Topological Phonons, Edge States, and Guest Modes. 5/17/2016 Zanjan School
|
|
|
- Cleopatra Stephens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Topological Phonons, Edge States, and Guest Modes
2 Topological Defects Closed path in real space Path in order parameter space: topological invariant Periodic Brillouin Zone Function on torus Torus It no defects on surface, topology is completely determined by two winding numbers, i.e., by a lattice vector Closed path of function
3 Topology and Adiabatic Continuity Insulators are topologically equivalent if they can be continuously deformed into one another without closing the energy gap genus = 0 Are there topological phases that are not adiabatically connected to the trivial insulator (ie the vacuum)? genus = 1
4 Topological Electronic States and Topological Insulators A major theme in theory or electronic states: Berry s phases Polyacetylene Quantum Hall effect Topological Insulators surface conducting states (Graphene + 3d): Charlie Kane, Gene Mele, Liang Fu, Shoucheng Zhang Kane and Mele, PRL 95, ; PRL (2005) Hasan and Kane, Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 3046 (2012) S. C. Zhang and B. Yan, Rept. Prog. Phys. 75, (2012) Gapped states can have different topological classifications leading to different surface states. Charlie Kane Gene Mele
5 Topology in hbar physics Polyacetalene: 1D chain with dimerization u = ± u 0 Su, Schrieffer, Heeger 79 u<0 A phase u>0 B phase A B 0 (x) E Two Dimensions: Quantum spin Hall insulator Kane and Mele 05 QSHI conduction band Conducting edge Insulating interior u(x) valence band E F /a 0 /a
6 Outline Topological index and edge states in the SSH model A Mechanical SSH model Kagome based lattices with distinct topological properties Topological count and edge states in kagomebased lattices Guest elastic modes Weyl modes and lines 3D Lattices Jamming
7 Su Schrieffer Heeger Model Two types of sites: 1 and 2: 1 connects to 2 but not 1 to 1 or 2 to 2 t 1 t 2 H = å ét + t l ê y y ë y y 1 l,1 l,2 2 l,2 l+,1 + hc.. ù úû Q = t d + t d ll 1 ll 2 l-1, l ; å = [ y Q y + y Q y ] ll,' l,1 ll l,2 l,2 ll' l',1 Q T ll ' = t d + t d = C 1 ll 2 l + 1, l ll å = Y () khk () Y() k; Y = ( y, y ) k 1 2 * Ck () = Q() k = t + te 1 2 ika Hk ( ) t 0 t e 1 2 ik t t e ik 0 * Q k ( ) Qk ( ) 0
8 Gapped Spectrum 2 2 E = Q( k) = t + t + 2tt coska t = t = t 1 2 ¾¾¾¾2 t cos( ka/2) t ka=p ¾¾¾¾ t Spectrum has zeros at ka = p when t = t and a gap of E = 2 t - t when t ¹ t. g
9 Zero modes localized at endpoints H(k) 0 Q(k) C(k) 0 t1 t t1 t2 0 Ck ( ) 0 0 t1 t Ey = t y + t y ; E = 0 l2 1 l1 2 l+ 1,1 y =-( t / t ) y ; l+ 1,1 1 2 l,1 y = -( t / t ) y ; y = 0 l-1,1 2 1 l,1 l,2 Ey = t y + t y ; E = 0 l1 1 l2 2 l-1,2 y =-( t / t ) y ; l-1,2 1 2 l,2 y = -( t / t ) y ; y = 0 l+ 1,2 2 1 l,2 l,1 Decaying sol'n on sites 1 from right if t < t ; 1 2 from left if t > t 1 2
10 Topological Charge of Gapped States Ck () = t + et º t+ zt = Cz () ( = 0, at z=-t / t) ik Cauchy s Argument Principle 2p 1 g'( z) 1 d n = ò dz = ò dk 2 pi gz ( ) 2pi dk 0 = # zeros - # poles = integer ik gz () = 0; z = e < 0; no poles Im k >0: decaying soln ik ln g( e ) Phase of C t 1 <t 2 P d dk dk ln Ck ( ) 1,0 t 2 <t 1
11 Domain wall states Tie right and left decaying states together to create a zeroenergy mode localized at the domain wall s Hs =-H z z For every state with energy E, there is a state with energy E ( particle hole symmetry ): There is a topologically protected zero mode at the boundary between the two distinct topological phases.
12 Graphene Various perturbations break the symmetry and lead to gaps at the Dirac points. Note similarity to gapping of phonon states in the twisted kagome lattice. [Graphene: rotational symmetry about vertical axis; kagome pattern for every q x.]
13 1D Topological Mechanical Model Blue SSH site > site: Red SSH site > bond
14 C, s s C c ( ) c ( ) C c E, s 1 s, 2, s1, s 1 2 1(2) ( q) c ( ) c ( ) e Mechanical SSH Model ( a 2rsin ) rcos k k a s,, s 4r cos l C 2 C iqa T s s,, s s k c c s T D 1 s 2 s1 2 Same spectrum as SSH: Zero mode on left (right) if c c c c Non linear mode B. G. G. Chen, N. Upadhyaya, V. Vitelli PNAS 111, (2014).
15 Topological Mechanics Show Conductor movie Bryan Chen, Nitin Upadhyaya, Vincenzo Vitelli (Leiden) PNAS, 111,13004,(2014)
16 2 D Maxwell Lattices: z=2d=4 Maxwell Lattice one that under periodic boundary conditions have z=2d exactly, i.e., z=4 in two dimensions and z=6 in three dimension (Isostatic later) Kagome Lattices
17 Topological States in Isostatic Lattices H 1 2 kqqt 1 2 kq(k)q (k) Not clear how to extract topological information from this: Introduce a model coupling sites to bonds. Remember that in the periodic case, N B = dn, and Q is a square matrix. H k 0 Q Q T 0 QQ T 0 ; H 2 k 2 0 Q T Q H 2 has the same spectrum as H, except for zero modes Topological information is contained in Q. To get nontrivial topological states, constraint of equal length (but not z=4) bonds must be relaxed.
18 Transitions between Topological States P T = 0 P T = 0 Different topological states,characterized by a polarization vector P T classes are separated by gapless states produced by states of self stress Transition state with states of self stress P =-a T 1 P =-a T 1
19 T 1 V cell P T 1 V BZ Choose symmetric unit cell; Calculate Q S dsp T Topological Polarization Polarizations i d 2 k BZ k Im Tr lnq R T n i a i ; b i a j 2 ij T N cell GR T /2; G k i b i i Place charge +2 at each site bond: zero net charge in unit cells; polarization is zero in symmetric cell L N cell GP L /2 P L R L Polarization of surface cell = d r s r b sites s bonds b L T n 0 s 1 1 : charge 2 a2 4 4 : charge -1 a2 6 6 : charge -1 a P 2a a a a L
20 b 2 Mode Count 1 1 First recall dn=n +2 B. Assign charge +2 to each site and 1 to each bond (like Pebble game Thorpe). The periodic lattice is charge neutral, but charge distribution within cells can have a dipole moment. b b b a 2 b 1 Spectrum is gapless with modes with frequency ~ q 2 a 3 a 1 Define: N S dn N L T L T 0 local count = surface charge Topological count = "Polarization" charge B
21 Symmetric and Surface Gauges w n e iqa n ; S n w n 1 detc sym g 1 S 2 S 3 g 2 S 3 S 2 g 3 S 1 S 2 g 0 S 1 S 2 S 3 a 1 b n w n c n w n n1 z x e iq x x ; z y e i 3q y y/2 3 3 n1 w 1 z x ; w 2 z x 1/2 z y ; w 2 z x 1/2 z y 1 One pole in z y detc surf e iqr L detc sym No poles, only zeros: Topological charge of surface compatible unit cells simply counts the totalnumberofzero modes atthesurface!
22 Twisted Kagome Surface States P T R T 0
23 Topological Surface States Non zero R T moves zero modes from one surface to the opposite one.
24 G b1 G b1 Domain Wall l G ( RT R 2 1 zero modes T r T ) l r G ( RT RT) 2 1 States of Self Stres T Modes of full H with zero modes from Q ( States of self stress) and form Q T (zero modes)
25 Stresses and zero modes at defects J. Paulose, B. G. G. Chen, V. Vitelli, Nature Physics 11, (2015). Stress is concentrated at selfstress domain wall causing mechanical failure Dislocations localize soft modes and self stress: J. Paulose, A. S. Meeussen, V. Vitelli, PNAS 112, (2015)
26 Guest Modes K æ G K K K ö æ xxxx xxyy xxxy G G u ö xx G u u æ ö xx xy K K K ; G = xxyy yyyy yyxy G G u u = u u yy K K K xy yy G ç è ø xxxy yyxy xyxy u èç ø èç xy ø Zeros to linear order in q qx G G q = ( u -detu ) y G xy u xx if
27 Elastic Energy a a 1 1 > < 0 0 : Negative Poisson ratio and R = 0; Q = O k T 2 det ( ) near origin : Positive Poisson ratio and R ¹ 0; T 3 Q = O k ) k = a x 1 det ( along k ; w ~ T T y k 2 Show Mathematica animation! a 1 >0 a 1 <0
28 Bulk Modes of Topological Lattices k = k k ^ = + ^ n + k zˆ nˆ; sin q cos q i a i a1 i(3 + a nˆ = Surface cos q k sin q ) d 2( cos q i a sin q) k 2 normal a a > 0:Im k ~ k 1 ^ Opposite signs on opposite surfaces < 0 :Im k ~ k 2 1 ^ Number surface modes (1 or 2) depends on q
29 Strain shifted zero modes Rocklin, Zhou, Sun, Mao, arxiv:
30 Topological Square Lattices Zeb Rocklin Michigan Bryan Chen UMass Vincenzo Vitelli Leiden +Martin Falk D. Z. Rocklin, B. G. g. Chen, M. Falk, V. Vitelli, TCL, arxiv: (2015) Two q=0 states of self stress but no elasticity. Weyl modes have interesting and nontrivial effect nonlinear dynamics (Bryan Chen) Rule rather than exception for large unit cell lattices Topological lattice with zero (Weyl) modes at q \neq 0 (like graphene Dirac point) with non zero winding number: Topological Polarization depends on surface q s, and zero modes change surfaces with q s. Sample traversing state of self stress when q s corresponds to Weyl q.
31 Weyl Phase diagram and domain wall zero modes (b) (c) (d) (e) (b) In region without Weyl modes like kagome (c) Region with a pair of Weyl modes enter at origin and disappear at zone edge (d) Transition region line of zero modes and SSS (e) Double critical lines of zero modes and SSS in two diretions ( UL, ) n ( q) = No. zero modes at q on free upper 0 (lower) surface n = No. of "binding bonds" added B n D () q = n U () q + n L () q -n B = No. of zero modes in DW
32 Topological Pyrochlore Lattices Olaf Stenull, CL Kane, TCL: Work in Progress Topologically distinct 3D phases, constructed following procedures developed for kagome lattices Weyl lines instead of Weyl points with associated transition of zero modes from one side of sample to other as Weyl lines are crossed. 3 zero modes at q=0: and 3 soft and 3 hard elastic directions (like origami).
33 Weyl points at jamming (a) Jammed Maxwell Lattice (b) Randomized quasicrystal approximate Probability distribution of inverse penetration depth: + on right, on left No. of zero modes on two surfaces and positions of Weyl modes. Two independent states of self stress at domain wall dividing two jammed Maxwell lattices
34 Large antagonistic unit cells Red: wall of states of self stress Blue: Zero energy domain wall
35 Origami In Progress Thanks to Chris Santangelo and Bryan Chen d=3; n=4; n b =12; dn n b =0: A Maxwell lattice Twisted kagome and topological versions gapped apparently no topological distinction between two 3 states of self stress and 3 zero modes at q=0: 3 soft elastic modes that involve 2d elasticity and change in thickness of membrane (zzstrain). Relax latter: One soft mode of inplane distortion, like flat kagome. Effective elastic energy has Helfrich bending energy (up down symmetry is broken) and strain curvature coupling (suggestive of Ron Resch)
36 In Progress Nonlinear response: Weyl Modes and their interactions with Guest Modes; Elastic and periodic Weyl modes mix producing interesting instabilities. (B. Chen, Z. Rocklin, V. Vitelli, TCL. Extend to 3D Weyl lines (O. Stenull, TCL) Real systems: Perfect physical Maxwell lattices do not exist. They either have bending forces between bonds at vertices or effective further neighbor interactions, but these interactions can be small in engineered materials. How does turning on small NNN or bending forces modify elastic response and zero modes (X. Mao, O. Stenull, Shu Yang, TCL) : Long wavelength: (d 1) Rayleigh modes on each surface; Shorter wavelengths; crossover to behavior similar to Maxwell lattice behavior but with low frequency surface modes Domain wall modes develop a finite frequency and become localized propagating phonons: Domain wall acts like a wave guide. Can we control phonon propagation by controlled placement of domain walls Self stress domain walls concentrate stress [Paulose, Meeussen,Vitelli PNAS 112, (2015)]. Can we control these stresses and places at which material breakdown occurs?
Frames near Mechanical Collapse
 Frames near Mechanical Collapse Xiaming Mao (Umich) Kai Sun (Umich) Charlie Kane (Penn) Anton Souslov (Ga Tech) Olaf Stenull (Penn) Zeb Rocklin (Umich) Bryan Chen (Leiden) Vincenzo Vitelli (Leiden) James
Frames near Mechanical Collapse Xiaming Mao (Umich) Kai Sun (Umich) Charlie Kane (Penn) Anton Souslov (Ga Tech) Olaf Stenull (Penn) Zeb Rocklin (Umich) Bryan Chen (Leiden) Vincenzo Vitelli (Leiden) James
Topological Insulators and Superconductors
 Topological Insulators and Superconductors Lecture #1: Topology and Band Theory Lecture #: Topological Insulators in and 3 dimensions Lecture #3: Topological Superconductors, Majorana Fermions an Topological
Topological Insulators and Superconductors Lecture #1: Topology and Band Theory Lecture #: Topological Insulators in and 3 dimensions Lecture #3: Topological Superconductors, Majorana Fermions an Topological
Symmetry, Topology and Phases of Matter
 Symmetry, Topology and Phases of Matter E E k=λ a k=λ b k=λ a k=λ b Topological Phases of Matter Many examples of topological band phenomena States adiabatically connected to independent electrons: - Quantum
Symmetry, Topology and Phases of Matter E E k=λ a k=λ b k=λ a k=λ b Topological Phases of Matter Many examples of topological band phenomena States adiabatically connected to independent electrons: - Quantum
Xiaoming Mao Physics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. IGERT Summer Institute 2017 Brandeis
 Xiaoming Mao Physics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor IGERT Summer Institute 2017 Brandeis Elastic Networks A family of discrete model networks involving masses connected by springs 1 2 kk( ll)2 Disordered
Xiaoming Mao Physics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor IGERT Summer Institute 2017 Brandeis Elastic Networks A family of discrete model networks involving masses connected by springs 1 2 kk( ll)2 Disordered
Organizing Principles for Understanding Matter
 Organizing Principles for Understanding Matter Symmetry Conceptual simplification Conservation laws Distinguish phases of matter by pattern of broken symmetries Topology Properties insensitive to smooth
Organizing Principles for Understanding Matter Symmetry Conceptual simplification Conservation laws Distinguish phases of matter by pattern of broken symmetries Topology Properties insensitive to smooth
Topological Physics in Band Insulators II
 Topological Physics in Band Insulators II Gene Mele University of Pennsylvania Topological Insulators in Two and Three Dimensions The canonical list of electric forms of matter is actually incomplete Conductor
Topological Physics in Band Insulators II Gene Mele University of Pennsylvania Topological Insulators in Two and Three Dimensions The canonical list of electric forms of matter is actually incomplete Conductor
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 16 Oct 2015
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 16 Oct 2015 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 16 Oct 2015](/thumbs/92/110516249.jpg) Mechanical Weyl Modes in Topological Maxwell Lattices arxiv:151.497v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 16 Oct 215 D. Zeb Rocklin, 1 Bryan Gin ge Chen, 2, Martin Falk, 3 Vincenzo Vitelli, 2 and T. C. Lubensky 4 1 Department
Mechanical Weyl Modes in Topological Maxwell Lattices arxiv:151.497v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 16 Oct 215 D. Zeb Rocklin, 1 Bryan Gin ge Chen, 2, Martin Falk, 3 Vincenzo Vitelli, 2 and T. C. Lubensky 4 1 Department
SSH Model. Alessandro David. November 3, 2016
 SSH Model Alessandro David November 3, 2016 Adapted from Lecture Notes at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1509.02295 and from article: Nature Physics 9, 795 (2013) Motivations SSH = Su-Schrieffer-Heeger Polyacetylene
SSH Model Alessandro David November 3, 2016 Adapted from Lecture Notes at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1509.02295 and from article: Nature Physics 9, 795 (2013) Motivations SSH = Su-Schrieffer-Heeger Polyacetylene
Introduction to topological insulators. Jennifer Cano
 Introduction to topological insulators Jennifer Cano Adapted from Charlie Kane s Windsor Lectures: http://www.physics.upenn.edu/~kane/ Review article: Hasan & Kane Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010 What is an insulator?
Introduction to topological insulators Jennifer Cano Adapted from Charlie Kane s Windsor Lectures: http://www.physics.upenn.edu/~kane/ Review article: Hasan & Kane Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010 What is an insulator?
Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator
 Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley Refs: Ran, Zhang A.V., Nature Physics 5, 289 (2009). Hosur, Ryu, AV arxiv: 0908.2691 Part 1: Outline A toy model of
Topological Defects inside a Topological Band Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley Refs: Ran, Zhang A.V., Nature Physics 5, 289 (2009). Hosur, Ryu, AV arxiv: 0908.2691 Part 1: Outline A toy model of
Topological Physics in Band Insulators. Gene Mele Department of Physics University of Pennsylvania
 Topological Physics in Band Insulators Gene Mele Department of Physics University of Pennsylvania A Brief History of Topological Insulators What they are How they were discovered Why they are important
Topological Physics in Band Insulators Gene Mele Department of Physics University of Pennsylvania A Brief History of Topological Insulators What they are How they were discovered Why they are important
Symmetry Protected Topological Insulators and Semimetals
 Symmetry Protected Topological Insulators and Semimetals I. Introduction : Many examples of topological band phenomena II. Recent developments : - Line node semimetal Kim, Wieder, Kane, Rappe, PRL 115,
Symmetry Protected Topological Insulators and Semimetals I. Introduction : Many examples of topological band phenomena II. Recent developments : - Line node semimetal Kim, Wieder, Kane, Rappe, PRL 115,
Topological Physics in Band Insulators. Gene Mele DRL 2N17a
 Topological Physics in Band Insulators Gene Mele DRL 2N17a Electronic States of Matter Benjamin Franklin (University of Pennsylvania) That the Electrical Fire freely removes from Place to Place in and
Topological Physics in Band Insulators Gene Mele DRL 2N17a Electronic States of Matter Benjamin Franklin (University of Pennsylvania) That the Electrical Fire freely removes from Place to Place in and
Topological Phases of Matter Out of Equilibrium
 Topological Phases of Matter Out of Equilibrium Nigel Cooper T.C.M. Group, Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge Solvay Workshop on Quantum Simulation ULB, Brussels, 18 February 2019 Max McGinley
Topological Phases of Matter Out of Equilibrium Nigel Cooper T.C.M. Group, Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge Solvay Workshop on Quantum Simulation ULB, Brussels, 18 February 2019 Max McGinley
Topological Electromagnetic and Thermal Responses of Time-Reversal Invariant Superconductors and Chiral-Symmetric band insulators
 Topological Electromagnetic and Thermal Responses of Time-Reversal Invariant Superconductors and Chiral-Symmetric band insulators Satoshi Fujimoto Dept. Phys., Kyoto University Collaborator: Ken Shiozaki
Topological Electromagnetic and Thermal Responses of Time-Reversal Invariant Superconductors and Chiral-Symmetric band insulators Satoshi Fujimoto Dept. Phys., Kyoto University Collaborator: Ken Shiozaki
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Nov 2013
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Nov 2013 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Nov 2013](/thumbs/84/91227656.jpg) Topological Boundary Modes in Isostatic Lattices C. L. Kane and T. C. Lubensky Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 1914 arxiv:138.554v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Nov
Topological Boundary Modes in Isostatic Lattices C. L. Kane and T. C. Lubensky Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 1914 arxiv:138.554v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Nov
Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry
 Phys620.nb 101 7 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry Q: Can we get a topological insulator that preserves the time-reversal symmetry? A: Yes, with the help of the spin degree of freedom.
Phys620.nb 101 7 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry Q: Can we get a topological insulator that preserves the time-reversal symmetry? A: Yes, with the help of the spin degree of freedom.
Measuring many-body topological invariants using polarons
 1 Anyon workshop, Kaiserslautern, 12/15/2014 Measuring many-body topological invariants using polarons Fabian Grusdt Physics Department and Research Center OPTIMAS, University of Kaiserslautern, Germany
1 Anyon workshop, Kaiserslautern, 12/15/2014 Measuring many-body topological invariants using polarons Fabian Grusdt Physics Department and Research Center OPTIMAS, University of Kaiserslautern, Germany
Topological Kondo Insulator SmB 6. Tetsuya Takimoto
 Topological Kondo Insulator SmB 6 J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80 123720, (2011). Tetsuya Takimoto Department of Physics, Hanyang University Collaborator: Ki-Hoon Lee (POSTECH) Content 1. Introduction of SmB 6 in-gap
Topological Kondo Insulator SmB 6 J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80 123720, (2011). Tetsuya Takimoto Department of Physics, Hanyang University Collaborator: Ki-Hoon Lee (POSTECH) Content 1. Introduction of SmB 6 in-gap
2D Materials with Strong Spin-orbit Coupling: Topological and Electronic Transport Properties
 2D Materials with Strong Spin-orbit Coupling: Topological and Electronic Transport Properties Artem Pulkin California Institute of Technology (Caltech), Pasadena, CA 91125, US Institute of Physics, Ecole
2D Materials with Strong Spin-orbit Coupling: Topological and Electronic Transport Properties Artem Pulkin California Institute of Technology (Caltech), Pasadena, CA 91125, US Institute of Physics, Ecole
The Quantum Spin Hall Effect
 The Quantum Spin Hall Effect Shou-Cheng Zhang Stanford University with Andrei Bernevig, Taylor Hughes Science, 314,1757 2006 Molenamp et al, Science, 318, 766 2007 XL Qi, T. Hughes, SCZ preprint The quantum
The Quantum Spin Hall Effect Shou-Cheng Zhang Stanford University with Andrei Bernevig, Taylor Hughes Science, 314,1757 2006 Molenamp et al, Science, 318, 766 2007 XL Qi, T. Hughes, SCZ preprint The quantum
Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators
 Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators Eduardo Fradkin University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Workshop on Field Theoretic Computer Simulations for Particle Physics and Condensed Matter
Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators Eduardo Fradkin University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Workshop on Field Theoretic Computer Simulations for Particle Physics and Condensed Matter
Structure and Topology of Band Structures in the 1651 Magnetic Space Groups
 Structure and Topology of Band Structures in the 1651 Magnetic Space Groups Haruki Watanabe University of Tokyo [Noninteracting] Sci Adv (2016) PRL (2016) Nat Commun (2017) (New) arxiv:1707.01903 [Interacting]
Structure and Topology of Band Structures in the 1651 Magnetic Space Groups Haruki Watanabe University of Tokyo [Noninteracting] Sci Adv (2016) PRL (2016) Nat Commun (2017) (New) arxiv:1707.01903 [Interacting]
Topological insulators. Pavel Buividovich (Regensburg)
 Topological insulators Pavel Buividovich (Regensburg) Hall effect Classical treatment Dissipative motion for point-like particles (Drude theory) Steady motion Classical Hall effect Cyclotron frequency
Topological insulators Pavel Buividovich (Regensburg) Hall effect Classical treatment Dissipative motion for point-like particles (Drude theory) Steady motion Classical Hall effect Cyclotron frequency
POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials
 POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials Nandini Trivedi L1: Spin Orbit Coupling L2: Topology and Topological Insulators Tutorials: May 24, 25 (2017) Scope of Lectures and Anchor Points: 1.Spin-Orbit Interaction
POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials Nandini Trivedi L1: Spin Orbit Coupling L2: Topology and Topological Insulators Tutorials: May 24, 25 (2017) Scope of Lectures and Anchor Points: 1.Spin-Orbit Interaction
5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry
 Phys62.nb 63 5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry It is impossible to have quantum Hall effect without breaking the time-reversal symmetry. xy xy. If we want xy to be invariant under, xy
Phys62.nb 63 5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry It is impossible to have quantum Hall effect without breaking the time-reversal symmetry. xy xy. If we want xy to be invariant under, xy
Notes on Topological Insulators and Quantum Spin Hall Effect. Jouko Nieminen Tampere University of Technology.
 Notes on Topological Insulators and Quantum Spin Hall Effect Jouko Nieminen Tampere University of Technology. Not so much discussed concept in this session: topology. In math, topology discards small details
Notes on Topological Insulators and Quantum Spin Hall Effect Jouko Nieminen Tampere University of Technology. Not so much discussed concept in this session: topology. In math, topology discards small details
Berry-phase Approach to Electric Polarization and Charge Fractionalization. Dennis P. Clougherty Department of Physics University of Vermont
 Berry-phase Approach to Electric Polarization and Charge Fractionalization Dennis P. Clougherty Department of Physics University of Vermont Outline Quick Review Berry phase in quantum systems adiabatic
Berry-phase Approach to Electric Polarization and Charge Fractionalization Dennis P. Clougherty Department of Physics University of Vermont Outline Quick Review Berry phase in quantum systems adiabatic
Topological Physics in Band Insulators IV
 Topological Physics in Band Insulators IV Gene Mele University of Pennsylvania Wannier representation and band projectors Modern view: Gapped electronic states are equivalent Kohn (1964): insulator is
Topological Physics in Band Insulators IV Gene Mele University of Pennsylvania Wannier representation and band projectors Modern view: Gapped electronic states are equivalent Kohn (1964): insulator is
Topological insulators and the quantum anomalous Hall state. David Vanderbilt Rutgers University
 Topological insulators and the quantum anomalous Hall state David Vanderbilt Rutgers University Outline Berry curvature and topology 2D quantum anomalous Hall (QAH) insulator TR-invariant insulators (Z
Topological insulators and the quantum anomalous Hall state David Vanderbilt Rutgers University Outline Berry curvature and topology 2D quantum anomalous Hall (QAH) insulator TR-invariant insulators (Z
Basics of topological insulator
 011/11/18 @ NTU Basics of topological insulator Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU A brief history of insulators Band insulator (Wilson, Bloch) Mott insulator Anderson insulator Quantum Hall insulator
011/11/18 @ NTU Basics of topological insulator Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU A brief history of insulators Band insulator (Wilson, Bloch) Mott insulator Anderson insulator Quantum Hall insulator
Single particle Green s functions and interacting topological insulators
 1 Single particle Green s functions and interacting topological insulators Victor Gurarie Nordita, Jan 2011 Topological insulators are free fermion systems characterized by topological invariants. 2 In
1 Single particle Green s functions and interacting topological insulators Victor Gurarie Nordita, Jan 2011 Topological insulators are free fermion systems characterized by topological invariants. 2 In
Takuya Kitagawa, Dima Abanin, Immanuel Bloch, Erez Berg, Mark Rudner, Liang Fu, Takashi Oka, Eugene Demler
 Exploring topological states with synthetic matter Takuya Kitagawa, Dima Abanin, Immanuel Bloch, Erez Berg, Mark Rudner, Liang Fu, Takashi Oka, Eugene Demler Harvard-MIT $$ NSF, AFOSR MURI, DARPA OLE,
Exploring topological states with synthetic matter Takuya Kitagawa, Dima Abanin, Immanuel Bloch, Erez Berg, Mark Rudner, Liang Fu, Takashi Oka, Eugene Demler Harvard-MIT $$ NSF, AFOSR MURI, DARPA OLE,
Phonons and elasticity in critically coordinated lattices
 REVIEW ARTICLE Phonons and elasticity in critically coordinated lattices Contents T C Lubensky 1, C L Kane 1, Xiaoming Mao 2, A Souslov 3 and Kai Sun 2 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University
REVIEW ARTICLE Phonons and elasticity in critically coordinated lattices Contents T C Lubensky 1, C L Kane 1, Xiaoming Mao 2, A Souslov 3 and Kai Sun 2 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University
Emergent topological phenomena in antiferromagnets with noncoplanar spins
 Emergent topological phenomena in antiferromagnets with noncoplanar spins - Surface quantum Hall effect - Dimensional crossover Bohm-Jung Yang (RIKEN, Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS), Japan)
Emergent topological phenomena in antiferromagnets with noncoplanar spins - Surface quantum Hall effect - Dimensional crossover Bohm-Jung Yang (RIKEN, Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS), Japan)
POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials
 POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials Nandini Trivedi L1: Spin Orbit Coupling L2: Topology and Topological Insulators Reference: Bernevig Topological Insulators and Topological Superconductors Tutorials:
POEM: Physics of Emergent Materials Nandini Trivedi L1: Spin Orbit Coupling L2: Topology and Topological Insulators Reference: Bernevig Topological Insulators and Topological Superconductors Tutorials:
On the K-theory classification of topological states of matter
 On the K-theory classification of topological states of matter (1,2) (1) Department of Mathematics Mathematical Sciences Institute (2) Department of Theoretical Physics Research School of Physics and Engineering
On the K-theory classification of topological states of matter (1,2) (1) Department of Mathematics Mathematical Sciences Institute (2) Department of Theoretical Physics Research School of Physics and Engineering
Topological nonsymmorphic crystalline superconductors
 UIUC, 10/26/2015 Topological nonsymmorphic crystalline superconductors Chaoxing Liu Department of Physics, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pennsylvania 16802, USA Chao-Xing Liu, Rui-Xing
UIUC, 10/26/2015 Topological nonsymmorphic crystalline superconductors Chaoxing Liu Department of Physics, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pennsylvania 16802, USA Chao-Xing Liu, Rui-Xing
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Apr 2010
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Apr 2010 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Apr 2010](/thumbs/93/114512366.jpg) Characterization of 3d topological insulators by 2d invariants Rahul Roy Rudolf Peierls Centre for Theoretical Physics, 1 Keble Road, Oxford, OX1 3NP, UK arxiv:1004.3507v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Apr 2010
Characterization of 3d topological insulators by 2d invariants Rahul Roy Rudolf Peierls Centre for Theoretical Physics, 1 Keble Road, Oxford, OX1 3NP, UK arxiv:1004.3507v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Apr 2010
From graphene to Z2 topological insulator
 From graphene to Z2 topological insulator single Dirac topological AL mass U U valley WL ordinary mass or ripples WL U WL AL AL U AL WL Rashba Ken-Ichiro Imura Condensed-Matter Theory / Tohoku Univ. Dirac
From graphene to Z2 topological insulator single Dirac topological AL mass U U valley WL ordinary mass or ripples WL U WL AL AL U AL WL Rashba Ken-Ichiro Imura Condensed-Matter Theory / Tohoku Univ. Dirac
Topological Properties of Quantum States of Condensed Matter: some recent surprises.
 Topological Properties of Quantum States of Condensed Matter: some recent surprises. F. D. M. Haldane Princeton University and Instituut Lorentz 1. Berry phases, zero-field Hall effect, and one-way light
Topological Properties of Quantum States of Condensed Matter: some recent surprises. F. D. M. Haldane Princeton University and Instituut Lorentz 1. Berry phases, zero-field Hall effect, and one-way light
Adiabatic particle pumping and anomalous velocity
 Adiabatic particle pumping and anomalous velocity November 17, 2015 November 17, 2015 1 / 31 Literature: 1 J. K. Asbóth, L. Oroszlány, and A. Pályi, arxiv:1509.02295 2 D. Xiao, M-Ch Chang, and Q. Niu,
Adiabatic particle pumping and anomalous velocity November 17, 2015 November 17, 2015 1 / 31 Literature: 1 J. K. Asbóth, L. Oroszlány, and A. Pályi, arxiv:1509.02295 2 D. Xiao, M-Ch Chang, and Q. Niu,
Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators
 Lecture 6 Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators Given the analogs between Berry s phase and vector potentials, it is not surprising that Berry s phase can be important in the Hall effect.
Lecture 6 Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators Given the analogs between Berry s phase and vector potentials, it is not surprising that Berry s phase can be important in the Hall effect.
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field
 Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
team Hans Peter Büchler Nicolai Lang Mikhail Lukin Norman Yao Sebastian Huber
 title 1 team 2 Hans Peter Büchler Nicolai Lang Mikhail Lukin Norman Yao Sebastian Huber motivation: topological states of matter 3 fermions non-interacting, filled band (single particle physics) topological
title 1 team 2 Hans Peter Büchler Nicolai Lang Mikhail Lukin Norman Yao Sebastian Huber motivation: topological states of matter 3 fermions non-interacting, filled band (single particle physics) topological
Konstantin Y. Bliokh, Daria Smirnova, Franco Nori. Center for Emergent Matter Science, RIKEN, Japan. Science 348, 1448 (2015)
 Konstantin Y. Bliokh, Daria Smirnova, Franco Nori Center for Emergent Matter Science, RIKEN, Japan Science 348, 1448 (2015) QSHE and topological insulators The quantum spin Hall effect means the presence
Konstantin Y. Bliokh, Daria Smirnova, Franco Nori Center for Emergent Matter Science, RIKEN, Japan Science 348, 1448 (2015) QSHE and topological insulators The quantum spin Hall effect means the presence
Disordered topological insulators with time-reversal symmetry: Z 2 invariants
 Keio Topo. Science (2016/11/18) Disordered topological insulators with time-reversal symmetry: Z 2 invariants Hosho Katsura Department of Physics, UTokyo Collaborators: Yutaka Akagi (UTokyo) Tohru Koma
Keio Topo. Science (2016/11/18) Disordered topological insulators with time-reversal symmetry: Z 2 invariants Hosho Katsura Department of Physics, UTokyo Collaborators: Yutaka Akagi (UTokyo) Tohru Koma
Classification of topological quantum matter with reflection symmetries
 Classification of topological quantum matter with reflection symmetries Andreas P. Schnyder Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research, Stuttgart June 14th, 2016 SPICE Workshop on New Paradigms in Dirac-Weyl
Classification of topological quantum matter with reflection symmetries Andreas P. Schnyder Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research, Stuttgart June 14th, 2016 SPICE Workshop on New Paradigms in Dirac-Weyl
First-Principles Calculation of Topological Invariants (Wannier Functions Approach) Alexey A. Soluyanov
 First-Principles Calculation of Topological Invariants (Wannier Functions Approach) Alexey A. Soluyanov ES'12, WFU, June 8, 212 The present work was done in collaboration with David Vanderbilt Outline:
First-Principles Calculation of Topological Invariants (Wannier Functions Approach) Alexey A. Soluyanov ES'12, WFU, June 8, 212 The present work was done in collaboration with David Vanderbilt Outline:
Topological insulator (TI)
 Topological insulator (TI) Haldane model: QHE without Landau level Quantized spin Hall effect: 2D topological insulators: Kane-Mele model for graphene HgTe quantum well InAs/GaSb quantum well 3D topological
Topological insulator (TI) Haldane model: QHE without Landau level Quantized spin Hall effect: 2D topological insulators: Kane-Mele model for graphene HgTe quantum well InAs/GaSb quantum well 3D topological
Classification of Symmetry Protected Topological Phases in Interacting Systems
 Classification of Symmetry Protected Topological Phases in Interacting Systems Zhengcheng Gu (PI) Collaborators: Prof. Xiao-Gang ang Wen (PI/ PI/MIT) Prof. M. Levin (U. of Chicago) Dr. Xie Chen(UC Berkeley)
Classification of Symmetry Protected Topological Phases in Interacting Systems Zhengcheng Gu (PI) Collaborators: Prof. Xiao-Gang ang Wen (PI/ PI/MIT) Prof. M. Levin (U. of Chicago) Dr. Xie Chen(UC Berkeley)
Ψ({z i }) = i<j(z i z j ) m e P i z i 2 /4, q = ± e m.
 Fractionalization of charge and statistics in graphene and related structures M. Franz University of British Columbia franz@physics.ubc.ca January 5, 2008 In collaboration with: C. Weeks, G. Rosenberg,
Fractionalization of charge and statistics in graphene and related structures M. Franz University of British Columbia franz@physics.ubc.ca January 5, 2008 In collaboration with: C. Weeks, G. Rosenberg,
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 May 2010
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 May 2010 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 May 2010](/thumbs/81/83686509.jpg) MIT-CTP/4147 Correlated Topological Insulators and the Fractional Magnetoelectric Effect B. Swingle, M. Barkeshli, J. McGreevy, and T. Senthil Department of Physics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
MIT-CTP/4147 Correlated Topological Insulators and the Fractional Magnetoelectric Effect B. Swingle, M. Barkeshli, J. McGreevy, and T. Senthil Department of Physics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
Topological Defects in the Topological Insulator
 Topological Defects in the Topological Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley arxiv:0810.5121 YING RAN Frank YI ZHANG Quantum Hall States Exotic Band Topology Topological band Insulators (quantum spin
Topological Defects in the Topological Insulator Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley arxiv:0810.5121 YING RAN Frank YI ZHANG Quantum Hall States Exotic Band Topology Topological band Insulators (quantum spin
Classification theory of topological insulators with Clifford algebras and its application to interacting fermions. Takahiro Morimoto.
 QMath13, 10 th October 2016 Classification theory of topological insulators with Clifford algebras and its application to interacting fermions Takahiro Morimoto UC Berkeley Collaborators Akira Furusaki
QMath13, 10 th October 2016 Classification theory of topological insulators with Clifford algebras and its application to interacting fermions Takahiro Morimoto UC Berkeley Collaborators Akira Furusaki
Topological insulators
 http://www.physik.uni-regensburg.de/forschung/fabian Topological insulators Jaroslav Fabian Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Regensburg Stara Lesna, 21.8.212 DFG SFB 689 what are topological
http://www.physik.uni-regensburg.de/forschung/fabian Topological insulators Jaroslav Fabian Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Regensburg Stara Lesna, 21.8.212 DFG SFB 689 what are topological
Exploring topological states with cold atoms and photons
 Exploring topological states with cold atoms and photons Theory: Takuya Kitagawa, Dima Abanin, Erez Berg, Mark Rudner, Liang Fu, Takashi Oka, Immanuel Bloch, Eugene Demler Experiments: I. Bloch s group
Exploring topological states with cold atoms and photons Theory: Takuya Kitagawa, Dima Abanin, Erez Berg, Mark Rudner, Liang Fu, Takashi Oka, Immanuel Bloch, Eugene Demler Experiments: I. Bloch s group
What is a topological insulator? Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU
 What is a topological insulator? Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU A mini course on topology extrinsic curvature K vs intrinsic (Gaussian) curvature G K 0 G 0 G>0 G=0 K 0 G=0 G
What is a topological insulator? Ming-Che Chang Dept of Physics, NTNU A mini course on topology extrinsic curvature K vs intrinsic (Gaussian) curvature G K 0 G 0 G>0 G=0 K 0 G=0 G
Topological Insulators
 Topological Insulators Aira Furusai (Condensed Matter Theory Lab.) = topological insulators (3d and 2d) Outline Introduction: band theory Example of topological insulators: integer quantum Hall effect
Topological Insulators Aira Furusai (Condensed Matter Theory Lab.) = topological insulators (3d and 2d) Outline Introduction: band theory Example of topological insulators: integer quantum Hall effect
Nanostructured Carbon Allotropes as Weyl-Like Semimetals
 Nanostructured Carbon Allotropes as Weyl-Like Semimetals Shengbai Zhang Department of Physics, Applied Physics & Astronomy Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute symmetry In quantum mechanics, symmetry can be
Nanostructured Carbon Allotropes as Weyl-Like Semimetals Shengbai Zhang Department of Physics, Applied Physics & Astronomy Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute symmetry In quantum mechanics, symmetry can be
KAVLI v F. Curved graphene revisited. María A. H. Vozmediano. Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Madrid CSIC
 KAVLI 2012 v F Curved graphene revisited María A. H. Vozmediano Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Madrid CSIC Collaborators ICMM(Graphene group) http://www.icmm.csic.es/gtg/ A. Cano E. V. Castro J.
KAVLI 2012 v F Curved graphene revisited María A. H. Vozmediano Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Madrid CSIC Collaborators ICMM(Graphene group) http://www.icmm.csic.es/gtg/ A. Cano E. V. Castro J.
synthetic condensed matter systems
 Ramsey interference as a probe of synthetic condensed matter systems Takuya Kitagawa (Harvard) DimaAbanin i (Harvard) Mikhael Knap (TU Graz/Harvard) Eugene Demler (Harvard) Supported by NSF, DARPA OLE,
Ramsey interference as a probe of synthetic condensed matter systems Takuya Kitagawa (Harvard) DimaAbanin i (Harvard) Mikhael Knap (TU Graz/Harvard) Eugene Demler (Harvard) Supported by NSF, DARPA OLE,
Quantum Hall effect. Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in I believe. WHY?? G xy = N e2 h.
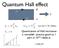 Quantum Hall effect V1 V2 R L I I x = N e2 h V y V x =0 G xy = N e2 h n.b. h/e 2 = 25 kohms Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in 10 10 I believe. WHY?? Robustness Why
Quantum Hall effect V1 V2 R L I I x = N e2 h V y V x =0 G xy = N e2 h n.b. h/e 2 = 25 kohms Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in 10 10 I believe. WHY?? Robustness Why
Weyl semi-metal: a New Topological State in Condensed Matter
 Weyl semi-metal: a New Topological State in Condensed Matter Sergey Savrasov Department of Physics, University of California, Davis Xiangang Wan Nanjing University Ari Turner and Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley
Weyl semi-metal: a New Topological State in Condensed Matter Sergey Savrasov Department of Physics, University of California, Davis Xiangang Wan Nanjing University Ari Turner and Ashvin Vishwanath UC Berkeley
Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter. Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti)
 Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Topological States of Matter System with bulk gap but non-trivial at energies below
Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Topological States of Matter System with bulk gap but non-trivial at energies below
Introductory lecture on topological insulators. Reza Asgari
 Introductory lecture on topological insulators Reza Asgari Workshop on graphene and topological insulators, IPM. 19-20 Oct. 2011 Outlines -Introduction New phases of materials, Insulators -Theory quantum
Introductory lecture on topological insulators Reza Asgari Workshop on graphene and topological insulators, IPM. 19-20 Oct. 2011 Outlines -Introduction New phases of materials, Insulators -Theory quantum
Weyl semimetals and topological phase transitions
 Weyl semimetals and topological phase transitions Shuichi Murakami 1 Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology 2 TIES, Tokyo Institute of Technology 3 CREST, JST Collaborators: R. Okugawa (Tokyo
Weyl semimetals and topological phase transitions Shuichi Murakami 1 Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology 2 TIES, Tokyo Institute of Technology 3 CREST, JST Collaborators: R. Okugawa (Tokyo
Valence Bonds in Random Quantum Magnets
 Valence Bonds in Random Quantum Magnets theory and application to YbMgGaO 4 Yukawa Institute, Kyoto, November 2017 Itamar Kimchi I.K., Adam Nahum, T. Senthil, arxiv:1710.06860 Valence Bonds in Random Quantum
Valence Bonds in Random Quantum Magnets theory and application to YbMgGaO 4 Yukawa Institute, Kyoto, November 2017 Itamar Kimchi I.K., Adam Nahum, T. Senthil, arxiv:1710.06860 Valence Bonds in Random Quantum
Topological response in Weyl metals. Anton Burkov
 Topological response in Weyl metals Anton Burkov NanoPiter, Saint-Petersburg, Russia, June 26, 2014 Outline Introduction: Weyl semimetal as a 3D generalization of IQHE. Anomalous Hall Effect in metallic
Topological response in Weyl metals Anton Burkov NanoPiter, Saint-Petersburg, Russia, June 26, 2014 Outline Introduction: Weyl semimetal as a 3D generalization of IQHE. Anomalous Hall Effect in metallic
Topological Insulators and Ferromagnets: appearance of flat surface bands
 Topological Insulators and Ferromagnets: appearance of flat surface bands Thomas Dahm University of Bielefeld T. Paananen and T. Dahm, PRB 87, 195447 (2013) T. Paananen et al, New J. Phys. 16, 033019 (2014)
Topological Insulators and Ferromagnets: appearance of flat surface bands Thomas Dahm University of Bielefeld T. Paananen and T. Dahm, PRB 87, 195447 (2013) T. Paananen et al, New J. Phys. 16, 033019 (2014)
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 11 Oct 2016
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 11 Oct 2016 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 11 Oct 2016](/thumbs/77/74977843.jpg) Nonsymmorphic symmetry-required band crossings in topological semimetals arxiv:1606.03698v [cond-mat.mes-hall] 11 Oct 016 Y. X. Zhao 1, and Andreas P. Schnyder 1, 1 Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State
Nonsymmorphic symmetry-required band crossings in topological semimetals arxiv:1606.03698v [cond-mat.mes-hall] 11 Oct 016 Y. X. Zhao 1, and Andreas P. Schnyder 1, 1 Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State
Modern Topics in Solid-State Theory: Topological insulators and superconductors
 Modern Topics in Solid-State Theory: Topological insulators and superconductors Andreas P. Schnyder Max-Planck-Institut für Festkörperforschung, Stuttgart Universität Stuttgart January 2016 Lecture Four:
Modern Topics in Solid-State Theory: Topological insulators and superconductors Andreas P. Schnyder Max-Planck-Institut für Festkörperforschung, Stuttgart Universität Stuttgart January 2016 Lecture Four:
Introduction to topological insulators
 Introduction to topological insulators Janos Asboth1, Laszlo Oroszlany2, Andras Palyi3 1: Wigner Research Centre for Physics, Hungarian Academy of Sciences 2: Eotvos University, Budapest 3: Technical University,
Introduction to topological insulators Janos Asboth1, Laszlo Oroszlany2, Andras Palyi3 1: Wigner Research Centre for Physics, Hungarian Academy of Sciences 2: Eotvos University, Budapest 3: Technical University,
Ultrafast study of Dirac fermions in out of equilibrium Topological Insulators
 Ultrafast study of Dirac fermions in out of equilibrium Topological Insulators Marino Marsi Laboratoire de Physique des Solides CNRS Univ. Paris-Sud - Université Paris-Saclay IMPACT, Cargèse, August 26
Ultrafast study of Dirac fermions in out of equilibrium Topological Insulators Marino Marsi Laboratoire de Physique des Solides CNRS Univ. Paris-Sud - Université Paris-Saclay IMPACT, Cargèse, August 26
Floquet theory of photo-induced topological phase transitions: Application to graphene
 Floquet theory of photo-induced topological phase transitions: Application to graphene Takashi Oka (University of Tokyo) T. Kitagawa (Harvard) L. Fu (Harvard) E. Demler (Harvard) A. Brataas (Norweigian
Floquet theory of photo-induced topological phase transitions: Application to graphene Takashi Oka (University of Tokyo) T. Kitagawa (Harvard) L. Fu (Harvard) E. Demler (Harvard) A. Brataas (Norweigian
Energy Spectrum and Broken spin-surface locking in Topological Insulator quantum dots
 Energy Spectrum and Broken spin-surface locking in Topological Insulator quantum dots A. Kundu 1 1 Heinrich-Heine Universität Düsseldorf, Germany The Capri Spring School on Transport in Nanostructures
Energy Spectrum and Broken spin-surface locking in Topological Insulator quantum dots A. Kundu 1 1 Heinrich-Heine Universität Düsseldorf, Germany The Capri Spring School on Transport in Nanostructures
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 22 Oct 2018
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 22 Oct 2018 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 22 Oct 2018](/thumbs/88/114697358.jpg) Pseudo topological insulators C. Yuce Department of Physics, Anadolu University, Turkey Department of Physics, Eskisehir Technical University, Turkey (Dated: October 23, 2018) arxiv:1808.07862v2 [cond-mat.str-el]
Pseudo topological insulators C. Yuce Department of Physics, Anadolu University, Turkey Department of Physics, Eskisehir Technical University, Turkey (Dated: October 23, 2018) arxiv:1808.07862v2 [cond-mat.str-el]
Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor
 Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor Sharmistha Sahoo Zhao Zhang Jeffrey Teo Outline Introduction Brief description of time reversal symmetric topological superconductor. Coupled wire model
Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor Sharmistha Sahoo Zhao Zhang Jeffrey Teo Outline Introduction Brief description of time reversal symmetric topological superconductor. Coupled wire model
Paramagnetic phases of Kagome lattice quantum Ising models p.1/16
 Paramagnetic phases of Kagome lattice quantum Ising models Predrag Nikolić In collaboration with T. Senthil Massachusetts Institute of Technology Paramagnetic phases of Kagome lattice quantum Ising models
Paramagnetic phases of Kagome lattice quantum Ising models Predrag Nikolić In collaboration with T. Senthil Massachusetts Institute of Technology Paramagnetic phases of Kagome lattice quantum Ising models
Two Dimensional Chern Insulators, the Qi-Wu-Zhang and Haldane Models
 Two Dimensional Chern Insulators, the Qi-Wu-Zhang and Haldane Models Matthew Brooks, Introduction to Topological Insulators Seminar, Universität Konstanz Contents QWZ Model of Chern Insulators Haldane
Two Dimensional Chern Insulators, the Qi-Wu-Zhang and Haldane Models Matthew Brooks, Introduction to Topological Insulators Seminar, Universität Konstanz Contents QWZ Model of Chern Insulators Haldane
where a is the lattice constant of the triangular Bravais lattice. reciprocal space is spanned by
 Contents 5 Topological States of Matter 1 5.1 Intro.......................................... 1 5.2 Integer Quantum Hall Effect..................... 1 5.3 Graphene......................................
Contents 5 Topological States of Matter 1 5.1 Intro.......................................... 1 5.2 Integer Quantum Hall Effect..................... 1 5.3 Graphene......................................
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 16 May 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 16 May 2018 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 16 May 2018](/thumbs/88/114583781.jpg) Extended Creutz ladder with spin-orbit coupling: a one-dimensional analog of the Kane-Mele model S. Gholizadeh and M. Yahyavi Department of Physics, Bilkent University, TR-68 Bilkent, Ankara, Turkey arxiv:186.1111v1
Extended Creutz ladder with spin-orbit coupling: a one-dimensional analog of the Kane-Mele model S. Gholizadeh and M. Yahyavi Department of Physics, Bilkent University, TR-68 Bilkent, Ankara, Turkey arxiv:186.1111v1
Crystalline Symmetry and Topology. YITP, Kyoto University Masatoshi Sato
 Crystalline Symmetry and Topology YITP, Kyoto University Masatoshi Sato In collaboration with Ken Shiozaki (YITP) Kiyonori Gomi (Shinshu University) Nobuyuki Okuma (YITP) Ai Yamakage (Nagoya University)
Crystalline Symmetry and Topology YITP, Kyoto University Masatoshi Sato In collaboration with Ken Shiozaki (YITP) Kiyonori Gomi (Shinshu University) Nobuyuki Okuma (YITP) Ai Yamakage (Nagoya University)
Symmetries in Quantum Transport : From Random Matrix Theory to Topological Insulators. Philippe Jacquod. U of Arizona
 Symmetries in Quantum Transport : From Random Matrix Theory to Topological Insulators Philippe Jacquod U of Arizona UA Phys colloquium - feb 1, 2013 Continuous symmetries and conservation laws Noether
Symmetries in Quantum Transport : From Random Matrix Theory to Topological Insulators Philippe Jacquod U of Arizona UA Phys colloquium - feb 1, 2013 Continuous symmetries and conservation laws Noether
Dirac semimetal in three dimensions
 Dirac semimetal in three dimensions Steve M. Young, Saad Zaheer, Jeffrey C. Y. Teo, Charles L. Kane, Eugene J. Mele, and Andrew M. Rappe University of Pennsylvania 6/7/12 1 Dirac points in Graphene Without
Dirac semimetal in three dimensions Steve M. Young, Saad Zaheer, Jeffrey C. Y. Teo, Charles L. Kane, Eugene J. Mele, and Andrew M. Rappe University of Pennsylvania 6/7/12 1 Dirac points in Graphene Without
K-theory in Condensed Matter Physics
 (1,2) (1) Department of Mathematics Mathematical Sciences Institute (2) Department of Theoretical Physics Research School of Physics and Engineering The Australian National University Canberra, AUSTRALIA
(1,2) (1) Department of Mathematics Mathematical Sciences Institute (2) Department of Theoretical Physics Research School of Physics and Engineering The Australian National University Canberra, AUSTRALIA
Topological Insulators in 3D and Bosonization
 Topological Insulators in 3D and Bosonization Andrea Cappelli, INFN Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Outline Topological states of matter: bulk and edge Fermions and bosons on the (1+1)-dimensional
Topological Insulators in 3D and Bosonization Andrea Cappelli, INFN Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Outline Topological states of matter: bulk and edge Fermions and bosons on the (1+1)-dimensional
Interaction-induced Symmetry Protected Topological Phase in Harper-Hofstadter models
 Interaction-induced Symmetry Protected Topological Phase in Harper-Hofstadter models arxiv:1609.03760 Lode Pollet Dario Hügel Hugo Strand, Philipp Werner (Uni Fribourg) Algorithmic developments diagrammatic
Interaction-induced Symmetry Protected Topological Phase in Harper-Hofstadter models arxiv:1609.03760 Lode Pollet Dario Hügel Hugo Strand, Philipp Werner (Uni Fribourg) Algorithmic developments diagrammatic
Topological insulators
 Oddelek za fiziko Seminar 1 b 1. letnik, II. stopnja Topological insulators Author: Žiga Kos Supervisor: prof. dr. Dragan Mihailović Ljubljana, June 24, 2013 Abstract In the seminar, the basic ideas behind
Oddelek za fiziko Seminar 1 b 1. letnik, II. stopnja Topological insulators Author: Žiga Kos Supervisor: prof. dr. Dragan Mihailović Ljubljana, June 24, 2013 Abstract In the seminar, the basic ideas behind
Quantum Spin Liquids and Majorana Metals
 Quantum Spin Liquids and Majorana Metals Maria Hermanns University of Cologne M.H., S. Trebst, PRB 89, 235102 (2014) M.H., K. O Brien, S. Trebst, PRL 114, 157202 (2015) M.H., S. Trebst, A. Rosch, arxiv:1506.01379
Quantum Spin Liquids and Majorana Metals Maria Hermanns University of Cologne M.H., S. Trebst, PRB 89, 235102 (2014) M.H., K. O Brien, S. Trebst, PRL 114, 157202 (2015) M.H., S. Trebst, A. Rosch, arxiv:1506.01379
Quantum Quenches in Chern Insulators
 Quantum Quenches in Chern Insulators Nigel Cooper Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge CUA Seminar M.I.T., November 10th, 2015 Marcello Caio & Joe Bhaseen (KCL), Stefan Baur (Cambridge) M.D. Caio,
Quantum Quenches in Chern Insulators Nigel Cooper Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge CUA Seminar M.I.T., November 10th, 2015 Marcello Caio & Joe Bhaseen (KCL), Stefan Baur (Cambridge) M.D. Caio,
Chern number and Z 2 invariant
 Chern number and Z 2 invariant Hikaru Sawahata Collabolators: Yo Pierre Mizuta, Naoya Yamaguchi, Fumiyuki Ishii Graduate School of Natural Science and Technology, Kanazawa University 2016/11/25 Hikaru
Chern number and Z 2 invariant Hikaru Sawahata Collabolators: Yo Pierre Mizuta, Naoya Yamaguchi, Fumiyuki Ishii Graduate School of Natural Science and Technology, Kanazawa University 2016/11/25 Hikaru
Dirac fermions in condensed matters
 Dirac fermions in condensed matters Bohm Jung Yang Department of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul National University Outline 1. Dirac fermions in relativistic wave equations 2. How do Dirac fermions appear
Dirac fermions in condensed matters Bohm Jung Yang Department of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul National University Outline 1. Dirac fermions in relativistic wave equations 2. How do Dirac fermions appear
Topological thermoelectrics
 Topological thermoelectrics JAIRO SINOVA Texas A&M University Institute of Physics ASCR Oleg Tretiakov, Artem Abanov, Suichi Murakami Great job candidate MRS Spring Meeting San Francisco April 28th 2011
Topological thermoelectrics JAIRO SINOVA Texas A&M University Institute of Physics ASCR Oleg Tretiakov, Artem Abanov, Suichi Murakami Great job candidate MRS Spring Meeting San Francisco April 28th 2011
Topological Photonics with Heavy-Photon Bands
 Topological Photonics with Heavy-Photon Bands Vassilios Yannopapas Dept. of Physics, National Technical University of Athens (NTUA) Quantum simulations and many-body physics with light, 4-11/6/2016, Hania,
Topological Photonics with Heavy-Photon Bands Vassilios Yannopapas Dept. of Physics, National Technical University of Athens (NTUA) Quantum simulations and many-body physics with light, 4-11/6/2016, Hania,
Hartmut Buhmann. Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Germany
 Hartmut Buhmann Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Germany Part I and II Insulators and Topological Insulators HgTe crystal structure Part III quantum wells Two-Dimensional TI Quantum Spin
Hartmut Buhmann Physikalisches Institut, EP3 Universität Würzburg Germany Part I and II Insulators and Topological Insulators HgTe crystal structure Part III quantum wells Two-Dimensional TI Quantum Spin
Topological Insulators
 Topological Insulators A new state of matter with three dimensional topological electronic order L. Andrew Wray Lawrence Berkeley National Lab Princeton University Surface States (Topological Order in
Topological Insulators A new state of matter with three dimensional topological electronic order L. Andrew Wray Lawrence Berkeley National Lab Princeton University Surface States (Topological Order in
Mapping the Berry Curvature of Optical Lattices
 Mapping the Berry Curvature of Optical Lattices Nigel Cooper Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge Quantum Simulations with Ultracold Atoms ICTP, Trieste, 16 July 2012 Hannah Price & NRC, PRA 85,
Mapping the Berry Curvature of Optical Lattices Nigel Cooper Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge Quantum Simulations with Ultracold Atoms ICTP, Trieste, 16 July 2012 Hannah Price & NRC, PRA 85,
Boundary Degeneracy of Topological Order
 Boundary Degeneracy of Topological Order Juven Wang (MIT/Perimeter Inst.) - and Xiao-Gang Wen Mar 15, 2013 @ PI arxiv.org/abs/1212.4863 Lattice model: Toric Code and String-net Flux Insertion What is?
Boundary Degeneracy of Topological Order Juven Wang (MIT/Perimeter Inst.) - and Xiao-Gang Wen Mar 15, 2013 @ PI arxiv.org/abs/1212.4863 Lattice model: Toric Code and String-net Flux Insertion What is?
