Computation of the Bernstein Coecients on Subdivided. are computed directly from the coecients on the subdivided triangle from the
|
|
|
- Giles Hampton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computation of the Bernstein Coecients on Subdivided riangles Ralf Hungerbuhler Fakultat fur Mathematik und Informatik, Universitat Konstanz, Postfach 5560 D 97, D{78434 Konstanz, Germany Jurgen Garlo (garloff@fh-konstanz.de) Fachbereich Informatik, Fachhochschule Konstanz, Postfach , D{78405 Konstanz, Germany Abstract. We present a procedure for computing the coecients of the expansion of a bivariate polynomial into Bernstein polynomials over subtriangles. hese triangles are generated by partitioning the standard simplex of IR. he coecients are computed directly from the coecients on the subdivided triangle from the preceding subdivision level. his allows a recursive computation of the coecients and facilitates the economical computation of bounds for the range of a bivariate polynomial over a given triangle. Keywords: Range enclosure, Bernstein polynomials, subdivision. Introduction Finding a tight enclosure for the range of a function over a compact set D IR l is a basic problem of interval computations, cf. [5],[6] and the references therein. If the function is a multivariate polynomial and D is a box, there exist several methods, for references cf. [4]. Compared to boxes, simplices allow more exibility since far more general geometries can be treated. In [4] we present a method for computing bounds for the range of a bivariate polynomial p(x; y) n ; 0 a x y with a C over a triangle. his method is based on the expansion of p into Bernstein polynomials. If p has only real coecients the minimum and the maximum of the coecients of this expansion, the so{called Bernstein coecients, provide lower and upper bounds for the range. All rounding errors appearing in the computation of the Bernstein coecients can be taken into account similarly as in [] for the univariate case. In the case Author to whom all correspondence should be directed. c 999 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. veroeffb.tex; /09/999; 7:37; p.
2 that p has complex coecients the convex hull of the Bernstein coecients encloses the range, for details see [4]. Without loss of generality we can assume that the given triangle is the unit triangle n(x; y) IR x; y 0 ^ x + y o since any nonempty triangle can be mapped by an ane transformation onto. he bounds are improved by subdivision. In partitioning we are led by the following useful fact []: When we subdivide a square by successively halving in both coordinate directions and calculate the Bernstein coecients on a generated subsquare then we obtain as a byproduct of the computation the Bernstein coecients on the neighbouring subsquares. his is one of the reasons why we partition into squares and triangles, cf. Figures and 3 in [4]. In this technical note we use the denitions and notations from [4] and present a procedure for computing the Bernstein coecients on the subtriangles and of the triangle t m, t ; : : :; m, m, which are subtriangles generated by subdivision; in the beginning these are the triangle and the subtriangles with vertex sets f(0, ), (, ), (0,)g and f(,0), (,0), (, )g. he Bernstein coecients are computed directly from the Bernstein coecients on the triangle t m. his allows a recursive computation of the Bernstein coecients on the subtriangles and facilitates the economical computation of the bounds for the range of the given polynomial over. In passing we note that the procedure presented in [4] for computing the Bernstein coecients on the four subsquares generated by halving [0; ] [0; ] in both coordinate directions can be generalized to the l{dimensional case. he resulting algorithm is rather technical. he procedure is therefore omitted here and the interested reader is referred to [3].. Main Result In this section we give the procedure for computing the Bernstein coecients on the subtriangles and of a triangle t m. In the following stands for or. PROCEDURE Let m and t f; : : :; m g. Start by setting (0) b ( m t ) for all (; ) I (n) ; veroeffb.tex; /09/999; 7:37; p.
3 3 then for 0; : : :; n (+) (+). ;+ + +; for (; ) I ((n)) ; (; ) I ((n)), (;) (;) (;) ; (n) ;+ + +; 0;+. ;. ; 9 > >; () ; 0; : : :; (n ) ; (). + ; 0; : : :; (n); + +;0. ; 0; : : :; (n); for nally for ;, 0; : : :; n and ; : : :; (n ) (; +) (; ) + (; ) ;+. ; 0; : : :; (n) : heorem he Bernstein coecients on the subtriangles at subdivision level can be obtained by the Procedure from the following relations with (i; j) I (n) 8>< b ij >: 8>< b ij >: (nij;j(ni)) 0 (i) 0j (i;(ni)j) j (nij;i(nj)) i (j) i0 (j;(nj)i) i : First one shows by induction on that 4 u v ;(n) (n); 4 u;v 0 u;v 0 u v if (n i) < j ; if (n i) j ; if (n i) > j ; if (n j) < i ; if (n j) i ; if (n j) > i : b +u;n(+u)(+v) (t m (3) ) ; b n(+u)(+v);+v ( m t ) veroeffb.tex; /09/999; 7:37; p.3
4 4 holds true for all (; ) I ((n)) for 0; : : :; n. hen one proves by induction on ; : : :; (n ) that the following identity is true for all ; and 0; : : :; n (; ) + (;) ;+h ; 0; : : :; (n) : h h 0 (4) We show the statements of the theorem only for the subtriangle and only in the case (n i) < j. he proof for the two remaining cases and for the subtriangle is analogous. o simplify notation, we mark the dependency from and t m of the quantities considered in the sequel by writing m + and m for short. From () and () it follows that for 0; : : :; (n ) (;) (m + ) (m + ) ;(n) (m + ) + ;(n) b +u;n(+u)v (m) u v u;v0 + b +u+;n(+u+)v (m) u v u;v0 + + b +u;n(+u)v (m) ; u v u0 v0 +;(n) (m + ). where the last but one identity follows from (3). Now we apply identity (4) to conclude from this result that j(ni) (j(ni))+ j(ni) jn nij+ u0 h0 nij v0 i(nij) nij v0 (nij;j(ni)) 0 (m + ) h0 j (n i) j (n i) h n i j + u n i j v h i n i j u0 v (nij;) h (m + ) minfu;j(ni)g h0 b h+u;n(h+u)v (m) j (n i) h veroeffb.tex; /09/999; 7:37; p.4
5 n i j + u h i(nij) i u0 b u;nuv (m) i nij v0 u n i j v b u;nuv (m) : o obtain the last but one identity we used the Vandermonde convolution formula, e.g., [7]. Now by Lemma 4. in [4] we can conclude (nij;j(ni)) 0 (m + ) b ij (m + ) : o compute the Bernstein coecients on the subtriangles 5 and by the Procedure requires 6 3 n3 + 4n n additions and the same amount of multiplications (binary shifts). Here we made use of the relations and (0) (0; ) (0) (0; ) for (; ) I (n) for ; : : :; n and 0; : : :; n : hen the cumulated operations count for the procedure for computing the Bernstein coecients on all subsquares and subtriangles lling the unit triangle at subdivision level i for all i ; : : :; m sums up to O(4 m n 3 ) additions and the same amount of multiplications (binary shifts). 3. Numerical Example It was shown in [4] that the convex hull of the Bernstein coecients on all subsquares and subtriangles generated at subdivision level m, denoted by C m, provides an enclosure for the range of p over. Obviously, a tighter enclosure for this range is given by taking the union of the convex hulls of the Bernstein coecients on each subregion at level m, i.e., where C S m rs : conv C 0 m [ S [ C S m rs r ;:::; m s ;:::; m r t ;:::; m C m t ; nb ij (S o mrs ) (n) (i; j) I S ; r ; : : :; m ; veroeffb.tex; /09/999; 7:37; p.5
6 6 and C m t n : conv b ij (t m ) (i; j) I (n) s ; : : :; m r o ; t ; : : :; m : We consider now the polynomial p(x; y) 3: + :i + (:8 + 4i)y + (:5 + i)x + (7 + 8i)xy : Figures and show C 0 m for m ; 4. Already three extreme points of C 0 are sharp, viz. b 00 S a00 p(0; 0) 3: + :i ; b 0 a00 + a 0 p(0; ) :3 + 5:i ; b 0 4 a00 + a 0 p(; 0) 5:6 + :i : y 6 0 Figure. Enclosure C 0 for the range of p over - x he edges connecting 3:+:i with the points :3+5:i and 5:6+:i are part of the range of p and are therefore sharp. Yet the rest of the boundary of C 0 provides a crude approximation of the image of the straight line connecting (0; ) with (; 0). veroeffb.tex; /09/999; 7:37; p.6
7 7 y x Figure. Enclosure C 0 4 for the range of p over he set C4 0 gives a much better approximation of the range of p. For illustration, the convex hulls of the Bernstein coecients which constitute C4 0 are displayed. he convex hulls of the Bernstein coecients on the subsquares are already identical to the respective ranges of p. Acknowledgements Support from the Ministry of Science and Research Baden{Wurttemberg and from the Ministry of Education, Science, Research, and echnology of the Federal Republic of Germany under the contract no is gratefully acknowledged. References. Fischer, H. C., \Range Computations and Applications," in \Contributions to Computer Arithmetic and Self{Validating Numerical Methods," C. Ullrich, Ed., J. C. Baltzer, Amsterdam, pp. 97{, Garlo, J., \he Bernstein Algorithm," Interval Computations, Vol., 993, pp. 54{ Hungerbuhler, R., \Bounds for the Range of a Multivariate Polynomial over riangles (in German)," diploma thesis, Faculty for Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Constance, Constance, Germany, 998. veroeffb.tex; /09/999; 7:37; p.7
8 8 4. Hungerbuhler, R. and Garlo, J., \Bounds for the Range of a Bivariate Polynomial over a riangle," Reliable Computing, Vol. 4, 998, pp. 3{3. 5. Neumaier, A., \Interval Methods for Systems of Equations," Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 990, Chapter. 6. Ratschek, H. and Rokne, J., \Computer Methods for the Range of Functions," Ellis Horwood Ltd., Chichester, Riordan, R., \Combinatorial Identities," Wiley and Sons, New York, 968, p. 8 and p.. veroeffb.tex; /09/999; 7:37; p.8
Investigation of a Subdivision Based Algorithm. for Solving Systems of Polynomial Equations. University of Applied Sciences / FH Konstanz
 to appear in the Proceedings of the 3rd World Congress of Nonlinear Analysts (WCNA 000), Catania, Sicily, Italy, July 9{6, 000, as a series of the Journal of Nonlinear Analysis Investigation of a Subdivision
to appear in the Proceedings of the 3rd World Congress of Nonlinear Analysts (WCNA 000), Catania, Sicily, Italy, July 9{6, 000, as a series of the Journal of Nonlinear Analysis Investigation of a Subdivision
Matrix Methods for the Bernstein Form and Their Application in Global Optimization
 Matrix Methods for the Bernstein Form and Their Application in Global Optimization June, 10 Jihad Titi Jürgen Garloff University of Konstanz Department of Mathematics and Statistics and University of Applied
Matrix Methods for the Bernstein Form and Their Application in Global Optimization June, 10 Jihad Titi Jürgen Garloff University of Konstanz Department of Mathematics and Statistics and University of Applied
The Bernstein Algorithm. Алгоритм Бернштейна
 Interval Computations No 2, 1993 The Bernstein Algorithm Jürgen Garloff We solve the problem of finding an enclosure for the range of a multivariate polynomial over a rectangular region by expanding the
Interval Computations No 2, 1993 The Bernstein Algorithm Jürgen Garloff We solve the problem of finding an enclosure for the range of a multivariate polynomial over a rectangular region by expanding the
A Lower Estimate for Entropy Numbers
 Journal of Approximation Theory 110, 120124 (2001) doi:10.1006jath.2000.3554, available online at http:www.idealibrary.com on A Lower Estimate for Entropy Numbers Thomas Ku hn Fakulta t fu r Mathematik
Journal of Approximation Theory 110, 120124 (2001) doi:10.1006jath.2000.3554, available online at http:www.idealibrary.com on A Lower Estimate for Entropy Numbers Thomas Ku hn Fakulta t fu r Mathematik
Jurgen Garlo. the inequality sign in all components having odd index sum. For these intervals in
 Intervals of Almost Totally Positive Matrices Jurgen Garlo University of Applied Sciences / FH Konstanz, Fachbereich Informatik, Postfach 100543, D-78405 Konstanz, Germany Abstract We consider the class
Intervals of Almost Totally Positive Matrices Jurgen Garlo University of Applied Sciences / FH Konstanz, Fachbereich Informatik, Postfach 100543, D-78405 Konstanz, Germany Abstract We consider the class
Numerical Integration for Multivariable. October Abstract. We consider the numerical integration of functions with point singularities over
 Numerical Integration for Multivariable Functions with Point Singularities Yaun Yang and Kendall E. Atkinson y October 199 Abstract We consider the numerical integration of functions with point singularities
Numerical Integration for Multivariable Functions with Point Singularities Yaun Yang and Kendall E. Atkinson y October 199 Abstract We consider the numerical integration of functions with point singularities
Convergence under Subdivision and Complexity of Polynomial Minimization in the Simplicial Bernstein Basis
 Convergence under Subdivision and Complexity of Polynomial Minimization in the Simplicial Bernstein Basis Richard Leroy IRMAR, University of Rennes 1 richard.leroy@ens-cachan.org Abstract In this article,
Convergence under Subdivision and Complexity of Polynomial Minimization in the Simplicial Bernstein Basis Richard Leroy IRMAR, University of Rennes 1 richard.leroy@ens-cachan.org Abstract In this article,
MULTIPLICITIES OF MONOMIAL IDEALS
 MULTIPLICITIES OF MONOMIAL IDEALS JÜRGEN HERZOG AND HEMA SRINIVASAN Introduction Let S = K[x 1 x n ] be a polynomial ring over a field K with standard grading, I S a graded ideal. The multiplicity of S/I
MULTIPLICITIES OF MONOMIAL IDEALS JÜRGEN HERZOG AND HEMA SRINIVASAN Introduction Let S = K[x 1 x n ] be a polynomial ring over a field K with standard grading, I S a graded ideal. The multiplicity of S/I
Geometric Constructions with Discretized Random Variables
 Geometric Constructions with Discretized Random Variables Hans-Peter Schröcker (hans-peter.schroecker@uibk.ac.at) Institut für Technische Mathematik, Geometrie und Bauinformatik, Universität Innsbruck,
Geometric Constructions with Discretized Random Variables Hans-Peter Schröcker (hans-peter.schroecker@uibk.ac.at) Institut für Technische Mathematik, Geometrie und Bauinformatik, Universität Innsbruck,
c 2009 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics
 SIAM J MATRIX ANAL APPL Vol 30, No 4, pp 1761 1772 c 2009 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics INTERVAL GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION WITH PIVOT TIGHTENING JÜRGEN GARLOFF Abstract We present a method
SIAM J MATRIX ANAL APPL Vol 30, No 4, pp 1761 1772 c 2009 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics INTERVAL GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION WITH PIVOT TIGHTENING JÜRGEN GARLOFF Abstract We present a method
(1.) For any subset P S we denote by L(P ) the abelian group of integral relations between elements of P, i.e. L(P ) := ker Z P! span Z P S S : For ea
 Torsion of dierentials on toric varieties Klaus Altmann Institut fur reine Mathematik, Humboldt-Universitat zu Berlin Ziegelstr. 13a, D-10099 Berlin, Germany. E-mail: altmann@mathematik.hu-berlin.de Abstract
Torsion of dierentials on toric varieties Klaus Altmann Institut fur reine Mathematik, Humboldt-Universitat zu Berlin Ziegelstr. 13a, D-10099 Berlin, Germany. E-mail: altmann@mathematik.hu-berlin.de Abstract
On the equivalence of regularity criteria for triangular and tetrahedral finite element partitions
 Computers and Mathematics with Applications 55 (2008) 2227 2233 www.elsevier.com/locate/camwa On the equivalence of regularity criteria for triangular and tetrahedral finite element partitions Jan Brandts
Computers and Mathematics with Applications 55 (2008) 2227 2233 www.elsevier.com/locate/camwa On the equivalence of regularity criteria for triangular and tetrahedral finite element partitions Jan Brandts
On Vector Product Algebras
 On Vector Product Algebras By Markus Rost. This text contains some remarks on vector product algebras and the graphical techniques. It is partially contained in the diploma thesis of D. Boos and S. Maurer.
On Vector Product Algebras By Markus Rost. This text contains some remarks on vector product algebras and the graphical techniques. It is partially contained in the diploma thesis of D. Boos and S. Maurer.
Technische Universität Ilmenau Institut für Mathematik
 Technische Universität Ilmenau Institut für Mathematik Preprint No. M 0/08 A lower bound on independence in terms of degrees Harant, Jochen August 00 Impressum: Hrsg.: Leiter des Instituts für Mathematik
Technische Universität Ilmenau Institut für Mathematik Preprint No. M 0/08 A lower bound on independence in terms of degrees Harant, Jochen August 00 Impressum: Hrsg.: Leiter des Instituts für Mathematik
Institute of Computer Science. Compact Form of the Hansen-Bliek-Rohn Enclosure
 Institute of Computer Science Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic Compact Form of the Hansen-Bliek-Rohn Enclosure Jiří Rohn http://uivtx.cs.cas.cz/~rohn Technical report No. V-1157 24.03.2012 Pod
Institute of Computer Science Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic Compact Form of the Hansen-Bliek-Rohn Enclosure Jiří Rohn http://uivtx.cs.cas.cz/~rohn Technical report No. V-1157 24.03.2012 Pod
arxiv:math/ v1 [math.co] 13 Jul 2005
![arxiv:math/ v1 [math.co] 13 Jul 2005 arxiv:math/ v1 [math.co] 13 Jul 2005](/thumbs/92/108537535.jpg) A NEW PROOF OF THE REFINED ALTERNATING SIGN MATRIX THEOREM arxiv:math/0507270v1 [math.co] 13 Jul 2005 Ilse Fischer Fakultät für Mathematik, Universität Wien Nordbergstrasse 15, A-1090 Wien, Austria E-mail:
A NEW PROOF OF THE REFINED ALTERNATING SIGN MATRIX THEOREM arxiv:math/0507270v1 [math.co] 13 Jul 2005 Ilse Fischer Fakultät für Mathematik, Universität Wien Nordbergstrasse 15, A-1090 Wien, Austria E-mail:
An Arrangement of Pseudocircles Not Realizable With Circles
 Beiträge zur Algebra und Geometrie Contributions to Algebra and Geometry Volume 46 (2005), No. 2, 351-356. An Arrangement of Pseudocircles Not Realizable With Circles Johann Linhart Ronald Ortner Institut
Beiträge zur Algebra und Geometrie Contributions to Algebra and Geometry Volume 46 (2005), No. 2, 351-356. An Arrangement of Pseudocircles Not Realizable With Circles Johann Linhart Ronald Ortner Institut
Geometric Constructions with Discretized Random Variables
 Geometric Constructions with Discretized Random Variables Hans-Peter Schröcker Johannes Wallner July 2005 We generalize the DEnv (Distribution envelope determination) method for bounding the result of
Geometric Constructions with Discretized Random Variables Hans-Peter Schröcker Johannes Wallner July 2005 We generalize the DEnv (Distribution envelope determination) method for bounding the result of
Constraint propagation for univariate quadratic constraints
 Constraint propagation for univariate quadratic constraints Arnold Neumaier Institut für Mathematik, Universität Wien Strudlhofgasse 4, A-1090 Wien, Austria email: Arnold.Neumaier@univie.ac.at WWW: http://www.mat.univie.ac.at/
Constraint propagation for univariate quadratic constraints Arnold Neumaier Institut für Mathematik, Universität Wien Strudlhofgasse 4, A-1090 Wien, Austria email: Arnold.Neumaier@univie.ac.at WWW: http://www.mat.univie.ac.at/
Fractional and circular 1-defective colorings of outerplanar graphs
 AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 6() (05), Pages Fractional and circular -defective colorings of outerplanar graphs Zuzana Farkasová Roman Soták Institute of Mathematics Faculty of Science,
AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 6() (05), Pages Fractional and circular -defective colorings of outerplanar graphs Zuzana Farkasová Roman Soták Institute of Mathematics Faculty of Science,
EULER-LIKE METHOD FOR THE SIMULTANEOUS INCLUSION OF POLYNOMIAL ZEROS WITH WEIERSTRASS CORRECTION
 EULER-LIKE METHOD FOR THE SIMULTANEOUS INCLUSION OF POLYNOMIAL ZEROS WITH WEIERSTRASS CORRECTION Miodrag S. Petković Faculty of Electronic Engineering, Department of Mathematics P.O. Box 73, 18000 Niš,
EULER-LIKE METHOD FOR THE SIMULTANEOUS INCLUSION OF POLYNOMIAL ZEROS WITH WEIERSTRASS CORRECTION Miodrag S. Petković Faculty of Electronic Engineering, Department of Mathematics P.O. Box 73, 18000 Niš,
Validating an A Priori Enclosure Using. High-Order Taylor Series. George F. Corliss and Robert Rihm. Abstract
 Validating an A Priori Enclosure Using High-Order Taylor Series George F. Corliss and Robert Rihm Abstract We use Taylor series plus an enclosure of the remainder term to validate the existence of a unique
Validating an A Priori Enclosure Using High-Order Taylor Series George F. Corliss and Robert Rihm Abstract We use Taylor series plus an enclosure of the remainder term to validate the existence of a unique
A Characterization of Distance-Regular Graphs with Diameter Three
 Journal of Algebraic Combinatorics 6 (1997), 299 303 c 1997 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. A Characterization of Distance-Regular Graphs with Diameter Three EDWIN R. VAN DAM
Journal of Algebraic Combinatorics 6 (1997), 299 303 c 1997 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. A Characterization of Distance-Regular Graphs with Diameter Three EDWIN R. VAN DAM
MULTIVARIATE BIRKHOFF-LAGRANGE INTERPOLATION SCHEMES AND CARTESIAN SETS OF NODES. 1. Introduction
 Acta Math. Univ. Comenianae Vol. LXXIII, 2(2004), pp. 217 221 217 MULTIVARIATE BIRKHOFF-LAGRANGE INTERPOLATION SCHEMES AND CARTESIAN SETS OF NODES N. CRAINIC Abstract. In this paper we study the relevance
Acta Math. Univ. Comenianae Vol. LXXIII, 2(2004), pp. 217 221 217 MULTIVARIATE BIRKHOFF-LAGRANGE INTERPOLATION SCHEMES AND CARTESIAN SETS OF NODES N. CRAINIC Abstract. In this paper we study the relevance
The local equivalence of two distances between clusterings: the Misclassification Error metric and the χ 2 distance
 The local equivalence of two distances between clusterings: the Misclassification Error metric and the χ 2 distance Marina Meilă University of Washington Department of Statistics Box 354322 Seattle, WA
The local equivalence of two distances between clusterings: the Misclassification Error metric and the χ 2 distance Marina Meilă University of Washington Department of Statistics Box 354322 Seattle, WA
9 Linear Interpolation and Estimation using Interval Analysis
 9 Linear Interpolation and Estimation using Interval Analysis S. M. Markov and E. D. Popova 1 ABSTRACT This chapter considers interpolation and curve tting using generalized polynomials under bounded measurement
9 Linear Interpolation and Estimation using Interval Analysis S. M. Markov and E. D. Popova 1 ABSTRACT This chapter considers interpolation and curve tting using generalized polynomials under bounded measurement
A Study of Numerical Elimination for the Solution of Multivariate Polynomial Systems
 A Study of Numerical Elimination for the Solution of Multivariate Polynomial Systems W Auzinger and H J Stetter Abstract In an earlier paper we had motivated and described am algorithm for the computation
A Study of Numerical Elimination for the Solution of Multivariate Polynomial Systems W Auzinger and H J Stetter Abstract In an earlier paper we had motivated and described am algorithm for the computation
Construction of `Wachspress type' rational basis functions over rectangles
 Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Math. Sci.), Vol. 110, No. 1, February 2000, pp. 69±77. # Printed in India Construction of `Wachspress type' rational basis functions over rectangles P L POWAR and S S RANA Department
Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Math. Sci.), Vol. 110, No. 1, February 2000, pp. 69±77. # Printed in India Construction of `Wachspress type' rational basis functions over rectangles P L POWAR and S S RANA Department
EXISTENCE VERIFICATION FOR SINGULAR ZEROS OF REAL NONLINEAR SYSTEMS
 EXISTENCE VERIFICATION FOR SINGULAR ZEROS OF REAL NONLINEAR SYSTEMS JIANWEI DIAN AND R BAKER KEARFOTT Abstract Traditional computational fixed point theorems, such as the Kantorovich theorem (made rigorous
EXISTENCE VERIFICATION FOR SINGULAR ZEROS OF REAL NONLINEAR SYSTEMS JIANWEI DIAN AND R BAKER KEARFOTT Abstract Traditional computational fixed point theorems, such as the Kantorovich theorem (made rigorous
290 J.M. Carnicer, J.M. Pe~na basis (u 1 ; : : : ; u n ) consisting of minimally supported elements, yet also has a basis (v 1 ; : : : ; v n ) which f
 Numer. Math. 67: 289{301 (1994) Numerische Mathematik c Springer-Verlag 1994 Electronic Edition Least supported bases and local linear independence J.M. Carnicer, J.M. Pe~na? Departamento de Matematica
Numer. Math. 67: 289{301 (1994) Numerische Mathematik c Springer-Verlag 1994 Electronic Edition Least supported bases and local linear independence J.M. Carnicer, J.M. Pe~na? Departamento de Matematica
Nonlinear Means in Geometric Modeling
 Nonlinear Means in Geometric Modeling Michael S. Floater SINTEF P. O. Box 124 Blindern, 0314 Oslo, Norway E-mail: Michael.Floater@math.sintef.no Charles A. Micchelli IBM Corporation T.J. Watson Research
Nonlinear Means in Geometric Modeling Michael S. Floater SINTEF P. O. Box 124 Blindern, 0314 Oslo, Norway E-mail: Michael.Floater@math.sintef.no Charles A. Micchelli IBM Corporation T.J. Watson Research
SPECTRA - a Maple library for solving linear matrix inequalities in exact arithmetic
 SPECTRA - a Maple library for solving linear matrix inequalities in exact arithmetic Didier Henrion Simone Naldi Mohab Safey El Din Version 1.0 of November 5, 2016 Abstract This document briefly describes
SPECTRA - a Maple library for solving linear matrix inequalities in exact arithmetic Didier Henrion Simone Naldi Mohab Safey El Din Version 1.0 of November 5, 2016 Abstract This document briefly describes
Diskrete Mathematik und Optimierung
 Diskrete Mathematik und Optimierung Winfried Hochstättler, Robert Nickel: Joins of Oriented Matroids Technical Report feu-dmo009.07 Contact: winfried.hochstaettler@fernuni-hagen.de robert.nickel@fernuni-hagen.de
Diskrete Mathematik und Optimierung Winfried Hochstättler, Robert Nickel: Joins of Oriented Matroids Technical Report feu-dmo009.07 Contact: winfried.hochstaettler@fernuni-hagen.de robert.nickel@fernuni-hagen.de
ETNA Kent State University
 Electronic Transactions on Numerical Analysis. Volume 37, pp. 166-172, 2010. Copyright 2010,. ISSN 1068-9613. ETNA A GRADIENT RECOVERY OPERATOR BASED ON AN OBLIQUE PROJECTION BISHNU P. LAMICHHANE Abstract.
Electronic Transactions on Numerical Analysis. Volume 37, pp. 166-172, 2010. Copyright 2010,. ISSN 1068-9613. ETNA A GRADIENT RECOVERY OPERATOR BASED ON AN OBLIQUE PROJECTION BISHNU P. LAMICHHANE Abstract.
Solving Global Optimization Problems by Interval Computation
 Solving Global Optimization Problems by Interval Computation Milan Hladík Department of Applied Mathematics, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic, http://kam.mff.cuni.cz/~hladik/
Solving Global Optimization Problems by Interval Computation Milan Hladík Department of Applied Mathematics, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic, http://kam.mff.cuni.cz/~hladik/
Bounding in Multi-Stage. Stochastic Programming. Problems. Olga Fiedler a Andras Prekopa b
 R utcor Research R eport Bounding in Multi-Stage Stochastic Programming Problems Olga Fiedler a Andras Prekopa b RRR 24-95, June 1995 RUTCOR Rutgers Center for Operations Research Rutgers University P.O.
R utcor Research R eport Bounding in Multi-Stage Stochastic Programming Problems Olga Fiedler a Andras Prekopa b RRR 24-95, June 1995 RUTCOR Rutgers Center for Operations Research Rutgers University P.O.
Optimal Fractal Coding is NP-Hard 1
 Optimal Fractal Coding is NP-Hard 1 (Extended Abstract) Matthias Ruhl, Hannes Hartenstein Institut für Informatik, Universität Freiburg Am Flughafen 17, 79110 Freiburg, Germany ruhl,hartenst@informatik.uni-freiburg.de
Optimal Fractal Coding is NP-Hard 1 (Extended Abstract) Matthias Ruhl, Hannes Hartenstein Institut für Informatik, Universität Freiburg Am Flughafen 17, 79110 Freiburg, Germany ruhl,hartenst@informatik.uni-freiburg.de
Bicriterial Delay Management
 Universität Konstanz Bicriterial Delay Management Csaba Megyeri Konstanzer Schriften in Mathematik und Informatik Nr. 198, März 2004 ISSN 1430 3558 c Fachbereich Mathematik und Statistik c Fachbereich
Universität Konstanz Bicriterial Delay Management Csaba Megyeri Konstanzer Schriften in Mathematik und Informatik Nr. 198, März 2004 ISSN 1430 3558 c Fachbereich Mathematik und Statistik c Fachbereich
A PLANAR INTEGRAL SELF-AFFINE TILE WITH CANTOR SET INTERSECTIONS WITH ITS NEIGHBORS
 #A INTEGERS 9 (9), 7-37 A PLANAR INTEGRAL SELF-AFFINE TILE WITH CANTOR SET INTERSECTIONS WITH ITS NEIGHBORS Shu-Juan Duan School of Math. and Computational Sciences, Xiangtan University, Hunan, China jjmmcn@6.com
#A INTEGERS 9 (9), 7-37 A PLANAR INTEGRAL SELF-AFFINE TILE WITH CANTOR SET INTERSECTIONS WITH ITS NEIGHBORS Shu-Juan Duan School of Math. and Computational Sciences, Xiangtan University, Hunan, China jjmmcn@6.com
Edge Isoperimetric Theorems for Integer Point Arrays
 Edge Isoperimetric Theorems for Integer Point Arrays R. Ahlswede, S.L. Bezrukov Universität Bielefeld, Fakultät für Mathematik Postfach 100131, 33501 Bielefeld, Germany Abstract We consider subsets of
Edge Isoperimetric Theorems for Integer Point Arrays R. Ahlswede, S.L. Bezrukov Universität Bielefeld, Fakultät für Mathematik Postfach 100131, 33501 Bielefeld, Germany Abstract We consider subsets of
COINCIDENCE AND THE COLOURING OF MAPS
 COINCIDENCE AND THE COLOURING OF MAPS JAN M. AARTS AND ROBBERT J. FOKKINK ABSTRACT In [8, 6] it was shown that for each k and n such that 2k n, there exists a contractible k-dimensional complex Y and a
COINCIDENCE AND THE COLOURING OF MAPS JAN M. AARTS AND ROBBERT J. FOKKINK ABSTRACT In [8, 6] it was shown that for each k and n such that 2k n, there exists a contractible k-dimensional complex Y and a
ON THE DIAMETER OF THE ATTRACTOR OF AN IFS Serge Dubuc Raouf Hamzaoui Abstract We investigate methods for the evaluation of the diameter of the attrac
 ON THE DIAMETER OF THE ATTRACTOR OF AN IFS Serge Dubuc Raouf Hamzaoui Abstract We investigate methods for the evaluation of the diameter of the attractor of an IFS. We propose an upper bound for the diameter
ON THE DIAMETER OF THE ATTRACTOR OF AN IFS Serge Dubuc Raouf Hamzaoui Abstract We investigate methods for the evaluation of the diameter of the attractor of an IFS. We propose an upper bound for the diameter
A Polytope for a Product of Real Linear Functions in 0/1 Variables
 Don Coppersmith Oktay Günlük Jon Lee Janny Leung A Polytope for a Product of Real Linear Functions in 0/1 Variables Original: 29 September 1999 as IBM Research Report RC21568 Revised version: 30 November
Don Coppersmith Oktay Günlük Jon Lee Janny Leung A Polytope for a Product of Real Linear Functions in 0/1 Variables Original: 29 September 1999 as IBM Research Report RC21568 Revised version: 30 November
Enclosure Methods. G. Alefeld Institut für Angewandte Mathematik Universität Karlsruhe Federal Republic of Germany
 Enclosure Methods G. Alefeld Institut für Angewandte Mathematik Universität Karlsruhe Federal Republic of Germany Abstract: We present an overview on existing methods for inc1uding the range of functions
Enclosure Methods G. Alefeld Institut für Angewandte Mathematik Universität Karlsruhe Federal Republic of Germany Abstract: We present an overview on existing methods for inc1uding the range of functions
An Introduction to Tropical Geometry
 An Introduction to Tropical Geometry Ryan Hart Doenges June 8, 2015 1 Introduction In their paper A Bit of Tropical Geometry [1], Erwan Brugallé and Kristin Shaw present an elementary introduction to the
An Introduction to Tropical Geometry Ryan Hart Doenges June 8, 2015 1 Introduction In their paper A Bit of Tropical Geometry [1], Erwan Brugallé and Kristin Shaw present an elementary introduction to the
Multicommodity Flows and Column Generation
 Lecture Notes Multicommodity Flows and Column Generation Marc Pfetsch Zuse Institute Berlin pfetsch@zib.de last change: 2/8/2006 Technische Universität Berlin Fakultät II, Institut für Mathematik WS 2006/07
Lecture Notes Multicommodity Flows and Column Generation Marc Pfetsch Zuse Institute Berlin pfetsch@zib.de last change: 2/8/2006 Technische Universität Berlin Fakultät II, Institut für Mathematik WS 2006/07
A CONTINUOUS MOVEMENT VERSION OF THE BANACH TARSKI PARADOX: A SOLUTION TO DE GROOT S PROBLEM
 The Journal of Symbolic Logic Volume 70, Number 3, Sept. 2005 A CONTINUOUS MOVEMENT VERSION OF THE BANACH TARSKI PARADOX: A SOLUTION TO DE GROOT S PROBLEM TREVOR M. WILSON Abstract. In 1924 Banach and
The Journal of Symbolic Logic Volume 70, Number 3, Sept. 2005 A CONTINUOUS MOVEMENT VERSION OF THE BANACH TARSKI PARADOX: A SOLUTION TO DE GROOT S PROBLEM TREVOR M. WILSON Abstract. In 1924 Banach and
Convexification and Multimodality of Random Probability Measures
 Convexification and Multimodality of Random Probability Measures George Kokolakis & George Kouvaras Department of Applied Mathematics National Technical University of Athens, Greece Isaac Newton Institute,
Convexification and Multimodality of Random Probability Measures George Kokolakis & George Kouvaras Department of Applied Mathematics National Technical University of Athens, Greece Isaac Newton Institute,
1. Introduction and background. Consider the primal-dual linear programs (LPs)
 SIAM J. OPIM. Vol. 9, No. 1, pp. 207 216 c 1998 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics ON HE DIMENSION OF HE SE OF RIM PERURBAIONS FOR OPIMAL PARIION INVARIANCE HARVEY J. REENBER, ALLEN. HOLDER,
SIAM J. OPIM. Vol. 9, No. 1, pp. 207 216 c 1998 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics ON HE DIMENSION OF HE SE OF RIM PERURBAIONS FOR OPIMAL PARIION INVARIANCE HARVEY J. REENBER, ALLEN. HOLDER,
Extremal Graphs Having No Stable Cutsets
 Extremal Graphs Having No Stable Cutsets Van Bang Le Institut für Informatik Universität Rostock Rostock, Germany le@informatik.uni-rostock.de Florian Pfender Department of Mathematics and Statistics University
Extremal Graphs Having No Stable Cutsets Van Bang Le Institut für Informatik Universität Rostock Rostock, Germany le@informatik.uni-rostock.de Florian Pfender Department of Mathematics and Statistics University
Limit Theorems in Probability and Number
 Limit Theorems in Probability and Number Theory Paderborn, January 14-15, 2011 Limit Theorems in Probability and Number Theory V. V. Buldygin K.-H. Indlekofer O. I. Klesov J. G. Steinebach Limit theorems
Limit Theorems in Probability and Number Theory Paderborn, January 14-15, 2011 Limit Theorems in Probability and Number Theory V. V. Buldygin K.-H. Indlekofer O. I. Klesov J. G. Steinebach Limit theorems
On alternating products of graph relations
 On alternating products of graph relations. Bodendiek Institut f. Mathematik und ihre Didaktik Christian-Albrechts-Universität Kiel.Lang Fachbereich Informatik Universität Hamburg Abstract It is well-known
On alternating products of graph relations. Bodendiek Institut f. Mathematik und ihre Didaktik Christian-Albrechts-Universität Kiel.Lang Fachbereich Informatik Universität Hamburg Abstract It is well-known
THE NUMBER OF SQUARE ISLANDS ON A RECTANGULAR SEA
 THE NUMBER OF SQUARE ISLANDS ON A RECTANGULAR SEA ESZTER K. HORVÁTH, GÁBOR HORVÁTH, ZOLTÁN NÉMETH, AND CSABA SZABÓ Abstract. The aim of the present paper is to carry on the research of Czédli in determining
THE NUMBER OF SQUARE ISLANDS ON A RECTANGULAR SEA ESZTER K. HORVÁTH, GÁBOR HORVÁTH, ZOLTÁN NÉMETH, AND CSABA SZABÓ Abstract. The aim of the present paper is to carry on the research of Czédli in determining
Constructive Proof of the Fan-Glicksberg Fixed Point Theorem for Sequentially Locally Non-constant Multi-functions in a Locally Convex Space
 Constructive Proof of the Fan-Glicksberg Fixed Point Theorem for Sequentially Locally Non-constant Multi-functions in a Locally Convex Space Yasuhito Tanaka, Member, IAENG, Abstract In this paper we constructively
Constructive Proof of the Fan-Glicksberg Fixed Point Theorem for Sequentially Locally Non-constant Multi-functions in a Locally Convex Space Yasuhito Tanaka, Member, IAENG, Abstract In this paper we constructively
arxiv: v1 [math.na] 28 Jun 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.na] 28 Jun 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.na] 28 Jun 2013](/thumbs/73/68618724.jpg) A New Operator and Method for Solving Interval Linear Equations Milan Hladík July 1, 2013 arxiv:13066739v1 [mathna] 28 Jun 2013 Abstract We deal with interval linear systems of equations We present a new
A New Operator and Method for Solving Interval Linear Equations Milan Hladík July 1, 2013 arxiv:13066739v1 [mathna] 28 Jun 2013 Abstract We deal with interval linear systems of equations We present a new
Lucas Polynomials and Power Sums
 Lucas Polynomials and Power Sums Ulrich Tamm Abstract The three term recurrence x n + y n = (x + y (x n + y n xy (x n + y n allows to express x n + y n as a polynomial in the two variables x + y and xy.
Lucas Polynomials and Power Sums Ulrich Tamm Abstract The three term recurrence x n + y n = (x + y (x n + y n xy (x n + y n allows to express x n + y n as a polynomial in the two variables x + y and xy.
The use of predicates to state constraints in Constraint Satisfaction is explained. If, as an
 of Constraint Satisfaction in Integer Programming H.P. Williams Hong Yan Faculty of Mathematical Studies, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK Department of Management, The Hong Kong Polytechnic
of Constraint Satisfaction in Integer Programming H.P. Williams Hong Yan Faculty of Mathematical Studies, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK Department of Management, The Hong Kong Polytechnic
besides your solutions of these problems. 1 1 We note, however, that there will be many factors in the admission decision
 The PRIMES 2015 Math Problem Set Dear PRIMES applicant! This is the PRIMES 2015 Math Problem Set. Please send us your solutions as part of your PRIMES application by December 1, 2015. For complete rules,
The PRIMES 2015 Math Problem Set Dear PRIMES applicant! This is the PRIMES 2015 Math Problem Set. Please send us your solutions as part of your PRIMES application by December 1, 2015. For complete rules,
Note on shortest and nearest lattice vectors
 Note on shortest and nearest lattice vectors Martin Henk Fachbereich Mathematik, Sekr. 6-1 Technische Universität Berlin Straße des 17. Juni 136 D-10623 Berlin Germany henk@math.tu-berlin.de We show that
Note on shortest and nearest lattice vectors Martin Henk Fachbereich Mathematik, Sekr. 6-1 Technische Universität Berlin Straße des 17. Juni 136 D-10623 Berlin Germany henk@math.tu-berlin.de We show that
APPENDIX A. Background Mathematics. A.1 Linear Algebra. Vector algebra. Let x denote the n-dimensional column vector with components x 1 x 2.
 APPENDIX A Background Mathematics A. Linear Algebra A.. Vector algebra Let x denote the n-dimensional column vector with components 0 x x 2 B C @. A x n Definition 6 (scalar product). The scalar product
APPENDIX A Background Mathematics A. Linear Algebra A.. Vector algebra Let x denote the n-dimensional column vector with components 0 x x 2 B C @. A x n Definition 6 (scalar product). The scalar product
Chapter 3 Conforming Finite Element Methods 3.1 Foundations Ritz-Galerkin Method
 Chapter 3 Conforming Finite Element Methods 3.1 Foundations 3.1.1 Ritz-Galerkin Method Let V be a Hilbert space, a(, ) : V V lr a bounded, V-elliptic bilinear form and l : V lr a bounded linear functional.
Chapter 3 Conforming Finite Element Methods 3.1 Foundations 3.1.1 Ritz-Galerkin Method Let V be a Hilbert space, a(, ) : V V lr a bounded, V-elliptic bilinear form and l : V lr a bounded linear functional.
On the mean connected induced subgraph order of cographs
 AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 71(1) (018), Pages 161 183 On the mean connected induced subgraph order of cographs Matthew E Kroeker Lucas Mol Ortrud R Oellermann University of Winnipeg Winnipeg,
AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 71(1) (018), Pages 161 183 On the mean connected induced subgraph order of cographs Matthew E Kroeker Lucas Mol Ortrud R Oellermann University of Winnipeg Winnipeg,
Interval Arithmetic An Elementary Introduction and Successful Applications
 Interval Arithmetic An Elementary Introduction and Successful Applications by R. Baker Kearfott Department of Mathematics University of Southwestern Louisiana U.S.L. Box 4-1010 Lafayette, LA 70504-1010
Interval Arithmetic An Elementary Introduction and Successful Applications by R. Baker Kearfott Department of Mathematics University of Southwestern Louisiana U.S.L. Box 4-1010 Lafayette, LA 70504-1010
Generation of Bode and Nyquist Plots for Nonrational Transfer Functions to Prescribed Accuracy
 Generation of Bode and Nyquist Plots for Nonrational Transfer Functions to Prescribed Accuracy P. S. V. Nataraj 1 and J. J. Barve 2 1 Associate Professor and 2 Research Scholar Systems and Control Engineering
Generation of Bode and Nyquist Plots for Nonrational Transfer Functions to Prescribed Accuracy P. S. V. Nataraj 1 and J. J. Barve 2 1 Associate Professor and 2 Research Scholar Systems and Control Engineering
Conflict-Free Colorings of Rectangles Ranges
 Conflict-Free Colorings of Rectangles Ranges Khaled Elbassioni Nabil H. Mustafa Max-Planck-Institut für Informatik, Saarbrücken, Germany felbassio, nmustafag@mpi-sb.mpg.de Abstract. Given the range space
Conflict-Free Colorings of Rectangles Ranges Khaled Elbassioni Nabil H. Mustafa Max-Planck-Institut für Informatik, Saarbrücken, Germany felbassio, nmustafag@mpi-sb.mpg.de Abstract. Given the range space
Generalized interval arithmetic on compact matrix Lie groups
 myjournal manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Generalized interval arithmetic on compact matrix Lie groups Hermann Schichl, Mihály Csaba Markót, Arnold Neumaier Faculty of Mathematics, University
myjournal manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Generalized interval arithmetic on compact matrix Lie groups Hermann Schichl, Mihály Csaba Markót, Arnold Neumaier Faculty of Mathematics, University
1 Convexity, Convex Relaxations, and Global Optimization
 1 Conveity, Conve Relaations, and Global Optimization Algorithms 1 1.1 Minima Consider the nonlinear optimization problem in a Euclidean space: where the feasible region. min f(), R n Definition (global
1 Conveity, Conve Relaations, and Global Optimization Algorithms 1 1.1 Minima Consider the nonlinear optimization problem in a Euclidean space: where the feasible region. min f(), R n Definition (global
Siegel s theorem, edge coloring, and a holant dichotomy
 Siegel s theorem, edge coloring, and a holant dichotomy Tyson Williams (University of Wisconsin-Madison) Joint with: Jin-Yi Cai and Heng Guo (University of Wisconsin-Madison) Appeared at FOCS 2014 1 /
Siegel s theorem, edge coloring, and a holant dichotomy Tyson Williams (University of Wisconsin-Madison) Joint with: Jin-Yi Cai and Heng Guo (University of Wisconsin-Madison) Appeared at FOCS 2014 1 /
Depth of some square free monomial ideals
 Bull. Math. Soc. Sci. Math. Roumanie Tome 56(104) No. 1, 2013, 117 124 Depth of some square free monomial ideals by Dorin Popescu and Andrei Zarojanu Dedicated to the memory of Nicolae Popescu (1937-2010)
Bull. Math. Soc. Sci. Math. Roumanie Tome 56(104) No. 1, 2013, 117 124 Depth of some square free monomial ideals by Dorin Popescu and Andrei Zarojanu Dedicated to the memory of Nicolae Popescu (1937-2010)
Distinguishing Cartesian powers of graphs
 Distinguishing Cartesian powers of graphs Wilfried Imrich Sandi Klavžar Abstract The distinguishing number D(G) of a graph is the least integer d such that there is a d-labeling of the vertices of G that
Distinguishing Cartesian powers of graphs Wilfried Imrich Sandi Klavžar Abstract The distinguishing number D(G) of a graph is the least integer d such that there is a d-labeling of the vertices of G that
VICTORIA POWERS AND THORSTEN W ORMANN Suppose there exists a real, symmetric, psd matrix B such that f = x B x T and rank t. Since B is real symmetric
 AN ALGORITHM FOR SUMS OF SQUARES OF REAL POLYNOMIALS Victoria Powers and Thorsten Wormann Introduction We present an algorithm to determine if a real polynomial is a sum of squares (of polynomials), and
AN ALGORITHM FOR SUMS OF SQUARES OF REAL POLYNOMIALS Victoria Powers and Thorsten Wormann Introduction We present an algorithm to determine if a real polynomial is a sum of squares (of polynomials), and
A Note on the 2 F 1 Hypergeometric Function
 A Note on the F 1 Hypergeometric Function Armen Bagdasaryan Institution of the Russian Academy of Sciences, V.A. Trapeznikov Institute for Control Sciences 65 Profsoyuznaya, 117997, Moscow, Russia E-mail:
A Note on the F 1 Hypergeometric Function Armen Bagdasaryan Institution of the Russian Academy of Sciences, V.A. Trapeznikov Institute for Control Sciences 65 Profsoyuznaya, 117997, Moscow, Russia E-mail:
On the Chvatál-Complexity of Binary Knapsack Problems. Gergely Kovács 1 Béla Vizvári College for Modern Business Studies, Hungary
 On the Chvatál-Complexity of Binary Knapsack Problems Gergely Kovács 1 Béla Vizvári 2 1 College for Modern Business Studies, Hungary 2 Eastern Mediterranean University, TRNC 2009. 1 Chvátal Cut and Complexity
On the Chvatál-Complexity of Binary Knapsack Problems Gergely Kovács 1 Béla Vizvári 2 1 College for Modern Business Studies, Hungary 2 Eastern Mediterranean University, TRNC 2009. 1 Chvátal Cut and Complexity
Inequalities among quasi-arithmetic means for continuous field of operators
 Filomat 26:5 202, 977 99 DOI 0.2298/FIL205977M Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat Inequalities among quasi-arithmetic
Filomat 26:5 202, 977 99 DOI 0.2298/FIL205977M Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat Inequalities among quasi-arithmetic
Bounded Expected Delay in Arithmetic Coding
 Bounded Expected Delay in Arithmetic Coding Ofer Shayevitz, Ram Zamir, and Meir Feder Tel Aviv University, Dept. of EE-Systems Tel Aviv 69978, Israel Email: {ofersha, zamir, meir }@eng.tau.ac.il arxiv:cs/0604106v1
Bounded Expected Delay in Arithmetic Coding Ofer Shayevitz, Ram Zamir, and Meir Feder Tel Aviv University, Dept. of EE-Systems Tel Aviv 69978, Israel Email: {ofersha, zamir, meir }@eng.tau.ac.il arxiv:cs/0604106v1
Global Optimization by Interval Analysis
 Global Optimization by Interval Analysis Milan Hladík Department of Applied Mathematics, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic, http://kam.mff.cuni.cz/~hladik/
Global Optimization by Interval Analysis Milan Hladík Department of Applied Mathematics, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic, http://kam.mff.cuni.cz/~hladik/
Legendre s Equation. PHYS Southern Illinois University. October 18, 2016
 Legendre s Equation PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University October 18, 2016 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Legendre s Equation October 18, 2016 1 / 11 Legendre s Equation Recall We are trying
Legendre s Equation PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University October 18, 2016 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Legendre s Equation October 18, 2016 1 / 11 Legendre s Equation Recall We are trying
Recursions for the Trapdoor Channel and an Upper Bound on its Capacity
 4 IEEE International Symposium on Information heory Recursions for the rapdoor Channel an Upper Bound on its Capacity obias Lutz Institute for Communications Engineering echnische Universität München Munich,
4 IEEE International Symposium on Information heory Recursions for the rapdoor Channel an Upper Bound on its Capacity obias Lutz Institute for Communications Engineering echnische Universität München Munich,
Generating Functions of Partitions
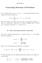 CHAPTER B Generating Functions of Partitions For a complex sequence {α n n 0,, 2, }, its generating function with a complex variable q is defined by A(q) : α n q n α n [q n ] A(q). When the sequence has
CHAPTER B Generating Functions of Partitions For a complex sequence {α n n 0,, 2, }, its generating function with a complex variable q is defined by A(q) : α n q n α n [q n ] A(q). When the sequence has
On the existence of an eigenvalue below the essential spectrum
 On the existence of an eigenvalue below the essential spectrum B.M.Brown, D.K.R.M c Cormack Department of Computer Science, Cardiff University of Wales, Cardiff, PO Box 916, Cardiff CF2 3XF, U.K. A. Zettl
On the existence of an eigenvalue below the essential spectrum B.M.Brown, D.K.R.M c Cormack Department of Computer Science, Cardiff University of Wales, Cardiff, PO Box 916, Cardiff CF2 3XF, U.K. A. Zettl
The Strong Largeur d Arborescence
 The Strong Largeur d Arborescence Rik Steenkamp (5887321) November 12, 2013 Master Thesis Supervisor: prof.dr. Monique Laurent Local Supervisor: prof.dr. Alexander Schrijver KdV Institute for Mathematics
The Strong Largeur d Arborescence Rik Steenkamp (5887321) November 12, 2013 Master Thesis Supervisor: prof.dr. Monique Laurent Local Supervisor: prof.dr. Alexander Schrijver KdV Institute for Mathematics
A better lower bound for quantum algorithms searching an ordered list
 A better lower bound for quantum algorithms searching an ordered list Andris Ambainis Computer Science Division University of California Berkeley, CA 94720, e-mail: ambainis@cs.berkeley.edu Abstract We
A better lower bound for quantum algorithms searching an ordered list Andris Ambainis Computer Science Division University of California Berkeley, CA 94720, e-mail: ambainis@cs.berkeley.edu Abstract We
Solving systems of polynomial equations and minimization of multivariate polynomials
 François Glineur, Polynomial solving & minimization - 1 - First Prev Next Last Full Screen Quit Solving systems of polynomial equations and minimization of multivariate polynomials François Glineur UCL/CORE
François Glineur, Polynomial solving & minimization - 1 - First Prev Next Last Full Screen Quit Solving systems of polynomial equations and minimization of multivariate polynomials François Glineur UCL/CORE
Choosability and fractional chromatic numbers
 Choosability and fractional chromatic numbers Noga Alon Zs. Tuza M. Voigt This copy was printed on October 11, 1995 Abstract A graph G is (a, b)-choosable if for any assignment of a list of a colors to
Choosability and fractional chromatic numbers Noga Alon Zs. Tuza M. Voigt This copy was printed on October 11, 1995 Abstract A graph G is (a, b)-choosable if for any assignment of a list of a colors to
IB Mathematics Standard Level Revision guide
 IB Mathematics Standard Level Revision guide F.G. Groeneveld TopClassTutors.ORG Copyright 2016 by F. Groeneveld All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted
IB Mathematics Standard Level Revision guide F.G. Groeneveld TopClassTutors.ORG Copyright 2016 by F. Groeneveld All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 Mar 2010
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 Mar 2010 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 Mar 2010](/thumbs/89/97670058.jpg) NUMBER OF COMPOSITIONS AND CONVOLVED FIBONACCI NUMBERS arxiv:10030981v1 [mathco] 4 Mar 2010 MILAN JANJIĆ Abstract We consider two type of upper Hessenberg matrices which determinants are Fibonacci numbers
NUMBER OF COMPOSITIONS AND CONVOLVED FIBONACCI NUMBERS arxiv:10030981v1 [mathco] 4 Mar 2010 MILAN JANJIĆ Abstract We consider two type of upper Hessenberg matrices which determinants are Fibonacci numbers
Quantum logics with given centres and variable state spaces Mirko Navara 1, Pavel Ptak 2 Abstract We ask which logics with a given centre allow for en
 Quantum logics with given centres and variable state spaces Mirko Navara 1, Pavel Ptak 2 Abstract We ask which logics with a given centre allow for enlargements with an arbitrary state space. We show in
Quantum logics with given centres and variable state spaces Mirko Navara 1, Pavel Ptak 2 Abstract We ask which logics with a given centre allow for enlargements with an arbitrary state space. We show in
Forcing unbalanced complete bipartite minors
 Forcing unbalanced complete bipartite minors Daniela Kühn Deryk Osthus Abstract Myers conjectured that for every integer s there exists a positive constant C such that for all integers t every graph of
Forcing unbalanced complete bipartite minors Daniela Kühn Deryk Osthus Abstract Myers conjectured that for every integer s there exists a positive constant C such that for all integers t every graph of
Acceptance of!-languages by Communicating Deterministic Turing Machines
 Acceptance of!-languages by Communicating Deterministic Turing Machines Rudolf Freund Institut für Computersprachen, Technische Universität Wien, Karlsplatz 13 A-1040 Wien, Austria Ludwig Staiger y Institut
Acceptance of!-languages by Communicating Deterministic Turing Machines Rudolf Freund Institut für Computersprachen, Technische Universität Wien, Karlsplatz 13 A-1040 Wien, Austria Ludwig Staiger y Institut
A Questionable Distance-Regular Graph
 A Questionable Distance-Regular Graph Rebecca Ross Abstract In this paper, we introduce distance-regular graphs and develop the intersection algebra for these graphs which is based upon its intersection
A Questionable Distance-Regular Graph Rebecca Ross Abstract In this paper, we introduce distance-regular graphs and develop the intersection algebra for these graphs which is based upon its intersection
1.1. The analytical denition. Denition. The Bernstein polynomials of degree n are dened analytically:
 DEGREE REDUCTION OF BÉZIER CURVES DAVE MORGAN Abstract. This paper opens with a description of Bézier curves. Then, techniques for the degree reduction of Bézier curves, along with a discussion of error
DEGREE REDUCTION OF BÉZIER CURVES DAVE MORGAN Abstract. This paper opens with a description of Bézier curves. Then, techniques for the degree reduction of Bézier curves, along with a discussion of error
On Multiplicity-free Products of Schur P -functions. 1 Introduction
 On Multiplicity-free Products of Schur P -functions Christine Bessenrodt Fakultät für Mathematik und Physik, Leibniz Universität Hannover, Welfengarten 3067 Hannover, Germany; bessen@math.uni-hannover.de
On Multiplicity-free Products of Schur P -functions Christine Bessenrodt Fakultät für Mathematik und Physik, Leibniz Universität Hannover, Welfengarten 3067 Hannover, Germany; bessen@math.uni-hannover.de
European Journal of Combinatorics
 European Journal of Combinatorics 30 (2009) 1686 1695 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Combinatorics ournal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ec Generalizations of Heilbronn
European Journal of Combinatorics 30 (2009) 1686 1695 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Combinatorics ournal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ec Generalizations of Heilbronn
Approximation Algorithms for Maximum. Coverage and Max Cut with Given Sizes of. Parts? A. A. Ageev and M. I. Sviridenko
 Approximation Algorithms for Maximum Coverage and Max Cut with Given Sizes of Parts? A. A. Ageev and M. I. Sviridenko Sobolev Institute of Mathematics pr. Koptyuga 4, 630090, Novosibirsk, Russia fageev,svirg@math.nsc.ru
Approximation Algorithms for Maximum Coverage and Max Cut with Given Sizes of Parts? A. A. Ageev and M. I. Sviridenko Sobolev Institute of Mathematics pr. Koptyuga 4, 630090, Novosibirsk, Russia fageev,svirg@math.nsc.ru
OPTIMAL INPUT SIGNAL DESIGN FOR IDENTIFICATION OF MAX PLUS LINEAR SYSTEMS
 OPTIMAL INPUT SIGNAL DESIGN FOR IDENTIFICATION OF MAX PLUS LINEAR SYSTEMS Gernot Schullerus, Volker Krebs, Bart De Schutter, Ton van den Boom Institut für Regelungs- und Steuerungssysteme, Universität
OPTIMAL INPUT SIGNAL DESIGN FOR IDENTIFICATION OF MAX PLUS LINEAR SYSTEMS Gernot Schullerus, Volker Krebs, Bart De Schutter, Ton van den Boom Institut für Regelungs- und Steuerungssysteme, Universität
2.1 Laplacian Variants
 -3 MS&E 337: Spectral Graph heory and Algorithmic Applications Spring 2015 Lecturer: Prof. Amin Saberi Lecture 2-3: 4/7/2015 Scribe: Simon Anastasiadis and Nolan Skochdopole Disclaimer: hese notes have
-3 MS&E 337: Spectral Graph heory and Algorithmic Applications Spring 2015 Lecturer: Prof. Amin Saberi Lecture 2-3: 4/7/2015 Scribe: Simon Anastasiadis and Nolan Skochdopole Disclaimer: hese notes have
Optimal global rates of convergence for interpolation problems with random design
 Optimal global rates of convergence for interpolation problems with random design Michael Kohler 1 and Adam Krzyżak 2, 1 Fachbereich Mathematik, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Schlossgartenstr. 7, 64289
Optimal global rates of convergence for interpolation problems with random design Michael Kohler 1 and Adam Krzyżak 2, 1 Fachbereich Mathematik, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Schlossgartenstr. 7, 64289
IMC 2015, Blagoevgrad, Bulgaria
 IMC 05, Blagoevgrad, Bulgaria Day, July 9, 05 Problem. For any integer n and two n n matrices with real entries, B that satisfy the equation + B ( + B prove that det( det(b. Does the same conclusion follow
IMC 05, Blagoevgrad, Bulgaria Day, July 9, 05 Problem. For any integer n and two n n matrices with real entries, B that satisfy the equation + B ( + B prove that det( det(b. Does the same conclusion follow
arxiv: v2 [math.ag] 24 Jun 2015
![arxiv: v2 [math.ag] 24 Jun 2015 arxiv: v2 [math.ag] 24 Jun 2015](/thumbs/94/118503236.jpg) TRIANGULATIONS OF MONOTONE FAMILIES I: TWO-DIMENSIONAL FAMILIES arxiv:1402.0460v2 [math.ag] 24 Jun 2015 SAUGATA BASU, ANDREI GABRIELOV, AND NICOLAI VOROBJOV Abstract. Let K R n be a compact definable set
TRIANGULATIONS OF MONOTONE FAMILIES I: TWO-DIMENSIONAL FAMILIES arxiv:1402.0460v2 [math.ag] 24 Jun 2015 SAUGATA BASU, ANDREI GABRIELOV, AND NICOLAI VOROBJOV Abstract. Let K R n be a compact definable set
arxiv: v3 [cs.dm] 18 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v3 [cs.dm] 18 Jan 2018 arxiv: v3 [cs.dm] 18 Jan 2018](/thumbs/81/83422292.jpg) On H-topological intersection graphs Steven Chaplick 1, Martin Töpfer 2, Jan Voborník 3, and Peter Zeman 3 1 Lehrstuhl für Informatik I, Universität Würzburg, Germany, www1.informatik.uni-wuerzburg.de/en/staff,
On H-topological intersection graphs Steven Chaplick 1, Martin Töpfer 2, Jan Voborník 3, and Peter Zeman 3 1 Lehrstuhl für Informatik I, Universität Würzburg, Germany, www1.informatik.uni-wuerzburg.de/en/staff,
