RESEARCH REGARDING FRICTION INFLUENCE OF WIRES TO JOINTS INTERIOR ON PRECISION POSITIONING OF A ROBOTIC ARM
|
|
|
- Samuel Nelson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Internatonal Journal of Modern Manufacturng Technologes ISSN , Vol. VIII, No. 1 / 2016 RESEARCH REGARDING FRICTION INFLUENCE OF WIRES TO JOINTS INTERIOR ON PRECISION POSITIONING OF A ROBOTIC ARM Catalna Cofu 1, Gheorghe Stan 2 1, 2 Vasle Alecsandr Unversty of Bacau, Department of Industral Engneerng Calea Marasest, No. 157, , Bacau, Romana Abstract: Robotc structures are used ncreasngly often n operatons from ndustral feld. By now, desgners came wth nnovatve robotc structures that mmc the movements nspred from nature (snake, octopus arm, elephant s trunk) to acheve flexble postonng. The specfc actuaton of elephant s trunk robotc arms wth wre-drven jonts through nner structure has several mportant advantages such as mnaturzaton possblty of the robotc arm dameter, flexble postonng through narrows spaces and a large workspace wth respect to robot sze. Inner actuaton causes elastc deformaton because of wres frcton to jonts nteror, whch contrbutes to the decreasng of jonts precson postonng. Elastc deformatons of drvng wres vary from jont to jont dependng upon the wnded surfaces number and wres length. In the analyss, we obtan varaton dagrams of postonng precson for each wre drven jont on Y and Z axes. The analytcal method s necessary for postonng precson optmzaton of the partcular robotc arm. Key words: actuatng wres frcton, nner actuaton, seral robotc structure, precson postonng, elastc deformaton. 1. INTRODUCTION The structure of elephant s trunk robotc arms conssts of serally connected jonts that enable flexble spatal postonng. Jonts of smlar structures are commonly drven by wres or cables to actuate them from dstance wth actuators dsposed at the base arm. Ths partcularty assures a low weght of the robotc arm. The actuaton of jonts wth pulley systems and drvng wres placed through structure arm nteror has the advantage of enablng small arm dameters along wth flexble postonng n narrow spaces. However, manpulaton n narrow spaces requres precson postonng that has dfferent sources of postonng errors. Ths paper hghlghts the nfluence of frcton between drvng wres and nner surfaces of robotc arm on postonng precson. Wre actuaton of jonts s commonly used at robotc hands for fngers drvng as t s a demand for mnmum dameters of fngers Correspondng author: Catalna Cofu, blgcatalna@yahoo.com 24 and, consequently for nner actuaton wth wres [1]. Robotc arms wth the structure smlar to elephant s trunk and a smaller number of actuators than the number of jonts have moton control ssues that are solved by an elastc tube mounted to arm s structure nteror [2, 3, 4]. Another robotc arm smlar to elephant s trunk structure has a PID devce for postonng errors compensaton of whch sources cannot be dentfed, [6]. More and more researchers are developng dfferent optmzaton methods of closed loop command systems and moton control usng PID devces to acheve accuracy and trajectory precson of elephant s trunk robotc arms, [5, 8]. The elastcty of drvng wres and ther frcton to jonts nteror surfaces ental the optmzaton ssue of precson postonng by errors compensaton of whch source s elastc deformaton of drvng wre,s [7]. Pulley system wth wres s commonly used as moton transmsson mechansm of elephant s trunk robotc arms. However, wre drven jonts presume postonng errors because of jonts backlashes and elastc deformatons of drvng wres. Determnaton of systematc errors caused by pulley system frctons s emphaszed n ths paper for a partcular desgn of elephant s trunk robotc arm wth 5 degrees of freedom. 2. TRANSMISSION MECHANISM AND ACTUATION SYSTEM OF SPECIFIC JOINTS STRUCTURE Structure desgn of jonts C from the partcular elephant s trunk robotc arm allows 1 degree of freedom and a rotaton of angle θ wthn drvng wres fxed to cylnder wth of radus R c wth opposte dametrcally bolts from structure nteror as descrbed n fg. 1. Each jont (=1...5) of the robotc arm conssts of a gudng element G through whch are crossng the drvng wres of next jont +1. The partcular jont s structure employs a specfc automatc command system, fg. 2, and the crossng of
2 Fg. 1. The crossng of drvng wres through nner jonts structure of robotc arm drvng wres through robotc arm s specfc to each jonts. Actuatng wres of jonts are wndng, one by one, the surfaces of radus R 2 and R 3 to whch corresponds frcton coeffcents μ 1 and μ 2 respectvely, before crossng the grooved wheel R c. Drvng mechansm of jonts C s a tangental transmsson mechansm of moton through wres and a pulley system wth drvng propertes. Each reducer shaft r s lnked to a grooved wheel R c whch transfers the rotaton to knematc jont through two wres fxed to grooved wheel at the bottom end and to cylnder of jont (C ) at the upper end, fg. 2. Actuaton system of each degree of freedom from the elephant s trunk robotc arm conssts of servomotors wth varable number of revolutons (M ), whch are responsble to move a correspondng weght by a rotaton moton and enable closed loop actuaton. Each degree of freedom employs the rotaton of dfferent weghts and a correspondng moment of nerta. The generated moments of nerta are C 5 C 4 G 4 C 3 G 3 G 3 C 2 G 2 G 2 G 2 C 1 R 3 R 2 R c1 R c2 R c3 R c4 R c5 r 1 r 2 r 3 r 4 r 5 ω T p1 1 ω T p2 2 ω T p3 3 ω T p4 4 ω T p5 5 M 1 M 2 M 3 M 4 M 5 FC 1 T v1 FC 2 T v2 FC 3 T v3 FC 4 T v4 FC 5 T v5 + - e 1v + - e 2v + - e 3v + - e 4v + - e 5v + - e 1p + - e 2p + - e 3p + - e 4p + - e 5p e 1 e 2 e 3 e 4 e 5 Control Assembly Fg. 2. The command structure of each degree of freedom 25
3 drectly proportonal wth masses correspondng to each degree of freedom. Thus, for hgh masses of jonts the performances of elephant s trunk robotc arm decrease. The servo drves answer to amplfer outputs and, thus, ther output s a proportonal command sgnal gven by a rotatonal moton ω and measured by a velocty transducer T v n the closed loop system. The poston of dstal end robotc arm s defned by rotaton θ of each jont and t s controlled by the poston loop wth a transducer T p whch s mounted on the gearbox output shaft of jont. Transmsson of moton mechansm between gearbox shaft and unversal jont shaft consst of wres and a pulley system wth transmsson rato R s Rc. Parameters R s and R c defne the radus of grooved wheel (R c ) and the radus of jont cylnder (C ) respectvely. Servo drves receve output sgnals from amplfers FC (frequency converter) and gve the requred moton of actuaton system, a rotatonal moton respectvely. Poston transducers dentfy output parameters and convert them n sgnals accepted by the servomechansms. Input sgnal of servomechansm s summed wth feedback sgnal ( e e ) and produce the proper command sgnal for drvng components of the system. Control assembly computes the reference parameters of servomotors M at each samplng perod. Each jont poston s controlled by the velocty loop and a dgtal poston transducer (T p ) mounted to the shaft of gearbox output, and the controlled sgnal s read by the assembly unt through poston loop. Feedback loops enable automatc error correcton of grooved wheel R c knematc parameters (poston, velocty and acceleraton). 3. DETERMINATION OF PULLEY FRICTION INFLUENCE ON JOINTS POSITIONING PRECISION The elephant s trunk robotc arm wth 5 degrees of freedom and wre drven jonts brngs on the ssue of wres frcton to nner structure surfaces of jonts. Frcton of wres to jonts nteror s a sldng frcton to wnded crcular surfaces. Drvng wres are made of stanless steel wth PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) coatng and are sldng on metallc surfaces (duralumn, steel) of robotc arm components. Frcton of drvng wres to crcular surfaces of gudng component G made of PTFE, fg. 2, s gnorable because of the angle of wndng about radans and the small coeffcent of frcton about 0.04 [9]. The drvng wres of jonts subjected to frcton on crcular surfaces from nner structure of robotc arm presume angles of wndng α 1, α 2 and coeffcents of frcton μ 1, μ 2 gven for crcular metallc surfaces wth radus R 2 and R 3 respectvely, fg. 3. p 26 The effect of frcton between drvng wres and nner structure of robotc arm s an addtonal elastc deformaton of drvng wres on sectons between angles of wndng α 1 ș α 2, fg. 3. Usng Euler s frcton equaton related to wre frcton we obtan equatons for forces that stress addtonally the drvng wres, equatons (1-2). A T 1 T T T e 1 1 (1) T T e 2 2 (2) l 1 Fg. 3. Wnded angles of jont drvng wre We note the pull-force appled at bottom end of drvng wre wth T 1 and the actuatng force of jont wtht 1. From the bottom to the top end of drvng wre, we note the hold-forces wtht, T andt, fg. 3. Therefore, wth gven forces and consderng frcton only, let us consder the followng equvalences T 1=T and T = T 1. We obtan the relaton between pull-force from bottom end of drvng wre and drvng force of jont usng equatons (1-2), equaton (3). l T T1 e (3) Thus, actuatng force of jont s smaller than the pullforce from bottom end of drvng wre as gven n equaton (4) where we note the amount of dvsor wth k, equaton (5). 1 T 1 T C T B α 2 α 1
4 T T k (4) k e (5) Parameter k gven n percentage defnes the coeffcent of effcency for transmsson mechansm of jont. Elastc deformaton of the wre l1 that actuates jont s the sum of elastc deformatons l 1 and l gven for each sectons length of drvng wre l and l respectvely, equaton (6), whch defne the length between tangent ponts of wnded surfaces accordng to fg. 3. l1 l1 l1 T l1 T l E A s (6) 1 l e1 1 l l T E A e s (7) Usng equatons (1-2) and (6), we obtan equaton (7) that defnes elastc deformaton of drvng wre as a consequence of frcton to jonts nteror whch depends on the value of pull-force T appled at wre end fxed to groove wheel R c. Length l defnes the secton length of drvng wre between grp pont A on grooved wheel and tangent pont B after wndng crcular surface wth angle α 1. Length l defnes the secton of drvng wre between tangent pont B and tangent pont C after wndng crcular surface wth angle α 2. Elastc deformatons of drvng wres ental postonng precson of jonts ssue and, thus, angular devatons, equaton (8). 180 l R (8) Angular devatons of jonts affect postonng precson of dstal end robotc arm and ental postonng errors because the pulley system s not part of closed loop command system. If we substtute the known structural and knematc parameters nto equaton (8) we obtan the nfluence of frcton between drvng wres and nteror structure of robotc arm on precson postonng of jonts. Frcton coeffcents depend on the surface qualty between PTFE coated stanless steel wre and nteror of jonts structure, the surfaces roughness of matng metals respectvely. The elephant s trunk robotc arm consst of metal components wth specfc roughness R a =1.6 of crcular surfaces from structure nteror that are wnded by drvng wres upon radus R 2 and R 3, fg. 2. Therefore, for the specfc structure of elephant s trunk robotc arm we have frcton coeffcents gven n table 1. The lengths of drvng wres before elastc c 27 deformaton, l, the lengths of drvng wres sectons subjected to frcton, l and l, the angles of frcton to nner crcular surfaces of robotc arm structure, α 1 and α 2, are also constructve gven. In real case each drvng wre of jonts from elephant s trunk robotc arm wth 5 degrees of freedom are subjected to dfferent pull-forces T. μ 1 μ 2 Table 1. Structural parameters C 1 C 2 C 3 C 4 C α [rad] α l [mm] l l [mm] In the analyss, we use the same value T = 1 N for all pull-forces appled n order to acheve the amount of jonts postonng errors proceeded from frcton between drvng wres and structure nteror of robotc arm. The radus of cylnder jont and the radus of grooved wheel are also constructve gven, R c =16 mm and R s =10 mm respectvely. Maxmum rotaton on X axs of unversal jonts s θ =±23 n both drectons. In calculus we consder that jonts are rotatng n left drecton by pullng the actve wre as shown n fg. 3, and, thus, the angle of jonts rotaton s θ =23. We also know: cross sectonal area of drvng wres A s =0.113 mm 2 and Young modulus E= MPa. Thus, we determne the ratos T / T gven by parameters k n table 2. Usng equatons (7) and (8) we obtan elastc deformatons of the 5 drvng wres and rotaton devatons of jonts respectvely, as a consequence of frcton to crcular surfaces from nner structure of elephant s trunk robotc arm, table 2. Table 2. Elastc deformatons and resulted postonng devatons C 1 C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 k 100 [%] l [μm] [ ] From table 2 we fnd that frcton of drvng wres to nner structure of jont 1 and of subsequent jonts reduce the effcency of transmsson mechansm wth maxmum 3.93 % and 3.70 % respectvely. The dfference of 0.23 % between last mentoned effcences comes from the value of angle α 2 dfferent at jont 1. Elastc deformatons of drvng wres are about mcrometers and do not exceed 10.7
5 μm at the wre that actuates jont 5. The varaton of postonng errors for each jont depends on angular devatons and results from the postonng equatons obtaned wth homogeneous transformaton matrces. Let us consder the world coordnate system O X Y Z of jont, fg. 4, wth poston coordnates x, y and z, whch defne nomnal poston of jont, equaton (9), towards base coordnate system O 0 X 0 Y 0 Z 0, x 0, y0, z0 0, 0, 0 respectvely. For the analyss, let us assume the poston of prevous jonts n the zero poston reference n order to acheve devatons of jonts that arse only from frcton between drvng wres and nners surfaces of robotc structure, equatons (16-17). Y 0 Z 0 X cos sn 0 0 sn cos x 0 y l z 1 1 l l l l l O 0 O 1 O 2 O 3 O 4 O 5 θ 1 θ 2 θ 3 θ 4 θ 5 (9) postons on Y and Z axes defne absolute postonng errors, equaton (16) and (17) respectvely. y y y (16) z z z (17) Fg. 5 and fg. 6 hghlght the varaton of postonng errors on Y and Z axes respectvely. Postonng errors of jonts reach varable values about mcrometers that are due to frcton between drvng wres and nner surfaces of robotc arm. Δy [μm] Δy 5 Δy 4 Δy 3 Δy 2 Δy θ [ ] Fg. 5. Dagram of postonng errors on Y axs Fg. 4. Elephant s trunk robotc arm knematcs We note the dstance between jonts wth l, fg. 4. From equaton (9) we obtan nomnal poston x, y and z of jont gven by equatons (10-12) towards the base coordnate system of robotc arm dependng upon rotaton angle. x 0 (10) y l sn (11) z l cos (12) The rotaton of jonts on X axs ental that poston coordnate x equals wth zero at each jont. We obtan vrtually poston of jonts on Y and Z axes by addng angular devatons nto postonng equatons of each jont, equatons (13) and (14) respectvely. y l sn (13) z l cos (14) The absolute dfference between vrtual and nomnal 28 Δz [μm] Fg. 6. Dagram of postonng errors on Z axs The maxmum postonng errors are obtaned at drvng wre of jont 5 that are about 50μm and 20μm on Y and Z axes respectvely. From varaton dagrams of postonng precson, we fnd that postonng errors from Y axs decrease as the angle of rotaton ncrease because of cosne functon. 4. CONCLUSION θ [ ] The elephant s trunk robotc arm wth 5 degrees of freedom, wre drven unversal jonts through nner structure and wre-pulley system presume frcton of Δz 5 Δz 4 Δz 3 Δz 2 Δz 1
6 drvng wres to jonts nteror ssue. The rotaton of jonts on X axs only mples postonng errors about mcrometers on Y and Z axes, y and z respectvely. In the analyss, we obtan that frcton between drvng wres and nner surfaces of robotc arm affects also the effcency of pulley system and goes to mnmum 96%. Drvng mechansm of the elephant s trunk robotc arm nclude AC servomotors that actuate the wres n a closed loop system. Thus, elephant s trunk robotc arms may reach mnmzed dameters and adequate precson of spatal postonng. However, postonng errors resulted from elastc deformaton of drvng wres due frcton to nner structure of robotc arm are found outsde the closed loop system and presume the use of compensaton methods. The obtaned elastc deformatons reach about 5μm at drvng wre of jont 1 and 10μm at drvng wre of jont 5. These deformatons affect precson postonng of jonts and mply maxmum rotaton devaton about mnutes of sexagesmal degrees, at jont 1 and at jont 5. The rotatonal devatons cause postonng errors that reach maxmum 50μm at the zero poston of jont 5 on Y axs. We obtaned postonng errors of jonts wthout takng nto consderaton the postonng devaton of prevous jonts and, thus, we assumed n the analyss that prevously jonts to the analyzed jont are n zero poston. We recommend the obtaned results for further research of maxmum postonng errors at end-effector usng the postonng equaton from drect knematcs when all prevously jonts reach maxmum rotaton. Elastc deformatons consdered as an effect of drvng wres frcton to nner structure surfaces of jonts are a part of total elastc deformatons supported by the drvng wres of jonts from consdered elephant s trunk robotc arm. Addtonally to the analyzed deformatons, there are elastc deformatons from resstance moments of each jont. Therefore, for a complete analyss on precson postonng of robotc arm we have to take nto consderaton both mentoned sources that affect elastc deformatons of drvng wres. Postonng errors obtaned n ths paper are systematc errors that are generally adjusted by adequate correcton appled n the programmng algorthm of robotc arm to elmnate postonng devatons obtaned n analytcal and expermental research. (1999), Ed. Frank Kreth, pp. 29, CRC Press LLC, Boca Raton. 2. L, J., Xu, C., Yao, Y., Dng, J., Fang, H., (2015), Predctng synchronous accuracy of the wre sheave drves, Precson Engneerng, 39, L, Z., Du, R., (2013), Desgn and Analyss of a Bo-Inspred Wre-Drven Mult-Secton Flexble Robot, Int J of Advanced Robotc Systems, 10, Lao, B., L, Z., Du, R., (2012), Robot Tadpole wth a Novel Bommetc Wre-drven Propulsor, Proceedngs of the 2012 IEEE Int Conf on Robotcs and Bommetcs, , Guangzhou, Chna 5. Hedar, S., Pltan, F., Shamsodn, M., Hedar, K., Zahmatkesh, S., (2013), Desgn New Nonlnear Controller wth Parallel Fuzzy Inference System Compensator to Control of Contnuum Robot Manpulator, Int J of Control and Automaton, 6 (4), Sadrna, O. R., Pltan, F., Jafar, M, Eram, M., Shamsodn, M., (2013), Desgn PID Estmator Fuzzy Plus Backsteppng to Control of Uncertan Contnuum Robot, Internatonal Journal of Hybrd Informaton Technology, 6 (4), Song. S., L, Z., Yu, H., Ren, H., (2015), Shape reconstructon for wre-drven flexble robots based on Bézer curve and electromagnetc postonng, Mechatroncs, 29, Xong, Y., L, Y., (2015), Modfed Internal Model Control Scheme for the Drve Part wth Elastc Jonts n Robotc System, J Intell Robot Syst, 79, Avalable from: box.com/frcton-coeffcents-d_778.html, Accesed: 15/04/ REFERENCES 1. Lews, F. L., et. al., End effectors and Toolng, Robotcs Mechancal Engneerng Handbook, 29 Receved: December 10, 2015 / Accepted: June 10, 2016 / Paper avalable onlne: June 20, 2016 Internatonal Journal of Modern Manufacturng Technologes.
Week 9 Chapter 10 Section 1-5
 Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
Advanced Mechanical Elements
 May 3, 08 Advanced Mechancal Elements (Lecture 7) Knematc analyss and moton control of underactuated mechansms wth elastc elements - Moton control of underactuated mechansms constraned by elastc elements
May 3, 08 Advanced Mechancal Elements (Lecture 7) Knematc analyss and moton control of underactuated mechansms wth elastc elements - Moton control of underactuated mechansms constraned by elastc elements
THE EFFECT OF TORSIONAL RIGIDITY BETWEEN ELEMENTS ON FREE VIBRATIONS OF A TELESCOPIC HYDRAULIC CYLINDER SUBJECTED TO EULER S LOAD
 Journal of Appled Mathematcs and Computatonal Mechancs 7, 6(3), 7- www.amcm.pcz.pl p-issn 99-9965 DOI:.75/jamcm.7.3. e-issn 353-588 THE EFFECT OF TORSIONAL RIGIDITY BETWEEN ELEMENTS ON FREE VIBRATIONS
Journal of Appled Mathematcs and Computatonal Mechancs 7, 6(3), 7- www.amcm.pcz.pl p-issn 99-9965 DOI:.75/jamcm.7.3. e-issn 353-588 THE EFFECT OF TORSIONAL RIGIDITY BETWEEN ELEMENTS ON FREE VIBRATIONS
Study on Active Micro-vibration Isolation System with Linear Motor Actuator. Gong-yu PAN, Wen-yan GU and Dong LI
 2017 2nd Internatonal Conference on Electrcal and Electroncs: echnques and Applcatons (EEA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-416-5 Study on Actve Mcro-vbraton Isolaton System wth Lnear Motor Actuator Gong-yu PAN,
2017 2nd Internatonal Conference on Electrcal and Electroncs: echnques and Applcatons (EEA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-416-5 Study on Actve Mcro-vbraton Isolaton System wth Lnear Motor Actuator Gong-yu PAN,
Study Guide For Exam Two
 Study Gude For Exam Two Physcs 2210 Albretsen Updated: 08/02/2018 All Other Prevous Study Gudes Modules 01-06 Module 07 Work Work done by a constant force F over a dstance s : Work done by varyng force
Study Gude For Exam Two Physcs 2210 Albretsen Updated: 08/02/2018 All Other Prevous Study Gudes Modules 01-06 Module 07 Work Work done by a constant force F over a dstance s : Work done by varyng force
ENGN 40 Dynamics and Vibrations Homework # 7 Due: Friday, April 15
 NGN 40 ynamcs and Vbratons Homework # 7 ue: Frday, Aprl 15 1. Consder a concal hostng drum used n the mnng ndustry to host a mass up/down. A cable of dameter d has the mass connected at one end and s wound/unwound
NGN 40 ynamcs and Vbratons Homework # 7 ue: Frday, Aprl 15 1. Consder a concal hostng drum used n the mnng ndustry to host a mass up/down. A cable of dameter d has the mass connected at one end and s wound/unwound
Week3, Chapter 4. Position and Displacement. Motion in Two Dimensions. Instantaneous Velocity. Average Velocity
 Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM
 ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM An elastc wave s a deformaton of the body that travels throughout the body n all drectons. We can examne the deformaton over a perod of tme by fxng our look
ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM An elastc wave s a deformaton of the body that travels throughout the body n all drectons. We can examne the deformaton over a perod of tme by fxng our look
Spin-rotation coupling of the angularly accelerated rigid body
 Spn-rotaton couplng of the angularly accelerated rgd body Loua Hassan Elzen Basher Khartoum, Sudan. Postal code:11123 E-mal: louaelzen@gmal.com November 1, 2017 All Rghts Reserved. Abstract Ths paper s
Spn-rotaton couplng of the angularly accelerated rgd body Loua Hassan Elzen Basher Khartoum, Sudan. Postal code:11123 E-mal: louaelzen@gmal.com November 1, 2017 All Rghts Reserved. Abstract Ths paper s
Indeterminate pin-jointed frames (trusses)
 Indetermnate pn-jonted frames (trusses) Calculaton of member forces usng force method I. Statcal determnacy. The degree of freedom of any truss can be derved as: w= k d a =, where k s the number of all
Indetermnate pn-jonted frames (trusses) Calculaton of member forces usng force method I. Statcal determnacy. The degree of freedom of any truss can be derved as: w= k d a =, where k s the number of all
A Multi-Axis Force Measurement System for a Space Docking Mechanism
 3rd Internatonal Conference on Materal, Mechancal and Manufacturng Engneerng (IC3ME 215) A Mult-Axs orce Measurement System for a Space Dockng Mechansm Gangfeng Lu a*, Changle L b and Zenghu Xe c Buldng
3rd Internatonal Conference on Materal, Mechancal and Manufacturng Engneerng (IC3ME 215) A Mult-Axs orce Measurement System for a Space Dockng Mechansm Gangfeng Lu a*, Changle L b and Zenghu Xe c Buldng
Finite Element Modelling of truss/cable structures
 Pet Schreurs Endhoven Unversty of echnology Department of Mechancal Engneerng Materals echnology November 3, 214 Fnte Element Modellng of truss/cable structures 1 Fnte Element Analyss of prestressed structures
Pet Schreurs Endhoven Unversty of echnology Department of Mechancal Engneerng Materals echnology November 3, 214 Fnte Element Modellng of truss/cable structures 1 Fnte Element Analyss of prestressed structures
COMPOSITE BEAM WITH WEAK SHEAR CONNECTION SUBJECTED TO THERMAL LOAD
 COMPOSITE BEAM WITH WEAK SHEAR CONNECTION SUBJECTED TO THERMAL LOAD Ákos Jósef Lengyel, István Ecsed Assstant Lecturer, Professor of Mechancs, Insttute of Appled Mechancs, Unversty of Mskolc, Mskolc-Egyetemváros,
COMPOSITE BEAM WITH WEAK SHEAR CONNECTION SUBJECTED TO THERMAL LOAD Ákos Jósef Lengyel, István Ecsed Assstant Lecturer, Professor of Mechancs, Insttute of Appled Mechancs, Unversty of Mskolc, Mskolc-Egyetemváros,
Part C Dynamics and Statics of Rigid Body. Chapter 5 Rotation of a Rigid Body About a Fixed Axis
 Part C Dynamcs and Statcs of Rgd Body Chapter 5 Rotaton of a Rgd Body About a Fxed Axs 5.. Rotatonal Varables 5.. Rotaton wth Constant Angular Acceleraton 5.3. Knetc Energy of Rotaton, Rotatonal Inerta
Part C Dynamcs and Statcs of Rgd Body Chapter 5 Rotaton of a Rgd Body About a Fxed Axs 5.. Rotatonal Varables 5.. Rotaton wth Constant Angular Acceleraton 5.3. Knetc Energy of Rotaton, Rotatonal Inerta
Iterative General Dynamic Model for Serial-Link Manipulators
 EEL6667: Knematcs, Dynamcs and Control of Robot Manpulators 1. Introducton Iteratve General Dynamc Model for Seral-Lnk Manpulators In ths set of notes, we are gong to develop a method for computng a general
EEL6667: Knematcs, Dynamcs and Control of Robot Manpulators 1. Introducton Iteratve General Dynamc Model for Seral-Lnk Manpulators In ths set of notes, we are gong to develop a method for computng a general
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Homework 7: Rigid Body Kinematics
 N40: ynamcs and Vbratons Homewor 7: Rgd Body Knematcs School of ngneerng Brown Unversty 1. In the fgure below, bar AB rotates counterclocwse at 4 rad/s. What are the angular veloctes of bars BC and C?.
N40: ynamcs and Vbratons Homewor 7: Rgd Body Knematcs School of ngneerng Brown Unversty 1. In the fgure below, bar AB rotates counterclocwse at 4 rad/s. What are the angular veloctes of bars BC and C?.
Modeling of Dynamic Systems
 Modelng of Dynamc Systems Ref: Control System Engneerng Norman Nse : Chapters & 3 Chapter objectves : Revew the Laplace transform Learn how to fnd a mathematcal model, called a transfer functon Learn how
Modelng of Dynamc Systems Ref: Control System Engneerng Norman Nse : Chapters & 3 Chapter objectves : Revew the Laplace transform Learn how to fnd a mathematcal model, called a transfer functon Learn how
An Algorithm to Solve the Inverse Kinematics Problem of a Robotic Manipulator Based on Rotation Vectors
 An Algorthm to Solve the Inverse Knematcs Problem of a Robotc Manpulator Based on Rotaton Vectors Mohamad Z. Al-az*, Mazn Z. Othman**, and Baker B. Al-Bahr* *AL-Nahran Unversty, Computer Eng. Dep., Baghdad,
An Algorthm to Solve the Inverse Knematcs Problem of a Robotc Manpulator Based on Rotaton Vectors Mohamad Z. Al-az*, Mazn Z. Othman**, and Baker B. Al-Bahr* *AL-Nahran Unversty, Computer Eng. Dep., Baghdad,
Model discrepancy in robotic calibration: its influence on the experimental parameter identification of a parallel space telescope
 213 IEEE/RSJ Internatonal Conference on Intellgent Robots and Systems (IROS) November 3-7, 213. Tokyo, Japan Model dscrepancy n robotc calbraton: ts nfluence on the expermental parameter dentfcaton of
213 IEEE/RSJ Internatonal Conference on Intellgent Robots and Systems (IROS) November 3-7, 213. Tokyo, Japan Model dscrepancy n robotc calbraton: ts nfluence on the expermental parameter dentfcaton of
Uncertainty in measurements of power and energy on power networks
 Uncertanty n measurements of power and energy on power networks E. Manov, N. Kolev Department of Measurement and Instrumentaton, Techncal Unversty Sofa, bul. Klment Ohrdsk No8, bl., 000 Sofa, Bulgara Tel./fax:
Uncertanty n measurements of power and energy on power networks E. Manov, N. Kolev Department of Measurement and Instrumentaton, Techncal Unversty Sofa, bul. Klment Ohrdsk No8, bl., 000 Sofa, Bulgara Tel./fax:
First Law: A body at rest remains at rest, a body in motion continues to move at constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force.
 Secton 1. Dynamcs (Newton s Laws of Moton) Two approaches: 1) Gven all the forces actng on a body, predct the subsequent (changes n) moton. 2) Gven the (changes n) moton of a body, nfer what forces act
Secton 1. Dynamcs (Newton s Laws of Moton) Two approaches: 1) Gven all the forces actng on a body, predct the subsequent (changes n) moton. 2) Gven the (changes n) moton of a body, nfer what forces act
829. An adaptive method for inertia force identification in cantilever under moving mass
 89. An adaptve method for nerta force dentfcaton n cantlever under movng mass Qang Chen 1, Mnzhuo Wang, Hao Yan 3, Haonan Ye 4, Guola Yang 5 1,, 3, 4 Department of Control and System Engneerng, Nanng Unversty,
89. An adaptve method for nerta force dentfcaton n cantlever under movng mass Qang Chen 1, Mnzhuo Wang, Hao Yan 3, Haonan Ye 4, Guola Yang 5 1,, 3, 4 Department of Control and System Engneerng, Nanng Unversty,
Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 11
 Physcs 111: Mechancs Lecture 11 Bn Chen NJIT Physcs Department Textbook Chapter 10: Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton q 10.1 Torque q 10. Torque and Angular Acceleraton for a Rgd Body q 10.3 Rgd-Body Rotaton
Physcs 111: Mechancs Lecture 11 Bn Chen NJIT Physcs Department Textbook Chapter 10: Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton q 10.1 Torque q 10. Torque and Angular Acceleraton for a Rgd Body q 10.3 Rgd-Body Rotaton
Experiment 1 Mass, volume and density
 Experment 1 Mass, volume and densty Purpose 1. Famlarze wth basc measurement tools such as verner calper, mcrometer, and laboratory balance. 2. Learn how to use the concepts of sgnfcant fgures, expermental
Experment 1 Mass, volume and densty Purpose 1. Famlarze wth basc measurement tools such as verner calper, mcrometer, and laboratory balance. 2. Learn how to use the concepts of sgnfcant fgures, expermental
Comparison of Novel Identification Method of Suspension Force Parameters and the Conventional Identification Method in Bearingless Motors
 Comparson of Novel Identfcaton ethod of Suspenson orce Parameters and the Conventonal Identfcaton ethod n Bearngless otors Yuma Otsu, Kouk Nakaya, Kmo Hjkata and Yasuhro Tanaka Department of echancal Systems
Comparson of Novel Identfcaton ethod of Suspenson orce Parameters and the Conventonal Identfcaton ethod n Bearngless otors Yuma Otsu, Kouk Nakaya, Kmo Hjkata and Yasuhro Tanaka Department of echancal Systems
Modeling and Simulation of a Hexapod Machine Tool for the Dynamic Stability Analysis of Milling Processes. C. Henninger, P.
 Smpack User Meetng 27 Modelng and Smulaton of a Heapod Machne Tool for the Dynamc Stablty Analyss of Mllng Processes C. Hennnger, P. Eberhard Insttute of Engneerng project funded by the DFG wthn the framework
Smpack User Meetng 27 Modelng and Smulaton of a Heapod Machne Tool for the Dynamc Stablty Analyss of Mllng Processes C. Hennnger, P. Eberhard Insttute of Engneerng project funded by the DFG wthn the framework
Design and Analysis of Landing Gear Mechanic Structure for the Mine Rescue Carrier Robot
 Sensors & Transducers 214 by IFSA Publshng, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Desgn and Analyss of Landng Gear Mechanc Structure for the Mne Rescue Carrer Robot We Juan, Wu Ja-Long X an Unversty of Scence
Sensors & Transducers 214 by IFSA Publshng, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Desgn and Analyss of Landng Gear Mechanc Structure for the Mne Rescue Carrer Robot We Juan, Wu Ja-Long X an Unversty of Scence
OFF-AXIS MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FRP COMPOSITES
 ICAMS 204 5 th Internatonal Conference on Advanced Materals and Systems OFF-AXIS MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FRP COMPOSITES VLAD LUPĂŞTEANU, NICOLAE ŢĂRANU, RALUCA HOHAN, PAUL CIOBANU Gh. Asach Techncal Unversty
ICAMS 204 5 th Internatonal Conference on Advanced Materals and Systems OFF-AXIS MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FRP COMPOSITES VLAD LUPĂŞTEANU, NICOLAE ŢĂRANU, RALUCA HOHAN, PAUL CIOBANU Gh. Asach Techncal Unversty
Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson 6 Theory of Quantzaton Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:
Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson 6 Theory of Quantzaton Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:
FUZZY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 FUZZY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD RELIABILITY TRUCTURE ANALYI UING PROBABILITY 3.. Maxmum Normal tress Internal force s the shear force, V has a magntude equal to the load P and bendng moment, M. Bendng moments
FUZZY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD RELIABILITY TRUCTURE ANALYI UING PROBABILITY 3.. Maxmum Normal tress Internal force s the shear force, V has a magntude equal to the load P and bendng moment, M. Bendng moments
CHAPTER 10 ROTATIONAL MOTION
 CHAPTER 0 ROTATONAL MOTON 0. ANGULAR VELOCTY Consder argd body rotates about a fxed axs through pont O n x-y plane as shown. Any partcle at pont P n ths rgd body rotates n a crcle of radus r about O. The
CHAPTER 0 ROTATONAL MOTON 0. ANGULAR VELOCTY Consder argd body rotates about a fxed axs through pont O n x-y plane as shown. Any partcle at pont P n ths rgd body rotates n a crcle of radus r about O. The
NMT EE 589 & UNM ME 482/582 ROBOT ENGINEERING. Dr. Stephen Bruder NMT EE 589 & UNM ME 482/582
 NMT EE 589 & UNM ME 48/58 ROBOT ENGINEERING Dr. Stephen Bruder NMT EE 589 & UNM ME 48/58 7. Robot Dynamcs 7.5 The Equatons of Moton Gven that we wsh to fnd the path q(t (n jont space) whch mnmzes the energy
NMT EE 589 & UNM ME 48/58 ROBOT ENGINEERING Dr. Stephen Bruder NMT EE 589 & UNM ME 48/58 7. Robot Dynamcs 7.5 The Equatons of Moton Gven that we wsh to fnd the path q(t (n jont space) whch mnmzes the energy
Econ107 Applied Econometrics Topic 3: Classical Model (Studenmund, Chapter 4)
 I. Classcal Assumptons Econ7 Appled Econometrcs Topc 3: Classcal Model (Studenmund, Chapter 4) We have defned OLS and studed some algebrac propertes of OLS. In ths topc we wll study statstcal propertes
I. Classcal Assumptons Econ7 Appled Econometrcs Topc 3: Classcal Model (Studenmund, Chapter 4) We have defned OLS and studed some algebrac propertes of OLS. In ths topc we wll study statstcal propertes
coordinates. Then, the position vectors are described by
 Revewng, what we have dscussed so far: Generalzed coordnates Any number of varables (say, n) suffcent to specfy the confguraton of the system at each nstant to tme (need not be the mnmum number). In general,
Revewng, what we have dscussed so far: Generalzed coordnates Any number of varables (say, n) suffcent to specfy the confguraton of the system at each nstant to tme (need not be the mnmum number). In general,
Appendix B: Resampling Algorithms
 407 Appendx B: Resamplng Algorthms A common problem of all partcle flters s the degeneracy of weghts, whch conssts of the unbounded ncrease of the varance of the mportance weghts ω [ ] of the partcles
407 Appendx B: Resamplng Algorthms A common problem of all partcle flters s the degeneracy of weghts, whch conssts of the unbounded ncrease of the varance of the mportance weghts ω [ ] of the partcles
Adaptive RFID Indoor Positioning Technology for Wheelchair Home Health Care Robot. T. C. Kuo
 Adaptve RFID Indoor Postonng Technology for Wheelchar Home Health Care Robot Contents Abstract Introducton RFID Indoor Postonng Method Fuzzy Neural Netor System Expermental Result Concluson -- Abstract
Adaptve RFID Indoor Postonng Technology for Wheelchar Home Health Care Robot Contents Abstract Introducton RFID Indoor Postonng Method Fuzzy Neural Netor System Expermental Result Concluson -- Abstract
9 Derivation of Rate Equations from Single-Cell Conductance (Hodgkin-Huxley-like) Equations
 Physcs 171/271 - Chapter 9R -Davd Klenfeld - Fall 2005 9 Dervaton of Rate Equatons from Sngle-Cell Conductance (Hodgkn-Huxley-lke) Equatons We consder a network of many neurons, each of whch obeys a set
Physcs 171/271 - Chapter 9R -Davd Klenfeld - Fall 2005 9 Dervaton of Rate Equatons from Sngle-Cell Conductance (Hodgkn-Huxley-lke) Equatons We consder a network of many neurons, each of whch obeys a set
FUZZY GOAL PROGRAMMING VS ORDINARY FUZZY PROGRAMMING APPROACH FOR MULTI OBJECTIVE PROGRAMMING PROBLEM
 Internatonal Conference on Ceramcs, Bkaner, Inda Internatonal Journal of Modern Physcs: Conference Seres Vol. 22 (2013) 757 761 World Scentfc Publshng Company DOI: 10.1142/S2010194513010982 FUZZY GOAL
Internatonal Conference on Ceramcs, Bkaner, Inda Internatonal Journal of Modern Physcs: Conference Seres Vol. 22 (2013) 757 761 World Scentfc Publshng Company DOI: 10.1142/S2010194513010982 FUZZY GOAL
Moments of Inertia. and reminds us of the analogous equation for linear momentum p= mv, which is of the form. The kinetic energy of the body is.
 Moments of Inerta Suppose a body s movng on a crcular path wth constant speed Let s consder two quanttes: the body s angular momentum L about the center of the crcle, and ts knetc energy T How are these
Moments of Inerta Suppose a body s movng on a crcular path wth constant speed Let s consder two quanttes: the body s angular momentum L about the center of the crcle, and ts knetc energy T How are these
Structure and Drive Paul A. Jensen Copyright July 20, 2003
 Structure and Drve Paul A. Jensen Copyrght July 20, 2003 A system s made up of several operatons wth flow passng between them. The structure of the system descrbes the flow paths from nputs to outputs.
Structure and Drve Paul A. Jensen Copyrght July 20, 2003 A system s made up of several operatons wth flow passng between them. The structure of the system descrbes the flow paths from nputs to outputs.
In this section is given an overview of the common elasticity models.
 Secton 4.1 4.1 Elastc Solds In ths secton s gven an overvew of the common elastcty models. 4.1.1 The Lnear Elastc Sold The classcal Lnear Elastc model, or Hooean model, has the followng lnear relatonshp
Secton 4.1 4.1 Elastc Solds In ths secton s gven an overvew of the common elastcty models. 4.1.1 The Lnear Elastc Sold The classcal Lnear Elastc model, or Hooean model, has the followng lnear relatonshp
Please initial the statement below to show that you have read it
 EN40: Dynamcs and Vbratons Mdterm Examnaton Thursday March 5 009 Dvson of Engneerng rown Unversty NME: Isaac Newton General Instructons No collaboraton of any knd s permtted on ths examnaton. You may brng
EN40: Dynamcs and Vbratons Mdterm Examnaton Thursday March 5 009 Dvson of Engneerng rown Unversty NME: Isaac Newton General Instructons No collaboraton of any knd s permtted on ths examnaton. You may brng
The Analysis of Coriolis Effect on a Robot Manipulator
 Internatonal Journal of Innovatons n Engneerng and echnology (IJIE) he Analyss of Corols Effect on a Robot Manpulator Pratap P homas Assstant Professor Department of Mechancal Engneerng K G Reddy college
Internatonal Journal of Innovatons n Engneerng and echnology (IJIE) he Analyss of Corols Effect on a Robot Manpulator Pratap P homas Assstant Professor Department of Mechancal Engneerng K G Reddy college
Chapter 13: Multiple Regression
 Chapter 13: Multple Regresson 13.1 Developng the multple-regresson Model The general model can be descrbed as: It smplfes for two ndependent varables: The sample ft parameter b 0, b 1, and b are used to
Chapter 13: Multple Regresson 13.1 Developng the multple-regresson Model The general model can be descrbed as: It smplfes for two ndependent varables: The sample ft parameter b 0, b 1, and b are used to
Please review the following statement: I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam.
 Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: Instructor s Name and Secton: (Crcle Your Secton) Sectons:
Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: Instructor s Name and Secton: (Crcle Your Secton) Sectons:
Homework 2: Kinematics and Dynamics of Particles Due Friday Feb 7, 2014 Max Score 45 Points + 8 Extra Credit
 EN40: Dynamcs and Vbratons School of Engneerng Brown Unversty Homework : Knematcs and Dynamcs of Partcles Due Frday Feb 7, 014 Max Score 45 Ponts + 8 Extra Credt 1. An expermental mcro-robot (see a descrpton
EN40: Dynamcs and Vbratons School of Engneerng Brown Unversty Homework : Knematcs and Dynamcs of Partcles Due Frday Feb 7, 014 Max Score 45 Ponts + 8 Extra Credt 1. An expermental mcro-robot (see a descrpton
Irregular vibrations in multi-mass discrete-continuous systems torsionally deformed
 (2) 4 48 Irregular vbratons n mult-mass dscrete-contnuous systems torsonally deformed Abstract In the paper rregular vbratons of dscrete-contnuous systems consstng of an arbtrary number rgd bodes connected
(2) 4 48 Irregular vbratons n mult-mass dscrete-contnuous systems torsonally deformed Abstract In the paper rregular vbratons of dscrete-contnuous systems consstng of an arbtrary number rgd bodes connected
Inductance Calculation for Conductors of Arbitrary Shape
 CRYO/02/028 Aprl 5, 2002 Inductance Calculaton for Conductors of Arbtrary Shape L. Bottura Dstrbuton: Internal Summary In ths note we descrbe a method for the numercal calculaton of nductances among conductors
CRYO/02/028 Aprl 5, 2002 Inductance Calculaton for Conductors of Arbtrary Shape L. Bottura Dstrbuton: Internal Summary In ths note we descrbe a method for the numercal calculaton of nductances among conductors
Regulation No. 117 (Tyres rolling noise and wet grip adhesion) Proposal for amendments to ECE/TRANS/WP.29/GRB/2010/3
 Transmtted by the expert from France Informal Document No. GRB-51-14 (67 th GRB, 15 17 February 2010, agenda tem 7) Regulaton No. 117 (Tyres rollng nose and wet grp adheson) Proposal for amendments to
Transmtted by the expert from France Informal Document No. GRB-51-14 (67 th GRB, 15 17 February 2010, agenda tem 7) Regulaton No. 117 (Tyres rollng nose and wet grp adheson) Proposal for amendments to
Second Order Analysis
 Second Order Analyss In the prevous classes we looked at a method that determnes the load correspondng to a state of bfurcaton equlbrum of a perfect frame by egenvalye analyss The system was assumed to
Second Order Analyss In the prevous classes we looked at a method that determnes the load correspondng to a state of bfurcaton equlbrum of a perfect frame by egenvalye analyss The system was assumed to
MEASUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTIA
 1. measurement MESUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTI The am of ths measurement s to determne the moment of nerta of the rotor of an electrc motor. 1. General relatons Rotatng moton and moment of nerta Let us
1. measurement MESUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTI The am of ths measurement s to determne the moment of nerta of the rotor of an electrc motor. 1. General relatons Rotatng moton and moment of nerta Let us
Chapter 6 Electrical Systems and Electromechanical Systems
 ME 43 Systems Dynamcs & Control Chapter 6: Electrcal Systems and Electromechancal Systems Chapter 6 Electrcal Systems and Electromechancal Systems 6. INTODUCTION A. Bazoune The majorty of engneerng systems
ME 43 Systems Dynamcs & Control Chapter 6: Electrcal Systems and Electromechancal Systems Chapter 6 Electrcal Systems and Electromechancal Systems 6. INTODUCTION A. Bazoune The majorty of engneerng systems
APPLICATION OF EDDY CURRENT PRINCIPLES FOR MEASUREMENT OF TUBE CENTERLINE
 APPLICATION OF EDDY CURRENT PRINCIPLES FOR MEASUREMENT OF TUBE CENTERLINE DEFLECTION E. J. Chern Martn Maretta Laboratores 1450 South Rollng Road Baltmore, MD 21227 INTRODUCTION Tubes are a vtal component
APPLICATION OF EDDY CURRENT PRINCIPLES FOR MEASUREMENT OF TUBE CENTERLINE DEFLECTION E. J. Chern Martn Maretta Laboratores 1450 South Rollng Road Baltmore, MD 21227 INTRODUCTION Tubes are a vtal component
The classical spin-rotation coupling
 LOUAI H. ELZEIN 2018 All Rghts Reserved The classcal spn-rotaton couplng Loua Hassan Elzen Basher Khartoum, Sudan. Postal code:11123 louaelzen@gmal.com Abstract Ths paper s prepared to show that a rgd
LOUAI H. ELZEIN 2018 All Rghts Reserved The classcal spn-rotaton couplng Loua Hassan Elzen Basher Khartoum, Sudan. Postal code:11123 louaelzen@gmal.com Abstract Ths paper s prepared to show that a rgd
B and H sensors for 3-D magnetic property testing
 B and H sensors for 3-D magnetc property testng Zh We Ln, Jan Guo Zhu, You Guang Guo, Jn Jang Zhong, and Ha We Lu Faculty of Engneerng, Unversty of Technology, Sydney, PO Bo 123, Broadway, SW 2007, Australa
B and H sensors for 3-D magnetc property testng Zh We Ln, Jan Guo Zhu, You Guang Guo, Jn Jang Zhong, and Ha We Lu Faculty of Engneerng, Unversty of Technology, Sydney, PO Bo 123, Broadway, SW 2007, Australa
MEV442 Introduction to Robotics Module 2. Dr. Santhakumar Mohan Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering National Institute of Technology Calicut
 MEV442 Introducton to Robotcs Module 2 Dr. Santhakumar Mohan Assstant Professor Mechancal Engneerng Natonal Insttute of Technology Calcut Jacobans: Veloctes and statc forces Introducton Notaton for tme-varyng
MEV442 Introducton to Robotcs Module 2 Dr. Santhakumar Mohan Assstant Professor Mechancal Engneerng Natonal Insttute of Technology Calcut Jacobans: Veloctes and statc forces Introducton Notaton for tme-varyng
Statistical Evaluation of WATFLOOD
 tatstcal Evaluaton of WATFLD By: Angela MacLean, Dept. of Cvl & Envronmental Engneerng, Unversty of Waterloo, n. ctober, 005 The statstcs program assocated wth WATFLD uses spl.csv fle that s produced wth
tatstcal Evaluaton of WATFLD By: Angela MacLean, Dept. of Cvl & Envronmental Engneerng, Unversty of Waterloo, n. ctober, 005 The statstcs program assocated wth WATFLD uses spl.csv fle that s produced wth
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. D Alembert s Principle and The Lagrangian-1
 P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
THE CURRENT BALANCE Physics 258/259
 DSH 1988, 005 THE CURRENT BALANCE Physcs 58/59 The tme average force between two parallel conductors carryng an alternatng current s measured by balancng ths force aganst the gravtatonal force on a set
DSH 1988, 005 THE CURRENT BALANCE Physcs 58/59 The tme average force between two parallel conductors carryng an alternatng current s measured by balancng ths force aganst the gravtatonal force on a set
SWITCHING PROCESS IN LIMITED SLIP DIFFERENTIAL
 6th Internatonal DAAAM Baltc Conference INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING 24-26 Aprl 2008, Tallnn, Estona SWITCHING PROCESS IN LIMITED SLIP DIFFERENTIAL Resev, J.; Roosmölder, L.; Stas, M. Abstract: The energy flow
6th Internatonal DAAAM Baltc Conference INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING 24-26 Aprl 2008, Tallnn, Estona SWITCHING PROCESS IN LIMITED SLIP DIFFERENTIAL Resev, J.; Roosmölder, L.; Stas, M. Abstract: The energy flow
Research on the Fuzzy Control for Vehicle Semi-active Suspension. Xiaoming Hu 1, a, Wanli Li 1,b
 Advanced Materals Research Onlne: 0-0- ISSN: -9, Vol., pp -9 do:0.0/www.scentfc.net/amr.. 0 Trans Tech Publcatons, Swterland Research on the Fuy Control for Vehcle Sem-actve Suspenson Xaomng Hu, a, Wanl
Advanced Materals Research Onlne: 0-0- ISSN: -9, Vol., pp -9 do:0.0/www.scentfc.net/amr.. 0 Trans Tech Publcatons, Swterland Research on the Fuy Control for Vehcle Sem-actve Suspenson Xaomng Hu, a, Wanl
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics. Calculus of Variations II
 1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Calculus of Varatons II 2 Calculus of Varatons: Generalzaton (no constrant yet) Suppose now that F depends on several dependent varables : We need to fnd such that has a statonary
1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Calculus of Varatons II 2 Calculus of Varatons: Generalzaton (no constrant yet) Suppose now that F depends on several dependent varables : We need to fnd such that has a statonary
Pulse Coded Modulation
 Pulse Coded Modulaton PCM (Pulse Coded Modulaton) s a voce codng technque defned by the ITU-T G.711 standard and t s used n dgtal telephony to encode the voce sgnal. The frst step n the analog to dgtal
Pulse Coded Modulaton PCM (Pulse Coded Modulaton) s a voce codng technque defned by the ITU-T G.711 standard and t s used n dgtal telephony to encode the voce sgnal. The frst step n the analog to dgtal
T f. Geometry. R f. R i. Homogeneous transformation. y x. P f. f 000. Homogeneous transformation matrix. R (A): Orientation P : Position
 Homogeneous transformaton Geometr T f R f R T f Homogeneous transformaton matr Unverst of Genova T f Phlppe Martnet = R f 000 P f 1 R (A): Orentaton P : Poston 123 Modelng and Control of Manpulator robots
Homogeneous transformaton Geometr T f R f R T f Homogeneous transformaton matr Unverst of Genova T f Phlppe Martnet = R f 000 P f 1 R (A): Orentaton P : Poston 123 Modelng and Control of Manpulator robots
Transfer Functions. Convenient representation of a linear, dynamic model. A transfer function (TF) relates one input and one output: ( ) system
 Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Chapter 7: Application Issues
 Chapter 7: Applcaton Issues hs chapter wll brefly summarze several of the ssues that arse n mplementaton of the Carpal Wrst. he specfc ssues nvolved n puttng ths wrst nto producton are both task and manpulator
Chapter 7: Applcaton Issues hs chapter wll brefly summarze several of the ssues that arse n mplementaton of the Carpal Wrst. he specfc ssues nvolved n puttng ths wrst nto producton are both task and manpulator
Assessment of Site Amplification Effect from Input Energy Spectra of Strong Ground Motion
 Assessment of Ste Amplfcaton Effect from Input Energy Spectra of Strong Ground Moton M.S. Gong & L.L Xe Key Laboratory of Earthquake Engneerng and Engneerng Vbraton,Insttute of Engneerng Mechancs, CEA,
Assessment of Ste Amplfcaton Effect from Input Energy Spectra of Strong Ground Moton M.S. Gong & L.L Xe Key Laboratory of Earthquake Engneerng and Engneerng Vbraton,Insttute of Engneerng Mechancs, CEA,
1 Derivation of Rate Equations from Single-Cell Conductance (Hodgkin-Huxley-like) Equations
 Physcs 171/271 -Davd Klenfeld - Fall 2005 (revsed Wnter 2011) 1 Dervaton of Rate Equatons from Sngle-Cell Conductance (Hodgkn-Huxley-lke) Equatons We consder a network of many neurons, each of whch obeys
Physcs 171/271 -Davd Klenfeld - Fall 2005 (revsed Wnter 2011) 1 Dervaton of Rate Equatons from Sngle-Cell Conductance (Hodgkn-Huxley-lke) Equatons We consder a network of many neurons, each of whch obeys
Rotational Dynamics. Physics 1425 Lecture 19. Michael Fowler, UVa
 Rotatonal Dynamcs Physcs 1425 Lecture 19 Mchael Fowler, UVa Rotatonal Dynamcs Newton s Frst Law: a rotatng body wll contnue to rotate at constant angular velocty as long as there s no torque actng on t.
Rotatonal Dynamcs Physcs 1425 Lecture 19 Mchael Fowler, UVa Rotatonal Dynamcs Newton s Frst Law: a rotatng body wll contnue to rotate at constant angular velocty as long as there s no torque actng on t.
VIBRATION FATIGUE DESIGN METHODOLOGY OF A LARGE SCALE HEAVY DUTY ROBOT
 ICSV14 Carns Australa 9-12 July, 2007 VIBRATION FATIGUE DESIGN METHODOLOGY OF A LARGE SCALE HEAVY DUTY ROBOT Jong Hw Seo 1, Jae Chul Hwang 1, Yong Won Cho 1, Dong Il Km 1, Hong Jae Ym 2 1 Robotcs Technology
ICSV14 Carns Australa 9-12 July, 2007 VIBRATION FATIGUE DESIGN METHODOLOGY OF A LARGE SCALE HEAVY DUTY ROBOT Jong Hw Seo 1, Jae Chul Hwang 1, Yong Won Cho 1, Dong Il Km 1, Hong Jae Ym 2 1 Robotcs Technology
2010 Black Engineering Building, Department of Mechanical Engineering. Iowa State University, Ames, IA, 50011
 Interface Energy Couplng between -tungsten Nanoflm and Few-layered Graphene Meng Han a, Pengyu Yuan a, Jng Lu a, Shuyao S b, Xaolong Zhao b, Yanan Yue c, Xnwe Wang a,*, Xangheng Xao b,* a 2010 Black Engneerng
Interface Energy Couplng between -tungsten Nanoflm and Few-layered Graphene Meng Han a, Pengyu Yuan a, Jng Lu a, Shuyao S b, Xaolong Zhao b, Yanan Yue c, Xnwe Wang a,*, Xangheng Xao b,* a 2010 Black Engneerng
Pivot-Wheel Drive Crab with a Twist! Clem McKown Team November-2009 (eq 1 edited 29-March-2010)
 Pvot-Wheel Drve Crab wth a Twst! Clem McKown Team 1640 13-November-2009 (eq 1 edted 29-March-2010) 4-Wheel Independent Pvot-Wheel Drve descrbes a 4wd drve-tran n whch each of the (4) wheels are ndependently
Pvot-Wheel Drve Crab wth a Twst! Clem McKown Team 1640 13-November-2009 (eq 1 edted 29-March-2010) 4-Wheel Independent Pvot-Wheel Drve descrbes a 4wd drve-tran n whch each of the (4) wheels are ndependently
Tensor Smooth Length for SPH Modelling of High Speed Impact
 Tensor Smooth Length for SPH Modellng of Hgh Speed Impact Roman Cherepanov and Alexander Gerasmov Insttute of Appled mathematcs and mechancs, Tomsk State Unversty 634050, Lenna av. 36, Tomsk, Russa RCherepanov82@gmal.com,Ger@npmm.tsu.ru
Tensor Smooth Length for SPH Modellng of Hgh Speed Impact Roman Cherepanov and Alexander Gerasmov Insttute of Appled mathematcs and mechancs, Tomsk State Unversty 634050, Lenna av. 36, Tomsk, Russa RCherepanov82@gmal.com,Ger@npmm.tsu.ru
ˆ (0.10 m) E ( N m /C ) 36 ˆj ( j C m)
 7.. = = 3 = 4 = 5. The electrc feld s constant everywhere between the plates. Ths s ndcated by the electrc feld vectors, whch are all the same length and n the same drecton. 7.5. Model: The dstances to
7.. = = 3 = 4 = 5. The electrc feld s constant everywhere between the plates. Ths s ndcated by the electrc feld vectors, whch are all the same length and n the same drecton. 7.5. Model: The dstances to
Georgia Tech PHYS 6124 Mathematical Methods of Physics I
 Georga Tech PHYS 624 Mathematcal Methods of Physcs I Instructor: Predrag Cvtanovć Fall semester 202 Homework Set #7 due October 30 202 == show all your work for maxmum credt == put labels ttle legends
Georga Tech PHYS 624 Mathematcal Methods of Physcs I Instructor: Predrag Cvtanovć Fall semester 202 Homework Set #7 due October 30 202 == show all your work for maxmum credt == put labels ttle legends
Physics 53. Rotational Motion 3. Sir, I have found you an argument, but I am not obliged to find you an understanding.
 Physcs 53 Rotatonal Moton 3 Sr, I have found you an argument, but I am not oblged to fnd you an understandng. Samuel Johnson Angular momentum Wth respect to rotatonal moton of a body, moment of nerta plays
Physcs 53 Rotatonal Moton 3 Sr, I have found you an argument, but I am not oblged to fnd you an understandng. Samuel Johnson Angular momentum Wth respect to rotatonal moton of a body, moment of nerta plays
RELIABILITY ASSESSMENT
 CHAPTER Rsk Analyss n Engneerng and Economcs RELIABILITY ASSESSMENT A. J. Clark School of Engneerng Department of Cvl and Envronmental Engneerng 4a CHAPMAN HALL/CRC Rsk Analyss for Engneerng Department
CHAPTER Rsk Analyss n Engneerng and Economcs RELIABILITY ASSESSMENT A. J. Clark School of Engneerng Department of Cvl and Envronmental Engneerng 4a CHAPMAN HALL/CRC Rsk Analyss for Engneerng Department
A Hybrid Variational Iteration Method for Blasius Equation
 Avalable at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 1932-9466 Vol. 10, Issue 1 (June 2015), pp. 223-229 Applcatons and Appled Mathematcs: An Internatonal Journal (AAM) A Hybrd Varatonal Iteraton Method
Avalable at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 1932-9466 Vol. 10, Issue 1 (June 2015), pp. 223-229 Applcatons and Appled Mathematcs: An Internatonal Journal (AAM) A Hybrd Varatonal Iteraton Method
Conservation of Angular Momentum = "Spin"
 Page 1 of 6 Conservaton of Angular Momentum = "Spn" We can assgn a drecton to the angular velocty: drecton of = drecton of axs + rght hand rule (wth rght hand, curl fngers n drecton of rotaton, thumb ponts
Page 1 of 6 Conservaton of Angular Momentum = "Spn" We can assgn a drecton to the angular velocty: drecton of = drecton of axs + rght hand rule (wth rght hand, curl fngers n drecton of rotaton, thumb ponts
Please review the following statement: I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam.
 ME 270 Summer 2014 Fnal Exam NAME (Last, Frst): Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS
ME 270 Summer 2014 Fnal Exam NAME (Last, Frst): Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS
Speeding up Computation of Scalar Multiplication in Elliptic Curve Cryptosystem
 H.K. Pathak et. al. / (IJCSE) Internatonal Journal on Computer Scence and Engneerng Speedng up Computaton of Scalar Multplcaton n Ellptc Curve Cryptosystem H. K. Pathak Manju Sangh S.o.S n Computer scence
H.K. Pathak et. al. / (IJCSE) Internatonal Journal on Computer Scence and Engneerng Speedng up Computaton of Scalar Multplcaton n Ellptc Curve Cryptosystem H. K. Pathak Manju Sangh S.o.S n Computer scence
November 5, 2002 SE 180: Earthquake Engineering SE 180. Final Project
 SE 8 Fnal Project Story Shear Frame u m Gven: u m L L m L L EI ω ω Solve for m Story Bendng Beam u u m L m L Gven: m L L EI ω ω Solve for m 3 3 Story Shear Frame u 3 m 3 Gven: L 3 m m L L L 3 EI ω ω ω
SE 8 Fnal Project Story Shear Frame u m Gven: u m L L m L L EI ω ω Solve for m Story Bendng Beam u u m L m L Gven: m L L EI ω ω Solve for m 3 3 Story Shear Frame u 3 m 3 Gven: L 3 m m L L L 3 EI ω ω ω
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics. Newtonian Mechanics
 1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Newtonan Mechancs Quck Revew of Newtonan Mechancs Basc Descrpton: -An dealzed pont partcle or a system of pont partcles n an nertal reference frame [Rgd bodes (ch. 5 later)]
1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Newtonan Mechancs Quck Revew of Newtonan Mechancs Basc Descrpton: -An dealzed pont partcle or a system of pont partcles n an nertal reference frame [Rgd bodes (ch. 5 later)]
LAB 4: Modulus of elasticity
 LAB 4: Modulus of elastcty 1. Preparaton: modulus of elastcty (chapter15, p.79) Hook s law graphcal determnaton of modulus of elastcty (p.8) determnaton of modulus of elastcty n tenson and flexural stress
LAB 4: Modulus of elastcty 1. Preparaton: modulus of elastcty (chapter15, p.79) Hook s law graphcal determnaton of modulus of elastcty (p.8) determnaton of modulus of elastcty n tenson and flexural stress
x = , so that calculated
 Stat 4, secton Sngle Factor ANOVA notes by Tm Plachowsk n chapter 8 we conducted hypothess tests n whch we compared a sngle sample s mean or proporton to some hypotheszed value Chapter 9 expanded ths to
Stat 4, secton Sngle Factor ANOVA notes by Tm Plachowsk n chapter 8 we conducted hypothess tests n whch we compared a sngle sample s mean or proporton to some hypotheszed value Chapter 9 expanded ths to
CHAPTER 14 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY
 CHAPTER 4 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY 4 Introducton A partcle n orbt around a pont mass or a sphercally symmetrc mass dstrbuton s movng n a gravtatonal potental of the form GM / r In ths potental t moves
CHAPTER 4 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY 4 Introducton A partcle n orbt around a pont mass or a sphercally symmetrc mass dstrbuton s movng n a gravtatonal potental of the form GM / r In ths potental t moves
Statics Modeling of an Underactuated Wire-Driven Flexible Robotic Arm
 2014 5th IEEE RAS & EMBS Internatonal Conference on Bomedcal Robotcs and Bomechatroncs (BoRob) August 12-15, 2014. São Paulo, Brazl Statcs Modelng of an Underactuated Wre-Drven Flexble Robotc Arm Zheng
2014 5th IEEE RAS & EMBS Internatonal Conference on Bomedcal Robotcs and Bomechatroncs (BoRob) August 12-15, 2014. São Paulo, Brazl Statcs Modelng of an Underactuated Wre-Drven Flexble Robotc Arm Zheng
High Efficient Dynamics Calculation Approach for Computed-Force Control of Robots with Parallel Structures
 Proceedngs of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decson and Control, and the European Control Conference 25 Sevlle, Span, December 12-15, 25 MoIC19.2 Hgh Effcent Dynamcs Calculaton Approach for Computed-Force
Proceedngs of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decson and Control, and the European Control Conference 25 Sevlle, Span, December 12-15, 25 MoIC19.2 Hgh Effcent Dynamcs Calculaton Approach for Computed-Force
A Tale of Friction Basic Rollercoaster Physics. Fahrenheit Rollercoaster, Hershey, PA max height = 121 ft max speed = 58 mph
 A Tale o Frcton Basc Rollercoaster Physcs Fahrenhet Rollercoaster, Hershey, PA max heght = 11 t max speed = 58 mph PLAY PLAY PLAY PLAY Rotatonal Movement Knematcs Smlar to how lnear velocty s dened, angular
A Tale o Frcton Basc Rollercoaster Physcs Fahrenhet Rollercoaster, Hershey, PA max heght = 11 t max speed = 58 mph PLAY PLAY PLAY PLAY Rotatonal Movement Knematcs Smlar to how lnear velocty s dened, angular
CHAPTER 6. LAGRANGE S EQUATIONS (Analytical Mechanics)
 CHAPTER 6 LAGRANGE S EQUATIONS (Analytcal Mechancs) 1 Ex. 1: Consder a partcle movng on a fxed horzontal surface. r P Let, be the poston and F be the total force on the partcle. The FBD s: -mgk F 1 x O
CHAPTER 6 LAGRANGE S EQUATIONS (Analytcal Mechancs) 1 Ex. 1: Consder a partcle movng on a fxed horzontal surface. r P Let, be the poston and F be the total force on the partcle. The FBD s: -mgk F 1 x O
VARIATION OF CONSTANT SUM CONSTRAINT FOR INTEGER MODEL WITH NON UNIFORM VARIABLES
 VARIATION OF CONSTANT SUM CONSTRAINT FOR INTEGER MODEL WITH NON UNIFORM VARIABLES BÂRZĂ, Slvu Faculty of Mathematcs-Informatcs Spru Haret Unversty barza_slvu@yahoo.com Abstract Ths paper wants to contnue
VARIATION OF CONSTANT SUM CONSTRAINT FOR INTEGER MODEL WITH NON UNIFORM VARIABLES BÂRZĂ, Slvu Faculty of Mathematcs-Informatcs Spru Haret Unversty barza_slvu@yahoo.com Abstract Ths paper wants to contnue
Automatic PID Controller Tuning for Robots with Nonlinear Friction at the Joints
 Automatc PID Controller unng for Robots wth Nonlnear Frcton at the Jonts Abílo Azenha, Ph.D. Abstract hs paper descrbes an approach to automatc tunng of PID poston controllers for manpulators wth nonlnear
Automatc PID Controller unng for Robots wth Nonlnear Frcton at the Jonts Abílo Azenha, Ph.D. Abstract hs paper descrbes an approach to automatc tunng of PID poston controllers for manpulators wth nonlnear
Modeling curves. Graphs: y = ax+b, y = sin(x) Implicit ax + by + c = 0, x 2 +y 2 =r 2 Parametric:
 Modelng curves Types of Curves Graphs: y = ax+b, y = sn(x) Implct ax + by + c = 0, x 2 +y 2 =r 2 Parametrc: x = ax + bxt x = cos t y = ay + byt y = snt Parametrc are the most common mplct are also used,
Modelng curves Types of Curves Graphs: y = ax+b, y = sn(x) Implct ax + by + c = 0, x 2 +y 2 =r 2 Parametrc: x = ax + bxt x = cos t y = ay + byt y = snt Parametrc are the most common mplct are also used,
Harmonic Detection Algorithm based on DQ Axis with Fourier Analysis for Hybrid Power Filters
 Harmonc Detecton Algorthm based on DQ Axs wth Fourer Analyss for Hybrd Power Flters K-L. AREERAK Power Qualty Research Unt, School of Electrcal Engneerng Insttute of Engneerng, Suranaree Unversty of Technology
Harmonc Detecton Algorthm based on DQ Axs wth Fourer Analyss for Hybrd Power Flters K-L. AREERAK Power Qualty Research Unt, School of Electrcal Engneerng Insttute of Engneerng, Suranaree Unversty of Technology
Chapter 9: Statistical Inference and the Relationship between Two Variables
 Chapter 9: Statstcal Inference and the Relatonshp between Two Varables Key Words The Regresson Model The Sample Regresson Equaton The Pearson Correlaton Coeffcent Learnng Outcomes After studyng ths chapter,
Chapter 9: Statstcal Inference and the Relatonshp between Two Varables Key Words The Regresson Model The Sample Regresson Equaton The Pearson Correlaton Coeffcent Learnng Outcomes After studyng ths chapter,
Winter 2008 CS567 Stochastic Linear/Integer Programming Guest Lecturer: Xu, Huan
 Wnter 2008 CS567 Stochastc Lnear/Integer Programmng Guest Lecturer: Xu, Huan Class 2: More Modelng Examples 1 Capacty Expanson Capacty expanson models optmal choces of the tmng and levels of nvestments
Wnter 2008 CS567 Stochastc Lnear/Integer Programmng Guest Lecturer: Xu, Huan Class 2: More Modelng Examples 1 Capacty Expanson Capacty expanson models optmal choces of the tmng and levels of nvestments
THE EFFECT OF BEAM TO COLUMN CONNECTION IN ARC PORTAL FRAME
 THE EFFECT OF BEAM TO COLUMN CONNECTON N ARC PORTAL FRAME Asko Keronen Rakenteden Mekankka, Vol. 26 No 2 1993, ss. 35-5 SUMMARY A full scale rc (renforced concrete) portal frame has been bult n order to
THE EFFECT OF BEAM TO COLUMN CONNECTON N ARC PORTAL FRAME Asko Keronen Rakenteden Mekankka, Vol. 26 No 2 1993, ss. 35-5 SUMMARY A full scale rc (renforced concrete) portal frame has been bult n order to
Chapter Newton s Method
 Chapter 9. Newton s Method After readng ths chapter, you should be able to:. Understand how Newton s method s dfferent from the Golden Secton Search method. Understand how Newton s method works 3. Solve
Chapter 9. Newton s Method After readng ths chapter, you should be able to:. Understand how Newton s method s dfferent from the Golden Secton Search method. Understand how Newton s method works 3. Solve
Section 8.1 Exercises
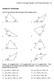 Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
NON LINEAR ANALYSIS OF STRUCTURES ACCORDING TO NEW EUROPEAN DESIGN CODE
 October 1-17, 008, Bejng, Chna NON LINEAR ANALYSIS OF SRUCURES ACCORDING O NEW EUROPEAN DESIGN CODE D. Mestrovc 1, D. Czmar and M. Pende 3 1 Professor, Dept. of Structural Engneerng, Faculty of Cvl Engneerng,
October 1-17, 008, Bejng, Chna NON LINEAR ANALYSIS OF SRUCURES ACCORDING O NEW EUROPEAN DESIGN CODE D. Mestrovc 1, D. Czmar and M. Pende 3 1 Professor, Dept. of Structural Engneerng, Faculty of Cvl Engneerng,
