Semiconductor light sources Outline
|
|
|
- Godwin Wood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Light soures Semiondutor light soures Outline Thermal (blakbody) radiation Light / matter interations & LEDs Lasers Robert R. MLeod, University of Colorado Pedrotti 3, Chapter 6 3
2 Blakbody light Blakbody soures Ideal inoherent soures Radiate energy, but unless T > 700 o K, emit very little visible radiation and thus appear blak. Plank s explanation of the blakbody spetrum in 900 was the beginning of the development of quantum mehanis. The radiane of a blakbody, L, does not depend on angle, and they are thus ideal Lambertian soures. 3 h 3 L W/m /Sr 5 h λkt λ e b λ Max, b µ T E σt 4 ( ) [ ] [ m K] W -8 W [ ], σ [ 4 ] m m K Plank s equation Wein s displaement law Stephan-Boltzman law for total emittane T7000 o K, λ Max.44 µm T5500 o K, λ Max.57 µm T4500 o K, λ Max.645 µm The surfae of the sun is roughly 5500 o K and radiates in the green. Humans at body temperature radiate in the infrared at about 9.5 µm. Robert R. MLeod, University of Colorado 4
3 Light / matter interation Interation of photons and matter aka Einstein oeffiients (Stimulated) absorption Photon inident, eletron in low energy state E E photon hν R St.Abs. B ( ν ) g E I N Photon absorbed, eletron in higher energy state, E E -E ~ h ν E E Simulated emission Photon inident, eletron in high energy state E E photon hν R St.Em. B ( ν ) g I N Photon emitted, eletron in low energy state. New photon idential to inident. E E E Spontaneous emission R Sp.Em. [ A ] N NO photon inident, eletron in high energy state Note: no I on right Photon emitted, eletron in low energy state. New photon diretion random. E E E E Robert R. MLeod, University of Colorado 5
4 Light / matter interation Appliation to light generation The rate onstant for stimulated emission and absorption are equal B B. Therefore, the relative rates of the two proesses is given by the population of the two states R R St.Em. St.Abs. B B ( ν ) g g I ( ν ) N In thermal equilibrium ( normal onditions ), the ratio of the population densities is given by their energy differene via the Boltzmann distribution N N I N N ( E E ) ( K T ) B e < So higher energy states are oupied, but less than lower energy states. At room temperature, the thermal energy, K B T ev and the energy of a green photon is E photon h / λ.4 / 0.5 µm.48 ev or N 0-4 N! Thus emission happens, but at a rate << less than absorption. Conlusion: In general, matter absorbs and does not amplify light (probably a good thing). Corollary: If we ould ahieve a population inversion in whih N > N, the opposite would be true. That is, the matter would at as an amplifier. LASER Light Amplifiation via Stimulated Emission of Radiation N In ontrast, an LED reates N in exess of the equilibrium. These exited states radiate via spontaneous emission. 6 Robert R. MLeod, University of Colorado
5 Light / matter interation Fluoresene and phosphoresene Energy diagram blonski/lightandolor/index.html Intersystem rossing Singlet Absorption Emission Absorption Emission Triplet Spin states Singlet ground Singlet exited Triplet exited Fluoresene spetra & mirosopy appliation niques/fluoresene/anatomy/fluoromir oanatomy.html Robert R. MLeod, University of Colorado 7
6 Light / matter interation LEDs Simplified juntion struture Lensed pakage Output is from juntion is ~isotropi. Only fration of photons not trapped by total internal refletion an esape. Enapsulant and lens is often inluded in pakage to inrease TIR angle and to onentrate radiation into forward diretion. Bandwih measured in 0 s of nm. By varying material, enter wavelength now ranges from infrared to near ultraviolet. Unpolarized. Can typially be modulated in a few ns. More effiient than inandesent bulbs and possibly fluoresent lamps. Organi LED displays beoming important. Robert R. MLeod, University of Colorado 8
7 Laser Basis of the laser Energy in to reate population inversion Mirror Mirror Filter Transverse modes Photons Gain medium d Effetive avity length in index Gain Cavity gain and loss Cavity longitudinal modes Filter transmission ( N ) ( N ) ( ) d Bandwih of rounrip gain d N d d Loss ν [ Hz] Resonant modes require d N λ N / ν Linewih related to avity loss ν [ Hz] Can be periodi and/or polarization sensitive ν [ Hz] Output spetrum Robert R. MLeod, University of Colorado Frequeny quite sensitive to d and thus temperature of avity. ν [ Hz] 9
8 Laser Lasers vs. lamps Spetrum Laser Inandesent lamp Effiieny Wall-plug effiieny is optial power out to eletrial power in. As high as 60% for diode lasers, 30% for diode-pumped solid states. Luminous effiieny is power in visible spetrum / eletrial power in. As low as % for inandesent bulbs. Filters an redue spetral wih but dramatially redue effiieny. Brightness L φ [ W] ( π w [ m] ) M [ ] φ λ ( ) 0 n w rad n M 0 [W/m /Sr] for a perfet W laser at λ um in air. π λ 0 L φ [ W] ( filament area [ m ]) 4π [ Sr] ( ) 0 5 [W/m /Sr] for a bulb with a mm filament emitting W Robert R. MLeod, University of Colorado 0
9 Laser Laser diodes Heterostruture laser diode Transistor outline pakage Output is typially anamorphi (elliptial), astigmati (diff urvature), single transverse mode, multi-longitudinal mode, polarized. Typial output faet x3 µm. Ciruit diagram Photodiode integrated into pakage for power monitoring and feedbak ontrol. Thermal ontrol with a thermo-eletri (Peltier) ooler is also ommon. Robert R. MLeod, University of Colorado
10 Laser Typial red LD spes Temperamental beasts Threshold urrent gain has overome loss in the avity and the devie is operating as a laser, not an LED. Varies between and within models. Max rated power faet (mirror) damage ours above this optial output power. Temperature dependene LDs are less effiient as their temperature inreases. Thus as they hange temperature, the bias urrent must be modified to keep the power onstant (and not blow it up). Range of urrent operation between the threshold and the urrent whih ahieves the max rated power. Both depend on temperature This range an be a small fration (0%) of the threshold urrent How to blow up a LD: Reverse urrent or urrent transients, partiularly during on/off Exessive optial power blows faets. Robert R. MLeod, University of Colorado
Line Radiative Transfer
 http://www.v.nrao.edu/ourse/astr534/ineradxfer.html ine Radiative Transfer Einstein Coeffiients We used armor's equation to estimate the spontaneous emission oeffiients A U for À reombination lines. A
http://www.v.nrao.edu/ourse/astr534/ineradxfer.html ine Radiative Transfer Einstein Coeffiients We used armor's equation to estimate the spontaneous emission oeffiients A U for À reombination lines. A
Physics 486. Classical Newton s laws Motion of bodies described in terms of initial conditions by specifying x(t), v(t).
 Physis 486 Tony M. Liss Leture 1 Why quantum mehanis? Quantum vs. lassial mehanis: Classial Newton s laws Motion of bodies desribed in terms of initial onditions by speifying x(t), v(t). Hugely suessful
Physis 486 Tony M. Liss Leture 1 Why quantum mehanis? Quantum vs. lassial mehanis: Classial Newton s laws Motion of bodies desribed in terms of initial onditions by speifying x(t), v(t). Hugely suessful
Particle Properties of Wave
 1 Chapter-1 Partile Properties o Wave Contains: (Blakbody radiation, photoeletri eet, Compton eet).1: Blakbody radiation A signiiant hint o the ailure o lassial physis arose rom investigations o thermalradiation
1 Chapter-1 Partile Properties o Wave Contains: (Blakbody radiation, photoeletri eet, Compton eet).1: Blakbody radiation A signiiant hint o the ailure o lassial physis arose rom investigations o thermalradiation
Introduction to Quantum Chemistry
 Chem. 140B Dr. J.A. Mak Introdution to Quantum Chemistry Without Quantum Mehanis, how would you explain: Periodi trends in properties of the elements Struture of ompounds e.g. Tetrahedral arbon in ethane,
Chem. 140B Dr. J.A. Mak Introdution to Quantum Chemistry Without Quantum Mehanis, how would you explain: Periodi trends in properties of the elements Struture of ompounds e.g. Tetrahedral arbon in ethane,
Blackbody radiation and Plank s law
 lakbody radiation and Plank s law blakbody problem: alulating the intensity o radiation at a given wavelength emitted by a body at a speii temperature Max Plank, 900 quantization o energy o radiation-emitting
lakbody radiation and Plank s law blakbody problem: alulating the intensity o radiation at a given wavelength emitted by a body at a speii temperature Max Plank, 900 quantization o energy o radiation-emitting
Class XII - Physics Electromagnetic Waves Chapter-wise Problems
 Class XII - Physis Eletromagneti Waves Chapter-wise Problems Multiple Choie Question :- 8 One requires ev of energy to dissoiate a arbon monoxide moleule into arbon and oxygen atoms The minimum frequeny
Class XII - Physis Eletromagneti Waves Chapter-wise Problems Multiple Choie Question :- 8 One requires ev of energy to dissoiate a arbon monoxide moleule into arbon and oxygen atoms The minimum frequeny
LECTURE 22. Electromagnetic. Spectrum 11/11/15. White Light: A Mixture of Colors (DEMO) White Light: A Mixture of Colors (DEMO)
 LECTURE 22 Eletromagneti Spetrum 2 White Light: A Mixture of Colors (DEMO) White Light: A Mixture of Colors (DEMO) 1. Add together magenta, yan, and yellow. Play with intensities of eah to get white light.
LECTURE 22 Eletromagneti Spetrum 2 White Light: A Mixture of Colors (DEMO) White Light: A Mixture of Colors (DEMO) 1. Add together magenta, yan, and yellow. Play with intensities of eah to get white light.
High Energy Astrophysics
 High Energ Astrophsis Essentials Giampaolo Pisano Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophsis - Uniersit of Manhester giampaolo.pisano@manhester.a.uk - http://www.jb.man.a.uk/~gp/ Februar 01 Essentials - Eletromagneti
High Energ Astrophsis Essentials Giampaolo Pisano Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophsis - Uniersit of Manhester giampaolo.pisano@manhester.a.uk - http://www.jb.man.a.uk/~gp/ Februar 01 Essentials - Eletromagneti
Monte Carlo Simulation of Electron and Radiative Emission from Silicon Diodes
 SIMULATION OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES AND PROCESSES Vol. 4 Edited by W. Fihtner, D. Aemmer - Zurih (Switzerland) September 12-14,1991 - Hartung-Gorre 521 Monte Carlo Simulation of Eletron and Radiative Emission
SIMULATION OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES AND PROCESSES Vol. 4 Edited by W. Fihtner, D. Aemmer - Zurih (Switzerland) September 12-14,1991 - Hartung-Gorre 521 Monte Carlo Simulation of Eletron and Radiative Emission
PID: ToF principle. PID: ToF principle
 16 16 PID: ToF priniple PID: ToF priniple It requires very good time resolution and a suffiient path L Given partiles m 1 and m with veloities β 1 and β : Sine from p = γmv = γmβ and E = γm Given a beam
16 16 PID: ToF priniple PID: ToF priniple It requires very good time resolution and a suffiient path L Given partiles m 1 and m with veloities β 1 and β : Sine from p = γmv = γmβ and E = γm Given a beam
Supplementary Information. Infrared Transparent Visible Opaque Fabrics (ITVOF) for Personal Cooling
 Supplementary Information Infrared Transparent Visible Opaque Fabris (ITVOF) for Personal Cooling Jonathan K. Tong 1,Ɨ, Xiaopeng Huang 1,Ɨ, Svetlana V. Boriskina 1, James Loomis 1, Yanfei Xu 1, and Gang
Supplementary Information Infrared Transparent Visible Opaque Fabris (ITVOF) for Personal Cooling Jonathan K. Tong 1,Ɨ, Xiaopeng Huang 1,Ɨ, Svetlana V. Boriskina 1, James Loomis 1, Yanfei Xu 1, and Gang
Recapitulate. Prof. Shiva Prasad, Department of Physics, IIT Bombay
 18 1 Reapitulate We disussed how light an be thought of onsisting of partiles known as photons. Compton Effet demonstrated that they an be treated as a partile with zero rest mass having nonzero energy
18 1 Reapitulate We disussed how light an be thought of onsisting of partiles known as photons. Compton Effet demonstrated that they an be treated as a partile with zero rest mass having nonzero energy
Part G-4: Sample Exams
 Part G-4: Sample Exams 1 Cairo University M.S.: Eletronis Cooling Faulty of Engineering Final Exam (Sample 1) Mehanial Power Engineering Dept. Time allowed 2 Hours Solve as muh as you an. 1. A heat sink
Part G-4: Sample Exams 1 Cairo University M.S.: Eletronis Cooling Faulty of Engineering Final Exam (Sample 1) Mehanial Power Engineering Dept. Time allowed 2 Hours Solve as muh as you an. 1. A heat sink
THEORETICAL PROBLEM No. 3 WHY ARE STARS SO LARGE?
 THEORETICAL PROBLEM No. 3 WHY ARE STARS SO LARGE? The stars are spheres of hot gas. Most of them shine beause they are fusing hydrogen into helium in their entral parts. In this problem we use onepts of
THEORETICAL PROBLEM No. 3 WHY ARE STARS SO LARGE? The stars are spheres of hot gas. Most of them shine beause they are fusing hydrogen into helium in their entral parts. In this problem we use onepts of
(E B) Rate of Absorption and Stimulated Emission. π 2 E 0 ( ) 2. δ(ω k. p. 59. The rate of absorption induced by the field is. w k
 p. 59 Rate of Absorption and Stimulated Emission The rate of absorption indued by the field is π w k ( ω) ω E 0 ( ) k ˆ µ δω ( k ω) The rate is learly dependent on the strength of the field. The variable
p. 59 Rate of Absorption and Stimulated Emission The rate of absorption indued by the field is π w k ( ω) ω E 0 ( ) k ˆ µ δω ( k ω) The rate is learly dependent on the strength of the field. The variable
Processi di Radiazione e MHD
 Proessi di Radiazione e MHD 0. Overview of elestial bodies and sky at various frequenies 1. Definition of main astrophysial observables. Radiative transfer 3. Blak body radiation 4. basi theory of radiation
Proessi di Radiazione e MHD 0. Overview of elestial bodies and sky at various frequenies 1. Definition of main astrophysial observables. Radiative transfer 3. Blak body radiation 4. basi theory of radiation
 New Methods for Measuring the hermal Emissivity of Semi-transparent and Opaque Materials By D. Demange, M. Bejet, and B. Dufour ONERA - DMSC - Fort de Palaiseau, Chemin de la Hunière 91761 Palaiseau, Frane
New Methods for Measuring the hermal Emissivity of Semi-transparent and Opaque Materials By D. Demange, M. Bejet, and B. Dufour ONERA - DMSC - Fort de Palaiseau, Chemin de la Hunière 91761 Palaiseau, Frane
(Chapter 10) EE 403/503 Introduction to Plasma Processing
 (Chapter 10) EE 403/503 Introdution to Plasma Proessing November 9, 011 Average Eletron Energy, [ev] P = 100 Hz P = 10 KHz P = 1 MHz P = 13.56 MHz P = 100 MHz P =.45 GHz P = 10 GHz P = 1 THz T e,mw > T
(Chapter 10) EE 403/503 Introdution to Plasma Proessing November 9, 011 Average Eletron Energy, [ev] P = 100 Hz P = 10 KHz P = 1 MHz P = 13.56 MHz P = 100 MHz P =.45 GHz P = 10 GHz P = 1 THz T e,mw > T
PHY 108: Optical Physics. Solution to Midterm Test
 PHY 108: Optial Physis Solution to Midterm Test TA: Xun Jia 1 May 14, 2008 1 Email: jiaxun@physis.ula.edu Spring 2008 Physis 108 Xun Jia (May 14, 2008) Problem #1 For a two mirror resonant avity, the resonane
PHY 108: Optial Physis Solution to Midterm Test TA: Xun Jia 1 May 14, 2008 1 Email: jiaxun@physis.ula.edu Spring 2008 Physis 108 Xun Jia (May 14, 2008) Problem #1 For a two mirror resonant avity, the resonane
Phys 2310 Fri. Dec. 12, 2014 Today s Topics. Begin Chapter 13: Lasers Reading for Next Time
 Phys 2310 Fri. Dec. 12, 2014 Today s Topics Begin Chapter 13: Lasers Reading for Next Time 1 Reading this Week By Fri.: Ch. 13 (13.1, 13.3) Lasers, Holography 2 Homework this Week No Homework this chapter.
Phys 2310 Fri. Dec. 12, 2014 Today s Topics Begin Chapter 13: Lasers Reading for Next Time 1 Reading this Week By Fri.: Ch. 13 (13.1, 13.3) Lasers, Holography 2 Homework this Week No Homework this chapter.
Principle Concepts behind IBM Q D. Stancil, Quantum Computing Seminar, 15 Feb 2018
 Priniple Conepts behind IBM Q D. Stanil, Quantum Computing Seminar, 15 Feb 018 V. Bouhiat, et al, Quantum Coherene with a Single Cooper Pair, Physia Sripta, Vol. T76, 165-170 (1998) A. Blais, et al, Cavity
Priniple Conepts behind IBM Q D. Stanil, Quantum Computing Seminar, 15 Feb 018 V. Bouhiat, et al, Quantum Coherene with a Single Cooper Pair, Physia Sripta, Vol. T76, 165-170 (1998) A. Blais, et al, Cavity
Lecture #1: Quantum Mechanics Historical Background Photoelectric Effect. Compton Scattering
 561 Fall 2017 Leture #1 page 1 Leture #1: Quantum Mehanis Historial Bakground Photoeletri Effet Compton Sattering Robert Field Experimental Spetrosopist = Quantum Mahinist TEXTBOOK: Quantum Chemistry,
561 Fall 2017 Leture #1 page 1 Leture #1: Quantum Mehanis Historial Bakground Photoeletri Effet Compton Sattering Robert Field Experimental Spetrosopist = Quantum Mahinist TEXTBOOK: Quantum Chemistry,
Accelerator Physics Particle Acceleration. G. A. Krafft Old Dominion University Jefferson Lab Lecture 4
 Aelerator Physis Partile Aeleration G. A. Krafft Old Dominion University Jefferson Lab Leture 4 Graduate Aelerator Physis Fall 15 Clarifiations from Last Time On Crest, RI 1 RI a 1 1 Pg RL Pg L V Pg RL
Aelerator Physis Partile Aeleration G. A. Krafft Old Dominion University Jefferson Lab Leture 4 Graduate Aelerator Physis Fall 15 Clarifiations from Last Time On Crest, RI 1 RI a 1 1 Pg RL Pg L V Pg RL
BEC-BCS cross-over in the exciton gas
 BEC-BCS ross-over in the exiton gas Monique Combesot Institut des NanoSienes de Paris, CNRS Université Pierre et Marie Curie Evora ot. 2012 1 1)Dilute limit: BEC ondensate of linearly polarized dark exitons
BEC-BCS ross-over in the exiton gas Monique Combesot Institut des NanoSienes de Paris, CNRS Université Pierre et Marie Curie Evora ot. 2012 1 1)Dilute limit: BEC ondensate of linearly polarized dark exitons
Chapter-4 Stimulated emission devices LASERS
 Semiconductor Laser Diodes Chapter-4 Stimulated emission devices LASERS The Road Ahead Lasers Basic Principles Applications Gas Lasers Semiconductor Lasers Semiconductor Lasers in Optical Networks Improvement
Semiconductor Laser Diodes Chapter-4 Stimulated emission devices LASERS The Road Ahead Lasers Basic Principles Applications Gas Lasers Semiconductor Lasers Semiconductor Lasers in Optical Networks Improvement
Theory. Coupled Rooms
 Theory of Coupled Rooms For: nternal only Report No.: R/50/TCR Prepared by:. N. taey B.., MO Otober 00 .00 Objet.. The objet of this doument is present the theory alulations to estimate the reverberant
Theory of Coupled Rooms For: nternal only Report No.: R/50/TCR Prepared by:. N. taey B.., MO Otober 00 .00 Objet.. The objet of this doument is present the theory alulations to estimate the reverberant
Revision checklist SP4 5. SP4 Waves. SP4a Describing waves. SP4b Wave speeds. SP4c Refraction
 SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency, wavelength, amplitude, period and velocity. Describe
SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency, wavelength, amplitude, period and velocity. Describe
Class Test 1 ( ) Subject Code :Applied Physics (17202/17207/17210) Total Marks :25. Model Answer. 3. Photon travels with the speed of light
 Class Test (0-) Sujet Code :Applied Physis (70/707/70) Total Marks :5 Sem. :Seond Model Answer Q Attempt any FOUR of the following 8 a State the properties of photon Ans:.Photon is eletrially neutral.
Class Test (0-) Sujet Code :Applied Physis (70/707/70) Total Marks :5 Sem. :Seond Model Answer Q Attempt any FOUR of the following 8 a State the properties of photon Ans:.Photon is eletrially neutral.
ICPY471. November 20, 2017 Udom Robkob, Physics-MUSC
 ICPY471 19 Laser Physics and Systems November 20, 2017 Udom Robkob, Physics-MUSC Topics Laser light Stimulated emission Population inversion Laser gain Laser threshold Laser systems Laser Light LASER=
ICPY471 19 Laser Physics and Systems November 20, 2017 Udom Robkob, Physics-MUSC Topics Laser light Stimulated emission Population inversion Laser gain Laser threshold Laser systems Laser Light LASER=
Stabilization of the Precision Positioning Stage Working in the Vacuum Environment by Using the Disturbance Observer
 Proeedings of the 4th IIAE International Conferene on Industrial Appliation Engineering 216 Stabilization of the Preision Positioning Stage Working in the Vauum Environment by Using the Disturbane Observer
Proeedings of the 4th IIAE International Conferene on Industrial Appliation Engineering 216 Stabilization of the Preision Positioning Stage Working in the Vauum Environment by Using the Disturbane Observer
Thermal Radiation By: Prof. K M Joshi
 Thermal Radiation By: Prof. K M Joshi Radiation originate due to emission of matter and its subsequent transports does not required any matter / medium. Que: Then what is the nature of this transport???
Thermal Radiation By: Prof. K M Joshi Radiation originate due to emission of matter and its subsequent transports does not required any matter / medium. Que: Then what is the nature of this transport???
SPECTRUM OF THE COMA CLUSTER RADIO HALO SYNCHROTRON RADIATION
 SPECTRUM OF THE COMA CLUSTER RADIO HALO SYNCHROTRON RADIATION OUTLINE OF THE LESSON REMINDER SPECIAL RELATIVITY: BEAMING, RELATIVISTIC LARMOR FORMULA CYCLOTRON EMISSION SYNCHROTRON POWER AND SPECTRUM EMITTED
SPECTRUM OF THE COMA CLUSTER RADIO HALO SYNCHROTRON RADIATION OUTLINE OF THE LESSON REMINDER SPECIAL RELATIVITY: BEAMING, RELATIVISTIC LARMOR FORMULA CYCLOTRON EMISSION SYNCHROTRON POWER AND SPECTRUM EMITTED
Duct Acoustics. Chap.4 Duct Acoustics. Plane wave
 Chap.4 Dut Aoustis Dut Aoustis Plane wave A sound propagation in pipes with different ross-setional area f the wavelength of sound is large in omparison with the diameter of the pipe the sound propagates
Chap.4 Dut Aoustis Dut Aoustis Plane wave A sound propagation in pipes with different ross-setional area f the wavelength of sound is large in omparison with the diameter of the pipe the sound propagates
Heat exchangers: Heat exchanger types:
 Heat exhangers: he proess of heat exhange between two fluids that are at different temperatures and separated by a solid wall ours in many engineering appliations. he devie used to implement this exhange
Heat exhangers: he proess of heat exhange between two fluids that are at different temperatures and separated by a solid wall ours in many engineering appliations. he devie used to implement this exhange
Tutorial 8: Solutions
 Tutorial 8: Solutions 1. * (a) Light from the Sun arrives at the Earth, an average of 1.5 10 11 m away, at the rate 1.4 10 3 Watts/m of area perpendiular to the diretion of the light. Assume that sunlight
Tutorial 8: Solutions 1. * (a) Light from the Sun arrives at the Earth, an average of 1.5 10 11 m away, at the rate 1.4 10 3 Watts/m of area perpendiular to the diretion of the light. Assume that sunlight
PAST YEAR EXAM PAPER SOLUTION SEMESTER II, ACADEMIC YEAR PAP261 Introduction to Lasers (Solution by: Phann Sophearin)
 SPMS Physis Club PAST YEAR EXAM PAPER SOLUTION SEMESTER II, ACADEMIC YEAR 009-0 PAP6 Introdution to Lasers (Solution by: Phann Sophearin) Question (a) - Three basi eleents required: avity, gain, and pup.
SPMS Physis Club PAST YEAR EXAM PAPER SOLUTION SEMESTER II, ACADEMIC YEAR 009-0 PAP6 Introdution to Lasers (Solution by: Phann Sophearin) Question (a) - Three basi eleents required: avity, gain, and pup.
Revision checklist. Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it! Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it!
 SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency,
SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency,
If velocity of A relative to ground = velocity of B relative to ground = the velocity of A relative to B =
 L Physis MC nswers Year:1989 Question Number: 3,0,,4,6,9,30,31,36,40,4 1989MC (3) If eloity of relatie to ground = and eloity of relatie to ground =, then the eloity of relatie to = X X Y Y Suppose that
L Physis MC nswers Year:1989 Question Number: 3,0,,4,6,9,30,31,36,40,4 1989MC (3) If eloity of relatie to ground = and eloity of relatie to ground =, then the eloity of relatie to = X X Y Y Suppose that
MultiPhysics Analysis of Trapped Field in Multi-Layer YBCO Plates
 Exerpt from the Proeedings of the COMSOL Conferene 9 Boston MultiPhysis Analysis of Trapped Field in Multi-Layer YBCO Plates Philippe. Masson Advaned Magnet Lab *7 Main Street, Bldg. #4, Palm Bay, Fl-95,
Exerpt from the Proeedings of the COMSOL Conferene 9 Boston MultiPhysis Analysis of Trapped Field in Multi-Layer YBCO Plates Philippe. Masson Advaned Magnet Lab *7 Main Street, Bldg. #4, Palm Bay, Fl-95,
ATMO/OPTI 656b Spring 2009
 Nomenclature and Definition of Radiation Quantities The various Radiation Quantities are defined in Table 2-1. Keeping them straight is difficult and the meanings may vary from textbook to textbook. I
Nomenclature and Definition of Radiation Quantities The various Radiation Quantities are defined in Table 2-1. Keeping them straight is difficult and the meanings may vary from textbook to textbook. I
What are Lasers? Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation LASER Light emitted at very narrow wavelength bands (monochromatic) Light
 What are Lasers? What are Lasers? Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation LASER Light emitted at very narrow wavelength bands (monochromatic) Light emitted in a directed beam Light is coherenent
What are Lasers? What are Lasers? Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation LASER Light emitted at very narrow wavelength bands (monochromatic) Light emitted in a directed beam Light is coherenent
PHYS2627/PHYS2265 Introductory quantum physics LABORATORYMANUAL Experiment 1: Experiments of Thermal Radiation
 I. Introduction PHYS2627/PHYS2265 Introductory quantum physics 2265-1LABORATORYMANUAL Experiment 1: Experiments of Thermal Radiation The electromagnetic radiation emitted by a body as a result of its temperature
I. Introduction PHYS2627/PHYS2265 Introductory quantum physics 2265-1LABORATORYMANUAL Experiment 1: Experiments of Thermal Radiation The electromagnetic radiation emitted by a body as a result of its temperature
Physics of Relaxation. Outline
 Physis of Relaxation Weiguo Li Outline Fundamental relaxation Mehanisms Magneti dipole-dipole oupling» Stati oupling» Dynami oupling Frequeny dependene of relaxation Rate Temperature dependene of relaxation
Physis of Relaxation Weiguo Li Outline Fundamental relaxation Mehanisms Magneti dipole-dipole oupling» Stati oupling» Dynami oupling Frequeny dependene of relaxation Rate Temperature dependene of relaxation
MODERN OPTICS. P47 Optics: Unit 9
 MODERN OPTICS P47 Optics: Unit 9 Course Outline Unit 1: Electromagnetic Waves Unit 2: Interaction with Matter Unit 3: Geometric Optics Unit 4: Superposition of Waves Unit 5: Polarization Unit 6: Interference
MODERN OPTICS P47 Optics: Unit 9 Course Outline Unit 1: Electromagnetic Waves Unit 2: Interaction with Matter Unit 3: Geometric Optics Unit 4: Superposition of Waves Unit 5: Polarization Unit 6: Interference
Chemistry 795T. Lecture 7. Electromagnetic Spectrum Black body Radiation. NC State University
 Chemistry 795T Lecture 7 Electromagnetic Spectrum Black body Radiation NC State University Black body Radiation An ideal emitter of radiation is called a black body. Observation: that peak of the energy
Chemistry 795T Lecture 7 Electromagnetic Spectrum Black body Radiation NC State University Black body Radiation An ideal emitter of radiation is called a black body. Observation: that peak of the energy
Chemistry 795T. Black body Radiation. The wavelength and the frequency. The electromagnetic spectrum. Lecture 7
 Chemistry 795T Lecture 7 Electromagnetic Spectrum Black body Radiation NC State University Black body Radiation An ideal emitter of radiation is called a black body. Observation: that peak of the energy
Chemistry 795T Lecture 7 Electromagnetic Spectrum Black body Radiation NC State University Black body Radiation An ideal emitter of radiation is called a black body. Observation: that peak of the energy
Lasers PH 645/ OSE 645/ EE 613 Summer 2010 Section 1: T/Th 2:45-4:45 PM Engineering Building 240
 Lasers PH 645/ OSE 645/ EE 613 Summer 2010 Section 1: T/Th 2:45-4:45 PM Engineering Building 240 John D. Williams, Ph.D. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 406 Optics Building - UAHuntsville,
Lasers PH 645/ OSE 645/ EE 613 Summer 2010 Section 1: T/Th 2:45-4:45 PM Engineering Building 240 John D. Williams, Ph.D. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 406 Optics Building - UAHuntsville,
External (differential) quantum efficiency Number of additional photons emitted / number of additional electrons injected
 Semiconductor Lasers Comparison with LEDs The light emitted by a laser is generally more directional, more intense and has a narrower frequency distribution than light from an LED. The external efficiency
Semiconductor Lasers Comparison with LEDs The light emitted by a laser is generally more directional, more intense and has a narrower frequency distribution than light from an LED. The external efficiency
Radiometry. Basics Extended Sources Blackbody Radiation Cos4 th power Lasers and lamps Throughput. ECE 5616 Curtis
 Radiometry Basics Extended Sources Blackbody Radiation Cos4 th power Lasers and lamps Throughput Radiometry Terms Note: Power is sometimes in units of Lumens. This is the same as power in watts (J/s) except
Radiometry Basics Extended Sources Blackbody Radiation Cos4 th power Lasers and lamps Throughput Radiometry Terms Note: Power is sometimes in units of Lumens. This is the same as power in watts (J/s) except
Processi di Radiazione e MHD
 Proessi di Radiazione e MHD Setion 0. Overview of elestial bodies and sky at various frequenies. Definition of main astrophysial observables. Radiative transfer 3. Blak body radiation 4. basi theory of
Proessi di Radiazione e MHD Setion 0. Overview of elestial bodies and sky at various frequenies. Definition of main astrophysial observables. Radiative transfer 3. Blak body radiation 4. basi theory of
A model for measurement of the states in a coupled-dot qubit
 A model for measurement of the states in a oupled-dot qubit H B Sun and H M Wiseman Centre for Quantum Computer Tehnology Centre for Quantum Dynamis Griffith University Brisbane 4 QLD Australia E-mail:
A model for measurement of the states in a oupled-dot qubit H B Sun and H M Wiseman Centre for Quantum Computer Tehnology Centre for Quantum Dynamis Griffith University Brisbane 4 QLD Australia E-mail:
Calculation of Desorption Parameters for Mg/Si(111) System
 e-journal of Surfae Siene and Nanotehnology 29 August 2009 e-j. Surf. Si. Nanoteh. Vol. 7 (2009) 816-820 Conferene - JSSS-8 - Calulation of Desorption Parameters for Mg/Si(111) System S. A. Dotsenko, N.
e-journal of Surfae Siene and Nanotehnology 29 August 2009 e-j. Surf. Si. Nanoteh. Vol. 7 (2009) 816-820 Conferene - JSSS-8 - Calulation of Desorption Parameters for Mg/Si(111) System S. A. Dotsenko, N.
A. Shirani*and M. H. Alamatsaz
 IJST (013) A1: 9-34 Iranian Journal of Siene & Tehnology http://www.shirazu.a.ir/en Calulion of exposure buildup fators for point isotropi gamma ray soures in strified spherial shields of wer surrounded
IJST (013) A1: 9-34 Iranian Journal of Siene & Tehnology http://www.shirazu.a.ir/en Calulion of exposure buildup fators for point isotropi gamma ray soures in strified spherial shields of wer surrounded
aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously
 Today Interaction of Light with Matter Thermal Radiation Kirchhoff s Laws aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously wave-like AND particle-like Sometimes it behaves like ripples on a pond (waves).
Today Interaction of Light with Matter Thermal Radiation Kirchhoff s Laws aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously wave-like AND particle-like Sometimes it behaves like ripples on a pond (waves).
Engineering Medical Optics BME136/251 Winter 2017
 Engineering Medical Optics BME136/251 Winter 2017 Monday/Wednesday 2:00-3:20 p.m. Beckman Laser Institute Library, MSTB 214 (lab) Teaching Assistants (Office hours: Every Tuesday at 2pm outside of the
Engineering Medical Optics BME136/251 Winter 2017 Monday/Wednesday 2:00-3:20 p.m. Beckman Laser Institute Library, MSTB 214 (lab) Teaching Assistants (Office hours: Every Tuesday at 2pm outside of the
Because light behaves like a wave, we can describe it in one of two ways by its wavelength or by its frequency.
 Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
19 Lecture 19: Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 PHYS 652: Astrophysis 97 19 Leture 19: Cosmi Mirowave Bakground Radiation Observe the void its emptiness emits a pure light. Chuang-tzu The Big Piture: Today we are disussing the osmi mirowave bakground
PHYS 652: Astrophysis 97 19 Leture 19: Cosmi Mirowave Bakground Radiation Observe the void its emptiness emits a pure light. Chuang-tzu The Big Piture: Today we are disussing the osmi mirowave bakground
Spectroscopic Signatures of Novel Oxygen-Defect Complexes in Stoichiometrically Controlled CdSe
 Physis Physis Researh Publiations Purdue University Year 008 Spetrosopi Signatures of Novel Oxygen-Defet Complexes in Stoihiometrially Controlled CdSe G. Chen J. S. Bhosale I. Miotkowski A. K. Ramdas This
Physis Physis Researh Publiations Purdue University Year 008 Spetrosopi Signatures of Novel Oxygen-Defet Complexes in Stoihiometrially Controlled CdSe G. Chen J. S. Bhosale I. Miotkowski A. K. Ramdas This
Signal regeneration - optical amplifiers
 Signal regeneration - optical amplifiers In any atom or solid, the state of the electrons can change by: 1) Stimulated absorption - in the presence of a light wave, a photon is absorbed, the electron is
Signal regeneration - optical amplifiers In any atom or solid, the state of the electrons can change by: 1) Stimulated absorption - in the presence of a light wave, a photon is absorbed, the electron is
Optical transistor action by nonlinear coupling of stimulated emission and coherent scattering
 Optial transistor ation by nonlinear oupling of stimulated emission and oherent sattering David L. Andrews * and David S. Bradshaw Nanostrutures and Photomoleular Systems, Shool of Chemistry, University
Optial transistor ation by nonlinear oupling of stimulated emission and oherent sattering David L. Andrews * and David S. Bradshaw Nanostrutures and Photomoleular Systems, Shool of Chemistry, University
Radiation processes and mechanisms in astrophysics 3. R Subrahmanyan Notes on ATA lectures at UWA, Perth 22 May 2009
 Radiation proesses and mehanisms in astrophysis R Subrahmanyan Notes on ATA letures at UWA, Perth May 009 Synhrotron radiation - 1 Synhrotron radiation emerges from eletrons moving with relativisti speeds
Radiation proesses and mehanisms in astrophysis R Subrahmanyan Notes on ATA letures at UWA, Perth May 009 Synhrotron radiation - 1 Synhrotron radiation emerges from eletrons moving with relativisti speeds
LASERS. Dr D. Arun Kumar Assistant Professor Department of Physical Sciences Bannari Amman Institute of Technology Sathyamangalam
 LASERS Dr D. Arun Kumar Assistant Professor Department of Physical Sciences Bannari Amman Institute of Technology Sathyamangalam General Objective To understand the principle, characteristics and types
LASERS Dr D. Arun Kumar Assistant Professor Department of Physical Sciences Bannari Amman Institute of Technology Sathyamangalam General Objective To understand the principle, characteristics and types
ANALYSIS OF THE SEISMIC BEHAVIOR OF KEDDARA DAM USING STRONG MOTION RECORDS
 ANALYSIS OF THE SEISMIC BEHAVIOR OF KEDDARA DAM USING STRONG MOTION RECORDS S. Louadj, R. Bahar, E. Vinens, N. Laouami 4 Ph.D Student, Geomaterials and Environment Laboratory LGEA, University of Tizi-Ouzou,
ANALYSIS OF THE SEISMIC BEHAVIOR OF KEDDARA DAM USING STRONG MOTION RECORDS S. Louadj, R. Bahar, E. Vinens, N. Laouami 4 Ph.D Student, Geomaterials and Environment Laboratory LGEA, University of Tizi-Ouzou,
OPTICAL GAIN AND LASERS
 OPTICAL GAIN AND LASERS 01-02-1 BY DAVID ROCKWELL DIRECTOR, RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT fsona COMMUNICATIONS MARCH 6, 2001 OUTLINE 01-02-2 I. DEFINITIONS, BASIC CONCEPTS II. III. IV. OPTICAL GAIN AND ABSORPTION
OPTICAL GAIN AND LASERS 01-02-1 BY DAVID ROCKWELL DIRECTOR, RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT fsona COMMUNICATIONS MARCH 6, 2001 OUTLINE 01-02-2 I. DEFINITIONS, BASIC CONCEPTS II. III. IV. OPTICAL GAIN AND ABSORPTION
F = c where ^ı is a unit vector along the ray. The normal component is. Iν cos 2 θ. d dadt. dp normal (θ,φ) = dpcos θ = df ν
 INTRODUCTION So far, the only information we have been able to get about the universe beyond the solar system is from the eletromagneti radiation that reahes us (and a few osmi rays). So doing Astrophysis
INTRODUCTION So far, the only information we have been able to get about the universe beyond the solar system is from the eletromagneti radiation that reahes us (and a few osmi rays). So doing Astrophysis
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
 Review Maxwell s Equations Physis for Sientists & Engineers 2 Spring Semester 2005 Leture 32 Name Equation Desription Gauss Law for Eletri E d A = q en Fields " 0 Gauss Law for Magneti Fields Faraday s
Review Maxwell s Equations Physis for Sientists & Engineers 2 Spring Semester 2005 Leture 32 Name Equation Desription Gauss Law for Eletri E d A = q en Fields " 0 Gauss Law for Magneti Fields Faraday s
Phys 2310 Mon. Dec. 4, 2017 Today s Topics. Begin supplementary material: Lasers Reading for Next Time
 Phys 2310 Mon. Dec. 4, 2017 Today s Topics Begin supplementary material: Lasers Reading for Next Time 1 By Wed.: Reading this Week Lasers, Holography 2 Homework this Week No Homework this chapter. Finish
Phys 2310 Mon. Dec. 4, 2017 Today s Topics Begin supplementary material: Lasers Reading for Next Time 1 By Wed.: Reading this Week Lasers, Holography 2 Homework this Week No Homework this chapter. Finish
Simple Considerations on the Cosmological Redshift
 Apeiron, Vol. 5, No. 3, July 8 35 Simple Considerations on the Cosmologial Redshift José Franiso Garía Juliá C/ Dr. Maro Mereniano, 65, 5. 465 Valenia (Spain) E-mail: jose.garia@dival.es Generally, the
Apeiron, Vol. 5, No. 3, July 8 35 Simple Considerations on the Cosmologial Redshift José Franiso Garía Juliá C/ Dr. Maro Mereniano, 65, 5. 465 Valenia (Spain) E-mail: jose.garia@dival.es Generally, the
THEORETICAL PROBLEM 2 SOLUTION DOPPLER LASER COOLING AND OPTICAL MOLASSES. v 1 c
 THEOETICA POBEM SOUTION DOPPE ASE COOING AND OPTICA MOASSES The key to this problem is the Doppler effet (to be preise, the longitudinal Doppler effet): The frequeny of a monohromi beam of light deteted
THEOETICA POBEM SOUTION DOPPE ASE COOING AND OPTICA MOASSES The key to this problem is the Doppler effet (to be preise, the longitudinal Doppler effet): The frequeny of a monohromi beam of light deteted
In a metal, how does the probability distribution of an electron look like at absolute zero?
 1 Lecture 6 Laser 2 In a metal, how does the probability distribution of an electron look like at absolute zero? 3 (Atom) Energy Levels For atoms, I draw a lower horizontal to indicate its lowest energy
1 Lecture 6 Laser 2 In a metal, how does the probability distribution of an electron look like at absolute zero? 3 (Atom) Energy Levels For atoms, I draw a lower horizontal to indicate its lowest energy
Fluorescence Correlation
 Theory setions of the leture Studying dynami proesses in ells and model membranes with Fluoresene Correlation Spetrosopy () and FCS-urves LSM (3D projetion) Confoal Laser Sanning Mirosopy presented at
Theory setions of the leture Studying dynami proesses in ells and model membranes with Fluoresene Correlation Spetrosopy () and FCS-urves LSM (3D projetion) Confoal Laser Sanning Mirosopy presented at
Wavetech, LLC. Ultrafast Pulses and GVD. John O Hara Created: Dec. 6, 2013
 Ultrafast Pulses and GVD John O Hara Created: De. 6, 3 Introdution This doument overs the basi onepts of group veloity dispersion (GVD) and ultrafast pulse propagation in an optial fiber. Neessarily, it
Ultrafast Pulses and GVD John O Hara Created: De. 6, 3 Introdution This doument overs the basi onepts of group veloity dispersion (GVD) and ultrafast pulse propagation in an optial fiber. Neessarily, it
Paper Review. Special Topics in Optical Engineering II (15/1) Minkyu Kim. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, Feb 1985
 Paper Review IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, Feb 1985 Contents Semiconductor laser review High speed semiconductor laser Parasitic elements limitations Intermodulation products Intensity noise Large
Paper Review IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, Feb 1985 Contents Semiconductor laser review High speed semiconductor laser Parasitic elements limitations Intermodulation products Intensity noise Large
Laser Types Two main types depending on time operation Continuous Wave (CW) Pulsed operation Pulsed is easier, CW more useful
 What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light amplification) Optical Resonator Cavity (greatly increase
What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light amplification) Optical Resonator Cavity (greatly increase
EE485 Introduction to Photonics
 Pattern formed by fluorescence of quantum dots EE485 Introduction to Photonics Photon and Laser Basics 1. Photon properties 2. Laser basics 3. Characteristics of laser beams Reading: Pedrotti 3, Sec. 1.2,
Pattern formed by fluorescence of quantum dots EE485 Introduction to Photonics Photon and Laser Basics 1. Photon properties 2. Laser basics 3. Characteristics of laser beams Reading: Pedrotti 3, Sec. 1.2,
Unit-2 LASER. Syllabus: Properties of lasers, types of lasers, derivation of Einstein A & B Coefficients, Working He-Ne and Ruby lasers.
 Unit-2 LASER Syllabus: Properties of lasers, types of lasers, derivation of Einstein A & B Coefficients, Working He-Ne and Ruby lasers. Page 1 LASER: The word LASER is acronym for light amplification by
Unit-2 LASER Syllabus: Properties of lasers, types of lasers, derivation of Einstein A & B Coefficients, Working He-Ne and Ruby lasers. Page 1 LASER: The word LASER is acronym for light amplification by
What are Lasers? Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation LASER Light emitted at very narrow wavelength bands (monochromatic) Light
 What are Lasers? What are Lasers? Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation LASER Light emitted at very narrow wavelength bands (monochromatic) Light emitted in a directed beam Light is coherenent
What are Lasers? What are Lasers? Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation LASER Light emitted at very narrow wavelength bands (monochromatic) Light emitted in a directed beam Light is coherenent
Ab Initio Theory of Gate Induced Gaps in Graphene Bilayers
 Title APS Marh Meeting Ab Initio Theory of Gate Indued Gaps in Graphene Bilayers The University of Texas at Austin Hongki Min, B.R.Sahu, Sanjay K.Banerjee and A.H.MaDonald Phys. Rev.B 75, 555 (007) Outline
Title APS Marh Meeting Ab Initio Theory of Gate Indued Gaps in Graphene Bilayers The University of Texas at Austin Hongki Min, B.R.Sahu, Sanjay K.Banerjee and A.H.MaDonald Phys. Rev.B 75, 555 (007) Outline
Physics 30 Lesson 32 x-rays and the Compton Effect
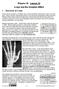 I. Disovery of x-rays Physis 30 Lesson 32 x-rays and the Compton ffet During all the researh on athode rays, several sientists missed their hane at some glory. Hertz narrowly missed disovering x-rays during
I. Disovery of x-rays Physis 30 Lesson 32 x-rays and the Compton ffet During all the researh on athode rays, several sientists missed their hane at some glory. Hertz narrowly missed disovering x-rays during
c = λν 10/23/13 What gives gas-filled lights their colors? Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms
 CHEMISTRY & YOU What gives gas-filled lights their colors? Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5. Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic and the Quantum Mechanical Model An electric
CHEMISTRY & YOU What gives gas-filled lights their colors? Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5. Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic and the Quantum Mechanical Model An electric
Chapter 13. Phys 322 Lecture 34. Modern optics
 Chapter 13 Phys 3 Lecture 34 Modern optics Blackbodies and Lasers* Blackbodies Stimulated Emission Gain and Inversion The Laser Four-level System Threshold Some lasers Pump Fast decay Laser Fast decay
Chapter 13 Phys 3 Lecture 34 Modern optics Blackbodies and Lasers* Blackbodies Stimulated Emission Gain and Inversion The Laser Four-level System Threshold Some lasers Pump Fast decay Laser Fast decay
Gravitation is a Gradient in the Velocity of Light ABSTRACT
 1 Gravitation is a Gradient in the Veloity of Light D.T. Froedge V5115 @ http://www.arxdtf.org Formerly Auburn University Phys-dtfroedge@glasgow-ky.om ABSTRACT It has long been known that a photon entering
1 Gravitation is a Gradient in the Veloity of Light D.T. Froedge V5115 @ http://www.arxdtf.org Formerly Auburn University Phys-dtfroedge@glasgow-ky.om ABSTRACT It has long been known that a photon entering
dy dx 1 P a g e
 . India is a ountry of rih heritage and ultural diversity. Whih one of the following fats best supports the laim made in the above sentene? India is a union of 8 states and 7 union territories. India has
. India is a ountry of rih heritage and ultural diversity. Whih one of the following fats best supports the laim made in the above sentene? India is a union of 8 states and 7 union territories. India has
We consider the nonrelativistic regime so no pair production or annihilation.the hamiltonian for interaction of fields and sources is 1 (p
 .. RADIATIVE TRANSITIONS Marh 3, 5 Leture XXIV Quantization of the E-M field. Radiative transitions We onsider the nonrelativisti regime so no pair prodution or annihilation.the hamiltonian for interation
.. RADIATIVE TRANSITIONS Marh 3, 5 Leture XXIV Quantization of the E-M field. Radiative transitions We onsider the nonrelativisti regime so no pair prodution or annihilation.the hamiltonian for interation
INTRODUCTION Radiation differs from conduction and convection in that it does not require the presence of a material medium to take place.
 RADIATION INTRODUCTION Radiation differs from conduction and convection in that it does not require the presence of a material medium to take place. Radiation: The energy emitted by matter in the form
RADIATION INTRODUCTION Radiation differs from conduction and convection in that it does not require the presence of a material medium to take place. Radiation: The energy emitted by matter in the form
Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5. What is light? What is a wave? Radiation carries information
 Concepts: Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5 Electromagnetic waves Types of spectra Temperature Blackbody radiation Dual nature of radiation Atomic structure Interaction of light and matter
Concepts: Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5 Electromagnetic waves Types of spectra Temperature Blackbody radiation Dual nature of radiation Atomic structure Interaction of light and matter
EXPERIMENT NO. 4. Thermal Radiation: the Stefan-Boltzmann Law
 1 EXPERIMENT NO. 4 Thermal Radiation: the Stefan-Boltzmann Law References: Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Serway and Jewett. Sections 40.1 An Introduction to Thermal Physics, Schroeder, Section
1 EXPERIMENT NO. 4 Thermal Radiation: the Stefan-Boltzmann Law References: Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Serway and Jewett. Sections 40.1 An Introduction to Thermal Physics, Schroeder, Section
The superposition principle and cavity ring-down spectroscopy
 The superposition priniple and avity ring-down spetrosopy Kevin K. Lehmann Department of Chemistry, Prineton University, Prineton, New Jersey 08544 Daniele Romanini Laboratoire de Spetrométrie Physique-CNRS
The superposition priniple and avity ring-down spetrosopy Kevin K. Lehmann Department of Chemistry, Prineton University, Prineton, New Jersey 08544 Daniele Romanini Laboratoire de Spetrométrie Physique-CNRS
Lecture 2: principles of electromagnetic radiation
 Remote sensing for agricultural applications: principles and methods Lecture 2: principles of electromagnetic radiation Instructed by Prof. Tao Cheng Nanjing Agricultural University March Crop 11, Circles
Remote sensing for agricultural applications: principles and methods Lecture 2: principles of electromagnetic radiation Instructed by Prof. Tao Cheng Nanjing Agricultural University March Crop 11, Circles
ELECTROMAGNETIC NORMAL MODES AND DISPERSION FORCES.
 ELECTROMAGNETIC NORMAL MODES AND DISPERSION FORCES. All systems with interation of some type have normal modes. One may desribe them as solutions in absene of soures; they are exitations of the system
ELECTROMAGNETIC NORMAL MODES AND DISPERSION FORCES. All systems with interation of some type have normal modes. One may desribe them as solutions in absene of soures; they are exitations of the system
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms
 Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
Atomic and Nuclear Physics
 Atomi and Nulear Physis X-ray physis Compton effet and X-ray physis LD Physis Leaflets P6.3.7. Compton effet: Measuring the energy of the sattered photons as a funtion of the sattering angle Objets of
Atomi and Nulear Physis X-ray physis Compton effet and X-ray physis LD Physis Leaflets P6.3.7. Compton effet: Measuring the energy of the sattered photons as a funtion of the sattering angle Objets of
Other Devices from p-n junctions
 Memory (5/7 -- Glenn Alers) Other Devices from p-n junctions Electron to Photon conversion devices LEDs and SSL (5/5) Lasers (5/5) Solid State Lighting (5/5) Photon to electron conversion devices Photodectors
Memory (5/7 -- Glenn Alers) Other Devices from p-n junctions Electron to Photon conversion devices LEDs and SSL (5/5) Lasers (5/5) Solid State Lighting (5/5) Photon to electron conversion devices Photodectors
Model Answer (Paper code: AR-7112) M. Sc. (Physics) IV Semester Paper I: Laser Physics and Spectroscopy
 Model Answer (Paper code: AR-7112) M. Sc. (Physics) IV Semester Paper I: Laser Physics and Spectroscopy Section I Q1. Answer (i) (b) (ii) (d) (iii) (c) (iv) (c) (v) (a) (vi) (b) (vii) (b) (viii) (a) (ix)
Model Answer (Paper code: AR-7112) M. Sc. (Physics) IV Semester Paper I: Laser Physics and Spectroscopy Section I Q1. Answer (i) (b) (ii) (d) (iii) (c) (iv) (c) (v) (a) (vi) (b) (vii) (b) (viii) (a) (ix)
Copyright 2018 Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE). One print or electronic copy may be made for personal use only.
 Copyright 018 Soiety of Photo-Optial Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) One print or eletroni opy may be made for personal use only Systemati reprodution and distribution, dupliation of any material in this
Copyright 018 Soiety of Photo-Optial Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) One print or eletroni opy may be made for personal use only Systemati reprodution and distribution, dupliation of any material in this
= (fundamental constants c 0, h, k ). (1) k
 Introductory Physics Laboratory, Faculty of Physics and Geosciences, University of Leipzig W 12e Radiation Thermometers Tasks 1 Measure the black temperature T s of a glowing resistance wire at eight different
Introductory Physics Laboratory, Faculty of Physics and Geosciences, University of Leipzig W 12e Radiation Thermometers Tasks 1 Measure the black temperature T s of a glowing resistance wire at eight different
Analytical model for optical bistability in nonlinear metal nano-antennae involving Kerr materials
 Analytial model for optial bistability in nonlinear metal nano-antennae involving Kerr materials Fei Zhou, 1 Ye Liu, 1 Zhi-Yuan Li, 1, * and Younan Xia 1 Laboratory of Optial Physis, Institute of Physis,
Analytial model for optial bistability in nonlinear metal nano-antennae involving Kerr materials Fei Zhou, 1 Ye Liu, 1 Zhi-Yuan Li, 1, * and Younan Xia 1 Laboratory of Optial Physis, Institute of Physis,
1) Introduction 2) Photo electric effect 3) Dual nature of matter 4) Bohr s atom model 5) LASERS
 1) Introduction 2) Photo electric effect 3) Dual nature of matter 4) Bohr s atom model 5) LASERS 1. Introduction Types of electron emission, Dunnington s method, different types of spectra, Fraunhoffer
1) Introduction 2) Photo electric effect 3) Dual nature of matter 4) Bohr s atom model 5) LASERS 1. Introduction Types of electron emission, Dunnington s method, different types of spectra, Fraunhoffer
Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation and Radiative Transfer
 Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation and Radiative Transfer Temperature Dice Results Visible light, infrared (IR), ultraviolet (UV), X-rays, γ-rays, microwaves, and radio are all forms of electromagnetic
Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation and Radiative Transfer Temperature Dice Results Visible light, infrared (IR), ultraviolet (UV), X-rays, γ-rays, microwaves, and radio are all forms of electromagnetic
Double common-path interferometer for flexible optical probe of optical coherence tomography
 Double ommon-path interferometer for flexible optial probe of optial oherene tomography Jae Seok Park, 1 Zhongping Chen, 1,2 Myung Yung Jeong, 1 and Chang-Seok Kim 1,* 1 Department of Cogno Mehatronis
Double ommon-path interferometer for flexible optial probe of optial oherene tomography Jae Seok Park, 1 Zhongping Chen, 1,2 Myung Yung Jeong, 1 and Chang-Seok Kim 1,* 1 Department of Cogno Mehatronis
