A World of Color. Session 2. OLLI at Illinois Spring D. H. Tracy
|
|
|
- Wilfrid Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A World of Color Session 2 OLLI at Illinois Spring 2018 D. H. Tracy
2 Course Outline 1. Overview, History and Spectra 2. Nature and Sources of Light 3. Eyes and Color Vision 4. Origins of Colors of Things 5. Propagation and Modification of Light 6. Visual Perception: Neurons and the Brain 7. Color Recording and Reproduction, Media 8. Color in Arts and Culture, Emotive Aspects 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 2
3 Session 2 Outline Photons How Light is Produced Light Sources Hot bodies Electric Discharges Electroluminescence Photon Impact (Fluorescence) Particle Impact Chemical 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 3
4 EM Waves Wavelength λ Institute of Sound and Vibration Research, U. of Southampton, UK 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 4
5 The Broad ElectroMagnetic Spectrum 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 5
6 Hot Things Glow 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 6
7 The Solar Spectrum in Detail O 3 Yellow areas lost on the way down 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 7
8 Triumph of 19 th Century Physics Lord Kelvin, 1900 There is nothing new to be discovered in physics now. All that remains is more and more precise measurement. 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 8
9 Ultraviolet Catastrophe Solar Spectrum 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 9
10 Ultraviolet Catastrophe Huge Discrepancy between Measurements and 19 th Century Theory 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 10
11 Solution was Quantum Theory Quantum Theory Max Planck Albert Einstein /1/2018 World of Color 2 11
12 The answer was. Duality: Part Wave Part Particle 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 12
13 Wave Picture is Fine for Optical Instruments But For Creating Light we need the Photon Picture Likewise Detection of light needs Photon Model 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 13
14 Color Perception Train Source Brain Optic Nerve Object Medium Eye 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 14
15 Color Perception Train: Sources Source Brain Optic Nerve Object Medium Eye 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 15
16 Logically, if Light is an EM Wave We should wave some electric charges up and down to generate light at the right (high) frequency of course Wavelength λ Institute of Sound and Vibration Research, U. of Southampton, UK 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 16
17 That s how radio transmitters work AM Radio Station 650 khz Cell Phone Radio Transmitter MHz Antenna Radio Frequency Generator Chips 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 17
18 But these wavelengths are still far too big We need 500,000 x shorter λ Electronics are not remotely capable of this frequency* * with one exception to be mentioned We need a different way to generate visible light one by one as photons 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 18
19 *Exception: Synchrotron Radiation Electrons whirling around at 99.9% of the speed of light sling off photons of all frequencies up to x-rays RIKEN Storage Ring, Japan 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 19
20 We ll Generate Photons via Electronic Transitions in Matter Atoms Molecules Solids Plasmas 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 20
21 Example: Hydrogen, the simplest case Photon Emission Balmer Lines Photon Absorption 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 21
22 How do we get electrons excited? Heat (thermal) Electric discharge Photon Impact (Fluorescence, Phosphorescence) Particle Impact Electroluminescence LEDs, Lasers, etc. Chemical Reactions 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 22
23 Thermal Excitation (Heat) 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 23
24 Thermally Excited Radiation 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 24
25 Thermally Excited Radiation Key concept is the Black Body An ideal Black Body: Absorbs all wavelengths of light perfectly It also emits all wavelengths according to the Plank law Temperature determines the intensity and spectrum shape Problem: How do you actually make a BB? 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 25
26 Pie in oven eventually reaches thermal equilibrium with oven 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 26
27 Cavity Black Body Glass Blowing Glory Hole Uniform Temperature T Radiation inside cavity reaches Blackbody Equilibrium Accurate Black Body Spectrum even if cavity walls are not black! Peephole 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 27
28 Plank Blackbody Spectra 8500 F (nm) 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 28
29 Emissivity: Blackness If a hot emitter is not black, reduced BlackBody emission is obtained Emissivity Factor ε measures the blackness ε = 100% means perfectly black ε = 0 means perfectly reflecting no emission Examples: Tungsten metal: ε 35-45% Silver metal: ε 3% Fire Brick: ε 75% Lamp Black ε 95% 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 29
30 Some Blackbodies (nearly) Sun 5,800 K (9,940 F) ~1500 K (2200F) cooler Black Soot Particle ~1500 K (2200F) 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 30
31 Some Blackbodies (nearly) Sun 5,800 K (9,940 F) ~1500 K (2200F) cooler Black Soot Particle ~1500 K (2200F) The blue flame is NOT Blackbody Radiation. It is Molecular Band emission, thermally excited 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 31
32 Some Blackbodies (nearly) Sun 5,800 K (9,940 F) ~1500 K Gas Burner (2200F) Similar cooler Black Soot Particle ~1500 K (2200F) The blue flame is NOT Blackbody Radiation. It is Molecular Band emission, thermally excited 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 32
33 Some Blackbodies (nearly) Sun 5,800 K (9,940 F) ~1500 K Foil Slit (2200F) View Band Spectrum at home cooler Black Soot Particle ~1500 K (2200F) The blue flame is NOT Blackbody Radiation. It is Molecular Band emission, thermally excited 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 33
34 Incandescent Lamps Tungsten Filaments ε 35-45% Efficiency ~ 2-5% 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 34
35 How do we get electrons excited? Heat (thermal) Electric discharge Photon Impact (Fluorescence, Phosphorescence) Particle Impact Electroluminescence LEDs, Lasers, etc. Chemical Reactions 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 35
36 Lightning T ~ 30,000 K 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 36
37 Xenon Arc Electric Discharge Lamps T 6-7K Xenon Arc Plasma Graybody T eff K Hotter than the Sun 15 kw IMAX Projector Lamp HID Headlamps 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 37
38 High Pressure Sodium Note dip in spectrum at 589 nm 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 38
39 High Pressure Sodium Coolish Sodium atoms near the glass envelope absorb the yellow 589 nm line. 589 nm 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 39
40 Low Pressure Electric Discharge: Mercury nm 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 40
41 Low Pressure Electric Discharge: Mercury Compact Fluorescent (CFL) Black Lights Germicidal Lamps DNA 546 nm 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 41
42 Low Pressure Electric Discharge: Neon Rare Gas Line Emission 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 42
43 Blackbody Sources Let s take a look Gas Discharge Lamp 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 43
44 How do we get electrons excited? Heat (thermal) Electric discharge Electroluminescence LEDs, Lasers, etc. Photon Impact (Fluorescence, Phosphorescence) Gentle excitation by electric currents: Particle Impact Chemical Reactions Little Heat 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 46
45 Electroluminescent Panels 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 47
46 Light Emitting Diodes First visible red LEDs 1961 (GE) First blue LEDs 1994 (Nichia) Light emitted at PN junction in certain semiconductor crystals Opposite of a Solar Cell Band Gap determines color 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 48
47 LED Materials vs. color Typical LED Peaks ~ 20 nm Wavelength (nm) 3 LED Dies on a board 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 49 from Wikipedia Light-emitting diode
48 Made as Wafers LED Features High Efficiency Long Life if not Overheated Typically 25-50% (or more) Electricity to Photons Christopher Jobson /1/2018 World of Color 2 50
49 Organic LEDs (OLEDs) Can be printed via dot-matrix techniques to make very small LEDs individual pixels in display 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 51
50 Lasers Strong Excitation Light Emitting Medium (Gas Discharge, LED, etc.) 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 52
51 Lasers Strong Excitation 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 53
52 But Photons are Bosons They come in bunches Satyendra Bose Calcutta ( ) 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 54
53 But Photons are Bosons They stick with the herd Satyendra Bose Calcutta ( ) 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 55
54 But Photons are Bosons Satyendra Bose Calcutta ( ) They follow the leader 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 56
55 Lasers Strong Excitation When this is a semiconductor diode, we basically have a Glorified LED (Diode Laser) All the Photons emerge as clones in lockstep Same direction Same wavelength Same polarization Same phase 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 57
56 Inside a Diode Laser Wikipedia Laser diode 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 58
57 Key Features of Laser Illumination Monochromatic Single Wavelength Very Bright Coherent Wave nature of light very apparent Speckle 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 59
58 Coherence isn t only a Laser problem LED Lamps can be somewhat coherent 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 60
59 Let s take a look Colored LEDs Diode Lasers 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 61
60 How do we get electrons excited? Heat (thermal) Electric discharge Electroluminescence LEDs, Lasers, etc. Photon Impact (Fluorescence, Phosphorescence) Particle Impact Chemical Reactions 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 63
61 Photon Impact: Simple Idea 1. Energetic Photon Excites target Dye molecule or Phosphor Solid 2. Target Re-Emits less Energetic Photon (redder) Re-emission can be immediate (~10 nano-seconds) or After a delay ( say > 1 milli-second up to days) Fluorescence or Scintillation Phosphorescence 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 64
62 Examples of Fluorescence Black Light (ultraviolet) Fluorescent Dye Blue and UV Sunlight Excites Whitener Dyes in clothing Result: Whiter than White 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 65
63 Examples of Fluorescence Black Light (ultraviolet) Fluorescent Dye Whitener (Blankophore BCH) Blue and UV Sunlight Excites Whitener Dyes in clothing Result: Whiter than White 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 66
64 Phosphorescence Glow-in-the-dark toys Charge up solid phosphor using bright light Decays slowly, emitting photons Decay time of minutes or hours Because very slow, not very bright Typical phosphor: Zinc Sulfide with Copper doping as activator (5 ppm) 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 67
65 Examples of Fluorescence using UV LED Flashlight Fluorescence 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 68
66 Fluorescent Lamps Scintillation in Lighting UV Photons from Mercury Discharge excite Phosphor coating on inside of glass tube White LED lamps Phosphor coating over powerful blue LED converts part of light to green and red. 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 69
67 Compact Fluorescent Lamp Spectra 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 70
68 Cerium: YAG Phosphor Typical White LED Lamp Blue LED Phosphor Blue LED Die 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 71
69 Great Flexibility in Phosphors for White LED (Animation) Fluorescence from Phosphor Mix excited by deep blue LED Blue LED yujintl.com 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 72
70 Innards of a White Light LED Bulb Power Supply (~ 2v per LED) 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 73
71 White LEDs Can Also Use RGB Mixing (3 separate colored LEDs) Advantage: Color balance can be adjusted 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 74
72 Fluorescent Lamps Let s take a look White LEDs 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 75
73 Comparing White Lamp Spectra HoveyElectric.com 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 77
74 How do we get electrons excited? Heat (thermal) Electric discharge Electroluminescence LEDs, Lasers, etc. Photon Impact (Fluorescence, Phosphorescence) Particle Impact Chemical Reactions 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 78
75 Light from Electron Impact Cathode Ray Tube 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 79
76 More Light from Electron Impact: 100 Miles Up N+ O N 2 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 80 (nm)
77 How do we get electrons excited? Heat (thermal) Electric discharge Electroluminescence LEDs, Lasers, etc. Photon Impact (Fluorescence, Phosphorescence) Particle Impact Chemical Reactions 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 81
78 Bioluminescence Biomolecule Luciferin is oxidized with the help of the enzyme Luciferase to generate light. L + O 2 Luciferase > oxy-l + Photon + junk Firefly Luciferin Protein Luciferase 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 82
79 Bioluminescence Biomolecule Luciferin is oxidized with the help of the enzyme Luciferase to generate light. L + O 2 Luciferase > oxy-l + Photon + junk Firefly Luciferin Protein Luciferase 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 83
80 Chemiluminescence (Glow Sticks etc.) Mix two chemicals: Luminol or similar in tube break glass vial of hydrogen peroxide Luminol + H 2 O 2 3-APA* 3- APA* 3-APA + Photon + Luminol H 2 O 2 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 84
81 Session 2 Outline Photons How Light is Produced Light Sources Hot bodies Electric Discharges Electroluminescence Photon Impact (Fluorescence) Particle Impact Chemical 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 85
82 Extra Content: Fraunhofer Spectra 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 86
83 The Solar Spectrum in Detail O 3 Yellow areas lost on the way down 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 87
84 Fraunhofer Lines Joseph von Fraunhofer , Bavarian Invented Spectroscope Discovered Hundreds of Absorption Lines in Solar Spectrum 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 88
85 How Fraunhofer Lines Form BlackBody ~ 5500K to Earth Relatively Cool Atoms in Atmosphere of Sun Absorb Certain Wavelengths 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 89
86 The Sun s Spectrum In Detail Echelle Spectrogram, very high resolution 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 90
87 Astronomy Determine elements present in stars 2. Measure velocities of stars or galaxies via Doppler Shift of spectra Synthetic Spectrum from a putative Galaxy far, far away 2/1/2018 World of Color 2 91
2. Discrete means unique, that other states don t overlap it. 3. Electrons in the outer electron shells have greater potential energy.
 30 Light Emission Answers and Solutions for Chapter 30 Reading Check Questions 1. At these high frequencies, ultraviolet light is emitted. 2. Discrete means unique, that other states don t overlap it.
30 Light Emission Answers and Solutions for Chapter 30 Reading Check Questions 1. At these high frequencies, ultraviolet light is emitted. 2. Discrete means unique, that other states don t overlap it.
Light Emission.
 Light Emission www.physics.sfasu.edu/friedfeld/ch29lec.ppt Radio waves are produced by electrons moving up and down an antenna. Visible light is produced by electrons changing energy states in an atom.
Light Emission www.physics.sfasu.edu/friedfeld/ch29lec.ppt Radio waves are produced by electrons moving up and down an antenna. Visible light is produced by electrons changing energy states in an atom.
OPAC 101 Introduction to Optics
 OPAC 101 Introduction to Optics Topic 2 Light Sources Department of http://www1.gantep.edu.tr/~bingul/opac101 Optical & Acustical Engineering Gaziantep University Sep 2017 Sayfa 1 Light Sources: maybe
OPAC 101 Introduction to Optics Topic 2 Light Sources Department of http://www1.gantep.edu.tr/~bingul/opac101 Optical & Acustical Engineering Gaziantep University Sep 2017 Sayfa 1 Light Sources: maybe
Light Emission. Today s Topics. Excitation/De-Excitation 10/26/2008. Excitation Emission Spectra Incandescence
 Light Emission Excitation Emission Spectra Incandescence Absorption Spectra Today s Topics Excitation/De-Excitation Electron raised to higher energy level Electron emits photon when it drops back down
Light Emission Excitation Emission Spectra Incandescence Absorption Spectra Today s Topics Excitation/De-Excitation Electron raised to higher energy level Electron emits photon when it drops back down
The Nature of Light I: Electromagnetic Waves Spectra Kirchoff s Laws Temperature Blackbody radiation
 The Nature of Light I: Electromagnetic Waves Spectra Kirchoff s Laws Temperature Blackbody radiation Electromagnetic Radiation (How we get most of our information about the cosmos) Examples of electromagnetic
The Nature of Light I: Electromagnetic Waves Spectra Kirchoff s Laws Temperature Blackbody radiation Electromagnetic Radiation (How we get most of our information about the cosmos) Examples of electromagnetic
Susan Cartwright Our Evolving Universe 1
 Atoms and Starlight Why do the stars shine? planets shine by reflected sunlight but what generates the Sun s light? What does starlight tell us about the stars? their temperature their chemical composition
Atoms and Starlight Why do the stars shine? planets shine by reflected sunlight but what generates the Sun s light? What does starlight tell us about the stars? their temperature their chemical composition
ASTRO Fall 2012 LAB #7: The Electromagnetic Spectrum
 ASTRO 1050 - Fall 2012 LAB #7: The Electromagnetic Spectrum ABSTRACT Astronomers rely on light to convey almost all of the information we have on distant astronomical objects. In addition to measuring
ASTRO 1050 - Fall 2012 LAB #7: The Electromagnetic Spectrum ABSTRACT Astronomers rely on light to convey almost all of the information we have on distant astronomical objects. In addition to measuring
Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5. What is light? What is a wave? Radiation carries information
 Concepts: Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5 Electromagnetic waves Types of spectra Temperature Blackbody radiation Dual nature of radiation Atomic structure Interaction of light and matter
Concepts: Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5 Electromagnetic waves Types of spectra Temperature Blackbody radiation Dual nature of radiation Atomic structure Interaction of light and matter
Classification of Electromagnetic Radiation
 Light and Energy Electromagnetic Radiation Radiant energy that exhibits wavelength-like behavior and travels through space at the speed of light in a vacuum. Example: The sun light, energy used in microwave
Light and Energy Electromagnetic Radiation Radiant energy that exhibits wavelength-like behavior and travels through space at the speed of light in a vacuum. Example: The sun light, energy used in microwave
Light is an important form of energy for all of us
 What is Light? Light is an important form of energy for all of us it allows us to see plants rely on light for photosynthesis many chemical reactions produce light life on Earth would not exist without
What is Light? Light is an important form of energy for all of us it allows us to see plants rely on light for photosynthesis many chemical reactions produce light life on Earth would not exist without
Name: Partner(s): 1102 or 3311: Desk # Date: Spectroscopy Part I
 Name: Partner(s): 1102 or 3311: Desk # Date: Spectroscopy Part I Purpose Investigate Kirchhoff s Laws for continuous, emission and absorption spectra Analyze the solar spectrum and identify unknown lines
Name: Partner(s): 1102 or 3311: Desk # Date: Spectroscopy Part I Purpose Investigate Kirchhoff s Laws for continuous, emission and absorption spectra Analyze the solar spectrum and identify unknown lines
Lights. And God said, "Let there be light"; and there was light. And God saw that the light was good; (Bible: Genesis I)
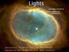 Lights Astronomy is based on observing lights from celestial bodies. And God said, "Let there be light"; and there was light. And God saw that the light was good; (Bible: Genesis I) Cat's Eye planetary
Lights Astronomy is based on observing lights from celestial bodies. And God said, "Let there be light"; and there was light. And God saw that the light was good; (Bible: Genesis I) Cat's Eye planetary
LIGHT. Question. Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light.
 LIGHT Question Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light. What kind of information can we get from light? 1 Light
LIGHT Question Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light. What kind of information can we get from light? 1 Light
Visible spectrum 1. Spectroscope. Name:
 Name: Visible spectrum 1 You know by now that different atoms have different configurations of electrons. You also know that electrons generate electromagnetic waves when they oscillate (remember that
Name: Visible spectrum 1 You know by now that different atoms have different configurations of electrons. You also know that electrons generate electromagnetic waves when they oscillate (remember that
PHYSICS 102N Spring Week 11 Light emission and absorption
 PHYSICS 102N Spring 2009 Week 11 Light emission and absorption Accelerated charges emit electromagnetic waves *) Examples: Radio antenna: Alternating voltage drives electrons back and forth 94.9 million
PHYSICS 102N Spring 2009 Week 11 Light emission and absorption Accelerated charges emit electromagnetic waves *) Examples: Radio antenna: Alternating voltage drives electrons back and forth 94.9 million
L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat flow. Conduction. Convection. Thermal Conductivity. heat conduction. Heat transfer
![L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat flow. Conduction. Convection. Thermal Conductivity. heat conduction. Heat transfer L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat flow. Conduction. Convection. Thermal Conductivity. heat conduction. Heat transfer](/thumbs/78/76842080.jpg) L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat transfer convection conduction emitters of seeing behind closed doors Greenhouse effect Heat Capacity How to boil water Heat flow HEAT the energy that flows from one system
L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat transfer convection conduction emitters of seeing behind closed doors Greenhouse effect Heat Capacity How to boil water Heat flow HEAT the energy that flows from one system
A100H Exploring the Universe: The interaction of light and matter. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100H Exploring the Universe: The interaction of light and matter Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu February 11, 2016 Read: Chap 5 02/11/16 slide 1 Exam #1: Thu 18 Feb
A100H Exploring the Universe: The interaction of light and matter Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu February 11, 2016 Read: Chap 5 02/11/16 slide 1 Exam #1: Thu 18 Feb
Light sources. Excited gas atoms are the primaty source of radiation in combustion and discharge lamps. lamps is not continuous!
 Light sources Excited gas atoms are the primaty source of radiation in combustion and discharge lamps. Continuous spectrum: black body radiation Characteristic spectrum: emission lines Absorption lines
Light sources Excited gas atoms are the primaty source of radiation in combustion and discharge lamps. Continuous spectrum: black body radiation Characteristic spectrum: emission lines Absorption lines
Atomic Theory C &03
 Atomic Theory Part One: Flame Tests Part Two: Atomic Spectra Part Three: Applications of Spectra (optional) C12-2-02 &03 This activity will focus on the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Atomic Theory Part One: Flame Tests Part Two: Atomic Spectra Part Three: Applications of Spectra (optional) C12-2-02 &03 This activity will focus on the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
What can laser light do for (or to) me?
 What can laser light do for (or to) me? Phys 1020, Day 15: Questions? Refection, refraction LASERS: 14.3 Next Up: Finish lasers Cameras and optics 1 Eyes to web: Final Project Info Light travels more slowly
What can laser light do for (or to) me? Phys 1020, Day 15: Questions? Refection, refraction LASERS: 14.3 Next Up: Finish lasers Cameras and optics 1 Eyes to web: Final Project Info Light travels more slowly
Light and Matter(LC)
 Light and Matter(LC) Every astronomy book that I ve seen has at least one chapter dedicated to the physics of light. Why are astronomers so interested in light? Everything* that we know about Astronomical
Light and Matter(LC) Every astronomy book that I ve seen has at least one chapter dedicated to the physics of light. Why are astronomers so interested in light? Everything* that we know about Astronomical
Lightbulbs. Lecture 18 : Blackbody spectrum Improving lightbulb efficiency
 Lightbulbs Lecture 18 : Blackbody spectrum Improving lightbulb efficiency Reminders: HW 7 due Monday at 10pm Simulations available in G116 Reading quiz on Tuesday, 10.1 EM radiation so far EM radiation
Lightbulbs Lecture 18 : Blackbody spectrum Improving lightbulb efficiency Reminders: HW 7 due Monday at 10pm Simulations available in G116 Reading quiz on Tuesday, 10.1 EM radiation so far EM radiation
Interested in exploring science or math teaching as a career?
 Interested in exploring science or math teaching as a career? Start with Step 1: EDUC 2020 (1 credit) Real experience teaching real kids! No commitment to continue with education courses Registration priority
Interested in exploring science or math teaching as a career? Start with Step 1: EDUC 2020 (1 credit) Real experience teaching real kids! No commitment to continue with education courses Registration priority
10/21/2015. Lightbulbs. Blackbody spectrum. Temperature and total emitted power (brightness) Blackbody spectrum and temperature
 Lightbulbs EM radiation so far EM radiation is a periodic modulation of the electric field: travels as a wave Wavelength (or frequency) determines: - type of EM radiation - if in visible range, wavelength
Lightbulbs EM radiation so far EM radiation is a periodic modulation of the electric field: travels as a wave Wavelength (or frequency) determines: - type of EM radiation - if in visible range, wavelength
Chapter 3. Electromagnetic Theory, Photons. and Light. Lecture 7
 Lecture 7 Chapter 3 Electromagnetic Theory, Photons. and Light Sources of light Emission of light by atoms The electromagnetic spectrum see supplementary material posted on the course website Electric
Lecture 7 Chapter 3 Electromagnetic Theory, Photons. and Light Sources of light Emission of light by atoms The electromagnetic spectrum see supplementary material posted on the course website Electric
Modern optics Lasers
 Chapter 13 Phys 322 Lecture 36 Modern optics Lasers Reminder: Please complete the online course evaluation Last lecture: Review discussion (no quiz) LASER = Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of
Chapter 13 Phys 322 Lecture 36 Modern optics Lasers Reminder: Please complete the online course evaluation Last lecture: Review discussion (no quiz) LASER = Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of
10.1 Properties of Light
 10.1 Properties of Light Every time you see, you are using light. You can t see anything in complete darkness! Whether you are looking at a light bulb, or a car, or this book, light brings information
10.1 Properties of Light Every time you see, you are using light. You can t see anything in complete darkness! Whether you are looking at a light bulb, or a car, or this book, light brings information
Chapter 4. Spectroscopy. Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah
 Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah Learning Goals: 4.1 Spectral Lines 4.2 Atoms and Radiation 4.3 Formation of the Spectral Lines 4.4 Molecules 4.5 Spectral Line Analysis 2 DR. T. AL-ABDULLAH
Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah Learning Goals: 4.1 Spectral Lines 4.2 Atoms and Radiation 4.3 Formation of the Spectral Lines 4.4 Molecules 4.5 Spectral Line Analysis 2 DR. T. AL-ABDULLAH
Chapter 5 Light and Matter
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter Stars and galaxies are too far for us to send a spacecraft or to visit (in our lifetimes). All we can receive from them is light But there is much we can learn (composition,
Chapter 5 Light and Matter Stars and galaxies are too far for us to send a spacecraft or to visit (in our lifetimes). All we can receive from them is light But there is much we can learn (composition,
Review: Properties of a wave
 Radiation travels as waves. Waves carry information and energy. Review: Properties of a wave wavelength (λ) crest amplitude (A) trough velocity (v) λ is a distance, so its units are m, cm, or mm, etc.
Radiation travels as waves. Waves carry information and energy. Review: Properties of a wave wavelength (λ) crest amplitude (A) trough velocity (v) λ is a distance, so its units are m, cm, or mm, etc.
hf = E 1 - E 2 hc = E 1 - E 2 λ FXA 2008 Candidates should be able to : EMISSION LINE SPECTRA
 1 Candidates should be able to : EMISSION LINE SPECTRA Explain how spectral lines are evidence for the existence of discrete energy levels in isolated atoms (i.e. in a gas discharge lamp). Describe the
1 Candidates should be able to : EMISSION LINE SPECTRA Explain how spectral lines are evidence for the existence of discrete energy levels in isolated atoms (i.e. in a gas discharge lamp). Describe the
9/16/08 Tuesday. Chapter 3. Properties of Light. Light the Astronomer s Tool. and sometimes it can be described as a particle!
 9/16/08 Tuesday Announce: Observations? Milky Way Center movie Moon s Surface Gravity movie Questions on Gravity from Ch. 2 Ch. 3 Newton Movie Chapter 3 Light and Atoms Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
9/16/08 Tuesday Announce: Observations? Milky Way Center movie Moon s Surface Gravity movie Questions on Gravity from Ch. 2 Ch. 3 Newton Movie Chapter 3 Light and Atoms Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
AST 102 chapter 5. Radiation and Spectra. Radiation and Spectra. Radiation and Spectra. What is light? What is radiation?
 5 Radiation and Spectra 1 Radiation and Spectra What is light? According to Webster: a.something that makes vision possible b.the sensation aroused by stimulation of the visual receptors c.electromagnetic
5 Radiation and Spectra 1 Radiation and Spectra What is light? According to Webster: a.something that makes vision possible b.the sensation aroused by stimulation of the visual receptors c.electromagnetic
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section IV
 ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section IV Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section IV Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use
Light. Mike Maloney Physics, SHS
 Light Mike Maloney Physics, SHS 1 Light What is LIGHT? WHERE DOES IT COME FROM? 2003 Mike Maloney 2 What is Light? Light is a wave, or rather acts like a wave. How do we know since we cannot see it? We
Light Mike Maloney Physics, SHS 1 Light What is LIGHT? WHERE DOES IT COME FROM? 2003 Mike Maloney 2 What is Light? Light is a wave, or rather acts like a wave. How do we know since we cannot see it? We
Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds
 - - Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds Absorption and emission from atoms, ions, and molecules Periodic Table of Elements The universe is mostly hydrogen H and helium He
- - Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds Absorption and emission from atoms, ions, and molecules Periodic Table of Elements The universe is mostly hydrogen H and helium He
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
 The Electromagnetic Spectrum Learning Objectives! What is Electromagnetic Radiation?! What are spectra? How could we measure a spectrum?! How do wavelengths correspond to colors for optical light? Does
The Electromagnetic Spectrum Learning Objectives! What is Electromagnetic Radiation?! What are spectra? How could we measure a spectrum?! How do wavelengths correspond to colors for optical light? Does
Parallax: Space Observatories. Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements. Stars, Galaxies & Universe Lecture #7 Outline
 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements HW#4: posted Thursday; due Monday (9/20) Reading Quiz on Ch. 16.5 Monday (9/20) Exam #1 (Next Wednesday 9/22) In class (50 minutes) first 20 minutes: review
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements HW#4: posted Thursday; due Monday (9/20) Reading Quiz on Ch. 16.5 Monday (9/20) Exam #1 (Next Wednesday 9/22) In class (50 minutes) first 20 minutes: review
Blackbody Radiation OBJECTIVES
 Name Class Date Skills Practice Lab Blackbody Radiation A perfect absorber of radiation also happens to be a perfect radiator of that radiation as well. Such objects are called blackbodies, because darker
Name Class Date Skills Practice Lab Blackbody Radiation A perfect absorber of radiation also happens to be a perfect radiator of that radiation as well. Such objects are called blackbodies, because darker
Classical and Planck picture. Planck s constant. Question. Quantum explanation for the Wein Effect.
 6.1 Quantum Physics. Particle Nature of Light Particle nature of Light Blackbody Radiation Photoelectric Effect Properties of photons Ionizing radiation Radiation damage x-rays Compton effect X-ray diffraction
6.1 Quantum Physics. Particle Nature of Light Particle nature of Light Blackbody Radiation Photoelectric Effect Properties of photons Ionizing radiation Radiation damage x-rays Compton effect X-ray diffraction
In class quiz - nature of light. Moonbow with Sailboats (Matt BenDaniel)
 In class quiz - nature of light Moonbow with Sailboats (Matt BenDaniel) Nature of light - review Light travels at very high but finite speed. Light is electromagnetic wave characterized by wavelength (or
In class quiz - nature of light Moonbow with Sailboats (Matt BenDaniel) Nature of light - review Light travels at very high but finite speed. Light is electromagnetic wave characterized by wavelength (or
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 38
 F UNDAMENTALS OF PHOTONICS Module 1.1 Nature and Properties of Light Linda J. Vandergriff Director of Photonics System Engineering Science Applications International Corporation McLean, Virginia Light
F UNDAMENTALS OF PHOTONICS Module 1.1 Nature and Properties of Light Linda J. Vandergriff Director of Photonics System Engineering Science Applications International Corporation McLean, Virginia Light
Chemistry 212 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY
 Chemistry 212 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY The emission and absorption of light energy of particular wavelengths by atoms and molecules is a common phenomenon. The emissions/absorptions are characteristic for each
Chemistry 212 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY The emission and absorption of light energy of particular wavelengths by atoms and molecules is a common phenomenon. The emissions/absorptions are characteristic for each
Today. Spectra. Thermal Radiation. Wien s Law. Stefan-Boltzmann Law. Kirchoff s Laws. Emission and Absorption. Spectra & Composition
 Today Spectra Thermal Radiation Wien s Law Stefan-Boltzmann Law Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Spectra & Composition Spectrum Originally, the range of colors obtained by passing sunlight through
Today Spectra Thermal Radiation Wien s Law Stefan-Boltzmann Law Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Spectra & Composition Spectrum Originally, the range of colors obtained by passing sunlight through
Light. October 14, ) Exam Review 2) Introduction 3) Light Waves 4) Atoms 5) Light Sources
 Light October 14, 2002 1) Exam Review 2) Introduction 3) Light Waves 4) Atoms 5) Light Sources Waves You know of many types of waves water, sound, seismic, etc A wave is something oscillating back and
Light October 14, 2002 1) Exam Review 2) Introduction 3) Light Waves 4) Atoms 5) Light Sources Waves You know of many types of waves water, sound, seismic, etc A wave is something oscillating back and
PHYSICS nd TERM Outline Notes (continued)
 PHYSICS 2800 2 nd TERM Outline Notes (continued) Section 6. Optical Properties (see also textbook, chapter 15) This section will be concerned with how electromagnetic radiation (visible light, in particular)
PHYSICS 2800 2 nd TERM Outline Notes (continued) Section 6. Optical Properties (see also textbook, chapter 15) This section will be concerned with how electromagnetic radiation (visible light, in particular)
Atomic Emission Spectra
 Atomic Emission Spectra Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are as follows: To build and calibrate a simple meter-stick spectroscope that is capable of measuring wavelengths of visible light.
Atomic Emission Spectra Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are as follows: To build and calibrate a simple meter-stick spectroscope that is capable of measuring wavelengths of visible light.
Taking Fingerprints of Stars, Galaxies, and Other Stuff. The Bohr Atom. The Bohr Atom Model of Hydrogen atom. Bohr Atom. Bohr Atom
 Periodic Table of Elements Taking Fingerprints of Stars, Galaxies, and Other Stuff Absorption and Emission from Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Universe is mostly (97%) Hydrogen and Helium (H and He) The ONLY
Periodic Table of Elements Taking Fingerprints of Stars, Galaxies, and Other Stuff Absorption and Emission from Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Universe is mostly (97%) Hydrogen and Helium (H and He) The ONLY
Chapter 4 Spectroscopy
 Chapter 4 Spectroscopy The beautiful visible spectrum of the star Procyon is shown here from red to blue, interrupted by hundreds of dark lines caused by the absorption of light in the hot star s cooler
Chapter 4 Spectroscopy The beautiful visible spectrum of the star Procyon is shown here from red to blue, interrupted by hundreds of dark lines caused by the absorption of light in the hot star s cooler
The Basics of Light. Sunrise from the Space Shuttle, STS-47 mission. The Basics of Light
 The Basics of Light The sun as it appears in X-ray light (left) and extreme ultraviolet light (right). Light as energy Light is remarkable. It is something we take for granted every day, but it's not something
The Basics of Light The sun as it appears in X-ray light (left) and extreme ultraviolet light (right). Light as energy Light is remarkable. It is something we take for granted every day, but it's not something
high energy state for the electron in the atom low energy state for the electron in the atom
 Atomic Spectra Objectives The objectives of this experiment are to: 1) Build and calibrate a simple spectroscope capable of measuring wavelengths of visible light. 2) Measure several wavelengths of light
Atomic Spectra Objectives The objectives of this experiment are to: 1) Build and calibrate a simple spectroscope capable of measuring wavelengths of visible light. 2) Measure several wavelengths of light
Wave - Particle Duality of Light
 Properties of Light Objectives Explain wave-particle duality State the speed of light Describe electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum Explain how light interacts with transparent and opaque
Properties of Light Objectives Explain wave-particle duality State the speed of light Describe electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum Explain how light interacts with transparent and opaque
Chapter 17, Electromagnetic Waves Physical Science, McDougal-Littell, 2008
 SECTION 1 (PP. 553-558): ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES HAVE UNIQUE TRAITS. Georgia Standards: S8P4a Identify the characteristics of electromagnetic and mechanical waves; S8P4d Describe how the behavior of waves
SECTION 1 (PP. 553-558): ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES HAVE UNIQUE TRAITS. Georgia Standards: S8P4a Identify the characteristics of electromagnetic and mechanical waves; S8P4d Describe how the behavior of waves
Experiment 24: Spectroscopy
 Experiment 24: Spectroscopy Figure 24.1: Spectroscopy EQUIPMENT High Voltage Power Supply Incandescent Light Source (3) Gas Discharge Tubes: 1. Helium 2. Hydrogen 3. Unknown Element Spectrometer Felt (1)
Experiment 24: Spectroscopy Figure 24.1: Spectroscopy EQUIPMENT High Voltage Power Supply Incandescent Light Source (3) Gas Discharge Tubes: 1. Helium 2. Hydrogen 3. Unknown Element Spectrometer Felt (1)
Light and Atoms. ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies. ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies !ATH REVIEW: #AST CLASS: "OMEWORK #1
 ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies!ATH REVIEW: Tonight, 5-6pm, in RAMY N1B23 "OMEWORK #1 -Due THU, Sept. 10, by 5pm, on Mastering Astronomy CLASS RECORDED STARTED - INFO WILL BE POSTED on CULEARN
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies!ATH REVIEW: Tonight, 5-6pm, in RAMY N1B23 "OMEWORK #1 -Due THU, Sept. 10, by 5pm, on Mastering Astronomy CLASS RECORDED STARTED - INFO WILL BE POSTED on CULEARN
Physics 1230: Light and Color
 Physics 1230: Light and Color Prof. Leo Radzihovsky! Susanna Todaro (lecturer)!!!! (TA/grader) Gamow Tower F623!! Help Room, 303-492-5436!!! Duane Physics radzihov@colorado.edu!! susanna.todaro@colorado.edu!
Physics 1230: Light and Color Prof. Leo Radzihovsky! Susanna Todaro (lecturer)!!!! (TA/grader) Gamow Tower F623!! Help Room, 303-492-5436!!! Duane Physics radzihov@colorado.edu!! susanna.todaro@colorado.edu!
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. How do we experience light? Colors of Light. How do light and matter interact?
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos How do we experience light? The warmth of sunlight tells us that light is a form of energy We can measure the amount of energy emitted by a
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos How do we experience light? The warmth of sunlight tells us that light is a form of energy We can measure the amount of energy emitted by a
Electromagnetic waves
 Lecture 21 Electromagnetic waves Atomic Physics Atomic Spectra Lasers Applications Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic Waves composed of electric and magnetic fields can be created by an oscillating
Lecture 21 Electromagnetic waves Atomic Physics Atomic Spectra Lasers Applications Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic Waves composed of electric and magnetic fields can be created by an oscillating
aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously
 Today Interaction of Light with Matter Thermal Radiation Kirchhoff s Laws aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously wave-like AND particle-like Sometimes it behaves like ripples on a pond (waves).
Today Interaction of Light with Matter Thermal Radiation Kirchhoff s Laws aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously wave-like AND particle-like Sometimes it behaves like ripples on a pond (waves).
What makes the color pink? Black and white TV summary. Different color phosphors. Color TV. Different color pixels
 Energy What makes the color pink? Black and white TV summary Picture made from a grid of dots (pixels) Dots illuminated when electron beam hits phosphor Beam scanned across entire screen ~ 50 times a second
Energy What makes the color pink? Black and white TV summary Picture made from a grid of dots (pixels) Dots illuminated when electron beam hits phosphor Beam scanned across entire screen ~ 50 times a second
SPECTROSCOPY PRELAB. 2) Name the 3 types of spectra and, in 1 sentence each, describe them.
 NAME: SPECTROSCOPY PRELAB 1) What is a spectrum? 2) Name the 3 types of spectra and, in 1 sentence each, describe them. a. b. c. 3) Use Wien s law to calculate the surface temperature of the star Alnilam
NAME: SPECTROSCOPY PRELAB 1) What is a spectrum? 2) Name the 3 types of spectra and, in 1 sentence each, describe them. a. b. c. 3) Use Wien s law to calculate the surface temperature of the star Alnilam
Lecture5PracticeQuiz.txt
 TAKEN FROM HORIZONS 7TH EDITION CHAPTER 6 TUTORIAL QUIZ 1. The difference between radiation and sound is that a. radiation exhibits the Doppler effect, whereas sound does not. b. radiation travels much
TAKEN FROM HORIZONS 7TH EDITION CHAPTER 6 TUTORIAL QUIZ 1. The difference between radiation and sound is that a. radiation exhibits the Doppler effect, whereas sound does not. b. radiation travels much
Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 5 June 1, 2018
 www.astro.yale.edu/astro120 Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 5 June 1, 2018 to understand how we know stuff about the universe we need to understand: 1. the spectral analysis of light 2. how light interacts with
www.astro.yale.edu/astro120 Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 5 June 1, 2018 to understand how we know stuff about the universe we need to understand: 1. the spectral analysis of light 2. how light interacts with
From Last Time Pearson Education, Inc.
 From Last Time Light: Absorption, Emission, Transmission, Reflection, and Scattering c=λ x f E=h x f Light (electromagnetic radiation) extends from gamma rays (high E, high f, small λ) to radio waves (small
From Last Time Light: Absorption, Emission, Transmission, Reflection, and Scattering c=λ x f E=h x f Light (electromagnetic radiation) extends from gamma rays (high E, high f, small λ) to radio waves (small
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. 5.1 Light in Everyday Life. How do we experience light?
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Light Energy & Solar Energy
 FORMS OF ENERGY LESSON PLAN 2.5 Light Energy & Solar Energy This lesson is designed for 3rd 5th grade students in a variety of school settings (public, private, STEM schools, and home schools) in the seven
FORMS OF ENERGY LESSON PLAN 2.5 Light Energy & Solar Energy This lesson is designed for 3rd 5th grade students in a variety of school settings (public, private, STEM schools, and home schools) in the seven
 Pre-Lab Reading Questions GS106 Lab 3 Answer Key - How We Use Light in Astronomy Life Cycle of a Wave: 1) initialized as oscillating vibrations ("disturbances"), 2) wave travel from origin to destination,
Pre-Lab Reading Questions GS106 Lab 3 Answer Key - How We Use Light in Astronomy Life Cycle of a Wave: 1) initialized as oscillating vibrations ("disturbances"), 2) wave travel from origin to destination,
Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds. Absorption and emission from atoms, ions, and molecules
 Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds Absorption and emission from atoms, ions, and molecules 1 Periodic Table of Elements The universe is mostly hydrogen H and helium He
Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds Absorption and emission from atoms, ions, and molecules 1 Periodic Table of Elements The universe is mostly hydrogen H and helium He
EXPERIMENT 09 OBSERVATION OF SPECTRA
 EXPERIMENT 09 OBSERVATION OF SPECTRA INTRODUCTION: In physics, as in very other area of study, one of the most valuable questions a student can learn to ask is, How do they know that? Thus, when you read
EXPERIMENT 09 OBSERVATION OF SPECTRA INTRODUCTION: In physics, as in very other area of study, one of the most valuable questions a student can learn to ask is, How do they know that? Thus, when you read
Astronomy The Nature of Light
 Astronomy The Nature of Light A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Measuring the speed of light Light is an electromagnetic wave The relationship between Light and temperature
Astronomy The Nature of Light A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Measuring the speed of light Light is an electromagnetic wave The relationship between Light and temperature
The Nature of Light. We have a dual model
 Light and Atoms Properties of Light We can come to understand the composition of distant bodies by analyzing the light they emit This analysis can tell us about the composition as well as the temperature
Light and Atoms Properties of Light We can come to understand the composition of distant bodies by analyzing the light they emit This analysis can tell us about the composition as well as the temperature
Unit 3 Part 1: Quantum Physics. introduce the idea of quanta as a new way of looking at light and sub atomic physical behaviour
 In this lesson you will Unit 3 Part 1: Quantum Physics consider and list some of the properties of light and sub atomic particles that were at odds with the classical wave theory of electromagnetic radiation
In this lesson you will Unit 3 Part 1: Quantum Physics consider and list some of the properties of light and sub atomic particles that were at odds with the classical wave theory of electromagnetic radiation
LECTURE # 17 Modern Optics Matter Waves
 PHYS 270-SPRING 2011 LECTURE # 17 Modern Optics Matter Waves April 5, 2011 1 Spectroscopy: Unlocking the Structure of Atoms There are two types of spectra, continuous spectra and discrete spectra: Hot,
PHYS 270-SPRING 2011 LECTURE # 17 Modern Optics Matter Waves April 5, 2011 1 Spectroscopy: Unlocking the Structure of Atoms There are two types of spectra, continuous spectra and discrete spectra: Hot,
What are the six common sources of light?
 What are the six common sources of light? Common light sources include incandescent, fluorescent, laser, neon, tungsten-halogen, and sodium-vapor bulbs. Objects that give off their own light are luminous.
What are the six common sources of light? Common light sources include incandescent, fluorescent, laser, neon, tungsten-halogen, and sodium-vapor bulbs. Objects that give off their own light are luminous.
Intro to Galaxies Light and Atoms - I
 Astrophysics Study of Light Study of Atoms Intro to Galaxies Light and Atoms - I 1 Atomic Physics elements: substances which cannot be broken down into simpler substances atom : smallest unit of an element
Astrophysics Study of Light Study of Atoms Intro to Galaxies Light and Atoms - I 1 Atomic Physics elements: substances which cannot be broken down into simpler substances atom : smallest unit of an element
A Warm Up Exercise. A Warm Up Exercise. A Warm Up Exercise. A Warm Up Exercise. The Solar Flux
 When you compare gamma ray photons with photons of radio waves, which of the following is true? Gamma rays have a shorter wavelength and less energy Gamma rays have a shorter wavelength and same energy
When you compare gamma ray photons with photons of radio waves, which of the following is true? Gamma rays have a shorter wavelength and less energy Gamma rays have a shorter wavelength and same energy
Experiment 7: Spectrum of the Hydrogen Atom
 Experiment 7: Spectrum of the Hydrogen Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30-6:30PM INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 Introduction The physics behind: The spectrum of
Experiment 7: Spectrum of the Hydrogen Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30-6:30PM INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 Introduction The physics behind: The spectrum of
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Light & Atoms. Electromagnetic [EM] Waves. Light and several other forms of radiation are called electromagnetic waves or electromagnetic radiation.
![Light & Atoms. Electromagnetic [EM] Waves. Light and several other forms of radiation are called electromagnetic waves or electromagnetic radiation. Light & Atoms. Electromagnetic [EM] Waves. Light and several other forms of radiation are called electromagnetic waves or electromagnetic radiation.](/thumbs/88/117441686.jpg) Light & Atoms Electromagnetic [EM] Waves Light and several other forms of radiation are called electromagnetic waves or electromagnetic radiation. These have both and electric part and a magnetic part
Light & Atoms Electromagnetic [EM] Waves Light and several other forms of radiation are called electromagnetic waves or electromagnetic radiation. These have both and electric part and a magnetic part
Chapter 5: Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos
 Chapter 5 Lecture Chapter 5: Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience
Chapter 5 Lecture Chapter 5: Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience
In this lab you will measure and quantify emission spectra from several different visible light sources.
 Lab 2 Spectroscopy In this lab you will measure and quantify emission spectra from several different visible light sources. 2.1 Spectral Lines In physics, we typically use the word spectrum to refer to
Lab 2 Spectroscopy In this lab you will measure and quantify emission spectra from several different visible light sources. 2.1 Spectral Lines In physics, we typically use the word spectrum to refer to
X Rays must be viewed from space used for detecting exotic objects such as neutron stars and black holes also observing the Sun.
 6/25 How do we get information from the telescope? 1. Galileo drew pictures. 2. With the invention of photography, we began taking pictures of the view in the telescope. With telescopes that would rotate
6/25 How do we get information from the telescope? 1. Galileo drew pictures. 2. With the invention of photography, we began taking pictures of the view in the telescope. With telescopes that would rotate
Astronomical Observations: Distance & Light 7/2/09. Astronomy 101
 Astronomical Observations: Distance & Light 7/2/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Something Cool: Lasers on the Moon Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day
Astronomical Observations: Distance & Light 7/2/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Something Cool: Lasers on the Moon Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day
Sunlight. 1 radiation.
 Sunlight The eye has evolved to see a narrow range of EM waves which we call 'visible light'. This visible range of frequency is due to the light comes from the Sun. The photosphere of the Sun is a blackbody
Sunlight The eye has evolved to see a narrow range of EM waves which we call 'visible light'. This visible range of frequency is due to the light comes from the Sun. The photosphere of the Sun is a blackbody
AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System. MIDTERM II: Tuesday, April 5 [covering Lectures 10 through 16]
![AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System. MIDTERM II: Tuesday, April 5 [covering Lectures 10 through 16] AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System. MIDTERM II: Tuesday, April 5 [covering Lectures 10 through 16]](/thumbs/78/77847540.jpg) AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System MIDTERM II: Tuesday, April 5 [covering Lectures 10 through 16] REVIEW Light as Information Bearer We can separate light into its different wavelengths (spectrum).
AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System MIDTERM II: Tuesday, April 5 [covering Lectures 10 through 16] REVIEW Light as Information Bearer We can separate light into its different wavelengths (spectrum).
What are the three basic types of spectra?
 Learning from Light Our goals for learning What are the three basic types of spectra? How does light tell us what things are made of? How does light tell us the temperatures of planets and stars? How do
Learning from Light Our goals for learning What are the three basic types of spectra? How does light tell us what things are made of? How does light tell us the temperatures of planets and stars? How do
Spectroscopy of Various Light Sources: The Interactions between Light and Matter ASTR 170B1, Spring 2017, Lab #2. 1 Introduction.
 Spectroscopy of Various Light Sources: The Interactions between Light and Matter ASTR 170B1, Spring 2017, Lab #2 DUE IN CLASS ON Thursday Sept 28! You CAN work in a group of 2, but you need only turn in
Spectroscopy of Various Light Sources: The Interactions between Light and Matter ASTR 170B1, Spring 2017, Lab #2 DUE IN CLASS ON Thursday Sept 28! You CAN work in a group of 2, but you need only turn in
AS 101: Day Lab #2 Summer Spectroscopy
 Spectroscopy Goals To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are related To see spectral lines from different elements in emission and
Spectroscopy Goals To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are related To see spectral lines from different elements in emission and
Laboratory Exercise. Atomic Spectra A Kirchoff Potpourri
 1 Name: Laboratory Exercise Atomic Spectra A Kirchoff Potpourri Purpose: To examine the atomic spectra from several gas filled tubes and understand the importance of spectroscopy to astronomy. Introduction
1 Name: Laboratory Exercise Atomic Spectra A Kirchoff Potpourri Purpose: To examine the atomic spectra from several gas filled tubes and understand the importance of spectroscopy to astronomy. Introduction
AST 301, Lecture 2. James Lattimer. Department of Physics & Astronomy 449 ESS Bldg. Stony Brook University. January 29, 2019
 AST 301, Lecture 2 James Lattimer Department of Physics & Astronomy 449 ESS Bldg. Stony Brook University January 29, 2019 Cosmic Catastrophes (AKA Collisions) james.lattimer@stonybrook.edu Properties of
AST 301, Lecture 2 James Lattimer Department of Physics & Astronomy 449 ESS Bldg. Stony Brook University January 29, 2019 Cosmic Catastrophes (AKA Collisions) james.lattimer@stonybrook.edu Properties of
Electromagnetic Radiation. Physical Principles of Remote Sensing
 Electromagnetic Radiation Physical Principles of Remote Sensing Outline for 4/3/2003 Properties of electromagnetic radiation The electromagnetic spectrum Spectral emissivity Radiant temperature vs. kinematic
Electromagnetic Radiation Physical Principles of Remote Sensing Outline for 4/3/2003 Properties of electromagnetic radiation The electromagnetic spectrum Spectral emissivity Radiant temperature vs. kinematic
Higher -o-o-o- Past Paper questions o-o-o- 3.4 Spectra
 Higher -o-o-o- Past Paper questions 1991-2010 -o-o-o- 3.4 Spectra 1992 Q37 The diagram below shows the energy levels for the hydrogen atom. (a) Between which two energy levels would an electron transition
Higher -o-o-o- Past Paper questions 1991-2010 -o-o-o- 3.4 Spectra 1992 Q37 The diagram below shows the energy levels for the hydrogen atom. (a) Between which two energy levels would an electron transition
Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. White light is made up of many different colors. Interactions of Light with Matter
 Chapter 5 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact?
Chapter 5 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact?
Recall: The Importance of Light
 Key Concepts: Lecture 19: Light Light: wave-like behavior Light: particle-like behavior Light: Interaction with matter - Kirchoff s Laws The Wave Nature of Electro-Magnetic Radiation Visible light is just
Key Concepts: Lecture 19: Light Light: wave-like behavior Light: particle-like behavior Light: Interaction with matter - Kirchoff s Laws The Wave Nature of Electro-Magnetic Radiation Visible light is just
Experiment 3 Electromagnetic Radiation and Atom Interaction
 Experiment 3 Electromagnetic Radiation and Atom Interaction B OBJECTIVES To be familiar with the relationship between emission line spectra and the energy levels of electrons in various atoms. B INTRODUCTION
Experiment 3 Electromagnetic Radiation and Atom Interaction B OBJECTIVES To be familiar with the relationship between emission line spectra and the energy levels of electrons in various atoms. B INTRODUCTION
X-Rays from Atoms. These are called K α X-rays See table 29.1 for the energy of K α X-rays produced by some elements. Section 29.3
 X-Rays from Atoms The highest photon energy available in a hydrogen atom is in the ultraviolet part of the electromagnetic spectrum Other atoms can emit much more energetic photons larger Z, more electric
X-Rays from Atoms The highest photon energy available in a hydrogen atom is in the ultraviolet part of the electromagnetic spectrum Other atoms can emit much more energetic photons larger Z, more electric
A fresh look at light: build your own spectrometer
 Image courtesy of National Optical Astronomy Observatory/Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy/National Science Foundation A fresh look at light: build your own spectrometer A high-resolution
Image courtesy of National Optical Astronomy Observatory/Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy/National Science Foundation A fresh look at light: build your own spectrometer A high-resolution
HOMEWORK - Chapter 4 Spectroscopy
 Astronomy 10 HOMEWORK - Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Use a calculator whenever necessary. For full credit, always show your work and explain how you got your answer in full, complete sentences on a separate
Astronomy 10 HOMEWORK - Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Use a calculator whenever necessary. For full credit, always show your work and explain how you got your answer in full, complete sentences on a separate
Chapter 6. Quantum Theory and the Electronic Structure of Atoms Part 1
 Chapter 6 Quantum Theory and the Electronic Structure of Atoms Part 1 The nature of light Quantum theory Topics Bohr s theory of the hydrogen atom Wave properties of matter Quantum mechanics Quantum numbers
Chapter 6 Quantum Theory and the Electronic Structure of Atoms Part 1 The nature of light Quantum theory Topics Bohr s theory of the hydrogen atom Wave properties of matter Quantum mechanics Quantum numbers
Announcements. One more bit of vocabulary about waves
 Announcements Homework 5 now available; due on Sunday, Nov. 16 before midnight No class on Tuesday, Nov. 11 (Veteran s Day) Midterm 2 on Wednesday, Nov. 12 Study materials now available on class web page;
Announcements Homework 5 now available; due on Sunday, Nov. 16 before midnight No class on Tuesday, Nov. 11 (Veteran s Day) Midterm 2 on Wednesday, Nov. 12 Study materials now available on class web page;
