Wave Motion In Terms of Field - Carrying Particles. Hisham B. Ghassib Royal Scientific Society Amman - Jordan
|
|
|
- Henry Nash
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Wave Motion In Terms of Field - Carrying Particles Hisham B. Ghassib Royal Scientific Society Amman - Jordan ABSTRACT In this paper, wave propagation is analyzed in terms of field-carrying particle kinematics. This analysis is used for kinematically dissecting classical field equations. The pedagogical value of this analysis is emphasized. It is also shown that, according to this analysis, proper mass could be interpreted as a measure of the deviation of a classical field from Huygens' propagation; a deviation which is externally generated and induced.
2 1- INTRODUCTION It is possible to assert, on purely theoretical grounds, that the concept of wave is pedagogically far more complicated and difficult to grasp than that other fundamental form of classical motion, the concept of particle(1). In fact, many a physics student has graduated from university with the uncomfortable feeling that, even though it is within his capacity to solve mathematically a number of wave equations under various conditions quite satisfactorily, he has not actually grasped the essence of the concept of wave. It would appear that this wide pedagogical gap between the two concepts is indeed an objective gap which has nothing to do with the specific psychology of the student as an individual, but is inherent in the very logico-empirical status of the two concepts. In the first place, wave motion is that fundamental form of classical motion which is characteristic of the transfer of energy in its pure field form. What is essentially transferred via wave motion is field energy, even though it may involve particle oscillation. Particle motion, on the other hand, is characteristic of the transfer of energy in its more tangible form, the mass form. The former is the fundamental building block of classical field dynamics, whereas the latter is the fundamental building block of classical matter dynamics. The intangibility and elusiveness of the classical concept of field, compared to the concept of mass, is one of the basic reasons for the aforementioned pedagogical gap().
3 In the second place, the correspondence between wave representations and physical phenomena involving wave motion is far less direct than that between the particle representation and its related phenomena. For example, the correspondence between the simple sinusoidal wave representation and light propagation is far less conspicuous than the correspondence between the particle representation and planetary motion. The concept of wave is usually introduced via a number of onedimensional and two-dimensional representations. The student usually grasps these representations as concrete systems and in their pure facticity without getting hold of the essence of the representation for which the latter has been designed in the first place. This is a danger latent in all representations, but especially so in wave representations. Accordingly, the student fails to make the leap, as it were, from the particular to the concrete general, and fails to grasp the physical significance of such general wave forms as electromagnetic and Schrodinger waves. In optics, the concept of wave is defined in terms of Huygens' Principle, the phenomena of interference and diffraction, and eventually the three-dimensional wave equation: 1 u t r,t
4 Interpreting wave propagation in terms of the continual generation of field sources a' la Huygens, one can account satisfactorily for the principal phenomena of wave motion. However, the exact mathematical and physical relationship between equation (1) and Huygens' Principle is never truly established. At least, it is not so established in a simple and straight-forward manner(3). The relationship is further confused when the Maxwell and Schrodinger equations are introduced in their capacity as exemplary wave equations(4). The student usually feels capable of grasping each one of these multifarious principles and representations on its own. However, when it comes to relating them dialectically in a comprehensive whole characteristic of the essence of wave motion, he feels utterly confused, and is at a loss. In this paper, we introduce the concept of field-carrying particle (point), and clarify wave propagation, including Huygens' principle, in terms of this concept. That is, we derive the wave equation from the kinematics of field-carrying particles. Then we use this method to dissect the Klein-Gordon equation, both in the absence and the presence of an electromagnetic field. This dissection leads us to view proper mass as a measure of the deviation from Huygens' propagation, and as an externally induced and generated interaction term. 4
5 - THE CONCEPT OF WAVE The concept of wave is rarely given a precise definition with clear boundaries and limits. It is used to describe all sorts of situations ranging from one-dimensional string waves to relativistic scalar fields. We shall therefore give a precise definition of wave motion which will assist us in classifying the various classical field equations. We shall specify the concept in terms of the answers to the following questions. Via what type of carrier the classical field travels in space and time? And, how do these field carriers propagate in space and time - i. e., what is the kinematics of waves? We start by viewing a scalar classical field as an infinite collection of field-carrying point particles moving in definite paths. The field,, carried by each particle is a function of both the position vector of the particle and the time. Thus, (r,t)...() We assume the following: - (I) changes with the position of the field particle and the time in such a way that it remains constant. This means that each particle carries a specific field value, just as classical Newtonian particles carry specific masses. It is in this sense that the particles are called fieldcarrying particles. Thus, 5
6 (ii) r,t for each particle. const...(3) That is, there is a level surface in four-dimensional (Minkowski) space for each particle. The field-carrying particles are continuously distributed in space such that ( r, t ) describes their space distribution at time t. It follows from (3) that: r. ( r,t) ( r, t) 0...(4) t where r(t) is the velocity of the field-carrying particle. Next, we interpret Huygens' principle to mean that each particle moves along a path which is always perpendicular to its level surface- i.e., r (t) is parallel to ( r, t ). Thus, r ( r,t) ( r,t)... (5) u t where u is the speed of the particles. Taking the divergence of each side of eq. (5), and then r,t, we obtain: r,t r,t u t t u t resubstituting for Thus, for constant speed fields, 1 r,t r, t 0...(7) u t...(6) 6
7 which is the generalized 3-D Huygens-type equation. We believe that this derivation of the wave equation clarifies its kinematic meaning and gives a precise mathematical form to Huygens' principle. 3- THE KLEIN-GORDON EQUATION Eq. (4) admits a wide variety of solutions, each of which is characterized by a specific type of wave propagation. We have dealt in some detail with the Huygen's (orthogonal) solution. The question is what other solutions are physically interesting and significant? To answer the question, we shall enquire into the structure of the free classical relativistic scalar field equation (the Klein-Gordon equation)-namely, 1 m c c t h 0 r,t r,t r,t...(8) where m o is the proper mass of the field, and c is the speed of light in vacuo. It is evident that eq. (8) differs fundamentally from eq. (6). Therefore, it cannot possibly belong to the Huygens' field variety. The question is, what solution of eq. (4) would generate eq. (8)? Let us consider the following solution. r c t r, t r, t...(9) 7
8 (u = c, the speed of light in this case). where is a three - dimensional vector. Eq. (9) is equivalent to Eq. (4) if. r 0...(10) that is, if is perpendicular to r. Now, taking the divergence of both sides of eq. (9), as before, we arrive at the following equation. 1 r, t r, t r, t...(11) c t which is identical to eq. (8) if moc...(1) h In eq. (9), is a measure of the deviation from Huygens' propagation. When is zero, the propagation is of the Huygens' variety. Therefore eq. (1) implies that proper mass is a measure of the deviation from Huygens' propagation. This is a new wave - geometric interpretation of mass, which follows from dissecting the familiar equation (8) with our unfamiliar methodology. Next, we ask the question, how is our solution modified in the presence of an external electromagnetic field? What effect does the electromagnetic field have on our "generator" shown in eq. (9)? 8
9 The classical relativistic scalar field equation assumes the following form in the presence of an external electromagnetic field(5). t e i c A r, t) 1 h ( ih e m c...(13) o c where e is the field charge, A is the externally induced vector potential, and is the externally induced scalar potential. To simplify the treatment, we assume that the scalar potential is a vanishing term, and the vector potential is time-independent, in which case eq.(13) is reduced to the following: ih e c A r,t h c t r,t m c r,t...(14 o ) What "generator" in the spirit of eq. (9) will generate eq. (14)? If we assume: (i) u is time-independent, (ii) A, u, form an orthonormal system (i.e., the wave propagates in a direction perpendicular to both A and ), then we can generate eq. (14) with the following generator: u c ie r, t mo... (15) c t h ch 9
10 It can easily be verified that eq. (15) obeys eq. (4) and generates eq. (14) subject to the two assumptions stated. This means that eq. (14) is a wave equation in the strict sense given to it in eq. (14). We notice that the mass term is similar, in both form and function, to the electromagnetic field term on the right-hand side of eq. (15). They are both " - terms", both perpendicular to the fieldparticle velocity, and both measures of the deviation from Huygens' propagation. This suggests that the mass term is some sort of a vector potential of an external field, which is, however, quite different from the electromagnetic vector potential. The former is real, whilst the latter is imaginary. Nevertheless, eq. (15) lends itself to a Machian interpretation of mass as an externally induced interaction term (6). It could be worth pursuing this suggestion by inquiring into the type of gauge field that would induce the mass term. 01
11 References 1- This statement, which is based on theoretical grounds, is, nevertheless, corroborated by the author's physics teaching experience and conversations with physics graduates in England and Jordan. - See, in particular, the detailed discussions of this fundamental difference in: Hisham B. Ghassib, Excursions into Scientific Thought, RSS, Amman (1985); The Process of Unification in Field Physics, RSS and ISESCO, Amman (1988); A Simplified Approach to the Concept of Wave Motion, RSS and ISESCO, Amman (1991). 3- In textbooks on optics, the general 3 - D wave equation is never kinematically derived. Its organic connection with Huygens (orthogonal) propagation is never directly shown. For example, in: R.S. Longhurst, Geometrical and Physical Optics, nd. Edition, Longmans (1967), p. 96, the 3-D wave equation is introduced for the first time as follows: "An investigation into the propagation of sound waves leads to the general result that the velocity potential satisfies the equation, 00
12 x y z 1 c t This is known as the general equation of wave motion". Only much later does he discuss Kirchhoff's formulation of Huygens' Principle, which starts with the wave equation and ends up by showing that the disturbance at a point is the sum of all retarded disturbances coming from a closed surface. Kirchhoff's formulation is, however, basically a theory of diffraction, and does not show how Huygens (orthogonal) propagation forms a constituent part of the wave equation. A similar treatment occurs in a classic, Arnold Sommerfeld's "Optics" [(translated by O. Laporte and P. Moldauer, Academic Press, New York (1964)]. This treatment seems to be typical of most textbooks on optics. 4- There is a detailed attempt at clarifying this relationship in the context of accounting for the Schrodinger equation in: Hisham Ghassib, How Wave Mechanics was Constructed, RSS and Dar-al-Furqan, Amman (1983). 5- See, for example: A.S. Kompaneyets, Theoretical Physics, Mir Publishers, Moscow (1965), p See, in this regard: J. Rosen, Extended Mach Principle, Am. J. Phys., 49 (3), March 1981, pp ; M. Semon and G. Schmieg, Note on the Analogy between Intertial and Electromagnetic Forces, Am. J. Phys., 49 (7), July 1981, pp ; Y. Gingras, Comment on 0
13 "What the Electromagnetic Vector Potential Describes", Am. J. Phys., 48 (1), Jan. 1980, p,
ESSEX COUNTY COLLEGE Mathematics and Physics Division PHY 203 General Physics III Course Outline
 ESSEX COUNTY COLLEGE Mathematics and Physics Division PHY 203 General Physics III Course Outline Course Number & Name: PHY 203 General Physics III Credit Hours: 5.0 Contact Hours: 7.0 Lecture/Lab: 7.0
ESSEX COUNTY COLLEGE Mathematics and Physics Division PHY 203 General Physics III Course Outline Course Number & Name: PHY 203 General Physics III Credit Hours: 5.0 Contact Hours: 7.0 Lecture/Lab: 7.0
Comment about Didactical formulation of the
 Comment about Didactical formulation of the Ampère law Hendrik van Hees Institute for Theoretical Physics, Goethe University Frankfurt, Max-von-Laue-Str. 1, D-60438 Frankfurt, Germany Frankfurt Institute
Comment about Didactical formulation of the Ampère law Hendrik van Hees Institute for Theoretical Physics, Goethe University Frankfurt, Max-von-Laue-Str. 1, D-60438 Frankfurt, Germany Frankfurt Institute
Physics 209 Fall 2002 Notes 5 Thomas Precession
 Physics 209 Fall 2002 Notes 5 Thomas Precession Jackson s discussion of Thomas precession is based on Thomas s original treatment, and on the later paper by Bargmann, Michel, and Telegdi. The alternative
Physics 209 Fall 2002 Notes 5 Thomas Precession Jackson s discussion of Thomas precession is based on Thomas s original treatment, and on the later paper by Bargmann, Michel, and Telegdi. The alternative
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.class-ph] 26 Sep 2003
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.class-ph] 26 Sep 2003 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.class-ph] 26 Sep 2003](/thumbs/87/95270988.jpg) arxiv:physics/0309112v1 [physics.class-ph] 26 Sep 2003 Electromagnetic vortex lines riding atop null solutions of the Maxwell equations Iwo Bialynicki-Birula Center for Theoretical Physics, Polish Academy
arxiv:physics/0309112v1 [physics.class-ph] 26 Sep 2003 Electromagnetic vortex lines riding atop null solutions of the Maxwell equations Iwo Bialynicki-Birula Center for Theoretical Physics, Polish Academy
Introduction. Chapter Presentation of Macroscopic Electrodynamics. 1.1 What is Electrodynamics?
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is Electrodynamics? Electrodynamics as a theory deals with electric charges which move in space and with electromagnetic fields that are produced by the charges and again
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is Electrodynamics? Electrodynamics as a theory deals with electric charges which move in space and with electromagnetic fields that are produced by the charges and again
FI 3103 Quantum Physics
 FI 3103 Quantum Physics Alexander A. Iskandar Physics of Magnetism and Photonics Research Group Institut Teknologi Bandung General Information Lecture schedule 17 18 9136 51 5 91 Tutorial Teaching Assistant
FI 3103 Quantum Physics Alexander A. Iskandar Physics of Magnetism and Photonics Research Group Institut Teknologi Bandung General Information Lecture schedule 17 18 9136 51 5 91 Tutorial Teaching Assistant
On Maxwell s discovery of electromagnetic waves and the gauge condition. P. T. Leung
 On Maxwell s discovery of electromagnetic waves and the gauge condition P. T. Leung Department of Physics, Portland State University, P. O. Box 751, Portland, OR 9707-0751 Abstract The original theoretical
On Maxwell s discovery of electromagnetic waves and the gauge condition P. T. Leung Department of Physics, Portland State University, P. O. Box 751, Portland, OR 9707-0751 Abstract The original theoretical
Nature of diffraction. Diffraction
 Nature of diffraction Diffraction From Grimaldi to Maxwell Definition of diffraction diffractio, Francesco Grimaldi (1665) The effect is a general characteristics of wave phenomena occurring whenever a
Nature of diffraction Diffraction From Grimaldi to Maxwell Definition of diffraction diffractio, Francesco Grimaldi (1665) The effect is a general characteristics of wave phenomena occurring whenever a
Diffractive Optics. Professor 송석호, Physics Department (Room #36-401) , ,
 Diffractive Optics Professor 송석호, Physics Department (Room #36-401) 2220-0923, 010-4546-1923, shsong@hanyang.ac.kr Office Hours Mondays 10:00-12:00, Wednesdays 10:00-12:00 TA 윤재웅 (Ph.D. student, Room #36-415)
Diffractive Optics Professor 송석호, Physics Department (Room #36-401) 2220-0923, 010-4546-1923, shsong@hanyang.ac.kr Office Hours Mondays 10:00-12:00, Wednesdays 10:00-12:00 TA 윤재웅 (Ph.D. student, Room #36-415)
TRANSIENT PHENOMENA IN QUANTUM MECHANICS: DIFFRACTION IN TIME
 Paths of Discovery Pontifical Academy of Sciences, Acta 18, Vatican City 2006 www.pas.va/content/dam/accademia/pdf/acta18/acta18-moshinsky.pdf TRANSIENT PHENOMENA IN QUANTUM MECHANICS: DIFFRACTION IN TIME
Paths of Discovery Pontifical Academy of Sciences, Acta 18, Vatican City 2006 www.pas.va/content/dam/accademia/pdf/acta18/acta18-moshinsky.pdf TRANSIENT PHENOMENA IN QUANTUM MECHANICS: DIFFRACTION IN TIME
Introduction. You know, it would be sufficient to really understand. If I can t picture it, I can t understand it.
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction You know, it would be sufficient to really understand the electron. Albert Einstein [2] If I can t picture it, I can t understand it. Albert Einstein [41] I think it is quite likely,
CHAPTER 1 Introduction You know, it would be sufficient to really understand the electron. Albert Einstein [2] If I can t picture it, I can t understand it. Albert Einstein [41] I think it is quite likely,
A simple and compact approach to hydrodynamic using geometric algebra. Abstract
 A simple and compact approach to hydrodynamic using geometric algebra Xiong Wang (a) Center for Chaos and Complex Networks (b) Department of Electronic Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong
A simple and compact approach to hydrodynamic using geometric algebra Xiong Wang (a) Center for Chaos and Complex Networks (b) Department of Electronic Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong
The Other Meaning of Special Relativity
 The Other Meaning of Special Relativity Robert A. Close* ABSTRACT Einstein s special theory of relativity postulates that the speed of light is a constant for all inertial observers. This postulate can
The Other Meaning of Special Relativity Robert A. Close* ABSTRACT Einstein s special theory of relativity postulates that the speed of light is a constant for all inertial observers. This postulate can
Science Curriculum Matrix
 Science Curriculum Matrix Physics Version 1.0 beta June 2, 2008 This curriculum (core matrix) document will eventually become part of the Science Curriculum Matrix. We envision the Science Curriculum Matrix
Science Curriculum Matrix Physics Version 1.0 beta June 2, 2008 This curriculum (core matrix) document will eventually become part of the Science Curriculum Matrix. We envision the Science Curriculum Matrix
Chapter 1. Preliminaries
 Chapter 1 Preliminaries 1.1 The Vector Concept Revisited The concept of a vector has been one of the most fruitful ideas in all of mathematics, and it is not surprising that we receive repeated exposure
Chapter 1 Preliminaries 1.1 The Vector Concept Revisited The concept of a vector has been one of the most fruitful ideas in all of mathematics, and it is not surprising that we receive repeated exposure
Physics General Physics II. Electricity, Magnetism and Optics Lecture 20 Chapter Wave Optics. Fall 2015 Semester Prof.
 Physics 21900 General Physics II Electricity, Magnetism and Optics Lecture 20 Chapter 23.1-2 Wave Optics Fall 2015 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones Announcement Exam #2 will be on Thursday, November 5 th (tomorrow)
Physics 21900 General Physics II Electricity, Magnetism and Optics Lecture 20 Chapter 23.1-2 Wave Optics Fall 2015 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones Announcement Exam #2 will be on Thursday, November 5 th (tomorrow)
4 credits, 3-hrs. lecture/2-hrs. lab/2-hrs. recitation Lecture:
 PHY 220 HOSTOS COMMUNITY COLLEGE GENERAL PHYSICS II 4 credits, 3-hrs. lecture/2-hrs. lab/2-hrs. recitation Lecture: Schedule Laboratory: Recitation: Instructor: E-mail: Office: Phone: Office Hours: Required
PHY 220 HOSTOS COMMUNITY COLLEGE GENERAL PHYSICS II 4 credits, 3-hrs. lecture/2-hrs. lab/2-hrs. recitation Lecture: Schedule Laboratory: Recitation: Instructor: E-mail: Office: Phone: Office Hours: Required
Notes on Huygens Principle 2000 Lawrence Rees
 Notes on Huygens Principle 2000 Lawrence Rees In the 17 th Century, Christiaan Huygens (1629 1695) proposed what we now know as Huygens Principle. We often invoke Huygens Principle as one of the fundamental
Notes on Huygens Principle 2000 Lawrence Rees In the 17 th Century, Christiaan Huygens (1629 1695) proposed what we now know as Huygens Principle. We often invoke Huygens Principle as one of the fundamental
The particle model for the Higgs condensate and the anomalous geometrical diffraction
 The particle model for the Higgs condensate and the anomalous geometrical diffraction Jiří Souček Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Arts U Kříže 8, Prague 5, 158 00, Czech Republic jiri.soucek@ff.cuni.cz
The particle model for the Higgs condensate and the anomalous geometrical diffraction Jiří Souček Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Arts U Kříže 8, Prague 5, 158 00, Czech Republic jiri.soucek@ff.cuni.cz
Motion Fundamentals. 1 Postulates. 2 Natural Progression. Thomas Kirk
 Motion Fundamentals Thomas Kirk I was asked by the Editor to respond to comments by the editorial referee on my article, Derivation of Reciprocal System Mathematics", and also to comment on K.V.K. Nehru
Motion Fundamentals Thomas Kirk I was asked by the Editor to respond to comments by the editorial referee on my article, Derivation of Reciprocal System Mathematics", and also to comment on K.V.K. Nehru
Lecture 9: Waves in Classical Physics
 PHYS419 Lecture 9 Waves in Classical Physics 1 Lecture 9: Waves in Classical Physics If I say the word wave in no particular context, the image which most probably springs to your mind is one of a roughly
PHYS419 Lecture 9 Waves in Classical Physics 1 Lecture 9: Waves in Classical Physics If I say the word wave in no particular context, the image which most probably springs to your mind is one of a roughly
On the quantum theory of rotating electrons
 Zur Quantentheorie des rotierenden Elektrons Zeit. f. Phys. 8 (98) 85-867. On the quantum theory of rotating electrons By Friedrich Möglich in Berlin-Lichterfelde. (Received on April 98.) Translated by
Zur Quantentheorie des rotierenden Elektrons Zeit. f. Phys. 8 (98) 85-867. On the quantum theory of rotating electrons By Friedrich Möglich in Berlin-Lichterfelde. (Received on April 98.) Translated by
Physical Optics 2018 Dr. Muwafaq Fadhil Al-Mishlab Third lecture [ Huygens Principle, Interference of light]
![Physical Optics 2018 Dr. Muwafaq Fadhil Al-Mishlab Third lecture [ Huygens Principle, Interference of light] Physical Optics 2018 Dr. Muwafaq Fadhil Al-Mishlab Third lecture [ Huygens Principle, Interference of light]](/thumbs/96/128206880.jpg) Physical Optics 2018 Dr. Muwafaq Fadhil Al-Mishlab Third lecture [ Huygens Principle, Interference of light] 1. Huygens principle Long before people understood the electromagnetic character of light, Christian
Physical Optics 2018 Dr. Muwafaq Fadhil Al-Mishlab Third lecture [ Huygens Principle, Interference of light] 1. Huygens principle Long before people understood the electromagnetic character of light, Christian
Lecture notes for QFT I (662)
 Preprint typeset in JHEP style - PAPER VERSION Lecture notes for QFT I (66) Martin Kruczenski Department of Physics, Purdue University, 55 Northwestern Avenue, W. Lafayette, IN 47907-036. E-mail: markru@purdue.edu
Preprint typeset in JHEP style - PAPER VERSION Lecture notes for QFT I (66) Martin Kruczenski Department of Physics, Purdue University, 55 Northwestern Avenue, W. Lafayette, IN 47907-036. E-mail: markru@purdue.edu
Plasma Physics Prof. V. K. Tripathi Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Plasma Physics Prof. V. K. Tripathi Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. # 09 Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Inhomogeneous Plasma (Refer Slide Time: 00:33) Today, I
Plasma Physics Prof. V. K. Tripathi Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture No. # 09 Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Inhomogeneous Plasma (Refer Slide Time: 00:33) Today, I
Light Quantum Hypothesis
 50 My God, He Plays Dice! Light Quantum Hypothesis Light Quantum Hypothesis 51 Light Quantum Hypothesis In his miracle year of 1905, Einstein wrote four extraordinary papers, one of which won him the 1921
50 My God, He Plays Dice! Light Quantum Hypothesis Light Quantum Hypothesis 51 Light Quantum Hypothesis In his miracle year of 1905, Einstein wrote four extraordinary papers, one of which won him the 1921
Physics 20 Work Plan
 Units/Topics Time Frame Major Learning Outcomes Unit Major Resource(s) Assessment methods Unit 2 Wave Motion A. Properties of waves 1. Wave terminology 2. Universal wave equation 3. Principle of Superposition
Units/Topics Time Frame Major Learning Outcomes Unit Major Resource(s) Assessment methods Unit 2 Wave Motion A. Properties of waves 1. Wave terminology 2. Universal wave equation 3. Principle of Superposition
RESEARCH PROJECT: Investigation of Relativistic Longitudinal Gauge Fields. and their Interactions. Abstract
 RESEARCH PROJECT: Investigation of Relativistic Longitudinal Gauge Fields and their Interactions By: Dale Alan Woodside, Ph.D. Department of Physics, Macquarie University Sydney, New South Wales 2109,
RESEARCH PROJECT: Investigation of Relativistic Longitudinal Gauge Fields and their Interactions By: Dale Alan Woodside, Ph.D. Department of Physics, Macquarie University Sydney, New South Wales 2109,
The Klein-Gordon string A tool I ve never heard of before Sergej Faletič
 The Klein-Gordon string A tool I ve never heard of before Sergej Faletič,, Jadranska 9, Ljubljana, E-mail: sergej.faletic@fmf.uni-lj.si Klein-Gordon string SEEMPE 5 Sergej Faletič springs/ elastic bands
The Klein-Gordon string A tool I ve never heard of before Sergej Faletič,, Jadranska 9, Ljubljana, E-mail: sergej.faletic@fmf.uni-lj.si Klein-Gordon string SEEMPE 5 Sergej Faletič springs/ elastic bands
Introduction to Polar Coordinates in Mechanics (for AQA Mechanics 5)
 Introduction to Polar Coordinates in Mechanics (for AQA Mechanics 5) Until now, we have dealt with displacement, velocity and acceleration in Cartesian coordinates - that is, in relation to fixed perpendicular
Introduction to Polar Coordinates in Mechanics (for AQA Mechanics 5) Until now, we have dealt with displacement, velocity and acceleration in Cartesian coordinates - that is, in relation to fixed perpendicular
OAKTON COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS. I. Course Course Course Prefix Number Name Credit: Lecture Lab. PHY 132 College Physics II 4 3 2
 OAKTON COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS I. Course Course Course Prefix Number Name Credit: Lecture Lab PHY 132 College Physics II 4 3 2 II. Prerequisites: PHY 131 III. Course (catalog) Description: Course
OAKTON COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS I. Course Course Course Prefix Number Name Credit: Lecture Lab PHY 132 College Physics II 4 3 2 II. Prerequisites: PHY 131 III. Course (catalog) Description: Course
CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
 CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Outlines 1. Waves in one dimension 2. Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum 3. Electromagnetic waves in Matter 4. Absorption and Dispersion 5. Guided Waves 2 Skip 9.1.1 and 9.1.2
CHAPTER 9 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Outlines 1. Waves in one dimension 2. Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum 3. Electromagnetic waves in Matter 4. Absorption and Dispersion 5. Guided Waves 2 Skip 9.1.1 and 9.1.2
Wilson Area School District Planned Course Guide
 Wilson Area School District Planned Course Guide Title of planned course: AP Physics C Independent Study Subject Area: Science Grade Level: 12 Course Description: AP Physics is our advanced placement course
Wilson Area School District Planned Course Guide Title of planned course: AP Physics C Independent Study Subject Area: Science Grade Level: 12 Course Description: AP Physics is our advanced placement course
ENV level elective. ENV 200 Intro to Environmental Science 4 credits ENV 330 Ecosystems and Ecological Design 4 credits
 PHYSICS Andrew Dawes, Chair; James Butler, Stephen Hall The program in physics is designed to prepare students for a variety of career paths including (but not limited to) physics and engineering graduate
PHYSICS Andrew Dawes, Chair; James Butler, Stephen Hall The program in physics is designed to prepare students for a variety of career paths including (but not limited to) physics and engineering graduate
CHAPTER 4 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN CYLINDRICAL SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 4 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN CYLINDRICAL SYSTEMS The vector Helmholtz equations satisfied by the phasor) electric and magnetic fields are where. In low-loss media and for a high frequency, i.e.,
CHAPTER 4 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN CYLINDRICAL SYSTEMS The vector Helmholtz equations satisfied by the phasor) electric and magnetic fields are where. In low-loss media and for a high frequency, i.e.,
MASTER SYLLABUS
 MASTER SYLLABUS 2019-2020 A. Academic Division: Business, Industry and Technology B. Discipline: Physics C. Course Number and Title: PHYS1130 General Physics II D. Course Coordinator: Gary Wood Assistant
MASTER SYLLABUS 2019-2020 A. Academic Division: Business, Industry and Technology B. Discipline: Physics C. Course Number and Title: PHYS1130 General Physics II D. Course Coordinator: Gary Wood Assistant
Basics of Radiation Fields
 Basics of Radiation Fields Initial questions: How could you estimate the distance to a radio source in our galaxy if you don t have a parallax? We are now going to shift gears a bit. In order to understand
Basics of Radiation Fields Initial questions: How could you estimate the distance to a radio source in our galaxy if you don t have a parallax? We are now going to shift gears a bit. In order to understand
A.K.Aringazin Department of Theoretical Physics Karaganda State University Karaganda , Kazakhstan. February 14, 1989
 LIE-ISOTOPIC FINSLERIAN LIFTING OF THE LORENTZ GROUP AND BLOKHINTSEV-REDEI-LIKE BEHAVIOR OF THE MESON LIFE-TIMES AND OF THE PARAMETERS OF THE K 0 K 0 SYSTEM A.K.Aringazin Department of Theoretical Physics
LIE-ISOTOPIC FINSLERIAN LIFTING OF THE LORENTZ GROUP AND BLOKHINTSEV-REDEI-LIKE BEHAVIOR OF THE MESON LIFE-TIMES AND OF THE PARAMETERS OF THE K 0 K 0 SYSTEM A.K.Aringazin Department of Theoretical Physics
Orbital Alignments. March 25, 2003
 Orbital Alignments March 25, 2003 1 Introduction In discussions of twisted ethylene derivatives, Figure 1, and similar discussions concerning Woodward Hoffman rules 1 the cos χ (χ is the twist angle dependence
Orbital Alignments March 25, 2003 1 Introduction In discussions of twisted ethylene derivatives, Figure 1, and similar discussions concerning Woodward Hoffman rules 1 the cos χ (χ is the twist angle dependence
With Modern Physics For Scientists and Engineers
 With Modern Physics For Scientists and Engineers Third Edition Richard Wolfson Middlebury College Jay M. Pasachoff Williams College ^ADDISON-WESLEY An imprint of Addison Wesley Longman, Inc. Reading, Massachusetts
With Modern Physics For Scientists and Engineers Third Edition Richard Wolfson Middlebury College Jay M. Pasachoff Williams College ^ADDISON-WESLEY An imprint of Addison Wesley Longman, Inc. Reading, Massachusetts
Program Learning Outcomes (Undergraduate Program):
 Program Learning s (Undergraduate Program):. Knowledge: The student will demonstrate knowledge and comprehension of the basic and applied fields of physics. 2. Problem Solving: The student will develop
Program Learning s (Undergraduate Program):. Knowledge: The student will demonstrate knowledge and comprehension of the basic and applied fields of physics. 2. Problem Solving: The student will develop
Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 2 (9/11/06) Schrödinger Wave Equation
 22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 2 (9/11/06) Schrödinger Wave Equation References -- R. M. Eisberg, Fundamentals of Modern Physics (Wiley & Sons, New York, 1961). R. L. Liboff, Introductory
22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 2 (9/11/06) Schrödinger Wave Equation References -- R. M. Eisberg, Fundamentals of Modern Physics (Wiley & Sons, New York, 1961). R. L. Liboff, Introductory
02 Coupled Oscillators
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Foundations of Wave Phenomena Library Digital Monographs 8-04 0 Coupled Oscillators Charles G. Torre Department of Physics, Utah State University, Charles.Torre@usu.edu
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Foundations of Wave Phenomena Library Digital Monographs 8-04 0 Coupled Oscillators Charles G. Torre Department of Physics, Utah State University, Charles.Torre@usu.edu
Evans Field Theory of Neutrino Oscillations
 22 Evans Field Theory of Neutrino Oscillations Summary. Neutrino oscillations are described with the generally covariant Evans field theory, showing that gravitation is able to influence the transmutation
22 Evans Field Theory of Neutrino Oscillations Summary. Neutrino oscillations are described with the generally covariant Evans field theory, showing that gravitation is able to influence the transmutation
. LORENTZ MAGNETIC FORCE LAW NOT PRECISELY VERIFIED
 . LORENTZ MAGNETIC FORCE LAW NOT PRECISELY VERIFIED CHAN RASJID KAH CHEW 2 March 2019 ABSTRACT. The Lorentz magnetic force law has not been precisely verified. The experimental basis of it is in the early
. LORENTZ MAGNETIC FORCE LAW NOT PRECISELY VERIFIED CHAN RASJID KAH CHEW 2 March 2019 ABSTRACT. The Lorentz magnetic force law has not been precisely verified. The experimental basis of it is in the early
HS AP Physics 1 Science
 Scope And Sequence Timeframe Unit Instructional Topics 5 Day(s) 20 Day(s) 5 Day(s) Kinematics Course AP Physics 1 is an introductory first-year, algebra-based, college level course for the student interested
Scope And Sequence Timeframe Unit Instructional Topics 5 Day(s) 20 Day(s) 5 Day(s) Kinematics Course AP Physics 1 is an introductory first-year, algebra-based, college level course for the student interested
Chapter 9. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 9. Electromagnetic Waves 9.1 Waves in One Dimension 9.1.1 The Wave Equation What is a "wave?" Let's start with the simple case: fixed shape, constant speed: How would you represent such a string
Chapter 9. Electromagnetic Waves 9.1 Waves in One Dimension 9.1.1 The Wave Equation What is a "wave?" Let's start with the simple case: fixed shape, constant speed: How would you represent such a string
arxiv:quant-ph/ v1 22 Dec 2004
 Quantum mechanics needs no interpretation L. Skála 1,2 and V. Kapsa 1 1 Charles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Ke Karlovu 3, 12116 Prague 2, Czech Republic and 2 University of Waterloo,
Quantum mechanics needs no interpretation L. Skála 1,2 and V. Kapsa 1 1 Charles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Ke Karlovu 3, 12116 Prague 2, Czech Republic and 2 University of Waterloo,
8.20 MIT Introduction to Special Relativity IAP 2005 Tentative Outline
 8.20 MIT Introduction to Special Relativity IAP 2005 Tentative Outline 1 Main Headings I Introduction and relativity pre Einstein II Einstein s principle of relativity and a new concept of spacetime III
8.20 MIT Introduction to Special Relativity IAP 2005 Tentative Outline 1 Main Headings I Introduction and relativity pre Einstein II Einstein s principle of relativity and a new concept of spacetime III
Physical substantiation of Huygens principle and the reciprocity theorem
 Physical substantiation of Huygens principle and the reciprocity theorem F. F. Mende http://fmnauka.narod.ru/works.html mende_fedor@mail.ru Abstract Huygens principle is the basic postulate of geometric
Physical substantiation of Huygens principle and the reciprocity theorem F. F. Mende http://fmnauka.narod.ru/works.html mende_fedor@mail.ru Abstract Huygens principle is the basic postulate of geometric
09 The Wave Equation in 3 Dimensions
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Foundations of Wave Phenomena Physics, Department of --2004 09 The Wave Equation in 3 Dimensions Charles G. Torre Department of Physics, Utah State University,
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Foundations of Wave Phenomena Physics, Department of --2004 09 The Wave Equation in 3 Dimensions Charles G. Torre Department of Physics, Utah State University,
Why quantum field theory?
 Why quantum field theory? It is often said that quantum field theory is the natural marriage of Einstein s special theory of relativity and the quantum theory. The point of this section will be to motivate
Why quantum field theory? It is often said that quantum field theory is the natural marriage of Einstein s special theory of relativity and the quantum theory. The point of this section will be to motivate
Special Theory of Relativity Prof. Shiva Prasad Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Special Theory of Relativity Prof. Shiva Prasad Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 24 Current Density Four Vector and Maxwell Equation Hello, so we have now come to
Special Theory of Relativity Prof. Shiva Prasad Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 24 Current Density Four Vector and Maxwell Equation Hello, so we have now come to
Introduction. Introductory Remarks
 Introductory Remarks This is probably your first real course in quantum mechanics. To be sure, it is understood that you have encountered an introduction to some of the basic concepts, phenomenology, history,
Introductory Remarks This is probably your first real course in quantum mechanics. To be sure, it is understood that you have encountered an introduction to some of the basic concepts, phenomenology, history,
3 Dimensional String Theory
 3 Dimensional String Theory New ideas for interactions and particles Abstract...1 Asymmetry in the interference occurrences of oscillators...1 Spontaneously broken symmetry in the Planck distribution law...3
3 Dimensional String Theory New ideas for interactions and particles Abstract...1 Asymmetry in the interference occurrences of oscillators...1 Spontaneously broken symmetry in the Planck distribution law...3
Bachelor s Degree in Chemistry. 1 st YEAR Mechanics and Thermodynamics ECTS credits: 6 Semester: 1. Teaching objectives
 1 st YEAR 5263 Mechanics and Thermodynamics ECTS credits: 6 Semester: 1 The student should be able to: 1. Understand the concepts and describe the fundamental aspects of Mechanics and Thermodynamics. 2.
1 st YEAR 5263 Mechanics and Thermodynamics ECTS credits: 6 Semester: 1 The student should be able to: 1. Understand the concepts and describe the fundamental aspects of Mechanics and Thermodynamics. 2.
Gravitational radiation
 Lecture 28: Gravitational radiation Gravitational radiation Reading: Ohanian and Ruffini, Gravitation and Spacetime, 2nd ed., Ch. 5. Gravitational equations in empty space The linearized field equations
Lecture 28: Gravitational radiation Gravitational radiation Reading: Ohanian and Ruffini, Gravitation and Spacetime, 2nd ed., Ch. 5. Gravitational equations in empty space The linearized field equations
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Classical Mechanics and Electrodynamics
 Classical Mechanics and Electrodynamics Lecture notes FYS 3120 Jon Magne Leinaas Department of Physics, University of Oslo December 2009 2 Preface These notes are prepared for the physics course FYS 3120,
Classical Mechanics and Electrodynamics Lecture notes FYS 3120 Jon Magne Leinaas Department of Physics, University of Oslo December 2009 2 Preface These notes are prepared for the physics course FYS 3120,
In electromagnetism Faraday s law and the Ampere- Maxwell law describe changes in the magnetic B and electric E fields:
 Causality in classical electrodynamics C. M. Savage Department of Quantum Science, The Australian National University The Physics Teacher, in press. craig.savage@anu.edu.au Causality in electrodynamics
Causality in classical electrodynamics C. M. Savage Department of Quantum Science, The Australian National University The Physics Teacher, in press. craig.savage@anu.edu.au Causality in electrodynamics
CHM 532 Notes on Wavefunctions and the Schrödinger Equation
 CHM 532 Notes on Wavefunctions and the Schrödinger Equation In class we have discussed a thought experiment 1 that contrasts the behavior of classical particles, classical waves and quantum particles.
CHM 532 Notes on Wavefunctions and the Schrödinger Equation In class we have discussed a thought experiment 1 that contrasts the behavior of classical particles, classical waves and quantum particles.
Lecture Sound Waves EM Waves. Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org. The Doppler Effect 11/11/2014
 Lecture 1102 Sound Waves EM Waves Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org The Doppler Effect The Doppler effect (or Doppler shift) is the change in frequency (or wavelength) of a wave for an observer moving
Lecture 1102 Sound Waves EM Waves Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org The Doppler Effect The Doppler effect (or Doppler shift) is the change in frequency (or wavelength) of a wave for an observer moving
Overview : Table Of Content :
 Book Title:-Physics for JEE (Main) and Other Engineering Entrance Examinations Author :-BASE ISBN :-9788131528501 Price :-INR 775 Pages :-1070 Edition :-1 Binding :-Paperback Imprint :-CL India Year :-2015
Book Title:-Physics for JEE (Main) and Other Engineering Entrance Examinations Author :-BASE ISBN :-9788131528501 Price :-INR 775 Pages :-1070 Edition :-1 Binding :-Paperback Imprint :-CL India Year :-2015
Class Notes Introduction to Modern Physics Physics 321 Plan II Under Construction
 Class Notes Introduction to Modern Physics Physics 321 Plan II Under Construction Austin M. Gleeson 1 Department of Physics University of Texas at Austin Austin, TX 78712 January 15, 2010 1 gleeson@physics.utexas.edu
Class Notes Introduction to Modern Physics Physics 321 Plan II Under Construction Austin M. Gleeson 1 Department of Physics University of Texas at Austin Austin, TX 78712 January 15, 2010 1 gleeson@physics.utexas.edu
01 Harmonic Oscillations
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Foundations of Wave Phenomena Library Digital Monographs 8-2014 01 Harmonic Oscillations Charles G. Torre Department of Physics, Utah State University, Charles.Torre@usu.edu
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Foundations of Wave Phenomena Library Digital Monographs 8-2014 01 Harmonic Oscillations Charles G. Torre Department of Physics, Utah State University, Charles.Torre@usu.edu
Exploring Excel spreadsheets in the teaching and learning of certain concepts of Statistical physics and Thermodynamics
 Exploring Excel spreadsheets in the teaching and learning of certain concepts of Statistical physics and Thermodynamics Ionel Grigore 1,2, Cristina Miron 1, Emil-Stefan Barna 1 (1) Faculty of Physics,
Exploring Excel spreadsheets in the teaching and learning of certain concepts of Statistical physics and Thermodynamics Ionel Grigore 1,2, Cristina Miron 1, Emil-Stefan Barna 1 (1) Faculty of Physics,
Physics For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach 3 rd Edition, AP Edition, 2013 Knight
 For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach 3 rd Edition, AP Edition, 2013 Knight To the Advanced Placement Topics for C *Advanced Placement, Advanced Placement Program, AP, and Pre-AP are registered
For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach 3 rd Edition, AP Edition, 2013 Knight To the Advanced Placement Topics for C *Advanced Placement, Advanced Placement Program, AP, and Pre-AP are registered
2 u 1-D: 3-D: x + 2 u
 c 2013 C.S. Casari - Politecnico di Milano - Introduction to Nanoscience 2013-14 Onde 1 1 Waves 1.1 wave propagation 1.1.1 field Field: a physical quantity (measurable, at least in principle) function
c 2013 C.S. Casari - Politecnico di Milano - Introduction to Nanoscience 2013-14 Onde 1 1 Waves 1.1 wave propagation 1.1.1 field Field: a physical quantity (measurable, at least in principle) function
Plane waves and spatial frequency. A plane wave
 Plane waves and spatial frequency A plane wave Complex representation E(,) zt Ecos( tkz) E cos( tkz) o Ezt (,) Ee Ee j( tkz) j( tkz) o 1 cos(2 ) cos( ) 2 A B t Re atbt () () ABcos(2 t ) Complex representation
Plane waves and spatial frequency A plane wave Complex representation E(,) zt Ecos( tkz) E cos( tkz) o Ezt (,) Ee Ee j( tkz) j( tkz) o 1 cos(2 ) cos( ) 2 A B t Re atbt () () ABcos(2 t ) Complex representation
Light as a Transverse Wave.
 Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Mind Association. Oxford University Press and Mind Association are collaborating with JSTOR to digitize, preserve and extend access to Mind.
 Mind Association Response to Colyvan Author(s): Joseph Melia Source: Mind, New Series, Vol. 111, No. 441 (Jan., 2002), pp. 75-79 Published by: Oxford University Press on behalf of the Mind Association
Mind Association Response to Colyvan Author(s): Joseph Melia Source: Mind, New Series, Vol. 111, No. 441 (Jan., 2002), pp. 75-79 Published by: Oxford University Press on behalf of the Mind Association
Optics. n n. sin c. sin
 Optics Geometrical optics (model) Light-ray: extremely thin parallel light beam Using this model, the explanation of several optical phenomena can be given as the solution of simple geometric problems.
Optics Geometrical optics (model) Light-ray: extremely thin parallel light beam Using this model, the explanation of several optical phenomena can be given as the solution of simple geometric problems.
Toward Completing Classical Physics
 Toward Completing Classical Physics Intro to waves Intro to electro-magnetism HW3 due on Thursday, Feb 8 th. Quiz next Thursday, Feb 15 th on relativity: short answers. 20 mins. Closed book. Materials
Toward Completing Classical Physics Intro to waves Intro to electro-magnetism HW3 due on Thursday, Feb 8 th. Quiz next Thursday, Feb 15 th on relativity: short answers. 20 mins. Closed book. Materials
The de Broglie hypothesis for the wave nature of matter was to simply re-write the equations describing light's dual nature: Elight = hf
 Modern Physics (PHY 3305) Lecture Notes Modern Physics (PHY 3305) Lecture Notes Describing Nature as Waves (Ch. 4.3-4.4) SteveSekula, 10 February 010 (created 13 December 009) Review tags: lecture We concluded
Modern Physics (PHY 3305) Lecture Notes Modern Physics (PHY 3305) Lecture Notes Describing Nature as Waves (Ch. 4.3-4.4) SteveSekula, 10 February 010 (created 13 December 009) Review tags: lecture We concluded
4 Electrodynamics and Relativity
 4 Electrodynamics and Relativity The first time I experienced beauty in physics was when I learned how Einstein s special relativity is hidden in the equations of Maxwell s theory of electricity and magnetism.
4 Electrodynamics and Relativity The first time I experienced beauty in physics was when I learned how Einstein s special relativity is hidden in the equations of Maxwell s theory of electricity and magnetism.
AP PHYSICS (B) SYLLABUS. Text: Physics, Sixth Edition by Cutnell and Johnson ISBN , Wiley and Sons, 2004 COURSE OVERVIEW
 AP PHYSICS (B) SYLLABUS Text: Physics, Sixth Edition by Cutnell and Johnson ISBN 0471-15183-1, Wiley and Sons, 2004 COURSE OVERVIEW Advanced Placement Physics is an intensive and rigorous college level
AP PHYSICS (B) SYLLABUS Text: Physics, Sixth Edition by Cutnell and Johnson ISBN 0471-15183-1, Wiley and Sons, 2004 COURSE OVERVIEW Advanced Placement Physics is an intensive and rigorous college level
A. B. Lahanas University of Athens, Physics Department, Nuclear and Particle Physics Section, Athens , Greece
 SPECIAL RELATIVITY A. B. Lahanas University of Athens, Physics Department, Nuclear and Particle Physics Section, Athens 157 71, Greece Abstract We give an introduction to Einstein s Special Theory of Relativity.
SPECIAL RELATIVITY A. B. Lahanas University of Athens, Physics Department, Nuclear and Particle Physics Section, Athens 157 71, Greece Abstract We give an introduction to Einstein s Special Theory of Relativity.
Lectures on Certain Problems in the Theory of Oscillations
 Lectures on Certain Problems in the Theory of Oscillations L. I. Mandel shtam May 5, 1944 Abstract [By the translator] This lecture covers the problems of energy velocity and its relation to group velocity.
Lectures on Certain Problems in the Theory of Oscillations L. I. Mandel shtam May 5, 1944 Abstract [By the translator] This lecture covers the problems of energy velocity and its relation to group velocity.
I N T R O D U C T I O N T O
 A. La Rosa Lecture Notes SU-hysics H 411/511 ECE 598 I N T R O D U C T I O N T O Q U A N T U M M E C H A N I C S How does light "really" decides which path to follow? An elementary Quantum Dynamics point
A. La Rosa Lecture Notes SU-hysics H 411/511 ECE 598 I N T R O D U C T I O N T O Q U A N T U M M E C H A N I C S How does light "really" decides which path to follow? An elementary Quantum Dynamics point
1 Lagrangian for a continuous system
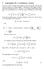 Lagrangian for a continuous system Let s start with an example from mechanics to get the big idea. The physical system of interest is a string of length and mass per unit length fixed at both ends, and
Lagrangian for a continuous system Let s start with an example from mechanics to get the big idea. The physical system of interest is a string of length and mass per unit length fixed at both ends, and
E = mc 2. Inertial Reference Frames. Inertial Reference Frames. The Special Theory of Relativity. Slide 1 / 63. Slide 2 / 63.
 Slide 1 / 63 The Special Theory of Relativity E = mc 2 Inertial Reference Frames Slide 2 / 63 Newton's laws are only valid in inertial reference frames: n inertial reference frame is one which is not accelerating
Slide 1 / 63 The Special Theory of Relativity E = mc 2 Inertial Reference Frames Slide 2 / 63 Newton's laws are only valid in inertial reference frames: n inertial reference frame is one which is not accelerating
Relativistic Constant Acceleration Distance Factor. Copyright 2010 Joseph A. Rybczyk
 Relativistic Constant Acceleration Distance Factor Copyright 2010 Joseph A. Rybczyk Abstract A formalized treatment of a previously discovered principle involving relativistic constant acceleration distances
Relativistic Constant Acceleration Distance Factor Copyright 2010 Joseph A. Rybczyk Abstract A formalized treatment of a previously discovered principle involving relativistic constant acceleration distances
AP Physics Syllabus Course Overview. Text: Physics by Giancoli, 5th edition Course Outline
 AP Physics Syllabus Course Overview Advanced Placement Physics B is an algebra-based course in general physics. It is equivalent to an introductory algebra-based university level physics course, whose
AP Physics Syllabus Course Overview Advanced Placement Physics B is an algebra-based course in general physics. It is equivalent to an introductory algebra-based university level physics course, whose
Clock synchronization, a universal light speed, and the terrestrial redshift experiment
 Clock synchronization, a universal light speed, and the terrestrial redshift experiment Alan Macdonald Department of Mathematics Luther College, Decorah, IA 52101, U.S.A. macdonal@luther.edu Am. J. Phys.
Clock synchronization, a universal light speed, and the terrestrial redshift experiment Alan Macdonald Department of Mathematics Luther College, Decorah, IA 52101, U.S.A. macdonal@luther.edu Am. J. Phys.
So, according to classical theory, electrical and gravitational forces are absolutely separate and distinct phenomena.
 Chapter 21 Magnetic Forces and Magnetic Fields Thursday, March 11, 2010 8:26 PM According to classical theory, there is no connection between electric charge and gravitational forces. Gravitational forces
Chapter 21 Magnetic Forces and Magnetic Fields Thursday, March 11, 2010 8:26 PM According to classical theory, there is no connection between electric charge and gravitational forces. Gravitational forces
Lecture PowerPoint. Chapter 32 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoint Chapter 32 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Lecture PowerPoint Chapter 32 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Theory of Everything by Illusion 2.0
 Theory of Everything by Illusion 2.0 Kimmo Rouvari September 25, 2015 Abstract Theory of Everything is The Holy Grail in physics. Physicists and like all over the world have searched the theory for a very
Theory of Everything by Illusion 2.0 Kimmo Rouvari September 25, 2015 Abstract Theory of Everything is The Holy Grail in physics. Physicists and like all over the world have searched the theory for a very
THREE DIMENSIONAL INVERSE SCATTERING FOR THE CLASSICAL WAVE EQUATION WITH
 THREE DIMENSIONAL INVERSE SCATTERING FOR THE CLASSICAL WAVE EQUATION WITH VARIABLE SPEED Margaret Cheney, James H. Rose, and Brian DeFacio Department of Mathematics, Duke University, Durham, NC 27706 Ames
THREE DIMENSIONAL INVERSE SCATTERING FOR THE CLASSICAL WAVE EQUATION WITH VARIABLE SPEED Margaret Cheney, James H. Rose, and Brian DeFacio Department of Mathematics, Duke University, Durham, NC 27706 Ames
The Weber Force. Introduction
 The Weber Force Eamon McAlea Contact@forbinsystems.com December 7th 2010 Abstract: In this paper It will be shown how the Weber Force law emerges as an averaged effect between two electrically neutral
The Weber Force Eamon McAlea Contact@forbinsystems.com December 7th 2010 Abstract: In this paper It will be shown how the Weber Force law emerges as an averaged effect between two electrically neutral
MATHEMATICAL MODELLING IN ONE DIMENSION
 MATHEMATICAL MODELLING IN ONE DIMENSION African Institute of Mathematics Library Series The African Institute of Mathematical Sciences (AIMS), founded in 2003 in Muizenberg, South Africa, provides a one-year
MATHEMATICAL MODELLING IN ONE DIMENSION African Institute of Mathematics Library Series The African Institute of Mathematical Sciences (AIMS), founded in 2003 in Muizenberg, South Africa, provides a one-year
Kutztown Area School District Curriculum (Unit Map) High School Physics Written by Kevin Kinney
 Kutztown Area School District Curriculum (Unit Map) High School Physics Written by Kevin Kinney Course Description: This introductory course is for students who intend to pursue post secondary studies.
Kutztown Area School District Curriculum (Unit Map) High School Physics Written by Kevin Kinney Course Description: This introductory course is for students who intend to pursue post secondary studies.
This course supports the assessments for Physics: Waves and Optics. The course covers 6 competencies and represents 3 competency units.
 This course supports the assessments for Physics: Waves and Optics. The course covers 6 competencies and represents 3 competency units. Introduction Overview Physics: Waves and Optics addresses foundational
This course supports the assessments for Physics: Waves and Optics. The course covers 6 competencies and represents 3 competency units. Introduction Overview Physics: Waves and Optics addresses foundational
Physics 142 Mechanical Waves Page 1. Mechanical Waves
 Physics 142 Mechanical Waves Page 1 Mechanical Waves This set of notes contains a review of wave motion in mechanics, emphasizing the mathematical formulation that will be used in our discussion of electromagnetic
Physics 142 Mechanical Waves Page 1 Mechanical Waves This set of notes contains a review of wave motion in mechanics, emphasizing the mathematical formulation that will be used in our discussion of electromagnetic
On Objectivity and Models for Measuring. G. Rasch. Lecture notes edited by Jon Stene.
 On Objectivity and Models for Measuring By G. Rasch Lecture notes edited by Jon Stene. On Objectivity and Models for Measuring By G. Rasch Lectures notes edited by Jon Stene. 1. The Basic Problem. Among
On Objectivity and Models for Measuring By G. Rasch Lecture notes edited by Jon Stene. On Objectivity and Models for Measuring By G. Rasch Lectures notes edited by Jon Stene. 1. The Basic Problem. Among
Physics 106a/196a Problem Set 7 Due Dec 2, 2005
 Physics 06a/96a Problem Set 7 Due Dec, 005 Version 3, Nov 7, 005 In this set we finish up the SHO and study coupled oscillations/normal modes and waves. Problems,, and 3 are for 06a students only, 4, 5,
Physics 06a/96a Problem Set 7 Due Dec, 005 Version 3, Nov 7, 005 In this set we finish up the SHO and study coupled oscillations/normal modes and waves. Problems,, and 3 are for 06a students only, 4, 5,
Introduction. Introductory Remarks
 Introductory Remarks This is probably your first real course in quantum mechanics. To be sure, it is understood that you have encountered an introduction to some of the basic concepts, phenomenology, history,
Introductory Remarks This is probably your first real course in quantum mechanics. To be sure, it is understood that you have encountered an introduction to some of the basic concepts, phenomenology, history,
PHYS 3313 Section 001. Lecture #3
 PHYS 3313 Section 001 Classical Physics Lecture #3 Concept of Waves and Particles Conservation Laws and Fundamental Forces Atomic Theory of Matter Unsolved Questions of 1895 and the New Horizon 1 Reminder:
PHYS 3313 Section 001 Classical Physics Lecture #3 Concept of Waves and Particles Conservation Laws and Fundamental Forces Atomic Theory of Matter Unsolved Questions of 1895 and the New Horizon 1 Reminder:
Light Waves and Polarization
 Light Waves and Polarization Xavier Fernando Ryerson Communications Lab http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~fernando The Nature of Light There are three theories explain the nature of light: Quantum Theory Light
Light Waves and Polarization Xavier Fernando Ryerson Communications Lab http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~fernando The Nature of Light There are three theories explain the nature of light: Quantum Theory Light
Northwestern CT Community College Course Syllabus. Course Title: CALCULUS-BASED PHYSICS I with Lab Course #: PHY 221
 Northwestern CT Community College Course Syllabus Course Title: CALCULUS-BASED PHYSICS I with Lab Course #: PHY 221 Course Description: 4 credits (3 class hours and 3 laboratory hours per week) Physics
Northwestern CT Community College Course Syllabus Course Title: CALCULUS-BASED PHYSICS I with Lab Course #: PHY 221 Course Description: 4 credits (3 class hours and 3 laboratory hours per week) Physics
BRAZOSPORT COLLEGE LAKE JACKSON, TEXAS SYLLABUS PHYS MECHANICS AND HEAT
 BRAZOSPORT COLLEGE LAKE JACKSON, TEXAS SYLLABUS PHYS 2325 - MECHANICS AND HEAT CATALOG DESCRIPTION: PHYS 2325 Mechanics and Heat. CIP 4008015403 A calculus-based approach to the principles of mechanics
BRAZOSPORT COLLEGE LAKE JACKSON, TEXAS SYLLABUS PHYS 2325 - MECHANICS AND HEAT CATALOG DESCRIPTION: PHYS 2325 Mechanics and Heat. CIP 4008015403 A calculus-based approach to the principles of mechanics
