0 < f(y) - fix) - (x*, y - x) < e\\y - x\\
|
|
|
- William Pope
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 121, Number 4, August 1994 A NOTE ON THE DIFFERENTIABILITY OF CONVEX FUNCTIONS WU CONGXIN AND CHENG LIXIN (Communicated by Palle E. T. Jorgensen) Abstract. Every real-valued convex and locally Lipschitzian function / defined on a nonempty closed convex set D of a Banach space E is the local restriction of a convex Lipschitzian function defined on E. Moreover, if E is separable and int D ± 0, then, for each Gateaux differentiability point x (6 int/j) of f, there is a closed convex set C C intd with the nonsupport points set N(C) ^ 0 and with x e N(C) such that fc (the restriction of / on C) is Fréchet differentiable at x. Rainwater [1] and Verona [2] recently generalized Asplund's theorems [5] in the following manner Theorem [Rainwater]. Suppose that E is an Asplund space (a Banach space of class (S)). Then, for every closed convex subset C of E such that the nonsupport points set NÍC) of C is nonempty and for every convex function f on C which is locally Lipschitzian on NÍC), the set of points Q, where f is Fréchet ÍGateaux) differentiable, is a dense G subset of C. Notation. We denote by C, Cx, and N(C) a closed convex set of a Banach space E, the cone generated by C from x, and the nonsupport points set of C, respectively. The open and the closed balls centered at x and with radius r are denoted by 5(x, r) and 5(x, r), respectively. All convex functions /, if nothing is added, are assumed real valued. Definition. We say that a function denoted by / is a local extension of f at u dom(/) and that / is a local restriction of / at u provided there is a neighborhood U of u such that / = / in U n dom(/ ). Definition. We say that / is Gateaux (Fréchet) differentiable at x NÍC) provided there exists a unique x* E* such that (x\y-x)< fiy) - px) for all y G C (for all e > 0 there exists ô > 0 such that whenever y C n B(x, Ô)). 0 < f(y) - fix) - (x*, y - x) < e\\y - x\\ Received by the editors October 28, Mathematics Subject Classification. Primary 26E15, 46G American Mathematical Society /94 $1.00+ $.25 per page
2 1058 WU CONGXIN AND CHENG LIXIN Lemma 1. Suppose that f is convex and locally Lipschitzian on C. Then (a) for every u C, there exist a neighborhood U of u and a convex Lipschitzian function fu defined on E such that f = fu in U n C ; (b) dom(d/) = dom(/) = C; (c) there exists a selection y far df on C such that y/ is locally bounded on C ; in particular [1], if NÍC) # 0, then df is itself locally bounded on N(C). Recall that the extended real-valued lower semicontinuous convex function f on E is said to be proper provided fix) > -oo for all x E and its iconvex) essential domain domf = {x: fix) < +00} is nonempty. For such f, we define the inf-convolutions as fnix) = inf{fiy) + n\\x -y\\: y E}. Then we have isee, for instance, [3, 4, 6]). Lemma 2. With f and {/ } as above, the sequence {/ } has the following properties : Í1 ) Each fn is convex and Lipschitzian on E with Lipschitz constant n ; (2) f ix) < f +iix) < fix) far each x E and each n > 1 ; (3) fnix) = fix) if and only if d fix) HnB* {where B* denotes the unit ball of E*) is nonempty or, equivalently, if and only if dfn(x) = dfix) n nb*. Proof of Lemma 1. Since / is locally Lipschitzian on C, there exists B(u, r) for some r > 0 and L > 0 such that \f(y) - /C*) ^ -^11v ~ xll whenever x, y G B(u, r) n C = Bciu,r). We define the extended real-valued convex function / on E by fix) - fix) if x Bciu, r), and fix) - 00, otherwise. Hence / is proper lower semicontinuous convex and bounded below on E and Lipschitzian on 2?c(«,r) with Lipschitz constant L. Let {/ } be the sequence of the inf-convolutions by /. Now we will show (a). Suppose, to the contrary, that the neighborhood U of u does not exist. Let Bn = Bciu, 1/n). Then, for each integer n > 1, there is x Bn such that / (x ) < /(x ), by the definition of /. For each such xn, we can choose y E such that f(xn)>fiyn) + n\\yn-xn\\, n = 1,2,..., that is, fixn) - fiy ) > n\\y -xn\\ for n = 1, 2,.... Clearly, we have y Bc(u, r). Note that xn Bc(u, r) whenever 1/n < r and / is Lipschitzian on Bc(u, r) with Lipschitz constant L. We have \f(x ) - f(yn)\ <L\\x -y \\ whenever l/n < r ; this is a contradiction which proved assertion (a). From the proof of assertion (a), it is easy to see that fn = fin Bc(u, r) by taking n [L] + 1 (where [L] denotes the maximal integer m satisfying m < L) ; that is, by Lemma 2, df(x)r\nb* is nonempty for each x Bc(u, r). Hence df(x) n nb* is nonempty for each x ß(w, r). Now we showed that there is a selection for df on B(u,r) which is bounded by n. The arbitrariness of u says that there is a selection ^ for 9/ on C which is locally bounded; hence we proved assertions (b) and (c). With / and / as in Lemma 1, by Lemma 2, we have dfu(x) c df(x) for each x G U n C. If C is closed and N(C) 0, note that x N(C) if
3 A NOTE ON THE DIFFERENTIABILITY OF CONVEX FUNCTIONS 1059 and only if Cx is dense in E [1]. By a simply convexity and differentiability argument, we see df = dfu in U C\ N(C). Hence we have Proposition 3. Suppose that C is closed with N(C) ^ 0 and f is locally Lipschitzian on N(C). Then the following versions are equivalent: (a) / is Gateaux differentiable at u N(C). (b) Every fu is Gateaux differentiable at u N(C). (c) Every selection for df on N(C) is norm-to-weak* continuous at u. (d) There is a selection for df on N(C) which is norm-to-weak* continuous at u. Corollary 4. Suppose that C is a closed convex set of the weak Asplund space E, and suppose that the convex function f is locally Lipschitzian on N(C). Then the set of points G, where f is Gateaux differentiable, is a Gs set of C. It is easy to see that if u N(C) is the Fréchet differentiability point of fu, then so is the one of f. The following example shows that if the interior of C is empty, then the Fréchet differentiability of fu is really stronger than the one off. ' Example 5. The function / defined by f(x) - \\x\\p on C = {x ll, x > 0 for n = 1,2,...} shows that / is Fréchet differentiable at each point of N(C) {x lx, xn > 0 for «= 1,2,...}, but the extension / of / (where fu II II/' on /') is nowhere Fréchet differentiable. More generally, we have Theorem 6. Suppose that E is separable, D is a nonempty open convex set of E, and f is a continuous convex function on D. Then, for each Gateaux differentiability point x D of f, there exists a closed convex subset C of D with N(C) t 0 and x N(C) such that fc (the restriction of f to C) is Fréchet differentiable at x. Proof. Let 0 < e < \. By [8] there are two sequences {xf} and {Xj} in E and in E*, respectively, satisfying (1) ^ = 1 for 7 = 1,2,...; (2) x; <l+e for; = 1,2,...; (3) x*(xj) = Sij (=1 if 1=/, =0 otherwise); (4) cl(span(x, for j = 1, 2,...)) = E. Suppose that x D is a Gateaux differentiability point of /. each n > 1, there exists 1 > 5n > 0 (5n > 0) such that (1) f(x±2ô xn)-fix)-(x*,±2ônxn) <2_n {x. = df{x)) Then, for Let En = span(x, for j = 1, 2,...,«), F = cë(±y for n = 1,2,...), and C = x + F, where y = ô x for n = 1,2,... Clearly, C (c D) is closed and convex and Cx is dense in E, and hence xéjv(c). Now we prove that point x is a Fréchet differentiability point of f. Suppose, to the contrary, that fc is not Fréchet differentiable at x. Then there is en > 0 such that for each
4 1060 WU CONGXIN AND CHENG LIXIN Sn there is z C with 0 < \\z - x\\ < dn such that fc(zn)-fc(x)-(x*,z -x) ^ ( - >*> y where x* = dfix). By the density of coi±yn for n = 1, 2,... ) in F, we can assume that {z - x} c coi±y for n = 1,2,...), that is, for each n > 1, there is a sequence {k{"]} with k{"] > 0 for i = 1, 2,... and, JL[.B) = 1 such that zn -x = ^/^ "'(iy/) Therefore, we have, by the properties of {x } and llz«- *ll > 7 max x*(z - x)\ (2), ;, = -^ max k{"]\\yj\\ = maxä,. l+e j J " ;" l+e j J ' Fix «o such that (1 + e) ~> = (1 + e)2-*> < e0/2. Let «o oo un=x + 2Y/l,n)(±yi) and vn = x + 2 X?\±yi). 1=1 i'=no + l Since z x, we can claim m,ü ë D for n = 1,2. Now we have z = ("«+ "" )/2, therefore, /c(z ) = /(z ) = /((«+ vn)/2) < \[fiun) + f(vn)]. Let w (u - x)/6 (where 6 - \\z - x\\). Then IKH = \\u -x\\/e <YlMln)\\yi\\/0n = 2Yix<?)âi/e (3),=1 '=' < il+e)-2y/^l")ài/maxxf)ôj < 2(1 +e)n0; that is, {wn} is contained by 2(1 + e)nob 0, where B 0 is the unit ball of the «o-dimensional subspace E 0 of E. (oo \ / oo ftp x + 2 Xf(±yi)\=fi k\"\x±2yl) + Y/k^x (=«0+1 / \/'=/io+l 1=1 oo «o < *.(i")f(x±2yi) + y ix?).f(x). i'=no+l '=1
5 A NOTE ON THE DIFFERENTIABILITY OF CONVEX FUNCTIONS 1061 Hence o < f(zn) - fix) - (x*, zn -x) < {[fjun) + fjvn)]/2 - fjx) - (X*, Z - x)} e f(u ) - f(x) - (X*,Un-x) f(v ) - f(x) - (X*,Vn-x) n < f(un) - fjx) - (X*, Un-X) 26n + ZT=n0+i^](f(x± 2yt) - f(x) - (x*, ±2y,» 26 (2) f(u ) - f(x) - (X*, U -X) 2dn (1 + e) T,T=n0+i in)(f(x ± 2v,) - fix) - (x*, ±2y,)) 2maxjXfôj (xjf(un)-f(x)-(x*,u -x) (1 c) 2_j j=n0+l f(u )-f(x)-(x*,u -x) q 26n + 2 = fix + enwn) - f(x) - (x*, enwn) " Since 2(1 + e)«o^/io is a bounded set of the «o-dimensional subspace E 0 of, u) ë2(1+ s)nob 0, and ö -» 0, and since / is Gateaux differentiable at x, we must have fjx + dnw ) - fjx) - (x*, d w ) for sufficiently large n. Hence fjx + enwn)- fjx)- (X*, d W ), 0 «0, «0 e - 2^-+ T< 2" + T = e for sufficiently large «, and this is a contradiction which completes our proof. Remark. The recent work of Preiss, Phelps, and Namioka [7] showed that if E admits an equivalent smooth norm, then it is of class (S). Hence, for the Gateaux differentiability, the Rainwater theorem still holds for smoothable Banach spaces. Acknowledgment The second author specially thanks Professors R. R. Phelps and I. Namioka for their hospitality and helpful conversations on this note.
6 1062 WU CONGXIN AND CHENG LIXIN References 1. J. Rainwater, Yet more on the differentiability of convex functions, Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. 103(1988), M. E. Verona, More on the differentiability of convex functions, Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. 103 (1988), J. B. Hiriart Urruty, Lipschitz r-continuity of the approximate subdifferential of a convex junction, Math. Scand. 47 (1980), P. J. Laurent, Approximation et optimisation, Hermann, Paris, E. Asplund, Fréchet differentiability of convex functions, Acta. Math. 121 (1968), S. Fitzpatrick and R. R. Phelps, Bounded approximants to monotone operators on Banach spaces (to appear). 7. D. Preiss, R. R. Phelps, and I. Namioka, Smooth Banach spaces, weak Asplund spaces and monotone or USCO mappings (to appear). 8. J. Lindenstrauss and L. Tzafiri, Classical Banach spaces. I, Springer-Verlag, New York, Department of Mathematics, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, , People's Republic of China
YET MORE ON THE DIFFERENTIABILITY OF CONVEX FUNCTIONS
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 103, Number 3, July 1988 YET MORE ON THE DIFFERENTIABILITY OF CONVEX FUNCTIONS JOHN RAINWATER (Communicated by William J. Davis) ABSTRACT. Generic
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 103, Number 3, July 1988 YET MORE ON THE DIFFERENTIABILITY OF CONVEX FUNCTIONS JOHN RAINWATER (Communicated by William J. Davis) ABSTRACT. Generic
FRAGMENTABILITY OF ROTUND BANACH SPACES. Scott Sciffer. lim <Jl(x+A.y)- $(x) A-tO A
 222 FRAGMENTABILITY OF ROTUND BANACH SPACES Scott Sciffer Introduction A topological. space X is said to be fragmented by a metric p if for every e > 0 and every subset Y of X there exists a nonempty relatively
222 FRAGMENTABILITY OF ROTUND BANACH SPACES Scott Sciffer Introduction A topological. space X is said to be fragmented by a metric p if for every e > 0 and every subset Y of X there exists a nonempty relatively
DIFFERENTIABILITY OF DISTANCE FUNCTIONS AND A PROXIMINAL PROPERTY INDUCING CONVEXITY
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 104, Number 2, October 1988 DIFFERENTIABILITY OF DISTANCE FUNCTIONS AND A PROXIMINAL PROPERTY INDUCING CONVEXITY J. R. GILES (Communicated by William
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 104, Number 2, October 1988 DIFFERENTIABILITY OF DISTANCE FUNCTIONS AND A PROXIMINAL PROPERTY INDUCING CONVEXITY J. R. GILES (Communicated by William
Subdifferential representation of convex functions: refinements and applications
 Subdifferential representation of convex functions: refinements and applications Joël Benoist & Aris Daniilidis Abstract Every lower semicontinuous convex function can be represented through its subdifferential
Subdifferential representation of convex functions: refinements and applications Joël Benoist & Aris Daniilidis Abstract Every lower semicontinuous convex function can be represented through its subdifferential
Examples of Convex Functions and Classifications of Normed Spaces
 Journal of Convex Analysis Volume 1 (1994), No.1, 61 73 Examples of Convex Functions and Classifications of Normed Spaces Jon Borwein 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Simon Fraser University
Journal of Convex Analysis Volume 1 (1994), No.1, 61 73 Examples of Convex Functions and Classifications of Normed Spaces Jon Borwein 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Simon Fraser University
Differentiability of Convex Functions on a Banach Space with Smooth Bump Function 1
 Journal of Convex Analysis Volume 1 (1994), No.1, 47 60 Differentiability of Convex Functions on a Banach Space with Smooth Bump Function 1 Li Yongxin, Shi Shuzhong Nankai Institute of Mathematics Tianjin,
Journal of Convex Analysis Volume 1 (1994), No.1, 47 60 Differentiability of Convex Functions on a Banach Space with Smooth Bump Function 1 Li Yongxin, Shi Shuzhong Nankai Institute of Mathematics Tianjin,
Epiconvergence and ε-subgradients of Convex Functions
 Journal of Convex Analysis Volume 1 (1994), No.1, 87 100 Epiconvergence and ε-subgradients of Convex Functions Andrei Verona Department of Mathematics, California State University Los Angeles, CA 90032,
Journal of Convex Analysis Volume 1 (1994), No.1, 87 100 Epiconvergence and ε-subgradients of Convex Functions Andrei Verona Department of Mathematics, California State University Los Angeles, CA 90032,
Sum of two maximal monotone operators in a general Banach space is maximal
 arxiv:1505.04879v1 [math.fa] 19 May 2015 Sum of two maximal monotone operators in a general Banach space is maximal S R Pattanaik, D K Pradhan and S Pradhan May 20, 2015 Abstract In a real Banach space,
arxiv:1505.04879v1 [math.fa] 19 May 2015 Sum of two maximal monotone operators in a general Banach space is maximal S R Pattanaik, D K Pradhan and S Pradhan May 20, 2015 Abstract In a real Banach space,
ON GAP FUNCTIONS OF VARIATIONAL INEQUALITY IN A BANACH SPACE. Sangho Kum and Gue Myung Lee. 1. Introduction
 J. Korean Math. Soc. 38 (2001), No. 3, pp. 683 695 ON GAP FUNCTIONS OF VARIATIONAL INEQUALITY IN A BANACH SPACE Sangho Kum and Gue Myung Lee Abstract. In this paper we are concerned with theoretical properties
J. Korean Math. Soc. 38 (2001), No. 3, pp. 683 695 ON GAP FUNCTIONS OF VARIATIONAL INEQUALITY IN A BANACH SPACE Sangho Kum and Gue Myung Lee Abstract. In this paper we are concerned with theoretical properties
Optimality Conditions for Nonsmooth Convex Optimization
 Optimality Conditions for Nonsmooth Convex Optimization Sangkyun Lee Oct 22, 2014 Let us consider a convex function f : R n R, where R is the extended real field, R := R {, + }, which is proper (f never
Optimality Conditions for Nonsmooth Convex Optimization Sangkyun Lee Oct 22, 2014 Let us consider a convex function f : R n R, where R is the extended real field, R := R {, + }, which is proper (f never
Monotone operators and bigger conjugate functions
 Monotone operators and bigger conjugate functions Heinz H. Bauschke, Jonathan M. Borwein, Xianfu Wang, and Liangjin Yao August 12, 2011 Abstract We study a question posed by Stephen Simons in his 2008
Monotone operators and bigger conjugate functions Heinz H. Bauschke, Jonathan M. Borwein, Xianfu Wang, and Liangjin Yao August 12, 2011 Abstract We study a question posed by Stephen Simons in his 2008
THE UNIQUE MINIMAL DUAL REPRESENTATION OF A CONVEX FUNCTION
 THE UNIQUE MINIMAL DUAL REPRESENTATION OF A CONVEX FUNCTION HALUK ERGIN AND TODD SARVER Abstract. Suppose (i) X is a separable Banach space, (ii) C is a convex subset of X that is a Baire space (when endowed
THE UNIQUE MINIMAL DUAL REPRESENTATION OF A CONVEX FUNCTION HALUK ERGIN AND TODD SARVER Abstract. Suppose (i) X is a separable Banach space, (ii) C is a convex subset of X that is a Baire space (when endowed
SOME PROPERTIES ON THE CLOSED SUBSETS IN BANACH SPACES
 ARCHIVUM MATHEMATICUM (BRNO) Tomus 42 (2006), 167 174 SOME PROPERTIES ON THE CLOSED SUBSETS IN BANACH SPACES ABDELHAKIM MAADEN AND ABDELKADER STOUTI Abstract. It is shown that under natural assumptions,
ARCHIVUM MATHEMATICUM (BRNO) Tomus 42 (2006), 167 174 SOME PROPERTIES ON THE CLOSED SUBSETS IN BANACH SPACES ABDELHAKIM MAADEN AND ABDELKADER STOUTI Abstract. It is shown that under natural assumptions,
Yuqing Chen, Yeol Je Cho, and Li Yang
 Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 39 (2002), No. 4, pp. 535 541 NOTE ON THE RESULTS WITH LOWER SEMI-CONTINUITY Yuqing Chen, Yeol Je Cho, and Li Yang Abstract. In this paper, we introduce the concept of lower semicontinuous
Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 39 (2002), No. 4, pp. 535 541 NOTE ON THE RESULTS WITH LOWER SEMI-CONTINUITY Yuqing Chen, Yeol Je Cho, and Li Yang Abstract. In this paper, we introduce the concept of lower semicontinuous
("-1/' .. f/ L) I LOCAL BOUNDEDNESS OF NONLINEAR, MONOTONE OPERA TORS. R. T. Rockafellar. MICHIGAN MATHEMATICAL vol. 16 (1969) pp.
 I l ("-1/'.. f/ L) I LOCAL BOUNDEDNESS OF NONLINEAR, MONOTONE OPERA TORS R. T. Rockafellar from the MICHIGAN MATHEMATICAL vol. 16 (1969) pp. 397-407 JOURNAL LOCAL BOUNDEDNESS OF NONLINEAR, MONOTONE OPERATORS
I l ("-1/'.. f/ L) I LOCAL BOUNDEDNESS OF NONLINEAR, MONOTONE OPERA TORS R. T. Rockafellar from the MICHIGAN MATHEMATICAL vol. 16 (1969) pp. 397-407 JOURNAL LOCAL BOUNDEDNESS OF NONLINEAR, MONOTONE OPERATORS
The local equicontinuity of a maximal monotone operator
 arxiv:1410.3328v2 [math.fa] 3 Nov 2014 The local equicontinuity of a maximal monotone operator M.D. Voisei Abstract The local equicontinuity of an operator T : X X with proper Fitzpatrick function ϕ T
arxiv:1410.3328v2 [math.fa] 3 Nov 2014 The local equicontinuity of a maximal monotone operator M.D. Voisei Abstract The local equicontinuity of an operator T : X X with proper Fitzpatrick function ϕ T
NOWHERE LOCALLY UNIFORMLY CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS
 NOWHERE LOCALLY UNIFORMLY CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS K. Jarosz Southern Illinois University at Edwardsville, IL 606, and Bowling Green State University, OH 43403 kjarosz@siue.edu September, 995 Abstract. Suppose
NOWHERE LOCALLY UNIFORMLY CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS K. Jarosz Southern Illinois University at Edwardsville, IL 606, and Bowling Green State University, OH 43403 kjarosz@siue.edu September, 995 Abstract. Suppose
(convex combination!). Use convexity of f and multiply by the common denominator to get. Interchanging the role of x and y, we obtain that f is ( 2M ε
 1. Continuity of convex functions in normed spaces In this chapter, we consider continuity properties of real-valued convex functions defined on open convex sets in normed spaces. Recall that every infinitedimensional
1. Continuity of convex functions in normed spaces In this chapter, we consider continuity properties of real-valued convex functions defined on open convex sets in normed spaces. Recall that every infinitedimensional
Brøndsted-Rockafellar property of subdifferentials of prox-bounded functions. Marc Lassonde Université des Antilles et de la Guyane
 Conference ADGO 2013 October 16, 2013 Brøndsted-Rockafellar property of subdifferentials of prox-bounded functions Marc Lassonde Université des Antilles et de la Guyane Playa Blanca, Tongoy, Chile SUBDIFFERENTIAL
Conference ADGO 2013 October 16, 2013 Brøndsted-Rockafellar property of subdifferentials of prox-bounded functions Marc Lassonde Université des Antilles et de la Guyane Playa Blanca, Tongoy, Chile SUBDIFFERENTIAL
A Note on the Class of Superreflexive Almost Transitive Banach Spaces
 E extracta mathematicae Vol. 23, Núm. 1, 1 6 (2008) A Note on the Class of Superreflexive Almost Transitive Banach Spaces Jarno Talponen University of Helsinki, Department of Mathematics and Statistics,
E extracta mathematicae Vol. 23, Núm. 1, 1 6 (2008) A Note on the Class of Superreflexive Almost Transitive Banach Spaces Jarno Talponen University of Helsinki, Department of Mathematics and Statistics,
MAT 570 REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES. Contents. 1. Sets Functions Countability Axiom of choice Equivalence relations 9
 MAT 570 REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES PROFESSOR: JOHN QUIGG SEMESTER: FALL 204 Contents. Sets 2 2. Functions 5 3. Countability 7 4. Axiom of choice 8 5. Equivalence relations 9 6. Real numbers 9 7. Extended
MAT 570 REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES PROFESSOR: JOHN QUIGG SEMESTER: FALL 204 Contents. Sets 2 2. Functions 5 3. Countability 7 4. Axiom of choice 8 5. Equivalence relations 9 6. Real numbers 9 7. Extended
Differentiability and Measures in Banach Spaces
 Differentiability and Measures in Banach Spaces David Preiss Department of Mathematics, University College London, London WC1E 6BT, UK The purpose of this contribution is to give information about new
Differentiability and Measures in Banach Spaces David Preiss Department of Mathematics, University College London, London WC1E 6BT, UK The purpose of this contribution is to give information about new
WEAK CONVERGENCE OF RESOLVENTS OF MAXIMAL MONOTONE OPERATORS AND MOSCO CONVERGENCE
 Fixed Point Theory, Volume 6, No. 1, 2005, 59-69 http://www.math.ubbcluj.ro/ nodeacj/sfptcj.htm WEAK CONVERGENCE OF RESOLVENTS OF MAXIMAL MONOTONE OPERATORS AND MOSCO CONVERGENCE YASUNORI KIMURA Department
Fixed Point Theory, Volume 6, No. 1, 2005, 59-69 http://www.math.ubbcluj.ro/ nodeacj/sfptcj.htm WEAK CONVERGENCE OF RESOLVENTS OF MAXIMAL MONOTONE OPERATORS AND MOSCO CONVERGENCE YASUNORI KIMURA Department
ON THE RANGE OF THE SUM OF MONOTONE OPERATORS IN GENERAL BANACH SPACES
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 124, Number 11, November 1996 ON THE RANGE OF THE SUM OF MONOTONE OPERATORS IN GENERAL BANACH SPACES HASSAN RIAHI (Communicated by Palle E. T. Jorgensen)
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 124, Number 11, November 1996 ON THE RANGE OF THE SUM OF MONOTONE OPERATORS IN GENERAL BANACH SPACES HASSAN RIAHI (Communicated by Palle E. T. Jorgensen)
Iterative Convex Optimization Algorithms; Part One: Using the Baillon Haddad Theorem
 Iterative Convex Optimization Algorithms; Part One: Using the Baillon Haddad Theorem Charles Byrne (Charles Byrne@uml.edu) http://faculty.uml.edu/cbyrne/cbyrne.html Department of Mathematical Sciences
Iterative Convex Optimization Algorithms; Part One: Using the Baillon Haddad Theorem Charles Byrne (Charles Byrne@uml.edu) http://faculty.uml.edu/cbyrne/cbyrne.html Department of Mathematical Sciences
The sum of two maximal monotone operator is of type FPV
 CJMS. 5(1)(2016), 17-21 Caspian Journal of Mathematical Sciences (CJMS) University of Mazandaran, Iran http://cjms.journals.umz.ac.ir ISSN: 1735-0611 The sum of two maximal monotone operator is of type
CJMS. 5(1)(2016), 17-21 Caspian Journal of Mathematical Sciences (CJMS) University of Mazandaran, Iran http://cjms.journals.umz.ac.ir ISSN: 1735-0611 The sum of two maximal monotone operator is of type
On restricted weak upper semicontinuous set valued mappings and reflexivity
 On restricted weak upper semicontinuous set valued mappings and reflexivity Julio Benítez Vicente Montesinos Dedicated to Professor Manuel Valdivia. Abstract It is known that if a Banach space is quasi
On restricted weak upper semicontinuous set valued mappings and reflexivity Julio Benítez Vicente Montesinos Dedicated to Professor Manuel Valdivia. Abstract It is known that if a Banach space is quasi
ON THE INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol. 64, No 1, 1976 ON THE INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM F. H. CLARKE The classical inverse function theorem gives conditions under which a C r function admits (locally) a C Γ
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol. 64, No 1, 1976 ON THE INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM F. H. CLARKE The classical inverse function theorem gives conditions under which a C r function admits (locally) a C Γ
On super-weakly compact sets and uniformly convexifiable sets
 STUDIA MATHEMATICA 199 () (010) On super-weakly compact sets and uniformly convexifiable sets by Lixin Cheng, Qingjin Cheng, Bo Wang and Wen Zhang (Xiamen) Abstract. This paper mainly concerns the topological
STUDIA MATHEMATICA 199 () (010) On super-weakly compact sets and uniformly convexifiable sets by Lixin Cheng, Qingjin Cheng, Bo Wang and Wen Zhang (Xiamen) Abstract. This paper mainly concerns the topological
A NICE PROOF OF FARKAS LEMMA
 A NICE PROOF OF FARKAS LEMMA DANIEL VICTOR TAUSK Abstract. The goal of this short note is to present a nice proof of Farkas Lemma which states that if C is the convex cone spanned by a finite set and if
A NICE PROOF OF FARKAS LEMMA DANIEL VICTOR TAUSK Abstract. The goal of this short note is to present a nice proof of Farkas Lemma which states that if C is the convex cone spanned by a finite set and if
Real Analysis Math 131AH Rudin, Chapter #1. Dominique Abdi
 Real Analysis Math 3AH Rudin, Chapter # Dominique Abdi.. If r is rational (r 0) and x is irrational, prove that r + x and rx are irrational. Solution. Assume the contrary, that r+x and rx are rational.
Real Analysis Math 3AH Rudin, Chapter # Dominique Abdi.. If r is rational (r 0) and x is irrational, prove that r + x and rx are irrational. Solution. Assume the contrary, that r+x and rx are rational.
MATH 409 Advanced Calculus I Lecture 12: Uniform continuity. Exponential functions.
 MATH 409 Advanced Calculus I Lecture 12: Uniform continuity. Exponential functions. Uniform continuity Definition. A function f : E R defined on a set E R is called uniformly continuous on E if for every
MATH 409 Advanced Calculus I Lecture 12: Uniform continuity. Exponential functions. Uniform continuity Definition. A function f : E R defined on a set E R is called uniformly continuous on E if for every
Necessary Optimality Conditions for ε e Pareto Solutions in Vector Optimization with Empty Interior Ordering Cones
 Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor Necessary Optimality Conditions for ε e Pareto Solutions in Vector Optimization with Empty Interior Ordering Cones Truong Q. Bao Suvendu R. Pattanaik
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor Necessary Optimality Conditions for ε e Pareto Solutions in Vector Optimization with Empty Interior Ordering Cones Truong Q. Bao Suvendu R. Pattanaik
Topological properties
 CHAPTER 4 Topological properties 1. Connectedness Definitions and examples Basic properties Connected components Connected versus path connected, again 2. Compactness Definition and first examples Topological
CHAPTER 4 Topological properties 1. Connectedness Definitions and examples Basic properties Connected components Connected versus path connected, again 2. Compactness Definition and first examples Topological
ON THE MAZUR-ULAM THEOREM AND THE ALEKSANDROV PROBLEM FOR UNIT DISTANCE PRESERVING MAPPINGS
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 118, Number 3, July 1993 ON THE MAZUR-ULAM THEOREM AND THE ALEKSANDROV PROBLEM FOR UNIT DISTANCE PRESERVING MAPPINGS THEMISTOCLES M. RASSIAS AND
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 118, Number 3, July 1993 ON THE MAZUR-ULAM THEOREM AND THE ALEKSANDROV PROBLEM FOR UNIT DISTANCE PRESERVING MAPPINGS THEMISTOCLES M. RASSIAS AND
A characterization of essentially strictly convex functions on reflexive Banach spaces
 A characterization of essentially strictly convex functions on reflexive Banach spaces Michel Volle Département de Mathématiques Université d Avignon et des Pays de Vaucluse 74, rue Louis Pasteur 84029
A characterization of essentially strictly convex functions on reflexive Banach spaces Michel Volle Département de Mathématiques Université d Avignon et des Pays de Vaucluse 74, rue Louis Pasteur 84029
RENORMINGS OF L p (L q )
 RENORMINGS OF L p (L q ) by arxiv:math/9804002v1 [math.fa] 1 Apr 1998 R. Deville, R. Gonzalo and J. A. Jaramillo (*) Laboratoire de Mathématiques, Université Bordeaux I, 351, cours de la Libération, 33400
RENORMINGS OF L p (L q ) by arxiv:math/9804002v1 [math.fa] 1 Apr 1998 R. Deville, R. Gonzalo and J. A. Jaramillo (*) Laboratoire de Mathématiques, Université Bordeaux I, 351, cours de la Libération, 33400
Continuity of convex functions in normed spaces
 Continuity of convex functions in normed spaces In this chapter, we consider continuity properties of real-valued convex functions defined on open convex sets in normed spaces. Recall that every infinitedimensional
Continuity of convex functions in normed spaces In this chapter, we consider continuity properties of real-valued convex functions defined on open convex sets in normed spaces. Recall that every infinitedimensional
INSTITUTE OF MATHEMATICS THE CZECH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES. Separable reductions and rich families in theory of Fréchet subdifferentials.
 INSTITUTE OF MATHEMATICS THE CZECH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Separable reductions and rich families in theory of Fréchet subdifferentials Marián Fabian Preprint No. 86-2015 PRAHA 2015 Spring School on Variational
INSTITUTE OF MATHEMATICS THE CZECH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Separable reductions and rich families in theory of Fréchet subdifferentials Marián Fabian Preprint No. 86-2015 PRAHA 2015 Spring School on Variational
1 Topology Definition of a topology Basis (Base) of a topology The subspace topology & the product topology on X Y 3
 Index Page 1 Topology 2 1.1 Definition of a topology 2 1.2 Basis (Base) of a topology 2 1.3 The subspace topology & the product topology on X Y 3 1.4 Basic topology concepts: limit points, closed sets,
Index Page 1 Topology 2 1.1 Definition of a topology 2 1.2 Basis (Base) of a topology 2 1.3 The subspace topology & the product topology on X Y 3 1.4 Basic topology concepts: limit points, closed sets,
Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics
 Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics http://jipam.vu.edu.au/ Volume 4, Issue 4, Article 67, 2003 ON GENERALIZED MONOTONE MULTIFUNCTIONS WITH APPLICATIONS TO OPTIMALITY CONDITIONS IN
Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics http://jipam.vu.edu.au/ Volume 4, Issue 4, Article 67, 2003 ON GENERALIZED MONOTONE MULTIFUNCTIONS WITH APPLICATIONS TO OPTIMALITY CONDITIONS IN
Optimization and Optimal Control in Banach Spaces
 Optimization and Optimal Control in Banach Spaces Bernhard Schmitzer October 19, 2017 1 Convex non-smooth optimization with proximal operators Remark 1.1 (Motivation). Convex optimization: easier to solve,
Optimization and Optimal Control in Banach Spaces Bernhard Schmitzer October 19, 2017 1 Convex non-smooth optimization with proximal operators Remark 1.1 (Motivation). Convex optimization: easier to solve,
Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics
 Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics EPI-DIFFERENTIABILITY AND OPTIMALITY CONDITIONS FOR AN EXTREMAL PROBLEM UNDER INCLUSION CONSTRAINTS T. AMAHROQ, N. GADHI AND PR H. RIAHI Université
Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics EPI-DIFFERENTIABILITY AND OPTIMALITY CONDITIONS FOR AN EXTREMAL PROBLEM UNDER INCLUSION CONSTRAINTS T. AMAHROQ, N. GADHI AND PR H. RIAHI Université
APPROXIMATE ISOMETRIES ON FINITE-DIMENSIONAL NORMED SPACES
 APPROXIMATE ISOMETRIES ON FINITE-DIMENSIONAL NORMED SPACES S. J. DILWORTH Abstract. Every ε-isometry u between real normed spaces of the same finite dimension which maps the origin to the origin may by
APPROXIMATE ISOMETRIES ON FINITE-DIMENSIONAL NORMED SPACES S. J. DILWORTH Abstract. Every ε-isometry u between real normed spaces of the same finite dimension which maps the origin to the origin may by
Analysis Finite and Infinite Sets The Real Numbers The Cantor Set
 Analysis Finite and Infinite Sets Definition. An initial segment is {n N n n 0 }. Definition. A finite set can be put into one-to-one correspondence with an initial segment. The empty set is also considered
Analysis Finite and Infinite Sets Definition. An initial segment is {n N n n 0 }. Definition. A finite set can be put into one-to-one correspondence with an initial segment. The empty set is also considered
From now on, we will represent a metric space with (X, d). Here are some examples: i=1 (x i y i ) p ) 1 p, p 1.
 Chapter 1 Metric spaces 1.1 Metric and convergence We will begin with some basic concepts. Definition 1.1. (Metric space) Metric space is a set X, with a metric satisfying: 1. d(x, y) 0, d(x, y) = 0 x
Chapter 1 Metric spaces 1.1 Metric and convergence We will begin with some basic concepts. Definition 1.1. (Metric space) Metric space is a set X, with a metric satisfying: 1. d(x, y) 0, d(x, y) = 0 x
^-,({«}))=ic^if<iic/n^ir=iic/, where e(n) is the sequence defined by e(n\m) = 8^, (the Kronecker delta).
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 70, Number 1, June 1978 COMPOSITION OPERATOR ON F AND ITS ADJOINT R. K. SINGH AND B. S. KOMAL Abstract. A necessary and sufficient condition for
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 70, Number 1, June 1978 COMPOSITION OPERATOR ON F AND ITS ADJOINT R. K. SINGH AND B. S. KOMAL Abstract. A necessary and sufficient condition for
SOME REMARKS ON SUBDIFFERENTIABILITY OF CONVEX FUNCTIONS
 Applied Mathematics E-Notes, 5(2005), 150-156 c ISSN 1607-2510 Available free at mirror sites of http://www.math.nthu.edu.tw/ amen/ SOME REMARKS ON SUBDIFFERENTIABILITY OF CONVEX FUNCTIONS Mohamed Laghdir
Applied Mathematics E-Notes, 5(2005), 150-156 c ISSN 1607-2510 Available free at mirror sites of http://www.math.nthu.edu.tw/ amen/ SOME REMARKS ON SUBDIFFERENTIABILITY OF CONVEX FUNCTIONS Mohamed Laghdir
Convex Optimization Notes
 Convex Optimization Notes Jonathan Siegel January 2017 1 Convex Analysis This section is devoted to the study of convex functions f : B R {+ } and convex sets U B, for B a Banach space. The case of B =
Convex Optimization Notes Jonathan Siegel January 2017 1 Convex Analysis This section is devoted to the study of convex functions f : B R {+ } and convex sets U B, for B a Banach space. The case of B =
Abstract. The connectivity of the efficient point set and of some proper efficient point sets in locally convex spaces is investigated.
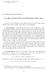 APPLICATIONES MATHEMATICAE 25,1 (1998), pp. 121 127 W. SONG (Harbin and Warszawa) ON THE CONNECTIVITY OF EFFICIENT POINT SETS Abstract. The connectivity of the efficient point set and of some proper efficient
APPLICATIONES MATHEMATICAE 25,1 (1998), pp. 121 127 W. SONG (Harbin and Warszawa) ON THE CONNECTIVITY OF EFFICIENT POINT SETS Abstract. The connectivity of the efficient point set and of some proper efficient
Weak-Star Convergence of Convex Sets
 Journal of Convex Analysis Volume 13 (2006), No. 3+4, 711 719 Weak-Star Convergence of Convex Sets S. Fitzpatrick A. S. Lewis ORIE, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA aslewis@orie.cornell.edu www.orie.cornell.edu/
Journal of Convex Analysis Volume 13 (2006), No. 3+4, 711 719 Weak-Star Convergence of Convex Sets S. Fitzpatrick A. S. Lewis ORIE, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA aslewis@orie.cornell.edu www.orie.cornell.edu/
arxiv:math/ v1 [math.fa] 4 Feb 1993
![arxiv:math/ v1 [math.fa] 4 Feb 1993 arxiv:math/ v1 [math.fa] 4 Feb 1993](/thumbs/85/91545657.jpg) Lectures on Maximal Monotone Operators R. R. Phelps Dept. Math. GN 50, Univ. of Wash., Seattle WA 98195; phelps@math.washington.edu (Lectures given at Prague/Paseky Summer School, Czech Republic, August
Lectures on Maximal Monotone Operators R. R. Phelps Dept. Math. GN 50, Univ. of Wash., Seattle WA 98195; phelps@math.washington.edu (Lectures given at Prague/Paseky Summer School, Czech Republic, August
Weak* Sequential Compactness and Bornological Limit Derivatives
 Journal of Convex Analysis Volume 2 (1995), No.1/2, 59 67 Weak* Sequential Compactness and Bornological Limit Derivatives Jonathan Borwein 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Simon Fraser University,
Journal of Convex Analysis Volume 2 (1995), No.1/2, 59 67 Weak* Sequential Compactness and Bornological Limit Derivatives Jonathan Borwein 1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Simon Fraser University,
UNIQUENESS OF THE UNIFORM NORM
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 116, Number 2, October 1992 UNIQUENESS OF THE UNIFORM NORM WITH AN APPLICATION TO TOPOLOGICAL ALGEBRAS S. J. BHATT AND D. J. KARIA (Communicated
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 116, Number 2, October 1992 UNIQUENESS OF THE UNIFORM NORM WITH AN APPLICATION TO TOPOLOGICAL ALGEBRAS S. J. BHATT AND D. J. KARIA (Communicated
Math General Topology Fall 2012 Homework 11 Solutions
 Math 535 - General Topology Fall 2012 Homework 11 Solutions Problem 1. Let X be a topological space. a. Show that the following properties of a subset A X are equivalent. 1. The closure of A in X has empty
Math 535 - General Topology Fall 2012 Homework 11 Solutions Problem 1. Let X be a topological space. a. Show that the following properties of a subset A X are equivalent. 1. The closure of A in X has empty
A PROOF OF A CONVEX-VALUED SELECTION THEOREM WITH THE CODOMAIN OF A FRÉCHET SPACE. Myung-Hyun Cho and Jun-Hui Kim. 1. Introduction
 Comm. Korean Math. Soc. 16 (2001), No. 2, pp. 277 285 A PROOF OF A CONVEX-VALUED SELECTION THEOREM WITH THE CODOMAIN OF A FRÉCHET SPACE Myung-Hyun Cho and Jun-Hui Kim Abstract. The purpose of this paper
Comm. Korean Math. Soc. 16 (2001), No. 2, pp. 277 285 A PROOF OF A CONVEX-VALUED SELECTION THEOREM WITH THE CODOMAIN OF A FRÉCHET SPACE Myung-Hyun Cho and Jun-Hui Kim Abstract. The purpose of this paper
Problem Set 5. 2 n k. Then a nk (x) = 1+( 1)k
 Problem Set 5 1. (Folland 2.43) For x [, 1), let 1 a n (x)2 n (a n (x) = or 1) be the base-2 expansion of x. (If x is a dyadic rational, choose the expansion such that a n (x) = for large n.) Then the
Problem Set 5 1. (Folland 2.43) For x [, 1), let 1 a n (x)2 n (a n (x) = or 1) be the base-2 expansion of x. (If x is a dyadic rational, choose the expansion such that a n (x) = for large n.) Then the
Peak Point Theorems for Uniform Algebras on Smooth Manifolds
 Peak Point Theorems for Uniform Algebras on Smooth Manifolds John T. Anderson and Alexander J. Izzo Abstract: It was once conjectured that if A is a uniform algebra on its maximal ideal space X, and if
Peak Point Theorems for Uniform Algebras on Smooth Manifolds John T. Anderson and Alexander J. Izzo Abstract: It was once conjectured that if A is a uniform algebra on its maximal ideal space X, and if
Strong subdifferentiability of norms and geometry of Banach spaces. G. Godefroy, V. Montesinos and V. Zizler
 Strong subdifferentiability of norms and geometry of Banach spaces G. Godefroy, V. Montesinos and V. Zizler Dedicated to the memory of Josef Kolomý Abstract. The strong subdifferentiability of norms (i.e.
Strong subdifferentiability of norms and geometry of Banach spaces G. Godefroy, V. Montesinos and V. Zizler Dedicated to the memory of Josef Kolomý Abstract. The strong subdifferentiability of norms (i.e.
DIFFERENTIABILITY VIA DIRECTIONAL DERIVATIVES
 PROCEEDINGS OK THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 70, Number 1, lune 1978 DIFFERENTIABILITY VIA DIRECTIONAL DERIVATIVES KA-SING LAU AND CLIFFORD E. WEIL Abstract. Let F be a continuous function from
PROCEEDINGS OK THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 70, Number 1, lune 1978 DIFFERENTIABILITY VIA DIRECTIONAL DERIVATIVES KA-SING LAU AND CLIFFORD E. WEIL Abstract. Let F be a continuous function from
A CHARACTERIZATION OF STRICT LOCAL MINIMIZERS OF ORDER ONE FOR STATIC MINMAX PROBLEMS IN THE PARAMETRIC CONSTRAINT CASE
 Journal of Applied Analysis Vol. 6, No. 1 (2000), pp. 139 148 A CHARACTERIZATION OF STRICT LOCAL MINIMIZERS OF ORDER ONE FOR STATIC MINMAX PROBLEMS IN THE PARAMETRIC CONSTRAINT CASE A. W. A. TAHA Received
Journal of Applied Analysis Vol. 6, No. 1 (2000), pp. 139 148 A CHARACTERIZATION OF STRICT LOCAL MINIMIZERS OF ORDER ONE FOR STATIC MINMAX PROBLEMS IN THE PARAMETRIC CONSTRAINT CASE A. W. A. TAHA Received
Convex Analysis and Economic Theory AY Elementary properties of convex functions
 Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences Ec 181 KC Border Convex Analysis and Economic Theory AY 2018 2019 Topic 6: Convex functions I 6.1 Elementary properties of convex functions We may occasionally
Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences Ec 181 KC Border Convex Analysis and Economic Theory AY 2018 2019 Topic 6: Convex functions I 6.1 Elementary properties of convex functions We may occasionally
Locally convex spaces, the hyperplane separation theorem, and the Krein-Milman theorem
 56 Chapter 7 Locally convex spaces, the hyperplane separation theorem, and the Krein-Milman theorem Recall that C(X) is not a normed linear space when X is not compact. On the other hand we could use semi
56 Chapter 7 Locally convex spaces, the hyperplane separation theorem, and the Krein-Milman theorem Recall that C(X) is not a normed linear space when X is not compact. On the other hand we could use semi
On the use of semi-closed sets and functions in convex analysis
 Open Math. 2015; 13: 1 5 Open Mathematics Open Access Research Article Constantin Zălinescu* On the use of semi-closed sets and functions in convex analysis Abstract: The main aim of this short note is
Open Math. 2015; 13: 1 5 Open Mathematics Open Access Research Article Constantin Zălinescu* On the use of semi-closed sets and functions in convex analysis Abstract: The main aim of this short note is
arxiv: v1 [math.oc] 21 Mar 2015
![arxiv: v1 [math.oc] 21 Mar 2015 arxiv: v1 [math.oc] 21 Mar 2015](/thumbs/88/117708247.jpg) Convex KKM maps, monotone operators and Minty variational inequalities arxiv:1503.06363v1 [math.oc] 21 Mar 2015 Marc Lassonde Université des Antilles, 97159 Pointe à Pitre, France E-mail: marc.lassonde@univ-ag.fr
Convex KKM maps, monotone operators and Minty variational inequalities arxiv:1503.06363v1 [math.oc] 21 Mar 2015 Marc Lassonde Université des Antilles, 97159 Pointe à Pitre, France E-mail: marc.lassonde@univ-ag.fr
Subdifferentiability and the Duality Gap
 Subdifferentiability and the Duality Gap Neil E. Gretsky (neg@math.ucr.edu) Department of Mathematics, University of California, Riverside Joseph M. Ostroy (ostroy@econ.ucla.edu) Department of Economics,
Subdifferentiability and the Duality Gap Neil E. Gretsky (neg@math.ucr.edu) Department of Mathematics, University of California, Riverside Joseph M. Ostroy (ostroy@econ.ucla.edu) Department of Economics,
1. Bounded linear maps. A linear map T : E F of real Banach
 DIFFERENTIABLE MAPS 1. Bounded linear maps. A linear map T : E F of real Banach spaces E, F is bounded if M > 0 so that for all v E: T v M v. If v r T v C for some positive constants r, C, then T is bounded:
DIFFERENTIABLE MAPS 1. Bounded linear maps. A linear map T : E F of real Banach spaces E, F is bounded if M > 0 so that for all v E: T v M v. If v r T v C for some positive constants r, C, then T is bounded:
THE INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM
 THE INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM W. PATRICK HOOPER The implicit function theorem is the following result: Theorem 1. Let f be a C 1 function from a neighborhood of a point a R n into R n. Suppose A = Df(a)
THE INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM W. PATRICK HOOPER The implicit function theorem is the following result: Theorem 1. Let f be a C 1 function from a neighborhood of a point a R n into R n. Suppose A = Df(a)
PREVALENCE OF SOME KNOWN TYPICAL PROPERTIES. 1. Introduction
 Acta Math. Univ. Comenianae Vol. LXX, 2(2001), pp. 185 192 185 PREVALENCE OF SOME KNOWN TYPICAL PROPERTIES H. SHI Abstract. In this paper, some known typical properties of function spaces are shown to
Acta Math. Univ. Comenianae Vol. LXX, 2(2001), pp. 185 192 185 PREVALENCE OF SOME KNOWN TYPICAL PROPERTIES H. SHI Abstract. In this paper, some known typical properties of function spaces are shown to
The structure of ideals, point derivations, amenability and weak amenability of extended Lipschitz algebras
 Int. J. Nonlinear Anal. Appl. 8 (2017) No. 1, 389-404 ISSN: 2008-6822 (electronic) http://dx.doi.org/10.22075/ijnaa.2016.493 The structure of ideals, point derivations, amenability and weak amenability
Int. J. Nonlinear Anal. Appl. 8 (2017) No. 1, 389-404 ISSN: 2008-6822 (electronic) http://dx.doi.org/10.22075/ijnaa.2016.493 The structure of ideals, point derivations, amenability and weak amenability
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES: COMPACT SETS AND FINITE-DIMENSIONAL SPACES. 1. Compact Sets
 FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES: COMPACT SETS AND FINITE-DIMENSIONAL SPACES CHRISTOPHER HEIL 1. Compact Sets Definition 1.1 (Compact and Totally Bounded Sets). Let X be a metric space, and let E X be
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES: COMPACT SETS AND FINITE-DIMENSIONAL SPACES CHRISTOPHER HEIL 1. Compact Sets Definition 1.1 (Compact and Totally Bounded Sets). Let X be a metric space, and let E X be
Exercises from other sources REAL NUMBERS 2,...,
 Exercises from other sources REAL NUMBERS 1. Find the supremum and infimum of the following sets: a) {1, b) c) 12, 13, 14, }, { 1 3, 4 9, 13 27, 40 } 81,, { 2, 2 + 2, 2 + 2 + } 2,..., d) {n N : n 2 < 10},
Exercises from other sources REAL NUMBERS 1. Find the supremum and infimum of the following sets: a) {1, b) c) 12, 13, 14, }, { 1 3, 4 9, 13 27, 40 } 81,, { 2, 2 + 2, 2 + 2 + } 2,..., d) {n N : n 2 < 10},
Economics 204 Summer/Fall 2011 Lecture 5 Friday July 29, 2011
 Economics 204 Summer/Fall 2011 Lecture 5 Friday July 29, 2011 Section 2.6 (cont.) Properties of Real Functions Here we first study properties of functions from R to R, making use of the additional structure
Economics 204 Summer/Fall 2011 Lecture 5 Friday July 29, 2011 Section 2.6 (cont.) Properties of Real Functions Here we first study properties of functions from R to R, making use of the additional structure
TOPOLOGICAL GROUPS MATH 519
 TOPOLOGICAL GROUPS MATH 519 The purpose of these notes is to give a mostly self-contained topological background for the study of the representations of locally compact totally disconnected groups, as
TOPOLOGICAL GROUPS MATH 519 The purpose of these notes is to give a mostly self-contained topological background for the study of the representations of locally compact totally disconnected groups, as
SOME REMARKS ON THE SPACE OF DIFFERENCES OF SUBLINEAR FUNCTIONS
 APPLICATIONES MATHEMATICAE 22,3 (1994), pp. 419 426 S. G. BARTELS and D. PALLASCHKE (Karlsruhe) SOME REMARKS ON THE SPACE OF DIFFERENCES OF SUBLINEAR FUNCTIONS Abstract. Two properties concerning the space
APPLICATIONES MATHEMATICAE 22,3 (1994), pp. 419 426 S. G. BARTELS and D. PALLASCHKE (Karlsruhe) SOME REMARKS ON THE SPACE OF DIFFERENCES OF SUBLINEAR FUNCTIONS Abstract. Two properties concerning the space
Math 5052 Measure Theory and Functional Analysis II Homework Assignment 7
 Math 5052 Measure Theory and Functional Analysis II Homework Assignment 7 Prof. Wickerhauser Due Friday, February 5th, 2016 Please do Exercises 3, 6, 14, 16*, 17, 18, 21*, 23*, 24, 27*. Exercises marked
Math 5052 Measure Theory and Functional Analysis II Homework Assignment 7 Prof. Wickerhauser Due Friday, February 5th, 2016 Please do Exercises 3, 6, 14, 16*, 17, 18, 21*, 23*, 24, 27*. Exercises marked
FIXED POINT ITERATION FOR PSEUDOCONTRACTIVE MAPS
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 127, Number 4, April 1999, Pages 1163 1170 S 0002-9939(99)05050-9 FIXED POINT ITERATION FOR PSEUDOCONTRACTIVE MAPS C. E. CHIDUME AND CHIKA MOORE
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 127, Number 4, April 1999, Pages 1163 1170 S 0002-9939(99)05050-9 FIXED POINT ITERATION FOR PSEUDOCONTRACTIVE MAPS C. E. CHIDUME AND CHIKA MOORE
CHAPTER 9. Embedding theorems
 CHAPTER 9 Embedding theorems In this chapter we will describe a general method for attacking embedding problems. We will establish several results but, as the main final result, we state here the following:
CHAPTER 9 Embedding theorems In this chapter we will describe a general method for attacking embedding problems. We will establish several results but, as the main final result, we state here the following:
OPTIMALITY CONDITIONS FOR D.C. VECTOR OPTIMIZATION PROBLEMS UNDER D.C. CONSTRAINTS. N. Gadhi, A. Metrane
 Serdica Math. J. 30 (2004), 17 32 OPTIMALITY CONDITIONS FOR D.C. VECTOR OPTIMIZATION PROBLEMS UNDER D.C. CONSTRAINTS N. Gadhi, A. Metrane Communicated by A. L. Dontchev Abstract. In this paper, we establish
Serdica Math. J. 30 (2004), 17 32 OPTIMALITY CONDITIONS FOR D.C. VECTOR OPTIMIZATION PROBLEMS UNDER D.C. CONSTRAINTS N. Gadhi, A. Metrane Communicated by A. L. Dontchev Abstract. In this paper, we establish
arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 30 Jun 2014
![arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 30 Jun 2014 arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 30 Jun 2014](/thumbs/80/81263552.jpg) Maximality of the sum of the subdifferential operator and a maximally monotone operator arxiv:1406.7664v1 [math.fa] 30 Jun 2014 Liangjin Yao June 29, 2014 Abstract The most important open problem in Monotone
Maximality of the sum of the subdifferential operator and a maximally monotone operator arxiv:1406.7664v1 [math.fa] 30 Jun 2014 Liangjin Yao June 29, 2014 Abstract The most important open problem in Monotone
THE NEARLY ADDITIVE MAPS
 Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 46 (009), No., pp. 199 07 DOI 10.4134/BKMS.009.46..199 THE NEARLY ADDITIVE MAPS Esmaeeil Ansari-Piri and Nasrin Eghbali Abstract. This note is a verification on the relations between
Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 46 (009), No., pp. 199 07 DOI 10.4134/BKMS.009.46..199 THE NEARLY ADDITIVE MAPS Esmaeeil Ansari-Piri and Nasrin Eghbali Abstract. This note is a verification on the relations between
Smarandachely Precontinuous maps. and Preopen Sets in Topological Vector Spaces
 International J.Math. Combin. Vol.2 (2009), 21-26 Smarandachely Precontinuous maps and Preopen Sets in Topological Vector Spaces Sayed Elagan Department of Mathematics and Statistics Faculty of Science,
International J.Math. Combin. Vol.2 (2009), 21-26 Smarandachely Precontinuous maps and Preopen Sets in Topological Vector Spaces Sayed Elagan Department of Mathematics and Statistics Faculty of Science,
g 2 (x) (1/3)M 1 = (1/3)(2/3)M.
 COMPACTNESS If C R n is closed and bounded, then by B-W it is sequentially compact: any sequence of points in C has a subsequence converging to a point in C Conversely, any sequentially compact C R n is
COMPACTNESS If C R n is closed and bounded, then by B-W it is sequentially compact: any sequence of points in C has a subsequence converging to a point in C Conversely, any sequentially compact C R n is
UNIFORMLY GÂTEAUX SMOOTH APPROXIMATIONS ON c 0 (Γ)
 UNIFORMLY GÂTEAUX SMOOTH APPROXIMATIONS ON c 0 Γ) PETR HÁJEK AND MICHAL JOHANIS Abstract. Every Lipschitz mapping from c 0 Γ) into a Banach space Y can be uniformly approximated by Lipschitz mappings that
UNIFORMLY GÂTEAUX SMOOTH APPROXIMATIONS ON c 0 Γ) PETR HÁJEK AND MICHAL JOHANIS Abstract. Every Lipschitz mapping from c 0 Γ) into a Banach space Y can be uniformly approximated by Lipschitz mappings that
A continuous operator extending fuzzy ultrametrics
 A continuous operator extending fuzzy ultrametrics I. Stasyuk, E.D. Tymchatyn November 30, 200 Abstract We consider the problem of simultaneous extension of fuzzy ultrametrics defined on closed subsets
A continuous operator extending fuzzy ultrametrics I. Stasyuk, E.D. Tymchatyn November 30, 200 Abstract We consider the problem of simultaneous extension of fuzzy ultrametrics defined on closed subsets
MAXIMALITY OF SUMS OF TWO MAXIMAL MONOTONE OPERATORS
 MAXIMALITY OF SUMS OF TWO MAXIMAL MONOTONE OPERATORS JONATHAN M. BORWEIN, FRSC Abstract. We use methods from convex analysis convex, relying on an ingenious function of Simon Fitzpatrick, to prove maximality
MAXIMALITY OF SUMS OF TWO MAXIMAL MONOTONE OPERATORS JONATHAN M. BORWEIN, FRSC Abstract. We use methods from convex analysis convex, relying on an ingenious function of Simon Fitzpatrick, to prove maximality
On pseudomonotone variational inequalities
 An. Şt. Univ. Ovidius Constanţa Vol. 14(1), 2006, 83 90 On pseudomonotone variational inequalities Silvia Fulina Abstract Abstract. There are mainly two definitions of pseudomonotone mappings. First, introduced
An. Şt. Univ. Ovidius Constanţa Vol. 14(1), 2006, 83 90 On pseudomonotone variational inequalities Silvia Fulina Abstract Abstract. There are mainly two definitions of pseudomonotone mappings. First, introduced
On Semicontinuity of Convex-valued Multifunctions and Cesari s Property (Q)
 On Semicontinuity of Convex-valued Multifunctions and Cesari s Property (Q) Andreas Löhne May 2, 2005 (last update: November 22, 2005) Abstract We investigate two types of semicontinuity for set-valued
On Semicontinuity of Convex-valued Multifunctions and Cesari s Property (Q) Andreas Löhne May 2, 2005 (last update: November 22, 2005) Abstract We investigate two types of semicontinuity for set-valued
REPRESENTABLE BANACH SPACES AND UNIFORMLY GÂTEAUX-SMOOTH NORMS. Julien Frontisi
 Serdica Math. J. 22 (1996), 33-38 REPRESENTABLE BANACH SPACES AND UNIFORMLY GÂTEAUX-SMOOTH NORMS Julien Frontisi Communicated by G. Godefroy Abstract. It is proved that a representable non-separable Banach
Serdica Math. J. 22 (1996), 33-38 REPRESENTABLE BANACH SPACES AND UNIFORMLY GÂTEAUX-SMOOTH NORMS Julien Frontisi Communicated by G. Godefroy Abstract. It is proved that a representable non-separable Banach
ECARES Université Libre de Bruxelles MATH CAMP Basic Topology
 ECARES Université Libre de Bruxelles MATH CAMP 03 Basic Topology Marjorie Gassner Contents: - Subsets, Cartesian products, de Morgan laws - Ordered sets, bounds, supremum, infimum - Functions, image, preimage,
ECARES Université Libre de Bruxelles MATH CAMP 03 Basic Topology Marjorie Gassner Contents: - Subsets, Cartesian products, de Morgan laws - Ordered sets, bounds, supremum, infimum - Functions, image, preimage,
Chapter 2 Convex Analysis
 Chapter 2 Convex Analysis The theory of nonsmooth analysis is based on convex analysis. Thus, we start this chapter by giving basic concepts and results of convexity (for further readings see also [202,
Chapter 2 Convex Analysis The theory of nonsmooth analysis is based on convex analysis. Thus, we start this chapter by giving basic concepts and results of convexity (for further readings see also [202,
ON THE HYPERBANACH SPACES. P. Raja. S.M. Vaezpour. 1. Introduction
 italian journal of pure and applied mathematics n. 28 2011 (261 272) 261 ON THE HYPERBANACH SPACES P. Raja Department O Mathematics Shahid Beheshti University P.O. Box 1983963113, Tehran Iran e-mail: pandoora
italian journal of pure and applied mathematics n. 28 2011 (261 272) 261 ON THE HYPERBANACH SPACES P. Raja Department O Mathematics Shahid Beheshti University P.O. Box 1983963113, Tehran Iran e-mail: pandoora
On constraint qualifications with generalized convexity and optimality conditions
 On constraint qualifications with generalized convexity and optimality conditions Manh-Hung Nguyen, Do Van Luu To cite this version: Manh-Hung Nguyen, Do Van Luu. On constraint qualifications with generalized
On constraint qualifications with generalized convexity and optimality conditions Manh-Hung Nguyen, Do Van Luu To cite this version: Manh-Hung Nguyen, Do Van Luu. On constraint qualifications with generalized
Immerse Metric Space Homework
 Immerse Metric Space Homework (Exercises -2). In R n, define d(x, y) = x y +... + x n y n. Show that d is a metric that induces the usual topology. Sketch the basis elements when n = 2. Solution: Steps
Immerse Metric Space Homework (Exercises -2). In R n, define d(x, y) = x y +... + x n y n. Show that d is a metric that induces the usual topology. Sketch the basis elements when n = 2. Solution: Steps
Shih-sen Chang, Yeol Je Cho, and Haiyun Zhou
 J. Korean Math. Soc. 38 (2001), No. 6, pp. 1245 1260 DEMI-CLOSED PRINCIPLE AND WEAK CONVERGENCE PROBLEMS FOR ASYMPTOTICALLY NONEXPANSIVE MAPPINGS Shih-sen Chang, Yeol Je Cho, and Haiyun Zhou Abstract.
J. Korean Math. Soc. 38 (2001), No. 6, pp. 1245 1260 DEMI-CLOSED PRINCIPLE AND WEAK CONVERGENCE PROBLEMS FOR ASYMPTOTICALLY NONEXPANSIVE MAPPINGS Shih-sen Chang, Yeol Je Cho, and Haiyun Zhou Abstract.
ON A HYBRID PROXIMAL POINT ALGORITHM IN BANACH SPACES
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 80, Iss. 3, 2018 ISSN 1223-7027 ON A HYBRID PROXIMAL POINT ALGORITHM IN BANACH SPACES Vahid Dadashi 1 In this paper, we introduce a hybrid projection algorithm for a countable
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 80, Iss. 3, 2018 ISSN 1223-7027 ON A HYBRID PROXIMAL POINT ALGORITHM IN BANACH SPACES Vahid Dadashi 1 In this paper, we introduce a hybrid projection algorithm for a countable
IN AN ALGEBRA OF OPERATORS
 Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 54 (2017), No. 2, pp. 443 454 https://doi.org/10.4134/bkms.b160011 pissn: 1015-8634 / eissn: 2234-3016 q-frequent HYPERCYCLICITY IN AN ALGEBRA OF OPERATORS Jaeseong Heo, Eunsang
Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 54 (2017), No. 2, pp. 443 454 https://doi.org/10.4134/bkms.b160011 pissn: 1015-8634 / eissn: 2234-3016 q-frequent HYPERCYCLICITY IN AN ALGEBRA OF OPERATORS Jaeseong Heo, Eunsang
(c) For each α R \ {0}, the mapping x αx is a homeomorphism of X.
 A short account of topological vector spaces Normed spaces, and especially Banach spaces, are basic ambient spaces in Infinite- Dimensional Analysis. However, there are situations in which it is necessary
A short account of topological vector spaces Normed spaces, and especially Banach spaces, are basic ambient spaces in Infinite- Dimensional Analysis. However, there are situations in which it is necessary
Viscosity Iterative Approximating the Common Fixed Points of Non-expansive Semigroups in Banach Spaces
 Viscosity Iterative Approximating the Common Fixed Points of Non-expansive Semigroups in Banach Spaces YUAN-HENG WANG Zhejiang Normal University Department of Mathematics Yingbing Road 688, 321004 Jinhua
Viscosity Iterative Approximating the Common Fixed Points of Non-expansive Semigroups in Banach Spaces YUAN-HENG WANG Zhejiang Normal University Department of Mathematics Yingbing Road 688, 321004 Jinhua
REAL AND COMPLEX ANALYSIS
 REAL AND COMPLE ANALYSIS Third Edition Walter Rudin Professor of Mathematics University of Wisconsin, Madison Version 1.1 No rights reserved. Any part of this work can be reproduced or transmitted in any
REAL AND COMPLE ANALYSIS Third Edition Walter Rudin Professor of Mathematics University of Wisconsin, Madison Version 1.1 No rights reserved. Any part of this work can be reproduced or transmitted in any
