Exam 3 Solutions. ClO g. At 200 K and a total pressure of 1.0 bar, the partial pressure ratio for the chlorine-containing compounds is p ClO2
|
|
|
- Kelley Gregory
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chemistry 360 Dr. Jean M. Standard Fall 2016 Name KEY Exam 3 Solutions 1.) (14 points) Consider the gas phase decomposition of chlorine dioxide, ClO 2, ClO 2 ( g) ClO ( g) + O ( g). At 200 K and a total pressure of 1.0 bar, the partial pressure ratio for the chlorine-containing compounds is p ClO2 / p ClO Determine the extent of reaction and equilibrium constant for the reaction at 200 K, assuming that there is 1 mole of ClO 2 initially present in the system. We first need to determine the mole fractions at equilibrium and the equilibrium constant expression. Starting from 1 mole of ClO 2 initially, we have ( ) ( ) + O ( g). ClO 2 g ClO g molesinit molesreacted molesequil. 1 x i The equilibrium constant is P ClO P P O P P ClO2 P P x P O P P 2 P P x O 2 P P. Substituting the mole fractions expressed in terms of the extent of reaction yields x O 2 P P P 1 P. 1+ Simplifying the expression above (not a required step but helpful later) leads to the result 2 ( 1+) 1 ( ) P P P P. The information in the problem does not include the value of the equilibrium constant; however, the ratio p ClO2 / p ClO is provided.
2 1. Continued 2 Expressing the ratio p ClO2 / p ClO in terms of the extent of reaction will allow us to determine, Solving for, p ClO2 p ClO p ClO2 p ClO 2 P P p ClO2 p ClO Finally, the equilibrium constant may be calculated by substitution, 2 ( 1+) P P ( ) P P bar 2 1 bar P P.
3 3 2.) (14 points) Sketch a temperature-composition (T-x) diagram for a binary liquid-vapor system with two components, A and B, that form ideal solutions. Make sure to label the axes as well as the various phases present in each region, along with the bubble and dew point lines. In addition, you should label the boiling points of the pure components, T A and TB. Assume that component A is the more volatile component. For any temperature T lying between the two pure boiling points, draw a tie line and describe its purpose. Discuss whether or not you expect the vapor phase mole fraction to be enriched or depleted in component A relative to the liquid phase. A sketch of a T-x diagram is shown below. The vapor phase lies in the upper part of the diagram, at higher temperatures. The liquid phase lies in the lower part of the diagram, at lower temperatures. The liquid-vapor equilibrium region is in between. The boundaries of the liquid-vapor equilibrium region are the dew point and bubble point lines. The points labeled T A and T B are the boiling points (vaporization temperatures) of pure components A and B, respectively. The more volatile component in this case, A, is the lower boiling component. V T B Dew Point L + V Tie Line Bubble Point T A L x A y A 0 1 x A, y A A tie line in the region of liquid-vapor equilibrium is shown in red. The end points label the compositions of the liquid and vapor phases. The composition of the liquid phase, x A, comes from the intersection of the tie line with the bubble point line, shown in this case as the dashed line on the left of the diagram. The composition of the liquid phase, y A, comes from the intersection of the tie line with the dew point line, shown in this case as the dashed line on the right of the diagram. The vapor phase will be enriched in the more volatile component. Thus, since A is more volatile than B in this case, we would expect to find more A in the vapor phase, such that y A > x A, as seen above.
4 3.) (14 points) The melting point of mercury is 38.9 C at 1 bar and 19.9 C at 3540 bar. The density of liquid mercury is g/ml and the density of solid mercury is g/ml. Determine the molar enthalpy of fusion. [The atomic mass of Hg is g/mol.] 4 The Clapeyron equation for solid-liquid phase equilibrium is dp dt ΔH fus,m T fus ΔV m. We can approximate the left side of the equation as dp dt ΔP ΔT. Substituting, ΔP ΔT ΔH fus,m T fus ΔV m. We can now solve for the desired molar enthalpy of fusion, ΔH fus,m ΔP ΔT T fus ΔV m. The molar volume of each phase can be calculated from the molecular weight M and the density D. For solid mercury, For liquid mercury, the molar volume is V s,m M D # 1L & % ( $ 1000 ml ' # g mol 1 & # 1L & % $ g ml 1 ( % ( ' $ 1000 ml ' V s,m L/mol. V l,m M D # 1L & % ( $ 1000 ml ' # g mol 1 & # 1L & % $ g ml 1 ( % ( ' $ 1000 ml ' V l,m L/mol. Substituting the information for the solid to liquid phase transition, # ΔP & ΔH fus,m % ( T fus ΔV m $ ΔT ' # bar & % ( K $ K ' # 100 J & Lbar/mol % ( $ 1 Lbar ' ΔH fus,m 2253 J/mol. ( )( L/mol)
5 4.) (15 points) True/false, short answer, multiple choice. 5 a.) True or False : The Clapeyron equation is valid only for the solid-liquid phase coexistence curve in one-component systems. b.) True or False: The reaction CO (g) + 3 H 2 (g) CH 4 (g) + H 2 O (g) is expected to shift to the left if hydrogen gas is removed from the system. c.) Short answer A maximum or minimum boiling solution for a binary liquid-vapor system is referred to as an azeotrope. d.) Short answer The van't Hoff Equation gives the temperature dependence of the equilibrium constant. e.) Multiple Choice For the three graphs shown below, circle the one that exhibits the correct behavior for a typical reaction which reaches chemical equilibrium. G G G (a) (b) (c)
6 6 5.) (14 points) Mixtures of benzene and cyclohexane exhibit ideal behavior. A solution was created containing 1.5 moles of liquid benzene and 2.5 moles of liquid cyclohexane, and at 50ºC the total vapor pressure of the solution was measured to be 340 torr. Another solution was created containing 1.5 moles of liquid benzene and 3.5 moles of liquid cyclohexane, and at 50ºC the measured total vapor pressure was 370 torr. Calculate the vapor pressures of pure benzene and pure cyclohexane at 50ºC. The ideal solution can be described by Raoult's Law, P i x i P i. The total pressure of the mixture is given by the sum of partial pressures, P P b + P c or P x b P b + x c P c. Here b refers to benzene and c refers to cyclohexane. We are given the total pressure for two different liquid phase compositions, and are asked to determine the pure vapor pressures. In the first case, the mole fractions are x b x b mol 1.5mol + 2.5mol and x c 1 x b x c In the second case, the mole fractions are x b x b mol 1.5mol + 3.5mol and x c 1 x c x c The total pressure, given by P x b P b + x c P c, in the first case is 340 torr 0.375P b P c. The total pressure in the second case is 370 torr P b P c.
7 5.) Continued 7 There are two equations and two unknowns. One way to solve this is to solve the first equation for P b and substitute into the second equation. So, solving the first equation for P b yields P b or P b P c P c. Substituting this result into the second equation leads to the vapor pressure of pure cyclohexane, P b P c ( ) P c 370 ( 0.300) P c P c P c P c P c 490 torr. From the first equation, we had P b P c. Substituting the vapor pressure of pure cyclohexane allows us to determine the vapor pressure of pure benzene, P b P b P b P c ( 490 torr) 90 torr.
8 6.) (14 points) Chlorine monoxide, ClO, a key component in the destruction of the ozone layer in the polar stratospheric regions, dimerizes to form Cl 2 O 2 according to the reaction 8 2ClO( g) Cl 2 O 2 ( g). At 200 K and a total pressure of 1 bar, ΔH R kj/mol and ΔS R 144 J mol 1 K 1. (a.) Determine the standard molar Gibbs free energy ΔG R bar. and equilibrium constant at 200 K and 1 We can use the equation ΔG R Substituting, ΔH R TΔS R. to calculate the standard molar Gibbs free energy. ΔG R ΔG R ΔH R TΔS R Jmol 1 ( 200 K) ( 144 Jmol 1 K 1 ) Jmol 1, or kjmol 1. Next, the following expression may be used to determine the equilibrium constant, ΔG R RT ln, # or exp ΔG & R $ ' % RT (. Substituting, exp ΔG R RT exp e ( J/mol) 8.314Jmol 1 K 1 ( ) 200 K ( )
9 6.) Continued 9 (b.) Discuss whether increasing the total pressure (at constant temperature) will increase or decrease the extent of reaction. Explain your answer. The effect of pressure on the extent of reaction depends on whether there are more moles of gas on the product side or on the reactant side. In this case, there is one mole of gas on the product side and there are two moles of gas on the reactant side. Therefore, increasing the total pressure will put stress on the reactant side, and the system will shift to the right to alleviate this stress. As a result the extent of reaction will increase if the pressure is increased. An alternate explanation is based upon the expression for the equilibrium constant. For the reaction 2ClO( g) Cl 2 O 2 ( g). the equilibrium constant expressed in terms of mole fractions is # " # " P Cl2 O 2 P P ClO P $ & % $ & % 2 x Cl2 O 2 P $ # " P & % P $ # " P & % 2. Simplifying, we have x Cl2 O 2 P 2 P. Notice that the equilibrium constant expression for this reaction includes the total pressure in the denominator. Therefore, if the total pressure increases, the P P term will decrease. In order for the numerical value of the equilibrium constant to remain the same, that means that the other term, x Cl 2 O 2, 2 must increase. For this to occur, x Cl2 O 2 (the mole fraction of the product) must increase and (the mole fraction of the reactant) must decrease; this has the effect of increasing the extent of reaction.
10 6.) Continued 10 (c.) Discuss whether increasing the temperature (at constant pressure) will increase or decrease the equilibrium constant. Explain your answer. The temperature dependence of the equilibrium constant depends on the sign of the molar enthalpy of reaction. We are given above that ΔH R kj/mol, so it is an exothermic reaction. One way to write the reaction including the heat released is 2ClO( g) Cl 2 O 2 ( g) + heat. Increasing the temperature puts stress on the product side (since that is where the heat resides). To alleviate this stress, the reaction shifts to the left, and the equilibrium constant decreases. An alternative explanation can be given using the van't Hoff plot, shown below. Exothermic case ln slope -ΔH o /R > 0 T high 1/T T low Since the enthalpy of reaction is negative, the slope of the van't Hoff plot is positive. When the temperature increases, 1/T decreases. We can see that this leads to a smaller value of ln and hence a smaller value of ; thus, the equilibrium constant decreases as the temperature increases.
11 7.) (15 points) True/false, short answer, multiple choice. 11 a.) True or False : For the liquid-to-vapor phase transition in a one-component system, the Gibbs free energy change is negative ( ΔG < 0 ). b.) True or False: A chemical equilibrium is an example of a dynamic equilibrium. c.) Short answer The triple point is the place on the phase diagram of a one-component system where the number of thermodynamic degrees of freedom equals zero. d.) Short answer The extent of reaction provides a measure of how far a chemical reaction has progressed from reactants to products. e.) Multiple Choice Henry's Law is generally expected to be valid for which component or components of a solution? 1) the solute 2) the solvent 3) both the solute and the solvent
Problem Set 10 Solutions
 Chemistry 360 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 10 Solutions 1 Sketch (roughly to scale) a phase diagram for molecular oxygen given the following information: the triple point occurs at 543 K and 114 torr;
Chemistry 360 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 10 Solutions 1 Sketch (roughly to scale) a phase diagram for molecular oxygen given the following information: the triple point occurs at 543 K and 114 torr;
Chemistry 360 Spring 2017 Dr. Jean M. Standard April 19, Exam points
 Chemistry 360 pring 2017 Dr. Jean M. tandard April 19, 2017 Name Exam 3 100 points Note: You must show your work on problems in order to receive full credit for any answers. You must turn in your equation
Chemistry 360 pring 2017 Dr. Jean M. tandard April 19, 2017 Name Exam 3 100 points Note: You must show your work on problems in order to receive full credit for any answers. You must turn in your equation
The Second Law of Thermodynamics (Chapter 4)
 The Second Law of Thermodynamics (Chapter 4) First Law: Energy of universe is constant: ΔE system = - ΔE surroundings Second Law: New variable, S, entropy. Changes in S, ΔS, tell us which processes made
The Second Law of Thermodynamics (Chapter 4) First Law: Energy of universe is constant: ΔE system = - ΔE surroundings Second Law: New variable, S, entropy. Changes in S, ΔS, tell us which processes made
 3.012 PS 7 3.012 Issued: 11.05.04 Fall 2004 Due: 11.12.04 THERMODYNAMICS 1. single-component phase diagrams. Shown below is a hypothetical phase diagram for a single-component closed system. Answer the
3.012 PS 7 3.012 Issued: 11.05.04 Fall 2004 Due: 11.12.04 THERMODYNAMICS 1. single-component phase diagrams. Shown below is a hypothetical phase diagram for a single-component closed system. Answer the
There are five problems on the exam. Do all of the problems. Show your work.
 CHM 3410 - Physical Chemistry 1 Second Hour Exam October 22, 2010 There are five problems on the exam. Do all of the problems. Show your work. R = 0.08206 L. atm/mole. K N A = 6.022 x 10 23 R = 0.08314
CHM 3410 - Physical Chemistry 1 Second Hour Exam October 22, 2010 There are five problems on the exam. Do all of the problems. Show your work. R = 0.08206 L. atm/mole. K N A = 6.022 x 10 23 R = 0.08314
B. Correct! Good work. F = C P + 2 = = 2 degrees of freedom. Good try. Hint: Think about the meaning of components and phases.
 Physical Chemistry - Problem Drill 06: Phase Equilibrium No. 1 of 10 1. The Gibbs Phase Rule is F = C P + 2, how many degrees of freedom does a system have that has two independent components and two phases?
Physical Chemistry - Problem Drill 06: Phase Equilibrium No. 1 of 10 1. The Gibbs Phase Rule is F = C P + 2, how many degrees of freedom does a system have that has two independent components and two phases?
Chem 260 Quiz - Chapter 4 (11/19/99)
 Chem 260 Quiz - Chapter 4 (11/19/99) Name (print) Signature Terms in bold: phase transitions transition temperature phase diagram phase boundaries vapor pressure thermal analysis dynamic equilibrium boiling
Chem 260 Quiz - Chapter 4 (11/19/99) Name (print) Signature Terms in bold: phase transitions transition temperature phase diagram phase boundaries vapor pressure thermal analysis dynamic equilibrium boiling
Chem 1A, Fall 2015, Midterm Exam 3. Version A November 17, 2015 (Prof. Head-Gordon) 2. Student ID: TA:
 Chem 1A, Fall 2015, Midterm Exam 3. Version A November 17, 2015 (Prof. Head-Gordon) 2 Name: Student ID: TA: Contents: 6 pages A. Multiple choice (10 points) B. Thermochemistry and Equilibria (12 points)
Chem 1A, Fall 2015, Midterm Exam 3. Version A November 17, 2015 (Prof. Head-Gordon) 2 Name: Student ID: TA: Contents: 6 pages A. Multiple choice (10 points) B. Thermochemistry and Equilibria (12 points)
There are five problems on the exam. Do all of the problems. Show your work
 CHM 3400 Fundamentals of Physical Chemistry Second Hour Exam March 8, 2017 There are five problems on the exam. Do all of the problems. Show your work R = 0.08206 L atm/mole K N A = 6.022 x 10 23 R = 0.08314
CHM 3400 Fundamentals of Physical Chemistry Second Hour Exam March 8, 2017 There are five problems on the exam. Do all of the problems. Show your work R = 0.08206 L atm/mole K N A = 6.022 x 10 23 R = 0.08314
CHEM 1032 PRACTICE EXAM I CLASS SPRING 2017
 1 CHEM 1032 PRACTICE EXAM I CLASS SPRING 2017 1. Select the characteristic(s) of the liquid phase: (You may need a periodic table. Useful information appears on page 5.) (i) adopts the shape of the container
1 CHEM 1032 PRACTICE EXAM I CLASS SPRING 2017 1. Select the characteristic(s) of the liquid phase: (You may need a periodic table. Useful information appears on page 5.) (i) adopts the shape of the container
Homework Problem Set 8 Solutions
 Chemistry 360 Dr. Jean M. Standard Homework roblem Set 8 Solutions. Starting from G = H S, derive the fundamental equation for G. o begin, we take the differential of G, dg = dh d( S) = dh ds Sd. Next,
Chemistry 360 Dr. Jean M. Standard Homework roblem Set 8 Solutions. Starting from G = H S, derive the fundamental equation for G. o begin, we take the differential of G, dg = dh d( S) = dh ds Sd. Next,
Thermodynamic condition for equilibrium between two phases a and b is G a = G b, so that during an equilibrium phase change, G ab = G a G b = 0.
 CHAPTER 5 LECTURE NOTES Phases and Solutions Phase diagrams for two one component systems, CO 2 and H 2 O, are shown below. The main items to note are the following: The lines represent equilibria between
CHAPTER 5 LECTURE NOTES Phases and Solutions Phase diagrams for two one component systems, CO 2 and H 2 O, are shown below. The main items to note are the following: The lines represent equilibria between
MCGILL UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE MIDTERM EXAMINATION CHEM 120 MONDAY MARCH 16, :30PM 8:30PM VERSION NUMBER: 1
 MCGILL UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE MIDTERM EXAMINATION CHEM 120 MONDAY MARCH 16, 2009 6:30PM 8:30PM VERSION NUMBER: 1 Instructions: BEFORE YOU BEGIN: Enter your student number and name on the computer
MCGILL UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE MIDTERM EXAMINATION CHEM 120 MONDAY MARCH 16, 2009 6:30PM 8:30PM VERSION NUMBER: 1 Instructions: BEFORE YOU BEGIN: Enter your student number and name on the computer
Phase Diagrams. NC State University
 Chemistry 433 Lecture 18 Phase Diagrams NC State University Definition of a phase diagram A phase diagram is a representation of the states of matter, solid, liquid, or gas as a function of temperature
Chemistry 433 Lecture 18 Phase Diagrams NC State University Definition of a phase diagram A phase diagram is a representation of the states of matter, solid, liquid, or gas as a function of temperature
x =!b ± b2! 4ac 2a moles particles solution (expt) moles solute dissolved (calculated conc ) i =
 Properties of Solution Practice Exam Solutions Name (last) (First) Read all questions before you start. Show all work and explain your answers. Report all numerical answers to the proper number of sig.
Properties of Solution Practice Exam Solutions Name (last) (First) Read all questions before you start. Show all work and explain your answers. Report all numerical answers to the proper number of sig.
FACULTY OF SCIENCE MID-TERM EXAMINATION 2 MARCH 18, :30 TO 8:30 PM CHEMISTRY 120 GENERAL CHEMISTRY
 FACULTY OF SCIENCE MID-TERM EXAMINATION 2 MARCH 18, 2011. 6:30 TO 8:30 PM CHEMISTRY 120 GENERAL CHEMISTRY Examiners: Prof. B. Siwick Prof. A. Mittermaier Dr. A. Fenster Name: Associate Examiner: A. Fenster
FACULTY OF SCIENCE MID-TERM EXAMINATION 2 MARCH 18, 2011. 6:30 TO 8:30 PM CHEMISTRY 120 GENERAL CHEMISTRY Examiners: Prof. B. Siwick Prof. A. Mittermaier Dr. A. Fenster Name: Associate Examiner: A. Fenster
Physical Chemistry I Exam points
 Chemistry 360 Fall 2018 Dr. Jean M. tandard October 17, 2018 Name Physical Chemistry I Exam 2 100 points Note: You must show your work on problems in order to receive full credit for any answers. You must
Chemistry 360 Fall 2018 Dr. Jean M. tandard October 17, 2018 Name Physical Chemistry I Exam 2 100 points Note: You must show your work on problems in order to receive full credit for any answers. You must
Chemistry 123: Physical and Organic Chemistry Topic 2: Thermochemistry
 Recall the equation. w = -PΔV = -(1.20 atm)(1.02 L)( = -1.24 10 2 J -101 J 1 L atm Where did the conversion factor come from? Compare two versions of the gas constant and calculate. 8.3145 J/mol K 0.082057
Recall the equation. w = -PΔV = -(1.20 atm)(1.02 L)( = -1.24 10 2 J -101 J 1 L atm Where did the conversion factor come from? Compare two versions of the gas constant and calculate. 8.3145 J/mol K 0.082057
CHM 2046 Test 2 Review: Chapter 12, Chapter 13, & Chapter 14
 Chapter 12: 1. In an 80.0 L home aquarium, the total pressure is 1 atm and the mole fraction of nitrogen is 0.78. Henry s law constant for N 2 in water at 25 is 6.1 x 10 4. What mass of nitrogen is dissolved
Chapter 12: 1. In an 80.0 L home aquarium, the total pressure is 1 atm and the mole fraction of nitrogen is 0.78. Henry s law constant for N 2 in water at 25 is 6.1 x 10 4. What mass of nitrogen is dissolved
Chemistry II Midterm Exam April 24, 2009
 Chemistry II Midterm Exam April 24, 2009 Constants R = 8.314 J / mol K = 0.08314 Lbar / K mol = 8.314 L kpa / K mol F = 9.6485 10 4 C/mol h = 6.63 10-34 J s h = 1.05 10-34 J s k = 1.3806504 10 23 J / K
Chemistry II Midterm Exam April 24, 2009 Constants R = 8.314 J / mol K = 0.08314 Lbar / K mol = 8.314 L kpa / K mol F = 9.6485 10 4 C/mol h = 6.63 10-34 J s h = 1.05 10-34 J s k = 1.3806504 10 23 J / K
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY CHEM330
 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY CHEM330 Duration: 3 hours Total Marks: 100 Internal Examiner: External Examiner: Professor B S Martincigh Professor J C Swarts University of the Free State INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer five
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY CHEM330 Duration: 3 hours Total Marks: 100 Internal Examiner: External Examiner: Professor B S Martincigh Professor J C Swarts University of the Free State INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer five
P(N,V,T) = NRT V. = P(N,V,T) dv
 CHEM-443, Fall 2016, Section 010 Student Name Quiz 1 09/09/2016 Directions: Please answer each question to the best of your ability. Make sure your response is legible, precise, includes relevant dimensional
CHEM-443, Fall 2016, Section 010 Student Name Quiz 1 09/09/2016 Directions: Please answer each question to the best of your ability. Make sure your response is legible, precise, includes relevant dimensional
Chemistry 1A, Spring 2007 Midterm Exam 3 April 9, 2007 (90 min, closed book)
 Chemistry 1A, Spring 2007 Midterm Exam 3 April 9, 2007 (90 min, closed book) Name: KEY SID: TA Name: 1.) Write your name on every page of this exam. 2.) This exam has 34 multiple choice questions. Fill
Chemistry 1A, Spring 2007 Midterm Exam 3 April 9, 2007 (90 min, closed book) Name: KEY SID: TA Name: 1.) Write your name on every page of this exam. 2.) This exam has 34 multiple choice questions. Fill
CHEM Exam 2 - October 11, INFORMATION PAGE (Use for reference and for scratch paper)
 CHEM 5200 - Exam 2 - October 11, 2018 INFORMATION PAGE (Use for reference and for scratch paper) Constants and Conversion Factors: R = 0.082 L-atm/mol-K = 8.31 J/mol-K = 8.31 kpa-l/mol-k 1 L-atm = 101
CHEM 5200 - Exam 2 - October 11, 2018 INFORMATION PAGE (Use for reference and for scratch paper) Constants and Conversion Factors: R = 0.082 L-atm/mol-K = 8.31 J/mol-K = 8.31 kpa-l/mol-k 1 L-atm = 101
Exam 1 Solutions 100 points
 Chemistry 360 Fall 018 Dr. Jean M. Standard September 19, 018 Name KEY Exam 1 Solutions 100 points 1.) (14 points) A chunk of gold metal weighing 100.0 g at 800 K is dropped into 100.0 g of liquid water
Chemistry 360 Fall 018 Dr. Jean M. Standard September 19, 018 Name KEY Exam 1 Solutions 100 points 1.) (14 points) A chunk of gold metal weighing 100.0 g at 800 K is dropped into 100.0 g of liquid water
Homework 11 - Second Law & Free Energy
 HW11 - Second Law & Free Energy Started: Nov 1 at 9:0am Quiz Instructions Homework 11 - Second Law & Free Energy Question 1 In order for an endothermic reaction to be spontaneous, endothermic reactions
HW11 - Second Law & Free Energy Started: Nov 1 at 9:0am Quiz Instructions Homework 11 - Second Law & Free Energy Question 1 In order for an endothermic reaction to be spontaneous, endothermic reactions
Chapter 12 Intermolecular Forces of Attraction
 Chapter 12 Intermolecular Forces of Attraction Intermolecular Forces Attractive or Repulsive Forces between molecules. Molecule - - - - - - Molecule Intramolecular Forces bonding forces within the molecule.
Chapter 12 Intermolecular Forces of Attraction Intermolecular Forces Attractive or Repulsive Forces between molecules. Molecule - - - - - - Molecule Intramolecular Forces bonding forces within the molecule.
Name: Discussion Section:
 CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2017, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 FORM B March 23, 2017 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed lease show
CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2017, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 FORM B March 23, 2017 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed lease show
Phase Equilibria in a One-Component System I
 5.60 spring 2005 Lecture #17 page 1 Phase Equilibria in a One-Component System I Goal: Understand the general phenomenology of phase transitions and phase coexistence conditions for a single component
5.60 spring 2005 Lecture #17 page 1 Phase Equilibria in a One-Component System I Goal: Understand the general phenomenology of phase transitions and phase coexistence conditions for a single component
LECTURE 6 NON ELECTROLYTE SOLUTION
 LECTURE 6 NON ELECTROLYTE SOLUTION Ch 45.5 pplied Phy Chem First Sem 2014-15 Ch 45.5 Exam II September 1/3 (Multiple Choice/Problem Solving) Coverage: Second/Third Laws of Thermodynamics Nonelectrolyte
LECTURE 6 NON ELECTROLYTE SOLUTION Ch 45.5 pplied Phy Chem First Sem 2014-15 Ch 45.5 Exam II September 1/3 (Multiple Choice/Problem Solving) Coverage: Second/Third Laws of Thermodynamics Nonelectrolyte
(name) Place the letter of the correct answer in the place provided. Work must be shown for non-multiple choice problems
 (name) Place the letter of the correct answer in the place provided. Work must be shown for non-multiple choice problems 1. According to Raoults Lab the change in the vapor pressure of a solution containing
(name) Place the letter of the correct answer in the place provided. Work must be shown for non-multiple choice problems 1. According to Raoults Lab the change in the vapor pressure of a solution containing
Class XI Chapter 6 Thermodynamics Chemistry
 Class XI Chapter 6 Chemistry Question 6.1: Choose the correct answer. A thermodynamic state function is a quantity (i) used to determine heat changes (ii) whose value is independent of path (iii) used
Class XI Chapter 6 Chemistry Question 6.1: Choose the correct answer. A thermodynamic state function is a quantity (i) used to determine heat changes (ii) whose value is independent of path (iii) used
Name. Chem 116 Sample Examination #2
 page 1 of 8 Name Last 5 digits of Student Number: XXX X Chem 116 Sample Examination #2 This exam consists of eight (8) pages, including this cover page. Be sure your copy is complete before beginning your
page 1 of 8 Name Last 5 digits of Student Number: XXX X Chem 116 Sample Examination #2 This exam consists of eight (8) pages, including this cover page. Be sure your copy is complete before beginning your
AP CHEMISTRY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP CHEMISTRY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 1 A sample of solid U O 8 is placed in a rigid 1.500 L flask. Chlorine gas, Cl 2 (g), is added, and the flask is heated to 862 C. The equation for
AP CHEMISTRY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 1 A sample of solid U O 8 is placed in a rigid 1.500 L flask. Chlorine gas, Cl 2 (g), is added, and the flask is heated to 862 C. The equation for
CH302 Spring 2009 Practice Exam 1 (a fairly easy exam to test basic concepts)
 CH302 Spring 2009 Practice Exam 1 (a fairly easy exam to test basic concepts) 1) Complete the following statement: We can expect vapor pressure when the molecules of a liquid are held together by intermolecular
CH302 Spring 2009 Practice Exam 1 (a fairly easy exam to test basic concepts) 1) Complete the following statement: We can expect vapor pressure when the molecules of a liquid are held together by intermolecular
DATA THAT YOU MAY USE UNITS Conventional Volume ml or cm 3 = cm 3 or 10-3 dm 3 Liter (L) = dm 3 Pressure atm = 760 torr = Pa CONSTANTS
 DATA THAT YOU MAY USE UNITS Conventional S.I. Volume ml or cm 3 = cm 3 or 0-3 dm 3 Liter (L) = dm 3 Pressure atm = 760 torr =.03 0 5 Pa torr = 33.3 Pa Temperature C 0 C = 73.5 K PV L-atm =.03 0 5 dm 3
DATA THAT YOU MAY USE UNITS Conventional S.I. Volume ml or cm 3 = cm 3 or 0-3 dm 3 Liter (L) = dm 3 Pressure atm = 760 torr =.03 0 5 Pa torr = 33.3 Pa Temperature C 0 C = 73.5 K PV L-atm =.03 0 5 dm 3
Thermochemistry: the study of energy (in the from of heat) changes that accompany physical & chemical changes
 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry: the study of energy (in the from of heat) changes that accompany physical & chemical changes heat flows from high to low (hot cool) endothermic reactions: absorb energy
Thermochemistry Thermochemistry: the study of energy (in the from of heat) changes that accompany physical & chemical changes heat flows from high to low (hot cool) endothermic reactions: absorb energy
= (25.0 g)(0.137 J/g C)[61.2 C - (-31.4 C)] = 317 J (= kj)
![= (25.0 g)(0.137 J/g C)[61.2 C - (-31.4 C)] = 317 J (= kj) = (25.0 g)(0.137 J/g C)[61.2 C - (-31.4 C)] = 317 J (= kj)](/thumbs/89/101004910.jpg) CHEM 101A ARMSTRONG SOLUTIONS TO TOPIC D PROBLEMS 1) For all problems involving energy, you may give your answer in either joules or kilojoules, unless the problem specifies a unit. (In general, though,
CHEM 101A ARMSTRONG SOLUTIONS TO TOPIC D PROBLEMS 1) For all problems involving energy, you may give your answer in either joules or kilojoules, unless the problem specifies a unit. (In general, though,
Lecture 4-6 Equilibrium
 Lecture 4-6 Equilibrium Discontinuity in the free energy, G verses T graph is an indication of phase transition. For one-component system, existing in two phases, the chemical potentials of each of these
Lecture 4-6 Equilibrium Discontinuity in the free energy, G verses T graph is an indication of phase transition. For one-component system, existing in two phases, the chemical potentials of each of these
PX-III Chem 1411 Chaps 11 & 12 Ebbing
 PX-III Chem 1411 Chaps 11 & 12 Ebbing 1. What is the name for the following phase change? I 2 (s) I 2 (g) A) melting B) condensation C) sublimation D) freezing E) vaporization 2. Which of the following
PX-III Chem 1411 Chaps 11 & 12 Ebbing 1. What is the name for the following phase change? I 2 (s) I 2 (g) A) melting B) condensation C) sublimation D) freezing E) vaporization 2. Which of the following
2) C 2 H 2 (g) + 2 H 2 (g) ---> C 2 H 6 (g) Information about the substances
 Thermochemistry 1) 2 C 4 H 10 (g) + 13 O 2 (g) ------> 8 CO 2 (g) + 10 H 2 O(l) The reaction represented above is spontaneous at 25 C. Assume that all reactants and products are in their standard states.
Thermochemistry 1) 2 C 4 H 10 (g) + 13 O 2 (g) ------> 8 CO 2 (g) + 10 H 2 O(l) The reaction represented above is spontaneous at 25 C. Assume that all reactants and products are in their standard states.
CHEMISTRY 102 FALL 2010 EXAM 1 FORM C SECTION 502 DR. KEENEY-KENNICUTT PART 1
 NAME CHEMISTRY 102 FALL 2010 EXAM 1 FORM C SECTION 502 DR. KEENEY-KENNICUTT Directions: (1) Put your name on PART 1 and your name and signature on PART 2 of the exam where indicated. (2) Sign the Aggie
NAME CHEMISTRY 102 FALL 2010 EXAM 1 FORM C SECTION 502 DR. KEENEY-KENNICUTT Directions: (1) Put your name on PART 1 and your name and signature on PART 2 of the exam where indicated. (2) Sign the Aggie
CHEM Exam 3 - March 30, Given in the individual questions on this test.
 CHEM 3530 - Exam 3 - March 30, 2018 Constants and Conversion Factors NA = 6.02x10 23 mol -1 R = 8.31 J/mol-K = 8.31 kpa-l/mol-k 1 bar = 100 kpa = 750 torr 1 kpa = 7.50 torr 1 J = 1 kpa-l 1 kcal = 4.18
CHEM 3530 - Exam 3 - March 30, 2018 Constants and Conversion Factors NA = 6.02x10 23 mol -1 R = 8.31 J/mol-K = 8.31 kpa-l/mol-k 1 bar = 100 kpa = 750 torr 1 kpa = 7.50 torr 1 J = 1 kpa-l 1 kcal = 4.18
P a g e What is the algebraic sign for enthalpy of solution? A. positive B. negative C. not enough information is given
 P a g e 1 Chem 123 Practice Questions for EXAM II Spring 2014 Exam II on Wed 3/12/14 This HAS BEEN updated after Monday s lecture (3/10/14) JUST studying these questions is not sufficient preparation.
P a g e 1 Chem 123 Practice Questions for EXAM II Spring 2014 Exam II on Wed 3/12/14 This HAS BEEN updated after Monday s lecture (3/10/14) JUST studying these questions is not sufficient preparation.
What is the volume of the unit cell of Ni in ml?
 P a g e 1 Chem 123 Practice Questions for EXAM II Fall 2014 Exam II on Mon 10/13/14 This HAS BEEN updated after Wed s lecture (10/8/14) JUST studying these questions is not sufficient preparation. There
P a g e 1 Chem 123 Practice Questions for EXAM II Fall 2014 Exam II on Mon 10/13/14 This HAS BEEN updated after Wed s lecture (10/8/14) JUST studying these questions is not sufficient preparation. There
Physical Chemistry I FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS
 Physical Chemistry I FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS Work any 8. Identify the 2 not to be graded! 1. In last year's final, students were asked to derive an expression for the isothermal Joule-Thompson Coefficient
Physical Chemistry I FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS Work any 8. Identify the 2 not to be graded! 1. In last year's final, students were asked to derive an expression for the isothermal Joule-Thompson Coefficient
Chem 75 February, 2017 Practice Exam 2
 As before, here is last year s Exam 2 in two forms: just the questions, and then the questions followed by their solutions. 1. (2 + 6 + 8 points) At high temperature, aluminum nitride, AlN(s), decomposes
As before, here is last year s Exam 2 in two forms: just the questions, and then the questions followed by their solutions. 1. (2 + 6 + 8 points) At high temperature, aluminum nitride, AlN(s), decomposes
Homework Problem Set 6 Solutions
 Chemistry 360 Dr. Jean M. Standard Homework Problem Set 6 Solutions 1. Determine the amount of pressure-volume work performed by 50.0 g of liquid water freezing to ice at 0 C and 1 atm pressure. The density
Chemistry 360 Dr. Jean M. Standard Homework Problem Set 6 Solutions 1. Determine the amount of pressure-volume work performed by 50.0 g of liquid water freezing to ice at 0 C and 1 atm pressure. The density
FORMULA SHEET (tear off)
 FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9 ) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5 )( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9 ) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5 )( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
Born-Haber Cycle: ΔH hydration
 Born-Haber Cycle: ΔH hydration ΔH solution,nacl = ΔH hydration,nacl(aq) U NaCl ΔH hydration,nacl(aq) = ΔH hydration,na + (g) + ΔH hydration,cl (g) Enthalpies of Hydration 1 Sample Exercise 11.3 Use the
Born-Haber Cycle: ΔH hydration ΔH solution,nacl = ΔH hydration,nacl(aq) U NaCl ΔH hydration,nacl(aq) = ΔH hydration,na + (g) + ΔH hydration,cl (g) Enthalpies of Hydration 1 Sample Exercise 11.3 Use the
Dr. White Chem 1B Saddleback College 1. Experiment 15 Thermodynamics of the Solution Process
 Dr. White Chem 1B Saddleback College 1 Experiment 15 Thermodynamics of the Solution Process Objectives To learn about the relationship between K and ΔG. To learn how the van't Hoff equation can be used
Dr. White Chem 1B Saddleback College 1 Experiment 15 Thermodynamics of the Solution Process Objectives To learn about the relationship between K and ΔG. To learn how the van't Hoff equation can be used
Name: Discussion Section:
 CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2017, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 FORM A March 23, 2017 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed Please show
CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2017, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 FORM A March 23, 2017 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed Please show
Phase Equilibrium: Preliminaries
 Phase Equilibrium: Preliminaries Phase diagrams for two one component systems, CO 2 and H 2 O, are shown below. The main items to note are the following: The lines represent equilibria between two phases.
Phase Equilibrium: Preliminaries Phase diagrams for two one component systems, CO 2 and H 2 O, are shown below. The main items to note are the following: The lines represent equilibria between two phases.
Solution W2009 NYB Final exam
 Solution W009 NYB Final exam Question Consider one liter of solution with [H SO 4 3.75 mol/l. Then : Mass of solution: 000 ml x.3 g/ml 30 g solution mass of H SO 4 : 3.75 mol /L x 98.078 g/mol 368 g mass
Solution W009 NYB Final exam Question Consider one liter of solution with [H SO 4 3.75 mol/l. Then : Mass of solution: 000 ml x.3 g/ml 30 g solution mass of H SO 4 : 3.75 mol /L x 98.078 g/mol 368 g mass
Chem 401 Unit 1 (Kinetics & Thermo) Review
 KINETICS 1. For the equation 2 H 2(g) + O 2(g) 2 H 2 O (g) How is the rate of formation of H 2 O mathematically related to the rate of disappearance of O 2? 2. Determine the relative reaction rates of
KINETICS 1. For the equation 2 H 2(g) + O 2(g) 2 H 2 O (g) How is the rate of formation of H 2 O mathematically related to the rate of disappearance of O 2? 2. Determine the relative reaction rates of
CHAPTER 4 Physical Transformations of Pure Substances.
 I. Generalities. CHAPTER 4 Physical Transformations of Pure Substances. A. Definitions: 1. A phase of a substance is a form of matter that is uniform throughout in chemical composition and physical state.
I. Generalities. CHAPTER 4 Physical Transformations of Pure Substances. A. Definitions: 1. A phase of a substance is a form of matter that is uniform throughout in chemical composition and physical state.
Chem 401 Unit 1 (Kinetics & Thermo) Review
 KINETICS 1. For the equation 2 H 2(g) + O 2(g) 2 H 2 O (g) How is the rate of formation of H 2 O mathematically related to the rate of disappearance of O 2? 1 Δ [H2O] Δ[O 2] = 2 Δt Δt 2. Determine the
KINETICS 1. For the equation 2 H 2(g) + O 2(g) 2 H 2 O (g) How is the rate of formation of H 2 O mathematically related to the rate of disappearance of O 2? 1 Δ [H2O] Δ[O 2] = 2 Δt Δt 2. Determine the
Exam 4, Enthalpy and Gases
 CHEM 1100 Dr. Stone November 8, 2017 Name_ G Exam 4, Enthalpy and Gases Equations and constants you may need: ΔE system = q + w PV = nrt R = 0.0821 (L*atm)/(mole*K) w = -PΔV K.E. = 1 2 m *µ 2 rms µ rms=
CHEM 1100 Dr. Stone November 8, 2017 Name_ G Exam 4, Enthalpy and Gases Equations and constants you may need: ΔE system = q + w PV = nrt R = 0.0821 (L*atm)/(mole*K) w = -PΔV K.E. = 1 2 m *µ 2 rms µ rms=
Chem 112 Dr. Kevin Moore
 Chem 112 Dr. Kevin Moore Gas Liquid Solid Polar Covalent Bond Partial Separation of Charge Electronegativity: H 2.1 Cl 3.0 H Cl δ + δ - Dipole Moment measure of the net polarity in a molecule Q Q magnitude
Chem 112 Dr. Kevin Moore Gas Liquid Solid Polar Covalent Bond Partial Separation of Charge Electronegativity: H 2.1 Cl 3.0 H Cl δ + δ - Dipole Moment measure of the net polarity in a molecule Q Q magnitude
CH2351 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II Unit I, II Phase Equilibria. Dr. M. Subramanian
 CH2351 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II Unit I, II Phase Equilibria Dr. M. Subramanian Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam
CH2351 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II Unit I, II Phase Equilibria Dr. M. Subramanian Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam
Unit 12. Thermochemistry
 Unit 12 Thermochemistry A reaction is spontaneous if it will occur without a continuous input of energy However, it may require an initial input of energy to get it started (activation energy) For Thermochemistry
Unit 12 Thermochemistry A reaction is spontaneous if it will occur without a continuous input of energy However, it may require an initial input of energy to get it started (activation energy) For Thermochemistry
Since the coefficients are only determined up to a multiplicative constant, set c 1 1 and solve for the coefficients: c 1 1 c c 3 1
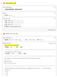 In[1]:= dipole moment of S4 Input interpretation: sulfur tetrafluoride dipole moment Result:.632 D (debyes) Unit conversions: 2.18 1-18 pc m (picocoulomb meters) 2.18 1-21 nc m (nanocoulomb meters) 2.18
In[1]:= dipole moment of S4 Input interpretation: sulfur tetrafluoride dipole moment Result:.632 D (debyes) Unit conversions: 2.18 1-18 pc m (picocoulomb meters) 2.18 1-21 nc m (nanocoulomb meters) 2.18
First Law of Thermodynamics
 First Law of Thermodynamics Remember: ΔE univ = 0 Total energy of the universe is constant. Energy can be transferred: ΔE = q + w q = heat w = work (F*D) = ΔPV 1 st Law, review For constant volume process:
First Law of Thermodynamics Remember: ΔE univ = 0 Total energy of the universe is constant. Energy can be transferred: ΔE = q + w q = heat w = work (F*D) = ΔPV 1 st Law, review For constant volume process:
Chapter 8 Phase Diagram, Relative Stability of Solid, Liquid, and Gas
 Chapter 8 Phase Diagram, Relative Stability of Solid, Liquid, and Gas Three states of matter: solid, liquid, gas (plasma) At low T: Solid is most stable. At high T: liquid or gas is most stable. Ex: Most
Chapter 8 Phase Diagram, Relative Stability of Solid, Liquid, and Gas Three states of matter: solid, liquid, gas (plasma) At low T: Solid is most stable. At high T: liquid or gas is most stable. Ex: Most
CHEMISTRY XL-14A PHYSICAL EQUILIBRIUM. August 13, 2011 Robert Iafe
 CHEMISTRY XL-14A PHYSICAL EQUILIBRIUM August 13, 2011 Robert Iafe Chapter Overview 2 Phases and Phase Transitions Solubility Colligative Properties Binary Liquid Mixtures Phases and Phase Transitions 3
CHEMISTRY XL-14A PHYSICAL EQUILIBRIUM August 13, 2011 Robert Iafe Chapter Overview 2 Phases and Phase Transitions Solubility Colligative Properties Binary Liquid Mixtures Phases and Phase Transitions 3
Last Name or Student ID
 10/06/08, Chem433 Exam # 1 Last Name or Student ID 1. (3 pts) 2. (3 pts) 3. (3 pts) 4. (2 pts) 5. (2 pts) 6. (2 pts) 7. (2 pts) 8. (2 pts) 9. (6 pts) 10. (5 pts) 11. (6 pts) 12. (12 pts) 13. (22 pts) 14.
10/06/08, Chem433 Exam # 1 Last Name or Student ID 1. (3 pts) 2. (3 pts) 3. (3 pts) 4. (2 pts) 5. (2 pts) 6. (2 pts) 7. (2 pts) 8. (2 pts) 9. (6 pts) 10. (5 pts) 11. (6 pts) 12. (12 pts) 13. (22 pts) 14.
Chapter 19. Chemical Thermodynamics. Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19 Enthalpy A thermodynamic quantity that equal to the internal energy of a system plus the product of its volume and pressure exerted on it by its surroundings; Enthalpy is the amount of energy
Chapter 19 Enthalpy A thermodynamic quantity that equal to the internal energy of a system plus the product of its volume and pressure exerted on it by its surroundings; Enthalpy is the amount of energy
1. How much heat is required to warm 400. g of ethanol from 25.0ºC to 40.0ºC?
 Heat and q=mcδt 1. How much heat is required to warm 400. g of ethanol from 25.0ºC to 40.0ºC? 2. What mass of water can be heated from 0.00ºC to 25.0ºC with 90,000. J of energy? 3. If 7,500. J of energy
Heat and q=mcδt 1. How much heat is required to warm 400. g of ethanol from 25.0ºC to 40.0ºC? 2. What mass of water can be heated from 0.00ºC to 25.0ºC with 90,000. J of energy? 3. If 7,500. J of energy
CHEMISTRY 109 #25 - REVIEW
 CHEMISTRY 109 Help Sheet #25 - REVIEW Chapter 4 (Part I); Sections 4.1-4.6; Ch. 9, Section 9.4a-9.4c (pg 387) ** Review the appropriate topics for your lecture section ** Prepared by Dr. Tony Jacob http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc
CHEMISTRY 109 Help Sheet #25 - REVIEW Chapter 4 (Part I); Sections 4.1-4.6; Ch. 9, Section 9.4a-9.4c (pg 387) ** Review the appropriate topics for your lecture section ** Prepared by Dr. Tony Jacob http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc
 HEMISTRY 110 EXAM 3 April 6, 2011 FORM A When the path is blocked, back up and see more of the way. 1. A 250 L vessel is evacuated and then connected to a 50.0 L bulb with compressed nitrogen. The pressure
HEMISTRY 110 EXAM 3 April 6, 2011 FORM A When the path is blocked, back up and see more of the way. 1. A 250 L vessel is evacuated and then connected to a 50.0 L bulb with compressed nitrogen. The pressure
CHEMISTRY 102 FALL 2010 EXAM 1 FORM D SECTION 502 DR. KEENEY-KENNICUTT PART 1
 NAME CHEMISTRY 102 FALL 2010 EXAM 1 FORM D SECTION 502 DR. KEENEY-KENNICUTT Directions: (1) Put your name on PART 1 and your name and signature on PART 2 of the exam where indicated. (2) Sign the Aggie
NAME CHEMISTRY 102 FALL 2010 EXAM 1 FORM D SECTION 502 DR. KEENEY-KENNICUTT Directions: (1) Put your name on PART 1 and your name and signature on PART 2 of the exam where indicated. (2) Sign the Aggie
General Chemistry revisited
 General Chemistry revisited A(g) + B(g) C(g) + D(g) We said that G = H TS where, eg, H = f H(C) + f H(D) - f H(A) - f H(B) G < 0 implied spontaneous to right G > 0 implied spontaneous to left In a very
General Chemistry revisited A(g) + B(g) C(g) + D(g) We said that G = H TS where, eg, H = f H(C) + f H(D) - f H(A) - f H(B) G < 0 implied spontaneous to right G > 0 implied spontaneous to left In a very
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Spontaneous Processes Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics The Molecular Interpretation of Entropy Entropy Changes in Chemical Reactions Gibbs Free Energy Free
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Spontaneous Processes Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics The Molecular Interpretation of Entropy Entropy Changes in Chemical Reactions Gibbs Free Energy Free
Exam 2 Solutions. for a gas obeying the equation of state. Z = PV m RT = 1 + BP + CP 2,
 Chemistry 360 Dr. Jean M. Standard Fall 016 Name KEY 1.) (14 points) Determine # H & % ( $ ' Exam Solutions for a gas obeying the equation of state Z = V m R = 1 + B + C, where B and C are constants. Since
Chemistry 360 Dr. Jean M. Standard Fall 016 Name KEY 1.) (14 points) Determine # H & % ( $ ' Exam Solutions for a gas obeying the equation of state Z = V m R = 1 + B + C, where B and C are constants. Since
Thermochemistry Chapter 8
 Thermochemistry Chapter 8 Thermochemistry First law of thermochemistry: Internal energy of an isolated system is constant; energy cannot be created or destroyed; however, energy can be converted to different
Thermochemistry Chapter 8 Thermochemistry First law of thermochemistry: Internal energy of an isolated system is constant; energy cannot be created or destroyed; however, energy can be converted to different
ln( P vap(s) / torr) = T / K ln( P vap(l) / torr) = T / K
 Chem 4501 Introduction to Thermodynamics, 3 Credits Kinetics, and Statistical Mechanics Fall Semester 2017 Homework Problem Set Number 9 Solutions 1. McQuarrie and Simon, 9-4. Paraphrase: Given expressions
Chem 4501 Introduction to Thermodynamics, 3 Credits Kinetics, and Statistical Mechanics Fall Semester 2017 Homework Problem Set Number 9 Solutions 1. McQuarrie and Simon, 9-4. Paraphrase: Given expressions
CHEMISTRY - CLUTCH CH CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: THERMOCHEMICAL PROCESSES is the branch of physical science concerned with heat and its transformations to and from other forms of energy. In terms of a chemical reaction,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: THERMOCHEMICAL PROCESSES is the branch of physical science concerned with heat and its transformations to and from other forms of energy. In terms of a chemical reaction,
Use your time wisely. Do not get stuck on one question. WORK MUST BE SHOWN CAREFULLY, WITH UNITS AT EVERY STEP OF SETUP.
 Spring 2014 CCBC-Catonsville (Wed 3/12/14) Use your time wisely. Do not get stuck on one question. WORK MUST BE SHOWN CAREFULLY, WITH UNITS AT EVERY STEP OF SETUP. PAGE TOTAL SCORE POSSIBLE YOUR SCORE
Spring 2014 CCBC-Catonsville (Wed 3/12/14) Use your time wisely. Do not get stuck on one question. WORK MUST BE SHOWN CAREFULLY, WITH UNITS AT EVERY STEP OF SETUP. PAGE TOTAL SCORE POSSIBLE YOUR SCORE
Chemistry 102 Spring 2019 Discussion #4 Chapters 11 and 12 Student name TA name Section
 Chemistry 102 Spring 2019 Discussion #4 Chapters 11 and 12 Student name TA name Section Things you should know when you finish the Discussion hand out: Average molar kinetic energy = E = M u 2 rms 2 =
Chemistry 102 Spring 2019 Discussion #4 Chapters 11 and 12 Student name TA name Section Things you should know when you finish the Discussion hand out: Average molar kinetic energy = E = M u 2 rms 2 =
A) sublimation. B) liquefaction. C) evaporation. D) condensation. E) freezing. 11. Below is a phase diagram for a substance.
 PX0411-1112 1. Which of the following statements concerning liquids is incorrect? A) The volume of a liquid changes very little with pressure. B) Liquids are relatively incompressible. C) Liquid molecules
PX0411-1112 1. Which of the following statements concerning liquids is incorrect? A) The volume of a liquid changes very little with pressure. B) Liquids are relatively incompressible. C) Liquid molecules
Week 12/Th: Lecture Units 31 & 32
 Week 12/Th: Lecture Units 31 & 32 Unit 30: Chemical Spontaneity -- entropy, 2 nd Law of Thermo -- free energy -- spontaneity Unit 31: Phase Equilibria -- liquid / gas -- phase diagrams -- phase boundaries
Week 12/Th: Lecture Units 31 & 32 Unit 30: Chemical Spontaneity -- entropy, 2 nd Law of Thermo -- free energy -- spontaneity Unit 31: Phase Equilibria -- liquid / gas -- phase diagrams -- phase boundaries
Let's look at how different properties affect vapor pressure. P =0 P =vapor pressure P =vapor pressure. first all liquid
 Let's look at how different properties affect vapor pressure P =0 P =vapor pressure P =vapor pressure Quick Quiz You have two containers. one has a total volume of 2 L and one has a total volume of 1 L
Let's look at how different properties affect vapor pressure P =0 P =vapor pressure P =vapor pressure Quick Quiz You have two containers. one has a total volume of 2 L and one has a total volume of 1 L
Chapter 11: Properties of Solutions - Their Concentrations and Colligative Properties. Chapter Outline
 Chapter 11: Properties of Solutions - Their Concentrations and Colligative Properties Chapter Outline 11.1 Energy Changes when Substances Dissolve 11.2 Vapor Pressure 11.3 Mixtures of Volatile Substances
Chapter 11: Properties of Solutions - Their Concentrations and Colligative Properties Chapter Outline 11.1 Energy Changes when Substances Dissolve 11.2 Vapor Pressure 11.3 Mixtures of Volatile Substances
CHAPTER THERMODYNAMICS
 54 CHAPTER THERMODYNAMICS 1. If ΔH is the change in enthalpy and ΔE the change in internal energy accompanying a gaseous reaction, then ΔHis always greater than ΔE ΔH< ΔE only if the number of moles of
54 CHAPTER THERMODYNAMICS 1. If ΔH is the change in enthalpy and ΔE the change in internal energy accompanying a gaseous reaction, then ΔHis always greater than ΔE ΔH< ΔE only if the number of moles of
temperature begins to change noticeably. Feedback D. Incorrect. Putting an object on a hot plate will always cause the temperature to increase.
 SAT Chemistry - Problem Drill 22: Thermodynamics No. 1 of 10 1. A metal with a high heat capacity is placed on top of a hot plate that is turned on. What will happen to the temperature of the piece of
SAT Chemistry - Problem Drill 22: Thermodynamics No. 1 of 10 1. A metal with a high heat capacity is placed on top of a hot plate that is turned on. What will happen to the temperature of the piece of
OCR Chemistry A H432
 All the energy changes we have considered so far have been in terms of enthalpy, and we have been able to predict whether a reaction is likely to occur on the basis of the enthalpy change associated with
All the energy changes we have considered so far have been in terms of enthalpy, and we have been able to predict whether a reaction is likely to occur on the basis of the enthalpy change associated with
MATSCI 204 Thermodynamics and Phase Equilibria Winter Chapter #4 Practice problems
 MATSCI 204 Thermodynamics and Phase Equilibria Winter 2013 Chapter #4 Practice problems Problem: 1-Show that for any extensive property Ω of a binary system A-B: d ( "# ) "# B, = "# + 1$ x B 2- If "# has
MATSCI 204 Thermodynamics and Phase Equilibria Winter 2013 Chapter #4 Practice problems Problem: 1-Show that for any extensive property Ω of a binary system A-B: d ( "# ) "# B, = "# + 1$ x B 2- If "# has
CHEMISTRY 202 Hour Exam II. Dr. D. DeCoste T.A (60 pts.) 31 (20 pts.) 32 (40 pts.)
 CHEMISTRY 202 Hour Exam II October 27, 2015 Dr. D. DeCoste Name Signature T.A. This exam contains 32 questions on 11 numbered pages. Check now to make sure you have a complete exam. You have two hours
CHEMISTRY 202 Hour Exam II October 27, 2015 Dr. D. DeCoste Name Signature T.A. This exam contains 32 questions on 11 numbered pages. Check now to make sure you have a complete exam. You have two hours
Chapter 5. Simple Mixtures Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201)
 Chapter 5. Simple Mixtures 2011 Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201) Contents The thermodynamic description of mixtures 5.1 Partial molar quantities 5.2 The thermodynamic of Mixing 5.3 The chemical
Chapter 5. Simple Mixtures 2011 Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201) Contents The thermodynamic description of mixtures 5.1 Partial molar quantities 5.2 The thermodynamic of Mixing 5.3 The chemical
Chapter 11 Spontaneous Change and Equilibrium
 Chapter 11 Spontaneous Change and Equilibrium 11-1 Enthalpy and Spontaneous Change 11-2 Entropy 11-3 Absolute Entropies and Chemical Reactions 11-4 The Second Law of Thermodynamics 11-5 The Gibbs Function
Chapter 11 Spontaneous Change and Equilibrium 11-1 Enthalpy and Spontaneous Change 11-2 Entropy 11-3 Absolute Entropies and Chemical Reactions 11-4 The Second Law of Thermodynamics 11-5 The Gibbs Function
Chem 1B Dr. White 1 Chapter 17: Thermodynamics. Review From Chem 1A (Chapter 6, section 1) A. The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chem 1B Dr. White 1 Chapter 17: Thermodynamics Review From Chem 1A (Chapter 6, section 1) A. The First Law of Thermodynamics 17.1 Spontaneous Processes and Entropy A. Spontaneous Change Chem 1B Dr. White
Chem 1B Dr. White 1 Chapter 17: Thermodynamics Review From Chem 1A (Chapter 6, section 1) A. The First Law of Thermodynamics 17.1 Spontaneous Processes and Entropy A. Spontaneous Change Chem 1B Dr. White
General Chemistry 1 CHM201 Unit 3 Practice Test
 General Chemistry 1 CHM201 Unit 3 Practice Test 1. Heat is best defined as a. a substance that increases the temperature and causes water to boil. b. a form of potential energy. c. a form of work. d. the
General Chemistry 1 CHM201 Unit 3 Practice Test 1. Heat is best defined as a. a substance that increases the temperature and causes water to boil. b. a form of potential energy. c. a form of work. d. the
CH 302 Spring 2008 Worksheet 4 Answer Key Practice Exam 1
 CH 302 Spring 2008 Worksheet 4 Answer Key Practice Exam 1 1. Predict the signs of ΔH and ΔS for the sublimation of CO 2. a. ΔH > 0, ΔS > 0 b. ΔH > 0, ΔS < 0 c. ΔH < 0, ΔS > 0 d. ΔH < 0, ΔS < 0 Answer:
CH 302 Spring 2008 Worksheet 4 Answer Key Practice Exam 1 1. Predict the signs of ΔH and ΔS for the sublimation of CO 2. a. ΔH > 0, ΔS > 0 b. ΔH > 0, ΔS < 0 c. ΔH < 0, ΔS > 0 d. ΔH < 0, ΔS < 0 Answer:
CHEMISTRY 102 FALL 2009 EXAM 1 FORM A SECTION 501 DR. KEENEY-KENNICUTT PART 1
 NAME CHEMISTRY 102 FALL 2009 EXAM 1 FORM A SECTION 501 DR. KEENEY-KENNICUTT Directions: (1) Put your name on PART 1 and your name and signature on PART 2 of the exam where indicated. (2) Sign the Aggie
NAME CHEMISTRY 102 FALL 2009 EXAM 1 FORM A SECTION 501 DR. KEENEY-KENNICUTT Directions: (1) Put your name on PART 1 and your name and signature on PART 2 of the exam where indicated. (2) Sign the Aggie
Chapter 12.4 Colligative Properties of Solutions Objectives List and define the colligative properties of solutions. Relate the values of colligative
 Chapter 12.4 Colligative Properties of Solutions Objectives List and define the colligative properties of solutions. Relate the values of colligative properties to the concentrations of solutions. Calculate
Chapter 12.4 Colligative Properties of Solutions Objectives List and define the colligative properties of solutions. Relate the values of colligative properties to the concentrations of solutions. Calculate
CHM 1046 FINAL REVIEW
 CHM 1046 FINAL REVIEW Prepared & Presented By: Marian Ayoub PART I Chapter Description 6 Thermochemistry 11 States of Matter; Liquids and Solids 12 Solutions 13 Rates of Reactions 18 Thermodynamics and
CHM 1046 FINAL REVIEW Prepared & Presented By: Marian Ayoub PART I Chapter Description 6 Thermochemistry 11 States of Matter; Liquids and Solids 12 Solutions 13 Rates of Reactions 18 Thermodynamics and
Name: Date: 3. Which is more concentrated (circle one.): 14.0 ppm CO 2 OR ppb CO 2?
 Name: Date: There are 25 questions totaling 90 points (scored out of 100 pts with Internship Activity). PLEASE look over the entire examination (8 pages total) BEFORE you begin to ensure your packet is
Name: Date: There are 25 questions totaling 90 points (scored out of 100 pts with Internship Activity). PLEASE look over the entire examination (8 pages total) BEFORE you begin to ensure your packet is
Phase Change (State Change): A change in physical form but not the chemical identity of a substance.
 CHM 123 Chapter 11 11.1-11.2 Phase change, evaporation, vapor pressure, and boiling point Phase Change (State Change): A change in physical form but not the chemical identity of a substance. Heat (Enthalpy)
CHM 123 Chapter 11 11.1-11.2 Phase change, evaporation, vapor pressure, and boiling point Phase Change (State Change): A change in physical form but not the chemical identity of a substance. Heat (Enthalpy)
CHE 107 Spring 2018 Exam 2
 CHE 107 Spring 2018 Exam 2 Your Name: Your ID: Question #: 1 Which substance has the smallest standard molar entropy ( S)? A He(g) B H2O(g) C CH4(g) D F2(g) Question #: 2 Phosgene, a chemical weapon used
CHE 107 Spring 2018 Exam 2 Your Name: Your ID: Question #: 1 Which substance has the smallest standard molar entropy ( S)? A He(g) B H2O(g) C CH4(g) D F2(g) Question #: 2 Phosgene, a chemical weapon used
Name: First three letters of last name
 Name: First three letters of last name Chemistry 342 Third Exam April 22, 2005 2:00 PM in C6 Lecture Center Write all work you want graded in the spaces provided. Both the logical solution to the problem
Name: First three letters of last name Chemistry 342 Third Exam April 22, 2005 2:00 PM in C6 Lecture Center Write all work you want graded in the spaces provided. Both the logical solution to the problem
