arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.other] 18 Jun 2005
|
|
|
- Charity Blankenship
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 How to distinguish between stick-slip and arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.other] 18 Jun 2005 pure slip oscillations J.Szkutnik, K.Ku lakowski Faculty of Physics and Applied Computer Science, AGH University of Science and Technology, al. Mickiewicza 30, Cracow, Poland Corresponding author. Abstract Numerical simulations are performed for the stick-slip motion in the Burridge- Knopoff model of one block. Calculated amplitude increases with the driving velocity. We argue that this effect can be a criterion to distinguish between the stick-slip and pure slip oscillations. PACS: Qp, a, x Keywords: friction, simulations 1 Introduction Understanding and control of frictional properties of matter remains a challenge for a wide spectrum of sciences [1]. In particular, physical effects which appear in the low velocity regime are of interest [2,3,4,5]. While details of rubbing surfaces depend on mechanical properties of the probing system [6], our understanding of these detail is to be built up from simple models. Here we concentrate on the simplest version of the Burridge-Knopoff model [7,8] of one block, connected with a spring to a driving mechanism moving with a constant velocity v 0. The block moves on a substrate under forces of spring and friction. The core of the problem is the friction force F dependence of the velocity v. As it was recognized by multiple authors, the origin of the instability of the uniform motion is that F(v) decreases at least near v = 0. This remains true for a chain of any number of blocks [9]. Preprint submitted to Elsevier Science 2 March 2017
2 We note that a more detailed model of friction is known [10,2] includes the d ependence of the friction force on the age of contact. This approach, known as Rice-Ruina model from names of its authors, has some shortcomings; in its simplest form it does not reproduce stable orbits. An argument, somewhat lengthy, was presented by us in Ref. [11]. However, more strong theorem can be proved very briefly, basing on the Dulac criterion [12]. The proof is shown in the Appendix. Here we are interested in the stable orbits, then we work with the Burridge-Knopoff model. It is often assumed that the only alternative for the uniform motion is the stick-slip motion, where the block periodically switches from motion to rest and motion again. However, as it was recently demonstrated within an analytical approximation, within some range of the driving velocity the stick phase disappears, but still the uniform motion is not stable [13]. The motion was termed pure-slip oscillations. The stick-slip, pure slip and uniform motion are then three distinct possibilities, one succeeding another when the velocity v 0 increases. From the results of Ref. [13], a criterion can be derived to distinguish stick-slip and pure slip phases. The amplitude of the oscillations increases with the driving velocity v 0 for the stick-slip phase and it decreases for the pure slip phase. In a recent report [14], oscillations of motion of a PMMA polymer sample scratched by a conical diamond intender were measured as dependent on the driving velocity and normal load. The amplitude and period of oscillations are found to decrease with the driving velocity. A question appears, if the oscillations are of stick-slip or pure slip kind? The range of velocities, which are of order of µm/s, do not allow to observe the stick effect directly. We note that in another experiment with PMMA ([15], Fig.5), the amplitude of the oscillations increases with the velocity. On the other hand, one could argue that the validity of analytical calculations in Ref.[13] is limited by the assumed shape of the function F(v), which was a polynomial function of third order. The aim of this paper is to provide new argument in this discussion by numerical calculations, for the shape of the function F(v) other than in Ref. [13]. After Ref. [9], we assume this function to be proportional to (1+av) 1. Alternatively we add a linear term bv to the same function, to reproduce the transition from the stick-slip to the uniform motion. However, here we are interested only in the stick-slip phase. The goal is to check if the amplitude of 2
3 the oscillations increases or decreases with the driving velocity v 0. In the next section we present the assumed equations of motion, the model parameters and the numerical results. Conclusions which can be derived from these results are presented in Section III. The text is closed by the above remarked Appendix on the Rice-Ruina model. 2 The model and the results For two versions of the formula for the friction force F i (v), i = 1,2, the equation of motion is mẍ = k(x v 0 t) F i (ẋ) (1) where m and x are the block mass and the block position, k is the spring constant, v 0 t is the position of the driving mechanism, F 1 (v) = µ 0 W/(1+av), F 2 = F 1 + bv, and µ 0 W = F i (0) is the static friction force. This equation is equivalent to a dimensionless equation ü = ντ u 1 pu (2) 1+cu where τ = k kx t, u =, ν = βv m µ 0 W 0, β = km, ẋ = dx µ 0, c = a/β and p = b/β. W dτ Thisversion, controlledby two (F = F 1 )orthree(f = F 2 )parameters, isused for the numerical calculations. The values of the parameters can be reproduced at least partially from the experimental data [14]. The normal load W = 196 mn, the velocity v 0 is from 5 to 1000 µm/s. From the fitting of the results to the time dependence of the spring force (Fig. 2 in Ref. [14]) we can get µ 0 = 0.46, a = 160 s/m and k = 62 N/m. The sample mass is about 1 g, but it is certainly much less that the mass m of the movable part of the setup, which cannot be deduced from the content of Ref. [14]. It seems reasonable to evaluate its order of magnitude to be about 1000 g. In Fig. 1 we show the time dependence of the spring force. This is to be compared with Fig. 2 of Ref. [14]. The accordance is good. This plot proves only that the fit is successful. However, the calculated velocity dependence of the amplitude of the spring force is entirely different from the experimental data. Both the curve obtained 3
4 F=k(vt-x) (mn) t(s) Fig. 1. Calculated time dependence of the spring force. The range of force is taken as the amplitude. The results are to be compared with Fig. 2 in Ref. [14]. for b = 0 and the experimental points are shown in Fig. 2. Other calculated curves are the driving velocity dependence of the period of oscillations and the period and amplitude dependences on the normal load. These curves agree with the experimental data in the sense that they increase or decrease in the same way as in experiment. More detailed comparison is difficult, because we do not know the parameters: the mass m and the coefficients a and b. However, the results of the simulations make clear that the calculated amplitude increases with the driving velocity. The only exception is when the mass is very small, less than 1 g, but even in this case the obtained dependence is very weak and incomparable with the experimental data. In the same Fig. 2 we show also the data for p = This value is small enough to keep the range of the driving velocity in the stick-slip regime. However, our qualitative conclusions remain unchanged. Acomparison ofourresults withtheexperimental dataofref.[15]canbeonly qualitative. The experimental setup is different from a simple block plus spring. However, some quantities are analogous to the previous case. For example, the spring constant is substituted by an elastic constant of the PMMA sample. On the other hand, numerical value of the coefficient β remains unknown. The value of a is about 250 s/m [15]. The coefficient b is set to zero. In Fig.3 we show the amplitude dependence on the driving velocity for three values of β: the same asinref. [14] (β = 42 s/m), 158 s/mand418s/m. The amplitude is in arbitrary units. For all investigated cases (three shown plus several others) the amplitude either remains constant or increases with v 0. The increase of 4
5 the experimental results of Ref. [15] can be reproduced for β = 158 s/m. The vertical scale of each curve depends on the coefficient µ 0 W. 3 Conclusions Summarizing the experimental data[14,15], we are faced with two experiments with opposite behaviour of the amplitude of the oscillations with the driving velocity. In the case of Ref. [14], the amplitude decreases about two times when the velocity increases by two orders of magnitude. In the case of Ref. [15], it increases about two times when the velocity increases by one order of magnitude. This qualitative difference of behaviour calls for an explanation with qualitatively different mechanisms. We postulate a solution that the dependence of the amplitude on the driving velocity, as calculated in Ref. [13], should be treated as a criterion to distinguish between the stick-slip and pure slip oscillations. With this criterion, the data of Ref. [14] should be assigned to pure slip oscillations, and the data of Ref. [15] - to the stick-slip phase. Acknowledgements The authors are grateful to Tristan Baumberger, Piotr Grabowski and Wojciech S lomczyński for helpful discussions and remarks. Appendix The equations of motion in the Rice-Ruina model are k W (v 0t x) = µ 0 +Bln Φ Φ 0 +Aln ẋ V r (3) Φ = 1 ẋφ D 0 (4) where x v 0 t is the block position with respect to the driving mechanism, v 0 is the driving velocity, k is the spring constant, W is the normal force, µ 0 is a reference value of the friction coefficient for steady sliding at some velocity V r. During sliding, the microcontacts are refreshed, on average, after a distance D 0. The state of these microcontacts is described by the variable Φ, which interpolates between the time of stick for the block sticked and D 0 /v 0 for 5
6 steady sliding. Finally, Φ 0 = D 0 /V r and A, B are unitless material constants. We note that B > A in the experimental data [16]. The equations can be transformed to an autonomous form. Denoting (x v 0 t)/d 0 = α, Φ/Φ 0 = φ, V r t/d 0 = τ, V/V r = ω, exp( µ 0 /A) = γ, KD 0 /W = κ, we get dimensionless equations κ α = ω +γφ B A exp[ α] (5) A κ φ = 1 γφ 1 B A exp[ α] (6) A where the time derivative is over τ. To apply the Dulac criterion [12], we need an auxiliary function g(α,φ); here the simplest g = 1 is sufficient. The divergence is (B A κ) γ κ A φ B A exp[ α] (7) A and it is different from zero except at the transition point from the uniform to the stick-slip motion. Then, there is no periodic orbits if B A κ 0. References [1] Socoliuc A, Bennewitz R, Gnecco E, Meyer E. Transition from stick-slip to continuous sliding in atomic friction: entering a new regime of ultralow friction. Phys Rev Lett 2004; 92 (13): [2] Heslot F, Baumberger T, Perrin B, Caroli B, Caroli C. Creep, stick-slip, and dry-friction dynamics: Experiments and a heuristic model. Phys Rev E 1994; 49 (6): [3] Braun O M, Dauxois T, Peyrard M. Friction in a thin commensurate contact. Phys Rev B 1997; 56 (8): [4] Albert R, Pfeifer M A, Barabási A-L, Schiffer P. Slow drag in a granular medium. Phys Rev Lett 1999; 82 (1): [5] Krylov S Yu, Jinesh K B, Valk H, Dienwiebel M, Frenken J W M. Thermally induced suppression of friction at the atomic scale. Phys Rev E 2005; 71 (6):
7 [6] Rozman M G, Urbakh M, Klafter J. Controlling chaotic frictional forces. Phys. Rev. E 1998; 57 (6): [7] Burridge R, Knopoff L. Model and theoretical seismicity. Bull Sei Soc Am 1967; 57 (3): [8] Carlson J M, Langer J S. Properties of earthquakes generated by fault dynamics. Phys Rev Lett 1989; 62 (22): [9] de Sousa Vieira M. Chaos in a simple spring-block system. Phys Lett A 1995; 198 (5-6): [10] Rice J R, Ruina A L. Stability of steady frictional slipping. J Appl Mech 1983; 50: [11] Szkutnik J, Ku lakowski K. Transition from Uniform Motion to Stick-Slip in the Rice-Ruina Model of One and Two Blocks. 17-th Marian Smoluchowski Symposium on Statistical Physics, Fundamentals and Applications, Zakopane, Poland, September 4-9, 2004 (nlin.si/ ). [12] Glendinning P. Stability, Instability and Chaos: an Introduction to the Theory of Nonlinear Differential Equations. Cambridge; Cambridge UP [13] Thomsen J J, Fidlin A. Analytical approximations for stick-slip vibrations amplitude. J Non-Linear Mech 2003; 38 (3): [14] Zhang S L, Valentine J M. Stick-slip and temperature effect on the scratching of materials. Tribology Letters 2002; 12 (4): [15] Briscoe B J, Chateauminois A, Chiu J, Vickery V. Acoustic noise emission in a model PMMA/steel fretting contact. In : Dalmaz D, et al., editors. Tribology Research: From Model Experiments to Industrial Problem. Tribology Series, 39. Elsevier, 2001, p [16] Baumberger T, Caroli C, Perrin B, Ronsin O. Nonlinear analysis of the stickslip bifurcation in the creep-controlled regime of dry friction. Phys Rev E 1995; 51 (5):
8 100 Amplitude (mn) v 0 (µm/s) Fig. 2. Amplitude of the friction force as dependent on the driving velocity v 0. Calculations are performed for b = 0 (solid line) and b = 100 s/m (dotted line). Experimental points are taken from Fig. 4 in Ref. [14]. 1 Amplitude (a. u.) v 0 (µm/s) Fig. 3. Amplitude of the friction force as dependent on the driving velocity v 0. Calculations are performed for b = 0 and three different values of β, from 42 s/m (highest curve) till 418 s/m (lowest curve). Experimental points are taken from Fig. 4 in Ref. [15]. 8
arxiv:nlin/ v1 [nlin.cd] 6 Aug 2004
![arxiv:nlin/ v1 [nlin.cd] 6 Aug 2004 arxiv:nlin/ v1 [nlin.cd] 6 Aug 2004](/thumbs/88/115435834.jpg) Complex dynamics in a one block model for earthquakes arxiv:nlin/0408016v1 [nlin.cd] 6 Aug 2004 Abstract Raúl Montagne and G. L. Vasconcelos Laboratório de Física Teórica e Computacional, Departamento
Complex dynamics in a one block model for earthquakes arxiv:nlin/0408016v1 [nlin.cd] 6 Aug 2004 Abstract Raúl Montagne and G. L. Vasconcelos Laboratório de Física Teórica e Computacional, Departamento
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Mar 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Mar 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Mar 2004](/thumbs/92/108548732.jpg) A Simple Model for Sheared Granular Layers Akira Furukawa and Hisao Hayakawa arxiv:cond-mat/0403529v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Mar 2004 Department of Physics, Graduateschool of Science, Kyoto University, Kyoto
A Simple Model for Sheared Granular Layers Akira Furukawa and Hisao Hayakawa arxiv:cond-mat/0403529v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Mar 2004 Department of Physics, Graduateschool of Science, Kyoto University, Kyoto
Nonsmooth dynamics of friction in modeling of earthquakes. Vladimir Ryabov Future University-Hakodate, Japan
 Nonsmooth dynamics of friction in modeling of earthquakes Vladimir Ryabov Future University-Hakodate, Japan Earthquakes are caused by friction between tectonic plates From: http://seismo.berkeley.edu/
Nonsmooth dynamics of friction in modeling of earthquakes Vladimir Ryabov Future University-Hakodate, Japan Earthquakes are caused by friction between tectonic plates From: http://seismo.berkeley.edu/
Experiments for Stick-Slip Motions in One-dimensional Mass-Spring Systems
 Letter Forma, 20, 39 46, 2005 Experiments for Stick-Slip Motions in One-dimensional Mass-Spring Systems Takayuki HIGUCHI, Hideaki KURIHARA and Osamu HIRAYAMA* Institute of Symbiotic Science and Technology,
Letter Forma, 20, 39 46, 2005 Experiments for Stick-Slip Motions in One-dimensional Mass-Spring Systems Takayuki HIGUCHI, Hideaki KURIHARA and Osamu HIRAYAMA* Institute of Symbiotic Science and Technology,
Nonlinear dynamics of dry friction
 J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 30 (1997) 6057 6063. Printed in the UK PII: S0305-4470(97)79385-5 Nonlinear dynamics of dry friction Franz-Josef Elmer Institut für Physik, Universität Basel, CH-4056 Basel, Switzerland
J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 30 (1997) 6057 6063. Printed in the UK PII: S0305-4470(97)79385-5 Nonlinear dynamics of dry friction Franz-Josef Elmer Institut für Physik, Universität Basel, CH-4056 Basel, Switzerland
Origin of stick-slip motion in a driven two-wave potential
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 54, NUMBER 6 DECEMBER 1996 Origin of stick-slip motion in a driven two-wave potential M. G. Rozman * NORDITA, Blegdamsvej 17, DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark M. Urbakh and J. Klafter
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 54, NUMBER 6 DECEMBER 1996 Origin of stick-slip motion in a driven two-wave potential M. G. Rozman * NORDITA, Blegdamsvej 17, DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark M. Urbakh and J. Klafter
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 18 Mar 2003
 Hysteresis loop of a nanoscopic magnetic array A. Kaczanowski, K. Malarz and K. Ku lakowski arxiv:cond-mat/3333v1 18 Mar 23 Department of Applied Computer Science, Faculty of Physics and Nuclear Techniques,
Hysteresis loop of a nanoscopic magnetic array A. Kaczanowski, K. Malarz and K. Ku lakowski arxiv:cond-mat/3333v1 18 Mar 23 Department of Applied Computer Science, Faculty of Physics and Nuclear Techniques,
Existence and Stability Analysis of Spring-Block Model Solutions with Rate and State Friction
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 36, 1785-1795 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com Existence and Stability Analysis of Spring-Block Model Solutions with Rate and State Friction Kodwo Annan Department
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 36, 1785-1795 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com Existence and Stability Analysis of Spring-Block Model Solutions with Rate and State Friction Kodwo Annan Department
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 9, 21 Sep. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Rate and State Friction Velocity step test to measure RSF parameters SHS test to measure RSF parameters
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 9, 21 Sep. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Rate and State Friction Velocity step test to measure RSF parameters SHS test to measure RSF parameters
TIME-DELAY IN SPRING-BLOCK MODEL FOR APERIODICITY IN EARTHQUAKES
 TIME-DELAY IN SPRING-BLOCK MODEL FOR APERIODICITY IN EARTHQUAKES S Kostic & N Vasovic University of Belgrade Faculty of Mining and Geology, Serbia I Franovic University of Belgrade Faculty of Physics,
TIME-DELAY IN SPRING-BLOCK MODEL FOR APERIODICITY IN EARTHQUAKES S Kostic & N Vasovic University of Belgrade Faculty of Mining and Geology, Serbia I Franovic University of Belgrade Faculty of Physics,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 4 Aug 1998
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 4 Aug 1998 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 4 Aug 1998](/thumbs/88/115379805.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/98646v2 [cond-mat.soft] 4 Aug 1998 Transition to Centrifugal Particle Motion in Rotating Drums Gerald H. Ristow Fachbereich Physik, Philipps Universität Renthof 6, D 3532 Marburg, Germany
arxiv:cond-mat/98646v2 [cond-mat.soft] 4 Aug 1998 Transition to Centrifugal Particle Motion in Rotating Drums Gerald H. Ristow Fachbereich Physik, Philipps Universität Renthof 6, D 3532 Marburg, Germany
Sliding Friction in the Frenkel-Kontorova Model
 arxiv:cond-mat/9510058v1 12 Oct 1995 to appear in "The Physics of Sliding Friction", Ed. B.N.J. Persson (Kluwer Academic Publishers), 1995 Sliding Friction in the Frenkel-Kontorova Model E. Granato I.N.P.E.,
arxiv:cond-mat/9510058v1 12 Oct 1995 to appear in "The Physics of Sliding Friction", Ed. B.N.J. Persson (Kluwer Academic Publishers), 1995 Sliding Friction in the Frenkel-Kontorova Model E. Granato I.N.P.E.,
Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities
 Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities Strasbourg, 15 Nov. 2007 François Renard LGCA, CNRS-OSUG, University of Grenoble, France PGP, University of Oslo, Norway Collaborators:
Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities Strasbourg, 15 Nov. 2007 François Renard LGCA, CNRS-OSUG, University of Grenoble, France PGP, University of Oslo, Norway Collaborators:
An improved brake squeal source model in the presence of kinematic and friction nonlinearities
 An improved brake squeal source model in the presence of kinematic and friction nonlinearities Osman Taha Sen, Jason T. Dreyer, and Rajendra Singh 3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Istanbul Technical
An improved brake squeal source model in the presence of kinematic and friction nonlinearities Osman Taha Sen, Jason T. Dreyer, and Rajendra Singh 3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Istanbul Technical
How to count trees? arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 7 Apr 2005
![How to count trees? arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 7 Apr 2005 How to count trees? arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 7 Apr 2005](/thumbs/93/111803874.jpg) How to count trees? arxiv:cond-mat/0501594v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 7 Apr 2005 Sebastian Piec, Krzysztof Malarz and Krzysztof Ku lakowski AGH University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Physics and
How to count trees? arxiv:cond-mat/0501594v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 7 Apr 2005 Sebastian Piec, Krzysztof Malarz and Krzysztof Ku lakowski AGH University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Physics and
Modeling friction on a mesoscale: Master equation for the earthquake-like model.
 Modeling friction on a mesoscale: Master equation for the earthquake-like model. Oleg Braun, Michel Peyrard To cite this version: Oleg Braun, Michel Peyrard. Modeling friction on a mesoscale: Master equation
Modeling friction on a mesoscale: Master equation for the earthquake-like model. Oleg Braun, Michel Peyrard To cite this version: Oleg Braun, Michel Peyrard. Modeling friction on a mesoscale: Master equation
FRICTION FORCE FOR BOUNDARY LUBRICATION
 Nanomaterials: Applications and Properties (NAP-11). Vol. 1, Part I 7 FRICTION FORCE FOR BOUNDARY LUBRICATION Iakov A. Lyashenko * Sumy State University, R-Korsakov, 47, Sumy, Ukraine ABSTRACT A thermodynamic
Nanomaterials: Applications and Properties (NAP-11). Vol. 1, Part I 7 FRICTION FORCE FOR BOUNDARY LUBRICATION Iakov A. Lyashenko * Sumy State University, R-Korsakov, 47, Sumy, Ukraine ABSTRACT A thermodynamic
The Stick-Slip Vibration and Bifurcation of a Vibro-Impact System with Dry Friction
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 308 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2014, 8, 308-313 Open Access The Stick-Slip Vibration and Bifurcation of a Vibro-Impact System with Dry
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 308 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2014, 8, 308-313 Open Access The Stick-Slip Vibration and Bifurcation of a Vibro-Impact System with Dry
Bifurcations from steady sliding to stick slip in boundary lubrication
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 57, NUMBER 5 MAY 1998 Bifurcations from steady sliding to stick slip in boundary lubrication A. A. Batista and J. M. Carlson Department of Physics, University of California, Santa
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 57, NUMBER 5 MAY 1998 Bifurcations from steady sliding to stick slip in boundary lubrication A. A. Batista and J. M. Carlson Department of Physics, University of California, Santa
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics
 Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
Bifurcation of Sound Waves in a Disturbed Fluid
 American Journal of Modern Physics 7; 6(5: 9-95 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajmp doi:.68/j.ajmp.765.3 ISSN: 36-8867 (Print; ISSN: 36-889 (Online Bifurcation of Sound Waves in a Disturbed Fluid
American Journal of Modern Physics 7; 6(5: 9-95 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajmp doi:.68/j.ajmp.765.3 ISSN: 36-8867 (Print; ISSN: 36-889 (Online Bifurcation of Sound Waves in a Disturbed Fluid
Periodic Skeletons of Nonlinear Dynamical Systems in the Problems of Global Bifurcation Analysis
 Periodic Skeletons of Nonlinear Dynamical Systems in the Problems of Global Bifurcation Analysis M Zakrzhevsky, I Schukin, A Klokov and E Shilvan PERIODIC SKELETONS OF NONLINEAR DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS IN THE
Periodic Skeletons of Nonlinear Dynamical Systems in the Problems of Global Bifurcation Analysis M Zakrzhevsky, I Schukin, A Klokov and E Shilvan PERIODIC SKELETONS OF NONLINEAR DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS IN THE
Friction of F-actin knots
 Friction of F-actin knots Helmut O. Kirchner a, Sebastien Neukirch b a INM Leibniz Institute for New Materials Campus D, D-6613 Saarbrücken, Germany b CNS & UPMC Univ Paris 06 UM 7190, Institut Jean Le
Friction of F-actin knots Helmut O. Kirchner a, Sebastien Neukirch b a INM Leibniz Institute for New Materials Campus D, D-6613 Saarbrücken, Germany b CNS & UPMC Univ Paris 06 UM 7190, Institut Jean Le
GEL ELECTROPHORESIS OF DNA NEW MEASUREMENTS AND THE REPTON MODEL AT HIGH FIELDS
 Vol. 36 (2005) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA B No 5 GEL ELECTROPHORESIS OF DNA NEW MEASUREMENTS AND THE REPTON MODEL AT HIGH FIELDS M.J. Krawczyk, P. Paściak, A. Dydejczyk, K. Kułakowski Faculty of Physics and
Vol. 36 (2005) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA B No 5 GEL ELECTROPHORESIS OF DNA NEW MEASUREMENTS AND THE REPTON MODEL AT HIGH FIELDS M.J. Krawczyk, P. Paściak, A. Dydejczyk, K. Kułakowski Faculty of Physics and
Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law
 Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law Naoyuki Kato (1), Kazuro Hirahara (2) and Mikio Iizuka (3) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University
Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law Naoyuki Kato (1), Kazuro Hirahara (2) and Mikio Iizuka (3) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 5 Jun 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 5 Jun 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 5 Jun 2004](/thumbs/74/70280953.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0406141v1 [cond-mat.other] 5 Jun 2004 Moving Beyond a Simple Model of Luminescence Rings in Quantum Well Structures D. Snoke 1, S. Denev 1, Y. Liu 1, S. Simon 2, R. Rapaport 2, G. Chen 2,
arxiv:cond-mat/0406141v1 [cond-mat.other] 5 Jun 2004 Moving Beyond a Simple Model of Luminescence Rings in Quantum Well Structures D. Snoke 1, S. Denev 1, Y. Liu 1, S. Simon 2, R. Rapaport 2, G. Chen 2,
The problem of singularity in impacting systems
 The problem of singularity in impacting systems Soumitro Banerjee, Department of Physics Indian Institute of Science Education & Research, Kolkata, India The problem of singularity in impacting systems
The problem of singularity in impacting systems Soumitro Banerjee, Department of Physics Indian Institute of Science Education & Research, Kolkata, India The problem of singularity in impacting systems
Experimental investigation of micro-chaos
 Experimental investigation of micro-chaos Gergely Gyebrószki Gábor Csernák Csaba Budai Department of Applied Mechanics Budapest University of Technology and Economics Budapest Hungary MTA-BME Research
Experimental investigation of micro-chaos Gergely Gyebrószki Gábor Csernák Csaba Budai Department of Applied Mechanics Budapest University of Technology and Economics Budapest Hungary MTA-BME Research
Chaos Control of the Chaotic Symmetric Gyroscope System
 48 Chaos Control of the Chaotic Symmetric Gyroscope System * Barış CEVHER, Yılmaz UYAROĞLU and 3 Selçuk EMIROĞLU,,3 Faculty of Engineering, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Sakarya
48 Chaos Control of the Chaotic Symmetric Gyroscope System * Barış CEVHER, Yılmaz UYAROĞLU and 3 Selçuk EMIROĞLU,,3 Faculty of Engineering, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Sakarya
Synchronization of Limit Cycle Oscillators by Telegraph Noise. arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Aug 2014
![Synchronization of Limit Cycle Oscillators by Telegraph Noise. arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Aug 2014 Synchronization of Limit Cycle Oscillators by Telegraph Noise. arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Aug 2014](/thumbs/73/69324282.jpg) Synchronization of Limit Cycle Oscillators by Telegraph Noise Denis S. Goldobin arxiv:148.135v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Aug 214 Department of Physics, University of Potsdam, Postfach 61553, D-14415 Potsdam,
Synchronization of Limit Cycle Oscillators by Telegraph Noise Denis S. Goldobin arxiv:148.135v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Aug 214 Department of Physics, University of Potsdam, Postfach 61553, D-14415 Potsdam,
Derivation of border-collision maps from limit cycle bifurcations
 Derivation of border-collision maps from limit cycle bifurcations Alan Champneys Department of Engineering Mathematics, University of Bristol Mario di Bernardo, Chris Budd, Piotr Kowalczyk Gabor Licsko,...
Derivation of border-collision maps from limit cycle bifurcations Alan Champneys Department of Engineering Mathematics, University of Bristol Mario di Bernardo, Chris Budd, Piotr Kowalczyk Gabor Licsko,...
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (212) 189, 1797 186 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-246X.212.5464.x A new paradigm for simulating pulse-like ruptures: the pulse energy equation Ahmed E. Elbanna 1
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (212) 189, 1797 186 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-246X.212.5464.x A new paradigm for simulating pulse-like ruptures: the pulse energy equation Ahmed E. Elbanna 1
Problem Set Number 01, MIT (Winter-Spring 2018)
 Problem Set Number 01, 18.377 MIT (Winter-Spring 2018) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., room 2-337, Cambridge, MA 02139) February 28, 2018 Due Thursday, March 8, 2018. Turn it in (by 3PM) at the Math.
Problem Set Number 01, 18.377 MIT (Winter-Spring 2018) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept., room 2-337, Cambridge, MA 02139) February 28, 2018 Due Thursday, March 8, 2018. Turn it in (by 3PM) at the Math.
Derivation of Table 2 in Okada (1992)
 Derivation of Table 2 in Okada (1992) [ I ] Derivation of Eqs.(4) through (6) Eq.(1) of Okada (1992) can be rewritten, where is the displacement at due to a j-th direction single force of unit magnitude
Derivation of Table 2 in Okada (1992) [ I ] Derivation of Eqs.(4) through (6) Eq.(1) of Okada (1992) can be rewritten, where is the displacement at due to a j-th direction single force of unit magnitude
Tribology in Industry. Some Aspects Concerning the Behaviour of Friction Materials at Low and Very Low Sliding Speeds
 RESEARCH Vol. 37, No. 3 (2015) 374-379 Tribology in Industry www.tribology.fink.rs Some Aspects Concerning the Behaviour of Friction Materials at Low and Very Low Sliding Speeds N.A. Stoica a, A. Tudor
RESEARCH Vol. 37, No. 3 (2015) 374-379 Tribology in Industry www.tribology.fink.rs Some Aspects Concerning the Behaviour of Friction Materials at Low and Very Low Sliding Speeds N.A. Stoica a, A. Tudor
Hopf Bifurcation Analysis and Approximation of Limit Cycle in Coupled Van Der Pol and Duffing Oscillators
 The Open Acoustics Journal 8 9-3 9 Open Access Hopf ifurcation Analysis and Approximation of Limit Cycle in Coupled Van Der Pol and Duffing Oscillators Jianping Cai *a and Jianhe Shen b a Department of
The Open Acoustics Journal 8 9-3 9 Open Access Hopf ifurcation Analysis and Approximation of Limit Cycle in Coupled Van Der Pol and Duffing Oscillators Jianping Cai *a and Jianhe Shen b a Department of
DYNAMICS OF ELASTIC EXCITABLE MEDIA
 International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vol. 9, No. 11 (1999) 2197 2202 c World Scientific Publishing Company DYNAMICS OF ELASTIC EXCITABLE MEDIA JULYAN H. E. CARTWRIGHT Instituto Andaluz de Ciencias
International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vol. 9, No. 11 (1999) 2197 2202 c World Scientific Publishing Company DYNAMICS OF ELASTIC EXCITABLE MEDIA JULYAN H. E. CARTWRIGHT Instituto Andaluz de Ciencias
Superlubricity on the nanometer scale
 Friction 2(2): 106 113 (2014) ISSN 2223-7690 DOI 10.1007/s40544-014-0052-4 CN 10-1237/TH REVIEW ARTICLE Superlubricity on the nanometer scale Ernst MEYER 1,*, Enrico GNECCO 2 1 Department of Physics, University
Friction 2(2): 106 113 (2014) ISSN 2223-7690 DOI 10.1007/s40544-014-0052-4 CN 10-1237/TH REVIEW ARTICLE Superlubricity on the nanometer scale Ernst MEYER 1,*, Enrico GNECCO 2 1 Department of Physics, University
Molecular dynamics simulations of sliding friction in a dense granular material
 Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 6 (998) 7 77. Printed in the UK PII: S965-393(98)9635- Molecular dynamics simulations of sliding friction in a dense granular material T Matthey and J P Hansen Department
Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 6 (998) 7 77. Printed in the UK PII: S965-393(98)9635- Molecular dynamics simulations of sliding friction in a dense granular material T Matthey and J P Hansen Department
The dynamics of a nonautonomous oscillator with friction memory
 The dynamics of a nonautonomous oscillator with friction memory L. A. Igumnov 1, V. S. Metrikin 2, M. V. Zaytzev 3 1, 2 Research Institute for mechanics, National Research Lobachevsky State University
The dynamics of a nonautonomous oscillator with friction memory L. A. Igumnov 1, V. S. Metrikin 2, M. V. Zaytzev 3 1, 2 Research Institute for mechanics, National Research Lobachevsky State University
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Mar 1997
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Mar 1997 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Mar 1997](/thumbs/89/98058524.jpg) Light scattering from a periodically modulated two dimensional arxiv:cond-mat/9703119v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Mar 1997 electron gas with partially filled Landau levels Arne Brataas 1 and C. Zhang 2 and
Light scattering from a periodically modulated two dimensional arxiv:cond-mat/9703119v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Mar 1997 electron gas with partially filled Landau levels Arne Brataas 1 and C. Zhang 2 and
Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors
 Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors Chris Marone, The Pennsylvania State University John Leeman, Marco Scuderi, Elisa Tinti, Cristiano
Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors Chris Marone, The Pennsylvania State University John Leeman, Marco Scuderi, Elisa Tinti, Cristiano
Transition from smooth sliding to stick-slip motion in a single frictional contact
 Transition from smooth sliding to stick-slip motion in a single frictional contact O. M. Braun* Institute of Physics, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, 03028 Kiev, Ukraine M. Peyrard Laboratoire
Transition from smooth sliding to stick-slip motion in a single frictional contact O. M. Braun* Institute of Physics, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, 03028 Kiev, Ukraine M. Peyrard Laboratoire
Dynamics of Non-Smooth Systems
 Dynamics of Non-Smooth Systems P Chandramouli Indian Institute of Technology Madras October 5, 2013 Mouli, IIT Madras Non-Smooth System Dynamics 1/39 Introduction Filippov Systems Behaviour around hyper-surface
Dynamics of Non-Smooth Systems P Chandramouli Indian Institute of Technology Madras October 5, 2013 Mouli, IIT Madras Non-Smooth System Dynamics 1/39 Introduction Filippov Systems Behaviour around hyper-surface
FRICTIONAL BEHAVIOUR OF THE INTERFACE IN SiC MONOFILAMENT MODEL COMPOSITES WITH BOROSILICATE GLASS MATRIX
 FRICTIONAL BEHAVIOUR OF THE INTERFACE IN SiC MONOFILAMENT MODEL COMPOSITES WITH BOROSILICATE GLASS MATRIX H. Cherouali, N. Louet, P. Reynaud and D. Rouby Groupe d Etudes de Métallurgie Physique et de Physique
FRICTIONAL BEHAVIOUR OF THE INTERFACE IN SiC MONOFILAMENT MODEL COMPOSITES WITH BOROSILICATE GLASS MATRIX H. Cherouali, N. Louet, P. Reynaud and D. Rouby Groupe d Etudes de Métallurgie Physique et de Physique
Analytical Approaches for Friction Induced Vibration and Stability Analysis
 Approaches for Friction Induced Vibration and Stability Analysis Anooshiravan FarshidianFar a, Mehrdad Noei Aghaee a Mechanical Engineering Department, Ferdowsi University, Azadi Square, P.O. Box: 91775-1111,
Approaches for Friction Induced Vibration and Stability Analysis Anooshiravan FarshidianFar a, Mehrdad Noei Aghaee a Mechanical Engineering Department, Ferdowsi University, Azadi Square, P.O. Box: 91775-1111,
Phase Desynchronization as a Mechanism for Transitions to High-Dimensional Chaos
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 35 (2001) pp. 682 688 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 35, No. 6, June 15, 2001 Phase Desynchronization as a Mechanism for Transitions to High-Dimensional
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 35 (2001) pp. 682 688 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 35, No. 6, June 15, 2001 Phase Desynchronization as a Mechanism for Transitions to High-Dimensional
A review of friction laws and their application for simulation of microseismicity prior to hydraulic fracturing
 A review of friction laws and their application for simulation of microseismicity prior to hydraulic fracturing Jiyang Ye, Mirko Van Der Baan (Email: jiyang1@ualberta.ca, Mirko.VanderBaan@ualberta.ca)
A review of friction laws and their application for simulation of microseismicity prior to hydraulic fracturing Jiyang Ye, Mirko Van Der Baan (Email: jiyang1@ualberta.ca, Mirko.VanderBaan@ualberta.ca)
Dynamical behaviour of a controlled vibro-impact system
 Vol 17 No 7, July 2008 c 2008 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1674-1056/2008/17(07)/2446-05 Chinese Physics B and IOP Publishing Ltd Dynamical behaviour of a controlled vibro-impact system Wang Liang( ), Xu Wei( ), and
Vol 17 No 7, July 2008 c 2008 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1674-1056/2008/17(07)/2446-05 Chinese Physics B and IOP Publishing Ltd Dynamical behaviour of a controlled vibro-impact system Wang Liang( ), Xu Wei( ), and
Introduction to structural dynamics
 Introduction to structural dynamics p n m n u n p n-1 p 3... m n-1 m 3... u n-1 u 3 k 1 c 1 u 1 u 2 k 2 m p 1 1 c 2 m2 p 2 k n c n m n u n p n m 2 p 2 u 2 m 1 p 1 u 1 Static vs dynamic analysis Static
Introduction to structural dynamics p n m n u n p n-1 p 3... m n-1 m 3... u n-1 u 3 k 1 c 1 u 1 u 2 k 2 m p 1 1 c 2 m2 p 2 k n c n m n u n p n m 2 p 2 u 2 m 1 p 1 u 1 Static vs dynamic analysis Static
The effect of inertia, viscous damping, temperature and normal stress on chaotic behaviour of the rate and state friction model
 J. Earth Syst. Sci. (018) 17:45 c Indian Academy of Sciences https://doi.org/10.1007/s1040-018-0935- The effect of inertia, viscous damping, temperature and normal stress on chaotic behaviour of the rate
J. Earth Syst. Sci. (018) 17:45 c Indian Academy of Sciences https://doi.org/10.1007/s1040-018-0935- The effect of inertia, viscous damping, temperature and normal stress on chaotic behaviour of the rate
Travelling waves. Chapter 8. 1 Introduction
 Chapter 8 Travelling waves 1 Introduction One of the cornerstones in the study of both linear and nonlinear PDEs is the wave propagation. A wave is a recognizable signal which is transferred from one part
Chapter 8 Travelling waves 1 Introduction One of the cornerstones in the study of both linear and nonlinear PDEs is the wave propagation. A wave is a recognizable signal which is transferred from one part
Giacomo Boffi. Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano
 http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano April 21, 2017 Outline of Structural Members Elastic-plastic Idealization
http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano April 21, 2017 Outline of Structural Members Elastic-plastic Idealization
Difference Resonances in a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator involving time. delay
 Difference Resonances in a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator involving time delay This paper was published in the journal Chaos, Solitions & Fractals, vol.4, no., pp.975-98, Oct 9 J.C. Ji, N. Zhang,
Difference Resonances in a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator involving time delay This paper was published in the journal Chaos, Solitions & Fractals, vol.4, no., pp.975-98, Oct 9 J.C. Ji, N. Zhang,
Decay mechanisms of oscillating quartz tuning fork immersed in He II
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Decay mechanisms of oscillating quartz tuning fork immersed in He II To cite this article: I Gritsenko et al 202 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 400 02068 View the article online
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Decay mechanisms of oscillating quartz tuning fork immersed in He II To cite this article: I Gritsenko et al 202 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 400 02068 View the article online
Abstract. We have devised an original laboratory experiment where we investigate
 1 1 Long Term Friction: from Stick-Slip to Stable Sliding 2 3 4 Christophe Voisin 1, François Renard 1,2 and Jean-Robert Grasso 1 1 Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique, CNRS, Observatoire
1 1 Long Term Friction: from Stick-Slip to Stable Sliding 2 3 4 Christophe Voisin 1, François Renard 1,2 and Jean-Robert Grasso 1 1 Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique, CNRS, Observatoire
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law
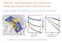 Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Strange dynamics of bilinear oscillator close to grazing
 Strange dynamics of bilinear oscillator close to grazing Ekaterina Pavlovskaia, James Ing, Soumitro Banerjee and Marian Wiercigroch Centre for Applied Dynamics Research, School of Engineering, King s College,
Strange dynamics of bilinear oscillator close to grazing Ekaterina Pavlovskaia, James Ing, Soumitro Banerjee and Marian Wiercigroch Centre for Applied Dynamics Research, School of Engineering, King s College,
TORSION PENDULUM: THE MECHANICAL NONLINEAR OSCILLATOR
 TORSION PENDULUM: THE MECHANICAL NONLINEAR OSCILLATOR Samo Lasič, Gorazd Planinšič,, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics University of Ljubljana, Slovenija Giacomo Torzo, Department of Physics, University
TORSION PENDULUM: THE MECHANICAL NONLINEAR OSCILLATOR Samo Lasič, Gorazd Planinšič,, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics University of Ljubljana, Slovenija Giacomo Torzo, Department of Physics, University
COMPLEX DYNAMICS AND CHAOS CONTROL IN DUFFING-VAN DER POL EQUATION WITH TWO EXTERNAL PERIODIC FORCING TERMS
 International J. of Math. Sci. & Engg. Appls. (IJMSEA) ISSN 0973-9424, Vol. 9 No. III (September, 2015), pp. 197-210 COMPLEX DYNAMICS AND CHAOS CONTROL IN DUFFING-VAN DER POL EQUATION WITH TWO EXTERNAL
International J. of Math. Sci. & Engg. Appls. (IJMSEA) ISSN 0973-9424, Vol. 9 No. III (September, 2015), pp. 197-210 COMPLEX DYNAMICS AND CHAOS CONTROL IN DUFFING-VAN DER POL EQUATION WITH TWO EXTERNAL
Theory of bifurcation amplifiers utilizing the nonlinear dynamical response of an optically damped mechanical oscillator
 Theory of bifurcation amplifiers utilizing the nonlinear dynamical response of an optically damped mechanical oscillator Research on optomechanical systems is of relevance to gravitational wave detection
Theory of bifurcation amplifiers utilizing the nonlinear dynamical response of an optically damped mechanical oscillator Research on optomechanical systems is of relevance to gravitational wave detection
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7)
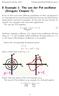 8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
Experimental Validation of Damping Model for a MEMS Bistable Electrostatic Energy Harvester
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series 557 (24) 24 doi:.88/742-6596/557//24 Experimental Validation of Damping Model for a MEMS Bistable Electrostatic Energy Harvester C H Nguyen, D S Nguyen 2 and E Halvorsen
Journal of Physics: Conference Series 557 (24) 24 doi:.88/742-6596/557//24 Experimental Validation of Damping Model for a MEMS Bistable Electrostatic Energy Harvester C H Nguyen, D S Nguyen 2 and E Halvorsen
Using controlling chaos technique to suppress self-modulation in a delayed feedback traveling wave tube oscillator
 Using controlling chaos technique to suppress self-modulation in a delayed feedback traveling wave tube oscillator N.M. Ryskin, O.S. Khavroshin and V.V. Emelyanov Dept. of Nonlinear Physics Saratov State
Using controlling chaos technique to suppress self-modulation in a delayed feedback traveling wave tube oscillator N.M. Ryskin, O.S. Khavroshin and V.V. Emelyanov Dept. of Nonlinear Physics Saratov State
Structural model for the dynamic buckling of a column under constant rate compression
 Structural model for the dynamic buckling of a column under constant rate compression Vitaly A. Kuzkin 1 Institute for Problems in Mechanical Engineering RAS Saint Petersburg Polytechnical University arxiv:1506.0047v
Structural model for the dynamic buckling of a column under constant rate compression Vitaly A. Kuzkin 1 Institute for Problems in Mechanical Engineering RAS Saint Petersburg Polytechnical University arxiv:1506.0047v
friction friction a-b slow fast increases during sliding
 µ increases during sliding faster sliding --> stronger fault --> slows sliding leads to stable slip: no earthquakes can start velocity-strengthening friction slow fast µ velocity-strengthening friction
µ increases during sliding faster sliding --> stronger fault --> slows sliding leads to stable slip: no earthquakes can start velocity-strengthening friction slow fast µ velocity-strengthening friction
Time-Resolved Studies of Stick-Slip Friction in Sheared Granular Layers
 Time-Resolved Studies of Stick-Slip Friction in Sheared Granular Layers S. Nasuno 1,2,*, A. Kudrolli 1,#, A Bak 1, and J.P. Gollub 1,3,+ 1 Physics Department, Haverford College, Haverford PA 19041 and
Time-Resolved Studies of Stick-Slip Friction in Sheared Granular Layers S. Nasuno 1,2,*, A. Kudrolli 1,#, A Bak 1, and J.P. Gollub 1,3,+ 1 Physics Department, Haverford College, Haverford PA 19041 and
Hitoshi Hirose (1), and Kazuro Hirahara (2) Abstract. Introduction
 Three dimensional simulation for the earthquake cycle at a subduction zone based on a rate- and state-dependent friction law: Insight into a finiteness and a variety of dip-slip earthquakes Hitoshi Hirose
Three dimensional simulation for the earthquake cycle at a subduction zone based on a rate- and state-dependent friction law: Insight into a finiteness and a variety of dip-slip earthquakes Hitoshi Hirose
Slow crack growth in polycarbonate films
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 5 July 5 Europhys. Lett., 7 (), pp. 4 48 (5) DOI:.9/epl/i5-77-3 Slow crack growth in polycarbonate films P. P. Cortet, S. Santucci, L. Vanel and S. Ciliberto Laboratoire de Physique,
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 5 July 5 Europhys. Lett., 7 (), pp. 4 48 (5) DOI:.9/epl/i5-77-3 Slow crack growth in polycarbonate films P. P. Cortet, S. Santucci, L. Vanel and S. Ciliberto Laboratoire de Physique,
Simulation study of the one-dimensional Burridge-Knopoff model of earthquakes
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jb003942, 2006 Simulation study of the one-dimensional Burridge-Knopoff model of earthquakes Takahiro Mori 1 and Hikaru Kawamura 1 Received 14
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jb003942, 2006 Simulation study of the one-dimensional Burridge-Knopoff model of earthquakes Takahiro Mori 1 and Hikaru Kawamura 1 Received 14
Development of a test apparatus that consistently generates squeak to rate squeak propensity of a pair of materials
 Development of a test apparatus that consistently generates squeak to rate squeak propensity of a pair of materials Gil Jun LEE 1 ; Jay KIM 2 1, 2 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, University
Development of a test apparatus that consistently generates squeak to rate squeak propensity of a pair of materials Gil Jun LEE 1 ; Jay KIM 2 1, 2 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, University
Friction Drive Simulation of a SAW Motor with Slider Surface Texture Variation
 Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 54 (28) pp 366-371 online at http://www.scientific.net (28) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Online available since 28/Sep/2 Friction Drive Simulation of a SAW
Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 54 (28) pp 366-371 online at http://www.scientific.net (28) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Online available since 28/Sep/2 Friction Drive Simulation of a SAW
Tracking a Harmonic Oscillator using a webcam
 Tracking a Harmonic Oscillator using a webcam Sohaib Shamim, Wasif Zia and Muhammad Sabieh Anwar LUMS School of Science and Engineering September 29, 2017 Version 2017-1 Is there any thing that in this
Tracking a Harmonic Oscillator using a webcam Sohaib Shamim, Wasif Zia and Muhammad Sabieh Anwar LUMS School of Science and Engineering September 29, 2017 Version 2017-1 Is there any thing that in this
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 8 Jan 2004
 Multifractality and nonextensivity at the edge of chaos of unimodal maps E. Mayoral and A. Robledo arxiv:cond-mat/0401128 v1 8 Jan 2004 Instituto de Física, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Apartado
Multifractality and nonextensivity at the edge of chaos of unimodal maps E. Mayoral and A. Robledo arxiv:cond-mat/0401128 v1 8 Jan 2004 Instituto de Física, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Apartado
Application of Reconstruction of Variational Iteration Method on the Laminar Flow in a Porous Cylinder with Regressing Walls
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 21, No. 2 (2017) 379 387 c Lodz University of Technology Application of Reconstruction of Variational Iteration Method on the Laminar Flow in a Porous Cylinder
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 21, No. 2 (2017) 379 387 c Lodz University of Technology Application of Reconstruction of Variational Iteration Method on the Laminar Flow in a Porous Cylinder
Application of Binary Sequences to Problems of Chaos
 Application of Binary Sequences to Problems of Chaos P. Singh, P. Mohr, D.D. Joseph Department of Aerospace Engineering and Mechanics, University of Minnesota 107 Akerman Hall, Minneapolis, M 55455 ABSTRACT
Application of Binary Sequences to Problems of Chaos P. Singh, P. Mohr, D.D. Joseph Department of Aerospace Engineering and Mechanics, University of Minnesota 107 Akerman Hall, Minneapolis, M 55455 ABSTRACT
Complex Dynamic Systems: Qualitative vs Quantitative analysis
 Complex Dynamic Systems: Qualitative vs Quantitative analysis Complex Dynamic Systems Chiara Mocenni Department of Information Engineering and Mathematics University of Siena (mocenni@diism.unisi.it) Dynamic
Complex Dynamic Systems: Qualitative vs Quantitative analysis Complex Dynamic Systems Chiara Mocenni Department of Information Engineering and Mathematics University of Siena (mocenni@diism.unisi.it) Dynamic
Stick-slip motions in the friction force microscope: Effects of tip compliance
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Birck and NCN Publications Birck Nanotechnology Center January 2008 Stick-slip motions in the friction force microscope: Effects of tip compliance William G. Conley Purdue
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Birck and NCN Publications Birck Nanotechnology Center January 2008 Stick-slip motions in the friction force microscope: Effects of tip compliance William G. Conley Purdue
EXPERIMENTS ON THE PFLÜGER COLUMN: FLUTTER FROM FRICTION
 EXPERIMENTS ON THE PFLÜGER COLUMN: FLUTTER FROM FRICTION Davide Bigoni 1, Oleg Kirillov 2, Diego Misseroni 1, Giovanni Noselli 3, Mirko Tommasini 1 1 DICAM, University of Trento, Trento, Italy 2 Russian
EXPERIMENTS ON THE PFLÜGER COLUMN: FLUTTER FROM FRICTION Davide Bigoni 1, Oleg Kirillov 2, Diego Misseroni 1, Giovanni Noselli 3, Mirko Tommasini 1 1 DICAM, University of Trento, Trento, Italy 2 Russian
AXIAL STICK-SLIP LIMIT CYCLING IN DRILL-STRING DYNAMICS WITH DELAY
 ENOC-2005, Eindhoven, Netherlands, 7-12 August 2005 AXIAL STICK-SLIP LIMIT CYCLING IN DRILL-STRING DYNAMICS WITH DELAY Christophe Germay Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University
ENOC-2005, Eindhoven, Netherlands, 7-12 August 2005 AXIAL STICK-SLIP LIMIT CYCLING IN DRILL-STRING DYNAMICS WITH DELAY Christophe Germay Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University
Frictional rheologies have a wide range of applications in engineering
 A liquid-crystal model for friction C. H. A. Cheng, L. H. Kellogg, S. Shkoller, and D. L. Turcotte Departments of Mathematics and Geology, University of California, Davis, CA 95616 ; Contributed by D.
A liquid-crystal model for friction C. H. A. Cheng, L. H. Kellogg, S. Shkoller, and D. L. Turcotte Departments of Mathematics and Geology, University of California, Davis, CA 95616 ; Contributed by D.
Self-Excited Vibration in Hydraulic Ball Check Valve
 Self-Excited Vibration in Hydraulic Ball Check Valve L. Grinis, V. Haslavsky, U. Tzadka Abstract This paper describes an experimental, theoretical model and numerical study of concentrated vortex flow
Self-Excited Vibration in Hydraulic Ball Check Valve L. Grinis, V. Haslavsky, U. Tzadka Abstract This paper describes an experimental, theoretical model and numerical study of concentrated vortex flow
Ordinal Analysis of Time Series
 Ordinal Analysis of Time Series K. Keller, M. Sinn Mathematical Institute, Wallstraße 0, 2552 Lübeck Abstract In order to develop fast and robust methods for extracting qualitative information from non-linear
Ordinal Analysis of Time Series K. Keller, M. Sinn Mathematical Institute, Wallstraße 0, 2552 Lübeck Abstract In order to develop fast and robust methods for extracting qualitative information from non-linear
Friction. Modeling, Identification, & Analysis
 Friction Modeling, Identification, & Analysis Objectives Understand the friction phenomenon as it relates to motion systems. Develop a control-oriented model with appropriate simplifying assumptions for
Friction Modeling, Identification, & Analysis Objectives Understand the friction phenomenon as it relates to motion systems. Develop a control-oriented model with appropriate simplifying assumptions for
Problem Set Number 2, j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014)
 Problem Set Number 2, 18.385j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept.,Cambridge, MA 02139) Due Mon., September 29, 2014. 1 Inverse function problem #01. Statement: Inverse function
Problem Set Number 2, 18.385j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept.,Cambridge, MA 02139) Due Mon., September 29, 2014. 1 Inverse function problem #01. Statement: Inverse function
Experimental and numerical realization of higher order autonomous Van der Pol-Duffing oscillator
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 47, November 2009, pp. 823-827 Experimental and numerical realization of higher order autonomous Van der Pol-Duffing oscillator V Balachandran, * & G Kandiban
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 47, November 2009, pp. 823-827 Experimental and numerical realization of higher order autonomous Van der Pol-Duffing oscillator V Balachandran, * & G Kandiban
Phase transitions in Nowak-Sznajd opinion dynamics
 arxiv:physics/69178v1 [physics.soc-ph] 21 Sep 26 Phase transitions in Nowak-Sznajd opinion dynamics Maciej Wo loszyn, Dietrich Stauffer* and Krzysztof Ku lakowski Faculty of Physics and Applied Computer
arxiv:physics/69178v1 [physics.soc-ph] 21 Sep 26 Phase transitions in Nowak-Sznajd opinion dynamics Maciej Wo loszyn, Dietrich Stauffer* and Krzysztof Ku lakowski Faculty of Physics and Applied Computer
Is Partial Slip Under Transverse Oscillatory Loading a Transient Event?
 Is Partial Slip Under Transverse Oscillatory Loading a Transient Event? Frederick Meyer, 1 Daniel Forchheimer, 2 Arne Langhoff, 1 Diethelm Johannsmann* 1 1 Institute of Physical Chemistry, TU Clausthal,
Is Partial Slip Under Transverse Oscillatory Loading a Transient Event? Frederick Meyer, 1 Daniel Forchheimer, 2 Arne Langhoff, 1 Diethelm Johannsmann* 1 1 Institute of Physical Chemistry, TU Clausthal,
Mechanisms for slow strengthening in granular materials
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 61, NUMBER 4 APRIL 2000 Mechanisms for slow strengthening in granular materials W. Losert, 1 J.-C. Géminard, 1,2 S. Nasuno, 1,3 and J. P. Gollub 1,4 1 Physics Department, Haverford
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 61, NUMBER 4 APRIL 2000 Mechanisms for slow strengthening in granular materials W. Losert, 1 J.-C. Géminard, 1,2 S. Nasuno, 1,3 and J. P. Gollub 1,4 1 Physics Department, Haverford
Chaotic dynamics in shear-thickening surfactant solutions
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 January 1996 Europhys. Lett., 23 (1), pp. 1-5 (1993) arxiv:cond-mat/0012489v2 [cond-mat.soft] 21 Aug 2001 Chaotic dynamics in shear-thickening surfactant solutions Ranjini Bandyopadhyay
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 January 1996 Europhys. Lett., 23 (1), pp. 1-5 (1993) arxiv:cond-mat/0012489v2 [cond-mat.soft] 21 Aug 2001 Chaotic dynamics in shear-thickening surfactant solutions Ranjini Bandyopadhyay
Steady Flow and its Instability of Gravitational Granular Flow
 Steady Flow and its Instability of Gravitational Granular Flow Namiko Mitarai Department of Chemistry and Physics of Condensed Matter, Graduate School of Science, Kyushu University, Japan. A thesis submitted
Steady Flow and its Instability of Gravitational Granular Flow Namiko Mitarai Department of Chemistry and Physics of Condensed Matter, Graduate School of Science, Kyushu University, Japan. A thesis submitted
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PD hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a preprint version which may differ from the publisher's version. or additional information about this
PD hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a preprint version which may differ from the publisher's version. or additional information about this
Influence of friction coefficient on rubbing behavior of oil bearing rotor system
 Influence of friction coefficient on rubbing behavior of oil bearing rotor system Changliang Tang 1, Jinfu ang 2, Dongjiang Han 3, Huan Lei 4, Long Hao 5, Tianyu Zhang 6 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 Institute of Engineering
Influence of friction coefficient on rubbing behavior of oil bearing rotor system Changliang Tang 1, Jinfu ang 2, Dongjiang Han 3, Huan Lei 4, Long Hao 5, Tianyu Zhang 6 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 Institute of Engineering
In this article, we study linear and non-linear stability of the three state variables rate and state
 Nonlin. Processes Geophys. Discuss., doi:0./npg-0-, 0 Published: February 0 c Author(s) 0. CC-BY.0 License. 0 0 Linear and Non-linear Stability Analysis of the Rate and State Friction Model with Three
Nonlin. Processes Geophys. Discuss., doi:0./npg-0-, 0 Published: February 0 c Author(s) 0. CC-BY.0 License. 0 0 Linear and Non-linear Stability Analysis of the Rate and State Friction Model with Three
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ).
 Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
µ=µ 0 + a ln (V/V 0 ) + b ln(v θ/d c ),
 1 Long Term Friction: from Stick-Slip to Stable Sliding Christophe Voisin 1, François Renard 1,2 and Jean-Robert Grasso 1 1LGIT-CNRS-OSUG, Université Joseph Fourier, Grenoble, France 2 Physics of Geological
1 Long Term Friction: from Stick-Slip to Stable Sliding Christophe Voisin 1, François Renard 1,2 and Jean-Robert Grasso 1 1LGIT-CNRS-OSUG, Université Joseph Fourier, Grenoble, France 2 Physics of Geological
Subharmonic Oscillations and Chaos in Dynamic Atomic Force Microscopy
 Subharmonic Oscillations and Chaos in Dynamic Atomic Force Microscopy John H. CANTRELL 1, Sean A. CANTRELL 2 1 NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia 23681, USA 2 NLS Analytics, LLC, Glencoe,
Subharmonic Oscillations and Chaos in Dynamic Atomic Force Microscopy John H. CANTRELL 1, Sean A. CANTRELL 2 1 NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia 23681, USA 2 NLS Analytics, LLC, Glencoe,
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Jun 2010
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Jun 2010 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Jun 2010](/thumbs/81/83040079.jpg) Chaos in Sandpile Models Saman Moghimi-Araghi and Ali Mollabashi Physics department, Sharif University of Technology, P.O. Box 55-96, Tehran, Iran We have investigated the weak chaos exponent to see if
Chaos in Sandpile Models Saman Moghimi-Araghi and Ali Mollabashi Physics department, Sharif University of Technology, P.O. Box 55-96, Tehran, Iran We have investigated the weak chaos exponent to see if
Research Article Water Effects on the First-Order Transition in a Model of Earthquakes
 ISRN Geophysics, Article ID 160378, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/014/160378 Research Article Water Effects on the First-Order Transition in a Model of Earthquakes M.W.Dongmo,L.Y.Kagho,F.B.Pelap,G.B.Tanekou,Y.L.Makenne,andA.Fomethe
ISRN Geophysics, Article ID 160378, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/014/160378 Research Article Water Effects on the First-Order Transition in a Model of Earthquakes M.W.Dongmo,L.Y.Kagho,F.B.Pelap,G.B.Tanekou,Y.L.Makenne,andA.Fomethe
Koivisto, Juha; Illa Tortos, Xavier; Rosti, Jari; Alava, Mikko Line Creep in Paper Peeling
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Koivisto, Juha; Illa Tortos, Xavier;
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Koivisto, Juha; Illa Tortos, Xavier;
