CorrelationbetweenVoronoivolumesindiscpackings
|
|
|
- Dwight Atkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 February EPL, 97()344 doi:.9/95-575/97/344 CorrelationbetweenVoronoivolumesindiscpackings Song-ChuanZhao (a),stacysidle,harryl.swinney andmatthiasschröter (b) Max-Planck-InstitutfürDynamikundSelbstorganisation-Bunsenstr.,D-3773Göttingen,Germany,EU CenterforNonlinearDynamicsandDepartmentofPhysics,UniversityofTexasatAustin Austin, TX 787, USA received 9 September ; accepted in final form December published online 3 January PACS n Granular systems PACS 45.7.Cc Static sandpiles; granular compaction PACS j Disordered solids Abstract We measure the two-point correlation of free Voronoi volumes in binary disc packings, wherethepackingfractionφ avgrangesfrom.875to.838.weobserveshort-rangedcorrelations overthewholerangeofφ avgandanticorrelationsforφ avg>.877.thespatialextentoftheanticorrelationincreaseswithφ avgwhilethepositionofthemaximumoftheanticorrelationandthe extentofthepositivecorrelationshrinkwithφ avg.weconjecturethattheonsetofanticorrelation corresponds to dilatancy onset in this system. Copyright c EPLA, Introduction. Dry granular matter interacts only via elastic and frictional forces, which require particles to be in contact; spatially extended interactions like Van der Waals forces typically play no role. However, granular particles form networks of force chains [], which implies the existence of local correlations. Lechenault etal. have shown that the logarithm of the distribution of free volumes in granular matter scales in a non-extensive way with the cluster size, which implies the existence of correlations between Voronoi cells[]. A similar scaling was also observed in monodisperse sphere packings[3]. These experimental observations raise the question how the spatial extent of such correlations changes with packing fraction. This question is especially important for granular systems with glassy behavior, where a number of groups have studied the length scale related to spatially heterogeneous dynamics[4 7]. In this paper we demonstrate the existence of both correlations and anticorrelationinthefreevoronoivolumes,andwemeasuretheir spatial extent as a function of volume fraction. Experiment. Experiments are performed in a two-dimensional air fluidized bed, as sketched in fig. (a). TheparticlesareabinarymixtureofTeflondiscswith diametersofd s =6mmandd l =9mm.Theyareconfined (a) songchuan.zhao@ds.mpg.de (b) matthias.schroeter@ds.mpg.de ThefreeVoronoivolumeisthedifferencebetweentheactual Voronoivolumeofacellandthevolumeofacellinahexagonal packing. between two vertical glass plates (thickness mm) separated by a distance slightly larger than the thickness of the discs(3.86 mm). The bed contains approximately 75discsofeachsize. Thediscpackingistappedfrombelowbyairpulses flowing through a distributor of open-porous foam(duocel 4 PPI aluminium foam). Electrostatic charging is minimized by grounding the distributor. The duration and strength of air pulses are controlled by two Waston Smith 6B464 mechanical pressure regulators and two pairs of Jefferson 6 series electronic valves. Three sensors below the distributor are used to measure air pressure (Validyne DP5), humidity(honeywell HIH-36) and temperature(ysi 4433). Typical humidities and temperatures are3.8±.3%and4.8±.4 C. Theaveragepackingfractionφ avg valueiscontrolled bythetypeanddurationoftheairpulses.theuseof different tapping modes(cf. fig. (b)) enables us to vary φ avg from.875 to.838, as shown in table. The mostcompactbedsareobtainedbyfirstdrivingthebed toanewconfigurationusingaprimarypulse,andthen following that by shorter secondary pulses to compactify the bed. The duration of the primary pulse and the strengthofairflowarefixed,butthenumberandduration of the secondary pulses are adjustable. Looser packings are obtained using two airflow pathways with different flow rates; when the primary pulse stops, the secondary pathway still provides some small flow, which slows down the settling discs. 344-p
2 Song-Chuan Zhao etal. (a) (b) (c).8 primary pulse secondary pulses Pressure (bar).6.4. valve valve distributor time (s) extended pulse 5mm Reg Reg Pressure (bar).6.4. air source..6. time (s) 9mm Fig. :(Color online)(a) Sketch of the experimental setup(particles not drawn to scale).(b) Examples of the different tapping modes. The pressure is measured below the distributor.(c) Image of the experimental packing. Table : Parameters of the air pulses. All the experiments start with the same primary pulse(3. bar measured at the regulator, ms), either followed by several secondary pulses with the same pressure or accompanied by an extended pulse. φ avg Extendedpulse Secondarypulses bar ms bar ms ms ms.856 5ms ms ms ms ms ms+5 5ms ms+3 5ms Aftereachtap,thepackingisallowedtorelaxforfour seconds. Then an image of the packing is taken by a CCDcamerawithaNikkor5mmlens.Onlythecentral region of the packing (5 9mm ), five small disc diameters away from boundaries, is captured. The spatial resolution is.7 mm per pixel. For each experiment 8 configurations are imaged. Image processing. To analyze the configuration we compute the Voronoi tessellation of the packing. Because we consider a D system, volume and area are used interchangeably in the following. In a first step the centers andsizesofthediscsarecalculatedwithanaccuracyof. pixel using a template correlation technique. TherearetwomethodstoidentifyVoronoicellsina bidisperse system, radical tessellation[8] and navigation map [9]. Radical tessellation takes the boundaries of the cells as the collection of points whose tangents to neighboring particles are equal length. The navigation maptakesthecellsasthecollectionofpointscloserto the surface of the corresponding particles than others in the system. In this work the navigation map is computed numerically on a grid of /6 pixel resolution. An example ofthenavigationmapisshowninfig.(a). Our packing is prepared under gravity. Sidewalls introduce slow convection rolls during an air flow pulse, and distributor inhomogeneities introduce gradients in the airflow.itisthereforenotsurprisingtofindgradientsof thepackingfractioninthesystem.theanalysisisdone for the central spatially most homogeneous region. The spatial variance of the local packing fraction (averaged over the whole 8 taps) is calculated for circles of diameter8d s (seethewhitedashedcircleinfig.(a)).thenthe region with the smallest variance(in all cases smaller than.43) is chosen as the analysis region for the experiment. Additionally, the evolution of the global packing fraction and the geometrical contact number in that region are examined to make sure that no segregation occurs during thecourseoftheexperiment. Results. Individual Voronoi volumes and free volume distribution. The distribution of individual Voronoi volumes v Thespatialvarianceofthewholesystemis p
3 Voronoi volume correlation (a) (b) (c) log(p(v/v s )) Voronoi volume v/v s (d) P(v/v s ) 8 x 3 6 small φ=.875 both 4 large (e) P(v/v s ) 8 x large small both φ= Voronoi volume v/v s Voronoi volume v/v s Fig. :(Color online)(a) Voronoi cells computed using the navigation map for the packing in fig. (c) and labeled with different colors. The white dashed circle indicates the size of the region over which we perform further analysis for over 8 individual configurations.(b)theprobabilitydistributionofthevolumeofindividualvoronoicells;thetwopeakscorrespondtothetwo sizesofdiscs.(c)anillustrationoftheconstructionofpairsbyahexagonalwheel.thewheelvertices(darkdots)definepairs of points. The free volume of the Voronoi cells to which the vertices belong is used for the two-point correlation measurement. (d), (e) Free volume distributions of small discs, large discs, and both for two different packing fractions. The volume is normalizedbythevolumeofsmallparticlesv s=πd s/4.theprobabilitiesarenormalizedbythenumberofsmall,large,and both discs, respectively. can be computed directly from the results of the navigationmap.anexampleisshowninfig.(b).becausewe do not want to distinguish between small and large discs, we follow Lechenault etal.[] and use in the subsequent analysisthefreevoronoivolumev f =v v min.theminimumvolumev min isthevolumethatagrainwouldoccupy inahexagonalpackingofidenticaldiscs.itequals 3 d, wheredisthediameterofthecorrespondinglarge(d l ) discsorsmall(d s )discs.whiletherespectivemeanfree volumesofsmallandlargediscsstilldiffer( v s=.35 f and v f l =.58inunitsofv s=πd s/4forφ avg =.838), the success of the subsequent analysis justifies this step by hindsight. The free volume distributions of small and large discs and both types together are presented for two packing fractionsinfig.(d)and(e).forlargevolumesthedecay is exponential but besides this feature none of the free volume distributions and volume distributions in fig. (b), (d) and (e) could be fitted reasonably with a gamma distribution. This result differs from D and 3D monodisperse packings[ ]. Therelativeheightofthetwopeaksinthefreevolume distributions changes with φ avg. A recent study of the probability distributions of quadron volumes (an alternative tessellation introduced in [3]) showed that the positionandheightofthesepeakscanbetracedtoconditional probabilities of cell volumes at given coordination numbers[4].sothechangesvisibleinfig.(d)and(e) mayalsoberelatedtoachangeofcontactnumber. Two-point correlation of free Voronoi volume. To quantify the correlations between Voronoi volumes we use the two-point correlation function: C ij (L)= (v i v i )(v j v j ) σ, () where i, j correspond to two points in a distance L belongingtotwovoronoivolumes,andv i,v j arethefree volumes of these Voronoi cells.... indicates averages over all the 8 different packings created by flow pulses. v i and v j are the mean free volumes at these points (computed separately to remedy the effect of remainingsmallgradients),andσ =(σi +σ j )/isthe corresponding variance. To obtain better statistics, 4 pairs of points with the samelareselected.foreachpairc ij (L)iscomputed using eq. (). In practice the pairs are selected in the following way: We construct a hexagonal wheel centered intheanalysisregion.thelengthofeachedgeofthewheel issettobel(cf.fig.(c)).thesixouterpointsandthe centerformpairsthatareseparatedbyadistancel. Foreachsuchpair,thefreevolumeofthetwoVoronoi cells to which the two vertices belong are taken as v i andv j ineq.().thenthehexagonistranslatedtofive different positions and rotated to four different angles for each position. However, the whole wheel stays inside the whitecircleinfig.(a).thenthe4pairsareaveraged: corr(l)= 4 C ij (L). () i,j 344-p3
4 Song-Chuan Zhao etal. corr(l).. φ =.875 φ =.838 corr(l).. vertical horizontal L/d s L/d s Fig. 3: (Color online) Depending on φ, corr(l) exhibits both correlations and anticorrelations. Inset: the anisotropy measurementforφ avg=.838.thetwopointcorrelationof pairsplacedhorizontally(darkgreen)andvertically(brown), rather than constructed from the hexagon. corr(l).8.4 L C Aneg.. A neg φ avg L min exp(-l/l AC ) L/d s Fig. 4: (Color online) Three characteristic lengths: L C, obtainedfromalinearfit(dashedblackline)tocorr(l)for small L; L min, corresponding to the minimum of corr(l); and L AC, obtained from an exponential fit (green line) to corr(l)forl>l min.theinsetshowsthenegativeareaa neg ofcorr(l)asafunctionofφ avg. The correlation function corr(l) is shown for two values of φ avg in fig. 3. For low φ avg, corr(l) decays to zero and then fluctuates around it. Positive values of corr(l) indicate that the two free Voronoi volumes deviate from theaverageinthesamedirection.forhighφ avg,corr(l) decreases to a negative minimum and then increases towards. Negative values of corr(l) characterize anticorrelations: Voronoi cells at this distance deviate in opposite directions from the average free volume. We define three characteristic lengths to describe corr(l)(seefig.4).firstwedoalinearfittocorr(l)for arangecenteredathalfofthemaximumofcorr(l)with width±/d s.thepointwherethisfitcrosseszeroyields the length L C. For measurements of corr(l) showing anticorrelationwedefineasecondlength,l min,whichis extracted from a local parabolic fit around the minimum characteristic length/d avg 3.5 φ AC L AC L min L C φ avg Fig. 5: (Color online) Packing fraction dependence of the characteristic lengths of correlation L C and anticorrelation L minandl AC.Thelengthsarenormalizedusingtheaverage discdiameterd avg,whichcorrespondsto.3.8timesd s. ofcorr(l).thethirdlength,l AC,isobtainedfroman exponentialfitrangingfroml min totheendofcorr(l) (weallowforasmalloffsetinthisfit,butthemagnitude ofthisoffsetislessthan.6inallcases). Tofindtheonsetoftheanticorrelations,theareaA neg wherecorr(l)<(cf.fig.4)isplottedasafunctionof φ avg,asshownintheinsetoffig.4 3.Anextrapolation of a linear fit to A neg to zero defines the threshold foranticorrelations,φ AC =.877±.5.Forφ>φ AC, corr(l) can be both positive and negative; therefore, it cannotbedescribedbyapowerlaw[]. ThedependenceofL C,L min,andl AC onφ avg isshown infig.5:l C andl min slowlydecreasemonotonicallywith φ avg,whilel AC growsapproximatelylinearly.thefinite extent of correlations and anticorrelations can also be seen infig.6,whichshowshowthevarianceofthefreevolume of a cluster scales with the number N of particles in thecluster.inthelargen limitalinearrelationshipis recovered as predicted by the central limit theorem in the absence of correlations. Gravity breaks the isotropy in our experimental setup; this anisotropy is visible in the correlations plotted in the inset of fig. 3, where pairs of horizontal and vertical points are averaged separately. While the qualitative features of corr(l) are independent of direction, the lower statistics of this analysis does not allow us to extract the corresponding characteristic lengths. We have also performed our analysis with the radical tessellation and have found that all features stay qualitatively the same. Quantitatively there are slight differences: φ AC =.88±.;L C,L min andl AC are6%,%and 3% larger on average. 3 WhencomputingA neg wetakeintoaccounttheoffsetofthe exponentialfitdeterminingl AC. 344-p4
5 Voronoi volume correlation ) log (σ N f L 8d s cluster 3 log (N).76 Fig. 6: (Color online) The correlations have finite spatial extent,asshownbythevarianceσ f N oftheaveragefreevolume ofacompactclusterasafunctionofthenumbernofgrains included (open blue circles). In the absence of correlations the central-limit theorem predicts a slope of one. While the slopeforsmallclusters(n<)is.76,inthelargenlimita slopeofoneisrecovered.alsotheslopeofahexagonalwheel cluster withsidelengthl 8d s(opentriangles)equalsone. Hereφ avg=.838;datasetsareshiftedforclarity. Discussion. This is the first observation of anticorrelation between Voronoi volumes in a granular system. Onereasonforthisisthatearlierstudiesofvolumefluctuations focused on the cluster composed of neighboring particles[,3]. There the variance of average free volume pergrainσn asafunctionofthenumberofgrainsincluded N wasmeasured,andthescalingσn N α withα< indicated the existence of correlations. However, the scalingbetweenσn andnisameasureofthecorrelationintegratedoverthewholeclustersize.inthelargenlimit,the relationbetweenn α andcorr(l)is N α = C N L(N) corr(l)ldl, (3) where C is a constant proportional to the density of the cluster (πl (N) would be the size of the cluster). The relatively small contribution of anticorrelations to the integral in eq. (3) would be hard to distinguish from experimental noise(cf. fig. 6). Therefore, a direct measurement of two-point correlation is necessary to find anticorrelation. In recent years a statistical mechanics approach for granular systems has been developed where the Hamilton function is replaced by a volume function[5]. Voronoi cells have been used to construct this function[,6,7]. While the discovery of anticorrelation has consequences for such an approach, some properties like the distribution of the local packing fraction have been shown to not depend on correlations[8]. It is possible that not only the extent but even the existence of positive correlation is an artifact of Voronoi tessellation. By definition the Voronoi tessellation assigns spacetoeachparticleinacertain equal way.inthe caseofthenavigationmap,theedgeofavoronoicell isthecollectionofpointsthathaveequaldistancerto the surface of the neighboring particles. The increase in avoronoivolumecouldroughlybeseenastheincrease in r, therefore ther of its neighboring Voronoi cell. Consequently the Voronoi tessellation itself gives rise to a positive correlation between neighboring Voronoi volumes. To verify whether this effect dominates the evolution of L C,weestimatetheaveragesized vor ofvoronoicellsin the system in the following way. In a homogeneous system, φ avg couldbewrittenastheratiooftheaverageparticle volumetotheaveragevoronoivolume,φ avg =d avg/d vor. Giventhebidispersenatureofoursystemd avg isinthe rangeof.3.8d s.thisestimationleavesusd vor = d avg / φ avg.rescalingl C withd vor showsthatl C decays slightly faster than explained by simple compaction. This could stem from the appearance of the anticorrelation beyondφ AC.Itwillbeinterestingtotestthishypothesis with another way of tessellation, such as quadrons[3]. Aboveφ AC thefluctuationofthevolumeofonegrain causes more and more grains to be anticorrelated, which isindicatedbytheincreaseofl AC andthedecreaseof L min.concerningthephysicalinterpretationoftheseanticorrelations,weconjecturethatφ AC mightcorrespondto theonsetofdilatancy.in3dsystemsitiswellestablished that loose granular material collapses under shear, while granular material denser than dilatancy onset expands [9,]. This expansion can be understood as competition between the grains for free volume. Our results show that correlations between the volumes of subunits depend on the specific system under consideration. For example, in froths there exist anticorrelations of the number of faces between neighboring cells[ 4]. At thesametimethevolumeofafoamcellisproportional to the number of faces[,5]. These features combined indicate that the volume of neighboring cells should be anticorrelated. ItwouldbeinterestingtoknowhowL AC woulddevelop at even higher density. However, we can not compactify the system above φ =.838 without partial segregation. In this case no anticorrelations occur within the segregated patches.theonlysurvivinglengthisl C,whichcharacterizes the size of the segregated patches. Conclusion. Our measurements of the two-point correlation function for binary disc packings yield a shortranged positive correlation over the whole range of packing fractions Above a volume fraction of.877 ±.5 we observe anticorrelation in the free Voronoi volumes. These anticorrelations reach a maximum at a distance of about 3.5 small particle diameters. They then decay exponentially with distance, with an exponent growing linearly with packing fraction. 344-p5
6 Song-Chuan Zhao etal. WethankS.Nagel,U.KrafftandW.Keiderling for their technical support. REFERENCES [] MajmudarT.S.andBehringerR.,Nature,435(5) 79. [] LechenaultF.,daCruzF.,DauchotO.andBertin E.,J.Stat.Mech.(6)P79. [3] AsteT.andMatteoT.D.,Eur.Phys.J.E,(7) 35. [4] GoldmanD.I.andSwinneyH.L.,Phys.Rev.Lett.,96 (6)457. [5] DauchotO.andMartyG.,Phys.Rev.Lett.,95(5) 657. [6] Keys A. S., Abate A., Glotzer S. C. anddurian D.J.,Nat.Phys.,3(7)6. [7] Lechenault F., Dauchot O., Biroli G. and BouchaudJ.P.,EPL,83(8)463. [8] GellatlyB.J.andFinneyJ.L.,J.Non-Cryst.Solids, 5(98)33. [9] RichardP.,OgerL.,TroadecJ.P.andGervoisA., Eur.Phys.J.E,6()95. [] AsteT.,DiMatteoT.,SaadatfarM.,SendenT.J., Schröter M. and Swinney H. L., EPL, 79 (7) 43. [] SlotterbackS.,ToiyaM.,GoffL.,DouglasJ.F. andlosertw.,phys.rev.lett.,(8)58. [] KumarV.S.andKumaranV.,J.Chem.Phys.,3 (5)45. [3] Blumenfeld R. andedwards S. F., Phys. Rev. Lett., 9(3)433. [4] FrenkelG.,BlumenfeldR.,GrofZ.andKingP.R., Phys.Rev.E,77(8)434. [5] EdwardsS.F.andOakeshottR.B.S.,PhysicaA, 57(989)8. [6] AsteT.andDiMatteoT.,Phys.Rev.E,77(8) 39. [7] Song C., Wang P. and Makse H. A., Nature, 453 (8)69. [8] Puckett J. G., Lechenault F. anddaniels K. E., Phys.Rev.E,83()43. [9] KablaA.J.andSendenT.J.,Phys.Rev.Lett., (9)83. [] Gravish N., Umbanhowar P. B. andgoldman D. I., Phys.Rev.Lett.,5()83. [] O DonovanC.B.andMöbiusM.E.,Phys.Rev.E,84 ()3(R). [] OgerL.,GervoisA.,TroadecJ.P.andRivierN., Philos.Mag.B,74(996)77. [3] HilhorstH.J.,Eur.Phys.J.B,64(8)437. [4] KumarS.,KurtzS.andWeaireD.,Philos.Mag.B, 69(994)43. [5] StoyanD.,KendalW.S.andMeckeJ.,Stochastic GeometryanditsApplications(Wiley, Chichester) p6
An invariant distribution in static granular media
 July 27 EPL, 79 (27) 243 doi: 1.129/295-575/79/243 www.epljournal.org An invariant distribution in static granular media T. Aste 1,T.DiMatteo 1,M.Saadatfar 1,2,T.J.Senden 1, Matthias Schröter 3 and Harry
July 27 EPL, 79 (27) 243 doi: 1.129/295-575/79/243 www.epljournal.org An invariant distribution in static granular media T. Aste 1,T.DiMatteo 1,M.Saadatfar 1,2,T.J.Senden 1, Matthias Schröter 3 and Harry
Resistance distribution in the hopping percolation model
 Resistance distribution in the hopping percolation model Yakov M. Strelniker, Shlomo Havlin, Richard Berkovits, and Aviad Frydman Minerva Center, Jack and Pearl Resnick Institute of Advanced Technology,
Resistance distribution in the hopping percolation model Yakov M. Strelniker, Shlomo Havlin, Richard Berkovits, and Aviad Frydman Minerva Center, Jack and Pearl Resnick Institute of Advanced Technology,
Dilatancy Transition in a Granular Model. David Aristoff and Charles Radin * Mathematics Department, University of Texas, Austin, TX 78712
 Dilatancy Transition in a Granular Model by David Aristoff and Charles Radin * Mathematics Department, University of Texas, Austin, TX 78712 Abstract We introduce a model of granular matter and use a stress
Dilatancy Transition in a Granular Model by David Aristoff and Charles Radin * Mathematics Department, University of Texas, Austin, TX 78712 Abstract We introduce a model of granular matter and use a stress
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29750 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Wortel, Geert Title: Granular flows : fluidization and anisotropy Issue Date: 2015-11-19
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29750 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Wortel, Geert Title: Granular flows : fluidization and anisotropy Issue Date: 2015-11-19
Mechanisms in the size segregation of a binary granular mixture
 Mechanisms in the size segregation of a binary granular mixture Matthias Schröter,* Stephan Ulrich, Jennifer Kreft, Jack B. Swift, and Harry L. Swinney Center for Nonlinear Dynamics and Department of Physics,
Mechanisms in the size segregation of a binary granular mixture Matthias Schröter,* Stephan Ulrich, Jennifer Kreft, Jack B. Swift, and Harry L. Swinney Center for Nonlinear Dynamics and Department of Physics,
The Needle in the Haystack: the physics of prolate granular piles
 Scott Franklin svfsps@rit.edu http://piggy.rit.edu/franklin Undergraduate Researchers Kevin Stokely Ari Diacou Jesus Benhumea Ken Desmond Saul Lapidus Peter Gee The Needle in the Haystack: the physics
Scott Franklin svfsps@rit.edu http://piggy.rit.edu/franklin Undergraduate Researchers Kevin Stokely Ari Diacou Jesus Benhumea Ken Desmond Saul Lapidus Peter Gee The Needle in the Haystack: the physics
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Mar 2008
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Mar 2008 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Mar 2008](/thumbs/86/93817801.jpg) CD2dBS-v2 Convergence dynamics of 2-dimensional isotropic and anisotropic Bak-Sneppen models Burhan Bakar and Ugur Tirnakli Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Ege University, 35100 Izmir, Turkey
CD2dBS-v2 Convergence dynamics of 2-dimensional isotropic and anisotropic Bak-Sneppen models Burhan Bakar and Ugur Tirnakli Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Ege University, 35100 Izmir, Turkey
LAMMPS Simulation of a Microgravity Shear Cell 299r Progress Report 2 Taiyo Wilson. Introduction:
 Introduction: After our initial simulations outlined in the first progress report, we determined that a shear cell with a bidisperse composition of particles would be a promising system to explore. However,
Introduction: After our initial simulations outlined in the first progress report, we determined that a shear cell with a bidisperse composition of particles would be a promising system to explore. However,
Kent Academic Repository
 Kent Academic Repository Full text document (pdf) Citation for published version Jerkins, Melissa and Schröter, Matthias and Swinney, Harry and Senden, Tim and Saadatfar, Mohammad and Aste, Tomaso (2008)
Kent Academic Repository Full text document (pdf) Citation for published version Jerkins, Melissa and Schröter, Matthias and Swinney, Harry and Senden, Tim and Saadatfar, Mohammad and Aste, Tomaso (2008)
LAMMPS Simulation of a Microgravity Shear Cell 299r Progress Report Taiyo Wilson. Units/Parameters:
 Units/Parameters: In our simulations, we chose to express quantities in terms of three fundamental values: m (particle mass), d (particle diameter), and τ (timestep, which is equivalent to (g/d)^0.5, where
Units/Parameters: In our simulations, we chose to express quantities in terms of three fundamental values: m (particle mass), d (particle diameter), and τ (timestep, which is equivalent to (g/d)^0.5, where
Aging in laponite water suspensions. P. K. Bhattacharyya Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 Aging in laponite water suspensions. P. K. Bhattacharyya Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies Massachusetts Institute of Technology Outline Laponite Basic background. Laponite in suspension Bonn et al.,
Aging in laponite water suspensions. P. K. Bhattacharyya Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies Massachusetts Institute of Technology Outline Laponite Basic background. Laponite in suspension Bonn et al.,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 28 Mar 2007
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 28 Mar 2007 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 28 Mar 2007](/thumbs/93/111468426.jpg) Universal Anisotropy in Force Networks under Shear Srdjan Ostojic, 1, Thijs J. H. Vlugt, 2 and Bernard Nienhuis 1 arxiv:cond-mat/0610483v2 [cond-mat.soft] 28 Mar 2007 1 Institute for Theoretical Physics,
Universal Anisotropy in Force Networks under Shear Srdjan Ostojic, 1, Thijs J. H. Vlugt, 2 and Bernard Nienhuis 1 arxiv:cond-mat/0610483v2 [cond-mat.soft] 28 Mar 2007 1 Institute for Theoretical Physics,
Correlation between local structure and dynamic heterogeneity in a metallic glass-forming liquid
 Correlation between local structure and dynamic heterogeneity in a metallic glass-forming liquid S. P. Pan a,b,*, S. D. Feng c, J. W. Qiao a,b, W. M. Wang d, and J. Y. Qin d a College of Materials Science
Correlation between local structure and dynamic heterogeneity in a metallic glass-forming liquid S. P. Pan a,b,*, S. D. Feng c, J. W. Qiao a,b, W. M. Wang d, and J. Y. Qin d a College of Materials Science
Clusters in granular flows : elements of a non-local rheology
 CEA-Saclay/SPEC; Group Instabilities and Turbulence Clusters in granular flows : elements of a non-local rheology Olivier Dauchot together with many contributors: D. Bonamy, E. Bertin, S. Deboeuf, B. Andreotti,
CEA-Saclay/SPEC; Group Instabilities and Turbulence Clusters in granular flows : elements of a non-local rheology Olivier Dauchot together with many contributors: D. Bonamy, E. Bertin, S. Deboeuf, B. Andreotti,
Jamming and critical outlet size in the discharge of a two-dimensional silo
 November 2008 EPL, 84 (2008) 44002 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/84/44002 www.epljournal.org Jamming and critical outlet size in the discharge of a two-dimensional silo A. Janda 1(a), I. Zuriguel 1,A.Garcimartín
November 2008 EPL, 84 (2008) 44002 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/84/44002 www.epljournal.org Jamming and critical outlet size in the discharge of a two-dimensional silo A. Janda 1(a), I. Zuriguel 1,A.Garcimartín
kgamma distributions in granular packs
 kgamma distributions in granular packs T. Aste,, G. W Delaney and T. Di Matteo School of Physical Sciences, University of Kent, Canterbury, Kent, CT2 7NH, UK. Department of Applied Mathematics, Research
kgamma distributions in granular packs T. Aste,, G. W Delaney and T. Di Matteo School of Physical Sciences, University of Kent, Canterbury, Kent, CT2 7NH, UK. Department of Applied Mathematics, Research
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 10 Dec 2010
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 10 Dec 2010 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 10 Dec 2010](/thumbs/90/101597834.jpg) epl draft The role of interstitial gas in determining the impact response of granular beds arxiv:112.2399v1 [cond-mat.soft] 1 Dec 21 John R. Royer 1 (a), Bryan Conyers 1, Eric I. Corwin 1 (b), Peter J.
epl draft The role of interstitial gas in determining the impact response of granular beds arxiv:112.2399v1 [cond-mat.soft] 1 Dec 21 John R. Royer 1 (a), Bryan Conyers 1, Eric I. Corwin 1 (b), Peter J.
Particle resuspension
 86 Chapter 6 Particle resuspension 6.1 Motivation In previous chapters, the relative effective viscosity of a flow with particles denser than the interstitial liquid was discussed. Such results show that
86 Chapter 6 Particle resuspension 6.1 Motivation In previous chapters, the relative effective viscosity of a flow with particles denser than the interstitial liquid was discussed. Such results show that
The role of tap duration for the steady state density of vibrated granular media
 epl draft The role of tap duration for the steady state density of vibrated granular media Joshua A. Dijksman 1 and Martin van Hecke 1 1 Kamerlingh Onnes Lab, Universiteit Leiden, Postbus 9504, 2300 RA
epl draft The role of tap duration for the steady state density of vibrated granular media Joshua A. Dijksman 1 and Martin van Hecke 1 1 Kamerlingh Onnes Lab, Universiteit Leiden, Postbus 9504, 2300 RA
Fig.8-1 Scheme of the fluidization column
 8 Fluidization Lenka Schreiberová, Martin Kohout I Basic relations and definitions Fluidization is a process where the liquid flows in opposite direction the gravitation and creates a suspension together
8 Fluidization Lenka Schreiberová, Martin Kohout I Basic relations and definitions Fluidization is a process where the liquid flows in opposite direction the gravitation and creates a suspension together
The Temperature and Relative Humidity Change in Wheat Bulk under the Condition of Temperature Differences
 Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference of Fluid Flow, Heat and Mass Transfer (FFHMT'17) Toronto, Canada August 21 23, 2017 Paper No. 147 DOI: 10.11159/ffhmt17.147 The Temperature and Relative
Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference of Fluid Flow, Heat and Mass Transfer (FFHMT'17) Toronto, Canada August 21 23, 2017 Paper No. 147 DOI: 10.11159/ffhmt17.147 The Temperature and Relative
Mixing Process of Binary Polymer Particles in Different Type of Mixers
 Vol. 3, No. 6 Mixing Process of Binary Polymer Particles in Different Type of Mixers S.M.Tasirin, S.K.Kamarudin & A.M.A. Hweage Department of Chemical and Process Engineering, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia
Vol. 3, No. 6 Mixing Process of Binary Polymer Particles in Different Type of Mixers S.M.Tasirin, S.K.Kamarudin & A.M.A. Hweage Department of Chemical and Process Engineering, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia
collisions inelastic, energy is dissipated and not conserved
 LECTURE 1 - Introduction to Granular Materials Jamming, Random Close Packing, The Isostatic State Granular materials particles only interact when they touch hard cores: rigid, incompressible, particles
LECTURE 1 - Introduction to Granular Materials Jamming, Random Close Packing, The Isostatic State Granular materials particles only interact when they touch hard cores: rigid, incompressible, particles
Granular Micro-Structure and Avalanche Precursors
 Granular Micro-Structure and Avalanche Precursors L. Staron, F. Radjai & J.-P. Vilotte Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, Cambridge CB3 0WA, UK. Laboratoire de Mécanique et Génie
Granular Micro-Structure and Avalanche Precursors L. Staron, F. Radjai & J.-P. Vilotte Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, Cambridge CB3 0WA, UK. Laboratoire de Mécanique et Génie
Citation PHYSICAL REVIEW E (2002), 65(6) RightCopyright 2002 American Physical So
 TitleStatistical mechanics of two hard d Author(s) Munakata, T; Hu, G Citation PHYSICAL REVIEW E (2002), 65(6) Issue Date 2002-06 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/50310 RightCopyright 2002 American Physical
TitleStatistical mechanics of two hard d Author(s) Munakata, T; Hu, G Citation PHYSICAL REVIEW E (2002), 65(6) Issue Date 2002-06 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/50310 RightCopyright 2002 American Physical
This is the accepted manuscript made available via CHORUS. The article has been published as:
 This is the accepted manuscript made available via CHORUS. The article has been published as: Similarity of the Signatures of the Initial Stages of Phase Separation in Metastable and Unstable Polymer Blends
This is the accepted manuscript made available via CHORUS. The article has been published as: Similarity of the Signatures of the Initial Stages of Phase Separation in Metastable and Unstable Polymer Blends
Influence of Interparticle Forces on Powder Behaviour Martin Rhodes
 Influence of Interparticle Forces on Powder Behaviour Martin Rhodes RSC Meeting Powder Flow 2018: Cohesive Powder Flow 12 April 2018 London Interparticle Forces Capillary Forces Due the presence of liquid
Influence of Interparticle Forces on Powder Behaviour Martin Rhodes RSC Meeting Powder Flow 2018: Cohesive Powder Flow 12 April 2018 London Interparticle Forces Capillary Forces Due the presence of liquid
Turbulentlike Quantitative Analysis on Energy Dissipation in Vibrated Granular Media
 Copyright 011 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.71, no., pp.149-155, 011 Turbulentlike Quantitative Analysis on Energy Dissipation in Vibrated Granular Media Zhi Yuan Cui 1, Jiu Hui Wu 1 and Di Chen Li 1 Abstract:
Copyright 011 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.71, no., pp.149-155, 011 Turbulentlike Quantitative Analysis on Energy Dissipation in Vibrated Granular Media Zhi Yuan Cui 1, Jiu Hui Wu 1 and Di Chen Li 1 Abstract:
Logarithmically modified scaling of temperature structure functions in thermal convection
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 January 2005 Europhys. Lett., 69 (1), pp. 75 80 (2005) DOI: 10.1209/epl/i2004-10373-4 Logarithmically modified scaling of temperature structure functions in thermal convection A.
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 January 2005 Europhys. Lett., 69 (1), pp. 75 80 (2005) DOI: 10.1209/epl/i2004-10373-4 Logarithmically modified scaling of temperature structure functions in thermal convection A.
Topological Persistence and Dynamical Heterogeneities Near Jamming
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Department of Physics Papers Department of Physics 8-3-27 Topological Persistence and Dynamical Heterogeneities Near Jamming Adam Ross Abate University of Pennsylvania,
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Department of Physics Papers Department of Physics 8-3-27 Topological Persistence and Dynamical Heterogeneities Near Jamming Adam Ross Abate University of Pennsylvania,
Segregation in a noninteracting binary mixture
 Segregation in a noninteracting binary mixture Filip Krzyżewski and Magdalena A. Załuska-Kotur,2 Institute of Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, Al. Lotników 32/46, 02-668 Warsaw, Poland 2 Faculty of
Segregation in a noninteracting binary mixture Filip Krzyżewski and Magdalena A. Załuska-Kotur,2 Institute of Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, Al. Lotników 32/46, 02-668 Warsaw, Poland 2 Faculty of
Force and flow at the onset of drag in plowed granular media
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 89, 4222 (24) Force and flow at the onset of drag in plowed granular media Nick Gravish School of Physics, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia 3332, USA Paul B. Umbanhowar
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 89, 4222 (24) Force and flow at the onset of drag in plowed granular media Nick Gravish School of Physics, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia 3332, USA Paul B. Umbanhowar
THE ONSET OF FLUIDIZATION OF FINE POWDERS IN ROTATING DRUMS
 The Mater.Phys.Mech.3 Onset of Fluidization (1) 57-6 of Fine Powders in Rotating Drums 57 THE ONSET OF FLUIDIZATION OF FINE POWDERS IN ROTATING DRUMS A. Castellanos, M.A. Sánchez and J.M. Valverde Departamento
The Mater.Phys.Mech.3 Onset of Fluidization (1) 57-6 of Fine Powders in Rotating Drums 57 THE ONSET OF FLUIDIZATION OF FINE POWDERS IN ROTATING DRUMS A. Castellanos, M.A. Sánchez and J.M. Valverde Departamento
Length Scales Related to Alpha and Beta Relaxation in Glass Forming Liquids
 Length Scales Related to Alpha and Beta Relaxation in Glass Forming Liquids Chandan Dasgupta Centre for Condensed Matter Theory Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science With Smarajit Karmakar
Length Scales Related to Alpha and Beta Relaxation in Glass Forming Liquids Chandan Dasgupta Centre for Condensed Matter Theory Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science With Smarajit Karmakar
Summer School: Granular Materials from Simulations to Astrophysical Applications
 Summer School: Granular Materials from Simulations to Astrophysical Applications Hosted by CSCAMM and the University of Maryland Burgers Program in Fluid Dynamics Organizers: Derek Richardson, Astronomy
Summer School: Granular Materials from Simulations to Astrophysical Applications Hosted by CSCAMM and the University of Maryland Burgers Program in Fluid Dynamics Organizers: Derek Richardson, Astronomy
Superdiffusive, heterogeneous, and collective particle motion near the fluid-solid transition in athermal disordered materials
 OFFPRINT Superdiffusive, heterogeneous, and collective particle motion near the fluid-solid transition in athermal disordered materials C. Heussinger, L. Berthier and J.-L. Barrat EPL, 90 (2010) 20005
OFFPRINT Superdiffusive, heterogeneous, and collective particle motion near the fluid-solid transition in athermal disordered materials C. Heussinger, L. Berthier and J.-L. Barrat EPL, 90 (2010) 20005
Continuum Model of Avalanches in Granular Media
 Continuum Model of Avalanches in Granular Media David Chen May 13, 2010 Abstract A continuum description of avalanches in granular systems is presented. The model is based on hydrodynamic equations coupled
Continuum Model of Avalanches in Granular Media David Chen May 13, 2010 Abstract A continuum description of avalanches in granular systems is presented. The model is based on hydrodynamic equations coupled
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Sep 2016
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Sep 2016 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Sep 2016](/thumbs/95/123667841.jpg) Anomalous Stress Fluctuations in Two Dimensional Isotropic Packings of Frictionless Disks Above the Jamming Transition arxiv:1609.09265v1 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Sep 2016 Yegang Wu, 1 Kamran Karimi, 2 Craig
Anomalous Stress Fluctuations in Two Dimensional Isotropic Packings of Frictionless Disks Above the Jamming Transition arxiv:1609.09265v1 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Sep 2016 Yegang Wu, 1 Kamran Karimi, 2 Craig
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Bloch point formation during skyrmion annihilation. Skyrmion number in layers with different z-coordinate during the annihilation of a skyrmion. As the skyrmion
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Bloch point formation during skyrmion annihilation. Skyrmion number in layers with different z-coordinate during the annihilation of a skyrmion. As the skyrmion
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing.
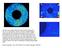 This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
A RESISTIVE FORCE MODEL FOR LEGGED LOCOMOTION ON GRANULAR MEDIA *
 A RESISTIVE FORCE MODEL FOR LEGGED LOCOMOTION ON GRANULAR MEDIA * CHEN LI, TINGNAN ZHANG, AND DANIEL I. GOLDMAN School of Physics, Georgia Institute of Technology, 837 State St NW Atlanta, GA 30332, USA
A RESISTIVE FORCE MODEL FOR LEGGED LOCOMOTION ON GRANULAR MEDIA * CHEN LI, TINGNAN ZHANG, AND DANIEL I. GOLDMAN School of Physics, Georgia Institute of Technology, 837 State St NW Atlanta, GA 30332, USA
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 56 Module 4: Lecture 7 on Stress-strain relationship and Shear strength of soils Contents Stress state, Mohr s circle analysis and Pole, Principal stressspace, Stress pathsin p-q space; Mohr-Coulomb failure
56 Module 4: Lecture 7 on Stress-strain relationship and Shear strength of soils Contents Stress state, Mohr s circle analysis and Pole, Principal stressspace, Stress pathsin p-q space; Mohr-Coulomb failure
CHARACTERISING THE FAILURE AND REPOSE ANGLES OF IRREGULARLY SHAPED THREE-DIMENSIONAL PARTICLES USING DEM
 Ninth International Conference on CFD in the Minerals and Process Industries CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia 10-12 December 2012 CHARACTERISING THE FAILURE AND REPOSE ANGLES OF IRREGULARLY SHAPED THREE-DIMENSIONAL
Ninth International Conference on CFD in the Minerals and Process Industries CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia 10-12 December 2012 CHARACTERISING THE FAILURE AND REPOSE ANGLES OF IRREGULARLY SHAPED THREE-DIMENSIONAL
Measurements of the yield stress in frictionless granular systems
 Measurements of the yield stress in frictionless granular systems Ning Xu 1 and Corey S. O Hern 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06520-8284, USA 2 Department
Measurements of the yield stress in frictionless granular systems Ning Xu 1 and Corey S. O Hern 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06520-8284, USA 2 Department
Effect of column diameter on dynamics of gas-solid fluidized bed: A statistical approach
 Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 16, January 2009, pp. 17-24 Effect of column diameter on dynamics of gas-solid fluidized bed: A statistical approach Y K Mohanty*, G K Roy & K C Biswal Department
Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 16, January 2009, pp. 17-24 Effect of column diameter on dynamics of gas-solid fluidized bed: A statistical approach Y K Mohanty*, G K Roy & K C Biswal Department
Proceedings of the ASME th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2016 June 19-24, 2016, Busan, South Korea
 Proceedings of the ASME 26 35th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE26 June 9-24, 26, Busan, South Korea OMAE26-54554 LOCAL STRAIN AND STRESS CALCULATION METHODS OF IRREGULAR
Proceedings of the ASME 26 35th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE26 June 9-24, 26, Busan, South Korea OMAE26-54554 LOCAL STRAIN AND STRESS CALCULATION METHODS OF IRREGULAR
A model for the transmission of contact forces in granular piles
 Author: Javier Cristín. Facultat de Física, Universitat de Barcelona, Diagonal 645, 08028 Barcelona, Spain Advisor: Carmen Miguel. Abstract:Granular matter is fundamentally different from other, more conventional,
Author: Javier Cristín. Facultat de Física, Universitat de Barcelona, Diagonal 645, 08028 Barcelona, Spain Advisor: Carmen Miguel. Abstract:Granular matter is fundamentally different from other, more conventional,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 25 Feb 1994
 A Model for Fracture in Fibrous Materials A. T. Bernardes Departamento de Física - ICEB arxiv:cond-mat/9402110v1 25 Feb 1994 Universidade Federal de Ouro Preto Campus do Morro do Cruzeiro 35410-000 Ouro
A Model for Fracture in Fibrous Materials A. T. Bernardes Departamento de Física - ICEB arxiv:cond-mat/9402110v1 25 Feb 1994 Universidade Federal de Ouro Preto Campus do Morro do Cruzeiro 35410-000 Ouro
Numerical evaluation of the upper critical dimension of percolation in scale-free networks
 umerical evaluation of the upper critical dimension of percolation in scale-free networks Zhenhua Wu, 1 Cecilia Lagorio, 2 Lidia A. Braunstein, 1,2 Reuven Cohen, 3 Shlomo Havlin, 3 and H. Eugene Stanley
umerical evaluation of the upper critical dimension of percolation in scale-free networks Zhenhua Wu, 1 Cecilia Lagorio, 2 Lidia A. Braunstein, 1,2 Reuven Cohen, 3 Shlomo Havlin, 3 and H. Eugene Stanley
Incipient sediment motion across the river to debris-flow transition
 Movie DR1 Movie DR2 Movie DR3 Movie DR4 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2014067 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS FOR Incipient sediment motion across the river to debris-flow transition Jeff P. Prancevic, Michael P. Lamb,
Movie DR1 Movie DR2 Movie DR3 Movie DR4 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2014067 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS FOR Incipient sediment motion across the river to debris-flow transition Jeff P. Prancevic, Michael P. Lamb,
The role of interparticle forces in the fluidization of micro and nanoparticles
 The role of interparticle forces in the fluidization of micro and nanoparticles A. Castellanos POWDER FLOW 2009 London, December 16 Acknowledgements The experimental work presented here has been done in
The role of interparticle forces in the fluidization of micro and nanoparticles A. Castellanos POWDER FLOW 2009 London, December 16 Acknowledgements The experimental work presented here has been done in
Microstructure evolution during impact on granular matter
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 85,011305(2012) Microstructure evolution during impact on granular matter L. Kondic, 1 X. Fang, 1 W. Losert, 2 C. S. O Hern, 3 and R. P. Behringer 4 1 Department of Mathematical Sciences,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 85,011305(2012) Microstructure evolution during impact on granular matter L. Kondic, 1 X. Fang, 1 W. Losert, 2 C. S. O Hern, 3 and R. P. Behringer 4 1 Department of Mathematical Sciences,
HRW 7e Chapter 2 Page 1 of 13
 HRW 7e Chapter Page of 3 Halliday/Resnick/Walker 7e Chapter. Huber s speed is v 0 =(00 m)/(6.509 s)=30.7 m/s = 0.6 km/h, where we have used the conversion factor m/s = 3.6 km/h. Since Whittingham beat
HRW 7e Chapter Page of 3 Halliday/Resnick/Walker 7e Chapter. Huber s speed is v 0 =(00 m)/(6.509 s)=30.7 m/s = 0.6 km/h, where we have used the conversion factor m/s = 3.6 km/h. Since Whittingham beat
Part I: Multiple Choice Questions
 Name: Part I: Multiple Choice Questions. What is the slope of the line y=3 A) 0 B) -3 ) C) 3 D) Undefined. What is the slope of the line perpendicular to the line x + 4y = 3 A) -/ B) / ) C) - D) 3. Find
Name: Part I: Multiple Choice Questions. What is the slope of the line y=3 A) 0 B) -3 ) C) 3 D) Undefined. What is the slope of the line perpendicular to the line x + 4y = 3 A) -/ B) / ) C) - D) 3. Find
Mechanistic Study of Nano-Particle Fluidization
 Refereed Proceedings The 1th International Conference on Fluidization - New Horizons in Fluidization Engineering Engineering Conferences International Year 007 Mechanistic Study of Nano-Particle Fluidization
Refereed Proceedings The 1th International Conference on Fluidization - New Horizons in Fluidization Engineering Engineering Conferences International Year 007 Mechanistic Study of Nano-Particle Fluidization
HSC PHYSICS ONLINE B F BA. repulsion between two negatively charged objects. attraction between a negative charge and a positive charge
 HSC PHYSICS ONLINE DYNAMICS TYPES O ORCES Electrostatic force (force mediated by a field - long range: action at a distance) the attractive or repulsion between two stationary charged objects. AB A B BA
HSC PHYSICS ONLINE DYNAMICS TYPES O ORCES Electrostatic force (force mediated by a field - long range: action at a distance) the attractive or repulsion between two stationary charged objects. AB A B BA
Approach to Jamming in an Air-Fluidized Granular Bed
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Department of Physics Papers Department of Physics 9-25-26 Approach to Jamming in an Air-Fluidized Granular Bed Adam Ross Abate University of Pennsylvania, aabate@physics.upenn.edu
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Department of Physics Papers Department of Physics 9-25-26 Approach to Jamming in an Air-Fluidized Granular Bed Adam Ross Abate University of Pennsylvania, aabate@physics.upenn.edu
Nonconservative Abelian sandpile model with the Bak-Tang-Wiesenfeld toppling rule
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 62, NUMBER 6 DECEMBER 2000 Nonconservative Abelian sandpile model with the Bak-Tang-Wiesenfeld toppling rule Alexei Vázquez 1,2 1 Abdus Salam International Center for Theoretical
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 62, NUMBER 6 DECEMBER 2000 Nonconservative Abelian sandpile model with the Bak-Tang-Wiesenfeld toppling rule Alexei Vázquez 1,2 1 Abdus Salam International Center for Theoretical
CURRICULUM MAP. Course/Subject: Honors Math I Grade: 10 Teacher: Davis. Month: September (19 instructional days)
 Month: September (19 instructional days) Numbers, Number Systems and Number Relationships Standard 2.1.11.A: Use operations (e.g., opposite, reciprocal, absolute value, raising to a power, finding roots,
Month: September (19 instructional days) Numbers, Number Systems and Number Relationships Standard 2.1.11.A: Use operations (e.g., opposite, reciprocal, absolute value, raising to a power, finding roots,
From time series to superstatistics
 From time series to superstatistics Christian Beck School of Mathematical Sciences, Queen Mary, University of London, Mile End Road, London E 4NS, United Kingdom Ezechiel G. D. Cohen The Rockefeller University,
From time series to superstatistics Christian Beck School of Mathematical Sciences, Queen Mary, University of London, Mile End Road, London E 4NS, United Kingdom Ezechiel G. D. Cohen The Rockefeller University,
Mechanisms for slow strengthening in granular materials
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 61, NUMBER 4 APRIL 2000 Mechanisms for slow strengthening in granular materials W. Losert, 1 J.-C. Géminard, 1,2 S. Nasuno, 1,3 and J. P. Gollub 1,4 1 Physics Department, Haverford
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 61, NUMBER 4 APRIL 2000 Mechanisms for slow strengthening in granular materials W. Losert, 1 J.-C. Géminard, 1,2 S. Nasuno, 1,3 and J. P. Gollub 1,4 1 Physics Department, Haverford
Solving the Schrödinger equation for the Sherrington Kirkpatrick model in a transverse field
 J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 30 (1997) L41 L47. Printed in the UK PII: S0305-4470(97)79383-1 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Solving the Schrödinger equation for the Sherrington Kirkpatrick model in a transverse field
J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 30 (1997) L41 L47. Printed in the UK PII: S0305-4470(97)79383-1 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Solving the Schrödinger equation for the Sherrington Kirkpatrick model in a transverse field
Universality class of triad dynamics on a triangular lattice
 Universality class of triad dynamics on a triangular lattice Filippo Radicchi,* Daniele Vilone, and Hildegard Meyer-Ortmanns School of Engineering and Science, International University Bremen, P. O. Box
Universality class of triad dynamics on a triangular lattice Filippo Radicchi,* Daniele Vilone, and Hildegard Meyer-Ortmanns School of Engineering and Science, International University Bremen, P. O. Box
Local Anisotropy In Globally Isotropic Granular Packings. Kamran Karimi Craig E Maloney
 Local Anisotropy In Globally Isotropic Granular Packings Kamran Karimi Craig E Maloney Granular Materials 2 A Granular Material Is A Conglomeration Of Discrete Solid, Natural Macroscopic Particles Characterized
Local Anisotropy In Globally Isotropic Granular Packings Kamran Karimi Craig E Maloney Granular Materials 2 A Granular Material Is A Conglomeration Of Discrete Solid, Natural Macroscopic Particles Characterized
Analyzing f, f, and f Solutions
 Analyzing f, f, and f Solutions We have intentionally included more material than can be covered in most Student Study Sessions to account for groups that are able to answer the questions at a faster rate.
Analyzing f, f, and f Solutions We have intentionally included more material than can be covered in most Student Study Sessions to account for groups that are able to answer the questions at a faster rate.
Microstructure Evolution during Impact on Granular Matter
 Microstructure Evolution during Impact on Granular Matter L. Kondic 1, X. Fang 1, W. Losert 2, C. S. O Hern 3, and R.P. Behringer 4 1 Department of Mathematical Sciences, New Jersey Institute of Technology,
Microstructure Evolution during Impact on Granular Matter L. Kondic 1, X. Fang 1, W. Losert 2, C. S. O Hern 3, and R.P. Behringer 4 1 Department of Mathematical Sciences, New Jersey Institute of Technology,
A B C D. Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment
 Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
cooperative motion in sheared granular matter Takahiro Hatano
 cooperative motion in sheared granular matter Takahiro Hatano (Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo) amorphous particulate systems: structure? 2D granular matter close to jamming spontaneous
cooperative motion in sheared granular matter Takahiro Hatano (Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo) amorphous particulate systems: structure? 2D granular matter close to jamming spontaneous
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 7 Nov 2012
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 7 Nov 2012 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 7 Nov 2012](/thumbs/96/127079609.jpg) Spin torque switching in perpendicular films at finite temperature, HP-13 Ru Zhu and P B Visscher arxiv:12111665v1 [cond-matmtrl-sci] 7 Nov 212 MINT Center and Department of Physics and Astronomy University
Spin torque switching in perpendicular films at finite temperature, HP-13 Ru Zhu and P B Visscher arxiv:12111665v1 [cond-matmtrl-sci] 7 Nov 212 MINT Center and Department of Physics and Astronomy University
Effects of horizontal vibration on hopper flows of granular materials
 PHYSICS OF FLUIDS VOLUME 11, NUMBER 1 JANUARY 1999 Effects of horizontal vibration on hopper flows of granular materials M. L. Hunt, R. C. Weathers, A. T. Lee, and C. E. Brennen Division of Engineering
PHYSICS OF FLUIDS VOLUME 11, NUMBER 1 JANUARY 1999 Effects of horizontal vibration on hopper flows of granular materials M. L. Hunt, R. C. Weathers, A. T. Lee, and C. E. Brennen Division of Engineering
Femtosecond laser-tissue interactions. G. Fibich. University of California, Los Angeles, Department of Mathematics ABSTRACT
 Femtosecond laser-tissue interactions G. Fibich University of California, Los Angeles, Department of Mathematics Los-Angeles, CA 90095 ABSTRACT Time dispersion plays an important role in the propagation
Femtosecond laser-tissue interactions G. Fibich University of California, Los Angeles, Department of Mathematics Los-Angeles, CA 90095 ABSTRACT Time dispersion plays an important role in the propagation
Fluctuations in shear-jammed states: A statistical ensemble approach
 May 2013 EPL, 2 (2013) 34002 doi:.1209/029-07/2/34002 www.epljournal.org Fluctuations in shear-jammed states: A statistical ensemble approach Dapeng Bi 1, Jie Zhang 2,R.P.Behringer 3 and Bulbul Chakraborty
May 2013 EPL, 2 (2013) 34002 doi:.1209/029-07/2/34002 www.epljournal.org Fluctuations in shear-jammed states: A statistical ensemble approach Dapeng Bi 1, Jie Zhang 2,R.P.Behringer 3 and Bulbul Chakraborty
Random close packing revisited: Ways to pack frictionless disks
 Random close packing revisited: Ways to pack frictionless disks Ning Xu, 1 Jerzy Blawzdziewicz, 1 and Corey S. O Hern 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut
Random close packing revisited: Ways to pack frictionless disks Ning Xu, 1 Jerzy Blawzdziewicz, 1 and Corey S. O Hern 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut
Mathematics: Pre-Algebra Eight
 Mathematics: Pre-Algebra Eight Students in 8 th Grade Pre-Algebra will study expressions and equations using one or two unknown values. Students will be introduced to the concept of a mathematical function
Mathematics: Pre-Algebra Eight Students in 8 th Grade Pre-Algebra will study expressions and equations using one or two unknown values. Students will be introduced to the concept of a mathematical function
1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle.
 Master 8.17 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 8.1 Properties of Tangents to a Circle 1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle. 2. Point O is the centre of the circle. Points
Master 8.17 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 8.1 Properties of Tangents to a Circle 1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle. 2. Point O is the centre of the circle. Points
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 80, Experimental demonstration of nonuniform frequency distributions of granular packings
 Experimental demonstration of nonuniform frequency distributions of granular pacings Guo-Jie Gao, 1 Jerzy Blawzdziewicz, 1,2 Corey S. O Hern, 1,2 and Mar Shattuc 3 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Experimental demonstration of nonuniform frequency distributions of granular pacings Guo-Jie Gao, 1 Jerzy Blawzdziewicz, 1,2 Corey S. O Hern, 1,2 and Mar Shattuc 3 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
3 Flow properties of bulk solids
 3 Flow properties of bulk solids The flow properties of bulk solids depend on many parameters, e.g.: particle size distribution, particle shape, chemical composition of the particles, moisture, temperature.
3 Flow properties of bulk solids The flow properties of bulk solids depend on many parameters, e.g.: particle size distribution, particle shape, chemical composition of the particles, moisture, temperature.
Numerical modeling of sliding contact
 Numerical modeling of sliding contact J.F. Molinari 1) Atomistic modeling of sliding contact; P. Spijker, G. Anciaux 2) Continuum modeling; D. Kammer, V. Yastrebov, P. Spijker pj ICTP/FANAS Conference
Numerical modeling of sliding contact J.F. Molinari 1) Atomistic modeling of sliding contact; P. Spijker, G. Anciaux 2) Continuum modeling; D. Kammer, V. Yastrebov, P. Spijker pj ICTP/FANAS Conference
Phase Transitions in Relaxor Ferroelectrics
 Phase Transitions in Relaxor Ferroelectrics Matthew Delgado December 13, 2005 Abstract This paper covers the properties of relaxor ferroelectrics and considers the transition from the paraelectric state
Phase Transitions in Relaxor Ferroelectrics Matthew Delgado December 13, 2005 Abstract This paper covers the properties of relaxor ferroelectrics and considers the transition from the paraelectric state
Phases of granular segregation in a binary mixture
 Phases of granular segregation in a binary mixture P. M. Reis, 1, * T. Sykes, 2 and T. Mullin 2 1 Laboratoire PMMH (UMR 7636 CNRS-ESPCI-P6-P7), 10 Rue Vauquelin, 75231 Paris, France 2 Manchester Center
Phases of granular segregation in a binary mixture P. M. Reis, 1, * T. Sykes, 2 and T. Mullin 2 1 Laboratoire PMMH (UMR 7636 CNRS-ESPCI-P6-P7), 10 Rue Vauquelin, 75231 Paris, France 2 Manchester Center
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 18 Dec 2006
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 18 Dec 2006 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 18 Dec 2006](/thumbs/82/86963356.jpg) The Jamming Transition in Granular Systems arxiv:cond-mat/61645v2 [cond-mat.soft] 18 Dec 26 T. S. Majmudar 1, M. Sperl 1, S. Luding 2, R.P. Behringer 1 1 Duke University, Department of Physics, Box 935,
The Jamming Transition in Granular Systems arxiv:cond-mat/61645v2 [cond-mat.soft] 18 Dec 26 T. S. Majmudar 1, M. Sperl 1, S. Luding 2, R.P. Behringer 1 1 Duke University, Department of Physics, Box 935,
Experimentally determined distribution of granular-flow characteristics in collisional bed load transport
 Experimentally determined distribution of granular-flow characteristics in collisional bed load transport Václav Matoušek 1,*, Štěpán Zrostlík 1, Luigi Fraccarollo 2, Anna Prati 2, and Michele Larcher
Experimentally determined distribution of granular-flow characteristics in collisional bed load transport Václav Matoušek 1,*, Štěpán Zrostlík 1, Luigi Fraccarollo 2, Anna Prati 2, and Michele Larcher
The Analysis of the Equilibrium Cluster Structure in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
 American Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 3, 899-904 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajac.2012.312a119 Published Online December 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajac) The Analysis of the Equilibrium
American Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 3, 899-904 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajac.2012.312a119 Published Online December 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajac) The Analysis of the Equilibrium
ACTA PHYSICA DEBRECINA XLVIII, 1 (2014) EMERGENCE OF ENERGY DEPENDENCE IN THE FRAGMENTATION OF HETEROGENEOUS MATERIALS. Abstract
 ACTA PHYSICA DEBRECINA XLVIII, 1 (2014) EMERGENCE OF ENERGY DEPENDENCE IN THE FRAGMENTATION OF HETEROGENEOUS MATERIALS Gergő Pál 1, Imre Varga 2, and Ferenc Kun 1 1 Department of Theoretical Physics, University
ACTA PHYSICA DEBRECINA XLVIII, 1 (2014) EMERGENCE OF ENERGY DEPENDENCE IN THE FRAGMENTATION OF HETEROGENEOUS MATERIALS Gergő Pál 1, Imre Varga 2, and Ferenc Kun 1 1 Department of Theoretical Physics, University
Anomalous Behavior of a Liquid-Particle System with Horizontal Vibration
 Original Paper Forma, 17, 339 347, 2002 Anomalous Behavior of a Liquid-Particle System with Horizontal Vibration Yusaku NAGATA, Akihiro KAWAKITA and Ryuji TAKAKI* Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology,
Original Paper Forma, 17, 339 347, 2002 Anomalous Behavior of a Liquid-Particle System with Horizontal Vibration Yusaku NAGATA, Akihiro KAWAKITA and Ryuji TAKAKI* Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology,
Math Review ECON 300: Spring 2014 Benjamin A. Jones MATH/CALCULUS REVIEW
 MATH/CALCULUS REVIEW SLOPE, INTERCEPT, and GRAPHS REVIEW (adapted from Paul s Online Math Notes) Let s start with some basic review material to make sure everybody is on the same page. The slope of a line
MATH/CALCULUS REVIEW SLOPE, INTERCEPT, and GRAPHS REVIEW (adapted from Paul s Online Math Notes) Let s start with some basic review material to make sure everybody is on the same page. The slope of a line
Table of Contents. Preface... xiii
 Preface... xiii PART I. ELEMENTS IN FLUID MECHANICS... 1 Chapter 1. Local Equations of Fluid Mechanics... 3 1.1. Forces, stress tensor, and pressure... 4 1.2. Navier Stokes equations in Cartesian coordinates...
Preface... xiii PART I. ELEMENTS IN FLUID MECHANICS... 1 Chapter 1. Local Equations of Fluid Mechanics... 3 1.1. Forces, stress tensor, and pressure... 4 1.2. Navier Stokes equations in Cartesian coordinates...
PHY 221 Lab 9 Work and Energy
 PHY 221 Lab 9 Work and Energy Name: Partners: Before coming to lab, please read this packet and do the prelab on page 13 of this handout. Goals: While F = ma may be one of the most important equations
PHY 221 Lab 9 Work and Energy Name: Partners: Before coming to lab, please read this packet and do the prelab on page 13 of this handout. Goals: While F = ma may be one of the most important equations
Hydraulic properties of porous media
 PART 5 Hydraulic properties of porous media Porosity Definition: Void space: n V void /V total total porosity e V void /V solid Primary porosity - between grains Secondary porosity - fracture or solution
PART 5 Hydraulic properties of porous media Porosity Definition: Void space: n V void /V total total porosity e V void /V solid Primary porosity - between grains Secondary porosity - fracture or solution
Discrete particle analysis of 2D pulsating fluidized bed. T. Kawaguchi, A. Miyoshi, T. Tanaka, Y. Tsuji
 Discrete particle analysis of 2D pulsating fluidized bed T. Kawaguchi, A. Miyoshi, T. Tanaka, Y. Tsuji Department of Mechanical Engineering, Osaka University, Yamada-Oka 2-, Suita, Osaka, 565-087, Japan
Discrete particle analysis of 2D pulsating fluidized bed T. Kawaguchi, A. Miyoshi, T. Tanaka, Y. Tsuji Department of Mechanical Engineering, Osaka University, Yamada-Oka 2-, Suita, Osaka, 565-087, Japan
Frequency distribution of mechanically stable disk packings
 Frequency distribution of mechanically stable disk packings Guo-Jie Gao, 1 Jerzy Bławzdziewicz, 1 and Corey S. O Hern 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut
Frequency distribution of mechanically stable disk packings Guo-Jie Gao, 1 Jerzy Bławzdziewicz, 1 and Corey S. O Hern 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut
PERCOLATION AND COARSE CONFORMAL UNIFORMIZATION. 1. Introduction
 PERCOLATION AND COARSE CONFORMAL UNIFORMIZATION ITAI BENJAMINI Abstract. We formulate conjectures regarding percolation on planar triangulations suggested by assuming (quasi) invariance under coarse conformal
PERCOLATION AND COARSE CONFORMAL UNIFORMIZATION ITAI BENJAMINI Abstract. We formulate conjectures regarding percolation on planar triangulations suggested by assuming (quasi) invariance under coarse conformal
arxiv:nlin/ v1 [nlin.cd] 29 Jan 2004
![arxiv:nlin/ v1 [nlin.cd] 29 Jan 2004 arxiv:nlin/ v1 [nlin.cd] 29 Jan 2004](/thumbs/74/70747676.jpg) Clusterization and intermittency of temperature fluctuations in turbulent convection A. Bershadskii 1,2, J.J. Niemela 1, A. Praskovsky 3 and K.R. Sreenivasan 1 1 International Center for Theoretical Physics,
Clusterization and intermittency of temperature fluctuations in turbulent convection A. Bershadskii 1,2, J.J. Niemela 1, A. Praskovsky 3 and K.R. Sreenivasan 1 1 International Center for Theoretical Physics,
The response of an idealized granular material to an incremental shear strain
 The response of an idealized granular material to an incremental shear strain Luigi La Ragione and Vanessa Magnanimo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Ambientale, Politecnico di Bari, Italy E-mail: l.laragione@poliba.it;
The response of an idealized granular material to an incremental shear strain Luigi La Ragione and Vanessa Magnanimo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Ambientale, Politecnico di Bari, Italy E-mail: l.laragione@poliba.it;
Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers CHAPTER 2. Nature of Materials
 Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers CHAPTER 2 Nature of Materials Bonds 1. Primary Bond: forms when atoms interchange or share electrons in order to fill the outer (valence) shells like noble
Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers CHAPTER 2 Nature of Materials Bonds 1. Primary Bond: forms when atoms interchange or share electrons in order to fill the outer (valence) shells like noble
Fluidisational velocity, resistance of permeable material layer
 Fluidisational velocity, resistance of permeable material layer Fluidisation is a process whereby a granular material is converted from a static solidlike state to a dynamic fluid-like state. This process
Fluidisational velocity, resistance of permeable material layer Fluidisation is a process whereby a granular material is converted from a static solidlike state to a dynamic fluid-like state. This process
8. The graph below shows a beetle s movement along a plant stem.
 Name: Block: Date: Introductory Physics: Midyear Review 1. Motion and Forces Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. 1.1 Compare and contrast
Name: Block: Date: Introductory Physics: Midyear Review 1. Motion and Forces Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. 1.1 Compare and contrast
Application of Discrete Element Method to Study Mechanical Behaviors of Ceramic Breeder Pebble Beds. Zhiyong An, Alice Ying, and Mohamed Abdou UCLA
 Application of Discrete Element Method to Study Mechanical Behaviors of Ceramic Breeder Pebble Beds Zhiyong An, Alice Ying, and Mohamed Abdou UCLA Presented at CBBI-4 Petten, The Netherlands September
Application of Discrete Element Method to Study Mechanical Behaviors of Ceramic Breeder Pebble Beds Zhiyong An, Alice Ying, and Mohamed Abdou UCLA Presented at CBBI-4 Petten, The Netherlands September
THE PHYSICS OF FOAM. Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics. July 1-26, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter. 1.
 THE PHYSICS OF FOAM Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics July 1-26, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter 1. Introduction Formation Microscopics 2. Structure Experiment Simulation
THE PHYSICS OF FOAM Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics July 1-26, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter 1. Introduction Formation Microscopics 2. Structure Experiment Simulation
Size Segregation in the Brazil Nut Effect
 Size Segregation in the Brazil Nut Effect Aline C. Soterroni and Fernando M. Ramos Applied Computing Program, National Institute for Space Research, São José dos Campos, Brazil Laboratory of Computing
Size Segregation in the Brazil Nut Effect Aline C. Soterroni and Fernando M. Ramos Applied Computing Program, National Institute for Space Research, São José dos Campos, Brazil Laboratory of Computing
