NOTES 5: APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION
|
|
|
- Louise Evans
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NOTES 5: APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: LESSON 5.1 EXTREMA ON AN INTERVAL Definition of Etrema Let f be defined on an interval I containing c. 1. f () c is the MINIMUM of f on I if f () c f() in I. f () c is the MAXIMUM of f on I if f () c f () in I Figures on pg 314: - Etreme values or Etrema are the minimum and maimum of a function on an interval - On an interval: Maimum ABSOLUTE ma Mininum ABSOLUTE min Theorem 5.1: The Etreme Value Theorem If f is continuous on a closed interval [ ab,, ] then f has both a minimum and a maimum on the interval. Note: In order for f () c to be an etreme value, f () c must eist (or must be defined). In other words: If f is defined at every c between a and b, and at the endpoints, then f must have the lowest and the highest points on ab., the graph over [ ] Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 1
2 Definition of Relative Etrema Relative Etrema can occur in two ways: If there is an open interval containing c on which: 1. f () c is a maimum, then ( c, f( c )) is called a RELATIVE MAXIMUM of f.. f () c is a minimum, then ( c, f( c )) is called a RELATIVE MINIMUM of f. Smooth and rounded curve horizontal tangent line derivative is 0. In other words: Relative etrema are hills or valleys of the graph. Sharp and peaked turn not differentiable. f ( ) f ( ) Eample 1: f( ) + 1 Find the derivative at, 1 ( 0,1 ) and ( ) f '( ) f '(0) What can you conclude 0,1 and about points ( ) (, 1)? Evaluate graph: Note: 0 and are the CRITICAL NUMBERS f '() Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page
3 Definition of a Critical Number Let f be defined at c. If f '( c ) 0 or if f is not differentiable at c, then c is a critical number of f. Evaluate Eample 1: Theorem 5.: Relative Etrema Occur Only at Critical Numbers Guidelines for Finding ABSOLUTE EXTREMA on a Closed Interval If f has a relative minimum or relative maimum at c, then c is a critical number of f. Note: The critical numbers of a function need not produce relative etrema. To find the etrema of a continuous function f on a closed ab,, use the following steps. interval [ ] 1. Find the critical numbers of f in ( a, b ).. Evaluate f at each critical number in ( a, b ). 3. Evaluate f at each endpoint [ ab., ] 4. The least of these values is the minimum. The greatest is the maimum. Eample : Find the ABSOLUTE Etrema of 4 3 f ( ) 3 4 1, on [ ] Step 1: To find the Critical Numbers: find f '( ), set f '( ) 0 and solve for Step : Find f ( CN ) f '( ) Step 3: Find f ( a ) f ( 1) Step 4: Find f ( b ) f () Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 3
4 Practice Problem 1: Find the ABSOLUTE Etrema of g ( ) 3 on [ 1, 1] Practice Problem : Find the ABSOLUTE Etrema of g ( ) 3 1 on ( 1, 4 ] 4 Practice Problem 3: Find the Critical Numbers of f( ) + 1 Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 4
5 LESSON 5. ROLLE S THEOREM AND THE MEAN VALUE THEOREM Theorem 5.3: Rolle s Theorem Let f be continuous on the closed ab, and differentiable interval [ ] on the interval ( a, b ). If f ( a) f ( b), then there is at least a, b such that one number c in ( ) f '( c ) 0. Eample 1: Find the two - intercepts of the function f and show that f '( ) 0 at some point between the two intercepts given f( ) + 4 Consider the following conditions before using Rolle s theorem: a. Is the function a, b? continuous in ( ) b. Is f ( a) f( b)? Eample : Let 3 f( ). + Find all values c in [ 1, 3] such that f '( c ) 0. Consider the following conditions before using Rolle s theorem: a. Is the function a, b? continuous in ( ) b. Is f ( a) f ( b)? Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 5
6 Theorem 5.4: The Mean Value Theorem Let f be continuous on the closed ab, and differentiable interval [ ] on the interval ( a, b ), then there eists a number c in ( a, b ) such that f '( c) f ( b) f( a). b a f( b) f( a) y y1 Note: b a 1 Alternative form of Mean Value Theorem f ( b) f( a) f '( c) b a ( ) f '( c) b a f( b) f( a) ( ) f '( c) b a + f( a) f( b) ( ) f ( b) f( a) + b a f '( c) Eample 3: Use the Mean Value Theorem to find all values of c in ( a, b ) such that f ( b) f( a) f '( c) b a given f( ) ( ). 1, 1 in [ ] Consider the following conditions before using the Mean Value theorem: a. Is the function a, b? continuous in ( ) b. What is f ( b) f( a) f '( c)? b a Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 6
7 LESSON 5.3 INCREASING AND DECREASING FUNCTIONS AND THE FIRST DERIVATIVE TEST Definition of Increasing and Decreasing Functions Decreasing: (, a) Negative derivative: f '( ) < 0 A function f is increasing on an interval if for any two numbers 1 and in the interval, 1 < f( 1) < f( ) and decreasing when < f( ) > f( ) 1 1 Constant: ( a, b ) Zero derivative: f '( ) 0 Increasing: ( b, ) Positive derivative: f '( ) > 0 Theorem 5.5: Test for Increasing and Decreasing Functions Guidelines for Finding Intervals on Which a Function Is Increasing or Decreasing Let f be a function that is continuous on the closed interval [ ab, ] and differentiable on the interval ( a, b ) 1. f '( ) > 0 in ( a, b) f is increasing on [ ab., ]. f '( ) < 0 in ( a, b) f is decreasing on [ ab., ] 3. f '( ) 0 in ( a, b) f is constant on [ ab., ] Let f be a function that is continuous on the interval ( a, b. ) To find the open intervals on which f is increasing or decreasing. 1. Locate the critical numbers of f in ( a, b ) by setting the derivative of f equal to 0. Use these numbers to determine the test intervals.. Determine the sign of f '( ) at one test value in each of the intervals. f '( ) < 0 Decreasin g 3. If f '( ) 0 Constan t f '( ) > 0 Increasin g Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 7
8 Practice Problems: Identify the open intervals on which the function is increasing, decreasing, or constant. 1. f ( ) 7 3 Intervals Test Values (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) < < < < < < < < f '( TV ) Conclusions. f( ) + 1 Intervals Test Values (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) < < < < < < < < f '( TV ) Conclusions Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 8
9 A Strictly Monotonic Function Theorem 5.6: The First Derivative Test (to find RELATIVE Etrema, not Absolute Etrema) A function is either increasing or decreasing on the entire interval. Let c be a critical number of a function f that is continuous on an open interval I containing c. If f is differentiable on the interval, ecept possibly at c, then f () c can be classified as follows. 1. If f '( ) changes from negative to positive at c, then f () c is a RELATIVE MINIMUM of f.. If f '( ) changes from positive to negative at c, then f () c is a RELATIVE MAXIMUM of f. 3. If f '( ) does not change sign at c, then f () c is neither a relative minimum nor relative maimum. Eample: f ( ) Relative Minimum Relative Maimum 3 Neither a ma nor a min Practice Problems: Find the relative etrema of the following functions 3. f( ) ( ) Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 9
10 Intervals Test Values (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) < < < < < < < < f '( TV ) Conclusions Identify Relative Etrema 4. f( ) 9 Intervals Test Values (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) < < < < < < < < f '( TV ) Conclusions Identify Relative Etrema Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 10
11 LESSON 5.4 CONCAVITY AND THE SECOND DERIVATIVE TEST Definition of Concavity Theorem 5.7: Test for Concavity Let f be differentiable on an open interval I. The graph of f is CONCAVE UPWARD on I if f '( ) is increasing on the interval and CONCAVE DOWNWARD on I if f '( ) is decreasing on the interval. Concave upward graph f lies above all of its tangent lines Concave downward graph f lies below all of its tangent lines Let f be a function whose nd derivative eists on an open interval I 1. f ''( ) > 0 in I graph is concave upward.. f ''( ) < 0 in I graph is concave downward. 3. f ''( ) 0 in I graph is linear, no concavity. Figures on pg 338 To find the intervals: 1. Find f ''( ). Set f ''( ) 0, and solve for. 3. Set the denominator of f (if any) 0 and solve for. Practice Problem 1: Determine concavity for 4 f( ) Check for continuity:. f '( ) 3. f ''( ) 4. Solve for possible points of inflection Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 11
12 Intervals Test Values (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) < < < < < < < < f ''( TV ) Conclusions Practice Problem : Determine concavity for 1 f( ) Check for continuity:. f '( ) 3. f ''( ) 4. Solve for possible points of inflection Intervals Test Values (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) < < < < < < < < f ''( TV ) Conclusions Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 1
13 Definition of Point of Inflection A point where the concavity of f changes. Figures on pg 340 Theorem 5.8: Points of Inflection If ( c, f( c )) is a point of inflection of the graph f, then either f ''( ) 0 or f ''( ) does not eist at c. Practice Problem 3: Determine the points of inflection and discuss the concavity f( ) 4 ( ) 3 1. Check for continuity:. f '( ) 3. f ''( ) 4. Solve for possible points of inflection Intervals Test Values (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) < < < < < < < < f ''( TV ) Conclusions Identify Points of Inflection Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 13
14 Theorem 5.9: Second Derivative Test Let f be a function such that f '( c ) 0 and the second derivative of f eists on an open interval containing c. 1. f ''( c ) > 0 RMin at ( c, f( c )). f ''( c ) < 0 RMa at ( c, f( c )) 3. f ''( c ) 0 No conclusion, need to use the First Derivative Test Practice Problem 4: Find the relative etrema for f ( ) Using 1 st Derivative Test 1. Determine continuity. f '( ) Using nd Derivative Test Repeat steps 1-3 in the First Derivative Test.. f ''( ) Graph: 3. Find CN s: 3. Test CN s in the nd Derivative 4. Test Table: 4. Conclusions: 5. Conclusions: Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 14
15 LESSON 5.5 LIMITS AT INFINITY Review: How to find horizontal, vertical and slant asymptotes n n 1 a n + an a + a 1 + a0 f( ) m m 1 b m + bm b + b 1 + b0 Vertical Set the denominator equal to zero then solve for Note: Vertical asymptotes are in the form of the zeros Horizontal i. n < m y 0 Note: Horizontal ii. n m an asymptotes are in the form y b of y... m iii. n > m no horizontal asymptotes Slant When n > m by 1 the slant asymptote is the quotient of the rational epression. (If n > m by or more, the function has neither horizontal nor slant asymptotes) Note: Slant asymptotes are in the form y m + b Note: These guidelines can be used to check for LIMITS at INFINITY of RATIONAL functions only. Eamples: Determine the VA, HA and SA for the following functions f( ) f( ) f( ) VA: HA: SA: VA: HA: SA: VA: HA: SA: Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 15
16 Limits at Infinity Everything for larger then M fits inside the given ε window around L. Definition of a Horizontal Asymptote Theorem 5.10: Limits at Infinity The line y L is a horizontal asymptote of the graph f is lim f ( ) L or lim f ( ) L. If r is a positive rational number and c is c any real number, then lim 0. r r Furthermore, if is defined when < 0, c then lim 0. r Remember: Given lim f ( ) L and c lim g ( ) K, then c lim f ( ) ± g( ) L± K c [ ] [ f g] lim ( ) ( ) c LK In other words: cons tant lim 0 or r cons tant lim 0 r Practice Problems: Evaluate the following limits and find their HA lim lim 5 HA: HA: Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 16
17 Practice Problems: Evaluate the following limits and find their HA. 3. lim 9 Note: when you encounter an indeterminate form, the suggested method is to DIVIDE the NUMERATOR and the DENOMINATOR by the HIGHEST POWER of in the DENOMINATOR. Practice Problems: Evaluate the following limits by finding the actual limits, then compare the answers to their HA s using the guidelines lim lim lim Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 17
18 Functions with two horizontal asymptotes and non-rational functions. a. lim Note: Eample 4: Find the following limits b. lim Graph: y Functions with Infinite Limits at Infinity a. lim Note: Eample 5: Find the following limits b. lim Graph: y Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 18
19 LESSON 5.6 A SUMMARY OF CURVE SKETCHING Absolute Etrema How to find Absolute Etrema on ab, [ ] An interval [ ab, ] is given AMa Highest point AMin Lowest point 1. Find the Critical Numbers: Find the 1 st derivative Set f '( ) 0 Solve for. Evaluate: f ( a ) f ( b ) f ( CN ) 3. The least of these values is the minimum. The greatest is the maimum. Eample: Find the ABSOLUTE Etrema of 1 hs () s on [ 0, ) Relative Etrema (hills and valleys) First Derivative Test 1. Find the CN: a, b, c. Set up the intervals using the CN 3. Choose a test value in each interval 4. Find f '( TV ) in each interval (, a) ( ab, ) (,) bc f '( TV ) > 0 Inc f '( TV ) < 0 f '( TV ) < 0 (, c ) f '( TV ) > 0 Dec Dec Inc a, f( a ) RMin( c, f( c )) RMa ( ) Second Derivative test 1. Find the CN: a, b, c. Find the nd derivative 3. Evaluate f ''( CN ' s ) 1. f ''( a ) > 0 RMin at ( a, f( a )). f ''( b ) < 0 RMa at ( b, f( b )) 3. f ''( c ) 0 No conclusion, need to use the First Derivative Test Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 19
20 Points of Inflection and Concavity 1. Find the 1 st derivative. Find the nd derivative 3. Set f ''( ) 0 4. Solve for to obtain POSSIBLE POINTS OF INFLECTION: ( a, f( a )), ( b, f( b )), ( c, f( c )) 5. Set up the intervals using the PP of I (, a) f ''( TV ) > 0 Upward ( ab, ) f ''( TV ) < 0 Downward, ( ) (,) bc f ''( TV ) < 0 Downward (, c ) f ''( TV ) > 0 Upward c, f( c ) P of I at ( a f a ) P of I ( ) Practice Problem: Use charts to show intervals of increasing and decreasing functions, label all relative etrema if applicable, find the intervals of concavity and points of inflection, find all vertical and horizontal asymptotes. Sketch the following graphs. (Find - and y-intercepts if they help you with your graph). Must show all work for full credit. Graphing calculator is just a checking device. 4 3 f ( ) f '( ) CN: Inc: Dec: RMin: RMa: f "( ) Label your grid carefully! Upward: Downward: P of I: -int: VA: HA: Mrs. Nguyen Honors PreCalculus Chapter 5 Notes Page 0
Name: NOTES 4: APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION. Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: WARM UP:
 NOTES 4: APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: WARM UP: Assume that f ( ) and g ( ) are differentiable functions: f ( ) f '( ) g ( ) g'( ) - 3 1-5 8-1 -9 7 4 1 0 5
NOTES 4: APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: WARM UP: Assume that f ( ) and g ( ) are differentiable functions: f ( ) f '( ) g ( ) g'( ) - 3 1-5 8-1 -9 7 4 1 0 5
?
 NOTES 4: APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION Name: Date: Period: WARM UP: Assume that f( ) and g ( ) are differentiable functions: f( ) f '( ) g ( ) g'( ) - 3 1-5 8-1 -9 7 4 1 0 5 9 9-3 1 3-3 6-5 3 8? 1. Let
NOTES 4: APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION Name: Date: Period: WARM UP: Assume that f( ) and g ( ) are differentiable functions: f( ) f '( ) g ( ) g'( ) - 3 1-5 8-1 -9 7 4 1 0 5 9 9-3 1 3-3 6-5 3 8? 1. Let
Pre-Calculus Mathematics Limit Process Calculus
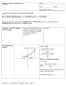 NOTES : LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: LESSON.1 THE TANGENT AND VELOCITY PROBLEMS Pre-Calculus Mathematics Limit Process Calculus The type of it that is used to find
NOTES : LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: LESSON.1 THE TANGENT AND VELOCITY PROBLEMS Pre-Calculus Mathematics Limit Process Calculus The type of it that is used to find
Math Honors Calculus I Final Examination, Fall Semester, 2013
 Math 2 - Honors Calculus I Final Eamination, Fall Semester, 2 Time Allowed: 2.5 Hours Total Marks:. (2 Marks) Find the following: ( (a) 2 ) sin 2. (b) + (ln 2)/(+ln ). (c) The 2-th Taylor polynomial centered
Math 2 - Honors Calculus I Final Eamination, Fall Semester, 2 Time Allowed: 2.5 Hours Total Marks:. (2 Marks) Find the following: ( (a) 2 ) sin 2. (b) + (ln 2)/(+ln ). (c) The 2-th Taylor polynomial centered
f'(x) = x 4 (2)(x - 6)(1) + (x - 6) 2 (4x 3 ) f'(x) = (x - 2) -1/3 = x 2 ; domain of f: (-, ) f'(x) = (x2 + 1)4x! 2x 2 (2x) 4x f'(x) =
 85. f() = 4 ( - 6) 2 f'() = 4 (2)( - 6)(1) + ( - 6) 2 (4 3 ) = 2 3 ( - 6)[ + 2( - 6)] = 2 3 ( - 6)(3-12) = 6 3 ( - 4)( - 6) Thus, the critical values are = 0, = 4, and = 6. Now we construct the sign chart
85. f() = 4 ( - 6) 2 f'() = 4 (2)( - 6)(1) + ( - 6) 2 (4 3 ) = 2 3 ( - 6)[ + 2( - 6)] = 2 3 ( - 6)(3-12) = 6 3 ( - 4)( - 6) Thus, the critical values are = 0, = 4, and = 6. Now we construct the sign chart
MATH section 3.4 Curve Sketching Page 1 of 29
 MATH section. Curve Sketching Page of 9 The step by step procedure below is for regular rational and polynomial functions. If a function contains radical or trigonometric term, then proceed carefully because
MATH section. Curve Sketching Page of 9 The step by step procedure below is for regular rational and polynomial functions. If a function contains radical or trigonometric term, then proceed carefully because
4.3 - How Derivatives Affect the Shape of a Graph
 4.3 - How Derivatives Affect the Shape of a Graph 1. Increasing and Decreasing Functions Definition: A function f is (strictly) increasing on an interval I if for every 1, in I with 1, f 1 f. A function
4.3 - How Derivatives Affect the Shape of a Graph 1. Increasing and Decreasing Functions Definition: A function f is (strictly) increasing on an interval I if for every 1, in I with 1, f 1 f. A function
Applications of Derivatives
 Applications of Derivatives Extrema on an Interval Objective: Understand the definition of extrema of a function on an interval. Understand the definition of relative extrema of a function on an open interval.
Applications of Derivatives Extrema on an Interval Objective: Understand the definition of extrema of a function on an interval. Understand the definition of relative extrema of a function on an open interval.
ch 3 applications of differentiation notebook.notebook January 17, 2018 Extrema on an Interval
 Extrema on an Interval Extrema, or extreme values, are the minimum and maximum of a function. They are also called absolute minimum and absolute maximum (or global max and global min). Extrema that occur
Extrema on an Interval Extrema, or extreme values, are the minimum and maximum of a function. They are also called absolute minimum and absolute maximum (or global max and global min). Extrema that occur
CURVE SKETCHING. Let's take an arbitrary function like the one whose graph is given below:
 I. THE FIRST DERIVATIVE TEST: CURVE SKETCHING Let's take an arbitrary function like the one whose graph is given below: As goes from a to p, the graph rises as moves to the right towards the interval P,
I. THE FIRST DERIVATIVE TEST: CURVE SKETCHING Let's take an arbitrary function like the one whose graph is given below: As goes from a to p, the graph rises as moves to the right towards the interval P,
Maximum and Minimum Values
 Maimum and Minimum Values y Maimum Minimum MATH 80 Lecture 4 of 6 Definitions: A function f has an absolute maimum at c if f ( c) f ( ) for all in D, where D is the domain of f. The number f (c) is called
Maimum and Minimum Values y Maimum Minimum MATH 80 Lecture 4 of 6 Definitions: A function f has an absolute maimum at c if f ( c) f ( ) for all in D, where D is the domain of f. The number f (c) is called
Graphing Rational Functions
 Graphing Rational Functions Let s use all of the material we have developed to graph some rational functions EXAMPLE 37 Graph y = f () = +3 3 lude both vertical and horizontal asymptotes SOLUTION First
Graphing Rational Functions Let s use all of the material we have developed to graph some rational functions EXAMPLE 37 Graph y = f () = +3 3 lude both vertical and horizontal asymptotes SOLUTION First
To do this which theorem did you use? b) Determine which points are inflections and mark the concavity on a number line for f.
 Math 13, Lab 11 1 a) Let f() = + 4 Determine which critical points are local maima, minima, and which are not etreme and mark this on a number line for b) Determine which points are inflections and mark
Math 13, Lab 11 1 a) Let f() = + 4 Determine which critical points are local maima, minima, and which are not etreme and mark this on a number line for b) Determine which points are inflections and mark
+ 2 on the interval [-1,3]
![+ 2 on the interval [-1,3] + 2 on the interval [-1,3]](/thumbs/89/98527152.jpg) Section.1 Etrema on an Interval 1. Understand the definition of etrema of a function on an interval.. Understand the definition of relative etrema of a function on an open interval.. Find etrema on a closed
Section.1 Etrema on an Interval 1. Understand the definition of etrema of a function on an interval.. Understand the definition of relative etrema of a function on an open interval.. Find etrema on a closed
3.1 ANALYSIS OF FUNCTIONS I INCREASE, DECREASE, AND CONCAVITY
 MATH00 (Calculus).1 ANALYSIS OF FUNCTIONS I INCREASE, DECREASE, AND CONCAVITY Name Group No. KEYWORD: increasing, decreasing, constant, concave up, concave down, and inflection point Eample 1. Match the
MATH00 (Calculus).1 ANALYSIS OF FUNCTIONS I INCREASE, DECREASE, AND CONCAVITY Name Group No. KEYWORD: increasing, decreasing, constant, concave up, concave down, and inflection point Eample 1. Match the
November 13, 2018 MAT186 Week 8 Justin Ko
 1 Mean Value Theorem Theorem 1 (Mean Value Theorem). Let f be a continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b). There eists a c (a, b) such that f f(b) f(a) (c) =. b a Eample 1: The Mean Value Theorem
1 Mean Value Theorem Theorem 1 (Mean Value Theorem). Let f be a continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b). There eists a c (a, b) such that f f(b) f(a) (c) =. b a Eample 1: The Mean Value Theorem
Math 1314 Lesson 13: Analyzing Other Types of Functions
 Math 1314 Lesson 13: Analyzing Other Types of Functions If the function you need to analyze is something other than a polynomial function, you will have some other types of information to find and some
Math 1314 Lesson 13: Analyzing Other Types of Functions If the function you need to analyze is something other than a polynomial function, you will have some other types of information to find and some
Review Guideline for Final
 Review Guideline for Final Here is the outline of the required skills for the final exam. Please read it carefully and find some corresponding homework problems in the corresponding sections to practice.
Review Guideline for Final Here is the outline of the required skills for the final exam. Please read it carefully and find some corresponding homework problems in the corresponding sections to practice.
UNIT 3. Rational Functions Limits at Infinity (Horizontal and Slant Asymptotes) Infinite Limits (Vertical Asymptotes) Graphing Rational Functions
 UNIT 3 Rational Functions Limits at Infinity (Horizontal and Slant Asymptotes) Infinite Limits (Vertical Asymptotes) Graphing Rational Functions Recall From Unit Rational Functions f() is a rational function
UNIT 3 Rational Functions Limits at Infinity (Horizontal and Slant Asymptotes) Infinite Limits (Vertical Asymptotes) Graphing Rational Functions Recall From Unit Rational Functions f() is a rational function
MATH 1325 Business Calculus Guided Notes
 MATH 135 Business Calculus Guided Notes LSC North Harris By Isabella Fisher Section.1 Functions and Theirs Graphs A is a rule that assigns to each element in one and only one element in. Set A Set B Set
MATH 135 Business Calculus Guided Notes LSC North Harris By Isabella Fisher Section.1 Functions and Theirs Graphs A is a rule that assigns to each element in one and only one element in. Set A Set B Set
So, t = 1 is a point of inflection of s(). Use s () t to find the velocity at t = Because 0, use 144.
 AP Eam Practice Questions for Chapter AP Eam Practice Questions for Chapter f 4 + 6 7 9 f + 7 0 + 6 0 ( + )( ) 0,. The critical numbers of f( ) are and.. Evaluate each point. A: d d C: d d B: D: d d d
AP Eam Practice Questions for Chapter AP Eam Practice Questions for Chapter f 4 + 6 7 9 f + 7 0 + 6 0 ( + )( ) 0,. The critical numbers of f( ) are and.. Evaluate each point. A: d d C: d d B: D: d d d
Fundamental Theorem of Algebra (NEW): A polynomial function of degree n > 0 has n complex zeros. Some of these zeros may be repeated.
 .5 and.6 Comple Numbers, Comple Zeros and the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Pre Calculus.5 COMPLEX NUMBERS 1. Understand that - 1 is an imaginary number denoted by the letter i.. Evaluate the square root
.5 and.6 Comple Numbers, Comple Zeros and the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Pre Calculus.5 COMPLEX NUMBERS 1. Understand that - 1 is an imaginary number denoted by the letter i.. Evaluate the square root
MA Lesson 25 Notes Section 5.3 (2 nd half of textbook)
 MA 000 Lesson 5 Notes Section 5. ( nd half of tetbook) Higher Derivatives: In this lesson, we will find a derivative of a derivative. A second derivative is a derivative of the first derivative. A third
MA 000 Lesson 5 Notes Section 5. ( nd half of tetbook) Higher Derivatives: In this lesson, we will find a derivative of a derivative. A second derivative is a derivative of the first derivative. A third
AP Exam Practice Questions for Chapter 3
 AP Eam Practice Questions for Chapter AP Eam Practice Questions for Chapter f + 6 7 9 f + 7 0 + 6 0 ( + )( ) 0,. The critical numbers of f are and. So, the answer is B.. Evaluate each statement. I: Because
AP Eam Practice Questions for Chapter AP Eam Practice Questions for Chapter f + 6 7 9 f + 7 0 + 6 0 ( + )( ) 0,. The critical numbers of f are and. So, the answer is B.. Evaluate each statement. I: Because
Section 3.3 Limits Involving Infinity - Asymptotes
 76 Section. Limits Involving Infinity - Asymptotes We begin our discussion with analyzing its as increases or decreases without bound. We will then eplore functions that have its at infinity. Let s consider
76 Section. Limits Involving Infinity - Asymptotes We begin our discussion with analyzing its as increases or decreases without bound. We will then eplore functions that have its at infinity. Let s consider
Asymptotes are additional pieces of information essential for curve sketching.
 Mathematics 00a Summary Notes page 57 4. Curve Sketching Asymptotes are additional pieces of information essential for curve sketching. Vertical Asymptotes The line a is a vertical asymptote of the graph
Mathematics 00a Summary Notes page 57 4. Curve Sketching Asymptotes are additional pieces of information essential for curve sketching. Vertical Asymptotes The line a is a vertical asymptote of the graph
PACKET Unit 4 Honors ICM Functions and Limits 1
 PACKET Unit 4 Honors ICM Functions and Limits 1 Day 1 Homework For each of the rational functions find: a. domain b. -intercept(s) c. y-intercept Graph #8 and #10 with at least 5 EXACT points. 1. f 6.
PACKET Unit 4 Honors ICM Functions and Limits 1 Day 1 Homework For each of the rational functions find: a. domain b. -intercept(s) c. y-intercept Graph #8 and #10 with at least 5 EXACT points. 1. f 6.
Solutions Exam 4 (Applications of Differentiation) 1. a. Applying the Quotient Rule we compute the derivative function of f as follows:
 MAT 4 Solutions Eam 4 (Applications of Differentiation) a Applying the Quotient Rule we compute the derivative function of f as follows: f () = 43 e 4 e (e ) = 43 4 e = 3 (4 ) e Hence f '( ) 0 for = 0
MAT 4 Solutions Eam 4 (Applications of Differentiation) a Applying the Quotient Rule we compute the derivative function of f as follows: f () = 43 e 4 e (e ) = 43 4 e = 3 (4 ) e Hence f '( ) 0 for = 0
Work the following on notebook paper. You may use your calculator to find
 CALCULUS WORKSHEET ON 3.1 Work the following on notebook paper. You may use your calculator to find f values. 1. For each of the labeled points, state whether the function whose graph is shown has an absolute
CALCULUS WORKSHEET ON 3.1 Work the following on notebook paper. You may use your calculator to find f values. 1. For each of the labeled points, state whether the function whose graph is shown has an absolute
Math 108, Solution of Midterm Exam 3
 Math 108, Solution of Midterm Exam 3 1 Find an equation of the tangent line to the curve x 3 +y 3 = xy at the point (1,1). Solution. Differentiating both sides of the given equation with respect to x,
Math 108, Solution of Midterm Exam 3 1 Find an equation of the tangent line to the curve x 3 +y 3 = xy at the point (1,1). Solution. Differentiating both sides of the given equation with respect to x,
UNIT 3. Recall From Unit 2 Rational Functions
 UNIT 3 Recall From Unit Rational Functions f() is a rational function if where p() and q() are and. Rational functions often approach for values of. Rational Functions are not graphs There various types
UNIT 3 Recall From Unit Rational Functions f() is a rational function if where p() and q() are and. Rational functions often approach for values of. Rational Functions are not graphs There various types
Chapter 3.5: Rational Functions
 Chapter.5: Rational Functions A rational number is a ratio of two integers. A rational function is a quotient of two polynomials. All rational numbers are, therefore, rational functions as well. Let s
Chapter.5: Rational Functions A rational number is a ratio of two integers. A rational function is a quotient of two polynomials. All rational numbers are, therefore, rational functions as well. Let s
x π. Determine all open interval(s) on which f is decreasing
 Calculus Maimus Increasing, Decreasing, and st Derivative Test Show all work. No calculator unless otherwise stated. Multiple Choice = /5 + _ /5 over. Determine the increasing and decreasing open intervals
Calculus Maimus Increasing, Decreasing, and st Derivative Test Show all work. No calculator unless otherwise stated. Multiple Choice = /5 + _ /5 over. Determine the increasing and decreasing open intervals
MATH section 4.4 Concavity and Curve Sketching Page 1. is increasing on I. is decreasing on I. = or. x c
 MATH 0100 section 4.4 Concavity and Curve Sketching Page 1 Definition: The graph of a differentiable function y = (a) concave up on an open interval I if df f( x) (b) concave down on an open interval I
MATH 0100 section 4.4 Concavity and Curve Sketching Page 1 Definition: The graph of a differentiable function y = (a) concave up on an open interval I if df f( x) (b) concave down on an open interval I
of multiplicity two. The sign of the polynomial is shown in the table below
 161 Precalculus 1 Review 5 Problem 1 Graph the polynomial function P( ) ( ) ( 1). Solution The polynomial is of degree 4 and therefore it is positive to the left of its smallest real root and to the right
161 Precalculus 1 Review 5 Problem 1 Graph the polynomial function P( ) ( ) ( 1). Solution The polynomial is of degree 4 and therefore it is positive to the left of its smallest real root and to the right
MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND
 MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS FINAL EXAMINATION Solutions Mathematics 1000 FALL 2010 Marks [12] 1. Evaluate the following limits, showing your work. Assign
MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS FINAL EXAMINATION Solutions Mathematics 1000 FALL 2010 Marks [12] 1. Evaluate the following limits, showing your work. Assign
The First Derivative Test for Rise and Fall Suppose that a function f has a derivative at every poin x of an interval A. Then
 Derivatives - Applications - c CNMiKnO PG - 1 Increasing and Decreasing Functions A function y = f(x) is said to increase throughout an interval A if y increases as x increases. That is, whenever x 2 >
Derivatives - Applications - c CNMiKnO PG - 1 Increasing and Decreasing Functions A function y = f(x) is said to increase throughout an interval A if y increases as x increases. That is, whenever x 2 >
Section 4.3 Concavity and Curve Sketching 1.5 Lectures. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 4.3 Concavity and Curve Sketching 1.5 Lectures College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Concavity 1 / 29 Concavity Increasing Function has three cases (University of Bahrain)
Section 4.3 Concavity and Curve Sketching 1.5 Lectures College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Concavity 1 / 29 Concavity Increasing Function has three cases (University of Bahrain)
Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule
 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule In this section, we will learn: How to evaluate functions whose values cannot be found at certain points. INDETERMINATE FORM TYPE
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule In this section, we will learn: How to evaluate functions whose values cannot be found at certain points. INDETERMINATE FORM TYPE
1. Find all critical numbers of the function. 2. Find any critical numbers of the function.
 1. Find all critical numbers of the function. a. critical numbers: *b. critical numbers: c. critical numbers: d. critical numbers: e. no critical numbers 2. Find any critical numbers of the function. a.
1. Find all critical numbers of the function. a. critical numbers: *b. critical numbers: c. critical numbers: d. critical numbers: e. no critical numbers 2. Find any critical numbers of the function. a.
1.2 Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus
 1. Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus 1. FUNCTIONS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Learning Targets for 1. 1. Determine whether a set of numbers or a graph is a function. Find the domain of a function given
1. Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus 1. FUNCTIONS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Learning Targets for 1. 1. Determine whether a set of numbers or a graph is a function. Find the domain of a function given
If C(x) is the total cost (in dollars) of producing x items of a product, then
 Supplemental Review Problems for Unit Test : 1 Marginal Analysis (Sec 7) Be prepared to calculate total revenue given the price - demand function; to calculate total profit given total revenue and total
Supplemental Review Problems for Unit Test : 1 Marginal Analysis (Sec 7) Be prepared to calculate total revenue given the price - demand function; to calculate total profit given total revenue and total
4.3 How derivatives affect the shape of a graph. The first derivative test and the second derivative test.
 Chapter 4: Applications of Differentiation In this chapter we will cover: 41 Maimum and minimum values The critical points method for finding etrema 43 How derivatives affect the shape of a graph The first
Chapter 4: Applications of Differentiation In this chapter we will cover: 41 Maimum and minimum values The critical points method for finding etrema 43 How derivatives affect the shape of a graph The first
4. (6 points) Express the domain of the following function in interval notation:
 Eam 1-A L. Ballou Name Math 131 Calculus I September 1, 016 NO Calculator Allowed BOX YOUR ANSWER! Show all work for full credit! 1. (4 points) Write an equation of a line with y-intercept 4 and -intercept
Eam 1-A L. Ballou Name Math 131 Calculus I September 1, 016 NO Calculator Allowed BOX YOUR ANSWER! Show all work for full credit! 1. (4 points) Write an equation of a line with y-intercept 4 and -intercept
Graphing Rational Functions KEY. (x 4) (x + 2) Factor denominator. y = 0 x = 4, x = -2
 6 ( 6) Factor numerator 1) f ( ) 8 ( 4) ( + ) Factor denominator n() is of degree: 1 -intercepts: d() is of degree: 6 y 0 4, - Plot the -intercepts. Draw the asymptotes with dotted lines. Then perform
6 ( 6) Factor numerator 1) f ( ) 8 ( 4) ( + ) Factor denominator n() is of degree: 1 -intercepts: d() is of degree: 6 y 0 4, - Plot the -intercepts. Draw the asymptotes with dotted lines. Then perform
Pre-Calculus Module 4
 Pre-Calculus Module 4 4 th Nine Weeks Table of Contents Precalculus Module 4 Unit 9 Rational Functions Rational Functions with Removable Discontinuities (1 5) End Behavior of Rational Functions (6) Rational
Pre-Calculus Module 4 4 th Nine Weeks Table of Contents Precalculus Module 4 Unit 9 Rational Functions Rational Functions with Removable Discontinuities (1 5) End Behavior of Rational Functions (6) Rational
1.2 Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus
 1. Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus 1. FUNCTIONS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Learning Targets for 1. 1. Determine whether a set of numbers or a graph is a function. Find the domain of a function given
1. Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus 1. FUNCTIONS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Learning Targets for 1. 1. Determine whether a set of numbers or a graph is a function. Find the domain of a function given
Math 180, Final Exam, Spring 2008 Problem 1 Solution. 1. For each of the following limits, determine whether the limit exists and, if so, evaluate it.
 Math 80, Final Eam, Spring 008 Problem Solution. For each of the following limits, determine whether the limit eists and, if so, evaluate it. + (a) lim 0 (b) lim ( ) 3 (c) lim Solution: (a) Upon substituting
Math 80, Final Eam, Spring 008 Problem Solution. For each of the following limits, determine whether the limit eists and, if so, evaluate it. + (a) lim 0 (b) lim ( ) 3 (c) lim Solution: (a) Upon substituting
Suppose that f is continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b). Then
![Suppose that f is continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b). Then Suppose that f is continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b). Then](/thumbs/74/71325034.jpg) Lectures 1/18 Derivatives and Graphs When we have a picture of the graph of a function f(x), we can make a picture of the derivative f (x) using the slopes of the tangents to the graph of f. In this section
Lectures 1/18 Derivatives and Graphs When we have a picture of the graph of a function f(x), we can make a picture of the derivative f (x) using the slopes of the tangents to the graph of f. In this section
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment
 AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Name: When you come back to school, it is my epectation that you will have this packet completed. You will be way behind at the beginning of the year if you haven t attempted
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Name: When you come back to school, it is my epectation that you will have this packet completed. You will be way behind at the beginning of the year if you haven t attempted
QUIZ ON CHAPTER 4 APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES; MATH 150 FALL 2016 KUNIYUKI 105 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 100 POINTS
 Math 150 Name: QUIZ ON CHAPTER 4 APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES; MATH 150 FALL 2016 KUNIYUKI 105 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 100 POINTS = 100% Show all work, simplify as appropriate, and use good form and procedure
Math 150 Name: QUIZ ON CHAPTER 4 APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES; MATH 150 FALL 2016 KUNIYUKI 105 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 100 POINTS = 100% Show all work, simplify as appropriate, and use good form and procedure
term from the numerator yields 2
 APPM 1350 Eam 2 Fall 2013 1. The following parts are not related: (a) (12 pts) Find y given: (i) y = (ii) y = sec( 2 1) tan() (iii) ( 2 + y 2 ) 2 = 2 2 2y 2 1 (b) (8 pts) Let f() be a function such that
APPM 1350 Eam 2 Fall 2013 1. The following parts are not related: (a) (12 pts) Find y given: (i) y = (ii) y = sec( 2 1) tan() (iii) ( 2 + y 2 ) 2 = 2 2 2y 2 1 (b) (8 pts) Let f() be a function such that
Introduction. A rational function is a quotient of polynomial functions. It can be written in the form
 RATIONAL FUNCTIONS Introduction A rational function is a quotient of polynomial functions. It can be written in the form where N(x) and D(x) are polynomials and D(x) is not the zero polynomial. 2 In general,
RATIONAL FUNCTIONS Introduction A rational function is a quotient of polynomial functions. It can be written in the form where N(x) and D(x) are polynomials and D(x) is not the zero polynomial. 2 In general,
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment
 AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Name: When you come back to school, you will be epected to have attempted every problem. These skills are all different tools that you will pull out of your toolbo this
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Name: When you come back to school, you will be epected to have attempted every problem. These skills are all different tools that you will pull out of your toolbo this
4.3 Mean-Value Theorem and Monotonicity
 .3 Mean-Value Theorem and Monotonicit 1. Mean Value Theorem Theorem: Suppose that f is continuous on the interval a, b and differentiable on the interval a, b. Then there eists a number c in a, b such
.3 Mean-Value Theorem and Monotonicit 1. Mean Value Theorem Theorem: Suppose that f is continuous on the interval a, b and differentiable on the interval a, b. Then there eists a number c in a, b such
Things to remember: x n a 1. x + a 0. x n + a n-1. P(x) = a n. Therefore, lim g(x) = 1. EXERCISE 3-2
 lim f() = lim (0.8-0.08) = 0, " "!10!10 lim f() = lim 0 = 0.!10!10 Therefore, lim f() = 0.!10 lim g() = lim (0.8 - "!10!10 0.042-3) = 1, " lim g() = lim 1 = 1.!10!0 Therefore, lim g() = 1.!10 EXERCISE
lim f() = lim (0.8-0.08) = 0, " "!10!10 lim f() = lim 0 = 0.!10!10 Therefore, lim f() = 0.!10 lim g() = lim (0.8 - "!10!10 0.042-3) = 1, " lim g() = lim 1 = 1.!10!0 Therefore, lim g() = 1.!10 EXERCISE
Section 3.4: Concavity and the second Derivative Test. Find any points of inflection of the graph of a function.
 Unit 3: Applications o Dierentiation Section 3.4: Concavity and the second Derivative Test Determine intervals on which a unction is concave upward or concave downward. Find any points o inlection o the
Unit 3: Applications o Dierentiation Section 3.4: Concavity and the second Derivative Test Determine intervals on which a unction is concave upward or concave downward. Find any points o inlection o the
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 7 The Quadratic Function (Vertex Form): Translations. and axis of symmetry is at x a.
 Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 7 Verte form of Quadratic Relations The epression a p q defines a quadratic relation called the verte form with a horizontal translation of p units and vertical translation of
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 7 Verte form of Quadratic Relations The epression a p q defines a quadratic relation called the verte form with a horizontal translation of p units and vertical translation of
MA 137 Calculus 1 with Life Science Applications Monotonicity and Concavity (Section 5.2) Extrema, Inflection Points, and Graphing (Section 5.
 MA 137 Calculus 1 with Life Science Applications Monotonicity and Concavity (Section 52) Extrema, Inflection Points, and Graphing (Section 53) Alberto Corso albertocorso@ukyedu Department of Mathematics
MA 137 Calculus 1 with Life Science Applications Monotonicity and Concavity (Section 52) Extrema, Inflection Points, and Graphing (Section 53) Alberto Corso albertocorso@ukyedu Department of Mathematics
3.1 Power Functions & Polynomial Functions
 3.1 Power Functions & Polynomial Functions A power function is a function that can be represented in the form f() = p, where the base is a variable and the eponent, p, is a number. The Effect of the Power
3.1 Power Functions & Polynomial Functions A power function is a function that can be represented in the form f() = p, where the base is a variable and the eponent, p, is a number. The Effect of the Power
Math 75B Practice Problems for Midterm II Solutions Ch. 16, 17, 12 (E), , 2.8 (S)
 Math 75B Practice Problems for Midterm II Solutions Ch. 6, 7, 2 (E),.-.5, 2.8 (S) DISCLAIMER. This collection of practice problems is not guaranteed to be identical, in length or content, to the actual
Math 75B Practice Problems for Midterm II Solutions Ch. 6, 7, 2 (E),.-.5, 2.8 (S) DISCLAIMER. This collection of practice problems is not guaranteed to be identical, in length or content, to the actual
Calculus 1st Semester Final Review
 Calculus st Semester Final Review Use the graph to find lim f ( ) (if it eists) 0 9 Determine the value of c so that f() is continuous on the entire real line if f ( ), c /, > 0 Find the limit: lim 6+
Calculus st Semester Final Review Use the graph to find lim f ( ) (if it eists) 0 9 Determine the value of c so that f() is continuous on the entire real line if f ( ), c /, > 0 Find the limit: lim 6+
Unit 5: Applications of Differentiation
 Unit 5: Applications of Differentiation DAY TOPIC ASSIGNMENT 1 Implicit Differentiation (p. 1) p. 7-73 Implicit Differentiation p. 74-75 3 Implicit Differentiation Review 4 QUIZ 1 5 Related Rates (p. 8)
Unit 5: Applications of Differentiation DAY TOPIC ASSIGNMENT 1 Implicit Differentiation (p. 1) p. 7-73 Implicit Differentiation p. 74-75 3 Implicit Differentiation Review 4 QUIZ 1 5 Related Rates (p. 8)
MATH140 Exam 2 - Sample Test 1 Detailed Solutions
 www.liontutors.com 1. D. reate a first derivative number line MATH140 Eam - Sample Test 1 Detailed Solutions cos -1 0 cos -1 cos 1 cos 1/ p + æp ö p æp ö ç è 4 ø ç è ø.. reate a second derivative number
www.liontutors.com 1. D. reate a first derivative number line MATH140 Eam - Sample Test 1 Detailed Solutions cos -1 0 cos -1 cos 1 cos 1/ p + æp ö p æp ö ç è 4 ø ç è ø.. reate a second derivative number
5.6 Asymptotes; Checking Behavior at Infinity
 5.6 Asymptotes; Checking Behavior at Infinity checking behavior at infinity DEFINITION asymptote In this section, the notion of checking behavior at infinity is made precise, by discussing both asymptotes
5.6 Asymptotes; Checking Behavior at Infinity checking behavior at infinity DEFINITION asymptote In this section, the notion of checking behavior at infinity is made precise, by discussing both asymptotes
The First Derivative Test
 The First Derivative Test We have already looked at this test in the last section even though we did not put a name to the process we were using. We use a y number line to test the sign of the first derivative
The First Derivative Test We have already looked at this test in the last section even though we did not put a name to the process we were using. We use a y number line to test the sign of the first derivative
1. Find the domain of the following functions. Write your answer using interval notation. (9 pts.)
 MATH- Sample Eam Spring 7. Find the domain of the following functions. Write your answer using interval notation. (9 pts.) a. 9 f ( ) b. g ( ) 9 8 8. Write the equation of the circle in standard form given
MATH- Sample Eam Spring 7. Find the domain of the following functions. Write your answer using interval notation. (9 pts.) a. 9 f ( ) b. g ( ) 9 8 8. Write the equation of the circle in standard form given
What makes f '(x) undefined? (set the denominator = 0)
 Chapter 3A Review 1. Find all critical numbers for the function ** Critical numbers find the first derivative and then find what makes f '(x) = 0 or undefined Q: What is the domain of this function (especially
Chapter 3A Review 1. Find all critical numbers for the function ** Critical numbers find the first derivative and then find what makes f '(x) = 0 or undefined Q: What is the domain of this function (especially
Limits and Their Properties
 Chapter 1 Limits and Their Properties Course Number Section 1.1 A Preview of Calculus Objective: In this lesson you learned how calculus compares with precalculus. I. What is Calculus? (Pages 42 44) Calculus
Chapter 1 Limits and Their Properties Course Number Section 1.1 A Preview of Calculus Objective: In this lesson you learned how calculus compares with precalculus. I. What is Calculus? (Pages 42 44) Calculus
(d by dx notation aka Leibniz notation)
 n Prerequisites: Differentiating, sin and cos ; sum/difference and chain rules; finding ma./min.; finding tangents to curves; finding stationary points and their nature; optimising a function. Maths Applications:
n Prerequisites: Differentiating, sin and cos ; sum/difference and chain rules; finding ma./min.; finding tangents to curves; finding stationary points and their nature; optimising a function. Maths Applications:
Section 5-1 First Derivatives and Graphs
 Name Date Class Section 5-1 First Derivatives and Graphs Goal: To use the first derivative to analyze graphs Theorem 1: Increasing and Decreasing Functions For the interval (a,b), if f '( x ) > 0, then
Name Date Class Section 5-1 First Derivatives and Graphs Goal: To use the first derivative to analyze graphs Theorem 1: Increasing and Decreasing Functions For the interval (a,b), if f '( x ) > 0, then
Extrema and the Extreme Value Theorem
 Extrema and the Extreme Value Theorem Local and Absolute Extrema. Extrema are the points where we will find a maximum or minimum on the curve. If they are local or relative extrema, then they will be the
Extrema and the Extreme Value Theorem Local and Absolute Extrema. Extrema are the points where we will find a maximum or minimum on the curve. If they are local or relative extrema, then they will be the
( ) = 1 x. g( x) = x3 +2
 Rational Functions are ratios (quotients) of polynomials, written in the form f x N ( x ) and D x ( ) are polynomials, and D x ( ) does not equal zero. The parent function for rational functions is f x
Rational Functions are ratios (quotients) of polynomials, written in the form f x N ( x ) and D x ( ) are polynomials, and D x ( ) does not equal zero. The parent function for rational functions is f x
AP CALCULUS AB Study Guide for Midterm Exam 2017
 AP CALCULUS AB Study Guide for Midterm Exam 2017 CHAPTER 1: PRECALCULUS REVIEW 1.1 Real Numbers, Functions and Graphs - Write absolute value as a piece-wise function - Write and interpret open and closed
AP CALCULUS AB Study Guide for Midterm Exam 2017 CHAPTER 1: PRECALCULUS REVIEW 1.1 Real Numbers, Functions and Graphs - Write absolute value as a piece-wise function - Write and interpret open and closed
The Detective s Hat Function
 The Detective s Hat Function (,) (,) (,) (,) (, ) (4, ) The graph of the function f shown above is a piecewise continuous function defined on [, 4]. The graph of f consists of five line segments. Let g
The Detective s Hat Function (,) (,) (,) (,) (, ) (4, ) The graph of the function f shown above is a piecewise continuous function defined on [, 4]. The graph of f consists of five line segments. Let g
MTH 241: Business and Social Sciences Calculus
 MTH 241: Business and Social Sciences Calculus F. Patricia Medina Department of Mathematics. Oregon State University January 28, 2015 Section 2.1 Increasing and decreasing Definition 1 A function is increasing
MTH 241: Business and Social Sciences Calculus F. Patricia Medina Department of Mathematics. Oregon State University January 28, 2015 Section 2.1 Increasing and decreasing Definition 1 A function is increasing
Math 1120, Section 1 Calculus Final Exam
 May 7, 2014 Name Each of the first 17 problems are worth 10 points The other problems are marked The total number of points available is 285 Throughout the free response part of this test, to get credit
May 7, 2014 Name Each of the first 17 problems are worth 10 points The other problems are marked The total number of points available is 285 Throughout the free response part of this test, to get credit
4.3 Exercises. local maximum or minimum. The second derivative is. e 1 x 2x 1. f x x 2 e 1 x 1 x 2 e 1 x 2x x 4
 SECTION 4.3 HOW DERIVATIVES AFFECT THE SHAPE OF A GRAPH 297 local maimum or minimum. The second derivative is f 2 e 2 e 2 4 e 2 4 Since e and 4, we have f when and when 2 f. So the curve is concave downward
SECTION 4.3 HOW DERIVATIVES AFFECT THE SHAPE OF A GRAPH 297 local maimum or minimum. The second derivative is f 2 e 2 e 2 4 e 2 4 Since e and 4, we have f when and when 2 f. So the curve is concave downward
4.3 Division of Polynomials
 4.3 Division of Polynomials Learning Objectives Divide a polynomials by a monomial. Divide a polynomial by a binomial. Rewrite and graph rational functions. Introduction A rational epression is formed
4.3 Division of Polynomials Learning Objectives Divide a polynomials by a monomial. Divide a polynomial by a binomial. Rewrite and graph rational functions. Introduction A rational epression is formed
MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 20
 official website http://uoft.me/mat137 MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 20 Today: 4.6 Concavity 4.7 Asypmtotes Next: 4.8 Curve Sketching Indeterminate Forms for Limits Which of the following are indeterminate
official website http://uoft.me/mat137 MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 20 Today: 4.6 Concavity 4.7 Asypmtotes Next: 4.8 Curve Sketching Indeterminate Forms for Limits Which of the following are indeterminate
Review: Limits of Functions - 10/7/16
 Review: Limits of Functions - 10/7/16 1 Right and Left Hand Limits Definition 1.0.1 We write lim a f() = L to mean that the function f() approaches L as approaches a from the left. We call this the left
Review: Limits of Functions - 10/7/16 1 Right and Left Hand Limits Definition 1.0.1 We write lim a f() = L to mean that the function f() approaches L as approaches a from the left. We call this the left
Absolute and Local Extrema. Critical Points In the proof of Rolle s Theorem, we actually demonstrated the following
 Absolute and Local Extrema Definition 1 (Absolute Maximum). A function f has an absolute maximum at c S if f(x) f(c) x S. We call f(c) the absolute maximum of f on S. Definition 2 (Local Maximum). A function
Absolute and Local Extrema Definition 1 (Absolute Maximum). A function f has an absolute maximum at c S if f(x) f(c) x S. We call f(c) the absolute maximum of f on S. Definition 2 (Local Maximum). A function
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval................... 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem...... 0 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval................... 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem...... 0 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and
Quick Review 4.1 (For help, go to Sections 1.2, 2.1, 3.5, and 3.6.)
 Section 4. Etreme Values of Functions 93 EXPLORATION Finding Etreme Values Let f,.. Determine graphicall the etreme values of f and where the occur. Find f at these values of.. Graph f and f or NDER f,,
Section 4. Etreme Values of Functions 93 EXPLORATION Finding Etreme Values Let f,.. Determine graphicall the etreme values of f and where the occur. Find f at these values of.. Graph f and f or NDER f,,
lim 2 x lim lim sin 3 (9) l)
 MAC FINAL EXAM REVIEW. Find each of the following its if it eists, a) ( 5). (7) b). c). ( 5 ) d). () (/) e) (/) f) (-) sin g) () h) 5 5 5. DNE i) (/) j) (-/) 7 8 k) m) ( ) (9) l) n) sin sin( ) 7 o) DNE
MAC FINAL EXAM REVIEW. Find each of the following its if it eists, a) ( 5). (7) b). c). ( 5 ) d). () (/) e) (/) f) (-) sin g) () h) 5 5 5. DNE i) (/) j) (-/) 7 8 k) m) ( ) (9) l) n) sin sin( ) 7 o) DNE
APPM 1345, Fall 2013: Exam 1 September 25, 2013
 APPM 1345, Fall 2013: Eam 1 September 25, 2013 Instructions: Please show all of our work and make our methods and reasoning clear. Answers out of the blue with no supporting work will receive no credit.
APPM 1345, Fall 2013: Eam 1 September 25, 2013 Instructions: Please show all of our work and make our methods and reasoning clear. Answers out of the blue with no supporting work will receive no credit.
AP Calculus AB. Chapter IV Lesson B. Curve Sketching
 AP Calculus AB Chapter IV Lesson B Curve Sketching local maxima Absolute maximum F I A B E G C J Absolute H K minimum D local minima Summary of trip along curve critical points occur where the derivative
AP Calculus AB Chapter IV Lesson B Curve Sketching local maxima Absolute maximum F I A B E G C J Absolute H K minimum D local minima Summary of trip along curve critical points occur where the derivative
1/100 Range: 1/10 1/ 2. 1) Constant: choose a value for the constant that can be graphed on the coordinate grid below.
 Name 1) Constant: choose a value or the constant that can be graphed on the coordinate grid below a y Toolkit Functions Lab Worksheet thru inverse trig ) Identity: y ) Reciprocal: 1 ( ) y / 1/ 1/1 1/ 1
Name 1) Constant: choose a value or the constant that can be graphed on the coordinate grid below a y Toolkit Functions Lab Worksheet thru inverse trig ) Identity: y ) Reciprocal: 1 ( ) y / 1/ 1/1 1/ 1
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 7 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 7 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative
Example 1a ~ Like # 1-39
 Example 1a ~ Like # 1-39 f(x) = A. The domain is {x x 2 1 0} = {x x 1} DOM: (, 1) ( 1, 1) (1, ) B. The x- and y-intercepts are both 0. C. Since f( x) = f(x), the function f is even. The curve is symmetric
Example 1a ~ Like # 1-39 f(x) = A. The domain is {x x 2 1 0} = {x x 1} DOM: (, 1) ( 1, 1) (1, ) B. The x- and y-intercepts are both 0. C. Since f( x) = f(x), the function f is even. The curve is symmetric
Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 119 Mark Sparks 2012
 Unit # Understanding the Derivative Homework Packet f ( h) f ( Find lim for each of the functions below. Then, find the equation of the tangent line to h 0 h the graph of f( at the given value of. 1. f
Unit # Understanding the Derivative Homework Packet f ( h) f ( Find lim for each of the functions below. Then, find the equation of the tangent line to h 0 h the graph of f( at the given value of. 1. f
MATH 152 FINAL EXAMINATION Spring Semester 2014
 Math 15 Final Eam Spring 1 MATH 15 FINAL EXAMINATION Spring Semester 1 NAME: RAW SCORE: Maimum raw score possible is 8. INSTRUCTOR: SECTION NUMBER: MAKE and MODEL of CALCULATOR USED: Answers are to be
Math 15 Final Eam Spring 1 MATH 15 FINAL EXAMINATION Spring Semester 1 NAME: RAW SCORE: Maimum raw score possible is 8. INSTRUCTOR: SECTION NUMBER: MAKE and MODEL of CALCULATOR USED: Answers are to be
Section 1.1: A Preview of Calculus When you finish your homework, you should be able to
 Section 1.1: A Preview of Calculus When you finish your homework, you should be able to π Understand what calculus is and how it compares with precalculus π Understand that the tangent line problem is
Section 1.1: A Preview of Calculus When you finish your homework, you should be able to π Understand what calculus is and how it compares with precalculus π Understand that the tangent line problem is
Math 1500 Fall 2010 Final Exam Review Solutions
 Math 500 Fall 00 Final Eam Review Solutions. Verify that the function f() = 4 + on the interval [, 5] satisfies the hypotheses of the Mean Value Theorem on the given interval. Then find all numbers c that
Math 500 Fall 00 Final Eam Review Solutions. Verify that the function f() = 4 + on the interval [, 5] satisfies the hypotheses of the Mean Value Theorem on the given interval. Then find all numbers c that
Math 1314 Lesson 12 Curve Sketching
 Math 1314 Lesson 12 Curve Sketching One of our objectives in this part of the course is to be able to graph functions. In this lesson, we ll add to some tools we already have to be able to sketch an accurate
Math 1314 Lesson 12 Curve Sketching One of our objectives in this part of the course is to be able to graph functions. In this lesson, we ll add to some tools we already have to be able to sketch an accurate
Unit 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 50 Unit 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions Polynomial Functions A polynomial function y p() is a function of the form p( ) a a a... a a a n n n n n n 0 where an, an,..., a, a, a0 are real constants and
50 Unit 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions Polynomial Functions A polynomial function y p() is a function of the form p( ) a a a... a a a n n n n n n 0 where an, an,..., a, a, a0 are real constants and
Student s Printed Name:
 MATH 1060 Test 1 Fall 018 Calculus of One Variable I Version B KEY Sections 1.3 3. Student s Printed Name: Instructor: XID: C Section: No questions will be answered during this eam. If you consider a question
MATH 1060 Test 1 Fall 018 Calculus of One Variable I Version B KEY Sections 1.3 3. Student s Printed Name: Instructor: XID: C Section: No questions will be answered during this eam. If you consider a question
4.3 How Derivatives Aect the Shape of a Graph
 11/3/2010 What does f say about f? Increasing/Decreasing Test Fact Increasing/Decreasing Test Fact If f '(x) > 0 on an interval, then f interval. is increasing on that Increasing/Decreasing Test Fact If
11/3/2010 What does f say about f? Increasing/Decreasing Test Fact Increasing/Decreasing Test Fact If f '(x) > 0 on an interval, then f interval. is increasing on that Increasing/Decreasing Test Fact If
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 07 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 07 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
AP Calculus Review Assignment Answer Sheet 1. Name: Date: Per. Harton Spring Break Packet 2015
 AP Calculus Review Assignment Answer Sheet 1 Name: Date: Per. Harton Spring Break Packet 015 This is an AP Calc Review packet. As we get closer to the eam, it is time to start reviewing old concepts. Use
AP Calculus Review Assignment Answer Sheet 1 Name: Date: Per. Harton Spring Break Packet 015 This is an AP Calc Review packet. As we get closer to the eam, it is time to start reviewing old concepts. Use
