Topology of the Fermi surface wavefunctions and magnetic oscillations in metals
|
|
|
- Shawn Roberts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Topology of the Fermi surface wavefunctions and magnetic oscillations in metals A. Alexandradinata L.I. Glazman Yale University arxiv: , arxiv: in preparation Physics Next Workshop 2017 LI/East End
2 Topology of the Fermi surface wavefunctions and magnetic oscillations in metals Aris Alexandradinata
3 Outline Normal metal in a magnetic field, Peierls substitution Classical and quantum magnetic oscillations Periodicity of oscillations and Onsager phase factor Quantization of degenerate bands (beyond Peierls) Symmetry constraints on the Onsager phase factor Transitions between the symmetry classes and magnetic breakdown Some applications
4 Electron in a periodic potential of crystal lattice Eigenvalues of yield the band structure Metals: partially filled band(s) 0 Low-energy properties defined by excitations (Landau quasiparticles) with small energies ξ(k) measured from the Fermi surface, Fermiology : study of dynamics of excitations near the Fermi surface (FS)
5 Measuring Fermi surface by using electron dynamics Pb Bi Learning about FS from the magnetic oscillations phenomena Quasiparticles dynamics in a weak magnetic field
6 Peierls substitution, dynamics of quasiparticles Peierls, 1933 Classical dynamics of Landau Fermi-liquid quasiparticles: Hamilton equations of motion for with orbits in k-space, circle around the FS,, at fixed along cyclotron (or helicon) orbits in real space
7 Classical magneto-oscillations Commensurability of the diameter or period of the cyclotron motion with the wavelength or period of the external perturbation affects the linear response Magneto-acoustic oscillations Cyclotron resonance (Azbel & Kaner, 1956) small skin depth for RF cross-sectional area of FS (Shockley, 1950) Attenuation (of sound or EM wave) peaks at resonances with extremal trajectories for a given FS and given field direction
8 Periodicity of classical magneto-oscillations Attenuation (of sound or EM wave) peaks at resonances with extremal trajectories for a given FS and given field direction (in related context: Onsager 1952, I.M. Lifshitz~1952, Lifshitz & Kosevich, 1954) Magneto-acoustic oscillations Cyclotron resonance Information about the geometry of FS
9 Semiclassical quantization of spectrum Onsager-Lifshitz: Bohr-Sommerfeld quantization of motion in quasi-momentum space of particles with Hamiltonian, where Onsager phase factor discrete levels at fixed, Maslov correction (two turning points in the1d WKB problem) approximately equidistant levels at cyclotron mass
10 Quantum magneto-oscillations Landau levels successively pass through the Fermi level upon variation of the field (field-independent) intercept, Onsager phase factor
11 de Haas van Alpen oscillations of magnetization (Lifshitz & Kosevich, 1954) Comes from asymptotic evaluation of magnetization at Similar: Shubnikov de Haas oscillations of conductivity Direct measurement of Landau levels: STM (especially interesting in 2D, where oscillates with field) (Madhavani group, 2015)
12 Limitations of the Peierls substitution Onsager-Lifshitz: Bohr-Sommerfeld quantization of motion in quasi-momentum space of particles with Hamiltonian, where Onsager phase factor Maslov correction (two turning points in the1d WKB problem) (1) Single band, deformable to a circle, non-degenerate orbit [, Fermi energy cuts out a single orbit a given non-degenerate band], (2) Operator acts only on the plane-wave factor of the Bloch function
13 Cell-periodic function does matter: an example Two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) with Rashba spin-orbit coupling term spinor depending on k two orbits, differ by helicity, here is one of them: 2π rotation of k results in
14 Cell-periodic function does matter: an example 2π rotation of k results in Two ways to look at the additional term: (a) By symmetry, spin confined to the plane; full rotation encompasses solid angle 2π (b) In quantization, one needs to account for the Berry connection, (this is beyond Peierls substitution)
15 Landau levels beyond Peierls substitution We consider electron spectrum with D degenerate bands, each band may create L trajectories related by spatial symmetry to each other (total degeneracy of the trajectories is DxL), and: (1) Generalize the semiclassical quantization condition, (2) Find the rank-dl matrix which defines the phases in terms of the Hamiltonian. Our theory is manifestly gauge-invariant (i.e., independent of the phases of basis functions ) (3) Establish symmetry constraints on. There are 10 and only 10 symmetry classes of closed Fermi surface extremal orbits.
16 2DEG, no SO coupling, with Simple examples 2DEG, with Rashba SOC (deformed) graphene: D=2, L=2
17 Expansion of the Hamiltonian in powers of B To next order in B, interband transitions occur between P and Q The sub-leading in terms: encodes the geometric phase (Berry), orbital moment (Roth), and Zeeman effect: acts on
18 Beyond the Peierls-Onsager theory
19 Wilson loop in the WKB wavefunction
20 Symmetries of the loop propagator Apply all non-trivial elements of the point-group symmetry (g) to the ordered exponent
21 Why only 10 classes of symmetric orbits
22 The 10 classes LL degeneracy symmetric spltng symmetric spltng LL degeneracy reflection (yes/no): u=(1/0) time reversal (yes/no): s=(1/0) symmetry relates disconnected orbits to each other (yes)/(no): (II-B)/(I and II-A)
23 The 10 classes Graphene; strained WTe 2, B rot.axis Surface of Bi 2 Se 3 ; Na 3 Bi, B trig.axis Surface of SnTe Bilayer graphene Deformed graphene, WSe 2 LL degeneracy symmetric spltng symmetric spltng LL degeneracy reflection (yes/no): u=(1/0) time reversal (yes/no): s=(1/0) symmetry relates disconnected orbits to each other (yes)/(no): (II-B)/(I and II-A)
24 Additional considerations (contractibility) Orbit not contractible to a point reflection (yes/no): u=(1/0) time reversal (yes/no): s=(1/0) Orbit contractible to a point
25 Lifshitz transition between II-A and II-B (u=1, s=0) II-A: symmetry within single orbit II-B: symmetry between distinct orbits reflection (yes/no): u=(1/0) time reversal (yes/no): s=(1/0)
26 Magnetic breakdown at the saddle point (dispense with phase of ) (includes geometrical phase, in addition to Azbel, 1961) topological trivial
27 Some applications (a) Strained graphene with broken spatial-inversion symmetry (HBN substrate) (b) WSe 2 [II-B, u=0, s=1] (one of the valleys)
28 Some applications (c) Na 3 Bi with B trigonal axis; [II-A, u=0, s=1]; (d) Strained WTe 2 (Weyl point), angular field dependence, z rotation axis [I-A, u=0, s=1]; (d)
29 Conclusions Shape and size of Fermi surface, Fermiology Topological band parameters, Topo-Fermiology intercept, Onsager phase factor
Orbital magnetization, geometric phase, and a modern theory of magnetic breakdown
 Orbital magnetization, geometric phase, and a modern theory of magnetic breakdown A. Alexandradinata Yale Wang Chong Tsinghua Leonid Glazman Yale Semiclassical theory of Bloch electrons in a magnetic field
Orbital magnetization, geometric phase, and a modern theory of magnetic breakdown A. Alexandradinata Yale Wang Chong Tsinghua Leonid Glazman Yale Semiclassical theory of Bloch electrons in a magnetic field
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 26 Sep 2013
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 26 Sep 2013 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 26 Sep 2013](/thumbs/83/88173709.jpg) Berry phase and the unconventional quantum Hall effect in graphene Jiamin Xue Microelectronic Research Center, The University arxiv:1309.6714v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 26 Sep 2013 of Texas at Austin, Austin,
Berry phase and the unconventional quantum Hall effect in graphene Jiamin Xue Microelectronic Research Center, The University arxiv:1309.6714v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 26 Sep 2013 of Texas at Austin, Austin,
Physics of Semiconductors
 Physics of Semiconductors 13 th 2016.7.11 Shingo Katsumoto Department of Physics and Institute for Solid State Physics University of Tokyo Outline today Laughlin s justification Spintronics Two current
Physics of Semiconductors 13 th 2016.7.11 Shingo Katsumoto Department of Physics and Institute for Solid State Physics University of Tokyo Outline today Laughlin s justification Spintronics Two current
Metals: the Drude and Sommerfeld models p. 1 Introduction p. 1 What do we know about metals? p. 1 The Drude model p. 2 Assumptions p.
 Metals: the Drude and Sommerfeld models p. 1 Introduction p. 1 What do we know about metals? p. 1 The Drude model p. 2 Assumptions p. 2 The relaxation-time approximation p. 3 The failure of the Drude model
Metals: the Drude and Sommerfeld models p. 1 Introduction p. 1 What do we know about metals? p. 1 The Drude model p. 2 Assumptions p. 2 The relaxation-time approximation p. 3 The failure of the Drude model
PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS AND THEIR HETEROSTRUCTURES
 PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS AND THEIR HETEROSTRUCTURES Jasprit Singh University of Michigan McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas Lisbon London Madrid Mexico Milan Montreal
PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS AND THEIR HETEROSTRUCTURES Jasprit Singh University of Michigan McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas Lisbon London Madrid Mexico Milan Montreal
Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators
 Lecture 6 Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators Given the analogs between Berry s phase and vector potentials, it is not surprising that Berry s phase can be important in the Hall effect.
Lecture 6 Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators Given the analogs between Berry s phase and vector potentials, it is not surprising that Berry s phase can be important in the Hall effect.
Interband effects and orbital suceptibility of multiband tight-binding models
 Interband effects and orbital suceptibility of multiband tight-binding models Frédéric Piéchon LPS (Orsay) with A. Raoux, J-N. Fuchs and G. Montambaux Orbital suceptibility Berry curvature ky? kx GDR Modmat,
Interband effects and orbital suceptibility of multiband tight-binding models Frédéric Piéchon LPS (Orsay) with A. Raoux, J-N. Fuchs and G. Montambaux Orbital suceptibility Berry curvature ky? kx GDR Modmat,
Tutorial: Berry phase and Berry curvature in solids
 Tutorial: Berry phase and Berry curvature in solids Justin Song Division of Physics, Nanyang Technological University (Singapore) & Institute of High Performance Computing (Singapore) Funding: (Singapore)
Tutorial: Berry phase and Berry curvature in solids Justin Song Division of Physics, Nanyang Technological University (Singapore) & Institute of High Performance Computing (Singapore) Funding: (Singapore)
Coulomb Drag in Graphene
 Graphene 2017 Coulomb Drag in Graphene -Toward Exciton Condensation Philip Kim Department of Physics, Harvard University Coulomb Drag Drag Resistance: R D = V 2 / I 1 Onsager Reciprocity V 2 (B)/ I 1 =
Graphene 2017 Coulomb Drag in Graphene -Toward Exciton Condensation Philip Kim Department of Physics, Harvard University Coulomb Drag Drag Resistance: R D = V 2 / I 1 Onsager Reciprocity V 2 (B)/ I 1 =
The Superfluid Phase s of Helium 3
 The Superfluid Phase s of Helium 3 DIETER VOLLHARD T Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen, Federal Republic of German y PETER WÖLFL E Universität Karlsruhe Federal Republic of Germany PREFACE
The Superfluid Phase s of Helium 3 DIETER VOLLHARD T Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen, Federal Republic of German y PETER WÖLFL E Universität Karlsruhe Federal Republic of Germany PREFACE
Topological insulators. Pavel Buividovich (Regensburg)
 Topological insulators Pavel Buividovich (Regensburg) Hall effect Classical treatment Dissipative motion for point-like particles (Drude theory) Steady motion Classical Hall effect Cyclotron frequency
Topological insulators Pavel Buividovich (Regensburg) Hall effect Classical treatment Dissipative motion for point-like particles (Drude theory) Steady motion Classical Hall effect Cyclotron frequency
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature12186 S1. WANNIER DIAGRAM B 1 1 a φ/φ O 1/2 1/3 1/4 1/5 1 E φ/φ O n/n O 1 FIG. S1: Left is a cartoon image of an electron subjected to both a magnetic field, and a square periodic lattice.
doi:1.138/nature12186 S1. WANNIER DIAGRAM B 1 1 a φ/φ O 1/2 1/3 1/4 1/5 1 E φ/φ O n/n O 1 FIG. S1: Left is a cartoon image of an electron subjected to both a magnetic field, and a square periodic lattice.
Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum
 Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum H.A. Fertig, Indiana University Luis Brey, CSIC, Madrid I. Introduction: Graphene Edge States (Non-Interacting) II. III. Quantum Hall Ferromagnetism and
Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum H.A. Fertig, Indiana University Luis Brey, CSIC, Madrid I. Introduction: Graphene Edge States (Non-Interacting) II. III. Quantum Hall Ferromagnetism and
Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators
 Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators Eduardo Fradkin University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Workshop on Field Theoretic Computer Simulations for Particle Physics and Condensed Matter
Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators Eduardo Fradkin University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Workshop on Field Theoretic Computer Simulations for Particle Physics and Condensed Matter
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2002 Outline
 Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2002 Outline 1. General structure of quantum mechanics. 8.04 was based primarily on wave mechanics. We review that foundation with the intent to build a more formal basis
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2002 Outline 1. General structure of quantum mechanics. 8.04 was based primarily on wave mechanics. We review that foundation with the intent to build a more formal basis
Vortices and vortex states of Rashba spin-orbit coupled condensates
 Vortices and vortex states of Rashba spin-orbit coupled condensates Predrag Nikolić George Mason University Institute for Quantum Matter @ Johns Hopkins University March 5, 2014 P.N, T.Duric, Z.Tesanovic,
Vortices and vortex states of Rashba spin-orbit coupled condensates Predrag Nikolić George Mason University Institute for Quantum Matter @ Johns Hopkins University March 5, 2014 P.N, T.Duric, Z.Tesanovic,
Quantum Physics III (8.06) Spring 2007 FINAL EXAMINATION Monday May 21, 9:00 am You have 3 hours.
 Quantum Physics III (8.06) Spring 2007 FINAL EXAMINATION Monday May 21, 9:00 am You have 3 hours. There are 10 problems, totalling 180 points. Do all problems. Answer all problems in the white books provided.
Quantum Physics III (8.06) Spring 2007 FINAL EXAMINATION Monday May 21, 9:00 am You have 3 hours. There are 10 problems, totalling 180 points. Do all problems. Answer all problems in the white books provided.
Spin orbit interaction in graphene monolayers & carbon nanotubes
 Spin orbit interaction in graphene monolayers & carbon nanotubes Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik, Düsseldorf Alessandro De Martino Andreas Schulz, Artur Hütten MPI Dresden, 25.10.2011 Overview
Spin orbit interaction in graphene monolayers & carbon nanotubes Reinhold Egger Institut für Theoretische Physik, Düsseldorf Alessandro De Martino Andreas Schulz, Artur Hütten MPI Dresden, 25.10.2011 Overview
Quantum Oscillations in underdoped cuprate superconductors
 Quantum Oscillations in underdoped cuprate superconductors Aabhaas Vineet Mallik Journal Club Talk 4 April, 2013 Aabhaas Vineet Mallik (Journal Club Talk) Quantum Oscillations in underdoped cuprate superconductors
Quantum Oscillations in underdoped cuprate superconductors Aabhaas Vineet Mallik Journal Club Talk 4 April, 2013 Aabhaas Vineet Mallik (Journal Club Talk) Quantum Oscillations in underdoped cuprate superconductors
Topological insulators and the quantum anomalous Hall state. David Vanderbilt Rutgers University
 Topological insulators and the quantum anomalous Hall state David Vanderbilt Rutgers University Outline Berry curvature and topology 2D quantum anomalous Hall (QAH) insulator TR-invariant insulators (Z
Topological insulators and the quantum anomalous Hall state David Vanderbilt Rutgers University Outline Berry curvature and topology 2D quantum anomalous Hall (QAH) insulator TR-invariant insulators (Z
List of Comprehensive Exams Topics
 List of Comprehensive Exams Topics Mechanics 1. Basic Mechanics Newton s laws and conservation laws, the virial theorem 2. The Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Formalism The Lagrange formalism and the principle
List of Comprehensive Exams Topics Mechanics 1. Basic Mechanics Newton s laws and conservation laws, the virial theorem 2. The Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Formalism The Lagrange formalism and the principle
TOPOLOGICAL BANDS IN GRAPHENE SUPERLATTICES
 TOPOLOGICAL BANDS IN GRAPHENE SUPERLATTICES 1) Berry curvature in superlattice bands 2) Energy scales for Moire superlattices 3) Spin-Hall effect in graphene Leonid Levitov (MIT) @ ISSP U Tokyo MIT Manchester
TOPOLOGICAL BANDS IN GRAPHENE SUPERLATTICES 1) Berry curvature in superlattice bands 2) Energy scales for Moire superlattices 3) Spin-Hall effect in graphene Leonid Levitov (MIT) @ ISSP U Tokyo MIT Manchester
Effects of spin-orbit coupling on the BKT transition and the vortexantivortex structure in 2D Fermi Gases
 Effects of spin-orbit coupling on the BKT transition and the vortexantivortex structure in D Fermi Gases Carlos A. R. Sa de Melo Georgia Institute of Technology QMath13 Mathematical Results in Quantum
Effects of spin-orbit coupling on the BKT transition and the vortexantivortex structure in D Fermi Gases Carlos A. R. Sa de Melo Georgia Institute of Technology QMath13 Mathematical Results in Quantum
Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 (Refer Slide Time: 00:22) Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 25 Pauli paramagnetism and Landau diamagnetism So far, in our
(Refer Slide Time: 00:22) Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 25 Pauli paramagnetism and Landau diamagnetism So far, in our
Les états de bord d un. isolant de Hall atomique
 Les états de bord d un isolant de Hall atomique séminaire Atomes Froids 2/9/22 Nathan Goldman (ULB), Jérôme Beugnon and Fabrice Gerbier Outline Quantum Hall effect : bulk Landau levels and edge states
Les états de bord d un isolant de Hall atomique séminaire Atomes Froids 2/9/22 Nathan Goldman (ULB), Jérôme Beugnon and Fabrice Gerbier Outline Quantum Hall effect : bulk Landau levels and edge states
POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials
 POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials Nandini Trivedi L1: Spin Orbit Coupling L2: Topology and Topological Insulators Tutorials: May 24, 25 (2017) Scope of Lectures and Anchor Points: 1.Spin-Orbit Interaction
POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials Nandini Trivedi L1: Spin Orbit Coupling L2: Topology and Topological Insulators Tutorials: May 24, 25 (2017) Scope of Lectures and Anchor Points: 1.Spin-Orbit Interaction
What is a topological insulator? Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU
 What is a topological insulator? Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU A mini course on topology extrinsic curvature K vs intrinsic (Gaussian) curvature G K 0 G 0 G>0 G=0 K 0 G=0 G
What is a topological insulator? Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU A mini course on topology extrinsic curvature K vs intrinsic (Gaussian) curvature G K 0 G 0 G>0 G=0 K 0 G=0 G
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Crystal structure of 1T -MoTe 2. (a) HAADF-STEM image of 1T -MoTe 2, looking down the [001] zone (scale bar, 0.5 nm). The area indicated by the red rectangle
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Crystal structure of 1T -MoTe 2. (a) HAADF-STEM image of 1T -MoTe 2, looking down the [001] zone (scale bar, 0.5 nm). The area indicated by the red rectangle
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field
 Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Magnetism in Condensed Matter
 Magnetism in Condensed Matter STEPHEN BLUNDELL Department of Physics University of Oxford OXFORD 'UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Magnetic moments 1 1 1.1.1 Magnetic moments and angular momentum
Magnetism in Condensed Matter STEPHEN BLUNDELL Department of Physics University of Oxford OXFORD 'UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Magnetic moments 1 1 1.1.1 Magnetic moments and angular momentum
Notes on Topological Insulators and Quantum Spin Hall Effect. Jouko Nieminen Tampere University of Technology.
 Notes on Topological Insulators and Quantum Spin Hall Effect Jouko Nieminen Tampere University of Technology. Not so much discussed concept in this session: topology. In math, topology discards small details
Notes on Topological Insulators and Quantum Spin Hall Effect Jouko Nieminen Tampere University of Technology. Not so much discussed concept in this session: topology. In math, topology discards small details
Minimal Update of Solid State Physics
 Minimal Update of Solid State Physics It is expected that participants are acquainted with basics of solid state physics. Therefore here we will refresh only those aspects, which are absolutely necessary
Minimal Update of Solid State Physics It is expected that participants are acquainted with basics of solid state physics. Therefore here we will refresh only those aspects, which are absolutely necessary
Correlated 2D Electron Aspects of the Quantum Hall Effect
 Correlated 2D Electron Aspects of the Quantum Hall Effect Magnetic field spectrum of the correlated 2D electron system: Electron interactions lead to a range of manifestations 10? = 4? = 2 Resistance (arb.
Correlated 2D Electron Aspects of the Quantum Hall Effect Magnetic field spectrum of the correlated 2D electron system: Electron interactions lead to a range of manifestations 10? = 4? = 2 Resistance (arb.
Contents. 1.1 Prerequisites and textbooks Physical phenomena and theoretical tools The path integrals... 9
 Preface v Chapter 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Prerequisites and textbooks......................... 1 1.2 Physical phenomena and theoretical tools................. 5 1.3 The path integrals..............................
Preface v Chapter 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Prerequisites and textbooks......................... 1 1.2 Physical phenomena and theoretical tools................. 5 1.3 The path integrals..............................
Electromagnetism II. Instructor: Andrei Sirenko Spring 2013 Thursdays 1 pm 4 pm. Spring 2013, NJIT 1
 Electromagnetism II Instructor: Andrei Sirenko sirenko@njit.edu Spring 013 Thursdays 1 pm 4 pm Spring 013, NJIT 1 PROBLEMS for CH. 6 http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/phys433/phys433eandm013.htm Can obtain
Electromagnetism II Instructor: Andrei Sirenko sirenko@njit.edu Spring 013 Thursdays 1 pm 4 pm Spring 013, NJIT 1 PROBLEMS for CH. 6 http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/phys433/phys433eandm013.htm Can obtain
Quantum spin liquids and the Mott transition. T. Senthil (MIT)
 Quantum spin liquids and the Mott transition T. Senthil (MIT) Friday, December 9, 2011 Band versus Mott insulators Band insulators: even number of electrons per unit cell; completely filled bands Mott
Quantum spin liquids and the Mott transition T. Senthil (MIT) Friday, December 9, 2011 Band versus Mott insulators Band insulators: even number of electrons per unit cell; completely filled bands Mott
Chemistry 483 Lecture Topics Fall 2009
 Chemistry 483 Lecture Topics Fall 2009 Text PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY A Molecular Approach McQuarrie and Simon A. Background (M&S,Chapter 1) Blackbody Radiation Photoelectric effect DeBroglie Wavelength Atomic
Chemistry 483 Lecture Topics Fall 2009 Text PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY A Molecular Approach McQuarrie and Simon A. Background (M&S,Chapter 1) Blackbody Radiation Photoelectric effect DeBroglie Wavelength Atomic
Physics 622: Quantum Mechanics -- Part II --
 Physics 622: Quantum Mechanics -- Part II -- Instructors Prof. Seth Aubin Office: room 255, Small Hall, tel: 1-3545 Lab: room 069, Small Hall (new wing), tel: 1-3532 e-mail: saaubi@wm.edu web: http://www.physics.wm.edu/~saubin/index.html
Physics 622: Quantum Mechanics -- Part II -- Instructors Prof. Seth Aubin Office: room 255, Small Hall, tel: 1-3545 Lab: room 069, Small Hall (new wing), tel: 1-3532 e-mail: saaubi@wm.edu web: http://www.physics.wm.edu/~saubin/index.html
Kondo effect in multi-level and multi-valley quantum dots. Mikio Eto Faculty of Science and Technology, Keio University, Japan
 Kondo effect in multi-level and multi-valley quantum dots Mikio Eto Faculty of Science and Technology, Keio University, Japan Outline 1. Introduction: next three slides for quantum dots 2. Kondo effect
Kondo effect in multi-level and multi-valley quantum dots Mikio Eto Faculty of Science and Technology, Keio University, Japan Outline 1. Introduction: next three slides for quantum dots 2. Kondo effect
3.15. Some symmetry properties of the Berry curvature and the Chern number.
 50 Phys620.nb z M 3 at the K point z M 3 3 t ' sin 3 t ' sin (3.36) (3.362) Therefore, as long as M 3 3 t ' sin, the system is an topological insulator ( z flips sign). If M 3 3 t ' sin, z is always positive
50 Phys620.nb z M 3 at the K point z M 3 3 t ' sin 3 t ' sin (3.36) (3.362) Therefore, as long as M 3 3 t ' sin, the system is an topological insulator ( z flips sign). If M 3 3 t ' sin, z is always positive
Electrons in a weak periodic potential
 Electrons in a weak periodic potential Assumptions: 1. Static defect-free lattice perfectly periodic potential. 2. Weak potential perturbative effect on the free electron states. Perfect periodicity of
Electrons in a weak periodic potential Assumptions: 1. Static defect-free lattice perfectly periodic potential. 2. Weak potential perturbative effect on the free electron states. Perfect periodicity of
Quantum Confinement in Graphene
 Quantum Confinement in Graphene from quasi-localization to chaotic billards MMM dominikus kölbl 13.10.08 1 / 27 Outline some facts about graphene quasibound states in graphene numerical calculation of
Quantum Confinement in Graphene from quasi-localization to chaotic billards MMM dominikus kölbl 13.10.08 1 / 27 Outline some facts about graphene quasibound states in graphene numerical calculation of
Dirac fermions in Graphite:
 Igor Lukyanchuk Amiens University, France, Yakov Kopelevich University of Campinas, Brazil Dirac fermions in Graphite: I. Lukyanchuk, Y. Kopelevich et al. - Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 166402 (2004) - Phys. Rev.
Igor Lukyanchuk Amiens University, France, Yakov Kopelevich University of Campinas, Brazil Dirac fermions in Graphite: I. Lukyanchuk, Y. Kopelevich et al. - Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 166402 (2004) - Phys. Rev.
3D topological insulators and half- Heusler compounds
 3D topological insulators and half- Heusler compounds Ram Seshadri Materials Department, and Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Materials Research Laboratory University of California, Santa Barbara
3D topological insulators and half- Heusler compounds Ram Seshadri Materials Department, and Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Materials Research Laboratory University of California, Santa Barbara
MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPY
 MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPY First Edition Jeanne L. McHale University of Idaho PRENTICE HALL, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 CONTENTS PREFACE xiii 1 INTRODUCTION AND REVIEW 1 1.1 Historical Perspective
MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPY First Edition Jeanne L. McHale University of Idaho PRENTICE HALL, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 CONTENTS PREFACE xiii 1 INTRODUCTION AND REVIEW 1 1.1 Historical Perspective
3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI. Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea
 3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea Content 3D Dirac metals Search for 3D generalization of graphene Bi 1-x
3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea Content 3D Dirac metals Search for 3D generalization of graphene Bi 1-x
Spin-Orbit Interactions in Semiconductor Nanostructures
 Spin-Orbit Interactions in Semiconductor Nanostructures Branislav K. Nikolić Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, U.S.A. http://www.physics.udel.edu/~bnikolic Spin-Orbit Hamiltonians
Spin-Orbit Interactions in Semiconductor Nanostructures Branislav K. Nikolić Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, U.S.A. http://www.physics.udel.edu/~bnikolic Spin-Orbit Hamiltonians
Lecture 4 Quantum mechanics in more than one-dimension
 Lecture 4 Quantum mechanics in more than one-dimension Background Previously, we have addressed quantum mechanics of 1d systems and explored bound and unbound (scattering) states. Although general concepts
Lecture 4 Quantum mechanics in more than one-dimension Background Previously, we have addressed quantum mechanics of 1d systems and explored bound and unbound (scattering) states. Although general concepts
Quantum Mechanics: Fundamentals
 Kurt Gottfried Tung-Mow Yan Quantum Mechanics: Fundamentals Second Edition With 75 Figures Springer Preface vii Fundamental Concepts 1 1.1 Complementarity and Uncertainty 1 (a) Complementarity 2 (b) The
Kurt Gottfried Tung-Mow Yan Quantum Mechanics: Fundamentals Second Edition With 75 Figures Springer Preface vii Fundamental Concepts 1 1.1 Complementarity and Uncertainty 1 (a) Complementarity 2 (b) The
Matrix product states for the fractional quantum Hall effect
 Matrix product states for the fractional quantum Hall effect Roger Mong (California Institute of Technology) University of Virginia Feb 24, 2014 Collaborators Michael Zaletel UC Berkeley (Stanford/Station
Matrix product states for the fractional quantum Hall effect Roger Mong (California Institute of Technology) University of Virginia Feb 24, 2014 Collaborators Michael Zaletel UC Berkeley (Stanford/Station
Dirac and Weyl fermions in condensed matter systems: an introduction
 Dirac and Weyl fermions in condensed matter systems: an introduction Fa Wang ( 王垡 ) ICQM, Peking University 第二届理论物理研讨会 Preamble: Dirac/Weyl fermions Dirac equation: reconciliation of special relativity
Dirac and Weyl fermions in condensed matter systems: an introduction Fa Wang ( 王垡 ) ICQM, Peking University 第二届理论物理研讨会 Preamble: Dirac/Weyl fermions Dirac equation: reconciliation of special relativity
QUANTUM MECHANICS. Franz Schwabl. Translated by Ronald Kates. ff Springer
 Franz Schwabl QUANTUM MECHANICS Translated by Ronald Kates Second Revised Edition With 122Figures, 16Tables, Numerous Worked Examples, and 126 Problems ff Springer Contents 1. Historical and Experimental
Franz Schwabl QUANTUM MECHANICS Translated by Ronald Kates Second Revised Edition With 122Figures, 16Tables, Numerous Worked Examples, and 126 Problems ff Springer Contents 1. Historical and Experimental
Maxwell s equations. electric field charge density. current density
 Maxwell s equations based on S-54 Our next task is to find a quantum field theory description of spin-1 particles, e.g. photons. Classical electrodynamics is governed by Maxwell s equations: electric field
Maxwell s equations based on S-54 Our next task is to find a quantum field theory description of spin-1 particles, e.g. photons. Classical electrodynamics is governed by Maxwell s equations: electric field
Quantum Field Theory. Kerson Huang. Second, Revised, and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH. From Operators to Path Integrals
 Kerson Huang Quantum Field Theory From Operators to Path Integrals Second, Revised, and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA I vh Contents Preface XIII 1 Introducing Quantum Fields
Kerson Huang Quantum Field Theory From Operators to Path Integrals Second, Revised, and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA I vh Contents Preface XIII 1 Introducing Quantum Fields
Criticality in topologically ordered systems: a case study
 Criticality in topologically ordered systems: a case study Fiona Burnell Schulz & FJB 16 FJB 17? Phases and phase transitions ~ 194 s: Landau theory (Liquids vs crystals; magnets; etc.) Local order parameter
Criticality in topologically ordered systems: a case study Fiona Burnell Schulz & FJB 16 FJB 17? Phases and phase transitions ~ 194 s: Landau theory (Liquids vs crystals; magnets; etc.) Local order parameter
Quantum Hall effect. Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in I believe. WHY?? G xy = N e2 h.
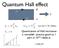 Quantum Hall effect V1 V2 R L I I x = N e2 h V y V x =0 G xy = N e2 h n.b. h/e 2 = 25 kohms Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in 10 10 I believe. WHY?? Robustness Why
Quantum Hall effect V1 V2 R L I I x = N e2 h V y V x =0 G xy = N e2 h n.b. h/e 2 = 25 kohms Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in 10 10 I believe. WHY?? Robustness Why
Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions
 Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions Dima Abanin (MIT) Collaboration: Leonid Levitov, Patrick Lee, Harvard and Columbia groups UIUC January 14, 2008 Electron transport in graphene monolayer New
Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions Dima Abanin (MIT) Collaboration: Leonid Levitov, Patrick Lee, Harvard and Columbia groups UIUC January 14, 2008 Electron transport in graphene monolayer New
(Recall: Right-hand rule!)
 1.10 The Vector Model of the Atom Classical Physics: If you go back to your first year physics textbook, you will find momentum p (= m v) has an angular counterpart, angular momentum l (= r x p), as shown
1.10 The Vector Model of the Atom Classical Physics: If you go back to your first year physics textbook, you will find momentum p (= m v) has an angular counterpart, angular momentum l (= r x p), as shown
Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator
 Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley Refs: Ran, Zhang A.V., Nature Physics 5, 289 (2009). Hosur, Ryu, AV arxiv: 0908.2691 Part 1: Outline A toy model of
Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley Refs: Ran, Zhang A.V., Nature Physics 5, 289 (2009). Hosur, Ryu, AV arxiv: 0908.2691 Part 1: Outline A toy model of
Transport Experiments on 3D Topological insulators
 TheoryWinter School, NHMFL, Jan 2014 Transport Experiments on 3D Topological insulators Part I N. P. Ong, Princeton Univ. 1. Transport in non-metallic Bi2Se3 and Bi2Te3 2. A TI with very large bulk ρ Bi2Te2Se
TheoryWinter School, NHMFL, Jan 2014 Transport Experiments on 3D Topological insulators Part I N. P. Ong, Princeton Univ. 1. Transport in non-metallic Bi2Se3 and Bi2Te3 2. A TI with very large bulk ρ Bi2Te2Se
Topological Insulators
 Topological Insulators Aira Furusai (Condensed Matter Theory Lab.) = topological insulators (3d and 2d) Outline Introduction: band theory Example of topological insulators: integer quantum Hall effect
Topological Insulators Aira Furusai (Condensed Matter Theory Lab.) = topological insulators (3d and 2d) Outline Introduction: band theory Example of topological insulators: integer quantum Hall effect
SYNTHETIC GAUGE FIELDS IN ULTRACOLD ATOMIC GASES
 Congresso Nazionale della Società Italiana di Fisica Università della Calabria 17/21 Settembre 2018 SYNTHETIC GAUGE FIELDS IN ULTRACOLD ATOMIC GASES Sandro Stringari Università di Trento CNR-INO - Bose-Einstein
Congresso Nazionale della Società Italiana di Fisica Università della Calabria 17/21 Settembre 2018 SYNTHETIC GAUGE FIELDS IN ULTRACOLD ATOMIC GASES Sandro Stringari Università di Trento CNR-INO - Bose-Einstein
Loop current order in optical lattices
 JQI Summer School June 13, 2014 Loop current order in optical lattices Xiaopeng Li JQI/CMTC Outline Ultracold atoms confined in optical lattices 1. Why we care about lattice? 2. Band structures and Berry
JQI Summer School June 13, 2014 Loop current order in optical lattices Xiaopeng Li JQI/CMTC Outline Ultracold atoms confined in optical lattices 1. Why we care about lattice? 2. Band structures and Berry
3.14. The model of Haldane on a honeycomb lattice
 4 Phys60.n..7. Marginal case: 4 t Dirac points at k=(,). Not an insulator. No topological index...8. case IV: 4 t All the four special points has z 0. We just use u I for the whole BZ. No singularity.
4 Phys60.n..7. Marginal case: 4 t Dirac points at k=(,). Not an insulator. No topological index...8. case IV: 4 t All the four special points has z 0. We just use u I for the whole BZ. No singularity.
Contents Preface Physical Constants, Units, Mathematical Signs and Symbols Introduction Kinetic Theory and the Boltzmann Equation
 V Contents Preface XI Physical Constants, Units, Mathematical Signs and Symbols 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Carbon Nanotubes 1 1.2 Theoretical Background 4 1.2.1 Metals and Conduction Electrons 4 1.2.2 Quantum
V Contents Preface XI Physical Constants, Units, Mathematical Signs and Symbols 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Carbon Nanotubes 1 1.2 Theoretical Background 4 1.2.1 Metals and Conduction Electrons 4 1.2.2 Quantum
Symmetries in Quantum Transport : From Random Matrix Theory to Topological Insulators. Philippe Jacquod. U of Arizona
 Symmetries in Quantum Transport : From Random Matrix Theory to Topological Insulators Philippe Jacquod U of Arizona UA Phys colloquium - feb 1, 2013 Continuous symmetries and conservation laws Noether
Symmetries in Quantum Transport : From Random Matrix Theory to Topological Insulators Philippe Jacquod U of Arizona UA Phys colloquium - feb 1, 2013 Continuous symmetries and conservation laws Noether
FYS Vår 2017 (Kondenserte fasers fysikk)
 FYS3410 - Vår 2017 (Kondenserte fasers fysikk) http://www.uio.no/studier/emner/matnat/fys/fys3410/v16/index.html Pensum: Introduction to Solid State Physics by Charles Kittel (Chapters 1-9, 11, 17, 18,
FYS3410 - Vår 2017 (Kondenserte fasers fysikk) http://www.uio.no/studier/emner/matnat/fys/fys3410/v16/index.html Pensum: Introduction to Solid State Physics by Charles Kittel (Chapters 1-9, 11, 17, 18,
Dirac fermions in condensed matters
 Dirac fermions in condensed matters Bohm Jung Yang Department of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul National University Outline 1. Dirac fermions in relativistic wave equations 2. How do Dirac fermions appear
Dirac fermions in condensed matters Bohm Jung Yang Department of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul National University Outline 1. Dirac fermions in relativistic wave equations 2. How do Dirac fermions appear
Quantum Physics in the Nanoworld
 Hans Lüth Quantum Physics in the Nanoworld Schrödinger's Cat and the Dwarfs 4) Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 General and Historical Remarks 1 1.2 Importance for Science and Technology 3 1.3 Philosophical
Hans Lüth Quantum Physics in the Nanoworld Schrödinger's Cat and the Dwarfs 4) Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 General and Historical Remarks 1 1.2 Importance for Science and Technology 3 1.3 Philosophical
2.4. Quantum Mechanical description of hydrogen atom
 2.4. Quantum Mechanical description of hydrogen atom Atomic units Quantity Atomic unit SI Conversion Ang. mom. h [J s] h = 1, 05459 10 34 Js Mass m e [kg] m e = 9, 1094 10 31 kg Charge e [C] e = 1, 6022
2.4. Quantum Mechanical description of hydrogen atom Atomic units Quantity Atomic unit SI Conversion Ang. mom. h [J s] h = 1, 05459 10 34 Js Mass m e [kg] m e = 9, 1094 10 31 kg Charge e [C] e = 1, 6022
Spins and spin-orbit coupling in semiconductors, metals, and nanostructures
 B. Halperin Spin lecture 1 Spins and spin-orbit coupling in semiconductors, metals, and nanostructures Behavior of non-equilibrium spin populations. Spin relaxation and spin transport. How does one produce
B. Halperin Spin lecture 1 Spins and spin-orbit coupling in semiconductors, metals, and nanostructures Behavior of non-equilibrium spin populations. Spin relaxation and spin transport. How does one produce
Spin-injection Spectroscopy of a Spin-orbit coupled Fermi Gas
 Spin-injection Spectroscopy of a Spin-orbit coupled Fermi Gas Tarik Yefsah Lawrence Cheuk, Ariel Sommer, Zoran Hadzibabic, Waseem Bakr and Martin Zwierlein July 20, 2012 ENS Why spin-orbit coupling? A
Spin-injection Spectroscopy of a Spin-orbit coupled Fermi Gas Tarik Yefsah Lawrence Cheuk, Ariel Sommer, Zoran Hadzibabic, Waseem Bakr and Martin Zwierlein July 20, 2012 ENS Why spin-orbit coupling? A
Basic Semiconductor Physics
 Chihiro Hamaguchi Basic Semiconductor Physics With 177 Figures and 25 Tables Springer 1. Energy Band Structures of Semiconductors 1 1.1 Free-Electron Model 1 1.2 Bloch Theorem 3 1.3 Nearly Free Electron
Chihiro Hamaguchi Basic Semiconductor Physics With 177 Figures and 25 Tables Springer 1. Energy Band Structures of Semiconductors 1 1.1 Free-Electron Model 1 1.2 Bloch Theorem 3 1.3 Nearly Free Electron
Applied Asymptotic Analysis
 Applied Asymptotic Analysis Peter D. Miller Graduate Studies in Mathematics Volume 75 American Mathematical Society Providence, Rhode Island Preface xiii Part 1. Fundamentals Chapter 0. Themes of Asymptotic
Applied Asymptotic Analysis Peter D. Miller Graduate Studies in Mathematics Volume 75 American Mathematical Society Providence, Rhode Island Preface xiii Part 1. Fundamentals Chapter 0. Themes of Asymptotic
Symmetry, Topology and Phases of Matter
 Symmetry, Topology and Phases of Matter E E k=λ a k=λ b k=λ a k=λ b Topological Phases of Matter Many examples of topological band phenomena States adiabatically connected to independent electrons: - Quantum
Symmetry, Topology and Phases of Matter E E k=λ a k=λ b k=λ a k=λ b Topological Phases of Matter Many examples of topological band phenomena States adiabatically connected to independent electrons: - Quantum
Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures
 Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures Jasprit Singh University of Michigan, Ann Arbor CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS PREFACE INTRODUCTION xiii xiv 1.1 SURVEY OF ADVANCES
Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures Jasprit Singh University of Michigan, Ann Arbor CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS PREFACE INTRODUCTION xiii xiv 1.1 SURVEY OF ADVANCES
POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials
 POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials Nandini Trivedi L1: Spin Orbit Coupling L2: Topology and Topological Insulators Reference: Bernevig Topological Insulators and Topological Superconductors Tutorials:
POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials Nandini Trivedi L1: Spin Orbit Coupling L2: Topology and Topological Insulators Reference: Bernevig Topological Insulators and Topological Superconductors Tutorials:
Topological insulator part I: Phenomena
 Phys60.nb 5 Topological insulator part I: Phenomena (Part II and Part III discusses how to understand a topological insluator based band-structure theory and gauge theory) (Part IV discusses more complicated
Phys60.nb 5 Topological insulator part I: Phenomena (Part II and Part III discusses how to understand a topological insluator based band-structure theory and gauge theory) (Part IV discusses more complicated
Vortex States in a Non-Abelian Magnetic Field
 Vortex States in a Non-Abelian Magnetic Field Predrag Nikolić George Mason University Institute for Quantum Matter @ Johns Hopkins University SESAPS November 10, 2016 Acknowledgments Collin Broholm IQM
Vortex States in a Non-Abelian Magnetic Field Predrag Nikolić George Mason University Institute for Quantum Matter @ Johns Hopkins University SESAPS November 10, 2016 Acknowledgments Collin Broholm IQM
Lecture Notes. Quantum Theory. Prof. Maximilian Kreuzer. Institute for Theoretical Physics Vienna University of Technology. covering the contents of
 Lecture Notes Quantum Theory by Prof. Maximilian Kreuzer Institute for Theoretical Physics Vienna University of Technology covering the contents of 136.019 Quantentheorie I and 136.027 Quantentheorie II
Lecture Notes Quantum Theory by Prof. Maximilian Kreuzer Institute for Theoretical Physics Vienna University of Technology covering the contents of 136.019 Quantentheorie I and 136.027 Quantentheorie II
Lecture 4: Basic elements of band theory
 Phys 769 Selected Topics in Condensed Matter Physics Summer 010 Lecture 4: Basic elements of band theory Lecturer: Anthony J. Leggett TA: Bill Coish 1 Introduction Most matter, in particular most insulating
Phys 769 Selected Topics in Condensed Matter Physics Summer 010 Lecture 4: Basic elements of band theory Lecturer: Anthony J. Leggett TA: Bill Coish 1 Introduction Most matter, in particular most insulating
Hamiltonian approach to Yang- Mills Theories in 2+1 Dimensions: Glueball and Meson Mass Spectra
 Hamiltonian approach to Yang- Mills Theories in 2+1 Dimensions: Glueball and Meson Mass Spectra Aleksandr Yelnikov Virginia Tech based on hep-th/0512200 hep-th/0604060 with Rob Leigh and Djordje Minic
Hamiltonian approach to Yang- Mills Theories in 2+1 Dimensions: Glueball and Meson Mass Spectra Aleksandr Yelnikov Virginia Tech based on hep-th/0512200 hep-th/0604060 with Rob Leigh and Djordje Minic
Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons
 Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons Introduction Physics of E. graphene Y. Andrei Experiments Rutgers University Transport electric field effect Quantum Hall Effect chiral fermions STM Dirac
Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons Introduction Physics of E. graphene Y. Andrei Experiments Rutgers University Transport electric field effect Quantum Hall Effect chiral fermions STM Dirac
Spin Currents in Mesoscopic Systems
 Spin Currents in Mesoscopic Systems Philippe Jacquod - U of Arizona I Adagideli (Sabanci) J Bardarson (Berkeley) M Duckheim (Berlin) D Loss (Basel) J Meair (Arizona) K Richter (Regensburg) M Scheid (Regensburg)
Spin Currents in Mesoscopic Systems Philippe Jacquod - U of Arizona I Adagideli (Sabanci) J Bardarson (Berkeley) M Duckheim (Berlin) D Loss (Basel) J Meair (Arizona) K Richter (Regensburg) M Scheid (Regensburg)
Drag force and superfluidity in the supersolid striped phase of a spin-orbit-coupled Bose gas
 / 6 Drag force and superfluidity in the supersolid striped phase of a spin-orbit-coupled Bose gas Giovanni Italo Martone with G. V. Shlyapnikov Worhshop on Exploring Nuclear Physics with Ultracold Atoms
/ 6 Drag force and superfluidity in the supersolid striped phase of a spin-orbit-coupled Bose gas Giovanni Italo Martone with G. V. Shlyapnikov Worhshop on Exploring Nuclear Physics with Ultracold Atoms
Topology driven quantum phase transitions
 Topology driven quantum phase transitions Dresden July 2009 Simon Trebst Microsoft Station Q UC Santa Barbara Charlotte Gils Alexei Kitaev Andreas Ludwig Matthias Troyer Zhenghan Wang Topological quantum
Topology driven quantum phase transitions Dresden July 2009 Simon Trebst Microsoft Station Q UC Santa Barbara Charlotte Gils Alexei Kitaev Andreas Ludwig Matthias Troyer Zhenghan Wang Topological quantum
LCI -birthplace of liquid crystal display. May, protests. Fashion school is in top-3 in USA. Clinical Psychology program is Top-5 in USA
 LCI -birthplace of liquid crystal display May, 4 1970 protests Fashion school is in top-3 in USA Clinical Psychology program is Top-5 in USA Topological insulators driven by electron spin Maxim Dzero Kent
LCI -birthplace of liquid crystal display May, 4 1970 protests Fashion school is in top-3 in USA Clinical Psychology program is Top-5 in USA Topological insulators driven by electron spin Maxim Dzero Kent
Emergent topological phenomena in antiferromagnets with noncoplanar spins
 Emergent topological phenomena in antiferromagnets with noncoplanar spins - Surface quantum Hall effect - Dimensional crossover Bohm-Jung Yang (RIKEN, Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS), Japan)
Emergent topological phenomena in antiferromagnets with noncoplanar spins - Surface quantum Hall effect - Dimensional crossover Bohm-Jung Yang (RIKEN, Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS), Japan)
QUANTUM MECHANICS SECOND EDITION G. ARULDHAS
 QUANTUM MECHANICS SECOND EDITION G. ARULDHAS Formerly, Professor and Head of Physics and Dean, Faculty of Science University of Kerala New Delhi-110001 2009 QUANTUM MECHANICS, 2nd Ed. G. Aruldhas 2009
QUANTUM MECHANICS SECOND EDITION G. ARULDHAS Formerly, Professor and Head of Physics and Dean, Faculty of Science University of Kerala New Delhi-110001 2009 QUANTUM MECHANICS, 2nd Ed. G. Aruldhas 2009
Fermi Surfaces and their Geometries
 Fermi Surfaces and their Geometries Didier Ndengeyintwali Physics Department, Drexel University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19104, USA (Dated: May 17, 2010) 1. Introduction The Pauli exclusion principle
Fermi Surfaces and their Geometries Didier Ndengeyintwali Physics Department, Drexel University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19104, USA (Dated: May 17, 2010) 1. Introduction The Pauli exclusion principle
Fundamentals and New Frontiers of Bose Einstein Condensation
 Contents Preface v 1. Fundamentals of Bose Einstein Condensation 1 1.1 Indistinguishability of Identical Particles.......... 1 1.2 Ideal Bose Gas in a Uniform System............ 3 1.3 Off-Diagonal Long-Range
Contents Preface v 1. Fundamentals of Bose Einstein Condensation 1 1.1 Indistinguishability of Identical Particles.......... 1 1.2 Ideal Bose Gas in a Uniform System............ 3 1.3 Off-Diagonal Long-Range
Ultracold Fermi and Bose Gases and Spinless Bose Charged Sound Particles
 October, 011 PROGRESS IN PHYSICS olume 4 Ultracold Fermi Bose Gases Spinless Bose Charged Sound Particles ahan N. Minasyan alentin N. Samoylov Scientific Center of Applied Research, JINR, Dubna, 141980,
October, 011 PROGRESS IN PHYSICS olume 4 Ultracold Fermi Bose Gases Spinless Bose Charged Sound Particles ahan N. Minasyan alentin N. Samoylov Scientific Center of Applied Research, JINR, Dubna, 141980,
Fundamentals of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing. Course Outline 2009
 Fundamentals of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing Course Outline 2009 Part I. Fundamentals of Quantum Mechanics Chapter 1. Concepts of Quantum and Experimental Facts 1.1. Blackbody Radiation and
Fundamentals of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing Course Outline 2009 Part I. Fundamentals of Quantum Mechanics Chapter 1. Concepts of Quantum and Experimental Facts 1.1. Blackbody Radiation and
Preface Introduction to the electron liquid
 Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry
 Phys62.nb 63 5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry It is impossible to have quantum Hall effect without breaking the time-reversal symmetry. xy xy. If we want xy to be invariant under, xy
Phys62.nb 63 5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry It is impossible to have quantum Hall effect without breaking the time-reversal symmetry. xy xy. If we want xy to be invariant under, xy
Quantum Phase Transitions
 Quantum Phase Transitions Subir Sachdev Department of Physics Yale University P.O. Box 208120, New Haven, CT 06520-8120 USA E-mail: subir.sachdev@yale.edu May 19, 2004 To appear in Encyclopedia of Mathematical
Quantum Phase Transitions Subir Sachdev Department of Physics Yale University P.O. Box 208120, New Haven, CT 06520-8120 USA E-mail: subir.sachdev@yale.edu May 19, 2004 To appear in Encyclopedia of Mathematical
J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2)
 Part I - Mechanics J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) s α l θ g z x A uniform rod of length l and mass m moves in the x-z plane. One end of the rod is suspended from a straight
Part I - Mechanics J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) s α l θ g z x A uniform rod of length l and mass m moves in the x-z plane. One end of the rod is suspended from a straight
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Landau Quantization and Quasiparticle Interference in the Three-Dimensional Dirac Semimetal Cd 3 As 2 Sangjun Jeon 1*, Brian B. Zhou 1*, Andras Gyenis 1, Benjamin E. Feldman 1, Itamar Kimchi 2, Andrew
Landau Quantization and Quasiparticle Interference in the Three-Dimensional Dirac Semimetal Cd 3 As 2 Sangjun Jeon 1*, Brian B. Zhou 1*, Andras Gyenis 1, Benjamin E. Feldman 1, Itamar Kimchi 2, Andrew
Spin Hall and quantum spin Hall effects. Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology PRESTO, JST
 YKIS2007 (Kyoto) Nov.16, 2007 Spin Hall and quantum spin Hall effects Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology PRESTO, JST Introduction Spin Hall effect spin Hall effect in
YKIS2007 (Kyoto) Nov.16, 2007 Spin Hall and quantum spin Hall effects Shuichi Murakami Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology PRESTO, JST Introduction Spin Hall effect spin Hall effect in
Practical Quantum Mechanics
 Siegfried Flügge Practical Quantum Mechanics With 78 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents Volume I I. General Concepts 1. Law of probability
Siegfried Flügge Practical Quantum Mechanics With 78 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents Volume I I. General Concepts 1. Law of probability
