Oppenheimer and His Physics CUNY Grad Center, 14 Oct 08, 6:30 pm By David C. Cassidy
|
|
|
- Justin Cooper
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Oppenheimer and His Physics CUNY Grad Center, 14 Oct 08, 6:30 pm By David C. Cassidy Among his many accomplishments, J. Robert Oppenheimer is probably best known for his staring role on the world stage of history as the atomic doctor, the scientific head of the Manhattan Project that built the atomic bomb. But he played other historical roles as well. He was for a time after the war the public personification of science, the government s inside authority on nuclear weapons, the nation s most public scientific victim of cold war McCarthyism. And during the 1930s he was simultaneously the left-wing intellectual, Berkeley Bohemian, Sanskit linguist, and-- by the way a theoretical physicist. Where did the physics come from? How is it that J. Robert Oppenheimer, the man of so many humanistic talents and pursuits, become one of the most influential theoretical physicists of his time? In what ways was he influential? And what did he actually do in physics? In attempting to answer such questions, I must of necessity be very brief and I will be mercifully non-technical. The physics began to arise at Harvard from where, in 1925, he set off for Cambridge University following graduation in search of a doctorate in experimental physics. A frustrating year of fumbling around in Cambridge physics laboratories gradually convinced Oppenheimer that experimental work was not his field. The only bright spot that year was his good fortune to have been in Cambridge at the birth of quantum mechanics. Shortly before Oppenheimer arrived in Cambridge, German physicist Werner Heisenberg had delivered a public lecture there on atomic spectra, as well as the private news to theorist Ralph Fowler and his student, Paul Dirac, that he had made what became the first breakthrough to quantum mechanics in the form of abstract matrix mechanics. Oppenheimer began attending lectures by the 2-year-older Dirac on the results of his efforts to help bring the new quantum mechanics to completion. Soon Oppenheimer was applying Dirac s work to practical problems under Fowler. By May 1926 he had his first two papers ready for publication. One of these, on the quantum mechanics of colliding electrons, interested another German visitor to Cambridge that year--professor Max Born, who presided over the birth of quantum mechanics in Göttingen, Germany. Born was so impressed with the young American that he invited him to Göttingen for the coming year. Oppenheimer jumped at the offer. I felt completely relieved of the responsibility to go back into a laboratory, he wrote. I hadn t been good, I hadn t done anybody any good, and I hadn t had any fun whatever; and here was something I felt just driven to try. It was for him another audition. But he easily landed the part and made it his own at stage center of the quantum revolution. This same pattern repeated itself over the next two decades. Superiors who recognized his great talents encouraged his work and selected him for promotion up the professional ranks of theoretical physics. Soon it was the Americans who made the selection and they did so for a specific
2 purpose: to bring American physics to the forefront of world research. Their strategy was 3-fold: to select a few of the very best physics postdocs for advanced training in quantum physics in Europe nd and the United States, 2 to build up a few selected universities into elite research institutions, and rd 3 to place their proteges in key teaching positions at those universities, where they would create research schools to rival the Europeans. Oppenheimer became a favorite candidate for this strategy when American recruiters came to Göttingen in search of talent--and it continued right through his selection to head the Manhattan project 17 years later. The once fumbling Oppenheimer completed his doctorate under Max Born within months of his arrival in Göttingen in Fall His dissertation, which he published in a German physics journal, was on the quantum mechanics of continuous spectra emitted by atoms and accelerated charges. Several other papers utilizing the new quantum mechanics quickly followed. One of these contained the famous Born-Oppenheimer approximation for calculating the properties of molecules. Again, a pattern was set. Oppenheimer eventually published 12 research papers while in Göttingen and in subsequent European locations before settling in California in late All were marked by orginality, innovation, and complete mastery of the difficult mathematics of the new physics. But, being just 2-4 years younger than the creators of quantum mechanics, Oppenheimer had to settle mainly for applications of the new physics to explanations of old and new phenomena, rather than fundamental contributions to the new theory. His papers in that period included studies of the band spectra of molecules, the scattering of alpha rays, the polarization of scattered light, the capture of electrons by atoms, and the Ramsauer effect in spectroscopy. With a doctorate in theoretical physics from Göttingen, Oppenheimer returned to the States in 1927 a hot commodity. Sponsored the National Research Council, or NRC, Oppenheimer split the academic year between Harvard and Caltech. The following year, , he went back to Europe as one of only 3 physics postdocs selected by the International Educ. Board of the Rockefeller Foundation. One of the other two was Isidor I. Rabi, who became a life-long friend. Working with Paul Ehrenfest in Leiden and Wolfgang Pauli in Zurich and visiting Heisenberg in Leipzig, Oppenheimer was fully prepared to bring what Rabi called the European taste and style for physics to American institutions. Rabi said: Americans who had studied in Europe and came back...decided that there was no reason things like that shouldn t be going in this country, and we went to work on it. (p115) And work on it they did. Oppenheimer returned to the States for good in August 1929 to begin teaching at the Univ of Calif. at Berkeley. At the request of Caltech s president, Robert A. Millikan, he agreed to spend a portion of each year working at Caltech in Pasadena. UC Berkeley was then one of the mediocre state colleges selected by Millikan and the NRC for transformation into an elite research institution, and Oppenheimer went there precisely for the opportunities it 2
3 afforded. He was joined by another NRC fellow, the experimentalist Ernest O. Lawrence. Within a decade Oppenheimer and Lawrence succeeded in their mission to help bring California physics to the forefront of American and world research. During the 1930s, Berkeley and Caltech were two of the top 5 producers of American physics doctorates. (The others were Michigan, Chicago, and Cornell.) Together, Berkeley and Caltech accounted for 1/3 of all physics doctorates in the US during the 1930s, and they have remained among the leaders ever since. Lawrence s Radiation Laboratory centered around his invention of the cyclotron in With massive funding from the Rockefeller Foundation, it became the early nucleus of the Manhattan Project and the model for post-war big science. Oppenheimer s theorists worked closely with Lawrence s big machine experimenters. In addition, every summer and during school vacations Oppenheimer and an entourage of 10 or so graduate students and postdocs migrated South to Pasadena to work with Cal Tech experimentalists Carl Anderson, Seth Neddermeyer and others on the mysteries of nuclei and cosmic rays. These collaborations were so successful that Oppenheimer s California School of theoretical physics soon did rival the European schools, as well as the many newly emerging American schools at selected eastern universities. There were plenty of experimental discoveries for the theorists to work on, some occurring right in California. The so-called miracle year of 1932 alone brought Anderson s discovery of the positive electron at Caltech, the British discovery of showers of created particles in collisions of high energy cosmic rays, the discoveries of the neutron and the deuteron, Heisenberg s neutronproton model of the nucleus, and Pauli s prediction of a new elementary particle, the neutrino. But how successful was Oppenheimer s school, and what did he and it actually produce in physics? Upon closer look, it is evident that Oppenheimer was, in those years, neither a popular teacher nor an excellent bureaucrat. Students avoided his courses because of his high demands and poor teaching style. But, wrote Hans Bethe, for those who could follow him he gave his students a feeling of the beauty of the subject, and he conveyed his excitement about its development. (155) Perhaps because of his demanding style, Oppenheimer did not produce a large number of doctorates only 22 in the period from 1930 until he left for Los Alamos in 1943, and only 6 through During the same period, , the entire department produced 70 doctorates. Oppenheimer s other 16 doctorates thru 1943 all graduated during the early 1940s, when the collaboration with Lawrence and his new accelerator were at their height. [3 others] He did not mentor any Caltech doctoral students, nor was he even listed as an examiner of any of the graduates. During the California years, Oppenheimer authored or co-authored 36 research papers and 16 abstracts of conference papers. Most of his papers were aimed at unraveling data in nuclear and high energy physics. The papers covered such topics as the nuclear photoelectric effect, the theory of electrons and positrons, and the build up of cosmic ray showers through quantum electromagnetic processes. 3
4 Compared with similar research elsewhere at the time, Oppenheimer and collaborators did not always produce the most innovative work. Oppenheimer obviously had many other things on this mind at the time as we know. But he and his students did produce solid work on the emerging problems of the day. And together with Lawrence s radiation lab, they helped form a solid foundation for the big-physics profession to follow during and after the coming war. Perhaps Oppenheimer s greatest success in physics occurred with his school s most speculative and least experimentally driven work--that on the collapse of dying stars which led to the prediction of what are now called neutron stars and Black Holes. On several occasions during the 1930s, Oppenheimer spoke in Pasadena on the application of nuclear theory to astrophysics, and he and his students began work on nuclear fusion as the source of the sun s energy. Unfortunately, just as they prepared to present their results in 1937, Hans Bethe published a full-scale theory of stellar energy, for which he received the Nobel Prize 30 years later. Scooped by Bethe, Oppenheimer and his students were encouraged by Richard Tolman at Caltech to consider the application of nuclear physics together with general relativity theory, not to the flourishing of a star, but to its death -- the events occurring in the sudden collapse of a star in a cataclysmic explosion that we sometimes observe from earth as a nova, or supernova. Oppenheimer and his students discovered that stars about 1 ½ to 3 times the mass of the sun would collapse into what became known as a neutron star, sort of a huge nucleus. For larger stars, they found that the pressure at the center of the collapsing star would become so great that it would be mathematically undefined, or infinite, in value a mathematical singularity from which, they predicted, not even light could escape. John Wheeler later called it a Black Hole. This was research of potential Nobel Prize quality. Unfortunately, it went nowhere. Mathematicians at the time avoided singularities even more than they do now, and observational astronomers were still trying to unravel the mysteries of galaxies, nebulae, and the expanding universe. The study of black holes did not take center stage until the evidence for their existence began to mount during the 1990s with the vistas opened by the Hubble Space Telescope. Oppenheimer returned to Berkeley after the war, where he mentored his last three doctoral candidates. At the same time, he continued his role as the impresario of group efforts when he presided over the famous Shelter Island conference that enabled the advance of postwar high-energy quantum physics. In 1947 he moved to Princeton as the director of the Institute for Advanced Study. During his tenure, the institute was heavily weighted toward physics and mathematics with the presence of such luminaries as Albert Einstein, John von Neumann, Hermann Weyl, and Kurt Gödel. 4 But Oppenheimer never again published a research paper in physics. Oppenheimer died in
5 rd Princeton of throat cancer in 1967, 2 months short of his 63 birthday. Thank you. 5
Featured Alumna Sarah Caudill ( 06)
 Featured Alumna Sarah Caudill ( 06) As a high school student applying to colleges, I had a choice between Stetson and the University of Florida. I reasoned that I would receive a more personalized education
Featured Alumna Sarah Caudill ( 06) As a high school student applying to colleges, I had a choice between Stetson and the University of Florida. I reasoned that I would receive a more personalized education
Do you know the man that dropped out of school and still was one of the greatest physicists of the 20th century? That is Albert Einstein.
 Do you know the man that dropped out of school and still was one of the greatest physicists of the 20th century? That is Albert Einstein. Albert was a man that thought for himself and changed the world
Do you know the man that dropped out of school and still was one of the greatest physicists of the 20th century? That is Albert Einstein. Albert was a man that thought for himself and changed the world
2008 Michigan Quantum Summer School
 2008 Michigan Quantum Summer School Historical introduction Jens Zorn, University of Michigan The spirit of the early Michigan Summer Symposia in Theoretical Physics now continues as a joint effort by
2008 Michigan Quantum Summer School Historical introduction Jens Zorn, University of Michigan The spirit of the early Michigan Summer Symposia in Theoretical Physics now continues as a joint effort by
Nobel Prize Winner Erwin Schrodinger. in Vienna. His father, Rudolf Schrodinger was married to the Alexander Bauer s daughter.
 Jamal Waked 4/26/12 Pd.2 Nobel Prize Winner Erwin Schrodinger Famous for his theory Schrodinger s Cat, based on the observation that electrons behave differently when being watched, Erwin Schrodinger was
Jamal Waked 4/26/12 Pd.2 Nobel Prize Winner Erwin Schrodinger Famous for his theory Schrodinger s Cat, based on the observation that electrons behave differently when being watched, Erwin Schrodinger was
New forms of matter near absolute zero temperature
 New forms of matter near absolute zero temperature Wolfgang Ketterle Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, USA Abstract. First, I want to make some remarks about my career. In 1990, I made
New forms of matter near absolute zero temperature Wolfgang Ketterle Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, USA Abstract. First, I want to make some remarks about my career. In 1990, I made
Edwin Hubble Changed Our Ideas About the Universe
 Edwin Hubble Changed Our Ideas About the Universe Astronomers continue to use the Hubble Space Telescope named after him. Transcript of radio broadcast: 28 April 2009 ANNOUNCER: EXPLORATIONS -- a program
Edwin Hubble Changed Our Ideas About the Universe Astronomers continue to use the Hubble Space Telescope named after him. Transcript of radio broadcast: 28 April 2009 ANNOUNCER: EXPLORATIONS -- a program
Ekman and Källén. Two world famous theoreticians from Lund.
 181 Ekman and Källén Two world famous theoreticians from Lund. The Ekman Spiral Walfrid Ekman came from Stockholm and studied in Uppsala. He is most well-known for his theories on how the wind, the Earth
181 Ekman and Källén Two world famous theoreticians from Lund. The Ekman Spiral Walfrid Ekman came from Stockholm and studied in Uppsala. He is most well-known for his theories on how the wind, the Earth
Enrico Fermi. Joshua Wells. ELEC 424: Solid State Devices. Dr. Dunlop
 Enrico Fermi Joshua Wells ELEC 424: Solid State Devices Dr. Dunlop March 4, 2003 Wells 2 If the 19th century was the century of chemistry, the 20th was the century of physics (Rhodes 1). So begins Time
Enrico Fermi Joshua Wells ELEC 424: Solid State Devices Dr. Dunlop March 4, 2003 Wells 2 If the 19th century was the century of chemistry, the 20th was the century of physics (Rhodes 1). So begins Time
What we don t know, we teach one another. Robert Oppenheimer, describing the profession of theoretical physics, in 1946
 What we don t know, we teach one another Robert Oppenheimer, describing the profession of theoretical physics, in 1946 My Undergraduate Teachers 1940-41 Black Mountain College Nathan Rosen taught me calculus
What we don t know, we teach one another Robert Oppenheimer, describing the profession of theoretical physics, in 1946 My Undergraduate Teachers 1940-41 Black Mountain College Nathan Rosen taught me calculus
Wave properties of light
 Wave properties of light Light is energy whose wavelength is the distance traveled in order to complete one cycle. The frequency of light refers to the number of cycles in one second. Low-energy light
Wave properties of light Light is energy whose wavelength is the distance traveled in order to complete one cycle. The frequency of light refers to the number of cycles in one second. Low-energy light
A trip to Quantum Physics
 A trip to Quantum Physics - Schrödinger s cats, Einstein s nightmares and quantum technology - Diego Porras School of Mathematical & Physical Sciences A bit of history Quantum weirdness Complexity in quantum
A trip to Quantum Physics - Schrödinger s cats, Einstein s nightmares and quantum technology - Diego Porras School of Mathematical & Physical Sciences A bit of history Quantum weirdness Complexity in quantum
FASTER, SMALLER, CHEAPER
 FASTER, SMALLER, CHEAPER DISCOVERING THE UNIVERSE ON A SHOESTRING BUDGET Pagels Public Lecture, Aspen Center for Physics Jonathan Feng, University of California, Irvine 9 August 2018 9 Aug 2018 Feng 1
FASTER, SMALLER, CHEAPER DISCOVERING THE UNIVERSE ON A SHOESTRING BUDGET Pagels Public Lecture, Aspen Center for Physics Jonathan Feng, University of California, Irvine 9 August 2018 9 Aug 2018 Feng 1
Lecture 18 : Black holes. Astronomy 111
 Lecture 18 : Black holes Astronomy 111 Gravity's final victory A star more massive than about 18 M sun would leave behind a post-supernova core this is larger than 2-3 M sun :Neutron degeneracy pressure
Lecture 18 : Black holes Astronomy 111 Gravity's final victory A star more massive than about 18 M sun would leave behind a post-supernova core this is larger than 2-3 M sun :Neutron degeneracy pressure
Topic Page: Einstein, Albert ( )
 Topic Page: Einstein, Albert (1879-1955) Definition: Einstein, Albert from Philip's Encyclopedia US physicist, b. Germany, who devised the famous theories of relativity. Einstein published many important
Topic Page: Einstein, Albert (1879-1955) Definition: Einstein, Albert from Philip's Encyclopedia US physicist, b. Germany, who devised the famous theories of relativity. Einstein published many important
Chapter One. The Old Quantum Theory. 1-1 Why Quantum Mechanics.
 Chapter One The Old Quantum Theory 1-1 Why Quantum Mechanics. The birth of quantum mechanics can be dated to 1925, when physicists such as Werner Heisenberg and Erwin Schrödinger invented mathematical
Chapter One The Old Quantum Theory 1-1 Why Quantum Mechanics. The birth of quantum mechanics can be dated to 1925, when physicists such as Werner Heisenberg and Erwin Schrödinger invented mathematical
PCES 5.1. Kaiser Wilhelm Institute (Berlin) in Hahn & Strassmann the discovery of nuclear fission in Berlin (1938)
 The ATOMIC NUCLEUS NUCLEAR FISSION- a Tunneling Process Nuclear fission, described on p. 4.30, is an extremely rare process. A U nucleus will on average take 4.5 billion yrs. to undergo fission- although
The ATOMIC NUCLEUS NUCLEAR FISSION- a Tunneling Process Nuclear fission, described on p. 4.30, is an extremely rare process. A U nucleus will on average take 4.5 billion yrs. to undergo fission- although
BETHE - SALPETER EQUATION THE ORIGINS Edwin E. Salpeter October 2008
 1. INTRODUCTION BETHE - SALPETER EQUATION THE ORIGINS Edwin E. Salpeter October 2008 The Bethe-Salpeter equation was first given at an American Physical Society meeting at the beginning of 1951 (Bethe-Salpeter
1. INTRODUCTION BETHE - SALPETER EQUATION THE ORIGINS Edwin E. Salpeter October 2008 The Bethe-Salpeter equation was first given at an American Physical Society meeting at the beginning of 1951 (Bethe-Salpeter
1. What does this poster contain?
 This poster presents the elementary constituents of matter (the particles) and their interactions, the latter having other particles as intermediaries. These elementary particles are point-like and have
This poster presents the elementary constituents of matter (the particles) and their interactions, the latter having other particles as intermediaries. These elementary particles are point-like and have
A REVIEW OF RADIO ASTRONOMY IN THE USA I. INTRODUCTION
 A REVIEW OF RADIO ASTRONOMY IN THE USA I. INTRODUCTION It has been suggested that the present time would be opportune for a review to be made of the whole field of radio astronomy in the country. In this
A REVIEW OF RADIO ASTRONOMY IN THE USA I. INTRODUCTION It has been suggested that the present time would be opportune for a review to be made of the whole field of radio astronomy in the country. In this
Quiz name: Chapter 12 Classwork Assignment Famous Scientist Edwin Hubble
 Name: Quiz name: Chapter 12 Classwork Assignment Famous Scientist Edwin Hubble Date: 1. was born on November 20, 1889. 2. He graduated from the University of Chicago and served in WWI before settling down
Name: Quiz name: Chapter 12 Classwork Assignment Famous Scientist Edwin Hubble Date: 1. was born on November 20, 1889. 2. He graduated from the University of Chicago and served in WWI before settling down
The Death of Stars. Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages ) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars
 The Death of Stars Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages 296-323) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars White dwarfs Roughly the size of the Earth with the mass of
The Death of Stars Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages 296-323) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars White dwarfs Roughly the size of the Earth with the mass of
CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 DIVISION OF THE HUMANITIES AND SOCIAL SCIENCES CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY PASADENA, CALIFORNIA 91125 THE ORIGINS OF NUCLEAR ASTROPHYSICS AT CAL TECH John L. Greenberg and Judith R. Goodstein Paper
DIVISION OF THE HUMANITIES AND SOCIAL SCIENCES CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY PASADENA, CALIFORNIA 91125 THE ORIGINS OF NUCLEAR ASTROPHYSICS AT CAL TECH John L. Greenberg and Judith R. Goodstein Paper
Big Bang Theory PowerPoint
 Big Bang Theory PowerPoint Name: # Period: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Recombination Photon Epoch Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Hadron Epoch Hadron Epoch Quark Epoch The Primordial Era Electroweak Epoch Inflationary Epoch
Big Bang Theory PowerPoint Name: # Period: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Recombination Photon Epoch Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Hadron Epoch Hadron Epoch Quark Epoch The Primordial Era Electroweak Epoch Inflationary Epoch
Lived Alfred Wegener was born on November 1, 1880, in Germany s capital city, Berlin.
 Alfred Wegener Lived 1880 1930. Alfred Wegener proposed the theory of continental drift the idea that Earth s continents move. Despite publishing a large body of compelling fossil and rock evidence for
Alfred Wegener Lived 1880 1930. Alfred Wegener proposed the theory of continental drift the idea that Earth s continents move. Despite publishing a large body of compelling fossil and rock evidence for
PHYSICS 107. Lecture 27 What s Next?
 PHYSICS 107 Lecture 27 What s Next? The origin of the elements Apart from the expansion of the universe and the cosmic microwave background radiation, the Big Bang theory makes another important set of
PHYSICS 107 Lecture 27 What s Next? The origin of the elements Apart from the expansion of the universe and the cosmic microwave background radiation, the Big Bang theory makes another important set of
How to Build a Habitable Planet Summary. Chapter 1 The Setting
 How to Build a Habitable Planet Summary Chapter 1 The Setting The universe as we know it began about 15 billion years ago with an explosion that is called the big bang. There is no record of any prior
How to Build a Habitable Planet Summary Chapter 1 The Setting The universe as we know it began about 15 billion years ago with an explosion that is called the big bang. There is no record of any prior
Stellar Evolution. The lives of low-mass stars. And the lives of massive stars
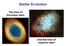 Stellar Evolution The lives of low-mass stars And the lives of massive stars Stars of High Mass High mass stars fuse H He, but do so in a different reaction: the CNO cycle Carbon is a catalyst, speeding
Stellar Evolution The lives of low-mass stars And the lives of massive stars Stars of High Mass High mass stars fuse H He, but do so in a different reaction: the CNO cycle Carbon is a catalyst, speeding
Unit 2: Atomic Theory Notes
 Unit 2: Atomic Theory Notes The changing of a substance into one or more new substances is known as a chemical reaction. Law of conservation of mass: mass is neither created nor destroyed during ordinary
Unit 2: Atomic Theory Notes The changing of a substance into one or more new substances is known as a chemical reaction. Law of conservation of mass: mass is neither created nor destroyed during ordinary
JJ Thomson Group 2 1. What are cathode rays? Cathode rays are a stream of electrons following through vacuum tube. Electrons
 Dalton Group 1 1. What did Democritus say about the atom? Democritus asked whether it is possible to divide a sample of matter forever into smaller and smaller pieces. After much thought, he concluded
Dalton Group 1 1. What did Democritus say about the atom? Democritus asked whether it is possible to divide a sample of matter forever into smaller and smaller pieces. After much thought, he concluded
FXA Candidates should be able to :
 1 Candidates should be able to : MATTER AND ANTIMATTER Explain that since protons and neutrons contain charged constituents called quarks, they are therefore, not fundamental particles. Every particle
1 Candidates should be able to : MATTER AND ANTIMATTER Explain that since protons and neutrons contain charged constituents called quarks, they are therefore, not fundamental particles. Every particle
The Enrico Fermi exhibition as museum prototype: experience and prospects
 The Enrico Fermi exhibition as museum prototype: experience and prospects L. Cifarelli & R. Nania The Centro Fermi in Rome A brief biography of E. Fermi The exhibition in Genova and Bologna Ideas for the
The Enrico Fermi exhibition as museum prototype: experience and prospects L. Cifarelli & R. Nania The Centro Fermi in Rome A brief biography of E. Fermi The exhibition in Genova and Bologna Ideas for the
The Search for a Fundamental Theory of the Universe
 The Search for a Fundamental Theory of the Universe Lecture 1- History & basic concepts, including Newton, Maxwell, Einstein & Quantum Mechanics Lecture 2 - Where are we now? General relativity & the Standard
The Search for a Fundamental Theory of the Universe Lecture 1- History & basic concepts, including Newton, Maxwell, Einstein & Quantum Mechanics Lecture 2 - Where are we now? General relativity & the Standard
University of California High-Performance AstroComputing Center JOEL PRIMACK UCSC
 University of California High-Performance AstroComputing Center JOEL PRIMACK UCSC http://hipacc.ucsc.edu/ As computing and observational power continue to increase rapidly, the most difficult problems
University of California High-Performance AstroComputing Center JOEL PRIMACK UCSC http://hipacc.ucsc.edu/ As computing and observational power continue to increase rapidly, the most difficult problems
Light Quantum Hypothesis
 50 My God, He Plays Dice! Light Quantum Hypothesis Light Quantum Hypothesis 51 Light Quantum Hypothesis In his miracle year of 1905, Einstein wrote four extraordinary papers, one of which won him the 1921
50 My God, He Plays Dice! Light Quantum Hypothesis Light Quantum Hypothesis 51 Light Quantum Hypothesis In his miracle year of 1905, Einstein wrote four extraordinary papers, one of which won him the 1921
A Universe Filled with Questions
 Volume 19 Issue 1 Spring 2010 Illinois Wesleyan University Magazine Article 2 2010 A Universe Filled with Questions Tim Obermiller Illinois Wesleyan University, iwumag@iwu.edu Recommended Citation Obermiller,
Volume 19 Issue 1 Spring 2010 Illinois Wesleyan University Magazine Article 2 2010 A Universe Filled with Questions Tim Obermiller Illinois Wesleyan University, iwumag@iwu.edu Recommended Citation Obermiller,
Quantum Theory. The most accurate and complete description of physical reality
 Quantum Theory The most accurate and complete description of physical reality Originating 1900 to 1930 and still under active development Set of ideas Scientist use to study microscopic world Nature is
Quantum Theory The most accurate and complete description of physical reality Originating 1900 to 1930 and still under active development Set of ideas Scientist use to study microscopic world Nature is
GRAVITATIONAL COLLAPSE
 GRAVITATIONAL COLLAPSE Landau and Chandrasekhar first realised the importance of General Relativity for Stars (1930). If we increase their mass and/or density, the effects of gravitation become increasingly
GRAVITATIONAL COLLAPSE Landau and Chandrasekhar first realised the importance of General Relativity for Stars (1930). If we increase their mass and/or density, the effects of gravitation become increasingly
Olbers Paradox. Why is the sky dark? Possible answers:
 Olbers Paradox Why is the sky dark? If the universe were infinitely big and infinitely old, there should be no dark patches in the sky (Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers (1757-- 1840) ) Possible answers: Dust? No,
Olbers Paradox Why is the sky dark? If the universe were infinitely big and infinitely old, there should be no dark patches in the sky (Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers (1757-- 1840) ) Possible answers: Dust? No,
Chapter 26: Cosmology
 Chapter 26: Cosmology Cosmology means the study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe as a whole. First of all, we need to know whether the universe has changed with time, or if it has
Chapter 26: Cosmology Cosmology means the study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe as a whole. First of all, we need to know whether the universe has changed with time, or if it has
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE
 Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
The Beginning of the Nuclear Age
 Questions 1. Otto Hahn received the 1945 Nobel prize for the experimental discovery of fission. His former colleague Lise Meitner, who explained the phenomenon did not. Do you consider that a fair decision
Questions 1. Otto Hahn received the 1945 Nobel prize for the experimental discovery of fission. His former colleague Lise Meitner, who explained the phenomenon did not. Do you consider that a fair decision
Chapter 16 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Star Birth Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Star Birth The dust and gas between the star in our galaxy is referred to as the Interstellar medium (ISM).
Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Star Birth The dust and gas between the star in our galaxy is referred to as the Interstellar medium (ISM).
Ryan Stillwell Paper: /10/2014. Neutrino Astronomy. A hidden universe. Prepared by: Ryan Stillwell. Tutor: Patrick Bowman
 Neutrino Astronomy A hidden universe Prepared by: Ryan Stillwell Tutor: Patrick Bowman Paper: 124.129 Date: 10 October 2014 i Table of Contents 1. Introduction pg 1 1.1 Background pg 1 2. Findings & Discussion
Neutrino Astronomy A hidden universe Prepared by: Ryan Stillwell Tutor: Patrick Bowman Paper: 124.129 Date: 10 October 2014 i Table of Contents 1. Introduction pg 1 1.1 Background pg 1 2. Findings & Discussion
The Big Bang Theory. Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra
 The Big Bang Theory Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra Theories from Before the Big Bang came from a black hole from another universe? our universe is part of a multiverse? just random particles? The Big
The Big Bang Theory Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra Theories from Before the Big Bang came from a black hole from another universe? our universe is part of a multiverse? just random particles? The Big
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens
 Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Beyond Our Solar System Earth Science, 13e Chapter 24 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Properties of stars Distance Distances to the stars are very
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Beyond Our Solar System Earth Science, 13e Chapter 24 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Properties of stars Distance Distances to the stars are very
5) Which stage lasts the longest? a) viii b) I c) iv d) iii e) vi
 1) Which of the following statements about globular clusters is false? a) Globular cluster stars are very metal- poor relative to the Sun. b) Globular cluster stars are more than 12 billion years old.
1) Which of the following statements about globular clusters is false? a) Globular cluster stars are very metal- poor relative to the Sun. b) Globular cluster stars are more than 12 billion years old.
AN OVERVIEW OF LIGO Adapted from material developed by Brock Wells Robert L. Olds Junior High School, Connell, WA August 2001
 AN OVERVIEW OF LIGO Adapted from material developed by Brock Wells Robert L. Olds Junior High School, Connell, WA August 2001 The purpose of this guide is to provide background about the LIGO project at
AN OVERVIEW OF LIGO Adapted from material developed by Brock Wells Robert L. Olds Junior High School, Connell, WA August 2001 The purpose of this guide is to provide background about the LIGO project at
Lecture 14: Einstein & The Expanding Universe
 Lecture 14: Einstein & The Expanding Universe As with all course material (including homework, exams), these lecture notes are not be reproduced, redistributed, or sold in any form. From Lecture 13: Hubble
Lecture 14: Einstein & The Expanding Universe As with all course material (including homework, exams), these lecture notes are not be reproduced, redistributed, or sold in any form. From Lecture 13: Hubble
Wolfgang Pauli. From the beginning, education and science were prominent pieces of Wolfgang s life; with
 2011-2012 School year 5 th 6 weeks Darius Ajabshir Mr. Smith PIB Physics 1 28 November 2011 Wolfgang Pauli On April 25 th 1900, Wolfgang Pauli was born to Wolfgang Pauli Sr. and Bertha Schütz. From the
2011-2012 School year 5 th 6 weeks Darius Ajabshir Mr. Smith PIB Physics 1 28 November 2011 Wolfgang Pauli On April 25 th 1900, Wolfgang Pauli was born to Wolfgang Pauli Sr. and Bertha Schütz. From the
Laboratory for Nuclear Science
 The Laboratory for Nuclear Science (LNS) provides support for research by faculty and research staff members in the fields of particle, nuclear, and theoretical plasma physics. This includes activities
The Laboratory for Nuclear Science (LNS) provides support for research by faculty and research staff members in the fields of particle, nuclear, and theoretical plasma physics. This includes activities
The summer before my junior year, I went to attend the Secondary Student Training
 Personal Section The summer before my junior year, I went to attend the Secondary Student Training Program at the University of Iowa. There, I interned for Professor Ugur Akgun to simulate the unfolding
Personal Section The summer before my junior year, I went to attend the Secondary Student Training Program at the University of Iowa. There, I interned for Professor Ugur Akgun to simulate the unfolding
UNVEILING THE ULTIMATE LAWS OF NATURE: DARK MATTER, SUPERSYMMETRY, AND THE LHC. Gordon Kane, Michigan Center for Theoretical Physics Warsaw, June 2009
 UNVEILING THE ULTIMATE LAWS OF NATURE: DARK MATTER, SUPERSYMMETRY, AND THE LHC Gordon Kane, Michigan Center for Theoretical Physics Warsaw, June 2009 OUTLINE! Some things we ve learned about the physical
UNVEILING THE ULTIMATE LAWS OF NATURE: DARK MATTER, SUPERSYMMETRY, AND THE LHC Gordon Kane, Michigan Center for Theoretical Physics Warsaw, June 2009 OUTLINE! Some things we ve learned about the physical
Gamma-Ray Astronomy. Astro 129: Chapter 1a
 Gamma-Ray Bursts Gamma-Ray Astronomy Gamma rays are photons with energies > 100 kev and are produced by sub-atomic particle interactions. They are absorbed by our atmosphere making observations from satellites
Gamma-Ray Bursts Gamma-Ray Astronomy Gamma rays are photons with energies > 100 kev and are produced by sub-atomic particle interactions. They are absorbed by our atmosphere making observations from satellites
STELLAR DEATH, AND OTHER THINGS THAT GO BOOM IN THE NIGHT. Kevin Moore - UCSB
 STELLAR DEATH, AND OTHER THINGS THAT GO BOOM IN THE NIGHT Kevin Moore - UCSB Overview Stellar evolution basics! Fates of stars related to their mass! Mass transfer adds many possibilities Historical supernovae
STELLAR DEATH, AND OTHER THINGS THAT GO BOOM IN THE NIGHT Kevin Moore - UCSB Overview Stellar evolution basics! Fates of stars related to their mass! Mass transfer adds many possibilities Historical supernovae
PHYS1118 Astronomy II
 PHYS1118 Astronomy II Course Description: This course is designed for non-science students. A study of astronomy as related to humans and society. Topics include elements of Newtonian physics, Relativity,
PHYS1118 Astronomy II Course Description: This course is designed for non-science students. A study of astronomy as related to humans and society. Topics include elements of Newtonian physics, Relativity,
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System 25.1 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System 25.1 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical
Marie and Pierre Curie. In 1903, the Nobel Prize was awarded to Marie and Pierre Curie for their work
 Molly Hellier Period 1 January 24,2011 Extra Credit Paper Marie and Pierre Curie In 1903, the Nobel Prize was awarded to Marie and Pierre Curie for their work with radiation. The couple made great strides
Molly Hellier Period 1 January 24,2011 Extra Credit Paper Marie and Pierre Curie In 1903, the Nobel Prize was awarded to Marie and Pierre Curie for their work with radiation. The couple made great strides
Einstein s Theory Relativistic 0 < v < c. No Absolute Time. Quantization, Zero point energy position & momentum obey Heisenberg uncertainity rule
 Lecture: March 27, 2019 Classical Mechanics Particle is described by position & velocity Quantum Mechanics Particle is described by wave function Probabilistic description Newton s equation non-relativistic
Lecture: March 27, 2019 Classical Mechanics Particle is described by position & velocity Quantum Mechanics Particle is described by wave function Probabilistic description Newton s equation non-relativistic
Dark Energy and Dark Matter
 Dark Energy and Dark Matter Attendance Quiz Are you here today? (a) yes (b) no Here! (c) The Dark Lord wants his ring back! Final Exam The final exam is Thursday, 6/8, from 11:30am to 1:30pm (2 hours),
Dark Energy and Dark Matter Attendance Quiz Are you here today? (a) yes (b) no Here! (c) The Dark Lord wants his ring back! Final Exam The final exam is Thursday, 6/8, from 11:30am to 1:30pm (2 hours),
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 10, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 10, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Before the term black hole was coined in 1967, these
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 10, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Before the term black hole was coined in 1967, these
NSDL/NSTA Web Seminar: Celebrating Astronomy: A Star s Story
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP NSDL/NSTA Web Seminar: Celebrating Astronomy: A Star s Story Thursday, September 25, 2008 6:30 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. Eastern time Agenda: 1. Introductions 2. Tech-help
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP NSDL/NSTA Web Seminar: Celebrating Astronomy: A Star s Story Thursday, September 25, 2008 6:30 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. Eastern time Agenda: 1. Introductions 2. Tech-help
John Ellis King s College London (& CERN) Welcome! Introduction to CERN. CERN: Accelerating Science and Innovation
 Welcome! John Ellis King s College London (& CERN) Introduction to CERN CERN: Accelerating Science and Innovation The Mission of CERN Push back the frontiers of knowledge E.g. the secrets of the Big Bang
Welcome! John Ellis King s College London (& CERN) Introduction to CERN CERN: Accelerating Science and Innovation The Mission of CERN Push back the frontiers of knowledge E.g. the secrets of the Big Bang
v = H o d Hubble s Law: Distant galaxies move away fastest Velocity (v) is proportional to Distance (d):
 Hubble s Law: Distant galaxies move away fastest Velocity (v) is proportional to Distance (d): v = H o d The Hubble Constant was measured after decades of observation: H 0 = 70 km/s/mpc Velocity (km/s)
Hubble s Law: Distant galaxies move away fastest Velocity (v) is proportional to Distance (d): v = H o d The Hubble Constant was measured after decades of observation: H 0 = 70 km/s/mpc Velocity (km/s)
Death of stars is based on. one thing mass.
 Death of stars is based on one thing mass. Not the mass they have when born, but the mass they have when they die. Star Death for mass 1.4 solar masses and less. These stars started big 7.5-10 solar masses.
Death of stars is based on one thing mass. Not the mass they have when born, but the mass they have when they die. Star Death for mass 1.4 solar masses and less. These stars started big 7.5-10 solar masses.
Comparing a Supergiant to the Sun
 The Lifetime of Stars Once a star has reached the main sequence stage of it life, it derives its energy from the fusion of hydrogen to helium Stars remain on the main sequence for a long time and most
The Lifetime of Stars Once a star has reached the main sequence stage of it life, it derives its energy from the fusion of hydrogen to helium Stars remain on the main sequence for a long time and most
If classical physics is wrong, why do we still use it?
 If classical physics is wrong, why do we still use it? Introduction The word quantum came from the Latin word which means "how great" or "how much." In quantum mechanics, it refers to a discrete unit that
If classical physics is wrong, why do we still use it? Introduction The word quantum came from the Latin word which means "how great" or "how much." In quantum mechanics, it refers to a discrete unit that
Lecture 25: Cosmology: The end of the Universe, Dark Matter, and Dark Energy. Astronomy 111 Wednesday November 29, 2017
 Lecture 25: Cosmology: The end of the Universe, Dark Matter, and Dark Energy Astronomy 111 Wednesday November 29, 2017 Reminders Online homework #11 due Monday at 3pm One more lecture after today Monday
Lecture 25: Cosmology: The end of the Universe, Dark Matter, and Dark Energy Astronomy 111 Wednesday November 29, 2017 Reminders Online homework #11 due Monday at 3pm One more lecture after today Monday
Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Chapter 29 THE UNIVERSE
 Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Constellations are groups of stars named over antiquity. A familiar constellation is Ursa Major, the Great Bear. Chapter 29 THE UNIVERSE The monthly
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Constellations are groups of stars named over antiquity. A familiar constellation is Ursa Major, the Great Bear. Chapter 29 THE UNIVERSE The monthly
ASTRO 114 Lecture Okay. We re now gonna continue discussing and conclude discussing the entire
 ASTRO 114 Lecture 55 1 Okay. We re now gonna continue discussing and conclude discussing the entire universe. So today we re gonna learn about everything, everything that we know of. There s still a lot
ASTRO 114 Lecture 55 1 Okay. We re now gonna continue discussing and conclude discussing the entire universe. So today we re gonna learn about everything, everything that we know of. There s still a lot
Properties of Stars. Characteristics of Stars
 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical characters. The sky contains 88 constellations. Star Color and Temperature Color
Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical characters. The sky contains 88 constellations. Star Color and Temperature Color
 Physics The study of the energy, matter, and forces in the Universe Why do stars move in the sky? How can heat be changed into electricity? What is the difference between an atom of one substance and an
Physics The study of the energy, matter, and forces in the Universe Why do stars move in the sky? How can heat be changed into electricity? What is the difference between an atom of one substance and an
1. Convective throughout deliver heat from core to surface purely by convection.
 6/30 Post Main Sequence Evolution: Low-Mass Stars 1. Convective throughout deliver heat from core to surface purely by convection. 2. Convection mixes the material of the star is the material carries the
6/30 Post Main Sequence Evolution: Low-Mass Stars 1. Convective throughout deliver heat from core to surface purely by convection. 2. Convection mixes the material of the star is the material carries the
Neutron Stars. We now know that SN 1054 was a Type II supernova that ended the life of a massive star and left behind a neutron star.
 Neutron Stars Neutron Stars The emission from the supernova that produced the crab nebula was observed in 1054 AD by Chinese, Japanese, Native Americans, and Persian/Arab astronomers as being bright enough
Neutron Stars Neutron Stars The emission from the supernova that produced the crab nebula was observed in 1054 AD by Chinese, Japanese, Native Americans, and Persian/Arab astronomers as being bright enough
MODERN ASTROPHYSICS PCES 4.55
 MODERN ASTROPHYSICS PCES 4.55 The 20 th century brought an appreciation of the colossal scale of the universe, and an explanation of how it all worked. The understanding of the stars came from nuclear
MODERN ASTROPHYSICS PCES 4.55 The 20 th century brought an appreciation of the colossal scale of the universe, and an explanation of how it all worked. The understanding of the stars came from nuclear
Stars Star birth and kinds Elemental furnaces Star death and heavy elements
 Stars Star birth and kinds Elemental furnaces Star death and heavy elements Matter was not uniformly distributed as the universe expanded after the Big Bang. This lumpy universe coalesced under the force
Stars Star birth and kinds Elemental furnaces Star death and heavy elements Matter was not uniformly distributed as the universe expanded after the Big Bang. This lumpy universe coalesced under the force
According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a. Chapter 34: Cosmology. Cosmology: How the Universe Works
 Chapter 34: Cosmology According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a a) Cloud of hydrogen gas b) Protostar c) Neutron star d) Black hole e) White dwarf id you
Chapter 34: Cosmology According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a a) Cloud of hydrogen gas b) Protostar c) Neutron star d) Black hole e) White dwarf id you
Complete Cosmos Chapter 24: Big Bang, Big Crunch Outline Sub-chapters
 Complete Cosmos Chapter 24: Big Bang, Big Crunch Theory of the Big Bang. From that cataclysmic explosion, the Universe continues to expand. But will it stop and reverse? Outline How did the Universe begin?
Complete Cosmos Chapter 24: Big Bang, Big Crunch Theory of the Big Bang. From that cataclysmic explosion, the Universe continues to expand. But will it stop and reverse? Outline How did the Universe begin?
11/1/16. Important Stuff (Section 001: 9:45 am) Important Stuff (Section 002, 1:00 pm) 14.1 White Dwarfs. Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard
 Important Stuff (Section 001: 9:45 am) The Second Midterm is Thursday, November 10 The Second Midterm will be given in a different room: Willey 175 Bring 2 pencils and a photo-id. In accordance with the
Important Stuff (Section 001: 9:45 am) The Second Midterm is Thursday, November 10 The Second Midterm will be given in a different room: Willey 175 Bring 2 pencils and a photo-id. In accordance with the
Carl David Anderson ( )
 Carl David Anderson (1905-1991) Carl David Anderson was born on September 3 rd, 1905, in New York City. At the age of 7, his family moved to Los Angeles where he attended public school. Shortly after the
Carl David Anderson (1905-1991) Carl David Anderson was born on September 3 rd, 1905, in New York City. At the age of 7, his family moved to Los Angeles where he attended public school. Shortly after the
Astronomy Ch. 21 Stellar Explosions. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 21 Stellar Explosions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A surface explosion on a white dwarf, caused
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 21 Stellar Explosions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A surface explosion on a white dwarf, caused
Light. Transverse electromagnetic wave, or electromagnetic radiation. Includes radio waves, microwaves, infra-red, visible, UV, X-rays, and gamma rays
 Light Transverse electromagnetic wave, or electromagnetic radiation Includes radio waves, microwaves, infra-red, visible, UV, X-rays, and gamma rays The type of light is determined purely by wavelength.
Light Transverse electromagnetic wave, or electromagnetic radiation Includes radio waves, microwaves, infra-red, visible, UV, X-rays, and gamma rays The type of light is determined purely by wavelength.
11/1/17. Important Stuff (Section 001: 9:45 am) Important Stuff (Section 002, 1:00 pm) 14.1 White Dwarfs. Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard
 11/1/17 Important Stuff (Section 001: 9:45 am) The Second Midterm is Thursday, November 9 The Second Midterm will be given in a different room: Willey 175 Bring 2 pencils and a photo-id. In accordance
11/1/17 Important Stuff (Section 001: 9:45 am) The Second Midterm is Thursday, November 9 The Second Midterm will be given in a different room: Willey 175 Bring 2 pencils and a photo-id. In accordance
Finding the Higgs. Facts And Mysteries In Elementary Particle Physics Downloaded from
 285 10 Finding the Higgs The Standard Model has been very successful. All the detailed couplings and particles needed for the cancellations between the diagrams have been found, and the more complicated
285 10 Finding the Higgs The Standard Model has been very successful. All the detailed couplings and particles needed for the cancellations between the diagrams have been found, and the more complicated
PHY1033C/HIS3931/IDH 3931 : Discovering Physics: The Universe and Humanity s Place in It Fall 2016
 PHY1033C/HIS3931/IDH 3931 : Discovering Physics: The Universe and Humanity s Place in It Fall 2016 Online evaluations open Announcements Final Exam Thursday, 15 December, 10am - 12, noon In-class NPB 1002
PHY1033C/HIS3931/IDH 3931 : Discovering Physics: The Universe and Humanity s Place in It Fall 2016 Online evaluations open Announcements Final Exam Thursday, 15 December, 10am - 12, noon In-class NPB 1002
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES
 SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
Beyond the Solar System 2006 Oct 17 Page 1 of 5
 I. Stars have color, brightness, mass, temperature and size. II. Distances to stars are measured using stellar parallax a. The further away, the less offset b. Parallax angles are extremely small c. Measured
I. Stars have color, brightness, mass, temperature and size. II. Distances to stars are measured using stellar parallax a. The further away, the less offset b. Parallax angles are extremely small c. Measured
Era of Atoms 5/3/18. Our Schedule and Topics
 5/3/18 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Cosmic Web Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 30 Thur 3 May 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Our Schedule and Topics Final Exam on Wed May
5/3/18 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Cosmic Web Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 30 Thur 3 May 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Our Schedule and Topics Final Exam on Wed May
The Big Bang. Mr. Mike Partridge Earth & Space Science J.H. Reagan High School, Houston, TX
 The Big Bang Mr. Mike Partridge Earth & Space Science J.H. Reagan High School, Houston, TX Notes Outlines Theories of the Universe Static Universe What is the Big Bang Theory What is the evidence supporting
The Big Bang Mr. Mike Partridge Earth & Space Science J.H. Reagan High School, Houston, TX Notes Outlines Theories of the Universe Static Universe What is the Big Bang Theory What is the evidence supporting
Introduction to me, High-Energy Physics and research at Belle
 Introduction to me, High-Energy Physics and research at Belle Jan Schümann Belle Collaboration Tsukuba, Japan Where I come from: Europe Germany Henstedt-Ulzburg... small village of 25.000 citizens My village...
Introduction to me, High-Energy Physics and research at Belle Jan Schümann Belle Collaboration Tsukuba, Japan Where I come from: Europe Germany Henstedt-Ulzburg... small village of 25.000 citizens My village...
W. M. KECK OBSERVATORY AWARDED NSF GRANT TO DEVELOP NEXT-GENERATION ADAPTIVE OPTICS SYSTEM
 Media Contact Mari-Ela Chock Telephone (808) 881-3827 Cell (808) 554-0567 Email mchock@keck.hawaii.edu Website www.keckobservatory.org FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE October 4, 2018 W. M. KECK OBSERVATORY AWARDED
Media Contact Mari-Ela Chock Telephone (808) 881-3827 Cell (808) 554-0567 Email mchock@keck.hawaii.edu Website www.keckobservatory.org FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE October 4, 2018 W. M. KECK OBSERVATORY AWARDED
Chapter 18 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 18 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning: What is a white dwarf? What can happen to
Chapter 18 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning: What is a white dwarf? What can happen to
Catching waves with Kip Thorne
 1997 2009, Millennium Mathematics Project, University of Cambridge. Permission is granted to print and copy this page on paper for non commercial use. For other uses, including electronic redistribution,
1997 2009, Millennium Mathematics Project, University of Cambridge. Permission is granted to print and copy this page on paper for non commercial use. For other uses, including electronic redistribution,
Test Natural Sciences 102 Section 8 noon --- VERSION A February 28, 2007
 Correct responses indicated in boldface. 1. An astronomer is designing a new telescope to use in space. The Hubble Space Telescope operates at wavelengths close to 500nm ( 1nm = 10-9 meter). The new telescope
Correct responses indicated in boldface. 1. An astronomer is designing a new telescope to use in space. The Hubble Space Telescope operates at wavelengths close to 500nm ( 1nm = 10-9 meter). The new telescope
News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons
 www.breaking News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons 1,000 IDEAS & ACTIVITIES FOR LANGUAGE TEACHERS The Breaking News English.com Resource Book http://www.breakingnewsenglish.com/book.html NASA
www.breaking News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons 1,000 IDEAS & ACTIVITIES FOR LANGUAGE TEACHERS The Breaking News English.com Resource Book http://www.breakingnewsenglish.com/book.html NASA
chapter 31 Stars and Galaxies
 chapter 31 Stars and Galaxies Day 1:Technology and the Big Bang Studying the Stars A. Telescopes - Electromagnetic radiation emitted by stars and other objects include light, radio, and X-ray Space telescopes
chapter 31 Stars and Galaxies Day 1:Technology and the Big Bang Studying the Stars A. Telescopes - Electromagnetic radiation emitted by stars and other objects include light, radio, and X-ray Space telescopes
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe Chapter Wrap-Up What makes up the universe and how does
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe Chapter Wrap-Up What makes up the universe and how does
How do we measure properties of a star? Today. Some Clicker Questions - #1. Some Clicker Questions - #1
 Today Announcements: HW#8 due Friday 4/9 at 8:00 am. The size of the Universe (It s expanding!) The Big Bang Video on the Big Bang NOTE: I will take several questions on exam 3 and the final from the videos
Today Announcements: HW#8 due Friday 4/9 at 8:00 am. The size of the Universe (It s expanding!) The Big Bang Video on the Big Bang NOTE: I will take several questions on exam 3 and the final from the videos
White dwarfs are the remaining cores of dead stars. Electron degeneracy pressure supports them against the crush of gravity. The White Dwarf Limit
 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Chapter 18 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning: What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? Seventh
The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Chapter 18 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning: What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? Seventh
PHY138Y Nuclear and Radiation
 PHY138Y Nuclear and Radiation Professor Tony Key MP401 key@physics.utoronto.ca You can hear Tom Lehrer s Elements at http://www.privatehand.com/flash/elements.html Van Kranendonk Prize for an Outstanding
PHY138Y Nuclear and Radiation Professor Tony Key MP401 key@physics.utoronto.ca You can hear Tom Lehrer s Elements at http://www.privatehand.com/flash/elements.html Van Kranendonk Prize for an Outstanding
Unravelling the Mysteries of Matter with the CERN Large Hadron Collider An Introduction/Overview of Particle Physics
 Unravelling the Mysteries of Matter with the CERN Large Hadron Collider An Introduction/Overview of Particle Physics Introductory Lecture August 3rd 2014 International Centre for Theoretical Physics and
Unravelling the Mysteries of Matter with the CERN Large Hadron Collider An Introduction/Overview of Particle Physics Introductory Lecture August 3rd 2014 International Centre for Theoretical Physics and
