Math 1070 Exam 2. March 16, 2006
|
|
|
- Vanessa Lloyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 1070 Exam 2 Name: March 16, Solve each of the following systems of equations using the indicated method: (a) Solve by graphing (include a sketch of your graph, indicating the graphing window, as well as the equations you graphed): 2x 1 3x 2 9 x 1 + 2x 2 8 I don t know how to get a graph in here, but two different possibilities for sets of equations work, which I show side by side. Solving for x 1 in the left column and x 2 in the right column would give 3 x 1 2 x x 2 3 x 1 3 x 1 2x x x The intersection points would be (1, 6) and (6, 1) respectively and, associating each coordinate to the correct variable, we get, in both cases, (b) Solve by substitution x 1 6 x 2 1 2x 1 + 5x 2 7 x 1 2x 2 4 From the second equation, x x 2, so the first equation is 2 (4 + 2x 2 ) + 5x 2 7, which simplifies to x Then, plugging this into x x 2, we get x ( 1 9 So x and x (c) Solve using elimination by addition 2x 1 + 3x x 1 6x 2 9 ) Add the second to the first to get 0x 1 3x 2 6. Then x 2 2. Substitute this into the first to get 2x , and thus x So x , and x
2 2. Do the following for each of the following matrices: State whether the matrix is in reduced form. If it is not perform an appropriate row operation to put it in reduced form. Then indicate whether the related system of equations has a unique solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solutions. (a) This satisfies all of the conditions of the reduced form. Further, since each column (except the constant terms) contains a leading one, we can conclude that there is a unique solution. (b) Not in reduced form because the leading 1 in the third row has 1 above it. Perform R 2 R 3 R 2 to get the reduced form: Since the last line corresponds to 0 1, there are no solutions. (c) Not in reduced form because the leading ones are not left to right as we go down. R 1 R 2 to get the reduced form: Perform Since we have a column with no leading ones and no line corresponds to 0 1, there are infinitely many solutions. 2
3 3. Consider the following matrices and perform the indicated operations (if possible) by hand: A B C D (a) BCA BCA B (CA) ( ) (b) 2D + A D + A (c) C 1 C
4 4. Consider the following system of equations: 3x 1 6x x 1 x 2 13 (a) Set up the augmented matrix for the system (b) Use Gauss-Jordan elimination to find the reduced row echelon form of this augmented matrix by hand. Show all work /3R R R R 1 R /3R R R R 2 R (c) Use the reduced row echelon form of the augmented matrix to determine the solution to the system of equations. x 1 5 x 2 3 4
5 5. Gizmos Incorporated manufactures three different gizmos: the Thingamajig, the Whatchacallit, and the Thing-bob. An overly simplified model of their production splits their manufacturing process into two steps: assembly and finishing. The following chart gives the time each step takes for each product. If the assembly department has a total of 300 hours available in a week and the finishing department has a total of 150 hours available in a week, what production schedule will allow Gizmos Incorporated to operate at full capacity? Production Step Thingamajig Whatchacallit Thing-bob Assembly Finishing The matrix for this comes right out of the table when we add the total hours available to the end of each row. We then find the reduced form (using a calculator) as follows: The reduced matrix corresponds to the following equations, where x 1, x 2, and x 3 represent the number of Thingamajigs, Whatchacallits and Thing-bobs produced respectively. Solving for x 1 and x 2, we get x 1 4x 3 0 x 2 + 3x x 1 4x 3 x x 3 Using the parameter t for x 3, we notice that t must be positive and that 3t must be less than 300, so that we have the following solution set: with 0 t 100, t an integer. x 1 4t x t x 3 t 5
6 6. Gizmos Incorporated, after a rapid expansion, operates plants in Cityburg and Townville. For various reasons, the hourly wages paid to employees differ at the two plants and for the different production steps, as given by the following table: Plant Assembly Finishing Cityburg $10.50 $11.00 Townville $13.00 $14.50 If we define matrix A as the matrix obtained directly from the table in question 5 and matrix B as the matrix obtained directly from the table in this question, (a) Compute the matrix BA (You may use a calculator). B and A , so that BA (b) Discuss the meanings of each entry in the matrix BA in terms of manufacturing. Each column represents a product (as it did in matrix A), and each row represents a plant (as it did in matrix B). The terms are determined by adding up the product of the hourly cost and hours needed in assembly and the product of the hourly cost and hours needed in finishing. Thus, the terms represent the total labor costs of manufacturing a given product (its column) at a given plant (its row). 6
7 7. The continuing saga of Gizmos Incorporated: Gizmos Incorporated discontinues production of the Thing-bob and reconfigures both of their plants to give the following hourly production schedule (entries indicating the number of units produced per hour): Plant Cityburg Townville Thingamajigs 10 8 Whatchacallits 5 8 The hours of operation for each plant are determined by the orders received each week. With the following orders, how long should each plant be operated to have the orders exactly filled? Thingamajigs Whatchacallits We are looking for six quantities: the hours for each plant and for each order. This corresponds to a 2 3 matrix. We have the following overall system, where c represents the hours of operation for Cityburg and t for Townville: c1 c 2 c t 1 t 2 t Then, multiplying both sides on the left by the inverse of the 2 2 matrix, we find that c1 c 2 c t 1 t 2 t Thus we have the following table for hours of operation for each order: Cityburg Townville
Math 1070 Exam 2. March 16, 2006
 Math 1070 Exam 2 Name: March 16, 2006 1. Solve each of the following systems of equations using the indicated method: (a) Solve by graphing (include a sketch of your graph, indicating the graphing window,
Math 1070 Exam 2 Name: March 16, 2006 1. Solve each of the following systems of equations using the indicated method: (a) Solve by graphing (include a sketch of your graph, indicating the graphing window,
Math 1314 Week #14 Notes
 Math 3 Week # Notes Section 5.: A system of equations consists of two or more equations. A solution to a system of equations is a point that satisfies all the equations in the system. In this chapter,
Math 3 Week # Notes Section 5.: A system of equations consists of two or more equations. A solution to a system of equations is a point that satisfies all the equations in the system. In this chapter,
Math x + 3y 5z = 14 3x 2y + 3z = 17 4x + 3y 2z = 1
 Math 210 1. Solve the system: x + y + z = 1 2x + 3y + 4z = 5 (a z = 2, y = 1 and x = 0 (b z =any value, y = 3 2z and x = z 2 (c z =any value, y = 3 2z and x = z + 2 (d z =any value, y = 3 + 2z and x =
Math 210 1. Solve the system: x + y + z = 1 2x + 3y + 4z = 5 (a z = 2, y = 1 and x = 0 (b z =any value, y = 3 2z and x = z 2 (c z =any value, y = 3 2z and x = z + 2 (d z =any value, y = 3 + 2z and x =
9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables
 9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables Recall that a system of equations consists of two or more equations each with two or more variables. A solution to a system in two variables is an ordered
9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables Recall that a system of equations consists of two or more equations each with two or more variables. A solution to a system in two variables is an ordered
Linear Algebra Practice Problems
 Math 7, Professor Ramras Linear Algebra Practice Problems () Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables x, y, and z, in which the constants a and b are real numbers. x y + z = a
Math 7, Professor Ramras Linear Algebra Practice Problems () Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables x, y, and z, in which the constants a and b are real numbers. x y + z = a
5x 2 = 10. x 1 + 7(2) = 4. x 1 3x 2 = 4. 3x 1 + 9x 2 = 8
 1 To solve the system x 1 + x 2 = 4 2x 1 9x 2 = 2 we find an (easier to solve) equivalent system as follows: Replace equation 2 with (2 times equation 1 + equation 2): x 1 + x 2 = 4 Solve equation 2 for
1 To solve the system x 1 + x 2 = 4 2x 1 9x 2 = 2 we find an (easier to solve) equivalent system as follows: Replace equation 2 with (2 times equation 1 + equation 2): x 1 + x 2 = 4 Solve equation 2 for
LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
 LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS MA1111: LINEAR ALGEBRA I, MICHAELMAS 2016 1 Linear equations We now switch gears to discuss the topic of solving linear equations, and more interestingly, systems
LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS MA1111: LINEAR ALGEBRA I, MICHAELMAS 2016 1 Linear equations We now switch gears to discuss the topic of solving linear equations, and more interestingly, systems
Exercise Sketch these lines and find their intersection.
 These are brief notes for the lecture on Friday August 21, 2009: they are not complete, but they are a guide to what I want to say today. They are not guaranteed to be correct. 1. Solving systems of linear
These are brief notes for the lecture on Friday August 21, 2009: they are not complete, but they are a guide to what I want to say today. They are not guaranteed to be correct. 1. Solving systems of linear
Review for Exam Find all a for which the following linear system has no solutions, one solution, and infinitely many solutions.
 Review for Exam. Find all a for which the following linear system has no solutions, one solution, and infinitely many solutions. x + y z = 2 x + 2y + z = 3 x + y + (a 2 5)z = a 2 The augmented matrix for
Review for Exam. Find all a for which the following linear system has no solutions, one solution, and infinitely many solutions. x + y z = 2 x + 2y + z = 3 x + y + (a 2 5)z = a 2 The augmented matrix for
Section 6.2 Larger Systems of Linear Equations
 Section 6.2 Larger Systems of Linear Equations Gaussian Elimination In general, to solve a system of linear equations using its augmented matrix, we use elementary row operations to arrive at a matrix
Section 6.2 Larger Systems of Linear Equations Gaussian Elimination In general, to solve a system of linear equations using its augmented matrix, we use elementary row operations to arrive at a matrix
Gauss-Jordan Row Reduction and Reduced Row Echelon Form
 Gauss-Jordan Row Reduction and Reduced Row Echelon Form If we put the augmented matrix of a linear system in reduced row-echelon form, then we don t need to back-substitute to solve the system. To put
Gauss-Jordan Row Reduction and Reduced Row Echelon Form If we put the augmented matrix of a linear system in reduced row-echelon form, then we don t need to back-substitute to solve the system. To put
Linear System Equations
 King Saud University September 24, 2018 Table of contents 1 2 3 4 Definition A linear system of equations with m equations and n unknowns is defined as follows: a 1,1 x 1 + a 1,2 x 2 + + a 1,n x n = b
King Saud University September 24, 2018 Table of contents 1 2 3 4 Definition A linear system of equations with m equations and n unknowns is defined as follows: a 1,1 x 1 + a 1,2 x 2 + + a 1,n x n = b
System of Linear Equations. Slide for MA1203 Business Mathematics II Week 1 & 2
 System of Linear Equations Slide for MA1203 Business Mathematics II Week 1 & 2 Function A manufacturer would like to know how his company s profit is related to its production level. How does one quantity
System of Linear Equations Slide for MA1203 Business Mathematics II Week 1 & 2 Function A manufacturer would like to know how his company s profit is related to its production level. How does one quantity
Solutions to Homework 5 - Math 3410
 Solutions to Homework 5 - Math 34 (Page 57: # 489) Determine whether the following vectors in R 4 are linearly dependent or independent: (a) (, 2, 3, ), (3, 7,, 2), (, 3, 7, 4) Solution From x(, 2, 3,
Solutions to Homework 5 - Math 34 (Page 57: # 489) Determine whether the following vectors in R 4 are linearly dependent or independent: (a) (, 2, 3, ), (3, 7,, 2), (, 3, 7, 4) Solution From x(, 2, 3,
Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables. Break Even. Example. 240x x This is when total cost equals total revenue.
 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 1 Break Even This is when total cost equals total revenue C(x) = R(x) A company breaks even when the profit is zero P(x) = R(x) C(x) = 0 2 R x 565x C x 6000
Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables 1 Break Even This is when total cost equals total revenue C(x) = R(x) A company breaks even when the profit is zero P(x) = R(x) C(x) = 0 2 R x 565x C x 6000
Linear Algebra I Lecture 8
 Linear Algebra I Lecture 8 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta January 25, 2019 Outline 1 2 Gauss-Jordan Elimination Given a system of linear equations f 1 (x 1, x 2,..., x n ) = 0 f 2 (x 1, x 2,..., x n
Linear Algebra I Lecture 8 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta January 25, 2019 Outline 1 2 Gauss-Jordan Elimination Given a system of linear equations f 1 (x 1, x 2,..., x n ) = 0 f 2 (x 1, x 2,..., x n
7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix
 7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Verify that two matrices are inverses of each other. Use Gauss-Jordan elimination to find inverses
7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Verify that two matrices are inverses of each other. Use Gauss-Jordan elimination to find inverses
If A is a 4 6 matrix and B is a 6 3 matrix then the dimension of AB is A. 4 6 B. 6 6 C. 4 3 D. 3 4 E. Undefined
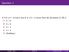 Question 1 If A is a 4 6 matrix and B is a 6 3 matrix then the dimension of AB is A. 4 6 B. 6 6 C. 4 3 D. 3 4 E. Undefined Quang T. Bach Math 18 October 18, 2017 1 / 17 Question 2 1 2 Let A = 3 4 1 2 3
Question 1 If A is a 4 6 matrix and B is a 6 3 matrix then the dimension of AB is A. 4 6 B. 6 6 C. 4 3 D. 3 4 E. Undefined Quang T. Bach Math 18 October 18, 2017 1 / 17 Question 2 1 2 Let A = 3 4 1 2 3
EXAM. Exam #1. Math 2360, Second Summer Session, April 24, 2001 ANSWERS
 i i EXAM Exam #1 Math 2360, Second Summer Session, 2002 April 24, 2001 ANSWERS i 50 pts. Problem 1. In each part you are given the augmented matrix of a system of linear equations, with the coefficent
i i EXAM Exam #1 Math 2360, Second Summer Session, 2002 April 24, 2001 ANSWERS i 50 pts. Problem 1. In each part you are given the augmented matrix of a system of linear equations, with the coefficent
Systems of Linear Equations
 Systems of Linear Equations Linear Equation Definition Any equation that is equivalent to the following format a a ann b (.) where,,, n are unknown variables and a, a,, an, b are known numbers (the so
Systems of Linear Equations Linear Equation Definition Any equation that is equivalent to the following format a a ann b (.) where,,, n are unknown variables and a, a,, an, b are known numbers (the so
Section 1.1 System of Linear Equations. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 211: Linear Algebra
 Section 1.1 System of Linear Equations College of Science MATHS 211: Linear Algebra (University of Bahrain) Linear System 1 / 33 Goals:. 1 Define system of linear equations and their solutions. 2 To represent
Section 1.1 System of Linear Equations College of Science MATHS 211: Linear Algebra (University of Bahrain) Linear System 1 / 33 Goals:. 1 Define system of linear equations and their solutions. 2 To represent
Matrices and Determinants
 Math Assignment Eperts is a leading provider of online Math help. Our eperts have prepared sample assignments to demonstrate the quality of solution we provide. If you are looking for mathematics help
Math Assignment Eperts is a leading provider of online Math help. Our eperts have prepared sample assignments to demonstrate the quality of solution we provide. If you are looking for mathematics help
Lecture 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices, Continued
 Lecture 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices, Continued Math 19620 Outline of Lecture Algorithm for putting a matrix in row reduced echelon form - i.e. Gauss-Jordan Elimination Number of Solutions
Lecture 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices, Continued Math 19620 Outline of Lecture Algorithm for putting a matrix in row reduced echelon form - i.e. Gauss-Jordan Elimination Number of Solutions
1 - Systems of Linear Equations
 1 - Systems of Linear Equations 1.1 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations Almost every problem in linear algebra will involve solving a system of equations. ü LINEAR EQUATIONS IN n VARIABLES We are
1 - Systems of Linear Equations 1.1 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations Almost every problem in linear algebra will involve solving a system of equations. ü LINEAR EQUATIONS IN n VARIABLES We are
Lecture 6 & 7. Shuanglin Shao. September 16th and 18th, 2013
 Lecture 6 & 7 Shuanglin Shao September 16th and 18th, 2013 1 Elementary matrices 2 Equivalence Theorem 3 A method of inverting matrices Def An n n matrice is called an elementary matrix if it can be obtained
Lecture 6 & 7 Shuanglin Shao September 16th and 18th, 2013 1 Elementary matrices 2 Equivalence Theorem 3 A method of inverting matrices Def An n n matrice is called an elementary matrix if it can be obtained
Recall, we solved the system below in a previous section. Here, we learn another method. x + 4y = 14 5x + 3y = 2
 We will learn how to use a matrix to solve a system of equations. College algebra Class notes Matrices and Systems of Equations (section 6.) Recall, we solved the system below in a previous section. Here,
We will learn how to use a matrix to solve a system of equations. College algebra Class notes Matrices and Systems of Equations (section 6.) Recall, we solved the system below in a previous section. Here,
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Using Matrices
 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Using Matrices What is a Matrix? A matrix is a compact grid or array of numbers. It can be created from a system of equations and used to solve the system of equations.
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Using Matrices What is a Matrix? A matrix is a compact grid or array of numbers. It can be created from a system of equations and used to solve the system of equations.
Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations
 What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
Solutions to Exam I MATH 304, section 6
 Solutions to Exam I MATH 304, section 6 YOU MUST SHOW ALL WORK TO GET CREDIT. Problem 1. Let A = 1 2 5 6 1 2 5 6 3 2 0 0 1 3 1 1 2 0 1 3, B =, C =, I = I 0 0 0 1 1 3 4 = 4 4 identity matrix. 3 1 2 6 0
Solutions to Exam I MATH 304, section 6 YOU MUST SHOW ALL WORK TO GET CREDIT. Problem 1. Let A = 1 2 5 6 1 2 5 6 3 2 0 0 1 3 1 1 2 0 1 3, B =, C =, I = I 0 0 0 1 1 3 4 = 4 4 identity matrix. 3 1 2 6 0
Methods for Solving Linear Systems Part 2
 Methods for Solving Linear Systems Part 2 We have studied the properties of matrices and found out that there are more ways that we can solve Linear Systems. In Section 7.3, we learned that we can use
Methods for Solving Linear Systems Part 2 We have studied the properties of matrices and found out that there are more ways that we can solve Linear Systems. In Section 7.3, we learned that we can use
Matrices. A matrix is a method of writing a set of numbers using rows and columns. Cells in a matrix can be referenced in the form.
 Matrices A matrix is a method of writing a set of numbers using rows and columns. 1 2 3 4 3 2 1 5 7 2 5 4 2 0 5 10 12 8 4 9 25 30 1 1 Reading Information from a Matrix Cells in a matrix can be referenced
Matrices A matrix is a method of writing a set of numbers using rows and columns. 1 2 3 4 3 2 1 5 7 2 5 4 2 0 5 10 12 8 4 9 25 30 1 1 Reading Information from a Matrix Cells in a matrix can be referenced
Pre-Calculus I. For example, the system. x y 2 z. may be represented by the augmented matrix
 Pre-Calculus I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Pre-Calculus I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
MIDTERM 1 - SOLUTIONS
 MIDTERM - SOLUTIONS MATH 254 - SUMMER 2002 - KUNIYUKI CHAPTERS, 2, GRADED OUT OF 75 POINTS 2 50 POINTS TOTAL ) Use either Gaussian elimination with back-substitution or Gauss-Jordan elimination to solve
MIDTERM - SOLUTIONS MATH 254 - SUMMER 2002 - KUNIYUKI CHAPTERS, 2, GRADED OUT OF 75 POINTS 2 50 POINTS TOTAL ) Use either Gaussian elimination with back-substitution or Gauss-Jordan elimination to solve
Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination
 Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination DEFINITION: A linear equation in the variables x 1,..., x n is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 +...+a n x n = b, where a 1,...,a n
Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination DEFINITION: A linear equation in the variables x 1,..., x n is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 +...+a n x n = b, where a 1,...,a n
Problem Sheet 1 with Solutions GRA 6035 Mathematics
 Problem Sheet 1 with Solutions GRA 6035 Mathematics BI Norwegian Business School 2 Problems 1. From linear system to augmented matrix Write down the coefficient matrix and the augmented matrix of the following
Problem Sheet 1 with Solutions GRA 6035 Mathematics BI Norwegian Business School 2 Problems 1. From linear system to augmented matrix Write down the coefficient matrix and the augmented matrix of the following
Section 6.3. Matrices and Systems of Equations
 Section 6.3 Matrices and Systems of Equations Introduction Definitions A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. Definitions A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. For example: [ 4 7 π 3 2 5 Definitions
Section 6.3 Matrices and Systems of Equations Introduction Definitions A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. Definitions A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. For example: [ 4 7 π 3 2 5 Definitions
Finite Mathematics Chapter 2. where a, b, c, d, h, and k are real numbers and neither a and b nor c and d are both zero.
 Finite Mathematics Chapter 2 Section 2.1 Systems of Linear Equations: An Introduction Systems of Equations Recall that a system of two linear equations in two variables may be written in the general form
Finite Mathematics Chapter 2 Section 2.1 Systems of Linear Equations: An Introduction Systems of Equations Recall that a system of two linear equations in two variables may be written in the general form
1. (7pts) Find the points of intersection, if any, of the following planes. 3x + 9y + 6z = 3 2x 6y 4z = 2 x + 3y + 2z = 1
 Math 125 Exam 1 Version 1 February 20, 2006 1. (a) (7pts) Find the points of intersection, if any, of the following planes. Solution: augmented R 1 R 3 3x + 9y + 6z = 3 2x 6y 4z = 2 x + 3y + 2z = 1 3 9
Math 125 Exam 1 Version 1 February 20, 2006 1. (a) (7pts) Find the points of intersection, if any, of the following planes. Solution: augmented R 1 R 3 3x + 9y + 6z = 3 2x 6y 4z = 2 x + 3y + 2z = 1 3 9
MODEL ANSWERS TO THE THIRD HOMEWORK
 MODEL ANSWERS TO THE THIRD HOMEWORK 1 (i) We apply Gaussian elimination to A First note that the second row is a multiple of the first row So we need to swap the second and third rows 1 3 2 1 2 6 5 7 3
MODEL ANSWERS TO THE THIRD HOMEWORK 1 (i) We apply Gaussian elimination to A First note that the second row is a multiple of the first row So we need to swap the second and third rows 1 3 2 1 2 6 5 7 3
Systems of Linear Equations. By: Tri Atmojo Kusmayadi and Mardiyana Mathematics Education Sebelas Maret University
 Systems of Linear Equations By: Tri Atmojo Kusmayadi and Mardiyana Mathematics Education Sebelas Maret University Standard of Competency: Understanding the properties of systems of linear equations, matrices,
Systems of Linear Equations By: Tri Atmojo Kusmayadi and Mardiyana Mathematics Education Sebelas Maret University Standard of Competency: Understanding the properties of systems of linear equations, matrices,
1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry
 1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry R. Craigen Office: MH 523 Email: craigenr@umanitoba.ca May-June 2017 Introduction: linear equations Read 1.1 (in the text that is!) Go to course, class webpages.
1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry R. Craigen Office: MH 523 Email: craigenr@umanitoba.ca May-June 2017 Introduction: linear equations Read 1.1 (in the text that is!) Go to course, class webpages.
Linear Algebra 1 Exam 1 Solutions 6/12/3
 Linear Algebra 1 Exam 1 Solutions 6/12/3 Question 1 Consider the linear system in the variables (x, y, z, t, u), given by the following matrix, in echelon form: 1 2 1 3 1 2 0 1 1 3 1 4 0 0 0 1 2 3 Reduce
Linear Algebra 1 Exam 1 Solutions 6/12/3 Question 1 Consider the linear system in the variables (x, y, z, t, u), given by the following matrix, in echelon form: 1 2 1 3 1 2 0 1 1 3 1 4 0 0 0 1 2 3 Reduce
Chapter Practice Test Name: Period: Date:
 Name: Period: Date: 1. Draw the graph of the following system: 3 x+ 5 y+ 13 = 0 29 x 11 y 7 = 0 3 13 y = x 3x+ 5y+ 13= 0 5 5 29x 11y 7 = 0 29 7 y = x 11 11 Practice Test Page 1 2. Determine the ordered
Name: Period: Date: 1. Draw the graph of the following system: 3 x+ 5 y+ 13 = 0 29 x 11 y 7 = 0 3 13 y = x 3x+ 5y+ 13= 0 5 5 29x 11y 7 = 0 29 7 y = x 11 11 Practice Test Page 1 2. Determine the ordered
6-1 Study Guide and Intervention Multivariable Linear Systems and Row Operations
 6-1 Study Guide and Intervention Multivariable Linear Systems and Row Operations Gaussian Elimination You can solve a system of linear equations using matrices. Solving a system by transforming it into
6-1 Study Guide and Intervention Multivariable Linear Systems and Row Operations Gaussian Elimination You can solve a system of linear equations using matrices. Solving a system by transforming it into
Linear Algebra I Lecture 10
 Linear Algebra I Lecture 10 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta January 30, 2019 Outline 1 Gauss-Jordan Algorithm ] Let A = [a ij m n be an m n matrix. To reduce A to a reduced row echelon form using elementary
Linear Algebra I Lecture 10 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta January 30, 2019 Outline 1 Gauss-Jordan Algorithm ] Let A = [a ij m n be an m n matrix. To reduce A to a reduced row echelon form using elementary
Chapter 1. Vectors, Matrices, and Linear Spaces
 1.4 Solving Systems of Linear Equations 1 Chapter 1. Vectors, Matrices, and Linear Spaces 1.4. Solving Systems of Linear Equations Note. We give an algorithm for solving a system of linear equations (called
1.4 Solving Systems of Linear Equations 1 Chapter 1. Vectors, Matrices, and Linear Spaces 1.4. Solving Systems of Linear Equations Note. We give an algorithm for solving a system of linear equations (called
Name: Section Registered In:
 Name: Section Registered In: Math 125 Exam 1 Version 1 February 21, 2006 60 points possible 1. (a) (3pts) Define what it means for a linear system to be inconsistent. Solution: A linear system is inconsistent
Name: Section Registered In: Math 125 Exam 1 Version 1 February 21, 2006 60 points possible 1. (a) (3pts) Define what it means for a linear system to be inconsistent. Solution: A linear system is inconsistent
March 19 - Solving Linear Systems
 March 19 - Solving Linear Systems Welcome to linear algebra! Linear algebra is the study of vectors, vector spaces, and maps between vector spaces. It has applications across data analysis, computer graphics,
March 19 - Solving Linear Systems Welcome to linear algebra! Linear algebra is the study of vectors, vector spaces, and maps between vector spaces. It has applications across data analysis, computer graphics,
FINAL (CHAPTERS 7-10) MATH 141 FALL 2018 KUNIYUKI 250 POINTS TOTAL
 Math 141 Name: FINAL (CHAPTERS 7-10) MATH 141 FALL 2018 KUNIYUKI 250 POINTS TOTAL Show all work, simplify as appropriate, and use good form and procedure (as in class). Box in your final answers! No notes
Math 141 Name: FINAL (CHAPTERS 7-10) MATH 141 FALL 2018 KUNIYUKI 250 POINTS TOTAL Show all work, simplify as appropriate, and use good form and procedure (as in class). Box in your final answers! No notes
Section Gaussian Elimination
 Section. - Gaussian Elimination A matrix is said to be in row echelon form (REF) if it has the following properties:. The first nonzero entry in any row is a. We call this a leading one or pivot one..
Section. - Gaussian Elimination A matrix is said to be in row echelon form (REF) if it has the following properties:. The first nonzero entry in any row is a. We call this a leading one or pivot one..
CHAPTER 9: Systems of Equations and Matrices
 MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 9: Systems of Equations and Matrices 9.1 Systems of Equations in Two Variables 9.2 Systems of Equations in Three Variables
MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 9: Systems of Equations and Matrices 9.1 Systems of Equations in Two Variables 9.2 Systems of Equations in Three Variables
Row Reduced Echelon Form
 Math 40 Row Reduced Echelon Form Solving systems of linear equations lies at the heart of linear algebra. In high school we learn to solve systems in or variables using elimination and substitution of
Math 40 Row Reduced Echelon Form Solving systems of linear equations lies at the heart of linear algebra. In high school we learn to solve systems in or variables using elimination and substitution of
Chapter 2. Systems of Equations and Augmented Matrices. Creighton University
 Chapter Section - Systems of Equations and Augmented Matrices D.S. Malik Creighton University Systems of Linear Equations Common ways to solve a system of equations: Eliminationi Substitution Elimination
Chapter Section - Systems of Equations and Augmented Matrices D.S. Malik Creighton University Systems of Linear Equations Common ways to solve a system of equations: Eliminationi Substitution Elimination
3. Replace any row by the sum of that row and a constant multiple of any other row.
 Section. Solution of Linear Systems by Gauss-Jordan Method A matrix is an ordered rectangular array of numbers, letters, symbols or algebraic expressions. A matrix with m rows and n columns has size or
Section. Solution of Linear Systems by Gauss-Jordan Method A matrix is an ordered rectangular array of numbers, letters, symbols or algebraic expressions. A matrix with m rows and n columns has size or
Lecture 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices
 Lecture 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Math 19620 Outline of Course Linear Equations and Matrices Linear Transformations, Inverses Bases, Linear Independence, Subspaces Abstract Vector Spaces
Lecture 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Math 19620 Outline of Course Linear Equations and Matrices Linear Transformations, Inverses Bases, Linear Independence, Subspaces Abstract Vector Spaces
7.5 Operations with Matrices. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 7.5 Operations with Matrices Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Decide whether two matrices are equal. Add and subtract matrices and multiply matrices by scalars. Multiply
7.5 Operations with Matrices Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Decide whether two matrices are equal. Add and subtract matrices and multiply matrices by scalars. Multiply
1111: Linear Algebra I
 1111: Linear Algebra I Dr. Vladimir Dotsenko (Vlad) Michaelmas Term 2015 Dr. Vladimir Dotsenko (Vlad) 1111: Linear Algebra I Michaelmas Term 2015 1 / 15 From equations to matrices For example, if we consider
1111: Linear Algebra I Dr. Vladimir Dotsenko (Vlad) Michaelmas Term 2015 Dr. Vladimir Dotsenko (Vlad) 1111: Linear Algebra I Michaelmas Term 2015 1 / 15 From equations to matrices For example, if we consider
The matrix will only be consistent if the last entry of row three is 0, meaning 2b 3 + b 2 b 1 = 0.
 ) Find all solutions of the linear system. Express the answer in vector form. x + 2x + x + x 5 = 2 2x 2 + 2x + 2x + x 5 = 8 x + 2x + x + 9x 5 = 2 2 Solution: Reduce the augmented matrix [ 2 2 2 8 ] to
) Find all solutions of the linear system. Express the answer in vector form. x + 2x + x + x 5 = 2 2x 2 + 2x + 2x + x 5 = 8 x + 2x + x + 9x 5 = 2 2 Solution: Reduce the augmented matrix [ 2 2 2 8 ] to
is Use at most six elementary row operations. (Partial
 MATH 235 SPRING 2 EXAM SOLUTIONS () (6 points) a) Show that the reduced row echelon form of the augmented matrix of the system x + + 2x 4 + x 5 = 3 x x 3 + x 4 + x 5 = 2 2x + 2x 3 2x 4 x 5 = 3 is. Use
MATH 235 SPRING 2 EXAM SOLUTIONS () (6 points) a) Show that the reduced row echelon form of the augmented matrix of the system x + + 2x 4 + x 5 = 3 x x 3 + x 4 + x 5 = 2 2x + 2x 3 2x 4 x 5 = 3 is. Use
6-2 Matrix Multiplication, Inverses and Determinants
 Find AB and BA, if possible. 1. A = A = ; A is a 1 2 matrix and B is a 2 2 matrix. Because the number of columns of A is equal to the number of rows of B, AB exists. To find the first entry of AB, find
Find AB and BA, if possible. 1. A = A = ; A is a 1 2 matrix and B is a 2 2 matrix. Because the number of columns of A is equal to the number of rows of B, AB exists. To find the first entry of AB, find
Matrix Solutions to Linear Equations
 Matrix Solutions to Linear Equations Augmented matrices can be used as a simplified way of writing a system of linear equations. In an augmented matrix, a vertical line is placed inside the matrix to represent
Matrix Solutions to Linear Equations Augmented matrices can be used as a simplified way of writing a system of linear equations. In an augmented matrix, a vertical line is placed inside the matrix to represent
Notes on Row Reduction
 Notes on Row Reduction Francis J. Narcowich Department of Mathematics Texas A&M University September The Row-Reduction Algorithm The row-reduced form of a matrix contains a great deal of information, both
Notes on Row Reduction Francis J. Narcowich Department of Mathematics Texas A&M University September The Row-Reduction Algorithm The row-reduced form of a matrix contains a great deal of information, both
1111: Linear Algebra I
 1111: Linear Algebra I Dr. Vladimir Dotsenko (Vlad) Lecture 6 Dr. Vladimir Dotsenko (Vlad) 1111: Linear Algebra I Lecture 6 1 / 14 Gauss Jordan elimination Last time we discussed bringing matrices to reduced
1111: Linear Algebra I Dr. Vladimir Dotsenko (Vlad) Lecture 6 Dr. Vladimir Dotsenko (Vlad) 1111: Linear Algebra I Lecture 6 1 / 14 Gauss Jordan elimination Last time we discussed bringing matrices to reduced
Math 301 Test I. M. Randall Holmes. September 8, 2008
 Math 0 Test I M. Randall Holmes September 8, 008 This exam will begin at 9:40 am and end at 0:5 am. You may use your writing instrument, a calculator, and your test paper; books, notes and neighbors to
Math 0 Test I M. Randall Holmes September 8, 008 This exam will begin at 9:40 am and end at 0:5 am. You may use your writing instrument, a calculator, and your test paper; books, notes and neighbors to
Math 2331 Linear Algebra
 1.1 Linear System Math 2331 Linear Algebra 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations Shang-Huan Chiu Department of Mathematics, University of Houston schiu@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ schiu/ Shang-Huan Chiu, University
1.1 Linear System Math 2331 Linear Algebra 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations Shang-Huan Chiu Department of Mathematics, University of Houston schiu@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ schiu/ Shang-Huan Chiu, University
Math "Matrix Approach to Solving Systems" Bibiana Lopez. November Crafton Hills College. (CHC) 6.3 November / 25
 Math 102 6.3 "Matrix Approach to Solving Systems" Bibiana Lopez Crafton Hills College November 2010 (CHC) 6.3 November 2010 1 / 25 Objectives: * Define a matrix and determine its order. * Write the augmented
Math 102 6.3 "Matrix Approach to Solving Systems" Bibiana Lopez Crafton Hills College November 2010 (CHC) 6.3 November 2010 1 / 25 Objectives: * Define a matrix and determine its order. * Write the augmented
4.3 Row operations. As we have seen in Section 4.1 we can simplify a system of equations by either:
 4.3 Row operations As we have seen in Section 4.1 we can simplify a system of equations by either: 1. Swapping the order of the equations around. For example: can become 3x 1 + 7x 2 = 9 x 1 2x 1 = 2 x
4.3 Row operations As we have seen in Section 4.1 we can simplify a system of equations by either: 1. Swapping the order of the equations around. For example: can become 3x 1 + 7x 2 = 9 x 1 2x 1 = 2 x
Midterm 1 Review. Written by Victoria Kala SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015
 Midterm 1 Review Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015 Summary This Midterm Review contains notes on sections 1.1 1.5 and 1.7 in your
Midterm 1 Review Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015 Summary This Midterm Review contains notes on sections 1.1 1.5 and 1.7 in your
MATH 115: Review for Chapter 6
 MATH 115: Review for Chapter 6 In order to prepare for our test on Chapter 6, ou need to understand and be able to work problems involving the following topics: I SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS CONTAINING
MATH 115: Review for Chapter 6 In order to prepare for our test on Chapter 6, ou need to understand and be able to work problems involving the following topics: I SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS CONTAINING
Week 1 (8/24/2004-8/30/2004) Read 2.1: Solution of linear system by the Echelon method
 Week 1 (8/24/2004-8/30/2004) Read 2.1: Solution of linear system by the Echelon method Important Terms and Concepts: Possibilities for the solutions of a system of two linear equations in two unknowns
Week 1 (8/24/2004-8/30/2004) Read 2.1: Solution of linear system by the Echelon method Important Terms and Concepts: Possibilities for the solutions of a system of two linear equations in two unknowns
Elementary Linear Algebra
 Elementary Linear Algebra Linear algebra is the study of; linear sets of equations and their transformation properties. Linear algebra allows the analysis of; rotations in space, least squares fitting,
Elementary Linear Algebra Linear algebra is the study of; linear sets of equations and their transformation properties. Linear algebra allows the analysis of; rotations in space, least squares fitting,
CHAPTER 7: Systems and Inequalities
 (Exercises for Chapter 7: Systems and Inequalities) E.7.1 CHAPTER 7: Systems and Inequalities (A) means refer to Part A, (B) means refer to Part B, etc. (Calculator) means use a calculator. Otherwise,
(Exercises for Chapter 7: Systems and Inequalities) E.7.1 CHAPTER 7: Systems and Inequalities (A) means refer to Part A, (B) means refer to Part B, etc. (Calculator) means use a calculator. Otherwise,
3 Fields, Elementary Matrices and Calculating Inverses
 3 Fields, Elementary Matrices and Calculating Inverses 3. Fields So far we have worked with matrices whose entries are real numbers (and systems of equations whose coefficients and solutions are real numbers).
3 Fields, Elementary Matrices and Calculating Inverses 3. Fields So far we have worked with matrices whose entries are real numbers (and systems of equations whose coefficients and solutions are real numbers).
4 Elementary matrices, continued
 4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. If you check the previous examples, you ll find that these matrices are constructed
4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. If you check the previous examples, you ll find that these matrices are constructed
22A-2 SUMMER 2014 LECTURE 5
 A- SUMMER 0 LECTURE 5 NATHANIEL GALLUP Agenda Elimination to the identity matrix Inverse matrices LU factorization Elimination to the identity matrix Previously, we have used elimination to get a system
A- SUMMER 0 LECTURE 5 NATHANIEL GALLUP Agenda Elimination to the identity matrix Inverse matrices LU factorization Elimination to the identity matrix Previously, we have used elimination to get a system
is a 3 4 matrix. It has 3 rows and 4 columns. The first row is the horizontal row [ ]
![is a 3 4 matrix. It has 3 rows and 4 columns. The first row is the horizontal row [ ] is a 3 4 matrix. It has 3 rows and 4 columns. The first row is the horizontal row [ ]](/thumbs/82/86615780.jpg) Matrices: Definition: An m n matrix, A m n is a rectangular array of numbers with m rows and n columns: a, a, a,n a, a, a,n A m,n =...... a m, a m, a m,n Each a i,j is the entry at the i th row, j th column.
Matrices: Definition: An m n matrix, A m n is a rectangular array of numbers with m rows and n columns: a, a, a,n a, a, a,n A m,n =...... a m, a m, a m,n Each a i,j is the entry at the i th row, j th column.
CHAPTER 9: Systems of Equations and Matrices
 MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 9: Systems of Equations and Matrices 9.1 Systems of Equations in Two Variables 9.2 Systems of Equations in Three Variables
MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 9: Systems of Equations and Matrices 9.1 Systems of Equations in Two Variables 9.2 Systems of Equations in Three Variables
Relationships Between Planes
 Relationships Between Planes Definition: consistent (system of equations) A system of equations is consistent if there exists one (or more than one) solution that satisfies the system. System 1: {, System
Relationships Between Planes Definition: consistent (system of equations) A system of equations is consistent if there exists one (or more than one) solution that satisfies the system. System 1: {, System
Elementary matrices, continued. To summarize, we have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding
 Elementary matrices, continued To summarize, we have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. If you check the previous examples, you ll find that these matrices
Elementary matrices, continued To summarize, we have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. If you check the previous examples, you ll find that these matrices
Miller Objectives Alignment Math
 Miller Objectives Alignment Math 1050 1 College Algebra Course Objectives Spring Semester 2016 1. Use algebraic methods to solve a variety of problems involving exponential, logarithmic, polynomial, and
Miller Objectives Alignment Math 1050 1 College Algebra Course Objectives Spring Semester 2016 1. Use algebraic methods to solve a variety of problems involving exponential, logarithmic, polynomial, and
Name: MATH 3195 :: Fall 2011 :: Exam 2. No document, no calculator, 1h00. Explanations and justifications are expected for full credit.
 Name: MATH 3195 :: Fall 2011 :: Exam 2 No document, no calculator, 1h00. Explanations and justifications are expected for full credit. 1. ( 4 pts) Say which matrix is in row echelon form and which is not.
Name: MATH 3195 :: Fall 2011 :: Exam 2 No document, no calculator, 1h00. Explanations and justifications are expected for full credit. 1. ( 4 pts) Say which matrix is in row echelon form and which is not.
A. Incorrect! Replacing is not a method for solving systems of equations.
 ACT Math and Science - Problem Drill 20: Systems of Equations No. 1 of 10 1. What methods were presented to solve systems of equations? (A) Graphing, replacing, and substitution. (B) Solving, replacing,
ACT Math and Science - Problem Drill 20: Systems of Equations No. 1 of 10 1. What methods were presented to solve systems of equations? (A) Graphing, replacing, and substitution. (B) Solving, replacing,
4 Elementary matrices, continued
 4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. To repeat the recipe: These matrices are constructed by performing the given row
4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. To repeat the recipe: These matrices are constructed by performing the given row
MAC1105-College Algebra. Chapter 5-Systems of Equations & Matrices
 MAC05-College Algebra Chapter 5-Systems of Equations & Matrices 5. Systems of Equations in Two Variables Solving Systems of Two Linear Equations/ Two-Variable Linear Equations A system of equations is
MAC05-College Algebra Chapter 5-Systems of Equations & Matrices 5. Systems of Equations in Two Variables Solving Systems of Two Linear Equations/ Two-Variable Linear Equations A system of equations is
CHAPTER 8: Matrices and Determinants
 (Exercises for Chapter 8: Matrices and Determinants) E.8.1 CHAPTER 8: Matrices and Determinants (A) means refer to Part A, (B) means refer to Part B, etc. Most of these exercises can be done without a
(Exercises for Chapter 8: Matrices and Determinants) E.8.1 CHAPTER 8: Matrices and Determinants (A) means refer to Part A, (B) means refer to Part B, etc. Most of these exercises can be done without a
Math 313 Chapter 1 Review
 Math 313 Chapter 1 Review Howard Anton, 9th Edition May 2010 Do NOT write on me! Contents 1 1.1 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations 2 2 1.2 Gaussian Elimination 3 3 1.3 Matrices and Matrix Operations
Math 313 Chapter 1 Review Howard Anton, 9th Edition May 2010 Do NOT write on me! Contents 1 1.1 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations 2 2 1.2 Gaussian Elimination 3 3 1.3 Matrices and Matrix Operations
DM559 Linear and Integer Programming. Lecture 2 Systems of Linear Equations. Marco Chiarandini
 DM559 Linear and Integer Programming Lecture Marco Chiarandini Department of Mathematics & Computer Science University of Southern Denmark Outline 1. Outline 1. 3 A Motivating Example You are organizing
DM559 Linear and Integer Programming Lecture Marco Chiarandini Department of Mathematics & Computer Science University of Southern Denmark Outline 1. Outline 1. 3 A Motivating Example You are organizing
Chapter 4. Solving Systems of Equations. Chapter 4
 Solving Systems of Equations 3 Scenarios for Solutions There are three general situations we may find ourselves in when attempting to solve systems of equations: 1 The system could have one unique solution.
Solving Systems of Equations 3 Scenarios for Solutions There are three general situations we may find ourselves in when attempting to solve systems of equations: 1 The system could have one unique solution.
MATH 54 - WORKSHEET 1 MONDAY 6/22
 MATH 54 - WORKSHEET 1 MONDAY 6/22 Row Operations: (1 (Replacement Add a multiple of one row to another row. (2 (Interchange Swap two rows. (3 (Scaling Multiply an entire row by a nonzero constant. A matrix
MATH 54 - WORKSHEET 1 MONDAY 6/22 Row Operations: (1 (Replacement Add a multiple of one row to another row. (2 (Interchange Swap two rows. (3 (Scaling Multiply an entire row by a nonzero constant. A matrix
Intermediate Algebra
 Intermediate Algebra George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 102 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Intermediate Algebra August 2013 1 / 33 Outline 1 Systems
Intermediate Algebra George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 102 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Intermediate Algebra August 2013 1 / 33 Outline 1 Systems
Perform the same three operations as above on the values in the matrix, where some notation is given as a shorthand way to describe each operation:
 SECTION 2.1: SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS WITH A UNIQUE SOLUTION In Chapter 1 we took a look at finding the intersection point of two lines on a graph. Chapter 2 begins with a look at a more formal approach
SECTION 2.1: SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS WITH A UNIQUE SOLUTION In Chapter 1 we took a look at finding the intersection point of two lines on a graph. Chapter 2 begins with a look at a more formal approach
Math Studio College Algebra
 Math 100 - Studio College Algebra Rekha Natarajan Kansas State University November 19, 2014 Systems of Equations Systems of Equations A system of equations consists of Systems of Equations A system of
Math 100 - Studio College Algebra Rekha Natarajan Kansas State University November 19, 2014 Systems of Equations Systems of Equations A system of equations consists of Systems of Equations A system of
ANSWERS. Answer: Perform combo(3,2,-1) on I then combo(1,3,-4) on the result. The elimination matrix is
 MATH 227-2 Sample Exam 1 Spring 216 ANSWERS 1. (1 points) (a) Give a counter example or explain why it is true. If A and B are n n invertible, and C T denotes the transpose of a matrix C, then (AB 1 )
MATH 227-2 Sample Exam 1 Spring 216 ANSWERS 1. (1 points) (a) Give a counter example or explain why it is true. If A and B are n n invertible, and C T denotes the transpose of a matrix C, then (AB 1 )
Lecture 4: Gaussian Elimination and Homogeneous Equations
 Lecture 4: Gaussian Elimination and Homogeneous Equations Reduced Row Echelon Form An augmented matrix associated to a system of linear equations is said to be in Reduced Row Echelon Form (RREF) if the
Lecture 4: Gaussian Elimination and Homogeneous Equations Reduced Row Echelon Form An augmented matrix associated to a system of linear equations is said to be in Reduced Row Echelon Form (RREF) if the
System of Linear Equations
 Chapter 7 - S&B Gaussian and Gauss-Jordan Elimination We will study systems of linear equations by describing techniques for solving such systems. The preferred solution technique- Gaussian elimination-
Chapter 7 - S&B Gaussian and Gauss-Jordan Elimination We will study systems of linear equations by describing techniques for solving such systems. The preferred solution technique- Gaussian elimination-
Section 12.4 Algebra of Matrices
 244 Section 2.4 Algebra of Matrices Before we can discuss Matrix Algebra, we need to have a clear idea what it means to say that two matrices are equal. Let's start a definition. Equal Matrices Two matrices
244 Section 2.4 Algebra of Matrices Before we can discuss Matrix Algebra, we need to have a clear idea what it means to say that two matrices are equal. Let's start a definition. Equal Matrices Two matrices
Lecture 12: Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Gaussian Elimination
 Lecture 12: Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Gaussian Elimination Winfried Just, Ohio University September 22, 2017 Review: The coefficient matrix Consider a system of m linear equations in n variables.
Lecture 12: Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Gaussian Elimination Winfried Just, Ohio University September 22, 2017 Review: The coefficient matrix Consider a system of m linear equations in n variables.
Chapter 1 Linear Equations. 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations
 Chapter Linear Equations. Systems of Linear Equations A linear equation in the n variables x, x 2,..., x n is one that can be expressed in the form a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a, a 2,..., a n and
Chapter Linear Equations. Systems of Linear Equations A linear equation in the n variables x, x 2,..., x n is one that can be expressed in the form a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a, a 2,..., a n and
Finite Mathematics. Linear Equations (Chapter 4) Optimization (Chapter 5) Finite Probability (Chapter 6) Markov Chains (Chapter 9) Finite Mathematics
 Finite Mathematics Linear Equations (Chapter ) Optimization (Chapter ) Finite Probability (Chapter 6) Markov Chains (Chapter 9) Finite Mathematics Linear Algebra Probability Linear Equations Simple Method
Finite Mathematics Linear Equations (Chapter ) Optimization (Chapter ) Finite Probability (Chapter 6) Markov Chains (Chapter 9) Finite Mathematics Linear Algebra Probability Linear Equations Simple Method
Solutions of Linear system, vector and matrix equation
 Goals: Solutions of Linear system, vector and matrix equation Solutions of linear system. Vectors, vector equation. Matrix equation. Math 112, Week 2 Suggested Textbook Readings: Sections 1.3, 1.4, 1.5
Goals: Solutions of Linear system, vector and matrix equation Solutions of linear system. Vectors, vector equation. Matrix equation. Math 112, Week 2 Suggested Textbook Readings: Sections 1.3, 1.4, 1.5
