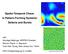
3D computer simulation of Rayleigh-Benard instability in a square box
|
|
|
- Aldous Collins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3D computer simulation of Rayleigh-Benard instability in a square box V.V. KOLMYCHKOV, O.S. MAZHOROVA, YU.P. POPOV, O.V.SHCHERITSA Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics RAS,4,Miusskaya sq., Moscow, , Russia Résumé : La stabilité des rouleaux bidimensionels est étudié au moyen des calculations bi- et tridimensionels utilisant le nombre de Rayleigh < Ra < , nombre de vague de rouleau 0.5 < k 0 < 7.0, nombre de Prandtl P r = 0.71; 1. Les scénarios differents d évolution de mode d écoulement en partant de mouvement potentiellement instable jusqu à mouvement stable sont discutés. En particulier, nous avons observés trois instabilités vraiment tridimensionels, le varicose oblique, l instabilité oscillatoire et le si-nommé spiral defect chaos. Les resultats sont comparés aux donneés theoretiques de Busse et colleagues sur la stabilité de couche horizontale de liquide (Busse s balloon)[1],[2] et aux donneés experimentales. Abstract : The stability of two-dimensional rolls is investigated by means of 2D and 3D calculations for Rayleigh number in the range < Ra < , roll s wave number 0.5 < k 0 < 7.0 and Prandtl number P r = 0.71; 1. Different scenarios for the flow pattern evolution from potentially unstable motion to a stable one are discussed. In particulary truly three dimensional forms of instabilities, such as skewed varicose, oscillatory, spiral defect chaos, have been observed. The results are compared with Busse and coworkers theoretical data on the stability of horizontal layer of fluid (so called Busse s balloon) [1],[2] and experimental data. Mots clefs : Rayleigh-Benard instability, computer simulation 1 Introduction Rayleigh-Benard convection, i.e. convection in a horizontal layer heated from below, permanently attracts attention of the researchers as a meaty example of hydrodynamical system in which transition to various types of instabilities can be studied. When the temperature difference between lower and upper plate is large enough, buoyancy forces lead to the destabilization of the quiescent state and convection evolves. The first stable convection pattern takes the form of rolls, i.e., two-dimensional structures with roughly circular streamlines in alternating directions. The strength of buoyancy forces are determined by Rayleigh number Ra, the size of rolls are described by wave number k. For different values of Prandtl number stability area of roll structures in the plane (Ra, k) has been obtained in [1]. Though RB system has been extensively studied both theoretically and experimentally, there is a lack of quantitative and reliable comparisons between theory and experiment. The theory usually deals with infinite layers, the short, linear stages of flow development, ideal flow patterns and etc. The main goal of the paper is to study numerically evolution and stability of roll structures and to produce in calculations overriding types of instabilities predicted by theoretical data. 2 Governing Equations and Numerical Procedure Rayleigh-Benard problem is governed by 3D time-dependent fluid flow and heat transfer equations. Fluid motion is described by Navier-Stokes equations in the Oberbeck - Boussinesq approximation. In Cartesian coordinates (x, y, z) the non dimensional equations take the form t V + (V )V = p + V + GrT e z (1) V = 0 (2) t T + (V )T = 1 T P r (3) where ξ ξ, = ( x, y, z ), = 2 = 2 xx + 2 yy + 2 zz, (x, y, z) D, D = [0, L] [0, L] [0, 1], V = (V x, V y, V z ) is the velocity vector, t - time. The non-dimensional variables are introduced by scaling the 1
2 length with the liquid depth (H), time is scaled with H 2 /ν, temperature with δt. On the domain boundary the velocity satisfies the no-slip and non-penetration condition : V = 0. Border conditions for temperature are : T = 1 at z = 0, T = 0 at z = 1 and n T = 0 on the remainder of the boundary, where n is the normal to the boundary. Initially the fluid is at rest and T = 1 z. To solve the governing equations a sequential procedure is applied. The velocity is advanced using the temperature from the previous layer in the force term. The calculated velocity field is inserted into the heat transfer equations. The problem is approximated at staggered grid using control-volume approach. Approximation of convective terms ensure kinetic and heat energy conservation [3]. The scheme is implicit, has second order in space and first in time. Algorithm was successfully used for simulation of subcritical thermo-diffusion convection [4], 3 Numerical results In a series of papers [1],[2], Busse and coworkers determined the region in (k, Ra) plane, so called Busse Balloon, where steady rolls are predicted to be stable with respect to infinitesimal disturbances, outside the region, rolls are destabilized by different kinds of secondary instabilities. There are Eckhaus mode that is the only 2D type of instability, zig-zag, skewed varicose, knot, oscillatory instability, etc. [5],[6]. All the results relate to the infinite horizontal layer D simulation Firstly we have done a set of 2D calculations to estimate the effect of sidewalls on the rolls stability. To initiate convective flow in the form of rolls with the wave number k dis, the temperature field in the plane z = 0.5 is disturbed with perturbation in the form 0.02cos(k dis x), 0.5 < k dis < 7.0. Horizontal domain size L is chosen to be a multiple of π/k dis and around 15. The grid size in space is The calculation has been done for Rayleigh number in the range < Ra < Numerical results show that the presence of sidewalls, no matter how distant, substantially restrict the possible wave-numbers which can occur in the bulk of the system. Near the convective threshold the band of available wave numbers is reduced to a range k (Ra Ra cr )/Ra cr instead of a size k [(Ra Ra cr )/Ra cr ] 1/2 predicted for Eckhaus instability in the infinite systems, (Ra cr = 1708 is the critical Rayleigh number). This is compatible with theoretical data [7]. Two scenarios of the flow pattern evolution, entitled quasi stable and roll diffusion, have been registered in our 2D calculations. Under quasi stable scenario, the initial disturbance evolves into well developed roll pattern with k = k dis all over the domain. Then, after a certain period of quasi stability, flow transition occurs : rolls adjoining the sidewalls are extruded from the region by the neighbouring ones and the wave number of the roll structure decreases. Such flow transitions can recur several times until stable roll pattern with k e k dis is set on. Another scenario of flow evolution is roll diffusion. In this case inside the bulk the initial perturbation grows slowly, while near the side walls, appears the roll structures with a new wave number k k dis, which is near stable. The cells with new wave number quickly gain the kinetic energy. Then next pair of rolls with the same wave number k appears near the first one and gradually the roll structure fills up the whole box. FIG. 1 roll diffusion. Evolution of the stream function for k dis = 6.8 k e = 3.8 (left) and k dis = 1.2 k e = 3.2 (right), Ra = 3Ra cr 2D calculations are refined by the series of time - dependent 3D simulations with similar initial data have been done. In this case we have observed the scenarios mentioned above as well as the essentially three dimensional flow pattern evolution. There are some results of the simulation. 2
3 3.2 3D simulation To study evolution and stability of roll structures, computer simulation has been done for < Ra < , P r = 0.71; 1. Spatial grid of size has been used, time step has been varied from 10 4 to In the calculations the stability threshold is about Ra 1750, which is close to theoretical critical value Ra cr = At Ra = 1750 the flow has roll pattern with wave number k k cr = 3.117, where k cr - the wave number that corresponds to Ra cr. The flow structure keeps the same with mesh refinement in space and time. It means that the grid size we use provide a good compromise between the computation time and accuracy. For Ra > 1750 amplitude of the initial perturbation grows uniformly throughout the space, when k 0 is close to k cr. When k 0 strongly differs from k cr, convective structures with wave number k form near the vertical boundaries and begin to spread into the bulk. Resulting flow has a roll structure and again can be stable or not depending on Ra and wave number values. At this stage, 3-dimensional results are similar to two-dimensional data. Further flow transition can be two or three dimensional. As an example let s analyse the flow structure evolution for P r = 1, Ra = 3500, k dis = 5.8 (fig.2). FIG. 2 Flow evolution : a t=0.2,b t=1, roll diffusion ; c t=5,d t=8, e t=9,f t=62, skewed varicose instability. Ra = 2Ra cr, P r = 1, k begin = 5.8 L x = Temperature field in the plane z = 0.5 plane. Light areas are hot, dark are cold. The wave number of initial disturbance is k dis = 5.8 that is close to neutral curve and has low amplitude growth rate. Rolls parallel to OY with k = 3.5 appears near the walls at t = 0.2t ν. The flow velocity is still small and this stage of flow evolution can be considered as a linear one. The amplitude growth rate of the new wave number is higher than the initial one. With time rolls with the new wave number penetrate into the bulk (fig.2b). 2D calculations show that rolls with the wave number k = 3.5 are stable, but according to Busse s balloon this value is unstable with respect to skewed varicose instability [2]. This type of instability leads to rolls curvature and their periodical compression. In our calculations at t = 5t ν straight rolls start to bend, then parts of the neighbour rolls glue to each other (the patchy process [2]) and complicated flow pattern is formed (fig. 2c-d). Newly formed flow pattern tends to form rolls with the wave number k = 2.5 that lies inside the Busse s balloon (fig. 2f). Theoretical and experimental data shows that wave number of the freely evolving rolls decreases with Ra [8]. Numerical calculations show similar dynamics and results are close to [8]. For P r = 0.71, Ra = 2500, k = 3.5 and Ra = 3500, k = 3, developed roll structures also unstable and skewed varicose instability arises. For Ra in the range 4000 < Ra < 7000 evolution of skewed varicose instability leads to spiral defects chaos (fig.3). Another example of instability is oscillatory. We have registered it for Ra = 9000, P r = 0.71, k = 1.5(fig.4) Period of oscillations is about and wave length is approximately , that is close to experimental data. 3
4 FIG. 3 Spiral defect chaos. Ra = 4Ra cr, P r = 0.71,k dis = Conclusions FIG. 4 Oscillatory convection Ra = 5.4Ra cr, P r = 0.71,k dis = 1.8 Convective stability of two-dimensional rolls in a closed box is investigated by means of 2D and 3D computer simulation. Different types of instability, well known from the theory of nonlinear stability, have been observed in calculations. Results are in good agreement with Busse and coworkers theoretical data on the stability of horizontal layer of fluid (so called Busse s balloon) [2] and experimental data. Références [1] Schlüter A., Lortz D., and Busse F. On the stability of steady finite amplitude convection. J. of Fluid Mechanics, 23(1), , [2] Busse F. and Clever R. Instabilities of convection rolls in a fluid of moderate prandtl number. J. of Fluid Mechanics, 91(2), , [3] Kolmychkov V., Mazhorova O., and Popov Y. Analysis of algorithms for the solution of 3d navier-stokes equations in natural variables. J. Differential equations, 42(7), , [4] Kolmychkov V., Mazhorova O., Popov Y., Bontoux P., and Ganaoui M. Identification of the convective instability in a multi-component solution by 3d simulations. J. Comptes Rendus Mecanique, 333(10), , [5] Busse F. The oscillatory instability of convection rolls in a low prandtl number. J. of Fluid Mechanics, 52(1), , [6] Clever R. and Busse F. Transition to time-dependent convection. J. of Fluid Mechanics, 65(4), ,
5 [7] Cross M., Daniels P., Hohenberg P., and Siggia E. Phase-winding solution in a finite container above the convection threshold. J. of Fluid Mechanics, 127(1), , [8] Willis J. S. R., G.and Deardorff. Roll-diameter dependence in rayleigh convection and its effect upon the heat flux. J. of Fluid Mechanics, 54(2), ,
Laurette TUCKERMAN Rayleigh-Bénard Convection and Lorenz Model
 Laurette TUCKERMAN laurette@pmmh.espci.fr Rayleigh-Bénard Convection and Lorenz Model Rayleigh-Bénard Convection Rayleigh-Bénard Convection Boussinesq Approximation Calculation and subtraction of the basic
Laurette TUCKERMAN laurette@pmmh.espci.fr Rayleigh-Bénard Convection and Lorenz Model Rayleigh-Bénard Convection Rayleigh-Bénard Convection Boussinesq Approximation Calculation and subtraction of the basic
Analysis of Turbulent Free Convection in a Rectangular Rayleigh-Bénard Cell
 Proceedings of the 8 th International Symposium on Experimental and Computational Aerothermodynamics of Internal Flows Lyon, July 2007 Paper reference : ISAIF8-00130 Analysis of Turbulent Free Convection
Proceedings of the 8 th International Symposium on Experimental and Computational Aerothermodynamics of Internal Flows Lyon, July 2007 Paper reference : ISAIF8-00130 Analysis of Turbulent Free Convection
Simulation Study on the Generation and Distortion Process of the Geomagnetic Field in Earth-like Conditions
 Chapter 1 Earth Science Simulation Study on the Generation and Distortion Process of the Geomagnetic Field in Earth-like Conditions Project Representative Yozo Hamano Authors Ataru Sakuraba Yusuke Oishi
Chapter 1 Earth Science Simulation Study on the Generation and Distortion Process of the Geomagnetic Field in Earth-like Conditions Project Representative Yozo Hamano Authors Ataru Sakuraba Yusuke Oishi
Natural convection adjacent to a sidewall with three fins in a differentially heated cavity
 ANZIAM J. 48 (CTAC2006) pp.c806 C819, 2007 C806 Natural convection adjacent to a sidewall with three fins in a differentially heated cavity F. Xu 1 J. C. Patterson 2 C. Lei 3 (Received 31 August 2006;
ANZIAM J. 48 (CTAC2006) pp.c806 C819, 2007 C806 Natural convection adjacent to a sidewall with three fins in a differentially heated cavity F. Xu 1 J. C. Patterson 2 C. Lei 3 (Received 31 August 2006;
Pattern Formation and Chaos
 Developments in Experimental Pattern Formation - Isaac Newton Institute, 2005 1 Pattern Formation and Chaos Insights from Large Scale Numerical Simulations of Rayleigh-Bénard Convection Collaborators:
Developments in Experimental Pattern Formation - Isaac Newton Institute, 2005 1 Pattern Formation and Chaos Insights from Large Scale Numerical Simulations of Rayleigh-Bénard Convection Collaborators:
Boundary and Interior Layers in Turbulent Thermal Convection
 Boundary and Interior Layers in Turbulent Thermal Convection Olga Shishkina & Claus Wagner DLR - Institute for Aerodynamics and Flow Technology, Bunsenstrasse 10, 37073 Göttingen, Germany Olga.Shishkina@dlr.de,
Boundary and Interior Layers in Turbulent Thermal Convection Olga Shishkina & Claus Wagner DLR - Institute for Aerodynamics and Flow Technology, Bunsenstrasse 10, 37073 Göttingen, Germany Olga.Shishkina@dlr.de,
UNIT II CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER
 UNIT II CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER Convection is the mode of heat transfer between a surface and a fluid moving over it. The energy transfer in convection is predominately due to the bulk motion of the fluid
UNIT II CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER Convection is the mode of heat transfer between a surface and a fluid moving over it. The energy transfer in convection is predominately due to the bulk motion of the fluid
Spatiotemporal Dynamics
 KITP, October 2003: Rayleigh-Bénard Convection 1 Spatiotemporal Dynamics Mark Paul, Keng-Hwee Chiam, Janet Scheel and Michael Cross (Caltech) Henry Greenside and Anand Jayaraman (Duke) Paul Fischer (ANL)
KITP, October 2003: Rayleigh-Bénard Convection 1 Spatiotemporal Dynamics Mark Paul, Keng-Hwee Chiam, Janet Scheel and Michael Cross (Caltech) Henry Greenside and Anand Jayaraman (Duke) Paul Fischer (ANL)
OSCILLATORY INSTABILITY OF THREE- DIMENSIONAL NATURAL CONVECTION OF AIR IN A LATERALLY HEATED CUBIC BOX
 OSCILLATORY INSTABILITY OF THREE- DIMENSIONAL NATURAL CONVECTION OF AIR IN A LATERALLY HEATED CUBIC BOX Alexander Yu. Gelfgat School of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tel-Aviv University,
OSCILLATORY INSTABILITY OF THREE- DIMENSIONAL NATURAL CONVECTION OF AIR IN A LATERALLY HEATED CUBIC BOX Alexander Yu. Gelfgat School of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tel-Aviv University,
SELF-SUSTAINED OSCILLATIONS AND BIFURCATIONS OF MIXED CONVECTION IN A MULTIPLE VENTILATED ENCLOSURE
 Computational Thermal Sciences, 3 (1): 63 72 (2011) SELF-SUSTAINED OSCILLATIONS AND BIFURCATIONS OF MIXED CONVECTION IN A MULTIPLE VENTILATED ENCLOSURE M. Zhao, 1, M. Yang, 1 M. Lu, 1 & Y. W. Zhang 2 1
Computational Thermal Sciences, 3 (1): 63 72 (2011) SELF-SUSTAINED OSCILLATIONS AND BIFURCATIONS OF MIXED CONVECTION IN A MULTIPLE VENTILATED ENCLOSURE M. Zhao, 1, M. Yang, 1 M. Lu, 1 & Y. W. Zhang 2 1
NUMERICAL STUDIES OF TRANSITION FROM STEADY TO UNSTEADY COUPLED THERMAL BOUNDARY LAYERS
 International Journal of Computational Methods Vol. 11, Suppl. 1 (214) 13442 (15 pages) c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 1.1142/S2198762134427 NUMERICAL STUDIES OF TRANSITION FROM STEADY TO UNSTEADY
International Journal of Computational Methods Vol. 11, Suppl. 1 (214) 13442 (15 pages) c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 1.1142/S2198762134427 NUMERICAL STUDIES OF TRANSITION FROM STEADY TO UNSTEADY
Spatiotemporal Chaos in Rayleigh-Bénard Convection
 Spatiotemporal Chaos in Rayleigh-Bénard Convection Michael Cross California Institute of Technology Beijing Normal University June 2006 Janet Scheel, Keng-Hwee Chiam, Mark Paul Henry Greenside, Anand Jayaraman
Spatiotemporal Chaos in Rayleigh-Bénard Convection Michael Cross California Institute of Technology Beijing Normal University June 2006 Janet Scheel, Keng-Hwee Chiam, Mark Paul Henry Greenside, Anand Jayaraman
Influence of wall modes on the onset of bulk convection in a rotating cylinder
 Influence of wall modes on the onset of bulk convection in a rotating cylinder F. Marques 1 and J. M. Lopez 2 1 Departament de Física Aplicada, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, 08034, Barcelona, Spain
Influence of wall modes on the onset of bulk convection in a rotating cylinder F. Marques 1 and J. M. Lopez 2 1 Departament de Física Aplicada, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, 08034, Barcelona, Spain
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS IN RAYLEIGH-BÉNARD CONVECTION
 Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2000. 32:709 778 Copyright 2000 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved RECENT DEVELOPMENTS IN RAYLEIGH-BÉNARD CONVECTION Eberhard Bodenschatz, Werner Pesch, and Guenter Ahlers Laboratory
Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2000. 32:709 778 Copyright 2000 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved RECENT DEVELOPMENTS IN RAYLEIGH-BÉNARD CONVECTION Eberhard Bodenschatz, Werner Pesch, and Guenter Ahlers Laboratory
Pattern Formation and Spatiotemporal Chaos in Systems Far from Equilibrium
 Pattern Formation and Spatiotemporal Chaos in Systems Far from Equilibrium Michael Cross California Institute of Technology Beijing Normal University May 2006 Michael Cross (Caltech, BNU) Pattern Formation
Pattern Formation and Spatiotemporal Chaos in Systems Far from Equilibrium Michael Cross California Institute of Technology Beijing Normal University May 2006 Michael Cross (Caltech, BNU) Pattern Formation
FREE CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER FROM AN OBJECT AT LOW RAYLEIGH NUMBER
 Free Convective Heat Transfer From an Object at Low Rayleigh Number FREE CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER FROM AN OBJECT AT LOW RAYLEIGH NUMBER Md. Golam Kader and Khandkar Aftab Hossain * Department of Mechanical
Free Convective Heat Transfer From an Object at Low Rayleigh Number FREE CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER FROM AN OBJECT AT LOW RAYLEIGH NUMBER Md. Golam Kader and Khandkar Aftab Hossain * Department of Mechanical
Experiments with Rayleigh-Bénard convection
 Experiments with Rayleigh-Bénard convection Guenter Ahlers Department of Physics and IQUEST, University of California Santa Barbara CA 93106 USA e-mail: guenter@physics.ucsb.edu Summary. After a brief
Experiments with Rayleigh-Bénard convection Guenter Ahlers Department of Physics and IQUEST, University of California Santa Barbara CA 93106 USA e-mail: guenter@physics.ucsb.edu Summary. After a brief
Boundary-Layer Theory
 Hermann Schlichting Klaus Gersten Boundary-Layer Theory With contributions from Egon Krause and Herbert Oertel Jr. Translated by Katherine Mayes 8th Revised and Enlarged Edition With 287 Figures and 22
Hermann Schlichting Klaus Gersten Boundary-Layer Theory With contributions from Egon Krause and Herbert Oertel Jr. Translated by Katherine Mayes 8th Revised and Enlarged Edition With 287 Figures and 22
Study of Forced and Free convection in Lid driven cavity problem
 MIT Study of Forced and Free convection in Lid driven cavity problem 18.086 Project report Divya Panchanathan 5-11-2014 Aim To solve the Navier-stokes momentum equations for a lid driven cavity problem
MIT Study of Forced and Free convection in Lid driven cavity problem 18.086 Project report Divya Panchanathan 5-11-2014 Aim To solve the Navier-stokes momentum equations for a lid driven cavity problem
Pattern Formation and Spatiotemporal Chaos
 Pattern Formation and Spatiotemporal Chaos - Chennai, 2004 1 Pattern Formation and Spatiotemporal Chaos Insights from Large Scale Numerical Simulations of Rayleigh-Bénard convection Collaborators: Mark
Pattern Formation and Spatiotemporal Chaos - Chennai, 2004 1 Pattern Formation and Spatiotemporal Chaos Insights from Large Scale Numerical Simulations of Rayleigh-Bénard convection Collaborators: Mark
Coherent structures in stably stratified plane Couette flow
 Coherent structures in stably stratified plane Couette flow D. Olvera * & R. R. Kerswell School of Mathematics, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK. * do2542@bristol.ac.uk Abstract A large body of recent
Coherent structures in stably stratified plane Couette flow D. Olvera * & R. R. Kerswell School of Mathematics, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK. * do2542@bristol.ac.uk Abstract A large body of recent
RAYLEIGH-BÉNARD CONVECTION IN A CYLINDER WITH AN ASPECT RATIO OF 8
 HEFAT01 9 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 01 Malta RAYLEIGH-BÉNARD CONVECTION IN A CYLINDER WITH AN ASPECT RATIO OF 8 Leong S.S. School of Mechanical
HEFAT01 9 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 01 Malta RAYLEIGH-BÉNARD CONVECTION IN A CYLINDER WITH AN ASPECT RATIO OF 8 Leong S.S. School of Mechanical
Effect of an adiabatic fin on natural convection heat transfer in a triangular enclosure
 American Journal of Applied Mathematics 2013; 1(4): 78-83 Published online November 10, 2013 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajam) doi: 10.11648/j.ajam.20130104.16 Effect of an adiabatic fin on
American Journal of Applied Mathematics 2013; 1(4): 78-83 Published online November 10, 2013 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajam) doi: 10.11648/j.ajam.20130104.16 Effect of an adiabatic fin on
MYcsvtu Notes HEAT TRANSFER BY CONVECTION
 www.mycsvtunotes.in HEAT TRANSFER BY CONVECTION CONDUCTION Mechanism of heat transfer through a solid or fluid in the absence any fluid motion. CONVECTION Mechanism of heat transfer through a fluid in
www.mycsvtunotes.in HEAT TRANSFER BY CONVECTION CONDUCTION Mechanism of heat transfer through a solid or fluid in the absence any fluid motion. CONVECTION Mechanism of heat transfer through a fluid in
Spatio-Temporal Chaos in Pattern-Forming Systems: Defects and Bursts
 Spatio-Temporal Chaos in Pattern-Forming Systems: Defects and Bursts with Santiago Madruga, MPIPKS Dresden Werner Pesch, U. Bayreuth Yuan-Nan Young, New Jersey Inst. Techn. DPG Frühjahrstagung 31.3.2006
Spatio-Temporal Chaos in Pattern-Forming Systems: Defects and Bursts with Santiago Madruga, MPIPKS Dresden Werner Pesch, U. Bayreuth Yuan-Nan Young, New Jersey Inst. Techn. DPG Frühjahrstagung 31.3.2006
Spatiotemporal Chaos in Rayleigh-Bénard Convection
 Spatiotemporal Chaos in Rayleigh-Bénard Convection Thesis by Keng-Hwee Chiam In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy California Institute of Technology Pasadena,
Spatiotemporal Chaos in Rayleigh-Bénard Convection Thesis by Keng-Hwee Chiam In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy California Institute of Technology Pasadena,
Chapter 9: Differential Analysis
 9-1 Introduction 9-2 Conservation of Mass 9-3 The Stream Function 9-4 Conservation of Linear Momentum 9-5 Navier Stokes Equation 9-6 Differential Analysis Problems Recall 9-1 Introduction (1) Chap 5: Control
9-1 Introduction 9-2 Conservation of Mass 9-3 The Stream Function 9-4 Conservation of Linear Momentum 9-5 Navier Stokes Equation 9-6 Differential Analysis Problems Recall 9-1 Introduction (1) Chap 5: Control
Chapter 7: Natural Convection
 7-1 Introduction 7- The Grashof Number 7-3 Natural Convection over Surfaces 7-4 Natural Convection Inside Enclosures 7-5 Similarity Solution 7-6 Integral Method 7-7 Combined Natural and Forced Convection
7-1 Introduction 7- The Grashof Number 7-3 Natural Convection over Surfaces 7-4 Natural Convection Inside Enclosures 7-5 Similarity Solution 7-6 Integral Method 7-7 Combined Natural and Forced Convection
Linear Biglobal Stability Analysis of Poiseuille-Rayleigh-Bénard Duct Flows in Binary Fluids with Soret Effect
 2012 International Conference on Fluid Dynamics and Thermodynamics Technologies (FDTT 2012) IPCSIT vol.33(2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Linear Biglobal Stability Analysis of Poiseuille-Rayleigh-Bénard
2012 International Conference on Fluid Dynamics and Thermodynamics Technologies (FDTT 2012) IPCSIT vol.33(2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Linear Biglobal Stability Analysis of Poiseuille-Rayleigh-Bénard
EFFECT OF VARYING THE HEATED LOWER REGION ON FLOW WITHIN A HORIZONTAL CYLINDER
 ISTP-1, 5, PRAGUE 1 TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON TRANSPORT PHENOMENA EFFECT OF VARYING THE HEATED LOWER REGION ON FLOW WITHIN A HORIZONTAL CYLINDER S. S. Leong School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering
ISTP-1, 5, PRAGUE 1 TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON TRANSPORT PHENOMENA EFFECT OF VARYING THE HEATED LOWER REGION ON FLOW WITHIN A HORIZONTAL CYLINDER S. S. Leong School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering
TRANSITION TO CHAOS OF RAYLEIGH-BÉNARD CELLS IN A CONFINED RECTANGULAR CONTAINER HEATED LOCALLY FROM BELOW
 TRANSITION TO CAOS OF RAYEIG-BÉNAR CES IN A CONFINE RECTANGUAR CONTAINER EATE OCAY FROM BEO iroyoshi Koizumi epartment of Mechanical Engineering & Intelligent Systems, The University of Electro-Communications,
TRANSITION TO CAOS OF RAYEIG-BÉNAR CES IN A CONFINE RECTANGUAR CONTAINER EATE OCAY FROM BEO iroyoshi Koizumi epartment of Mechanical Engineering & Intelligent Systems, The University of Electro-Communications,
Chapter 9: Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow
 of Fluid Flow Objectives 1. Understand how the differential equations of mass and momentum conservation are derived. 2. Calculate the stream function and pressure field, and plot streamlines for a known
of Fluid Flow Objectives 1. Understand how the differential equations of mass and momentum conservation are derived. 2. Calculate the stream function and pressure field, and plot streamlines for a known
Numerical Study of the Moving Boundary Problem During Melting Process in a Rectangular Cavity Heated from Below
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (4): 25-256, 2007 ISSN 546-9239 2007 Science Publications Corresponding Author: Numerical Study of the Moving Boundary Problem During Melting Process in a Rectangular
American Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (4): 25-256, 2007 ISSN 546-9239 2007 Science Publications Corresponding Author: Numerical Study of the Moving Boundary Problem During Melting Process in a Rectangular
Numerical Investigation of Combined Buoyancy and Surface Tension Driven Convection in an Axi-Symmetric Cylindrical Annulus
 Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, 2007, Vol. 12, No. 4, 541 552 Numerical Investigation of Combined Buoyancy and Surface Tension Driven Convection in an Axi-Symmetric Cylindrical Annulus M. Sankar
Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, 2007, Vol. 12, No. 4, 541 552 Numerical Investigation of Combined Buoyancy and Surface Tension Driven Convection in an Axi-Symmetric Cylindrical Annulus M. Sankar
Convection. forced convection when the flow is caused by external means, such as by a fan, a pump, or atmospheric winds.
 Convection The convection heat transfer mode is comprised of two mechanisms. In addition to energy transfer due to random molecular motion (diffusion), energy is also transferred by the bulk, or macroscopic,
Convection The convection heat transfer mode is comprised of two mechanisms. In addition to energy transfer due to random molecular motion (diffusion), energy is also transferred by the bulk, or macroscopic,
A Theory of Spatiotemporal Chaos: What s it mean, and how close are we?
 A Theory of Spatiotemporal Chaos: What s it mean, and how close are we? Michael Dennin UC Irvine Department of Physics and Astronomy Funded by: NSF DMR9975497 Sloan Foundation Research Corporation Outline
A Theory of Spatiotemporal Chaos: What s it mean, and how close are we? Michael Dennin UC Irvine Department of Physics and Astronomy Funded by: NSF DMR9975497 Sloan Foundation Research Corporation Outline
Hydrothermal waves in a disk of fluid
 Hydrothermal waves in a disk of fluid Nicolas Garnier, Arnaud Chiffaudel, and François Daviaud Rayleigh-Bénard and Bénard-Marangoni instabilities have been studied for roughly a century and have served
Hydrothermal waves in a disk of fluid Nicolas Garnier, Arnaud Chiffaudel, and François Daviaud Rayleigh-Bénard and Bénard-Marangoni instabilities have been studied for roughly a century and have served
MERGING OF SHEET PLUMES IN TURBULENT CONVECTION
 Proceedings of the 37 th International & 4 th National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power FMFP 2010 December 16-18, 2010, IIT Madras, Chennai, India FMFP 2010 MERGING OF SHEET PLUMES IN TURBULENT
Proceedings of the 37 th International & 4 th National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power FMFP 2010 December 16-18, 2010, IIT Madras, Chennai, India FMFP 2010 MERGING OF SHEET PLUMES IN TURBULENT
Rayleigh-Bénard convection in a homeotropically aligned nematic liquid crystal
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 58, NUMBER 5 NOVEMBER 1998 Rayleigh-Bénard convection in a homeotropically aligned nematic liquid crystal Leif Thomas, 1 Werner Pesch, 2 and Guenter Ahlers 1 1 Department of Physics
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 58, NUMBER 5 NOVEMBER 1998 Rayleigh-Bénard convection in a homeotropically aligned nematic liquid crystal Leif Thomas, 1 Werner Pesch, 2 and Guenter Ahlers 1 1 Department of Physics
Roll convection of binary fluid mixtures in porous media
 J. Fluid Mech. (21), vol. 649, pp. 165 186. c Cambridge University Press 21 doi:1.117/s22112999332 165 Roll convection of binary fluid mixtures in porous media R. U M L A, M. AUGUSTIN, B. HUKE AND M. L
J. Fluid Mech. (21), vol. 649, pp. 165 186. c Cambridge University Press 21 doi:1.117/s22112999332 165 Roll convection of binary fluid mixtures in porous media R. U M L A, M. AUGUSTIN, B. HUKE AND M. L
Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics. Laurette Tuckerman PMMH-ESPCI-CNRS
 Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics Laurette Tuckerman PMMH-ESPCI-CNRS laurette@pmmh.espci.fr Hydrodynamic Instabilities: Convection and Lorenz Model Web sites used in demonstrations
Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics Laurette Tuckerman PMMH-ESPCI-CNRS laurette@pmmh.espci.fr Hydrodynamic Instabilities: Convection and Lorenz Model Web sites used in demonstrations
Convection Workshop. Academic Resource Center
 Convection Workshop Academic Resource Center Presentation Outline Understanding the concepts Correlations External Convection (Chapter 7) Internal Convection (Chapter 8) Free Convection (Chapter 9) Solving
Convection Workshop Academic Resource Center Presentation Outline Understanding the concepts Correlations External Convection (Chapter 7) Internal Convection (Chapter 8) Free Convection (Chapter 9) Solving
Ageostrophic instabilities of a front in a stratified rotating fluid
 8 ème Congrès Français de Mécanique Grenoble, 27-3 août 27 Ageostrophic instabilities of a front in a stratified rotating fluid J. Gula, R. Plougonven & V. Zeitlin Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique
8 ème Congrès Français de Mécanique Grenoble, 27-3 août 27 Ageostrophic instabilities of a front in a stratified rotating fluid J. Gula, R. Plougonven & V. Zeitlin Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique
Natural Convection in Parabolic Enclosure Heated from Below
 www.ccsenet.org/mas Modern Applied Science Vol. 5, No. 3; June 011 Natural Convection in Parabolic Enclosure Heated from Below Dr. Ahmed W. Mustafa (Corresponding auther) University of Tikrit, College
www.ccsenet.org/mas Modern Applied Science Vol. 5, No. 3; June 011 Natural Convection in Parabolic Enclosure Heated from Below Dr. Ahmed W. Mustafa (Corresponding auther) University of Tikrit, College
Convection Due to Spatially Distributed Heating
 Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository December Convection Due to Spatially Distributed Heating Mohammad Zakir Hossain The University of Western Ontario Supervisor
Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository December Convection Due to Spatially Distributed Heating Mohammad Zakir Hossain The University of Western Ontario Supervisor
OSCILLATING INSTABILITY IN ONE-DIMENSIONAL RAYLEIGH-BENARD CONVECTION
 OSCILLATING INSTABILITY IN ONE-DIMENSIONAL RAYLEIGH-BENARD CONVECTION F. Daviaud, P. Berge, M. Dubois To cite this version: F. Daviaud, P. Berge, M. Dubois. OSCILLATING INSTABILITY IN ONE-DIMENSIONAL RAYLEIGH-BENARD
OSCILLATING INSTABILITY IN ONE-DIMENSIONAL RAYLEIGH-BENARD CONVECTION F. Daviaud, P. Berge, M. Dubois To cite this version: F. Daviaud, P. Berge, M. Dubois. OSCILLATING INSTABILITY IN ONE-DIMENSIONAL RAYLEIGH-BENARD
Towards a Numerical Benchmark for 3D Low Mach Number Mixed Flows in a Rectangular Channel Heated from Below
 Copyright 2008 Tech Science Press FDMP, vol.4, no.4, pp.263-269, 2008 Towards a Numerical Benchmark for 3D Low Mach Number Mixed Flows in a Rectangular Channel Heated from Below G. Accary 1, S. Meradji
Copyright 2008 Tech Science Press FDMP, vol.4, no.4, pp.263-269, 2008 Towards a Numerical Benchmark for 3D Low Mach Number Mixed Flows in a Rectangular Channel Heated from Below G. Accary 1, S. Meradji
NATURAL CONVECTION FLOW IN A SQUARE CAVITY WITH INTERNAL HEAT GENERATION AND A FLUSH MOUNTED HEATER ON A SIDE WALL
 Journal of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering December, 2010 DOI: 10.3329/jname.v7i2.3292 http://www.banglajol.info NATURAL CONVECTION FLOW IN A SQUARE CAVITY WITH INTERNAL HEAT GENERATION AND A
Journal of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering December, 2010 DOI: 10.3329/jname.v7i2.3292 http://www.banglajol.info NATURAL CONVECTION FLOW IN A SQUARE CAVITY WITH INTERNAL HEAT GENERATION AND A
A Finite Element Analysis on MHD Free Convection Flow in Open Square Cavity Containing Heated Circular Cylinder
 American Journal of Computational Mathematics, 2015, 5, 41-54 Published Online March 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajcm http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajcm.2015.51003 A Finite Element Analysis
American Journal of Computational Mathematics, 2015, 5, 41-54 Published Online March 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajcm http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajcm.2015.51003 A Finite Element Analysis
Experiments on Thermally Driven Convection
 Experiments on Thermally Driven Convection Guenter Ahlers ABSTRACT Experimental results for thermally driven convection in a thin horizontal layer of a nematic liquid crystal heated from below or above
Experiments on Thermally Driven Convection Guenter Ahlers ABSTRACT Experimental results for thermally driven convection in a thin horizontal layer of a nematic liquid crystal heated from below or above
Rotating Rayleigh-Bénard Convection: Aspect Ratio Dependence of the Initial Bifurcations
 arxiv:patt-sol/9303001v1 11 Mar 1993 Rotating Rayleigh-Bénard Convection: Aspect Ratio Dependence of the Initial Bifurcations Li Ning and Robert E. Ecke Physics Division and Center for Nonlinear Studies
arxiv:patt-sol/9303001v1 11 Mar 1993 Rotating Rayleigh-Bénard Convection: Aspect Ratio Dependence of the Initial Bifurcations Li Ning and Robert E. Ecke Physics Division and Center for Nonlinear Studies
Wake of oblate spheroids and flat cylinders
 Institut de Mécanique des Fluides et des Solides, Université de Strasbourg/CNRS, France Parametric study of the transition scenario in the wake of oblate spheroids and flat cylinders Summary 1 Introduction
Institut de Mécanique des Fluides et des Solides, Université de Strasbourg/CNRS, France Parametric study of the transition scenario in the wake of oblate spheroids and flat cylinders Summary 1 Introduction
Abstract. Introduction
 Combined forced and natural convection in a square cavity - numerical solution and scale analysis A.T. Franco/ M.M. Ganzarolli'' "DAMEC, CEFET, PR 80230-901, Curitiba, PR Brasil >>DE, FEM, UNICAMP 13081-970,
Combined forced and natural convection in a square cavity - numerical solution and scale analysis A.T. Franco/ M.M. Ganzarolli'' "DAMEC, CEFET, PR 80230-901, Curitiba, PR Brasil >>DE, FEM, UNICAMP 13081-970,
MIXED CONVECTION IN A SQUARE CAVITY WITH A HEAT-CONDUCTING HORIZONTAL SQUARE CYLINDER
 Suranaree J. Sci. Technol. Vol. 17 No. 2; April - June 2010 139 MIXED CONVECTION IN A SQUARE CAVITY WITH A HEAT-CONDUCTING HORIZONTAL SQUARE CYLINDER Md. Mustafizur Rahman 1 *, M. A. Alim 1 and Sumon Saha
Suranaree J. Sci. Technol. Vol. 17 No. 2; April - June 2010 139 MIXED CONVECTION IN A SQUARE CAVITY WITH A HEAT-CONDUCTING HORIZONTAL SQUARE CYLINDER Md. Mustafizur Rahman 1 *, M. A. Alim 1 and Sumon Saha
Analysis of the flow and heat transfer characteristics for MHD free convection in an enclosure with a heated obstacle
 Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, 2011, Vol. 16, No. 1, 89 99 89 Analysis of the flow and heat transfer characteristics for MHD free convection in an enclosure with a heated obstacle S. Parvin,
Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control, 2011, Vol. 16, No. 1, 89 99 89 Analysis of the flow and heat transfer characteristics for MHD free convection in an enclosure with a heated obstacle S. Parvin,
Traveling waves in rotating Rayleigh-Bénard convection
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 69, 056301 (2004) Traveling waves in rotating Rayleigh-Bénard convection Wooyoung Choi, 1,2, * Dilip Prasad, 1,2, Roberto Camassa, 1,2 and Robert E. Ecke 2,3 1 Theoretical Division, Los
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 69, 056301 (2004) Traveling waves in rotating Rayleigh-Bénard convection Wooyoung Choi, 1,2, * Dilip Prasad, 1,2, Roberto Camassa, 1,2 and Robert E. Ecke 2,3 1 Theoretical Division, Los
Figure 11.1: A fluid jet extruded where we define the dimensionless groups
 11. Fluid Jets 11.1 The shape of a falling fluid jet Consider a circular orifice of a radius a ejecting a flux Q of fluid density ρ and kinematic viscosity ν (see Fig. 11.1). The resulting jet accelerates
11. Fluid Jets 11.1 The shape of a falling fluid jet Consider a circular orifice of a radius a ejecting a flux Q of fluid density ρ and kinematic viscosity ν (see Fig. 11.1). The resulting jet accelerates
HEAT TRANSFER BY CONVECTION. Dr. Şaziye Balku 1
 HEAT TRANSFER BY CONVECTION Dr. Şaziye Balku 1 CONDUCTION Mechanism of heat transfer through a solid or fluid in the absence any fluid motion. CONVECTION Mechanism of heat transfer through a fluid in the
HEAT TRANSFER BY CONVECTION Dr. Şaziye Balku 1 CONDUCTION Mechanism of heat transfer through a solid or fluid in the absence any fluid motion. CONVECTION Mechanism of heat transfer through a fluid in the
Abstract: This paper numerically investigates the physical mechanism of flow instability
 Hua-Shu Dou*, Gang Jiang, Numerical simulation of flow instability and heat transfer of natural convection in a differentially heated cavity, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 103 (2016)
Hua-Shu Dou*, Gang Jiang, Numerical simulation of flow instability and heat transfer of natural convection in a differentially heated cavity, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 103 (2016)
Change of ow patterns in thermocapillary convection in liquid bridge
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Acta Astronautica 54 (2004) 493 501 www.elsevier.com/locate/actaastro Change of ow patterns in thermocapillary convection in liquid bridge V.M. Shevtsova, D.E.
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Acta Astronautica 54 (2004) 493 501 www.elsevier.com/locate/actaastro Change of ow patterns in thermocapillary convection in liquid bridge V.M. Shevtsova, D.E.
STABILITY ANALYSIS FOR BUOYANCY-OPPOSED FLOWS IN POLOIDAL DUCTS OF THE DCLL BLANKET. N. Vetcha, S. Smolentsev and M. Abdou
 STABILITY ANALYSIS FOR BUOYANCY-OPPOSED FLOWS IN POLOIDAL DUCTS OF THE DCLL BLANKET N. Vetcha S. Smolentsev and M. Abdou Fusion Science and Technology Center at University of California Los Angeles CA
STABILITY ANALYSIS FOR BUOYANCY-OPPOSED FLOWS IN POLOIDAL DUCTS OF THE DCLL BLANKET N. Vetcha S. Smolentsev and M. Abdou Fusion Science and Technology Center at University of California Los Angeles CA
Module 6: Free Convections Lecture 26: Evaluation of Nusselt Number. The Lecture Contains: Heat transfer coefficient. Objectives_template
 The Lecture Contains: Heat transfer coefficient file:///d /Web%20Course%20(Ganesh%20Rana)/Dr.%20gautam%20biswas/Final/convective_heat_and_mass_transfer/lecture26/26_1.html[12/24/2014 6:08:23 PM] Heat transfer
The Lecture Contains: Heat transfer coefficient file:///d /Web%20Course%20(Ganesh%20Rana)/Dr.%20gautam%20biswas/Final/convective_heat_and_mass_transfer/lecture26/26_1.html[12/24/2014 6:08:23 PM] Heat transfer
Open boundary conditions in numerical simulations of unsteady incompressible flow
 Open boundary conditions in numerical simulations of unsteady incompressible flow M. P. Kirkpatrick S. W. Armfield Abstract In numerical simulations of unsteady incompressible flow, mass conservation can
Open boundary conditions in numerical simulations of unsteady incompressible flow M. P. Kirkpatrick S. W. Armfield Abstract In numerical simulations of unsteady incompressible flow, mass conservation can
Convection Patterns. Physics 221A, Spring 2017 Lectures: P. H. Diamond Notes: Jiacong Li
 Convection Patterns Physics 1A, Spring 017 Lectures: P. H. Diamond Notes: Jiacong Li 1 Introduction In previous lectures, we have studied the basics of dynamics, which include dimensions of (strange) attractors,
Convection Patterns Physics 1A, Spring 017 Lectures: P. H. Diamond Notes: Jiacong Li 1 Introduction In previous lectures, we have studied the basics of dynamics, which include dimensions of (strange) attractors,
10. Buoyancy-driven flow
 10. Buoyancy-driven flow For such flows to occur, need: Gravity field Variation of density (note: not the same as variable density!) Simplest case: Viscous flow, incompressible fluid, density-variation
10. Buoyancy-driven flow For such flows to occur, need: Gravity field Variation of density (note: not the same as variable density!) Simplest case: Viscous flow, incompressible fluid, density-variation
Effect of Gravity Modulation and Internal Heat Generation on Rayleigh-Bénard Convection in Couple Stress Fluid with Maxwell-Cattaneo Law
 Effect of Gravity Modulation and Internal Heat Generation on Rayleigh-Bénard Convection in Couple Stress Fluid with Maxwell-Cattaneo Law Maria Thomas Research scholar, Department of Mathematics, CHRIST
Effect of Gravity Modulation and Internal Heat Generation on Rayleigh-Bénard Convection in Couple Stress Fluid with Maxwell-Cattaneo Law Maria Thomas Research scholar, Department of Mathematics, CHRIST
Contents. I Introduction 1. Preface. xiii
 Contents Preface xiii I Introduction 1 1 Continuous matter 3 1.1 Molecules................................ 4 1.2 The continuum approximation.................... 6 1.3 Newtonian mechanics.........................
Contents Preface xiii I Introduction 1 1 Continuous matter 3 1.1 Molecules................................ 4 1.2 The continuum approximation.................... 6 1.3 Newtonian mechanics.........................
Visualization of Natural Convection in Enclosure. Filled with Porous Medium by Sinusoidally. Temperature on the One Side
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol., 2012, no. 97, 801-812 Visualization of Natural Convection in Enclosure Filled with Porous Medium by Sinusoidally Temperature on the One Side Paweena Khansila Department
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol., 2012, no. 97, 801-812 Visualization of Natural Convection in Enclosure Filled with Porous Medium by Sinusoidally Temperature on the One Side Paweena Khansila Department
Destabilization of free convection by weak rotation
 Destabilization of free convection by weak rotation A. Yu. Gelfgat School of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tel-Aviv University, 69978, Tel-Aviv, Israel Abstract This study offers an explanation
Destabilization of free convection by weak rotation A. Yu. Gelfgat School of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tel-Aviv University, 69978, Tel-Aviv, Israel Abstract This study offers an explanation
Principles of Convection
 Principles of Convection Point Conduction & convection are similar both require the presence of a material medium. But convection requires the presence of fluid motion. Heat transfer through the: Solid
Principles of Convection Point Conduction & convection are similar both require the presence of a material medium. But convection requires the presence of fluid motion. Heat transfer through the: Solid
LINEAR STABILITY ANALYSIS AND DIRECT NUMERICAL SIMUALATION OF DOUBLE-LAYER RAYLEIGH-BÉNARD CONVECTION
 LINEAR STABILITY ANALYSIS AND DIRECT NUMERICAL SIMUALATION OF DOUBLE-LAYER RAYLEIGH-BÉNARD CONVECTION É. FONTANA 1, E. MANCUSI 1,2, A. A. ULSON DE SOUZA 1, S. M. A. GUELLI U. SOUZA 1 1 Universidade Federal
LINEAR STABILITY ANALYSIS AND DIRECT NUMERICAL SIMUALATION OF DOUBLE-LAYER RAYLEIGH-BÉNARD CONVECTION É. FONTANA 1, E. MANCUSI 1,2, A. A. ULSON DE SOUZA 1, S. M. A. GUELLI U. SOUZA 1 1 Universidade Federal
Applications of parabolized stability equation for predicting transition position in boundary layers
 Appl. Math. Mech. -Engl. Ed., 33(6), 679 686 (2012) DOI 10.1007/s10483-012-1579-7 c Shanghai University and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2012 Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) Applications
Appl. Math. Mech. -Engl. Ed., 33(6), 679 686 (2012) DOI 10.1007/s10483-012-1579-7 c Shanghai University and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2012 Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) Applications
Flow patterns and heat transfer in square cavities with perfectly conducting horizontal walls: the case of high Rayleigh numbers ( )
 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VII 391 Flow patterns and heat transfer in square cavities with perfectly conducting horizontal walls: the case of high Rayleigh numbers (10 6 10 9 ) R. L. Frederick & S. Courtin
Advances in Fluid Mechanics VII 391 Flow patterns and heat transfer in square cavities with perfectly conducting horizontal walls: the case of high Rayleigh numbers (10 6 10 9 ) R. L. Frederick & S. Courtin
MECHANISMS OF INSTABILITY IN RAYLEIGH-BÉNARD CONVECTION
 MECHANISMS OF INSTABILITY IN RAYLEIGH-BÉNARD CONVECTION A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by Adam C. Perkins In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy in the
MECHANISMS OF INSTABILITY IN RAYLEIGH-BÉNARD CONVECTION A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by Adam C. Perkins In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy in the
Magnetic field effects on liquid metal free convection
 Magnetic field effects on liquid metal free convection S Renaudière de Vaux R Zamansky W Bergez Ph Tordjeman V Bouyer P Piluso J.F. Haquet To cite this version: S Renaudière de Vaux R Zamansky W Bergez
Magnetic field effects on liquid metal free convection S Renaudière de Vaux R Zamansky W Bergez Ph Tordjeman V Bouyer P Piluso J.F. Haquet To cite this version: S Renaudière de Vaux R Zamansky W Bergez
Validation of an adjoint method for compressible channel flow sensitivities
 9 ème Congrès Français de Mécanique Marseille, -8 août 9 Validation of an method for compressible channel flow sensitivities L. MORE-GABARRO, P. CAHALIFAUD, C. AIRIAU Université de oulouse ; CNRS, INP,
9 ème Congrès Français de Mécanique Marseille, -8 août 9 Validation of an method for compressible channel flow sensitivities L. MORE-GABARRO, P. CAHALIFAUD, C. AIRIAU Université de oulouse ; CNRS, INP,
Lattice Boltzmann Method for Fluid Simulations
 Lattice Boltzmann Method for Fluid Simulations Yuanxun Bill Bao & Justin Meskas April 14, 2011 1 Introduction In the last two decades, the Lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) has emerged as a promising tool
Lattice Boltzmann Method for Fluid Simulations Yuanxun Bill Bao & Justin Meskas April 14, 2011 1 Introduction In the last two decades, the Lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) has emerged as a promising tool
INFLUENCE OF GEOMETRICAL ASPECT RATIO ON THE OSCILLATORY MARANGONI CONVECTION IN LIQUID BRIDGES R. MONTI, R. SAVINO, M. LAPPA *
 AUTHOR S POST PRINT (Romeo Colour: Green) Acta Astronautica (ISSN: 94-5765) Vol. 47, No., pp. 753-76, 2. DOI.6/S94-5765()26- Publisher version available at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s94576526
AUTHOR S POST PRINT (Romeo Colour: Green) Acta Astronautica (ISSN: 94-5765) Vol. 47, No., pp. 753-76, 2. DOI.6/S94-5765()26- Publisher version available at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s94576526
NATURAL CONVECTION AND RADIATION IN CIRCULAR AND ARC CAVITY
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 9 (ICME9) - 8 December 9, Dhaka, Bangladesh ICME9-TH- NATURAL CONVECTION AND RADIATION IN CIRCULAR AND ARC CAVITY Naheed Ferdous, Md.
Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 9 (ICME9) - 8 December 9, Dhaka, Bangladesh ICME9-TH- NATURAL CONVECTION AND RADIATION IN CIRCULAR AND ARC CAVITY Naheed Ferdous, Md.
Numerical Study of Free Convection Heat Transfer in a Square Cavity with a Fin Attached to Its Cold Wall
 Heat Transfer Research, 2011, Vol. 42, No. 3 Numerical Study of Free Convection Heat Transfer in a Square Cavity with a Fin Attached to Its Cold Wall SAEID JANI, 1* MEYSAM AMINI, 2 and MOSTAFA MAHMOODI
Heat Transfer Research, 2011, Vol. 42, No. 3 Numerical Study of Free Convection Heat Transfer in a Square Cavity with a Fin Attached to Its Cold Wall SAEID JANI, 1* MEYSAM AMINI, 2 and MOSTAFA MAHMOODI
CFD STUDY OF MASS TRANSFER IN SPACER FILLED MEMBRANE MODULE
 GANIT J. Bangladesh Math. Soc. (ISSN 1606-3694) 31 (2011) 33-41 CFD STUDY OF MASS TRANSFER IN SPACER FILLED MEMBRANE MODULE Sharmina Hussain Department of Mathematics and Natural Science BRAC University,
GANIT J. Bangladesh Math. Soc. (ISSN 1606-3694) 31 (2011) 33-41 CFD STUDY OF MASS TRANSFER IN SPACER FILLED MEMBRANE MODULE Sharmina Hussain Department of Mathematics and Natural Science BRAC University,
NUMERICAL STUDY OF THE THERMOSOLUTAL CONVECTION IN A THREE- DIMENSIONAL CAVITY SUBMITTED TO CROSS GRADIENTS OF TEMPERATURE AND CONCENTRATION
 NUMERICAL STUDY OF THE THERMOSOLUTAL CONVECTION IN A THREE- DIMENSIONAL CAVITY SUBMITTED TO CROSS GRADIENTS OF TEMPERATURE AND CONCENTRATION Meriem OUZAOUIT 1 *, Btissam ABOURIDA 1, Lahoucine BELARCHE
NUMERICAL STUDY OF THE THERMOSOLUTAL CONVECTION IN A THREE- DIMENSIONAL CAVITY SUBMITTED TO CROSS GRADIENTS OF TEMPERATURE AND CONCENTRATION Meriem OUZAOUIT 1 *, Btissam ABOURIDA 1, Lahoucine BELARCHE
PHYSFLU - Physics of Fluids
 Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 748 - FIS - Department of Physics Academic year: Degree: 2018 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ENGINEERING PHYSICS
Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 748 - FIS - Department of Physics Academic year: Degree: 2018 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ENGINEERING PHYSICS
Long-Wave Instability in the Raylegh-Benard Problem with High Frequency Vibrations
 World Applied Sciences Journal 7 (8): 1005-1009, 013 ISSN 1818-95 IDOSI Publications, 013 DOI: 10.589/idosi.wasj.013.7.08.13695 Long-Wave Instability in the Raylegh-Benard Problem with High Frequency Vibrations
World Applied Sciences Journal 7 (8): 1005-1009, 013 ISSN 1818-95 IDOSI Publications, 013 DOI: 10.589/idosi.wasj.013.7.08.13695 Long-Wave Instability in the Raylegh-Benard Problem with High Frequency Vibrations
NATURAL CONVECTION WITHIN TRAPEZOIDAL ENCLOSURE WITH TWO BAFFLES: EFFECT OF VARIOUS ANGLES OF INCLINATION
 NATURAL CONVECTION WITHIN TRAPEZOIDAL ENCLOSURE WITH TWO BAFFLES: EFFECT OF VARIOUS ANGLES OF INCLINATION Éliton Fontana, eliton_fontana@hotmail.com Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina - UFSC Adriano
NATURAL CONVECTION WITHIN TRAPEZOIDAL ENCLOSURE WITH TWO BAFFLES: EFFECT OF VARIOUS ANGLES OF INCLINATION Éliton Fontana, eliton_fontana@hotmail.com Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina - UFSC Adriano
Fluid Dynamics: Theory, Computation, and Numerical Simulation Second Edition
 Fluid Dynamics: Theory, Computation, and Numerical Simulation Second Edition C. Pozrikidis m Springer Contents Preface v 1 Introduction to Kinematics 1 1.1 Fluids and solids 1 1.2 Fluid parcels and flow
Fluid Dynamics: Theory, Computation, and Numerical Simulation Second Edition C. Pozrikidis m Springer Contents Preface v 1 Introduction to Kinematics 1 1.1 Fluids and solids 1 1.2 Fluid parcels and flow
PHYS 432 Physics of Fluids: Instabilities
 PHYS 432 Physics of Fluids: Instabilities 1. Internal gravity waves Background state being perturbed: A stratified fluid in hydrostatic balance. It can be constant density like the ocean or compressible
PHYS 432 Physics of Fluids: Instabilities 1. Internal gravity waves Background state being perturbed: A stratified fluid in hydrostatic balance. It can be constant density like the ocean or compressible
Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computation (JAMC), 2018, 2(7),
 Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computation (JAMC), 2018, 2(7), 266-270 http://www.hillpublisher.org/journal/jamc ISSN Online:2576-0645 ISSN Print:2576-0653 The Solution Of 2D Hydrodynamic Equations
Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computation (JAMC), 2018, 2(7), 266-270 http://www.hillpublisher.org/journal/jamc ISSN Online:2576-0645 ISSN Print:2576-0653 The Solution Of 2D Hydrodynamic Equations
Marangoni-Natural Convection in Liquid Metals in the Presence of a Tilted Magnetic Field
 Copyright 2010 Tech Science Press FDMP, vol.6, no.4, pp.369-384, 2010 Marangoni-Natural Convection in Liquid Metals in the Presence of a Tilted Magnetic Field S. Hamimid 1 and A. Amroune 1 Abstract: The
Copyright 2010 Tech Science Press FDMP, vol.6, no.4, pp.369-384, 2010 Marangoni-Natural Convection in Liquid Metals in the Presence of a Tilted Magnetic Field S. Hamimid 1 and A. Amroune 1 Abstract: The
Homogeneous Rayleigh-Bénard convection
 Slide 1 Homogeneous Rayleigh-Bénard convection scaling, heat transport and structures E. Calzavarini and F. Toschi, D. Lohse, R. Tripiccione, C. R. Doering, J. D. Gibbon, A. Tanabe Euromech Colloquium
Slide 1 Homogeneous Rayleigh-Bénard convection scaling, heat transport and structures E. Calzavarini and F. Toschi, D. Lohse, R. Tripiccione, C. R. Doering, J. D. Gibbon, A. Tanabe Euromech Colloquium
Tertiary and quaternary solutions for plane Couette flow
 J. Fluid Mech. (1997), vol. 344, pp. 137 153. Printed in the United Kingdom c 1997 Cambridge University Press 137 Tertiary and quaternary solutions for plane Couette flow By R. M. CLEVER 1 AND F. H. BUSSE
J. Fluid Mech. (1997), vol. 344, pp. 137 153. Printed in the United Kingdom c 1997 Cambridge University Press 137 Tertiary and quaternary solutions for plane Couette flow By R. M. CLEVER 1 AND F. H. BUSSE
Interfacial waves in steady and oscillatory, two-layer Couette flows
 Interfacial waves in steady and oscillatory, two-layer Couette flows M. J. McCready Department of Chemical Engineering University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556 Page 1 Acknowledgments Students: M.
Interfacial waves in steady and oscillatory, two-layer Couette flows M. J. McCready Department of Chemical Engineering University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556 Page 1 Acknowledgments Students: M.
2004 American Physical Society
 PUBLISHED VERSION Cox, Stephen Michael; Matthews, P. C.; Pollicott, S. L. Swift-Hohenberg model for magnetoconvection Physical Review E, 004; 69(6):066314 004 American Physical Society http://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/physreve.69.066314
PUBLISHED VERSION Cox, Stephen Michael; Matthews, P. C.; Pollicott, S. L. Swift-Hohenberg model for magnetoconvection Physical Review E, 004; 69(6):066314 004 American Physical Society http://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/physreve.69.066314
Direct numerical simulation and global stability analysis of three-dimensional instabilities in a lid-driven cavity
 C. R. Mecanique 336 (2008 586 591 http://france.elsevier.com/direct/cras2b/ Direct numerical simulation and global stability analysis of three-dimensional instabilities in a lid-driven cavity Jérèmie Chicheportiche,
C. R. Mecanique 336 (2008 586 591 http://france.elsevier.com/direct/cras2b/ Direct numerical simulation and global stability analysis of three-dimensional instabilities in a lid-driven cavity Jérèmie Chicheportiche,
Candidates must show on each answer book the type of calculator used. Log Tables, Statistical Tables and Graph Paper are available on request.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Spring Semester Examination 2004 FLUID DYNAMICS Time allowed: 3 hours Attempt Question 1 and FOUR other questions. Candidates must show on each answer book
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Spring Semester Examination 2004 FLUID DYNAMICS Time allowed: 3 hours Attempt Question 1 and FOUR other questions. Candidates must show on each answer book
Complex Patterns in a Simple System
 Complex Patterns in a Simple System arxiv:patt-sol/9304003v1 17 Apr 1993 John E. Pearson Center for Nonlinear Studies Los Alamos National Laboratory February 4, 2008 Abstract Numerical simulations of a
Complex Patterns in a Simple System arxiv:patt-sol/9304003v1 17 Apr 1993 John E. Pearson Center for Nonlinear Studies Los Alamos National Laboratory February 4, 2008 Abstract Numerical simulations of a
Homology and symmetry breaking in Rayleigh-Bénard convection: Experiments and simulations
 PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 19, 117105 2007 Homology and symmetry breaking in Rayleigh-Bénard convection: Experiments and simulations Kapilanjan Krishan, a Huseyin Kurtuldu, and Michael F. Schatz b Center for Nonlinear
PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 19, 117105 2007 Homology and symmetry breaking in Rayleigh-Bénard convection: Experiments and simulations Kapilanjan Krishan, a Huseyin Kurtuldu, and Michael F. Schatz b Center for Nonlinear
Coupling of Lattice Boltzmann Equation and Finite Volume Method to Simulate Heat Transfer in a Square Cavity
 Copyright 2009 Tech Science Press FDMP, vol.5, no.3, pp.283-295, 2009 Coupling of Lattice Boltzmann Equation and Finite Volume Method to Simulate Heat Transfer in a Square Cavity Ahmed Mezrhab 1 and Hassan
Copyright 2009 Tech Science Press FDMP, vol.5, no.3, pp.283-295, 2009 Coupling of Lattice Boltzmann Equation and Finite Volume Method to Simulate Heat Transfer in a Square Cavity Ahmed Mezrhab 1 and Hassan
Chapter 3 NATURAL CONVECTION
 Fundamentals of Thermal-Fluid Sciences, 3rd Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Robert H. Turner, John M. Cimbala McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 3 NATURAL CONVECTION Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Fundamentals of Thermal-Fluid Sciences, 3rd Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Robert H. Turner, John M. Cimbala McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 3 NATURAL CONVECTION Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer. Week 9
 Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer Week 9 補充! Multidimensional Effects Transient problems with heat transfer in two or three dimensions can be considered using the solutions obtained for one dimensional
Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer Week 9 補充! Multidimensional Effects Transient problems with heat transfer in two or three dimensions can be considered using the solutions obtained for one dimensional
