ENGINEERING MECHANICS
|
|
|
- Agnes Grant
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ENGINEERING MECHANICS
2
3 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (In SI Units) For BE/B.Tech. Ist YEAR Strictly as per the latest syllabus prescribed by Mahamaya Technical University, Noida By Dr. R.K. BANSAL B.Sc. Engg. (Mech.), M.Tech., Hons. (IIT, Delhi), Ph.D., M.I.E. (India) Formerly Professor in Mechanical Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering Delhi College of Engineering Delhi Presently Dean (Academics) Northern India Engineering College Delhi LAXMI PUBLICATIONS (P) LTD BANGALORE CHENNAI COCHIN GUWAHATI HYDERABAD JALANDHAR KOLKATA LUCKNOW MUMBAI RANCHI NEW DELHI BOSTON, USA
4 All rights reserved with the Publisher and Authors. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise without the prior written permission of authors and the publisher. Published by LAXMI PUBLICATIONS (P) LTD 113, Golden House, Daryaganj, New Delhi Phone : Fax : info@laxmipublications.com Compiled by : Smt. Nirmal Bansal Price : ` Only. First Edition : 2013 OFFICES Bangalore Jalandhar Chennai Kolkata Cochin , Lucknow Guwahati , Mumbai , Hyderabad Ranchi EEM ENGG MECHANICS (MTU)-BAN Typeset at : Excellent Graphics, Delhi. C 2179/010/09 Printed at : Ajit Printers
5 Contents Chapters Pages UNIT-I 1. Two Dimensional Concurrent Force Systems Basic Concepts Units (System of Units) Force Systems Laws of Motion Moment and Couple Vectors Vector Representation of Forces and Moments Vector Operations The Principle of Transmissibility of Forces Resultant of a Force System Equilibrium and Equations of Equilibrium Equilibrium Conditions Free Body Diagram Determination of Reaction Resultant of Two Dimensional Concurrent Forces Applications of Concurrent Forces Highlights Exercise UNIT-II 2. Two Dimensional Non-Concurrent Force Systems Basic Concepts Varignon s Theorem (or Principle of Moments) Transfer of a Force to Parallel Position Distributed Force System Highlights 2A.. 79 Exercise 2A Types of Supports and Their Reactions Converting Force into Couples and Vice-Versa Highlights 2B Exercise 2B ( v )
6 ( vi ) Chapters Pages 3. Friction Introduction Laws of Coulomb Friction Equilibrium of Bodies Involving Dry Friction Equilibrium of a Body Lying on a Rough Inclined Plane Ladder Friction Belt Friction Highlights Exercise Truss (or Frames) Introduction Types of Frames Perfect Frame Imperfect Frame Assumptions in Truss Analysis Analysis of a Frame Method of Joints Method of Sections Highlights Exercise UNIT-III 5. Centroid and Moment of Inertia Centre of Gravity Centroid Centroid or Centre of Gravity of Simple Plane Figures Centroid of Composite Bodies Problems of Finding Centroid or Centre of Gravity of Areas by Integration Method Centroid of Volume Moment of Inertia of Plane Area Theorem of the Perpendicular Axis Theorem of Parallel Axis Determination of Area Moment of Inertia Mass Moment of Inertia Mass Moment of Inertia of a Rectangular Plate Mass Moment of Inertia of Circular Ring Mass Moment of Inertia of a Disc or Circular Plate Mass Moment of Inertia of a Circular Cylinder Mass Moment of Inertia of a Sphere
7 Chapters ( vii ) Pages Mass Moment of Inertia of a Cone about its Axis of Symmetry Pappus Theorems Polar Moment of Inertia Highlights Exercise UNIT-IV 6. Kinematics of Rigid Bodies Introduction Plane Rectilinear Motion Rectilinear Motion Under Constant Acceleration Rectilinear Motion Under Variable Acceleration Highlights 6A Exercise 6A Plane Curvilinear Motion of Rigid Body Curvilinear Motion Under Constant Angular Acceleration Curvilinear Motion Under Variable Angular Acceleration Types of Motion Velocity of Link Having Translation and Rotation Motion by Instantaneous Centre Velocity and Acceleration of a Body Under Translation and Rotational Motion or Kinematics of Plane Motion Relative Motion Highlights 6B Exercise 6B UNIT-V 7. Kinetics of Rigid Bodies Introduction Force, Mass and Acceleration Newton s Laws of Motion Kinetics of Rigid Bodies Momentum and Angular Momentum (or Moment of Momentum) Laws for Rotary Motion Work and Energy Work-Energy Principle Law of Conservation of Energy Impulse and Momentum D Alembert s Principle and Dynamic Equilibrium Highlights Exercise
8 ( viii ) 8. Virtual Work Virtual Displacement and Virtual Work Principle of Virtual Work Stability of Equilibrium The Principle of Virtual Work for Problems on Framed Structure Application of Virtual Work on Ladders The Principle of Virtual Work for Problems on Lifting Machines Highlights Exercise Objective Type Questions Additional Questions
9 Preface The course contents of this edition of the book entitled, Engineering Mechanics are planned in such a way that the book covers the complete content of first year course of all disciplines of Mahamaya Technical University, Noida strictly as per the latest syllabus prescribed by Mahamaya Technical University, Noida. The book contains following five units : Unit I : Two Dimensional Concurrent Force Systems, Basic Concepts, Resultant of a Force System, Free Body Diagrams, Equilibrium and Equation of Equilibrium. Unit II : Two Dimensional Non-Concurrent Force Systems, Basic Concepts, Varignon s Theorem, Types of Supports and their Reactions, Friction and Structure (Truss) Unit III : Centroid and Moment of Inertia. Unit IV : Kinematics of Rigid Body. Unit V : Kinetics of Rigid Body. The book is written in a simple and easy-to-follow language so that even an average student can grasp the subject by self-study. At the end of each chapter, highlights, theoretical questions and many unsolved problems with answers are given for the students to solve them. Mrs Nirmal Bansal deserves special credit as she not only provided an ideal atmosphere at home for book writing but also gave inspiration and valuable suggestions. Though every care has been taken in checking the manuscripts and proofreading, yet claiming perfection is very difficult. We shall be very grateful to the readers and users of this book for pointing any mistake that might have crept in. Suggestions for improvement are most welcome and would be incorporated in the next edition with a view to make the book more useful. Dr. R.K. BANSAL ( ix )
10 SYLLABUS (EME-102 / 202 : ENGINEERING MECHANICS) UNIT I Two Dimensional Concurrent Force Systems : Basic concepts, Laws of motion, Principle of Transmissibility of forces, Transfer of a force to parallel position, Resultant of a force system, Simplest Resultant of Two dimensional Concurrent and Non-concurrent Force systems, Distributed force system, Free body diagrams, Equilibrium and Equations of Equilibrium, Applications. 5 UNIT II Friction : Introduction, Laws of coulomb friction, Equilibrium of bodies involving dryfriction, Belt friction, Application. 3 Trusses : Introduction, Simple Truss and Solution of Simple Truss, Method of Joints and Method of Sections. 3 UNIT III Centroid and Moment of Inertia : Centroid of plane, curve, area, volume and composite bodies, Moment of inertia of plane area, Parallel Axes Theorem, Perpendicular axes theorems, Principal Moment of Inertia, Mass Moment of Inertia of Circular Ring, Disc, Cylinder, Sphere and Cone about their Axis of Symmetry. 6 UNIT IV Kinematics of Rigid Body : Introduction, Plane Motion of Rigid Body, Velocity and Acceleration under Translation and Rotational Motion, Relative Velocity. 4 UNIT V Kinetics of Rigid Body : Introduction, Force, Mass and Acceleration, Work and Energy, Impulse and Momentum, D Alembert s Principles and Dynamic Equilibrium. 4 ( x )
11 UNIT I 1. Two Dimensional Concurrent Force Systems
12
13 1 Two Dimensional Concurrent Force Systems 1.1. BASIC CONCEPTS Engineering mechanics is that branch of science which deals with the behaviour of a body when the body is at rest or in motion. The engineering mechanics may be divided into Statics and Dynamics. The branch of science, which deals with the study of a body when the body is at rest, is known as Statics while the branch of science which deals with the study of a body when the body is in motion, is known as Dynamics. Dynamics is further divided into kinematics and kinetics. The study of a body in motion, when the forces which cause the motion are not considered, is called kinematics and if the forces are also considered for the body in motion, that branch of science is called kinetics. The classification of Engineering Mechanics are shown in Fig. 1.1 below. ENGINEERING MECHANICS 1. Statics (Body is at rest) 2. Dynamics (Body is in motion) ( i) Kinematics (Forces which cause motion are not considered) Fig. 1.1 ( ii) Kinetics (Forces are considered) Note. Statics deals with equilibrium of bodies at rest, whereas dynamics deals with the motion of bodies and the forces that cause them Vector Quantity. A quantity which is completely specified by magnitude and direction, is known as a vector quantity. Some examples of vector quantities are : velocity, acceleration, force and momentum. A vector quantity is represented by means of a straight line with an arrow as shown in Fig The length of the straight line (i.e., AB) A B represents the magnitude and arrow represents the direction of the vector. The symbol AB Fig Vector Quantity. also represents this vector, which means it is acting from A to B. 3
14 4 ENGINEERING MECHANICS Scalar Quantity. A quantity, which is completely specified by magnitude only, is known as a scalar quantity. Some examples of scalar quantity are : mass, length, time and temperature A Particle. A particle is a body of infinitely small volume (or a particle is a body of negligible dimensions) and the mass of the particle is considered to be concentrated at a point. Hence a particle is assumed to a point and the mass of the particle is concentrated at this point Law of Parallelogram of Forces. The law of parallelogram of forces is used to determine the resultant* of two forces acting at a point in a plane. It states, If two forces, acting at a point be represented in magnitude and direction by the two adjacent sides of a parallelogram, then their resultant is represented in magnitude and direction by the diagonal of the parallelogram passing through that point. Let two forces P and Q act at a point O as shown in Fig The force P is represented in magnitude and direction by OA whereas the force Q is presented in magnitude and direction by OB. Let the angle between the two forces be α. The resultant of these two forces will be obtained in magnitude and direction by the diagonal (passing through O) of the parallelogram of which OA and OB are two adjacent sides. Hence draw the parallelogram with OA and OB as adjacent sides as shown in Fig The resultant R is represented by OC in magnitude and direction. B B C Q Q R O α P A α θ α O P A D Fig. 1.3 Fig. 1.4 Magnitude of Resultant (R) From C draw CD perpendicular to OA produced. Let α = Angle between two forces P and Q = AOB Now DAC = AOB (Corresponding angles) = α In parallelogram OACB, AC is parallel and equal to OB. AC = Q. In triangle ACD, AD = AC cos α = Q cos α and CD = AC sin α = Q sin α. In triangle OCD, OC 2 = OD 2 + DC 2. *The resultant of a system of forces may be defined as a single force which has the same effect as system of forces acting on the body.
15 TWO DIMENSIONAL CONCURRENT FORCE SYSTEMS 5 But OC = R, OD = OA + AD = P + Q cos α and DC = Q sin α. R 2 = (P + Q cos α) 2 + (Q sin α) 2 = P 2 + Q 2 cos 2 α + 2PQ cos α + Q 2 sin 2 α = P 2 + Q 2 (cos 2 α + sin 2 α) + 2PQ cos α = P 2 + Q 2 + 2PQ cos α ( cos 2 α + sin 2 α = 1) 2 2 R = P + Q + 2PQcos α...(1.1) Equation (1.1) gives the magnitude of resultant force R. Direction of Resultant Let θ = Angle made by resultant with OA. Then from triangle OCD, tan θ = CD Q sin α = OD P + Qcos α θ = tan 1 Equation (1.2) gives the direction of resultant (R). The direction of resultant can also be obtained by using sine rule [In triangle OAC, OA = P, AC = Q, OC = R, angle OAC = (180 α), angle ACO = 180 [θ α] = (α θ)] F HG I Q sin α...(1.2) P + Qcos αkj C sin q sin (180 - a) sin ( a - q) = = AC OC OA O sin q sin (180 - a) sin ( a - q) = = Q R P Two cases are important. 1st Case. If the two forces P and Q act at right angles, then α = 90 From equation (1.1), we get the magnitude of resultant as R = P + Q + 2PQcos α = P + Q + 2PQcos 90 = 2 2 P + Q ( cos 90 = 0)...(1.2 A) From equation (1.2), the direction of resultant is obtained as θ = tan 1 = tan 1 F HG F HG Q sin α P + Qcos α Q sin 90 P + Qcos 90 I KJ I = KJ tan 1 Q P ( sin 90 = 1 and cos 90 = 0) 2nd Case. The two forces P and Q are equal and are acting at an angle α between them. Then the magnitude and direction of resultant is given as R = P + Q + 2PQcos α = P + P + 2P P cos α ( P = Q) = 2P + 2P cos α = 2P ( 1+ cos α) R (180 ) P A Fig. 1.4 (a) ( ) Q
16 Engineering Mechanics (MTU) By Dr. R.K. Bansal 40% OFF Publisher : Laxmi Publications ISBN : Author : Dr. R.K. Bansal Type the URL : 10 Get this ebook
A TEXTBOOK APPLIED MECHANICS
 A TEXTBOOK OF APPLIED MECHANICS A TEXTBOOK OF APPLIED MECHANICS (Including Laboratory Practicals) S.I. UNITS By R.K. RAJPUT M.E. (Heat Power Engg.) Hons. Gold Medallist ; Grad. (Mech. Engg. & Elect. Engg.)
A TEXTBOOK OF APPLIED MECHANICS A TEXTBOOK OF APPLIED MECHANICS (Including Laboratory Practicals) S.I. UNITS By R.K. RAJPUT M.E. (Heat Power Engg.) Hons. Gold Medallist ; Grad. (Mech. Engg. & Elect. Engg.)
THEORY OF MACHINES I
 THEORY OF MACHINES I (Kinematics of Machines) (In SI Units) For BE/B.Tech. 3rd YEAR (Strictly as per the latest syllabus prescribed by U.P.T.U., U.P.) By Dr. R.K. BANSAL B.Sc. Engg. (Mech.), M.Tech., Hons.
THEORY OF MACHINES I (Kinematics of Machines) (In SI Units) For BE/B.Tech. 3rd YEAR (Strictly as per the latest syllabus prescribed by U.P.T.U., U.P.) By Dr. R.K. BANSAL B.Sc. Engg. (Mech.), M.Tech., Hons.
ENGINEERING MECHANICS: STATICS AND DYNAMICS
 ENGINEERING MECHANICS: STATICS AND DYNAMICS Dr. A.K. Tayal ENGINEERING MECHANICS STATICS AND DYNAMICS A.K. Tayal Ph. D. Formerly Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Delhi College of Engineering
ENGINEERING MECHANICS: STATICS AND DYNAMICS Dr. A.K. Tayal ENGINEERING MECHANICS STATICS AND DYNAMICS A.K. Tayal Ph. D. Formerly Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Delhi College of Engineering
CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY
 CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY MATHS SERIES CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY By N.P. BALI FIREWALL MEDIA (An Imprint of Laxmi Publications Pvt. Ltd.) BANGALORE CHENNAI COCHIN GUWAHATI HYDERABAD JALANDHAR KOLKATA LUCKNOW MUMBAI
CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY MATHS SERIES CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY By N.P. BALI FIREWALL MEDIA (An Imprint of Laxmi Publications Pvt. Ltd.) BANGALORE CHENNAI COCHIN GUWAHATI HYDERABAD JALANDHAR KOLKATA LUCKNOW MUMBAI
STATICS Chapter 1 Introductory Concepts
 Contents Preface to Adapted Edition... (v) Preface to Third Edition... (vii) List of Symbols and Abbreviations... (xi) PART - I STATICS Chapter 1 Introductory Concepts 1-1 Scope of Mechanics... 1 1-2 Preview
Contents Preface to Adapted Edition... (v) Preface to Third Edition... (vii) List of Symbols and Abbreviations... (xi) PART - I STATICS Chapter 1 Introductory Concepts 1-1 Scope of Mechanics... 1 1-2 Preview
2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS
 Set No - 1 I B.Tech I Semester Regular/Supple. Examinations Nov./Dec. 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to CE, ME, CSE, PCE, IT, Chem. E, Aero E, AME, Min E, PE, Metal E, Textile Engg.) Time: 3 hours
Set No - 1 I B.Tech I Semester Regular/Supple. Examinations Nov./Dec. 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to CE, ME, CSE, PCE, IT, Chem. E, Aero E, AME, Min E, PE, Metal E, Textile Engg.) Time: 3 hours
Foundations and Applications of Engineering Mechanics
 Foundations and Applications of Engineering Mechanics 4843/24, 2nd Floor, Ansari Road, Daryaganj, Delhi - 110002, India Cambridge University Press is part of the University of Cambridge. It furthers the
Foundations and Applications of Engineering Mechanics 4843/24, 2nd Floor, Ansari Road, Daryaganj, Delhi - 110002, India Cambridge University Press is part of the University of Cambridge. It furthers the
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MECHANICS QUESTION BANK UNIT I - PART-A
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MECHANICS QUESTION BANK Sub. Code: CE1151 Sub. Name: Engg. Mechanics UNIT I - PART-A Sem / Year II / I 1.Distinguish the following system of forces with a suitable
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MECHANICS QUESTION BANK Sub. Code: CE1151 Sub. Name: Engg. Mechanics UNIT I - PART-A Sem / Year II / I 1.Distinguish the following system of forces with a suitable
Set No - 1 I B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations Jan./Feb ENGINEERING MECHANICS
 3 Set No - 1 I B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations Jan./Feb. 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to CE, ME, CSE, PCE, IT, Chem E, Aero E, AME, Min E, PE, Metal E) Time: 3 hours Question Paper Consists
3 Set No - 1 I B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations Jan./Feb. 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to CE, ME, CSE, PCE, IT, Chem E, Aero E, AME, Min E, PE, Metal E) Time: 3 hours Question Paper Consists
ENGINEERING MECHANICS
 ENGINEERING MECHANICS BASUDEB BHATTACHARYYA Assistant Professor Department of Applied Mechanics Bengal Engineering and Science University Shibpur, Howrah OXJFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Foreword Preface
ENGINEERING MECHANICS BASUDEB BHATTACHARYYA Assistant Professor Department of Applied Mechanics Bengal Engineering and Science University Shibpur, Howrah OXJFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Foreword Preface
where G is called the universal gravitational constant.
 UNIT-I BASICS & STATICS OF PARTICLES 1. What are the different laws of mechanics? First law: A body does not change its state of motion unless acted upon by a force or Every object in a state of uniform
UNIT-I BASICS & STATICS OF PARTICLES 1. What are the different laws of mechanics? First law: A body does not change its state of motion unless acted upon by a force or Every object in a state of uniform
BASIC ENGINEERING MECHANICS
 BASIC ENGINEERING MECHANICS Other titles of interest to engineers An Introduction to Engineering Fluid Mechanics J. A. Fox Principles of Engineering Thermodynamics E. M. Goodger Analysis and Presentation
BASIC ENGINEERING MECHANICS Other titles of interest to engineers An Introduction to Engineering Fluid Mechanics J. A. Fox Principles of Engineering Thermodynamics E. M. Goodger Analysis and Presentation
2. a) Explain the equilibrium of i) Concurrent force system, and ii) General force system.
 Code No: R21031 R10 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 2013 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Com to ME, AE, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions
Code No: R21031 R10 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 2013 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Com to ME, AE, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING BRANCH: MECHANICAL YEAR / SEMESTER: I / II UNIT 1 PART- A 1. State Newton's three laws of motion? 2.
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING BRANCH: MECHANICAL YEAR / SEMESTER: I / II UNIT 1 PART- A 1. State Newton's three laws of motion? 2.
Where, m = slope of line = constant c = Intercept on y axis = effort required to start the machine
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Model Answer: Summer 07 Code: 70 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Model Answer: Summer 07 Code: 70 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
STATICS & DYNAMICS. Engineering Mechanics. Gary L. Gray. Francesco Costanzo. Michael E. Plesha. University of Wisconsin-Madison
 Engineering Mechanics STATICS & DYNAMICS SECOND EDITION Francesco Costanzo Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics Penn State University Michael E. Plesha Department of Engineering Physics University
Engineering Mechanics STATICS & DYNAMICS SECOND EDITION Francesco Costanzo Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics Penn State University Michael E. Plesha Department of Engineering Physics University
ISBN :
 ISBN : 978-81-909042-4-7 - www.airwalkpublications.com ANNA UNIVERSITY - R2013 GE6253 ENGINEERING MECHANICS UNIT I: BASICS AND STATICS OF PARTICLES 12 Introduction Units and Dimensions Laws of Mechanics
ISBN : 978-81-909042-4-7 - www.airwalkpublications.com ANNA UNIVERSITY - R2013 GE6253 ENGINEERING MECHANICS UNIT I: BASICS AND STATICS OF PARTICLES 12 Introduction Units and Dimensions Laws of Mechanics
2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS
 Set No - 1 I B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations Aug. 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to CE, ME, CSE, PCE, IT, Chem E, Aero E, AME, Min E, PE, Metal E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question
Set No - 1 I B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations Aug. 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to CE, ME, CSE, PCE, IT, Chem E, Aero E, AME, Min E, PE, Metal E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question
ELEMENTARY ENGINEERING MECHANICS
 ELEMENTARY ENGINEERING MECHANICS Other title by the same author Applied Mechanics Made Simple (Heinemann: 'Made Simple' series) Other Macmllian titles of related interest Basic Engineering Mechanics J.
ELEMENTARY ENGINEERING MECHANICS Other title by the same author Applied Mechanics Made Simple (Heinemann: 'Made Simple' series) Other Macmllian titles of related interest Basic Engineering Mechanics J.
The Great Indian Hornbill
 The Great Indian Hornbill Our mascot The Great Indian Hornbill is on the verge of extinction and features in International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) red list of endangered species. Now these
The Great Indian Hornbill Our mascot The Great Indian Hornbill is on the verge of extinction and features in International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) red list of endangered species. Now these
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING DEFINITIONS AND TERMINOLOGY Course Name : ENGINEERING MECHANICS Course Code : AAEB01 Program :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING DEFINITIONS AND TERMINOLOGY Course Name : ENGINEERING MECHANICS Course Code : AAEB01 Program :
Bergen Community College Division of Math, Science and Technology Department of Physical Sciences. Course Syllabus PHY 294 Engineering Mechanics
 Bergen Community College Division of Math, Science and Technology Department of Physical Sciences Course Syllabus PHY 294 Engineering Mechanics Semester and year: Course Number: Meeting Times and Locations:
Bergen Community College Division of Math, Science and Technology Department of Physical Sciences Course Syllabus PHY 294 Engineering Mechanics Semester and year: Course Number: Meeting Times and Locations:
Description Subject Teaching Methodology L T P C
 Course/ Code Engineering Mechanics 3 1-3 Teaching Total contact hours - 64 Engineering Physics Course Objectives: The students completing this course are expected to understand the concepts of forces and
Course/ Code Engineering Mechanics 3 1-3 Teaching Total contact hours - 64 Engineering Physics Course Objectives: The students completing this course are expected to understand the concepts of forces and
K.GNANASEKARAN. M.E.,M.B.A.,(Ph.D)
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG. Engineering Mechanics I YEAR 2th SEMESTER) Two Marks Question Bank UNIT-I Basics and statics of particles 1. Define Engineering Mechanics Engineering Mechanics is defined
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGG. Engineering Mechanics I YEAR 2th SEMESTER) Two Marks Question Bank UNIT-I Basics and statics of particles 1. Define Engineering Mechanics Engineering Mechanics is defined
Engineering Mechanics I Year B.Tech
 Engineering Mechanics I Year B.Tech By N.SRINIVASA REDDY., M.Tech. Sr. Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Vardhaman College of Engineering Basic concepts of Mathematics & Physics
Engineering Mechanics I Year B.Tech By N.SRINIVASA REDDY., M.Tech. Sr. Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Vardhaman College of Engineering Basic concepts of Mathematics & Physics
ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS
 A TEXTBOOK OF ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS For B.Sc. (Engg.), B.E., B. Tech., M.E. and Equivalent Professional Examinations By N.P. BALI Formerly Principal S.B. College, Gurgaon Haryana Dr. MANISH GOYAL M.Sc.
A TEXTBOOK OF ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS For B.Sc. (Engg.), B.E., B. Tech., M.E. and Equivalent Professional Examinations By N.P. BALI Formerly Principal S.B. College, Gurgaon Haryana Dr. MANISH GOYAL M.Sc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Preface...
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Preface...................................... xiv 1 Introduction........................................ 1 1.1 Engineering and Statics.............................. 1 1.2 A Brief History
TABLE OF CONTENTS Preface...................................... xiv 1 Introduction........................................ 1 1.1 Engineering and Statics.............................. 1 1.2 A Brief History
Academic Course Description. BHARATH UNIVERSITY Faculty of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering
 BME202 - ENGINEERING MECHANICS Course (catalog) description Academic Course Description BHARATH UNIVERSITY Faculty of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering BME202 - ENGINEERING
BME202 - ENGINEERING MECHANICS Course (catalog) description Academic Course Description BHARATH UNIVERSITY Faculty of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering BME202 - ENGINEERING
 Subject : Engineering Mechanics Subject Code : 1704 Page No: 1 / 6 ----------------------------- Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
Subject : Engineering Mechanics Subject Code : 1704 Page No: 1 / 6 ----------------------------- Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
ENGINEERING MECHANICS
 Set No - 1 I B. Tech II Semester Regular/Supply Examinations July/Aug. - 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to ECE, EEE, EIE, Bio-Tech, E Com.E, Agri. E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question Paper Consists
Set No - 1 I B. Tech II Semester Regular/Supply Examinations July/Aug. - 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to ECE, EEE, EIE, Bio-Tech, E Com.E, Agri. E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question Paper Consists
Model Answers Attempt any TEN of the following :
 (ISO/IEC - 70-005 Certified) Model Answer: Winter 7 Sub. Code: 17 Important Instructions to Examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
(ISO/IEC - 70-005 Certified) Model Answer: Winter 7 Sub. Code: 17 Important Instructions to Examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
Fundamental Principles
 Fundamental Principles Newton s First Law: If the resultant force on a particle is zero, the particle will remain at rest or continue to move in a straight line. First Law: A. body will remain at rest
Fundamental Principles Newton s First Law: If the resultant force on a particle is zero, the particle will remain at rest or continue to move in a straight line. First Law: A. body will remain at rest
ENGINEERING MECHANICS - Question Bank
 E Semester-_IST YEAR (CIVIL, MECH, AUTO, CHEM, RUER, PLASTIC, ENV,TT,AERO) ENGINEERING MECHANICS - Question ank All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 Define space,time matter and force, scalar
E Semester-_IST YEAR (CIVIL, MECH, AUTO, CHEM, RUER, PLASTIC, ENV,TT,AERO) ENGINEERING MECHANICS - Question ank All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 Define space,time matter and force, scalar
ME101: Engineering Mechanics ( )
 ME101: Engineering Mechanics (3 1 0 8) 2016-2017 (II Semester); Division IV Budhaditya Hazra Room N-307 Department of Civil Engineering budhaditya.hazra@iitg.ernet.in Phone: 258 3334/5334 Web: www.iitg.ernet.in/budhaditya.hazra
ME101: Engineering Mechanics (3 1 0 8) 2016-2017 (II Semester); Division IV Budhaditya Hazra Room N-307 Department of Civil Engineering budhaditya.hazra@iitg.ernet.in Phone: 258 3334/5334 Web: www.iitg.ernet.in/budhaditya.hazra
VED e\monish-k\tit-5kch IInd Kerala (Semester V)
 e\monish-k\tit-5kch IInd 4-01-1 A TEXTBOOK OF ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS A TEXTBOOK OF ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS For BTECH (5 th Semester) Computer Science and Information Technology FOR MAHATMA GANDHI UNIVERSITY,
e\monish-k\tit-5kch IInd 4-01-1 A TEXTBOOK OF ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS A TEXTBOOK OF ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS For BTECH (5 th Semester) Computer Science and Information Technology FOR MAHATMA GANDHI UNIVERSITY,
PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION (Section 17.2)
 PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION (Section 17.2) We will limit our study of planar kinetics to rigid bodies that are symmetric with respect to a fixed reference plane. As discussed in Chapter 16, when
PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION (Section 17.2) We will limit our study of planar kinetics to rigid bodies that are symmetric with respect to a fixed reference plane. As discussed in Chapter 16, when
STATICS SECOND EDITION
 Engineering Mechanics STATICS SECOND EDITION Michael E. Plesha Department of Engineering Physics University of Wisconsin-Madison Gary L. Gray Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics Penn State
Engineering Mechanics STATICS SECOND EDITION Michael E. Plesha Department of Engineering Physics University of Wisconsin-Madison Gary L. Gray Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics Penn State
A. Objective of the Course: Objectives of introducing this subject at second year level in civil branches are: 1. Introduction 02
 Subject Code: 0CL030 Subject Name: Mechanics of Solids B.Tech. II Year (Sem-3) Mechanical & Automobile Engineering Teaching Credits Examination Marks Scheme Theory Marks Practical Marks Total L 4 T 0 P
Subject Code: 0CL030 Subject Name: Mechanics of Solids B.Tech. II Year (Sem-3) Mechanical & Automobile Engineering Teaching Credits Examination Marks Scheme Theory Marks Practical Marks Total L 4 T 0 P
PHYSICS. Course Structure. Unit Topics Marks. Physical World and Measurement. 1 Physical World. 2 Units and Measurements.
 PHYSICS Course Structure Unit Topics Marks I Physical World and Measurement 1 Physical World 2 Units and Measurements II Kinematics 3 Motion in a Straight Line 23 4 Motion in a Plane III Laws of Motion
PHYSICS Course Structure Unit Topics Marks I Physical World and Measurement 1 Physical World 2 Units and Measurements II Kinematics 3 Motion in a Straight Line 23 4 Motion in a Plane III Laws of Motion
A TEXTBOOK APPLIED MECHANICS
 A TEXTBOOK OF APPLIED MECHANICS A TEXTBOOK OF APPLIED MECHANICS (Including Laboratory Practicals) S.I. UNITS By R.K. RAJPUT M.E. (Heat Power Engg.) Hons. Gold Medallist ; Grad. (Mech. Engg. & Elect. Engg.)
A TEXTBOOK OF APPLIED MECHANICS A TEXTBOOK OF APPLIED MECHANICS (Including Laboratory Practicals) S.I. UNITS By R.K. RAJPUT M.E. (Heat Power Engg.) Hons. Gold Medallist ; Grad. (Mech. Engg. & Elect. Engg.)
Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module No. - 01 Basics of Statics Lecture No. - 01 Fundamental of Engineering Mechanics
Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module No. - 01 Basics of Statics Lecture No. - 01 Fundamental of Engineering Mechanics
Engineering Mechanics
 2019 MPROVEMENT Mechanical Engineering Engineering Mechanics Answer Key of Objective & Conventional Questions 1 System of forces, Centoriod, MOI 1. (c) 2. (b) 3. (a) 4. (c) 5. (b) 6. (c) 7. (b) 8. (b)
2019 MPROVEMENT Mechanical Engineering Engineering Mechanics Answer Key of Objective & Conventional Questions 1 System of forces, Centoriod, MOI 1. (c) 2. (b) 3. (a) 4. (c) 5. (b) 6. (c) 7. (b) 8. (b)
Miami-Dade Community College. PHY 1025 Basic Physics. This course may be used to satisfy one of the Natural Science requirements.
 Miami-Dade Community College PHY 1025 Basic Physics PHY 1025 3 credits Course Description This course will facilitate the transition from high school to college/university physics. Content includes units
Miami-Dade Community College PHY 1025 Basic Physics PHY 1025 3 credits Course Description This course will facilitate the transition from high school to college/university physics. Content includes units
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS Credit Hours: 6
 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS Credit Hours: 6 Teaching Scheme Theory Tutorials Practical Total Credit Hours/week 4 0 6 6 Marks 00 0 50 50 6 A. Objective of the Course: Objectives of introducing this subject at second
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS Credit Hours: 6 Teaching Scheme Theory Tutorials Practical Total Credit Hours/week 4 0 6 6 Marks 00 0 50 50 6 A. Objective of the Course: Objectives of introducing this subject at second
Simplified Structural Analysis and Design for Architects
 Simplified Structural Analysis and Design for Architects Second Edition Rima Taher, PhD, PE New Jersey Institute of Technology Bassim Hamadeh, CEO and Publisher Kassie Graves, Director of Acquisitions
Simplified Structural Analysis and Design for Architects Second Edition Rima Taher, PhD, PE New Jersey Institute of Technology Bassim Hamadeh, CEO and Publisher Kassie Graves, Director of Acquisitions
GOPALAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT Department of Civil Engineering COURSE PLAN
 Appendix - C GOPALAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT Department of Civil Engineering Academic Year: 2017-18 Semester: EVEN COURSE PLAN Semester: II Subject Code& Name: 15CIV23& Elements of Civil
Appendix - C GOPALAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT Department of Civil Engineering Academic Year: 2017-18 Semester: EVEN COURSE PLAN Semester: II Subject Code& Name: 15CIV23& Elements of Civil
PESIT-BSC Department of Science & Humanities
 Class No. 1. 2. 3. LESSON PLAN 15CIV13/23 ELEMENTS OF CIVIL ENGINEERING Course objectives: AND ENGINEERING MECHANICS The objectives of this course is to make students to learn basics of Civil Engineering
Class No. 1. 2. 3. LESSON PLAN 15CIV13/23 ELEMENTS OF CIVIL ENGINEERING Course objectives: AND ENGINEERING MECHANICS The objectives of this course is to make students to learn basics of Civil Engineering
Get Discount Coupons for your Coaching institute and FREE Study Material at Force System
 Get Discount Coupons for your Coaching institute and FEE Study Material at www.pickmycoaching.com Mechanics Force System When a member of forces simultaneously acting on the body, it is known as force
Get Discount Coupons for your Coaching institute and FEE Study Material at www.pickmycoaching.com Mechanics Force System When a member of forces simultaneously acting on the body, it is known as force
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE DESCRIPTION
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURE DECRIPTION Course Code Course Title : A10302 : ENGINEERING MECHANIC Course tructure : Lectures Tutorials Practical Credits 3 - - 6 Course Coordinator : Dr.D.Govardhan,
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURE DECRIPTION Course Code Course Title : A10302 : ENGINEERING MECHANIC Course tructure : Lectures Tutorials Practical Credits 3 - - 6 Course Coordinator : Dr.D.Govardhan,
JNTU World. Subject Code: R13110/R13 '' '' '' ''' '
 Set No - 1 I B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations Sept. - 2014 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to CE, ME, CSE, PCE, IT, Chem E, Aero E, AME, Min E, PE, Metal E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question
Set No - 1 I B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations Sept. - 2014 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to CE, ME, CSE, PCE, IT, Chem E, Aero E, AME, Min E, PE, Metal E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question
Engineering Mechanics Objective module 1 with solutions: A K GAIKAR
 Engineering Mechanics Objective module 1 with solutions: A K GAIKAR 1. What is the branch of engineering mechanics which refers to the study of stationary rigid body? A. Statics B. Kinetics C. Kinematics
Engineering Mechanics Objective module 1 with solutions: A K GAIKAR 1. What is the branch of engineering mechanics which refers to the study of stationary rigid body? A. Statics B. Kinetics C. Kinematics
STATICS AND DYNAMICS
 ENGINEERING MECHANICS STATICS AND DYNAMICS FOURTEENTH EDITION R. C. HIBBELER PEARSON Hoboken Boston Columbus San Francisco New York Indianapolis London Toronto Sydney Singapore Tokyo Montreal Dubai Madrid
ENGINEERING MECHANICS STATICS AND DYNAMICS FOURTEENTH EDITION R. C. HIBBELER PEARSON Hoboken Boston Columbus San Francisco New York Indianapolis London Toronto Sydney Singapore Tokyo Montreal Dubai Madrid
Course syllabus Engineering Mechanics - Dynamics
 Course syllabus Engineering Mechanics - Dynamics COURSE DETAILS Type of study programme Study programme Course title Course code ECTS (Number of credits allocated) Course status Year of study Course Web
Course syllabus Engineering Mechanics - Dynamics COURSE DETAILS Type of study programme Study programme Course title Course code ECTS (Number of credits allocated) Course status Year of study Course Web
2016 ENGINEERING MECHANICS
 Set No 1 I B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec 2016 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Com. to AE, AME, BOT, CHEM, CE, EEE, ME, MTE, MM, PCE, PE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question Paper Consists of Part-A
Set No 1 I B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Dec 2016 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Com. to AE, AME, BOT, CHEM, CE, EEE, ME, MTE, MM, PCE, PE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question Paper Consists of Part-A
Mechanics. In the Science Program, Mechanics contributes to the following program goals described in the Exit Profile:
 Mechanics Objectives: 00UR Discipline: Physics Ponderation: 3-2-3 Course Code: 203-NYA-05 Prerequisite: Sec. V Physics 534, Mathematics 536 (or equivalent) Course Credit: 2 2/3 Corequisite: 00UP (Calculus
Mechanics Objectives: 00UR Discipline: Physics Ponderation: 3-2-3 Course Code: 203-NYA-05 Prerequisite: Sec. V Physics 534, Mathematics 536 (or equivalent) Course Credit: 2 2/3 Corequisite: 00UP (Calculus
inertia of a body, principal axes of inertia, invariants of an inertia tensor, and inertia triangle inequalities are illustrated and discussed.
 Preface This book belongs to a series of three books written simultaneously (the remaining two are titled Classical Mechanics: Dynamics and Classical Mechanics: Applied MechanicsandMechatronics). This
Preface This book belongs to a series of three books written simultaneously (the remaining two are titled Classical Mechanics: Dynamics and Classical Mechanics: Applied MechanicsandMechatronics). This
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE ENGS STATICS
 STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE PREPARED BY: ARTHUR HURLBUT, Ph.D. P.E.(October 2006) UPDATED BY: MICHAEL J. NEWTOWN, P.E. (October 2006) REVISED BY:
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE PREPARED BY: ARTHUR HURLBUT, Ph.D. P.E.(October 2006) UPDATED BY: MICHAEL J. NEWTOWN, P.E. (October 2006) REVISED BY:
DIVIDED SYLLABUS ( ) - CLASS XI PHYSICS (CODE 042) COURSE STRUCTURE APRIL
 DIVIDED SYLLABUS (2015-16 ) - CLASS XI PHYSICS (CODE 042) COURSE STRUCTURE APRIL Unit I: Physical World and Measurement Physics Need for measurement: Units of measurement; systems of units; SI units, fundamental
DIVIDED SYLLABUS (2015-16 ) - CLASS XI PHYSICS (CODE 042) COURSE STRUCTURE APRIL Unit I: Physical World and Measurement Physics Need for measurement: Units of measurement; systems of units; SI units, fundamental
Igor Emri Arkady Voloshin. Statics. Learning from Engineering Examples
 Statics Igor Emri Arkady Voloshin Statics Learning from Engineering Examples Igor Emri University of Ljubljana Ljubljana, Slovenia Arkady Voloshin Lehigh University Bethlehem, PA, USA ISBN 978-1-4939-2100-3
Statics Igor Emri Arkady Voloshin Statics Learning from Engineering Examples Igor Emri University of Ljubljana Ljubljana, Slovenia Arkady Voloshin Lehigh University Bethlehem, PA, USA ISBN 978-1-4939-2100-3
.VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 .VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF GENERAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK II SEMESTER GE 8292- Engineering Mechanics Regulation 2017 Academic Year 2017 18 VALLIAMMAI
.VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF GENERAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK II SEMESTER GE 8292- Engineering Mechanics Regulation 2017 Academic Year 2017 18 VALLIAMMAI
USHA RAMA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
 Set No - 1 I B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations Feb. - 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to ECE, EEE, EIE, Bio-Tech, E Com.E, Agri. E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question Paper Consists
Set No - 1 I B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations Feb. - 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to ECE, EEE, EIE, Bio-Tech, E Com.E, Agri. E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question Paper Consists
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY BASIC ENGINEERING MECHANICS MCQ TUTORIAL SHEET OF MEC Concurrent forces are those forces whose lines of action
 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY BASIC ENGINEERING MECHANICS MCQ TUTORIAL SHEET OF MEC 107 1. Concurrent forces are those forces whose lines of action 1. Meet on the same plane 2. Meet at one point 3. Lie
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY BASIC ENGINEERING MECHANICS MCQ TUTORIAL SHEET OF MEC 107 1. Concurrent forces are those forces whose lines of action 1. Meet on the same plane 2. Meet at one point 3. Lie
Department of Mechanical Engineering Course plan
 Faculty of Engineering & Technology, SRM University, Kattankulathur 603203 School of Mechanical Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering Course plan Course code : ME1002 Date : 19 th December 2013
Faculty of Engineering & Technology, SRM University, Kattankulathur 603203 School of Mechanical Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering Course plan Course code : ME1002 Date : 19 th December 2013
ENGINEERING MECHANICS
 ENGINEERING MECHANICS Engineering Mechanics Volume 2: Stresses, Strains, Displacements by C. HARTSUIJKER Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands and J.W. WELLEMAN Delft University of Technology,
ENGINEERING MECHANICS Engineering Mechanics Volume 2: Stresses, Strains, Displacements by C. HARTSUIJKER Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands and J.W. WELLEMAN Delft University of Technology,
Dept of ECE, SCMS Cochin
 B B2B109 Pages: 3 Reg. No. Name: APJ ABDUL KALAM TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SECOND SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2017 Course Code: BE 100 Course Name: ENGINEERING MECHANICS Max. Marks: 100 Duration:
B B2B109 Pages: 3 Reg. No. Name: APJ ABDUL KALAM TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SECOND SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2017 Course Code: BE 100 Course Name: ENGINEERING MECHANICS Max. Marks: 100 Duration:
Class XI Physics Syllabus One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70
 Class XI Physics Syllabus 2013 One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70 Class XI Weightage Unit I Physical World & Measurement 03 Unit II Kinematics 10 Unit III Laws of Motion 10 Unit IV Work, Energy & Power
Class XI Physics Syllabus 2013 One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70 Class XI Weightage Unit I Physical World & Measurement 03 Unit II Kinematics 10 Unit III Laws of Motion 10 Unit IV Work, Energy & Power
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE SYLLABUS FOR ENGR 2301 Engineering Mechanics - Statics. Semester Hours Credit: 3
 CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE SYLLABUS FOR ENGR 2301 Engineering Mechanics - Statics Semester Hours Credit: 3 I. INTRODUCTION A. ENGR 2301, Engineering Mechanics Statics, is a three-semester hour course that is
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE SYLLABUS FOR ENGR 2301 Engineering Mechanics - Statics Semester Hours Credit: 3 I. INTRODUCTION A. ENGR 2301, Engineering Mechanics Statics, is a three-semester hour course that is
F R. + F 3x. + F 2y. = (F 1x. j + F 3x. i + F 2y. i F 3y. i + F 1y. j F 2x. ) i + (F 1y. ) j. F 2x. F 3y. = (F ) i + (F ) j. ) j
 General comments: closed book and notes but optional one page crib sheet allowed. STUDY: old exams, homework and power point lectures! Key: make sure you can solve your homework problems and exam problems.
General comments: closed book and notes but optional one page crib sheet allowed. STUDY: old exams, homework and power point lectures! Key: make sure you can solve your homework problems and exam problems.
D.A.V. PUBLIC SCHOOL, UPPAL S SOUTHEND, SECTOR 49, GURUGRAM CLASS XI (PHYSICS) Academic plan for
 D.A.V. PUBLIC SCHOOL, UPPAL S SOUTHEND, SECTOR 49, GURUGRAM CLASS XI (PHYSICS) Academic plan for 2017-2018 UNIT NAME OF UNIT WEIGHTAGE 1. 2. 3. Physical World and Measurement Kinemetics Laws of Motion
D.A.V. PUBLIC SCHOOL, UPPAL S SOUTHEND, SECTOR 49, GURUGRAM CLASS XI (PHYSICS) Academic plan for 2017-2018 UNIT NAME OF UNIT WEIGHTAGE 1. 2. 3. Physical World and Measurement Kinemetics Laws of Motion
Moments of Inertia (7 pages; 23/3/18)
 Moments of Inertia (7 pages; 3/3/8) () Suppose that an object rotates about a fixed axis AB with angular velocity θ. Considering the object to be made up of particles, suppose that particle i (with mass
Moments of Inertia (7 pages; 3/3/8) () Suppose that an object rotates about a fixed axis AB with angular velocity θ. Considering the object to be made up of particles, suppose that particle i (with mass
BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS)
 BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS) All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 (a) Write the SI units of following quantities and also mention whether it is scalar or vector: (i)
BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS) All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 (a) Write the SI units of following quantities and also mention whether it is scalar or vector: (i)
COMPLEX ANALYSIS-I. DR. P.K. SRIVASTAVA Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics Galgotia s College of Engg. & Technology, Gr.
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS-I DR. P.K. SRIVASTAVA Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics Galgotia s College of Engg. & Technology, Gr. Noida An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Company Vayu Education of India 2/25,
COMPLEX ANALYSIS-I DR. P.K. SRIVASTAVA Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics Galgotia s College of Engg. & Technology, Gr. Noida An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Company Vayu Education of India 2/25,
Pharmaceutical Mathematics with Application to Pharmacy
 Pharmaceutical Mathematics with Application to Pharmacy (ii) (iii) Pharmaceutical Mathe ematics with Application to Pharmacy D.H. Panchaksharappa Gowda Assistant Professor, J.S.S. College of Pharmacy,
Pharmaceutical Mathematics with Application to Pharmacy (ii) (iii) Pharmaceutical Mathe ematics with Application to Pharmacy D.H. Panchaksharappa Gowda Assistant Professor, J.S.S. College of Pharmacy,
PART-A. a. 60 N b. -60 N. c. 30 N d. 120 N. b. How you can get direction of Resultant R when number of forces acting on a particle in plane.
 V.S.. ENGINEERING OLLEGE, KRUR EPRTMENT OF MEHNIL ENGINEERING EMI YER: 2009-2010 (EVEN SEMESTER) ENGINEERING MEHNIS (MEH II SEM) QUESTION NK UNIT I PRT- EM QUESTION NK 1. efine Mechanics 2. What is meant
V.S.. ENGINEERING OLLEGE, KRUR EPRTMENT OF MEHNIL ENGINEERING EMI YER: 2009-2010 (EVEN SEMESTER) ENGINEERING MEHNIS (MEH II SEM) QUESTION NK UNIT I PRT- EM QUESTION NK 1. efine Mechanics 2. What is meant
Civil Engineering. Structural Analysis. Comprehensive Theory with Solved Examples and Practice Questions. Publications
 Civil Engineering Structural Analysis Comprehensive Theory with Solved Examples and Practice Questions Publications Publications MADE EASY Publications Corporate Office: 44-A/4, Kalu Sarai (Near Hauz Khas
Civil Engineering Structural Analysis Comprehensive Theory with Solved Examples and Practice Questions Publications Publications MADE EASY Publications Corporate Office: 44-A/4, Kalu Sarai (Near Hauz Khas
Appendix. Vectors, Systems of Equations
 ppendix Vectors, Systems of Equations Vectors, Systems of Equations.1.1 Vectors Scalar physical quantities (e.g., time, mass, density) possess only magnitude. Vectors are physical quantities (e.g., force,
ppendix Vectors, Systems of Equations Vectors, Systems of Equations.1.1 Vectors Scalar physical quantities (e.g., time, mass, density) possess only magnitude. Vectors are physical quantities (e.g., force,
Vector Mechanics For Engineers Statics Solution Manual 10th Edition
 Vector Mechanics For Engineers Statics Solution Manual 10th Edition We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on
Vector Mechanics For Engineers Statics Solution Manual 10th Edition We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on
Vector Mechanics For Engineers Statics And Dynamics
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with vector mechanics for
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with vector mechanics for
SPRING SEMESTER AE 262 DYNAMICS. (02) Dr. Yavuz YAMAN
 2012-2013 SPRING SEMESTER AE 262 DYNAMICS INSTRUCTOR (01) Dr. Yavuz YAMAN (02) Dr. Yavuz YAMAN TEXTBOOK Vector Mechanics for Engineers DYNAMICS F.P. Beer, E.R. Johnston Jr. and W.E. Clausen Eighth Edition
2012-2013 SPRING SEMESTER AE 262 DYNAMICS INSTRUCTOR (01) Dr. Yavuz YAMAN (02) Dr. Yavuz YAMAN TEXTBOOK Vector Mechanics for Engineers DYNAMICS F.P. Beer, E.R. Johnston Jr. and W.E. Clausen Eighth Edition
Introduction to CLASSICAL MECHANICS
 Introduction to CLASSICAL MECHANICS Introduction to CLASSICAL MECHANICS A.P. FRENCH Massachusetts Institute oj Technology M.G. EBISON The Institute oj Physics, London KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS DORDRECHT
Introduction to CLASSICAL MECHANICS Introduction to CLASSICAL MECHANICS A.P. FRENCH Massachusetts Institute oj Technology M.G. EBISON The Institute oj Physics, London KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS DORDRECHT
Vector Mechanics For Engineers Statics 8th Edition
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with vector mechanics for
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with vector mechanics for
FIRST MULTICOLOUR EDITION
 FIRST MULTICOLOUR EDITION Including Balancing of Equations By Ion-Electron Method By Oxidation Number Method G.D. TULI Ex-Principal Shyamlal College Delhi University, Delhi P.L. SONI Formerly, Head of
FIRST MULTICOLOUR EDITION Including Balancing of Equations By Ion-Electron Method By Oxidation Number Method G.D. TULI Ex-Principal Shyamlal College Delhi University, Delhi P.L. SONI Formerly, Head of
A Text book of MATHEMATICS-I. Career Institute of Technology and Management, Faridabad. Manav Rachna Publishing House Pvt. Ltd.
 A Tet book of ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS-I by Prof. R.S. Goel E. Principal, Aggarwal College, Ballabhgarh Senior Faculty of Mathematics Career Institute of Technology and Management, Faridabad Dr. Y.K. Sharma
A Tet book of ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS-I by Prof. R.S. Goel E. Principal, Aggarwal College, Ballabhgarh Senior Faculty of Mathematics Career Institute of Technology and Management, Faridabad Dr. Y.K. Sharma
Statics deal with the condition of equilibrium of bodies acted upon by forces.
 Mechanics It is defined as that branch of science, which describes and predicts the conditions of rest or motion of bodies under the action of forces. Engineering mechanics applies the principle of mechanics
Mechanics It is defined as that branch of science, which describes and predicts the conditions of rest or motion of bodies under the action of forces. Engineering mechanics applies the principle of mechanics
Written as per the revised G Scheme syllabus prescribed by the Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education (MSBTE) w.e.f. academic year
 Written as per the revised G Scheme syllabus prescribed by the Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education (MSBTE) w.e.f. academic year 2012-2013 Basic MATHEMATICS First Year Diploma Semester - I First
Written as per the revised G Scheme syllabus prescribed by the Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education (MSBTE) w.e.f. academic year 2012-2013 Basic MATHEMATICS First Year Diploma Semester - I First
Vidyalanakar F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CE/CH/CR/CS/CV/EE/EP/FE/ME/MH/MI/PG/PT/PS] Engineering Mechanics
![Vidyalanakar F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CE/CH/CR/CS/CV/EE/EP/FE/ME/MH/MI/PG/PT/PS] Engineering Mechanics Vidyalanakar F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CE/CH/CR/CS/CV/EE/EP/FE/ME/MH/MI/PG/PT/PS] Engineering Mechanics](/thumbs/77/74871041.jpg) Vidyalanakar F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CE/CH/CR/CS/CV/EE/EP/FE/ME/MH/MI/PG/PT/PS] Engineering Mechanics Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1 Attempt any TEN of the following
Vidyalanakar F.Y. Diploma : Sem. II [AE/CE/CH/CR/CS/CV/EE/EP/FE/ME/MH/MI/PG/PT/PS] Engineering Mechanics Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1 Attempt any TEN of the following
Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Paper Reference(s) 6678/01 Edexcel GCE Mechanics M2 Silver Level S2 Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included with question papers Nil Candidates
Paper Reference(s) 6678/01 Edexcel GCE Mechanics M2 Silver Level S2 Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included with question papers Nil Candidates
Bachelor of Technology Civil Engineering. 01CI0301: Mechanics of Solids
 01CI0301: Mechanics of Solids Objective of the Course Objectives of introducing this subject at second year level in civil branches are: To study about identification of different types of forces, systematic
01CI0301: Mechanics of Solids Objective of the Course Objectives of introducing this subject at second year level in civil branches are: To study about identification of different types of forces, systematic
Lesson Plan. Name of the Faculty : SANDEEP (VTF in CIVIL ENGG.) Lesson plan duration : 15 Weeks(July 2018 to Nov 2018)
 Lesson Plan Name of the Faculty : SANDEEP (VTF in CIVIL ENGG.) Discipline : CIVIL Engg. Semester : 3 rd Subject : Applied Mechanics Lesson plan duration : 15 s(july 2018 to Nov 2018) - 1 2 3 Theory Practical
Lesson Plan Name of the Faculty : SANDEEP (VTF in CIVIL ENGG.) Discipline : CIVIL Engg. Semester : 3 rd Subject : Applied Mechanics Lesson plan duration : 15 s(july 2018 to Nov 2018) - 1 2 3 Theory Practical
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD.
 ENGINEERING MECHANICS 1. RATIONALE Engineering Mechanics is a branch of Applied Science where laws of physics are applied to solve engineering problems. Broadly speaking Engineering Mechanics can be classified
ENGINEERING MECHANICS 1. RATIONALE Engineering Mechanics is a branch of Applied Science where laws of physics are applied to solve engineering problems. Broadly speaking Engineering Mechanics can be classified
APPLIED MATHEMATICS IM 02
 IM SYLLABUS (2013) APPLIED MATHEMATICS IM 02 SYLLABUS Applied Mathematics IM 02 Syllabus (Available in September) 1 Paper (3 hours) Applied Mathematics (Mechanics) Aims A course based on this syllabus
IM SYLLABUS (2013) APPLIED MATHEMATICS IM 02 SYLLABUS Applied Mathematics IM 02 Syllabus (Available in September) 1 Paper (3 hours) Applied Mathematics (Mechanics) Aims A course based on this syllabus
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 STATICS AND MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr, John T. DeWolf David E Mazurek \Cawect Mc / iur/» Craw SugomcT Hilt Introduction 1 1.1 What is Mechanics? 2 1.2 Fundamental
STATICS AND MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr, John T. DeWolf David E Mazurek \Cawect Mc / iur/» Craw SugomcT Hilt Introduction 1 1.1 What is Mechanics? 2 1.2 Fundamental
Chapter 2 Mechanical Equilibrium
 Chapter 2 Mechanical Equilibrium I. Force (2.1) A. force is a push or pull 1. A force is needed to change an object s state of motion 2. State of motion may be one of two things a. At rest b. Moving uniformly
Chapter 2 Mechanical Equilibrium I. Force (2.1) A. force is a push or pull 1. A force is needed to change an object s state of motion 2. State of motion may be one of two things a. At rest b. Moving uniformly
E 490 FE Exam Prep. Engineering Mechanics
 E 490 FE Exam Prep Engineering Mechanics 2008 E 490 Course Topics Statics Newton s Laws of Motion Resultant Force Systems Moment of Forces and Couples Equilibrium Pulley Systems Trusses Centroid of an
E 490 FE Exam Prep Engineering Mechanics 2008 E 490 Course Topics Statics Newton s Laws of Motion Resultant Force Systems Moment of Forces and Couples Equilibrium Pulley Systems Trusses Centroid of an
SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS AND TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ONTARIO COURSE OUTLINE
 SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS AND TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ONTARIO COURSE OUTLINE COURSE TITLE: CODE NO. : SEMESTER: Two PROGRAM: AUTHOR: Aviation Technology Flight Douglas McKinnon DATE: Jan 2013
SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS AND TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ONTARIO COURSE OUTLINE COURSE TITLE: CODE NO. : SEMESTER: Two PROGRAM: AUTHOR: Aviation Technology Flight Douglas McKinnon DATE: Jan 2013
Chapter 4 Statics and dynamics of rigid bodies
 Chapter 4 Statics and dynamics of rigid bodies Bachelor Program in AUTOMATION ENGINEERING Prof. Rong-yong Zhao (zhaorongyong@tongji.edu.cn) First Semester,2014-2015 Content of chapter 4 4.1 Static equilibrium
Chapter 4 Statics and dynamics of rigid bodies Bachelor Program in AUTOMATION ENGINEERING Prof. Rong-yong Zhao (zhaorongyong@tongji.edu.cn) First Semester,2014-2015 Content of chapter 4 4.1 Static equilibrium
Reg. No. : Question Paper Code : B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER Second Semester.
 Ws11 Reg. No. : Question Paper Code : 27275 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2015. Second Semester Civil Engineering GE 6253 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to all branches except Electrical
Ws11 Reg. No. : Question Paper Code : 27275 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2015. Second Semester Civil Engineering GE 6253 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to all branches except Electrical
AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives
 AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives I. KINEMATICS A. Motion in One Dimension 1. The relationships among position, velocity and acceleration a. Given a graph of position vs. time, identify or sketch a graph
AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives I. KINEMATICS A. Motion in One Dimension 1. The relationships among position, velocity and acceleration a. Given a graph of position vs. time, identify or sketch a graph
Rigid Body Kinetics :: Force/Mass/Acc
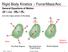 Rigid Body Kinetics :: Force/Mass/Acc General Equations of Motion G is the mass center of the body Action Dynamic Response 1 Rigid Body Kinetics :: Force/Mass/Acc Fixed Axis Rotation All points in body
Rigid Body Kinetics :: Force/Mass/Acc General Equations of Motion G is the mass center of the body Action Dynamic Response 1 Rigid Body Kinetics :: Force/Mass/Acc Fixed Axis Rotation All points in body
A PRACTICAL MANUAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL ENGINEERING
 A PRACTICAL MANUAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL ENGINEERING A PRACTICAL MANUAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL ENGINEERING P.S. SONA M Pharma Associate Professor, Department of Pharmaceutics Parul Institute of Pharmacy, Limda,
A PRACTICAL MANUAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL ENGINEERING A PRACTICAL MANUAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL ENGINEERING P.S. SONA M Pharma Associate Professor, Department of Pharmaceutics Parul Institute of Pharmacy, Limda,
