WHAT IS STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELING (SEM)?
|
|
|
- Suzanna Morrison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WHAT IS STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELING (SEM)? 1
2 LINEAR STRUCTURAL RELATIONS 2
3 Terminología LINEAR LATENT VARIABLE MODELS T.W. Anderson (1989), Journal of Econometrics MULTIVARIATE LINEAR RELATIONS T.W. Anderson (1987), 2nd International Temp. Conference in Statistics LINEAR STATISTICAL RELATIONSHIPS T.W. Anderson (1984), Annals of Statistics, 12 COVARIANCE STRUCTURES Browne, Shapiro, Satorra,... Jöreskog (1973, 1977) Wiley (1979) Keesling (1972) Koopmans and Hovel (1953) 3
4 Computer programs LISREL EQS LISCOMP / Mplus COSAN MOMENTS CALIS AMOS RAMONA Mx Jöreskog and Sörbom Bentler Muthén McDonalds Schoenberg SAS Arbunckle Browne Neale 4
5 Computer programs SEM software: EQS LISREL MPLUS AMOS Mx 5
6 ... books Bollen (1989) Dwyer (1983) Hayduk (1987) Mueller (1996) Saris and Stronkhorst (1984)... 6
7 ... many research papers Austin and Wolfle (1991): Annotated bibliography of structural equation modeling: Technical Works. BJMSP, 99, pp Austin, J.T. and Calteron, R.F. (1996). Theoretical and technical contributions to structural equation modeling: An updated annotated bibliography. SEM, pp
8 Information on SEM: bibliography, courses.. General information on SEM: Jason Newsom's Structural Equation Modeling Reference List David A. Kenny s course Jouni Kuha s Model Assessment and Model Choice: An Annotated Bibliography 8
9 ... web sites SEM webs: jcrawford/psychom.htm computing the scaling factor for the difference of chi squares 9
10 Introduction to SEM: Data: Data matrix ( raw data ) Sufficient statistics (sample means, variances and covariances) Indiv. vars Data Matrix (n x p) Sample Moments: Vector of means Variance and covariance matrix (p x p) Fourth order moments: Γ (p* x p*) p* = p(p+1)/2, p=20--> p* =210 10
11 Moment Structure S sample covariance matrix Σ population covariance matrix Σ = Σ(θ) 11
12 Fitting S to Σ(θ): Min f(s,σ) Σ ^ ^ = Σ(θ) ^ S Σ ^ S Σ 0 12
13 Type of variables Manifest Variables: Y i, X i Measurement Model: ε 3 X 3 λ 32 ξ 2 ε 4 X 4 λ 42 Measurement error, disturbances: ε i, δ i 13
14 The form of structural equation models Latent constructs: - Endogenous η i - Exogenous ξ i Structural Model: - Regression of η 1 on ξ 2 : γ 12 - Regression of η 1 on η 2 : β 12 Structural Error: ζ i 14
15 LISREL model: η (m x 1) = Β (m x m) η (m x 1) + Γ (m x n) ξ (n x 1) + ζ (m x 1) y (p x 1) = Λ y(p x m) η (m x 1) + ε (p x 1) x (q x 1) = Λ x(q x n) ξ (n x 1) + δ (q x 1) 15
16 ... path diagram (LISREL) ε 1 ε 2 ε 3 Y 1 Y 2 Y 3 δ 1 X 1 γ 11 ζ 1 ζ 2 ξ 1 η 1 δ 2 X 2 β 31 δ 3 X 3 θ 21 η 3 Y 6 Y 7 ε 6 ε 7 δ 4 X 4 ξ 2 γ 22 η 2 β 32 ζ 3 δ 5 X 5 Y 4 Y 5 ε 4 ε 5 16
17 SEM: i=1,2,..., n g, donde: z i : vector de variables observables, η i : vector de variables endógenas ξ i : vector de variables exógenas v i = (η i, ξ i ) : vector de variables observables y latentes, U (g) : matriz de selección completamente especificada, B, Γ y Φ = E(ξ i ξ i ): matrices de parámetros del modelo 17
18 El modelo general: donde: Φ = var ξ 18
19 ... path diagram (EQS) Ε 6 Ε 7 Ε 8 V 6 V 7 V 8 Ε 1 Ε 2 V 1 V 2 F 1 F 3 D 3 D 5 V 11 Ε 11 Ε 3 Ε 4 V 3 V 4 F 2 F 4 F 5 V 12 Ε 12 D 4 Ε 5 V 5 V 9 V 10 Ε 9 Ε 10 19
20 Main virtues of SEM (ctd.) Flexibility on the type of data: Continuous and ordinal variables multiple sample Informative missingness (MCA, MAR) Finite mixture distributions Multilevel models Samples with complex design General longitudinal type of data... 20
21 RESEARCH DESINGS 21
22 Data collection designs Cross-sectional N independent units observed or measured at one time Time-series One unit observed or measured al T occasions Longitudinal N independent units observed or measured at two or more occasions 22
23 .. data collection designs Longitudinal a) Retrospective b) Prospective c) Repeated measures d) panel e) Rotating panel Experimental, quasi-experimental data Observational or non-experimental 23
24 Type of Variables VARIABLES Continous Ordinal Nominal SCALE TYPE Interval or ratio Ordinal Ordered categories Underordered caterogies Censored, truncated 24
25 Ordinal Variables Is is assumed that there is a continuous unobserved variable x* underlying the observed ordinal variable x. A threshold model is specified, as in ordinal probit regression, but here we contemplate multivariate regression. It is the underlying variable x* that is acting in the SEM model. 25
26 Polychorical correlation 26
27 Polyserial correlation 27
28 Threshold model 28
29 Modelling the effect on behaviour Correla =.83 Affect Cognition U.65 Behaviour A policy that changes Affect will have more influence on B than one that Bagozzi and Burnkrant (1979), changes cognition Attitude organization and the attitude behaviour relationship, Journal Of Personality and Social Psychology, 37, Influence of affect on Behaviour is almost Three times stronger (on a standardized scale) Than the effect of Cognition. 29
30 Causal model with reciprocal effects U 1 W I U 2 P = price D = demand I = Income W = Wages D + - P 30
31 Examples with Coupon data (Bagozzi, 1994) 31
32 Example: Data of Bagozzi, Baumgartner, and Yi (1992), on coupon usage : Sample A: Action oriented women (n = 85) Intentions # Intentions # Behavior Attitudes # Attitudes # Attitudes # Sample B: State oriented women (n = 64) Intentions # Intentions # Behavior Attitudes # Attitudes # Attitudes #
33 Variables /LABELS V1 = Intentions1; V2 = Intentions2; V3 = Behavior; V4 = Attitudes1; V5 = Attitudes2; V6 = Attitudes3; F1 = Attitudes F2 = Intentions V3 = Behavior 33
34 SEM multiple indicators E4 E5 E6 V4 V5 V6 F1 F2 D2 E3 V1 V2 E1 E2 V3 F1 = Attitudes F2 = Intentions V3 = Behavior 34
35 INTENTIO=V1 = F E1 INTENTIO=V2 = 1.014*F E CHI-SQUARE = 5.426, 7 DEGREES OF FREEDOM PROBABILITY VALUE IS BEHAVIOR=V3 =.330*F *F E VARIANCES OF INDEPENDENT VARIABLES ATTITUDE=V4 = 1.020*F E ATTITUDE=V5 =.951*F E ATTITUDE=V6 = 1.269*F E INTENTIO=F2 = 1.311*F D E1 -INTENTIO 2.020*I I I I E2 -INTENTIO I I I I E3 -BEHAVIOR I I I I E4 -ATTITUDE I I I I E5 -ATTITUDE I E D *I D2 -INTENTIO.255 I I I.565*I.257 I I I 1.311*I.213 I I I.875*I.161 I I I.576*I.115 I 35
36 ... adding parameters? LAGRANGE MULTIPLIER TEST (FOR ADDING PARAMETERS) ORDERED UNIVARIATE TEST STATISTICS: NO CODE PARAMETER CHI-SQUARE PROBABILITY PARAMETER CHANGE V2,F V1,F V4,F V5,F V6,F V3,F F1,F F2,D V1,F
37 Hopkins and Hopkins (1997): Strategic planningfinancial performance relationships in banks: a causal examination. Strategic Management Journal, Vol 18 (8), pp. ( ) 37
38 Data to be analyzed Sample: 112 comercial bancs Data obtained by survey Dependent variable: Intensity of strategic plannification Finance results Independent variables: Directive factors Contour factors Organizative factors 38
39 39
40 40
41 41
42 42
43 43
44 44
45 Covariance matrix:: Means: S.D.:
INTRODUCTION TO STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS
 I. Description of the course. INTRODUCTION TO STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS A. Objectives and scope of the course. B. Logistics of enrollment, auditing, requirements, distribution of notes, access to programs.
I. Description of the course. INTRODUCTION TO STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS A. Objectives and scope of the course. B. Logistics of enrollment, auditing, requirements, distribution of notes, access to programs.
Jan. 22, An Overview of Structural Equation. Karl Joreskog and LISREL: A personal story
 Jan., 8 Karl Joreskog and LISREL: A personal stor Modeling HC Weng //8 95, /5, born in Amal, Swedan Uppsala: 955-96 Ambition was to stud mathematics and phsics and become a high school teacher Princeton:
Jan., 8 Karl Joreskog and LISREL: A personal stor Modeling HC Weng //8 95, /5, born in Amal, Swedan Uppsala: 955-96 Ambition was to stud mathematics and phsics and become a high school teacher Princeton:
Exploring Cultural Differences with Structural Equation Modelling
 Exploring Cultural Differences with Structural Equation Modelling Wynne W. Chin University of Calgary and City University of Hong Kong 1996 IS Cross Cultural Workshop slide 1 The objectives for this presentation
Exploring Cultural Differences with Structural Equation Modelling Wynne W. Chin University of Calgary and City University of Hong Kong 1996 IS Cross Cultural Workshop slide 1 The objectives for this presentation
Computationally Efficient Estimation of Multilevel High-Dimensional Latent Variable Models
 Computationally Efficient Estimation of Multilevel High-Dimensional Latent Variable Models Tihomir Asparouhov 1, Bengt Muthen 2 Muthen & Muthen 1 UCLA 2 Abstract Multilevel analysis often leads to modeling
Computationally Efficient Estimation of Multilevel High-Dimensional Latent Variable Models Tihomir Asparouhov 1, Bengt Muthen 2 Muthen & Muthen 1 UCLA 2 Abstract Multilevel analysis often leads to modeling
General structural model Part 2: Categorical variables and beyond. Psychology 588: Covariance structure and factor models
 General structural model Part 2: Categorical variables and beyond Psychology 588: Covariance structure and factor models Categorical variables 2 Conventional (linear) SEM assumes continuous observed variables
General structural model Part 2: Categorical variables and beyond Psychology 588: Covariance structure and factor models Categorical variables 2 Conventional (linear) SEM assumes continuous observed variables
Structural Equation Modeling and Confirmatory Factor Analysis. Types of Variables
 /4/04 Structural Equation Modeling and Confirmatory Factor Analysis Advanced Statistics for Researchers Session 3 Dr. Chris Rakes Website: http://csrakes.yolasite.com Email: Rakes@umbc.edu Twitter: @RakesChris
/4/04 Structural Equation Modeling and Confirmatory Factor Analysis Advanced Statistics for Researchers Session 3 Dr. Chris Rakes Website: http://csrakes.yolasite.com Email: Rakes@umbc.edu Twitter: @RakesChris
Latent variable interactions
 Latent variable interactions Bengt Muthén & Tihomir Asparouhov Mplus www.statmodel.com November 2, 2015 1 1 Latent variable interactions Structural equation modeling with latent variable interactions has
Latent variable interactions Bengt Muthén & Tihomir Asparouhov Mplus www.statmodel.com November 2, 2015 1 1 Latent variable interactions Structural equation modeling with latent variable interactions has
Misspecification in Nonrecursive SEMs 1. Nonrecursive Latent Variable Models under Misspecification
 Misspecification in Nonrecursive SEMs 1 Nonrecursive Latent Variable Models under Misspecification Misspecification in Nonrecursive SEMs 2 Abstract A problem central to structural equation modeling is
Misspecification in Nonrecursive SEMs 1 Nonrecursive Latent Variable Models under Misspecification Misspecification in Nonrecursive SEMs 2 Abstract A problem central to structural equation modeling is
SEM for Categorical Outcomes
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS WITH LATENT VARIABLES
 STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS WITH LATENT VARIABLES Albert Satorra Departament d Economia i Empresa Universitat Pompeu Fabra Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) is widely used in behavioural, social and economic
STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS WITH LATENT VARIABLES Albert Satorra Departament d Economia i Empresa Universitat Pompeu Fabra Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) is widely used in behavioural, social and economic
Nesting and Equivalence Testing
 Nesting and Equivalence Testing Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén August 13, 2018 Abstract In this note, we discuss the nesting and equivalence testing (NET) methodology developed in Bentler and Satorra
Nesting and Equivalence Testing Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén August 13, 2018 Abstract In this note, we discuss the nesting and equivalence testing (NET) methodology developed in Bentler and Satorra
Testing Structural Equation Models: The Effect of Kurtosis
 Testing Structural Equation Models: The Effect of Kurtosis Tron Foss, Karl G Jöreskog & Ulf H Olsson Norwegian School of Management October 18, 2006 Abstract Various chi-square statistics are used for
Testing Structural Equation Models: The Effect of Kurtosis Tron Foss, Karl G Jöreskog & Ulf H Olsson Norwegian School of Management October 18, 2006 Abstract Various chi-square statistics are used for
Ruth E. Mathiowetz. Chapel Hill 2010
 Evaluating Latent Variable Interactions with Structural Equation Mixture Models Ruth E. Mathiowetz A thesis submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment
Evaluating Latent Variable Interactions with Structural Equation Mixture Models Ruth E. Mathiowetz A thesis submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment
Measurement error models with uncertainty about the error variance. Daniel L. Oberski
 Measurement error models with uncertainty about the error variance 1 Running head: MEASUREMENT ERROR MODELS WITH UNCERTAINTY ABOUT THE ERROR VARIANCE Measurement error models with uncertainty about the
Measurement error models with uncertainty about the error variance 1 Running head: MEASUREMENT ERROR MODELS WITH UNCERTAINTY ABOUT THE ERROR VARIANCE Measurement error models with uncertainty about the
Evaluating the Sensitivity of Goodness-of-Fit Indices to Data Perturbation: An Integrated MC-SGR Approach
 Evaluating the Sensitivity of Goodness-of-Fit Indices to Data Perturbation: An Integrated MC-SGR Approach Massimiliano Pastore 1 and Luigi Lombardi 2 1 Department of Psychology University of Cagliari Via
Evaluating the Sensitivity of Goodness-of-Fit Indices to Data Perturbation: An Integrated MC-SGR Approach Massimiliano Pastore 1 and Luigi Lombardi 2 1 Department of Psychology University of Cagliari Via
Specifying Latent Curve and Other Growth Models Using Mplus. (Revised )
 Ronald H. Heck 1 University of Hawai i at Mānoa Handout #20 Specifying Latent Curve and Other Growth Models Using Mplus (Revised 12-1-2014) The SEM approach offers a contrasting framework for use in analyzing
Ronald H. Heck 1 University of Hawai i at Mānoa Handout #20 Specifying Latent Curve and Other Growth Models Using Mplus (Revised 12-1-2014) The SEM approach offers a contrasting framework for use in analyzing
A Cautionary Note on the Use of LISREL s Automatic Start Values in Confirmatory Factor Analysis Studies R. L. Brown University of Wisconsin
 A Cautionary Note on the Use of LISREL s Automatic Start Values in Confirmatory Factor Analysis Studies R. L. Brown University of Wisconsin The accuracy of parameter estimates provided by the major computer
A Cautionary Note on the Use of LISREL s Automatic Start Values in Confirmatory Factor Analysis Studies R. L. Brown University of Wisconsin The accuracy of parameter estimates provided by the major computer
2/26/2017. PSY 512: Advanced Statistics for Psychological and Behavioral Research 2
 PSY 512: Advanced Statistics for Psychological and Behavioral Research 2 What is SEM? When should we use SEM? What can SEM tell us? SEM Terminology and Jargon Technical Issues Types of SEM Models Limitations
PSY 512: Advanced Statistics for Psychological and Behavioral Research 2 What is SEM? When should we use SEM? What can SEM tell us? SEM Terminology and Jargon Technical Issues Types of SEM Models Limitations
4. Path Analysis. In the diagram: The technique of path analysis is originated by (American) geneticist Sewell Wright in early 1920.
 4. Path Analysis The technique of path analysis is originated by (American) geneticist Sewell Wright in early 1920. The relationships between variables are presented in a path diagram. The system of relationships
4. Path Analysis The technique of path analysis is originated by (American) geneticist Sewell Wright in early 1920. The relationships between variables are presented in a path diagram. The system of relationships
Multiple group models for ordinal variables
 Multiple group models for ordinal variables 1. Introduction In practice, many multivariate data sets consist of observations of ordinal variables rather than continuous variables. Most statistical methods
Multiple group models for ordinal variables 1. Introduction In practice, many multivariate data sets consist of observations of ordinal variables rather than continuous variables. Most statistical methods
RANDOM INTERCEPT ITEM FACTOR ANALYSIS. IE Working Paper MK8-102-I 02 / 04 / Alberto Maydeu Olivares
 RANDOM INTERCEPT ITEM FACTOR ANALYSIS IE Working Paper MK8-102-I 02 / 04 / 2003 Alberto Maydeu Olivares Instituto de Empresa Marketing Dept. C / María de Molina 11-15, 28006 Madrid España Alberto.Maydeu@ie.edu
RANDOM INTERCEPT ITEM FACTOR ANALYSIS IE Working Paper MK8-102-I 02 / 04 / 2003 Alberto Maydeu Olivares Instituto de Empresa Marketing Dept. C / María de Molina 11-15, 28006 Madrid España Alberto.Maydeu@ie.edu
EVALUATION OF STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS
 1 EVALUATION OF STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS I. Issues related to the initial specification of theoretical models of interest 1. Model specification: a. Measurement model: (i) EFA vs. CFA (ii) reflective
1 EVALUATION OF STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS I. Issues related to the initial specification of theoretical models of interest 1. Model specification: a. Measurement model: (i) EFA vs. CFA (ii) reflective
Scaled and adjusted restricted tests in. multi-sample analysis of moment structures. Albert Satorra. Universitat Pompeu Fabra.
 Scaled and adjusted restricted tests in multi-sample analysis of moment structures Albert Satorra Universitat Pompeu Fabra July 15, 1999 The author is grateful to Peter Bentler and Bengt Muthen for their
Scaled and adjusted restricted tests in multi-sample analysis of moment structures Albert Satorra Universitat Pompeu Fabra July 15, 1999 The author is grateful to Peter Bentler and Bengt Muthen for their
Assessing Factorial Invariance in Ordered-Categorical Measures
 Multivariate Behavioral Research, 39 (3), 479-515 Copyright 2004, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. Assessing Factorial Invariance in Ordered-Categorical Measures Roger E. Millsap and Jenn Yun-Tein Arizona
Multivariate Behavioral Research, 39 (3), 479-515 Copyright 2004, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. Assessing Factorial Invariance in Ordered-Categorical Measures Roger E. Millsap and Jenn Yun-Tein Arizona
Factor Analysis. Qian-Li Xue
 Factor Analysis Qian-Li Xue Biostatistics Program Harvard Catalyst The Harvard Clinical & Translational Science Center Short course, October 7, 06 Well-used latent variable models Latent variable scale
Factor Analysis Qian-Li Xue Biostatistics Program Harvard Catalyst The Harvard Clinical & Translational Science Center Short course, October 7, 06 Well-used latent variable models Latent variable scale
Compiled by: Assoc. Prof. Dr Bahaman Abu Samah Department of Professional Developmentand Continuing Education Faculty of Educational Studies
 Compiled by: Assoc. Prof. Dr Bahaman Abu Samah Department of Professional Developmentand Continuing Education Faculty of Educational Studies Universiti Putra Malaysia Serdang Structural Equation Modeling
Compiled by: Assoc. Prof. Dr Bahaman Abu Samah Department of Professional Developmentand Continuing Education Faculty of Educational Studies Universiti Putra Malaysia Serdang Structural Equation Modeling
An Efficient State Space Approach to Estimate Univariate and Multivariate Multilevel Regression Models
 An Efficient State Space Approach to Estimate Univariate and Multivariate Multilevel Regression Models Fei Gu Kristopher J. Preacher Wei Wu 05/21/2013 Overview Introduction: estimate MLM as SEM (Bauer,
An Efficient State Space Approach to Estimate Univariate and Multivariate Multilevel Regression Models Fei Gu Kristopher J. Preacher Wei Wu 05/21/2013 Overview Introduction: estimate MLM as SEM (Bauer,
CHAPTER 3. SPECIALIZED EXTENSIONS
 03-Preacher-45609:03-Preacher-45609.qxd 6/3/2008 3:36 PM Page 57 CHAPTER 3. SPECIALIZED EXTENSIONS We have by no means exhausted the possibilities of LGM with the examples presented thus far. As scientific
03-Preacher-45609:03-Preacher-45609.qxd 6/3/2008 3:36 PM Page 57 CHAPTER 3. SPECIALIZED EXTENSIONS We have by no means exhausted the possibilities of LGM with the examples presented thus far. As scientific
FORMATIVE AND REFLECTIVE MODELS: STATE OF THE ART. Anna Simonetto *
 Electronic Journal of Applied Statistical Analysis EJASA (2012), Electron. J. App. Stat. Anal., Vol. 5, Issue 3, 452 457 e-issn 2070-5948, DOI 10.1285/i20705948v5n3p452 2012 Università del Salento http://siba-ese.unile.it/index.php/ejasa/index
Electronic Journal of Applied Statistical Analysis EJASA (2012), Electron. J. App. Stat. Anal., Vol. 5, Issue 3, 452 457 e-issn 2070-5948, DOI 10.1285/i20705948v5n3p452 2012 Università del Salento http://siba-ese.unile.it/index.php/ejasa/index
A Measurement Model of Child Health: Latent Variables Approach
 Journal of Health & Population in Developing Countries / URL: http://www.jhpdc.unc.edu/ Date Published 9 February, 2004 A Measurement Model of Child Health: Latent Variables Approach Shafqat Shehzad PhD
Journal of Health & Population in Developing Countries / URL: http://www.jhpdc.unc.edu/ Date Published 9 February, 2004 A Measurement Model of Child Health: Latent Variables Approach Shafqat Shehzad PhD
Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling
 Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling Notes Prepared by: Lisa Lix, PhD Manitoba Centre for Health Policy Topics Section I: Introduction Section II: Review of Statistical Concepts and Regression
Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling Notes Prepared by: Lisa Lix, PhD Manitoba Centre for Health Policy Topics Section I: Introduction Section II: Review of Statistical Concepts and Regression
Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling: Issues and Practical Considerations
 An NCME Instructional Module on Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling: Issues and Practical Considerations Pui-Wa Lei and Qiong Wu, The Pennsylvania State University Structural equation modeling
An NCME Instructional Module on Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling: Issues and Practical Considerations Pui-Wa Lei and Qiong Wu, The Pennsylvania State University Structural equation modeling
Multilevel Analysis of Grouped and Longitudinal Data
 Multilevel Analysis of Grouped and Longitudinal Data Joop J. Hox Utrecht University Second draft, to appear in: T.D. Little, K.U. Schnabel, & J. Baumert (Eds.). Modeling longitudinal and multiple-group
Multilevel Analysis of Grouped and Longitudinal Data Joop J. Hox Utrecht University Second draft, to appear in: T.D. Little, K.U. Schnabel, & J. Baumert (Eds.). Modeling longitudinal and multiple-group
Inference with Heywood cases
 Inference with Joint work with Kenneth Bollen (UNC) and Victoria Savalei (UBC) NSF support from SES-0617193 with funds from SSA September 18, 2009 What is a case? (1931) considered characterization of
Inference with Joint work with Kenneth Bollen (UNC) and Victoria Savalei (UBC) NSF support from SES-0617193 with funds from SSA September 18, 2009 What is a case? (1931) considered characterization of
A Guide to Modern Econometric:
 A Guide to Modern Econometric: 4th edition Marno Verbeek Rotterdam School of Management, Erasmus University, Rotterdam B 379887 )WILEY A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication Contents Preface xiii 1 Introduction
A Guide to Modern Econometric: 4th edition Marno Verbeek Rotterdam School of Management, Erasmus University, Rotterdam B 379887 )WILEY A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication Contents Preface xiii 1 Introduction
Richard N. Jones, Sc.D. HSPH Kresge G2 October 5, 2011
 Harvard Catalyst Biostatistical Seminar Neuropsychological Proles in Alzheimer's Disease and Cerebral Infarction: A Longitudinal MIMIC Model An Overview of Structural Equation Modeling using Mplus Richard
Harvard Catalyst Biostatistical Seminar Neuropsychological Proles in Alzheimer's Disease and Cerebral Infarction: A Longitudinal MIMIC Model An Overview of Structural Equation Modeling using Mplus Richard
Principles and Practice in Reporting Structural Equation Analyses
 Psychological Methods Copyright 2002 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 2002, Vol. 7, No. 1, 64 82 1082-989X/02/$5.00 DOI: 10.1037//1082-989X.7.1.64 Principles and Practice in Reporting Structural
Psychological Methods Copyright 2002 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 2002, Vol. 7, No. 1, 64 82 1082-989X/02/$5.00 DOI: 10.1037//1082-989X.7.1.64 Principles and Practice in Reporting Structural
Multilevel Structural Equation Modeling
 Multilevel Structural Equation Modeling Joop Hox Utrecht University j.hox@uu.nl http://www.joophox.net 14_15_mlevsem Multilevel Regression Three level data structure Groups at different levels may have
Multilevel Structural Equation Modeling Joop Hox Utrecht University j.hox@uu.nl http://www.joophox.net 14_15_mlevsem Multilevel Regression Three level data structure Groups at different levels may have
SHOPPING FOR EFFICIENT CONFIDENCE INTERVALS IN STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS. Donna Mohr and Yong Xu. University of North Florida
 SHOPPING FOR EFFICIENT CONFIDENCE INTERVALS IN STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS Donna Mohr and Yong Xu University of North Florida Authors Note Parts of this work were incorporated in Yong Xu s Masters Thesis
SHOPPING FOR EFFICIENT CONFIDENCE INTERVALS IN STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS Donna Mohr and Yong Xu University of North Florida Authors Note Parts of this work were incorporated in Yong Xu s Masters Thesis
ABSTRACT. Chair, Dr. Gregory R. Hancock, Department of. interactions as a function of the size of the interaction effect, sample size, the loadings of
 ABSTRACT Title of Document: A COMPARISON OF METHODS FOR TESTING FOR INTERACTION EFFECTS IN STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELING Brandi A. Weiss, Doctor of Philosophy, 00 Directed By: Chair, Dr. Gregory R. Hancock,
ABSTRACT Title of Document: A COMPARISON OF METHODS FOR TESTING FOR INTERACTION EFFECTS IN STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELING Brandi A. Weiss, Doctor of Philosophy, 00 Directed By: Chair, Dr. Gregory R. Hancock,
Do not copy, quote, or cite without permission LECTURE 4: THE GENERAL LISREL MODEL
 LECTURE 4: THE GENERAL LISREL MODEL I. QUICK REVIEW OF A LITTLE MATRIX ALGEBRA. II. A SIMPLE RECURSIVE MODEL IN LATENT VARIABLES. III. THE GENERAL LISREL MODEL IN MATRIX FORM. A. SPECIFYING STRUCTURAL
LECTURE 4: THE GENERAL LISREL MODEL I. QUICK REVIEW OF A LITTLE MATRIX ALGEBRA. II. A SIMPLE RECURSIVE MODEL IN LATENT VARIABLES. III. THE GENERAL LISREL MODEL IN MATRIX FORM. A. SPECIFYING STRUCTURAL
DOCUMENTOS DE TRABAJO BILTOKI. Spanish Customer Satisfaction Indices by Cumulative Panel Data.
 DOCUMENTOS DE TRABAJO BILTOKI D.T. 2003.12 Spanish Customer Satisfaction Indices by Cumulative Panel Data. Cristina López Caro, Karmele Fernández Aguirre y Petr Mariel Facultad de Ciencias Económicas.
DOCUMENTOS DE TRABAJO BILTOKI D.T. 2003.12 Spanish Customer Satisfaction Indices by Cumulative Panel Data. Cristina López Caro, Karmele Fernández Aguirre y Petr Mariel Facultad de Ciencias Económicas.
A Threshold-Free Approach to the Study of the Structure of Binary Data
 International Journal of Statistics and Probability; Vol. 2, No. 2; 2013 ISSN 1927-7032 E-ISSN 1927-7040 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education A Threshold-Free Approach to the Study of
International Journal of Statistics and Probability; Vol. 2, No. 2; 2013 ISSN 1927-7032 E-ISSN 1927-7040 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education A Threshold-Free Approach to the Study of
Ridge Structural Equation Modeling with Correlation Matrices for Ordinal and Continuous Data. Ke-Hai Yuan University of Notre Dame
 Ridge Structural Equation Modeling with Correlation Matrices for Ordinal and Continuous Data Ke-Hai Yuan University of Notre Dame Rui Wu Beihang University Peter M. Bentler University of California, Los
Ridge Structural Equation Modeling with Correlation Matrices for Ordinal and Continuous Data Ke-Hai Yuan University of Notre Dame Rui Wu Beihang University Peter M. Bentler University of California, Los
Advanced Structural Equations Models I
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
THE GENERAL STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODEL WITH LATENT VARIATES
 THE GENERAL STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODEL WITH LATENT VARIATES I. Specification: A full structural equation model with latent variables consists of two parts: a latent variable model (which specifies the relations
THE GENERAL STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODEL WITH LATENT VARIATES I. Specification: A full structural equation model with latent variables consists of two parts: a latent variable model (which specifies the relations
Estimating and Using Propensity Score in Presence of Missing Background Data. An Application to Assess the Impact of Childbearing on Wellbeing
 Estimating and Using Propensity Score in Presence of Missing Background Data. An Application to Assess the Impact of Childbearing on Wellbeing Alessandra Mattei Dipartimento di Statistica G. Parenti Università
Estimating and Using Propensity Score in Presence of Missing Background Data. An Application to Assess the Impact of Childbearing on Wellbeing Alessandra Mattei Dipartimento di Statistica G. Parenti Università
Journal of Multivariate Analysis. Use of prior information in the consistent estimation of regression coefficients in measurement error models
 Journal of Multivariate Analysis 00 (2009) 498 520 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Multivariate Analysis journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jmva Use of prior information in
Journal of Multivariate Analysis 00 (2009) 498 520 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Multivariate Analysis journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jmva Use of prior information in
Financial Econometrics
 Financial Econometrics Multivariate Time Series Analysis: VAR Gerald P. Dwyer Trinity College, Dublin January 2013 GPD (TCD) VAR 01/13 1 / 25 Structural equations Suppose have simultaneous system for supply
Financial Econometrics Multivariate Time Series Analysis: VAR Gerald P. Dwyer Trinity College, Dublin January 2013 GPD (TCD) VAR 01/13 1 / 25 Structural equations Suppose have simultaneous system for supply
MULTILEVEL IMPUTATION 1
 MULTILEVEL IMPUTATION 1 Supplement B: MCMC Sampling Steps and Distributions for Two-Level Imputation This document gives technical details of the full conditional distributions used to draw regression
MULTILEVEL IMPUTATION 1 Supplement B: MCMC Sampling Steps and Distributions for Two-Level Imputation This document gives technical details of the full conditional distributions used to draw regression
The comparison of estimation methods on the parameter estimates and fit indices in SEM model under 7-point Likert scale
 The comparison of estimation methods on the parameter estimates and fit indices in SEM model under 7-point Likert scale Piotr Tarka Abstract In this article, the author discusses the issues and problems
The comparison of estimation methods on the parameter estimates and fit indices in SEM model under 7-point Likert scale Piotr Tarka Abstract In this article, the author discusses the issues and problems
Using SAS PROC TCALIS for multigroup structural equation modelling with mean structures
 516 British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology (2011), 64, 516 537 C 2011 The British Psychological Society The British Psychological Society www.wileyonlinelibrary.com Expert Tutorial
516 British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology (2011), 64, 516 537 C 2011 The British Psychological Society The British Psychological Society www.wileyonlinelibrary.com Expert Tutorial
Factor Analysis and Latent Structure of Categorical Data
 Factor Analysis and Latent Structure of Categorical Data Irini Moustaki Athens University of Economics and Business Outline Objectives Factor analysis model Literature Approaches Item Response Theory Models
Factor Analysis and Latent Structure of Categorical Data Irini Moustaki Athens University of Economics and Business Outline Objectives Factor analysis model Literature Approaches Item Response Theory Models
General structural model Part 1: Covariance structure and identification. Psychology 588: Covariance structure and factor models
 General structural model Part 1: Covariance structure and identification Psychology 588: Covariance structure and factor models Latent variables 2 Interchangeably used: constructs --- substantively defined
General structural model Part 1: Covariance structure and identification Psychology 588: Covariance structure and factor models Latent variables 2 Interchangeably used: constructs --- substantively defined
Title. Description. Remarks and examples. stata.com. stata.com. Variable notation. methods and formulas for sem Methods and formulas for sem
 Title stata.com methods and formulas for sem Methods and formulas for sem Description Remarks and examples References Also see Description The methods and formulas for the sem commands are presented below.
Title stata.com methods and formulas for sem Methods and formulas for sem Description Remarks and examples References Also see Description The methods and formulas for the sem commands are presented below.
SAS/STAT 14.1 User s Guide. Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling with Latent Variables
 SAS/STAT 14.1 User s Guide Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling with Latent Variables This document is an individual chapter from SAS/STAT 14.1 User s Guide. The correct bibliographic citation
SAS/STAT 14.1 User s Guide Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling with Latent Variables This document is an individual chapter from SAS/STAT 14.1 User s Guide. The correct bibliographic citation
Factor Analysis & Structural Equation Models. CS185 Human Computer Interaction
 Factor Analysis & Structural Equation Models CS185 Human Computer Interaction MoodPlay Recommender (Andjelkovic et al, UMAP 2016) Online system available here: http://ugallery.pythonanywhere.com/ 2 3 Structural
Factor Analysis & Structural Equation Models CS185 Human Computer Interaction MoodPlay Recommender (Andjelkovic et al, UMAP 2016) Online system available here: http://ugallery.pythonanywhere.com/ 2 3 Structural
Using Structural Equation Modeling to Conduct Confirmatory Factor Analysis
 Using Structural Equation Modeling to Conduct Confirmatory Factor Analysis Advanced Statistics for Researchers Session 3 Dr. Chris Rakes Website: http://csrakes.yolasite.com Email: Rakes@umbc.edu Twitter:
Using Structural Equation Modeling to Conduct Confirmatory Factor Analysis Advanced Statistics for Researchers Session 3 Dr. Chris Rakes Website: http://csrakes.yolasite.com Email: Rakes@umbc.edu Twitter:
Structural equation modeling
 Structural equation modeling Rex B Kline Concordia University Montréal ISTQL Set B B1 Data, path models Data o N o Form o Screening B2 B3 Sample size o N needed: Complexity Estimation method Distributions
Structural equation modeling Rex B Kline Concordia University Montréal ISTQL Set B B1 Data, path models Data o N o Form o Screening B2 B3 Sample size o N needed: Complexity Estimation method Distributions
Using Mplus individual residual plots for. diagnostics and model evaluation in SEM
 Using Mplus individual residual plots for diagnostics and model evaluation in SEM Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén Mplus Web Notes: No. 20 October 31, 2017 1 Introduction A variety of plots are available
Using Mplus individual residual plots for diagnostics and model evaluation in SEM Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén Mplus Web Notes: No. 20 October 31, 2017 1 Introduction A variety of plots are available
Correlations with Categorical Data
 Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Multiple Correlations and Canonical Correlations with Categorical Data Sik-Yum Lee The Chinese University of Hong Kong Wal-Yin Poon University of California, Los Angeles
Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Multiple Correlations and Canonical Correlations with Categorical Data Sik-Yum Lee The Chinese University of Hong Kong Wal-Yin Poon University of California, Los Angeles
Running head: AUTOCORRELATION IN THE COFM. The Effects of Autocorrelation on the Curve-of-Factors Growth Model
 Autocorrelation in the COFM 1 Running head: AUTOCORRELATION IN THE COFM The Effects of Autocorrelation on the Curve-of-Factors Growth Model Daniel L. Murphy Pearson S. Natasha Beretvas and Keenan A. Pituch
Autocorrelation in the COFM 1 Running head: AUTOCORRELATION IN THE COFM The Effects of Autocorrelation on the Curve-of-Factors Growth Model Daniel L. Murphy Pearson S. Natasha Beretvas and Keenan A. Pituch
Chapter 8. Models with Structural and Measurement Components. Overview. Characteristics of SR models. Analysis of SR models. Estimation of SR models
 Chapter 8 Models with Structural and Measurement Components Good people are good because they've come to wisdom through failure. Overview William Saroyan Characteristics of SR models Estimation of SR models
Chapter 8 Models with Structural and Measurement Components Good people are good because they've come to wisdom through failure. Overview William Saroyan Characteristics of SR models Estimation of SR models
Citation for published version (APA): Jak, S. (2013). Cluster bias: Testing measurement invariance in multilevel data
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Cluster bias: Testing measurement invariance in multilevel data Jak, S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Jak, S. (2013). Cluster bias: Testing
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Cluster bias: Testing measurement invariance in multilevel data Jak, S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Jak, S. (2013). Cluster bias: Testing
STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELING. Khaled Bedair Statistics Department Virginia Tech LISA, Summer 2013
 STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELING Khaled Bedair Statistics Department Virginia Tech LISA, Summer 2013 Introduction: Path analysis Path Analysis is used to estimate a system of equations in which all of the
STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELING Khaled Bedair Statistics Department Virginia Tech LISA, Summer 2013 Introduction: Path analysis Path Analysis is used to estimate a system of equations in which all of the
Outline
 2559 Outline cvonck@111zeelandnet.nl 1. Review of analysis of variance (ANOVA), simple regression analysis (SRA), and path analysis (PA) 1.1 Similarities and differences between MRA with dummy variables
2559 Outline cvonck@111zeelandnet.nl 1. Review of analysis of variance (ANOVA), simple regression analysis (SRA), and path analysis (PA) 1.1 Similarities and differences between MRA with dummy variables
Selection endogenous dummy ordered probit, and selection endogenous dummy dynamic ordered probit models
 Selection endogenous dummy ordered probit, and selection endogenous dummy dynamic ordered probit models Massimiliano Bratti & Alfonso Miranda In many fields of applied work researchers need to model an
Selection endogenous dummy ordered probit, and selection endogenous dummy dynamic ordered probit models Massimiliano Bratti & Alfonso Miranda In many fields of applied work researchers need to model an
NELS 88. Latent Response Variable Formulation Versus Probability Curve Formulation
 NELS 88 Table 2.3 Adjusted odds ratios of eighth-grade students in 988 performing below basic levels of reading and mathematics in 988 and dropping out of school, 988 to 990, by basic demographics Variable
NELS 88 Table 2.3 Adjusted odds ratios of eighth-grade students in 988 performing below basic levels of reading and mathematics in 988 and dropping out of school, 988 to 990, by basic demographics Variable
Old and new approaches for the analysis of categorical data in a SEM framework
 Old and new approaches for the analysis of categorical data in a SEM framework Yves Rosseel Department of Data Analysis Belgium Myrsini Katsikatsou Department of Statistics London Scool of Economics UK
Old and new approaches for the analysis of categorical data in a SEM framework Yves Rosseel Department of Data Analysis Belgium Myrsini Katsikatsou Department of Statistics London Scool of Economics UK
Psychology 830. Introduction to Covariance Structure Modeling
 Psychology 830 Introduction to Covariance Structure Modeling Class Notes Winter 2004 Michael W. Browne Ohio State University These notes have been developed collaboratively by Professors Michael Browne
Psychology 830 Introduction to Covariance Structure Modeling Class Notes Winter 2004 Michael W. Browne Ohio State University These notes have been developed collaboratively by Professors Michael Browne
Generalized Linear Models for Non-Normal Data
 Generalized Linear Models for Non-Normal Data Today s Class: 3 parts of a generalized model Models for binary outcomes Complications for generalized multivariate or multilevel models SPLH 861: Lecture
Generalized Linear Models for Non-Normal Data Today s Class: 3 parts of a generalized model Models for binary outcomes Complications for generalized multivariate or multilevel models SPLH 861: Lecture
What is Structural Equation Modelling?
 methods@manchester What is Structural Equation Modelling? Nick Shryane Institute for Social Change University of Manchester 1 Topics Where SEM fits in the families of statistical models Causality SEM is
methods@manchester What is Structural Equation Modelling? Nick Shryane Institute for Social Change University of Manchester 1 Topics Where SEM fits in the families of statistical models Causality SEM is
LISREL Workshop at M3 Conference 2015
 LISREL Workshop at M3 Conference 2015 Karl G Jöreskog Norwegian Business School & Uppsala University May 11, 2015 Karl G Jöreskog ( ) LISREL Workshop at M3 Conference 2015 May 11, 2015 1 / 73 Ways of Working
LISREL Workshop at M3 Conference 2015 Karl G Jöreskog Norwegian Business School & Uppsala University May 11, 2015 Karl G Jöreskog ( ) LISREL Workshop at M3 Conference 2015 May 11, 2015 1 / 73 Ways of Working
Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling Dominique Zephyr Applied Statistics Lab
 Applied Statistics Lab Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling Dominique Zephyr Applied Statistics Lab SEM Model 3.64 7.32 Education 2.6 Income 2.1.6.83 Charac. of Individuals 1 5.2e-06 -.62 2.62
Applied Statistics Lab Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling Dominique Zephyr Applied Statistics Lab SEM Model 3.64 7.32 Education 2.6 Income 2.1.6.83 Charac. of Individuals 1 5.2e-06 -.62 2.62
Supplemental material to accompany Preacher and Hayes (2008)
 Supplemental material to accompany Preacher and Hayes (2008) Kristopher J. Preacher University of Kansas Andrew F. Hayes The Ohio State University The multivariate delta method for deriving the asymptotic
Supplemental material to accompany Preacher and Hayes (2008) Kristopher J. Preacher University of Kansas Andrew F. Hayes The Ohio State University The multivariate delta method for deriving the asymptotic
Structural Equation Modeling An Econometrician s Introduction
 S Structural Equation Modeling An Econometrician s Introduction PD Dr. Stefan Klößner Winter Term 2016/17 U N I V E R S I T A S A R A V I E N I S S Overview NOT: easy to digest introduction for practitioners
S Structural Equation Modeling An Econometrician s Introduction PD Dr. Stefan Klößner Winter Term 2016/17 U N I V E R S I T A S A R A V I E N I S S Overview NOT: easy to digest introduction for practitioners
Residual analysis for structural equation modeling
 Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2013 Residual analysis for structural equation modeling Laura Hildreth Iowa State University Follow this and additional works at: http://lib.dr.iastate.edu/etd
Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2013 Residual analysis for structural equation modeling Laura Hildreth Iowa State University Follow this and additional works at: http://lib.dr.iastate.edu/etd
ECON 4160: Econometrics-Modelling and Systems Estimation Lecture 9: Multiple equation models II
 ECON 4160: Econometrics-Modelling and Systems Estimation Lecture 9: Multiple equation models II Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics University of Oslo 9 October 2018 The reference to this lecture is:
ECON 4160: Econometrics-Modelling and Systems Estimation Lecture 9: Multiple equation models II Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics University of Oslo 9 October 2018 The reference to this lecture is:
Estimating the validity of administrative and survey variables through structural equation modeling
 13 2 Estimating the validity of administrative and survey variables through structural equation modeling A simulation study on robustness Sander Scholtus and Bart F.M. Bakker The views expressed in this
13 2 Estimating the validity of administrative and survey variables through structural equation modeling A simulation study on robustness Sander Scholtus and Bart F.M. Bakker The views expressed in this
STA 216, GLM, Lecture 16. October 29, 2007
 STA 216, GLM, Lecture 16 October 29, 2007 Efficient Posterior Computation in Factor Models Underlying Normal Models Generalized Latent Trait Models Formulation Genetic Epidemiology Illustration Structural
STA 216, GLM, Lecture 16 October 29, 2007 Efficient Posterior Computation in Factor Models Underlying Normal Models Generalized Latent Trait Models Formulation Genetic Epidemiology Illustration Structural
Bayesian Analysis of Latent Variable Models using Mplus
 Bayesian Analysis of Latent Variable Models using Mplus Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén Version 2 June 29, 2010 1 1 Introduction In this paper we describe some of the modeling possibilities that are
Bayesian Analysis of Latent Variable Models using Mplus Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén Version 2 June 29, 2010 1 1 Introduction In this paper we describe some of the modeling possibilities that are
Chapter 5. Introduction to Path Analysis. Overview. Correlation and causation. Specification of path models. Types of path models
 Chapter 5 Introduction to Path Analysis Put simply, the basic dilemma in all sciences is that of how much to oversimplify reality. Overview H. M. Blalock Correlation and causation Specification of path
Chapter 5 Introduction to Path Analysis Put simply, the basic dilemma in all sciences is that of how much to oversimplify reality. Overview H. M. Blalock Correlation and causation Specification of path
Preface. List of examples
 Contents Preface List of examples i xix 1 LISREL models and methods 1 1.1 The general LISREL model 1 Assumptions 2 The covariance matrix of the observations as implied by the LISREL model 3 Fixed, free,
Contents Preface List of examples i xix 1 LISREL models and methods 1 1.1 The general LISREL model 1 Assumptions 2 The covariance matrix of the observations as implied by the LISREL model 3 Fixed, free,
Applied Econometrics Lecture 1
 Lecture 1 1 1 Università di Urbino Università di Urbino PhD Programme in Global Studies Spring 2018 Outline of this module Beyond OLS (very brief sketch) Regression and causality: sources of endogeneity
Lecture 1 1 1 Università di Urbino Università di Urbino PhD Programme in Global Studies Spring 2018 Outline of this module Beyond OLS (very brief sketch) Regression and causality: sources of endogeneity
On the robustness of LISREL (maximum likelihood estimation) against small sample size and non-normality. Boomsma, Anne
 University of Groningen On the robustness of LISREL (maximum likelihood estimation) against small sample size and non-normality. Boomsma, Anne IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
University of Groningen On the robustness of LISREL (maximum likelihood estimation) against small sample size and non-normality. Boomsma, Anne IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
Inference using structural equations with latent variables
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
SEM Day 1 Lab Exercises SPIDA 2007 Dave Flora
 SEM Day 1 Lab Exercises SPIDA 2007 Dave Flora 1 Today we will see how to estimate CFA models and interpret output using both SAS and LISREL. In SAS, commands for specifying SEMs are given using linear
SEM Day 1 Lab Exercises SPIDA 2007 Dave Flora 1 Today we will see how to estimate CFA models and interpret output using both SAS and LISREL. In SAS, commands for specifying SEMs are given using linear
Moderation 調節 = 交互作用
 Moderation 調節 = 交互作用 Kit-Tai Hau 侯傑泰 JianFang Chang 常建芳 The Chinese University of Hong Kong Based on Marsh, H. W., Hau, K. T., Wen, Z., Nagengast, B., & Morin, A. J. S. (in press). Moderation. In Little,
Moderation 調節 = 交互作用 Kit-Tai Hau 侯傑泰 JianFang Chang 常建芳 The Chinese University of Hong Kong Based on Marsh, H. W., Hau, K. T., Wen, Z., Nagengast, B., & Morin, A. J. S. (in press). Moderation. In Little,
Course title SD206. Introduction to Structural Equation Modelling
 10 th ECPR Summer School in Methods and Techniques, 23 July - 8 August University of Ljubljana, Slovenia Course Description Form 1-2 week course (30 hrs) Course title SD206. Introduction to Structural
10 th ECPR Summer School in Methods and Techniques, 23 July - 8 August University of Ljubljana, Slovenia Course Description Form 1-2 week course (30 hrs) Course title SD206. Introduction to Structural
ADVANCED QUANTITATIVE METHODS READING LIST. January LOGISTIC/PROBIT & RELATED REGRESSION METHODS
 ADVANCED QUANTITATIVE METHODS READING LIST January 1999 OUTLINE 1. LINEAR REGRESSION 2. LOGISTIC/PROBIT & RELATED REGRESSION METHODS 3. STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS 4. LONGITUDINAL DATA ANALYSIS 5. MULTILEVEL
ADVANCED QUANTITATIVE METHODS READING LIST January 1999 OUTLINE 1. LINEAR REGRESSION 2. LOGISTIC/PROBIT & RELATED REGRESSION METHODS 3. STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS 4. LONGITUDINAL DATA ANALYSIS 5. MULTILEVEL
Functioning of global fit statistics in latent growth curve modeling
 University of Northern Colorado Scholarship & Creative Works @ Digital UNC Dissertations Student Research 12-1-2009 Functioning of global fit statistics in latent growth curve modeling Kathryn K. DeRoche
University of Northern Colorado Scholarship & Creative Works @ Digital UNC Dissertations Student Research 12-1-2009 Functioning of global fit statistics in latent growth curve modeling Kathryn K. DeRoche
SC705: Advanced Statistics Instructor: Natasha Sarkisian Class notes: Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling (SEM)
 SC705: Advanced Statistics Instructor: Natasha Sarkisian Class notes: Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) SEM is a family of statistical techniques which builds upon multiple regression,
SC705: Advanced Statistics Instructor: Natasha Sarkisian Class notes: Introduction to Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) SEM is a family of statistical techniques which builds upon multiple regression,
CHAPTER 9 EXAMPLES: MULTILEVEL MODELING WITH COMPLEX SURVEY DATA
 Examples: Multilevel Modeling With Complex Survey Data CHAPTER 9 EXAMPLES: MULTILEVEL MODELING WITH COMPLEX SURVEY DATA Complex survey data refers to data obtained by stratification, cluster sampling and/or
Examples: Multilevel Modeling With Complex Survey Data CHAPTER 9 EXAMPLES: MULTILEVEL MODELING WITH COMPLEX SURVEY DATA Complex survey data refers to data obtained by stratification, cluster sampling and/or
SRMR in Mplus. Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén. May 2, 2018
 SRMR in Mplus Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén May 2, 2018 1 Introduction In this note we describe the Mplus implementation of the SRMR standardized root mean squared residual) fit index for the models
SRMR in Mplus Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén May 2, 2018 1 Introduction In this note we describe the Mplus implementation of the SRMR standardized root mean squared residual) fit index for the models
Joint Modeling of Longitudinal Item Response Data and Survival
 Joint Modeling of Longitudinal Item Response Data and Survival Jean-Paul Fox University of Twente Department of Research Methodology, Measurement and Data Analysis Faculty of Behavioural Sciences Enschede,
Joint Modeling of Longitudinal Item Response Data and Survival Jean-Paul Fox University of Twente Department of Research Methodology, Measurement and Data Analysis Faculty of Behavioural Sciences Enschede,
Testing structural equation models: the effect of kurtosis. Tron Foss BI Norwegian Business School. Karl G. Jøreskog BI Norwegian Business School
 This file was downloaded from the institutional repository BI Brage - http://brage.bibsys.no/bi (Open Access) Testing structural equation models: the effect of kurtosis Tron Foss BI Norwegian Business
This file was downloaded from the institutional repository BI Brage - http://brage.bibsys.no/bi (Open Access) Testing structural equation models: the effect of kurtosis Tron Foss BI Norwegian Business
Can Variances of Latent Variables be Scaled in Such a Way That They Correspond to Eigenvalues?
 International Journal of Statistics and Probability; Vol. 6, No. 6; November 07 ISSN 97-703 E-ISSN 97-7040 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Can Variances of Latent Variables be Scaled
International Journal of Statistics and Probability; Vol. 6, No. 6; November 07 ISSN 97-703 E-ISSN 97-7040 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Can Variances of Latent Variables be Scaled
Econometric Analysis of Cross Section and Panel Data
 Econometric Analysis of Cross Section and Panel Data Jeffrey M. Wooldridge / The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England Contents Preface Acknowledgments xvii xxiii I INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND
Econometric Analysis of Cross Section and Panel Data Jeffrey M. Wooldridge / The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England Contents Preface Acknowledgments xvii xxiii I INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND
Package SEMModComp. R topics documented: February 19, Type Package Title Model Comparisons for SEM Version 1.0 Date Author Roy Levy
 Type Package Title Model Comparisons for SEM Version 1.0 Date 2009-02-23 Author Roy Levy Package SEMModComp Maintainer Roy Levy February 19, 2015 Conduct tests of difference in fit for
Type Package Title Model Comparisons for SEM Version 1.0 Date 2009-02-23 Author Roy Levy Package SEMModComp Maintainer Roy Levy February 19, 2015 Conduct tests of difference in fit for
How to run the RI CLPM with Mplus By Ellen Hamaker March 21, 2018
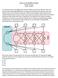 How to run the RI CLPM with Mplus By Ellen Hamaker March 21, 2018 The random intercept cross lagged panel model (RI CLPM) as proposed by Hamaker, Kuiper and Grasman (2015, Psychological Methods) is a model
How to run the RI CLPM with Mplus By Ellen Hamaker March 21, 2018 The random intercept cross lagged panel model (RI CLPM) as proposed by Hamaker, Kuiper and Grasman (2015, Psychological Methods) is a model
