SOLUTION OF WHITEHEAD EQUATION ON GROUPS
|
|
|
- Brittany Ford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 138(2013) MATHEMATICA BOHEMICA No. 2, SOLUTION OF WHITEHEAD EQUATION ON GROUPS Valeriĭ A. Faĭziev, Tver, Prasanna K. Sahoo, Louisville (Received December 21, 2011) Abstract. Let G be a group and H an abelian group. Let J (G, H)be the set of solutions f: G HoftheJensenfunctionalequation f(xy)+f(xy 1 )=2f(x)satisfying thecondition f(xyz) f(xzy)=f(yz) f(zy)forall x, y,z G. Let Q (G, H)bethe setofsolutions f: G H ofthequadraticequation f(xy)+f(xy 1 )=2f(x)+2f(y) satisfyingthekannappancondition f(xyz)=f(xzy)forall x,y, z G. Inthispaperwe determine solutions of the Whitehead equation on groups. We show that every solution f: G HoftheWhiteheadequationisoftheform4f=2ϕ+2ψ,where2ϕ J (G, H) and2ψ Q (G, H).Moreover,if Hhastheadditionalpropertythat2h=0implies h=0 forall h H,theneverysolution f: G H ofthewhiteheadequationisoftheform 2f= ϕ+ψ,where ϕ J (G, H)and2ψ(x)=B(x,x)forsomesymmetricbihomomorphism B: G G H. Keywords: homomorphism, Fréchet functional equation, Jensen functional equation, symmetric bihomomorphism, Whitehead functional equation MSC2010:39B52 1. Introduction Let Gbeagroupand Hanabeliangroup. Let f : G Hbeafunction. The Cauchydifferenceof f, C (1) f : G G H,isgivenby (1.1) C (1) f (x, y) = f(xy) f(x) f(y) forall x, y G. TheCauchydifferenceof f measureshowmuch f deviatesfrom beingagrouphomomorphismofthegroup Gintothegroup H.ThesecondCauchy differenceof f, C (2) f : G G G H,isgivenby (1.2) C (2) f (x, y, z) = C f(xy, z) C f (x, z) C f (y, z) ThisworkwassupportedbyagrantfromtheofficeoftheVicePresidentofResearch, University of Louisville. 171
2 forall x, y, z G.If C (2) (x, y, z) = 0,thenonearrivesatthefunctionalequation f (1.3) f(xyz) + f(x) + f(y) + f(z) = f(xy) + f(xz) + f(yz) forall x, y, z G.Thisequationfirstappearedinapaper[5]ofJ.H.C.Whitehead in In that paper he solved the functional equation(1.3) on abelian groups assumingthat fsatisfiesthecondition f(x 1 ) = f(x).onanamsmeetingprofessor Deeba of University of Houston asked for the solution of equation(1.3). Kannappan in[1]solvedthisequationformappings f : V Kwhere V isavectorspaceand Kisafieldwithcharacteristicdifferentfrom2. Thesolution f : G Hofthefunctionalequation (1.4) f(xyz) + f(x) + f(y) + f(z) = f(xy) + f(yz) + f(zx) forall x, y, z Gcanbefoundinthebook[2]byKannappan. Thefunctional equation(1.4) is referred to as the Fréchet functional equation in[2]. On an abelian group G the functional equations(1.3) and(1.4) are equivalent. However, on an arbitrary group G, Whitehead and Fréchet functional equations are not equivalent. Itiseasytoseethatif f : G Hsatisfies(1.3),then f(e) = 0,where eisthe identity(orneutral)elementofthegroup G.Let W(G, H)bethesetofallfunctions thatsatisfythewhiteheadfunctionalequation(1.3). Let J(G, H)bethesetofall solutions of the Jensen functional equation (1.5) f(xy) + f(xy 1 ) = 2f(x), x, y G andlet J 0 (G, H)denotethesetofallsolutions f : G HoftheJensenfunctional equation(1.5) together with the normalization condition f(e) = 0. Moreover, denoteby J (G, H)thesubspaceof J 0 (G, H)consistingoffunctions ϕsatisfyingthe additional condition (1.6) ϕ(xyz) ϕ(xzy) = ϕ(yz) ϕ(zy) forevery x, y, z G. Ongroups,theJensenfunctionalequationwasextensively studiedbyngin[3]. Afunction f : G H issaidtosatisfythekannappanconditionifforany x, y, z G,therelation (1.7) f(xyz) = f(xzy) holds.thekannappanconditionon f : G Hisequivalentto fbeingafunction ontheabeliangroup G/[G, G],where [G, G]isthecommutatorssubgroupof G. 172
3 Theset Q(G, H)willstandforthesetofsolutions g: G Hofthequadratic functional equation (1.8) g(xy) + g(xy 1 ) = 2g(x) + 2g(y), x, y G. Denoteby Q (G, H)thesubsetof Q(G, H)consistingoffunctionssatisfyingthe Kannappan condition(1.7). The quadratic functional equation on groups was studied in[4]and[6]. InSection2ofthepresentpaperwedeterminethegeneralsolutionsoftheequation (1.3) on arbitrary groups. Using these results proved for the Whitehead equation, in Section 3 we find the solutions of the Fréchet functional equation. 2. Solution of the Whitehead equation Inthissection,wefirstpresentseverallemmasthatwillbeusedtoprovethemain result of this paper. Lemma2.1.Let Gbeagroupand Hanabeliangroup. Ifafunction f : G H satisfies the Whitehead equation (1.3), then it satisfies the following system of equations: (2.1) f(xy) + f(xy 1 ) = 2f(x) + f(y) + f(y 1 ), f(yx) + f(y 1 x) = 2f(x) + f(y) + f(y 1 ), f(xyz) f(xzy) = f(yz) f(zy), f(zyx) f(yzx) = f(zy) f(yz). Proof. Letting x = y = z = ein(1.3),weseethat f(e) = 0. Nowifweset z = y 1 thenfrom(1.3)weget f(x) + f(x) + f(y) + f(y 1 ) = f(xy) + f(xy 1 ), which is (2.2) f(xy) + f(xy 1 ) = 2f(x) + f(y) + f(y 1 ). Nowifweput y = x 1 weget f(z) + f(x) + f(x 1 ) + f(z) = f(xz) + f(x 1 z) 173
4 and hence Nowchanging xto yand zto xweget f(xz) + f(x 1 z) = 2f(z) + f(x) + f(x 1 ). (2.3) f(yx) + f(y 1 x) = 2f(x) + f(y) + f(y 1 ). Interchanging ywith zin(1.3)weobtain (2.4) f(xzy) + f(x) + f(y) + f(z) = f(xy) + f(xz) + f(zy), and subtracting(2.4) from the equation(1.3) we get (2.5) f(xyz) f(xzy) = f(yz) f(zy). Similarly,weobtainthelastequationofthesystem(2.1). Thusweseethatifa function f satisfies equation(1.3) then it satisfies the system(2.1), and the proof of the lemma is now complete. Lemma2.2. Let Gbeagroupand Hanabeliangroup.Ifafunction f : G H satisfies the system of equations (2.6) f(xy) + f(xy 1 ) = 2f(x) + f(y) + f(y 1 ), f(yx) + f(y 1 x) = 2f(x) + f(y) + f(y 1 ), f(xyz) f(xzy) = f(yz) f(zy), f(zyx) f(yzx) = f(zy) f(yz), then 2f = ϕ + ψforsome ϕ J (G, H)and ψ Q (G, H). Proof. Foranyfunction φ: G H,denoteby φ thefunctiondefinedbythe rule φ (x) = φ(x 1 ). Itisclearthat φ satisfiesthesystem(2.6)ifandonlyif φ satisfies this system. Now suppose that a function f satisfies the system(2.6). Then functions (2.7) ϕ(x) = f(x) f (x), ψ(x) = f(x) + f (x) satisfythesamesystemand 2f = ϕ + ψ. Fromthefirstequationofthesystem (2.6)itfollowsthat ϕ J(G, H)and ψ Q(G, H). Fromthethirdequationof (2.6)itfollowsthat ϕ J (G, H). Nowconsiderthefunction ψ. Itisclearthat ψ(x) = ψ(x 1 )and ψsatisfiesthesystem(2.6)ifandonlyifitsatisfiesthesystem (2.8) ψ(xy) + ψ(xy 1 ) = 2ψ(x) + 2ψ(y), 174 ψ(xyz) ψ(xzy) = ψ(yz) ψ(zy).
5 Letusverifythat,forany x, y G,thefunction ψsatisfiestherelation ψ(xy) = ψ(yx). Indeed, we have ψ(xy) + ψ(xy 1 ) = 2ψ(x) + 2ψ(y), ψ(yx) + ψ(yx 1 ) = 2ψ(y) + 2ψ(x). Subtracting the latter equation from the former and taking into account the relation ψ(yx 1 ) = ψ((xy 1 ) 1 ) = ψ(xy 1 ),weobtain ψ(xy) = ψ(yx) forall x, y G.Hencefrom(2.8)weseethat ψsatisfiesthesystem (2.9) ψ(xy) + ψ(xy 1 ) = 2ψ(x) + 2ψ(y), ψ(xyz) = ψ(xzy). Therefore ψ is a quadratic function satisfying the Kannappan condition ψ(xyz) = ψ(xzy)andthus ψ Q (G, H).Theproofofthelemmaisnowcomplete. Foranyabeliangroup Handany n N,let nh = {g; g = nh, h H},that is,thesubgroup nhconsistsofelementsoftheform g = nh. Lemma2.3.Let Gbeagroupand Hanabeliangroup. (a) If ϕ J (G, H),then 2ϕ W(G, H). (b) If ψ Q (G, H),then 2ψ W(G, H). Proof. Toprove(a),let ϕ J (G, H).Hence φsatisfiestherelations (2.10) ϕ(xy) + ϕ(xy 1 ) = 2ϕ(x) and ϕ(yx) + ϕ(yx 1 ) = 2ϕ(y). Hencebyaddingthelasttwoequations,wehave (2.11) ϕ(xy) + ϕ(xy 1 ) + ϕ(yx) + ϕ(yx 1 ) = 2ϕ(x) + 2ϕ(y). Since ϕisanoddfunction, ϕ(xy 1 ) = ϕ(yx 1 ),andthus(2.11)yields (2.12) ϕ(xy) + ϕ(yx) = 2ϕ(x) + 2ϕ(y) forall x, y G. 175
6 Replacing xby xyand yby zin(2.10),weobtain (2.13) ϕ(xyz) + ϕ(xyz 1 ) = 2ϕ(xy). Similarly, again replacing x by xz in(2.10), we have (2.14) ϕ(xzy) + ϕ(xzy 1 ) = 2ϕ(xz). Adding last two equalities and using the fact that we have ϕ ( xyz 1) + ϕ ( xzy 1) = ϕ ( x(yz 1 ) ) + ϕ ( x(yz 1 ) 1) ϕ(xyz) + ϕ(xzy) + ϕ ( x(yz 1 ) ) + ϕ ( x(yz 1 ) 1) = 2ϕ(xy) + 2ϕ(xz) forall x, y, z G.Usingtheequation(2.10)inthelastequation,wehave (2.15) ϕ(xyz) + ϕ(xzy) + 2ϕ(x) = 2ϕ(xy) + 2ϕ(xz) forall x, y, z G.Takingthesumof(1.6)and(2.15),weget (2.16) 2ϕ(xyz) + 2ϕ(x) = 2ϕ(xy) + 2ϕ(xz) + ϕ(yz) ϕ(zy). From(2.12), we have (2.17) 2ϕ(y) + 2ϕ(z) = ϕ(yz) + ϕ(zy). Takingthesumof(2.17)and(2.16),weobtain 2ϕ(xyz) + 2ϕ(x) + 2ϕ(y) + 2ϕ(z) = 2ϕ(xy) + 2ϕ(xz) + 2ϕ(yz). Hence 2ϕ W(G, H).Thiscompletestheproofof(a). Toprove(b),let ψ Q (G, H). Hence ψiseven,thatis, ψ(x 1 ) = ψ(x)forall x G.Replacing yby yzin(1.8),wehave (2.18) ψ(xyz) + ψ(xz 1 y 1 ) 2ψ(x) 2ψ(yz) = 0. Similarly,replacing xby xz 1 and yby y 1 in(1.8)andusingthefactthat ψis even, we obtain (2.19) ψ(xz 1 y 1 ) + ψ(xz 1 y) 2ψ(xz 1 ) 2ψ(y) =
7 Againreplacing xby xyand yby z 1,weseethat (2.20) ψ(xyz 1 ) + ψ(xyz) 2ψ(xy) 2ψ(z) = 0. Finally,replacing yby z 1,weobtain (2.21) 2ψ(xz 1 ) + 2ψ(xz) 4ψ(x) 4ψ(z) = 0. Subtractingthesumof(2.19)and(2.21)formthesumof(2.18)and(2.20)andusing the Kannappan condition(1.7), we obtain 2ψ(xyz) + 2ψ(x) + 2ψ(y) + 2ψ(z) 2ψ(xy) 2ψ(xz) 2ψ(yz) = 0. Therefore, 2ψ W(G, H).Further,itiseasytoseethat 2J (G, H)and 2Q (G, H) aresubgroupsof W(G, H).Thiscompletestheproofofthelemma. Whenagroup Gisthedirectsumofsubgroups H and K,thensymbolically wedenotethisbywriting G = H K. Thefollowingtheoremeasilyfollowsfrom Lemma2.1,Lemma2.2andLemma2.3. Theorem2.4.Supposethat Gisagroupand H isanabeliangroup. If f W(G, H),then (2.22) 4f = 2ϕ + 2ψ, where ϕ J(G, H), 2ϕ J(G, H) W(G, H) = J (G, H), ψ Q(G, H), and 2ψ Q(G, H) W(G, H) = Q (G, H).Therefore (2.23) 4W(G, H) = 2J (G, H) 2Q (G, H). Remark2.1. If Hhastheproperty (2.24) 2h = 0 implies h = 0 forall h H,thenfrom(2.23)weget (2.25) 2W(G, H) = J (G, H) Q (G, H). Lemma2.5.Let Gbeagroupand H anabeliangroup. Let ω Q(G, H) W(G, H).Thenthereisasymmetricbimorphism B: G G Hsuchthat 2ω(x) = B(x, x). 177
8 Proof. Let B(x, y) = ω(xy) ω(x) ω(y),thenwehave B(x, yz) B(x, y) B(x, z) = ω(xyz) ω(x) ω(yz) ω(xy) + ω(x) + ω(y) ω(xz) + ω(x) + ω(z) = 0 and B(xy, z) B(x, z) B(y, z) = ω(xyz) ω(xy) ω(z) ω(xz) + ω(x) + ω(z) ω(yz) + ω(y) + ω(z) = 0. Therefore B(x, y) is a bimorphism. Since ω(xy) = ω(yx) it follows that B(x, y) is a symmetricbimorphism.nowsince ω(x 2 ) = 4ω(x),weget B(x, x) = ω(x 2 ) 2ω(x) = 4ω(x) 2ω(x) = 2ω(x). This completes the proof of the lemma. Theorem2.6.Let Gbeagroupand Hanabeliangroupwiththepropertythat 2h = 0implies h = 0forall h H.Theneverysolution f : G HoftheWhitehead equation (1.3)isoftheform 2f = ϕ + ψ,where ϕ J (G, H)and 2ψ(x) = B(x, x) forsomesymmetricbihomomorphism B: G G H. 3. Fréchet equation In this section, we determine the solution of Fréchet equation using the results obtained in the previous section. Consider the Fréchet equation (3.1) f(xyz) + f(x) + f(y) + f(z) = f(xy) + f(yz) + f(zx), where f : G H.Thesetofsolutionsof(3.1)letusdenoteby F(G, H). Lemma3.1.Let Gbeagroupand Hanabeliangroup. (a) F(G, H) W(G, H). (b) Let f W(G, H),then f F(G, H)ifandonlyifitsatisfiesthecondition f(xy) = f(yx)forany x, y G. 178
9 Proof. Toprove(a),let f F(G, H).Then fsatisfies (3.2) f(zxy) + f(x) + f(y) + f(z) = f(zx) + f(xy) + f(yz). Subtracting(3.2) from(3.1), we obtain (3.3) f(zxy) = f(xyz). Putting y = 1,weget (3.4) f(zx) = f(xz). It follows that every solution of(3.1) satisfies equation(1.3). Therefore F(G, H) W(G, H). Next,weprove(b).Let f W(G, H).Itisclearthatif fsatisfiesthecondition f(xy) = f(yx)forany x, y G,then f F(G, H).Therefore F(G, H)isasubgroup of W(G, H) consisting of functions satisfying the condition(3.4). Lemma3.2.Let Gbeagroupand Hanabeliangroup. If f J(G, H)and satisfies f(xy) = f(yx)forall x, y G,then 2f Hom(G, H). Moreover,if Hhas theproperty (2.24),then f Hom(G, H). Proof. Let f J(G, H).Then fsatisfies f(xy) + f(xy 1 ) = 2f(x) forall x, y G.Interchanging xand y,wehave f(yx) + f(yx 1 ) = 2f(y). Takingasumoftheseequationsandusingrelations f(xy) = f(yx)and f(yx 1 ) = f(xy 1 )weobtain 2f(xy) = 2f(x) + 2f(y) forall x, y G,andhence 2f Hom(G, H). The following theorem easily follows. Theorem3.3.Let Gbeagroupand Hanabeliangroup.Suppose f F(G, H). Then (3.5) 4f = ξ + 2ψ, where ξ Hom(G, H), 2ψ Q(G, H) W(G, H) = Q (G, H),and ψ Q(G, H). Therefore 4W(G, H) = Hom(G, H) 2Q(G, H). 179
10 References [1] Pl. Kannappan: Quadratic functional equation and inner product spaces. Results Math. 27(1995), zbl MR [2] Pl. Kannappan: Functional Equations and Inequalities with Applications. Springer Monographs in Mathematics, Springer, New York, zbl MR [3] C. T. Ng: Jensen s functional equation on groups. Aequationes Math. 39(1990), zbl MR [4] P. de Place Friis, H. Stetkær: On the quadratic functional equation on groups. Publ. Math. Debrecen 69(2006), zbl MR [5] J.H.C.Whitehead:Acertainexactsequence.Ann.Math.(2)52(1950), zblmr [6] D. Yang: The quadratic functional equation on groups. Publ. Math. Debrecen 66(2005), zbl MR Authors addresses: Valeriĭ A. Faĭziev, Tver State Agricultural Academy, Tver Sakharovo, Russia, valeriy.faiz@mail.ru; Prasanna K. Sahoo, Department of Mathematics, University of Louisville, Louisville, Kentucky USA, sahoo@ louisville.edu. 180
Yet another variant of the Drygas functional equation on groups
 Proyecciones Journal of Mathematics Vol. 36, N o 1, pp. 13-27, March 2017. Universidad Católica del Norte Antofagasta - Chile Yet another variant of the Drygas functional equation on groups Prasanna K.
Proyecciones Journal of Mathematics Vol. 36, N o 1, pp. 13-27, March 2017. Universidad Católica del Norte Antofagasta - Chile Yet another variant of the Drygas functional equation on groups Prasanna K.
Several functional equations defined on groups arising from stochastic distance measures.
 University of Louisville ThinkIR: The University of Louisville's Institutional Repository Electronic Theses and Dissertations 8-2014 Several functional equations defined on groups arising from stochastic
University of Louisville ThinkIR: The University of Louisville's Institutional Repository Electronic Theses and Dissertations 8-2014 Several functional equations defined on groups arising from stochastic
AJEBBAR OMAR AND ELQORACHI ELQORACHI. Abstract. In this paper we establish the stability of the functional equation
 STABILITY OF THE COSINE-SINE FUNCTIONAL EQUATION ON AMENABLE GROUPS arxiv:1809.0764v1 [math.ra] 19 Sep 018 AJEBBAR OMAR AND ELQORACHI ELQORACHI Abstract. In this paper we establish the stability of the
STABILITY OF THE COSINE-SINE FUNCTIONAL EQUATION ON AMENABLE GROUPS arxiv:1809.0764v1 [math.ra] 19 Sep 018 AJEBBAR OMAR AND ELQORACHI ELQORACHI Abstract. In this paper we establish the stability of the
ON A FUNCTIONAL EQUATION ASSOCIATED WITH THE TRAPEZOIDAL RULE - II
 Bulletin of the Institute of Mathematics Academia Sinica New Series) Vol. 4 009), No., pp. 9-3 ON A FUNCTIONAL EQUATION ASSOCIATED WITH THE TRAPEZOIDAL RULE - II BY PRASANNA K. SAHOO Astract In this paper,
Bulletin of the Institute of Mathematics Academia Sinica New Series) Vol. 4 009), No., pp. 9-3 ON A FUNCTIONAL EQUATION ASSOCIATED WITH THE TRAPEZOIDAL RULE - II BY PRASANNA K. SAHOO Astract In this paper,
arxiv:math/ v1 [math.fa] 12 Nov 2005
![arxiv:math/ v1 [math.fa] 12 Nov 2005 arxiv:math/ v1 [math.fa] 12 Nov 2005](/thumbs/93/113384465.jpg) arxiv:math/051130v1 [math.fa] 1 Nov 005 STABILITY OF GENERALIZED JENSEN EQUATION ON RESTRICTED DOMAINS S.-M. JUNG, M. S. MOSLEHIAN, AND P. K. SAHOO Abstract. In this paper, we establish the conditional
arxiv:math/051130v1 [math.fa] 1 Nov 005 STABILITY OF GENERALIZED JENSEN EQUATION ON RESTRICTED DOMAINS S.-M. JUNG, M. S. MOSLEHIAN, AND P. K. SAHOO Abstract. In this paper, we establish the conditional
Functional Equations Problems. Amir Hossein Parvardi June 13, Dedicated to pco.
 Functional Equations Problems Amir Hossein Parvardi June 13, 2011 Dedicated to pco. email: ahpwsog@gmail.com, blog: http://math-olympiad.blogsky.com. 1 1 Definitions N is the set of positive integers.
Functional Equations Problems Amir Hossein Parvardi June 13, 2011 Dedicated to pco. email: ahpwsog@gmail.com, blog: http://math-olympiad.blogsky.com. 1 1 Definitions N is the set of positive integers.
Research Article A Fixed Point Approach to the Stability of Quadratic Functional Equation with Involution
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Fixed Point Theory and Applications Volume 008, Article ID 73086, 11 pages doi:10.1155/008/73086 Research Article A Fixed Point Approach to the Stability of Quadratic Functional
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Fixed Point Theory and Applications Volume 008, Article ID 73086, 11 pages doi:10.1155/008/73086 Research Article A Fixed Point Approach to the Stability of Quadratic Functional
STABILITY OF THE COSINE-SINE FUNCTIONAL EQUATION WITH INVOLUTION
 Adv. Oper. Theory (017), no. 4, 531 546 http://doi.org/10.034/aot.1706-1190 ISSN: 538-5X (electronic) http://aot-math.org STABILITY OF THE COSINE-SINE FUNCTIONAL EQUATION WITH INVOLUTION JEONGWOOK CHANG,
Adv. Oper. Theory (017), no. 4, 531 546 http://doi.org/10.034/aot.1706-1190 ISSN: 538-5X (electronic) http://aot-math.org STABILITY OF THE COSINE-SINE FUNCTIONAL EQUATION WITH INVOLUTION JEONGWOOK CHANG,
STABILITY OF n-th ORDER FLETT S POINTS AND LAGRANGE S POINTS
 SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol.2 (4) (2006), 4 48 STABILITY OF n-th ORDER FLETT S POINTS AND LAGRANGE S POINTS IWONA PAWLIKOWSKA Abstract. In this article we show the stability of Flett s points and
SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol.2 (4) (2006), 4 48 STABILITY OF n-th ORDER FLETT S POINTS AND LAGRANGE S POINTS IWONA PAWLIKOWSKA Abstract. In this article we show the stability of Flett s points and
THE STABILITY OF THE SINE AND COSINE FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS LÁSZLÓ SZÉKELYHIDI
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 110, Number 1, September 1990 THE STABILITY OF THE SINE AND COSINE FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS LÁSZLÓ SZÉKELYHIDI (Communicated by Kenneth R. Meyer) Abstract.
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 110, Number 1, September 1990 THE STABILITY OF THE SINE AND COSINE FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS LÁSZLÓ SZÉKELYHIDI (Communicated by Kenneth R. Meyer) Abstract.
Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A
 Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A 116 (2009) 1080 1086 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A www.elsevier.com/locate/jcta Note Quasifields of symplectic
Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A 116 (2009) 1080 1086 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A www.elsevier.com/locate/jcta Note Quasifields of symplectic
Extra Problems and Examples
 Extra Problems and Examples Steven Bellenot October 11, 2007 1 Separation of Variables Find the solution u(x, y) to the following equations by separating variables. 1. u x + u y = 0 2. u x u y = 0 answer:
Extra Problems and Examples Steven Bellenot October 11, 2007 1 Separation of Variables Find the solution u(x, y) to the following equations by separating variables. 1. u x + u y = 0 2. u x u y = 0 answer:
HYERS ULAM STABILITY OF FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS IN SEVERAL VARIABLES. Gian Luigi Forti. Contents
 HYERS ULAM STABILITY OF FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS IN SEVERAL VARIABLES Gian Luigi Forti Contents 1. Introduction. Historical background. 2. The additive Cauchy equation; Jensen s equation. 3. The quadratic
HYERS ULAM STABILITY OF FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS IN SEVERAL VARIABLES Gian Luigi Forti Contents 1. Introduction. Historical background. 2. The additive Cauchy equation; Jensen s equation. 3. The quadratic
The general solution of a quadratic functional equation and Ulam stability
 Available online at www.tjnsa.com J. Nonlinear Sci. Appl. 8 (05), 60 69 Research Article The general solution of a quadratic functional equation and Ulam stability Yaoyao Lan a,b,, Yonghong Shen c a College
Available online at www.tjnsa.com J. Nonlinear Sci. Appl. 8 (05), 60 69 Research Article The general solution of a quadratic functional equation and Ulam stability Yaoyao Lan a,b,, Yonghong Shen c a College
Zygfryd Kominek REMARKS ON THE STABILITY OF SOME QUADRATIC FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS
 Opuscula Mathematica Vol. 8 No. 4 008 To the memory of Professor Andrzej Lasota Zygfryd Kominek REMARKS ON THE STABILITY OF SOME QUADRATIC FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS Abstract. Stability problems concerning the
Opuscula Mathematica Vol. 8 No. 4 008 To the memory of Professor Andrzej Lasota Zygfryd Kominek REMARKS ON THE STABILITY OF SOME QUADRATIC FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS Abstract. Stability problems concerning the
Midterm 1 Solutions Thursday, February 26
 Math 59 Dr. DeTurck Midterm 1 Solutions Thursday, February 26 1. First note that since f() = f( + ) = f()f(), we have either f() = (in which case f(x) = f(x + ) = f(x)f() = for all x, so c = ) or else
Math 59 Dr. DeTurck Midterm 1 Solutions Thursday, February 26 1. First note that since f() = f( + ) = f()f(), we have either f() = (in which case f(x) = f(x + ) = f(x)f() = for all x, so c = ) or else
ON POSITIVE, LINEAR AND QUADRATIC BOOLEAN FUNCTIONS
 Kragujevac Journal of Mathematics Volume 36 Number 2 (2012), Pages 177 187. ON POSITIVE, LINEAR AND QUADRATIC BOOLEAN FUNCTIONS SERGIU RUDEANU Abstract. In [1], [2] it was proved that a function f : {0,
Kragujevac Journal of Mathematics Volume 36 Number 2 (2012), Pages 177 187. ON POSITIVE, LINEAR AND QUADRATIC BOOLEAN FUNCTIONS SERGIU RUDEANU Abstract. In [1], [2] it was proved that a function f : {0,
Research Article On the Stability of Quadratic Functional Equations in F-Spaces
 Function Spaces Volume 2016, Article ID 5636101, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5636101 Research Article On the Stability of Quadratic Functional Equations in F-Spaces Xiuzhong Yang College of
Function Spaces Volume 2016, Article ID 5636101, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5636101 Research Article On the Stability of Quadratic Functional Equations in F-Spaces Xiuzhong Yang College of
KKM THEOREM WITH APPLICATIONS TO LOWER AND UPPER BOUNDS EQUILIBRIUM PROBLEM IN G-CONVEX SPACES
 IJMMS 2003:51, 3267 3276 PII. S0161171203211261 http://ijmms.hindawi.com Hindawi Publishing Corp. KKM THEOREM WITH APPLICATIONS TO LOWER AND UPPER BOUNDS EQUILIBRIUM PROBLEM IN G-CONVEX SPACES M. FAKHAR
IJMMS 2003:51, 3267 3276 PII. S0161171203211261 http://ijmms.hindawi.com Hindawi Publishing Corp. KKM THEOREM WITH APPLICATIONS TO LOWER AND UPPER BOUNDS EQUILIBRIUM PROBLEM IN G-CONVEX SPACES M. FAKHAR
HYERS-ULAM-RASSIAS STABILITY OF JENSEN S EQUATION AND ITS APPLICATION
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 16, Number 11, November 1998, Pages 3137 3143 S 000-9939(9804680- HYERS-ULAM-RASSIAS STABILITY OF JENSEN S EQUATION AND ITS APPLICATION SOON-MO JUNG
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 16, Number 11, November 1998, Pages 3137 3143 S 000-9939(9804680- HYERS-ULAM-RASSIAS STABILITY OF JENSEN S EQUATION AND ITS APPLICATION SOON-MO JUNG
Commutative Banach algebras 79
 8. Commutative Banach algebras In this chapter, we analyze commutative Banach algebras in greater detail. So we always assume that xy = yx for all x, y A here. Definition 8.1. Let A be a (commutative)
8. Commutative Banach algebras In this chapter, we analyze commutative Banach algebras in greater detail. So we always assume that xy = yx for all x, y A here. Definition 8.1. Let A be a (commutative)
Solutions to Homework # 1 Math 381, Rice University, Fall (x y) y 2 = 0. Part (b). We make a convenient change of variables:
 Hildebrand, Ch. 8, # : Part (a). We compute Subtracting, we eliminate f... Solutions to Homework # Math 38, Rice University, Fall 2003 x = f(x + y) + (x y)f (x + y) y = f(x + y) + (x y)f (x + y). x = 2f(x
Hildebrand, Ch. 8, # : Part (a). We compute Subtracting, we eliminate f... Solutions to Homework # Math 38, Rice University, Fall 2003 x = f(x + y) + (x y)f (x + y) y = f(x + y) + (x y)f (x + y). x = 2f(x
Stability of Adjointable Mappings in Hilbert
 Stability of Adjointable Mappings in Hilbert arxiv:math/0501139v2 [math.fa] 1 Aug 2005 C -Modules M. S. Moslehian Abstract The generalized Hyers Ulam Rassias stability of adjointable mappings on Hilbert
Stability of Adjointable Mappings in Hilbert arxiv:math/0501139v2 [math.fa] 1 Aug 2005 C -Modules M. S. Moslehian Abstract The generalized Hyers Ulam Rassias stability of adjointable mappings on Hilbert
ARCS IN FINITE PROJECTIVE SPACES. Basic objects and definitions
 ARCS IN FINITE PROJECTIVE SPACES SIMEON BALL Abstract. These notes are an outline of a course on arcs given at the Finite Geometry Summer School, University of Sussex, June 26-30, 2017. Let K denote an
ARCS IN FINITE PROJECTIVE SPACES SIMEON BALL Abstract. These notes are an outline of a course on arcs given at the Finite Geometry Summer School, University of Sussex, June 26-30, 2017. Let K denote an
On KS-Semigroup Homomorphism
 International Mathematical Forum, 4, 2009, no. 23, 1129-1138 On KS-Semigroup Homomorphism Jocelyn S. Paradero-Vilela and Mila Cawi Department of Mathematics, College of Science and Mathematics MSU-Iligan
International Mathematical Forum, 4, 2009, no. 23, 1129-1138 On KS-Semigroup Homomorphism Jocelyn S. Paradero-Vilela and Mila Cawi Department of Mathematics, College of Science and Mathematics MSU-Iligan
MATH 436 Notes: Cyclic groups and Invariant Subgroups.
 MATH 436 Notes: Cyclic groups and Invariant Subgroups. Jonathan Pakianathan September 30, 2003 1 Cyclic Groups Now that we have enough basic tools, let us go back and study the structure of cyclic groups.
MATH 436 Notes: Cyclic groups and Invariant Subgroups. Jonathan Pakianathan September 30, 2003 1 Cyclic Groups Now that we have enough basic tools, let us go back and study the structure of cyclic groups.
Fixed and Common Fixed Point Theorems in Metric Spaces
 Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 6, 2012, no. 4, 173-180 Fixed and Common Fixed Point Theorems in Metric Spaces Saleh A. Al-Mezel Department of Mathematics University of Tabuk P.O. Box 741, Tabuk 7149,
Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 6, 2012, no. 4, 173-180 Fixed and Common Fixed Point Theorems in Metric Spaces Saleh A. Al-Mezel Department of Mathematics University of Tabuk P.O. Box 741, Tabuk 7149,
Theory of Positive Definite Kernel and Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Space
 Theory of Positive Definite Kernel and Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Space Statistical Inference with Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Space Kenji Fukumizu Institute of Statistical Mathematics, ROIS Department
Theory of Positive Definite Kernel and Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Space Statistical Inference with Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Space Kenji Fukumizu Institute of Statistical Mathematics, ROIS Department
x y More precisely, this equation means that given any ε > 0, there exists some δ > 0 such that
 Chapter 2 Limits and continuity 21 The definition of a it Definition 21 (ε-δ definition) Let f be a function and y R a fixed number Take x to be a point which approaches y without being equal to y If there
Chapter 2 Limits and continuity 21 The definition of a it Definition 21 (ε-δ definition) Let f be a function and y R a fixed number Take x to be a point which approaches y without being equal to y If there
Module 2: First-Order Partial Differential Equations
 Module 2: First-Order Partial Differential Equations The mathematical formulations of many problems in science and engineering reduce to study of first-order PDEs. For instance, the study of first-order
Module 2: First-Order Partial Differential Equations The mathematical formulations of many problems in science and engineering reduce to study of first-order PDEs. For instance, the study of first-order
1. (7 points)state and PROVE Cayley s Theorem.
 Math 546, Final Exam, Fall 2004 The exam is worth 100 points. Write your answers as legibly as you can on the blank sheets of paper provided. Use only one side of each sheet. Take enough space for each
Math 546, Final Exam, Fall 2004 The exam is worth 100 points. Write your answers as legibly as you can on the blank sheets of paper provided. Use only one side of each sheet. Take enough space for each
arxiv:math/ v2 [math.ct] 21 Feb 2007
![arxiv:math/ v2 [math.ct] 21 Feb 2007 arxiv:math/ v2 [math.ct] 21 Feb 2007](/thumbs/93/114165114.jpg) 1 INTRODUCTION TO ANN-CATEGORIES Nguyen Tien Quang arxiv:math/0702588v2 [math.ct] 21 Feb 2007 Abstract. In this paper, we present new concepts of Ann-categories, Ann-functors, and a transmission of the
1 INTRODUCTION TO ANN-CATEGORIES Nguyen Tien Quang arxiv:math/0702588v2 [math.ct] 21 Feb 2007 Abstract. In this paper, we present new concepts of Ann-categories, Ann-functors, and a transmission of the
NECESSARY AND SUFFICIENT CONDITIONS FOR SOLUTION OF THE FOURTH ORDER CAUCHY DIFFERENCE EQUATION ON SYMMETRIC GROUPS. K. Thangavelu 1, M.
 International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 117 No. 1 2017, 45-57 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu doi: 10.12732/ijpam.v117i1.5
International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 117 No. 1 2017, 45-57 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu doi: 10.12732/ijpam.v117i1.5
THE NEARLY ADDITIVE MAPS
 Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 46 (009), No., pp. 199 07 DOI 10.4134/BKMS.009.46..199 THE NEARLY ADDITIVE MAPS Esmaeeil Ansari-Piri and Nasrin Eghbali Abstract. This note is a verification on the relations between
Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 46 (009), No., pp. 199 07 DOI 10.4134/BKMS.009.46..199 THE NEARLY ADDITIVE MAPS Esmaeeil Ansari-Piri and Nasrin Eghbali Abstract. This note is a verification on the relations between
The Australian Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications
 The Australian Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications http://ajmaa.org Volume 8, Issue, Article 3, pp. -8, 0 ULAM STABILITY OF RECIPROCAL DIFFERENCE AND ADJOINT FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS K. RAVI,
The Australian Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications http://ajmaa.org Volume 8, Issue, Article 3, pp. -8, 0 ULAM STABILITY OF RECIPROCAL DIFFERENCE AND ADJOINT FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS K. RAVI,
On a Cauchy equation in norm
 http://www.mathematik.uni-karlsruhe.de/ semlv Seminar LV, No. 27, 11 pp., 02.10.2006 On a Cauchy equation in norm by R O M A N G E R (Katowice) and P E T E R V O L K M A N N (Karlsruhe) Abstract. We deal
http://www.mathematik.uni-karlsruhe.de/ semlv Seminar LV, No. 27, 11 pp., 02.10.2006 On a Cauchy equation in norm by R O M A N G E R (Katowice) and P E T E R V O L K M A N N (Karlsruhe) Abstract. We deal
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIABILITY IN R n.
 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIABILITY IN R n. MATANIA BEN-ARTZI April 2015 Functions here are defined on a subset T R n and take values in R m, where m can be smaller, equal or greater than n. The (open) ball
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIABILITY IN R n. MATANIA BEN-ARTZI April 2015 Functions here are defined on a subset T R n and take values in R m, where m can be smaller, equal or greater than n. The (open) ball
arxiv: v3 [math.ap] 25 May 2017
![arxiv: v3 [math.ap] 25 May 2017 arxiv: v3 [math.ap] 25 May 2017](/thumbs/94/119200272.jpg) ON THE STABILITY OF FIRST ORDER PDES ASSOCIATED TO VECTOR FIELDS MAYSAM MAYSAMI SADR arxiv:1604.03279v3 [math.ap] 25 May 2017 Abstract. Let M be a manifold, V be a vector field on M, and B be a Banach
ON THE STABILITY OF FIRST ORDER PDES ASSOCIATED TO VECTOR FIELDS MAYSAM MAYSAMI SADR arxiv:1604.03279v3 [math.ap] 25 May 2017 Abstract. Let M be a manifold, V be a vector field on M, and B be a Banach
A CLASS OF NEW TRIGONOMETRIC INEQUALITIES AND THEIR SHARPENINGS
 Journal of Mathematical Inequalities Volume, Number 3 (008), 49 436 A CLASS OF NEW TRIGONOMETRIC INEQUALITIES AND THEIR SHARPENINGS KUN ZHU, HONG ZHANG AND KAIQING WENG (communicated by V. Volenec) Abstract.
Journal of Mathematical Inequalities Volume, Number 3 (008), 49 436 A CLASS OF NEW TRIGONOMETRIC INEQUALITIES AND THEIR SHARPENINGS KUN ZHU, HONG ZHANG AND KAIQING WENG (communicated by V. Volenec) Abstract.
Functional equations of Cauchy s and d Alembert s Type on Compact Groups
 Proyecciones Journal of Mathematics Vol. 34, N o 3, pp. 297-305, September 2015. Universidad Católica del Norte Antofagasta - Chile Functional equations of Cauchy s and d Alembert s Type on Compact roups
Proyecciones Journal of Mathematics Vol. 34, N o 3, pp. 297-305, September 2015. Universidad Católica del Norte Antofagasta - Chile Functional equations of Cauchy s and d Alembert s Type on Compact roups
Lecture 5 - Lie Algebra Cohomology II
 Lecture 5 - Lie Algebra Cohomology II January 28, 2013 1 Motivation: Left-invariant modules over a group Given a vector bundle F ξ G over G where G has a representation on F, a left G- action on ξ is a
Lecture 5 - Lie Algebra Cohomology II January 28, 2013 1 Motivation: Left-invariant modules over a group Given a vector bundle F ξ G over G where G has a representation on F, a left G- action on ξ is a
4.6. Linear Operators on Hilbert Spaces
 4.6. Linear Operators on Hilbert Spaces 1 4.6. Linear Operators on Hilbert Spaces Note. This section explores a number of different kinds of bounded linear transformations (or, equivalently, operators
4.6. Linear Operators on Hilbert Spaces 1 4.6. Linear Operators on Hilbert Spaces Note. This section explores a number of different kinds of bounded linear transformations (or, equivalently, operators
arxiv: v2 [math.gr] 24 Feb 2010
![arxiv: v2 [math.gr] 24 Feb 2010 arxiv: v2 [math.gr] 24 Feb 2010](/thumbs/73/68980999.jpg) CONSTRUCTIONS OF COMMUTATIVE AUTOMORPHIC LOOPS arxiv:0810.2114v2 [math.gr] 24 Feb 2010 Abstract. A loop whose inner mappings are automorphisms is an automorphic loop (or A-loop). We characterize commutative
CONSTRUCTIONS OF COMMUTATIVE AUTOMORPHIC LOOPS arxiv:0810.2114v2 [math.gr] 24 Feb 2010 Abstract. A loop whose inner mappings are automorphisms is an automorphic loop (or A-loop). We characterize commutative
CHAPTER 2 POLYNOMIALS KEY POINTS
 CHAPTER POLYNOMIALS KEY POINTS 1. Polynomials of degrees 1, and 3 are called linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials respectively.. A quadratic polynomial in x with real coefficient is of the form a x
CHAPTER POLYNOMIALS KEY POINTS 1. Polynomials of degrees 1, and 3 are called linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials respectively.. A quadratic polynomial in x with real coefficient is of the form a x
On spectral analysis in varieties containing the solutions of inhomogeneous linear functional equations
 On spectral analysis in varieties containing the solutions of inhomogeneous linear functional equations arxiv:1704.04753v1 [math.cv] 16 Apr 2017 Gergely Kiss gergely.kiss@uni.lu Csaba Vincze csvincze@science.unideb.hu
On spectral analysis in varieties containing the solutions of inhomogeneous linear functional equations arxiv:1704.04753v1 [math.cv] 16 Apr 2017 Gergely Kiss gergely.kiss@uni.lu Csaba Vincze csvincze@science.unideb.hu
arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 21 Dec 2018
![arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 21 Dec 2018 arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 21 Dec 2018](/thumbs/92/109974295.jpg) arxiv:1812.09198v1 [math.fa] 21 Dec 2018 The Hahn-Banach Theorem: a proof of the equivalence between the analitic and geometric versions Fidel José Fernández y Fernández Arroyo Departamento de Matemáticas
arxiv:1812.09198v1 [math.fa] 21 Dec 2018 The Hahn-Banach Theorem: a proof of the equivalence between the analitic and geometric versions Fidel José Fernández y Fernández Arroyo Departamento de Matemáticas
Orthogonality equation with two unknown functions
 Aequat. Math. 90 (2016), 11 23 c The Author(s) 2015. This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com 0001-9054/16/010011-13 published online June 21, 2015 DOI 10.1007/s00010-015-0359-x Aequationes
Aequat. Math. 90 (2016), 11 23 c The Author(s) 2015. This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com 0001-9054/16/010011-13 published online June 21, 2015 DOI 10.1007/s00010-015-0359-x Aequationes
arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 15 Nov 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 15 Nov 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 15 Nov 2013](/thumbs/72/66429746.jpg) ISOMETRIC IMMERSIONS OF HIGHER CODIMENSION INTO THE PRODUCT S k H n+p k OF SPHERE AND HYPERBOLOID XINGXIAO LI AND TIANQUN ZHANG arxiv:1311.3849v1 [math.dg] 15 Nov 013 Abstract. In this paper, we obtain
ISOMETRIC IMMERSIONS OF HIGHER CODIMENSION INTO THE PRODUCT S k H n+p k OF SPHERE AND HYPERBOLOID XINGXIAO LI AND TIANQUN ZHANG arxiv:1311.3849v1 [math.dg] 15 Nov 013 Abstract. In this paper, we obtain
Research Article Solution and Stability of a General Mixed Type Cubic and Quartic Functional Equation
 Function Spaces and Applications Volume 203, Article ID 67380, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/203/67380 Research Article Solution and Stability of a General Mixed Type Cubic and Quartic Functional Equation
Function Spaces and Applications Volume 203, Article ID 67380, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/203/67380 Research Article Solution and Stability of a General Mixed Type Cubic and Quartic Functional Equation
Method of Lagrange Multipliers
 Method of Lagrange Multipliers A. Salih Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram September 2013 Lagrange multiplier method is a technique
Method of Lagrange Multipliers A. Salih Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram September 2013 Lagrange multiplier method is a technique
GENERALIZED POPOVICIU FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS IN BANACH MODULES OVER A C ALGEBRA AND APPROXIMATE ALGEBRA HOMOMORPHISMS. Chun Gil Park
 NEW ZEALAND JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 3 (003), 183 193 GENERALIZED POPOVICIU FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS IN BANACH MODULES OVER A C ALGEBRA AND APPROXIMATE ALGEBRA HOMOMORPHISMS Chun Gil Park (Received March
NEW ZEALAND JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 3 (003), 183 193 GENERALIZED POPOVICIU FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS IN BANACH MODULES OVER A C ALGEBRA AND APPROXIMATE ALGEBRA HOMOMORPHISMS Chun Gil Park (Received March
Equimultiple locus of embedded algebroid surfaces and blowing up in arbitrary characteristic
 arxiv:math/0703583v [math.ag] 20 Mar 2007 Equimultiple locus of embedded algebroid surfaces and blowing up in arbitrary characteristic Piedra, R. Depto. de Álgebra Universidad de Sevilla November, 2005
arxiv:math/0703583v [math.ag] 20 Mar 2007 Equimultiple locus of embedded algebroid surfaces and blowing up in arbitrary characteristic Piedra, R. Depto. de Álgebra Universidad de Sevilla November, 2005
Commentationes Mathematicae Universitatis Carolinae
 Commentationes Mathematicae Universitatis Carolinae John R. Giles; Scott Sciffer Fréchet directional differentiability and Fréchet differentiability Commentationes Mathematicae Universitatis Carolinae,
Commentationes Mathematicae Universitatis Carolinae John R. Giles; Scott Sciffer Fréchet directional differentiability and Fréchet differentiability Commentationes Mathematicae Universitatis Carolinae,
Solutions for Assignment 4 Math 402
 Solutions for Assignment 4 Math 402 Page 74, problem 6. Assume that φ : G G is a group homomorphism. Let H = φ(g). We will prove that H is a subgroup of G. Let e and e denote the identity elements of G
Solutions for Assignment 4 Math 402 Page 74, problem 6. Assume that φ : G G is a group homomorphism. Let H = φ(g). We will prove that H is a subgroup of G. Let e and e denote the identity elements of G
ON HYERS-ULAM STABILITY OF NONLINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 52 2015), No. 2, pp. 685 697 http://dx.doi.org/10.4134/bkms.2015.52.2.685 ON HYERS-ULAM STABILITY OF NONLINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Jinghao Huang, Soon-Mo Jung, and Yongjin Li
Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 52 2015), No. 2, pp. 685 697 http://dx.doi.org/10.4134/bkms.2015.52.2.685 ON HYERS-ULAM STABILITY OF NONLINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Jinghao Huang, Soon-Mo Jung, and Yongjin Li
Ternary Modified Collatz Sequences And Jacobsthal Numbers
 1 47 6 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 19 (016), Article 16.7.5 Ternary Modified Collatz Sequences And Jacobsthal Numbers Ji Young Choi Department of Mathematics Shippensburg University of Pennsylvania
1 47 6 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 19 (016), Article 16.7.5 Ternary Modified Collatz Sequences And Jacobsthal Numbers Ji Young Choi Department of Mathematics Shippensburg University of Pennsylvania
Q-cubic ideals of near-rings
 Inter national Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 113 No. 10 2017, 56 64 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Q-cubic ideals
Inter national Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 113 No. 10 2017, 56 64 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Q-cubic ideals
Homomorphisms in C -ternary algebras and JB -triples
 J. Math. Anal. Appl. 337 (2008 13 20 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmaa Homomorphisms in C -ternary algebras and J -triples Choonkil Park a,1, Themistocles M. Rassias b, a Department of Mathematics, Hanyang
J. Math. Anal. Appl. 337 (2008 13 20 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmaa Homomorphisms in C -ternary algebras and J -triples Choonkil Park a,1, Themistocles M. Rassias b, a Department of Mathematics, Hanyang
Characterization of quadratic mappings through a functional inequality
 J. Math. Anal. Appl. 32 (2006) 52 59 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmaa Characterization of quadratic mappings through a functional inequality Włodzimierz Fechner Institute of Mathematics, Silesian University,
J. Math. Anal. Appl. 32 (2006) 52 59 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmaa Characterization of quadratic mappings through a functional inequality Włodzimierz Fechner Institute of Mathematics, Silesian University,
arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 17 May 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 17 May 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 17 May 2013](/thumbs/72/67702327.jpg) arxiv:1305.4171v1 [math.fa] 17 May 013 The Continuity of Q + -Homogeneous Superadditive Correspondences Masoumeh Aghajani, Kourosh Nourouzi Department of Mathematics, K. N. Toosi University of Technology,
arxiv:1305.4171v1 [math.fa] 17 May 013 The Continuity of Q + -Homogeneous Superadditive Correspondences Masoumeh Aghajani, Kourosh Nourouzi Department of Mathematics, K. N. Toosi University of Technology,
2210 fall 2002 Exponential and log functions Positive Integer exponents Negative integer exponents Fractional exponents
 220 fall 2002 Exponential and log functions Exponential functions, even simple ones like 0 x, or 2 x, are relatively difficult to describe and to calculate because they involve taking high roots of integers,
220 fall 2002 Exponential and log functions Exponential functions, even simple ones like 0 x, or 2 x, are relatively difficult to describe and to calculate because they involve taking high roots of integers,
Relative Loss Bounds for Multidimensional Regression Problems
 Relative Loss Bounds for Multidimensional Regression Problems Jyrki Kivinen and Manfred Warmuth Presented by: Arindam Banerjee A Single Neuron For a training example (x, y), x R d, y [0, 1] learning solves
Relative Loss Bounds for Multidimensional Regression Problems Jyrki Kivinen and Manfred Warmuth Presented by: Arindam Banerjee A Single Neuron For a training example (x, y), x R d, y [0, 1] learning solves
14.3 Conservative Vector Fields
 hapter 14 Vector alculus Section 14.3 onservative Vector Fields Page 1 14.3 onservative Vector Fields This is an action-packed section in which several fundamental ideas come together. At the heart of
hapter 14 Vector alculus Section 14.3 onservative Vector Fields Page 1 14.3 onservative Vector Fields This is an action-packed section in which several fundamental ideas come together. At the heart of
INNER INVARIANT MEANS ON DISCRETE SEMIGROUPS WITH IDENTITY. B. Mohammadzadeh and R. Nasr-Isfahani. Received January 16, 2006
 Scientiae Mathematicae Japonicae Online, e-2006, 337 347 337 INNER INVARIANT MEANS ON DISCRETE SEMIGROUPS WITH IDENTITY B. Mohammadzadeh and R. Nasr-Isfahani Received January 16, 2006 Abstract. In the
Scientiae Mathematicae Japonicae Online, e-2006, 337 347 337 INNER INVARIANT MEANS ON DISCRETE SEMIGROUPS WITH IDENTITY B. Mohammadzadeh and R. Nasr-Isfahani Received January 16, 2006 Abstract. In the
DISTRIBUTIONAL SOLUTIONS OF WILSON S FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS WITH INVOLUTION AND THEIR ERDÖS PROBLEM
 Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 53 (016), No. 4, pp. 1157 1169 http://dx.doi.org/10.4134/bkms.b150584 pissn: 1015-8634 / eissn: 34-3016 DISTRIBUTIONAL SOLUTIONS OF WILSON S FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS WITH INVOLUTION
Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 53 (016), No. 4, pp. 1157 1169 http://dx.doi.org/10.4134/bkms.b150584 pissn: 1015-8634 / eissn: 34-3016 DISTRIBUTIONAL SOLUTIONS OF WILSON S FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS WITH INVOLUTION
Reverse Mathematics of Topology
 Reverse Mathematics of Topology William Chan 1 Abstract. This paper develops the Reverse Mathematics of second countable topologies, where the elements of the topological space exist. The notion of topology,
Reverse Mathematics of Topology William Chan 1 Abstract. This paper develops the Reverse Mathematics of second countable topologies, where the elements of the topological space exist. The notion of topology,
On Tabor groupoids and stability of some functional equations
 Aequat. Math. 87 (2014), 165 171 c The Author(s) 2013. This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com 0001-9054/14/010165-7 published online November 7, 2013 DOI 10.1007/s00010-013-0206-x
Aequat. Math. 87 (2014), 165 171 c The Author(s) 2013. This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com 0001-9054/14/010165-7 published online November 7, 2013 DOI 10.1007/s00010-013-0206-x
THE JORDAN-CHEVALLEY DECOMPOSITION
 THE JORDAN-CHEVALLEY DECOMPOSITION JOO HEON YOO Abstract. This paper illustrates the Jordan-Chevalley decomposition through two related problems. Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Linear Algebra Review 1 3.
THE JORDAN-CHEVALLEY DECOMPOSITION JOO HEON YOO Abstract. This paper illustrates the Jordan-Chevalley decomposition through two related problems. Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Linear Algebra Review 1 3.
T k b p M r will so ordered by Ike one who quits squuv. fe2m per year, or year, jo ad vaoce. Pleaie and THE ALTO SOLO
 q q P XXX F Y > F P Y ~ Y P Y P F q > ##- F F - 5 F F?? 5 7? F P P?? - - F - F F - P 7 - F P - F F % P - % % > P F 9 P 86 F F F F F > X7 F?? F P Y? F F F P F F
q q P XXX F Y > F P Y ~ Y P Y P F q > ##- F F - 5 F F?? 5 7? F P P?? - - F - F F - P 7 - F P - F F % P - % % > P F 9 P 86 F F F F F > X7 F?? F P Y? F F F P F F
QUADRATIC LEVEL QUASIGROUP EQUATIONS WITH FOUR VARIABLES I. Aleksandar Krapež
 PUBLICATIONS DE L INSTITUT MATHÉMATIQUE Nouvelle série, tome 81(95) (2007), 53 67 DOI 102298/PIM0795053K QUADRATIC LEVEL QUASIGROUP EQUATIONS WITH FOUR VARIABLES I Aleksandar Krapež Abstract. We consider
PUBLICATIONS DE L INSTITUT MATHÉMATIQUE Nouvelle série, tome 81(95) (2007), 53 67 DOI 102298/PIM0795053K QUADRATIC LEVEL QUASIGROUP EQUATIONS WITH FOUR VARIABLES I Aleksandar Krapež Abstract. We consider
2.1 Affine and Projective Coordinates
 1 Introduction Depending how you look at them, elliptic curves can be deceptively simple. Using one of the easier definitions, we are just looking at points (x,y) that satisfy a cubic equation, something
1 Introduction Depending how you look at them, elliptic curves can be deceptively simple. Using one of the easier definitions, we are just looking at points (x,y) that satisfy a cubic equation, something
13 More on free abelian groups
 13 More on free abelian groups Recall. G is a free abelian group if G = i I Z for some set I. 13.1 Definition. Let G be an abelian group. A set B G is a basis of G if B generates G if for some x 1,...x
13 More on free abelian groups Recall. G is a free abelian group if G = i I Z for some set I. 13.1 Definition. Let G be an abelian group. A set B G is a basis of G if B generates G if for some x 1,...x
1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why. (a b)(a c)(a d)(b c)(b d)(c d) a 2 + ab b = 2018.
 New Zealand Mathematical Olympiad Committee Camp Selection Problems 2018 Solutions Due: 28th September 2018 1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why must be a multiple of
New Zealand Mathematical Olympiad Committee Camp Selection Problems 2018 Solutions Due: 28th September 2018 1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why must be a multiple of
D-MATH Algebra I HS18 Prof. Rahul Pandharipande. Solution 1. Arithmetic, Zorn s Lemma.
 D-MATH Algebra I HS18 Prof. Rahul Pandharipande Solution 1 Arithmetic, Zorn s Lemma. 1. (a) Using the Euclidean division, determine gcd(160, 399). (b) Find m 0, n 0 Z such that gcd(160, 399) = 160m 0 +
D-MATH Algebra I HS18 Prof. Rahul Pandharipande Solution 1 Arithmetic, Zorn s Lemma. 1. (a) Using the Euclidean division, determine gcd(160, 399). (b) Find m 0, n 0 Z such that gcd(160, 399) = 160m 0 +
Graded modules over generalized Weyl algebras
 Graded modules over generalized Weyl algebras Advancement to Candidacy Robert Won Advised by: Dan Rogalski December 4, 2014 1 / 41 Overview 1 Preliminaries Graded rings and modules Noncommutative things
Graded modules over generalized Weyl algebras Advancement to Candidacy Robert Won Advised by: Dan Rogalski December 4, 2014 1 / 41 Overview 1 Preliminaries Graded rings and modules Noncommutative things
AMC Lecture Notes. Justin Stevens. Cybermath Academy
 AMC Lecture Notes Justin Stevens Cybermath Academy Contents 1 Systems of Equations 1 1 Systems of Equations 1.1 Substitution Example 1.1. Solve the system below for x and y: x y = 4, 2x + y = 29. Solution.
AMC Lecture Notes Justin Stevens Cybermath Academy Contents 1 Systems of Equations 1 1 Systems of Equations 1.1 Substitution Example 1.1. Solve the system below for x and y: x y = 4, 2x + y = 29. Solution.
arxiv: v3 [math.ca] 24 Aug 2010
![arxiv: v3 [math.ca] 24 Aug 2010 arxiv: v3 [math.ca] 24 Aug 2010](/thumbs/93/117941037.jpg) MULTI-VARIABLE TRANSLATION EQUATION WHICH ARISES FROM HOMOTHETY arxiv:0911.1513v3 [math.ca] 24 Aug 2010 GIEDRIUS ALKAUSKAS Abstract. In many regular cases, there exists a properly defined limit of iterations
MULTI-VARIABLE TRANSLATION EQUATION WHICH ARISES FROM HOMOTHETY arxiv:0911.1513v3 [math.ca] 24 Aug 2010 GIEDRIUS ALKAUSKAS Abstract. In many regular cases, there exists a properly defined limit of iterations
Jordan derivations on C -ternary algebras for a Cauchy-Jensen functional equation
 c 2010 International Press Adv. Theor. Math. Phys. 14 (2010 1 19 arxiv:1101.021v1 [math-ph] 1 Dec 2010 Jordan derivations on C -ternary algebras for a Cauchy-Jensen functional equation Choonkil Park 1,
c 2010 International Press Adv. Theor. Math. Phys. 14 (2010 1 19 arxiv:1101.021v1 [math-ph] 1 Dec 2010 Jordan derivations on C -ternary algebras for a Cauchy-Jensen functional equation Choonkil Park 1,
Hyers-Ulam Rassias stability of Pexiderized Cauchy functional equation in 2-Banach spaces
 Available online at www.tjnsa.com J. Nonlinear Sci. Appl. 5 (202), 459 465 Research Article Hyers-Ulam Rassias stability of Pexiderized Cauchy functional equation in 2-Banach spaces G. Zamani Eskandani
Available online at www.tjnsa.com J. Nonlinear Sci. Appl. 5 (202), 459 465 Research Article Hyers-Ulam Rassias stability of Pexiderized Cauchy functional equation in 2-Banach spaces G. Zamani Eskandani
arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 31 Jan 2016
![arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 31 Jan 2016 arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 31 Jan 2016](/thumbs/92/110643937.jpg) ASYMPTOTIC STABILITY OF THE CAUCHY AND JENSEN FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS ANNA BAHYRYCZ, ZSOLT PÁLES, AND MAGDALENA PISZCZEK arxiv:160.00300v1 [math.ca] 31 Jan 016 Abstract. The aim of this note is to investigate
ASYMPTOTIC STABILITY OF THE CAUCHY AND JENSEN FUNCTIONAL EQUATIONS ANNA BAHYRYCZ, ZSOLT PÁLES, AND MAGDALENA PISZCZEK arxiv:160.00300v1 [math.ca] 31 Jan 016 Abstract. The aim of this note is to investigate
Contractors and connectors of graph algebras
 Contractors and connectors of graph algebras László Lovász and Balázs Szegedy Microsoft Research One Microsoft Way April 2005; revised August 2005 Abstract We study generalizations of the contraction-deletion
Contractors and connectors of graph algebras László Lovász and Balázs Szegedy Microsoft Research One Microsoft Way April 2005; revised August 2005 Abstract We study generalizations of the contraction-deletion
Math 210, Final Exam, Practice Fall 2009 Problem 1 Solution AB AC AB. cosθ = AB BC AB (0)(1)+( 4)( 2)+(3)(2)
 Math 2, Final Exam, Practice Fall 29 Problem Solution. A triangle has vertices at the points A (,,), B (, 3,4), and C (2,,3) (a) Find the cosine of the angle between the vectors AB and AC. (b) Find an
Math 2, Final Exam, Practice Fall 29 Problem Solution. A triangle has vertices at the points A (,,), B (, 3,4), and C (2,,3) (a) Find the cosine of the angle between the vectors AB and AC. (b) Find an
4.1 Primary Decompositions
 4.1 Primary Decompositions generalization of factorization of an integer as a product of prime powers. unique factorization of ideals in a large class of rings. In Z, a prime number p gives rise to a prime
4.1 Primary Decompositions generalization of factorization of an integer as a product of prime powers. unique factorization of ideals in a large class of rings. In Z, a prime number p gives rise to a prime
1 FUNCTIONS _ 5 _ 1.0 RELATIONS
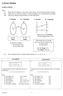 1 FUNCTIONS 1.0 RELATIONS Notes : (i) Four types of relations : one-to-one many-to-one one-to-many many-to-many. (ii) Three ways to represent relations : arrowed diagram set of ordered pairs graph. (iii)
1 FUNCTIONS 1.0 RELATIONS Notes : (i) Four types of relations : one-to-one many-to-one one-to-many many-to-many. (ii) Three ways to represent relations : arrowed diagram set of ordered pairs graph. (iii)
6. The Homomorphism Theorems In this section, we investigate maps between groups which preserve the groupoperations.
 6. The Homomorphism Theorems In this section, we investigate maps between groups which preserve the groupoperations. Definition. Let G and H be groups and let ϕ : G H be a mapping from G to H. Then ϕ is
6. The Homomorphism Theorems In this section, we investigate maps between groups which preserve the groupoperations. Definition. Let G and H be groups and let ϕ : G H be a mapping from G to H. Then ϕ is
GENERAL QUARTIC-CUBIC-QUADRATIC FUNCTIONAL EQUATION IN NON-ARCHIMEDEAN NORMED SPACES
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 72, Iss. 3, 200 ISSN 223-7027 GENERAL QUARTIC-CUBIC-QUADRATIC FUNCTIONAL EQUATION IN NON-ARCHIMEDEAN NORMED SPACES M. Eshaghi Gordji, H. Khodaei 2, R. Khodabakhsh 3 The
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 72, Iss. 3, 200 ISSN 223-7027 GENERAL QUARTIC-CUBIC-QUADRATIC FUNCTIONAL EQUATION IN NON-ARCHIMEDEAN NORMED SPACES M. Eshaghi Gordji, H. Khodaei 2, R. Khodabakhsh 3 The
ON T-FUZZY GROUPS. Inheung Chon
 Kangweon-Kyungki Math. Jour. 9 (2001), No. 2, pp. 149 156 ON T-FUZZY GROUPS Inheung Chon Abstract. We characterize some properties of t-fuzzy groups and t-fuzzy invariant groups and represent every subgroup
Kangweon-Kyungki Math. Jour. 9 (2001), No. 2, pp. 149 156 ON T-FUZZY GROUPS Inheung Chon Abstract. We characterize some properties of t-fuzzy groups and t-fuzzy invariant groups and represent every subgroup
arxiv:math/ v1 [math.fa] 1 Dec 2005
![arxiv:math/ v1 [math.fa] 1 Dec 2005 arxiv:math/ v1 [math.fa] 1 Dec 2005](/thumbs/87/96534831.jpg) arxiv:math/051007v1 [math.fa] 1 Dec 005 A FIXED POINT APPROACH TO STABILITY OF A QUADRATIC EQUATION M. MIRZAVAZIRI AND M. S. MOSLEHIAN Abstract. Using the fixed point alternative theorem we establish the
arxiv:math/051007v1 [math.fa] 1 Dec 005 A FIXED POINT APPROACH TO STABILITY OF A QUADRATIC EQUATION M. MIRZAVAZIRI AND M. S. MOSLEHIAN Abstract. Using the fixed point alternative theorem we establish the
Nonlinear Autonomous Dynamical systems of two dimensions. Part A
 Nonlinear Autonomous Dynamical systems of two dimensions Part A Nonlinear Autonomous Dynamical systems of two dimensions x f ( x, y), x(0) x vector field y g( xy, ), y(0) y F ( f, g) 0 0 f, g are continuous
Nonlinear Autonomous Dynamical systems of two dimensions Part A Nonlinear Autonomous Dynamical systems of two dimensions x f ( x, y), x(0) x vector field y g( xy, ), y(0) y F ( f, g) 0 0 f, g are continuous
SOME ESTIMATES FOR THE MINIMAL EIGENVALUE OF THE STURM-LIOUVILLE PROBLEM WITH THIRD-TYPE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS
 136211 MATHEMATICA BOHEMICA No. 4, 377 384 SOME ESTIMATES FOR THE MINIMAL EIGENVALUE OF THE STURM-LIOUVILLE PROBLEM WITH THIRD-TYPE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS Elena Karulina, Moskva Received October 15, 29 Abstract.
136211 MATHEMATICA BOHEMICA No. 4, 377 384 SOME ESTIMATES FOR THE MINIMAL EIGENVALUE OF THE STURM-LIOUVILLE PROBLEM WITH THIRD-TYPE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS Elena Karulina, Moskva Received October 15, 29 Abstract.
UNIFORMLY GÂTEAUX SMOOTH APPROXIMATIONS ON c 0 (Γ)
 UNIFORMLY GÂTEAUX SMOOTH APPROXIMATIONS ON c 0 Γ) PETR HÁJEK AND MICHAL JOHANIS Abstract. Every Lipschitz mapping from c 0 Γ) into a Banach space Y can be uniformly approximated by Lipschitz mappings that
UNIFORMLY GÂTEAUX SMOOTH APPROXIMATIONS ON c 0 Γ) PETR HÁJEK AND MICHAL JOHANIS Abstract. Every Lipschitz mapping from c 0 Γ) into a Banach space Y can be uniformly approximated by Lipschitz mappings that
Math 263 Assignment #4 Solutions. 0 = f 1 (x,y,z) = 2x 1 0 = f 2 (x,y,z) = z 2 0 = f 3 (x,y,z) = y 1
 Math 263 Assignment #4 Solutions 1. Find and classify the critical points of each of the following functions: (a) f(x,y,z) = x 2 + yz x 2y z + 7 (c) f(x,y) = e x2 y 2 (1 e x2 ) (b) f(x,y) = (x + y) 3 (x
Math 263 Assignment #4 Solutions 1. Find and classify the critical points of each of the following functions: (a) f(x,y,z) = x 2 + yz x 2y z + 7 (c) f(x,y) = e x2 y 2 (1 e x2 ) (b) f(x,y) = (x + y) 3 (x
STABILITY OF A GENERALIZED MIXED TYPE ADDITIVE, QUADRATIC, CUBIC AND QUARTIC FUNCTIONAL EQUATION
 Volume 0 009), Issue 4, Article 4, 9 pp. STABILITY OF A GENERALIZED MIXED TYPE ADDITIVE, QUADRATIC, CUBIC AND QUARTIC FUNCTIONAL EQUATION K. RAVI, J.M. RASSIAS, M. ARUNKUMAR, AND R. KODANDAN DEPARTMENT
Volume 0 009), Issue 4, Article 4, 9 pp. STABILITY OF A GENERALIZED MIXED TYPE ADDITIVE, QUADRATIC, CUBIC AND QUARTIC FUNCTIONAL EQUATION K. RAVI, J.M. RASSIAS, M. ARUNKUMAR, AND R. KODANDAN DEPARTMENT
WHEN LAGRANGEAN AND QUASI-ARITHMETIC MEANS COINCIDE
 Volume 8 (007, Issue 3, Article 71, 5 pp. WHEN LAGRANGEAN AND QUASI-ARITHMETIC MEANS COINCIDE JUSTYNA JARCZYK FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS, COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ECONOMETRICS, UNIVERSITY OF ZIELONA GÓRA SZAFRANA
Volume 8 (007, Issue 3, Article 71, 5 pp. WHEN LAGRANGEAN AND QUASI-ARITHMETIC MEANS COINCIDE JUSTYNA JARCZYK FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS, COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ECONOMETRICS, UNIVERSITY OF ZIELONA GÓRA SZAFRANA
arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 2 Jul 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 2 Jul 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 2 Jul 2013](/thumbs/94/118732290.jpg) HYPERSTABILITY OF A FUNCTIONAL EQUATION ESZTER GSELMANN arxiv:1307.0631v1 [math.ca] 2 Jul 2013 Abstract. The aim of this paper is to prove that the parametric fundamental equation of information is hyperstable
HYPERSTABILITY OF A FUNCTIONAL EQUATION ESZTER GSELMANN arxiv:1307.0631v1 [math.ca] 2 Jul 2013 Abstract. The aim of this paper is to prove that the parametric fundamental equation of information is hyperstable
Go l ab Schinzel equation on cylinders
 Aequat. Math. 91 (2017), 547 561 c The Author(s) 2017. This article is an open access publication 0001-9054/17/030547-15 published online March 27, 2017 DOI 10.1007/s00010-017-0475-x Aequationes Mathematicae
Aequat. Math. 91 (2017), 547 561 c The Author(s) 2017. This article is an open access publication 0001-9054/17/030547-15 published online March 27, 2017 DOI 10.1007/s00010-017-0475-x Aequationes Mathematicae
On the Stability of J -Homomorphisms
 On the Stability of J -Homomorphisms arxiv:math/0501158v2 [math.fa] 2 Sep 2005 Choonkil Baak and Mohammad Sal Moslehian Abstract The main purpose of this paper is to prove the generalized Hyers-Ulam-Rassias
On the Stability of J -Homomorphisms arxiv:math/0501158v2 [math.fa] 2 Sep 2005 Choonkil Baak and Mohammad Sal Moslehian Abstract The main purpose of this paper is to prove the generalized Hyers-Ulam-Rassias
Solution of the Higher Order Cauchy Difference Equation on Free Groups
 Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 13, Number 8 (2017, pp. 4141 4151 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/gjpam.htm Solution of the Higher Order Cauchy
Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 13, Number 8 (2017, pp. 4141 4151 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/gjpam.htm Solution of the Higher Order Cauchy
Test 2 Review Math 1111 College Algebra
 Test 2 Review Math 1111 College Algebra 1. Begin by graphing the standard quadratic function f(x) = x 2. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. g(x) = x 2 + 2 *a. b. c. d.
Test 2 Review Math 1111 College Algebra 1. Begin by graphing the standard quadratic function f(x) = x 2. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. g(x) = x 2 + 2 *a. b. c. d.

 Y G q G Y Y 29 8 $ 29 G 6 q )
Y G q G Y Y 29 8 $ 29 G 6 q )