Calculus II (Fall 2015) Practice Problems for Exam 1
|
|
|
- Brooke Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Calculus II (Fall 15) Practice Problems for Exam 1 Note: Section divisions and instructions below are the same as they will be on the exam, so you will have a better idea of what to expect, though I will leave spaces for answers on the actual exam. However, this is not quite a mock exam as there are more practice problems here than there will be on the actual exam. Nevertheless, I recommend you treat it as a mock exam (prepare first and try to finish on your own), with a rough goal of finishing in.5 hours. Then check your solutions with those posted on DL, ask questions if needed, and go back and make sure you can do the problems on your own. Instructions: Write your name and discussion section number (11 16) at the top. Read all instructions. No notes, text, calculators, etc. are allowed. Please answer the questions in the space provided below. You may use the back of the pages as scratch paper. If you run out of space for your answer on the front, you may continue it on the back provided you note that your answer continues on the back. Each section has additional instructions below. Maximum score: points. 1 True or False Instructions: Circle T or F for each question. No work is needed. Each problem is worth points. In this section, a and b are real numbers with a b, f(x) and g(x) denote a continuous functions on R, and R is the region between y = f(x) and y = g(x) from x = a to x = b. 1. T F If F (x) is an antiderivative of f(x), then b f(x) dx = F (b) F (a). a. T F Any continuous function on [a, b] is differentiable. 3. T F Any continuous function on [a, b] is integrable. 4. T F If a function is not continuous at some point in [a, b], then it is not integrable on [a, b]. 5. T F (f(x) + g(x)) dx = f(x)dx + g(x) dx 6. T F (f(x)g(x)) dx = f(x)dx g(x) dx 7. T F d b dx a sin(x4 ) dx = sin(x 4 ) 8. T F π π x cos x dx = π x cos x dx. 9. T F The area of R (as above) is b (f(x) g(x)) dx. a 1. T F If S is the solid obtained by rotating R around the x-axis, the volume of S is b a π(f(x) g(x) ) dx. 11. T F If S is the solid obtained by rotating R around the line x = a, the volume of S is b a π(x a)(f(x) g(x)) dx. 1
2 Quick questions Instructions: For each question in this section, you are not required to show any work. However, in the event that your answer is incorrect, you may receive partial credit for work you write down. Each problem is worth points. Box in your final answer. 1. Compute 3 (x + 1) dx. 13. Compute π/9 sin 3x dx. 14. Compute x cos(x 3 ) dx. 15. Compute ( x + 1) 5 dx. 16. Compute sec x tan x dx. 17. Compute cos x sin x dx. 18. Compute the area under y = x 5 from x = to x =. 19. Approximate the area under y = x between x = and x = 1 by computing the corresponding Riemann sum with n = 4 equal width partitions using the right endpoint rule. 3 Patient Problems Instructions: For each problem below, show your work. Each problem is worth points. You may use the following identities: n = n(n+1) and n = n(n+1)(n+1) 6. For calculations, box in your final answer.. Using Riemann sums and the definition of integrals, compute the area under the curve y = x from x = to x =. 1. Sketch the region bounded by the curves y = x 7 and y = 5 x, and compute the area.. Sketch the region bounded by the curves y = x, y = x and the x-axis. Compute its area. 3. Let R be the region in the xy-plane under the curve y = x between x = and x = 1, and let S be the solid obtained by rotating R about the line x =. Sketch R and S, and determine the volume of S. 4. Let R be the region in the xy-plane above the x-axis which is bounded by y = x and y = x 3. Let S be the solid obtained by rotating R about the y-axis. Sketch R and S, and determine the volume of S. 5. Suppose the Oscar Mayer Wienermobile, initially at rest at time, travels due north and accelerates at a rate of 3t mph/s at time t (measured in seconds). What is the average speed of the Wienermobile from time t = to t = 1?
3 Solutions For the first two parts, explanations are not required, but I ll provide some for your benefit. Sketches I will omit. Note: Answers can be simplified in different ways, so if what you wrote down is different, it s not necessarily wrong (e.g., # 15). Just check to make sure it equals what I wrote. And if you think you find an error in one of my solutions, please let me know so I can double check it. 1. T: this is FTC II. F: Think about x 3. T: true this follows from of FTC I. So integrals of continuous functions closed intervals always exist but derivatives do not (this is not true on open intervals e.g., think of 1 x ). 4. F: We can still integrate sometimes, e.g., jump discontinuities. 5. T 6. F 7. F: Read the question carefully the definite integral gives some constant, so the derivative is. 8. F: Since x is odd and cos x is even, x cos x is odd, thus by symmetry the integral on the left is. (A picture shows the integral on the right is not zero.) 9. F (but almost T): You need to assume f(x) g(x) on [a, b] for this to be true. In general, you need absolute values. 1. F (but almost T): You need something like f(x), g(x) on [a, b]. To see why, think about f(x) = x and g(x) = x. Then rotating R around the x-axis gives the same solid as rotating the region under y = x around the x-axis (a cone). Here when you rotate the top half R about the x-axis, it passes through the bottom part of R. So one point of view is that the issue is R is bigger than it needs to be to generate S. 11. F (but almost T): Actually, I meant to make this statement true, but I forgot to write down the assumption that f(x) g(x). If f(x) g(x), this is what you get from the method of cylindrical shells: we ll have cylinders of height f(x) g(x) ( f(x) g(x) in general) and radius x a. (Note since we rotate around x a, there is no issue about R being too big as in the previous problem.) ] 3 1. You get x3 3 + x = = 1. Neat! Maybe every answer will from now on just be the problem number. 13. Let u = 3x so du = 3dx, i.e., dx = du 3. Then the integral is u(π/9) u() sin u du ] π/3 3 = 1 3 cos u = 1 3 (1 1) = 1 6. Hmm... maybe not every answer will be the problem number. 14. Let u = x 3 so du = 3x dx. Then the integral is cos(u) du 3 = 1 3 sin u + C = 1 3 sin x3 + C. 3
4 15. Let u = x + 1 so du = x 1/ dx, i.e., dx = xdu. Note x = u 1. Then our integral is u 5 x du = u 5 ( u 1 ) du = 1 (u 6 u 5 ) du = 1 (u7 7 u6 6 ) + C. Then we can substitute back (and, if we want, factor out a u 6 ) to get 1 ( x + 1) 6 ( 1 7 ( x + 1) 1 6 ) + C. 16. This problem is neato-torpedo, because we can do it two ways to get two different answers which are both right! Solution 1: Let u = tan x so du = sec xdx. Then our integral is u du = u + C = tan x + C. Solution : Let u = sec x so du = sec x tan xdx. Then our integral is u du = u + C = sec x + C. What s going on here? Note that sec x tan x = 1 sin x cos x = cos x cos x = 1, in other words, tan x and sec x differ by a constant so the above expressions are really the same after appropriately modifying C. (This issue is one reason forgetting the +C will lead to mental anguish without the +C s you get two different answers which are not equal.) 17. Rewrite it as cos x 1 sin x sin x dx = cot x csc x dx = csc x + C. 18. The area is ] (x 5) dx = x3 3 5x = 8 1 = 3 3. The area is negative because most of the region lies below the x-axis. 19. The right end points are 1 4, 4, 3 4 and 4 4. So our Riemann sum is ( )1 4 = 1 8 ( ).. The n-th Riemann sum, using right endpoints, is n ( ) i R n = = n n i=1 }{{}}{{} n 3 ( (n) ). height width (Here the right endpoints are n, 4 n,..., n n so interval widths are all n.) Factoring out and using the formula for the sum of the first n squares I gave you, we get R n = 8 n 3 (1 + + n ) = 8n(n + 1)(n + 1) 6n 3 = 4 3 ( + 3 n + 1 n ) 8 3 as n. (Note: it is probably a good idea to double check your answer with what you get using the FTC/power rule.) 4
5 1. The points of intersection will happen when x 7 = 5 x, i.e., when 3x = 1, i.e., when x = ±. Let f(x) = 5 x and g(x) = x 7. Then f(x) g(x) on [, ], so the area is ((5 x ) (x 7)) dx = (1 3x ) dx = (I used symmetry in the middle, but of course you don t have to.). Can I go home now? Haven t we done enough? No? Okay. (1 3x ) dx = (1x x 3 )] = (4 8) = 3. Note x = x when x = 1, so the region is the region under y = x from to 1 together with the region under the curve y = x from 1 to. Thus the area is x dx + ( x) dx = 3 x3/] 1 1 ] + (x x ) = (4 ) ( 1 ) = 7 6. Alternatively, you could integrate dy if you do this, you don t need to break the region up into two integrals, since R is the region to the left of x = y and to the right of x = y for y 1. Thus you can also write the area as (( y) y ) dy = y y y3 3 ] 1 = ( ) = We can do this by cross-sections (discs/washers) or cylindrical shells. Again, you can do this either way, but you should be able to solve it both ways, just in case the problem you get is much harder one way than the other. Solution 1 (cross-sections): If we take horizontal cross-sections (with respect to y), we will get annuli (washers) with outer radius 3 and inner radius x + = y +. Thus the volume is π(3 (y + ) ) dy = π (5 4y y 4 ) dy = (5y 4y3 3 y5 5 ) ] 1 = 5π 15.. Solution (cylindrical shells): If we approximate by cylinders, the cylinder about x = through x has radius x + and height x. So our volume is π(x + ) x dx = π (x 3/ + x 1/ ) dx = π( 5 x5/ x3/ ) ] 1 = 5π Again, you can do this problem either with cross-sections or cylindrical shells. Here R is the region below y = x and above y = x 3 between x = and x = 1. I think cylindrical shells is slightly easier here so I will do that. We use cylinders of radius x and the height x x 3, so by our formula in class we see the volume is πx(x x 3 ) dx = π (x x 4 ) dx = π( x3 3 x5 5 ) ] 1 5. Write a(t) for acceleration and v(t) for velocity. We know 3t 3t v(t) = a(t) dt = dt = 4 + C = 4π 15. for some C. Since the Wienermobile starts off at rest, v() =, which means C =. The average velocity is 1 1 v(t) dt = 1 3t = 1 ] 1 t3 1 = 1 = 5 mph
6 1 (Remember the average value of a function f(x) on [a, b] is b a f(x) dx. But in this case, you should already know that average velocity is (distance traveled)/(time spent), so you could probably reason this out for yourself by realizing distance traveled is v(t) dt.) Note: since units are given in the problem, you are expected to include units (in this case, mph) in your final answer. If you re curious, note the speed of the Wienermobile after 1 seconds is v(1) = = 75 mph, so the average velocity over this period is considerably less than half the final velocity on this interval. To make sense of this, draw a graph of v(t). b a 6
Calculus II Practice Test 1 Problems: , 6.5, Page 1 of 10
 Calculus II Practice Test Problems: 6.-6.3, 6.5, 7.-7.3 Page of This is in no way an inclusive set of problems there can be other types of problems on the actual test. To prepare for the test: review homework,
Calculus II Practice Test Problems: 6.-6.3, 6.5, 7.-7.3 Page of This is in no way an inclusive set of problems there can be other types of problems on the actual test. To prepare for the test: review homework,
Integrals. D. DeTurck. January 1, University of Pennsylvania. D. DeTurck Math A: Integrals 1 / 61
 Integrals D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania January 1, 2018 D. DeTurck Math 104 002 2018A: Integrals 1 / 61 Integrals Start with dx this means a little bit of x or a little change in x If we add up
Integrals D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania January 1, 2018 D. DeTurck Math 104 002 2018A: Integrals 1 / 61 Integrals Start with dx this means a little bit of x or a little change in x If we add up
Prelim 1 Solutions V2 Math 1120
 Feb., Prelim Solutions V Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 9 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck! Problem ) ( Points) Calculate the following: x a)
Feb., Prelim Solutions V Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 9 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck! Problem ) ( Points) Calculate the following: x a)
Math 221 Exam III (50 minutes) Friday April 19, 2002 Answers
 Math Exam III (5 minutes) Friday April 9, Answers I. ( points.) Fill in the boxes as to complete the following statement: A definite integral can be approximated by a Riemann sum. More precisely, if a
Math Exam III (5 minutes) Friday April 9, Answers I. ( points.) Fill in the boxes as to complete the following statement: A definite integral can be approximated by a Riemann sum. More precisely, if a
M152: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review
 M52: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review Chapter 4. 4.2 : Mean Value Theorem. - Know the statement and idea of Mean Value Theorem. - Know how to find values of c making the theorem true. - Realize the importance
M52: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review Chapter 4. 4.2 : Mean Value Theorem. - Know the statement and idea of Mean Value Theorem. - Know how to find values of c making the theorem true. - Realize the importance
1.4 Techniques of Integration
 .4 Techniques of Integration Recall the following strategy for evaluating definite integrals, which arose from the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (see Section.3). To calculate b a f(x) dx. Find a function
.4 Techniques of Integration Recall the following strategy for evaluating definite integrals, which arose from the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (see Section.3). To calculate b a f(x) dx. Find a function
Spring 2017 Midterm 1 04/26/2017
 Math 2B Spring 2017 Midterm 1 04/26/2017 Time Limit: 50 Minutes Name (Print): Student ID This exam contains 10 pages (including this cover page) and 5 problems. Check to see if any pages are missing. Enter
Math 2B Spring 2017 Midterm 1 04/26/2017 Time Limit: 50 Minutes Name (Print): Student ID This exam contains 10 pages (including this cover page) and 5 problems. Check to see if any pages are missing. Enter
Chapter 4 Integration
 Chapter 4 Integration SECTION 4.1 Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integration Calculus: Chapter 4 Section 4.1 Antiderivative A function F is an antiderivative of f on an interval I if F '( x) f ( x) for
Chapter 4 Integration SECTION 4.1 Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integration Calculus: Chapter 4 Section 4.1 Antiderivative A function F is an antiderivative of f on an interval I if F '( x) f ( x) for
Review: Exam Material to be covered: 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.5 plus review of u, du substitution.
 Review: Exam. Goals for this portion of the course: Be able to compute the area between curves, the volume of solids of revolution, and understand the mean value of a function. We had three basic volumes:
Review: Exam. Goals for this portion of the course: Be able to compute the area between curves, the volume of solids of revolution, and understand the mean value of a function. We had three basic volumes:
Final Exam Review Exercise Set A, Math 1551, Fall 2017
 Final Exam Review Exercise Set A, Math 1551, Fall 2017 This review set gives a list of topics that we explored throughout this course, as well as a few practice problems at the end of the document. A complete
Final Exam Review Exercise Set A, Math 1551, Fall 2017 This review set gives a list of topics that we explored throughout this course, as well as a few practice problems at the end of the document. A complete
Calculus AB Topics Limits Continuity, Asymptotes
 Calculus AB Topics Limits Continuity, Asymptotes Consider f x 2x 1 x 3 1 x 3 x 3 Is there a vertical asymptote at x = 3? Do not give a Precalculus answer on a Calculus exam. Consider f x 2x 1 x 3 1 x 3
Calculus AB Topics Limits Continuity, Asymptotes Consider f x 2x 1 x 3 1 x 3 x 3 Is there a vertical asymptote at x = 3? Do not give a Precalculus answer on a Calculus exam. Consider f x 2x 1 x 3 1 x 3
MAT 132 Midterm 1 Spring 2017
 MAT Midterm Spring 7 Name: ID: Problem 5 6 7 8 Total ( pts) ( pts) ( pts) ( pts) ( pts) ( pts) (5 pts) (5 pts) ( pts) Score Instructions: () Fill in your name and Stony Brook ID number at the top of this
MAT Midterm Spring 7 Name: ID: Problem 5 6 7 8 Total ( pts) ( pts) ( pts) ( pts) ( pts) ( pts) (5 pts) (5 pts) ( pts) Score Instructions: () Fill in your name and Stony Brook ID number at the top of this
Have a Safe and Happy Break
 Math 121 Final EF: December 10, 2013 Name Directions: 1 /15 2 /15 3 /15 4 /15 5 /10 6 /10 7 /20 8 /15 9 /15 10 /10 11 /15 12 /20 13 /15 14 /10 Total /200 1. No book, notes, or ouiji boards. You may use
Math 121 Final EF: December 10, 2013 Name Directions: 1 /15 2 /15 3 /15 4 /15 5 /10 6 /10 7 /20 8 /15 9 /15 10 /10 11 /15 12 /20 13 /15 14 /10 Total /200 1. No book, notes, or ouiji boards. You may use
5 Integrals reviewed Basic facts U-substitution... 5
 Contents 5 Integrals reviewed 5. Basic facts............................... 5.5 U-substitution............................. 5 6 Integral Applications 0 6. Area between two curves.......................
Contents 5 Integrals reviewed 5. Basic facts............................... 5.5 U-substitution............................. 5 6 Integral Applications 0 6. Area between two curves.......................
Math 41 Final Exam December 9, 2013
 Math 41 Final Exam December 9, 2013 Name: SUID#: Circle your section: Valentin Buciumas Jafar Jafarov Jesse Madnick Alexandra Musat Amy Pang 02 (1:15-2:05pm) 08 (10-10:50am) 03 (11-11:50am) 06 (9-9:50am)
Math 41 Final Exam December 9, 2013 Name: SUID#: Circle your section: Valentin Buciumas Jafar Jafarov Jesse Madnick Alexandra Musat Amy Pang 02 (1:15-2:05pm) 08 (10-10:50am) 03 (11-11:50am) 06 (9-9:50am)
Name: Instructor: Exam 3 Solutions. Multiple Choice. 3x + 2 x ) 3x 3 + 2x 2 + 5x + 2 3x 3 3x 2x 2 + 2x + 2 2x 2 2 2x.
 . Exam 3 Solutions Multiple Choice.(6 pts.) Find the equation of the slant asymptote to the function We have so the slant asymptote is y = 3x +. f(x) = 3x3 + x + 5x + x + 3x + x + ) 3x 3 + x + 5x + 3x
. Exam 3 Solutions Multiple Choice.(6 pts.) Find the equation of the slant asymptote to the function We have so the slant asymptote is y = 3x +. f(x) = 3x3 + x + 5x + x + 3x + x + ) 3x 3 + x + 5x + 3x
MATH 1241 Common Final Exam Fall 2010
 MATH 1241 Common Final Exam Fall 2010 Please print the following information: Name: Instructor: Student ID: Section/Time: The MATH 1241 Final Exam consists of three parts. You have three hours for the
MATH 1241 Common Final Exam Fall 2010 Please print the following information: Name: Instructor: Student ID: Section/Time: The MATH 1241 Final Exam consists of three parts. You have three hours for the
10550 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS. x 2 4. x 2 x 2 5x +6 = lim x +2. x 2 x 3 = 4 1 = 4.
 55 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS. First notice that x 2 4 x 2x + 2 x 2 5x +6 x 2x. This function is undefined at x 2. Since, in the it as x 2, we only care about what happens near x 2 an for x less than
55 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS. First notice that x 2 4 x 2x + 2 x 2 5x +6 x 2x. This function is undefined at x 2. Since, in the it as x 2, we only care about what happens near x 2 an for x less than
MATH 153 FIRST MIDTERM EXAM
 NAME: Solutions MATH 53 FIRST MIDTERM EXAM October 2, 2005. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. 2. This exam has pages including this cover. There are 8 questions. 3. Write your name on
NAME: Solutions MATH 53 FIRST MIDTERM EXAM October 2, 2005. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. 2. This exam has pages including this cover. There are 8 questions. 3. Write your name on
MATH 162. Midterm Exam 1 - Solutions February 22, 2007
 MATH 62 Midterm Exam - Solutions February 22, 27. (8 points) Evaluate the following integrals: (a) x sin(x 4 + 7) dx Solution: Let u = x 4 + 7, then du = 4x dx and x sin(x 4 + 7) dx = 4 sin(u) du = 4 [
MATH 62 Midterm Exam - Solutions February 22, 27. (8 points) Evaluate the following integrals: (a) x sin(x 4 + 7) dx Solution: Let u = x 4 + 7, then du = 4x dx and x sin(x 4 + 7) dx = 4 sin(u) du = 4 [
Math 229 Mock Final Exam Solution
 Name: Math 229 Mock Final Exam Solution Disclaimer: This mock exam is for practice purposes only. No graphing calulators TI-89 is allowed on this test. Be sure that all of your work is shown and that it
Name: Math 229 Mock Final Exam Solution Disclaimer: This mock exam is for practice purposes only. No graphing calulators TI-89 is allowed on this test. Be sure that all of your work is shown and that it
Math 180 Written Homework Assignment #10 Due Tuesday, December 2nd at the beginning of your discussion class.
 Math 18 Written Homework Assignment #1 Due Tuesday, December 2nd at the beginning of your discussion class. Directions. You are welcome to work on the following problems with other MATH 18 students, but
Math 18 Written Homework Assignment #1 Due Tuesday, December 2nd at the beginning of your discussion class. Directions. You are welcome to work on the following problems with other MATH 18 students, but
Math 1: Calculus with Algebra Midterm 2 Thursday, October 29. Circle your section number: 1 Freund 2 DeFord
 Math 1: Calculus with Algebra Midterm 2 Thursday, October 29 Name: Circle your section number: 1 Freund 2 DeFord Please read the following instructions before starting the exam: This exam is closed book,
Math 1: Calculus with Algebra Midterm 2 Thursday, October 29 Name: Circle your section number: 1 Freund 2 DeFord Please read the following instructions before starting the exam: This exam is closed book,
MATH 250 TOPIC 13 INTEGRATION. 13B. Constant, Sum, and Difference Rules
 Math 5 Integration Topic 3 Page MATH 5 TOPIC 3 INTEGRATION 3A. Integration of Common Functions Practice Problems 3B. Constant, Sum, and Difference Rules Practice Problems 3C. Substitution Practice Problems
Math 5 Integration Topic 3 Page MATH 5 TOPIC 3 INTEGRATION 3A. Integration of Common Functions Practice Problems 3B. Constant, Sum, and Difference Rules Practice Problems 3C. Substitution Practice Problems
5 Integrals reviewed Basic facts U-substitution... 4
 Contents 5 Integrals reviewed 5. Basic facts............................... 5.5 U-substitution............................. 4 6 Integral Applications 0 6. Area between two curves.......................
Contents 5 Integrals reviewed 5. Basic facts............................... 5.5 U-substitution............................. 4 6 Integral Applications 0 6. Area between two curves.......................
Review for Final Exam, MATH , Fall 2010
 Review for Final Exam, MATH 170-002, Fall 2010 The test will be on Wednesday December 15 in ILC 404 (usual class room), 8:00 a.m - 10:00 a.m. Please bring a non-graphing calculator for the test. No other
Review for Final Exam, MATH 170-002, Fall 2010 The test will be on Wednesday December 15 in ILC 404 (usual class room), 8:00 a.m - 10:00 a.m. Please bring a non-graphing calculator for the test. No other
AB Calculus Diagnostic Test
 AB Calculus Diagnostic Test The Exam AP Calculus AB Exam SECTION I: Multiple-Choice Questions DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. At a Glance Total Time hour and 5 minutes Number of Questions
AB Calculus Diagnostic Test The Exam AP Calculus AB Exam SECTION I: Multiple-Choice Questions DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. At a Glance Total Time hour and 5 minutes Number of Questions
Applications of Differentiation
 Applications of Differentiation Definitions. A function f has an absolute maximum (or global maximum) at c if for all x in the domain D of f, f(c) f(x). The number f(c) is called the maximum value of f
Applications of Differentiation Definitions. A function f has an absolute maximum (or global maximum) at c if for all x in the domain D of f, f(c) f(x). The number f(c) is called the maximum value of f
In general, if we start with a function f and want to reverse the differentiation process, then we are finding an antiderivative of f.
 Math 1410 Worksheet #27: Section 4.9 Name: Our final application of derivatives is a prelude to what will come in later chapters. In many situations, it will be necessary to find a way to reverse the differentiation
Math 1410 Worksheet #27: Section 4.9 Name: Our final application of derivatives is a prelude to what will come in later chapters. In many situations, it will be necessary to find a way to reverse the differentiation
Math 152 Take Home Test 1
 Math 5 Take Home Test Due Monday 5 th October (5 points) The following test will be done at home in order to ensure that it is a fair and representative reflection of your own ability in mathematics I
Math 5 Take Home Test Due Monday 5 th October (5 points) The following test will be done at home in order to ensure that it is a fair and representative reflection of your own ability in mathematics I
Examples. 1. (Solution) (a) Suppose f is an increasing function, and let A(x) = x
 Math 31A Final Exam Practice Problems Austin Christian December 1, 15 Here are some practice problems for the final. You ll notice that these problems all come from material since the last exam. You are,
Math 31A Final Exam Practice Problems Austin Christian December 1, 15 Here are some practice problems for the final. You ll notice that these problems all come from material since the last exam. You are,
The Chain Rule. The Chain Rule. dy dy du dx du dx. For y = f (u) and u = g (x)
 AP Calculus Mrs. Jo Brooks The Chain Rule To find the derivative of more complicated functions, we use something called the chain rule. It can be confusing unless you keep yourself organized as you go
AP Calculus Mrs. Jo Brooks The Chain Rule To find the derivative of more complicated functions, we use something called the chain rule. It can be confusing unless you keep yourself organized as you go
1 + x 2 d dx (sec 1 x) =
 Page This exam has: 8 multiple choice questions worth 4 points each. hand graded questions worth 4 points each. Important: No graphing calculators! Any non-graphing, non-differentiating, non-integrating
Page This exam has: 8 multiple choice questions worth 4 points each. hand graded questions worth 4 points each. Important: No graphing calculators! Any non-graphing, non-differentiating, non-integrating
Math 1431 Final Exam Review
 Math 1431 Final Exam Review Comprehensive exam. I recommend you study all past reviews and practice exams as well. Know all rules/formulas. Make a reservation for the final exam. If you miss it, go back
Math 1431 Final Exam Review Comprehensive exam. I recommend you study all past reviews and practice exams as well. Know all rules/formulas. Make a reservation for the final exam. If you miss it, go back
Substitutions and by Parts, Area Between Curves. Goals: The Method of Substitution Areas Integration by Parts
 Week #7: Substitutions and by Parts, Area Between Curves Goals: The Method of Substitution Areas Integration by Parts 1 Week 7 The Indefinite Integral The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, b a f(x) dx =
Week #7: Substitutions and by Parts, Area Between Curves Goals: The Method of Substitution Areas Integration by Parts 1 Week 7 The Indefinite Integral The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, b a f(x) dx =
Chapter 5 Integrals. 5.1 Areas and Distances
 Chapter 5 Integrals 5.1 Areas and Distances We start with a problem how can we calculate the area under a given function ie, the area between the function and the x-axis? If the curve happens to be something
Chapter 5 Integrals 5.1 Areas and Distances We start with a problem how can we calculate the area under a given function ie, the area between the function and the x-axis? If the curve happens to be something
PLEASE MARK YOUR ANSWERS WITH AN X, not a circle! 1. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 2. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 4. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e)...
 Math, Exam III November 6, 7 The Honor Code is in effect for this examination. All work is to be your own. No calculators. The exam lasts for hour and min. Be sure that your name is on every page in case
Math, Exam III November 6, 7 The Honor Code is in effect for this examination. All work is to be your own. No calculators. The exam lasts for hour and min. Be sure that your name is on every page in case
Math 230 Mock Final Exam Detailed Solution
 Name: Math 30 Mock Final Exam Detailed Solution Disclaimer: This mock exam is for practice purposes only. No graphing calulators TI-89 is allowed on this test. Be sure that all of your work is shown and
Name: Math 30 Mock Final Exam Detailed Solution Disclaimer: This mock exam is for practice purposes only. No graphing calulators TI-89 is allowed on this test. Be sure that all of your work is shown and
MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS
 MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS Summer Assignment Welcome to Multivariable Calculus, Multivariable Calculus is a course commonly taken by second and third year college students. The general concept is to take the
MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS Summer Assignment Welcome to Multivariable Calculus, Multivariable Calculus is a course commonly taken by second and third year college students. The general concept is to take the
MATH 2300 review problems for Exam 1 ANSWERS
 MATH review problems for Exam ANSWERS. Evaluate the integral sin x cos x dx in each of the following ways: This one is self-explanatory; we leave it to you. (a) Integrate by parts, with u = sin x and dv
MATH review problems for Exam ANSWERS. Evaluate the integral sin x cos x dx in each of the following ways: This one is self-explanatory; we leave it to you. (a) Integrate by parts, with u = sin x and dv
MATH141: Calculus II Exam #4 7/21/2017 Page 1
 MATH141: Calculus II Exam #4 7/21/2017 Page 1 Write legibly and show all work. No partial credit can be given for an unjustified, incorrect answer. Put your name in the top right corner and sign the honor
MATH141: Calculus II Exam #4 7/21/2017 Page 1 Write legibly and show all work. No partial credit can be given for an unjustified, incorrect answer. Put your name in the top right corner and sign the honor
MA 113 Calculus I Fall 2016 Exam Final Wednesday, December 14, True/False 1 T F 2 T F 3 T F 4 T F 5 T F. Name: Section:
 MA 113 Calculus I Fall 2016 Exam Final Wednesday, December 14, 2016 Name: Section: Last 4 digits of student ID #: This exam has five true/false questions (two points each), ten multiple choice questions
MA 113 Calculus I Fall 2016 Exam Final Wednesday, December 14, 2016 Name: Section: Last 4 digits of student ID #: This exam has five true/false questions (two points each), ten multiple choice questions
x+1 e 2t dt. h(x) := Find the equation of the tangent line to y = h(x) at x = 0.
 Math Sample final problems Here are some problems that appeared on past Math exams. Note that you will be given a table of Z-scores for the standard normal distribution on the test. Don t forget to have
Math Sample final problems Here are some problems that appeared on past Math exams. Note that you will be given a table of Z-scores for the standard normal distribution on the test. Don t forget to have
Final Exam 12/11/ (16 pts) Find derivatives for each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 1+ x e + e π [Do not simplify your answer.
 Math 105 Final Exam 1/11/1 Name Read directions carefully and show all your work. Partial credit will be assigned based upon the correctness, completeness, and clarity of your answers. Correct answers
Math 105 Final Exam 1/11/1 Name Read directions carefully and show all your work. Partial credit will be assigned based upon the correctness, completeness, and clarity of your answers. Correct answers
5.5. The Substitution Rule
 INTEGRALS 5 INTEGRALS 5.5 The Substitution Rule In this section, we will learn: To substitute a new variable in place of an existing expression in a function, making integration easier. INTRODUCTION Due
INTEGRALS 5 INTEGRALS 5.5 The Substitution Rule In this section, we will learn: To substitute a new variable in place of an existing expression in a function, making integration easier. INTRODUCTION Due
Chapter 6: The Definite Integral
 Name: Date: Period: AP Calc AB Mr. Mellina Chapter 6: The Definite Integral v v Sections: v 6.1 Estimating with Finite Sums v 6.5 Trapezoidal Rule v 6.2 Definite Integrals 6.3 Definite Integrals and Antiderivatives
Name: Date: Period: AP Calc AB Mr. Mellina Chapter 6: The Definite Integral v v Sections: v 6.1 Estimating with Finite Sums v 6.5 Trapezoidal Rule v 6.2 Definite Integrals 6.3 Definite Integrals and Antiderivatives
Goal: Approximate the area under a curve using the Rectangular Approximation Method (RAM) RECTANGULAR APPROXIMATION METHODS
 AP Calculus 5. Areas and Distances Goal: Approximate the area under a curve using the Rectangular Approximation Method (RAM) Exercise : Calculate the area between the x-axis and the graph of y = 3 2x.
AP Calculus 5. Areas and Distances Goal: Approximate the area under a curve using the Rectangular Approximation Method (RAM) Exercise : Calculate the area between the x-axis and the graph of y = 3 2x.
Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 11.
 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through. Show all your work on the standard response
Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through. Show all your work on the standard response
AP Calculus AB Mrs. Mills Carlmont High School
 AP Calculus AB 015-016 Mrs. Mills Carlmont High School AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT NAME: READ THE FOLLOWING DIRECTIONS CAREFULLY! Read through the notes & eamples for each page and then solve all
AP Calculus AB 015-016 Mrs. Mills Carlmont High School AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT NAME: READ THE FOLLOWING DIRECTIONS CAREFULLY! Read through the notes & eamples for each page and then solve all
Level 1 Calculus Final Exam Day 1 50 minutes
 Level 1 Calculus Final Exam 2013 Day 1 50 minutes Name: Block: Circle Teacher Name LeBlanc Normile Instructions Write answers in the space provided and show all work. Calculators okay but observe instructions
Level 1 Calculus Final Exam 2013 Day 1 50 minutes Name: Block: Circle Teacher Name LeBlanc Normile Instructions Write answers in the space provided and show all work. Calculators okay but observe instructions
Integration and antiderivatives
 Integration and antiderivatives 1. Evaluate the following:. True or false: d dx lim x / x et dt x cos( 1 4 t ) dt sin x dx = sin(π/) 3. True or false: the following function F (x) is an antiderivative
Integration and antiderivatives 1. Evaluate the following:. True or false: d dx lim x / x et dt x cos( 1 4 t ) dt sin x dx = sin(π/) 3. True or false: the following function F (x) is an antiderivative
AP* Calculus Free-response Question Type Analysis and Notes Revised to include the 2013 Exam By Lin McMullin
 AP* Calculus Free-response Question Type Analysis and Notes Revised to include the 2013 Exam By Lin McMullin General note: AP Questions often test several diverse ideas or concepts in the same question.
AP* Calculus Free-response Question Type Analysis and Notes Revised to include the 2013 Exam By Lin McMullin General note: AP Questions often test several diverse ideas or concepts in the same question.
Topics and Concepts. 1. Limits
 Topics and Concepts 1. Limits (a) Evaluating its (Know: it exists if and only if the it from the left is the same as the it from the right) (b) Infinite its (give rise to vertical asymptotes) (c) Limits
Topics and Concepts 1. Limits (a) Evaluating its (Know: it exists if and only if the it from the left is the same as the it from the right) (b) Infinite its (give rise to vertical asymptotes) (c) Limits
Math 111, Introduction to the Calculus, Fall 2011 Midterm I Practice Exam 1 Solutions
 Math 111, Introduction to the Calculus, Fall 2011 Midterm I Practice Exam 1 Solutions For each question, there is a model solution (showing you the level of detail I expect on the exam) and then below
Math 111, Introduction to the Calculus, Fall 2011 Midterm I Practice Exam 1 Solutions For each question, there is a model solution (showing you the level of detail I expect on the exam) and then below
Exam 3 review for Math 1190
 Exam 3 review for Math 9 Be sure to be familiar with the following : Extreme Value Theorem Optimization The antiderivative u-substitution as a method for finding antiderivatives Reimann sums (e.g. L 6
Exam 3 review for Math 9 Be sure to be familiar with the following : Extreme Value Theorem Optimization The antiderivative u-substitution as a method for finding antiderivatives Reimann sums (e.g. L 6
Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review
 Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review c Trinity College 1 A note to the students from the lecturer: This course will be moving rather quickly, and it will be in your own best interests to
Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review c Trinity College 1 A note to the students from the lecturer: This course will be moving rather quickly, and it will be in your own best interests to
Mth Review Problems for Test 2 Stewart 8e Chapter 3. For Test #2 study these problems, the examples in your notes, and the homework.
 For Test # study these problems, the examples in your notes, and the homework. Derivative Rules D [u n ] = nu n 1 du D [ln u] = du u D [log b u] = du u ln b D [e u ] = e u du D [a u ] = a u ln a du D [sin
For Test # study these problems, the examples in your notes, and the homework. Derivative Rules D [u n ] = nu n 1 du D [ln u] = du u D [log b u] = du u ln b D [e u ] = e u du D [a u ] = a u ln a du D [sin
AP Calculus AB 2nd Semester Homework List
 AP Calculus AB 2nd Semester Homework List Date Assigned: 1/4 DUE Date: 1/6 Title: Typsetting Basic L A TEX and Sigma Notation Write the homework out on paper. Then type the homework on L A TEX. Use this
AP Calculus AB 2nd Semester Homework List Date Assigned: 1/4 DUE Date: 1/6 Title: Typsetting Basic L A TEX and Sigma Notation Write the homework out on paper. Then type the homework on L A TEX. Use this
HAND IN PART. Prof. Girardi Math 142 Spring Exam 1. NAME: key
 HAND IN PART Prof. Girardi Math 4 Spring 4..4 Exam MARK BOX problem points 7 % NAME: key PIN: INSTRUCTIONS The mark box above indicates the problems along with their points. Check that your copy of the
HAND IN PART Prof. Girardi Math 4 Spring 4..4 Exam MARK BOX problem points 7 % NAME: key PIN: INSTRUCTIONS The mark box above indicates the problems along with their points. Check that your copy of the
Math 106 Answers to Exam 3a Fall 2015
 Math 6 Answers to Exam 3a Fall 5.. Consider the curve given parametrically by x(t) = cos(t), y(t) = (t 3 ) 3, for t from π to π. (a) (6 points) Find all the points (x, y) where the graph has either a vertical
Math 6 Answers to Exam 3a Fall 5.. Consider the curve given parametrically by x(t) = cos(t), y(t) = (t 3 ) 3, for t from π to π. (a) (6 points) Find all the points (x, y) where the graph has either a vertical
MATH 1190 Exam 4 (Version 2) Solutions December 1, 2006 S. F. Ellermeyer Name
 MATH 90 Exam 4 (Version ) Solutions December, 006 S. F. Ellermeyer Name Instructions. Your work on this exam will be graded according to two criteria: mathematical correctness and clarity of presentation.
MATH 90 Exam 4 (Version ) Solutions December, 006 S. F. Ellermeyer Name Instructions. Your work on this exam will be graded according to two criteria: mathematical correctness and clarity of presentation.
Lecture : The Indefinite Integral MTH 124
 Up to this point we have investigated the definite integral of a function over an interval. In particular we have done the following. Approximated integrals using left and right Riemann sums. Defined the
Up to this point we have investigated the definite integral of a function over an interval. In particular we have done the following. Approximated integrals using left and right Riemann sums. Defined the
Math 122 Fall Unit Test 1 Review Problems Set A
 Math Fall 8 Unit Test Review Problems Set A We have chosen these problems because we think that they are representative of many of the mathematical concepts that we have studied. There is no guarantee
Math Fall 8 Unit Test Review Problems Set A We have chosen these problems because we think that they are representative of many of the mathematical concepts that we have studied. There is no guarantee
Grade: The remainder of this page has been left blank for your workings. VERSION D. Midterm D: Page 1 of 12
 First Name: Student-No: Last Name: Section: Grade: The remainder of this page has been left blank for your workings. Midterm D: Page of 2 Indefinite Integrals. 9 marks Each part is worth marks. Please
First Name: Student-No: Last Name: Section: Grade: The remainder of this page has been left blank for your workings. Midterm D: Page of 2 Indefinite Integrals. 9 marks Each part is worth marks. Please
No calculators, cell phones or any other electronic devices can be used on this exam. Clear your desk of everything excepts pens, pencils and erasers.
 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS. Do not open your exam until told to do so. No calculators, cell phones or any other electronic devices can be used on this exam. Clear
Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS. Do not open your exam until told to do so. No calculators, cell phones or any other electronic devices can be used on this exam. Clear
Math 250 Skills Assessment Test
 Math 5 Skills Assessment Test Page Math 5 Skills Assessment Test The purpose of this test is purely diagnostic (before beginning your review, it will be helpful to assess both strengths and weaknesses).
Math 5 Skills Assessment Test Page Math 5 Skills Assessment Test The purpose of this test is purely diagnostic (before beginning your review, it will be helpful to assess both strengths and weaknesses).
Applied Calculus I. Lecture 36
 Applied Calculus I Lecture 36 Computing the volume Consider a continuous function over an interval [a, b]. y a b x Computing the volume Consider a continuous function over an interval [a, b]. y y a b x
Applied Calculus I Lecture 36 Computing the volume Consider a continuous function over an interval [a, b]. y a b x Computing the volume Consider a continuous function over an interval [a, b]. y y a b x
Final Exam Solutions
 Final Exam Solutions Laurence Field Math, Section March, Name: Solutions Instructions: This exam has 8 questions for a total of points. The value of each part of each question is stated. The time allowed
Final Exam Solutions Laurence Field Math, Section March, Name: Solutions Instructions: This exam has 8 questions for a total of points. The value of each part of each question is stated. The time allowed
CHAIN RULE: DAY 2 WITH TRIG FUNCTIONS. Section 2.4A Calculus AP/Dual, Revised /30/2018 1:44 AM 2.4A: Chain Rule Day 2 1
 CHAIN RULE: DAY WITH TRIG FUNCTIONS Section.4A Calculus AP/Dual, Revised 018 viet.dang@humbleisd.net 7/30/018 1:44 AM.4A: Chain Rule Day 1 THE CHAIN RULE A. d dx f g x = f g x g x B. If f(x) is a differentiable
CHAIN RULE: DAY WITH TRIG FUNCTIONS Section.4A Calculus AP/Dual, Revised 018 viet.dang@humbleisd.net 7/30/018 1:44 AM.4A: Chain Rule Day 1 THE CHAIN RULE A. d dx f g x = f g x g x B. If f(x) is a differentiable
Friday 09/15/2017 Midterm I 50 minutes
 Fa 17: MATH 2924 040 Differential and Integral Calculus II Noel Brady Friday 09/15/2017 Midterm I 50 minutes Name: Student ID: Instructions. 1. Attempt all questions. 2. Do not write on back of exam sheets.
Fa 17: MATH 2924 040 Differential and Integral Calculus II Noel Brady Friday 09/15/2017 Midterm I 50 minutes Name: Student ID: Instructions. 1. Attempt all questions. 2. Do not write on back of exam sheets.
Bonus Homework and Exam Review - Math 141, Frank Thorne Due Friday, December 9 at the start of the final exam.
 Bonus Homework and Exam Review - Math 141, Frank Thorne (thornef@mailbox.sc.edu) Due Friday, December 9 at the start of the final exam. It is strongly recommended that you do as many of these problems
Bonus Homework and Exam Review - Math 141, Frank Thorne (thornef@mailbox.sc.edu) Due Friday, December 9 at the start of the final exam. It is strongly recommended that you do as many of these problems
Old Math 220 Exams. David M. McClendon. Department of Mathematics Ferris State University
 Old Math 0 Exams David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University Last updated to include exams from Spring 05 Contents Contents General information about these exams 4 Exams from 0
Old Math 0 Exams David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University Last updated to include exams from Spring 05 Contents Contents General information about these exams 4 Exams from 0
Math 241 Final Exam, Spring 2013
 Math 241 Final Exam, Spring 2013 Name: Section number: Instructor: Read all of the following information before starting the exam. Question Points Score 1 5 2 5 3 12 4 10 5 17 6 15 7 6 8 12 9 12 10 14
Math 241 Final Exam, Spring 2013 Name: Section number: Instructor: Read all of the following information before starting the exam. Question Points Score 1 5 2 5 3 12 4 10 5 17 6 15 7 6 8 12 9 12 10 14
MAT137 - Term 2, Week 2
 MAT137 - Term 2, Week 2 This lecture will assume you have watched all of the videos on the definition of the integral (but will remind you about some things). Today we re talking about: More on the definition
MAT137 - Term 2, Week 2 This lecture will assume you have watched all of the videos on the definition of the integral (but will remind you about some things). Today we re talking about: More on the definition
Solutions to Math 41 Final Exam December 10, 2012
 Solutions to Math 4 Final Exam December,. ( points) Find each of the following limits, with justification. If there is an infinite limit, then explain whether it is or. x ln(t + ) dt (a) lim x x (5 points)
Solutions to Math 4 Final Exam December,. ( points) Find each of the following limits, with justification. If there is an infinite limit, then explain whether it is or. x ln(t + ) dt (a) lim x x (5 points)
Give your answers in exact form, except as noted in particular problems.
 Math 125 Final Examination Spring 2010 Your Name Your Signature Student ID # Quiz Section Professor s Name TA s Name This exam is closed book. You may use one 8 2 1 11 sheet of handwritten notes (both
Math 125 Final Examination Spring 2010 Your Name Your Signature Student ID # Quiz Section Professor s Name TA s Name This exam is closed book. You may use one 8 2 1 11 sheet of handwritten notes (both
MATH 18.01, FALL PROBLEM SET # 6 SOLUTIONS
 MATH 181, FALL 17 - PROBLEM SET # 6 SOLUTIONS Part II (5 points) 1 (Thurs, Oct 6; Second Fundamental Theorem; + + + + + = 16 points) Let sinc(x) denote the sinc function { 1 if x =, sinc(x) = sin x if
MATH 181, FALL 17 - PROBLEM SET # 6 SOLUTIONS Part II (5 points) 1 (Thurs, Oct 6; Second Fundamental Theorem; + + + + + = 16 points) Let sinc(x) denote the sinc function { 1 if x =, sinc(x) = sin x if
7.1 Indefinite Integrals Calculus
 7.1 Indefinite Integrals Calculus Learning Objectives A student will be able to: Find antiderivatives of functions. Represent antiderivatives. Interpret the constant of integration graphically. Solve differential
7.1 Indefinite Integrals Calculus Learning Objectives A student will be able to: Find antiderivatives of functions. Represent antiderivatives. Interpret the constant of integration graphically. Solve differential
Examples from Section 6.3: Volume by Cylindrical Shells Page 1
 Examples from Section 6.3: Volume by Cylindrical Shells Page 1 Questions Example Find the volume of the region which is created when we rotate the region below y = x x 3 and above < x < about the y-axis.
Examples from Section 6.3: Volume by Cylindrical Shells Page 1 Questions Example Find the volume of the region which is created when we rotate the region below y = x x 3 and above < x < about the y-axis.
 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - DISCLAIMER - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - General Information: This midterm is a sample midterm. This means: The sample midterm contains problems that are of similar,
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - DISCLAIMER - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - General Information: This midterm is a sample midterm. This means: The sample midterm contains problems that are of similar,
MA FINAL EXAM Green May 5, You must use a #2 pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet).
 MA 600 FINAL EXAM Green May 5, 06 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME. You must use a # pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet).. Be sure the paper you are looking at right now is GREEN!
MA 600 FINAL EXAM Green May 5, 06 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME. You must use a # pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet).. Be sure the paper you are looking at right now is GREEN!
Math 112 (Calculus I) Midterm Exam 3 KEY
 Math 11 (Calculus I) Midterm Exam KEY Multiple Choice. Fill in the answer to each problem on your computer scored answer sheet. Make sure your name, section and instructor are on that sheet. 1. Which of
Math 11 (Calculus I) Midterm Exam KEY Multiple Choice. Fill in the answer to each problem on your computer scored answer sheet. Make sure your name, section and instructor are on that sheet. 1. Which of
Calculus is Cool. Math 160 Calculus for Physical Scientists I Exam 1 September 18, 2014, 5:00-6:50 pm. NAME: Instructor: Time your class meets:
 NAME: Instructor: Time your class meets: Math 160 Calculus for Physical Scientists I Exam 1 September 18, 2014, 5:00-6:50 pm How can it be that mathematics, being after all a product of human thought independent
NAME: Instructor: Time your class meets: Math 160 Calculus for Physical Scientists I Exam 1 September 18, 2014, 5:00-6:50 pm How can it be that mathematics, being after all a product of human thought independent
GENERAL TIPS WHEN TAKING THE AP CALC EXAM. Multiple Choice Portion
 GENERAL TIPS WHEN TAKING THE AP CALC EXAM. Multiple Choice Portion 1. You are hunting for apples, aka easy questions. Do not go in numerical order; that is a trap! 2. Do all Level 1s first. Then 2. Then
GENERAL TIPS WHEN TAKING THE AP CALC EXAM. Multiple Choice Portion 1. You are hunting for apples, aka easy questions. Do not go in numerical order; that is a trap! 2. Do all Level 1s first. Then 2. Then
University of Toronto MAT137Y1 Calculus! Test 2 1 December 2017 Time: 110 minutes
 University of Toronto MAT137Y1 Calculus! Test 2 1 December 2017 Time: 110 minutes Please complete this cover page with ALL CAPITAL LETTERS. Last name......................................................................................
University of Toronto MAT137Y1 Calculus! Test 2 1 December 2017 Time: 110 minutes Please complete this cover page with ALL CAPITAL LETTERS. Last name......................................................................................
Volume: The Disk Method. Using the integral to find volume.
 Volume: The Disk Method Using the integral to find volume. If a region in a plane is revolved about a line, the resulting solid is a solid of revolution and the line is called the axis of revolution. y
Volume: The Disk Method Using the integral to find volume. If a region in a plane is revolved about a line, the resulting solid is a solid of revolution and the line is called the axis of revolution. y
3.1 Day 1: The Derivative of a Function
 A P Calculus 3.1 Day 1: The Derivative of a Function I CAN DEFINE A DERIVATIVE AND UNDERSTAND ITS NOTATION. Last chapter we learned to find the slope of a tangent line to a point on a graph by using a
A P Calculus 3.1 Day 1: The Derivative of a Function I CAN DEFINE A DERIVATIVE AND UNDERSTAND ITS NOTATION. Last chapter we learned to find the slope of a tangent line to a point on a graph by using a
Example. Evaluate. 3x 2 4 x dx.
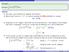 3x 2 4 x 3 + 4 dx. Solution: We need a new technique to integrate this function. Notice that if we let u x 3 + 4, and we compute the differential du of u, we get: du 3x 2 dx Going back to our integral,
3x 2 4 x 3 + 4 dx. Solution: We need a new technique to integrate this function. Notice that if we let u x 3 + 4, and we compute the differential du of u, we get: du 3x 2 dx Going back to our integral,
True or False. Circle T if the statement is always true; otherwise circle F. for all angles θ. T F. 1 sin θ
 Math 90 Practice Midterm III Solutions Ch. 8-0 (Ebersole), 3.3-3.8 (Stewart) DISCLAIMER. This collection of practice problems is not guaranteed to be identical, in length or content, to the actual exam.
Math 90 Practice Midterm III Solutions Ch. 8-0 (Ebersole), 3.3-3.8 (Stewart) DISCLAIMER. This collection of practice problems is not guaranteed to be identical, in length or content, to the actual exam.
Learning Objectives for Math 165
 Learning Objectives for Math 165 Chapter 2 Limits Section 2.1: Average Rate of Change. State the definition of average rate of change Describe what the rate of change does and does not tell us in a given
Learning Objectives for Math 165 Chapter 2 Limits Section 2.1: Average Rate of Change. State the definition of average rate of change Describe what the rate of change does and does not tell us in a given
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE The Final Exam takes place on Wednesday, June 13, 2018, from 10:30 AM to 12:30 PM in 1100 Donald Bren Hall (not the usual lecture room!!!) NO books/notes/calculators/cheat sheets
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE The Final Exam takes place on Wednesday, June 13, 2018, from 10:30 AM to 12:30 PM in 1100 Donald Bren Hall (not the usual lecture room!!!) NO books/notes/calculators/cheat sheets
1. There are 8 questions spanning 9 pages total (including this cover page). Please make sure that you have all 9 pages before starting.
 Instructor: K. Rotz Name: Solution PUID: 00000-00000 Instructions and tips: 1. There are 8 questions spanning 9 pages total (including this cover page). Please make sure that you have all 9 pages before
Instructor: K. Rotz Name: Solution PUID: 00000-00000 Instructions and tips: 1. There are 8 questions spanning 9 pages total (including this cover page). Please make sure that you have all 9 pages before
MATH 101 Midterm Examination Spring 2009
 MATH Midterm Eamination Spring 9 Date: May 5, 9 Time: 7 minutes Surname: (Please, print!) Given name(s): Signature: Instructions. This is a closed book eam: No books, no notes, no calculators are allowed!.
MATH Midterm Eamination Spring 9 Date: May 5, 9 Time: 7 minutes Surname: (Please, print!) Given name(s): Signature: Instructions. This is a closed book eam: No books, no notes, no calculators are allowed!.
Sec 4.1 Limits, Informally. When we calculated f (x), we first started with the difference quotient. f(x + h) f(x) h
 1 Sec 4.1 Limits, Informally When we calculated f (x), we first started with the difference quotient f(x + h) f(x) h and made h small. In other words, f (x) is the number f(x+h) f(x) approaches as h gets
1 Sec 4.1 Limits, Informally When we calculated f (x), we first started with the difference quotient f(x + h) f(x) h and made h small. In other words, f (x) is the number f(x+h) f(x) approaches as h gets
MLC Practice Final Exam. Recitation Instructor: Page Points Score Total: 200.
 Name: PID: Section: Recitation Instructor: DO NOT WRITE BELOW THIS LINE. GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. Page Points Score 3 20 4 30 5 20 6 20 7 20 8 20 9 25 10 25 11 20 Total: 200 Page 1 of 11 Name: Section:
Name: PID: Section: Recitation Instructor: DO NOT WRITE BELOW THIS LINE. GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. Page Points Score 3 20 4 30 5 20 6 20 7 20 8 20 9 25 10 25 11 20 Total: 200 Page 1 of 11 Name: Section:
HAND IN PART. Prof. Girardi Math 142 Spring Exam 3 PIN:
 HAND IN PART Prof. Girardi Math 142 Spring 2014 04.17.2014 Exam 3 MARK BOX problem points possible your score 0A 9 0B 8 0C 10 0D 12 NAME: PIN: solution key Total for 0 39 Total for 1 10 61 % 100 INSTRUCTIONS
HAND IN PART Prof. Girardi Math 142 Spring 2014 04.17.2014 Exam 3 MARK BOX problem points possible your score 0A 9 0B 8 0C 10 0D 12 NAME: PIN: solution key Total for 0 39 Total for 1 10 61 % 100 INSTRUCTIONS
Math 116 Final Exam April 26, 2013
 Math 116 Final Exam April 26, 2013 Name: Instructor: Section: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so. 2. This exam has 13 pages including this cover. There are 10 problems. Note that the
Math 116 Final Exam April 26, 2013 Name: Instructor: Section: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so. 2. This exam has 13 pages including this cover. There are 10 problems. Note that the
f(x) g(x) = [f (x)g(x) dx + f(x)g (x)dx
 Chapter 7 is concerned with all the integrals that can t be evaluated with simple antidifferentiation. Chart of Integrals on Page 463 7.1 Integration by Parts Like with the Chain Rule substitutions with
Chapter 7 is concerned with all the integrals that can t be evaluated with simple antidifferentiation. Chart of Integrals on Page 463 7.1 Integration by Parts Like with the Chain Rule substitutions with
Main topics for the First Midterm
 Main topics for the First Midterm Midterm 2 will cover Sections 7.7-7.9, 8.1-8.5, 9.1-9.2, 11.1-11.2. This is roughly the material from the first five homeworks and and three quizzes. In particular, I
Main topics for the First Midterm Midterm 2 will cover Sections 7.7-7.9, 8.1-8.5, 9.1-9.2, 11.1-11.2. This is roughly the material from the first five homeworks and and three quizzes. In particular, I
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
 AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA CALCULUS AB SECTION I, Part A Time 55 minutes Number of questions 8 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USED ON THIS PART OF THE EXAM. Directions: Solve each of the following problems,
AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA CALCULUS AB SECTION I, Part A Time 55 minutes Number of questions 8 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USED ON THIS PART OF THE EXAM. Directions: Solve each of the following problems,
