measure of the altitude drawn from the verte of the right angle of a right triangle to its hpotenuse is the segments of the. between the measures of the two b. If the altitude is drawn from the verte of the angle of a right triangle to its hpotenuse, then the measure of a is the of the of the triangle between the measure of the hpotenuse and the segment adjacent to that leg. c. If the altitude is drawn from the of the right angle of a right triangle to its Helping You Remember,then the two triangles formed are to the given triangle and to each other. 4. good wa to remember a new mathematical concept is to relate it to something ou alread know. How can the meaning of mean in a proportion help ou to remember how to find the geometric mean between two numbers? Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 355 Glencoe Geometr
10 7-1 Enrichment Mathematics and Music Pthagoras, a Greek philosopher who lived during the sith centur.., believed that all nature, beaut, and harmon could be epressed b wholenumber relationships. Most people remember Pthagoras for his teachings about right triangles. (The sum of the squares of the legs equals the square of the hpotenuse.) ut Pthagoras also discovered relationships between the musical notes of a scale. These relationships can be epressed as ratios. D E F G When ou pla a stringed instrument, ou produce different notes b placing our finger on different places on a string. This is the result of changing the length of the vibrating part of the string. The string can be used to produce F b placing a finger 3 4 of the wa along the string. 3 of string 4 Suppose a string has a length of 16 inches. Write and solve proportions to determine what length of string would have to vibrate to produce the remaining notes of the scale. 1. D 2. E 3. F 4. G omplete to show the distance between finger positions on the 16-inch string for each note. For eample, (16) D in. D E F G 9. etween two consecutive musical notes, there is either a whole step or a half step. Using the distances ou found in Eercise 8, determine what two pairs of notes have a half step between them. Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 356 Glencoe Geometr
11 7-2 Stud Guide and Intervention The Pthagorean Theorem and Its onverse The Pthagorean Theorem In a right triangle, the sum of the squares of the measures of the legs equals the square of the measure of the hpotenuse. is a right triangle, so a 2 b 2 c 2. c b a Eample 1 Prove the Pthagorean Theorem. With altitude D, each leg a and b is a geometric mean between hpotenuse c and the segment of the hpotenuse adjacent to that leg. c a a and c b b, so a2 c and b 2 c. dd the two equations and substitute c to get a 2 b 2 c c c( ) c 2. Eample 2 c D h a b a. Find a. a a 2 b 2 c 2 Pthagorean Theorem a b 12, c 13 a a 2 25 a 5 Simplif. Subtract. Take the square root of each side. b. Find c. 20 c 30 a 2 b 2 c 2 Pthagorean Theorem c 2 a 20, b c 2 Simplif c 2 dd c Take the square root of each side c Use a calculator. Lesson 7-2 Eercises Find Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 357 Glencoe Geometr
12 7-2 Stud Guide and Intervention (continued) The Pthagorean Theorem and Its onverse onverse of the Pthagorean Theorem If the sum of the squares of the measures of the two shorter sides of a triangle equals the square of the measure of the longest side, then the triangle is a right triangle. If the three whole numbers a, b, and c satisf the equation a 2 b 2 c 2, then the numbers a, b, and c form a Pthagorean triple. b If a 2 b 2 c 2, then is a right triangle. c a Eample Determine whether PQR is a right triangle. a 2 b 2 c 2 Pthagorean Theorem 10 2 (10 3 ) a 10, b 10 3, c Simplif dd. The sum of the squares of the two shorter sides equals the square of the longest side, so the triangle is a right triangle. R P 10 Q Eercises Determine whether each set of measures can be the measures of the sides of a right triangle. Then state whether the form a Pthagorean triple , 40, , 30, , 24, , 8, , 4 7, , 15, , 12, , 8, , 40, 41 famil of Pthagorean triples consists of multiples of known triples. For each Pthagorean triple, find two triples in the same famil , 4, , 12, , 24, 25 Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 358 Glencoe Geometr
13 7-2 Find. Skills Practice The Pthagorean Theorem and Its onverse Determine whether STU is a right triangle for the given vertices. Eplain. 7. S(5, 5), T(7, 3), U(3, 2) 8. S(3, 3), T(5, 5), U(6, 0) Lesson S(4, 6), T(9, 1), U(1, 3) 10. S(0, 3), T( 2, 5), U(4, 7) 11. S( 3, 2), T(2, 7), U( 1, 1) 12. S(2, 1), T(5, 4), U(6, 3) Determine whether each set of measures can be the measures of the sides of a right triangle. Then state whether the form a Pthagorean triple , 16, , 30, , 48, , 4 5, , 5, , 2 7, 6 5 Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 359 Glencoe Geometr
14 7-2 Find. Practice The Pthagorean Theorem and Its onverse Determine whether GHI is a right triangle for the given vertices. Eplain. 7. G(2, 7), H(3, 6), I( 4, 1) 8. G( 6, 2), H(1, 12), I( 2, 1) 9. G( 2, 1), H(3, 1), I( 4, 4) 10. G( 2, 4), H(4, 1), I( 1, 9) Determine whether each set of measures can be the measures of the sides of a right triangle. Then state whether the form a Pthagorean triple , 40, , 28, , 32, , 1 2, , 2 2, , 2 3, ONSTRUTION The bottom end of a ramp at a warehouse is 10 feet from the base of the main dock and is 11 feet long. How high is the dock? 11 ft ramp 10 ft? dock Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 360 Glencoe Geometr
15 7-2 Reading to Learn Mathematics The Pthagorean Theorem and Its onverse Pre-ctivit How are right triangles used to build suspension bridges? Read the introduction to Lesson 7-2 at the top of page 350 in our tetbook. Do the two right triangles shown in the drawing appear to be similar? Eplain our reasoning. Reading the Lesson 1. Eplain in our own words the difference between how the Pthagorean Theorem is used and how the onverse of the Pthagorean Theorem is used. 2. Refer to the figure. For this figure, which statements are true?. m 2 n 2 p 2. n 2 m 2 p 2. m 2 n 2 p 2 D. m 2 p 2 n 2 E. p 2 n 2 m 2 F. n 2 p 2 m 2 m n p Lesson 7-2 G. n m p 2 2 H. p m n Is the following statement true or false? Pthagorean triple is an group of three numbers for which the sum of the squares of the smaller two numbers is equal to the square of the largest number. Eplain our reasoning. 4. If,, and z form a Pthagorean triple and k is a positive integer, which of the following groups of numbers are also Pthagorean triples?. 3, 4, 5z. 3, 3, 3z. 3, 3, 3z D. k, k, kz Helping You Remember 5. Man students who studied geometr long ago remember the Pthagorean Theorem as the equation a 2 b 2 c 2, but cannot tell ou what this equation means. formula is useless if ou don t know what it means and how to use it. How could ou help someone who has forgotten the Pthagorean Theorem remember the meaning of the equation a 2 b 2 c 2? Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 361 Glencoe Geometr
16 7-2 Enrichment onverse of a Right Triangle Theorem You have learned that the measure of the altitude from the verte of the right angle of a right triangle to its hpotenuse is the geometric mean between the measures of the two segments of the hpotenuse. Is the converse of this theorem true? In order to find out, it will help to rewrite the original theorem in if-then form as follows. If Q is a right triangle with right angle at Q, then QP is the geometric mean between P and P, where P is between and and Q P is perpendicular to. Q P 1. Write the converse of the if-then form of the theorem. 2. Is the converse of the original theorem true? Refer to the figure at the right to eplain our answer. Q P You ma find it interesting to eamine the other theorems in hapter 7 to see whether their converses are true or false. You will need to restate the theorems carefull in order to write their converses. Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 362 Glencoe Geometr
17 7-3 Stud Guide and Intervention Special Right Triangles Properties of Triangles The sides of a right triangle have a special relationship. Eample 1 Eample 2 If the leg of a right triangle is units, show that the hpotenuse is 2 units Using the Pthagorean Theorem with a b, then c 2 a 2 b c Eercises Find. In a right triangle the hpotenuse is 2 times the leg. If the hpotenuse is 6 units, find the length of each leg. The hpotenuse is 2 times the leg, so divide the length of the hpotenuse b 2. a units Lesson Find the perimeter of a square with diagonal 12 centimeters. 8. Find the diagonal of a square with perimeter 20 inches. 9. Find the diagonal of a square with perimeter 28 meters. Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 363 Glencoe Geometr
18 7-3 Stud Guide and Intervention (continued) Special Right Triangles Properties of Triangles The sides of a right triangle also have a special relationship. Eample 1 In a right triangle, show that the hpotenuse is twice the shorter leg and the longer leg is 3 times the shorter leg. MNQ is a right triangle, and the length of the hpotenuse M N is two times the length of the shorter side N Q. Using the Pthagorean Theorem, a 2 (2) a M a P 60 Q 60 N MNP is an equilateral triangle. MNQ is a right triangle. Eample 2 In a right triangle, the hpotenuse is 5 centimeters. Find the lengths of the other two sides of the triangle. If the hpotenuse of a right triangle is 5 centimeters, then the length of the shorter leg is half of 5 or 2.5 centimeters. The length of the longer leg is 3 times the length of the shorter leg, or (2.5)( 3 ) centimeters. Eercises Find and The perimeter of an equilateral triangle is 32 centimeters. Find the length of an altitude of the triangle to the nearest tenth of a centimeter. 8. n altitude of an equilateral triangle is 8.3 meters. Find the perimeter of the triangle to the nearest tenth of a meter. Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 364 Glencoe Geometr
19 7-3 Find and. Skills Practice Special Right Triangles For Eercises 7 9, use the figure at the right. 7. If a 11, find b and c. c 60 a 30 b 8. If b 15, find a and c. 9. If c 9, find a and b. For Eercises 10 and 11, use the figure at the right. 10. The perimeter of the square is 30 inches. Find the length of. Lesson 7-3 D Find the length of the diagonal D. 12. The perimeter of the equilateral triangle is 60 meters. Find the length of an altitude. E D 60 G F 13. GE is a triangle with right angle at E, and E is the longer leg. Find the coordinates of G in Quadrant I for E(1, 1) and (4, 1). Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 365 Glencoe Geometr
20 7-3 Find and. Practice Special Right Triangles For Eercises 7 9, use the figure at the right. 7. If a 4 3, find b and c. c D 60 a 8. If 3 3, find a and D. 30 b 9. If a 4, find D, b, and. 10. The perimeter of an equilateral triangle is 39 centimeters. Find the length of an altitude of the triangle. 11. MIP is a triangle with right angle at I, and I P the longer leg. Find the coordinates of M in Quadrant I for I(3, 3) and P(12, 3). 12. TJK is a triangle with right angle at J. Find the coordinates of T in Quadrant II for J( 2, 3) and K(3, 3). 13. OTNIL GRDENS One of the displas at a botanical garden is an herb garden planted in the shape of a square. The square measures 6 ards on each side. Visitors can view the herbs from a diagonal pathwa through the garden. How long is the pathwa? 6 d 6 d 6 d 6 d Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 366 Glencoe Geometr
21 7-3 Reading to Learn Mathematics Special Triangles Pre-ctivit How is triangle tiling used in wallpaper design? Read the introduction to Lesson 7-3 at the top of page 357 in our tetbook. How can ou most completel describe the larger triangle and the two smaller triangles in tile 15? How can ou most completel describe the larger triangle and the two smaller triangles in tile 16? (Include angle measures in describing all the triangles.) Reading the Lesson 1. Suppl the correct number or numbers to complete each statement. a. In a triangle, to find the length of the hpotenuse, multipl the length of a leg b. b. In a triangle, to find the length of the hpotenuse, multipl the length of the shorter leg b. c. In a triangle, the longer leg is opposite the angle with a measure of. d. In a triangle, to find the length of the longer leg, multipl the length of the shorter leg b. e. In an isosceles right triangle, each leg is opposite an angle with a measure of. f. In a triangle, to find the length of the shorter leg, divide the length of the longer leg b. g. In triangle, to find the length of the longer leg, divide the length of the hpotenuse b and multipl the result b. h. To find the length of a side of a square, divide the length of the diagonal b. Lesson Indicate whether each statement is alwas, sometimes, or never true. a. The lengths of the three sides of an isosceles triangle satisf the Pthagorean Theorem. b. The lengths of the sides of a triangle form a Pthagorean triple. c. The lengths of all three sides of a triangle are positive integers. Helping You Remember 3. Some students find it easier to remember mathematical concepts in terms of specific numbers rather than variables. How can ou use specific numbers to help ou remember the relationship between the lengths of the three sides in a triangle? Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 367 Glencoe Geometr
22 7-3 Enrichment onstructing Values of Square Roots The diagram at the right shows a right isosceles triangle with two legs of length 1 inch. the Pthagorean Theorem, the length of the hpotenuse is 2 inches. constructing an adjacent right triangle with legs of 2 inches and 1 inch, ou can create a segment of length 3. continuing this process as shown below, ou can construct a wheel of square roots. This wheel is called the Wheel of Theodorus after a Greek philosopher who lived about ontinue constructing the wheel until ou make a segment of length Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 368 Glencoe Geometr
23 7-4 Stud Guide and Intervention Trigonometr Trigonometric Ratios The ratio of the lengths of two sides of a right triangle is called a trigonometric ratio. The three most common ratios are sine, cosine, and tangent, which are abbreviated sin, cos, and tan, respectivel. sin R leg opposite R leg adjacent to R cos R tan R hpotenuse hpotenuse r t s t r s S leg opposite R leg adjacent to R r T s t R Eample Find sin, cos, and tan. Epress each ratio as a decimal to the nearest thousandth sin o pposite leg hpotenuse cos a djacent leg hpotenuse opposite leg tan a djacent leg Eercises Find the indicated trigonometric ratio as a fraction and as a decimal. If necessar, round to the nearest ten-thousandth. 1. sin 2. tan E D F 3. cos 4. cos 5. sin D 6. tan E Lesson cos E 8. cos D Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 369 Glencoe Geometr
24 7-4 Stud Guide and Intervention (continued) Trigonometr Use Trigonometric Ratios In a right triangle, if ou know the measures of two sides or if ou know the measures of one side and an acute angle, then ou can use trigonometric ratios to find the measures of the missing sides or angles of the triangle. Eample Find,, and z. Round each measure to the nearest whole number. z a. Find b. Find. tan 1 8 tan tan c. Find z. cos 1 8 z cos z z cos z cos 58 z 34 Eercises Find. Round to the nearest tenth Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 370 Glencoe Geometr
25 7-4 Skills Practice Trigonometr Use RST to find sin R, cos R, tan R, sin S, cos S, and tan S. Epress each ratio as a fraction and as a decimal to the nearest hundredth. t S r 1. r 16, s 30, t r 10, s 24, t 26 R s T Use a calculator to find each value. Round to the nearest ten-thousandth. 3. sin 5 4. tan cos sin tan cos 52.9 Use the figure to find each trigonometric ratio. Epress answers as a fraction and as a decimal rounded to the nearest ten-thousandth. 9. tan 10. sin 11. cos Find the measure of each acute angle to the nearest tenth of a degree. 12. sin tan cos R tan cos sin Lesson 7-4 Find. Round to the nearest tenth L S U Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 371 Glencoe Geometr
26 7-4 Practice Trigonometr Use LMN to find sin L, cos L, tan L, sin M, cos M, and tan M. Epress each ratio as a fraction and as a decimal to the nearest hundredth. L 1. 15, m 36, n , m 12 3, n 24 N M Use a calculator to find each value. Round to the nearest ten-thousandth. 3. sin tan cos 64.8 Use the figure to find each trigonometric ratio. Epress answers as a fraction and as a decimal rounded to the nearest ten-thousandth. 6. cos 7. tan 8. sin Find the measure of each acute angle to the nearest tenth of a degree. 9. sin tan cos R Find. Round to the nearest tenth GEOGRPHY Diego used a theodolite to map a region of land for his class in geomorpholog. To determine the elevation of a vertical rock formation, he measured the distance from the base of the formation to his position and the angle between the ground and the line of sight to the top of the formation. The distance was 43 meters and the angle was 36 degrees. What is the height of the formation to the nearest meter? m Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 372 Glencoe Geometr
27 7-4 Reading to Learn Mathematics Trigonometr Pre-ctivit How can surveors determine angle measures? Read the introduction to Lesson 7-4 at the top of page 364 in our tetbook. Wh is it important to determine the relative positions accuratel in navigation? (Give two possible reasons.) Reading the Lesson What does calibrated mean? 1. Refer to the figure. Write a ratio using the side lengths in the figure to represent each of the following trigonometric ratios. M N. sin N. cos N P. tan N D. tan M E. sin M F. cos M 2. ssume that ou enter each of the epressions in the list on the left into our calculator. Match each of these epressions with a description from the list on the right to tell what ou are finding when ou enter this epression. a. sin 20 b. cos 20 c. sin d. tan e. tan 20 f. cos i. the degree measure of an acute angle whose cosine is 0.8 ii. the ratio of the length of the leg adjacent to the 20 angle to the length of hpotenuse in a triangle iii.the degree measure of an acute angle in a right triangle for which the ratio of the length of the opposite leg to the length of the adjacent leg is 0.8 iv. the ratio of the length of the leg opposite the 20 angle to the length of the leg adjacent to it in a triangle v. the ratio of the length of the leg opposite the 20 angle to the length of hpotenuse in a triangle vi. the degree measure of an acute angle in a right triangle for which the ratio of the length of the opposite leg to the length of the hpotenuse is 0.8 Lesson 7-4 Helping You Remember 3. How can the co in cosine help ou to remember the relationship between the sines and cosines of the two acute angles of a right triangle? Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 373 Glencoe Geometr
28 7-4 Enrichment Sine and osine of ngles The following diagram can be used to obtain approimate values for the sine and cosine of angles from 0 to 90. The radius of the circle is 1. So, the sine and cosine values can be read directl from the vertical and horizontal aes Eample Find approimate values for sin 40 and cos 40. onsider the triangle formed b the segment marked 40, as illustrated b the shaded triangle at right. sin 40 a c b or 0.64 cos 40 1 c or c 1 unit a sin b cos Use the diagram above to complete the chart of values sin 0.64 cos ompare the sine and cosine of two complementar angles (angles whose sum is 90 ). What do ou notice? Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 374 Glencoe Geometr
29 7-5 Stud Guide and Intervention ngles of Elevation and Depression ngles of Elevation Man real-world problems that involve looking up to an object can be described in terms of an angle of elevation, which is the angle between an observer s line of sight and a horizontal line. line of sight angle of elevation Eample The angle of elevation from point to the top of a cliff is 34. If point is 1000 feet from the base of the cliff, how high is the cliff? Let the height of the cliff. tan 34 tan o pposite adjacent 1000(tan 34 ) Multipl each side b Use a calculator ft The height of the cliff is about feet. Eercises Solve each problem. Round measures of segments to the nearest whole number and angles to the nearest degree. 1. The angle of elevation from point to the top of a hill is 49. If point is 400 feet from the base of the hill, how high is the hill?? ft 2. Find the angle of elevation of the sun when a 12.5-meter-tall telephone pole casts a 18-meter-long shadow. sun? 18 m 12.5 m 3. ladder leaning against a building makes an angle of 78 with the ground. The foot of the ladder is 5 feet from the building. How long is the ladder?? 78 5 ft 4. person whose ees are 5 feet above the ground is standing on the runwa of an airport 100 feet from the control tower. That person observes an air traffic controller at the window of the 132-foot tower. What is the angle of elevation? 5 ft? 100 ft 132 ft Lesson 7-5 Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 375 Glencoe Geometr
30 7-5 Stud Guide and Intervention (continued) ngles of Elevation and Depression ngles of Depression When an observer is looking down, the angle of depression is the angle between the observer s line of sight and a horizontal line. horizontal line of sight angle of depression Y Eample The angle of depression from the top of an 80-foot building to point on the ground is 42. How far is the foot of the building from point? Let the distance from point to the foot of the building. Since the horizontal line is parallel to the ground, the angle of depression D is congruent to. tan tan o pposite adjacent (tan 42 ) 80 Multipl each side b. 80 tan Use a calculator. Divide each side b tan 42. Point is about 89 feet from the base of the building. Eercises horizontal D angle of depression ft Solve each problem. Round measures of segments to the nearest whole number and angles to the nearest degree. 1. The angle of depression from the top of a sheer cliff to point on the ground is 35. If point is 280 feet from the base of the cliff, how tall is the cliff? 35? 280 ft 2. The angle of depression from a balloon on a 75-foot string to a person on the ground is 36. How high is the balloon? ft? 3. ski run is 1000 ards long with a vertical drop of 208 ards. Find the angle of depression from the top of the ski run to the bottom d? 208 d 4. From the top of a 120-foot-high tower, an air traffic controller observes an airplane on the runwa at an angle of depression of 19. How far from the base of the tower is the airplane?? ft Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 376 Glencoe Geometr
31 7-5 Skills Practice ngles of Elevation and Depression Name the angle of depression or angle of elevation in each figure F L S T T S R W 3. D 4. Z R W P 5. MOUNTIN IKING On a mountain bike trip along the Gemini ridges Trail in Moab, Utah, Nabuko stopped on the canon floor to get a good view of the twin sandstone bridges. Nabuko is standing about 60 meters from the base of the canon cliff, and the natural arch bridges are about 100 meters up the canon wall. If her line of sight is five feet above the ground, what is the angle of elevation to the top of the bridges? Round to the nearest tenth degree. 6. SHDOWS Suppose the sun casts a shadow off a 35-foot building. If the angle of elevation to the sun is 60, how long is the shadow to the nearest tenth of a foot? 60? 35 ft 7. LLOONING From her position in a hot-air balloon, ngie can see her car parked in a field. If the angle of depression is 8 and ngie is 38 meters above the ground, what is the straight-line distance from ngie to her car? Round to the nearest whole meter. 8. INDIRET MESUREMENT Kle is at the end of a pier 30 feet above the ocean. His ee level is 3 feet above the pier. He is using binoculars to watch a whale surface. If the angle of depression of the whale is 20, how far is the whale from Kle s binoculars? Round to the nearest tenth foot. whale 20 Kle s ees 3 ft pier 30 ft water level Lesson 7-5 Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 377 Glencoe Geometr
32 7-5 Practice ngles of Elevation and Depression Name the angle of depression or angle of elevation in each figure. 1. T R 2. R P Z Y L M 3. WTER TOWERS student can see a water tower from the closest point of the soccer field at San Lobos High School. The edge of the soccer field is about 110 feet from the water tower and the water tower stands at a height of 32.5 feet. What is the angle of elevation if the ee level of the student viewing the tower from the edge of the soccer field is 6 feet above the ground? Round to the nearest tenth degree. 4. ONSTRUTION roofer props a ladder against a wall so that the top of the ladder reaches a 30-foot roof that needs repair. If the angle of elevation from the bottom of the ladder to the roof is 55, how far is the ladder from the base of the wall? Round our answer to the nearest foot. 5. TOWN ORDINNES The town of elmont restricts the height of flagpoles to 25 feet on an propert. Lindsa wants to determine whether her school is in compliance with the regulation. Her ee level is 5.5 feet from the ground and she stands 36 feet from the flagpole. If the angle of elevation is about 25, what is the height of the flagpole to the nearest tenth foot? ft 36 ft 6. GEOGRPHY Stephan is standing on a mesa at the Painted Desert. The elevation of the mesa is about 1380 meters and Stephan s ee level is 1.8 meters above ground. If Stephan can see a band of multicolored shale at the bottom and the angle of depression is 29, about how far is the band of shale from his ees? Round to the nearest meter. 7. INDIRET MESUREMENT Mr. Dominguez is standing on a 40-foot ocean bluff near his home. He can see his two dogs on the beach below. If his line of sight is 6 feet above the ground and the angles of depression to his dogs are 34 and 48, how far apart are the dogs to the nearest foot? Mr. Dominguez 6 ft 40 ft bluff Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 378 Glencoe Geometr
33 7-5 Reading to Learn Mathematics ngles of Elevation and Depression Pre-ctivit How do airline pilots use angles of elevation and depression? Read the introduction to Lesson 7-5 at the top of page 371 in our tetbook. What does the angle measure tell the pilot? Reading the Lesson 1. Refer to the figure. The two observers are looking at one another. Select the correct choice for each question. a. What is the line of sight? (i) line RS (ii) line ST (iii) line RT (iv) line TU b. What is the angle of elevation? (i) RST (ii) SRT (iii) RTS (iv) UTR c. What is the angle of depression? (i) RST (ii) SRT (iii) RTS (iv) UTR observer on ground R U observer at T top of building S d. How are the angle of elevation and the angle of depression related? (i) The are complementar. (ii) The are congruent. (iii) The are supplementar. (iv) The angle of elevation is larger than the angle of depression. e. Which postulate or theorem that ou learned in hapter 3 supports our answer for part c? (i) orresponding ngles Postulate (ii) lternate Eterior ngles Theorem (iii) onsecutive Interior ngles Theorem (iv) lternate Interior ngles Theorem 2. student sas that the angle of elevation from his ee to the top of a flagpole is 135. What is wrong with the student s statement? Helping You Remember 3. good wa to remember something is to eplain it to someone else. Suppose a classmate finds it difficult to distinguish between angles of elevation and angles of depression. What are some hints ou can give her to help her get it right ever time? Lesson 7-5 Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 379 Glencoe Geometr
34 7-5 Enrichment Reading Mathematics The three most common trigonometric ratios are sine, cosine, and tangent. Three other ratios are the cosecant, secant, and cotangent. The chart below shows abbreviations and definitions for all si ratios. Refer to the triangle at the right. c a bbreviation Read as: Ratio leg opposite sin the sine of a c hpotenuse b leg adjacent to cos the cosine of b hpotenuse c leg opposite tan the tangent of a leg adjacent to b hpotenuse c csc the cosecant of leg opposite a hpotenuse c sec the secant of leg adjacent to b leg adjacent to cot the cotangent of b leg opposite a Use the abbreviations to rewrite each statement as an equation. 1. The secant of angle is equal to 1 divided b the cosine of angle. 2. The cosecant of angle is equal to 1 divided b the sine of angle. 3. The cotangent of angle is equal to 1 divided b the tangent of angle. 4. The cosecant of angle multiplied b the sine of angle is equal to The secant of angle multiplied b the cosine of angle is equal to The cotangent of angle times the tangent of angle is equal to 1. Use the triangle at right. Write each ratio. R 7. sec R 8. csc R 9. cot R 10. sec S 11. csc S 12. cot S s t 13. If sin 0.289, find the value of csc. T r S 14. If tan 1.376, find the value of cot. Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 380 Glencoe Geometr
35 7-6 Stud Guide and Intervention The Law of Sines The Law of Sines In an triangle, there is a special relationship between the angles of the triangle and the lengths of the sides opposite the angles. Law of Sines sin sin sin a b c Lesson 7-6 Eample 1 Eample b 30 In, find b. sin sin Law of Sines c b sin 45 sin 74 m 45, c 30, m b b sin sin 74 ross multipl. b 30 sin 74 Divide each side b sin 45. sin 45 b 40.8 Use a calculator. D E F sin D sin E d e si n D 28 sin In DEF, find m D. Law of Sines d 28, m E 58, e sin D 28 sin 58 ross multipl. sin D 28 s in D sin 1 28 s in D 81.6 Divide each side b 24. Use the inverse sine. Use a calculator. Eercises Find each measure using the given measures of. Round angle measures to the nearest degree and side measures to the nearest tenth. 1. If c 12, m 80, and m 40, find a. 2. If b 20, c 26, and m 52, find m. 3. If a 18, c 16, and m 84, find m. 4. If a 25, m 72, and m 17, find b. 5. If b 12, m 89, and m 80, find a. 6. If a 30, c 20, and m 60, find m. Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 381 Glencoe Geometr
36 7-6 Stud Guide and Intervention (continued) The Law of Sines Use the Law of Sines to Solve Problems You can use the Law of Sines to solve some problems that involve triangles. Law of Sines Let be an triangle with a, b, and c representing the measures of the sides opposite the angles with measures,, and, respectivel. Then sin a sin b sin c. Eample Isosceles has a base of 24 centimeters and a verte angle of 68. Find the perimeter of the triangle. The verte angle is 68, so the sum of the measures of the base angles is 112 and m m 56. sin sin b a Law of Sines c 68 b 24 a sin sin 56 m 68, b 24, m 56 a a sin sin 56 a 24 sin 56 sin ross multipl. Divide each side b sin 68. Use a calculator. The triangle is isosceles, so c The perimeter is or about 67 centimeters. Eercises Draw a triangle to go with each eercise and mark it with the given information. Then solve the problem. Round angle measures to the nearest degree and side measures to the nearest tenth. 1. One side of a triangular garden is 42.0 feet. The angles on each end of this side measure 66 and 82. Find the length of fence needed to enclose the garden. 2. Two radar stations and are 32 miles apart. The locate an airplane X at the same time. The three points form X, which measures 46, and X, which measures 52. How far is the airplane from each station? 3. civil engineer wants to determine the distances from points and to an inaccessible point in a river. measures 67 and measures 52. If points and are 82.0 feet apart, find the distance from to each point. 4. ranger tower at point is 42 kilometers north of a ranger tower at point. fire at point is observed from both towers. If measures 43 and measures 68, which ranger tower is closer to the fire? How much closer? Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 382 Glencoe Geometr
37 7-6 Skills Practice The Law of Sines Find each measure using the given measures from. Round angle measures to the nearest tenth degree and side measures to the nearest tenth. 1. If m 35, m 48, and b 28, find a. 2. If m 17, m 46, and c 18, find b. Lesson If m 86, m 51, and a 38, find c. 4. If a 17, b 8, and m 73, find m. 5. If c 38, b 34, and m 36, find m. 6. If a 12, c 20, and m 83, find m. 7. If m 22, a 18, and m 104, find b. Solve each PQR described below. Round measures to the nearest tenth. 8. p 27, q 40, m P q 12, r 11, m R p 29, q 34, m Q If m P 89, p 16, r If m Q 103, m P 63, p If m P 96, m R 82, r If m R 49, m Q 76, r If m Q 31, m P 52, p If q 8, m Q 28, m R If r 15, p 21, m P 128 Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 383 Glencoe Geometr
38 7-6 Practice The Law of Sines Find each measure using the given measures from EFG. Round angle measures to the nearest tenth degree and side measures to the nearest tenth. 1. If m G 14, m E 67, and e 14, find g. 2. If e 12.7, m E 42, and m F 61, find f. 3. If g 14, f 5.8, and m G 83, find m F. 4. If e 19.1, m G 34, and m E 56, find g. 5. If f 9.6, g 27.4, and m G 43, find m F. Solve each STU described below. Round measures to the nearest tenth. 6. m T 85, s 4.3, t s 40, u 12, m S m U 37, t 2.3, m T m S 62, m U 59, s t 28.4, u 21.7, m T m S 89, s 15.3, t m T 98, m U 74, u t 11.8, m S 84, m T INDIRET MESUREMENT To find the distance from the edge of the lake to the tree on the island in the lake, Hannah set up a triangular configuration as shown in the diagram. The distance from location to location is 85 meters. The measures of the angles at and are 51 and 83, respectivel. What is the distance from the edge of the lake at to the tree on the island at? Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 384 Glencoe Geometr
39 7-6 Reading to Learn Mathematics The Law of Sines Pre-ctivit How are triangles used in radio astronom? Read the introduction to Lesson 7-6 at the top of page 377 in our tetbook. Wh might several antennas be better than one single antenna when studing distant objects? Lesson 7-6 Reading the Lesson 1. Refer to the figure. ccording to the Law of Sines, which of the following are correct statements? m n p.. sin m si n n sin p sin M sin N sin P M N P. co s M cos N co s P m n p sin M D. sin N sin P m n p M n P p m N E. (sin M) 2 (sin N) 2 (sin P) 2 F. sin P sin M sin N p m n 2. State whether each of the following statements is true or false. If the statement is false, eplain wh. a. The Law of Sines applies to all triangles. b. The Pthagorean Theorem applies to all triangles. c. If ou are given the length of one side of a triangle and the measures of an two angles, ou can use the Law of Sines to find the lengths of the other two sides. d. If ou know the measures of two angles of a triangle, ou should use the Law of Sines to find the measure of the third angle. e. friend tells ou that in triangle RST, m R 132, r 24 centimeters, and s 31 centimeters. an ou use the Law of Sines to solve the triangle? Eplain. Helping You Remember 3. Man students remember mathematical equations and formulas better if the can state them in words. State the Law of Sines in our own words without using variables or mathematical smbols. Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 385 Glencoe Geometr
40 7-6 Enrichment Identities n identit is an equation that is true for all values of the variable for which both sides are defined. One wa to verif an identit is to use a right triangle and the definitions for trigonometric functions. c a Eample 1 is an identit. Verif that (sin ) 2 (cos ) 2 1 b (sin ) 2 (cos ) 2 a c 2 b c 2 b 2 a2 c c c 2 1 To check whether an equation ma be an identit, ou can test several values. However, since ou cannot test all values, ou cannot be certain that the equation is an identit. 2 Eample 2 Test sin 2 2 sin cos to see if it could be an identit. Tr 20. Use a calculator to evaluate each epression. sin 2 sin 40 2 sin cos 2 (sin 20)(cos 20) (0.342)(0.940) Since the left and right sides seem equal, the equation ma be an identit. Use triangle shown above. Verif that each equation is an identit. 1. c os 1 sin tan 2. t an 1 sin co s 3. tan cos sin 4. 1 (cos ) 2 (sin ) 2 Tr several values for to test whether each equation could be an identit. 5. cos 2 (cos ) 2 (sin ) 2 6. cos (90 ) sin Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 386 Glencoe Geometr
41 7-7 Stud Guide and Intervention The Law of osines The Law of osines nother relationship between the sides and angles of an triangle is called the Law of osines.you can use the Law of osines if ou know three sides of a triangle or if ou know two sides and the included angle of a triangle. Law of osines Let be an triangle with a, b, and c representing the measures of the sides opposite the angles with measures,, and, respectivel. Then the following equations are true. a 2 b 2 c 2 2bc cos b 2 a 2 c 2 2ac cos c 2 a 2 b 2 2ab cos Eample 1 In, find c. c 2 a 2 b 2 2ab cos Law of osines c (12)(10)cos 48 a 12, b 10, m 48 c (10)co 2(12) s 48 c 9.1 Use a calculator. Take the square root of each side c Lesson 7-7 Eample 2 In, find m. a 2 b 2 c 2 2bc cos Law of osines (5)(8) cos a 7, b 5, c cos Multipl cos Subtract 89 from each side. 1 cos Divide each side b cos 1 1 Use the inverse cosine Use a calculator Eercises Find each measure using the given measures from. Round angle measures to the nearest degree and side measures to the nearest tenth. 1. If b 14, c 12, and m 62, find a. 2. If a 11, b 10, and c 12, find m. 3. If a 24, b 18, and c 16, find m. 4. If a 20, c 25, and m 82, find b. 5. If b 18, c 28, and m 59, find a. 6. If a 15, b 19, and c 15, find m. Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 387 Glencoe Geometr
42 7-7 Stud Guide and Intervention (continued) The Law of osines Use the Law of osines to Solve Problems You can use the Law of osines to solve some problems involving triangles. Law of osines Let be an triangle with a, b, and c representing the measures of the sides opposite the angles with measures,, and, respectivel. Then the following equations are true. a 2 b 2 c 2 2bc cos b 2 a 2 c 2 2ac cos c 2 a 2 b 2 2ab cos Eample Ms. Jones wants to purchase a piece of land with the shape shown. Find the perimeter of the propert. Use the Law of osines to find the value of a. a 2 b 2 c 2 2bc cos Law of osines a (300)(200) cos 88 b 300, c 200, m 88 a 130, ,0 00 cos Take the square root of each side. Use a calculator. Use the Law of osines again to find the value of c. c 2 a 2 b 2 2ab cos Law of osines c (354.7)(300) cos 80 a 354.7, b 300, m 80 c 215, , cos Take the square root of each side. Use a calculator. The perimeter of the land is or about 1223 feet. Eercises 300 ft 80 a 300 ft ft c Draw a figure or diagram to go with each eercise and mark it with the given information. Then solve the problem. Round angle measures to the nearest degree and side measures to the nearest tenth. 1. triangular garden has dimensions 54 feet, 48 feet, and 62 feet. Find the angles at each corner of the garden. 2. parallelogram has a 68 angle and sides 8 and 12. Find the lengths of the diagonals. 3. n airplane is sighted from two locations, and its position forms an acute triangle with them. The distance to the airplane is 20 miles from one location with an angle of elevation 48.0, and 40 miles from the other location with an angle of elevation of How far apart are the two locations? 4. ranger tower at point is directl north of a ranger tower at point. fire at point is observed from both towers. The distance from the fire to tower is 60 miles, and the distance from the fire to tower is 50 miles. If m 62, find the distance between the towers. Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 388 Glencoe Geometr
43 7-7 Skills Practice The Law of osines In RST, given the following measures, find the measure of the missing side. 1. r 5, s 8, m T r 6, t 11, m S r 9, t 15, m S s 12, t 10, m R 58 In HIJ, given the lengths of the sides, find the measure of the stated angle to the nearest tenth. 5. h 12, i 18, j 7; m H Lesson h 15, i 16, j 22; m I 7. h 23, i 27, j 29; m J 8. h 37, i 21, j 30; m H Determine whether the Law of Sines or the Law of osines should be used first to solve each triangle. Then solve each triangle. Round angle measures to the nearest degree and side measures to the nearest tenth c M L 52 N 11. a 10, b 14, c a 12, b 10, m 27 Solve each RST described below. Round measures to the nearest tenth. 13. r 12, s 32, t r 30, s 25, m T r 15, s 11, m R r 21, s 28, t 30 Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 389 Glencoe Geometr
44 7-7 Practice The Law of osines In JKL, given the following measures, find the measure of the missing side. 1. j 1.3, k 10, m L j 9.6, 1.7, m K j 11, k 7, m L k 4.7, 5.2, m J 112 In MNQ, given the lengths of the sides, find the measure of the stated angle to the nearest tenth. 5. m 17, n 23, q 25; m Q 6. m 24, n 28, q 34; m M 7. m 12.9, n 18, q 20.5; m N 8. m 23, n 30.1, q 42; m Q Determine whether the Law of Sines or the Law of osines should be used first to solve. Then sole each triangle. Round angle measures to the nearest degree and side measure to the nearest tenth. 9. a 13, b 18, c a 6, b 19, m a 17, b 22, m a 15.5, b 18, m 72 Solve each FGH described below. Round measures to the nearest tenth. 13. m F 54, f 12.5, g f 20, g 23, m H f 15.8, g 11, h f 36, h 30, m G REL ESTTE The Esposito famil purchased a triangular plot of land on which the plan to build a barn and corral. The lengths of the sides of the plot are 320 feet, 286 feet, and 305 feet. What are the measures of the angles formed on each side of the propert? Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 390 Glencoe Geometr
45 7-7 Reading to Learn Mathematics The Law of osines Pre-ctivit How are triangles used in building design? Read the introduction to Lesson 7-7 at the top of page 385 in our tetbook. What could be a disadvantage of a triangular room? Reading the Lesson 1. Refer to the figure. ccording to the Law of osines, which statements are correct for DEF?. d 2 e 2 f 2 ef cos D. e 2 d 2 f 2 2df cos E. d 2 e 2 f 2 2ef cos D D. f 2 d 2 e 2 2ef cos F E. f 2 d 2 e 2 2de cos F F. d 2 e 2 f 2 G. sin D sin E sin F d e f H. d e 2 f f 2 2e D cos D e F f d E Lesson Each of the following describes three given parts of a triangle. In each case, indicate whether ou would use the Law of Sines or the Law of osines first in solving a triangle with those given parts. (In some cases, onl one of the two laws would be used in solving the triangle.) a. SSS b. S c. S d. SS e. SS 3. Indicate whether each statement is true or false. If the statement is false, eplain wh. a. The Law of osines applies to right triangles. b. The Pthagorean Theorem applies to acute triangles. c. The Law of osines is used to find the third side of a triangle when ou are given the measures of two sides and the nonincluded angle. d. The Law of osines can be used to solve a triangle in which the measures of the three sides are 5 centimeters, 8 centimeters, and 15 centimeters. Helping You Remember 4. good wa to remember a new mathematical formula is to relate it to one ou alread know. The Law of osines looks somewhat like the Pthagorean Theorem. oth formulas must be true for a right triangle. How can that be? Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 391 Glencoe Geometr
NAME DATE PERIOD. Find the geometric mean between each pair of numbers to the nearest tenth and and and 2
 8-1 Practice Geometric Mean Find the geometric mean between each pair of numbers to the nearest tenth. 1. 8 and 12 2. 3 7 and 6 7 3. 4 and 2 5 Find the measure of the altitude drawn to the hpotenuse. State
8-1 Practice Geometric Mean Find the geometric mean between each pair of numbers to the nearest tenth. 1. 8 and 12 2. 3 7 and 6 7 3. 4 and 2 5 Find the measure of the altitude drawn to the hpotenuse. State
Geometry. Chapter 7 Resource Masters
 Geometr hapter Resource Masters onsumable Workbooks Man of the worksheets contained in the hapter Resource Masters booklets are available as consumable workbooks. Stud Guide and Intervention Workbook 0-0-09-
Geometr hapter Resource Masters onsumable Workbooks Man of the worksheets contained in the hapter Resource Masters booklets are available as consumable workbooks. Stud Guide and Intervention Workbook 0-0-09-
8.5 angles of elevation and depression ink.notebook. March 05, Page 74 Page Angles of Elevation and Depression. Page 76.
 8.5 angles of elevation and depression ink.notebook 65 Page 74 Page 73 8.5 Angles of Elevation and Depression Page 75 Page 76 1 Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson Notes Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson
8.5 angles of elevation and depression ink.notebook 65 Page 74 Page 73 8.5 Angles of Elevation and Depression Page 75 Page 76 1 Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson Notes Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson
Geometry Unit 7 - Notes Right Triangles and Trigonometry
 Geometry Unit 7 - Notes Right Triangles and Trigonometry Review terms: 1) right angle ) right triangle 3) adjacent 4) Triangle Inequality Theorem Review topic: Geometric mean a = = d a d Syllabus Objective:
Geometry Unit 7 - Notes Right Triangles and Trigonometry Review terms: 1) right angle ) right triangle 3) adjacent 4) Triangle Inequality Theorem Review topic: Geometric mean a = = d a d Syllabus Objective:
Name: Period: Geometry Honors Unit 5: Trigonometry Homework. x a = 4, b= a = 7, b = a = 6, c =
 Name: Period: Geometr Honors Unit 5: Trigonometr Homework Section 5.1: Pthagorean Theorem Find the value of each variable or missing side. Leave answers in simplest radical form ND as a decimal rounded
Name: Period: Geometr Honors Unit 5: Trigonometr Homework Section 5.1: Pthagorean Theorem Find the value of each variable or missing side. Leave answers in simplest radical form ND as a decimal rounded
10-1 L E S S O N M A S T E R. Name. Vocabulary. 1. Refer to the diagram at the right. Fill in the blank. a. The leg adjacent to is.
 L E S S O N M S T E R Vocabular 10 Questions on SPUR Objectives 1. Refer to the diagram at the right. Fill in the blank. a. The leg adjacent to is. b. The leg opposite is. c. The hpotenuse is. C 2. Fill
L E S S O N M S T E R Vocabular 10 Questions on SPUR Objectives 1. Refer to the diagram at the right. Fill in the blank. a. The leg adjacent to is. b. The leg opposite is. c. The hpotenuse is. C 2. Fill
MORE TRIGONOMETRY
 MORE TRIGONOMETRY 5.1.1 5.1.3 We net introduce two more trigonometric ratios: sine and cosine. Both of them are used with acute angles of right triangles, just as the tangent ratio is. Using the diagram
MORE TRIGONOMETRY 5.1.1 5.1.3 We net introduce two more trigonometric ratios: sine and cosine. Both of them are used with acute angles of right triangles, just as the tangent ratio is. Using the diagram
Exercise Set 4.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios
 Eercise Set.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Answer the following. 9. 1. If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the opposite those sides are also congruent. 2. If two angles
Eercise Set.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Answer the following. 9. 1. If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the opposite those sides are also congruent. 2. If two angles
Geometry Rules! Chapter 8 Notes
 Geometr Rules! Chapter 8 Notes - 1 - Notes #6: The Pthagorean Theorem (Sections 8.2, 8.3) A. The Pthagorean Theorem Right Triangles: Triangles with right angle Hpotenuse: the side across from the angle
Geometr Rules! Chapter 8 Notes - 1 - Notes #6: The Pthagorean Theorem (Sections 8.2, 8.3) A. The Pthagorean Theorem Right Triangles: Triangles with right angle Hpotenuse: the side across from the angle
Name: Period: Geometry Unit 5: Trigonometry Homework. x a = 4, b= a = 7, b = a = 6, c = a = 3, b = 7
 Name: Period: Geometr Unit 5: Trigonometr Homework Section 5.1: Pthagorean Theorem Find the value of each variable or missing side. Leave answers in simplest radical form AND as a decimal rounded to the
Name: Period: Geometr Unit 5: Trigonometr Homework Section 5.1: Pthagorean Theorem Find the value of each variable or missing side. Leave answers in simplest radical form AND as a decimal rounded to the
9.3. Practice C For use with pages Tell whether the triangle is a right triangle.
 LESSON 9.3 NAME DATE For use with pages 543 549 Tell whether the triangle is a right triangle. 1. 21 2. 3. 75 6 2 2 17 72 63 66 16 2 4. 110 5. 4.3 6. 96 2 4.4 10 3 3 4.5 Decide whether the numbers can
LESSON 9.3 NAME DATE For use with pages 543 549 Tell whether the triangle is a right triangle. 1. 21 2. 3. 75 6 2 2 17 72 63 66 16 2 4. 110 5. 4.3 6. 96 2 4.4 10 3 3 4.5 Decide whether the numbers can
Trigonometric ratios:
 0 Trigonometric ratios: The six trigonometric ratios of A are: Sine Cosine Tangent sin A = opposite leg hypotenuse adjacent leg cos A = hypotenuse tan A = opposite adjacent leg leg and their inverses:
0 Trigonometric ratios: The six trigonometric ratios of A are: Sine Cosine Tangent sin A = opposite leg hypotenuse adjacent leg cos A = hypotenuse tan A = opposite adjacent leg leg and their inverses:
Prerequisite Skills. y x =
 Prerequisite Skills BLM 1 1... Solve Equations 1. Solve. 2x + 5 = 11 x 5 + 6 = 7 x 2 = 225 d) x 2 = 24 2 + 32 2 e) 60 2 + x 2 = 61 2 f) 13 2 12 2 = x 2 The Pythagorean Theorem 2. Find the measure of the
Prerequisite Skills BLM 1 1... Solve Equations 1. Solve. 2x + 5 = 11 x 5 + 6 = 7 x 2 = 225 d) x 2 = 24 2 + 32 2 e) 60 2 + x 2 = 61 2 f) 13 2 12 2 = x 2 The Pythagorean Theorem 2. Find the measure of the
Geometry Right Triangles and Trigonometry
 Geometry Right Triangles and Trigonometry Day Date lass Homework Th 2/16 F 2/17 N: Special Right Triangles & Pythagorean Theorem Right Triangle & Pythagorean Theorem Practice Mid-Winter reak WKS: Special
Geometry Right Triangles and Trigonometry Day Date lass Homework Th 2/16 F 2/17 N: Special Right Triangles & Pythagorean Theorem Right Triangle & Pythagorean Theorem Practice Mid-Winter reak WKS: Special
Trigonometry Math 076
 Trigonometry Math 076 133 Right ngle Trigonometry Trigonometry provides us with a way to relate the length of sides of a triangle to the measure of its angles. There are three important trigonometric functions
Trigonometry Math 076 133 Right ngle Trigonometry Trigonometry provides us with a way to relate the length of sides of a triangle to the measure of its angles. There are three important trigonometric functions
1.1 Angles and Degree Measure
 J. Jenkins - Math 060 Notes. Angles and Degree Measure An angle is often thought of as being formed b rotating one ra awa from a fied ra indicated b an arrow. The fied ra is the initial side and the rotated
J. Jenkins - Math 060 Notes. Angles and Degree Measure An angle is often thought of as being formed b rotating one ra awa from a fied ra indicated b an arrow. The fied ra is the initial side and the rotated
Using the Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse
 7 ig Idea 1 HPTR SUMMR IG IDS Using the Pythagorean Theorem and Its onverse For our Notebook The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle the square of the length of the hypotenuse c is equal
7 ig Idea 1 HPTR SUMMR IG IDS Using the Pythagorean Theorem and Its onverse For our Notebook The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle the square of the length of the hypotenuse c is equal
Special Right Triangles
 . Special Right Triangles Essential Question What is the relationship among the side lengths of - - 0 triangles? - - 0 triangles? Side Ratios of an Isosceles Right Triangle ATTENDING TO PRECISION To be
. Special Right Triangles Essential Question What is the relationship among the side lengths of - - 0 triangles? - - 0 triangles? Side Ratios of an Isosceles Right Triangle ATTENDING TO PRECISION To be
2018 Midterm Review Trigonometry: Midterm Review A Missive from the Math Department Trigonometry Work Problems Study For Understanding Read Actively
 Summer . Fill in the blank to correctl complete the sentence..4 written in degrees and minutes is..4 written in degrees and minutes is.. Find the complement and the supplement of the given angle. The complement
Summer . Fill in the blank to correctl complete the sentence..4 written in degrees and minutes is..4 written in degrees and minutes is.. Find the complement and the supplement of the given angle. The complement
Pre-AP Geometry 8-4 Study Guide: Angles of Elevation and Depression (pp ) Page! 1 of! 8
 Page! 1 of! 8 Attendance Problems. 1. Identify the the pair of alternate interior angles. 2. Use a calculator to find! tan 30 to the nearest ten-thousandth. 3. Solve! tan 54 = 2500 Round your answer to
Page! 1 of! 8 Attendance Problems. 1. Identify the the pair of alternate interior angles. 2. Use a calculator to find! tan 30 to the nearest ten-thousandth. 3. Solve! tan 54 = 2500 Round your answer to
Geometry. of Right Triangles. Pythagorean Theorem. Pythagorean Theorem. Angles of Elevation and Depression Law of Sines and Law of Cosines
 Geometry Pythagorean Theorem of Right Triangles Angles of Elevation and epression Law of Sines and Law of osines Pythagorean Theorem Recall that a right triangle is a triangle with a right angle. In a
Geometry Pythagorean Theorem of Right Triangles Angles of Elevation and epression Law of Sines and Law of osines Pythagorean Theorem Recall that a right triangle is a triangle with a right angle. In a
Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions
 SECTION 4.1 Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions Section 4.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Special Right Triangles Trigonometric Ratios
SECTION 4.1 Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions Section 4.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Special Right Triangles Trigonometric Ratios
Key Concept Trigonometric Ratios. length of leg opposite A length of hypotenuse. = a c. length of leg adjacent to A length of hypotenuse
 8-3 Trigonometry ommon ore State Standards G-SRT..8 Use trigonometric ratios and the Pythagorean Theorem to solve right triangles in applied problems. lso, G-SRT..7, G-MG..1 MP 1, MP 3, MP 4, MP Objective
8-3 Trigonometry ommon ore State Standards G-SRT..8 Use trigonometric ratios and the Pythagorean Theorem to solve right triangles in applied problems. lso, G-SRT..7, G-MG..1 MP 1, MP 3, MP 4, MP Objective
Essential Question How can you find a trigonometric function of an acute angle θ? opp. hyp. opp. adj. sec θ = hyp. adj.
 . Right Triangle Trigonometry Essential Question How can you find a trigonometric function of an acute angle? Consider one of the acute angles of a right triangle. Ratios of a right triangle s side lengths
. Right Triangle Trigonometry Essential Question How can you find a trigonometric function of an acute angle? Consider one of the acute angles of a right triangle. Ratios of a right triangle s side lengths
Name: Class: Date: Use a trigonometric ratio to determine the value of x. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
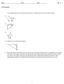 Class: Date: Ch 9 Questions 1. Use a trigonometric ratio to determine the value of x. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 2. 3. 4. Estimate m X to the nearest degree. 5. Katie and Matt are both flying
Class: Date: Ch 9 Questions 1. Use a trigonometric ratio to determine the value of x. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 2. 3. 4. Estimate m X to the nearest degree. 5. Katie and Matt are both flying
D) sin A = D) tan A = D) cos B =
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function requested. Write your answer as a fraction in lowest terms. 1) 1) Find sin A.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function requested. Write your answer as a fraction in lowest terms. 1) 1) Find sin A.
Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge
 Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge R Eponent Laws...50 R Epanding and Simplifing Polnomial Epressions...5 R 3 Factoring Polnomial Epressions...5 R Working with Rational Epressions...55 R 5 Slope
Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge R Eponent Laws...50 R Epanding and Simplifing Polnomial Epressions...5 R 3 Factoring Polnomial Epressions...5 R Working with Rational Epressions...55 R 5 Slope
Trigonometry Applications
 Name: Date: Period Trigonometry Applications Draw a picture (if one is not provided), write an equation, and solve each problem. Round answers to the nearest hundredths. 1. A 110-ft crane set at an angle
Name: Date: Period Trigonometry Applications Draw a picture (if one is not provided), write an equation, and solve each problem. Round answers to the nearest hundredths. 1. A 110-ft crane set at an angle
Geometry. Trigonometry of Right Triangles. Slide 1 / 240. Slide 2 / 240. Slide 3 / 240
 New Jersey enter for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 240 Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
New Jersey enter for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 240 Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
T.4 Applications of Right Angle Trigonometry
 424 section T4 T.4 Applications of Right Angle Trigonometry Solving Right Triangles Geometry of right triangles has many applications in the real world. It is often used by carpenters, surveyors, engineers,
424 section T4 T.4 Applications of Right Angle Trigonometry Solving Right Triangles Geometry of right triangles has many applications in the real world. It is often used by carpenters, surveyors, engineers,
Show all work for full credit. Do NOT use trig to solve special right triangle problems (half credit).
 Chapter 8 Retake Review 1 The length of the hypotenuse of a 30 60 90 triangle is 4. Find the perimeter. 2 What similarity statement can you write relating the three triangles in the diagram? 5 Find the
Chapter 8 Retake Review 1 The length of the hypotenuse of a 30 60 90 triangle is 4. Find the perimeter. 2 What similarity statement can you write relating the three triangles in the diagram? 5 Find the
Trigonometric. equations. Topic: Periodic functions and applications. Simple trigonometric. equations. Equations using radians Further trigonometric
 Trigonometric equations 6 sllabusref eferenceence Topic: Periodic functions and applications In this cha 6A 6B 6C 6D 6E chapter Simple trigonometric equations Equations using radians Further trigonometric
Trigonometric equations 6 sllabusref eferenceence Topic: Periodic functions and applications In this cha 6A 6B 6C 6D 6E chapter Simple trigonometric equations Equations using radians Further trigonometric
Triangles and Vectors
 Chapter 3 Triangles and Vectors As was stated at the start of Chapter 1, trigonometry had its origins in the study of triangles. In fact, the word trigonometry comes from the Greek words for triangle measurement.
Chapter 3 Triangles and Vectors As was stated at the start of Chapter 1, trigonometry had its origins in the study of triangles. In fact, the word trigonometry comes from the Greek words for triangle measurement.
Find the perimeter of the figure named and shown. Express the perimeter in the same unit of measure that appears on the given side or sides.
 Mth101 Chapter 8 HW Name Find the perimeter of the figure named and shown. Express the perimeter in the same unit of measure that appears on the given side or sides. 1) 1) Rectangle 6 in. 12 in. 12 in.
Mth101 Chapter 8 HW Name Find the perimeter of the figure named and shown. Express the perimeter in the same unit of measure that appears on the given side or sides. 1) 1) Rectangle 6 in. 12 in. 12 in.
Final Exam Review. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 ( Final Exam Review Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. is an isosceles triangle. is the longest side with length. = and =. Find. 4 x + 4 7
( Final Exam Review Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. is an isosceles triangle. is the longest side with length. = and =. Find. 4 x + 4 7
Name Date Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Class Work Unless otherwise directed, leave answers as reduced fractions or round to the nearest tenth.
 Name Date Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Class Work Unless otherwise directed, leave answers as reduced fractions or round to the nearest tenth. 1. Evaluate the sin, cos, and tan of θ(theta). 2. Evaluate
Name Date Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Class Work Unless otherwise directed, leave answers as reduced fractions or round to the nearest tenth. 1. Evaluate the sin, cos, and tan of θ(theta). 2. Evaluate
Find the length of an arc that subtends a central angle of 45 in a circle of radius 8 m. Round your answer to 3 decimal places.
 Chapter 6 Practice Test Find the radian measure of the angle with the given degree measure. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) 80 Find the degree measure of the angle with the given radian measure:
Chapter 6 Practice Test Find the radian measure of the angle with the given degree measure. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) 80 Find the degree measure of the angle with the given radian measure:
4.2 TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS: THE UNIT CIRCLE
 9 Chapter Trigonometr. TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS: THE UNIT CIRCLE What ou should learn Identif a unit circle and describe its relationship to real numbers. Evaluate trigonometric functions ug the unit circle.
9 Chapter Trigonometr. TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS: THE UNIT CIRCLE What ou should learn Identif a unit circle and describe its relationship to real numbers. Evaluate trigonometric functions ug the unit circle.
Trigonometric Functions
 Trigonometric Functions This section reviews radian measure and the basic trigonometric functions. C ' θ r s ' ngles ngles are measured in degrees or radians. The number of radians in the central angle
Trigonometric Functions This section reviews radian measure and the basic trigonometric functions. C ' θ r s ' ngles ngles are measured in degrees or radians. The number of radians in the central angle
Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Class Work
 Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Class Work Unless otherwise directed, leave answers as reduced fractions or round to the nearest tenth. 1. Evaluate the sin, cos, and tan of θ(theta). 2. Evaluate the
Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Class Work Unless otherwise directed, leave answers as reduced fractions or round to the nearest tenth. 1. Evaluate the sin, cos, and tan of θ(theta). 2. Evaluate the
The Primary Trigonometric Ratios Word Problems
 The Primary Trigonometric Ratios Word Problems A. Determining the measures of the sides and angles of right triangles using the primary ratios When we want to measure the height of an inaccessible object
The Primary Trigonometric Ratios Word Problems A. Determining the measures of the sides and angles of right triangles using the primary ratios When we want to measure the height of an inaccessible object
Ch. 2 Trigonometry Notes
 First Name: Last Name: Block: Ch. 2 Trigonometry Notes 2.1 THE TANGENT RATIO 2 Ch. 2.1 HW: p. 75 #3 16, 19 4 2.2 USING THE TANGENT RATIO TO CALCULATE LENGTHS 5 Ch. 2.2 HW: p. 82 # 3 5 (a, c), #6 14 6 2.4
First Name: Last Name: Block: Ch. 2 Trigonometry Notes 2.1 THE TANGENT RATIO 2 Ch. 2.1 HW: p. 75 #3 16, 19 4 2.2 USING THE TANGENT RATIO TO CALCULATE LENGTHS 5 Ch. 2.2 HW: p. 82 # 3 5 (a, c), #6 14 6 2.4
Lesson 16: Applications of Trig Ratios to Find Missing Angles
 : Applications of Trig Ratios to Find Missing Angles Learning Targets I can find a missing angle in a right triangle diagram and apply this to real world situation Opening Exercise Find the shadow cast
: Applications of Trig Ratios to Find Missing Angles Learning Targets I can find a missing angle in a right triangle diagram and apply this to real world situation Opening Exercise Find the shadow cast
North Carolina Math 2 Transition Edition Unit 5 Assessment: Trigonometry
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ North Carolina Math 2 Transition Edition Unit 5 Assessment: Trigonometry Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the
Name: Class: _ Date: _ North Carolina Math 2 Transition Edition Unit 5 Assessment: Trigonometry Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the
Ch6prac 1.Find the degree measure of the angle with the given radian measure. (Round your answer to the nearest whole number.) -2
 Ch6prac 1.Find the degree measure of the angle with the given radian measure. (Round your answer to the nearest whole number.) -2 2. Find the degree measure of the angle with the given radian measure.
Ch6prac 1.Find the degree measure of the angle with the given radian measure. (Round your answer to the nearest whole number.) -2 2. Find the degree measure of the angle with the given radian measure.
15 x. Substitute. Multiply. Add. Find the positive square root.
 hapter Review.1 The Pythagorean Theorem (pp. 3 70) Dynamic Solutions available at igideasmath.com Find the value of. Then tell whether the side lengths form a Pythagorean triple. c 2 = a 2 + b 2 Pythagorean
hapter Review.1 The Pythagorean Theorem (pp. 3 70) Dynamic Solutions available at igideasmath.com Find the value of. Then tell whether the side lengths form a Pythagorean triple. c 2 = a 2 + b 2 Pythagorean
Geometry. Trigonometry of Right Triangles. Slide 1 / 240. Slide 2 / 240. Slide 3 / 240
 New Jersey enter for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 240 Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
New Jersey enter for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 240 Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
Solve the equation for the specified variable. Use the distributive property to factor as necessary. 2) -9s + 8p = tp - 8 for p
 College Readiness Math Final Eam Review Sheet Solve the equation. 1) r + 6 = r + 8 3 6 Solve the equation for the specified variable. Use the distributive propert to factor as necessar. 2) -9s + 8p = tp
College Readiness Math Final Eam Review Sheet Solve the equation. 1) r + 6 = r + 8 3 6 Solve the equation for the specified variable. Use the distributive propert to factor as necessar. 2) -9s + 8p = tp
Diagnostic Tests Study Guide
 California State Universit, Sacramento Department of Mathematics and Statistics Diagnostic Tests Stud Guide Descriptions Stud Guides Sample Tests & Answers Table of Contents: Introduction Elementar Algebra
California State Universit, Sacramento Department of Mathematics and Statistics Diagnostic Tests Stud Guide Descriptions Stud Guides Sample Tests & Answers Table of Contents: Introduction Elementar Algebra
Analytic Trigonometry
 CHAPTER 5 Analtic Trigonometr 5. Fundamental Identities 5. Proving Trigonometric Identities 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities 5.4 Multiple-Angle Identities 5.5 The Law of Sines 5.6 The Law of Cosines It
CHAPTER 5 Analtic Trigonometr 5. Fundamental Identities 5. Proving Trigonometric Identities 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities 5.4 Multiple-Angle Identities 5.5 The Law of Sines 5.6 The Law of Cosines It
FINAL EXAM REVIEW Math 200 Spring 2007
 FINL EXM REVIEW Math 00 Spring 007 The final eam will be on Monda, Ma 14 from 7:00-9:00 in room. The eam will cover all material covered in class this semester, all of chapters 1,, 3, and 7. ll of the
FINL EXM REVIEW Math 00 Spring 007 The final eam will be on Monda, Ma 14 from 7:00-9:00 in room. The eam will cover all material covered in class this semester, all of chapters 1,, 3, and 7. ll of the
Inverse Trigonometric Functions. inverse sine, inverse cosine, and inverse tangent are given below. where tan = a and º π 2 < < π 2 (or º90 < < 90 ).
 Page 1 of 7 1. Inverse Trigonometric Functions What ou should learn GOAL 1 Evaluate inverse trigonometric functions. GOAL Use inverse trigonometric functions to solve real-life problems, such as finding
Page 1 of 7 1. Inverse Trigonometric Functions What ou should learn GOAL 1 Evaluate inverse trigonometric functions. GOAL Use inverse trigonometric functions to solve real-life problems, such as finding
Study Guide and Intervention
 6- NAME DATE PERID Stud Guide and Intervention Graphing Quadratic Functions Graph Quadratic Functions Quadratic Function A function defined b an equation of the form f () a b c, where a 0 b Graph of a
6- NAME DATE PERID Stud Guide and Intervention Graphing Quadratic Functions Graph Quadratic Functions Quadratic Function A function defined b an equation of the form f () a b c, where a 0 b Graph of a
Unit 3 Right Triangle Trigonometry - Classwork
 Unit 3 Right Triangle Trigonometry - Classwork We have spent time learning the definitions of trig functions and finding the trig functions of both quadrant and special angles. But what about other angles?
Unit 3 Right Triangle Trigonometry - Classwork We have spent time learning the definitions of trig functions and finding the trig functions of both quadrant and special angles. But what about other angles?
Transition to College Math
 Transition to College Math Date: Unit 3: Trigonometr Lesson 2: Angles of Rotation Name Period Essential Question: What is the reference angle for an angle of 15? Standard: F-TF.2 Learning Target: Eplain
Transition to College Math Date: Unit 3: Trigonometr Lesson 2: Angles of Rotation Name Period Essential Question: What is the reference angle for an angle of 15? Standard: F-TF.2 Learning Target: Eplain
b) Parallelogram Opposite Sides Converse c) Parallelogram Diagonals Converse d) Opposite sides Parallel and Congruent Theorem
 Chapter 7 1. State which theorem you can use to show that the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. a) Parallelogram Opposite Angles Converse b) Parallelogram Opposite Sides Converse c) Parallelogram Diagonals
Chapter 7 1. State which theorem you can use to show that the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. a) Parallelogram Opposite Angles Converse b) Parallelogram Opposite Sides Converse c) Parallelogram Diagonals
Assignment 1 and 2: Complete practice worksheet: Simplifying Radicals and check your answers
 Geometry 0-03 Summary Notes Right Triangles and Trigonometry These notes are intended to be a guide and a help as you work through Chapter 8. These are not the only thing you need to read, however. Rely
Geometry 0-03 Summary Notes Right Triangles and Trigonometry These notes are intended to be a guide and a help as you work through Chapter 8. These are not the only thing you need to read, however. Rely
Special Angles 1 Worksheet MCR3U Jensen
 Special Angles 1 Worksheet 1) a) Draw a right triangle that has one angle measuring 30. Label the sides using lengths 3, 2, and 1. b) Identify the adjacent and opposite sides relative to the 30 angle.
Special Angles 1 Worksheet 1) a) Draw a right triangle that has one angle measuring 30. Label the sides using lengths 3, 2, and 1. b) Identify the adjacent and opposite sides relative to the 30 angle.
Practice Questions for Midterm 2 - Math 1060Q - Fall 2013
 Eam Review Practice Questions for Midterm - Math 060Q - Fall 0 The following is a selection of problems to help prepare ou for the second midterm eam. Please note the following: anthing from Module/Chapter
Eam Review Practice Questions for Midterm - Math 060Q - Fall 0 The following is a selection of problems to help prepare ou for the second midterm eam. Please note the following: anthing from Module/Chapter
Int Math 2B EOC FIG Assessment ID: ib C. DE = DF. A. ABE ACD B. A + C = 90 C. C + D = B + E D. A = 38 and C = 38
 1 If ΔDEF and ΔJKL are two triangles such that D J, which of the following would be sufficient to prove the triangles are similar? A. DE = EF JK KL B. DE = EF JK JL C. DE = DF JK KL D. DE = DF JK JL 2
1 If ΔDEF and ΔJKL are two triangles such that D J, which of the following would be sufficient to prove the triangles are similar? A. DE = EF JK KL B. DE = EF JK JL C. DE = DF JK KL D. DE = DF JK JL 2
Geometry Final Review. Chapter 1. Name: Per: Vocab. Example Problems
 Geometry Final Review Name: Per: Vocab Word Acute angle Adjacent angles Angle bisector Collinear Line Linear pair Midpoint Obtuse angle Plane Pythagorean theorem Ray Right angle Supplementary angles Complementary
Geometry Final Review Name: Per: Vocab Word Acute angle Adjacent angles Angle bisector Collinear Line Linear pair Midpoint Obtuse angle Plane Pythagorean theorem Ray Right angle Supplementary angles Complementary
UNIT 5 SIMILARITY, RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY, AND PROOF Unit Assessment
 Unit 5 ircle the letter of the best answer. 1. line segment has endpoints at (, 5) and (, 11). point on the segment has a distance that is 1 of the length of the segment from endpoint (, 5). What are the
Unit 5 ircle the letter of the best answer. 1. line segment has endpoints at (, 5) and (, 11). point on the segment has a distance that is 1 of the length of the segment from endpoint (, 5). What are the
Throughout this chapter you will need: pencil ruler protractor. 7.1 Relationship Between Sides in Rightangled. 13 cm 10.5 cm
 7. Trigonometry In this chapter you will learn aout: the relationship etween the ratio of the sides in a right-angled triangle solving prolems using the trigonometric ratios finding the lengths of unknown
7. Trigonometry In this chapter you will learn aout: the relationship etween the ratio of the sides in a right-angled triangle solving prolems using the trigonometric ratios finding the lengths of unknown
8.6 Inverse Trigonometric Ratios
 www.ck12.org Chapter 8. Right Triangle Trigonometry 8.6 Inverse Trigonometric Ratios Learning Objectives Use the inverse trigonometric ratios to find an angle in a right triangle. Solve a right triangle.
www.ck12.org Chapter 8. Right Triangle Trigonometry 8.6 Inverse Trigonometric Ratios Learning Objectives Use the inverse trigonometric ratios to find an angle in a right triangle. Solve a right triangle.
Chapter 1. The word trigonometry comes from two Greek words, trigonon, meaning triangle, and. Trigonometric Ideas COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 Chapter Trigonometric Ideas The word trigonometr comes from two Greek words, trigonon, meaning triangle, and metria, meaning measurement This is the branch of mathematics that deals with the ratios between
Chapter Trigonometric Ideas The word trigonometr comes from two Greek words, trigonon, meaning triangle, and metria, meaning measurement This is the branch of mathematics that deals with the ratios between
Geometry Warm Up Right Triangles Day 8 Date
 Geometry Warm Up Right Triangles Day 8 Name Date Questions 1 4: Use the following diagram. Round decimals to the nearest tenth. P r q Q p R 1. If PR = 12 and m R = 19, find p. 2. If m P = 58 and r = 5,
Geometry Warm Up Right Triangles Day 8 Name Date Questions 1 4: Use the following diagram. Round decimals to the nearest tenth. P r q Q p R 1. If PR = 12 and m R = 19, find p. 2. If m P = 58 and r = 5,
9.1 Practice A. Name Date sin θ = and cot θ = to sketch and label the triangle. Then evaluate. the other four trigonometric functions of θ.
 .1 Practice A In Eercises 1 and, evaluate the si trigonometric functions of the angle. 1.. 8 1. Let be an acute angle of a right triangle. Use the two trigonometric functions 10 sin = and cot = to sketch
.1 Practice A In Eercises 1 and, evaluate the si trigonometric functions of the angle. 1.. 8 1. Let be an acute angle of a right triangle. Use the two trigonometric functions 10 sin = and cot = to sketch
Pre-calculus Notes: Chapter 5 The Trigonometric Functions. Use the word bank below to fill in the blanks below. You may use each term only once.
 Name: Pre-calculus Notes: Chapter 5 The Trigonometric Functions Section 1 Angles and Degree Measure Use the word bank below to fill in the blanks below. You may use each term only once. degree vertex negative
Name: Pre-calculus Notes: Chapter 5 The Trigonometric Functions Section 1 Angles and Degree Measure Use the word bank below to fill in the blanks below. You may use each term only once. degree vertex negative
: SINE, COSINE, & TANGENT RATIOS
 Geometry Notes Packet Name: 9.2 9.4: SINE, COSINE, & TANGENT RATIOS Trigonometric Ratios A ratio of the lengths of two sides of a right triangle. For any acute angle, there is a leg Opposite the angle
Geometry Notes Packet Name: 9.2 9.4: SINE, COSINE, & TANGENT RATIOS Trigonometric Ratios A ratio of the lengths of two sides of a right triangle. For any acute angle, there is a leg Opposite the angle
PRECALCULUS FINAL EXAM REVIEW
 PRECALCULUS FINAL EXAM REVIEW Evaluate the function at the indicated value of. Round our result to three decimal places.. f () 4(5 ); 0.8. f () e ; 0.78 Use the graph of f to describe the transformation
PRECALCULUS FINAL EXAM REVIEW Evaluate the function at the indicated value of. Round our result to three decimal places.. f () 4(5 ); 0.8. f () e ; 0.78 Use the graph of f to describe the transformation
THE KENNESAW STATE UNIVERSITY HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS COMPETITION PART I MULTIPLE CHOICE NO CALCULATORS 90 MINUTES
 THE 008 009 KENNESW STTE UNIVERSITY HIGH SHOOL MTHEMTIS OMPETITION PRT I MULTIPLE HOIE For each of the following questions, carefull blacken the appropriate bo on the answer sheet with a # pencil. o not
THE 008 009 KENNESW STTE UNIVERSITY HIGH SHOOL MTHEMTIS OMPETITION PRT I MULTIPLE HOIE For each of the following questions, carefull blacken the appropriate bo on the answer sheet with a # pencil. o not
Trigonometry Unit 5. Reflect previous TEST mark, Overall mark now. Looking back, what can you improve upon?
 1 U n i t 5 11C Date: Name: Tentative TEST date Trigonometry Unit 5 Reflect previous TEST mark, Overall mark now. Looking back, what can you improve upon? Learning Goals/Success Criteria Use the following
1 U n i t 5 11C Date: Name: Tentative TEST date Trigonometry Unit 5 Reflect previous TEST mark, Overall mark now. Looking back, what can you improve upon? Learning Goals/Success Criteria Use the following
Special Mathematics Notes
 Special Mathematics Notes Tetbook: Classroom Mathematics Stds 9 & 10 CHAPTER 6 Trigonometr Trigonometr is a stud of measurements of sides of triangles as related to the angles, and the application of this
Special Mathematics Notes Tetbook: Classroom Mathematics Stds 9 & 10 CHAPTER 6 Trigonometr Trigonometr is a stud of measurements of sides of triangles as related to the angles, and the application of this
Practice Lesson 11-1 Practice Algebra 1 Chapter 11 "256 "32 "96. "65 "2a "13. "48n. "6n 3 "180. "25x 2 "48 "10 "60 "12. "8x 6 y 7.
 Practice 11-1 Simplifying Radicals Simplify each radical epression. 1. "32 2. "22? "8 3. "147 4. 17 5. "a 2 b 5 Ä 144 6. 2 "256 7. "80 8. "27 9. 10. 8 "6 "32 "7 "96 11. "12 4 12. 13. "200 14. 12 15. "15?
Practice 11-1 Simplifying Radicals Simplify each radical epression. 1. "32 2. "22? "8 3. "147 4. 17 5. "a 2 b 5 Ä 144 6. 2 "256 7. "80 8. "27 9. 10. 8 "6 "32 "7 "96 11. "12 4 12. 13. "200 14. 12 15. "15?
1.1 Angles, Degrees, and Arcs
 MA140 Trig 2015 Homework p. 1 Name: 1.1 Angles, Degrees, and Arcs Find the fraction of a counterclockwise revolution that will form an angle with the indicated number of degrees. 3(a). 45 3(b). 150 3(c).
MA140 Trig 2015 Homework p. 1 Name: 1.1 Angles, Degrees, and Arcs Find the fraction of a counterclockwise revolution that will form an angle with the indicated number of degrees. 3(a). 45 3(b). 150 3(c).
Lesson 1: Trigonometry Angles and Quadrants
 Trigonometry Lesson 1: Trigonometry Angles and Quadrants An angle of rotation can be determined by rotating a ray about its endpoint or. The starting position of the ray is the side of the angle. The position
Trigonometry Lesson 1: Trigonometry Angles and Quadrants An angle of rotation can be determined by rotating a ray about its endpoint or. The starting position of the ray is the side of the angle. The position
~ 1 ~ Geometry 2 nd Semester Review Find the value for the variable for each of the following situations
 Geometry nd Semester Review 018 Find the value for the variable for each of the following situations. 7. 400 m 1. 7 8. y. 8.9 cm 0 0 9.. 19 6 60 1 11 10. 45 4. 58 5 11. 5. 11 6. 18 1 slide 4.1 meters long
Geometry nd Semester Review 018 Find the value for the variable for each of the following situations. 7. 400 m 1. 7 8. y. 8.9 cm 0 0 9.. 19 6 60 1 11 10. 45 4. 58 5 11. 5. 11 6. 18 1 slide 4.1 meters long
PRACTICE PROBLEMS CH 8 and Proofs
 GEOM PRACTICE PROBLEMS CH 8 and Proofs Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the length of the missing side. The triangle is not drawn to
GEOM PRACTICE PROBLEMS CH 8 and Proofs Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the length of the missing side. The triangle is not drawn to
Graph and Write Equations of Ellipses. You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas and circles. You will graph and write equations of ellipses.
 TEKS 9.4 a.5, A.5.B, A.5.C Before Now Graph and Write Equations of Ellipses You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas and circles. You will graph and write equations of ellipses. Wh? So ou can model
TEKS 9.4 a.5, A.5.B, A.5.C Before Now Graph and Write Equations of Ellipses You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas and circles. You will graph and write equations of ellipses. Wh? So ou can model
Math 0200 Final Exam Review Questions
 Math 000 Final Eam Review Questions 1. Simplif: 4 8i + 8 ( 7). Simplif: 11 ( 9) + 6(10 4) + 4. Simplif ( 5 + 7) ( ) 8 6 4. Simplif: (4 ) 9 i 5. Simplif: 4 7 6. Evaluate 4 + 5 when = and = Write each of
Math 000 Final Eam Review Questions 1. Simplif: 4 8i + 8 ( 7). Simplif: 11 ( 9) + 6(10 4) + 4. Simplif ( 5 + 7) ( ) 8 6 4. Simplif: (4 ) 9 i 5. Simplif: 4 7 6. Evaluate 4 + 5 when = and = Write each of
Math 123 Summary of Important Algebra & Trigonometry Concepts Chapter 1 & Appendix D, Stewart, Calculus Early Transcendentals
 Math Summar of Important Algebra & Trigonometr Concepts Chapter & Appendi D, Stewart, Calculus Earl Transcendentals Function a rule that assigns to each element in a set D eactl one element, called f (
Math Summar of Important Algebra & Trigonometr Concepts Chapter & Appendi D, Stewart, Calculus Earl Transcendentals Function a rule that assigns to each element in a set D eactl one element, called f (
Glossary. Also available at BigIdeasMath.com: multi-language glossary vocabulary flash cards
 Glossar This student friendl glossar is designed to be a reference for ke vocabular, properties, and mathematical terms. Several of the entries include a short eample to aid our understanding of important
Glossar This student friendl glossar is designed to be a reference for ke vocabular, properties, and mathematical terms. Several of the entries include a short eample to aid our understanding of important
November 14, Special Right Triangles Triangle Theorem: The length of the hypotenuse is times the length of a leg.
 November 14, 2013 5-1Special Right Triangles 1. 45 0-45 0-90 0 Triangle Theorem: The length of the hpotenuse is times the length of a leg. 3. Find the missing measures. e) If BC = 14 inches, find AC if
November 14, 2013 5-1Special Right Triangles 1. 45 0-45 0-90 0 Triangle Theorem: The length of the hpotenuse is times the length of a leg. 3. Find the missing measures. e) If BC = 14 inches, find AC if
Math 122 Final Review Guide
 Math 122 Final Review Guide Some questions are a combination of ideas from more than one section. Listed are the main sections that a question relates to. 5.4 1. Convert 97 to radians. 5.3 2. If 1035 is
Math 122 Final Review Guide Some questions are a combination of ideas from more than one section. Listed are the main sections that a question relates to. 5.4 1. Convert 97 to radians. 5.3 2. If 1035 is
MPE Review Section II: Trigonometry
 MPE Review Section II: Trigonometry Review similar triangles, right triangles, and the definition of the sine, cosine and tangent functions of angles of a right triangle In particular, recall that the
MPE Review Section II: Trigonometry Review similar triangles, right triangles, and the definition of the sine, cosine and tangent functions of angles of a right triangle In particular, recall that the
Fair Game Review. Chapter 10
 Name Date Chapter 0 Evaluate the expression. Fair Game Review. 9 +. + 6. 8 +. 9 00. ( 9 ) 6. 6 ( + ) 7. 6 6 8. 9 6 x 9. The number of visits to a website can be modeled b = +, where is hundreds of visits
Name Date Chapter 0 Evaluate the expression. Fair Game Review. 9 +. + 6. 8 +. 9 00. ( 9 ) 6. 6 ( + ) 7. 6 6 8. 9 6 x 9. The number of visits to a website can be modeled b = +, where is hundreds of visits
NOTES Show all necessary work. You are not allowed to use your unit circle on the test. The test will include a non-calculator portion
 Algebra Trig hapter 1 Review Problems omplete the following problems on a separate piece of paper. NOTES Show all necessary work. You are not allowed to use your unit circle on the test. The test will
Algebra Trig hapter 1 Review Problems omplete the following problems on a separate piece of paper. NOTES Show all necessary work. You are not allowed to use your unit circle on the test. The test will
4. Find the areas contained in the shapes. 7. Find the areas contained in the shapes.
 Geometry Name: Composite Area I Worksheet Period: Date: 4. Find the areas contained in the shapes. 7. Find the areas contained in the shapes. 4 mm 2 mm 2 mm 4 cm 3 cm 6 cm 4 cm 7 cm 9. Find the shaded
Geometry Name: Composite Area I Worksheet Period: Date: 4. Find the areas contained in the shapes. 7. Find the areas contained in the shapes. 4 mm 2 mm 2 mm 4 cm 3 cm 6 cm 4 cm 7 cm 9. Find the shaded
Chapter 2: Trigonometry
 Chapter 2: Trigonometry Section 2.1 Chapter 2: Trigonometry Section 2.1: The Tangent Ratio Sides of a Right Triangle with Respect to a Reference Angle Given a right triangle, we generally label its sides
Chapter 2: Trigonometry Section 2.1 Chapter 2: Trigonometry Section 2.1: The Tangent Ratio Sides of a Right Triangle with Respect to a Reference Angle Given a right triangle, we generally label its sides
Name Score Period Date. m = 2. Find the geometric mean of the two numbers. Copy and complete the statement.
 Chapter 6 Review Geometry Name Score Period Date Solve the proportion. 3 5 1. = m 1 3m 4 m = 2. 12 n = n 3 n = Find the geometric mean of the two numbers. Copy and complete the statement. 7 x 7? 3. 12
Chapter 6 Review Geometry Name Score Period Date Solve the proportion. 3 5 1. = m 1 3m 4 m = 2. 12 n = n 3 n = Find the geometric mean of the two numbers. Copy and complete the statement. 7 x 7? 3. 12
Use a calculator to find the value of the expression in radian measure rounded to 2 decimal places. 1 8) cos-1 6
 Math 180 - chapter 7 and 8.1-8. - New Edition - Spring 09 Name Find the value of the expression. 1) sin-1 0.5 ) tan-1-1 ) cos-1 (- ) 4) sin-1 Find the exact value of the expression. 5) sin [sin-1 (0.7)]
Math 180 - chapter 7 and 8.1-8. - New Edition - Spring 09 Name Find the value of the expression. 1) sin-1 0.5 ) tan-1-1 ) cos-1 (- ) 4) sin-1 Find the exact value of the expression. 5) sin [sin-1 (0.7)]
I. Degrees and Radians minutes equal 1 degree seconds equal 1 minute. 3. Also, 3600 seconds equal 1 degree. 3.
 0//0 I. Degrees and Radians A. A degree is a unit of angular measure equal to /80 th of a straight angle. B. A degree is broken up into minutes and seconds (in the DMS degree minute second sstem) as follows:.
0//0 I. Degrees and Radians A. A degree is a unit of angular measure equal to /80 th of a straight angle. B. A degree is broken up into minutes and seconds (in the DMS degree minute second sstem) as follows:.
9-1. The Function with Equation y = ax 2. Vocabulary. Graphing y = x 2. Lesson
 Chapter 9 Lesson 9-1 The Function with Equation = a BIG IDEA The graph of an quadratic function with equation = a, with a 0, is a parabola with verte at the origin. Vocabular parabola refl ection-smmetric
Chapter 9 Lesson 9-1 The Function with Equation = a BIG IDEA The graph of an quadratic function with equation = a, with a 0, is a parabola with verte at the origin. Vocabular parabola refl ection-smmetric
Trigonometric Ratios of Acute Angles. Evaluate reciprocal trigonometric ratios. LEARN ABOUT the Math. In ^MNP, determine the length of MN.
 Trigonometric Ratios of cute ngles GOL Evaluate reciprocal trigonometric ratios. LERN BOUT the Math P From a position some distance away from the base of a tree, Monique uses a clinometer to determine
Trigonometric Ratios of cute ngles GOL Evaluate reciprocal trigonometric ratios. LERN BOUT the Math P From a position some distance away from the base of a tree, Monique uses a clinometer to determine
Chapter 8 Resource Masters
 Chapter 8 Resource Masters CONSUMABLE WORKBOOKS Man of the worksheets contained in the Chapter Resource Masters booklets are available as consumable workbooks in both English and Spanish. ISBN10 ISBN13
Chapter 8 Resource Masters CONSUMABLE WORKBOOKS Man of the worksheets contained in the Chapter Resource Masters booklets are available as consumable workbooks in both English and Spanish. ISBN10 ISBN13
7.1 Ratios and Proportions Notes
 7.1 Ratios and Proportions Notes Ratio Proportion olve the proportions: 1. 5 = x 75 2. x 5 1 = 4 2. 2x + 1 5x 4 = 5 4. x 11 4 = 5. 4 7 = 2x + 5. = 7 x x + 1 7.1 Ratios and Proportions Notes Write and
7.1 Ratios and Proportions Notes Ratio Proportion olve the proportions: 1. 5 = x 75 2. x 5 1 = 4 2. 2x + 1 5x 4 = 5 4. x 11 4 = 5. 4 7 = 2x + 5. = 7 x x + 1 7.1 Ratios and Proportions Notes Write and
One of the most common applications of Calculus involves determining maximum or minimum values.
 8 LESSON 5- MAX/MIN APPLICATIONS (OPTIMIZATION) One of the most common applications of Calculus involves determining maimum or minimum values. Procedure:. Choose variables and/or draw a labeled figure..
8 LESSON 5- MAX/MIN APPLICATIONS (OPTIMIZATION) One of the most common applications of Calculus involves determining maimum or minimum values. Procedure:. Choose variables and/or draw a labeled figure..
GZW. How can you find exact trigonometric ratios?
 4. Special Angles Aircraft pilots often cannot see other nearb planes because of clouds, fog, or visual obstructions. Air Traffic Control uses software to track the location of aircraft to ensure that
4. Special Angles Aircraft pilots often cannot see other nearb planes because of clouds, fog, or visual obstructions. Air Traffic Control uses software to track the location of aircraft to ensure that
Geometry Midterm Exam Review 3. Square BERT is transformed to create the image B E R T, as shown.
 1. Reflect FOXY across line y = x. 3. Square BERT is transformed to create the image B E R T, as shown. 2. Parallelogram SHAQ is shown. Point E is the midpoint of segment SH. Point F is the midpoint of
1. Reflect FOXY across line y = x. 3. Square BERT is transformed to create the image B E R T, as shown. 2. Parallelogram SHAQ is shown. Point E is the midpoint of segment SH. Point F is the midpoint of
Geometry Honors Final Exam Review June 2018
 Geometry Honors Final Exam Review June 2018 1. Determine whether 128 feet, 136 feet, and 245 feet can be the lengths of the sides of a triangle. 2. Casey has a 13-inch television and a 52-inch television
Geometry Honors Final Exam Review June 2018 1. Determine whether 128 feet, 136 feet, and 245 feet can be the lengths of the sides of a triangle. 2. Casey has a 13-inch television and a 52-inch television
