Process Algebra CSP A Technique to Model Concurrent Programs
|
|
|
- Loren Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Process Algebr CSP A Technique to Model Concurrent Progrms Jnury 15, 2002 Hui Shi
2 1 Contents CSP-Processes Opertionl Semntics Trnsition systems nd stte mchines Bisimultion Firing rules for CSP Model-Checker FDR Denottionl Semntics Specifiction nd Refinement
3 2 Semntic pproches to CSP Opertionl semntics inteprets CSP processes s trnsition digrms, with visible nd invisivle ctions for moving between vrious progrm sttes. Denottionl semntics mps CSP into some bstrct models: trces, filures nd filures/divergences. Algebric semntics is defined by set of lgebric lws, from which process equivlence between CSP processes cn be derived.
4 Opertionl Semntics
5 Opertionl Semntics 4 Trnsition systems nd stte mchines Lbelled Trnsition System (LTD) set of nodes s process sttes strting node n 0 for ech Σ,, reltion between nodes, where Σ, = Σ {, } Σ is the lphbet of ll communictions of process
6 Opertionl Semntics 5 A b B D C E Exmple 1 (A lbelled trnsition system)
7 Opertionl Semntics 6 Strong bisimultion Definition 1 (Strong Bisimultion) IF S is n LTS, the reltion R on the set of nodes S of S is sid to be strong bisimultion if, nd only if, both the following hold: n 1, n 2, m 1 S. x Σ,. n 1 Rn 2 n 1 x m1 m 2 S.n 2 x m2 m 1 Rm 2 n 1, n 2, m 2 S. x Σ,. n 1 Rn 2 n 2 x m2 m 1 S.n 1 x m1 m 1 Rm 2 Two nodes in S re sid to be bisimilr if there is ny bisimultion which reltes them.
8 Opertionl Semntics 7 A X B C Y E D G Z F Exmple 2 (Bisimultion equivlence)
9 Opertionl Semntics 8 Firing rules for CSP Foundmentl opertors Skip Ω Ω denotes ny terminted process e P where, subs(,e,p) ( comms(e)) comms(e) is the set of communiction described by e subs(, e, P) is the result of substituting the prt of for ech identifier in P bound by e P Q P P Q Q
10 Opertionl Semntics 9 µ p.p P[µ p.p/p] P P Q P P Q Q P Q Q P Q P P P Q P ( ) Q Q P Q Q ( ) Exmple 3 ( P b Q nd P b Q)
11 Opertionl Semntics 10 Prllel opertors P P P Q P Q X X Q Q P Q P X X Q P P P Q P Q ( Σ\X ) Q Q P Q P Q ( Σ\X ) X X X X P P Q P Q P X X Q Q ( X ) P X P Q P Ω Q X P X Q Q P Ω Q X Ω Ω Ω X Exercise: Derive the trnsitions of the process SVAR(0) {red,write} (USER(1) USER(2))
12 Opertionl Semntics 11 Hiding nd renming P P\B x P x P \B (x B { }) P P P\B Ω P P\B P P \B ( B) P P P[ R ] P [ R ] P P[ R ] Ω P P P b ( R b) P[ R ] P [ R ] Sequentil composition P x P P; Q x P ; Q (x ) P.P P P; Q Q Time-out P P P Q P Q P P P Q P ( ) P Q Q
13 Opertionl Semntics 12 P b b b b Q P Q Exmple 4 (P Q nd (P Stop) Q ) P = P Q = b Q
14 Opertionl Semntics 13 Exercise: Derive the trnsitions of the following process: COPY >> COPY = (COPY [ right/mid ] COPY [ left/mid ]) \ {mid} {mid} where COPY = µ p.left?x right.x p
15 Opertionl Semntics 14 The Model-Checker FDR The bsic concept of FDR FDR (Filures-Divergence-Refinemen) is model-checking tool for lbelled trnsition systems with foundtions in CSP bsed minly on explict model-checking techniques. Explict model-checking techniques: the check proceeds by recursive induction which fully expnds the rechble stte-spce of the two systems nd visits ech pir of supposedly corresponding stte in turn.
16 Opertionl Semntics 15 The bsic opertion of FDR Clculte the opertionl semntics using firing rules. Normlise the specifiction process into LTS in which ll sttes re semnticlly distinct bsed minly on the strong bisimultion. Checke process properties in terms of refinemen reltions.
17 Opertionl Semntics 16 Exmple 5 (Model-checking) A concurrent system is dedlocked if no component cn mke ny progress, generlly becuse ech is witing for communiction with others. A concurrent system cn livelock, when network communictes infinitely internlly without ny component communicting externlly. Some exmples Five dining philosophers (dedlock check) Producer-consumer system with hiding (livelock check) Buffer (refinement check)
Bisimulation. R.J. van Glabbeek
 Bisimultion R.J. vn Glbbeek NICTA, Sydney, Austrli. School of Computer Science nd Engineering, The University of New South Wles, Sydney, Austrli. Computer Science Deprtment, Stnford University, CA 94305-9045,
Bisimultion R.J. vn Glbbeek NICTA, Sydney, Austrli. School of Computer Science nd Engineering, The University of New South Wles, Sydney, Austrli. Computer Science Deprtment, Stnford University, CA 94305-9045,
Strong Bisimulation. Overview. References. Actions Labeled transition system Transition semantics Simulation Bisimulation
 Strong Bisimultion Overview Actions Lbeled trnsition system Trnsition semntics Simultion Bisimultion References Robin Milner, Communiction nd Concurrency Robin Milner, Communicting nd Mobil Systems 32
Strong Bisimultion Overview Actions Lbeled trnsition system Trnsition semntics Simultion Bisimultion References Robin Milner, Communiction nd Concurrency Robin Milner, Communicting nd Mobil Systems 32
Hennessy-Milner Logic 1.
 Hennessy-Milner Logic 1. Colloquium in honor of Robin Milner. Crlos Olrte. Pontifici Universidd Jverin 28 April 2010. 1 Bsed on the tlks: [1,2,3] Prof. Robin Milner (R.I.P). LIX, Ecole Polytechnique. Motivtion
Hennessy-Milner Logic 1. Colloquium in honor of Robin Milner. Crlos Olrte. Pontifici Universidd Jverin 28 April 2010. 1 Bsed on the tlks: [1,2,3] Prof. Robin Milner (R.I.P). LIX, Ecole Polytechnique. Motivtion
Summer School Verification Technology, Systems & Applications
 VTSA 2011 Summer School Verifiction Technology, Systems & Applictions 4th edition since 2008: Liège (Belgium), Sep. 19 23, 2011 free prticiption, limited number of prticipnts ppliction dedline: July 22,
VTSA 2011 Summer School Verifiction Technology, Systems & Applictions 4th edition since 2008: Liège (Belgium), Sep. 19 23, 2011 free prticiption, limited number of prticipnts ppliction dedline: July 22,
Notes on specifying systems in EST
 Robert Meolic, Ttjn Kpus: Notes on specifying systems in EST 1 Notes on specifying systems in EST Robert Meolic, Ttjn Kpus Fculty of EE & CS University of Mribor Robert Meolic, Ttjn Kpus: Notes on specifying
Robert Meolic, Ttjn Kpus: Notes on specifying systems in EST 1 Notes on specifying systems in EST Robert Meolic, Ttjn Kpus Fculty of EE & CS University of Mribor Robert Meolic, Ttjn Kpus: Notes on specifying
Semantic reachability for simple process algebras. Richard Mayr. Abstract
 Semntic rechbility for simple process lgebrs Richrd Myr Abstrct This pper is n pproch to combine the rechbility problem with semntic notions like bisimultion equivlence. It dels with questions of the following
Semntic rechbility for simple process lgebrs Richrd Myr Abstrct This pper is n pproch to combine the rechbility problem with semntic notions like bisimultion equivlence. It dels with questions of the following
SAT-Solving in CSP Trace Refinement
 ST-Solving in CSP Trce Refinement Hristin Plikrev, Joël Ouknine nd. W. Roscoe Deprtment of Computer Science, Oxford University, UK bstrct In this pper, we ddress the problem of pplying ST-bsed bounded
ST-Solving in CSP Trce Refinement Hristin Plikrev, Joël Ouknine nd. W. Roscoe Deprtment of Computer Science, Oxford University, UK bstrct In this pper, we ddress the problem of pplying ST-bsed bounded
Semantic Reachability. Richard Mayr. Institut fur Informatik. Technische Universitat Munchen. Arcisstr. 21, D Munchen, Germany E. N. T. C. S.
 URL: http://www.elsevier.nl/locte/entcs/volume6.html?? pges Semntic Rechbility Richrd Myr Institut fur Informtik Technische Universitt Munchen Arcisstr. 21, D-80290 Munchen, Germny e-mil: myrri@informtik.tu-muenchen.de
URL: http://www.elsevier.nl/locte/entcs/volume6.html?? pges Semntic Rechbility Richrd Myr Institut fur Informtik Technische Universitt Munchen Arcisstr. 21, D-80290 Munchen, Germny e-mil: myrri@informtik.tu-muenchen.de
Concepts of Concurrent Computation Spring 2015 Lecture 9: Petri Nets
 Concepts of Concurrent Computtion Spring 205 Lecture 9: Petri Nets Sebstin Nnz Chris Poskitt Chir of Softwre Engineering Petri nets Petri nets re mthemticl models for describing systems with concurrency
Concepts of Concurrent Computtion Spring 205 Lecture 9: Petri Nets Sebstin Nnz Chris Poskitt Chir of Softwre Engineering Petri nets Petri nets re mthemticl models for describing systems with concurrency
Temporal logic CTL : syntax. Communication and Concurrency Lecture 6. Φ ::= tt ff Φ 1 Φ 2 Φ 1 Φ 2 [K]Φ K Φ AG Φ EF Φ AF Φ EG Φ A formula can be
![Temporal logic CTL : syntax. Communication and Concurrency Lecture 6. Φ ::= tt ff Φ 1 Φ 2 Φ 1 Φ 2 [K]Φ K Φ AG Φ EF Φ AF Φ EG Φ A formula can be Temporal logic CTL : syntax. Communication and Concurrency Lecture 6. Φ ::= tt ff Φ 1 Φ 2 Φ 1 Φ 2 [K]Φ K Φ AG Φ EF Φ AF Φ EG Φ A formula can be](/thumbs/93/111158524.jpg) Temporl logic CTL : syntx Communiction nd Concurrency Lecture 6 Colin Stirling (cps) Φ ::= tt ff Φ 1 Φ Φ 1 Φ [K]Φ K Φ A formul cn be School of Informtics 7th October 013 Temporl logic CTL : syntx Temporl
Temporl logic CTL : syntx Communiction nd Concurrency Lecture 6 Colin Stirling (cps) Φ ::= tt ff Φ 1 Φ Φ 1 Φ [K]Φ K Φ A formul cn be School of Informtics 7th October 013 Temporl logic CTL : syntx Temporl
Review of Control Flow Semantics
 Review of Control Flow Semntics Riccrdo Pucell Deprtment of Computer Science Cornell University April 19, 2001 I hve to dmit, I ws looking forwrd to reviewing this book. It nswered wht ws for me 6-yer
Review of Control Flow Semntics Riccrdo Pucell Deprtment of Computer Science Cornell University April 19, 2001 I hve to dmit, I ws looking forwrd to reviewing this book. It nswered wht ws for me 6-yer
Extending CSP with tests for availability
 Communicting rocess Architectures 2009 eter Welch, Hermn Roebbers nd Tobe Announced (Eds.) IOS ress, 2009 1 c 2009 The uthors nd IOS ress. All rights reserved. 1 Extending CS with tests for vilbility Gvin
Communicting rocess Architectures 2009 eter Welch, Hermn Roebbers nd Tobe Announced (Eds.) IOS ress, 2009 1 c 2009 The uthors nd IOS ress. All rights reserved. 1 Extending CS with tests for vilbility Gvin
Science of Computer Programming
 Science of Computer Progrmming 81 (2014) 3 52 Contents lists vilble t ScienceDirect Science of Computer Progrmming journl homepge: www.elsevier.com/locte/scico CSP-bsed counter bstrction for systems with
Science of Computer Progrmming 81 (2014) 3 52 Contents lists vilble t ScienceDirect Science of Computer Progrmming journl homepge: www.elsevier.com/locte/scico CSP-bsed counter bstrction for systems with
1 Introduction. Abstract
 LANGUAGES FOR CONCURRENCY Ctusci Plmidessi INRIA nd LIX, École Polytechnique ctusci@lix.polytechnique.fr Frnk D. Vlenci CNRS nd LIX, École Polytechnique frnk.vlenci@lix.polytechnique.fr Abstrct This essy
LANGUAGES FOR CONCURRENCY Ctusci Plmidessi INRIA nd LIX, École Polytechnique ctusci@lix.polytechnique.fr Frnk D. Vlenci CNRS nd LIX, École Polytechnique frnk.vlenci@lix.polytechnique.fr Abstrct This essy
An Introduction to Bisimulation and Coinduction
 An Introduction to Bisimultion nd Coinduction Dvide Sngiorgi Focus Tem, INRIA (Frnce)/University of Bologn (Itly) Emil: Dvide.Sngiorgi@cs.unibo.it http://www.cs.unibo.it/ sngio/ Microsoft Reserch Summer
An Introduction to Bisimultion nd Coinduction Dvide Sngiorgi Focus Tem, INRIA (Frnce)/University of Bologn (Itly) Emil: Dvide.Sngiorgi@cs.unibo.it http://www.cs.unibo.it/ sngio/ Microsoft Reserch Summer
Probabilistic Model Checking Michaelmas Term Dr. Dave Parker. Department of Computer Science University of Oxford
 Probbilistic Model Checking Michelms Term 2011 Dr. Dve Prker Deprtment of Computer Science University of Oxford Long-run properties Lst lecture: regulr sfety properties e.g. messge filure never occurs
Probbilistic Model Checking Michelms Term 2011 Dr. Dve Prker Deprtment of Computer Science University of Oxford Long-run properties Lst lecture: regulr sfety properties e.g. messge filure never occurs
CS 267: Automated Verification. Lecture 8: Automata Theoretic Model Checking. Instructor: Tevfik Bultan
 CS 267: Automted Verifiction Lecture 8: Automt Theoretic Model Checking Instructor: Tevfik Bultn LTL Properties Büchi utomt [Vrdi nd Wolper LICS 86] Büchi utomt: Finite stte utomt tht ccept infinite strings
CS 267: Automted Verifiction Lecture 8: Automt Theoretic Model Checking Instructor: Tevfik Bultn LTL Properties Büchi utomt [Vrdi nd Wolper LICS 86] Büchi utomt: Finite stte utomt tht ccept infinite strings
Refined interfaces for compositional verification
 Refined interfces for compositionl verifiction Frédéric Lng INRI Rhône-lpes http://www.inrilpes.fr/vsy Motivtion Enumertive verifiction of concurrent systems Prllel composition of synchronous processes
Refined interfces for compositionl verifiction Frédéric Lng INRI Rhône-lpes http://www.inrilpes.fr/vsy Motivtion Enumertive verifiction of concurrent systems Prllel composition of synchronous processes
Introduction to spefication and verification Lecture Notes, autumn 2011
 Introduction to spefiction nd verifiction Lecture Notes, utumn 2011 Timo Krvi UNIVERSITY OF HELSINKI FINLAND Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 The strting point............................ 1 1.2 Globl stte
Introduction to spefiction nd verifiction Lecture Notes, utumn 2011 Timo Krvi UNIVERSITY OF HELSINKI FINLAND Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 The strting point............................ 1 1.2 Globl stte
Designing and Understanding the Behaviour of Systems
 Designing nd Understnding the Behviour of Systems Jn Friso Groote & Michel Reniers Deprtment of Computer Science Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven Emil: J.F.Groote@tue.nl, M.A.Reniers@tue.nl
Designing nd Understnding the Behviour of Systems Jn Friso Groote & Michel Reniers Deprtment of Computer Science Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven Emil: J.F.Groote@tue.nl, M.A.Reniers@tue.nl
Process Algebras for Petri Nets
 Roberto Gorrieri Process Algebrs for Petri Nets The Alphbetiztion of Distributed Systems Roberto Gorrieri Diprtimento di Informtic - Scienz e Ingegneri Università di Bologn Bologn, Itly ISSN 1431-2654
Roberto Gorrieri Process Algebrs for Petri Nets The Alphbetiztion of Distributed Systems Roberto Gorrieri Diprtimento di Informtic - Scienz e Ingegneri Università di Bologn Bologn, Itly ISSN 1431-2654
Automata Theory 101. Introduction. Outline. Introduction Finite Automata Regular Expressions ω-automata. Ralf Huuck.
 Outline Automt Theory 101 Rlf Huuck Introduction Finite Automt Regulr Expressions ω-automt Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 1 Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 2 Acknowledgement Some slides re sed on Wolfgng Thoms excellent
Outline Automt Theory 101 Rlf Huuck Introduction Finite Automt Regulr Expressions ω-automt Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 1 Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 2 Acknowledgement Some slides re sed on Wolfgng Thoms excellent
A tutorial on sequential functions
 A tutoril on sequentil functions Jen-Éric Pin LIAFA, CNRS nd University Pris 7 30 Jnury 2006, CWI, Amsterdm Outline (1) Sequentil functions (2) A chrcteriztion of sequentil trnsducers (3) Miniml sequentil
A tutoril on sequentil functions Jen-Éric Pin LIAFA, CNRS nd University Pris 7 30 Jnury 2006, CWI, Amsterdm Outline (1) Sequentil functions (2) A chrcteriztion of sequentil trnsducers (3) Miniml sequentil
Process Algebra with Recursive Operations
 Process Algebr with Recursive Opertions Jn Bergstr 2,3 Wn Fokkink 1 Albn Ponse 1,3 1 CWI Kruisln 413, 1098 SJ Amsterdm, The Netherlnds url: http://www.cwi.nl/ 2 Utrecht University, Deprtment of Philosophy
Process Algebr with Recursive Opertions Jn Bergstr 2,3 Wn Fokkink 1 Albn Ponse 1,3 1 CWI Kruisln 413, 1098 SJ Amsterdm, The Netherlnds url: http://www.cwi.nl/ 2 Utrecht University, Deprtment of Philosophy
19 Optimal behavior: Game theory
 Intro. to Artificil Intelligence: Dle Schuurmns, Relu Ptrscu 1 19 Optiml behvior: Gme theory Adversril stte dynmics hve to ccount for worst cse Compute policy π : S A tht mximizes minimum rewrd Let S (,
Intro. to Artificil Intelligence: Dle Schuurmns, Relu Ptrscu 1 19 Optiml behvior: Gme theory Adversril stte dynmics hve to ccount for worst cse Compute policy π : S A tht mximizes minimum rewrd Let S (,
Kleene Theorems for Free Choice Nets Labelled with Distributed Alphabets
 Kleene Theorems for Free Choice Nets Lbelled with Distributed Alphbets Rmchndr Phwde Indin Institute of Technology Dhrwd, Dhrwd 580011, Indi Emil: prb@iitdh.c.in Abstrct. We provided [15] expressions for
Kleene Theorems for Free Choice Nets Lbelled with Distributed Alphbets Rmchndr Phwde Indin Institute of Technology Dhrwd, Dhrwd 580011, Indi Emil: prb@iitdh.c.in Abstrct. We provided [15] expressions for
CS 275 Automata and Formal Language Theory
 CS 275 Automt nd Forml Lnguge Theory Course Notes Prt II: The Recognition Problem (II) Chpter II.6.: Push Down Automt Remrk: This mteril is no longer tught nd not directly exm relevnt Anton Setzer (Bsed
CS 275 Automt nd Forml Lnguge Theory Course Notes Prt II: The Recognition Problem (II) Chpter II.6.: Push Down Automt Remrk: This mteril is no longer tught nd not directly exm relevnt Anton Setzer (Bsed
State Minimization for DFAs
 Stte Minimiztion for DFAs Red K & S 2.7 Do Homework 10. Consider: Stte Minimiztion 4 5 Is this miniml mchine? Step (1): Get rid of unrechle sttes. Stte Minimiztion 6, Stte is unrechle. Step (2): Get rid
Stte Minimiztion for DFAs Red K & S 2.7 Do Homework 10. Consider: Stte Minimiztion 4 5 Is this miniml mchine? Step (1): Get rid of unrechle sttes. Stte Minimiztion 6, Stte is unrechle. Step (2): Get rid
NFAs and Regular Expressions. NFA-ε, continued. Recall. Last class: Today: Fun:
 CMPU 240 Lnguge Theory nd Computtion Spring 2019 NFAs nd Regulr Expressions Lst clss: Introduced nondeterministic finite utomt with -trnsitions Tody: Prove n NFA- is no more powerful thn n NFA Introduce
CMPU 240 Lnguge Theory nd Computtion Spring 2019 NFAs nd Regulr Expressions Lst clss: Introduced nondeterministic finite utomt with -trnsitions Tody: Prove n NFA- is no more powerful thn n NFA Introduce
Exercises with (Some) Solutions
 Exercises with (Some) Solutions Techer: Luc Tesei Mster of Science in Computer Science - University of Cmerino Contents 1 Strong Bisimultion nd HML 2 2 Wek Bisimultion 31 3 Complete Lttices nd Fix Points
Exercises with (Some) Solutions Techer: Luc Tesei Mster of Science in Computer Science - University of Cmerino Contents 1 Strong Bisimultion nd HML 2 2 Wek Bisimultion 31 3 Complete Lttices nd Fix Points
Chapter 2 Finite Automata
 Chpter 2 Finite Automt 28 2.1 Introduction Finite utomt: first model of the notion of effective procedure. (They lso hve mny other pplictions). The concept of finite utomton cn e derived y exmining wht
Chpter 2 Finite Automt 28 2.1 Introduction Finite utomt: first model of the notion of effective procedure. (They lso hve mny other pplictions). The concept of finite utomton cn e derived y exmining wht
ɛ-closure, Kleene s Theorem,
 DEGefW5wiGH2XgYMEzUKjEmtCDUsRQ4d 1 A nice pper relevnt to this course is titled The Glory of the Pst 2 NICTA Resercher, Adjunct t the Austrlin Ntionl University nd Griffith University ɛ-closure, Kleene
DEGefW5wiGH2XgYMEzUKjEmtCDUsRQ4d 1 A nice pper relevnt to this course is titled The Glory of the Pst 2 NICTA Resercher, Adjunct t the Austrlin Ntionl University nd Griffith University ɛ-closure, Kleene
Expressiveness modulo Bisimilarity of Regular Expressions with Parallel Composition (Extended Abstract)
 Expressiveness modulo Bisimilrity of Regulr Expressions with Prllel Composition (Extended Abstrct) Jos C. M. Beten Eindhoven University of Technology, The Netherlnds j.c.m.beten@tue.nl Tim Muller University
Expressiveness modulo Bisimilrity of Regulr Expressions with Prllel Composition (Extended Abstrct) Jos C. M. Beten Eindhoven University of Technology, The Netherlnds j.c.m.beten@tue.nl Tim Muller University
Conjunction on processes: Full abstraction via ready-tree semantics
 Theoreticl Computer Science 373 (2007) 19 40 www.elsevier.com/locte/tcs Conjunction on processes: Full bstrction vi redy-tree semntics Gerld Lüttgen, Wlter Vogler b, Deprtment of Computer Science, University
Theoreticl Computer Science 373 (2007) 19 40 www.elsevier.com/locte/tcs Conjunction on processes: Full bstrction vi redy-tree semntics Gerld Lüttgen, Wlter Vogler b, Deprtment of Computer Science, University
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018
 Finite Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 10 An Bove April 23rd 2018 Recp: Regulr Lnguges We cn convert between FA nd RE; Hence both FA nd RE ccept/generte regulr lnguges; More
Finite Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 10 An Bove April 23rd 2018 Recp: Regulr Lnguges We cn convert between FA nd RE; Hence both FA nd RE ccept/generte regulr lnguges; More
Lecture 9: LTL and Büchi Automata
 Lecture 9: LTL nd Büchi Automt 1 LTL Property Ptterns Quite often the requirements of system follow some simple ptterns. Sometimes we wnt to specify tht property should only hold in certin context, clled
Lecture 9: LTL nd Büchi Automt 1 LTL Property Ptterns Quite often the requirements of system follow some simple ptterns. Sometimes we wnt to specify tht property should only hold in certin context, clled
Discrete Time Process Algebra with Relative Timing
 Discrete Time Process Alger with Reltive Timing J.C.M. Beten nd M.A. Reniers Deprtment of Mthemtics nd Computing Science, Eindhoven University of Technology, P.O. Box 513, NL-5600 MB Eindhoven, The Netherlnds
Discrete Time Process Alger with Reltive Timing J.C.M. Beten nd M.A. Reniers Deprtment of Mthemtics nd Computing Science, Eindhoven University of Technology, P.O. Box 513, NL-5600 MB Eindhoven, The Netherlnds
Informe Técnico / Technical Report
 DEPARTAMENTO DE SISTEMAS INFORMÁTICOS Y COMPUTACIÓN UNIVERSIDAD POLITÉCNICA DE VALENCIA P.O. Box: 22012 E-46071 Vlenci (SPAIN) Informe Técnico / Technicl Report Ref. No.: DSIC-II/03/10 Pges: 30 Title:
DEPARTAMENTO DE SISTEMAS INFORMÁTICOS Y COMPUTACIÓN UNIVERSIDAD POLITÉCNICA DE VALENCIA P.O. Box: 22012 E-46071 Vlenci (SPAIN) Informe Técnico / Technicl Report Ref. No.: DSIC-II/03/10 Pges: 30 Title:
Introduction to ω-autamata
 Fridy 25 th Jnury, 2013 Outline From finite word utomt ω-regulr lnguge ω-utomt Nondeterministic Models Deterministic Models Two Lower Bounds Conclusion Discussion Synthesis Preliminry From finite word
Fridy 25 th Jnury, 2013 Outline From finite word utomt ω-regulr lnguge ω-utomt Nondeterministic Models Deterministic Models Two Lower Bounds Conclusion Discussion Synthesis Preliminry From finite word
Equality and Inequality in the Dataflow Algebra. A. J. Cowling
 Verifiction nd Testing Reserch Group, Deprtment of Computer Science, University of Sheffield, Regent Court, 211, Portobello Street, Sheffield, S1 4DP, United Kingdom Emil: A.Cowling @ dcs.shef.c.uk Telephone:
Verifiction nd Testing Reserch Group, Deprtment of Computer Science, University of Sheffield, Regent Court, 211, Portobello Street, Sheffield, S1 4DP, United Kingdom Emil: A.Cowling @ dcs.shef.c.uk Telephone:
Non-Deterministic Finite Automata. Fall 2018 Costas Busch - RPI 1
 Non-Deterministic Finite Automt Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet ={} q q2 1 q 0 q 3 Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 2 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet
Non-Deterministic Finite Automt Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet ={} q q2 1 q 0 q 3 Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 2 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet
Categorical approaches to bisimilarity
 Ctegoricl pproches to bisimilrity PPS seminr, IRIF, Pris 7 Jérémy Dubut Ntionl Institute of Informtics Jpnese-French Lbortory for Informtics April 2nd Jérémy Dubut (NII & JFLI) Ctegoricl pproches to bisimilrity
Ctegoricl pproches to bisimilrity PPS seminr, IRIF, Pris 7 Jérémy Dubut Ntionl Institute of Informtics Jpnese-French Lbortory for Informtics April 2nd Jérémy Dubut (NII & JFLI) Ctegoricl pproches to bisimilrity
More on automata. Michael George. March 24 April 7, 2014
 More on utomt Michel George Mrch 24 April 7, 2014 1 Automt constructions Now tht we hve forml model of mchine, it is useful to mke some generl constructions. 1.1 DFA Union / Product construction Suppose
More on utomt Michel George Mrch 24 April 7, 2014 1 Automt constructions Now tht we hve forml model of mchine, it is useful to mke some generl constructions. 1.1 DFA Union / Product construction Suppose
KNOWLEDGE-BASED AGENTS INFERENCE
 AGENTS THAT REASON LOGICALLY KNOWLEDGE-BASED AGENTS Two components: knowledge bse, nd n inference engine. Declrtive pproch to building n gent. We tell it wht it needs to know, nd It cn sk itself wht to
AGENTS THAT REASON LOGICALLY KNOWLEDGE-BASED AGENTS Two components: knowledge bse, nd n inference engine. Declrtive pproch to building n gent. We tell it wht it needs to know, nd It cn sk itself wht to
Towards Algebraic Semantics of Circus Time
 Towrds Algeric Semntics of Circus Time Kun Wei nd Jim Woodcock Deprtment of Computer Science, University of York, York, YO10 5GH, UK {kun.wei,jim.woodcock}@york.c.uk Astrct. Over the yers, the Circus fmily
Towrds Algeric Semntics of Circus Time Kun Wei nd Jim Woodcock Deprtment of Computer Science, University of York, York, YO10 5GH, UK {kun.wei,jim.woodcock}@york.c.uk Astrct. Over the yers, the Circus fmily
Complexity and Decidability of Some Equivalence-Checking Problems
 Complexity nd Decidbility of Some Equivlence-Checking Problems Zdeněk Sw Ph.D. Thesis Fculty of Electricl Engineering nd Computer Science Technicl University of Ostrv 2005 ii Acknowledgements I would like
Complexity nd Decidbility of Some Equivlence-Checking Problems Zdeněk Sw Ph.D. Thesis Fculty of Electricl Engineering nd Computer Science Technicl University of Ostrv 2005 ii Acknowledgements I would like
We will see what is meant by standard form very shortly
 THEOREM: For fesible liner progrm in its stndrd form, the optimum vlue of the objective over its nonempty fesible region is () either unbounded or (b) is chievble t lest t one extreme point of the fesible
THEOREM: For fesible liner progrm in its stndrd form, the optimum vlue of the objective over its nonempty fesible region is () either unbounded or (b) is chievble t lest t one extreme point of the fesible
Process Algebra: An Algebraic Theory of Concurrency
 Process Alger: An Algeric Theory of Concurrency Wn Fokkink Vrije Universiteit Amsterdm, Deprtment of Theoreticl Computer Science, De Boeleln 1081, 1081 HV Amsterdm, The Netherlnds wnf@cs.vu.nl Astrct.
Process Alger: An Algeric Theory of Concurrency Wn Fokkink Vrije Universiteit Amsterdm, Deprtment of Theoreticl Computer Science, De Boeleln 1081, 1081 HV Amsterdm, The Netherlnds wnf@cs.vu.nl Astrct.
Towards a Mathematical Operational Semantics
 Towrds Mthemticl Opertionl Semntics Dniele Turi Gordon Plotkin Deprtment of Computer Science Lbortory for Foundtions of Computer Science University of Edinburgh, The
Towrds Mthemticl Opertionl Semntics Dniele Turi Gordon Plotkin Deprtment of Computer Science Lbortory for Foundtions of Computer Science University of Edinburgh, The
Regular Expressions (RE) Regular Expressions (RE) Regular Expressions (RE) Regular Expressions (RE) Kleene-*
 Regulr Expressions (RE) Regulr Expressions (RE) Empty set F A RE denotes the empty set Opertion Nottion Lnguge UNIX Empty string A RE denotes the set {} Alterntion R +r L(r ) L(r ) r r Symol Alterntion
Regulr Expressions (RE) Regulr Expressions (RE) Empty set F A RE denotes the empty set Opertion Nottion Lnguge UNIX Empty string A RE denotes the set {} Alterntion R +r L(r ) L(r ) r r Symol Alterntion
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2007
 CS 188: Artificil Intelligence Spring 2007 Lecture 3: Queue-Bsed Serch 1/23/2007 Srini Nrynn UC Berkeley Mny slides over the course dpted from Dn Klein, Sturt Russell or Andrew Moore Announcements Assignment
CS 188: Artificil Intelligence Spring 2007 Lecture 3: Queue-Bsed Serch 1/23/2007 Srini Nrynn UC Berkeley Mny slides over the course dpted from Dn Klein, Sturt Russell or Andrew Moore Announcements Assignment
Minimal DFA. minimal DFA for L starting from any other
 Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
a,b a 1 a 2 a 3 a,b 1 a,b a,b 2 3 a,b a,b a 2 a,b CS Determinisitic Finite Automata 1
 CS4 45- Determinisitic Finite Automt -: Genertors vs. Checkers Regulr expressions re one wy to specify forml lnguge String Genertor Genertes strings in the lnguge Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) re nother
CS4 45- Determinisitic Finite Automt -: Genertors vs. Checkers Regulr expressions re one wy to specify forml lnguge String Genertor Genertes strings in the lnguge Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) re nother
CSE : Exam 3-ANSWERS, Spring 2011 Time: 50 minutes
 CSE 260-002: Exm 3-ANSWERS, Spring 20 ime: 50 minutes Nme: his exm hs 4 pges nd 0 prolems totling 00 points. his exm is closed ook nd closed notes.. Wrshll s lgorithm for trnsitive closure computtion is
CSE 260-002: Exm 3-ANSWERS, Spring 20 ime: 50 minutes Nme: his exm hs 4 pges nd 0 prolems totling 00 points. his exm is closed ook nd closed notes.. Wrshll s lgorithm for trnsitive closure computtion is
Real-time Concepts for a Formal Specification Language for Software / Hardware Systems
 1 Rel-time Concepts for Forml Specifiction Lnguge for Softwre / Hrdwre Systems M.C.W. Geilen nd J.P.M. Voeten Abstrct Incresingly complex systems re being designed tht consist of concurrently operting
1 Rel-time Concepts for Forml Specifiction Lnguge for Softwre / Hrdwre Systems M.C.W. Geilen nd J.P.M. Voeten Abstrct Incresingly complex systems re being designed tht consist of concurrently operting
Chapter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automata. Formal Language, chapter 5, slide 1
 Chpter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automt Forml Lnguge, chpter 5, slide 1 1 A DFA hs exctly one trnsition from every stte on every symol in the lphet. By relxing this requirement we get relted ut more
Chpter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automt Forml Lnguge, chpter 5, slide 1 1 A DFA hs exctly one trnsition from every stte on every symol in the lphet. By relxing this requirement we get relted ut more
Bisimulation, Games & Hennessy Milner logic
 Bisimultion, Gmes & Hennessy Milner logi Leture 1 of Modelli Mtemtii dei Proessi Conorrenti Pweł Soboiński Univeristy of Southmpton, UK Bisimultion, Gmes & Hennessy Milner logi p.1/32 Clssil lnguge theory
Bisimultion, Gmes & Hennessy Milner logi Leture 1 of Modelli Mtemtii dei Proessi Conorrenti Pweł Soboiński Univeristy of Southmpton, UK Bisimultion, Gmes & Hennessy Milner logi p.1/32 Clssil lnguge theory
Administrivia CSE 190: Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction
 Administrivi CSE 190: Reinforcement Lerning: An Introduction Any emil sent to me bout the course should hve CSE 190 in the subject line! Chpter 4: Dynmic Progrmming Acknowledgment: A good number of these
Administrivi CSE 190: Reinforcement Lerning: An Introduction Any emil sent to me bout the course should hve CSE 190 in the subject line! Chpter 4: Dynmic Progrmming Acknowledgment: A good number of these
Event Structures for Arbitrary Disruption
 Fundment Informtice XX (2005) 1 28 1 IOS Press Event Structures for Arbitrry Disruption Hrld Fecher Christin Albrecht Universität zu Kiel Technische Fkultät, Institut für Informtik, Hermnn-Rodewldstr.
Fundment Informtice XX (2005) 1 28 1 IOS Press Event Structures for Arbitrry Disruption Hrld Fecher Christin Albrecht Universität zu Kiel Technische Fkultät, Institut für Informtik, Hermnn-Rodewldstr.
Uninformed Search Lecture 4
 Lecture 4 Wht re common serch strtegies tht operte given only serch problem? How do they compre? 1 Agend A quick refresher DFS, BFS, ID-DFS, UCS Unifiction! 2 Serch Problem Formlism Defined vi the following
Lecture 4 Wht re common serch strtegies tht operte given only serch problem? How do they compre? 1 Agend A quick refresher DFS, BFS, ID-DFS, UCS Unifiction! 2 Serch Problem Formlism Defined vi the following
How to simulate Turing machines by invertible one-dimensional cellular automata
 How to simulte Turing mchines by invertible one-dimensionl cellulr utomt Jen-Christophe Dubcq Déprtement de Mthémtiques et d Informtique, École Normle Supérieure de Lyon, 46, llée d Itlie, 69364 Lyon Cedex
How to simulte Turing mchines by invertible one-dimensionl cellulr utomt Jen-Christophe Dubcq Déprtement de Mthémtiques et d Informtique, École Normle Supérieure de Lyon, 46, llée d Itlie, 69364 Lyon Cedex
dierent process-lgebric theories in order to cpture dierent spects of system behvior; however, ech such formlism generlly includes the following chrct
 Process Algebr Rnce Clevelnd Deprtment of Computer Science P.O. Box 7534 North Crolin Stte University Rleigh, NC 27695-7534 USA Scott A. Smolk Deprtment of Computer Science Stte University of New York
Process Algebr Rnce Clevelnd Deprtment of Computer Science P.O. Box 7534 North Crolin Stte University Rleigh, NC 27695-7534 USA Scott A. Smolk Deprtment of Computer Science Stte University of New York
Let's start with an example:
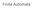 Finite Automt Let's strt with n exmple: Here you see leled circles tht re sttes, nd leled rrows tht re trnsitions. One of the sttes is mrked "strt". One of the sttes hs doule circle; this is terminl stte
Finite Automt Let's strt with n exmple: Here you see leled circles tht re sttes, nd leled rrows tht re trnsitions. One of the sttes is mrked "strt". One of the sttes hs doule circle; this is terminl stte
Acceptance Sampling by Attributes
 Introduction Acceptnce Smpling by Attributes Acceptnce smpling is concerned with inspection nd decision mking regrding products. Three spects of smpling re importnt: o Involves rndom smpling of n entire
Introduction Acceptnce Smpling by Attributes Acceptnce smpling is concerned with inspection nd decision mking regrding products. Three spects of smpling re importnt: o Involves rndom smpling of n entire
Reinforcement Learning
 Reinforcement Lerning Tom Mitchell, Mchine Lerning, chpter 13 Outline Introduction Comprison with inductive lerning Mrkov Decision Processes: the model Optiml policy: The tsk Q Lerning: Q function Algorithm
Reinforcement Lerning Tom Mitchell, Mchine Lerning, chpter 13 Outline Introduction Comprison with inductive lerning Mrkov Decision Processes: the model Optiml policy: The tsk Q Lerning: Q function Algorithm
Draft. Draft. Introduction to Coalgebra. Towards Mathematics of States and Observations. Bart Jacobs. Draft Copy.
 1 Introduction to Colgebr. Towrds Mthemtics of Sttes nd Observtions Brt Jcobs Institute for Computing nd Informtion Sciences, Rdboud University Nijmegen, P.O. Box 9010, 6500 GL Nijmegen, The Netherlnds.
1 Introduction to Colgebr. Towrds Mthemtics of Sttes nd Observtions Brt Jcobs Institute for Computing nd Informtion Sciences, Rdboud University Nijmegen, P.O. Box 9010, 6500 GL Nijmegen, The Netherlnds.
Designing finite automata II
 Designing finite utomt II Prolem: Design DFA A such tht L(A) consists of ll strings of nd which re of length 3n, for n = 0, 1, 2, (1) Determine wht to rememer out the input string Assign stte to ech of
Designing finite utomt II Prolem: Design DFA A such tht L(A) consists of ll strings of nd which re of length 3n, for n = 0, 1, 2, (1) Determine wht to rememer out the input string Assign stte to ech of
Coalgebra, Lecture 15: Equations for Deterministic Automata
 Colger, Lecture 15: Equtions for Deterministic Automt Julin Slmnc (nd Jurrin Rot) Decemer 19, 2016 In this lecture, we will study the concept of equtions for deterministic utomt. The notes re self contined
Colger, Lecture 15: Equtions for Deterministic Automt Julin Slmnc (nd Jurrin Rot) Decemer 19, 2016 In this lecture, we will study the concept of equtions for deterministic utomt. The notes re self contined
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2010
 CS 188: Artificil Intelligence Fll 2010 Lecture 18: Decision Digrms 10/28/2010 Dn Klein C Berkeley Vlue of Informtion 1 Decision Networks ME: choose the ction which mximizes the expected utility given
CS 188: Artificil Intelligence Fll 2010 Lecture 18: Decision Digrms 10/28/2010 Dn Klein C Berkeley Vlue of Informtion 1 Decision Networks ME: choose the ction which mximizes the expected utility given
MA 124 January 18, Derivatives are. Integrals are.
 MA 124 Jnury 18, 2018 Prof PB s one-minute introduction to clculus Derivtives re. Integrls re. In Clculus 1, we lern limits, derivtives, some pplictions of derivtives, indefinite integrls, definite integrls,
MA 124 Jnury 18, 2018 Prof PB s one-minute introduction to clculus Derivtives re. Integrls re. In Clculus 1, we lern limits, derivtives, some pplictions of derivtives, indefinite integrls, definite integrls,
Characterising Testing Preorders for Finite Probabilistic Processes
 Chrcterising Testing Preorders for Finite Probbilistic Processes Yuxin Deng Jio Tong University Shnghi, Chin Rob vn Glbbeek Ntionl ICT Austrli Sydney, Austrli School of CSE, University of New South Wles
Chrcterising Testing Preorders for Finite Probbilistic Processes Yuxin Deng Jio Tong University Shnghi, Chin Rob vn Glbbeek Ntionl ICT Austrli Sydney, Austrli School of CSE, University of New South Wles
Finite Automata. Informatics 2A: Lecture 3. John Longley. 22 September School of Informatics University of Edinburgh
 Lnguges nd Automt Finite Automt Informtics 2A: Lecture 3 John Longley School of Informtics University of Edinburgh jrl@inf.ed.c.uk 22 September 2017 1 / 30 Lnguges nd Automt 1 Lnguges nd Automt Wht is
Lnguges nd Automt Finite Automt Informtics 2A: Lecture 3 John Longley School of Informtics University of Edinburgh jrl@inf.ed.c.uk 22 September 2017 1 / 30 Lnguges nd Automt 1 Lnguges nd Automt Wht is
ad = cb (1) cf = ed (2) adf = cbf (3) cf b = edb (4)
 10 Most proofs re left s reding exercises. Definition 10.1. Z = Z {0}. Definition 10.2. Let be the binry reltion defined on Z Z by, b c, d iff d = cb. Theorem 10.3. is n equivlence reltion on Z Z. Proof.
10 Most proofs re left s reding exercises. Definition 10.1. Z = Z {0}. Definition 10.2. Let be the binry reltion defined on Z Z by, b c, d iff d = cb. Theorem 10.3. is n equivlence reltion on Z Z. Proof.
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring Regular Languages. Equivalences between Finite automata and REs. Haniel Barbosa
 CS:4330 Theory of Computtion Spring 208 Regulr Lnguges Equivlences between Finite utomt nd REs Hniel Brbos Redings for this lecture Chpter of [Sipser 996], 3rd edition. Section.3. Finite utomt nd regulr
CS:4330 Theory of Computtion Spring 208 Regulr Lnguges Equivlences between Finite utomt nd REs Hniel Brbos Redings for this lecture Chpter of [Sipser 996], 3rd edition. Section.3. Finite utomt nd regulr
Finite Automata. Informatics 2A: Lecture 3. Mary Cryan. 21 September School of Informatics University of Edinburgh
 Finite Automt Informtics 2A: Lecture 3 Mry Cryn School of Informtics University of Edinburgh mcryn@inf.ed.c.uk 21 September 2018 1 / 30 Lnguges nd Automt Wht is lnguge? Finite utomt: recp Some forml definitions
Finite Automt Informtics 2A: Lecture 3 Mry Cryn School of Informtics University of Edinburgh mcryn@inf.ed.c.uk 21 September 2018 1 / 30 Lnguges nd Automt Wht is lnguge? Finite utomt: recp Some forml definitions
Lecture 6 Regular Grammars
 Lecture 6 Regulr Grmmrs COT 4420 Theory of Computtion Section 3.3 Grmmr A grmmr G is defined s qudruple G = (V, T, S, P) V is finite set of vribles T is finite set of terminl symbols S V is specil vrible
Lecture 6 Regulr Grmmrs COT 4420 Theory of Computtion Section 3.3 Grmmr A grmmr G is defined s qudruple G = (V, T, S, P) V is finite set of vribles T is finite set of terminl symbols S V is specil vrible
Module 6 Value Iteration. CS 886 Sequential Decision Making and Reinforcement Learning University of Waterloo
 Module 6 Vlue Itertion CS 886 Sequentil Decision Mking nd Reinforcement Lerning University of Wterloo Mrkov Decision Process Definition Set of sttes: S Set of ctions (i.e., decisions): A Trnsition model:
Module 6 Vlue Itertion CS 886 Sequentil Decision Mking nd Reinforcement Lerning University of Wterloo Mrkov Decision Process Definition Set of sttes: S Set of ctions (i.e., decisions): A Trnsition model:
Equivalences on Observable Processes
 Equivlences on Observble Processes Irek Ulidowski Deprtment of Computing Imperil College of Science, Technology nd Medicine 180 Queens Gte London SW7 2BZ. E-mil: iu@doc.ic.c.uk Abstrct The im of this pper
Equivlences on Observble Processes Irek Ulidowski Deprtment of Computing Imperil College of Science, Technology nd Medicine 180 Queens Gte London SW7 2BZ. E-mil: iu@doc.ic.c.uk Abstrct The im of this pper
CS 301. Lecture 04 Regular Expressions. Stephen Checkoway. January 29, 2018
 CS 301 Lecture 04 Regulr Expressions Stephen Checkowy Jnury 29, 2018 1 / 35 Review from lst time NFA N = (Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F ) where δ Q Σ P (Q) mps stte nd n lphet symol (or ) to set of sttes We run n NFA
CS 301 Lecture 04 Regulr Expressions Stephen Checkowy Jnury 29, 2018 1 / 35 Review from lst time NFA N = (Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F ) where δ Q Σ P (Q) mps stte nd n lphet symol (or ) to set of sttes We run n NFA
Lesson 25: Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
 Lesson 2: Adding nd Subtrcting Rtionl Expressions Student Outcomes Students perform ddition nd subtrction of rtionl expressions. Lesson Notes This lesson reviews ddition nd subtrction of frctions using
Lesson 2: Adding nd Subtrcting Rtionl Expressions Student Outcomes Students perform ddition nd subtrction of rtionl expressions. Lesson Notes This lesson reviews ddition nd subtrction of frctions using
Electron Correlation Methods
 Electron Correltion Methods HF method: electron-electron interction is replced by n verge interction E HF c E 0 E HF E 0 exct ground stte energy E HF HF energy for given bsis set HF Ec 0 - represents mesure
Electron Correltion Methods HF method: electron-electron interction is replced by n verge interction E HF c E 0 E HF E 0 exct ground stte energy E HF HF energy for given bsis set HF Ec 0 - represents mesure
Non Deterministic Automata. Linz: Nondeterministic Finite Accepters, page 51
 Non Deterministic Automt Linz: Nondeterministic Finite Accepters, pge 51 1 Nondeterministic Finite Accepter (NFA) Alphbet ={} q 1 q2 q 0 q 3 2 Nondeterministic Finite Accepter (NFA) Alphbet ={} Two choices
Non Deterministic Automt Linz: Nondeterministic Finite Accepters, pge 51 1 Nondeterministic Finite Accepter (NFA) Alphbet ={} q 1 q2 q 0 q 3 2 Nondeterministic Finite Accepter (NFA) Alphbet ={} Two choices
New data structures to reduce data size and search time
 New dt structures to reduce dt size nd serch time Tsuneo Kuwbr Deprtment of Informtion Sciences, Fculty of Science, Kngw University, Hirtsuk-shi, Jpn FIT2018 1D-1, No2, pp1-4 Copyright (c)2018 by The Institute
New dt structures to reduce dt size nd serch time Tsuneo Kuwbr Deprtment of Informtion Sciences, Fculty of Science, Kngw University, Hirtsuk-shi, Jpn FIT2018 1D-1, No2, pp1-4 Copyright (c)2018 by The Institute
AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES. Definition 1.5: Finite Automaton
 25. Finite Automt AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES A system of computtion tht only hs finite numer of possile sttes cn e modeled using finite utomton A finite utomton is often illustrted s stte digrm d d d. d q
25. Finite Automt AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES A system of computtion tht only hs finite numer of possile sttes cn e modeled using finite utomton A finite utomton is often illustrted s stte digrm d d d. d q
Extended nonlocal games from quantum-classical games
 Extended nonlocl gmes from quntum-clssicl gmes Theory Seminr incent Russo niversity of Wterloo October 17, 2016 Outline Extended nonlocl gmes nd quntum-clssicl gmes Entngled vlues nd the dimension of entnglement
Extended nonlocl gmes from quntum-clssicl gmes Theory Seminr incent Russo niversity of Wterloo October 17, 2016 Outline Extended nonlocl gmes nd quntum-clssicl gmes Entngled vlues nd the dimension of entnglement
Analyzing Real-Time Systems 1
 Anlyzing Rel-Time Systems 1 Jürgen Ruf nd Thoms Kropf Wilhelm-Schickrd-Institute University of Tübingen, Snd 13, 7076 Tübingen, Germny {ruf,kropf}@informtik.uni-tuebingen.de http://www-ti.informtik.uni-tuebingen/~ruf
Anlyzing Rel-Time Systems 1 Jürgen Ruf nd Thoms Kropf Wilhelm-Schickrd-Institute University of Tübingen, Snd 13, 7076 Tübingen, Germny {ruf,kropf}@informtik.uni-tuebingen.de http://www-ti.informtik.uni-tuebingen/~ruf
Homework 3 Solutions
 CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 3 Solutions 1. Give NFAs with the specified numer of sttes recognizing ech of the following lnguges. In ll cses, the lphet is Σ = {,1}.
CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 3 Solutions 1. Give NFAs with the specified numer of sttes recognizing ech of the following lnguges. In ll cses, the lphet is Σ = {,1}.
MOdal logics and behavioural equivalences are very
 WU AND DENG: DISTRIBUTION-BASED BEHAVIOURAL DISTANCE FOR NONDETERMINISTIC FUZZY TRANSITION SYSTEMS 1 Distribution-Bsed Behviourl Distnce for Nondeterministic Fuzzy Trnsition Systems Hengyng Wu nd Yuxin
WU AND DENG: DISTRIBUTION-BASED BEHAVIOURAL DISTANCE FOR NONDETERMINISTIC FUZZY TRANSITION SYSTEMS 1 Distribution-Bsed Behviourl Distnce for Nondeterministic Fuzzy Trnsition Systems Hengyng Wu nd Yuxin
Anatomy of a Deterministic Finite Automaton. Deterministic Finite Automata. A machine so simple that you can understand it in less than one minute
 Victor Admchik Dnny Sletor Gret Theoreticl Ides In Computer Science CS 5-25 Spring 2 Lecture 2 Mr 3, 2 Crnegie Mellon University Deterministic Finite Automt Finite Automt A mchine so simple tht you cn
Victor Admchik Dnny Sletor Gret Theoreticl Ides In Computer Science CS 5-25 Spring 2 Lecture 2 Mr 3, 2 Crnegie Mellon University Deterministic Finite Automt Finite Automt A mchine so simple tht you cn
CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing
 CS375: Logic nd Theory of Computing Fuhu (Frnk) Cheng Deprtment of Computer Science University of Kentucky 1 Tble of Contents: Week 1: Preliminries (set lgebr, reltions, functions) (red Chpters 1-4) Weeks
CS375: Logic nd Theory of Computing Fuhu (Frnk) Cheng Deprtment of Computer Science University of Kentucky 1 Tble of Contents: Week 1: Preliminries (set lgebr, reltions, functions) (red Chpters 1-4) Weeks
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 188: Artificil Intelligence Lecture 19: Decision Digrms Pieter Abbeel --- C Berkeley Mny slides over this course dpted from Dn Klein, Sturt Russell, Andrew Moore Decision Networks ME: choose the ction
CS 188: Artificil Intelligence Lecture 19: Decision Digrms Pieter Abbeel --- C Berkeley Mny slides over this course dpted from Dn Klein, Sturt Russell, Andrew Moore Decision Networks ME: choose the ction
Decidability, Behavioural Equivalences and Infinite Transition Graphs. Hans Hüttel
 Decidbility, Behviourl Equivlences nd Infinite Trnsition Grphs Hns Hüttel Doctor of Philosophy University of Edinburgh 1991 Abstrct This thesis studies behviourl equivlences on lbelled infinite trnsition
Decidbility, Behviourl Equivlences nd Infinite Trnsition Grphs Hns Hüttel Doctor of Philosophy University of Edinburgh 1991 Abstrct This thesis studies behviourl equivlences on lbelled infinite trnsition
Numerical Linear Algebra Assignment 008
 Numericl Liner Algebr Assignment 008 Nguyen Qun B Hong Students t Fculty of Mth nd Computer Science, Ho Chi Minh University of Science, Vietnm emil. nguyenqunbhong@gmil.com blog. http://hongnguyenqunb.wordpress.com
Numericl Liner Algebr Assignment 008 Nguyen Qun B Hong Students t Fculty of Mth nd Computer Science, Ho Chi Minh University of Science, Vietnm emil. nguyenqunbhong@gmil.com blog. http://hongnguyenqunb.wordpress.com
Automata and Languages
 Automt nd Lnguges Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering Lb. The University of Aizu Jpn Grmmr Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
Automt nd Lnguges Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering Lb. The University of Aizu Jpn Grmmr Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informatica REPORTRAPPORT. Supervisory control for nondeterministic systems
 Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informtic REPORTRAPPORT Supervisory control for nondeterministic systems A. Overkmp Deprtment of Opertions Reserch, Sttistics, nd System Theory BS-R9411 1994 Supervisory Control
Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informtic REPORTRAPPORT Supervisory control for nondeterministic systems A. Overkmp Deprtment of Opertions Reserch, Sttistics, nd System Theory BS-R9411 1994 Supervisory Control
The Predom module. Predom calculates and plots isothermal 1-, 2- and 3-metal predominance area diagrams. Predom accesses only compound databases.
 Section 1 Section 2 The module clcultes nd plots isotherml 1-, 2- nd 3-metl predominnce re digrms. ccesses only compound dtbses. Tble of Contents Tble of Contents Opening the module Section 3 Stoichiometric
Section 1 Section 2 The module clcultes nd plots isotherml 1-, 2- nd 3-metl predominnce re digrms. ccesses only compound dtbses. Tble of Contents Tble of Contents Opening the module Section 3 Stoichiometric
Java II Finite Automata I
 Jv II Finite Automt I Bernd Kiefer Bernd.Kiefer@dfki.de Deutsches Forschungszentrum für künstliche Intelligenz Finite Automt I p.1/13 Processing Regulr Expressions We lredy lerned out Jv s regulr expression
Jv II Finite Automt I Bernd Kiefer Bernd.Kiefer@dfki.de Deutsches Forschungszentrum für künstliche Intelligenz Finite Automt I p.1/13 Processing Regulr Expressions We lredy lerned out Jv s regulr expression
Decision Networks. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Example: Decision Networks. Decision Networks. Decisions as Outcome Trees
 CS 188: Artificil Intelligence Fll 2011 Decision Networks ME: choose the ction which mximizes the expected utility given the evidence mbrell Lecture 17: Decision Digrms 10/27/2011 Cn directly opertionlize
CS 188: Artificil Intelligence Fll 2011 Decision Networks ME: choose the ction which mximizes the expected utility given the evidence mbrell Lecture 17: Decision Digrms 10/27/2011 Cn directly opertionlize
Foundations for Timed Systems
 Foundtions for Timed Systems Ptrici Bouyer LSV CNRS UMR 8643 & ENS de Cchn 6, venue du Président Wilson 9423 Cchn Frnce emil: bouyer@lsv.ens-cchn.fr Introduction Explicit timing constrints re nturlly present
Foundtions for Timed Systems Ptrici Bouyer LSV CNRS UMR 8643 & ENS de Cchn 6, venue du Président Wilson 9423 Cchn Frnce emil: bouyer@lsv.ens-cchn.fr Introduction Explicit timing constrints re nturlly present
State space systems analysis (continued) Stability. A. Definitions A system is said to be Asymptotically Stable (AS) when it satisfies
 Stte spce systems nlysis (continued) Stbility A. Definitions A system is sid to be Asymptoticlly Stble (AS) when it stisfies ut () = 0, t > 0 lim xt () 0. t A system is AS if nd only if the impulse response
Stte spce systems nlysis (continued) Stbility A. Definitions A system is sid to be Asymptoticlly Stble (AS) when it stisfies ut () = 0, t > 0 lim xt () 0. t A system is AS if nd only if the impulse response
