On Tornheim's double series
|
|
|
- Tyrone Lawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ACTA ARITHMETICA LXXV.2 (1996) On Tornheim's double series JAMES G. HUARD (Buffalo, N.Y.), KENNETH S. WILLIAMS (Ottawa, Ont.) and ZHANG NAN-YUE (Beijing) 1. Introduction. We call the double infinite series 03 1 T(r, = C (r, s, t nonnegative integers) p,v=l p'vs (p + v)t a Tornheim series, after Tornheim who made a systematic and thorough investigation of this interesting series in a paper [6] published in The Tornheim series T(r, 0, t), when rewritten in the form J arises in the study of the gamma function (see, for example, [3, p. 471). The series T(r, s, t) is finite if and only if (1.1) r+t>l, s+t>l, and r+s+t>2. The basic properties of T(r, s, t) (assuming (1.1)) are the following (1.2) T(r, s, t) = T(s, r, t), (1.3) T(7-7 s, 0) = <(r)<(s), (1.4) T(r, 0, t) + T(t, 0, r) = <(r)<(t) - <(r + t), r > 2, (1.5) T(r,s-l,t+l)+T(r-l,s,t+l)=T(r,s,t), r>1, s>1, where < denotes the Riemann zeta function Mathematics Subject Classification: Primary llm06; Secondary 30B99, 33320, 40A05, 40B05. Key words and phrases: Tornheim's double series, Riemann zeta function. Research of the second author supported by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada grant A Research of the third author supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China.
2 106 J. G. Huard et al. Properties (1.3) and (1.4) give us a glimpse of the fascinating interplay between Tornheim series and the Riemann zeta function which we explore in this paper. The key to understanding this interplay is the recurrence relation (1.5). For a fixed value N (1 3) of r + s + t, we place the (finite) T(r, s, t) in a hexagonal array TN of N rows by arranging those T(r, s, t) with t = k in the (N - k)th row in order of increasing s. For example, the array T5 is The Tornheim hexagon TN is symmetric about its vertical axis in view of (1.2). The recurrence relation (1.5) shows that each entry with r # 0 and s # 0 is the sum of the two entries immediately above it, as in Pascal's triangle. Applying this relation successively, we see that every entry can be expressed as a linear combination of those entries with r = 0 or s = 0, and thus (in view of the symmetry) just in terms of those with s = 0. For example, in 75, In general, if r and s are integers satisfying then where which is easily established by induction. We note that TN-i is not finite. From (1.4) we see that
3 Tomheim's double series 107 When r + s = N the left side of (1.6) is given by (1.3), and we obtain the following system of [N/2] - 1 linear equations for the Ti: (N- i ; 1) N-r (N - i - 1) Ti = C(r)C(N - r), T-2 zf C N-r-i i=l i= 1 Using (1.7) to replace Ti by C(i)C(N - i) - C(N) - TN-i for i = [N/2] + 1,..., N - 2, and using the value found by Tornheim [6, eq. (lo)], we obtain from (1.8) a system (SN) of [N/2] - 1 linear equations for the [N/2] - 1 quantities T2,..., TNl2]. In addition to (1.9), Tornheim has evaluated T(r, s, t) explicitly in certain other cases. For example he has shown for N > 3 that Further, when N = r + s + t is odd, he proved that T(r, s, t) is a polynomial in C(2),..., C(N) with rational coefficients but did not give the polynomial. The purpose of this paper is to determine T(r, s, t) explicitly when N = r + s + t is odd. We show that T(r, s, t) is an integral linear combination of the products C(2i)C(N - 2i), i = 0,1,..., (N - 3)/2, except when r = s = 0. We also indicate why our approach does not appear to work when r + s + t is even. We use the identity where k and r are positive integers, and u and v are nonnegative integers not both zero, which follows easily from [3, p. 48, eq. (9)]. When N is odd
4 108 J. G. Huard et al. we use (1.12) in Section 3 to show that the system (SN) uniquely determines T2,..., TLNj2]. We prove THEOREM 1. Let N be an odd integer with N 1 3. Then, for i = 1,..., N - 2, we have where we recall that [(O) = -112 However, when N is even the system (SN) is not in general sufficient to find all of the Ti, for example when N = 8,10,12,14,16,18. The value of a general T(r, s, t) when r + s + t is odd is obtained in Section 4 by using in (1.6) the values of the Ti given in Theorem 1 and appealing to a combinatorial identity (Lemma 2.1) to evaluate the resulting sums of binomial coefficients. We prove THEOREM 2. Let N be an odd integer with N _> 3. Let r and s be nonnegative integers satisfying 1 5 r + s 5 N - 1, r 5 N - 2, s 5 N - 2. Set Then T(T, S, N - r - s) = EN(T, S) + EN(s,T). Theorem 2 covers all nonnegative integers r, s, t for which T(r, s, t) is finite and r + s + t = N is odd except for the case r = s = 0, which is covered by (1.10), and the case t = 0, which is covered by (1.3). All of Tornheim's other evaluations [6] are special cases of the above theorem. Furthermore, taking r = s = t = 2k + 1 (k 1 0) in Theorem 2, we deduce the result
5 Tornheim's double series 109 The problem of evaluating T(2k + 1,2k + 1,2k + 1) was posed in 1958 by Mordell [2], who showed that T(2k, 2k, 2k) is a rational multiple of T~~ for k 2 1, but gave the multiple only for k = 1. In 1985 Subbarao and Sitaramachandrarao [5] gave the explicit evaluation (with a misprint corrected) which can be rewritten in the simpler form and then combined with (1.14) to give THEOREM 3. For r > 1, 2. A combinatorial identity. As usual the binomial coefficient (E) is defined for any real number x and any integer n. We just note the properties and, for any integer (r) m, (2.2) = 0 if and only if n < 0 or 0 5 m < n. The following identity is used in the proof of Theorem 2. LEMMA 2.1. For nonnegative integers m, n, p and q with p > q, we have Proof. We have
6 110 J. G. Huard et al. q-n-1 = (-l)m( m-p+q by the Vandermonde convolution (see [I, p. 221 or [4, p. 81). rn 3. Evaluation of T(i, 0, N - i), N (odd) 2 3. We begin this section with two recurrence relations involving the Tj. Each of these is obtained by summing the identity (1.12) and making use of (1.7) and (1.8). PROPOSITION 3.1. Let N be an integer with N > 3, and let i = 1,..., N-2. Then (b) ( ( - I ) ~ (-1y)Ti + ( - I ) ~ ( N-j-1 j=1 N-i-1 P r o o f. When i = 1, (a) holds by (1.9), and (b) follows from N-2 N-2
7 Tornheim's double series 111, Thus we may assume that 2 5 i 5 N - 2. (a) Collecting together the terms with j = 1 in (1.12) (with v = i, u = N - i), we have (-1)' = (N- j-1 ki(k + r)n-i j=2 Summing over all positive integers k and r, we obtain Hence by (1.7), (1.9) and (1.11). Appealing to (1.8), and noting that we deduce that
8 J. G. Huard et al. from which (a) follows. (b) Replacing i by N - i in (3.1), multiplying by (-I)~, and appealing to (1.7), we find that (r~~'),. and changing j to N - j in the second summation. Equation (b) now follows after rearranging, noting that (:I:) = P r o of of T he o r e m 1. As N is odd, adding equations (a) and (b) of Proposition 3.1 eliminates the term Tj, and we obtain (N;sl) -. j odd j even. from which Theorem 1 follows. When N is even, the left sides of (a) and (b) of Proposition 3.1 are the same, and equating their right sides, we obtain the following result.
9 Tornheim's double series 113 PROPOSITION 3.2. Let N be an even integer with N 2 4, and let i = 1,..., N/2. Then We remark that when i = 1 Proposition 3.2 is a well-known identity (see for example [6, p. 3081). We now discuss briefly the case when N (2 4) is even. Recall that (SN) is a system of [N/2] - 1 linear equations in the [N/2] - 1 quantities Ti (i = 2,..., [N/2]). When N is even, (1.7) gives Using this in (SN), we obtain a new system (Sh) of N/2-1 linear equations in the N/2-2 quantities Ti (i = 2,..., N/2-1). The system (Si) is trivial. When N = 6,8,...,18 the rank of the system (Sh) is [N/3] - 1. Thus (Sh) does not determine all of the Ti when N = 8,10,...,18, but does when N = 6. It would be of interest to know if the rank is given by [N/3] - 1 for N When N = 4, Proposition 3.2 gives the relation 2<(2)2 = 5<(4), which we use to obtain T(1,0,3) = i<(4) and T(2,0,2) = :<(4). When N = 6, the same proposition gives 4<(2)<(4) = 7<(6), and hence When N = 8, after a little algebra, we have 3<(2)<(6) = 5<(8), and 6<(4)2 = 7<(8). The system (Si) reduces to the single equation so we are unable to determine the values of T(2,0,6) and T(3,0,5). When N = 10, the system (Si,) determines only the quantities 7T(2,0,8) + 2T(3,0,7) and T(3,0,7) + T(4,0,6). 4. Evaluation of T(r,s, N - r - s) for N (odd) > 3: Proof of Theorem 2. Let N be an odd integer with N 2 3, and let r and s be nonnegative integers satisfying 1 < r + s 5 N - 1, r < N - 2, s < N - 2. When r = 0 or s = 0 Theorem 2 follows from Theorem 1 and (1.2). Thus we have only to prove Theorem 2 when r and s are positive integers. From
10 114 J. G. Huard et al. (1.6) we may write where In (1.6) the range of summation of each of the two sums may be extended up to j = (N - 3)/2 provided that the term C(i)C(N - i) is appended when i is odd and at least 3, since in this case there is a contribution from the term with j = (N - i)/2. We therefore obtain where S4(~,4 T+S-i-1 = 2 ( s-1 i=3 i odd Using Lemma 2.1 (with m = T - 1, n = s - 1, p = q = N - 2j - I ), we obtain
11 Tonzheim's double series 115 AgainusingLemma2.1 (withm = r, n = s-1,p = N-1, q = N-zj-l), we obtain Next, using (2.1) we have Clearly Also, 1 + 5{(-1)' - (-l)'}c(n - r - s)c(r + s), where the last term occurs since [(N- r - s)/2] = [(N- r - s - 1)/2] + 1 when r + s is odd. Now by (1.13) we have EN(~,s) = Sl(r,s) + S~(S,T) + S2(r, 5) + S3(5,~) 1 - -{(-I)' - (-l)'}c(n - r - s)c(r + s). 2
12 116 J. G. Huard et al. Hence EN(s,T) = SI(S,~)+S~(~,S)+S~(S,~)+S~(~,S) so that EN(T,s) + EN(s,T) = UN(T,S) + UN(S,T) = T(T,s, N - T - s). 5. Conclusion. It appears to be a difficult open problem to determine an explicit formula for T(r, s, t) when r + s + t = N is even. Such a formula is known for a general even N in the following cases (where we have taken r 2 s in view of (1.2)): r s t Reference 0 0 N [6, Theorem 51 r N-r 0 [6, eq- (6)l 1 1 N - 2 [6, eq. (8)l 1 0 N - 1 [6, eq. (lo)] r N - r [6, Theorem 31 N/2 0 N/2 [6, Theorem 61 N/3 N/3 N/3 [5, p N/3 N/3-1 N/3 + 1 (by preceding result and (1.5)) In each of these cases except the first (see (1.10)) the formula for T(r, s, t) can be given as a linear combination of <(N) and <(i)<(n - i), i = 2,3,..., N/2. It would be interesting to know if this is the case in general. Acknowledgements. The first and third authors would like to acknowledge the hospitality of the Centre for Research in Algebra and Number Theory during their stays at Carleton University. References [I] H. W. Gould, Combinatorial Identities, Morgantown, W.Va., [2] L. J. Mordell, On the evaluation of some multiple series, J. London Math. Soc. 33 (1958), [3] N. N i e 1s en, Die Gammafinktion, Chelsea, Bronx, [4] J. Riordan, Combinatorial Identities, Wiley; New York, 1968.
13 Tornheim's double series 117 [5] M. V. Subbarao and R. Sitaramachandrarao, On some infinite series of L. J. Mordell and their analogues, Pacific J. Math. 119 (1985), [6] L. Tornheim, Harmonic double series, Amer. J. Math. 72 (1950), Department of Mathematics Canisius College Buffalo, New York U.S.A. Centre for Research in Algebra and Number Theory Department of Mathematics and Statistics Carleton University Ottawa, Ontario, Canada K1S 5B6 Information Department The People's University of China Beijing, People's Republic of China Received on and in revised form on
On Tornheim s double series
 ACTA ARITHMETICA LXXV.2 (1996 On Tornheim s double series by James G. Huard (Buffalo, N.Y., Kenneth S. Williams (Ottawa, Ont. and Zhang Nan-Yue (Beijing 1. Introduction. We call the double infinite series
ACTA ARITHMETICA LXXV.2 (1996 On Tornheim s double series by James G. Huard (Buffalo, N.Y., Kenneth S. Williams (Ottawa, Ont. and Zhang Nan-Yue (Beijing 1. Introduction. We call the double infinite series
COLLOQUIUM MATHEMATICUM
 COLLOQUIUM MATHEMATICUM VOL. 74 1997 NO. 1 ON PASCAL'S TRIANGLE MODULO p2 JAMES G. H U A RD (BUFFALO, N.Y.), BLAIR K. S P E ARM A N (KELOWNA, B.C.), AND KENNETH S. W I L L I A M S (OTTAWA, ONT.) 1. Introduction.
COLLOQUIUM MATHEMATICUM VOL. 74 1997 NO. 1 ON PASCAL'S TRIANGLE MODULO p2 JAMES G. H U A RD (BUFFALO, N.Y.), BLAIR K. S P E ARM A N (KELOWNA, B.C.), AND KENNETH S. W I L L I A M S (OTTAWA, ONT.) 1. Introduction.
Sums of Products of Bernoulli Numbers*
 journal of number theory 60, 234 (996) article no. 00 Sums of Products of Bernoulli Numbers* Karl Dilcher Department of Mathematics, Statistics, and Computing Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova
journal of number theory 60, 234 (996) article no. 00 Sums of Products of Bernoulli Numbers* Karl Dilcher Department of Mathematics, Statistics, and Computing Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova
A MATRIX GENERALIZATION OF A THEOREM OF FINE
 A MATRIX GENERALIZATION OF A THEOREM OF FINE ERIC ROWLAND To Jeff Shallit on his 60th birthday! Abstract. In 1947 Nathan Fine gave a beautiful product for the number of binomial coefficients ( n, for m
A MATRIX GENERALIZATION OF A THEOREM OF FINE ERIC ROWLAND To Jeff Shallit on his 60th birthday! Abstract. In 1947 Nathan Fine gave a beautiful product for the number of binomial coefficients ( n, for m
Generalized Akiyama-Tanigawa Algorithm for Hypersums of Powers of Integers
 1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol 16 (2013, Article 1332 Generalized Aiyama-Tanigawa Algorithm for Hypersums of Powers of Integers José Luis Cereceda Distrito Telefónica, Edificio Este
1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol 16 (2013, Article 1332 Generalized Aiyama-Tanigawa Algorithm for Hypersums of Powers of Integers José Luis Cereceda Distrito Telefónica, Edificio Este
POLYNOMIAL SOLUTIONS OF PELL S EQUATION AND FUNDAMENTAL UNITS IN REAL QUADRATIC FIELDS
 J. London Math. Soc. 67 (2003) 16 28 C 2003 London Mathematical Society DOI: 10.1112/S002461070200371X POLYNOMIAL SOLUTIONS OF PELL S EQUATION AND FUNDAMENTAL UNITS IN REAL QUADRATIC FIELDS J. MCLAUGHLIN
J. London Math. Soc. 67 (2003) 16 28 C 2003 London Mathematical Society DOI: 10.1112/S002461070200371X POLYNOMIAL SOLUTIONS OF PELL S EQUATION AND FUNDAMENTAL UNITS IN REAL QUADRATIC FIELDS J. MCLAUGHLIN
Sloping Binary Numbers: A New Sequence Related to the Binary Numbers
 Sloping Binary Numbers: A New Sequence Related to the Binary Numbers David Applegate, Internet and Network Systems Research Center, AT&T Shannon Labs, 180 Park Avenue, Florham Park, NJ 0793 0971, USA (Email:
Sloping Binary Numbers: A New Sequence Related to the Binary Numbers David Applegate, Internet and Network Systems Research Center, AT&T Shannon Labs, 180 Park Avenue, Florham Park, NJ 0793 0971, USA (Email:
The genera representing a positive integer
 ACTA ARITHMETICA 102.4 (2002) The genera representing a positive integer by Pierre Kaplan (Nancy) and Kenneth S. Williams (Ottawa) 1. Introduction. A nonsquare integer d with d 0 or 1 (mod 4) is called
ACTA ARITHMETICA 102.4 (2002) The genera representing a positive integer by Pierre Kaplan (Nancy) and Kenneth S. Williams (Ottawa) 1. Introduction. A nonsquare integer d with d 0 or 1 (mod 4) is called
Polyexponentials. Khristo N. Boyadzhiev Ohio Northern University Departnment of Mathematics Ada, OH
 Polyexponentials Khristo N. Boyadzhiev Ohio Northern University Departnment of Mathematics Ada, OH 45810 k-boyadzhiev@onu.edu 1. Introduction. The polylogarithmic function [15] (1.1) and the more general
Polyexponentials Khristo N. Boyadzhiev Ohio Northern University Departnment of Mathematics Ada, OH 45810 k-boyadzhiev@onu.edu 1. Introduction. The polylogarithmic function [15] (1.1) and the more general
ON MORDELL-TORNHEIM AND OTHER MULTIPLE ZETA-FUNCTIONS. (m + n) s 3. n s 2
 ON MORDELL-TORNHEIM AND OTHER MULTIPLE ZETA-FUNCTIONS KOHJI MATSUMOTO. Introduction In 950, Tornheim [4] introduced the double series m s n s 2 (m + n) s 3 (.) m= n= of three variables, and studied its
ON MORDELL-TORNHEIM AND OTHER MULTIPLE ZETA-FUNCTIONS KOHJI MATSUMOTO. Introduction In 950, Tornheim [4] introduced the double series m s n s 2 (m + n) s 3 (.) m= n= of three variables, and studied its
{ 0! = 1 n! = n(n 1)!, n 1. n! =
 Summations Question? What is the sum of the first 100 positive integers? Counting Question? In how many ways may the first three horses in a 10 horse race finish? Multiplication Principle: If an event
Summations Question? What is the sum of the first 100 positive integers? Counting Question? In how many ways may the first three horses in a 10 horse race finish? Multiplication Principle: If an event
q-counting hypercubes in Lucas cubes
 Turkish Journal of Mathematics http:// journals. tubitak. gov. tr/ math/ Research Article Turk J Math (2018) 42: 190 203 c TÜBİTAK doi:10.3906/mat-1605-2 q-counting hypercubes in Lucas cubes Elif SAYGI
Turkish Journal of Mathematics http:// journals. tubitak. gov. tr/ math/ Research Article Turk J Math (2018) 42: 190 203 c TÜBİTAK doi:10.3906/mat-1605-2 q-counting hypercubes in Lucas cubes Elif SAYGI
Ternary Quadratic Forms and Eta Quotients
 Canad. Math. Bull. Vol. 58 (4), 015 pp. 858 868 http://dx.doi.org/10.4153/cmb-015-044-3 Canadian Mathematical Society 015 Ternary Quadratic Forms and Eta Quotients Kenneth S. Williams Abstract. Let η(z)
Canad. Math. Bull. Vol. 58 (4), 015 pp. 858 868 http://dx.doi.org/10.4153/cmb-015-044-3 Canadian Mathematical Society 015 Ternary Quadratic Forms and Eta Quotients Kenneth S. Williams Abstract. Let η(z)
Hypergeometric series and the Riemann zeta function
 ACTA ARITHMETICA LXXXII.2 (997) Hypergeometric series and the Riemann zeta function by Wenchang Chu (Roma) For infinite series related to the Riemann zeta function, De Doelder [4] established numerous
ACTA ARITHMETICA LXXXII.2 (997) Hypergeometric series and the Riemann zeta function by Wenchang Chu (Roma) For infinite series related to the Riemann zeta function, De Doelder [4] established numerous
Investigating Geometric and Exponential Polynomials with Euler-Seidel Matrices
 1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 14 (2011), Article 11.4.6 Investigating Geometric and Exponential Polynomials with Euler-Seidel Matrices Ayhan Dil and Veli Kurt Department of Mathematics
1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 14 (2011), Article 11.4.6 Investigating Geometric and Exponential Polynomials with Euler-Seidel Matrices Ayhan Dil and Veli Kurt Department of Mathematics
On squares of squares
 ACTA ARITHMETICA LXXXVIII.3 (1999) On squares of squares by Andrew Bremner (Tempe, Ariz.) 0. There is a long and intriguing history of the subject of magic squares, squares whose row, column, and diagonal
ACTA ARITHMETICA LXXXVIII.3 (1999) On squares of squares by Andrew Bremner (Tempe, Ariz.) 0. There is a long and intriguing history of the subject of magic squares, squares whose row, column, and diagonal
An Euler-Type Formula for ζ(2k + 1)
 An Euler-Type Formula for ζ(k + ) Michael J. Dancs and Tian-Xiao He Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Illinois Wesleyan University Bloomington, IL 670-900, USA Draft, June 30th, 004 Abstract
An Euler-Type Formula for ζ(k + ) Michael J. Dancs and Tian-Xiao He Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Illinois Wesleyan University Bloomington, IL 670-900, USA Draft, June 30th, 004 Abstract
On Systems of Diagonal Forms II
 On Systems of Diagonal Forms II Michael P Knapp 1 Introduction In a recent paper [8], we considered the system F of homogeneous additive forms F 1 (x) = a 11 x k 1 1 + + a 1s x k 1 s F R (x) = a R1 x k
On Systems of Diagonal Forms II Michael P Knapp 1 Introduction In a recent paper [8], we considered the system F of homogeneous additive forms F 1 (x) = a 11 x k 1 1 + + a 1s x k 1 s F R (x) = a R1 x k
Applications. More Counting Problems. Complexity of Algorithms
 Recurrences Applications More Counting Problems Complexity of Algorithms Part I Recurrences and Binomial Coefficients Paths in a Triangle P(0, 0) P(1, 0) P(1,1) P(2, 0) P(2,1) P(2, 2) P(3, 0) P(3,1) P(3,
Recurrences Applications More Counting Problems Complexity of Algorithms Part I Recurrences and Binomial Coefficients Paths in a Triangle P(0, 0) P(1, 0) P(1,1) P(2, 0) P(2,1) P(2, 2) P(3, 0) P(3,1) P(3,
Situation: Summing the Natural Numbers
 Situation: Summing the Natural Numbers Prepared at Penn State University Mid-Atlantic Center for Mathematics Teaching and Learning 14 July 005 Shari and Anna Edited at University of Georgia Center for
Situation: Summing the Natural Numbers Prepared at Penn State University Mid-Atlantic Center for Mathematics Teaching and Learning 14 July 005 Shari and Anna Edited at University of Georgia Center for
A LINEAR BINOMIAL RECURRENCE AND THE BELL NUMBERS AND POLYNOMIALS
 Applicable Analysis and Discrete Mathematics, 1 (27, 371 385. Available electronically at http://pefmath.etf.bg.ac.yu A LINEAR BINOMIAL RECURRENCE AND THE BELL NUMBERS AND POLYNOMIALS H. W. Gould, Jocelyn
Applicable Analysis and Discrete Mathematics, 1 (27, 371 385. Available electronically at http://pefmath.etf.bg.ac.yu A LINEAR BINOMIAL RECURRENCE AND THE BELL NUMBERS AND POLYNOMIALS H. W. Gould, Jocelyn
SQUARES THEOREM. Submitted by K. K. Azad. Absf ract. 0. Notation. As (n) = ~(k) ~ (- n sk), kot/s
 Far East J. Math. Sci. (FJMS) 3(6) (2001), 1001-1005 AN ARITHMETIC PROOF OF JACOBI'S EIGHT SQUARES THEOREM KENNETH S. WILLIAMS ( Received July 21, 2001 ) Submitted by K. K. Azad Absf ract An elementary
Far East J. Math. Sci. (FJMS) 3(6) (2001), 1001-1005 AN ARITHMETIC PROOF OF JACOBI'S EIGHT SQUARES THEOREM KENNETH S. WILLIAMS ( Received July 21, 2001 ) Submitted by K. K. Azad Absf ract An elementary
POLYNOMIAL SOLUTIONS TO PELL S EQUATION AND FUNDAMENTAL UNITS IN REAL QUADRATIC FIELDS arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 27 Dec 2018
![POLYNOMIAL SOLUTIONS TO PELL S EQUATION AND FUNDAMENTAL UNITS IN REAL QUADRATIC FIELDS arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 27 Dec 2018 POLYNOMIAL SOLUTIONS TO PELL S EQUATION AND FUNDAMENTAL UNITS IN REAL QUADRATIC FIELDS arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 27 Dec 2018](/thumbs/93/111465980.jpg) POLYNOMIAL SOLUTIONS TO PELL S EQUATION AND FUNDAMENTAL UNITS IN REAL QUADRATIC FIELDS arxiv:1812.10828v1 [math.nt] 27 Dec 2018 J. MC LAUGHLIN Abstract. Finding polynomial solutions to Pell s equation
POLYNOMIAL SOLUTIONS TO PELL S EQUATION AND FUNDAMENTAL UNITS IN REAL QUADRATIC FIELDS arxiv:1812.10828v1 [math.nt] 27 Dec 2018 J. MC LAUGHLIN Abstract. Finding polynomial solutions to Pell s equation
On integer solutions to x 2 dy 2 = 1, z 2 2dy 2 = 1
 ACTA ARITHMETICA LXXXII.1 (1997) On integer solutions to x 2 dy 2 = 1, z 2 2dy 2 = 1 by P. G. Walsh (Ottawa, Ont.) 1. Introduction. Let d denote a positive integer. In [7] Ono proves that if the number
ACTA ARITHMETICA LXXXII.1 (1997) On integer solutions to x 2 dy 2 = 1, z 2 2dy 2 = 1 by P. G. Walsh (Ottawa, Ont.) 1. Introduction. Let d denote a positive integer. In [7] Ono proves that if the number
Product distance matrix of a tree with matrix weights
 Product distance matrix of a tree with matrix weights R B Bapat Stat-Math Unit Indian Statistical Institute, Delhi 7-SJSS Marg, New Delhi 110 016, India email: rbb@isidacin Sivaramakrishnan Sivasubramanian
Product distance matrix of a tree with matrix weights R B Bapat Stat-Math Unit Indian Statistical Institute, Delhi 7-SJSS Marg, New Delhi 110 016, India email: rbb@isidacin Sivaramakrishnan Sivasubramanian
Fibonacci and Lucas Identities the Golden Way
 Fibonacci Lucas Identities the Golden Way Kunle Adegoe adegoe00@gmail.com arxiv:1810.12115v1 [math.nt] 25 Oct 2018 Department of Physics Engineering Physics, Obafemi Awolowo University, 220005 Ile-Ife,
Fibonacci Lucas Identities the Golden Way Kunle Adegoe adegoe00@gmail.com arxiv:1810.12115v1 [math.nt] 25 Oct 2018 Department of Physics Engineering Physics, Obafemi Awolowo University, 220005 Ile-Ife,
k 2r n k n n k) k 2r+1 k 2r (1.1)
 J. Number Theory 130(010, no. 1, 701 706. ON -ADIC ORDERS OF SOME BINOMIAL SUMS Hao Pan and Zhi-Wei Sun Abstract. We prove that for any nonnegative integers n and r the binomial sum ( n k r is divisible
J. Number Theory 130(010, no. 1, 701 706. ON -ADIC ORDERS OF SOME BINOMIAL SUMS Hao Pan and Zhi-Wei Sun Abstract. We prove that for any nonnegative integers n and r the binomial sum ( n k r is divisible
MATRIX REPRESENTATIONS FOR MULTIPLICATIVE NESTED SUMS. 1. Introduction. The harmonic sums, defined by [BK99, eq. 4, p. 1] sign (i 1 ) n 1 (N) :=
![MATRIX REPRESENTATIONS FOR MULTIPLICATIVE NESTED SUMS. 1. Introduction. The harmonic sums, defined by [BK99, eq. 4, p. 1] sign (i 1 ) n 1 (N) := MATRIX REPRESENTATIONS FOR MULTIPLICATIVE NESTED SUMS. 1. Introduction. The harmonic sums, defined by [BK99, eq. 4, p. 1] sign (i 1 ) n 1 (N) :=](/thumbs/88/114751236.jpg) MATRIX REPRESENTATIONS FOR MULTIPLICATIVE NESTED SUMS LIN JIU AND DIANE YAHUI SHI* Abstract We study the multiplicative nested sums which are generalizations of the harmonic sums and provide a calculation
MATRIX REPRESENTATIONS FOR MULTIPLICATIVE NESTED SUMS LIN JIU AND DIANE YAHUI SHI* Abstract We study the multiplicative nested sums which are generalizations of the harmonic sums and provide a calculation
IDENTITIES FOR OVERPARTITIONS WITH EVEN SMALLEST PARTS
 IDENTITIES FOR OVERPARTITIONS WITH EVEN SMALLEST PARTS MIN-JOO JANG AND JEREMY LOVEJOY Abstract. We prove several combinatorial identities involving overpartitions whose smallest parts are even. These
IDENTITIES FOR OVERPARTITIONS WITH EVEN SMALLEST PARTS MIN-JOO JANG AND JEREMY LOVEJOY Abstract. We prove several combinatorial identities involving overpartitions whose smallest parts are even. These
Some Congruences for the Partial Bell Polynomials
 3 47 6 3 Journal of Integer Seuences, Vol. 009), Article 09.4. Some Congruences for the Partial Bell Polynomials Miloud Mihoubi University of Science and Technology Houari Boumediene Faculty of Mathematics
3 47 6 3 Journal of Integer Seuences, Vol. 009), Article 09.4. Some Congruences for the Partial Bell Polynomials Miloud Mihoubi University of Science and Technology Houari Boumediene Faculty of Mathematics
1. Introduction. Let P and Q be non-zero relatively prime integers, α and β (α > β) be the zeros of x 2 P x + Q, and, for n 0, let
 C O L L O Q U I U M M A T H E M A T I C U M VOL. 78 1998 NO. 1 SQUARES IN LUCAS SEQUENCES HAVING AN EVEN FIRST PARAMETER BY PAULO R I B E N B O I M (KINGSTON, ONTARIO) AND WAYNE L. M c D A N I E L (ST.
C O L L O Q U I U M M A T H E M A T I C U M VOL. 78 1998 NO. 1 SQUARES IN LUCAS SEQUENCES HAVING AN EVEN FIRST PARAMETER BY PAULO R I B E N B O I M (KINGSTON, ONTARIO) AND WAYNE L. M c D A N I E L (ST.
ANALOGUES OF THE TRIPLE PRODUCT IDENTITY, LEBESGUE S IDENTITY AND EULER S PENTAGONAL NUMBER THEOREM
 q-hypergeometric PROOFS OF POLYNOMIAL ANALOGUES OF THE TRIPLE PRODUCT IDENTITY, LEBESGUE S IDENTITY AND EULER S PENTAGONAL NUMBER THEOREM S OLE WARNAAR Abstract We present alternative, q-hypergeometric
q-hypergeometric PROOFS OF POLYNOMIAL ANALOGUES OF THE TRIPLE PRODUCT IDENTITY, LEBESGUE S IDENTITY AND EULER S PENTAGONAL NUMBER THEOREM S OLE WARNAAR Abstract We present alternative, q-hypergeometric
A q-analogue OF THE GENERALIZED FACTORIAL NUMBERS
 J. Korean Math. Soc. 47 (2010), No. 3, pp. 645 657 DOI 10.4134/JKMS.2010.47.3.645 A q-analogue OF THE GENERALIZED FACTORIAL NUMBERS Seok-Zun Song, Gi-Sang Cheon, Young-Bae Jun, and LeRoy B. Beasley Abstract.
J. Korean Math. Soc. 47 (2010), No. 3, pp. 645 657 DOI 10.4134/JKMS.2010.47.3.645 A q-analogue OF THE GENERALIZED FACTORIAL NUMBERS Seok-Zun Song, Gi-Sang Cheon, Young-Bae Jun, and LeRoy B. Beasley Abstract.
Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics
 Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics ASYMPTOTIC EXPANSION OF THE EQUIPOISE CURVE OF A POLYNOMIAL INEQUALITY ROGER B. EGGLETON AND WILLIAM P. GALVIN Department of Mathematics Illinois
Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics ASYMPTOTIC EXPANSION OF THE EQUIPOISE CURVE OF A POLYNOMIAL INEQUALITY ROGER B. EGGLETON AND WILLIAM P. GALVIN Department of Mathematics Illinois
Polynomials with palindromic and unimodal coefficients
 Polynomials with palindromic and unimodal coefficients arxiv:60.05629v [math.co] 2 Jan 206 Hua Sun, Yi Wang, Hai-Xia Zhang School of Mathematical Sciences, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 6024,
Polynomials with palindromic and unimodal coefficients arxiv:60.05629v [math.co] 2 Jan 206 Hua Sun, Yi Wang, Hai-Xia Zhang School of Mathematical Sciences, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 6024,
On Certain Sums of Stirling Numbers with Binomial Coefficients
 1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 18 (2015, Article 15.9.6 On Certain Sums of Stirling Numbers with Binomial Coefficients H. W. Gould Department of Mathematics West Virginia University
1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 18 (2015, Article 15.9.6 On Certain Sums of Stirling Numbers with Binomial Coefficients H. W. Gould Department of Mathematics West Virginia University
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 20 Dec 2016
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 20 Dec 2016 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 20 Dec 2016](/thumbs/96/128277820.jpg) F-POLYNOMIAL FORMULA FROM CONTINUED FRACTIONS MICHELLE RABIDEAU arxiv:1612.06845v1 [math.co] 20 Dec 2016 Abstract. For cluster algebras from surfaces, there is a known formula for cluster variables and
F-POLYNOMIAL FORMULA FROM CONTINUED FRACTIONS MICHELLE RABIDEAU arxiv:1612.06845v1 [math.co] 20 Dec 2016 Abstract. For cluster algebras from surfaces, there is a known formula for cluster variables and
A DISCRETE VIEW OF FAÀ DI BRUNO. 1. Introduction. How are the following two problems related?
 ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 46, Number, 06 A DISCRETE VIEW OF FAÀ DI BRUNO RAYMOND A BEAUREGARD AND VLADIMIR A DOBRUSHKIN ABSTRACT It is shown how solving a discrete convolution problem
ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 46, Number, 06 A DISCRETE VIEW OF FAÀ DI BRUNO RAYMOND A BEAUREGARD AND VLADIMIR A DOBRUSHKIN ABSTRACT It is shown how solving a discrete convolution problem
Links Between Sums Over Paths in Bernoulli s Triangles and the Fibonacci Numbers
 Links Between Sums Over Paths in Bernoulli s Triangles and the Fibonacci Numbers arxiv:1611.09181v1 [math.co] 28 Nov 2016 Denis Neiter and Amsha Proag Ecole Polytechnique Route de Saclay 91128 Palaiseau
Links Between Sums Over Paths in Bernoulli s Triangles and the Fibonacci Numbers arxiv:1611.09181v1 [math.co] 28 Nov 2016 Denis Neiter and Amsha Proag Ecole Polytechnique Route de Saclay 91128 Palaiseau
MULTI-RESTRAINED STIRLING NUMBERS
 MULTI-RESTRAINED STIRLING NUMBERS JI YOUNG CHOI DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS SHIPPENSBURG UNIVERSITY SHIPPENSBURG, PA 17257, U.S.A. Abstract. Given positive integers n, k, and m, the (n, k)-th m- restrained
MULTI-RESTRAINED STIRLING NUMBERS JI YOUNG CHOI DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS SHIPPENSBURG UNIVERSITY SHIPPENSBURG, PA 17257, U.S.A. Abstract. Given positive integers n, k, and m, the (n, k)-th m- restrained
VALUES OF THE RIEMANN ZETA FUNCTION AND INTEGRALS INVOLVING log(2sinhf) AND log (2 sin f)
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol. 168, No. 2, 1995 VALUES OF THE RIEMANN ZETA FUNCTION AND INTEGRALS INVOLVING log(2sinhf) AND log (2 sin f) ZHANG NAN-YUE AND KENNETH S. WILLIAMS (1.1) Integrals involving
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol. 168, No. 2, 1995 VALUES OF THE RIEMANN ZETA FUNCTION AND INTEGRALS INVOLVING log(2sinhf) AND log (2 sin f) ZHANG NAN-YUE AND KENNETH S. WILLIAMS (1.1) Integrals involving
THE NUMBER OF LOCALLY RESTRICTED DIRECTED GRAPHS1
 THE NUMBER OF LOCALLY RESTRICTED DIRECTED GRAPHS1 LEO KATZ AND JAMES H. POWELL 1. Preliminaries. We shall be concerned with finite graphs of / directed lines on n points, or nodes. The lines are joins
THE NUMBER OF LOCALLY RESTRICTED DIRECTED GRAPHS1 LEO KATZ AND JAMES H. POWELL 1. Preliminaries. We shall be concerned with finite graphs of / directed lines on n points, or nodes. The lines are joins
Linear Recurrence Relations for Sums of Products of Two Terms
 Linear Recurrence Relations for Sums of Products of Two Terms Yan-Ping Mu College of Science, Tianjin University of Technology Tianjin 300384, P.R. China yanping.mu@gmail.com Submitted: Dec 27, 2010; Accepted:
Linear Recurrence Relations for Sums of Products of Two Terms Yan-Ping Mu College of Science, Tianjin University of Technology Tianjin 300384, P.R. China yanping.mu@gmail.com Submitted: Dec 27, 2010; Accepted:
Algorithmic Approach to Counting of Certain Types m-ary Partitions
 Algorithmic Approach to Counting of Certain Types m-ary Partitions Valentin P. Bakoev Abstract Partitions of integers of the type m n as a sum of powers of m (the so called m-ary partitions) and their
Algorithmic Approach to Counting of Certain Types m-ary Partitions Valentin P. Bakoev Abstract Partitions of integers of the type m n as a sum of powers of m (the so called m-ary partitions) and their
MULTISECTION METHOD AND FURTHER FORMULAE FOR π. De-Yin Zheng
 Indian J. pure appl. Math., 39(: 37-55, April 008 c Printed in India. MULTISECTION METHOD AND FURTHER FORMULAE FOR π De-Yin Zheng Department of Mathematics, Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou 30036,
Indian J. pure appl. Math., 39(: 37-55, April 008 c Printed in India. MULTISECTION METHOD AND FURTHER FORMULAE FOR π De-Yin Zheng Department of Mathematics, Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou 30036,
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 Mar 2010
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 Mar 2010 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 Mar 2010](/thumbs/89/97670058.jpg) NUMBER OF COMPOSITIONS AND CONVOLVED FIBONACCI NUMBERS arxiv:10030981v1 [mathco] 4 Mar 2010 MILAN JANJIĆ Abstract We consider two type of upper Hessenberg matrices which determinants are Fibonacci numbers
NUMBER OF COMPOSITIONS AND CONVOLVED FIBONACCI NUMBERS arxiv:10030981v1 [mathco] 4 Mar 2010 MILAN JANJIĆ Abstract We consider two type of upper Hessenberg matrices which determinants are Fibonacci numbers
A SHARP RESULT ON m-covers. Hao Pan and Zhi-Wei Sun
 Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. 35(2007), no., 355 3520. A SHARP RESULT ON m-covers Hao Pan and Zhi-Wei Sun Abstract. Let A = a s + Z k s= be a finite system of arithmetic sequences which forms an m-cover of Z
Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. 35(2007), no., 355 3520. A SHARP RESULT ON m-covers Hao Pan and Zhi-Wei Sun Abstract. Let A = a s + Z k s= be a finite system of arithmetic sequences which forms an m-cover of Z
2 Generating Functions
 2 Generating Functions In this part of the course, we re going to introduce algebraic methods for counting and proving combinatorial identities. This is often greatly advantageous over the method of finding
2 Generating Functions In this part of the course, we re going to introduce algebraic methods for counting and proving combinatorial identities. This is often greatly advantageous over the method of finding
THE LOG-BEHAVIOR OF THE SEQUENCE FOR THE PARTIAL SUM OF A LOG-CONVEX SEQUENCE. 1. Introduction
 SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol.13 (26), No.2, (2017), 163 178 DOI: 10.5644/SJM.13.2.04 THE LOG-BEHAVIOR OF THE SEQUENCE FOR THE PARTIAL SUM OF A LOG-CONVEX SEQUENCE FENG-ZHEN ZHAO Abstract. In this
SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol.13 (26), No.2, (2017), 163 178 DOI: 10.5644/SJM.13.2.04 THE LOG-BEHAVIOR OF THE SEQUENCE FOR THE PARTIAL SUM OF A LOG-CONVEX SEQUENCE FENG-ZHEN ZHAO Abstract. In this
ON THE CONTINUED FRACTION EXPANSION OF THE UNIQUE ROOT IN F(p) OF THE EQUATION x 4 + x 2 T x 1/12 = 0 AND OTHER RELATED HYPERQUADRATIC EXPANSIONS
 ON THE CONTINUED FRACTION EXPANSION OF THE UNIQUE ROOT IN F(p) OF THE EQUATION x 4 + x 2 T x 1/12 = 0 AND OTHER RELATED HYPERQUADRATIC EXPANSIONS by A. Lasjaunias Abstract.In 1986, Mills and Robbins observed
ON THE CONTINUED FRACTION EXPANSION OF THE UNIQUE ROOT IN F(p) OF THE EQUATION x 4 + x 2 T x 1/12 = 0 AND OTHER RELATED HYPERQUADRATIC EXPANSIONS by A. Lasjaunias Abstract.In 1986, Mills and Robbins observed
INFINITELY MANY ELLIPTIC CURVES OF RANK EXACTLY TWO. 1. Introduction
 INFINITELY MANY ELLIPTIC CURVES OF RANK EXACTLY TWO DONGHO BYEON AND KEUNYOUNG JEONG Abstract. In this note, we construct an infinite family of elliptic curves E defined over Q whose Mordell-Weil group
INFINITELY MANY ELLIPTIC CURVES OF RANK EXACTLY TWO DONGHO BYEON AND KEUNYOUNG JEONG Abstract. In this note, we construct an infinite family of elliptic curves E defined over Q whose Mordell-Weil group
Predictive criteria for the representation of primes by binary quadratic forms
 ACTA ARITHMETICA LXX3 (1995) Predictive criteria for the representation of primes by binary quadratic forms by Joseph B Muskat (Ramat-Gan), Blair K Spearman (Kelowna, BC) and Kenneth S Williams (Ottawa,
ACTA ARITHMETICA LXX3 (1995) Predictive criteria for the representation of primes by binary quadratic forms by Joseph B Muskat (Ramat-Gan), Blair K Spearman (Kelowna, BC) and Kenneth S Williams (Ottawa,
arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 11 Aug 2016
![arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 11 Aug 2016 arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 11 Aug 2016](/thumbs/89/98875665.jpg) INTEGERS REPRESENTABLE AS THE PRODUCT OF THE SUM OF FOUR INTEGERS WITH THE SUM OF THEIR RECIPROCALS arxiv:160803382v1 [mathnt] 11 Aug 2016 YONG ZHANG Abstract By the theory of elliptic curves we study
INTEGERS REPRESENTABLE AS THE PRODUCT OF THE SUM OF FOUR INTEGERS WITH THE SUM OF THEIR RECIPROCALS arxiv:160803382v1 [mathnt] 11 Aug 2016 YONG ZHANG Abstract By the theory of elliptic curves we study
A hyperfactorial divisibility Darij Grinberg *long version*
 A hyperfactorial divisibility Darij Grinberg *long version* Let us define a function H : N N by n H n k! for every n N Our goal is to prove the following theorem: Theorem 0 MacMahon We have H b + c H c
A hyperfactorial divisibility Darij Grinberg *long version* Let us define a function H : N N by n H n k! for every n N Our goal is to prove the following theorem: Theorem 0 MacMahon We have H b + c H c
Miller Objectives Alignment Math
 Miller Objectives Alignment Math 1050 1 College Algebra Course Objectives Spring Semester 2016 1. Use algebraic methods to solve a variety of problems involving exponential, logarithmic, polynomial, and
Miller Objectives Alignment Math 1050 1 College Algebra Course Objectives Spring Semester 2016 1. Use algebraic methods to solve a variety of problems involving exponential, logarithmic, polynomial, and
A Symbolic Operator Approach to Several Summation Formulas for Power Series
 A Symbolic Operator Approach to Several Summation Formulas for Power Series T. X. He, L. C. Hsu 2, P. J.-S. Shiue 3, and D. C. Torney 4 Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Illinois Wesleyan
A Symbolic Operator Approach to Several Summation Formulas for Power Series T. X. He, L. C. Hsu 2, P. J.-S. Shiue 3, and D. C. Torney 4 Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Illinois Wesleyan
Linear transformations preserving the strong q-log-convexity of polynomials
 Linear transformations preserving the strong q-log-convexity of polynomials Bao-Xuan Zhu School of Mathematics and Statistics Jiangsu Normal University Xuzhou, PR China bxzhu@jsnueducn Hua Sun College
Linear transformations preserving the strong q-log-convexity of polynomials Bao-Xuan Zhu School of Mathematics and Statistics Jiangsu Normal University Xuzhou, PR China bxzhu@jsnueducn Hua Sun College
New Multiple Harmonic Sum Identities
 New Multiple Harmonic Sum Identities Helmut Prodinger Department of Mathematics University of Stellenbosch 760 Stellenbosch, South Africa hproding@sun.ac.za Roberto Tauraso Dipartimento di Matematica Università
New Multiple Harmonic Sum Identities Helmut Prodinger Department of Mathematics University of Stellenbosch 760 Stellenbosch, South Africa hproding@sun.ac.za Roberto Tauraso Dipartimento di Matematica Università
Solving Systems of Linear Equations. Classification by Number of Solutions
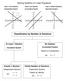 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
GENERALIZATION OF THE SIGN REVERSING INVOLUTION ON THE SPECIAL RIM HOOK TABLEAUX. Jaejin Lee
 Korean J. Math. 8 (00), No., pp. 89 98 GENERALIZATION OF THE SIGN REVERSING INVOLUTION ON THE SPECIAL RIM HOOK TABLEAUX Jaejin Lee Abstract. Eğecioğlu and Remmel [] gave a combinatorial interpretation
Korean J. Math. 8 (00), No., pp. 89 98 GENERALIZATION OF THE SIGN REVERSING INVOLUTION ON THE SPECIAL RIM HOOK TABLEAUX Jaejin Lee Abstract. Eğecioğlu and Remmel [] gave a combinatorial interpretation
Decomposition of Pascal s Kernels Mod p s
 San Jose State University SJSU ScholarWorks Faculty Publications Mathematics January 2002 Decomposition of Pascal s Kernels Mod p s Richard P. Kubelka San Jose State University, richard.kubelka@ssu.edu
San Jose State University SJSU ScholarWorks Faculty Publications Mathematics January 2002 Decomposition of Pascal s Kernels Mod p s Richard P. Kubelka San Jose State University, richard.kubelka@ssu.edu
Bounds for the Representations of Integers by Positive Quadratic Forms
 22 MATHEMATICS MAGAZINE Bounds for the Representations of Integers by Positive Quadratic Forms KENNETH S. WILLIAMS Carleton University Ottawa, ON, Canada kennethwilliams@cunet.carleton.ca The fact that
22 MATHEMATICS MAGAZINE Bounds for the Representations of Integers by Positive Quadratic Forms KENNETH S. WILLIAMS Carleton University Ottawa, ON, Canada kennethwilliams@cunet.carleton.ca The fact that
Explicit solution of a class of quartic Thue equations
 ACTA ARITHMETICA LXIV.3 (1993) Explicit solution of a class of quartic Thue equations by Nikos Tzanakis (Iraklion) 1. Introduction. In this paper we deal with the efficient solution of a certain interesting
ACTA ARITHMETICA LXIV.3 (1993) Explicit solution of a class of quartic Thue equations by Nikos Tzanakis (Iraklion) 1. Introduction. In this paper we deal with the efficient solution of a certain interesting
EVALUATION OF A FAMILY OF BINOMIAL DETERMINANTS
 EVALUATION OF A FAMILY OF BINOMIAL DETERMINANTS CHARLES HELOU AND JAMES A SELLERS Abstract Motivated by a recent work about finite sequences where the n-th term is bounded by n, we evaluate some classes
EVALUATION OF A FAMILY OF BINOMIAL DETERMINANTS CHARLES HELOU AND JAMES A SELLERS Abstract Motivated by a recent work about finite sequences where the n-th term is bounded by n, we evaluate some classes
Simple explicit formulas for the Frame-Stewart numbers
 Simple explicit formulas for the Frame-Stewart numbers Sandi Klavžar Department of Mathematics, PEF, University of Maribor Koroška cesta 160, 2000 Maribor, Slovenia sandi.klavzar@uni-lj.si Uroš Milutinović
Simple explicit formulas for the Frame-Stewart numbers Sandi Klavžar Department of Mathematics, PEF, University of Maribor Koroška cesta 160, 2000 Maribor, Slovenia sandi.klavzar@uni-lj.si Uroš Milutinović
Zhi-Wei Sun Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University Nanjing , People s Republic of China
 J. Number Theory 16(016), 190 11. A RESULT SIMILAR TO LAGRANGE S THEOREM Zhi-Wei Sun Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University Nanjing 10093, People s Republic of China zwsun@nju.edu.cn http://math.nju.edu.cn/
J. Number Theory 16(016), 190 11. A RESULT SIMILAR TO LAGRANGE S THEOREM Zhi-Wei Sun Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University Nanjing 10093, People s Republic of China zwsun@nju.edu.cn http://math.nju.edu.cn/
Symmetric functions and the Vandermonde matrix
 J ournal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 172 (2004) 49-64 Symmetric functions and the Vandermonde matrix Halil Oruç, Hakan K. Akmaz Department of Mathematics, Dokuz Eylül University Fen Edebiyat
J ournal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 172 (2004) 49-64 Symmetric functions and the Vandermonde matrix Halil Oruç, Hakan K. Akmaz Department of Mathematics, Dokuz Eylül University Fen Edebiyat
On the power-free parts of consecutive integers
 ACTA ARITHMETICA XC4 (1999) On the power-free parts of consecutive integers by B M M de Weger (Krimpen aan den IJssel) and C E van de Woestijne (Leiden) 1 Introduction and main results Considering the
ACTA ARITHMETICA XC4 (1999) On the power-free parts of consecutive integers by B M M de Weger (Krimpen aan den IJssel) and C E van de Woestijne (Leiden) 1 Introduction and main results Considering the
The Degree of the Splitting Field of a Random Polynomial over a Finite Field
 The Degree of the Splitting Field of a Random Polynomial over a Finite Field John D. Dixon and Daniel Panario School of Mathematics and Statistics Carleton University, Ottawa, Canada fjdixon,danielg@math.carleton.ca
The Degree of the Splitting Field of a Random Polynomial over a Finite Field John D. Dixon and Daniel Panario School of Mathematics and Statistics Carleton University, Ottawa, Canada fjdixon,danielg@math.carleton.ca
SERIES
 SERIES.... This chapter revisits sequences arithmetic then geometric to see how these ideas can be extended, and how they occur in other contexts. A sequence is a list of ordered numbers, whereas a series
SERIES.... This chapter revisits sequences arithmetic then geometric to see how these ideas can be extended, and how they occur in other contexts. A sequence is a list of ordered numbers, whereas a series
Partitions, rooks, and symmetric functions in noncommuting variables
 Partitions, rooks, and symmetric functions in noncommuting variables Mahir Bilen Can Department of Mathematics, Tulane University New Orleans, LA 70118, USA, mcan@tulane.edu and Bruce E. Sagan Department
Partitions, rooks, and symmetric functions in noncommuting variables Mahir Bilen Can Department of Mathematics, Tulane University New Orleans, LA 70118, USA, mcan@tulane.edu and Bruce E. Sagan Department
Summing Series: Solutions
 Sequences and Series Misha Lavrov Summing Series: Solutions Western PA ARML Practice December, 0 Switching the order of summation Prove useful identity 9 x x x x x x Riemann s zeta function ζ is defined
Sequences and Series Misha Lavrov Summing Series: Solutions Western PA ARML Practice December, 0 Switching the order of summation Prove useful identity 9 x x x x x x Riemann s zeta function ζ is defined
Series of Error Terms for Rational Approximations of Irrational Numbers
 2 3 47 6 23 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 4 20, Article..4 Series of Error Terms for Rational Approximations of Irrational Numbers Carsten Elsner Fachhochschule für die Wirtschaft Hannover Freundallee
2 3 47 6 23 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 4 20, Article..4 Series of Error Terms for Rational Approximations of Irrational Numbers Carsten Elsner Fachhochschule für die Wirtschaft Hannover Freundallee
A video College Algebra course & 6 Enrichment videos
 A video College Algebra course & 6 Enrichment videos Recorded at the University of Missouri Kansas City in 1998. All times are approximate. About 43 hours total. Available on YouTube at http://www.youtube.com/user/umkc
A video College Algebra course & 6 Enrichment videos Recorded at the University of Missouri Kansas City in 1998. All times are approximate. About 43 hours total. Available on YouTube at http://www.youtube.com/user/umkc
A talk given at the University of California at Irvine on Jan. 19, 2006.
 A talk given at the University of California at Irvine on Jan. 19, 2006. A SURVEY OF ZERO-SUM PROBLEMS ON ABELIAN GROUPS Zhi-Wei Sun Department of Mathematics Nanjing University Nanjing 210093 People s
A talk given at the University of California at Irvine on Jan. 19, 2006. A SURVEY OF ZERO-SUM PROBLEMS ON ABELIAN GROUPS Zhi-Wei Sun Department of Mathematics Nanjing University Nanjing 210093 People s
ON UNIVERSAL SUMS OF POLYGONAL NUMBERS
 Sci. China Math. 58(2015), no. 7, 1367 1396. ON UNIVERSAL SUMS OF POLYGONAL NUMBERS Zhi-Wei SUN Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University Nanjing 210093, People s Republic of China zwsun@nju.edu.cn
Sci. China Math. 58(2015), no. 7, 1367 1396. ON UNIVERSAL SUMS OF POLYGONAL NUMBERS Zhi-Wei SUN Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University Nanjing 210093, People s Republic of China zwsun@nju.edu.cn
#A20 INTEGERS 11 (2011) ON CONGRUENT NUMBERS WITH THREE PRIME FACTORS. Lindsey Reinholz
 #A20 INTEGERS 11 (2011) ON CONGRUENT NUMBERS WITH THREE PRIME FACTORS Lindsey Reinholz Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of British Columbia Okanagan, Kelowna, BC, Canada, V1V 1V7. reinholz@interchange.ubc.ca
#A20 INTEGERS 11 (2011) ON CONGRUENT NUMBERS WITH THREE PRIME FACTORS Lindsey Reinholz Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of British Columbia Okanagan, Kelowna, BC, Canada, V1V 1V7. reinholz@interchange.ubc.ca
MCR3U Unit 7 Lesson Notes
 7.1 Arithmetic Sequences Sequence: An ordered list of numbers identified by a pattern or rule that may stop at some number or continue indefinitely. Ex. 1, 2, 4, 8,... Ex. 3, 7, 11, 15 Term (of a sequence):
7.1 Arithmetic Sequences Sequence: An ordered list of numbers identified by a pattern or rule that may stop at some number or continue indefinitely. Ex. 1, 2, 4, 8,... Ex. 3, 7, 11, 15 Term (of a sequence):
MATH 117 LECTURE NOTES
 MATH 117 LECTURE NOTES XIN ZHOU Abstract. This is the set of lecture notes for Math 117 during Fall quarter of 2017 at UC Santa Barbara. The lectures follow closely the textbook [1]. Contents 1. The set
MATH 117 LECTURE NOTES XIN ZHOU Abstract. This is the set of lecture notes for Math 117 during Fall quarter of 2017 at UC Santa Barbara. The lectures follow closely the textbook [1]. Contents 1. The set
The k-fibonacci matrix and the Pascal matrix
 Cent Eur J Math 9(6 0 403-40 DOI: 0478/s533-0-0089-9 Central European Journal of Mathematics The -Fibonacci matrix and the Pascal matrix Research Article Sergio Falcon Department of Mathematics and Institute
Cent Eur J Math 9(6 0 403-40 DOI: 0478/s533-0-0089-9 Central European Journal of Mathematics The -Fibonacci matrix and the Pascal matrix Research Article Sergio Falcon Department of Mathematics and Institute
Spectra of Semidirect Products of Cyclic Groups
 Spectra of Semidirect Products of Cyclic Groups Nathan Fox 1 University of Minnesota-Twin Cities Abstract The spectrum of a graph is the set of eigenvalues of its adjacency matrix A group, together with
Spectra of Semidirect Products of Cyclic Groups Nathan Fox 1 University of Minnesota-Twin Cities Abstract The spectrum of a graph is the set of eigenvalues of its adjacency matrix A group, together with
NEW CONSTRUCTION OF THE EAGON-NORTHCOTT COMPLEX. Oh-Jin Kang and Joohyung Kim
 Korean J Math 20 (2012) No 2 pp 161 176 NEW CONSTRUCTION OF THE EAGON-NORTHCOTT COMPLEX Oh-Jin Kang and Joohyung Kim Abstract The authors [6 introduced the concept of a complete matrix of grade g > 3 to
Korean J Math 20 (2012) No 2 pp 161 176 NEW CONSTRUCTION OF THE EAGON-NORTHCOTT COMPLEX Oh-Jin Kang and Joohyung Kim Abstract The authors [6 introduced the concept of a complete matrix of grade g > 3 to
DISTRIBUTION OF FIBONACCI AND LUCAS NUMBERS MODULO 3 k
 DISTRIBUTION OF FIBONACCI AND LUCAS NUMBERS MODULO 3 k RALF BUNDSCHUH AND PETER BUNDSCHUH Dedicated to Peter Shiue on the occasion of his 70th birthday Abstract. Let F 0 = 0,F 1 = 1, and F n = F n 1 +F
DISTRIBUTION OF FIBONACCI AND LUCAS NUMBERS MODULO 3 k RALF BUNDSCHUH AND PETER BUNDSCHUH Dedicated to Peter Shiue on the occasion of his 70th birthday Abstract. Let F 0 = 0,F 1 = 1, and F n = F n 1 +F
Some theorems on the explicit evaluations of singular moduli 1
 General Mathematics Vol 17 No 1 009) 71 87 Some theorems on the explicit evaluations of singular moduli 1 K Sushan Bairy Abstract At scattered places in his notebooks Ramanujan recorded some theorems for
General Mathematics Vol 17 No 1 009) 71 87 Some theorems on the explicit evaluations of singular moduli 1 K Sushan Bairy Abstract At scattered places in his notebooks Ramanujan recorded some theorems for
The Degree of the Splitting Field of a Random Polynomial over a Finite Field
 The Degree of the Splitting Field of a Random Polynomial over a Finite Field John D. Dixon and Daniel Panario School of Mathematics and Statistics Carleton University, Ottawa, Canada {jdixon,daniel}@math.carleton.ca
The Degree of the Splitting Field of a Random Polynomial over a Finite Field John D. Dixon and Daniel Panario School of Mathematics and Statistics Carleton University, Ottawa, Canada {jdixon,daniel}@math.carleton.ca
Lecture Notes 6: Dynamic Equations Part A: First-Order Difference Equations in One Variable
 University of Warwick, EC9A0 Maths for Economists Peter J. Hammond 1 of 54 Lecture Notes 6: Dynamic Equations Part A: First-Order Difference Equations in One Variable Peter J. Hammond latest revision 2017
University of Warwick, EC9A0 Maths for Economists Peter J. Hammond 1 of 54 Lecture Notes 6: Dynamic Equations Part A: First-Order Difference Equations in One Variable Peter J. Hammond latest revision 2017
ON RANDOM DETERMINANTS I
 Studia Scientiarum Mathematicarum Hungarica, 2 (1967), pp. 125 132. ON RANDOM DETERMINANTS I András Prékopa (Budapest) Received: July 20, 1966 1 Introduction Consider the determinant with random entries
Studia Scientiarum Mathematicarum Hungarica, 2 (1967), pp. 125 132. ON RANDOM DETERMINANTS I András Prékopa (Budapest) Received: July 20, 1966 1 Introduction Consider the determinant with random entries
Combinatorial properties of the numbers of tableaux of bounded height
 Combinatorial properties of the numbers of tableaux of bounded height Marilena Barnabei, Flavio Bonetti, and Matteo Sibani Abstract We introduce an infinite family of lower triangular matrices Γ (s), where
Combinatorial properties of the numbers of tableaux of bounded height Marilena Barnabei, Flavio Bonetti, and Matteo Sibani Abstract We introduce an infinite family of lower triangular matrices Γ (s), where
Another Proof of Nathanson s Theorems
 1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 14 (2011), Article 11.8.4 Another Proof of Nathanson s Theorems Quan-Hui Yang School of Mathematical Sciences Nanjing Normal University Nanjing 210046
1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 14 (2011), Article 11.8.4 Another Proof of Nathanson s Theorems Quan-Hui Yang School of Mathematical Sciences Nanjing Normal University Nanjing 210046
Discrete Applied Mathematics
 Discrete Applied Mathematics 157 (2009 1696 1701 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Discrete Applied Mathematics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/dam Riordan group involutions and the -sequence
Discrete Applied Mathematics 157 (2009 1696 1701 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Discrete Applied Mathematics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/dam Riordan group involutions and the -sequence
INTEGRAL BASES FOR AN INFINITE FAMILY OF CYCLIC QUINTIC FIELDS*
 ASIAN J. MATH. Vol. 10, No. 4, pp. 765-772, December 2006 @ 2006 International Press 008 INTEGRAL BASES FOR AN INFINITE FAMILY OF CYCLIC QUINTIC FIELDS* DANIEL ELOFF?, BLAIR K. SPEAR MAN^^, AND KENNETH
ASIAN J. MATH. Vol. 10, No. 4, pp. 765-772, December 2006 @ 2006 International Press 008 INTEGRAL BASES FOR AN INFINITE FAMILY OF CYCLIC QUINTIC FIELDS* DANIEL ELOFF?, BLAIR K. SPEAR MAN^^, AND KENNETH
On the single-orbit conjecture for uncoverings-by-bases
 On the single-orbit conjecture for uncoverings-by-bases Robert F. Bailey School of Mathematics and Statistics Carleton University 1125 Colonel By Drive Ottawa, Ontario K1S 5B6 Canada Peter J. Cameron School
On the single-orbit conjecture for uncoverings-by-bases Robert F. Bailey School of Mathematics and Statistics Carleton University 1125 Colonel By Drive Ottawa, Ontario K1S 5B6 Canada Peter J. Cameron School
On the Convergence of the Summation Formulas Constructed by Using a Symbolic Operator Approach
 On the Convergence of the Summation Formulas Constructed by Using a Symbolic Operator Approach Tian-Xiao He 1, Leetsch C. Hsu 2, and Peter J.-S. Shiue 3 1 Department of Mathematics and Computer Science
On the Convergence of the Summation Formulas Constructed by Using a Symbolic Operator Approach Tian-Xiao He 1, Leetsch C. Hsu 2, and Peter J.-S. Shiue 3 1 Department of Mathematics and Computer Science
Colloq. Math. 145(2016), no. 1, ON SOME UNIVERSAL SUMS OF GENERALIZED POLYGONAL NUMBERS. 1. Introduction. x(x 1) (1.1) p m (x) = (m 2) + x.
 Colloq. Math. 145(016), no. 1, 149-155. ON SOME UNIVERSAL SUMS OF GENERALIZED POLYGONAL NUMBERS FAN GE AND ZHI-WEI SUN Abstract. For m = 3, 4,... those p m (x) = (m )x(x 1)/ + x with x Z are called generalized
Colloq. Math. 145(016), no. 1, 149-155. ON SOME UNIVERSAL SUMS OF GENERALIZED POLYGONAL NUMBERS FAN GE AND ZHI-WEI SUN Abstract. For m = 3, 4,... those p m (x) = (m )x(x 1)/ + x with x Z are called generalized
A RECIPROCAL SUM RELATED TO THE RIEMANN ζ FUNCTION. 1. Introduction. 1 n s, k 2 = n 1. k 3 = 2n(n 1),
 Journal of Mathematical Inequalities Volume, Number 07, 09 5 doi:0.753/jmi--0 A RECIPROCAL SUM RELATED TO THE RIEMANN ζ FUNCTION LIN XIN AND LI XIAOXUE Communicated by J. Pečarić Abstract. This paper,
Journal of Mathematical Inequalities Volume, Number 07, 09 5 doi:0.753/jmi--0 A RECIPROCAL SUM RELATED TO THE RIEMANN ζ FUNCTION LIN XIN AND LI XIAOXUE Communicated by J. Pečarić Abstract. This paper,
A PERIODIC APPROACH TO PLANE PARTITION CONGRUENCES
 A PERIODIC APPROACH TO PLANE PARTITION CONGRUENCES MATTHEW S. MIZUHARA, JAMES A. SELLERS, AND HOLLY SWISHER Abstract. Ramanujan s celebrated congruences of the partition function p(n have inspired a vast
A PERIODIC APPROACH TO PLANE PARTITION CONGRUENCES MATTHEW S. MIZUHARA, JAMES A. SELLERS, AND HOLLY SWISHER Abstract. Ramanujan s celebrated congruences of the partition function p(n have inspired a vast
A 4 -SEXTIC FIELDS WITH A POWER BASIS. Daniel Eloff, Blair K. Spearman, and Kenneth S. Williams
 A 4 -SEXTIC FIELDS WITH A POWER BASIS Daniel Eloff, Blair K. Spearman, and Kenneth S. Williams Abstract. An infinite family of monogenic sextic fields with Galois group A 4 is exhibited. 1. Introduction.
A 4 -SEXTIC FIELDS WITH A POWER BASIS Daniel Eloff, Blair K. Spearman, and Kenneth S. Williams Abstract. An infinite family of monogenic sextic fields with Galois group A 4 is exhibited. 1. Introduction.
Compositions of n with no occurrence of k. Phyllis Chinn, Humboldt State University Silvia Heubach, California State University Los Angeles
 Compositions of n with no occurrence of k Phyllis Chinn, Humboldt State University Silvia Heubach, California State University Los Angeles Abstract A composition of n is an ordered collection of one or
Compositions of n with no occurrence of k Phyllis Chinn, Humboldt State University Silvia Heubach, California State University Los Angeles Abstract A composition of n is an ordered collection of one or
arxiv: v1 [math.ag] 13 Mar 2019
![arxiv: v1 [math.ag] 13 Mar 2019 arxiv: v1 [math.ag] 13 Mar 2019](/thumbs/94/120330902.jpg) THE CONSTRUCTION PROBLEM FOR HODGE NUMBERS MODULO AN INTEGER MATTHIAS PAULSEN AND STEFAN SCHREIEDER arxiv:1903.05430v1 [math.ag] 13 Mar 2019 Abstract. For any integer m 2 and any dimension n 1, we show
THE CONSTRUCTION PROBLEM FOR HODGE NUMBERS MODULO AN INTEGER MATTHIAS PAULSEN AND STEFAN SCHREIEDER arxiv:1903.05430v1 [math.ag] 13 Mar 2019 Abstract. For any integer m 2 and any dimension n 1, we show
Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination
 Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination DEFINITION: A linear equation in the variables x 1,..., x n is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 +...+a n x n = b, where a 1,...,a n
Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination DEFINITION: A linear equation in the variables x 1,..., x n is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 +...+a n x n = b, where a 1,...,a n
