Fourier Transform and its Applications
|
|
|
- Owen Baker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fourier Transform and its Applications Prof. (Dr.) K.R. Chowdhary, Director COE webpage: JIET College of Engineering August 18, 2017 kr chowdhary Fourier Transform & its applications 1/ 15
2 Outlines: Joseph Fourier Motivation Applications Introduction to Fourier transform Finding frequency cntents of a function Fitting in Complex Numbers and Exponentials Fourier series Use of ScLab an open source software Resources for further reading kr chowdhary Fourier Transform & its applications 2/ 15
3 Joseph Fourier While working on the flow of heat, French mathematician [ Jean Baptiste] Joseph Fourier (March 21, 1768 May 16, 1830) discovered the equation for it that now bears his name. Fourier, the son of a tailor, born in Auxerre (France), was orphaned at the age of eight. Fourier was active politically during the upheaval of the French Revolution. In 1798 Fourier accompanied young General Napoleon Bonaparte on his Eastern expedition. After Fourier returned to Paris Napoleon made him an offer that was actually a command to serve as the Prefect kr chowdhary Fourier Transform & its applications 3/ 15
4 Motivation Ninety percent of all physics is concerned with vibrations and waves of one sort or another. An oscilloscope will display a graph of pressure against time, F(t), which is periodic. This waveform is not a pure sinusoid The waveform can be analysed to find the amplitudes of the overtones, kr chowdhary Fourier Transform & its applications 4/ 15
5 Motivation... A(v) is the Fourier transform of F(t). kr chowdhary Fourier Transform & its applications 5/ 15
6 Applications Actually it is the modular transform, but at this stage that is a detail. Suppose that the sound is not periodic Some uses of Fourier tran.: selection of a valuable violin; analysis of the sound of an aero-engine to detect a faulty gear-wheel; an electrocardiogram to detect a heart defect; light curve of a periodic variable star to determine the underlying physical causes of the variation, kr chowdhary Fourier Transform & its applications 6/ 15
7 Applications... Methods based on the Fourier transform are used in virtually all areas of engineering and science and by virtually all engineers and scientists. For starters: Circuit designers Spectroscopists Crystallographers Anyone working in signal processing and communications Anyone working in imaging - Fourier analysis was originally concerned with representing and analyzing periodic phenomena, via Fourier series, and later with extending those insights to nonperiodic phenomena, via the Fourier transform. - You can analyze the signal either in the time (or spatial) domain or in the frequency domain. kr chowdhary Fourier Transform & its applications 7/ 15
8 Introduction Fourier Transform The Fourier transform is among the most widely used tools for transforming data sequences and functions (single or multi-dimensional), from what is referred to as the time domain to the frequency domain. Functions as Combinations of Sinusoids: Any continuous, periodic function can be represented as a linear combination of sines and cosines. A sine is a function of the form: A sin(2πωt+ φ), where A - amplitude, ω - frequency, and φ - phase, which is used for getting values other than 0 at t =0. A cosine function has exactly the same components as the sine, and can be viewed as a shifted sine (i.e., a sine with phase π/2). kr chowdhary Fourier Transform & its applications 8/ 15
9 Introduction Fourier Transform... Thus, given a function f(t), we can usually rewrite it (or at least approximate it), for some n as: f(t)= n k=1 (A k cos(2πω k t)+b k sin(2πω k t)) (1) Both sines and cosines are combined, rather than only sines, to allow the expression of functions for which f(0) 0, in a way that is simpler than adding the phase to the sine in order to make it into a cosine. As an example of a linear combination of sinusoids consider the function: f 1 (t)=0.5sinπt+2sin4πt+4cos2πt (2) kr chowdhary Fourier Transform & its applications 9/ 15
10 Introduction Fourier Transform The function f 1 (t) consists of sines and cosines of 3 frequencies. kr chowdhary Fourier Transform & its applications 10/ 15
11 Frequency contents of the function f 1 (t) k Frequency (ω k ) Cosine amplitude (A k ) Sine Amplitude(B k ) 1 1/2 0 1/ The representation of a periodic function (or of a function that is defined only on a finite interval) as the linear combination of sines and cosines, is known as the Fourier series expansion of the function. The Fourier transform is a tool for obtaining such frequency and amplitude information for sequences and functions, which are not necessarily periodic. These sequences are just a special case of functions. kr chowdhary Fourier Transform & its applications 11/ 15
12 Fitting in Complex Numbers and Exponentials e iθ =cos(θ)+i sin(θ), e iθ =cos(θ) i sin(θ) Hence, cos(θ) = eiθ +e iθ 2, sin(θ)= eiθ e iθ 2i Thus, f(t)= n k=1 [ A k 2 (e2πiω kt +e 2πiωkt )+ B k 2i (e2πiω kt e 2πiωkt )] where C k = A k ib k 2 for k >0, and C k = A k+ib k 2 for k <0, and C 0 =0, and ω k = ω k, for k <0, and f(t)= n k= n [C k e 2πiω kt ] kr chowdhary Fourier Transform & its applications 12/ 15
13 Fourier series For a steady note, description requires only the fundamental frequency, its amplitude and the amplitudes of its harmonics. F(t)=a 0 +a 1 cos(2πv 0 t)+b 1 sin(2πv 0 t)+a 2 cos(4πv 0 t) +b 2 sin(4πv 0 t)+b 3 cos(6πv 0 t)+... (3) where v 0 is the fundamental frequency of the note. F(t)= n= a n cos(2πnv 0 t)+b n sin(2πnv 0 t) (4) The is for mathematical symmetry. Since cosx = cos( x), sinx = sin( x), F(t)=A 0 /2+ n=1 where A n =a n +a n, B n =b n b n A n cos(2πnv 0 t)+b n sin(2πnv 0 t) (5) kr chowdhary Fourier Transform & its applications 13/ 15
14 Fast Fourier Transform using SciLab s=sin(2 π 50 t)+sin(2 π 70 t+π/4)+grand(1,n, nor,0,1) y =fft(s) kr chowdhary Fourier Transform & its applications 14/ 15
15 Resources FourierTransformBib/Links/ FourierTransformBib lnk 1.html kr chowdhary Fourier Transform & its applications 15/ 15
Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier
 Center of Atmospheric Sciences, UNAM September 30, 2016 Jean-Baptiste Joseph Jean-Baptiste Joseph (1768 1830) was a French mathematician and physicist born in Auxerre and best known for initiating the
Center of Atmospheric Sciences, UNAM September 30, 2016 Jean-Baptiste Joseph Jean-Baptiste Joseph (1768 1830) was a French mathematician and physicist born in Auxerre and best known for initiating the
Analysis II: Fourier Series
 .... Analysis II: Fourier Series Kenichi Maruno Department of Mathematics, The University of Texas - Pan American May 3, 011 K.Maruno (UT-Pan American) Analysis II May 3, 011 1 / 16 Fourier series were
.... Analysis II: Fourier Series Kenichi Maruno Department of Mathematics, The University of Texas - Pan American May 3, 011 K.Maruno (UT-Pan American) Analysis II May 3, 011 1 / 16 Fourier series were
Weighted SS(E) = w 2 1( y 1 y1) y n. w n. Wy W y 2 = Wy WAx 2. WAx = Wy. (WA) T WAx = (WA) T b
 6.8 - Applications of Inner Product Spaces Weighted Least-Squares Sometimes you want to get a least-squares solution to a problem where some of the data points are less reliable than others. In this case,
6.8 - Applications of Inner Product Spaces Weighted Least-Squares Sometimes you want to get a least-squares solution to a problem where some of the data points are less reliable than others. In this case,
Today s lecture. The Fourier transform. Sampling, aliasing, interpolation The Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) algorithm
 Today s lecture The Fourier transform What is it? What is it useful for? What are its properties? Sampling, aliasing, interpolation The Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) algorithm Jean Baptiste Joseph Fourier
Today s lecture The Fourier transform What is it? What is it useful for? What are its properties? Sampling, aliasing, interpolation The Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) algorithm Jean Baptiste Joseph Fourier
Communication Signals (Haykin Sec. 2.4 and Ziemer Sec Sec. 2.4) KECE321 Communication Systems I
 Communication Signals (Haykin Sec..4 and iemer Sec...4-Sec..4) KECE3 Communication Systems I Lecture #3, March, 0 Prof. Young-Chai Ko 년 3 월 일일요일 Review Signal classification Phasor signal and spectra Representation
Communication Signals (Haykin Sec..4 and iemer Sec...4-Sec..4) KECE3 Communication Systems I Lecture #3, March, 0 Prof. Young-Chai Ko 년 3 월 일일요일 Review Signal classification Phasor signal and spectra Representation
CHAPTER 4 FOURIER SERIES S A B A R I N A I S M A I L
 CHAPTER 4 FOURIER SERIES 1 S A B A R I N A I S M A I L Outline Introduction of the Fourier series. The properties of the Fourier series. Symmetry consideration Application of the Fourier series to circuit
CHAPTER 4 FOURIER SERIES 1 S A B A R I N A I S M A I L Outline Introduction of the Fourier series. The properties of the Fourier series. Symmetry consideration Application of the Fourier series to circuit
Lab Fourier Analysis Do prelab before lab starts. PHSX 262 Spring 2011 Lecture 5 Page 1. Based with permission on lectures by John Getty
 Today /5/ Lecture 5 Fourier Series Time-Frequency Decomposition/Superposition Fourier Components (Ex. Square wave) Filtering Spectrum Analysis Windowing Fast Fourier Transform Sweep Frequency Analyzer
Today /5/ Lecture 5 Fourier Series Time-Frequency Decomposition/Superposition Fourier Components (Ex. Square wave) Filtering Spectrum Analysis Windowing Fast Fourier Transform Sweep Frequency Analyzer
Signals and Systems Lecture (S2) Orthogonal Functions and Fourier Series March 17, 2008
 Signals and Systems Lecture (S) Orthogonal Functions and Fourier Series March 17, 008 Today s Topics 1. Analogy between functions of time and vectors. Fourier series Take Away Periodic complex exponentials
Signals and Systems Lecture (S) Orthogonal Functions and Fourier Series March 17, 008 Today s Topics 1. Analogy between functions of time and vectors. Fourier series Take Away Periodic complex exponentials
Continuous-time Fourier Methods
 ELEC 321-001 SIGNALS and SYSTEMS Continuous-time Fourier Methods Chapter 6 1 Representing a Signal The convolution method for finding the response of a system to an excitation takes advantage of the linearity
ELEC 321-001 SIGNALS and SYSTEMS Continuous-time Fourier Methods Chapter 6 1 Representing a Signal The convolution method for finding the response of a system to an excitation takes advantage of the linearity
Lecture 5. The Digital Fourier Transform. (Based, in part, on The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing by Steven Smith)
 Lecture 5 The Digital Fourier Transform (Based, in part, on The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing by Steven Smith) 1 -. 8 -. 6 -. 4 -. 2-1 -. 8 -. 6 -. 4 -. 2 -. 2. 4. 6. 8 1
Lecture 5 The Digital Fourier Transform (Based, in part, on The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing by Steven Smith) 1 -. 8 -. 6 -. 4 -. 2-1 -. 8 -. 6 -. 4 -. 2 -. 2. 4. 6. 8 1
Chapter 4 Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) And Signal Spectrum
 Chapter 4 Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) And Signal Spectrum CEN352, DR. Nassim Ammour, King Saud University 1 Fourier Transform History Born 21 March 1768 ( Auxerre ). Died 16 May 1830 ( Paris ) French
Chapter 4 Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) And Signal Spectrum CEN352, DR. Nassim Ammour, King Saud University 1 Fourier Transform History Born 21 March 1768 ( Auxerre ). Died 16 May 1830 ( Paris ) French
SET 1. (1) Solve for x: (a) e 2x = 5 3x
 () Solve for x: (a) e x = 5 3x SET We take natural log on both sides: ln(e x ) = ln(5 3x ) x = 3 x ln(5) Now we take log base on both sides: log ( x ) = log (3 x ln 5) x = log (3 x ) + log (ln(5)) x x
() Solve for x: (a) e x = 5 3x SET We take natural log on both sides: ln(e x ) = ln(5 3x ) x = 3 x ln(5) Now we take log base on both sides: log ( x ) = log (3 x ln 5) x = log (3 x ) + log (ln(5)) x x
Lecture # 06. Image Processing in Frequency Domain
 Digital Image Processing CP-7008 Lecture # 06 Image Processing in Frequency Domain Fall 2011 Outline Fourier Transform Relationship with Image Processing CP-7008: Digital Image Processing Lecture # 6 2
Digital Image Processing CP-7008 Lecture # 06 Image Processing in Frequency Domain Fall 2011 Outline Fourier Transform Relationship with Image Processing CP-7008: Digital Image Processing Lecture # 6 2
4.5. Applications of Trigonometry to Waves. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Applications of Trigonometry to Waves 4.5 Introduction Waves and vibrations occur in many contexts. The water waves on the sea and the vibrations of a stringed musical instrument are just two everyday
Applications of Trigonometry to Waves 4.5 Introduction Waves and vibrations occur in many contexts. The water waves on the sea and the vibrations of a stringed musical instrument are just two everyday
Today s lecture. Local neighbourhood processing. The convolution. Removing uncorrelated noise from an image The Fourier transform
 Cris Luengo TD396 fall 4 cris@cbuuse Today s lecture Local neighbourhood processing smoothing an image sharpening an image The convolution What is it? What is it useful for? How can I compute it? Removing
Cris Luengo TD396 fall 4 cris@cbuuse Today s lecture Local neighbourhood processing smoothing an image sharpening an image The convolution What is it? What is it useful for? How can I compute it? Removing
Honors Algebra 2 Chapter 14 Page 1
 Section. (Introduction) Graphs of Trig Functions Objectives:. To graph basic trig functions using t-bar method. A. Sine and Cosecant. y = sinθ y y y y 0 --- --- 80 --- --- 30 0 0 300 5 35 5 35 60 50 0
Section. (Introduction) Graphs of Trig Functions Objectives:. To graph basic trig functions using t-bar method. A. Sine and Cosecant. y = sinθ y y y y 0 --- --- 80 --- --- 30 0 0 300 5 35 5 35 60 50 0
Chapter 2 Joseph Fourier
 Chapter 2 Joseph Fourier Joseph Fourier (1768 1830) 2.1 Introduction Fourier series are trigonometric series used to represent a function, and they are widely used throughout pure and applied mathematics.
Chapter 2 Joseph Fourier Joseph Fourier (1768 1830) 2.1 Introduction Fourier series are trigonometric series used to represent a function, and they are widely used throughout pure and applied mathematics.
Examples of the Fourier Theorem (Sect. 10.3). The Fourier Theorem: Continuous case.
 s of the Fourier Theorem (Sect. 1.3. The Fourier Theorem: Continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem: Piecewise continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem:
s of the Fourier Theorem (Sect. 1.3. The Fourier Theorem: Continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem: Piecewise continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem:
f (t) K(t, u) d t. f (t) K 1 (t, u) d u. Integral Transform Inverse Fourier Transform
 Integral Transforms Massoud Malek An integral transform maps an equation from its original domain into another domain, where it might be manipulated and solved much more easily than in the original domain.
Integral Transforms Massoud Malek An integral transform maps an equation from its original domain into another domain, where it might be manipulated and solved much more easily than in the original domain.
3 rd class Mech. Eng. Dept. hamdiahmed.weebly.com Fourier Series
 Definition 1 Fourier Series A function f is said to be piecewise continuous on [a, b] if there exists finitely many points a = x 1 < x 2
Definition 1 Fourier Series A function f is said to be piecewise continuous on [a, b] if there exists finitely many points a = x 1 < x 2
Topic 3: Fourier Series (FS)
 ELEC264: Signals And Systems Topic 3: Fourier Series (FS) o o o o Introduction to frequency analysis of signals CT FS Fourier series of CT periodic signals Signal Symmetry and CT Fourier Series Properties
ELEC264: Signals And Systems Topic 3: Fourier Series (FS) o o o o Introduction to frequency analysis of signals CT FS Fourier series of CT periodic signals Signal Symmetry and CT Fourier Series Properties
FOURIER SERIES. Chapter Introduction
 Chapter 1 FOURIER SERIES 1.1 Introduction Fourier series introduced by a French physicist Joseph Fourier (1768-1830), is a mathematical tool that converts some specific periodic signals into everlasting
Chapter 1 FOURIER SERIES 1.1 Introduction Fourier series introduced by a French physicist Joseph Fourier (1768-1830), is a mathematical tool that converts some specific periodic signals into everlasting
ECE Digital Image Processing and Introduction to Computer Vision. Outline
 ECE592-064 Digital mage Processing and ntroduction to Computer Vision Depart. of ECE, NC State University nstructor: Tianfu (Matt) Wu Spring 2017 1. Recap Outline 2. Thinking in the frequency domain Convolution
ECE592-064 Digital mage Processing and ntroduction to Computer Vision Depart. of ECE, NC State University nstructor: Tianfu (Matt) Wu Spring 2017 1. Recap Outline 2. Thinking in the frequency domain Convolution
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 28 FURTHER MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 3 TUTORIAL 1 - TRIGONOMETRICAL GRAPHS
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 28 FURTHER MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 3 TUTORIAL 1 - TRIGONOMETRICAL GRAPHS CONTENTS 3 Be able to understand how to manipulate trigonometric expressions and apply
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 28 FURTHER MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 3 TUTORIAL 1 - TRIGONOMETRICAL GRAPHS CONTENTS 3 Be able to understand how to manipulate trigonometric expressions and apply
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Fourier Analysis PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 08 It s all waves! Representation of information One of the big issues in perception (and cognition in general) is identifying how the brain represents information
Fourier Analysis PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 08 It s all waves! Representation of information One of the big issues in perception (and cognition in general) is identifying how the brain represents information
Section 6.1 Angles and Radian Measure Review If you measured the distance around a circle in terms of its radius, what is the unit of measure?
 Section 6.1 Angles and Radian Measure Review If you measured the distance around a circle in terms of its radius, what is the unit of measure? In relationship to a circle, if I go half way around the edge
Section 6.1 Angles and Radian Measure Review If you measured the distance around a circle in terms of its radius, what is the unit of measure? In relationship to a circle, if I go half way around the edge
Reference Text: The evolution of Applied harmonics analysis by Elena Prestini
 Notes for July 14. Filtering in Frequency domain. Reference Text: The evolution of Applied harmonics analysis by Elena Prestini It all started with: Jean Baptist Joseph Fourier (1768-1830) Mathematician,
Notes for July 14. Filtering in Frequency domain. Reference Text: The evolution of Applied harmonics analysis by Elena Prestini It all started with: Jean Baptist Joseph Fourier (1768-1830) Mathematician,
Fourier Analysis PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 08. Representation of information
 Fourier Analysis PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 08 It s all waves! Representation of information One of the big issues in perception (and cognition in general) is identifying how the brain represents information
Fourier Analysis PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 08 It s all waves! Representation of information One of the big issues in perception (and cognition in general) is identifying how the brain represents information
FOURIER ANALYSIS. (a) Fourier Series
 (a) Fourier Series FOURIER ANAYSIS (b) Fourier Transforms Useful books: 1. Advanced Mathematics for Engineers and Scientists, Schaum s Outline Series, M. R. Spiegel - The course text. We follow their notation
(a) Fourier Series FOURIER ANAYSIS (b) Fourier Transforms Useful books: 1. Advanced Mathematics for Engineers and Scientists, Schaum s Outline Series, M. R. Spiegel - The course text. We follow their notation
Fourier Transform in Image Processing. CS/BIOEN 6640 U of Utah Guido Gerig (slides modified from Marcel Prastawa 2012)
 Fourier Transform in Image Processing CS/BIOEN 6640 U of Utah Guido Gerig (slides modified from Marcel Prastawa 2012) Basis Decomposition Write a function as a weighted sum of basis functions f ( x) wibi(
Fourier Transform in Image Processing CS/BIOEN 6640 U of Utah Guido Gerig (slides modified from Marcel Prastawa 2012) Basis Decomposition Write a function as a weighted sum of basis functions f ( x) wibi(
Fourier Series and the Discrete Fourier Expansion
 2 2.5.5 Fourier Series and the Discrete Fourier Expansion Matthew Lincoln Adrienne Carter sillyajc@yahoo.com December 5, 2 Abstract This article is intended to introduce the Fourier series and the Discrete
2 2.5.5 Fourier Series and the Discrete Fourier Expansion Matthew Lincoln Adrienne Carter sillyajc@yahoo.com December 5, 2 Abstract This article is intended to introduce the Fourier series and the Discrete
Fast Fourier Transform
 Fast Fourier Transform December 8, 2016 FFT JPEG RGB Y C B C R (luma (brightness), chroma 2 (color)) chroma resolution is reduced image is split in blocks 8 8 pixels JPEG RGB Y C B C R (luma (brightness),
Fast Fourier Transform December 8, 2016 FFT JPEG RGB Y C B C R (luma (brightness), chroma 2 (color)) chroma resolution is reduced image is split in blocks 8 8 pixels JPEG RGB Y C B C R (luma (brightness),
Prof. Shayla Sawyer CP08 solution
 What does the time constant represent in an exponential function? How do you define a sinusoid? What is impedance? How is a capacitor affected by an input signal that changes over time? How is an inductor
What does the time constant represent in an exponential function? How do you define a sinusoid? What is impedance? How is a capacitor affected by an input signal that changes over time? How is an inductor
SEISMIC WAVE PROPAGATION. Lecture 2: Fourier Analysis
 SEISMIC WAVE PROPAGATION Lecture 2: Fourier Analysis Fourier Series & Fourier Transforms Fourier Series Review of trigonometric identities Analysing the square wave Fourier Transform Transforms of some
SEISMIC WAVE PROPAGATION Lecture 2: Fourier Analysis Fourier Series & Fourier Transforms Fourier Series Review of trigonometric identities Analysing the square wave Fourier Transform Transforms of some
Chapter 17: Fourier Series
 Section A Introduction to Fourier Series By the end of this section you will be able to recognise periodic functions sketch periodic functions determine the period of the given function Why are Fourier
Section A Introduction to Fourier Series By the end of this section you will be able to recognise periodic functions sketch periodic functions determine the period of the given function Why are Fourier
Name Date Period. Calculater Permitted MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 PreAP Precalculus Spring Final Exam Review Name Date Period Calculater Permitted MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the expression.
PreAP Precalculus Spring Final Exam Review Name Date Period Calculater Permitted MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the expression.
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves
 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system
Chapter 17. Fourier series
 Chapter 17. Fourier series We have already met the simple periodic functions, of the form cos(ωt θ). In this chapter we shall look at periodic functions of more complicated nature. 1. The basic results
Chapter 17. Fourier series We have already met the simple periodic functions, of the form cos(ωt θ). In this chapter we shall look at periodic functions of more complicated nature. 1. The basic results
8/19/16. Fourier Analysis. Fourier analysis: the dial tone phone. Fourier analysis: the dial tone phone
 Patrice Koehl Department of Biological Sciences National University of Singapore http://www.cs.ucdavis.edu/~koehl/teaching/bl5229 koehl@cs.ucdavis.edu Fourier analysis: the dial tone phone We use Fourier
Patrice Koehl Department of Biological Sciences National University of Singapore http://www.cs.ucdavis.edu/~koehl/teaching/bl5229 koehl@cs.ucdavis.edu Fourier analysis: the dial tone phone We use Fourier
(Refer Slide Time: 01:30)
 Networks and Systems Prof V.G K.Murti Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 11 Fourier Series (5) Continuing our discussion of Fourier series today, we will
Networks and Systems Prof V.G K.Murti Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 11 Fourier Series (5) Continuing our discussion of Fourier series today, we will
The Australia Telescope. The Australia Telescope National Facility. Why is it a National Facility? Who uses the AT? Ray Norris CSIRO ATNF
 The Australia Telescope National Facility The Australia Telescope Ray Norris CSIRO ATNF Why is it a National Facility? Funded by the federal government (through CSIRO) Provides radio-astronomical facilities
The Australia Telescope National Facility The Australia Telescope Ray Norris CSIRO ATNF Why is it a National Facility? Funded by the federal government (through CSIRO) Provides radio-astronomical facilities
Analytic Trigonometry. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Analytic Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 7.1 Trigonometric Identities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions Proving
Analytic Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 7.1 Trigonometric Identities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions Proving
The Fourier series are applicable to periodic signals. They were discovered by the
 3.1 Fourier Series The Fourier series are applicable to periodic signals. They were discovered by the famous French mathematician Joseph Fourier in 1807. By using the Fourier series, a periodic signal
3.1 Fourier Series The Fourier series are applicable to periodic signals. They were discovered by the famous French mathematician Joseph Fourier in 1807. By using the Fourier series, a periodic signal
Properties of Fourier Cosine and Sine Transforms
 International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR) ISSN 237-4531 (Print & Online) http://gssrr.org/index.php?journal=journalofbasicandapplied ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR) ISSN 237-4531 (Print & Online) http://gssrr.org/index.php?journal=journalofbasicandapplied ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 4 Sequences and Series
 Chapter 4 Sequences and Series 4.1 Sequence Review Sequence: a set of elements (numbers or letters or a combination of both). The elements of the set all follow the same rule (logical progression). The
Chapter 4 Sequences and Series 4.1 Sequence Review Sequence: a set of elements (numbers or letters or a combination of both). The elements of the set all follow the same rule (logical progression). The
(c) cos Arctan ( 3) ( ) PRECALCULUS ADVANCED REVIEW FOR FINAL FIRST SEMESTER
 PRECALCULUS ADVANCED REVIEW FOR FINAL FIRST SEMESTER Work the following on notebook paper ecept for the graphs. Do not use our calculator unless the problem tells ou to use it. Give three decimal places
PRECALCULUS ADVANCED REVIEW FOR FINAL FIRST SEMESTER Work the following on notebook paper ecept for the graphs. Do not use our calculator unless the problem tells ou to use it. Give three decimal places
Assignment 3 Solutions
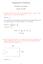 Assignment Solutions Networks and systems August 8, 7. Consider an LTI system with transfer function H(jw) = input is sin(t + π 4 ), what is the output? +jw. If the Solution : C For an LTI system with
Assignment Solutions Networks and systems August 8, 7. Consider an LTI system with transfer function H(jw) = input is sin(t + π 4 ), what is the output? +jw. If the Solution : C For an LTI system with
Solutions 2: Simple Harmonic Oscillator and General Oscillations
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology MITES 2017 Physics III Solutions 2: Simple Harmonic Oscillator and General Oscillations Due Wednesday June 21, at 9AM under Rene García s door Preface: This problem
Massachusetts Institute of Technology MITES 2017 Physics III Solutions 2: Simple Harmonic Oscillator and General Oscillations Due Wednesday June 21, at 9AM under Rene García s door Preface: This problem
ANoteonEuler sformula
 ANoteonEuler sformula Dr. Mike Wilkes ASC Chastain Indian River State College 4/1/014 1 Euler s Formula The general complex exponential function e z,wherez is any complex number of the form (a + ib), has
ANoteonEuler sformula Dr. Mike Wilkes ASC Chastain Indian River State College 4/1/014 1 Euler s Formula The general complex exponential function e z,wherez is any complex number of the form (a + ib), has
Fourier Series. Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta
 1 Lecture Notes on Partial Differential Equations Chapter IV Fourier Series Ilyasse Aksikas Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta aksikas@ualberta.ca DEFINITIONS 2 Before
1 Lecture Notes on Partial Differential Equations Chapter IV Fourier Series Ilyasse Aksikas Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta aksikas@ualberta.ca DEFINITIONS 2 Before
I. Signals & Sinusoids
 I. Signals & Sinusoids [p. 3] Signal definition Sinusoidal signal Plotting a sinusoid [p. 12] Signal operations Time shifting Time scaling Time reversal Combining time shifting & scaling [p. 17] Trigonometric
I. Signals & Sinusoids [p. 3] Signal definition Sinusoidal signal Plotting a sinusoid [p. 12] Signal operations Time shifting Time scaling Time reversal Combining time shifting & scaling [p. 17] Trigonometric
2.3 Oscillation. The harmonic oscillator equation is the differential equation. d 2 y dt 2 r y (r > 0). Its solutions have the form
 2. Oscillation So far, we have used differential equations to describe functions that grow or decay over time. The next most common behavior for a function is to oscillate, meaning that it increases and
2. Oscillation So far, we have used differential equations to describe functions that grow or decay over time. The next most common behavior for a function is to oscillate, meaning that it increases and
Phasor Young Won Lim 05/19/2015
 Phasor Copyright (c) 2009-2015 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version
Phasor Copyright (c) 2009-2015 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version
Dr. David A. Clifton Group Leader Computational Health Informatics (CHI) Lab Lecturer in Engineering Science, Balliol College
 Dr. David A. Clifton Group Leader Computational Health Informatics (CHI) Lab Lecturer in Engineering Science, Balliol College 1. Introduction to Fourier analysis, the Fourier series 2. Sampling and Aliasing
Dr. David A. Clifton Group Leader Computational Health Informatics (CHI) Lab Lecturer in Engineering Science, Balliol College 1. Introduction to Fourier analysis, the Fourier series 2. Sampling and Aliasing
Fourier Series and Fourier Transforms
 Fourier Series and Fourier Transforms EECS2 (6.082), MIT Fall 2006 Lectures 2 and 3 Fourier Series From your differential equations course, 18.03, you know Fourier s expression representing a T -periodic
Fourier Series and Fourier Transforms EECS2 (6.082), MIT Fall 2006 Lectures 2 and 3 Fourier Series From your differential equations course, 18.03, you know Fourier s expression representing a T -periodic
Chapter Thirteen: Traveling Waves and the Wave Equation in Air, Water and the Ether
 Chapter Thirteen: Traveling Waves and the Wave Equation in Air, Water and the Ether We have been discussing the waves that are found in the string of a guitar or violin and how they are the physical reality
Chapter Thirteen: Traveling Waves and the Wave Equation in Air, Water and the Ether We have been discussing the waves that are found in the string of a guitar or violin and how they are the physical reality
IMAGE ENHANCEMENT: FILTERING IN THE FREQUENCY DOMAIN. Francesca Pizzorni Ferrarese
 IMAGE ENHANCEMENT: FILTERING IN THE FREQUENCY DOMAIN Francesca Pizzorni Ferrarese Contents In this lecture we will look at image enhancement in the frequency domain Jean Baptiste Joseph Fourier The Fourier
IMAGE ENHANCEMENT: FILTERING IN THE FREQUENCY DOMAIN Francesca Pizzorni Ferrarese Contents In this lecture we will look at image enhancement in the frequency domain Jean Baptiste Joseph Fourier The Fourier
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 22 Review Spring 2013 Semester Matthew Jones Midterm Exam: Date: Wednesday, March 6 th Time: 8:00 10:00 pm Room: PHYS 203 Material: French, chapters 1-8 Review
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 22 Review Spring 2013 Semester Matthew Jones Midterm Exam: Date: Wednesday, March 6 th Time: 8:00 10:00 pm Room: PHYS 203 Material: French, chapters 1-8 Review
Inverse Trig Functions
 6.6i Inverse Trigonometric Functions Inverse Sine Function Does g(x) = sin(x) have an inverse? What restriction would we need to make so that at least a piece of this function has an inverse? Given f (x)
6.6i Inverse Trigonometric Functions Inverse Sine Function Does g(x) = sin(x) have an inverse? What restriction would we need to make so that at least a piece of this function has an inverse? Given f (x)
Sum-to-Product and Product-to-Sum Formulas
 Sum-to-Product and Product-to-Sum Formulas By: OpenStaxCollege The UCLA marching band (credit: Eric Chan, Flickr). A band marches down the field creating an amazing sound that bolsters the crowd. That
Sum-to-Product and Product-to-Sum Formulas By: OpenStaxCollege The UCLA marching band (credit: Eric Chan, Flickr). A band marches down the field creating an amazing sound that bolsters the crowd. That
Print Name : ID : ECE Test #1 9/22/2016
 Print Name : Email ID : ECE 2660 Test #1 9/22/2016 All answers must be recorded on the answer page (page 2). You must do all questions on the exam. For Part 4 you must show all your work and write your
Print Name : Email ID : ECE 2660 Test #1 9/22/2016 All answers must be recorded on the answer page (page 2). You must do all questions on the exam. For Part 4 you must show all your work and write your
Fourier Analysis Fourier Series C H A P T E R 1 1
 C H A P T E R Fourier Analysis 474 This chapter on Fourier analysis covers three broad areas: Fourier series in Secs...4, more general orthonormal series called Sturm iouville epansions in Secs..5 and.6
C H A P T E R Fourier Analysis 474 This chapter on Fourier analysis covers three broad areas: Fourier series in Secs...4, more general orthonormal series called Sturm iouville epansions in Secs..5 and.6
Solutions to the Homework Replaces Section 3.7, 3.8
 Solutions to the Homework Replaces Section 3.7, 3.8 1. Our text (p. 198) states that µ ω 0 = ( 1 γ2 4km ) 1/2 1 1 2 γ 2 4km How was this approximation made? (Hint: Linearize 1 x) SOLUTION: We linearize
Solutions to the Homework Replaces Section 3.7, 3.8 1. Our text (p. 198) states that µ ω 0 = ( 1 γ2 4km ) 1/2 1 1 2 γ 2 4km How was this approximation made? (Hint: Linearize 1 x) SOLUTION: We linearize
Math 1303 Part II. The opening of one of 360 equal central angles of a circle is what we chose to represent 1 degree
 Math 1303 Part II We have discussed two ways of measuring angles; degrees and radians The opening of one of 360 equal central angles of a circle is what we chose to represent 1 degree We defined a radian
Math 1303 Part II We have discussed two ways of measuring angles; degrees and radians The opening of one of 360 equal central angles of a circle is what we chose to represent 1 degree We defined a radian
10 Motivation for Fourier series
 10 Motivation for Fourier series Donkeys and scholars in the middle! French soldiers, forming defensive squares in Egypt, during Napoleon s campaign The central topic of our course is the so-called Fourier
10 Motivation for Fourier series Donkeys and scholars in the middle! French soldiers, forming defensive squares in Egypt, during Napoleon s campaign The central topic of our course is the so-called Fourier
Precalculus Honors Problem Set: Elementary Trigonometry
 Precalculus Honors Problem Set: Elementary Trigonometry Mr. Warkentin 03 Sprague Hall 017-018 Academic Year Directions: These questions are not presented in order of difficulty. Some of these questions
Precalculus Honors Problem Set: Elementary Trigonometry Mr. Warkentin 03 Sprague Hall 017-018 Academic Year Directions: These questions are not presented in order of difficulty. Some of these questions
Fourier Series & The Fourier Transform
 Fourier Series & The Fourier Transform What is the Fourier Transform? Anharmonic Waves Fourier Cosine Series for even functions Fourier Sine Series for odd functions The continuous limit: the Fourier transform
Fourier Series & The Fourier Transform What is the Fourier Transform? Anharmonic Waves Fourier Cosine Series for even functions Fourier Sine Series for odd functions The continuous limit: the Fourier transform
GATE EE Topic wise Questions SIGNALS & SYSTEMS
 www.gatehelp.com GATE EE Topic wise Questions YEAR 010 ONE MARK Question. 1 For the system /( s + 1), the approximate time taken for a step response to reach 98% of the final value is (A) 1 s (B) s (C)
www.gatehelp.com GATE EE Topic wise Questions YEAR 010 ONE MARK Question. 1 For the system /( s + 1), the approximate time taken for a step response to reach 98% of the final value is (A) 1 s (B) s (C)
19. The Fourier Transform in optics
 19. The Fourier Transform in optics What is the Fourier Transform? Anharmonic waves The spectrum of a light wave Fourier transform of an exponential The Dirac delta function The Fourier transform of e
19. The Fourier Transform in optics What is the Fourier Transform? Anharmonic waves The spectrum of a light wave Fourier transform of an exponential The Dirac delta function The Fourier transform of e
Chapter 5 Trigonometric Functions of Angles
 Chapter 5 Trigonometric Functions of Angles Section 3 Points on Circles Using Sine and Cosine Signs Signs I Signs (+, +) I Signs II (+, +) I Signs II (, +) (+, +) I Signs II (, +) (+, +) I III Signs II
Chapter 5 Trigonometric Functions of Angles Section 3 Points on Circles Using Sine and Cosine Signs Signs I Signs (+, +) I Signs II (+, +) I Signs II (, +) (+, +) I Signs II (, +) (+, +) I III Signs II
23.4. Convergence. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Convergence 3.4 Introduction In this Section we examine, briefly, the convergence characteristics of a Fourier series. We have seen that a Fourier series can be found for functions which are not necessarily
Convergence 3.4 Introduction In this Section we examine, briefly, the convergence characteristics of a Fourier series. We have seen that a Fourier series can be found for functions which are not necessarily
Fourier Analysis Partial Differential Equations (PDEs)
 PART C Fourier Analysis. Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) CHAPTER CHAPTER Fourier Analysis Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) Chapter and Chapter are directly related to each other in that Fourier
PART C Fourier Analysis. Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) CHAPTER CHAPTER Fourier Analysis Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) Chapter and Chapter are directly related to each other in that Fourier
Fourier transforms. R. C. Daileda. Partial Differential Equations April 17, Trinity University
 The Fourier Transform R. C. Trinity University Partial Differential Equations April 17, 214 The Fourier series representation For periodic functions Recall: If f is a 2p-periodic (piecewise smooth) function,
The Fourier Transform R. C. Trinity University Partial Differential Equations April 17, 214 The Fourier series representation For periodic functions Recall: If f is a 2p-periodic (piecewise smooth) function,
Fourier series. XE31EO2 - Pavel Máša. Electrical Circuits 2 Lecture1. XE31EO2 - Pavel Máša - Fourier Series
 Fourier series Electrical Circuits Lecture - Fourier Series Filtr RLC defibrillator MOTIVATION WHAT WE CAN'T EXPLAIN YET Source voltage rectangular waveform Resistor voltage sinusoidal waveform - Fourier
Fourier series Electrical Circuits Lecture - Fourier Series Filtr RLC defibrillator MOTIVATION WHAT WE CAN'T EXPLAIN YET Source voltage rectangular waveform Resistor voltage sinusoidal waveform - Fourier
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS: PAPER 3C1 HANDOUT 6a. Dr David Corrigan 1. Electronic and Electrical Engineering Dept.
 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS: PAPER 3C HANDOUT 6a. Dr David Corrigan. Electronic and Electrical Engineering Dept. corrigad@tcd.ie www.mee.tcd.ie/ corrigad FOURIER SERIES Have seen how the behaviour of systems can
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS: PAPER 3C HANDOUT 6a. Dr David Corrigan. Electronic and Electrical Engineering Dept. corrigad@tcd.ie www.mee.tcd.ie/ corrigad FOURIER SERIES Have seen how the behaviour of systems can
Complex Numbers. James K. Peterson. September 19, Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University
 Complex Numbers James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University September 19, 2013 Outline 1 Complex Numbers 2 Complex Number Calculations
Complex Numbers James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University September 19, 2013 Outline 1 Complex Numbers 2 Complex Number Calculations
Complex Numbers. Outline. James K. Peterson. September 19, Complex Numbers. Complex Number Calculations. Complex Functions
 Complex Numbers James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University September 19, 2013 Outline Complex Numbers Complex Number Calculations Complex
Complex Numbers James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University September 19, 2013 Outline Complex Numbers Complex Number Calculations Complex
Lab #2 - Two Degrees-of-Freedom Oscillator
 Lab #2 - Two Degrees-of-Freedom Oscillator Last Updated: March 0, 2007 INTRODUCTION The system illustrated in Figure has two degrees-of-freedom. This means that two is the minimum number of coordinates
Lab #2 - Two Degrees-of-Freedom Oscillator Last Updated: March 0, 2007 INTRODUCTION The system illustrated in Figure has two degrees-of-freedom. This means that two is the minimum number of coordinates
EA2.3 - Electronics 2 1
 In the previous lecture, I talked about the idea of complex frequency s, where s = σ + jω. Using such concept of complex frequency allows us to analyse signals and systems with better generality. In this
In the previous lecture, I talked about the idea of complex frequency s, where s = σ + jω. Using such concept of complex frequency allows us to analyse signals and systems with better generality. In this
Queens College, CUNY, Department of Computer Science Numerical Methods CSCI 361 / 761 Spring 2018 Instructor: Dr. Sateesh Mane.
 Queens College, CUNY, Department of Computer Science Numerical Methods CSCI 361 / 761 Spring 018 Instructor: Dr. Sateesh Mane c Sateesh R. Mane 018 30 Lecture 30 April 7, 018 Fourier Series In this lecture,
Queens College, CUNY, Department of Computer Science Numerical Methods CSCI 361 / 761 Spring 018 Instructor: Dr. Sateesh Mane c Sateesh R. Mane 018 30 Lecture 30 April 7, 018 Fourier Series In this lecture,
Chapter 16: Oscillations
 Chapter 16: Oscillations Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Periodic Motion Periodic Motion is any motion that repeats itself. The Period (T) is the time it takes for one complete cycle of motion.
Chapter 16: Oscillations Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Periodic Motion Periodic Motion is any motion that repeats itself. The Period (T) is the time it takes for one complete cycle of motion.
Using Fourier Analysis in Evaluating Program Office Estimates
 Using Fourier Analysis in Evaluating Program Office Estimates Stephen Cox, USA PEO Aviation Matthew Latham, USA AMCOM Angela Lemke, USA AMCOM June 2010 Special Thanks To: Wallace Willard, NASA Penny Pride,
Using Fourier Analysis in Evaluating Program Office Estimates Stephen Cox, USA PEO Aviation Matthew Latham, USA AMCOM Angela Lemke, USA AMCOM June 2010 Special Thanks To: Wallace Willard, NASA Penny Pride,
5.1: Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions
 5.1: Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Complete the table below ( we used increments of for the values of ) 4 0 sin 4 2 3 4 5 4 3 7 2 4 2 cos 1. Using the table, sketch the graph of y sin for 0 2 2. What
5.1: Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Complete the table below ( we used increments of for the values of ) 4 0 sin 4 2 3 4 5 4 3 7 2 4 2 cos 1. Using the table, sketch the graph of y sin for 0 2 2. What
Chapter 7: Trigonometric Equations and Identities
 Chapter 7: Trigonometric Equations and Identities In the last two chapters we have used basic definitions and relationships to simplify trigonometric expressions and equations. In this chapter we will
Chapter 7: Trigonometric Equations and Identities In the last two chapters we have used basic definitions and relationships to simplify trigonometric expressions and equations. In this chapter we will
Functions of Several Variables
 Functions of Several Variables Partial Derivatives Philippe B Laval KSU March 21, 2012 Philippe B Laval (KSU) Functions of Several Variables March 21, 2012 1 / 19 Introduction In this section we extend
Functions of Several Variables Partial Derivatives Philippe B Laval KSU March 21, 2012 Philippe B Laval (KSU) Functions of Several Variables March 21, 2012 1 / 19 Introduction In this section we extend
Sinusoids. Amplitude and Magnitude. Phase and Period. CMPT 889: Lecture 2 Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation
 Sinusoids CMPT 889: Lecture Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University September 6, 005 Sinusoids are
Sinusoids CMPT 889: Lecture Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University September 6, 005 Sinusoids are
7 PDES, FOURIER SERIES AND TRANSFORMS Last Updated: July 16, 2012
 Problem List 7.1 Fourier series expansion of absolute value function 7.2 Fourier series expansion of step function 7.3 Orthogonality of functions 7.4 Fourier transform of sinusoidal pulse 7.5 Introducing
Problem List 7.1 Fourier series expansion of absolute value function 7.2 Fourier series expansion of step function 7.3 Orthogonality of functions 7.4 Fourier transform of sinusoidal pulse 7.5 Introducing
A1 Time-Frequency Analysis
 A 20 / A Time-Frequency Analysis David Murray david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/2tf Hilary 20 A 20 2 / Content 8 Lectures: 6 Topics... From Signals to Complex Fourier Series 2
A 20 / A Time-Frequency Analysis David Murray david.murray@eng.ox.ac.uk www.robots.ox.ac.uk/ dwm/courses/2tf Hilary 20 A 20 2 / Content 8 Lectures: 6 Topics... From Signals to Complex Fourier Series 2
CMPT 889: Lecture 2 Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation
 CMPT 889: Lecture 2 Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University September 26, 2005 1 Sinusoids Sinusoids
CMPT 889: Lecture 2 Sinusoids, Complex Exponentials, Spectrum Representation Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University September 26, 2005 1 Sinusoids Sinusoids
Worksheet #2. Use trigonometry and logarithms to model natural phenomena from a periodic behavior perspective.
 math 112 Worksheet #2 Name Due Date: Objective: Use trigonometry and logarithms to model natural phenomena from a periodic behavior perspective. We revisit the varying of tree ring widths over time. We
math 112 Worksheet #2 Name Due Date: Objective: Use trigonometry and logarithms to model natural phenomena from a periodic behavior perspective. We revisit the varying of tree ring widths over time. We
Math 345: Applied Mathematics
 Math 345: Applied Mathematics Introduction to Fourier Series, I Tones, Harmonics, and Fourier s Theorem Marcus Pendergrass Hampden-Sydney College Fall 2012 1 Sounds as waveforms I ve got a bad feeling
Math 345: Applied Mathematics Introduction to Fourier Series, I Tones, Harmonics, and Fourier s Theorem Marcus Pendergrass Hampden-Sydney College Fall 2012 1 Sounds as waveforms I ve got a bad feeling
Signals and systems Lecture (S3) Square Wave Example, Signal Power and Properties of Fourier Series March 18, 2008
 Signals and systems Lecture (S3) Square Wave Example, Signal Power and Properties of Fourier Series March 18, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Derivation of a Fourier series representation of a square wave signal
Signals and systems Lecture (S3) Square Wave Example, Signal Power and Properties of Fourier Series March 18, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Derivation of a Fourier series representation of a square wave signal
An improper integral and an infinite series
 An improper integral and an infinite series A. Baltimore one of the old cities in the United States Yue Kwok Choy In summer of 2010, I had great time visiting my daughter, Wendy, who is living in a small
An improper integral and an infinite series A. Baltimore one of the old cities in the United States Yue Kwok Choy In summer of 2010, I had great time visiting my daughter, Wendy, who is living in a small
Notes on Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series
 Notes on Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series et f(x) be a piecewise linear function on [, ] (This means that f(x) may possess a finite number of finite discontinuities on the interval). Then f(x)
Notes on Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series et f(x) be a piecewise linear function on [, ] (This means that f(x) may possess a finite number of finite discontinuities on the interval). Then f(x)
Practice 14. imathesis.com By Carlos Sotuyo
 Practice 4 imathesis.com By Carlos Sotuyo Suggested solutions for Miscellaneous exercises 0, problems 5-0, pages 53 to 55 from Pure Mathematics, by Hugh Neil and Douglas Quailing, Cambridge University
Practice 4 imathesis.com By Carlos Sotuyo Suggested solutions for Miscellaneous exercises 0, problems 5-0, pages 53 to 55 from Pure Mathematics, by Hugh Neil and Douglas Quailing, Cambridge University
Complex numbers. Reference note to lecture 9 ECON 5101 Time Series Econometrics
 Complex numbers. Reference note to lecture 9 ECON 5101 Time Series Econometrics Ragnar Nymoen March 31 2014 1 Introduction This note gives the definitions and theorems related to complex numbers that are
Complex numbers. Reference note to lecture 9 ECON 5101 Time Series Econometrics Ragnar Nymoen March 31 2014 1 Introduction This note gives the definitions and theorems related to complex numbers that are
Solutions to the Homework Replaces Section 3.7, 3.8
 Solutions to the Homework Replaces Section 3.7, 3.8. Show that the period of motion of an undamped vibration of a mass hanging from a vertical spring is 2π L/g SOLUTION: With no damping, mu + ku = 0 has
Solutions to the Homework Replaces Section 3.7, 3.8. Show that the period of motion of an undamped vibration of a mass hanging from a vertical spring is 2π L/g SOLUTION: With no damping, mu + ku = 0 has
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 1 Objectives : sinusoidal functions Impedance use phasors to determine the forced response of a circuit subjected to sinusoidal excitation Apply techniques
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 1 Objectives : sinusoidal functions Impedance use phasors to determine the forced response of a circuit subjected to sinusoidal excitation Apply techniques
THE FOURIER TRANSFORM (Fourier series for a function whose period is very, very long) Reading: Main 11.3
 THE FOURIER TRANSFORM (Fourier series for a function whose period is very, very long) Reading: Main 11.3 Any periodic function f(t) can be written as a Fourier Series a 0 2 + a n cos( nωt) + b n sin n
THE FOURIER TRANSFORM (Fourier series for a function whose period is very, very long) Reading: Main 11.3 Any periodic function f(t) can be written as a Fourier Series a 0 2 + a n cos( nωt) + b n sin n
Lecture 10: Eigenvalue Estimation
 CS 880: Quantum Information Processing 9/7/010 Lecture 10: Eigenvalue Estimation Instructor: Dieter van Melkebeek Scribe: Dalibor Zelený Last time we discussed the quantum Fourier transform, and introduced
CS 880: Quantum Information Processing 9/7/010 Lecture 10: Eigenvalue Estimation Instructor: Dieter van Melkebeek Scribe: Dalibor Zelený Last time we discussed the quantum Fourier transform, and introduced
