From the Ideas of Edgeworth and Pareto in Exchange Economy to Multi-Objective Mathematical Programming
|
|
|
- Stephanie Arnold
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SCIRE Journal of Mathematics htt://scireaorg/journal/mathematics ril Volume 2 Issue 2 ril 207 From the Ideas of Edgeorth and Pareto in Echange Econom to Multi-Objective Mathematical Programming Zdravko Dimitrov Slavov Christina Slavova Evans 2 Varna Free niversit Varna ulgaria 2 The George Washington niversit Washington DC S bstract In this aer e consider the first general theories of multi-objective mathematical rogramming The stem from otimization techniques in economics and are attributed to the economists Francis Edgeorth and Vilfredo Pareto We ill focus our attention on these ideas from a mathematical oint of vie Keords: otimization multi-objective mathematical rogramming Edgeorth-bo Pareto-otimal equilibrium Introduction The ke concet of ever otimization roblem is to seek the best solution that maimizes or minimizes one or more objective functions During otimization one often needs to consider several objective functions simultaneousl When more than one objective functions are associated the otimization roblem becomes multi-objective in hich case the usual otimization techniques for a scalar function cannot be used This te of roblem is knon 5
2 as either multi-criteria or vector otimization Mathematicall it is knon as multi-objective mathematical rogramming (MOMP and the folloing records eist in 200 Mathematics Subject Classification: 90C - Mathematical rogramming 90C29 - Multi-objective and goal rogramming 65K - Mathematical rogramming otimization and variational techniques 65K05 - Mathematical rogramming methods 49M - Numerical methods and 49M37 - Methods of nonlinear rogramming te The standard form of a MOMP roblem is to find a variable ( 2 m R m so as to m maimize (or minimize f f f f ( 2 n subject to g ( 0 i J i h ( 0 i i J q [ a b ] i J i i i m here f : i J } are given objective functions n 2 g : i J } are given inequalit { i n { i constraint functions 0 h : i J } are given equalit constraint functions q 0 { i q and b i are the loer and uer bounds for i Let the feasible domain (or constraint set be denoted b a b and J m 2 m is the inde set gi( 0 i J m { ( 2 m R : hi ( 0 i Jq } ai i bi i Jm s usual let us assume that set is nonemt but the inde sets emt or nonemt i i a i J and J q can be either We ill discuss onl maimization roblems Hoever each minimization roblem can be transformed to a maimization roblem ver easil b considering the negative of the objective function values Since the objective functions f : i J } ma conflict ith each other it is usuall difficult { i n to obtain the global maimum for each objective function at the same time So if no single oint maimizes all of the several objective functions at once then n rg ma( f i i is emt Therefore the target of the maimization roblem is to obtain a set of solutions that are Pareto-otimal 6
3 2 Notions and Definitions Edgeorth and Pareto are often called the fathers of multi-objective mathematical rogramming The notion of Edgeorth-Pareto otimalit as introduced b the Irish economist Francis Edgeorth ( in 88 Hoever this concet is usuall attributed to the French-Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto ( ho in 896 develoed it further see Figure Edgeorth and Pareto ere studing the natural ordering in the image sace in mathematical models of a simle echange market [2] The first mathematical consideration of this roblem as done b Kuhn and Tucker in 95 [4] [0] [] Since that time multi-objective otimization has became an active research field Figure : The fathers of multi-objective mathematical rogramming In [0] Harold Kuhn and lbert Tucker cite the 975 Nobel Laureate in Economics Tjalling Koomans [8] hen the talk about "vector maimum of Koomans' efficient oint te for several functions" Kuhn and Tucker also cite the 972 Nobel Laureate in Economics Kenneth rro [] ho contributed to the foundations of multi-objective otimization The origins of the mathematical foundations of multi-objective otimization can be traced back to the eriod from 895 to 906 During that eriod Georg Cantor and Feli Hausdorff laid the foundations of infinite dimensional ordered saces [2] [4] [3] In countless books and research aers on multi-objective mathematical rogramming one can find a mathematical definition essentiall as folloing: 7
4 Definition (a oint is called an ideal Pareto-otimal solution if and onl if fi fi for all and all i Jn The set of ideal Pareto-otimal solutions of is denoted b f Pareto-otimal set IPO (the are the global maimum of f on and is called an ideal (b oint is called a Pareto-otimal solution if and onl if there does not eist a oint such that fi fi for all i Jn and f k f k for some k Jn The set of the Pareto-otimal solutions of is denoted b f PO and is called a Paretootimal set The image of a Pareto-otimal set under the objective function is called a Paretofront set ie ( PO f PF ( f (c oint eist a oint f is called a strictl Pareto-otimal solution if and onl if there does not such that fi fi for all i Jn and The set of strictl Pareto-otimal solutions of is denoted b f SPO and is called a strictl Paretootimal set (d oint eist a oint is called a eakl Pareto-otimal solution if and onl if there does not such that fi fi for all i Jn The set of eakl Pareto-otimal solutions of is denoted b f WPO and is called a eakl Pareto-otimal set The image of a eakl Pareto-otimal set under the objective function is called a eakl Paretofront set ie ( WPO f WPF ( f f The above definition qualifies Pareto-otimal solutions in the global sense In literature the term Pareto-otimal is frequentl used snonmousl ith Edgeorth-Pareto otimal efficient non-inferior and non-dominated In this aer let the given functions f : i J } g : i J } and h : i J } be all { i n { i { i q continuous on In this case it is eas to rove that the feasible domain is comact Remark In our otimization roblem it can be shon that: PO f and f nonemt but IPO f n rg ma( f i i and f WPO are SPO ma be emt or nonemt; IPO f PO f SPO f PO f PO f WPO f PF f WPF f f ( ; WPO f and f and [3] and WPF are comact see also [7] [9] 8
5 Note that strictl Pareto-otimal solutions are the multi-objective analogue of unique otimal solutions in scalar otimization Remark 2 It is ell-knon that PO f IPO f if and onl if f nonemt [3] If the ideal Pareto-otimal set f n rg ma( f i i IPO is IPO is emt then e ill accet the elements into the Pareto-otimal strictl Pareto-otimal and eak Pareto-otimal sets as three different solutions of our otimization roblem ( suall a Pareto-otimal solution is not necessaril uniquel determined instead there are several Pareto-otimal solutions 3 Edgeorth-bo Diagram Echange and Equilibrium The general idea of the Edgeorth-bo diagram (or geometric interretation of echange is that there are to consumers: consumer and consumer and to goods: good and good We ill assume for mathematical simlicit that ever good is erfect homogeneous and erfectl divisible The divisibilit assumtion is ver convenient in economic analsis since it allos us to use continuit arguments [6] The Edgeorth-bo diagram gives us a grah of different distributions of goods beteen consumers No suose that consumers and have utilit functions and (strictl increasing concave and continuous resectivel consumer has indifference curves 2 and 3 and consumer has indifference curves 2 and 3 locus of allocations of goods for hich the utilit function is constant is called an indifference curve In order to create an Edgeorth-bo diagram for consumer and consumer e must lace them ithin the same barter echange market To do this e siml take one of the consumers for eamle consumer reflect their indifference curves about the and aes and lace them on the same grah as the other consumer ie consumer see Figure 2 9
6 Figure 2: Edgeorth-bo diagram and Pareto-otimal set 3 arter Echange No e have to achieve otimal distributions of the to goods beteen the to consumers In this case e get an otimization roblem: maimize the utilit functions and of both consumers and subject to a limited amount of goods and nalticall for fied 0 and 0 e obtain a multi-objective otimization roblem as follos: maimize (2 subject to Observe resectivel and resectivel and reresent the quantit of good roert of consumers and and reresent the quantit of good roert of consumers and From the roerties of utilit functions to roblem (3 ritten as: maimize and it follos that roblem (2 is equivalent (3 20
7 subject to The basic idea is as follos: The indifference curves join all the oints that give consumers the same level of utilit connecting all oints of tangenc beteen the indifference curves of both consumers e construct the contract curve and it reresents all Pareto-otimal allocations ie curve O O is a geometrical image of the Pareto-otimal set Thus the Pareto-otimal allocation is the allocation here it is not ossible to make one consumer better off ithout making another orse off see also Figure 2 From a mathematical oint of vie the Pareto-otimal allocations are solutions of multi-objective otimization roblem (3 Here it is true that there are several Pareto-otimal solutions The Pareto-otimal set does not deend on the initial distribution of goods among consumers but it deends on the initial qualities of the various goods see also [2] It can also be seen that the Pareto-otimal allocations are not related to a rices sstem This means that e analzed a barter echange ie mathematical model of echange ithout rices 32 Cometitive Equilibrium In addition let goods and have rices and resectivel and let consumers and have an initial allocation and of goods and resectivel From an economic oint of vie an echange econom is characterized b initial allocation of the goods rices sstem and utilit functions of the consumers In this case e also have to achieve the otimal distribution of the to goods beteen the to consumers Hence e get a ne otimization roblem nalticall for fied and 0 such that 0 and 0 and to ositive arameters ( and ( e obtain a multiobjective otimization roblem ritten as: maimize (4 subject to 2
8 It is imortant to note that rices and of the goods is an additional result in the rocess to solving the multi-objective otimization roblem (4 ie the rices sstem is derivative and a ver imortant roduct of maimization of the utilit functions of the consumers in an echange econom gain from the roerties of utilit functions equivalent to roblem (5 ritten as: and maimize it follos that roblem (4 is (5 subject to It is knon that roblem (3 has a solution but obtaining a solution is difficult for roblem (5 Let us assume that there eist arameters 0 and 0 such that roblem (5 has a unique solution ie roblem (5 has an ideal Pareto-otimal solution In other ords e assume that e have a cometitive equilibrium allocation this is at oint E in Figure 3 and the equilibrium rices are and 22
9 23 Figure 3: Cometitive equilibrium allocation - oint E Remark 3 Note that the sloe in absolute value at oint E of the contract curves and 3 is equal to k see Figure 3 Let us assume that utilit functions and have first artial derivatives therefore e have that ( ( ( grad grad For : ( - marginal rate of substitution and : e obtain the tangenc beteen indifference curves is the oint here (for roblem (3 and if this oint is a cometitive equilibrium allocation then k (for roblem (5 [5] [6] Consider the linear sstem of constraints in roblem (5 ritten as: It is eas to sho mathematicall that the above sstem is equivalent to the folloing sstem:
10 Obviousl e obtain roblem (5 is equivalent to roblem (6 that is: maimize (6 subject to Remark 4 Note that each solution to roblem (6 is also a solution to roblem (3: therefore each cometitive equilibrium allocation is Pareto-otimal Remark 5 lgebraicall consumer trades q for q and similarl consumer trades q for q ; therefore q q It is eas to rove that the folloing statements are equivalent: (a (b ; ; (c (d ; In all above cases the consumers do not reall trade ie q 0 and q 0 If consumers trade goods then ( ( 0 and ( ( 0 Of course e can also consider these ideas in a ure echange econom ith n 2 consumers and m 2 goods 33 Numerical Eamle Here e consider an illustrative eamle to demonstrate the concets of otimalit and equilibrium in a simle echange econom ith to consumers and to goods 24
11 Let the consumers have Cobb-Douglas utilit functions and 0 0 and given b here (0 and 0 No e ill find the Pareto-otimal set and the cometitive equilibrium 0 0 ased on Remark 3 it is eas to sho that roblem (3 is equivalent to the folloing sstem: First e comute and ; therefore ie here 0 ( s a result e obtain that the Pareto-otimal set is equal to 4 {( R : ( 0 ( } and OO : ( infinite number of Pareto-otimal allocations Here there are three cases: ( If then and O O is a straight line (2 If then and O O is a conve curve (3 If then and O O is a concave curve see Figure 2 In fact there is an In this eamle all of the Pareto-otimal allocations are strictl Pareto-otimal and eakl Pareto-otimal and the ideal Pareto-otimal set is emt Clearl roblem (6 is equivalent to the folloing sstem: k k k k We solve this sstem and the result is as follos: 25
12 26 ( ; ( ; ; ; k If the rices lie on a unit simle ie then the rices are ( and ( ( In the general case e obtain s ( and s ( ( here R s or s and s ( here R s ; therefore ( and ( References [] K rro Social Choice and Individual Values Coles Commission for Research in Economics Monograh N:2 John Wile and Sons 95 [2] M Ehrgott Gandibleu Multi-criteria Otimization: State of the rt nnotated ibliograhic Surves Kluer cademic Press 2002 [3] M Ehrgott Multi-criteria Otimization Sringer 2005 [4] M Ehrgott Vilfredo Pareto and multi-objective otimization Documenta Mathematica Etra volume: Otimization Stories [5] Ellickson Cometitive Equilibrium: Theor and lications Cambridge niversit Press 997 [6] Feldman R Serrano Welfare Economics and Social Choice Theor Sringer 2006 [7] J Jahn Vector Otimization: Theor lications and Etensions Sringer 2004
13 [8] T Koomans nalsis of Production as an efficient Combination of ctivities in T Koomans editor Coles Commission for Research in Economics Monograh N:3 John Wile and Sons [9] D Luc Theor of Vector Otimization Sringer 989 [0] H Kuhn Tucker Nonlinear rogramming in J Neman editor Proceedings of the 2nd erkele Smosium on Mathematical Statistics and Probabilit niversit of California Press erkele C [] M Lutacik Mathematical Otimization and Economic nalsis Sringer 200 [2] Z Slavov Structure of the Pareto otimalit set ith fied resources and consumtion sets lied Mathematics and Comutation 54 ( [3] R Steuer Multile Criteria Otimization: Theor Comutation and lication John Wile and Sons
Micro I. Lesson 5 : Consumer Equilibrium
 Microecono mics I. Antonio Zabalza. Universit of Valencia 1 Micro I. Lesson 5 : Consumer Equilibrium 5.1 Otimal Choice If references are well behaved (smooth, conve, continuous and negativel sloed), then
Microecono mics I. Antonio Zabalza. Universit of Valencia 1 Micro I. Lesson 5 : Consumer Equilibrium 5.1 Otimal Choice If references are well behaved (smooth, conve, continuous and negativel sloed), then
Profit Maximization. Beattie, Taylor, and Watts Sections: 3.1b-c, 3.2c, , 5.2a-d
 Proit Maimization Beattie Talor and Watts Sections:.b-c.c 4.-4. 5.a-d Agenda Generalized Proit Maimization Proit Maimization ith One Inut and One Outut Proit Maimization ith To Inuts and One Outut Proit
Proit Maimization Beattie Talor and Watts Sections:.b-c.c 4.-4. 5.a-d Agenda Generalized Proit Maimization Proit Maimization ith One Inut and One Outut Proit Maimization ith To Inuts and One Outut Proit
ANSWERS TO ODD NUMBERED EXERCISES IN CHAPTER 5. The constraint is binding at the maximum therefore we can substitute for y
 John Rile Aril 0 ANSWERS TO ODD NUMBERED EXERCISES IN CHAPTER 5 Section 5: The Robinson Crusoe Econom Eercise 5-: Equilibrium (a) = ( + ω) = ( + 47, ) Then = 47 Substituting or in the / roduction unction,
John Rile Aril 0 ANSWERS TO ODD NUMBERED EXERCISES IN CHAPTER 5 Section 5: The Robinson Crusoe Econom Eercise 5-: Equilibrium (a) = ( + ω) = ( + 47, ) Then = 47 Substituting or in the / roduction unction,
, αβ, > 0 is strictly quasi-concave on
 John Riley 8 Setember 9 Econ Diagnostic Test Time allowed: 9 minutes. Attemt all three questions. Note that the last two arts of questions and 3 are marked with an asterisk (). These do not carry many
John Riley 8 Setember 9 Econ Diagnostic Test Time allowed: 9 minutes. Attemt all three questions. Note that the last two arts of questions and 3 are marked with an asterisk (). These do not carry many
Second Order Symmetric and Maxmin Symmetric Duality with Cone Constraints
 International Journal of Oerations Research International Journal of Oerations Research Vol. 4, No. 4, 99 5 7) Second Order Smmetric Mamin Smmetric Dualit with Cone Constraints I. Husain,, Abha Goel, M.
International Journal of Oerations Research International Journal of Oerations Research Vol. 4, No. 4, 99 5 7) Second Order Smmetric Mamin Smmetric Dualit with Cone Constraints I. Husain,, Abha Goel, M.
5.1 THE ROBINSON CRUSOE ECONOMY
 Essential Microeconomics -- 5 THE ROBINSON CRUSOE ECONOMY Ke ideas: Walrasian equilibrium allocation, otimal allocation, invisible hand at work A simle econom with roduction Two commodities, H consumers,
Essential Microeconomics -- 5 THE ROBINSON CRUSOE ECONOMY Ke ideas: Walrasian equilibrium allocation, otimal allocation, invisible hand at work A simle econom with roduction Two commodities, H consumers,
Planar Transformations and Displacements
 Chater Planar Transformations and Dislacements Kinematics is concerned with the roerties of the motion of oints. These oints are on objects in the environment or on a robot maniulator. Two features that
Chater Planar Transformations and Dislacements Kinematics is concerned with the roerties of the motion of oints. These oints are on objects in the environment or on a robot maniulator. Two features that
International Trade with a Public Intermediate Good and the Gains from Trade
 International Trade with a Public Intermediate Good and the Gains from Trade Nobuhito Suga Graduate School of Economics, Nagoya University Makoto Tawada Graduate School of Economics, Nagoya University
International Trade with a Public Intermediate Good and the Gains from Trade Nobuhito Suga Graduate School of Economics, Nagoya University Makoto Tawada Graduate School of Economics, Nagoya University
The. Consortium. Continuum Mechanics. Original notes by Professor Mike Gunn, South Bank University, London, UK Produced by the CRISP Consortium Ltd
 The C R I S P Consortium Continuum Mechanics Original notes b Professor Mike Gunn, South Bank Universit, London, UK Produced b the CRISP Consortium Ltd THOR OF STRSSS In a three dimensional loaded bod,
The C R I S P Consortium Continuum Mechanics Original notes b Professor Mike Gunn, South Bank Universit, London, UK Produced b the CRISP Consortium Ltd THOR OF STRSSS In a three dimensional loaded bod,
Theory of Externalities Partial Equilibrium Analysis
 Theory of Externalities Partial Equilibrium Analysis Definition: An externality is resent whenever the well being of a consumer or the roduction ossibilities of a firm are directly affected by the actions
Theory of Externalities Partial Equilibrium Analysis Definition: An externality is resent whenever the well being of a consumer or the roduction ossibilities of a firm are directly affected by the actions
PROFIT MAXIMIZATION. π = p y Σ n i=1 w i x i (2)
 PROFIT MAXIMIZATION DEFINITION OF A NEOCLASSICAL FIRM A neoclassical firm is an organization that controls the transformation of inuts (resources it owns or urchases into oututs or roducts (valued roducts
PROFIT MAXIMIZATION DEFINITION OF A NEOCLASSICAL FIRM A neoclassical firm is an organization that controls the transformation of inuts (resources it owns or urchases into oututs or roducts (valued roducts
Convex Analysis and Economic Theory Winter 2018
 Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences Ec 181 KC Border Conve Analysis and Economic Theory Winter 2018 Toic 16: Fenchel conjugates 16.1 Conjugate functions Recall from Proosition 14.1.1 that is
Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences Ec 181 KC Border Conve Analysis and Economic Theory Winter 2018 Toic 16: Fenchel conjugates 16.1 Conjugate functions Recall from Proosition 14.1.1 that is
ANSWERS TO ODD NUMBERED EXERCISES IN CHAPTER 3
 John Riley 5 Setember 0 NSWERS T DD NUMERED EXERCISES IN CHPTER 3 SECTIN 3: Equilibrium and Efficiency Exercise 3-: Prices with Quasi-linear references (a) Since references are convex, an allocation is
John Riley 5 Setember 0 NSWERS T DD NUMERED EXERCISES IN CHPTER 3 SECTIN 3: Equilibrium and Efficiency Exercise 3-: Prices with Quasi-linear references (a) Since references are convex, an allocation is
Economics 101. Lecture 7 - Monopoly and Oligopoly
 Economics 0 Lecture 7 - Monooly and Oligooly Production Equilibrium After having exlored Walrasian equilibria with roduction in the Robinson Crusoe economy, we will now ste in to a more general setting.
Economics 0 Lecture 7 - Monooly and Oligooly Production Equilibrium After having exlored Walrasian equilibria with roduction in the Robinson Crusoe economy, we will now ste in to a more general setting.
CMSC 425: Lecture 7 Geometric Programming: Sample Solutions
 CMSC 425: Lecture 7 Geometric Programming: Samle Solutions Samles: In the last few lectures, we have been discussing affine and Euclidean geometr, coordinate frames and affine transformations, and rotations.
CMSC 425: Lecture 7 Geometric Programming: Samle Solutions Samles: In the last few lectures, we have been discussing affine and Euclidean geometr, coordinate frames and affine transformations, and rotations.
(ii) An input requirement set for this technology is clearly not convex as it
 LONDON SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS Department of Economics Leonardo Felli 32L.4.02; 7525 Solutions to Assignment 5 EC487 Advanced Microeconomics Part I 1. Sketch of the answers: (i) The map of isoquants for this
LONDON SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS Department of Economics Leonardo Felli 32L.4.02; 7525 Solutions to Assignment 5 EC487 Advanced Microeconomics Part I 1. Sketch of the answers: (i) The map of isoquants for this
Note on Mathematical Development of Plate Theories
 Advanced Studies in Theoretical Phsics Vol. 9, 015, no. 1, 47-55 HIKARI Ltd,.m-hikari.com http://d.doi.org/10.1988/astp.015.411150 Note on athematical Development of Plate Theories Patiphan Chantaraichit
Advanced Studies in Theoretical Phsics Vol. 9, 015, no. 1, 47-55 HIKARI Ltd,.m-hikari.com http://d.doi.org/10.1988/astp.015.411150 Note on athematical Development of Plate Theories Patiphan Chantaraichit
Uniform Law on the Unit Sphere of a Banach Space
 Uniform Law on the Unit Shere of a Banach Sace by Bernard Beauzamy Société de Calcul Mathématique SA Faubourg Saint Honoré 75008 Paris France Setember 008 Abstract We investigate the construction of a
Uniform Law on the Unit Shere of a Banach Sace by Bernard Beauzamy Société de Calcul Mathématique SA Faubourg Saint Honoré 75008 Paris France Setember 008 Abstract We investigate the construction of a
1 Entropy 1. 3 Extensivity 4. 5 Convexity 5
 Contents CONEX FUNCIONS AND HERMODYNAMIC POENIALS 1 Entroy 1 2 Energy Reresentation 2 3 Etensivity 4 4 Fundamental Equations 4 5 Conveity 5 6 Legendre transforms 6 7 Reservoirs and Legendre transforms
Contents CONEX FUNCIONS AND HERMODYNAMIC POENIALS 1 Entroy 1 2 Energy Reresentation 2 3 Etensivity 4 4 Fundamental Equations 4 5 Conveity 5 6 Legendre transforms 6 7 Reservoirs and Legendre transforms
Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Polnomial and Rational Functions Figure -mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of ork b Horia Varlan;
Polnomial and Rational Functions Figure -mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of ork b Horia Varlan;
E-companion to A risk- and ambiguity-averse extension of the max-min newsvendor order formula
 e-comanion to Han Du and Zuluaga: Etension of Scarf s ma-min order formula ec E-comanion to A risk- and ambiguity-averse etension of the ma-min newsvendor order formula Qiaoming Han School of Mathematics
e-comanion to Han Du and Zuluaga: Etension of Scarf s ma-min order formula ec E-comanion to A risk- and ambiguity-averse etension of the ma-min newsvendor order formula Qiaoming Han School of Mathematics
DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF A VERSATILE METHOD FOR THE CALCULATION OF HEAT TRANSFER IN WATER-BASED RADIANT SYSTEMS METHODS
 Eleventh International IBPSA Conference Glasgo, Scotland July 27-30, 2009 DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF A VERSATILE METHOD FOR THE CALCULATION OF HEAT TRANSFER IN WATER-BASED RADIANT SYSTEMS Massimiliano
Eleventh International IBPSA Conference Glasgo, Scotland July 27-30, 2009 DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF A VERSATILE METHOD FOR THE CALCULATION OF HEAT TRANSFER IN WATER-BASED RADIANT SYSTEMS Massimiliano
4. CONTINUOUS VARIABLES AND ECONOMIC APPLICATIONS
 STATIC GAMES 4. CONTINUOUS VARIABLES AND ECONOMIC APPLICATIONS Universidad Carlos III de Madrid CONTINUOUS VARIABLES In many games, ure strategies that layers can choose are not only, 3 or any other finite
STATIC GAMES 4. CONTINUOUS VARIABLES AND ECONOMIC APPLICATIONS Universidad Carlos III de Madrid CONTINUOUS VARIABLES In many games, ure strategies that layers can choose are not only, 3 or any other finite
Lecture 7: Linear Classification Methods
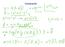 Homeork Homeork Lecture 7: Linear lassification Methods Final rojects? Grous oics Proosal eek 5 Lecture is oster session, Jacobs Hall Lobby, snacks Final reort 5 June. What is linear classification? lassification
Homeork Homeork Lecture 7: Linear lassification Methods Final rojects? Grous oics Proosal eek 5 Lecture is oster session, Jacobs Hall Lobby, snacks Final reort 5 June. What is linear classification? lassification
ECON 500 Fall Exam #2 Answer Key.
 ECO 500 Fall 004. Eam # Answer Key. ) While standing in line at your favourite movie theatre, you hear someone behind you say: I like ocorn, but I m not buying any because it isn t worth the high rice.
ECO 500 Fall 004. Eam # Answer Key. ) While standing in line at your favourite movie theatre, you hear someone behind you say: I like ocorn, but I m not buying any because it isn t worth the high rice.
Mathematics. Class 12th. CBSE Examination Paper 2015 (All India Set) (Detailed Solutions)
 CBSE Eamination Paer (All India Set) (Detailed Solutions) Mathematics Class th z z. We have, z On aling R R R, we get z z z z (/) Taking common ( z) from R common from R, we get ( z)( ) z ( z)( ) [ R R
CBSE Eamination Paer (All India Set) (Detailed Solutions) Mathematics Class th z z. We have, z On aling R R R, we get z z z z (/) Taking common ( z) from R common from R, we get ( z)( ) z ( z)( ) [ R R
Feedback-error control
 Chater 4 Feedback-error control 4.1 Introduction This chater exlains the feedback-error (FBE) control scheme originally described by Kawato [, 87, 8]. FBE is a widely used neural network based controller
Chater 4 Feedback-error control 4.1 Introduction This chater exlains the feedback-error (FBE) control scheme originally described by Kawato [, 87, 8]. FBE is a widely used neural network based controller
Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Polnomial and Rational Functions Figure -mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of ork b Horia Varlan;
Polnomial and Rational Functions Figure -mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of ork b Horia Varlan;
Generalized Least-Squares Regressions II: Theory and Classication
 Recent Advances in Intelligent Control, Modelling Comutational Science Generalized Least-Squares Regressions II Theor Classication NATANIEL GREENE Deartment of Mathematics Comuter Science Kingsorough Communit
Recent Advances in Intelligent Control, Modelling Comutational Science Generalized Least-Squares Regressions II Theor Classication NATANIEL GREENE Deartment of Mathematics Comuter Science Kingsorough Communit
Exercise 2: Equivalence of the first two definitions for a differentiable function. is a convex combination of
 March 07 Mathematical Foundations John Riley Module Marginal analysis and single variable calculus 6 Eercises Eercise : Alternative definitions of a concave function (a) For and that 0, and conve combination
March 07 Mathematical Foundations John Riley Module Marginal analysis and single variable calculus 6 Eercises Eercise : Alternative definitions of a concave function (a) For and that 0, and conve combination
λ. It is usually positive; if it is zero then the constraint is not binding.
 hater 4 Utilit Maimization and hoice rational consmer chooses his most referred bndle of commodities from the set of feasible choices to consme The rocess of obtaining this otimal bndle is called tilit-maimization
hater 4 Utilit Maimization and hoice rational consmer chooses his most referred bndle of commodities from the set of feasible choices to consme The rocess of obtaining this otimal bndle is called tilit-maimization
Pure exchange competitive equilibrium under uncertainty
 J Ambient Intell Human Comut 7) 8:759 768 DOI.7/s65-7-5-x ORIGINAL RESEARCH Pure exchange cometitive equilibrium under uncertainty Qiqiong Chen Yuanguo Zhu Received: 7 February 7 / Acceted: 4 Aril 7 /
J Ambient Intell Human Comut 7) 8:759 768 DOI.7/s65-7-5-x ORIGINAL RESEARCH Pure exchange cometitive equilibrium under uncertainty Qiqiong Chen Yuanguo Zhu Received: 7 February 7 / Acceted: 4 Aril 7 /
0.1 Practical Guide - Surface Integrals. C (0,0,c) A (0,b,0) A (a,0,0)
 . Practical Guide - urface Integrals urface integral,means to integrate over a surface. We begin with the stud of surfaces. The easiest wa is to give as man familiar eamles as ossible ) a lane surface
. Practical Guide - urface Integrals urface integral,means to integrate over a surface. We begin with the stud of surfaces. The easiest wa is to give as man familiar eamles as ossible ) a lane surface
Finding Shortest Hamiltonian Path is in P. Abstract
 Finding Shortest Hamiltonian Path is in P Dhananay P. Mehendale Sir Parashurambhau College, Tilak Road, Pune, India bstract The roblem of finding shortest Hamiltonian ath in a eighted comlete grah belongs
Finding Shortest Hamiltonian Path is in P Dhananay P. Mehendale Sir Parashurambhau College, Tilak Road, Pune, India bstract The roblem of finding shortest Hamiltonian ath in a eighted comlete grah belongs
10.2 Polar Equations and Graphs
 SECTIN 0. Polar Equations and Grahs 77 Elaining Concets: Discussion and Writing 85. In converting from olar coordinates to rectangular coordinates, what formulas will ou use? 86. Elain how ou roceed to
SECTIN 0. Polar Equations and Grahs 77 Elaining Concets: Discussion and Writing 85. In converting from olar coordinates to rectangular coordinates, what formulas will ou use? 86. Elain how ou roceed to
Export Subsidies, Productivity and Welfare under Firm-Level Heterogeneity
 Eport Subsidies, Productivit and Welare under Firm-Level Heterogeneit Svetlana Demidova Universit o Georgia Andres Rodriguez-Clare z Pennslvania State Universit and NBER Februar 2007 Abstract It is ell
Eport Subsidies, Productivit and Welare under Firm-Level Heterogeneit Svetlana Demidova Universit o Georgia Andres Rodriguez-Clare z Pennslvania State Universit and NBER Februar 2007 Abstract It is ell
Business Cycles: The Classical Approach
 San Francisco State University ECON 302 Business Cycles: The Classical Approach Introduction Michael Bar Recall from the introduction that the output per capita in the U.S. is groing steady, but there
San Francisco State University ECON 302 Business Cycles: The Classical Approach Introduction Michael Bar Recall from the introduction that the output per capita in the U.S. is groing steady, but there
A Method of Setting the Penalization Constants in the Suboptimal Linear Quadratic Tracking Method
 XXVI. ASR '21 Seminar, Instruments and Control, Ostrava, Aril 26-27, 21 Paer 57 A Method of Setting the Penalization Constants in the Subotimal Linear Quadratic Tracking Method PERŮTKA, Karel Ing., Deartment
XXVI. ASR '21 Seminar, Instruments and Control, Ostrava, Aril 26-27, 21 Paer 57 A Method of Setting the Penalization Constants in the Subotimal Linear Quadratic Tracking Method PERŮTKA, Karel Ing., Deartment
Comments on Problems. 3.1 This problem offers some practice in deriving utility functions from indifference curve specifications.
 CHAPTER 3 PREFERENCES AND UTILITY These problems provide some practice in eamining utilit unctions b looking at indierence curve maps and at a ew unctional orms. The primar ocus is on illustrating the
CHAPTER 3 PREFERENCES AND UTILITY These problems provide some practice in eamining utilit unctions b looking at indierence curve maps and at a ew unctional orms. The primar ocus is on illustrating the
MA202 Calculus III Fall, 2009 Laboratory Exploration 3: Vector Fields Solution Key
 MA0 Calculus III Fall, 009 Laborator Eloration 3: Vector Fields Solution Ke Introduction: This lab deals with several asects of vector elds. Read the handout on vector elds and electrostatics from Chater
MA0 Calculus III Fall, 009 Laborator Eloration 3: Vector Fields Solution Ke Introduction: This lab deals with several asects of vector elds. Read the handout on vector elds and electrostatics from Chater
7. Two Random Variables
 7. Two Random Variables In man eeriments the observations are eressible not as a single quantit but as a amil o quantities. or eamle to record the height and weight o each erson in a communit or the number
7. Two Random Variables In man eeriments the observations are eressible not as a single quantit but as a amil o quantities. or eamle to record the height and weight o each erson in a communit or the number
A Two-Warehouse Inventory Model with Imperfect Quality and Inspection Errors
 esearch Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technolog 4(0): 3896-3904, 0 ISSN: 040-7467 Maell Scientific Organization, 0 Submitted: ecember 8, 0 Accepted: April 3, 0 Published: October 5, 0 A
esearch Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technolog 4(0): 3896-3904, 0 ISSN: 040-7467 Maell Scientific Organization, 0 Submitted: ecember 8, 0 Accepted: April 3, 0 Published: October 5, 0 A
Consumer Theory. Budget Set. Isoquants. Budget Line. Budget Set x
 Consmer Theor Bdget Set M Y + Y M. Bdget Line Bdget Set M Isoqants 0.8 0.6 0.4 0. 0 0 0. 0.4 0.6 0.8 Isoqants Isoqants are contor sets of the tilit fnction Conve references means if consmer indifferent
Consmer Theor Bdget Set M Y + Y M. Bdget Line Bdget Set M Isoqants 0.8 0.6 0.4 0. 0 0 0. 0.4 0.6 0.8 Isoqants Isoqants are contor sets of the tilit fnction Conve references means if consmer indifferent
Recovering preferences in the household production framework: The case of averting behavior
 Udo Ebert Recovering references in the household roduction framework: The case of averting behavior February 2002 * Address: Deartment of Economics, University of Oldenburg, D-26 Oldenburg, ermany Tel.:
Udo Ebert Recovering references in the household roduction framework: The case of averting behavior February 2002 * Address: Deartment of Economics, University of Oldenburg, D-26 Oldenburg, ermany Tel.:
Exponential Ratio Type Estimators of Population Mean under Non-Response
 Oen Journal of Statistics, 0,, 97-0 Published Online Februar 0 (htt://www.scir.org/journal/ojs) htt://d.doi.org/0.6/ojs.0.00 Eonential Ratio Te Estimators of Poulation Mean under Non-Resonse Lovleen Kumar
Oen Journal of Statistics, 0,, 97-0 Published Online Februar 0 (htt://www.scir.org/journal/ojs) htt://d.doi.org/0.6/ojs.0.00 Eonential Ratio Te Estimators of Poulation Mean under Non-Resonse Lovleen Kumar
A continuous review inventory model with the controllable production rate of the manufacturer
 Intl. Trans. in O. Res. 12 (2005) 247 258 INTERNATIONAL TRANSACTIONS IN OERATIONAL RESEARCH A continuous review inventory model with the controllable roduction rate of the manufacturer I. K. Moon and B.
Intl. Trans. in O. Res. 12 (2005) 247 258 INTERNATIONAL TRANSACTIONS IN OERATIONAL RESEARCH A continuous review inventory model with the controllable roduction rate of the manufacturer I. K. Moon and B.
Optimization of Gear Design and Manufacture. Vilmos SIMON *
 7 International Conference on Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering (ICMME 7) ISBN: 978--6595-44- timization of Gear Design and Manufacture Vilmos SIMN * Budaest Universit of Technolog and Economics,
7 International Conference on Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering (ICMME 7) ISBN: 978--6595-44- timization of Gear Design and Manufacture Vilmos SIMN * Budaest Universit of Technolog and Economics,
A Generalization of a result of Catlin: 2-factors in line graphs
 AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 72(2) (2018), Pages 164 184 A Generalization of a result of Catlin: 2-factors in line graphs Ronald J. Gould Emory University Atlanta, Georgia U.S.A. rg@mathcs.emory.edu
AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 72(2) (2018), Pages 164 184 A Generalization of a result of Catlin: 2-factors in line graphs Ronald J. Gould Emory University Atlanta, Georgia U.S.A. rg@mathcs.emory.edu
Econ 401A: Economic Theory Mid-term. Answers
 . Labor suly Econ 40: Economic Theory Mid-term nswers (a) Let be labor suly. Then x 4 The key ste is setting u the budget constraint. x w w(4 x ) Thus the budget constraint can be rewritten as follows:
. Labor suly Econ 40: Economic Theory Mid-term nswers (a) Let be labor suly. Then x 4 The key ste is setting u the budget constraint. x w w(4 x ) Thus the budget constraint can be rewritten as follows:
Robust Beamforming via Matrix Completion
 Robust Beamforming via Matrix Comletion Shunqiao Sun and Athina P. Petroulu Deartment of Electrical and Comuter Engineering Rutgers, the State University of Ne Jersey Piscataay, Ne Jersey 8854-858 Email:
Robust Beamforming via Matrix Comletion Shunqiao Sun and Athina P. Petroulu Deartment of Electrical and Comuter Engineering Rutgers, the State University of Ne Jersey Piscataay, Ne Jersey 8854-858 Email:
CONSUMPTION. (Lectures 4, 5, and 6) Remark: (*) signals those exercises that I consider to be the most important
 CONSUMPTION (Lectures 4, 5, and 6) Remark: (*) signals those eercises that I consider to be the most imortant Eercise 0 (MWG, E. 1.B.1, 1.B.) Show that if is rational, then: 1. if y z, then z;. is both
CONSUMPTION (Lectures 4, 5, and 6) Remark: (*) signals those eercises that I consider to be the most imortant Eercise 0 (MWG, E. 1.B.1, 1.B.) Show that if is rational, then: 1. if y z, then z;. is both
2.2 BUDGET-CONSTRAINED CHOICE WITH TWO COMMODITIES
 Essential Miroeonomis -- 22 BUDGET-CONSTRAINED CHOICE WITH TWO COMMODITIES Continuity of demand 2 Inome effets 6 Quasi-linear, Cobb-Douglas and CES referenes 9 Eenditure funtion 4 Substitution effets and
Essential Miroeonomis -- 22 BUDGET-CONSTRAINED CHOICE WITH TWO COMMODITIES Continuity of demand 2 Inome effets 6 Quasi-linear, Cobb-Douglas and CES referenes 9 Eenditure funtion 4 Substitution effets and
Monopolist s mark-up and the elasticity of substitution
 Croatian Oerational Research Review 377 CRORR 8(7), 377 39 Monoolist s mark-u and the elasticity of substitution Ilko Vrankić, Mira Kran, and Tomislav Herceg Deartment of Economic Theory, Faculty of Economics
Croatian Oerational Research Review 377 CRORR 8(7), 377 39 Monoolist s mark-u and the elasticity of substitution Ilko Vrankić, Mira Kran, and Tomislav Herceg Deartment of Economic Theory, Faculty of Economics
Comparison of Estimators in Case of Low Correlation in Adaptive Cluster Sampling. Muhammad Shahzad Chaudhry 1 and Muhammad Hanif 2
 ISSN 684-8403 Journal of Statistics Volume 3, 06. pp. 4-57 Comparison of Estimators in Case of Lo Correlation in Muhammad Shahad Chaudhr and Muhammad Hanif Abstract In this paper, to Regression-Cum-Eponential
ISSN 684-8403 Journal of Statistics Volume 3, 06. pp. 4-57 Comparison of Estimators in Case of Lo Correlation in Muhammad Shahad Chaudhr and Muhammad Hanif Abstract In this paper, to Regression-Cum-Eponential
Boundedness Properties for Some Integral Transform
 Boundedness Proerties for Some Integral Transform V. D. Sharma, A. N. Rangari 2 Deartment of Mathematics, Arts, Commerce and Science College, Amravati- 444606(M.S), India Deartment of Mathematics, Adarsh
Boundedness Proerties for Some Integral Transform V. D. Sharma, A. N. Rangari 2 Deartment of Mathematics, Arts, Commerce and Science College, Amravati- 444606(M.S), India Deartment of Mathematics, Adarsh
CONTROL SYSTEMS, ROBOTICS, AND AUTOMATION Vol. III Stability Theory - Peter C. Müller
 STABILITY THEORY Peter C. Müller University of Wuertal, Germany Keywords: Asymtotic stability, Eonential stability, Linearization, Linear systems, Lyaunov equation, Lyaunov function, Lyaunov stability,
STABILITY THEORY Peter C. Müller University of Wuertal, Germany Keywords: Asymtotic stability, Eonential stability, Linearization, Linear systems, Lyaunov equation, Lyaunov function, Lyaunov stability,
ALTERNATIVE SOLUTION TO THE QUARTIC EQUATION by Farid A. Chouery 1, P.E. 2006, All rights reserved
 ALTERNATIVE SOLUTION TO THE QUARTIC EQUATION b Farid A. Chouer, P.E. 006, All rights reserved Abstract A new method to obtain a closed form solution of the fourth order olnomial equation is roosed in this
ALTERNATIVE SOLUTION TO THE QUARTIC EQUATION b Farid A. Chouer, P.E. 006, All rights reserved Abstract A new method to obtain a closed form solution of the fourth order olnomial equation is roosed in this
FUZZY CONTROL. Khurshid Ahmad, Professor of Computer Science, Department of Computer Science Trinity College, Dublin-2, IRELAND Nov 15-16th, 2011
 : Mamdani & akagi-sugeno Controllers Khurshid Ahmad, Professor of Comuter Science, Deartment of Comuter Science rinit College, Dublin-, IRELAND Nov 5-6th, 0 htts://www.cs.tcd.ie/khurshid.ahmad/eaching/eaching.html
: Mamdani & akagi-sugeno Controllers Khurshid Ahmad, Professor of Comuter Science, Deartment of Comuter Science rinit College, Dublin-, IRELAND Nov 5-6th, 0 htts://www.cs.tcd.ie/khurshid.ahmad/eaching/eaching.html
CHAPTER 3 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE POPULATION. From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum
 CHAPTER 3 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE POPULATION From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum 1997 19 CHAPTER 3 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE POPULATION 3.0. Introduction
CHAPTER 3 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE POPULATION From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum 1997 19 CHAPTER 3 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE POPULATION 3.0. Introduction
COBB-Douglas, Constant Elasticity of Substitution (CES) and Transcendental Logarithmic Production Functions in Non-linear Type of Special Functions
 ISSN: 3-9653; IC Value: 45.98; SJ Imact Factor :6.887 Volume 5 Issue XII December 07- Available at www.ijraset.com COBB-Douglas, Constant Elasticity of Substitution (CES) and Transcendental Logarithmic
ISSN: 3-9653; IC Value: 45.98; SJ Imact Factor :6.887 Volume 5 Issue XII December 07- Available at www.ijraset.com COBB-Douglas, Constant Elasticity of Substitution (CES) and Transcendental Logarithmic
Stationary Monetary Equilibria with Strictly Increasing Value Functions and Non-Discrete Money Holdings Distributions: An Indeterminacy Result
 CIRJE-F-615 Stationary Monetary Equilibria with Strictly Increasing Value Functions and Non-Discrete Money Holdings Distributions: An Indeterminacy Result Kazuya Kamiya University of Toyo Taashi Shimizu
CIRJE-F-615 Stationary Monetary Equilibria with Strictly Increasing Value Functions and Non-Discrete Money Holdings Distributions: An Indeterminacy Result Kazuya Kamiya University of Toyo Taashi Shimizu
4 Scheduling. Outline of the chapter. 4.1 Preliminaries
 4 Scheduling In this section, e consider so-called Scheduling roblems I.e., if there are altogether M machines or resources for each machine, a roduction sequence of all N jobs has to be found as ell as
4 Scheduling In this section, e consider so-called Scheduling roblems I.e., if there are altogether M machines or resources for each machine, a roduction sequence of all N jobs has to be found as ell as
Engineering Mathematics (E35 317) Final Exam December 15, 2006
 Engineering Mathematics (E35 317) Final Exam December 15, 2006 This exam contains six free-resonse roblems orth 36 oints altogether, eight short-anser roblems orth one oint each, seven multile-choice roblems
Engineering Mathematics (E35 317) Final Exam December 15, 2006 This exam contains six free-resonse roblems orth 36 oints altogether, eight short-anser roblems orth one oint each, seven multile-choice roblems
Factor Analysis of Convective Heat Transfer for a Horizontal Tube in the Turbulent Flow Region Using Artificial Neural Network
 COMPUTATIONAL METHODS IN ENGINEERING AND SCIENCE EPMESC X, Aug. -3, 6, Sanya, Hainan,China 6 Tsinghua University ess & Sringer-Verlag Factor Analysis of Convective Heat Transfer for a Horizontal Tube in
COMPUTATIONAL METHODS IN ENGINEERING AND SCIENCE EPMESC X, Aug. -3, 6, Sanya, Hainan,China 6 Tsinghua University ess & Sringer-Verlag Factor Analysis of Convective Heat Transfer for a Horizontal Tube in
Statics and dynamics: some elementary concepts
 1 Statics and dynamics: some elementary concets Dynamics is the study of the movement through time of variables such as heartbeat, temerature, secies oulation, voltage, roduction, emloyment, rices and
1 Statics and dynamics: some elementary concets Dynamics is the study of the movement through time of variables such as heartbeat, temerature, secies oulation, voltage, roduction, emloyment, rices and
Hadi s Method and It s Advantage in Ranking Fuzzy Numbers
 ustralian Journal of Basic and pplied Sciences, 4(1): 46-467, 1 ISSN 1991-8178 Hadi s Method and It s dvantage in anking Fuzz Numbers S.H. Nasseri, M. Sohrabi Department of Mathematical Sciences, Mazandaran
ustralian Journal of Basic and pplied Sciences, 4(1): 46-467, 1 ISSN 1991-8178 Hadi s Method and It s dvantage in anking Fuzz Numbers S.H. Nasseri, M. Sohrabi Department of Mathematical Sciences, Mazandaran
Research on the nonlinear spherical percolation model with quadratic pressure gradient and its percolation characteristics
 Vol., No., 98-105 (010) htt://dx.doi.org/10.436/ns.010.016 Natural Science Research on the nonlinear sherical ercolation model with quadratic ressure gradient and its ercolation characteristics Ren-Shi
Vol., No., 98-105 (010) htt://dx.doi.org/10.436/ns.010.016 Natural Science Research on the nonlinear sherical ercolation model with quadratic ressure gradient and its ercolation characteristics Ren-Shi
Voting and Lobbying - 3 Models
 Voting and obbying - 3 Models Series of 3 aers eloring the effects of olitical actions on market outcomes. Current theories of regulation unsatisfying (to me!: Toulouse School: Agency Model regulators
Voting and obbying - 3 Models Series of 3 aers eloring the effects of olitical actions on market outcomes. Current theories of regulation unsatisfying (to me!: Toulouse School: Agency Model regulators
Local Extreme Points and a Young-Type Inequality
 Alied Mathematical Sciences Vol. 08 no. 6 65-75 HIKARI Ltd www.m-hikari.com htts://doi.org/0.988/ams.08.886 Local Extreme Points a Young-Te Inequalit Loredana Ciurdariu Deartment of Mathematics Politehnica
Alied Mathematical Sciences Vol. 08 no. 6 65-75 HIKARI Ltd www.m-hikari.com htts://doi.org/0.988/ams.08.886 Local Extreme Points a Young-Te Inequalit Loredana Ciurdariu Deartment of Mathematics Politehnica
y(x) = x w + ε(x), (1)
 Linear regression We are ready to consider our first machine-learning problem: linear regression. Suppose that e are interested in the values of a function y(x): R d R, here x is a d-dimensional vector-valued
Linear regression We are ready to consider our first machine-learning problem: linear regression. Suppose that e are interested in the values of a function y(x): R d R, here x is a d-dimensional vector-valued
Two NP-hard Interchangeable Terminal Problems*
 o NP-hard Interchangeable erminal Problems* Sartaj Sahni and San-Yuan Wu Universit of Minnesota ABSRAC o subproblems that arise hen routing channels ith interchangeable terminals are shon to be NP-hard
o NP-hard Interchangeable erminal Problems* Sartaj Sahni and San-Yuan Wu Universit of Minnesota ABSRAC o subproblems that arise hen routing channels ith interchangeable terminals are shon to be NP-hard
Electromagnetics I Exam No. 3 December 1, 2003 Solution
 Electroagnetics Ea No. 3 Deceber 1, 2003 Solution Please read the ea carefull. Solve the folloing 4 probles. Each proble is 1/4 of the grade. To receive full credit, ou ust sho all ork. f cannot understand
Electroagnetics Ea No. 3 Deceber 1, 2003 Solution Please read the ea carefull. Solve the folloing 4 probles. Each proble is 1/4 of the grade. To receive full credit, ou ust sho all ork. f cannot understand
Session 5: Review of Classical Astrodynamics
 Session 5: Review of Classical Astrodynamics In revious lectures we described in detail the rocess to find the otimal secific imulse for a articular situation. Among the mission requirements that serve
Session 5: Review of Classical Astrodynamics In revious lectures we described in detail the rocess to find the otimal secific imulse for a articular situation. Among the mission requirements that serve
FOCUS ON THEORY. We recall that a function g(x) is differentiable at the point a if the limit
 FOCUS ON THEORY 653 DIFFERENTIABILITY Notes on Differentiabilit In Section 13.3 we gave an informal introduction to te concet of differentiabilit. We called a function f (; ) differentiable at a oint (a;
FOCUS ON THEORY 653 DIFFERENTIABILITY Notes on Differentiabilit In Section 13.3 we gave an informal introduction to te concet of differentiabilit. We called a function f (; ) differentiable at a oint (a;
Discussion Papers in Economics
 Discussion Paers in Economics No. No. 2004/09 2000/62 Dynamics of Multile Outut Growth, Equilibria Consumtion with Eternalities and Physical Caital in Two-Sector Models of Endogenous Growth by by Emanuela
Discussion Paers in Economics No. No. 2004/09 2000/62 Dynamics of Multile Outut Growth, Equilibria Consumtion with Eternalities and Physical Caital in Two-Sector Models of Endogenous Growth by by Emanuela
Optical Design with Zemax
 Otical Design with Zema Lecture 9: Imaging 13-1-8 Herbert Gross Winter term 1 www.ia.uni-jena.de Time schedule 1 16.1. Introduction Introduction, Zema interface, menues, file handling, references, Editors,
Otical Design with Zema Lecture 9: Imaging 13-1-8 Herbert Gross Winter term 1 www.ia.uni-jena.de Time schedule 1 16.1. Introduction Introduction, Zema interface, menues, file handling, references, Editors,
CMSC 425: Lecture 4 Geometry and Geometric Programming
 CMSC 425: Lecture 4 Geometry and Geometric Programming Geometry for Game Programming and Grahics: For the next few lectures, we will discuss some of the basic elements of geometry. There are many areas
CMSC 425: Lecture 4 Geometry and Geometric Programming Geometry for Game Programming and Grahics: For the next few lectures, we will discuss some of the basic elements of geometry. There are many areas
PERFORMANCE BASED DESIGN SYSTEM FOR CONCRETE MIXTURE WITH MULTI-OPTIMIZING GENETIC ALGORITHM
 PERFORMANCE BASED DESIGN SYSTEM FOR CONCRETE MIXTURE WITH MULTI-OPTIMIZING GENETIC ALGORITHM Takafumi Noguchi 1, Iei Maruyama 1 and Manabu Kanematsu 1 1 Deartment of Architecture, University of Tokyo,
PERFORMANCE BASED DESIGN SYSTEM FOR CONCRETE MIXTURE WITH MULTI-OPTIMIZING GENETIC ALGORITHM Takafumi Noguchi 1, Iei Maruyama 1 and Manabu Kanematsu 1 1 Deartment of Architecture, University of Tokyo,
Econ 201: Problem Set 3 Answers
 Econ 20: Problem Set 3 Ansers Instructor: Alexandre Sollaci T.A.: Ryan Hughes Winter 208 Question a) The firm s fixed cost is F C = a and variable costs are T V Cq) = 2 bq2. b) As seen in class, the optimal
Econ 20: Problem Set 3 Ansers Instructor: Alexandre Sollaci T.A.: Ryan Hughes Winter 208 Question a) The firm s fixed cost is F C = a and variable costs are T V Cq) = 2 bq2. b) As seen in class, the optimal
An Asymptotic Approximation for TCP Compound
 Noname manuscrit No. (will be inserted b the editor) An Asmtotic Aroimation for TCP Comound Sudheer Poojar Vinod Sharma Received: date / Acceted: date Abstract In this aer, we derive an aroimation for
Noname manuscrit No. (will be inserted b the editor) An Asmtotic Aroimation for TCP Comound Sudheer Poojar Vinod Sharma Received: date / Acceted: date Abstract In this aer, we derive an aroimation for
Research on Evaluation Method of Organization s Performance Based on Comparative Advantage Characteristics
 Vol.1, No.10, Ar 01,.67-7 Research on Evaluation Method of Organization s Performance Based on Comarative Advantage Characteristics WEN Xin 1, JIA Jianfeng and ZHAO Xi nan 3 Abstract It as under the guidance
Vol.1, No.10, Ar 01,.67-7 Research on Evaluation Method of Organization s Performance Based on Comarative Advantage Characteristics WEN Xin 1, JIA Jianfeng and ZHAO Xi nan 3 Abstract It as under the guidance
The decision-feedback equalizer optimization for Gaussian noise
 Journal of Theoretical and Alied Comuter Science Vol. 8 No. 4 4. 5- ISSN 99-634 (rinted 3-5653 (online htt://www.jtacs.org The decision-feedback eualizer otimization for Gaussian noise Arkadiusz Grzbowski
Journal of Theoretical and Alied Comuter Science Vol. 8 No. 4 4. 5- ISSN 99-634 (rinted 3-5653 (online htt://www.jtacs.org The decision-feedback eualizer otimization for Gaussian noise Arkadiusz Grzbowski
Symmetric and Asymmetric Equilibria in a Spatial Duopoly
 This version: February 003 Symmetric and Asymmetric Equilibria in a Satial Duooly Marcella Scrimitore Deartment of Economics, University of Lecce, Italy Jel Classification: L3, R39 Abstract We develo a
This version: February 003 Symmetric and Asymmetric Equilibria in a Satial Duooly Marcella Scrimitore Deartment of Economics, University of Lecce, Italy Jel Classification: L3, R39 Abstract We develo a
Introduction to Probability for Graphical Models
 Introduction to Probability for Grahical Models CSC 4 Kaustav Kundu Thursday January 4, 06 *Most slides based on Kevin Swersky s slides, Inmar Givoni s slides, Danny Tarlow s slides, Jaser Snoek s slides,
Introduction to Probability for Grahical Models CSC 4 Kaustav Kundu Thursday January 4, 06 *Most slides based on Kevin Swersky s slides, Inmar Givoni s slides, Danny Tarlow s slides, Jaser Snoek s slides,
The Fekete Szegő theorem with splitting conditions: Part I
 ACTA ARITHMETICA XCIII.2 (2000) The Fekete Szegő theorem with slitting conditions: Part I by Robert Rumely (Athens, GA) A classical theorem of Fekete and Szegő [4] says that if E is a comact set in the
ACTA ARITHMETICA XCIII.2 (2000) The Fekete Szegő theorem with slitting conditions: Part I by Robert Rumely (Athens, GA) A classical theorem of Fekete and Szegő [4] says that if E is a comact set in the
Greediness of higher rank Haar wavelet bases in L p w(r) spaces
 Stud. Univ. Babeş-Bolyai Math. 59(2014), No. 2, 213 219 Greediness of higher rank Haar avelet bases in L (R) saces Ekaterine Kaanadze Abstract. We rove that higher rank Haar avelet systems are greedy in
Stud. Univ. Babeş-Bolyai Math. 59(2014), No. 2, 213 219 Greediness of higher rank Haar avelet bases in L (R) saces Ekaterine Kaanadze Abstract. We rove that higher rank Haar avelet systems are greedy in
Cost and benefit including value of life and limb measured in time units
 Secial Worksho on Risk Accetance and Risk Communication March 26-27, 2007, Stanford University Cost and benefit including value of life and limb measured in time units Ove Ditlevsen and Peter Friis-Hansen
Secial Worksho on Risk Accetance and Risk Communication March 26-27, 2007, Stanford University Cost and benefit including value of life and limb measured in time units Ove Ditlevsen and Peter Friis-Hansen
Elements of Economic Analysis II Lecture VII: Equilibrium in a Competitive Market
 Elements of Economic Analysis II Lecture VII: Equilibrium in a Competitive Market Kai Hao Yang 10/31/2017 1 Partial Equilibrium in a Competitive Market In the previous lecture, e derived the aggregate
Elements of Economic Analysis II Lecture VII: Equilibrium in a Competitive Market Kai Hao Yang 10/31/2017 1 Partial Equilibrium in a Competitive Market In the previous lecture, e derived the aggregate
Conditioning and Independence
 Discrete Random Variables: Joint PMFs Conditioning and Indeendence Berlin Chen Deartment of Comuter Science & Information ngineering National Taiwan Normal Universit Reference: - D. P. Bertsekas J. N.
Discrete Random Variables: Joint PMFs Conditioning and Indeendence Berlin Chen Deartment of Comuter Science & Information ngineering National Taiwan Normal Universit Reference: - D. P. Bertsekas J. N.
Figure : An 8 bridge design grid. (a) Run this model using LOQO. What is the otimal comliance? What is the running time?
 5.094/SMA53 Systems Otimization: Models and Comutation Assignment 5 (00 o i n ts) Due Aril 7, 004 Some Convex Analysis (0 o i n ts) (a) Given ositive scalars L and E, consider the following set in three-dimensional
5.094/SMA53 Systems Otimization: Models and Comutation Assignment 5 (00 o i n ts) Due Aril 7, 004 Some Convex Analysis (0 o i n ts) (a) Given ositive scalars L and E, consider the following set in three-dimensional
Stable ion beam transport through periodic electrostatic structures: linear and non-linear effects
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com hsics rocedia rocedia 001 (008) (008) 000 000 87 97 www.elsevier.com/locate/rocedia www.elsevier.com/locate/ roceedings of the Seventh International Conference
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com hsics rocedia rocedia 001 (008) (008) 000 000 87 97 www.elsevier.com/locate/rocedia www.elsevier.com/locate/ roceedings of the Seventh International Conference
Improving AOR Method for a Class of Two-by-Two Linear Systems
 Alied Mathematics 2 2 236-24 doi:4236/am22226 Published Online February 2 (htt://scirporg/journal/am) Imroving AOR Method for a Class of To-by-To Linear Systems Abstract Cuixia Li Shiliang Wu 2 College
Alied Mathematics 2 2 236-24 doi:4236/am22226 Published Online February 2 (htt://scirporg/journal/am) Imroving AOR Method for a Class of To-by-To Linear Systems Abstract Cuixia Li Shiliang Wu 2 College
2x2x2 Heckscher-Ohlin-Samuelson (H-O-S) model with factor substitution
 2x2x2 Heckscher-Ohlin-amuelson (H-O- model with factor substitution The HAT ALGEBRA of the Heckscher-Ohlin model with factor substitution o far we were dealing with the easiest ossible version of the H-O-
2x2x2 Heckscher-Ohlin-amuelson (H-O- model with factor substitution The HAT ALGEBRA of the Heckscher-Ohlin model with factor substitution o far we were dealing with the easiest ossible version of the H-O-
2.9. V = u(x,y) + a(x-f(l x,t x )) + b(y-g(l y,t y )) + c(l o -L x -L y ) + d(t o -T x -T y ) (1) (a) Suggested Answer: V u a 0 (2) u x = -a b 0 (3)
 2.9 V = u(,) + a(-f(, )) + b(-g(, )) + c( o - - ) + d( o - - ) (1) (a) Suggested Answer: V u a 0 (2) u = -a V u b 0 (3) u = -b V f a d 0 (4) V V V b g d 0 (5) a f c 0 (6) b g c 0 (7) g c/ b c c/a f (b)
2.9 V = u(,) + a(-f(, )) + b(-g(, )) + c( o - - ) + d( o - - ) (1) (a) Suggested Answer: V u a 0 (2) u = -a V u b 0 (3) u = -b V f a d 0 (4) V V V b g d 0 (5) a f c 0 (6) b g c 0 (7) g c/ b c c/a f (b)
Microeconomics Fall 2017 Problem set 1: Possible answers
 Microeconomics Fall 07 Problem set Possible answers Each answer resents only one way of solving the roblem. Other right answers are ossible and welcome. Exercise For each of the following roerties, draw
Microeconomics Fall 07 Problem set Possible answers Each answer resents only one way of solving the roblem. Other right answers are ossible and welcome. Exercise For each of the following roerties, draw
Distributed Rule-Based Inference in the Presence of Redundant Information
 istribution Statement : roved for ublic release; distribution is unlimited. istributed Rule-ased Inference in the Presence of Redundant Information June 8, 004 William J. Farrell III Lockheed Martin dvanced
istribution Statement : roved for ublic release; distribution is unlimited. istributed Rule-ased Inference in the Presence of Redundant Information June 8, 004 William J. Farrell III Lockheed Martin dvanced
Combinatorics of topmost discs of multi-peg Tower of Hanoi problem
 Combinatorics of tomost discs of multi-eg Tower of Hanoi roblem Sandi Klavžar Deartment of Mathematics, PEF, Unversity of Maribor Koroška cesta 160, 000 Maribor, Slovenia Uroš Milutinović Deartment of
Combinatorics of tomost discs of multi-eg Tower of Hanoi roblem Sandi Klavžar Deartment of Mathematics, PEF, Unversity of Maribor Koroška cesta 160, 000 Maribor, Slovenia Uroš Milutinović Deartment of
Lecture Thermodynamics 9. Entropy form of the 1 st law. Let us start with the differential form of the 1 st law: du = d Q + d W
 Lecture hermodnamics 9 Entro form of the st law Let us start with the differential form of the st law: du = d Q + d W Consider a hdrostatic sstem. o know the required d Q and d W between two nearb states,
Lecture hermodnamics 9 Entro form of the st law Let us start with the differential form of the st law: du = d Q + d W Consider a hdrostatic sstem. o know the required d Q and d W between two nearb states,
Linear programming: Theory
 Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences Ec 181 KC Border Convex Analsis and Economic Theor Winter 2018 Topic 28: Linear programming: Theor 28.1 The saddlepoint theorem for linear programming The
Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences Ec 181 KC Border Convex Analsis and Economic Theor Winter 2018 Topic 28: Linear programming: Theor 28.1 The saddlepoint theorem for linear programming The
Nonlinear programming
 08-04- htt://staff.chemeng.lth.se/~berntn/courses/otimps.htm Otimization of Process Systems Nonlinear rogramming PhD course 08 Bernt Nilsson, Det of Chemical Engineering, Lund University Content Unconstraint
08-04- htt://staff.chemeng.lth.se/~berntn/courses/otimps.htm Otimization of Process Systems Nonlinear rogramming PhD course 08 Bernt Nilsson, Det of Chemical Engineering, Lund University Content Unconstraint
