Theoretical study of two-element array of equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate
|
|
|
- Milton Booth
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 3 journal of September 2005 physics pp Theoretical study of two-element array of equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate K K VERMA and K R SONI Microwave Laboratory, Department of Physics, Malaviya National Institute of Technology, Jaipur , India kkvermaphd@rediffmail.com MS received 6 November 2004; revised 11 April 2005; accepted 28 April 2005 Abstract. The radiation characteristics of a two-element array of equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on a ferrite substrate are studied theoretically by considering the presence of bias magnetic field in the direction of propagation of electromagnetic waves. It is found that the natural modes of propagation in the direction of magnetic field are left- and right-circularly polarized waves and these modes have different propagation constants. In loss-less isotropic warm plasma, this array antenna geometry excites both electromagnetic (EM) and electroacoustic plasma (P) waves in addition to a nonradiating surface wave. In the absence of an external magnetic field, the EM- and P-waves can be decoupled into two independent modes, the electroacoustic mode is longitudinal while the electromagnetic mode is transverse. The far-zone EM-mode and P-mode radiation fields are derived using vector wave function techniques and pattern multiplication approaches. The results are obtained in both plasma medium and free space. Some important antenna parameters such as radiation conductance, directivity and quality factor are plotted for different values of plasma-to-source frequency. Keywords. Microstrip array antenna; ferrite substrate; radiation properties; plasma. PACS Nos Ba; Fd 1. Introduction In recent years, ferrite substrates have been the subject of much interest for microstrip patch antennas and their arrays. The high dielectric constant of the ferrite substrates reduces the antenna dimensions and when biased with a DC magnetic field, the antenna exhibits a number of novel properties. These include frequency tuning agility, the generation of circular polarization, reduction of surface waves and radar cross-section control. Ferrite materials are also used to generate beam scanning antennas. Microstrip antennas mounted on aerospace vehicles encounter plasma medium during their travel in space, as a result of which radiation properties are altered significantly. This change is caused due to the generation of electroacoustic (P) waves in addition to electromagnetic (EM) waves [1 5]. 501
2 K K Verma and K R Soni Table 1. Design requirement and substrate characteristics of the ferrite substrate Ni 1.062Co 0.02Fe 1.948O 4. Design frequency (f) 1.0 GHz Relative permittivity (ε r) Dieletric loss tangent (tan δ e ) Magnetic loss tangent (tan δ m) Applied DC magnetic bias field (H 0 ) A/m Saturation magnetization (µ 0 M s ) 0.03 T Patch dimension (a) m Substrate thickness (h) m Gyromagnetic ratio (γ) rad /s T Ferrite and other magnetic materials have been extensively used in several microwave devices such as phase shifters, isolators, circulators, tunable filters, delay lines etc. Ferrite materials have a significant amount of anisotropy at microwave frequencies. This anisotropy gets induced by applying external DC magnetic field in ferrite or gyrotropic materials and brings about non-reciprocal behavior in them. This paper describes the radiation characteristics of a two-element array of equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on the ferrite substrate Ni Co 0.02 Fe O 4. Design requirement and substrate characteristics considered for this analysis are listed in table Radiation field expressions The top and side view of the configuration of array antenna is shown in figure 1. It consists of two identical triangular microstrip patch elements of arm length a, on a ferrite substrate Ni Co 0.02 Fe O 4 of thickness h and substrate permittivity ε r. The array elements are separated by a distance d and the progressive phase excitation difference between the patches is β 1. Each patch can be excited by a microstrip transmission line connected to the edge or by a coaxial line from the back at the plane φ = 0. We have considered the patch as a cavity which acts as a disc resonator. Among the various modes that may be excited in such a disc resonator, we have considered TM mn mode with respect to z-axis. Here n and m are the mode numbers associated with x and y directions respectively. The E z component of the field inside the cavity for dominant mode is given as E z = A 1,0, 1 [2 cos(2πx/ 3a + 2π/3) cos(2πy/3a) + cos(4πy/3a)]. (1) When the propagation of electromagnetic waves takes place along the direction of applied magnetic bias field, two plane wave modes the left-hand circularly polarized (LHCP) mode and the right-hand circularly polarized (RHCP) mode may exist. The magnetic properties of the ferrite substrate affect both these modes. Therefore, the effective permeability for right-hand circular polarization and lefthand circular polarization will be given as [6 8] µ effr = µ ω m ω 0 ω, (2) 502 Pramana J. Phys., Vol. 65, No. 3, September 2005
3 The radiation characteristics of a two-element array Figure 1. (a) 2D top view of the configuration of two-element triangular patch array microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate. (b) Side view of the configuration of two-element triangular patch microstrip array antenna on ferrite substrate. (c) 3D view of the configuration of two-element triangular patch microstrip array antenna on ferrite substrate. µ effl = µ ω m ω 0 + ω. (3) The expression of the resonant frequency of the considered equilateral triangular microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate in TM mn mode is given as f r = 2c µ 0 3a ε r µ eff. (4) Pramana J. Phys., Vol. 65, No. 3, September
4 K K Verma and K R Soni Other field components are obtained by solving Maxwell s equations. By image theory, the ground plane may be replaced by an image of the top conductor. The magnetic currents also exist along the edges of triangular conductor and may be evaluated from M = 2(E n), (5) where n is a unit vector normal to the aperture. Using linearized hydrodynamic theory of plasma, vector wave function technique and neglecting the coupling between the elements, the basic equations of far-zone fields of the two-element array of triangular microstrip patch antenna are given as [9 11] [ exp{ ι(βe r β 1 )} E θt = ιη 0 ω[ F x sin φ + F y cos φ] + exp{ ι(β er 2 0.5β 1 )} r 2 r 1 ], (6) [ exp{ ι(βe r β 1 )} E φt = ιη 0 ω[f x cos θ cos φ + F y cos θ sin φ] + exp{ ι(β er 2 0.5β 1 )} r 2 ]. (7) In the far-zone field region, the values of the radius vectors r 1, r 2 can be calculated from figure 1. and r 1 r + d/2 cos θ r 2 r d/2 cos θ, for phase variation r 1 r 2 r, for amplitude variation. Applying these approximations in eqs (6) and (7), we get: For EM-mode: r 1 E θt = ιη 0 ω[ F x sin φ + F y cos φ]2 cos[0.5(β e d cos θ + β 1 )] e iβer r (8) and for plasma-mode: E φt = ιη 0 ω[f x cos θ cos φ + F y cos θ sin φ]2 cos[0.5(β e d cos θ + β 1 ) e iβer r (9) E pt = 2hβ p ω 2 p/3aωε 0 (ω 2 ω 2 p) exp( ιβ p r)/r exp( ιβ p a sin θ cos φ/ 3) 2 cos[0.5(β p d cos θ + β 1 ) [E px + E py ], (10) 504 Pramana J. Phys., Vol. 65, No. 3, September 2005
5 The radiation characteristics of a two-element array where E θt, E φt are the components of total electric field vectors for EM-mode, E pt is the total electric field vector for plasma-mode, F x is the x-component of vector electric potential, F y is the y-component of vector electric potential, E px is the x-component of the electric field vector for plasma-mode, E py is the y-component of electric field vector for P-mode, β e is the phase propagation constant for EMmode given by 2πA/λ 0, β p is the phase propagation constant for plasma-mode given by β e c/v, c is the velocity of light, v is the root mean square thermal velocity of electron, A is the plasma frequency parameter given by (1 ωp/ω 2 0) 2 1/2, ω p is the angular plasma frequency, ω is the angular source frequency and β 1 is the progressive phase excitation difference between the patches. 3. Field patterns The expression for total field pattern R(θ, φ) is obtained as R(θ, φ) = E θt 2 + E φt 2. (11) Then, the radiation field patterns in the E-plane (φ = 0) and H-plane (φ = π/2) are given as R e (θ, φ) = E θt 2 + E φt 2 = η 2 0ω 2 0( F y 2 + F x 2 cos 2 θ) (E-plane), (12) R h (θ, φ) = E θt 2 + E φt 2 = η 2 0ω 2 0( F x 2 + F y 2 cos 2 θ) (H-plane). The values of R e and R h are calculated for a case taking f = 1 GHz, a = 2.2 cm, ε r = 14.78, applied DC magnetic bias field (H 0 ) = A/m, saturation magnetization (µ 0 M s ) = 0.03 T, d = λ/2 and the phase difference β 1 = π/2. The results are plotted in figures 2 and 3 for two different planes (φ = 0 and φ = π/2) for A = 1.0, i.e. in free space and in figures 4 and 5 for two different planes (φ = 0 and φ = π/2) for A = 0.5, i.e. in plasma medium. The variation of effective permeability for both RHCP and LHCP modes with applied magnetic bias field (H 0 ) is shown in figure 6. The P-mode fields are plotted in figure 7 for A = 0.5 for a limited range of 10 (from 60 to 70 ). The field patterns are also compared with single-element triangular patch microstrip antenna. (13) 4. Other antenna parameters 4.1 Radiation conductance The total power radiated can be calculated by employing Poynting s theorem and is given as ( ) ( ) { } 1 1 P r = Re (E H )ds. 2 2 S Pramana J. Phys., Vol. 65, No. 3, September
6 K K Verma and K R Soni Figure 2. Variation of R(θ, φ) for A = 1.0 (free space) for single-element and two-element (β 1 = π/2) equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate in E-plane. Figure 3. Variation of R(θ, φ) for A = 1.0 (free space) for single-element and two-element (β 1 = π/2) equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate in H-plane. The factor 1 2 is due to the fact that the power is radiated through the upper half space only and S is the total spherical surface area. ( ) { } 1 P r = Re (E θ Hφ E φ Hθ )ds. 4 S Thus, the expressions for radiated power in EM-modes is obtained using the relation [6]: P e = (A/4η 0 ) 2π π 0 0 { E θt 2 + E φt 2 }r 2 sin θdθdφ. (14) Here, A = (1 ω 2 p/ω 2 0) 1/2 and ω p /ω 0 is the plasma-to-source frequency ratio. 506 Pramana J. Phys., Vol. 65, No. 3, September 2005
7 The radiation characteristics of a two-element array Figure 4. Variation of R(θ, φ) for A = 0.5 (plasma) for single-element and two-element (β 1 = π/2) equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate in E-plane. Figure 5. Variation of R(θ, φ) for A = 0.5 (plasma) for single-element and two-element (β 1 = π/2) equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate in H-plane. The radiation conductance of an antenna in EM-mode can be defined as 4.2 Directivity G e = 2P e /V 2 0. (15) The directivity of an antenna is defined as the ratio of the maxium radiation intensity (power per unit solid angle) to the average radiation intensity. It can be expressed as / { 2π π } D e = 4π{max( E θt 2 + E φ 2 )} E θt 2 + E φt 2 r 2 sin θdθdφ. (16) 0 0 Pramana J. Phys., Vol. 65, No. 3, September
8 K K Verma and K R Soni Figure 6. Variation of effective permeability of substrate with applied bias field. Figure 7. Variation of plasma mode field pattern E pt 2 for A = 0.5 (plasma) for single-element and two-element (β 1 = π/2) equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate. 4.3 Quality factor A parameter specifying the frequency selectivity of a resonant circuit is the quality factor Q, which can be defined as the ratio between energy stored in the system and the energy lost. The total Q of a microstrip radiating element comprises contributions due to the radiation Q r, conductor loss Q c, and dielectric loss Q d quality factors. So 1/Q t = 1/Q r + 1/Q c + 1/Q d, (17) where Q r = ω 0 W t /P r, Q c = ω 0 W t /P c = (π f µ σ) 1/2 h and Q d = ω 0 W t /P d = 1/ tan δ. Here, W t is the energy stored in the antenna element, P c and P d are power 508 Pramana J. Phys., Vol. 65, No. 3, September 2005
9 The radiation characteristics of a two-element array Figure 8. Variation of radiation conductance G e for single-element and two-element equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate for EM-mode with plasma parameter A. loss factors due to the conductors and dielectric, respectively, σ is the conductivity of the conductors. The energy stored in the triangular radiating element is given by W t = (εh/2) E z (x, y) 2 dx dy. (18) 5. Conclusion The radiation characteristics of a two-element linear array of equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate have been studied by considering the presence of bias magnetic field in the direction of propagation of EM waves. The results of the array geometry are compared with those of single-element of equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna. It is found that there is a significant change in the radiation characteristics of array geometry. In the case of EM-mode, the shape of the field pattern has been modified to a great extent and redistributes the field intensities considerably. It is also observed that the radiation patterns of a singleelement antenna contain only one major lobe of considerably wide beam-width, while the array geometry produces a directive beam with a narrow beam-width. In the case of P-mode, the field patterns are similar to single-element microstrip antenna. It is further observed that the values of radiation conductance are considerably higher for array geometry and it increases continuously with increasing plasma parameter. The values of directivity for array geometry are also considerably higher than that of the single-element of equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna. The values of quality factor for array geometry are lower than that of single-element of equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna. The computed values of pattern characteristics of the present array are given in table 2. It is clear from this table that half-power beam-width of the patterns in free space is relatively small in comparison to plasma medium. Thus it reveals that the patterns are more directive in free-space than in plasma medium. Variation of radiation conductance G e for single-element and two-element equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate with plasma parameter A is shown in figure 8. From this figure, it is observed that the radiation conduction (G e ) of the two-element array antenna is more than that of the single-element antenna for all the plasma frequency. Pramana J. Phys., Vol. 65, No. 3, September
10 K K Verma and K R Soni Table 2. Pattern characteristics of the two-element array of triangular microstrip patch antenna on ferrite substrate. Pattern characteristics φ = 0 plane φ = 0 plane φ = π/2 plane φ = π/2 plane A = 1.0 A = 0.5 A = 1.0 A = 0.5 RHCP LHCP RHCP LHCP RHCP LHCP RHCP LHCP Half-power beam width (HPBW) Full null beam width (FNBW) Direction of max. radiation Figure 9. Variation of directivity D e for single-element and two-element equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate for EM mode with plasma parameter A. Figure 10. Variation of quality factor Q e for single-element and two-element equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate for EM-mode with plasma parameter A. It is maximum in free space and decreases on increasing plasma frequency. It is also observed that the radiation conduction (G e ) with LHCP waves is higher than that with RHCP waves. Variation of radiation conductance D e for single- 510 Pramana J. Phys., Vol. 65, No. 3, September 2005
11 The radiation characteristics of a two-element array Table 3. Antenna parameters for single-element and two-element equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate with RHCP waves. G e for two- D e for D e for Plasma G e for single element single two-element Q e for Q e for parameter element linear array element linear array single two-element (A) (mho) (mho) (db) (db) element linear array Table 4. Antenna parameters for single element and two-element equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate with LHCP waves. G e for two- D e for D e for Plasma G e for single element single two-element Q e for Q e for parameter element linear array element linear array single two-element (A) (mho) (mho) (db) (db) element linear array element and two-element equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate with plasma parameter A is shown in figure 9. From this figure, it is observed that the directivity (D e ) of this array with LHCP waves is higher than that with RHCP waves for free space and all plasma frequency. Variation of radiation conductance Q e for single-element and two-element equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna on ferrite substrate with plasma parameter A is shown in figure 10. From this figure, it is noticed that the low values of quality factor (Q e ) of this array antenna in free space indicate that antenna is radiating power more effectively Pramana J. Phys., Vol. 65, No. 3, September
12 K K Verma and K R Soni in free space. Hence at low values of A, more energy is radiated in the form of plasma waves, which increases the quality factor of antenna in plasma medium. If we are considering the effect of LHCP and RHCP modes, then the total quality factor of this array antenna with LHCP waves is lower than that with RHCP waves. Finally, it is concluded that two-element linear array of equilateral triangular patch microstrip antenna has unique radiation characteristics and can be employed in applications where high gain and narrow beam-width are required. The results of the present study are useful, particularly for space vehicles because such type of array antenna can be mounted on the flat surface as well as on the curved surface of the vehicles. References [1] I L Freeston and R K Gupta, Proc. IEE 18, 633 (1971) [2] J R James and G J Wilson, Microwaves optics and acoustic 1, 165 (1977) [3] J Helszajn and D S James, IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory and Techniques MTT-26, 95 (1978) [4] Y T Lo, D Soloman and W F Richards, IEEE Trans. Antenna and Propagation AP- 27, 137 (1979) [5] K R Carver and J W Mink, IEEE Trans. Antenna and Propagation AP-29, 2 (1981) [6] I J Bahl and P Bhartia, Microstrip antennas (Artech House, London, 1980) [7] C A Balanis, Antenna Theory analysis and design (Harper and Row, New York, 1982) [8] R E Collin, Foundations for microwave engineering (McGraw Hill, New York, 1992) [9] K K Verma and K R Soni, Indian J. Phys. B78, 1359 (2004) [10] K K Verma and K R Soni, Indian J. Phys. B78, 1397 (2004) [11] K K Verma and K R Soni, Pramana J. Phys. 64, 147 (2005) 512 Pramana J. Phys., Vol. 65, No. 3, September 2005
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 52, , 2005 FDTD ANALYSIS OF MICROSTRIP PATCH ANTENNA COVERED BY PLASMA SHEATH
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 52, 173 183, 25 FDTD ANALYSIS OF MICROSTRIP PATCH ANTENNA COVERED BY PLASMA SHEATH Z. H. Qian and R. S. Chen Department of Communication Engineering Nanjing
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 52, 173 183, 25 FDTD ANALYSIS OF MICROSTRIP PATCH ANTENNA COVERED BY PLASMA SHEATH Z. H. Qian and R. S. Chen Department of Communication Engineering Nanjing
Passive Coplanar Circulator with the Yig Thin Films
 Passive Coplanar Circulator with the Yig Thin Films Rahmouna El-Bouslemti 1,1, Faouzi Salah-Belkhodja 1, 1 LTTNS Laboratory, Department of Electronic, University of Djillali Liabès, Sidi Bel Abbés, Algeria
Passive Coplanar Circulator with the Yig Thin Films Rahmouna El-Bouslemti 1,1, Faouzi Salah-Belkhodja 1, 1 LTTNS Laboratory, Department of Electronic, University of Djillali Liabès, Sidi Bel Abbés, Algeria
PROPAGATION IN A FERRITE CIRCULAR WAVEGUIDE MAGNETIZED THROUGH A ROTARY FOUR-POLE MAGNETIC FIELD
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 68, 1 13, 2007 PROPAGATION IN A FERRITE CIRCULAR WAVEGUIDE MAGNETIZED THROUGH A ROTARY FOUR-POLE MAGNETIC FIELD M. Mazur Analog Techniques Department Telecommunication
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 68, 1 13, 2007 PROPAGATION IN A FERRITE CIRCULAR WAVEGUIDE MAGNETIZED THROUGH A ROTARY FOUR-POLE MAGNETIC FIELD M. Mazur Analog Techniques Department Telecommunication
Microstrip Antennas. Prof. Girish Kumar Electrical Engineering Department, IIT Bombay. (022)
 Microstrip Antennas Prof. Girish Kumar Electrical Engineering Department, IIT Bombay gkumar@ee.iitb.ac.in (022) 2576 7436 Rectangular Microstrip Antenna (RMSA) Y Top View W x X L Side View r Ground plane
Microstrip Antennas Prof. Girish Kumar Electrical Engineering Department, IIT Bombay gkumar@ee.iitb.ac.in (022) 2576 7436 Rectangular Microstrip Antenna (RMSA) Y Top View W x X L Side View r Ground plane
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 24, , 2011
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 24, 173 183, 2011 STUDY OF THE RADIATED POLARIZATIO OF A ATEA ARRAY WITH CIRCULAR GEOMETRY K. Louertani 1, *, R. Guinvarc h 2,. Ribière-Tharaud 3, and M. Hélier
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 24, 173 183, 2011 STUDY OF THE RADIATED POLARIZATIO OF A ATEA ARRAY WITH CIRCULAR GEOMETRY K. Louertani 1, *, R. Guinvarc h 2,. Ribière-Tharaud 3, and M. Hélier
NASA Contractor Report. Application of FEM to Estimate Complex Permittivity of Dielectric Material at Microwave Frequency Using Waveguide Measurements
 NASA Contractor Report Application of FEM to Estimate Complex Permittivity of Dielectric Material at Microwave Frequency Using Waveguide Measurements M. D.Deshpande VIGYAN Inc., Hampton, VA C. J. Reddy
NASA Contractor Report Application of FEM to Estimate Complex Permittivity of Dielectric Material at Microwave Frequency Using Waveguide Measurements M. D.Deshpande VIGYAN Inc., Hampton, VA C. J. Reddy
Omar M. Ramahi University of Waterloo Waterloo, Ontario, Canada
 Omar M. Ramahi University of Waterloo Waterloo, Ontario, Canada Traditional Material!! Electromagnetic Wave ε, μ r r The only properties an electromagnetic wave sees: 1. Electric permittivity, ε 2. Magnetic
Omar M. Ramahi University of Waterloo Waterloo, Ontario, Canada Traditional Material!! Electromagnetic Wave ε, μ r r The only properties an electromagnetic wave sees: 1. Electric permittivity, ε 2. Magnetic
Wavelength Dependent Microwave Devices Based on Metamaterial Technology. Professor Bal Virdee BSc(Eng) PhD CEng FIET
 Wavelength Dependent Microwave Devices Based on Metamaterial Technology by Professor Bal Virdee BSc(Eng) PhD CEng FIET EM response of materials are determined by the spatial distribution of its atoms and
Wavelength Dependent Microwave Devices Based on Metamaterial Technology by Professor Bal Virdee BSc(Eng) PhD CEng FIET EM response of materials are determined by the spatial distribution of its atoms and
Modelling and design of complete photonic band gaps in two-dimensional photonic crystals
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 70, No. 1 journal of January 2008 physics pp. 153 161 Modelling and design of complete photonic band gaps in two-dimensional photonic crystals YOGITA KALRA and
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 70, No. 1 journal of January 2008 physics pp. 153 161 Modelling and design of complete photonic band gaps in two-dimensional photonic crystals YOGITA KALRA and
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 71,
 Coupling of electromagnetic waves and superlattice vibrations in a piezomagnetic superlattice: Creation of a polariton through the piezomagnetic effect H. Liu, S. N. Zhu, Z. G. Dong, Y. Y. Zhu, Y. F. Chen,
Coupling of electromagnetic waves and superlattice vibrations in a piezomagnetic superlattice: Creation of a polariton through the piezomagnetic effect H. Liu, S. N. Zhu, Z. G. Dong, Y. Y. Zhu, Y. F. Chen,
RESONANCE FREQUENCIES AND FAR FIELD PATTERNS OF ELLIPTICAL DIELECTRIC RESONATOR ANTENNA: ANALYTICAL APPROACH
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 64, 81 98, 2006 RESONANCE FREQUENCIES AND FAR FIELD PATTERNS OF ELLIPTICAL DIELECTRIC RESONATOR ANTENNA: ANALYTICAL APPROACH A. Tadjalli and A. Sebak ECE Dept,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 64, 81 98, 2006 RESONANCE FREQUENCIES AND FAR FIELD PATTERNS OF ELLIPTICAL DIELECTRIC RESONATOR ANTENNA: ANALYTICAL APPROACH A. Tadjalli and A. Sebak ECE Dept,
Spectral Domain Analysis of Open Planar Transmission Lines
 Mikrotalasna revija Novembar 4. Spectral Domain Analysis of Open Planar Transmission Lines Ján Zehentner, Jan Mrkvica, Jan Macháč Abstract The paper presents a new code calculating the basic characteristics
Mikrotalasna revija Novembar 4. Spectral Domain Analysis of Open Planar Transmission Lines Ján Zehentner, Jan Mrkvica, Jan Macháč Abstract The paper presents a new code calculating the basic characteristics
Ansoft HFSS Material Manager
 Choose Perfect Conductor to define a perfectly conducting material that is, a material with infinite conductivity. No field solution is performed inside a perfect conductor. Solve Inside is set to No to
Choose Perfect Conductor to define a perfectly conducting material that is, a material with infinite conductivity. No field solution is performed inside a perfect conductor. Solve Inside is set to No to
1. Consider the biconvex thick lens shown in the figure below, made from transparent material with index n and thickness L.
 Optical Science and Engineering 2013 Advanced Optics Exam Answer all questions. Begin each question on a new blank page. Put your banner ID at the top of each page. Please staple all pages for each individual
Optical Science and Engineering 2013 Advanced Optics Exam Answer all questions. Begin each question on a new blank page. Put your banner ID at the top of each page. Please staple all pages for each individual
Microwave Phase Shift Using Ferrite Filled Waveguide Below Cutoff
 Microwave Phase Shift Using Ferrite Filled Waveguide Below Cutoff CHARLES R. BOYD, JR. Microwave Applications Group, Santa Maria, California, U. S. A. ABSTRACT Unlike conventional waveguides, lossless
Microwave Phase Shift Using Ferrite Filled Waveguide Below Cutoff CHARLES R. BOYD, JR. Microwave Applications Group, Santa Maria, California, U. S. A. ABSTRACT Unlike conventional waveguides, lossless
Microstrip Coupler with Complementary Split-Ring Resonator (CSRR)
 Microstrip Coupler with Complementary Split-Ring Resonator (CSRR) E-242 Course Project Report Submitted by, EMIL MATHEW JOSEPH 4810-411-091-07049 Guided by, Prof. K J VINOY Department of Electrical and
Microstrip Coupler with Complementary Split-Ring Resonator (CSRR) E-242 Course Project Report Submitted by, EMIL MATHEW JOSEPH 4810-411-091-07049 Guided by, Prof. K J VINOY Department of Electrical and
Analytical Solution for Capacitance and Characteristic Impedance of CPW with Defected Structures in Signal line
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 54, 79 84, 25 Analytical Solution for Capacitance and Characteristic Impedance of CPW with Defected Structures in Signal line Naibo Zhang, Zhongliang
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 54, 79 84, 25 Analytical Solution for Capacitance and Characteristic Impedance of CPW with Defected Structures in Signal line Naibo Zhang, Zhongliang
Arbitrary Patterning Techniques for Anisotropic Surfaces, and Line Waves
 Arbitrary Patterning Techniques for Anisotropic Surfaces, and Line Waves Dan Sievenpiper, Jiyeon Lee, and Dia a Bisharat January 11, 2016 1 Outline Arbitrary Anisotropic Surface Patterning Surface wave
Arbitrary Patterning Techniques for Anisotropic Surfaces, and Line Waves Dan Sievenpiper, Jiyeon Lee, and Dia a Bisharat January 11, 2016 1 Outline Arbitrary Anisotropic Surface Patterning Surface wave
Road Map. Potential Applications of Antennas with Metamaterial Loading
 Road Map Potential Applications of Antennas with Metamaterial Loading Filiberto Bilotti Department of Applied Electronics University of Roma Tre Rome, Italy The history of metamaterials Metamaterial terminology
Road Map Potential Applications of Antennas with Metamaterial Loading Filiberto Bilotti Department of Applied Electronics University of Roma Tre Rome, Italy The history of metamaterials Metamaterial terminology
Engineering Electromagnetics
 Nathan Ida Engineering Electromagnetics With 821 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface vu Vector Algebra 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Scalars and Vectors 2 1.3 Products of Vectors 13 1.4 Definition of Fields
Nathan Ida Engineering Electromagnetics With 821 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface vu Vector Algebra 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Scalars and Vectors 2 1.3 Products of Vectors 13 1.4 Definition of Fields
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 17, , 2010
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 17, 163 170, 2010 MINIATURE ELECTROMAGNETIC BAND-GAP STRUCTURE USING SPIRAL GROUND PLANE H.-H. Xie, Y.-C. Jiao, K. Song, and B. Yang National Key Laboratory
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 17, 163 170, 2010 MINIATURE ELECTROMAGNETIC BAND-GAP STRUCTURE USING SPIRAL GROUND PLANE H.-H. Xie, Y.-C. Jiao, K. Song, and B. Yang National Key Laboratory
5 RCS Management of Edge Diffracted Waves
 5 RCS Management of Edge Diffracted Waves 5.1 Introduction Radar absorbing materials (RAM s) applied as a coating on the surface of an object, partially transform the energy of an incident radar beam into
5 RCS Management of Edge Diffracted Waves 5.1 Introduction Radar absorbing materials (RAM s) applied as a coating on the surface of an object, partially transform the energy of an incident radar beam into
LECTURE 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.)
 LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) 1 Rectangular Horn Antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave bands (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high gain, low VSWR (with
LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) 1 Rectangular Horn Antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave bands (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high gain, low VSWR (with
AXIALLY SLOTTED ANTENNA ON A CIRCULAR OR ELLIPTIC CYLINDER COATED WITH METAMATERIALS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 1, 329 341, 2 AXIALLY SLOTTED ANTENNA ON A CIRCULAR OR ELLIPTIC CYLINDER COATED WITH METAMATERIALS A-K. Hamid Department of Electrical/Electronics and Computer
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 1, 329 341, 2 AXIALLY SLOTTED ANTENNA ON A CIRCULAR OR ELLIPTIC CYLINDER COATED WITH METAMATERIALS A-K. Hamid Department of Electrical/Electronics and Computer
Photonic band gap engineering in 2D photonic crystals
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 6 journal of December 2006 physics pp. 1155 1164 Photonic band gap engineering in 2D photonic crystals YOGITA KALRA and R K SINHA TIFAC-Center of Relevance
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 6 journal of December 2006 physics pp. 1155 1164 Photonic band gap engineering in 2D photonic crystals YOGITA KALRA and R K SINHA TIFAC-Center of Relevance
Research Article Trapped-Mode Resonance Regime of Thin Microwave Electromagnetic Arrays with Two Concentric Rings in Unit Cell
 Microwave Science and Technology Volume 2, Article ID 3688, 6 pages doi:.55/2/3688 Research Article Trapped-Mode Resonance Regime of Thin Microwave Electromagnetic Arrays with Two Concentric Rings in Unit
Microwave Science and Technology Volume 2, Article ID 3688, 6 pages doi:.55/2/3688 Research Article Trapped-Mode Resonance Regime of Thin Microwave Electromagnetic Arrays with Two Concentric Rings in Unit
APPLICATION OF NON-BIASED FERRITES
 IMS-004 Workshop WMH APPLICATION OF NON-BIASED FERRITES FOR THE SUPPRESSION OF EMI FROM RF TO MM WAVES Karén Kocharyan RENAISSANCE Electronics Corporation 1 Lancaster County Rd., Harvard, MA 01451 kkocharyan@rec-usa.com
IMS-004 Workshop WMH APPLICATION OF NON-BIASED FERRITES FOR THE SUPPRESSION OF EMI FROM RF TO MM WAVES Karén Kocharyan RENAISSANCE Electronics Corporation 1 Lancaster County Rd., Harvard, MA 01451 kkocharyan@rec-usa.com
The Effect of Cooling Systems on HTS Microstrip Antennas
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 28 176 The Effect of Cooling Systems on HTS Microstrip Antennas S. F. Liu 1 and S. D. Liu 2 1 Xidian University, Xi an 7171, China 2 Xi an Institute of Space Radio Technology,
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 28 176 The Effect of Cooling Systems on HTS Microstrip Antennas S. F. Liu 1 and S. D. Liu 2 1 Xidian University, Xi an 7171, China 2 Xi an Institute of Space Radio Technology,
Electromagnetic Scattering from a PEC Wedge Capped with Cylindrical Layers with Dielectric and Conductive Properties
 0. OZTURK, ET AL., ELECTROMAGNETIC SCATTERING FROM A PEC WEDGE CAPPED WIT CYLINDRICAL LAYERS... Electromagnetic Scattering from a PEC Wedge Capped with Cylindrical Layers with Dielectric and Conductive
0. OZTURK, ET AL., ELECTROMAGNETIC SCATTERING FROM A PEC WEDGE CAPPED WIT CYLINDRICAL LAYERS... Electromagnetic Scattering from a PEC Wedge Capped with Cylindrical Layers with Dielectric and Conductive
Electromagnetic Implosion Using a Lens
 Sensor and Simulation Notes Note 516 July 2006 Electromagnetic Implosion Using a Lens Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Albuquerque New Mexico 87131
Sensor and Simulation Notes Note 516 July 2006 Electromagnetic Implosion Using a Lens Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Albuquerque New Mexico 87131
MICROWAVE SURFACE IMPEDANCE OF A NEARLY FERROELECTRIC SUPERCONDUCTOR
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 73, 39 47, 2007 MICROWAVE SURFACE IMPEDANCE OF A NEARLY FERROELECTRIC SUPERCONDUCTOR C.-J. Wu Department of Applied Physics National University of Kaohsiung
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 73, 39 47, 2007 MICROWAVE SURFACE IMPEDANCE OF A NEARLY FERROELECTRIC SUPERCONDUCTOR C.-J. Wu Department of Applied Physics National University of Kaohsiung
Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics
 Keqian Zhang Dejie Li Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics Second Edition With 280 Figures and 13 Tables 4u Springer Basic Electromagnetic Theory 1 1.1 Maxwell's Equations 1 1.1.1
Keqian Zhang Dejie Li Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics Second Edition With 280 Figures and 13 Tables 4u Springer Basic Electromagnetic Theory 1 1.1 Maxwell's Equations 1 1.1.1
Sensitivity of surface resistance measurement of HTS thin films by cavity resonator, dielectric resonator and microstrip line resonator
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 58, Nos 5 & 6 journal of May & June 2002 physics pp. 7 77 Sensitivity of surface resistance measurement of HTS thin films by cavity resonator, dielectric resonator
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 58, Nos 5 & 6 journal of May & June 2002 physics pp. 7 77 Sensitivity of surface resistance measurement of HTS thin films by cavity resonator, dielectric resonator
Analyzing of Coupling Region for CRLH/RH TL Coupler with Lumped-elements
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 3, NO. 5, 27 564 Analyzing of Coupling Region for CRLH/RH TL Coupler with Lumped-elements Y. Wang 2, Y. Zhang, 2, and F. Liu 2 Pohl Institute of Solid State Physics, Tongji University,
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 3, NO. 5, 27 564 Analyzing of Coupling Region for CRLH/RH TL Coupler with Lumped-elements Y. Wang 2, Y. Zhang, 2, and F. Liu 2 Pohl Institute of Solid State Physics, Tongji University,
On Electromagnetic-Acoustic Analogies in Energetic Relations for Waves Interacting with Material Surfaces
 Vol. 114 2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 6 A Optical and Acoustical Methods in Science and Technology On Electromagnetic-Acoustic Analogies in Energetic Relations for Waves Interacting with Material
Vol. 114 2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 6 A Optical and Acoustical Methods in Science and Technology On Electromagnetic-Acoustic Analogies in Energetic Relations for Waves Interacting with Material
MEASURE THE COMPLEX PERMEABILITY OF FER- ROMAGNETIC THIN FILMS: COMPARISON SHORTED MICROSTRIP METHOD WITH MICROSTRIP TRANS- MISSION METHOD
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 11, 173 181, 2009 MEASURE THE COMPLEX PERMEABILITY OF FER- ROMAGNETIC THIN FILMS: COMPARISON SHORTED MICROSTRIP METHOD WITH MICROSTRIP TRANS- MISSION
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 11, 173 181, 2009 MEASURE THE COMPLEX PERMEABILITY OF FER- ROMAGNETIC THIN FILMS: COMPARISON SHORTED MICROSTRIP METHOD WITH MICROSTRIP TRANS- MISSION
Contribution of Feed Waveguide on the Admittance Characteristics Of Coplanar Slot Coupled E-H Tee Junction
 ISSN(Online): 30-9801 Contribution of Feed Waveguide on the Admittance Characteristics Of Coplanar Slot Coupled E-H Tee Junction M.Murali, Prof. G.S.N Raju Research Scholar, Dept.of ECE, Andhra University,
ISSN(Online): 30-9801 Contribution of Feed Waveguide on the Admittance Characteristics Of Coplanar Slot Coupled E-H Tee Junction M.Murali, Prof. G.S.N Raju Research Scholar, Dept.of ECE, Andhra University,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 1, , 2008
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B Vol. 1 09 18 008 DIFFRACTION EFFICIENCY ENHANCEMENT OF GUIDED OPTICAL WAVES BY MAGNETOSTATIC FORWARD VOLUME WAVES IN THE YTTRIUM-IRON-GARNET WAVEGUIDE COATED WITH
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B Vol. 1 09 18 008 DIFFRACTION EFFICIENCY ENHANCEMENT OF GUIDED OPTICAL WAVES BY MAGNETOSTATIC FORWARD VOLUME WAVES IN THE YTTRIUM-IRON-GARNET WAVEGUIDE COATED WITH
Evaluation of the Sacttering Matrix of Flat Dipoles Embedded in Multilayer Structures
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 5, 2008 536 Evaluation of the Sacttering Matrix of Flat Dipoles Embedded in Multilayer Structures S. J. S. Sant Anna 1, 2, J. C. da S. Lacava 2, and D. Fernandes 2 1 Instituto
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 5, 2008 536 Evaluation of the Sacttering Matrix of Flat Dipoles Embedded in Multilayer Structures S. J. S. Sant Anna 1, 2, J. C. da S. Lacava 2, and D. Fernandes 2 1 Instituto
Poynting Theory & Wave Polarization
 Poynting Theory & Wave Polarization Prepared By Dr. Eng. Sherif Hekal Assistant Professor Electronics and Communications Engineering 10/31/2017 1 Agenda Poynting Theory o Poynting Vector o Time average
Poynting Theory & Wave Polarization Prepared By Dr. Eng. Sherif Hekal Assistant Professor Electronics and Communications Engineering 10/31/2017 1 Agenda Poynting Theory o Poynting Vector o Time average
Physics (Theory) There are 30 questions in total. Question Nos. 1 to 8 are very short answer type questions and carry one mark each.
 Physics (Theory) Time allowed: 3 hours] [Maximum marks:70 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) (iii) (iii) (iv) (v) There are 30 questions in total. Question Nos. 1 to 8 are very
Physics (Theory) Time allowed: 3 hours] [Maximum marks:70 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) (iii) (iii) (iv) (v) There are 30 questions in total. Question Nos. 1 to 8 are very
LECTURE 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) Equation Section 18
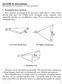 LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) quation Section 18 1 Rectangular horn antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave band (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high
LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) quation Section 18 1 Rectangular horn antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave band (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high
ARTIFICIAL DIELECTRIC SUBSTRATE FOR MICROWAVE APPLICATIONS
 ARTIFICIAL DIELECTRIC SUBSTRATE FOR MICROWAVE APPLICATIONS DOC. ING. JAN MACHÁČ, DRSC. PROF. ING. JÁN ZEHENTNER, DRSC. Abstract: This paper presents a new version of an artificial dielectric substrate.
ARTIFICIAL DIELECTRIC SUBSTRATE FOR MICROWAVE APPLICATIONS DOC. ING. JAN MACHÁČ, DRSC. PROF. ING. JÁN ZEHENTNER, DRSC. Abstract: This paper presents a new version of an artificial dielectric substrate.
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 6
 ECE 6341 Spring 2016 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 6 1 Leaky Modes v TM 1 Mode SW 1 v= utan u ε R 2 R kh 0 n1 r = ( ) 1 u Splitting point ISW f = f s f > f s We will examine the solutions as the
ECE 6341 Spring 2016 Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 6 1 Leaky Modes v TM 1 Mode SW 1 v= utan u ε R 2 R kh 0 n1 r = ( ) 1 u Splitting point ISW f = f s f > f s We will examine the solutions as the
J.-C. Zhang, Y.-Z. Yin, and J.-P. Ma National Laboratory of Antennas and Microwave Technology Xidian University Xi an, Shaanxi , P. R.
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 55 60, 2009 MULTIFUNCTIONAL MEANDER LINE POLARIZER J.-C. Zhang, Y.-Z. Yin, and J.-P. Ma National Laboratory of Antennas and Microwave Technology Xidian
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 55 60, 2009 MULTIFUNCTIONAL MEANDER LINE POLARIZER J.-C. Zhang, Y.-Z. Yin, and J.-P. Ma National Laboratory of Antennas and Microwave Technology Xidian
A Novel Single-Source Surface Integral Method to Compute Scattering from Dielectric Objects
 SUBMITTED TO IEEE ANTENNAS AND WIRELESS PROPAGATION LETTERS ON NOVEMBER 18, 2016 1 A Novel Single-Source Surface Integral Method to Compute Scattering from Dielectric Objects Utkarsh R. Patel, Student
SUBMITTED TO IEEE ANTENNAS AND WIRELESS PROPAGATION LETTERS ON NOVEMBER 18, 2016 1 A Novel Single-Source Surface Integral Method to Compute Scattering from Dielectric Objects Utkarsh R. Patel, Student
Optical Properties of Left-Handed Materials by Nathaniel Ferraro 01
 Optical Properties of Left-Handed Materials by Nathaniel Ferraro 1 Abstract Recently materials with the unusual property of having a simultaneously negative permeability and permittivity have been tested
Optical Properties of Left-Handed Materials by Nathaniel Ferraro 1 Abstract Recently materials with the unusual property of having a simultaneously negative permeability and permittivity have been tested
Unidirectional spin-wave heat conveyer
 Unidirectional spin-wave heat conveyer Figure S1: Calculation of spin-wave modes and their dispersion relations excited in a 0.4 mm-thick and 4 mm-diameter Y 3 Fe 5 O 12 disk. a, Experimentally obtained
Unidirectional spin-wave heat conveyer Figure S1: Calculation of spin-wave modes and their dispersion relations excited in a 0.4 mm-thick and 4 mm-diameter Y 3 Fe 5 O 12 disk. a, Experimentally obtained
Chapter 33. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost entirely on the physics of electromagnetic waves. The connection between electric and magnetic fields to produce light is own of
Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost entirely on the physics of electromagnetic waves. The connection between electric and magnetic fields to produce light is own of
Aperture Antennas 1 Introduction
 1 Introduction Very often, we have antennas in aperture forms, for example, the antennas shown below: Pyramidal horn antenna Conical horn antenna 1 Paraboloidal antenna Slot antenna Analysis Method for.1
1 Introduction Very often, we have antennas in aperture forms, for example, the antennas shown below: Pyramidal horn antenna Conical horn antenna 1 Paraboloidal antenna Slot antenna Analysis Method for.1
Eigenvalue Analysis of Waveguides and Planar Transmission Lines Loaded with Full Tensor Anisotropic Materials
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 5, NO. 5, 2009 471 Eigenvalue Analysis of Waveguides and Planar Transmission Lines Loaded with Full Tensor Anisotropic Materials C. S. Lavranos, D. G. Drogoudis, and G. A. Kyriacou Department
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 5, NO. 5, 2009 471 Eigenvalue Analysis of Waveguides and Planar Transmission Lines Loaded with Full Tensor Anisotropic Materials C. S. Lavranos, D. G. Drogoudis, and G. A. Kyriacou Department
Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics
 Keqian Zhang Dejie Li Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics Translated by authors With 259 Figures Springer Contents 1 Basic Electromagnetic Theory 1 1.1 Maxwell's Equations 1 1.1.1
Keqian Zhang Dejie Li Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics Translated by authors With 259 Figures Springer Contents 1 Basic Electromagnetic Theory 1 1.1 Maxwell's Equations 1 1.1.1
Electromagnetic Scattering From Arbitrarily Shaped Aperture Backed by Rectangular Cavity Recessed in Infinite Ground Plane
 NASA Technical Paper 3640 Electromagnetic Scattering From Arbitrarily Shaped Aperture Backed by Rectangular Cavity Recessed in Infinite Ground Plane C. R. Cockrell and Fred B. Beck Langley Research Center
NASA Technical Paper 3640 Electromagnetic Scattering From Arbitrarily Shaped Aperture Backed by Rectangular Cavity Recessed in Infinite Ground Plane C. R. Cockrell and Fred B. Beck Langley Research Center
Extinction properties of a sphere with negative permittivity and permeability
 PERGAMON Solid State Communications 116 (2000) 411 415 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Extinction properties of a sphere with negative permittivity and permeability R. Ruppin* Department of Physics and Applied
PERGAMON Solid State Communications 116 (2000) 411 415 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Extinction properties of a sphere with negative permittivity and permeability R. Ruppin* Department of Physics and Applied
Class 15 : Electromagnetic Waves
 Class 15 : Electromagnetic Waves Wave equations Why do electromagnetic waves arise? What are their properties? How do they transport energy from place to place? Recap (1) In a region of space containing
Class 15 : Electromagnetic Waves Wave equations Why do electromagnetic waves arise? What are their properties? How do they transport energy from place to place? Recap (1) In a region of space containing
EFFECTS OF SOIL PHYSICAL PROPERTIES ON LAND- MINES DETECTION USING MICROSTRIP ANTENNA AS A SENSOR
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 7, 13 24, 2009 EFFECTS OF SOIL PHYSICAL PROPERTIES ON LAND- MINES DETECTION USING MICROSTRIP ANTENNA AS A SENSOR S. H. Zainud-Deen, M. E. Badr, E. M. Ali,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 7, 13 24, 2009 EFFECTS OF SOIL PHYSICAL PROPERTIES ON LAND- MINES DETECTION USING MICROSTRIP ANTENNA AS A SENSOR S. H. Zainud-Deen, M. E. Badr, E. M. Ali,
III. Spherical Waves and Radiation
 III. Spherical Waves and Radiation Antennas radiate spherical waves into free space Receiving antennas, reciprocity, path gain and path loss Noise as a limit to reception Ray model for antennas above a
III. Spherical Waves and Radiation Antennas radiate spherical waves into free space Receiving antennas, reciprocity, path gain and path loss Noise as a limit to reception Ray model for antennas above a
COLLOCATED SIBC-FDTD METHOD FOR COATED CONDUCTORS AT OBLIQUE INCIDENCE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 3, 239 252, 213 COLLOCATED SIBC-FDTD METHOD FOR COATED CONDUCTORS AT OBLIQUE INCIDENCE Lijuan Shi 1, 3, Lixia Yang 2, *, Hui Ma 2, and Jianning Ding 3 1 School
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 3, 239 252, 213 COLLOCATED SIBC-FDTD METHOD FOR COATED CONDUCTORS AT OBLIQUE INCIDENCE Lijuan Shi 1, 3, Lixia Yang 2, *, Hui Ma 2, and Jianning Ding 3 1 School
General review: - a) Dot Product
 General review: - a) Dot Product If θ is the angle between the vectors a and b, then a b = a b cos θ NOTE: Two vectors a and b are orthogonal, if and only if a b = 0. Properties of the Dot Product If a,
General review: - a) Dot Product If θ is the angle between the vectors a and b, then a b = a b cos θ NOTE: Two vectors a and b are orthogonal, if and only if a b = 0. Properties of the Dot Product If a,
1 Chapter 8 Maxwell s Equations
 Electromagnetic Waves ECEN 3410 Prof. Wagner Final Review Questions 1 Chapter 8 Maxwell s Equations 1. Describe the integral form of charge conservation within a volume V through a surface S, and give
Electromagnetic Waves ECEN 3410 Prof. Wagner Final Review Questions 1 Chapter 8 Maxwell s Equations 1. Describe the integral form of charge conservation within a volume V through a surface S, and give
Absorption suppression in photonic crystals
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 77, 442 28 Absorption suppression in photonic crystals A. Figotin and I. Vitebskiy Department of Mathematics, University of California at Irvine, Irvine, California 92697, USA Received
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 77, 442 28 Absorption suppression in photonic crystals A. Figotin and I. Vitebskiy Department of Mathematics, University of California at Irvine, Irvine, California 92697, USA Received
ARTIFICIAL TRANSMISSION LINE WITH LEFT/RIGHT-HANDED BEHAVIOR BASED ON WIRE BONDED INTERDIGITAL CAPACITORS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 11, 245 264, 29 ARTIFICIAL TRANSMISSION LINE WITH LEFT/RIGHT-HANDED BEHAVIOR BASED ON WIRE BONDED INTERDIGITAL CAPACITORS J. J. Sánchez-Martínez, E. Márquez-Segura,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 11, 245 264, 29 ARTIFICIAL TRANSMISSION LINE WITH LEFT/RIGHT-HANDED BEHAVIOR BASED ON WIRE BONDED INTERDIGITAL CAPACITORS J. J. Sánchez-Martínez, E. Márquez-Segura,
Enhancing and suppressing radiation with some permeability-near-zero structures
 Enhancing and suppressing radiation with some permeability-near-zero structures Yi Jin 1,2 and Sailing He 1,2,3,* 1 Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical
Enhancing and suppressing radiation with some permeability-near-zero structures Yi Jin 1,2 and Sailing He 1,2,3,* 1 Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical
Plane Waves Part II. 1. For an electromagnetic wave incident from one medium to a second medium, total reflection takes place when
 Plane Waves Part II. For an electromagnetic wave incident from one medium to a second medium, total reflection takes place when (a) The angle of incidence is equal to the Brewster angle with E field perpendicular
Plane Waves Part II. For an electromagnetic wave incident from one medium to a second medium, total reflection takes place when (a) The angle of incidence is equal to the Brewster angle with E field perpendicular
Lecture Notes on Wave Optics (03/05/14) 2.71/2.710 Introduction to Optics Nick Fang
 Outline: A. Electromagnetism B. Frequency Domain (Fourier transform) C. EM waves in Cartesian coordinates D. Energy Flow and Poynting Vector E. Connection to geometrical optics F. Eikonal Equations: Path
Outline: A. Electromagnetism B. Frequency Domain (Fourier transform) C. EM waves in Cartesian coordinates D. Energy Flow and Poynting Vector E. Connection to geometrical optics F. Eikonal Equations: Path
ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION
 ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION Electromagnetic Waves and Their Propagation Through the Atmosphere ELECTRIC FIELD An Electric field exists in the presence of a charged body ELECTRIC FIELD INTENSITY (E) A
ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION Electromagnetic Waves and Their Propagation Through the Atmosphere ELECTRIC FIELD An Electric field exists in the presence of a charged body ELECTRIC FIELD INTENSITY (E) A
! #! % && ( ) ) +++,. # /0 % 1 /21/ 3 && & 44&, &&7 4/ 00
 ! #! % && ( ) ) +++,. # /0 % 1 /21/ 3 &&4 2 05 6. 4& 44&, &&7 4/ 00 8 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 56, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2008 345 Moment Method Analysis of an Archimedean Spiral Printed
! #! % && ( ) ) +++,. # /0 % 1 /21/ 3 &&4 2 05 6. 4& 44&, &&7 4/ 00 8 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 56, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2008 345 Moment Method Analysis of an Archimedean Spiral Printed
Electromagnetic Scattering from an Anisotropic Uniaxial-coated Conducting Sphere
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 25, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 43 Electromagnetic Scattering from an Anisotropic Uniaxial-coated Conducting Sphere You-Lin Geng 1,2, Xin-Bao Wu 3, and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 25, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 43 Electromagnetic Scattering from an Anisotropic Uniaxial-coated Conducting Sphere You-Lin Geng 1,2, Xin-Bao Wu 3, and
SPHERICAL RESONATOR WITH DB-BOUNDARY CON- DITIONS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 3 37, 2009 SPHERICAL RESONATOR WITH DB-BOUNDARY CON- DITIONS I. V. Lindell and A. H. Sihvola Electromagnetics Group Department of Radio Science and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 3 37, 2009 SPHERICAL RESONATOR WITH DB-BOUNDARY CON- DITIONS I. V. Lindell and A. H. Sihvola Electromagnetics Group Department of Radio Science and
Applications of Time Domain Vector Potential Formulation to 3-D Electromagnetic Problems
 Applications of Time Domain Vector Potential Formulation to 3-D Electromagnetic Problems F. De Flaviis, M. G. Noro, R. E. Diaz, G. Franceschetti and N. G. Alexopoulos Department of Electrical Engineering
Applications of Time Domain Vector Potential Formulation to 3-D Electromagnetic Problems F. De Flaviis, M. G. Noro, R. E. Diaz, G. Franceschetti and N. G. Alexopoulos Department of Electrical Engineering
Exciting High Frequency Oscillations in a Coaxial Transmission Line with a Magnetized Ferrite
 Journal of Magnetics 20(4), 460-465 (2015) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 http://dx.doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2015.20.4.460 Exciting High Frequency Oscillations in a Coaxial Transmission Line
Journal of Magnetics 20(4), 460-465 (2015) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 http://dx.doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2015.20.4.460 Exciting High Frequency Oscillations in a Coaxial Transmission Line
Efficiency and Bandwidth Improvement Using Metamaterial of Microstrip Patch Antenna
 Efficiency and Bandwidth Improvement Using Metamaterial of Microstrip Patch Antenna Aakash Mithari 1, Uday Patil 2 1Student Department of Electronics Technology Engg., Shivaji University, Kolhapur, Maharashtra,
Efficiency and Bandwidth Improvement Using Metamaterial of Microstrip Patch Antenna Aakash Mithari 1, Uday Patil 2 1Student Department of Electronics Technology Engg., Shivaji University, Kolhapur, Maharashtra,
Reflector Antennas. Summary. 1.Basic Concepts of Antennas. 2.Radiation by Aperture Antennas. 3.Reflector Antennas. 4.Design and Analysis Methods
 Reflector Antennas DR. RAFAEL ABRANTES PENCHEL Summary 1.Basic Concepts of Antennas 2.Radiation by Aperture Antennas 3.Reflector Antennas 4.Design and Analysis Methods 1 Basic Concepts of Antennas Coordinate
Reflector Antennas DR. RAFAEL ABRANTES PENCHEL Summary 1.Basic Concepts of Antennas 2.Radiation by Aperture Antennas 3.Reflector Antennas 4.Design and Analysis Methods 1 Basic Concepts of Antennas Coordinate
FORMULATION OF ANISOTROPIC MEDIUM IN SPATIAL NETWORK METHOD. N. Yoshida, S. Koike, N. Kukutsu, and T. Kashiwa
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 13, 293 362, 1996 FORMULATION OF ANISOTROPIC MEDIUM IN SPATIAL NETWORK METHOD N. Yoshida, S. Koike, N. Kukutsu, and T. Kashiwa 1. Introduction 2. Spatial Network
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 13, 293 362, 1996 FORMULATION OF ANISOTROPIC MEDIUM IN SPATIAL NETWORK METHOD N. Yoshida, S. Koike, N. Kukutsu, and T. Kashiwa 1. Introduction 2. Spatial Network
Full-Wave Analysis of Anisotropic Circular Microstrip Antenna with Air Gap Layer
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 34, 143 151, 214 Full-Wave Analysis of Anisotropic Circular Microstrip Antenna with Air Gap Layer Sami Bedra 1, *, Randa Bedra 1, Siham Benkouda 2, and Tarek
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 34, 143 151, 214 Full-Wave Analysis of Anisotropic Circular Microstrip Antenna with Air Gap Layer Sami Bedra 1, *, Randa Bedra 1, Siham Benkouda 2, and Tarek
CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
 CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Outlines 1. Waves in one dimension 2. Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum 3. Electromagnetic waves in Matter 4. Absorption and Dispersion 5. Guided Waves 2 Skip 9.1.1 and 9.1.2
CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Outlines 1. Waves in one dimension 2. Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum 3. Electromagnetic waves in Matter 4. Absorption and Dispersion 5. Guided Waves 2 Skip 9.1.1 and 9.1.2
MINIMIZING REFLECTION AND FOCUSSING OF INCIDENT WAVE TO ENHANCE ENERGY DEPOSITION IN PHOTODETECTOR S ACTIVE REGION
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 65, 71 80, 2006 MINIMIZING REFLECTION AND FOCUSSING OF INCIDENT WAVE TO ENHANCE ENERGY DEPOSITION IN PHOTODETECTOR S ACTIVE REGION A. A. Pavel, P. Kirawanich,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 65, 71 80, 2006 MINIMIZING REFLECTION AND FOCUSSING OF INCIDENT WAVE TO ENHANCE ENERGY DEPOSITION IN PHOTODETECTOR S ACTIVE REGION A. A. Pavel, P. Kirawanich,
Microwave Engineering 3e Author - D. Pozar
 Microwave Engineering 3e Author - D. Pozar Sections 3.6 3.8 Presented by Alex Higgins 1 Outline Section 3.6 Surface Waves on a Grounded Dielectric Slab Section 3.7 Stripline Section 3.8 Microstrip An Investigation
Microwave Engineering 3e Author - D. Pozar Sections 3.6 3.8 Presented by Alex Higgins 1 Outline Section 3.6 Surface Waves on a Grounded Dielectric Slab Section 3.7 Stripline Section 3.8 Microstrip An Investigation
Design of Composite Electromagnetic Wave Absorber Made of Fine Aluminum Particles Dispersed in Polystyrene Resin by Controlling Permeability
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 5, NO. 7, 9 663 Design of Composite Electromagnetic Wave Absorber Made of Fine Aluminum Particles Dispersed in Polystyrene Resin by Controlling Permeability K. Sakai, Y. Wada, Y. Sato,
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 5, NO. 7, 9 663 Design of Composite Electromagnetic Wave Absorber Made of Fine Aluminum Particles Dispersed in Polystyrene Resin by Controlling Permeability K. Sakai, Y. Wada, Y. Sato,
ANALYTICAL MODEL OF A METASURFACE CONSIST- ING OF A REGULAR ARRAY OF SUB-WAVELENGTH CIRCULAR HOLES IN A METAL SHEET
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 18, 209 219, 2011 ANALYTICAL MODEL OF A METASURFACE CONSIST- ING OF A REGULAR ARRAY OF SUB-WAVELENGTH CIRCULAR HOLES IN A METAL SHEET D. Ramaccia *, F. Bilotti,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 18, 209 219, 2011 ANALYTICAL MODEL OF A METASURFACE CONSIST- ING OF A REGULAR ARRAY OF SUB-WAVELENGTH CIRCULAR HOLES IN A METAL SHEET D. Ramaccia *, F. Bilotti,
Graduate Diploma in Engineering Circuits and waves
 9210-112 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Circuits and waves You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil, ruler No additional data is attached
9210-112 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Circuits and waves You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil, ruler No additional data is attached
Design of a Non-uniform High Impedance Surface for a Low Profile Antenna
 352 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 Design of a Non-uniform High Impedance Surface for a Low Profile Antenna M. Hosseini 2, A. Pirhadi 1,2, and M. Hakkak
352 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 Design of a Non-uniform High Impedance Surface for a Low Profile Antenna M. Hosseini 2, A. Pirhadi 1,2, and M. Hakkak
Lecture 3 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 3, Slide 1
 Lecture 3 Optical fibers as waveguides Maxwell s equations The wave equation Fiber modes Phase velocity, group velocity Dispersion Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 3, Slide 1 Maxwell s equations in
Lecture 3 Optical fibers as waveguides Maxwell s equations The wave equation Fiber modes Phase velocity, group velocity Dispersion Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 3, Slide 1 Maxwell s equations in
Electromagnetic Waves
 May 7, 2008 1 1 J.D.Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd Edition, Section 7 Maxwell Equations In a region of space where there are no free sources (ρ = 0, J = 0), Maxwell s equations reduce to a simple
May 7, 2008 1 1 J.D.Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd Edition, Section 7 Maxwell Equations In a region of space where there are no free sources (ρ = 0, J = 0), Maxwell s equations reduce to a simple
A Novel Tunable Dual-Band Bandstop Filter (DBBSF) Using BST Capacitors and Tuning Diode
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 67, 59 69, 2016 A Novel Tunable Dual-Band Bandstop Filter (DBBSF) Using BST Capacitors and Tuning Diode Hassan Aldeeb and Thottam S. Kalkur * Abstract A novel
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 67, 59 69, 2016 A Novel Tunable Dual-Band Bandstop Filter (DBBSF) Using BST Capacitors and Tuning Diode Hassan Aldeeb and Thottam S. Kalkur * Abstract A novel
Reconfigurable plasma antennas
 Reconfigurable plasma antennas Mohammad pourbagher 1, Javad nourinia 1 and Nader pourmahmud 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Urima University, Iran 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Urima
Reconfigurable plasma antennas Mohammad pourbagher 1, Javad nourinia 1 and Nader pourmahmud 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Urima University, Iran 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Urima
Ultrafast Optoelectronic Study of Superconducting Transmission Lines
 Ultrafast Optoelectronic Study of Superconducting Transmission Lines Shinho Cho, Chang-Sik Son and Jonghun Lyou Presented at the 8th International Conference on Electronic Materials (IUMRS-ICEM 2002, Xi
Ultrafast Optoelectronic Study of Superconducting Transmission Lines Shinho Cho, Chang-Sik Son and Jonghun Lyou Presented at the 8th International Conference on Electronic Materials (IUMRS-ICEM 2002, Xi
Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts
 NE 2 Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820) Faradays
NE 2 Chap. 1 Fundamental Concepts Important Laws in Electromagnetics Coulomb s Law (1785) Gauss s Law (1839) Ampere s Law (1827) Ohm s Law (1827) Kirchhoff s Law (1845) Biot-Savart Law (1820) Faradays
Periodic Leaky-Wave Antennas for Orbital Angular Momentum Multiplexing System Master Thesis Final Presentation
 Periodic Leaky-Wave Antennas for Orbital Angular Momentum Multiplexing System Master Thesis Final Presentation Amar Al-Bassam 23.06.2014 Outline I. INTRODUCTION II. CONCEPT OF GENERATION III. ELECTROMAGNETIC
Periodic Leaky-Wave Antennas for Orbital Angular Momentum Multiplexing System Master Thesis Final Presentation Amar Al-Bassam 23.06.2014 Outline I. INTRODUCTION II. CONCEPT OF GENERATION III. ELECTROMAGNETIC
INTRODUCTION TO TRANSMISSION LINES DR. FARID FARAHMAND FALL 2012
 INTRODUCTION TO TRANSMISSION LINES DR. FARID FARAHMAND FALL 2012 http://www.empowermentresources.com/stop_cointelpro/electromagnetic_warfare.htm RF Design In RF circuits RF energy has to be transported
INTRODUCTION TO TRANSMISSION LINES DR. FARID FARAHMAND FALL 2012 http://www.empowermentresources.com/stop_cointelpro/electromagnetic_warfare.htm RF Design In RF circuits RF energy has to be transported
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 35, , 2002
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 35, 315 334, 2002 NUMERICAL STUDIES OF LEFT HANDED METAMATERIALS C. D. Moss, T. M. Grzegorczyk, Y. Zhang, and J. A. Kong Research Laboratory of Electronics Massachusetts
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 35, 315 334, 2002 NUMERICAL STUDIES OF LEFT HANDED METAMATERIALS C. D. Moss, T. M. Grzegorczyk, Y. Zhang, and J. A. Kong Research Laboratory of Electronics Massachusetts
Analysis of Modified Bowtie Nanoantennas in the Excitation and Emission Regimes
 232 Analysis of Modified Bowtie Nanoantennas in the Excitation and Emission Regimes Karlo Q. da Costa, Victor A. Dmitriev, Federal University of Para, Belém-PA, Brazil, e-mails: karlo@ufpa.br, victor@ufpa.br
232 Analysis of Modified Bowtie Nanoantennas in the Excitation and Emission Regimes Karlo Q. da Costa, Victor A. Dmitriev, Federal University of Para, Belém-PA, Brazil, e-mails: karlo@ufpa.br, victor@ufpa.br
Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017
 Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017 1. a. Find the capacitance of a spherical capacitor with inner radius l i and outer radius l 0 filled with dielectric
Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017 1. a. Find the capacitance of a spherical capacitor with inner radius l i and outer radius l 0 filled with dielectric
A Highly Tunable Sub-Wavelength Chiral Structure for Circular Polarizer
 A Highly Tunable Sub-Wavelength Chiral Structure for Circular Polarizer Menglin. L. N. Chen 1, Li Jun Jiang 1, Wei E. I. Sha 1 and Tatsuo Itoh 2 1 Dept. Of EEE, The University Of Hong Kong 2 EE Dept.,
A Highly Tunable Sub-Wavelength Chiral Structure for Circular Polarizer Menglin. L. N. Chen 1, Li Jun Jiang 1, Wei E. I. Sha 1 and Tatsuo Itoh 2 1 Dept. Of EEE, The University Of Hong Kong 2 EE Dept.,
ANALYSIS OF DISPERSION RELATION OF PIECEWISE LINEAR RECURSIVE CONVOLUTION FDTD METHOD FOR SPACE-VARYING PLASMA
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 22, 83 93, 2011 ANALYSIS OF DISPERSION RELATION OF PIECEWISE LINEAR RECURSIVE CONVOLUTION FDTD METHOD FOR SPACE-VARYING PLASMA X. Ai Science and Technology
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 22, 83 93, 2011 ANALYSIS OF DISPERSION RELATION OF PIECEWISE LINEAR RECURSIVE CONVOLUTION FDTD METHOD FOR SPACE-VARYING PLASMA X. Ai Science and Technology
arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 10 Feb 2009
![arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 10 Feb 2009 arxiv: v1 [physics.class-ph] 10 Feb 2009](/thumbs/74/70654766.jpg) Ground-Plane Quasi-Cloaking for Free Space Efthymios Kallos, Christos Argyropoulos, and Yang Hao School of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science, Queen Mary University of London, Mile End Road, London,
Ground-Plane Quasi-Cloaking for Free Space Efthymios Kallos, Christos Argyropoulos, and Yang Hao School of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science, Queen Mary University of London, Mile End Road, London,
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations predict the propagation of electromagnetic energy away from time-varying sources (current and charge) in the form of waves. Consider a linear, homogeneous, isotropic
Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations predict the propagation of electromagnetic energy away from time-varying sources (current and charge) in the form of waves. Consider a linear, homogeneous, isotropic
PEMC PARABOLOIDAL REFLECTOR IN CHIRAL MEDIUM SUPPORTING POSITIVE PHASE VELOC- ITY AND NEGATIVE PHASE VELOCITY SIMULTANE- OUSLY
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 10, 77 86, 2009 PEMC PARABOLOIDAL REFLECTOR IN CHIRAL MEDIUM SUPPORTING POSITIVE PHASE VELOC- ITY AND NEGATIVE PHASE VELOCITY SIMULTANE- OUSLY T. Rahim
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 10, 77 86, 2009 PEMC PARABOLOIDAL REFLECTOR IN CHIRAL MEDIUM SUPPORTING POSITIVE PHASE VELOC- ITY AND NEGATIVE PHASE VELOCITY SIMULTANE- OUSLY T. Rahim
A Novel Design of Photonic Crystal Lens Based on Negative Refractive Index
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 2008 296 A Novel Design of Photonic Crystal Lens Based on Negative Refractive Index S. Haxha 1 and F. AbdelMalek 2 1 Photonics Group, Department of Electronics, University
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 2, 2008 296 A Novel Design of Photonic Crystal Lens Based on Negative Refractive Index S. Haxha 1 and F. AbdelMalek 2 1 Photonics Group, Department of Electronics, University
Electromagnetic Waves. Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition)
 PH 222-3A Spring 2007 Electromagnetic Waves Lecture 22 Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost
PH 222-3A Spring 2007 Electromagnetic Waves Lecture 22 Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost
