EE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DRAWING
|
|
|
- Linda Hodge
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DRAWING Akhil A. Balakrishnan 1 1 Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Jyothi Engineering College, Cheruthuruthy As on January 12, 2014 Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
2 We will go through... 1 INTRODUCTION 2 DC ARMATURE WINDING 3 AC MACHINE WINDING Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
3 OBJECTIVES * To make students to be able to plan and draw different views of electrical machines and transformers. * To make the students to draw different types of windings used in electrical machines. * Introduction to AutoCAD in Electrical engineering drawing. Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
4 SYLLABUS Module I (12 Hours) DC Windings: Simplex lap and wave dc armature windings. AC Windings: Mush and concentric type single layer three phase ac armature windings. Simplex lap and wave, integral and fractional slot, double layer three phase ac armature windings. Introduction to AutoCad:Developed winding diagrams (Auto Cad not included for Examination). Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
5 Module II (14 Hours) SYLLABUS 1 Sectional plan and elevation of a transformer limb with windings. 2 Sectional plan and elevation of the core assembly of a power transformer. 3 Sectional plan and elevation of a distribution transformer tank with its accessories. 4 Sketches of capacitor and oil filled type transformer bushings. 5 Layout and single line diagram of a distribution transformer. Substation Layouts: 1 Layouts and single line diagrams of outdoor and indoor substations. 2 Layout of a 220KV substation. 3 Layout of a captive power substation. 4 Single line diagram of a distribution centre. Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
6 Module III (26 Hours) DC Machines: SYLLABUS 1 Sectional front and side elevation of armature with commutator of a dc machine. 2 Sectional front and side elevation of the yoke and pole assembly with field winding of a dc machine. 3 Sectional front and side elevation of an assembled dc Machine. Alternators: 1 Sectional front and side elevation of a water wheel rotor assembly with winding. 2 Sectional front and side elevation of a salient pole alternator. 3 Sectional front and side elevation of a Turbo alternator. 4 Sketches of the methods of pole fixing and slot details of Turbo and Water wheel alternator. Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
7 Text Books REFERENCES 1 Narang K. L., A text book of Electrical Engineering Drawing, Tech India Publications 2 C. R. Dargan, Electrical Drawing and Estimation, New Asian Publishers Reference Books 1 Bhattacharya S. K., Electrical Engineering Drawing, Wiley Eastern. 2 Clayton and Hancock, Performance and design of dc machines, ELBS. 3 Sawhney, Electrical Machine Design, Dhanpath Rai & Sons. 4 Say M.G, Performance and design of AC machines, Pitman, ELBS. 5 A. Nagoorkani, A simplified text in Electrical Machine Design, RBA Publications Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
8 Internal Continuous Assessment (Maximum Marks - 30) 30% - Tests 60% - Assignments such as class work, home work 10% - Regularity in the class University Examination Pattern Q I - 2 questions A and B of 15 marks from Module I with choice to answer any one. Q II - 2 questions A and B of 20 marks from Module II with choice to answer any one. Q III - 2 questions of 35 marks from Module III with choice to answer any one Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
9 DC ARMATURE WINDING Armature Winding: Consists of number of coils connected in series and number of such series circuits are connected in parallel. DC machine armature are double layer windings, which means that each slot has two coil sides. Two types of double layer winding are Simplex Lap winding Finish of a coil is connected to start of next coil. No: of parallel paths = No: of poles Simplex Wave winding Finish of a coil is connected to start of a coil which is lying one pole pitch away from the finish. No: of parallel paths = 2 Ends of the coils are connected to commutators. Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
10 DC MACHINE WINDING Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
11 ELEMENTS OF AN ARMATURE WINDING Conductor: Active length of copper or aluminium wire in the slot. Turn: Two conductors connected to an end by an end connector. Two conductors of a turn are placed approximately a pole pitch apart. Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
12 ELEMENTS OF AN ARMATURE WINDING Coil Side: Active portions of the conductors in a coil. A coil have two sides. Upper (Top) coil side and Lower (Bottom) coil side. Distance between two coil sides is approximately kept as one pole pitch. Overhang: End portion of the coil connecting the two coil sides. Coil Span: Distance between two coil sides of a coil. Expressed in terms of number of slots or in electrical degrees. Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
13 ELEMENTS OF AN ARMATURE WINDING Coil : Several turns connected in series. Principal element of armature winding. Coil with single turn is called single turn coil and with several turns is called multi turn coil. Single Turn Coil Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
14 ELEMENTS OF AN ARMATURE WINDING Coil : Several turns connected in series. Principal element of armature winding. Coil with single turn is called single turn coil and with several turns is called multi turn coil. Two Turn Coil Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
15 ELEMENTS OF AN ARMATURE WINDING Coil : Several turns connected in series. Principal element of armature winding. Coil with single turn is called single turn coil and with several turns is called multi turn coil. Three Turn Coil Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
16 ELEMENTS OF AN ARMATURE WINDING Winding: Several coils connected in series. Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
17 ELEMENTS OF AN ARMATURE WINDING Pole Pitch: Peripheral distance between center of two adjacent poles in dc machine. Angle between centers of adjacent poles is 180 (electrical). Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
18 ELEMENTS OF AN ARMATURE WINDING Full pitched coil: Coil span is equal to pole pitch. Short pitched or chorded coil: Coil span is less than the pole pitch. Single layer winding: Coil sides are arranged in a single layer in a slot. Double layer winding: Coil sides are arranged in two layers in a slot. Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
19 IMPORTANT TERMS RELATED TO WINDING Back pitch(y b ): Distance between top and bottom coil sides of a coil measured around the back of armature. Always an odd number. Determines size of the coil (coil span) Equal to coil sides per pole or pole pitch. Front pitch(y f ): Distance between two coil sides connected to the same commutator segment. Winding pitch(y): Distance between the starts of two consecutive coils measured in terms of coil sides. Always an even integer. Y = Y b - Y f for lap winding Y = Y b + Y f for wave winding Commutator pitch(y c ): Distance between two commutator segments to which the ends (start & finish) of a coil are connected. Measured in terms of commutator segments. Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
20 LAP WINDING Y b = 2C/P ± K Y = Y b - Y f Y = ± 2 (Simplex) Y c = Y/2 = ± 1 (Simplex) Y f = Y b - Y A = P K = integer or fraction Back end : 1 + Y b = X 1 Front end : X 1 - Y f = X 2 Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
21 WAVE WINDING Y b = 2C/P ± K Y = Y b + Y f Y = (2C ± 2)/(P/2) Y c = Y/2 = (C ± 1)/(P/2) Y f = Y - Y b A = 2 K = integer or fraction Back end : 1 + Y b = X 1 Front end : X 1 + Y f = X 2 Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
22 TYPES OF WINDING Progressive Winding: Winding progresses in the direction of the coils are wound. Retrogressive Winding: After passing once round the armature, the winding falls in a slot to the left of its starting point. Progressive Winding Retrogressive Winding Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
23 EQUALISER RING In Lap winding, the EMF s induced in each parallel path may not be exactly equal. It results in internal circulating currents in the armature circuit and in the brushes. Causes : Excessive heating, sparking at the brushes and mechanical vibration. To overcome this, Equaliser rings are provided at the back of the armature. No of equaliser rings, m = Z 2P No of tappings to one equaliser ring = No of pair of poles(p/2) Distance between adjacent tappings = No of coils No of tappings = 2C mp Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
24 DESIGN OF WINDING No of slots = S No: of conductors or coil sides = Z No: of coils,c = Z/2 No of commutator segments = No: of coils No: of poles = P No: of parallel paths = No of brushes= A Coil Span = No: of slots per poles Coil sides per slot = Z S Coil sides per pole = Z P Back pitch = Y b Front pitch = Y f Winding pitch = Y Commutator pitch = Y c Y c, Y b and Y f will be always an odd integer Y is always an even integer Progressive Winding + sign, Retrogressive Winding - sign Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
25 DESIGN OF WINDING Bottom coil side of current coil = Top coil side of current coil + Back Pitch (Both Lap & Wave) Top coil side of next coil = Bottom coil side of current coil - Front Pitch (Lap) Top coil side of next coil = Bottom coil side of current coil + Front Pitch (Wave) Winding Calculations Back Connections Front Connections Winding Table Ring Diagram Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
26 Example 1 Design and draw the developed winding diagram for a 4 pole, 8 slots, double layer simplex lap winding for a DC generator. Show the connections to equalizer rings. P = 4, S = 8 C = 8 Coil sides per slot = 2 Z = 16 Coil sides per pole = Z P = 16 4 = 4 Y b = 2C 2 8 P ±K = 4 ±K = 5(Progressive) or 3(Retrogressive) Y c = ±1(Simplex) ; Y = ±2 (Yc = Y/2) Y f = Y b - Y = 5-2 = 3 No of equalizer rings, m = Z 2P or C P = 8 4 = 2 No of tappings to one equalizer rings = P 2 = 4 2 = 2 Distance between adjacent tappings = 2C mp = = 2 Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
27 Winding Calculations 1+5=6 6-3=3 3+5=8 8-3=5 5+5= =7 7+5= =9 9+5= = = = =18(2) 18-3= =20(4) 4-3=1 Back Connections (2) 15 20(4) Winding Table (2) 15 20(4) 1 Ring Diagram Front Connections Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
28 Lap Winding Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
29 Example 2 Design and draw the developed winding diagram for a 4 pole, 13 slots, double layer simplex wave winding with 13 commutator segments. P = 4, S = 13 C = 13 Coil sides per slot = 2 Z = 26 Coil sides per pole = Z P = 26 4 = 6.5 Coil sides per pole should be an integer, Coils sides per pole = 6 Y b = 2C 2 13 P ±K = 4 ±K = 7(Progressive) or 5(Retrogressive) Y = 2C±2 P/2 = 2 13±2 4/2 = 14, Y c should be always an odd integer Y f = Y - Y b = 14-7 = 7 Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
30 Winding Calculations 1+7=8 8+7= = =29(3) 3+7= = = =31(5) 5+7= = = =33(7) 7+7= = =28(2) 2+7=9 9+7= = =30(4) 4+7= = = =32(6) 6+7= = =27(1) Winding Table Back Connections (2) (4) (6) Front Connections (3) (5) (7) (1) Ring Diagram (3) (5) (7) (2) (4) (6) (1) Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
31 Wave Winding Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
32 Exercises 1 Design and draw the developed winding diagram for a 4 pole, 12 slots, double layer simplex lap winding for a DC generator with 12 commutator segments. 2 Design and draw the developed winding diagram for a 4 pole simplex wave winding having 25 slots, 25 coils and 25 commutator segments. 3 Design and draw the developed winding diagram for a 4 pole, 24 slots, double layer simplex lap winding for a DC generator with 24 commutator segments. Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
33 AC MACHINE WINDING Identical to DC machine winding In an AC winding, the commutator & its connection are not required. AC machine winding may be open, in the case of star windings and closed in the case of delta windings Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
34 CLASSIFICATION Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
35 IMPORTANT TERMS USED IN WINDING Slots per pole per phase(spp): To divide the slots into different phase-groups. spp is an integer : Integral Slot winding. spp is a fraction : Fractional Slot winding. Coil Pitch or coil span: Distance between two active coil sides of a coil in terms of slots. coil pitch = pole pitch Full pitched winding. coil span < pole pitch Short pitched winding. Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
36 SINGLE LAYER WINDING Three phase windings are of two types: Single Layer winding Rarely Used Double Layer winding. Disadvantages of single layer windings are: Inconvenience in arrangement of the overhang. High cost in production. Chording & use of fractional spp is not possible. Single layer windings have one coil side per slot A coil completely occupies 2 slots Classified into: Mush Type. Concentric Type. Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
37 MUSH WINDING All coils have same span One coil side is longer than the other Long and short coil side occupy alternate slots Coil span should be odd Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
38 Example 3 Draw a mush winding diagram for a 4 pole, 36 slots,three phase armature. P = 4, S = 36 Slots per pole per phase(spp) = = 3 One pole phase group consists of 3 slots Coil sides are arranged as alternate long and short coil sides. Coil span = pole pitch = 36 4 = 9 slots Angle between two consecutive slots = = 20 electrical Start of phase R is assumed to be in slot no: 1 Start of Y phase lies 120 electrical apart from Phase R Start of B phase lies again 120 electrical apart from Phase Y. No: of coils corresponding to 120 electrical= = 6 slots Start of coil side of phase Y lies in slot no: 7 and Start of coil side of phase B lies in slot no: 13 Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
39 Mush Winding Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
40 CONCENTRIC WINDING Made up of concentric coils of different pitches, for each pair of poles Divided into two main groups: Unbifurcated winding. A pair of adjacent pole phase groups form a concentric coil. Bifurcated winding. Each pole phase groups is split into two sets of concentric coil, sharing its return coil sides with another such group. Overhang should be accommodated in separate planes Pole pairs is even Can be accommodated in 2 planes. Pole pairs is a multiple of 3 Can be accommodated in 3 planes. If overhang has to be accommodated in 2 planes, a cranked coil group results. Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
41 Example 4 Draw a single layer concentric unbifurcated winding diagram with two plane overhang, for a three-phase, 48 slots, 8 pole, AC armature. P = 8, S = 48 Slots per pole per phase(spp) = = 2 One pole phase group consists of 2 slots Coil span = pole pitch = 48 8 = 6 slots Angle between two consecutive slots = = 30 electrical No: of coils corresponding to 120 electrical= = 4 slots One coil group is placed in four slots, one pole pitch apart. No: of coil groups = 48 4 = 12 No: of pole pairs is even, hence overhang is arranged in two planes Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
42 Unbifurcated Concentric Winding Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
43 Example 5 Develop a single layer winding concentric unbifurcated type winding diagram with two plane overhang for a three phase, 36 slots, 6 pole armature. P = 6, S = 36 Slots per pole per phase(spp) = = 2 One pole phase group consists of 2 slots Two coil sides are split into 2 sets of concentric coils sharing its return coil side with another group. Coil span = pole pitch = 36 6 = 6 slots Angle between two consecutive slots = = 30 electrical No: of coils corresponding to 120 electrical= = 4 slots No: of coil groups = 36 4 = 9, No: of pole pairs = 3 Overhang can be accommodated in 3 planes If the overhang is to be accommodated in 2 planes, we get cranked coil groups. Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
44 Unbifurcated Concentric Winding with Cranked Coil Group Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
45 Example 6 For a three phase AC machine, the armature is having 24 slots. A single layer concentric bifurcated winding for four poles is to be made. Draw the developed winding diagram with the overhang in three planes. P = 4, S = 24 Slots per pole per phase(spp) = = 2 One pole phase group consists of 2 slots Two coil sides are split into 2 sets of concentric coils sharing its return coil side with another group. Coil span = pole pitch = 24 4 = 6 slots Angle between two consecutive slots = = 30 electrical No: of coils corresponding to 120 electrical= = 4 slots One coil group is placed in two slots. No: of coil groups = 24 2 = 12. Overhang is accommodated in 3 planes. Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
46 Bifurcated Concentric Winding Akhil A. Balakrishnan (JECC) Lecture Notes As on January 12, / 44
EE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DRAWING
 EE09 605 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DRAWING Akhil A. Balakrishnan 1 1 Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Jyothi Engineering College, Cheruthuruthy As on February 24, 2014 Akhil A. Balakrishnan
EE09 605 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DRAWING Akhil A. Balakrishnan 1 1 Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Jyothi Engineering College, Cheruthuruthy As on February 24, 2014 Akhil A. Balakrishnan
UNIT I INTRODUCTION Part A- Two marks questions
 ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DESIGN OF ELECTRICAL MACHINES UNIT I INTRODUCTION 1. Define specific magnetic
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DESIGN OF ELECTRICAL MACHINES UNIT I INTRODUCTION 1. Define specific magnetic
ELECTRICALMACHINES-I QUESTUION BANK
 ELECTRICALMACHINES-I QUESTUION BANK UNIT-I INTRODUCTION OF MAGNETIC MATERIAL PART A 1. What are the three basic rotating Electric machines? 2. Name the three materials used in machine manufacture. 3. What
ELECTRICALMACHINES-I QUESTUION BANK UNIT-I INTRODUCTION OF MAGNETIC MATERIAL PART A 1. What are the three basic rotating Electric machines? 2. Name the three materials used in machine manufacture. 3. What
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I
 ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Unit I Introduction 1. What are the three basic types
ROEVER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ELAMBALUR, PERAMBALUR-621220 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Unit I Introduction 1. What are the three basic types
EC T32 - ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 EC T32 - ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING UNIT-I - TRANSFORMER 1. What is a transformer? 2. Briefly explain the principle of operation of transformers. 3. What are the parts of a transformer? 4. What are the types
EC T32 - ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING UNIT-I - TRANSFORMER 1. What is a transformer? 2. Briefly explain the principle of operation of transformers. 3. What are the parts of a transformer? 4. What are the types
DESIGN OF ELECTRICAL APPARATUS SOLVED PROBLEMS
 DESIGN OF ELECTRICAL APPARATUS SOLVED PROBLEMS 1. A 350 KW, 500V, 450rpm, 6-pole, dc generator is built with an armature diameter of 0.87m and core length of 0.32m. The lap wound armature has 660 conductors.
DESIGN OF ELECTRICAL APPARATUS SOLVED PROBLEMS 1. A 350 KW, 500V, 450rpm, 6-pole, dc generator is built with an armature diameter of 0.87m and core length of 0.32m. The lap wound armature has 660 conductors.
CHAPTER 3 CONVENTIONAL DESIGN SOLUTIONS
 31 CHAPTER 3 CONVENTIONAL DESIGN SOLUTIONS 3.1 CONVENTIONAL DESIGN Conventional design is a trial and error method. It makes use of empirical relations, approximations and assumptions. (Say 1958) A method
31 CHAPTER 3 CONVENTIONAL DESIGN SOLUTIONS 3.1 CONVENTIONAL DESIGN Conventional design is a trial and error method. It makes use of empirical relations, approximations and assumptions. (Say 1958) A method
Introduction. Energy is needed in different forms: Light bulbs and heaters need electrical energy Fans and rolling miles need mechanical energy
 Introduction Energy is needed in different forms: Light bulbs and heaters need electrical energy Fans and rolling miles need mechanical energy What does AC and DC stand for? Electrical machines Motors
Introduction Energy is needed in different forms: Light bulbs and heaters need electrical energy Fans and rolling miles need mechanical energy What does AC and DC stand for? Electrical machines Motors
PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
 QUESTION PAPER INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : /10/2016 Marks: 0 Subject & Code: BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING -15ELE15 Sec : F,G,H,I,J,K Name of faculty : Dhanashree Bhate, Hema B, Prashanth V Time :
QUESTION PAPER INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : /10/2016 Marks: 0 Subject & Code: BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING -15ELE15 Sec : F,G,H,I,J,K Name of faculty : Dhanashree Bhate, Hema B, Prashanth V Time :
D.C. Machine Design Problem (EE Electrical Machine Design I) By Pratik Mochi CSPIT, CHARUSAT
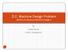 D.C. Machine Design Problem (EE401.01 Electrical Machine Design I) By Pratik Mochi CSPIT, CHARUSAT 1 2 Cross Section View of 4 pole DC Machine Design Problem Design a 250kW, 400V, 625A, 600 rpm, lap wound
D.C. Machine Design Problem (EE401.01 Electrical Machine Design I) By Pratik Mochi CSPIT, CHARUSAT 1 2 Cross Section View of 4 pole DC Machine Design Problem Design a 250kW, 400V, 625A, 600 rpm, lap wound
Design of Synchronous Machines
 Design of Synchronous Machines Introduction Synchronous machines are AC machines that have a field circuit supplied by an external DC source. Synchronous machines are having two major parts namely stationary
Design of Synchronous Machines Introduction Synchronous machines are AC machines that have a field circuit supplied by an external DC source. Synchronous machines are having two major parts namely stationary
Revision Guide for Chapter 15
 Revision Guide for Chapter 15 Contents tudent s Checklist Revision otes Transformer... 4 Electromagnetic induction... 4 Generator... 5 Electric motor... 6 Magnetic field... 8 Magnetic flux... 9 Force on
Revision Guide for Chapter 15 Contents tudent s Checklist Revision otes Transformer... 4 Electromagnetic induction... 4 Generator... 5 Electric motor... 6 Magnetic field... 8 Magnetic flux... 9 Force on
The principles of conservation of energy and charge apply to electrical circuits. Properties of magnetic fields apply in nature and technology.
 UIT E UMMARY KEY COCEPT CHAPTER UMMARY 11 The principles of conservation of energy and charge apply to electrical circuits. Electrical circuits Conventional current and electron flow Current, electrical
UIT E UMMARY KEY COCEPT CHAPTER UMMARY 11 The principles of conservation of energy and charge apply to electrical circuits. Electrical circuits Conventional current and electron flow Current, electrical
Basic Electrical Engineering SYLLABUS. Total No. of Lecture Hrs. : 50 Exam Marks : 80
 SYLLABUS Subject Code: /25 No. of Lecture Hrs./ Week : 04 IA Marks : 20 Exam Hours : 03 Total No. of Lecture Hrs. : 50 Exam Marks : 80 Course objectives: Impart a basic knowledge of electrical quantities
SYLLABUS Subject Code: /25 No. of Lecture Hrs./ Week : 04 IA Marks : 20 Exam Hours : 03 Total No. of Lecture Hrs. : 50 Exam Marks : 80 Course objectives: Impart a basic knowledge of electrical quantities
Revision Guide for Chapter 15
 Revision Guide for Chapter 15 Contents Revision Checklist Revision otes Transformer...4 Electromagnetic induction...4 Lenz's law...5 Generator...6 Electric motor...7 Magnetic field...9 Magnetic flux...
Revision Guide for Chapter 15 Contents Revision Checklist Revision otes Transformer...4 Electromagnetic induction...4 Lenz's law...5 Generator...6 Electric motor...7 Magnetic field...9 Magnetic flux...
Note that a current-carrying solenoid produces a dipole field similar to that of a bar magnet. The field is uniform within the coil.
 An electrical current produces a magnetic field that is directed around it. Conventional current is the flow of positive charge. Hence, it is directed from the positive terminal of the power supply, through
An electrical current produces a magnetic field that is directed around it. Conventional current is the flow of positive charge. Hence, it is directed from the positive terminal of the power supply, through
Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis
 Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis Lecture 12 : Sequence Modeling of Power Apparatus Objectives In this lecture we will discuss Per unit calculation and its advantages. Modeling aspects
Module 3 : Sequence Components and Fault Analysis Lecture 12 : Sequence Modeling of Power Apparatus Objectives In this lecture we will discuss Per unit calculation and its advantages. Modeling aspects
Chapter # 1 Three-Phase Winding, EMF's and MMF's
 Chapter # 1 Three-Phase Winding, EMF's and MMF's 1. Introduction standard A.C. generators or alternators (as they are usually called) operate on the same fundamental principles of electromagnetic induction
Chapter # 1 Three-Phase Winding, EMF's and MMF's 1. Introduction standard A.C. generators or alternators (as they are usually called) operate on the same fundamental principles of electromagnetic induction
CHAPTER 8 DC MACHINERY FUNDAMENTALS
 CHAPTER 8 DC MACHINERY FUNDAMENTALS Summary: 1. A Simple Rotating Loop between Curved Pole Faces - The Voltage Induced in a Rotating Loop - Getting DC voltage out of the Rotating Loop - The Induced Torque
CHAPTER 8 DC MACHINERY FUNDAMENTALS Summary: 1. A Simple Rotating Loop between Curved Pole Faces - The Voltage Induced in a Rotating Loop - Getting DC voltage out of the Rotating Loop - The Induced Torque
Design, analysis and fabrication of linear permanent magnet synchronous machine
 Design, analysis and fabrication of linear permanent magnet synchronous machine Monojit Seal Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIEST, Shibpur, Howrah - 711103 W.B., India. email: seal.monojit@gmail.com
Design, analysis and fabrication of linear permanent magnet synchronous machine Monojit Seal Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIEST, Shibpur, Howrah - 711103 W.B., India. email: seal.monojit@gmail.com
An Introduction to Electrical Machines. P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy
 An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
TOPIC: ELECTRODYNAMICS - MOTORS AND GENERATORS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT. (Taken from the DoE Physical Sciences Preparatory Examination Paper )
 TOPIC: ELECTRODYNAMICS - MOTORS AND GENERATORS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT SECTION A: TYPICAL EXAM QUESTIONS QUESTION 1: 13 minutes (Taken from the DoE Physical Sciences Preparatory Examination Paper 1 2008)
TOPIC: ELECTRODYNAMICS - MOTORS AND GENERATORS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT SECTION A: TYPICAL EXAM QUESTIONS QUESTION 1: 13 minutes (Taken from the DoE Physical Sciences Preparatory Examination Paper 1 2008)
Synchronous Machines
 Synchronous machine 1. Construction Generator Exciter View of a twopole round rotor generator and exciter. A Stator with laminated iron core C Slots with phase winding B A B Rotor with dc winding B N S
Synchronous machine 1. Construction Generator Exciter View of a twopole round rotor generator and exciter. A Stator with laminated iron core C Slots with phase winding B A B Rotor with dc winding B N S
EEE3405 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES 2 - TEST
 ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS (EACH QUESTION 20 Marks, FULL MAKS = 60) Given v 1 = 100 sin(100πt+π/6) (i) Find the MS, period and the frequency of v 1 (ii) If v 2 =75sin(100πt-π/10) find V 1, V 2, 2V 1 -V 2 (phasor)
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS (EACH QUESTION 20 Marks, FULL MAKS = 60) Given v 1 = 100 sin(100πt+π/6) (i) Find the MS, period and the frequency of v 1 (ii) If v 2 =75sin(100πt-π/10) find V 1, V 2, 2V 1 -V 2 (phasor)
Proposal of short armature core double-sided transverse flux type linear synchronous motor
 Proposal of short armature core double-sided transverse flux type linear synchronous motor Shin Jung-Seob a, Takafumi Koseki a and Kim Houng-Joong b a The University of Tokyo, Engineering Building #2 12F,7-3-1
Proposal of short armature core double-sided transverse flux type linear synchronous motor Shin Jung-Seob a, Takafumi Koseki a and Kim Houng-Joong b a The University of Tokyo, Engineering Building #2 12F,7-3-1
UNIT-I INTRODUCTION. 1. State the principle of electromechanical energy conversion.
 UNIT-I INTRODUCTION 1. State the principle of electromechanical energy conversion. The mechanical energy is converted in to electrical energy which takes place through either by magnetic field or electric
UNIT-I INTRODUCTION 1. State the principle of electromechanical energy conversion. The mechanical energy is converted in to electrical energy which takes place through either by magnetic field or electric
SECOND ENGINEER REG III/2 MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY. 1. Understands the physical construction and characteristics of basic components.
 SECOND ENGINEER REG III/ MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS A B C D Electric and Electronic Components Electric Circuit Principles Electromagnetism Electrical Machines The expected learning outcome
SECOND ENGINEER REG III/ MARINE ELECTRO-TECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS A B C D Electric and Electronic Components Electric Circuit Principles Electromagnetism Electrical Machines The expected learning outcome
Tutorial 1 (EMD) Rotary field winding
 Tutorial 1 (EMD) Rotary field winding The unchorded two-layer three-phase winding of a small synchronous fan drive for a computer has the following parameters: number of slots per pole and phase q = 1,
Tutorial 1 (EMD) Rotary field winding The unchorded two-layer three-phase winding of a small synchronous fan drive for a computer has the following parameters: number of slots per pole and phase q = 1,
Electric Machines I DC Machines - DC Generators. Dr. Firas Obeidat
 Electric Machines I DC Machines DC Generators Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 Construction of Simple Loop Generator 2 Working of Simple Loop Generator 3 Types of DC Generators 4 The Terminal Characteristic
Electric Machines I DC Machines DC Generators Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 Construction of Simple Loop Generator 2 Working of Simple Loop Generator 3 Types of DC Generators 4 The Terminal Characteristic
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK II SEMESTER BE8255 BASIC ELECTRICAL, ELECTRONICS AND MEASUREMENT ENGINEERING
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK II SEMESTER BE8255 BASIC ELECTRICAL, ELECTRONICS AND MEASUREMENT ENGINEERING
Generators for wind power conversion
 Generators for wind power conversion B. G. Fernandes Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Email : bgf@ee.iitb.ac.in Outline of The Talk Introduction Constant speed
Generators for wind power conversion B. G. Fernandes Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Email : bgf@ee.iitb.ac.in Outline of The Talk Introduction Constant speed
Equal Pitch and Unequal Pitch:
 Equal Pitch and Unequal Pitch: Equal-Pitch Multiple-Stack Stepper: For each rotor stack, there is a toothed stator segment around it, whose pitch angle is identical to that of the rotor (θs = θr). A stator
Equal Pitch and Unequal Pitch: Equal-Pitch Multiple-Stack Stepper: For each rotor stack, there is a toothed stator segment around it, whose pitch angle is identical to that of the rotor (θs = θr). A stator
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *5498152391* PHYSICS 0625/41 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) May/June 2018 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *5498152391* PHYSICS 0625/41 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) May/June 2018 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
TRACING OF MAXIMUM POWER DENSITY POINT FOR AXIAL FLUX TORUS TYPE MACHINES USING GENERAL PURPOSE SIZING EQUATIONS
 TRACING OF MAXIMUM POWER DENSITY POINT FOR AXIAL FLUX TORUS TYPE MACHINES USING GENERAL PURPOSE SIZING EQUATIONS M. Ramanjaneyulu Chowdary Dr.G.S Raju Mr.V.Rameshbabu M.Tech power electronics Former BHU
TRACING OF MAXIMUM POWER DENSITY POINT FOR AXIAL FLUX TORUS TYPE MACHINES USING GENERAL PURPOSE SIZING EQUATIONS M. Ramanjaneyulu Chowdary Dr.G.S Raju Mr.V.Rameshbabu M.Tech power electronics Former BHU
(a) Torsional spring-mass system. (b) Spring element.
 m v s T s v a (a) T a (b) T a FIGURE 2.1 (a) Torsional spring-mass system. (b) Spring element. by ky Wall friction, b Mass M k y M y r(t) Force r(t) (a) (b) FIGURE 2.2 (a) Spring-mass-damper system. (b)
m v s T s v a (a) T a (b) T a FIGURE 2.1 (a) Torsional spring-mass system. (b) Spring element. by ky Wall friction, b Mass M k y M y r(t) Force r(t) (a) (b) FIGURE 2.2 (a) Spring-mass-damper system. (b)
Physics 1051 Laboratory #10 Simple DC Motor The Simple DC Motor
 1 The 2 Prelab Write experiment title, your name and student number at top of the page. Prelab 1: Write the objective of this experiment. Prelab 2: Write the relevant theory of this experiment. Prelab
1 The 2 Prelab Write experiment title, your name and student number at top of the page. Prelab 1: Write the objective of this experiment. Prelab 2: Write the relevant theory of this experiment. Prelab
EN Power Electronics and Machines
 1/19 - Power Electronics and Machines Transformers Suryanarayana Doolla Department of Energy Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay suryad@iitb.ac.in Lecture Organization - Modules
1/19 - Power Electronics and Machines Transformers Suryanarayana Doolla Department of Energy Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay suryad@iitb.ac.in Lecture Organization - Modules
Generalized Theory of Electrical Machines- A Review
 Generalized Theory of Electrical Machines- A Review Dr. Sandip Mehta Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, JIET Group of Institutions, Jodhpur Abstract:-This paper provides an overview
Generalized Theory of Electrical Machines- A Review Dr. Sandip Mehta Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, JIET Group of Institutions, Jodhpur Abstract:-This paper provides an overview
Fig. 2.1 I =... A [2] Suggest why it would be impossible for overhead cables carrying an alternating current to float in the Earth s magnetic field.
![Fig. 2.1 I =... A [2] Suggest why it would be impossible for overhead cables carrying an alternating current to float in the Earth s magnetic field. Fig. 2.1 I =... A [2] Suggest why it would be impossible for overhead cables carrying an alternating current to float in the Earth s magnetic field.](/thumbs/78/78653113.jpg) 1 (a) Fig. 2.1 shows a horizontal current-carrying wire placed in a uniform magnetic field. I region of uniform magnetic field wire Fig. 2.1 The magnetic field of flux density 0.070 T is at right angles
1 (a) Fig. 2.1 shows a horizontal current-carrying wire placed in a uniform magnetic field. I region of uniform magnetic field wire Fig. 2.1 The magnetic field of flux density 0.070 T is at right angles
ENGG4420 LECTURE 7. CHAPTER 1 BY RADU MURESAN Page 1. September :29 PM
 CHAPTER 1 BY RADU MURESAN Page 1 ENGG4420 LECTURE 7 September 21 10 2:29 PM MODELS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Electric circuits contain sources of electric voltage and current and other electronic elements such
CHAPTER 1 BY RADU MURESAN Page 1 ENGG4420 LECTURE 7 September 21 10 2:29 PM MODELS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Electric circuits contain sources of electric voltage and current and other electronic elements such
AGA KHAN UNIVERSITY EXAMINATION BOARD SECONDARY SCHOOL CERTIFICATE CLASS X EXAMINATION MAY Physics Paper I. Time: 35 minutes Marks: 25
 Page 1 of 8 AGA KHAN UNIVERSITY EXAMINATION BOARD SECONDARY SCHOOL CERTIFICATE CLASS X EXAMINATION MAY 2015 Physics Paper I Time: 35 minutes Marks: 25 INSTRUCTIONS 1. Read each question carefully. 2. Answer
Page 1 of 8 AGA KHAN UNIVERSITY EXAMINATION BOARD SECONDARY SCHOOL CERTIFICATE CLASS X EXAMINATION MAY 2015 Physics Paper I Time: 35 minutes Marks: 25 INSTRUCTIONS 1. Read each question carefully. 2. Answer
International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies
 Volume 2, Issue 9, September 2014 ISSN: 2321 7782 (Online) International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Survey Paper / Case Study Available online
Volume 2, Issue 9, September 2014 ISSN: 2321 7782 (Online) International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Survey Paper / Case Study Available online
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3. OUTCOME 3 - MAGNETISM and INDUCTION
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 3 - MAGNETISM and INDUCTION 3 Understand the principles and properties of magnetism Magnetic field:
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 3 - MAGNETISM and INDUCTION 3 Understand the principles and properties of magnetism Magnetic field:
Term-End Examination December, calculator is permitted.
 No. of Printed Pages : 8 I BET-024 DIPLOMA IN CIVIL ENGINEERING (DCLE(G)) / DIPLOMA IN ELECTRICAL AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING (DEME) / DCLEVI / DMEVI / DELVI / DECVI / DCSVI C.1 C.IE):: 1_ Term-End Examination
No. of Printed Pages : 8 I BET-024 DIPLOMA IN CIVIL ENGINEERING (DCLE(G)) / DIPLOMA IN ELECTRICAL AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING (DEME) / DCLEVI / DMEVI / DELVI / DECVI / DCSVI C.1 C.IE):: 1_ Term-End Examination
Eddy Current Heating in Large Salient Pole Generators
 Eddy Current Heating in Large Salient Pole Generators C.P.Riley and A.M. Michaelides Vector Fields Ltd., 24 Bankside, Kidlington, Oxford OX5 1JE, UK phone: (+44) 1865 370151, fax: (+44) 1865 370277 e-mail:
Eddy Current Heating in Large Salient Pole Generators C.P.Riley and A.M. Michaelides Vector Fields Ltd., 24 Bankside, Kidlington, Oxford OX5 1JE, UK phone: (+44) 1865 370151, fax: (+44) 1865 370277 e-mail:
SAMPLE DEB Exams 1065
 L.35 PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2015 TIME 3 HOURS PHYSICS ORDINARY LEVEL Answer three questions from Section A and five questions from Section B. N.B. Relevant data are listed in the Formulae
L.35 PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2015 TIME 3 HOURS PHYSICS ORDINARY LEVEL Answer three questions from Section A and five questions from Section B. N.B. Relevant data are listed in the Formulae
Water-Cooled Direct Drive Permanent Magnet Motor Design in Consideration of its Efficiency and Structural Strength
 Journal of Magnetics 18(2), 125-129 (2013) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 http://dx.doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2013.18.2.125 Water-Cooled Direct Drive Permanent Magnet Motor Design in Consideration
Journal of Magnetics 18(2), 125-129 (2013) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 http://dx.doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2013.18.2.125 Water-Cooled Direct Drive Permanent Magnet Motor Design in Consideration
Chapter 6: Efficiency and Heating. 9/18/2003 Electromechanical Dynamics 1
 Chapter 6: Efficiency and Heating 9/18/2003 Electromechanical Dynamics 1 Losses As a machine transforms energy from one form to another there is always a certain power loss the loss is expressed as heat,
Chapter 6: Efficiency and Heating 9/18/2003 Electromechanical Dynamics 1 Losses As a machine transforms energy from one form to another there is always a certain power loss the loss is expressed as heat,
Electric Transformer Motor Theory
 Electric Transformer Motor Theory This whole article is written in assumption that the reader has a college level degree and several years experience with electronics. This document was written with the
Electric Transformer Motor Theory This whole article is written in assumption that the reader has a college level degree and several years experience with electronics. This document was written with the
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
 Subject Code : 17331 (ETE) Model Answer Page No : 1 of 23 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Subject Code : 17331 (ETE) Model Answer Page No : 1 of 23 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Texas A & M University Department of Mechanical Engineering MEEN 364 Dynamic Systems and Controls Dr. Alexander G. Parlos
 Texas A & M University Department of Mechanical Engineering MEEN 364 Dynamic Systems and Controls Dr. Alexander G. Parlos Lecture 6: Modeling of Electromechanical Systems Principles of Motor Operation
Texas A & M University Department of Mechanical Engineering MEEN 364 Dynamic Systems and Controls Dr. Alexander G. Parlos Lecture 6: Modeling of Electromechanical Systems Principles of Motor Operation
THREE PHASE SYSTEMS Part 1
 ERT105: ELECTRCAL TECHNOLOGY CHAPTER 3 THREE PHASE SYSTEMS Part 1 1 Objectives Become familiar with the operation of a three phase generator and the magnitude and phase relationship. Be able to calculate
ERT105: ELECTRCAL TECHNOLOGY CHAPTER 3 THREE PHASE SYSTEMS Part 1 1 Objectives Become familiar with the operation of a three phase generator and the magnitude and phase relationship. Be able to calculate
NCERT solutions Magnetic effects of current (In-text questions)
 NCERT solutions Magnetic effects of current (In-text questions) Page No: 224 Question 1 Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? Compass needle is a small permanent magnet.
NCERT solutions Magnetic effects of current (In-text questions) Page No: 224 Question 1 Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet? Compass needle is a small permanent magnet.
Synchronous Machine Design ( Dr. R. C. Goel & Nafees Ahmed )
 Synchronous Machine Design ( Dr. R. C. Goel & Nafees Ahmed ) y Nafees Ahmed Asstt. rof. Department of Electrical Engineering DIT, University, Dehradun, Uttarakhand References:. Notes by Dr. R. C. Goel.
Synchronous Machine Design ( Dr. R. C. Goel & Nafees Ahmed ) y Nafees Ahmed Asstt. rof. Department of Electrical Engineering DIT, University, Dehradun, Uttarakhand References:. Notes by Dr. R. C. Goel.
2002 Prentice Hall, Inc. Gene F. Franklin, J. David Powell, Abbas Emami-Naeini Feedback Control of Dynamic Systems, 4e
 u Figure 2.1 Cruise-control model x Friction force bx m x u Figure 2.2 Free-body diagram for cruise control S P 278 Figure 2.3 Automobile suspension y m 2 k s b v car x m 1 k w Road surface r Inertial
u Figure 2.1 Cruise-control model x Friction force bx m x u Figure 2.2 Free-body diagram for cruise control S P 278 Figure 2.3 Automobile suspension y m 2 k s b v car x m 1 k w Road surface r Inertial
Motor-CAD combined electromagnetic and thermal model (January 2015)
 Motor-CAD combined electromagnetic and thermal model (January 2015) Description The Motor-CAD allows the machine performance, losses and temperatures to be calculated for a BPM machine. In this tutorial
Motor-CAD combined electromagnetic and thermal model (January 2015) Description The Motor-CAD allows the machine performance, losses and temperatures to be calculated for a BPM machine. In this tutorial
Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark]
![Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark] Induction_P1. 1. [1 mark]](/thumbs/88/115570773.jpg) Induction_P1 1. [1 mark] Two identical circular coils are placed one below the other so that their planes are both horizontal. The top coil is connected to a cell and a switch. The switch is closed and
Induction_P1 1. [1 mark] Two identical circular coils are placed one below the other so that their planes are both horizontal. The top coil is connected to a cell and a switch. The switch is closed and
Current Balance. Introduction
 Current Balance Objectives a. To find the direction of magnetic field, current and the Lorentz force b. To find the relationship between Lorentz force and current c. To find the relationship between Lorentz
Current Balance Objectives a. To find the direction of magnetic field, current and the Lorentz force b. To find the relationship between Lorentz force and current c. To find the relationship between Lorentz
Optimisation of Inner Diameter to Outer Diameter Ratio of Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Generator
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 220-1, Volume 9, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov Dec. 2014), PP 4-47 Optimisation of Inner Diameter to Outer Diameter
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 220-1, Volume 9, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov Dec. 2014), PP 4-47 Optimisation of Inner Diameter to Outer Diameter
Electric Machines I Three Phase Induction Motor. Dr. Firas Obeidat
 Electric Machines I Three Phase Induction Motor Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 General Principles 2 Construction 3 Production of Rotating Field 4 Why Does the Rotor Rotate 5 The Slip and Rotor
Electric Machines I Three Phase Induction Motor Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 General Principles 2 Construction 3 Production of Rotating Field 4 Why Does the Rotor Rotate 5 The Slip and Rotor
Fea of a High Efficiency Brushless Dc Motor Design
 Fea of a High Efficiency Brushless Dc Motor Design Manoj Kumar Pandey, Dr. Anurag Tripathi and Dr. Bharti Dwivedi 1 Research Scholar, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, AKTU Lucknow UP- 226031, India.
Fea of a High Efficiency Brushless Dc Motor Design Manoj Kumar Pandey, Dr. Anurag Tripathi and Dr. Bharti Dwivedi 1 Research Scholar, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, AKTU Lucknow UP- 226031, India.
Scilab Textbook Companion for Electrical Machinery by Dr. P S Bimbhra 1
 Scilab Textbook Companion for Electrical Machinery by Dr. P S Bimbhra 1 Created by Tejash Ajay Sharma B.Tech Electrical Engineering Visvesvaraya National Institute of Technology College Teacher None Cross-Checked
Scilab Textbook Companion for Electrical Machinery by Dr. P S Bimbhra 1 Created by Tejash Ajay Sharma B.Tech Electrical Engineering Visvesvaraya National Institute of Technology College Teacher None Cross-Checked
ELECTRICIAN MODEL PAPER - 1 PART A MARKS: 70
 ELECTRICIAN MODEL PAPER - 1 PART A MARKS: 70 I. Answer the following Questions 1. What is purpose of Fuse? 2. a heater is rated as 1000 w, 250 v. What is the heater resistance? 3. In simple voltaic cell,
ELECTRICIAN MODEL PAPER - 1 PART A MARKS: 70 I. Answer the following Questions 1. What is purpose of Fuse? 2. a heater is rated as 1000 w, 250 v. What is the heater resistance? 3. In simple voltaic cell,
SEMESTER IV SEMESTER IV MA202 MATHEMATICS IV
 SEMESTER IV S.No. CODE COURSE OF STUDY L T P C 1. MA202 Mathematics - IV 3 0 0 3 2. EE202 DC Machines and Transformers 3 1 0 4 3. EE204 AC Machines 3 1 0 4 4. EE206 Transmission and Distribution of Electrical
SEMESTER IV S.No. CODE COURSE OF STUDY L T P C 1. MA202 Mathematics - IV 3 0 0 3 2. EE202 DC Machines and Transformers 3 1 0 4 3. EE204 AC Machines 3 1 0 4 4. EE206 Transmission and Distribution of Electrical
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *7907131038* PHYSICS 0625/33 Paper 3 Extended May/June 2014 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer on
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *7907131038* PHYSICS 0625/33 Paper 3 Extended May/June 2014 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer on
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
ELECTROMAGNETISM The study of the relationship between electricity and magnetism is called
 ELECTROMAGNETISM The study of the relationship between electricity and magnetism is called Electromagnetism Before, 1819 it was believed that there was no connection between electricity and magnetism.
ELECTROMAGNETISM The study of the relationship between electricity and magnetism is called Electromagnetism Before, 1819 it was believed that there was no connection between electricity and magnetism.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 22, NO. 1, JANUARY /$ IEEE
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 22, NO. 1, JANUARY 2007 195 Analysis of Half-Turn Effect in Power Transformers Using Nonlinear-Transient FE Formulation G. B. Kumbhar, S. V. Kulkarni, Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 22, NO. 1, JANUARY 2007 195 Analysis of Half-Turn Effect in Power Transformers Using Nonlinear-Transient FE Formulation G. B. Kumbhar, S. V. Kulkarni, Member,
MOTORS AND GENERATORS
 DO PHYSCS ONLNE MOTORS AND GENERATORS view 1 Charge q Q [coulomb C] view 2 Current i [ampere A] view 3 Potential difference v V [volt V] Electric ield E [V.m -1 N.C -1 ] view 4 Resistance R [ohm ] view
DO PHYSCS ONLNE MOTORS AND GENERATORS view 1 Charge q Q [coulomb C] view 2 Current i [ampere A] view 3 Potential difference v V [volt V] Electric ield E [V.m -1 N.C -1 ] view 4 Resistance R [ohm ] view
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number
 A LEVEL PHYSICS Specimen Assessment Materials 25 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number A LEVEL PHYSICS COMPONENT 2 Electricity and the Universe SPECIMEN PAPER 2 hours For Examiner s use only Question
A LEVEL PHYSICS Specimen Assessment Materials 25 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number A LEVEL PHYSICS COMPONENT 2 Electricity and the Universe SPECIMEN PAPER 2 hours For Examiner s use only Question
Downloaded from
 CLASS VI Mathematics (Knowing our Numbers) Worksheet-01 Choose correct option in questions 1 to 7. 1. Which is greatest? a. 234 b. 543 c. 657 56 2. Which is smallest? a. 4567 b. 3456 c. 2345 d. 1234 3.
CLASS VI Mathematics (Knowing our Numbers) Worksheet-01 Choose correct option in questions 1 to 7. 1. Which is greatest? a. 234 b. 543 c. 657 56 2. Which is smallest? a. 4567 b. 3456 c. 2345 d. 1234 3.
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. Generalised Approach to the Analysis of Asymmetrical Delta Connected Three-Phase Induction Motor
 AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Generalised Approach to the Analysis of Asymmetrical Delta Connected Three-Phase Induction Motor 1 Jafar
AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Generalised Approach to the Analysis of Asymmetrical Delta Connected Three-Phase Induction Motor 1 Jafar
LAB REPORT: THREE-PHASE INDUCTION MACHINE
 LAB REPORT: THREE-PHASE INDUCTION MACHINE ANDY BENNETT 1. Summary This report details the operation, modelling and characteristics of a three-phase induction machine. It attempts to provide a concise overview
LAB REPORT: THREE-PHASE INDUCTION MACHINE ANDY BENNETT 1. Summary This report details the operation, modelling and characteristics of a three-phase induction machine. It attempts to provide a concise overview
Physics 42 Exam 3 Fall 2013 PRINT Name:
 Physics 42 Exam 3 Fall 2013 PRINT Name: 1 2 3 4 Conceptual Questions : Circle the BEST answer. (1 point each) 1. A small plastic ball has an excess negative charge on it. If a magnet is placed close to
Physics 42 Exam 3 Fall 2013 PRINT Name: 1 2 3 4 Conceptual Questions : Circle the BEST answer. (1 point each) 1. A small plastic ball has an excess negative charge on it. If a magnet is placed close to
Broken Flux Generator
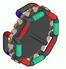 Broken Flux Generator The Broken Flux Generator The Broken Flux Generator operates on the principal of paths of magnetic flux being made or broken. Instead of rotating magnets or coils, a series of disks
Broken Flux Generator The Broken Flux Generator The Broken Flux Generator operates on the principal of paths of magnetic flux being made or broken. Instead of rotating magnets or coils, a series of disks
Intermediate Physics PHYS102
 Intermediate Physics PHYS102 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu My webpage: www.concord.edu/rcyburt
Intermediate Physics PHYS102 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu My webpage: www.concord.edu/rcyburt
Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University College of Engineering. Electrical Engineering Department EE 3360 Electrical Machines (II)
 Chapter # 4 Three-Phase Induction Machines 1- Introduction (General Principles) Generally, conversion of electrical power into mechanical power takes place in the rotating part of an electric motor. In
Chapter # 4 Three-Phase Induction Machines 1- Introduction (General Principles) Generally, conversion of electrical power into mechanical power takes place in the rotating part of an electric motor. In
: DJJ2022 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY. Upon completion of this course, students should be able to:
 PUO/KURIKULUM/JKM/DEM/DJJ2022/1.0/EFF JUNE 2014/(03) POLYTECHNICS MINISTRY OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SALINAN TERKAWAL COURSE : DJJ2022 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY CREDIT(S) : 2 PRE REQUISITE(S)
PUO/KURIKULUM/JKM/DEM/DJJ2022/1.0/EFF JUNE 2014/(03) POLYTECHNICS MINISTRY OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SALINAN TERKAWAL COURSE : DJJ2022 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY CREDIT(S) : 2 PRE REQUISITE(S)
PHENOMENA OF ALTERNATING CURRENTS
 PHENOMENA OF ALTERNATING CURRENTS Source : http://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/11498 http://www.fdp.nu/free_energy.asp?book=gen Scientific American Supplement. Vol. XXIV, No. 601. Scientific American established
PHENOMENA OF ALTERNATING CURRENTS Source : http://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/11498 http://www.fdp.nu/free_energy.asp?book=gen Scientific American Supplement. Vol. XXIV, No. 601. Scientific American established
Control of Wind Turbine Generators. James Cale Guest Lecturer EE 566, Fall Semester 2014 Colorado State University
 Control of Wind Turbine Generators James Cale Guest Lecturer EE 566, Fall Semester 2014 Colorado State University Review from Day 1 Review Last time, we started with basic concepts from physics such as
Control of Wind Turbine Generators James Cale Guest Lecturer EE 566, Fall Semester 2014 Colorado State University Review from Day 1 Review Last time, we started with basic concepts from physics such as
Electromagnetic Induction & Inductors
 Electromagnetic Induction & Inductors 1 Revision of Electromagnetic Induction and Inductors (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) Magnetic Field
Electromagnetic Induction & Inductors 1 Revision of Electromagnetic Induction and Inductors (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) Magnetic Field
UNIVERSITY POLYTECHNIC B.I.T., MESRA, RANCHI. COURSE STRUCTURE (W.E.F Batch Students) (Total Unit 7.5)
 COURSE STRUCTURE (W.E.F. 2011 Batch Students) (Total Unit 7.5) Course Code Theory Unit Course Code Sessional Unit DMA 3001 Mathematics III 1.0 DEC 3002 Basic Electronics Lab. 0.5 DEC 3001 Basic Electronics
COURSE STRUCTURE (W.E.F. 2011 Batch Students) (Total Unit 7.5) Course Code Theory Unit Course Code Sessional Unit DMA 3001 Mathematics III 1.0 DEC 3002 Basic Electronics Lab. 0.5 DEC 3001 Basic Electronics
Capacitance. A different kind of capacitor: Work must be done to charge a capacitor. Capacitors in circuits. Capacitor connected to a battery
 Capacitance The ratio C = Q/V is a conductor s self capacitance Units of capacitance: Coulomb/Volt = Farad A capacitor is made of two conductors with equal but opposite charge Capacitance depends on shape
Capacitance The ratio C = Q/V is a conductor s self capacitance Units of capacitance: Coulomb/Volt = Farad A capacitor is made of two conductors with equal but opposite charge Capacitance depends on shape
Synchronous Machines
 Synchronous Machines Synchronous generators or alternators are used to convert mechanical power derived from steam, gas, or hydraulic-turbine to ac electric power Synchronous generators are the primary
Synchronous Machines Synchronous generators or alternators are used to convert mechanical power derived from steam, gas, or hydraulic-turbine to ac electric power Synchronous generators are the primary
Module 3 Electrical Fundamentals
 3.1 Electron Theory Structure and distribution of electrical charges within: atoms, molecules, ions, compounds; Molecular structure of conductors, semiconductors and insulators. 3.2 Static Electricity
3.1 Electron Theory Structure and distribution of electrical charges within: atoms, molecules, ions, compounds; Molecular structure of conductors, semiconductors and insulators. 3.2 Static Electricity
Doubly salient reluctance machine or, as it is also called, switched reluctance machine. [Pyrhönen et al 2008]
![Doubly salient reluctance machine or, as it is also called, switched reluctance machine. [Pyrhönen et al 2008] Doubly salient reluctance machine or, as it is also called, switched reluctance machine. [Pyrhönen et al 2008]](/thumbs/86/93665357.jpg) Doubly salient reluctance machine or, as it is also called, switched reluctance machine [Pyrhönen et al 2008] Pros and contras of a switched reluctance machine Advantages Simple robust rotor with a small
Doubly salient reluctance machine or, as it is also called, switched reluctance machine [Pyrhönen et al 2008] Pros and contras of a switched reluctance machine Advantages Simple robust rotor with a small
3 d Calculate the product of the motor constant and the pole flux KΦ in this operating point. 2 e Calculate the torque.
 Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) 11 November 011 from 14.00 to 17.00. This exam consists of 5 problems on 4 pages. Page 5 can be used to answer problem 4 question b. The number before a question
Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) 11 November 011 from 14.00 to 17.00. This exam consists of 5 problems on 4 pages. Page 5 can be used to answer problem 4 question b. The number before a question
Applied Electronics and Electrical Machines
 School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Applied Electronics and Electrical Machines (ELEC 365) Fall 2015 DC Machines 1 DC Machines Key educational goals: Develop the basic principle of operation
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Applied Electronics and Electrical Machines (ELEC 365) Fall 2015 DC Machines 1 DC Machines Key educational goals: Develop the basic principle of operation
EDEXCEL NATIONALS UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES. ASSIGNMENT No. 3 - ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION
 EDEXCEL NATIONALS UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES ASSIGNMENT No. 3 - ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION NAME: I agree to the assessment as contained in this assignment. I confirm that the work submitted
EDEXCEL NATIONALS UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES ASSIGNMENT No. 3 - ELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION NAME: I agree to the assessment as contained in this assignment. I confirm that the work submitted
Sample assessment instrument and indicative responses
 Sample assessment instrument and indicative responses Supervised assessment This sample is intended to inform the design of assessment instruments in the senior phase of learning. It highlights the qualities
Sample assessment instrument and indicative responses Supervised assessment This sample is intended to inform the design of assessment instruments in the senior phase of learning. It highlights the qualities
Homework # Physics 2 for Students of Mechanical Engineering. Part A
 Homework #9 203-1-1721 Physics 2 for Students of Mechanical Engineering Part A 5. A 25-kV electron gun in a TV tube fires an electron beam having a diameter of 0.22 mm at the screen. The spot on the screen
Homework #9 203-1-1721 Physics 2 for Students of Mechanical Engineering Part A 5. A 25-kV electron gun in a TV tube fires an electron beam having a diameter of 0.22 mm at the screen. The spot on the screen
TEMPERATURE EFFECTS ON MOTOR PERFORMANCE
 TEMPERATURE EFFECTS ON MOTOR PERFORMANCE Authored By: Dan Montone Haydon Kerk Motion Solutions / Pittman Motors hen applying DC motors to any type of application, temperature effects need to be considered
TEMPERATURE EFFECTS ON MOTOR PERFORMANCE Authored By: Dan Montone Haydon Kerk Motion Solutions / Pittman Motors hen applying DC motors to any type of application, temperature effects need to be considered
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM, A. C. THEORY AND ELECTRONICS, ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS
 UNIT 2: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM, A. C. THEORY AND ELECTRONICS, ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS MODULE 1: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of this Module, students should: 1. understand
UNIT 2: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM, A. C. THEORY AND ELECTRONICS, ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS MODULE 1: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of this Module, students should: 1. understand
Homework (lecture 11): 3, 5, 9, 13, 21, 25, 29, 31, 40, 45, 49, 51, 57, 62
 Homework (lecture ): 3, 5, 9, 3,, 5, 9, 3, 4, 45, 49, 5, 57, 6 3. An electron that has velocity: moves through the uniform magnetic field (a) Find the force on the electron. (b) Repeat your calculation
Homework (lecture ): 3, 5, 9, 3,, 5, 9, 3, 4, 45, 49, 5, 57, 6 3. An electron that has velocity: moves through the uniform magnetic field (a) Find the force on the electron. (b) Repeat your calculation
 Question 6.1: Predict the direction of induced current in the situations described by the following Figs. 6.18(a) to (f ). (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) The direction of the induced current in a closed loop
Question 6.1: Predict the direction of induced current in the situations described by the following Figs. 6.18(a) to (f ). (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) The direction of the induced current in a closed loop
ELECTRICAL FUNDAMENTALS
 Part 66 Cat. B1 / B2 Module 3 ELECTRICAL FUNDAMENTALS Vilnius-2017 Issue 1. Effective date 2017-02-28 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY Page 1 of 280 If we look at electronic configuration of a carbon C atom,
Part 66 Cat. B1 / B2 Module 3 ELECTRICAL FUNDAMENTALS Vilnius-2017 Issue 1. Effective date 2017-02-28 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY Page 1 of 280 If we look at electronic configuration of a carbon C atom,
This is a repository copy of Improved analytical model for predicting the magnetic field distribution in brushless permanent-magnet machines.
 This is a repository copy of Improved analytical model for predicting the magnetic field distribution in brushless permanent-magnet machines. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/874/
This is a repository copy of Improved analytical model for predicting the magnetic field distribution in brushless permanent-magnet machines. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/874/
Motors and Generators
 Motors and Generators Joe Khachan and Chris Stewart Introduction This part of the syllabus draws upon many ideas and concepts from the old HSC syllabus, perhaps with a bit more of a historical twist thrown
Motors and Generators Joe Khachan and Chris Stewart Introduction This part of the syllabus draws upon many ideas and concepts from the old HSC syllabus, perhaps with a bit more of a historical twist thrown
EE 410/510: Electromechanical Systems Chapter 4
 EE 410/510: Electromechanical Systems Chapter 4 Chapter 4. Direct Current Electric Machines and Motion Devices Permanent Magnet DC Electric Machines Radial Topology Simulation and Experimental Studies
EE 410/510: Electromechanical Systems Chapter 4 Chapter 4. Direct Current Electric Machines and Motion Devices Permanent Magnet DC Electric Machines Radial Topology Simulation and Experimental Studies
Alternating current. Book pg
 Alternating current Book pg.440-442 Review of induced emf Emf = BLv, v = speed of rod Φ = BA flux density Emf = NΦ rate of change of flux density t Normal to surface Φ = BA cos θ θ = 0 Φ = BA θ = 90 0
Alternating current Book pg.440-442 Review of induced emf Emf = BLv, v = speed of rod Φ = BA flux density Emf = NΦ rate of change of flux density t Normal to surface Φ = BA cos θ θ = 0 Φ = BA θ = 90 0
