Elastic reciprocity and symmetry constraints on the stress field due to a surface-parallel distribution of dislocations
|
|
|
- Harry Williams
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Elastic reciprocity and symmetry constraints on the stress field due to a surface-parallel distribution of dislocations Robert C. Viesca a, James R. Rice a,b a School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA b Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA Abstract Elastic reciprocity and geometric symmetry are used to constrain the expressions for stresses due to introduction of line dislocations near a half-space surface. Specifically, a relationship is shown to exist between the changes induced by dislocations of orthogonal Burgers vectors (normal and parallel to the free surface). These results are used to address inconsistencies of solutions in the literature. Keywords: dislocation, half-space, elastic, reciprocity 1. Background There is currently a variance in the literature regarding the solution for an edge dislocation near a free surface which has persisted for more than 40 years. With reference to Figure 1, the point of disagreement is whether, at a point along the x axis, the change of the surface-normal stress σ yy due to the dislocation of Figure 1a is opposite or equal to the change of shear stress σ yx due to the dislocation of Figure 1b, for the same magnitude of Burgers vector (displacement discontinuity) in both 1a and 1b. The original solution of the dislocation problem by Head (1953), consistently with an independent solution by Dundurs and Sendecky (1965), indicated the relation to be opposite (as drawn in Figure 1). However, among his influential body of work on reducing crack and contact problems to singular integral equations and devising effective numerical solution techniques, one special case Preprint submitted to J. Mech. Phys. Solids January 9, 2011
2 addressed by Erdogan (1969) required that same dislocation solution. His result, repeated in Erdogan et al. (1973), can be seen to match the original Head solution with the exception of a difference of sign in one term. That difference indicates the relation discussed above to, instead, be equal. This discrepancy became apparent when examining the stress intensity factors for a uniformly pressurized subsurface crack, represented as a continuous distribution of such dislocations. These factors were first numerically calculated in the case of the equal relation by Erdogan (1969) and Erdogan et al. (1973), and in that of the opposite relation by Ashbaugh (1975), who first suggested the solution in Erdogan et al. (1973) required correction. Subsequently, Chen et al. (1980) also suggested the same correction, and, in addition to Higashida and Kamada (1982), also calculated the intensity factors in agreement with those of Ashbaugh (1975). It is the results of Higashida and Kamada (1982) that feature ambiguously alongside and in contrast with those of Erdogan et al. (1973) in a handbook of stress intensity solutions (Murakami, 1987, p. 167). However, there are indications that one of the solutions may be correct. Examining the stress intensity factors, K I and K II, in the limit of a very shallow crack using a beam approximation, Dyskin et al. (2000) note agreement with Higashida and Kamada (1982) over Erdogan et al. (1973). Additionally, several other authors have presented consistent solutions (Thouless et al., 1987; Yang and Li, 1997; the latter claim a misprint in the solution of Head, 1953, although we find no such misprint when comparing their solutions). Additionally, work by Erdogan (1971) for a crack parallel to a bimaterial interface between joined half-spaces indicates an opposite relation. Because that configuration reduces, in the limit of zero stiffness for the uncracked halfspace, to the problem considered in 1969 and 1973, there is an inconsistency among the set of papers. Further, Tada et al. (2000, p. 231) give a beam theory asymptote for the mode I stress intensity factor that is different from Dyskin et al. (2000) and seemingly in agreement with the results of Erdogan et al. (1973). However, if we assume that beam theory adequately describes energy transfer to the crack tip, hence implies KI 2 +K2 II, that mode-i asymptote requires that K II = 3K I, which deviates strongly from the trend in mode II of Erdogan et al. (1973). Furthermore, Paynter et al. (2006), aware of the sign mismatch leading to the dissimilar results, maintain that the solution of Erdogan et al. (1973) is correct. The matter appears to some extent unsettled and we aim here to conclusively address the discrepancy based not on re-deriving specific proposed solutions but, rather, appealing to general 2
3 a) y σ yy x σ xy b) y x Figure 1: Elements along the x-axis and at symmetric points about the y-axis indicate stress (σ xx omitted) due to an edge dislocation with Burgers vector a) parallel and b) perpendicular to a free surface a distance h away. Standard positive conventions for normal (in tension) and shear stresses are designated in a). 3
4 considerations of elastic reciprocity and symmetry. 2. Elastic reciprocity The Betti reciprocal theorem requires that for two elastic stress-displacement fields σ ıj (1), u (1) k and σ ıj (2), u (2) k in the half space, corresponding to different distributions of displacement discontinuity along a cut (e.g., to represent a crack) coincident with a portion of the x axis (which is parallel to the free surface), that ( ) ( ) nı σ ıj (1) u (2) j ds = nı σ ıj (2) u (1) j ds (1) S Here the origin of the y-axis is a distance h below the free surface, and the closed contour S runs along y = 0 ± along the length of the cut. We consider cases of balanced tractions along y = 0 ± so that, for ı = x, y, σ yı (x, 0 + ) = σ yı (x, 0 ) σ yı (x) along that contour. Then, defining displacement discontinuities δ ı (x) u ı (x, 0 + ) u ı (x, 0 ) along the cut, reciprocity requires [ σ (1) yx (x)δ (2) x (x) + σ (1) yy (x)δ (2) y (x) dx = S [ σ (2) yx (x)δ (1) x (x) + σ (2) yy (x)δ (1) y (x) dx (2) (with the integrands vanishing here and below for positions x outside the cut). The stresses σ yı (x) due to continuous distributions of dislocations of the types in Figure 1a and b, with local densities dδ k (x)/dx over the domain < x <, have the form σ yı (x) = µ 2π(1 ν) [ 1 dδ ı (t) + K ıj (t x) dδ j(t) dt (3) t x dt dt While labeling the kernels as K ıj (t x) versus a notation L ıj (x t) is an arbitrary and inconsequential choice, we have chosen to follow the implicit preference of Erdogan (1969). 4
5 Choosing δ x (2) (x) = 0, δ y (1) (x) = 0 and substituting the relations for stress [ K yx (t x) dδ(1) x (t) dt δ y (2) (x)dx = dt [ K xy (t x) dδ(2) y (t) dt δ x (1) (x)dx (4) dt Integrating the innermost integrals by parts, noting that the kernels must vanish as t x, and assuming that δ x (1) (t), δ y (2) (t) are bounded as t ±, [ K yx(t x)δ x (1) (t)dt δ y (2) (x)dx = [ K xy(t x)δ y (2) (t)dt δ x (1) (x)dx (5) where K ıj(θ) = dk ıj (θ)/dθ. Switching the symbols for the integration variables x and t on the left hand side and rearranging δ (1) x (x)δ (2) y (t) [ K xy(t x) K yx(x t) dtdx = 0 (6) That equation must be satisfied for an arbitrary choice of the functions in the product δ (1) (t), requiring that x (x)δ y (2) K xy(t x) = K yx(x t) (7) Then noting that K xy(θ) K yx( θ) = 0 is equivalent to d[k xy (θ)+k yx ( θ)/dθ = 0, we conclude that K xy (t x) = K yx (x t) (8) 3. Symmetry To further sharpen the constraint of Equation 8, consider the two cases δ x (1) (x) = b x x 2 x, δ(2) y (x) = b y x 2 x for x > 0 (9) with δ x (1) (0) = δ y (2) (0) = 0, and with δ y (1) (x) = δ x (2) (x) = 0 for all x. These describe a classical edge dislocation line running perpendicular to the x, y 5
6 plane through its origin, i.e., along the z direction, with Burgers vector components b x in case (1) and b y in case (2). The stress field created in case (1) is equivalent to that produced by insertion of a sliver of material of thickness b x along the portion of the y, z plane corresponding to y > 0 (Figure 1a). That created in case (2) is equivalent to that produced by insertion of a sliver of thickness b y along the portion of the x, z plane corresponding to x < 0 (Figure 1b). The resulting stresses on y = 0 in the two cases are, by Equation 3, σ (1) yx (x) = σ (2) µb x 2π(1 ν) [ 1 x K xx( x), σ (1) yx (x) = µb y 2π(1 ν) K xy( x), σ yy (2) (x) = yy (x) = µb x 2π(1 ν) K yx( x) (10) µb y 2π(1 ν) [ 1 x K yy( x) (11) Case (1) has mirror symmetry about the y, z plane, u (1) x (x, y) = u (1) x ( x, y), u (1) y (x, y) = u (1) y ( x, y), so that σ yx (1) (+x) = σ yx (1) ( x) and σ yy (1) (+x) = σ yy (1) ( x), assuring that K xx ( x) = K xx (+x) and K yx ( x) = K yx (+x) (12) Case (2) has pure antisymmetry about that y, z plane, requiring that u (2) x (x, y) = u (2) x ( x, y), u (2) y (x, y) = u (2) y ( x, y), so that σ yx (2) (+x) = σ yx (2) ( x) and σ yy (2) (+x) = σ yy (2) ( x), assuring that K xy ( x) = K xy (+x) and K yy (+x) = K yy ( x) (13) Thus both K xy (t x) and K yx (t x) are even functions of t x and our previous deduction that K xy (t x) = K yx (x t) can be rewritten as K xy (t x) = K yx (t x) (14) Reverting to the opening discussion, this result, based only on elastic reciprocity and symmetry, clearly shows that the opposite alternative must be the correct one. This result is not restricted to the coordinate choice of Figure 1, as we show next. 4. Coordinate changes Given K ıj (θ) for a particular choice of coordinates x, y, the components Kĩ j (θ) may be determined for an alternative choice x, ỹ. Consider the coordinates x = x, ỹ = y (e.g., Erdogan, 1969; Erdogan et al., 1973; Figure 2), 6
7 a) x b) ỹ x y Figure 2: Elements along the x-axis and at symmetric points about the ỹ-axis indicate stress (σ x x omitted) due to an edge dislocation with Burgers vector a) parallel and b) perpendicular to a free surface a distance h away. 7
8 for which the displacement discontinuities are δĩ( x) = u + ĩ ( x, 0+ ) u ĩ ( x, 0 ) for ĩ = x, ỹ, and the stress components take the form µ [ 1 dδĩ( t ) σỹĩ ( x) = + Kĩ j ( t x) dδ j( t ) d t (15) 2π(1 ν) t x d t d t We note that δ x ( x) = δ x (x) and δỹ( x) = δ y (x) and that σỹ x ( x) = σ yx (x), and σỹỹ ( x) = σ yy (x). Using these relations for displacement discontinuities and stress components between the two coordinate systems, the coordinate transformations themselves, and the anticipated even or odd nature of Kĩ j (θ), we may transform the expression for σỹĩ ( x) as an integral over t (Equation 15) to an expression for σ yı (x) as an integral over t. Doing so and comparing the resulting expression with Equation 3, we find the relation between the nonsingular kernels: K ıj (θ) = Kĩ j (θ) for ı = j and K ıj (θ) = Kĩ j (θ) for ı j. (Here the notation is such that if ı = x, then ĩ = x, etc.) That both K xy (θ) and K yx (θ) transform into the new coordinate system with the same sign preserves the conclusion of the previous section: K xỹ (θ) = Kỹ x (θ). This indicates that the solution proposed in Erdogan (1969) and Erdogan et al. (1973), in which K xỹ (θ) = Kỹ x (θ), must require correction, presumably due to an unnoticed sign error in transcription from notes or in derivation. From the above analysis alone, it is not possible to determine which of the two terms requires a sign change to arrive at K xỹ (θ) = Kỹ x (θ). However, using a correct solution in another coordinate set (e.g., Head, 1953) and the coordinate transformation above, the appropriate sign change may be determined (see Appendix). 5. Acknowledgment Our interest in clarifying ambiguities in the literature arose in studying models for fractures running parallel to surfaces of half-spaces as they arise in landslide and glacial mechanics, those studies being supported in the former application area by a Cooperative Research Agreement with Total E&P Recherche Developpement under award number FR , and in the latter by NSF Office of Polar Programs award ANT We are grateful to Victor C. Tsai for discussion. 8
9 Appendix A. Expressions for stress due to edge dislocations under change of coordinates, Burgers vector convention For the coordinates of Figure 1 and the positive Burgers vector convention represented by cases (1) and (2) (e.g., as in Thouless et al., 1987), stresses along y = 0 are σ (1) yx (x) + σ (2) yx (x) µ/ [2π(1 ν) σ (2) yy (x) + σ (1) yy (x) µ/ [2π(1 ν) = b x [ 1 x x 4h 2 + x 2 + b y [ 24h 3 x 2 32h 5 (4h 2 + x 2 ) 3 = b y [ 1 x x 4h 2 + x 2 b x [ 24h3 x 2 32h 5 (4h 2 + x 2 ) 3 8h 2 x (4h 2 + x 2 ) 2 + 4h2 x 3 48h 4 x (4h 2 + x 2 ) 3 + (A.1) 8h 2 x (4h 2 + x 2 ) 2 + 4h2 x 3 48h 4 x (4h 2 + x 2 ) 3 + (A.2) Comparing the above to eqs. (10 11), the components K ıj (θ) are θ K xx (θ) = 4h 2 + θ + 8h 2 θ 2 (4h 2 + θ 2 ) 2 + 4h2 θ 3 48h 4 θ (4h 2 + θ 2 ) 3 K xy (θ) = 24h3 θ 2 32h 5 (4h 2 + θ 2 ) 3 θ K yy (θ) = 4h 2 + θ 8h 2 θ 2 (4h 2 + θ 2 ) 2 + 4h2 θ 3 48h 4 θ (4h 2 + θ 2 ) 3 K yx (θ) = 24h3 θ 2 32h 5 (4h 2 + θ 2 ) 3 (A.3) The solution for the coordinates x, ỹ of the Erdogan 1969 and 1973 papers is then correctly given, using the transformation K xỹ (θ) = K xy (θ), Kỹ x (θ) = K yx (θ), and K x x (θ) = K xx (θ), Kỹỹ (θ) = K yy (θ), as K xỹ (θ) = Kỹ x (θ) = 24h3 θ 2 32h 5 (4h 2 + θ 2 ) 3 (A.4) with on-diagonal Kĩ j (θ) as above, whereas previously Erdogan (1969) stated K xỹ (θ) = Kỹ x (θ) = (24h 3 θ 2 32h 5 )/ (4h 2 + θ 2 ) 3. Erdogan (1971), using the same coordinates, is in agreement with these Kĩ j (θ) provided the sign is 9
10 changed for each of his kernel terms. That is appropriate for K x x and Kỹỹ because he reversed the sign convention for these terms in the 1971 paper, but not for K xỹ and Kỹ x. If we speculate that such was a misprint and that he intended to reverse the sign convention for the off-diagonal terms too, then results of his 1971 paper would be fully verified. References Ashbaugh, N., Stress solution for a crack at an arbitrary angle to an interface. Int. J. Fracture 11, Chen, S.H., Keer, L.M., Achenbach, J.D., Steady motion of a crack parallel to a bond-plane. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 18, Dundurs, J., Sendecky, G.P., Behavior of an edge dislocation near a bimetallic interface. J. Appl. Phys. 36, Dyskin, A.V., Germanovich, L.N., Ustinov, K.B., Asymptotic analysis of crack interaction with free boundary. Int. J. Solid. Struct. 37, Erdogan, F., Solutions of systems of singular integral equations. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. J. Appl. Math. 17, Erdogan, F., Bonded dissimilar materials containing cracks parallel to the interface. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 3, Erdogan, F., Gupta, G.D., Cook, T.S., Numerical solutions of singular integral equations, in: Sih, G.C. (Ed.), Mechanics of Fracture: Methods of Analysis and Solution of Crack Problems. Noordhoff Int. Pub., Leyden, Netherlands. chapter 7, pp Head, A.K., Edge dislocations in inhomogeneous media. Proc. Phys. Soc. B 66, Higashida, Y., Kamada, K., Stress fields around a crack lying parallel to a free surface. Int. J. Fracture 19, Murakami, Y. (Ed.), Stress Intensity Factors Handbook. volume 1. Pergamon Press, New York. 10
11 Paynter, R.J.H., Hills, D.A., Sackfield, A., The penny crack beneath the surface of a half-space: The penny crack beneath the surface of a halfspace: with application to the blister test. Int. J. Fracture 142, Tada, H., Paris, P.C., Irwin, G.R. (Eds.), The Stress Analysis of Cracks Handbook. ASME, New York. 3rd edition. Thouless, M.D., Evans, A.G., Ashby, M.F., Hutchinson, J.W., The edge cracking and spalling of brittle plates. Acta. Metall. 35, Yang, F., Li, J.C.M., Dislocation model of a subsurface crack. J. Appl. Phys. 82,
Two semi-infinite interfacial cracks between two bonded dissimilar elastic strips
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Faculty Publications from the Department of Engineering Mechanics Mechanical & Materials Engineering, Department of 9-2003
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Faculty Publications from the Department of Engineering Mechanics Mechanical & Materials Engineering, Department of 9-2003
Transactions on Engineering Sciences vol 6, 1994 WIT Press, ISSN
 Unitary weight functions for semi-infinite crack in the half-plane K.L. Molski Institute of Cranes and Heavy Machinery Engineering, Warsaw University of Technology, Narbutta 85, 02-524 Warsaw, Poland ABSTRACT
Unitary weight functions for semi-infinite crack in the half-plane K.L. Molski Institute of Cranes and Heavy Machinery Engineering, Warsaw University of Technology, Narbutta 85, 02-524 Warsaw, Poland ABSTRACT
INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE ON BEHAVIOR OF THE INTERFACIAL CRACK BETWEEN THE TWO LAYERS
 Djoković, J. M., et.al.: Influence of Temperature on Behavior of the Interfacial THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 010, Vol. 14, Suppl., pp. S59-S68 S59 INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE ON BEHAVIOR OF THE INTERFACIAL CRACK
Djoković, J. M., et.al.: Influence of Temperature on Behavior of the Interfacial THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 010, Vol. 14, Suppl., pp. S59-S68 S59 INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE ON BEHAVIOR OF THE INTERFACIAL CRACK
Elastic and Elastic-Plastic Behaviour of a Crack in a Residual Stress Field
 Residual Stresses 2016: IC-10 Elastic and Elastic-Plastic Behaviour of a Crack in a Residual Stress Field Guiyi Wu a, Chris Aird b, David Smith and Martyn Pavier c* Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Residual Stresses 2016: IC-10 Elastic and Elastic-Plastic Behaviour of a Crack in a Residual Stress Field Guiyi Wu a, Chris Aird b, David Smith and Martyn Pavier c* Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Homework Problems. ( σ 11 + σ 22 ) 2. cos (θ /2), ( σ θθ σ rr ) 2. ( σ 22 σ 11 ) 2
 Engineering Sciences 47: Fracture Mechanics J. R. Rice, 1991 Homework Problems 1) Assuming that the stress field near a crack tip in a linear elastic solid is singular in the form σ ij = rλ Σ ij (θ), it
Engineering Sciences 47: Fracture Mechanics J. R. Rice, 1991 Homework Problems 1) Assuming that the stress field near a crack tip in a linear elastic solid is singular in the form σ ij = rλ Σ ij (θ), it
The effect of a crack-tip radius on the validity of the singular solution
 693 The effect of a crack-tip radius on the validity of the singular solution D Dini and D A Hills* Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK Abstract: The influence of the finite
693 The effect of a crack-tip radius on the validity of the singular solution D Dini and D A Hills* Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK Abstract: The influence of the finite
Moving screw dislocations in piezoelectric bimaterials
 phys stat sol (b) 38 No 1 10 16 (003) / DOI 10100/pssb00301805 Moving screw dislocations in piezoelectric bimaterials Xiang-Fa Wu *1 Yuris A Dzenis 1 and Wen-Sheng Zou 1 Department of Engineering Mechanics
phys stat sol (b) 38 No 1 10 16 (003) / DOI 10100/pssb00301805 Moving screw dislocations in piezoelectric bimaterials Xiang-Fa Wu *1 Yuris A Dzenis 1 and Wen-Sheng Zou 1 Department of Engineering Mechanics
Integral equations for crack systems in a slightly heterogeneous elastic medium
 Boundary Elements and Other Mesh Reduction Methods XXXII 65 Integral equations for crack systems in a slightly heterogeneous elastic medium A. N. Galybin & S. M. Aizikovich Wessex Institute of Technology,
Boundary Elements and Other Mesh Reduction Methods XXXII 65 Integral equations for crack systems in a slightly heterogeneous elastic medium A. N. Galybin & S. M. Aizikovich Wessex Institute of Technology,
The Subsurface Crack Under Conditions of Slip and Stick Caused by a Surface Normal Force
 F.-K.Chang Maria Comninou Mem. ASME Sheri Sheppard Student Mem. ASME J. R. Barber Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Mich. 48109 The Subsurface
F.-K.Chang Maria Comninou Mem. ASME Sheri Sheppard Student Mem. ASME J. R. Barber Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Mich. 48109 The Subsurface
Mode II stress intensity factors determination using FE analysis
 Mode II stress intensity factors determination using FE analysis Paulo C. M. Azevedo IDMEC and Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto March 2008 Abstract The stress intensity factors K I and
Mode II stress intensity factors determination using FE analysis Paulo C. M. Azevedo IDMEC and Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto March 2008 Abstract The stress intensity factors K I and
17th European Conference on Fracture 2-5 September,2008, Brno, Czech Republic. Thermal Fracture of a FGM/Homogeneous Bimaterial with Defects
 -5 September,8, Brno, Czech Republic Thermal Fracture of a FGM/Homogeneous Bimaterial with Defects Vera Petrova, a, Siegfried Schmauder,b Voronezh State University, University Sq., Voronezh 3946, Russia
-5 September,8, Brno, Czech Republic Thermal Fracture of a FGM/Homogeneous Bimaterial with Defects Vera Petrova, a, Siegfried Schmauder,b Voronezh State University, University Sq., Voronezh 3946, Russia
A Piezoelectric Screw Dislocation Interacting with an Elliptical Piezoelectric Inhomogeneity Containing a Confocal Elliptical Rigid Core
 Commun. Theor. Phys. 56 774 778 Vol. 56, No. 4, October 5, A Piezoelectric Screw Dislocation Interacting with an Elliptical Piezoelectric Inhomogeneity Containing a Confocal Elliptical Rigid Core JIANG
Commun. Theor. Phys. 56 774 778 Vol. 56, No. 4, October 5, A Piezoelectric Screw Dislocation Interacting with an Elliptical Piezoelectric Inhomogeneity Containing a Confocal Elliptical Rigid Core JIANG
CRACK INITIATION CRITERIA FOR SINGULAR STRESS CONCENTRATIONS Part I: A Universal Assessment of Singular Stress Concentrations
 Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 14, 2007, No. 6, p. 399 408 399 CRACK INITIATION CRITERIA FOR SINGULAR STRESS CONCENTRATIONS Part I: A Universal Assessment of Singular Stress Concentrations Zdeněk Knésl, Jan
Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 14, 2007, No. 6, p. 399 408 399 CRACK INITIATION CRITERIA FOR SINGULAR STRESS CONCENTRATIONS Part I: A Universal Assessment of Singular Stress Concentrations Zdeněk Knésl, Jan
Fracture Mechanics, Damage and Fatigue Linear Elastic Fracture Mechanics - Energetic Approach
 University of Liège Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering Fracture Mechanics, Damage and Fatigue Linear Elastic Fracture Mechanics - Energetic Approach Ludovic Noels Computational & Multiscale Mechanics of
University of Liège Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering Fracture Mechanics, Damage and Fatigue Linear Elastic Fracture Mechanics - Energetic Approach Ludovic Noels Computational & Multiscale Mechanics of
The Effects of Transverse Shear on the Delamination of Edge-Notch Flexure and 3-Point Bend Geometries
 The Effects of Transverse Shear on the Delamination of Edge-Notch Flexure and 3-Point Bend Geometries M. D. Thouless Department of Mechanical Engineering Department of Materials Science & Engineering University
The Effects of Transverse Shear on the Delamination of Edge-Notch Flexure and 3-Point Bend Geometries M. D. Thouless Department of Mechanical Engineering Department of Materials Science & Engineering University
The influence of elastic mismatch on the size of the plastic zone of a crack terminating at a brittle-ductile interface
 International Journal of Fracture 65: 183-196, 1994. ~ 1994 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 183 The influence of elastic mismatch on the size of the plastic zone of a crack terminating
International Journal of Fracture 65: 183-196, 1994. ~ 1994 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 183 The influence of elastic mismatch on the size of the plastic zone of a crack terminating
Size effect in the strength of concrete structures
 Sādhanā Vol. 27 Part 4 August 2002 pp. 449 459. Printed in India Size effect in the strength of concrete structures B L KARIHALOO and Q Z XIAO Division of Civil Engineering School of Engineering Cardiff
Sādhanā Vol. 27 Part 4 August 2002 pp. 449 459. Printed in India Size effect in the strength of concrete structures B L KARIHALOO and Q Z XIAO Division of Civil Engineering School of Engineering Cardiff
First-Order Solutions for the Buckling Loads of Euler-Bernoulli Weakened Columns
 First-Order Solutions for the Buckling Loads of Euler-Bernoulli Weakened Columns J. A. Loya ; G. Vadillo 2 ; and J. Fernández-Sáez 3 Abstract: In this work, closed-form expressions for the buckling loads
First-Order Solutions for the Buckling Loads of Euler-Bernoulli Weakened Columns J. A. Loya ; G. Vadillo 2 ; and J. Fernández-Sáez 3 Abstract: In this work, closed-form expressions for the buckling loads
Fracture Mechanics of Composites with Residual Thermal Stresses
 J. A. Nairn Material Science & Engineering, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah 84 Fracture Mechanics of Composites with Residual Thermal Stresses The problem of calculating the energy release rate
J. A. Nairn Material Science & Engineering, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah 84 Fracture Mechanics of Composites with Residual Thermal Stresses The problem of calculating the energy release rate
VERIFICATION OF BRITTLE FRACTURE CRITERIA FOR BIMATERIAL STRUCTURES
 VERIFICATION OF BRITTLE FRACTURE CRITERIA FOR BIMATERIAL STRUCTURES Grzegorz MIECZKOWSKI *, Krzysztof MOLSKI * * Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Białystok University of Technology, ul. Wiejska 45C,
VERIFICATION OF BRITTLE FRACTURE CRITERIA FOR BIMATERIAL STRUCTURES Grzegorz MIECZKOWSKI *, Krzysztof MOLSKI * * Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Białystok University of Technology, ul. Wiejska 45C,
Transactions on Modelling and Simulation vol 9, 1995 WIT Press, ISSN X
 Elastic-plastic model of crack growth under fatigue using the boundary element method M. Scibetta, O. Pensis LTAS Fracture Mechanics, University ofliege, B-4000 Liege, Belgium Abstract Life of mechanic
Elastic-plastic model of crack growth under fatigue using the boundary element method M. Scibetta, O. Pensis LTAS Fracture Mechanics, University ofliege, B-4000 Liege, Belgium Abstract Life of mechanic
Materials and Structures
 Journal of Mechanics of Materials and Structures BRITTLE FRACTURE BEYOND THE STRESS INTENSITY FACTOR C. T. Sun and Haiyang Qian Volume 4, Nº 4 April 2009 mathematical sciences publishers JOURNAL OF MECHANICS
Journal of Mechanics of Materials and Structures BRITTLE FRACTURE BEYOND THE STRESS INTENSITY FACTOR C. T. Sun and Haiyang Qian Volume 4, Nº 4 April 2009 mathematical sciences publishers JOURNAL OF MECHANICS
Method for calculating the stress intensity factor for mode-i indentation with eccentric loads
 Acta Technica 6 (017), No. 4A, 481488 c 017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Method for calculating the stress intensity factor for mode-i indentation with eccentric loads DUO Yili 1,, XIE Yujun
Acta Technica 6 (017), No. 4A, 481488 c 017 Institute of Thermomechanics CAS, v.v.i. Method for calculating the stress intensity factor for mode-i indentation with eccentric loads DUO Yili 1,, XIE Yujun
Stress intensity factors for a crack in front of an inclusion
 Stress intensity factors for a crack in front of an inclusion Johan Helsing Department of Solid Mechanics and NADA, Royal Institute of Technology, SE-100 44 Stockholm, Sweden Email: helsing@nada.kth.se,
Stress intensity factors for a crack in front of an inclusion Johan Helsing Department of Solid Mechanics and NADA, Royal Institute of Technology, SE-100 44 Stockholm, Sweden Email: helsing@nada.kth.se,
Stress intensity factor analysis for an interface crack between dissimilar isotropic materials
 Stress intensity factor analysis for an interface crack between dissimilar isotropic materials under thermal stress T. Ikeda* & C. T. Sun* I Chemical Engineering Group, Department of Materials Process
Stress intensity factor analysis for an interface crack between dissimilar isotropic materials under thermal stress T. Ikeda* & C. T. Sun* I Chemical Engineering Group, Department of Materials Process
Stress intensity factors determination for an inclined central crack on a plate subjected to uniform tensile loading using FE analysis
 Stress intensity factors determination for an inclined central crack on a plate subjected to uniform tensile loading using FE analysis Paulo C. M. Azevedo IDMEC and Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade
Stress intensity factors determination for an inclined central crack on a plate subjected to uniform tensile loading using FE analysis Paulo C. M. Azevedo IDMEC and Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade
Fracture mechanics fundamentals. Stress at a notch Stress at a crack Stress intensity factors Fracture mechanics based design
 Fracture mechanics fundamentals Stress at a notch Stress at a crack Stress intensity factors Fracture mechanics based design Failure modes Failure can occur in a number of modes: - plastic deformation
Fracture mechanics fundamentals Stress at a notch Stress at a crack Stress intensity factors Fracture mechanics based design Failure modes Failure can occur in a number of modes: - plastic deformation
Elastic behaviour of an edge dislocation near a sharp crack emanating from a semi-elliptical blunt crack
 Chin. Phys. B Vol. 19, No. 1 010 01610 Elastic behaviour of an edge dislocation near a sharp crack emanating from a semi-elliptical blunt crack Fang Qi-Hong 方棋洪, Song Hao-Peng 宋豪鹏, and Liu You-Wen 刘又文
Chin. Phys. B Vol. 19, No. 1 010 01610 Elastic behaviour of an edge dislocation near a sharp crack emanating from a semi-elliptical blunt crack Fang Qi-Hong 方棋洪, Song Hao-Peng 宋豪鹏, and Liu You-Wen 刘又文
arxiv:patt-sol/ v1 5 Nov 1993
 Oscillatory instability of crack propagations in quasi-static fracture Shin-ichi Sasa Department of physics, Kyoto University, Kyoto 606, Japan arxiv:patt-sol/9311001v1 5 Nov 1993 Ken Sekimoto Department
Oscillatory instability of crack propagations in quasi-static fracture Shin-ichi Sasa Department of physics, Kyoto University, Kyoto 606, Japan arxiv:patt-sol/9311001v1 5 Nov 1993 Ken Sekimoto Department
TOUGHNESS OF PLASTICALLY-DEFORMING ASYMMETRIC JOINTS. Ford Research Laboratory, Ford Motor Company, Dearborn, MI 48121, U.S.A. 1.
 TOUGHNESS OF PLASTICALLY-DEFORMING ASYMMETRIC JOINTS M. D. Thouless, M. S. Kafkalidis, S. M. Ward and Y. Bankowski Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics, University of Michigan, Ann
TOUGHNESS OF PLASTICALLY-DEFORMING ASYMMETRIC JOINTS M. D. Thouless, M. S. Kafkalidis, S. M. Ward and Y. Bankowski Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics, University of Michigan, Ann
Surface crack subject to mixed mode loading
 Engineering Fracture Mechanics 65 (2000) 1±14 www.elsevier.com/locate/engfracmech Surface crack subject to mixed mode loading M.Y. He a, J.W. Hutchinson b, * a Materials Engineering Department, University
Engineering Fracture Mechanics 65 (2000) 1±14 www.elsevier.com/locate/engfracmech Surface crack subject to mixed mode loading M.Y. He a, J.W. Hutchinson b, * a Materials Engineering Department, University
CRACK-TIP DIFFRACTION IN A TRANSVERSELY ISOTROPIC SOLID. A.N. Norris and J.D. Achenbach
 CRACK-TIP DIFFRACTION IN A TRANSVERSELY ISOTROPIC SOLID A.N. Norris and J.D. Achenbach The Technological Institute Northwestern University Evanston, IL 60201 ABSTRACT Crack diffraction in a transversely
CRACK-TIP DIFFRACTION IN A TRANSVERSELY ISOTROPIC SOLID A.N. Norris and J.D. Achenbach The Technological Institute Northwestern University Evanston, IL 60201 ABSTRACT Crack diffraction in a transversely
Screw dislocation interacting with interface and interfacial cracks in piezoelectric bimaterials
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Faculty Publications from the Department of Engineering Mechanics Mechanical & Materials Engineering, Department of 4-2003
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Faculty Publications from the Department of Engineering Mechanics Mechanical & Materials Engineering, Department of 4-2003
Exercise: concepts from chapter 5
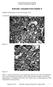 Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 5 1) Study the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. Figure 1a Figure 1b Figure 1. Nearly undeformed (1a) and significantly deformed (1b) oöids with spherulitic
Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 5 1) Study the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. Figure 1a Figure 1b Figure 1. Nearly undeformed (1a) and significantly deformed (1b) oöids with spherulitic
Finite element analysis of longitudinal debonding between fibre and matrix interface
 Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 11, February 2004, pp. 43-48 Finite element analysis of longitudinal debonding between fibre and matrix interface K Aslantaş & S Taşgetiren Department
Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 11, February 2004, pp. 43-48 Finite element analysis of longitudinal debonding between fibre and matrix interface K Aslantaş & S Taşgetiren Department
PROPAGATION OF CURVED CRACKS IN HOMOGENEOUS AND GRADED MATERIALS
 PROPAGATION OF CURVED CRACKS IN HOMOGENEOUS AND GRADED MATERIALS Abstract Matthew T. Tilbrook, Robert J. Moon and Mark Hoffman School of Materials Science and Engineering University of New South Wales,
PROPAGATION OF CURVED CRACKS IN HOMOGENEOUS AND GRADED MATERIALS Abstract Matthew T. Tilbrook, Robert J. Moon and Mark Hoffman School of Materials Science and Engineering University of New South Wales,
INFLUENCE OF THE LOCATION AND CRACK ANGLE ON THE MAGNITUDE OF STRESS INTENSITY FACTORS MODE I AND II UNDER UNIAXIAL TENSION STRESSES
 INFLUENCE OF THE LOCATION AND CRACK ANGLE ON THE MAGNITUDE OF STRESS INTENSITY FACTORS MODE I AND II UNDER UNIAXIAL TENSION STRESSES Najah Rustum Mohsin Southern Technical University, Technical Institute-Nasiriya,
INFLUENCE OF THE LOCATION AND CRACK ANGLE ON THE MAGNITUDE OF STRESS INTENSITY FACTORS MODE I AND II UNDER UNIAXIAL TENSION STRESSES Najah Rustum Mohsin Southern Technical University, Technical Institute-Nasiriya,
RUPTURE OF FRICTIONALLY HELD INCOHERENT INTERFACES UNDER DYNAMIC SHEAR LOADING
 RUPTURE OF FRICTIONALLY HELD INCOHERENT INTERFACES UNDER DYNAMIC SHEAR LOADING G. Lykotrafitis and A.J. Rosakis Graduate Aeronautical Laboratories, Mail Stop 105-50, California Institute of Technology,
RUPTURE OF FRICTIONALLY HELD INCOHERENT INTERFACES UNDER DYNAMIC SHEAR LOADING G. Lykotrafitis and A.J. Rosakis Graduate Aeronautical Laboratories, Mail Stop 105-50, California Institute of Technology,
Dynamic Stress Intensity Factors of Collinear Cracks under a Uniform Tensile Stress Wave 1
 Copyright 2013 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.93, no.2, pp.133-148, 2013 Dynamic Stress Intensity Factors of Collinear Cracks under a Uniform Tensile Stress Wave 1 K.-C. Wu 2, S.-M. Huang 2, S.-H. Chen 3
Copyright 2013 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.93, no.2, pp.133-148, 2013 Dynamic Stress Intensity Factors of Collinear Cracks under a Uniform Tensile Stress Wave 1 K.-C. Wu 2, S.-M. Huang 2, S.-H. Chen 3
For an imposed stress history consisting of a rapidly applied step-function jump in
 Problem 2 (20 points) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 0239 2.002 MECHANICS AND MATERIALS II SOLUTION for QUIZ NO. October 5, 2003 For
Problem 2 (20 points) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 0239 2.002 MECHANICS AND MATERIALS II SOLUTION for QUIZ NO. October 5, 2003 For
3 2 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) 3. a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1
 Math Problem a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1 3 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) = Au( t) with u (0) =. 3 1 u 1 =, u 1 3 = b- True or false and why 1. if A is
Math Problem a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1 3 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) = Au( t) with u (0) =. 3 1 u 1 =, u 1 3 = b- True or false and why 1. if A is
Introduction to fracture mechanics
 Introduction to fracture mechanics Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Dr. Giuseppe Abbiati, Dr. Konstantinos Agathos Lecture 6-9 November, 2017 Institute of Structural Engineering, ETH Zu rich November 9, 2017 Institute
Introduction to fracture mechanics Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Dr. Giuseppe Abbiati, Dr. Konstantinos Agathos Lecture 6-9 November, 2017 Institute of Structural Engineering, ETH Zu rich November 9, 2017 Institute
Topics in Ship Structures
 Topics in Ship Structures 8 Elastic-lastic Fracture Mechanics Reference : Fracture Mechanics by T.L. Anderson Lecture Note of Eindhoven University of Technology 17. 1 by Jang, Beom Seon Oen INteractive
Topics in Ship Structures 8 Elastic-lastic Fracture Mechanics Reference : Fracture Mechanics by T.L. Anderson Lecture Note of Eindhoven University of Technology 17. 1 by Jang, Beom Seon Oen INteractive
Strain analysis.
 Strain analysis ecalais@purdue.edu Plates vs. continuum Gordon and Stein, 1991 Most plates are rigid at the until know we have studied a purely discontinuous approach where plates are
Strain analysis ecalais@purdue.edu Plates vs. continuum Gordon and Stein, 1991 Most plates are rigid at the until know we have studied a purely discontinuous approach where plates are
WESTERGAARD COMPLEX STRESS FUNCTIONS (16)
 GG711c 1/1/03 1 WESTERGAARD COMPLEX STRESS FUNCTIONS (16) I Main topics A B Historical perspective Expression of the biharmonic function by harmonic functions C Boundary conditions D Use of symmetry and
GG711c 1/1/03 1 WESTERGAARD COMPLEX STRESS FUNCTIONS (16) I Main topics A B Historical perspective Expression of the biharmonic function by harmonic functions C Boundary conditions D Use of symmetry and
A modified quarter point element for fracture analysis of cracks
 ndian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 14, February 007, pp. 31-38 A modified quarter point element for fracture analysis of cracks Sayantan Paul & B N Rao* Structural Engineering Division,
ndian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 14, February 007, pp. 31-38 A modified quarter point element for fracture analysis of cracks Sayantan Paul & B N Rao* Structural Engineering Division,
The Effect of Cohesive-Law Parameters on Mixed-Mode Fracture
 The Effect of Cohesive-Law Parameters on Mixed-Mode Fracture R. B. Sills * and M. D. Thouless * Abstract * Department of Mechanical Engineering Department of Materials Science & Engineering University
The Effect of Cohesive-Law Parameters on Mixed-Mode Fracture R. B. Sills * and M. D. Thouless * Abstract * Department of Mechanical Engineering Department of Materials Science & Engineering University
Module 2: Reflecting on One s Problems
 MATH55 Module : Reflecting on One s Problems Main Math concepts: Translations, Reflections, Graphs of Equations, Symmetry Auxiliary ideas: Working with quadratics, Mobius maps, Calculus, Inverses I. Transformations
MATH55 Module : Reflecting on One s Problems Main Math concepts: Translations, Reflections, Graphs of Equations, Symmetry Auxiliary ideas: Working with quadratics, Mobius maps, Calculus, Inverses I. Transformations
CRACK-TIP DRIVING FORCE The model evaluates the eect of inhomogeneities by nding the dierence between the J-integral on two contours - one close to th
 ICF 100244OR Inhomogeneity eects on crack growth N. K. Simha 1,F.D.Fischer 2 &O.Kolednik 3 1 Department ofmechanical Engineering, University of Miami, P.O. Box 248294, Coral Gables, FL 33124-0624, USA
ICF 100244OR Inhomogeneity eects on crack growth N. K. Simha 1,F.D.Fischer 2 &O.Kolednik 3 1 Department ofmechanical Engineering, University of Miami, P.O. Box 248294, Coral Gables, FL 33124-0624, USA
FRACTURE MECHANICS OF COMPOSITES WITH RESIDUAL STRESSES, TRACTION-LOADED CRACKS, AND IMPERFECT INTERFACES
 Proc. 2 nd ESIS TC4 Conference on Polymers and Composites, in press, 1999 Author prepared reprint FRACTURE MECHANICS OF COMPOSITES WITH RESIDUAL STRESSES, TRACTION-LOADED CRACKS, AND IMPERFECT INTERFACES
Proc. 2 nd ESIS TC4 Conference on Polymers and Composites, in press, 1999 Author prepared reprint FRACTURE MECHANICS OF COMPOSITES WITH RESIDUAL STRESSES, TRACTION-LOADED CRACKS, AND IMPERFECT INTERFACES
Screw Dislocation Interacting with Interfacial Edge-Cracks in Piezoelectric Bimaterial Strips
 Freund Publishing House Ltd. International Journal of Nonlinear Sciences Numerical Simulation 5(4), 34-346, 4 Screw Dislocation Interacting with Interfacial Edge-Cracks in Piezoelectric Bimaterial Strips
Freund Publishing House Ltd. International Journal of Nonlinear Sciences Numerical Simulation 5(4), 34-346, 4 Screw Dislocation Interacting with Interfacial Edge-Cracks in Piezoelectric Bimaterial Strips
J. Sladek, V. Sladek & M. Hrina Institute of Construction and Architecture, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Bratislava, Slovakia
 Evaluation of fracture parameters for functionally gradient materials J. Sladek, V. Sladek & M. Hrina Institute of Construction and Architecture, Slovak Academy of Sciences, 842 20 Bratislava, Slovakia
Evaluation of fracture parameters for functionally gradient materials J. Sladek, V. Sladek & M. Hrina Institute of Construction and Architecture, Slovak Academy of Sciences, 842 20 Bratislava, Slovakia
' ' ' ' ). The midplane of the plate is chosen to FREE WAVE PROPAGATION IN PLATES OF GENERAL ANISOTROPIC MEDIA
 FREE WAVE PROPAGATON N PLATES OF GENERAL ANSOTROPC MEDA Adnan H. Nayfeh Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics University of Cincinnati Cincinnati, OH 45221 D.E. Chimenti Materials Laboratory
FREE WAVE PROPAGATON N PLATES OF GENERAL ANSOTROPC MEDA Adnan H. Nayfeh Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics University of Cincinnati Cincinnati, OH 45221 D.E. Chimenti Materials Laboratory
Analysis of interface cracks with contact in composites by 2D BEM
 CHAPTER 8 Analysis of interface cracks with contact in composites by 2D BEM V. Mantič 1, A. Blázquez 2, E. Correa 1 & F. París 1 1 Group of Elasticity and Strength of Materials, School of Engineering,
CHAPTER 8 Analysis of interface cracks with contact in composites by 2D BEM V. Mantič 1, A. Blázquez 2, E. Correa 1 & F. París 1 1 Group of Elasticity and Strength of Materials, School of Engineering,
Analysis of Order of Singularity at a Vertex in 3D Transversely Isotropic Piezoelectric Single-Step Bonded Joints
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) 203 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-047 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-09, pp-7-99 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) 203 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-047 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-09, pp-7-99 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access
MingHao Zhao, HaiTao Liu, CuiYing Fan, Ernian Pan & Tong-Yi Zhang
 A nonlinear bilayer beam model for an interfacial crack in dielectric bimaterials under mechanical/electrical loading MingHao Zhao HaiTao Liu CuiYing Fan Ernian Pan & Tong-Yi Zhang International Journal
A nonlinear bilayer beam model for an interfacial crack in dielectric bimaterials under mechanical/electrical loading MingHao Zhao HaiTao Liu CuiYing Fan Ernian Pan & Tong-Yi Zhang International Journal
(Received 5 May 1980; accepted for print 21 September 1980)
 MECHANICS RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS Vol. 7(6),351-358,1980. Printed in the USA. 0093-6413/80/060351-08502.00/0 Copyright (c) Pergamon Press Ltd ON THE DISPLACEMENT INDUCED IN A RIGID CIRCULAR PUNCH ON AN
MECHANICS RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS Vol. 7(6),351-358,1980. Printed in the USA. 0093-6413/80/060351-08502.00/0 Copyright (c) Pergamon Press Ltd ON THE DISPLACEMENT INDUCED IN A RIGID CIRCULAR PUNCH ON AN
A novel approach to predict the growth rate of short cracks under multiaxial loadings
 A novel approach to predict the growth rate of short cracks under multiaxial loadings F. Brugier 1&2, S. Pommier 1, R. de Moura Pinho 2, C. Mary 2 and D. Soria 2 1 LMT-Cachan, ENS Cachan / CNRS / UPMC
A novel approach to predict the growth rate of short cracks under multiaxial loadings F. Brugier 1&2, S. Pommier 1, R. de Moura Pinho 2, C. Mary 2 and D. Soria 2 1 LMT-Cachan, ENS Cachan / CNRS / UPMC
Stresses and Displacements in Functionally Graded Materials of Semi-Infinite Extent Induced by Rectangular Loadings
 Materials 2012, 5, 210-226; doi:10.3390/ma5020210 Article OPEN ACCESS materials ISSN 1996-1944 www.mdpi.com/journal/materials Stresses and Displacements in Functionally Graded Materials of Semi-Infinite
Materials 2012, 5, 210-226; doi:10.3390/ma5020210 Article OPEN ACCESS materials ISSN 1996-1944 www.mdpi.com/journal/materials Stresses and Displacements in Functionally Graded Materials of Semi-Infinite
Analysis of Square-shaped Crack in Layered Halfspace Subject to Uniform Loading over Rectangular Surface Area
 Copyright 2015 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.109-110, no.1, pp.55-80, 2015 Analysis of Square-shaped Crack in Layered Halfspace Subject to Uniform Loading over Rectangular Surface Area H. T. Xiao 1,2,3,
Copyright 2015 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.109-110, no.1, pp.55-80, 2015 Analysis of Square-shaped Crack in Layered Halfspace Subject to Uniform Loading over Rectangular Surface Area H. T. Xiao 1,2,3,
On the singularity of temperature gradient near an inclined crack terminating at bimaterial interface
 International Journal of Fracture 58:319-324, 1992. 1992 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 319 On the singularity of temperature gradient near an inclined crack terminating at bimaterial
International Journal of Fracture 58:319-324, 1992. 1992 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 319 On the singularity of temperature gradient near an inclined crack terminating at bimaterial
Thermal stress intensity factors of interface cracks in bimaterials
 International Journal of Fracture 57: 381-388, 1992. 1992 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 381 Thermal stress intensity factors of interface cracks in bimaterials M. MEYER and S.
International Journal of Fracture 57: 381-388, 1992. 1992 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 381 Thermal stress intensity factors of interface cracks in bimaterials M. MEYER and S.
Stress intensity factors for a mixed mode center crack in an anisotropic strip
 International Journal of Fracture 108: 367 381, 2001. 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. Stress intensity factors for a mixed mode center crack in an anisotropic strip HAIYING
International Journal of Fracture 108: 367 381, 2001. 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. Stress intensity factors for a mixed mode center crack in an anisotropic strip HAIYING
On the determinacy of repetitive structures
 Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 51 (2003) 383 391 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmps On the determinacy of repetitive structures S.D. Guest a;, J.W. Hutchinson b a Department of Engineering, University
Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 51 (2003) 383 391 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmps On the determinacy of repetitive structures S.D. Guest a;, J.W. Hutchinson b a Department of Engineering, University
Transactions on Engineering Sciences vol 6, 1994 WIT Press, ISSN
 The treatment of crack propagation in inhomogeneous materials using the boundary element method A. Boussekine," L. Ulmet," S. Caperaa* " Laboratoire de Genie Civil, Universite de Limoges, 19300 Egletons,
The treatment of crack propagation in inhomogeneous materials using the boundary element method A. Boussekine," L. Ulmet," S. Caperaa* " Laboratoire de Genie Civil, Universite de Limoges, 19300 Egletons,
Some improvements of Xfem for cracked domains
 Some improvements of Xfem for cracked domains E. Chahine 1, P. Laborde 2, J. Pommier 1, Y. Renard 3 and M. Salaün 4 (1) INSA Toulouse, laboratoire MIP, CNRS UMR 5640, Complexe scientifique de Rangueil,
Some improvements of Xfem for cracked domains E. Chahine 1, P. Laborde 2, J. Pommier 1, Y. Renard 3 and M. Salaün 4 (1) INSA Toulouse, laboratoire MIP, CNRS UMR 5640, Complexe scientifique de Rangueil,
Effects of partial closure and friction on a radial crack emanating from a circular hole
 International Journal of Fracture 28 (1985) 29-36. 1985 Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Dordrecht. Printed in The Netherlands. Effects of partial closure and friction on a radial crack emanating from a circular
International Journal of Fracture 28 (1985) 29-36. 1985 Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Dordrecht. Printed in The Netherlands. Effects of partial closure and friction on a radial crack emanating from a circular
Loss of constraint on fracture in thin film structures due to creep
 Acta Materialia 50 (2002) 4137 4148 www.actamat-journals.com Loss of constraint on fracture in thin film structures due to creep R. Huang a,, J.H. Prévost a, Z. Suo b a Department of Civil and Environmental
Acta Materialia 50 (2002) 4137 4148 www.actamat-journals.com Loss of constraint on fracture in thin film structures due to creep R. Huang a,, J.H. Prévost a, Z. Suo b a Department of Civil and Environmental
e = (l/27r)ln(l- p/l+p'
 Key Engineering Materials Vols. J83-I87 (2000) pp. 73-78 2000 Trans Tech Publications. Switzerland Kinking out of a Mixed Mode Interface Crack T. Ikeda\ Y. Komohara^, A. Nakamura^ and N. Miyazaki^ ^ Department
Key Engineering Materials Vols. J83-I87 (2000) pp. 73-78 2000 Trans Tech Publications. Switzerland Kinking out of a Mixed Mode Interface Crack T. Ikeda\ Y. Komohara^, A. Nakamura^ and N. Miyazaki^ ^ Department
S.P. Timoshenko Institute of Mechanics, National Academy of Sciences, Department of Fracture Mechanics, Kyiv, Ukraine
 CALCULATION OF THE PREFRACTURE ZONE AT THE CRACK TIP ON THE INTERFACE OF MEDIA A. Kaminsky a L. Kipnis b M. Dudik b G. Khazin b and A. Bykovtscev c a S.P. Timoshenko Institute of Mechanics National Academy
CALCULATION OF THE PREFRACTURE ZONE AT THE CRACK TIP ON THE INTERFACE OF MEDIA A. Kaminsky a L. Kipnis b M. Dudik b G. Khazin b and A. Bykovtscev c a S.P. Timoshenko Institute of Mechanics National Academy
Cracks Jacques Besson
 Jacques Besson Centre des Matériaux UMR 7633 Mines ParisTech PSL Research University Institut Mines Télécom Aγνωστ oς Θεoς Outline 1 Some definitions 2 in a linear elastic material 3 in a plastic material
Jacques Besson Centre des Matériaux UMR 7633 Mines ParisTech PSL Research University Institut Mines Télécom Aγνωστ oς Θεoς Outline 1 Some definitions 2 in a linear elastic material 3 in a plastic material
Toughness of Ni/Al 2 O 3 interfaces as dependent on micron-scale plasticity and atomistic-scale separation
 Philosophical Magazine Vol. 88, Nos. 30 32, 21 October 11 November 2008, 3841 3859 Toughness of Ni/Al 2 O 3 interfaces as dependent on micron-scale plasticity and atomistic-scale separation Y. Wei a and
Philosophical Magazine Vol. 88, Nos. 30 32, 21 October 11 November 2008, 3841 3859 Toughness of Ni/Al 2 O 3 interfaces as dependent on micron-scale plasticity and atomistic-scale separation Y. Wei a and
Studies of Bimaterial Interface Fracture with Peridynamics Fang Wang 1, Lisheng Liu 2, *, Qiwen Liu 1, Zhenyu Zhang 1, Lin Su 1 & Dan Xue 1
 International Power, Electronics and Materials Engineering Conference (IPEMEC 2015) Studies of Bimaterial Interface Fracture with Peridynamics Fang Wang 1, Lisheng Liu 2, *, Qiwen Liu 1, Zhenyu Zhang 1,
International Power, Electronics and Materials Engineering Conference (IPEMEC 2015) Studies of Bimaterial Interface Fracture with Peridynamics Fang Wang 1, Lisheng Liu 2, *, Qiwen Liu 1, Zhenyu Zhang 1,
Critical applied stresses for a crack initiation from a sharp V-notch
 Focussed on: Fracture and Structural Integrity related Issues Critical applied stresses for a crack initiation from a sharp V-notch L. Náhlík, P. Hutař Institute of Physics of Materials, Academy of Sciences
Focussed on: Fracture and Structural Integrity related Issues Critical applied stresses for a crack initiation from a sharp V-notch L. Náhlík, P. Hutař Institute of Physics of Materials, Academy of Sciences
Tentamen/Examination TMHL61
 Avd Hållfasthetslära, IKP, Linköpings Universitet Tentamen/Examination TMHL61 Tentamen i Skademekanik och livslängdsanalys TMHL61 lördagen den 14/10 2000, kl 8-12 Solid Mechanics, IKP, Linköping University
Avd Hållfasthetslära, IKP, Linköpings Universitet Tentamen/Examination TMHL61 Tentamen i Skademekanik och livslängdsanalys TMHL61 lördagen den 14/10 2000, kl 8-12 Solid Mechanics, IKP, Linköping University
Analytical formulation of Modified Upper Bound theorem
 CHAPTER 3 Analytical formulation of Modified Upper Bound theorem 3.1 Introduction In the mathematical theory of elasticity, the principles of minimum potential energy and minimum complimentary energy are
CHAPTER 3 Analytical formulation of Modified Upper Bound theorem 3.1 Introduction In the mathematical theory of elasticity, the principles of minimum potential energy and minimum complimentary energy are
A TIME-DEPENDENT DAMAGE LAW IN DEFORMABLE SOLID: A HOMOGENIZATION APPROACH
 9th HSTAM International Congress on Mechanics Limassol, Cyprus, - July, A TIME-DEPENDENT DAMAGE LAW IN DEFORMABLE SOLID: A HOMOGENIZATION APPROACH Cristian Dascalu, Bertrand François, Laboratoire Sols
9th HSTAM International Congress on Mechanics Limassol, Cyprus, - July, A TIME-DEPENDENT DAMAGE LAW IN DEFORMABLE SOLID: A HOMOGENIZATION APPROACH Cristian Dascalu, Bertrand François, Laboratoire Sols
An Accurate Quadrature for the Numerical Integration of Polynomial Functions
 International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics 2018; 4(1: 1-7 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijamtp doi: 10.11648/j.ijamtp.20180401.11 ISSN: 2575-5919 (Print; ISSN: 2575-5927
International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics 2018; 4(1: 1-7 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijamtp doi: 10.11648/j.ijamtp.20180401.11 ISSN: 2575-5919 (Print; ISSN: 2575-5927
CALCULATION OF FRACTURE MECHANICS PARAMETERS FOR AN ARBITRARY THREE-DIMENSIONAL CRACK, BY THE EQUIVALENT DOMAIN INTEGRAL METHOD 1
 CALCULATION OF FRACTURE MECHANICS PARAMETERS FOR AN ARBITRARY THREE-DIMENSIONAL CRACK, BY THE EQUIVALENT DOMAIN INTEGRAL METHOD 1 G. P. NIKISHKOV 2 and S. N. ATLURI 3 Center for the Advancement of Computational
CALCULATION OF FRACTURE MECHANICS PARAMETERS FOR AN ARBITRARY THREE-DIMENSIONAL CRACK, BY THE EQUIVALENT DOMAIN INTEGRAL METHOD 1 G. P. NIKISHKOV 2 and S. N. ATLURI 3 Center for the Advancement of Computational
Potential-dependent dynamic fracture of nanoporous gold
 Potential-dependent dynamic fracture of nanoporous gold Shaofeng Sun 1, Xiying Chen 1, Nilesh Badwe 1, Karl Sieradzki 1 * 1 Ira A. Fulton School of Engineering, Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona
Potential-dependent dynamic fracture of nanoporous gold Shaofeng Sun 1, Xiying Chen 1, Nilesh Badwe 1, Karl Sieradzki 1 * 1 Ira A. Fulton School of Engineering, Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona
A simple plane-strain solution for functionally graded multilayered isotropic cylinders
 Structural Engineering and Mechanics, Vol. 24, o. 6 (2006) 000-000 1 A simple plane-strain solution for functionally graded multilayered isotropic cylinders E. Pan Department of Civil Engineering, The
Structural Engineering and Mechanics, Vol. 24, o. 6 (2006) 000-000 1 A simple plane-strain solution for functionally graded multilayered isotropic cylinders E. Pan Department of Civil Engineering, The
DRIVING FORCES. and INCLUSION BOUNDARIES with transformation strain. Xanthippi Markenscoff
 DRIVING FORCES ON MOVING DEFECTS: DISLOCATIONS and INCLUSION BOUNDARIES with transformation strain Xanthippi Markenscoff UCSD Energy release rates (Driving forces) for moving defects: dislocations and
DRIVING FORCES ON MOVING DEFECTS: DISLOCATIONS and INCLUSION BOUNDARIES with transformation strain Xanthippi Markenscoff UCSD Energy release rates (Driving forces) for moving defects: dislocations and
Exercise: concepts from chapter 8
 Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 8 1) The following exercises explore elementary concepts associated with a linear elastic material that is isotropic and homogeneous with respect to elastic
Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 8 1) The following exercises explore elementary concepts associated with a linear elastic material that is isotropic and homogeneous with respect to elastic
MICROMECHANICAL MODELS FOR CONCRETE
 Chapter 5 MICROMECHANICAL MODELS FOR CONCRETE 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter three micromechanical models will be examined. The first two models are the differential scheme and the Mori-Tanaka model
Chapter 5 MICROMECHANICAL MODELS FOR CONCRETE 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter three micromechanical models will be examined. The first two models are the differential scheme and the Mori-Tanaka model
Analytical solutions for some defect problems in 1D hexagonal and 2D octagonal quasicrystals
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 70 No. 5 journal of May 008 physics pp. 911 933 Analytical solutions for some defect problems in 1D hexagonal and D octagonal quasicrystals X WANG 1 and E PAN
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 70 No. 5 journal of May 008 physics pp. 911 933 Analytical solutions for some defect problems in 1D hexagonal and D octagonal quasicrystals X WANG 1 and E PAN
Introduction to Fracture
 Introduction to Fracture Introduction Design of a component Yielding Strength Deflection Stiffness Buckling critical load Fatigue Stress and Strain based Vibration Resonance Impact High strain rates Fracture
Introduction to Fracture Introduction Design of a component Yielding Strength Deflection Stiffness Buckling critical load Fatigue Stress and Strain based Vibration Resonance Impact High strain rates Fracture
Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics (ZAMP) /88/ $ 2.70/0 Vol. 39, July BirkhS.user Verlag Basel, 1988
 Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics (ZAMP) 0044-2275/88/004573-06 $ 2.70/0 Vol. 39, July 1988 9 BirkhS.user Verlag Basel, 1988 Cracked orthotropic strip with clamped boundaries By H. G. Georgiadis*)
Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics (ZAMP) 0044-2275/88/004573-06 $ 2.70/0 Vol. 39, July 1988 9 BirkhS.user Verlag Basel, 1988 Cracked orthotropic strip with clamped boundaries By H. G. Georgiadis*)
PROPAGATION OF A MODE-I CRACK UNDER THE IRWIN AND KHRISTIANOVICH BARENBLATT CRITERIA
 Materials Science, Vol. 39, No. 3, 3 PROPAGATION OF A MODE-I CRACK UNDER THE IRWIN AND KHRISTIANOVICH BARENBLATT CRITERIA I. I. Argatov, M. Bach, and V. A. Kovtunenko UDC 539.3 We study the problem of
Materials Science, Vol. 39, No. 3, 3 PROPAGATION OF A MODE-I CRACK UNDER THE IRWIN AND KHRISTIANOVICH BARENBLATT CRITERIA I. I. Argatov, M. Bach, and V. A. Kovtunenko UDC 539.3 We study the problem of
G1RT-CT A. BASIC CONCEPTS F. GUTIÉRREZ-SOLANA S. CICERO J.A. ALVAREZ R. LACALLE W P 6: TRAINING & EDUCATION
 A. BASIC CONCEPTS 6 INTRODUCTION The final fracture of structural components is associated with the presence of macro or microstructural defects that affect the stress state due to the loading conditions.
A. BASIC CONCEPTS 6 INTRODUCTION The final fracture of structural components is associated with the presence of macro or microstructural defects that affect the stress state due to the loading conditions.
Cauchy principal integrals Assume that ( ) is well-defined over. Cauchy principal integrals Z ( ) Z ( ) = lim. ( ) ) for (1)
 Notes on Cauchy principal and Hadamard finite-part integrals by W. T. Ang Original version on May 009 Revised and corrected on July 0 (In the original version, a term is missing in the alternative definition
Notes on Cauchy principal and Hadamard finite-part integrals by W. T. Ang Original version on May 009 Revised and corrected on July 0 (In the original version, a term is missing in the alternative definition
Advanced Strength of Materials Prof S. K. Maiti Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture 27
 Advanced Strength of Materials Prof S. K. Maiti Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture 27 Last time we considered Griffith theory of brittle fracture, where in it was considered
Advanced Strength of Materials Prof S. K. Maiti Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture 27 Last time we considered Griffith theory of brittle fracture, where in it was considered
The Rotating Inhomogeneous Elastic Cylinders of. Variable-Thickness and Density
 Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences 23 2008, 237 257 An International Journal c 2008 Dixie W Publishing Corporation, U. S. A. The Rotating Inhomogeneous Elastic Cylinders of Variable-Thickness and
Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences 23 2008, 237 257 An International Journal c 2008 Dixie W Publishing Corporation, U. S. A. The Rotating Inhomogeneous Elastic Cylinders of Variable-Thickness and
Coherence and Polarization Properties of Far Fields Generated by Quasi-Homogeneous Planar Electromagnetic Sources
 University of Miami Scholarly Repository Physics Articles and Papers Physics --2005 Coherence and Polarization Properties of Far Fields Generated by Quasi-Homogeneous Planar Electromagnetic Sources Olga
University of Miami Scholarly Repository Physics Articles and Papers Physics --2005 Coherence and Polarization Properties of Far Fields Generated by Quasi-Homogeneous Planar Electromagnetic Sources Olga
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE OUT-OF-PLANE DISPLACEMENT FIELDS FOR DIFFERENT CRACK PROPAGATION VELOVITIES
 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE OUT-OF-PLANE DISPLACEMENT FIELDS FOR DIFFERENT CRACK PROPAGATION VELOVITIES S. Hédan, V. Valle and M. Cottron Laboratoire de Mécanique des Solides, UMR 6610 Université de Poitiers
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE OUT-OF-PLANE DISPLACEMENT FIELDS FOR DIFFERENT CRACK PROPAGATION VELOVITIES S. Hédan, V. Valle and M. Cottron Laboratoire de Mécanique des Solides, UMR 6610 Université de Poitiers
436 A. Barani and G.H. Rahimi assessment models have been employed to investigate the LBB of cracked pipes that are not for combined load [8]. Yun-Jae
![436 A. Barani and G.H. Rahimi assessment models have been employed to investigate the LBB of cracked pipes that are not for combined load [8]. Yun-Jae 436 A. Barani and G.H. Rahimi assessment models have been employed to investigate the LBB of cracked pipes that are not for combined load [8]. Yun-Jae](/thumbs/86/94473226.jpg) Scientia Iranica, Vol. 4, No. 5, pp 435{44 c Sharif University of Technology, October 27 Approximate Method for Evaluation of the J-Integral for Circumferentially Semi-Elliptical-Cracked Pipes Subjected
Scientia Iranica, Vol. 4, No. 5, pp 435{44 c Sharif University of Technology, October 27 Approximate Method for Evaluation of the J-Integral for Circumferentially Semi-Elliptical-Cracked Pipes Subjected
On the local and nonlocal components of solvation thermodynamics and their relation to solvation shell models
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 109, NUMBER 12 22 SEPTEMBER 1998 On the local and nonlocal components of solvation thermodynamics and their relation to solvation shell models Nobuyuki Matubayasi Institute
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 109, NUMBER 12 22 SEPTEMBER 1998 On the local and nonlocal components of solvation thermodynamics and their relation to solvation shell models Nobuyuki Matubayasi Institute
McMAT 2007 Micromechanics of Materials Austin, Texas, June 3 7, 2007
 McMAT 2007 Micromechanics of Materials Austin, Texas, June 3 7, 2007 RANDOM POLYCRYSTALS OF GRAINS WITH CRACKS: MODEL OF ELASTIC BEHAVIOR FOR FRACTURED SYSTEMS James G. Berryman Earth Sciences Division
McMAT 2007 Micromechanics of Materials Austin, Texas, June 3 7, 2007 RANDOM POLYCRYSTALS OF GRAINS WITH CRACKS: MODEL OF ELASTIC BEHAVIOR FOR FRACTURED SYSTEMS James G. Berryman Earth Sciences Division
Modified Maxwell-Garnett equation for the effective transport coefficients in inhomogeneous media
 J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 3 (998) 7227 7234. Printed in the UK PII: S0305-4470(98)93976-2 Modified Maxwell-Garnett equation for the effective transport coefficients in inhomogeneous media Juris Robert Kalnin
J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 3 (998) 7227 7234. Printed in the UK PII: S0305-4470(98)93976-2 Modified Maxwell-Garnett equation for the effective transport coefficients in inhomogeneous media Juris Robert Kalnin
Stress magnification due to stretching and bending of thin ligaments between voids
 Arch Appl Mech 6) DOI 1.17/s419-6-8-6 ORIGINAL V. A. Lubarda X. Markenscoff Stress magnification due to stretching and bending of thin ligaments between voids Received: 8 December 5 Springer-Verlag 6 Abstract
Arch Appl Mech 6) DOI 1.17/s419-6-8-6 ORIGINAL V. A. Lubarda X. Markenscoff Stress magnification due to stretching and bending of thin ligaments between voids Received: 8 December 5 Springer-Verlag 6 Abstract
Relaxation of a Strained Elastic Film on a Viscous Layer
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 695 Materials Research Society Relaxation of a Strained Elastic Film on a Viscous Layer R. Huang 1, H. Yin, J. Liang 3, K. D. Hobart 4, J. C. Sturm, and Z. Suo 3 1 Department
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 695 Materials Research Society Relaxation of a Strained Elastic Film on a Viscous Layer R. Huang 1, H. Yin, J. Liang 3, K. D. Hobart 4, J. C. Sturm, and Z. Suo 3 1 Department
