AN INDEX OF FACTORIAL SIMPLICITY* HENRY F. KAISER UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY AND UNITED STATES COAST GUARD ACADEMY
|
|
|
- Alvin Gervais McKinney
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PSYCHOMETRIKA--VOL. 39, NO. 1 MARCH, 1974 AN INDEX OF FACTORIAL SIMPLICITY* HENRY F. KAISER UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY AND UNITED STATES COAST GUARD ACADEMY An index of factorial simplicity, employing the quartimax transformational criteria of Carroll, Wrigley and Neuhaus, and Saunders, is developed. This index is both for each row separately and for a factor pattern matrix as a whole. The index varies between zero and one. The problem of calibrating the index is discussed. After a factor analysis has been completed, it is of interest to assess how good the solution is, in the sense of how simple--and thus how interpretable-- the final factor pattern matrix is. The ideal solution, most investigators would agree, is one that is unifactorial, i.e., a solution for which each row of the pattern matrix has one, and only one, non-zero loading. In this paper we propose an index, for each row of the factor matrix separately and for the matrix as a whole, which measures the tendency towards unifactoriality for a given row and the tendency toward unifactoriality for the entire factor pattern matrix. For this purpose, we turn to the quartimax criteria for analytic transformation of Carroll [1953], Wrigley and Neuhaus [1954], and Saunders [1953], and measure the value of their criteria for the data at hand relative to the optimum value of their criteria. Interestingly, it turns out that each of their three rationales leads to the same index of factorial simplicity when we scale the index to lie between zero and one. (It should be pointed out that, while we develop our index from the quartimax viewpoint, our results are applicable to any factor pattern matrix.) First we consider Carroll's [1953] criterion. For row j of the pattern matrix V, he proposes that (1) = 5: should be a minimum. Clearly the minimum value that C~ can reach is zero, and this occurs when only one of the q (the number of factors) elements in row i is non-zero. The worst possible value of Ci, i.e., when C~ is a maximum, * The research reported in this paper was supported in part by the Office of Computing Activities, National Science Foundation. 31
2 32 PSYCHOMETRIKA occurs when all q of the vi, in row j are equal in absolute value. It is seen that "this is given by (2) max C; = q(q- 1)(~E ] vi2/q) 2, a (3) = (q -- 1)(~-'~. v,.2)2/q. Let us take as our squared index of factorial simplicity, for row j of V, the quantity (4) (IFS(j))2= 1 C, max C; 2~, ~-, vi.2vi, 2 (5) = 1 -- "~' (q -- 1)(~E] vi2)/q 8 We define our IFS(J) in this way so that it can vary from zero to one, yielding a value of zero when all vi. are equal in absolute value--the worst possible situation--and reaching a value of one only when all vi, but one are zero--the best possible situation. (We discuss why we take the square root of (5) for the actual (IFS(J)) below under "the problem of calibration.") Noting that (6) E Y_,v,.% 2= (Z~,.2) 2- Z~;.', e#t s s and after a little algebra, we find q E v,.' - ( E v;.3)2 $ $ (7) (IFS(J)) 2 = (q _ )(Z] v,. ) a From Carroll's viewpoint, his overall criterion for the entire pattern matrix is (s) c = E c; = E E E v,.% 2. i i s#t If we define our overall squared index of factorial simplicity as (9) (IFS)2= 1 we readily find that (10) (IFS) 2 = C max C ' Y~ [q ~ v; 4 -- ( ~[] v;.2) 2] i s s ~E [(q - 1)(2E v;.)]22 i s which again can vary from zero--worst possible--to one--best possible. The latter occurs only when the entire matrix is unifactorial.
3 HENRY F. KAISER 33 From Wrigley and Neuhaus' [1954] point of view a row of V is ideal when the variance of the squared loadings is a maximum, i.e., when (11) W; = [q ~ vi, 4 -- (~ v,,2)2]/q 2 s is a maximum. The maximum value that Wi can attain is (12) max W; = [q(~] v;.2) 2 - (~] v,,2)2]/q 2. s $ From this viewpoint let us take as our squared index of factorial simplicity (13) (IFS(J))~ _ W, max Wi ' q ~]vi. 4- (~]vi,2) 2 8 a (14) (q -- 1)(~-v;.22), the same index we proposed when looking at the problem from Carroll's viewpoint. Overall--for the entire matrix--we define 8 i (15) (IFS)2 - ~ max Wi i E[q Ev;." - (E (16) -- ' ' [(q - *,;. ~ ) ]..., J as before. Finally, Saunders' [1953] version of the quartimax criterion proposes that, for row j, Z Vis (17) Si* - "- 2 2 should be a maximum. The maximum value of Si* occurs, as might be expected, when one and only one element in row j is non-zero, and is (18) max Si* = 1. When all elements in row j are equal in absolute value--the worst possible situation--si* is a minimum, and is (19) rain Si* = 1/q. Let us redefine Si* as (20) S~ = a -'k bsi* $ t
4 34 PSYCHOMETRIKA choosing a and b so that S; varies from zero to one (rather than Si*'s varying from 1/q to 1). For this purpose we have the simultaneous equations in a and b (21) and (22) yielding (23) and (24) from which (25) S~ = Elementary algebra yields a + b (max Si*) = a "4- b(1) = 1, a + b (min Si*) = a -4- b(1/q) = O, a = --1/(q- 1), b = q/(q-- 1), Z /)is q (q ) + (q - 1) Z: (~i.) ~ ~" q ~v;, 4 -- (y~vi2) 2 $ (26) S, = (IFS(J)) 2 = (q - 1)(~-v;,22) as before. For the entire pattern matrix we can again derive the overall squared IFS as Z E - (Z (27) (IFS)2 i, ~2 [(q - 1)( ]E -v;. ) 2 Thus, all roads lead to Rome: regardless of what version of the quartimax criterion we use, if we set out to define an index which varies from zero to one we find (7), (14), or (26) for a given row J, or (10), (16), or (27) for the entire factor pattern matrix. The Problem o] Calibration Although we know that an IFS can vary from a minimum of zero to a maximum of one, we still would like to know the meaning of values between these extremes. It would seem that only extensive numerical experience with real data will give us a solid feeling for, say, how big is big, etc. Ho~= ever, the following considerations may be helpful for this problem. Above we uniformly defined squared indices of factorial simplicity. The reason for this is that throughout we have dealt with fourth-power functions of loadings, and it would seem more consistent with other statistical a t
5 - 1) HENRY F. KAISER 35 measures, e.g., the correlation ratio, to deal with squared functions. Additionally, numerical appraisal indicates that, were we not to take square roots above, our indices would be too dramatically depressed for only slight departures from unifactoriality. Further help in the calibration of our index may be gained from considering the special case of a row of a factor matrix with q elements, c of which are non-zero and equal in absolute value, and (q - c) are zero (c is what is usually called the complexity of a variable represented by the row). Elementary analysis for this special case yields = q--c (28) (IFS(J))2 c(q- 1) and (29) lim(ifs(j)) 2 = lim q-c _ c(q - c In Table 1 are given values of IFS(J), as given by the square roots of (28) and (29), for various values of q and c. This table might possibly give the wrong impression about what IFSs are observed with real data. Most real world problems have an average complexity c of, so to speak, about one and one-half, and thus yield an IFS in the.70s or.80s. Subjective reflection, based upon Table 1 and primarily observing IFSs for a substantial number of factor analyses from the real world, suggests the following evaluation of levels of our index of factorial simplicity: in the.90s, marvelous in the.80s, meritorious in the.70s, middling in the.60s, mediocre in the.50s, miserable below.50, unacceptable Table I Indices of Factorial Simplicity as a Function of q, the NLmber of Factors, and c, the Complexity of a Variable's Loadings. oooo o " u ] i0 Ii 12 q = ntmlber of factors
6 36 PSYCHOMETRIKA Referring to Table 1, we see that an IFS will be at.50, the borderline of acceptability, when, for complexity two, there are three factors, for complexity three, there are nine factors, and for complexity four, there is an infinity of factors. For complexity c of five or greater, an acceptable IFS is not attainable. REFERENCES Carroll, J. B. An analytical solution for approximating simple structure in factor analysis. Psychometrika, 1953, 18, Saunders, D. R. An analytic method for rotation to orthogonal simple structure. American Psychologist, 1953, 8, 428 (Abstract). Wrigley, C. & Neuhaus, J. O. The quartimax method: An analytical approach to orthogonal simple structure. British Journal of Statistical Psychology, 1954, 7, Manuscript received 2/5/73 Revised manuscript received 9/5/73
Applied Multivariate Analysis
 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Vaasa, Finland Spring 2017 Dimension reduction Exploratory (EFA) Background While the motivation in PCA is to replace the original (correlated) variables
Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Vaasa, Finland Spring 2017 Dimension reduction Exploratory (EFA) Background While the motivation in PCA is to replace the original (correlated) variables
Penalized varimax. Abstract
 Penalized varimax 1 Penalized varimax Nickolay T. Trendafilov and Doyo Gragn Department of Mathematics and Statistics, The Open University, Walton Hall, Milton Keynes MK7 6AA, UK Abstract A common weakness
Penalized varimax 1 Penalized varimax Nickolay T. Trendafilov and Doyo Gragn Department of Mathematics and Statistics, The Open University, Walton Hall, Milton Keynes MK7 6AA, UK Abstract A common weakness
Exploratory Factor Analysis: dimensionality and factor scores. Psychology 588: Covariance structure and factor models
 Exploratory Factor Analysis: dimensionality and factor scores Psychology 588: Covariance structure and factor models How many PCs to retain 2 Unlike confirmatory FA, the number of factors to extract is
Exploratory Factor Analysis: dimensionality and factor scores Psychology 588: Covariance structure and factor models How many PCs to retain 2 Unlike confirmatory FA, the number of factors to extract is
CHAPTER 11 FACTOR TRANSFORMATIONS: ANALYTIC TRANSFORMATIONS. From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C.
 CHAPTER 11 FACTOR TRANSFORMATIONS: ANALYTIC TRANSFORMATIONS From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum 1997 363 CHAPTER 11 FACTOR TRANSFORMATIONS : ANALYTIC TRANSFORMATIONS
CHAPTER 11 FACTOR TRANSFORMATIONS: ANALYTIC TRANSFORMATIONS From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum 1997 363 CHAPTER 11 FACTOR TRANSFORMATIONS : ANALYTIC TRANSFORMATIONS
FACTOR ANALYSIS AS MATRIX DECOMPOSITION 1. INTRODUCTION
 FACTOR ANALYSIS AS MATRIX DECOMPOSITION JAN DE LEEUW ABSTRACT. Meet the abstract. This is the abstract. 1. INTRODUCTION Suppose we have n measurements on each of taking m variables. Collect these measurements
FACTOR ANALYSIS AS MATRIX DECOMPOSITION JAN DE LEEUW ABSTRACT. Meet the abstract. This is the abstract. 1. INTRODUCTION Suppose we have n measurements on each of taking m variables. Collect these measurements
Dimensionality Assessment: Additional Methods
 Dimensionality Assessment: Additional Methods In Chapter 3 we use a nonlinear factor analytic model for assessing dimensionality. In this appendix two additional approaches are presented. The first strategy
Dimensionality Assessment: Additional Methods In Chapter 3 we use a nonlinear factor analytic model for assessing dimensionality. In this appendix two additional approaches are presented. The first strategy
Unit 5: Fractional Factorial Experiments at Two Levels
 Unit 5: Fractional Factorial Experiments at Two Levels Source : Chapter 4 (sections 4.1-4.3, 4.4.1, 4.4.3, 4.5, part of 4.6). Effect aliasing, resolution, minimum aberration criteria. Analysis. Techniques
Unit 5: Fractional Factorial Experiments at Two Levels Source : Chapter 4 (sections 4.1-4.3, 4.4.1, 4.4.3, 4.5, part of 4.6). Effect aliasing, resolution, minimum aberration criteria. Analysis. Techniques
VAR2 VAR3 VAR4 VAR5. Or, in terms of basic measurement theory, we could model it as:
 1 Neuendorf Factor Analysis Assumptions: 1. Metric (interval/ratio) data 2. Linearity (in the relationships among the variables) -Factors are linear constructions of the set of variables (see #8 under
1 Neuendorf Factor Analysis Assumptions: 1. Metric (interval/ratio) data 2. Linearity (in the relationships among the variables) -Factors are linear constructions of the set of variables (see #8 under
Quantitative Trendspotting. Rex Yuxing Du and Wagner A. Kamakura. Web Appendix A Inferring and Projecting the Latent Dynamic Factors
 1 Quantitative Trendspotting Rex Yuxing Du and Wagner A. Kamakura Web Appendix A Inferring and Projecting the Latent Dynamic Factors The procedure for inferring the latent state variables (i.e., [ ] ),
1 Quantitative Trendspotting Rex Yuxing Du and Wagner A. Kamakura Web Appendix A Inferring and Projecting the Latent Dynamic Factors The procedure for inferring the latent state variables (i.e., [ ] ),
FACTOR ANALYSIS AND MULTIDIMENSIONAL SCALING
 FACTOR ANALYSIS AND MULTIDIMENSIONAL SCALING Vishwanath Mantha Department for Electrical and Computer Engineering Mississippi State University, Mississippi State, MS 39762 mantha@isip.msstate.edu ABSTRACT
FACTOR ANALYSIS AND MULTIDIMENSIONAL SCALING Vishwanath Mantha Department for Electrical and Computer Engineering Mississippi State University, Mississippi State, MS 39762 mantha@isip.msstate.edu ABSTRACT
The geometry of polynomial diagrams
 Theoretical Mathematics & Applications, vol.4, no.1, 014, 71-76 ISSN: 179-9687 (print), 179-9709 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 014 The geometry of polynomial diagrams Alennikov A. Maksim 1 Abstract In this
Theoretical Mathematics & Applications, vol.4, no.1, 014, 71-76 ISSN: 179-9687 (print), 179-9709 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 014 The geometry of polynomial diagrams Alennikov A. Maksim 1 Abstract In this
To link to this article:
 This article was downloaded by: [VUL Vanderbilt University] On: 17 February 2013, At: 12:05 Publisher: Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office:
This article was downloaded by: [VUL Vanderbilt University] On: 17 February 2013, At: 12:05 Publisher: Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office:
Stuart s tau measure of effect size for ordinal variables: Some methodological considerations
 Behavior Research Methods 2009, 41 (4), 1144-1148 doi:10.3758/brm.41.4.1144 Stuart s tau measure of effect size for ordinal variables: Some methodological considerations KENNETH J. BERRY Colorado State
Behavior Research Methods 2009, 41 (4), 1144-1148 doi:10.3758/brm.41.4.1144 Stuart s tau measure of effect size for ordinal variables: Some methodological considerations KENNETH J. BERRY Colorado State
Estimating Coefficients in Linear Models: It Don't Make No Nevermind
 Psychological Bulletin 1976, Vol. 83, No. 2. 213-217 Estimating Coefficients in Linear Models: It Don't Make No Nevermind Howard Wainer Department of Behavioral Science, University of Chicago It is proved
Psychological Bulletin 1976, Vol. 83, No. 2. 213-217 Estimating Coefficients in Linear Models: It Don't Make No Nevermind Howard Wainer Department of Behavioral Science, University of Chicago It is proved
Or, in terms of basic measurement theory, we could model it as:
 1 Neuendorf Factor Analysis Assumptions: 1. Metric (interval/ratio) data 2. Linearity (in relationships among the variables--factors are linear constructions of the set of variables; the critical source
1 Neuendorf Factor Analysis Assumptions: 1. Metric (interval/ratio) data 2. Linearity (in relationships among the variables--factors are linear constructions of the set of variables; the critical source
Problems with parallel analysis in data sets with oblique simple structure
 Methods of Psychological Research Online 2001, Vol.6, No.2 Internet: http://www.mpr-online.de Institute for Science Education 2001 IPN Kiel Problems with parallel analysis in data sets with oblique simple
Methods of Psychological Research Online 2001, Vol.6, No.2 Internet: http://www.mpr-online.de Institute for Science Education 2001 IPN Kiel Problems with parallel analysis in data sets with oblique simple
Principal Component Analysis & Factor Analysis. Psych 818 DeShon
 Principal Component Analysis & Factor Analysis Psych 818 DeShon Purpose Both are used to reduce the dimensionality of correlated measurements Can be used in a purely exploratory fashion to investigate
Principal Component Analysis & Factor Analysis Psych 818 DeShon Purpose Both are used to reduce the dimensionality of correlated measurements Can be used in a purely exploratory fashion to investigate
Jerome Kaltenhauser and Yuk Lee
 Correlation Coefficients for Binary Data In Factor Analysis Jerome Kaltenhauser and Yuk Lee The most commonly used factor analytic models employ a symmetric matrix of correlation coefficients as input.
Correlation Coefficients for Binary Data In Factor Analysis Jerome Kaltenhauser and Yuk Lee The most commonly used factor analytic models employ a symmetric matrix of correlation coefficients as input.
Exploratory Factor Analysis and Principal Component Analysis
 Exploratory Factor Analysis and Principal Component Analysis Today s Topics: What are EFA and PCA for? Planning a factor analytic study Analysis steps: Extraction methods How many factors Rotation and
Exploratory Factor Analysis and Principal Component Analysis Today s Topics: What are EFA and PCA for? Planning a factor analytic study Analysis steps: Extraction methods How many factors Rotation and
Robustness. James H. Steiger. Department of Psychology and Human Development Vanderbilt University. James H. Steiger (Vanderbilt University) 1 / 37
 Robustness James H. Steiger Department of Psychology and Human Development Vanderbilt University James H. Steiger (Vanderbilt University) 1 / 37 Robustness 1 Introduction 2 Robust Parameters and Robust
Robustness James H. Steiger Department of Psychology and Human Development Vanderbilt University James H. Steiger (Vanderbilt University) 1 / 37 Robustness 1 Introduction 2 Robust Parameters and Robust
Exploratory Factor Analysis and Principal Component Analysis
 Exploratory Factor Analysis and Principal Component Analysis Today s Topics: What are EFA and PCA for? Planning a factor analytic study Analysis steps: Extraction methods How many factors Rotation and
Exploratory Factor Analysis and Principal Component Analysis Today s Topics: What are EFA and PCA for? Planning a factor analytic study Analysis steps: Extraction methods How many factors Rotation and
Fast Near-Optimal Energy Allocation for Multimedia Loading on Multicarrier Systems
 Fast Near-Optimal Energy Allocation for Multimedia Loading on Multicarrier Systems Michael A. Enright and C.-C. Jay Kuo Department of Electrical Engineering and Signal and Image Processing Institute University
Fast Near-Optimal Energy Allocation for Multimedia Loading on Multicarrier Systems Michael A. Enright and C.-C. Jay Kuo Department of Electrical Engineering and Signal and Image Processing Institute University
Factor analysis. George Balabanis
 Factor analysis George Balabanis Key Concepts and Terms Deviation. A deviation is a value minus its mean: x - mean x Variance is a measure of how spread out a distribution is. It is computed as the average
Factor analysis George Balabanis Key Concepts and Terms Deviation. A deviation is a value minus its mean: x - mean x Variance is a measure of how spread out a distribution is. It is computed as the average
A Brief Discussion of Lebesgue Measure Theory
 A Brief Discussion of Lebesgue Measure Theory Introduction In class, we used the following function in our development of our definition of area under a curve: { if x is rational f(x) = 0 if x is irrational
A Brief Discussion of Lebesgue Measure Theory Introduction In class, we used the following function in our development of our definition of area under a curve: { if x is rational f(x) = 0 if x is irrational
401 Review. 6. Power analysis for one/two-sample hypothesis tests and for correlation analysis.
 401 Review Major topics of the course 1. Univariate analysis 2. Bivariate analysis 3. Simple linear regression 4. Linear algebra 5. Multiple regression analysis Major analysis methods 1. Graphical analysis
401 Review Major topics of the course 1. Univariate analysis 2. Bivariate analysis 3. Simple linear regression 4. Linear algebra 5. Multiple regression analysis Major analysis methods 1. Graphical analysis
Factor Analysis. Summary. Sample StatFolio: factor analysis.sgp
 Factor Analysis Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Statistical Model... 4 Analysis Summary... 5 Analysis Options... 7 Scree Plot... 9 Extraction Statistics... 10 Rotation Statistics... 11 D and 3D Scatterplots...
Factor Analysis Summary... 1 Data Input... 3 Statistical Model... 4 Analysis Summary... 5 Analysis Options... 7 Scree Plot... 9 Extraction Statistics... 10 Rotation Statistics... 11 D and 3D Scatterplots...
Backward Error Estimation
 Backward Error Estimation S. Chandrasekaran E. Gomez Y. Karant K. E. Schubert Abstract Estimation of unknowns in the presence of noise and uncertainty is an active area of study, because no method handles
Backward Error Estimation S. Chandrasekaran E. Gomez Y. Karant K. E. Schubert Abstract Estimation of unknowns in the presence of noise and uncertainty is an active area of study, because no method handles
Theory of Screening Procedures to Identify Robust Product Designs Using Fractional Factorial Experiments
 Theory of Screening Procedures to Identify Robust Product Designs Using Fractional Factorial Experiments Guohua Pan Biostatistics and Statistical Reporting Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation East Hanover,
Theory of Screening Procedures to Identify Robust Product Designs Using Fractional Factorial Experiments Guohua Pan Biostatistics and Statistical Reporting Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation East Hanover,
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast March 2019 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast March 2019 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College March 2, 2019 Summary: Dramatic flip from a mild winter to a top five coldest February on record in many locations
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast March 2019 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College March 2, 2019 Summary: Dramatic flip from a mild winter to a top five coldest February on record in many locations
CHAPTER 4 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE SAMPLE. From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum
 CHAPTER 4 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE SAMPLE From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum 1997 65 CHAPTER 4 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE SAMPLE 4.0. Introduction In Chapter
CHAPTER 4 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE SAMPLE From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum 1997 65 CHAPTER 4 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE SAMPLE 4.0. Introduction In Chapter
The Use of Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis in the General Chemistry Laboratory
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 59, Issue 1 (January, 1959) 1959-01 The Use of Quantitative and Qualitative
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 59, Issue 1 (January, 1959) 1959-01 The Use of Quantitative and Qualitative
A non-gaussian decomposition of Total Water Storage (TWS), using Independent Component Analysis (ICA)
 Titelmaster A non-gaussian decomposition of Total Water Storage (TWS, using Independent Component Analysis (ICA Ehsan Forootan and Jürgen Kusche Astronomical Physical & Mathematical Geodesy, Bonn University
Titelmaster A non-gaussian decomposition of Total Water Storage (TWS, using Independent Component Analysis (ICA Ehsan Forootan and Jürgen Kusche Astronomical Physical & Mathematical Geodesy, Bonn University
Sandia National Laboratories, P. O. Box 5800, Albuquerque, NM 87185, USA
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 23, 299 3, 22 LINEAR DIFFUSION INTO A FARADAY CAGE K. C. Chen *, Y. T. Lin, L. K. Warne, and K. O. Merewether Sandia National Laboratories, P. O. Box 58, Albuquerque,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 23, 299 3, 22 LINEAR DIFFUSION INTO A FARADAY CAGE K. C. Chen *, Y. T. Lin, L. K. Warne, and K. O. Merewether Sandia National Laboratories, P. O. Box 58, Albuquerque,
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Theory, Practice, and Examples
 Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Theory, Practice, and Examples Data Reduction summarization of data with many (p) variables by a smaller set of (k) derived (synthetic, composite) variables. p k n A
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Theory, Practice, and Examples Data Reduction summarization of data with many (p) variables by a smaller set of (k) derived (synthetic, composite) variables. p k n A
Forecasting the use, costs and benefits of HSR in the years ahead. Samer Madanat UC Berkeley
 Forecasting the use, costs and benefits of HSR in the years ahead Samer Madanat UC Berkeley Outline Demand models and ridership forecasts Errors in demand models and consequences Case study: the CA HSR
Forecasting the use, costs and benefits of HSR in the years ahead Samer Madanat UC Berkeley Outline Demand models and ridership forecasts Errors in demand models and consequences Case study: the CA HSR
Determination of accelerated condition for brush wear of small brush-type DC motor in using Design of Experiment (DOE) based on the Taguchi method
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 25 (2) (2011) 317~322 www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-010-1230-6 Determination of accelerated condition for brush wear of small brush-type
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 25 (2) (2011) 317~322 www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-010-1230-6 Determination of accelerated condition for brush wear of small brush-type
Change-point models and performance measures for sequential change detection
 Change-point models and performance measures for sequential change detection Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Patras, 26500 Rion, Greece moustaki@upatras.gr George V. Moustakides
Change-point models and performance measures for sequential change detection Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Patras, 26500 Rion, Greece moustaki@upatras.gr George V. Moustakides
over the parameters θ. In both cases, consequently, we select the minimizing
 MONOTONE REGRESSION JAN DE LEEUW Abstract. This is an entry for The Encyclopedia of Statistics in Behavioral Science, to be published by Wiley in 200. In linear regression we fit a linear function y =
MONOTONE REGRESSION JAN DE LEEUW Abstract. This is an entry for The Encyclopedia of Statistics in Behavioral Science, to be published by Wiley in 200. In linear regression we fit a linear function y =
Outline. March 2 is the day of the first midterm Heads up! Recap of electric forces Fields Examples. 2/17/17 Physics 132 1
 Outline March 2 is the day of the first midterm Heads up! Recap of electric forces Fields Examples 2/17/17 Physics 132 1 The Electric Field!!!! Fq ( r ) E (r ) = q 2/17/17 2 Physics 132 Foothold idea:
Outline March 2 is the day of the first midterm Heads up! Recap of electric forces Fields Examples 2/17/17 Physics 132 1 The Electric Field!!!! Fq ( r ) E (r ) = q 2/17/17 2 Physics 132 Foothold idea:
Best Guaranteed Result Principle and Decision Making in Operations with Stochastic Factors and Uncertainty
 Stochastics and uncertainty underlie all the processes of the Universe. N.N.Moiseev Best Guaranteed Result Principle and Decision Making in Operations with Stochastic Factors and Uncertainty by Iouldouz
Stochastics and uncertainty underlie all the processes of the Universe. N.N.Moiseev Best Guaranteed Result Principle and Decision Making in Operations with Stochastic Factors and Uncertainty by Iouldouz
Numerical Linear Algebra Homework Assignment - Week 2
 Numerical Linear Algebra Homework Assignment - Week 2 Đoàn Trần Nguyên Tùng Student ID: 1411352 8th October 2016 Exercise 2.1: Show that if a matrix A is both triangular and unitary, then it is diagonal.
Numerical Linear Algebra Homework Assignment - Week 2 Đoàn Trần Nguyên Tùng Student ID: 1411352 8th October 2016 Exercise 2.1: Show that if a matrix A is both triangular and unitary, then it is diagonal.
Understanding Mrs. Divitz
 Understanding Mrs. Divitz Metaphor and Computational Mathematics Charlie Van Loan Department of Computer Science Cornell University Householder XVIII: Tahoe City What Recent Math Test Scores Show... 4th
Understanding Mrs. Divitz Metaphor and Computational Mathematics Charlie Van Loan Department of Computer Science Cornell University Householder XVIII: Tahoe City What Recent Math Test Scores Show... 4th
Further Studies of the Whitetop Cloud-Seeding Experiment
 Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Vol. 68, No. 1, pp. 147-151, January 1971 Further Studies of the Whitetop Cloud-Seeding Experiment JEANNE L. LOVASICH, JERZY NEYMAN, ELIZABETH MARCELLA A.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Vol. 68, No. 1, pp. 147-151, January 1971 Further Studies of the Whitetop Cloud-Seeding Experiment JEANNE L. LOVASICH, JERZY NEYMAN, ELIZABETH MARCELLA A.
Lesson 3: Understanding Addition of Integers
 Classwork Exercise 1: Addition Using the Integer Game Play the Integer Game with your group without using a number line. Example 1: Counting On to Express the Sum as Absolute Value on a Number Line Model
Classwork Exercise 1: Addition Using the Integer Game Play the Integer Game with your group without using a number line. Example 1: Counting On to Express the Sum as Absolute Value on a Number Line Model
Introduction to Factor Analysis
 to Factor Analysis Lecture 10 August 2, 2011 Advanced Multivariate Statistical Methods ICPSR Summer Session #2 Lecture #10-8/3/2011 Slide 1 of 55 Today s Lecture Factor Analysis Today s Lecture Exploratory
to Factor Analysis Lecture 10 August 2, 2011 Advanced Multivariate Statistical Methods ICPSR Summer Session #2 Lecture #10-8/3/2011 Slide 1 of 55 Today s Lecture Factor Analysis Today s Lecture Exploratory
B. Maddah INDE 504 Discrete-Event Simulation. Output Analysis (1)
 B. Maddah INDE 504 Discrete-Event Simulation Output Analysis (1) Introduction The basic, most serious disadvantage of simulation is that we don t get exact answers. Two different runs of the same model
B. Maddah INDE 504 Discrete-Event Simulation Output Analysis (1) Introduction The basic, most serious disadvantage of simulation is that we don t get exact answers. Two different runs of the same model
Group Dependence of Some Reliability
 Group Dependence of Some Reliability Indices for astery Tests D. R. Divgi Syracuse University Reliability indices for mastery tests depend not only on true-score variance but also on mean and cutoff scores.
Group Dependence of Some Reliability Indices for astery Tests D. R. Divgi Syracuse University Reliability indices for mastery tests depend not only on true-score variance but also on mean and cutoff scores.
On properties of four IFS operators
 Fuzzy Sets Systems 15 (2005) 151 155 www.elsevier.com/locate/fss On properties of four IFS operators Deng-Feng Li a,b,c,, Feng Shan a, Chun-Tian Cheng c a Department of Sciences, Shenyang Institute of
Fuzzy Sets Systems 15 (2005) 151 155 www.elsevier.com/locate/fss On properties of four IFS operators Deng-Feng Li a,b,c,, Feng Shan a, Chun-Tian Cheng c a Department of Sciences, Shenyang Institute of
REDUNDANCY ANALYSIS AN ALTERNATIVE FOR CANONICAL CORRELATION ANALYSIS ARNOLD L. VAN DEN WOLLENBERG UNIVERSITY OF NIJMEGEN
 PSYCHOMETRIKA-VOL. 42, NO, 2 JUNE, 1977 REDUNDANCY ANALYSIS AN ALTERNATIVE FOR CANONICAL CORRELATION ANALYSIS ARNOLD L. VAN DEN WOLLENBERG UNIVERSITY OF NIJMEGEN A component method is presented maximizing
PSYCHOMETRIKA-VOL. 42, NO, 2 JUNE, 1977 REDUNDANCY ANALYSIS AN ALTERNATIVE FOR CANONICAL CORRELATION ANALYSIS ARNOLD L. VAN DEN WOLLENBERG UNIVERSITY OF NIJMEGEN A component method is presented maximizing
Psychology 405: Psychometric Theory Constructs, Components, and Factor Models
 Psychology 405: Psychometric Theory Constructs, Components, and Factor Models William Revelle Department of Psychology Northwestern University Evanston, Illinois USA April, 2012 1 / 58 Outline 1 Preliminaries
Psychology 405: Psychometric Theory Constructs, Components, and Factor Models William Revelle Department of Psychology Northwestern University Evanston, Illinois USA April, 2012 1 / 58 Outline 1 Preliminaries
Optimization of Muffler and Silencer
 Chapter 5 Optimization of Muffler and Silencer In the earlier chapter though various numerical methods are presented, they are not meant to optimize the performance of muffler/silencer for space constraint
Chapter 5 Optimization of Muffler and Silencer In the earlier chapter though various numerical methods are presented, they are not meant to optimize the performance of muffler/silencer for space constraint
MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD IN GENERALIZED FIXED SCORE FACTOR ANALYSIS 1. INTRODUCTION
 MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD IN GENERALIZED FIXED SCORE FACTOR ANALYSIS JAN DE LEEUW ABSTRACT. We study the weighted least squares fixed rank approximation problem in which the weight matrices depend on unknown
MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD IN GENERALIZED FIXED SCORE FACTOR ANALYSIS JAN DE LEEUW ABSTRACT. We study the weighted least squares fixed rank approximation problem in which the weight matrices depend on unknown
A Factor Analysis of Key Decision Factors for Implementing SOA-based Enterprise level Business Intelligence Systems
 icbst 2014 International Conference on Business, Science and Technology which will be held at Hatyai, Thailand on the 25th and 26th of April 2014. AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied
icbst 2014 International Conference on Business, Science and Technology which will be held at Hatyai, Thailand on the 25th and 26th of April 2014. AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied
arxiv: v2 [math.nt] 30 Oct 2015
![arxiv: v2 [math.nt] 30 Oct 2015 arxiv: v2 [math.nt] 30 Oct 2015](/thumbs/89/98213112.jpg) Journal Name, Vol. X, No. X, DATE YEAR, pp. xx-xx arxiv:1508.07562v2 [math.nt] 30 Oct 2015 A Note on Generating Almost Pythagorean Triples John Rafael M. Antalan and Mark D. Tomenes Department of Mathematics
Journal Name, Vol. X, No. X, DATE YEAR, pp. xx-xx arxiv:1508.07562v2 [math.nt] 30 Oct 2015 A Note on Generating Almost Pythagorean Triples John Rafael M. Antalan and Mark D. Tomenes Department of Mathematics
Linear Programming Applications. Transportation Problem
 Linear Programming Applications Transportation Problem 1 Introduction Transportation problem is a special problem of its own structure. Planning model that allocates resources, machines, materials, capital
Linear Programming Applications Transportation Problem 1 Introduction Transportation problem is a special problem of its own structure. Planning model that allocates resources, machines, materials, capital
DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS FOR NONPARAMETRIC MODELS I. INTRODUCTION
 The Annals of Statistics 1975, Vol. 3, No.5, 1038-1044 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS FOR NONPARAMETRIC MODELS I. INTRODUCTION BY P. J. BICKEL 1 AND E. L. LEHMANN 2 University of California, Berkeley An overview
The Annals of Statistics 1975, Vol. 3, No.5, 1038-1044 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS FOR NONPARAMETRIC MODELS I. INTRODUCTION BY P. J. BICKEL 1 AND E. L. LEHMANN 2 University of California, Berkeley An overview
How to run the RI CLPM with Mplus By Ellen Hamaker March 21, 2018
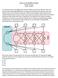 How to run the RI CLPM with Mplus By Ellen Hamaker March 21, 2018 The random intercept cross lagged panel model (RI CLPM) as proposed by Hamaker, Kuiper and Grasman (2015, Psychological Methods) is a model
How to run the RI CLPM with Mplus By Ellen Hamaker March 21, 2018 The random intercept cross lagged panel model (RI CLPM) as proposed by Hamaker, Kuiper and Grasman (2015, Psychological Methods) is a model
Nonparametric Online Item Calibration
 Nonparametric Online Item Calibration Fumiko Samejima University of Tennesee Keynote Address Presented June 7, 2007 Abstract In estimating the operating characteristic (OC) of an item, in contrast to parametric
Nonparametric Online Item Calibration Fumiko Samejima University of Tennesee Keynote Address Presented June 7, 2007 Abstract In estimating the operating characteristic (OC) of an item, in contrast to parametric
( ) about L in the ( ) so ( ).
 A Topological Definition of Limits for Use in Elementary Calculus Charles L. Cooper, Phd (ccooper@uco.edu) Michael S. McClendon, PhD (mmcclendon@uco.edu Department of Mathematics & Statistics University
A Topological Definition of Limits for Use in Elementary Calculus Charles L. Cooper, Phd (ccooper@uco.edu) Michael S. McClendon, PhD (mmcclendon@uco.edu Department of Mathematics & Statistics University
LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
 LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS MA1111: LINEAR ALGEBRA I, MICHAELMAS 2016 1 Linear equations We now switch gears to discuss the topic of solving linear equations, and more interestingly, systems
LECTURES 4/5: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS MA1111: LINEAR ALGEBRA I, MICHAELMAS 2016 1 Linear equations We now switch gears to discuss the topic of solving linear equations, and more interestingly, systems
Gauss s Law. Name. I. The Law: , where ɛ 0 = C 2 (N?m 2
 Name Gauss s Law I. The Law:, where ɛ 0 = 8.8510 12 C 2 (N?m 2 1. Consider a point charge q in three-dimensional space. Symmetry requires the electric field to point directly away from the charge in all
Name Gauss s Law I. The Law:, where ɛ 0 = 8.8510 12 C 2 (N?m 2 1. Consider a point charge q in three-dimensional space. Symmetry requires the electric field to point directly away from the charge in all
Definition (The carefully thought-out calculus version based on limits).
 4.1. Continuity and Graphs Definition 4.1.1 (Intuitive idea used in algebra based on graphing). A function, f, is continuous on the interval (a, b) if the graph of y = f(x) can be drawn over the interval
4.1. Continuity and Graphs Definition 4.1.1 (Intuitive idea used in algebra based on graphing). A function, f, is continuous on the interval (a, b) if the graph of y = f(x) can be drawn over the interval
2/26/2017. This is similar to canonical correlation in some ways. PSY 512: Advanced Statistics for Psychological and Behavioral Research 2
 PSY 512: Advanced Statistics for Psychological and Behavioral Research 2 What is factor analysis? What are factors? Representing factors Graphs and equations Extracting factors Methods and criteria Interpreting
PSY 512: Advanced Statistics for Psychological and Behavioral Research 2 What is factor analysis? What are factors? Representing factors Graphs and equations Extracting factors Methods and criteria Interpreting
SHOPPING FOR EFFICIENT CONFIDENCE INTERVALS IN STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS. Donna Mohr and Yong Xu. University of North Florida
 SHOPPING FOR EFFICIENT CONFIDENCE INTERVALS IN STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS Donna Mohr and Yong Xu University of North Florida Authors Note Parts of this work were incorporated in Yong Xu s Masters Thesis
SHOPPING FOR EFFICIENT CONFIDENCE INTERVALS IN STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELS Donna Mohr and Yong Xu University of North Florida Authors Note Parts of this work were incorporated in Yong Xu s Masters Thesis
On the Variance of Eigenvalues in PCA and MCA
 On the Variance of in PCA and MCA Jean-Luc Durand jean-luc.durand@univ-paris13.fr Laboratoire d Éthologie Expérimentale et Comparée - LEEC EA 4443 Université Paris 13 Sorbonne Paris Cité Naples, CARME
On the Variance of in PCA and MCA Jean-Luc Durand jean-luc.durand@univ-paris13.fr Laboratoire d Éthologie Expérimentale et Comparée - LEEC EA 4443 Université Paris 13 Sorbonne Paris Cité Naples, CARME
Principal Component Analysis
 Principal Component Analysis CS5240 Theoretical Foundations in Multimedia Leow Wee Kheng Department of Computer Science School of Computing National University of Singapore Leow Wee Kheng (NUS) Principal
Principal Component Analysis CS5240 Theoretical Foundations in Multimedia Leow Wee Kheng Department of Computer Science School of Computing National University of Singapore Leow Wee Kheng (NUS) Principal
Introduction to Factor Analysis
 to Factor Analysis Lecture 11 November 2, 2005 Multivariate Analysis Lecture #11-11/2/2005 Slide 1 of 58 Today s Lecture Factor Analysis. Today s Lecture Exploratory factor analysis (EFA). Confirmatory
to Factor Analysis Lecture 11 November 2, 2005 Multivariate Analysis Lecture #11-11/2/2005 Slide 1 of 58 Today s Lecture Factor Analysis. Today s Lecture Exploratory factor analysis (EFA). Confirmatory
r(equivalent): A Simple Effect Size Indicator
 r(equivalent): A Simple Effect Size Indicator The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Rosenthal, Robert, and
r(equivalent): A Simple Effect Size Indicator The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Rosenthal, Robert, and
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 INTRODUCTION We currently live in what is often termed the information age. Aided by new and emerging technologies, data are being collected at unprecedented rates in all walks
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 INTRODUCTION We currently live in what is often termed the information age. Aided by new and emerging technologies, data are being collected at unprecedented rates in all walks
More Linear Algebra. Edps/Soc 584, Psych 594. Carolyn J. Anderson
 More Linear Algebra Edps/Soc 584, Psych 594 Carolyn J. Anderson Department of Educational Psychology I L L I N O I S university of illinois at urbana-champaign c Board of Trustees, University of Illinois
More Linear Algebra Edps/Soc 584, Psych 594 Carolyn J. Anderson Department of Educational Psychology I L L I N O I S university of illinois at urbana-champaign c Board of Trustees, University of Illinois
Recovery of weak factor loadings in confirmatory factor analysis under conditions of model misspecification
 Behavior Research Methods 29, 41 (4), 138-152 doi:1.3758/brm.41.4.138 Recovery of weak factor loadings in confirmatory factor analysis under conditions of model misspecification CARMEN XIMÉNEZ Autonoma
Behavior Research Methods 29, 41 (4), 138-152 doi:1.3758/brm.41.4.138 Recovery of weak factor loadings in confirmatory factor analysis under conditions of model misspecification CARMEN XIMÉNEZ Autonoma
Chapter 14: Repeated-measures designs
 Chapter 14: Repeated-measures designs Oliver Twisted Please, Sir, can I have some more sphericity? The following article is adapted from: Field, A. P. (1998). A bluffer s guide to sphericity. Newsletter
Chapter 14: Repeated-measures designs Oliver Twisted Please, Sir, can I have some more sphericity? The following article is adapted from: Field, A. P. (1998). A bluffer s guide to sphericity. Newsletter
Set Point Control of a Thermal Load Population
 Set Point Control of a Thermal Load Population 1/15 Set Point Control of a Thermal Load Population CE 291F Final Project Travis Walter Civil Systems Program Civil and Environmental Engineering Department
Set Point Control of a Thermal Load Population 1/15 Set Point Control of a Thermal Load Population CE 291F Final Project Travis Walter Civil Systems Program Civil and Environmental Engineering Department
A Simulation Study to Compare CAT Strategies for Cognitive Diagnosis
 A Simulation Study to Compare CAT Strategies for Cognitive Diagnosis Xueli Xu Department of Statistics,University of Illinois Hua-Hua Chang Department of Educational Psychology,University of Texas Jeff
A Simulation Study to Compare CAT Strategies for Cognitive Diagnosis Xueli Xu Department of Statistics,University of Illinois Hua-Hua Chang Department of Educational Psychology,University of Texas Jeff
SIMPLIFIED CALCULATION OF PRINCIPAL COMPONENTS HAROLD HOTELLING
 PSYCHOMETRIKA--VOL. 1, NO. 1 SIMPLIFIED CALCULATION OF PRINCIPAL COMPONENTS HAROLD HOTELLING The resolution of a set of n tests or other variates into components 7~, each of which accounts for the greatest
PSYCHOMETRIKA--VOL. 1, NO. 1 SIMPLIFIED CALCULATION OF PRINCIPAL COMPONENTS HAROLD HOTELLING The resolution of a set of n tests or other variates into components 7~, each of which accounts for the greatest
A Sensitivity Analysis of the Social Vulnerability Index
 Risk Analysis, Vol. 28, No. 4, 2008 DOI: 10.1111/j.1539-6924.2008.01072.x A Sensitivity Analysis of the Social Vulnerability Index Mathew C. Schmidtlein, 1 Roland C. Deutsch, 2 Walter W. Piegorsch, 3 and
Risk Analysis, Vol. 28, No. 4, 2008 DOI: 10.1111/j.1539-6924.2008.01072.x A Sensitivity Analysis of the Social Vulnerability Index Mathew C. Schmidtlein, 1 Roland C. Deutsch, 2 Walter W. Piegorsch, 3 and
Composite scales and scores
 Combining variables University of York Department of Health Sciences Measurement in Health and Disease Composite scales and scores Sometimes we have several outcome variables and we are interested in the
Combining variables University of York Department of Health Sciences Measurement in Health and Disease Composite scales and scores Sometimes we have several outcome variables and we are interested in the
Math Bootcamp 2012 Miscellaneous
 Math Bootcamp 202 Miscellaneous Factorial, combination and permutation The factorial of a positive integer n denoted by n!, is the product of all positive integers less than or equal to n. Define 0! =.
Math Bootcamp 202 Miscellaneous Factorial, combination and permutation The factorial of a positive integer n denoted by n!, is the product of all positive integers less than or equal to n. Define 0! =.
UCLA STAT 233 Statistical Methods in Biomedical Imaging
 UCLA STAT 233 Statistical Methods in Biomedical Imaging Instructor: Ivo Dinov, Asst. Prof. In Statistics and Neurology University of California, Los Angeles, Spring 2004 http://www.stat.ucla.edu/~dinov/
UCLA STAT 233 Statistical Methods in Biomedical Imaging Instructor: Ivo Dinov, Asst. Prof. In Statistics and Neurology University of California, Los Angeles, Spring 2004 http://www.stat.ucla.edu/~dinov/
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 INTRODUCTION We currently live in what is often termed the information age. Aided by new and emerging technologies, data are being collected at unprecedented rates in all walks
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 INTRODUCTION We currently live in what is often termed the information age. Aided by new and emerging technologies, data are being collected at unprecedented rates in all walks
Multivariate Fundamentals: Rotation. Exploratory Factor Analysis
 Multivariate Fundamentals: Rotation Exploratory Factor Analysis PCA Analysis A Review Precipitation Temperature Ecosystems PCA Analysis with Spatial Data Proportion of variance explained Comp.1 + Comp.2
Multivariate Fundamentals: Rotation Exploratory Factor Analysis PCA Analysis A Review Precipitation Temperature Ecosystems PCA Analysis with Spatial Data Proportion of variance explained Comp.1 + Comp.2
The t-statistic. Student s t Test
 The t-statistic 1 Student s t Test When the population standard deviation is not known, you cannot use a z score hypothesis test Use Student s t test instead Student s t, or t test is, conceptually, very
The t-statistic 1 Student s t Test When the population standard deviation is not known, you cannot use a z score hypothesis test Use Student s t test instead Student s t, or t test is, conceptually, very
Two-Level Designs to Estimate All Main Effects and Two-Factor Interactions
 Technometrics ISSN: 0040-1706 (Print) 1537-2723 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/utch20 Two-Level Designs to Estimate All Main Effects and Two-Factor Interactions Pieter T. Eendebak
Technometrics ISSN: 0040-1706 (Print) 1537-2723 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/utch20 Two-Level Designs to Estimate All Main Effects and Two-Factor Interactions Pieter T. Eendebak
EXAM # 3 PLEASE SHOW ALL WORK!
 Stat 311, Summer 2018 Name EXAM # 3 PLEASE SHOW ALL WORK! Problem Points Grade 1 30 2 20 3 20 4 30 Total 100 1. A socioeconomic study analyzes two discrete random variables in a certain population of households
Stat 311, Summer 2018 Name EXAM # 3 PLEASE SHOW ALL WORK! Problem Points Grade 1 30 2 20 3 20 4 30 Total 100 1. A socioeconomic study analyzes two discrete random variables in a certain population of households
UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS LIBRARY AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS
 UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS LIBRARY AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS i CENTRAL CIRCULATION BOOKSTACKS The person charging this material is responsible for its renewal or its return to the library from which it
UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS LIBRARY AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS i CENTRAL CIRCULATION BOOKSTACKS The person charging this material is responsible for its renewal or its return to the library from which it
4.3 Equations in 3-space
 4.3 Equations in 3-space istance can be used to define functions from a 3-space R 3 to the line R. Let P be a fixed point in the 3-space R 3 (say, with coordinates P (2, 5, 7)). Consider a function f :
4.3 Equations in 3-space istance can be used to define functions from a 3-space R 3 to the line R. Let P be a fixed point in the 3-space R 3 (say, with coordinates P (2, 5, 7)). Consider a function f :
Moment Aberration Projection for Nonregular Fractional Factorial Designs
 Moment Aberration Projection for Nonregular Fractional Factorial Designs Hongquan Xu Department of Statistics University of California Los Angeles, CA 90095-1554 (hqxu@stat.ucla.edu) Lih-Yuan Deng Department
Moment Aberration Projection for Nonregular Fractional Factorial Designs Hongquan Xu Department of Statistics University of California Los Angeles, CA 90095-1554 (hqxu@stat.ucla.edu) Lih-Yuan Deng Department
GI07/COMPM012: Mathematical Programming and Research Methods (Part 2) 2. Least Squares and Principal Components Analysis. Massimiliano Pontil
 GI07/COMPM012: Mathematical Programming and Research Methods (Part 2) 2. Least Squares and Principal Components Analysis Massimiliano Pontil 1 Today s plan SVD and principal component analysis (PCA) Connection
GI07/COMPM012: Mathematical Programming and Research Methods (Part 2) 2. Least Squares and Principal Components Analysis Massimiliano Pontil 1 Today s plan SVD and principal component analysis (PCA) Connection
The derivative: Definition
 The derivative: Definition The derivative of a function at a point x = a is defined as * +,' -*(+) lim ' ) ' = f (a) Alternative notation: let h = x a = δx * 5 -*(+) 7* lim = lim = f (a) 5 + 5-+ 75 ) 75
The derivative: Definition The derivative of a function at a point x = a is defined as * +,' -*(+) lim ' ) ' = f (a) Alternative notation: let h = x a = δx * 5 -*(+) 7* lim = lim = f (a) 5 + 5-+ 75 ) 75
DISTRIBUTION OF STRESS IN GROUND-SUPPORTED SLABS
 Structural Concrete Software System TN207_sog_stresses_10 122005 DISTRIBUTION OF STRESS IN GROUND-SUPPORTED SLABS Bijan O Aalami 1 This Technical Note describes the distribution of stress in ground-supported
Structural Concrete Software System TN207_sog_stresses_10 122005 DISTRIBUTION OF STRESS IN GROUND-SUPPORTED SLABS Bijan O Aalami 1 This Technical Note describes the distribution of stress in ground-supported
Sections 2.1, 2.2 and 2.4: Limit of a function Motivation:
 Sections 2.1, 2.2 and 2.4: Limit of a function Motivation: There are expressions which can be computed only using Algebra, meaning only using the operations +,, and. Examples which can be computed using
Sections 2.1, 2.2 and 2.4: Limit of a function Motivation: There are expressions which can be computed only using Algebra, meaning only using the operations +,, and. Examples which can be computed using
ME EN 363 Elementary Instrumentation
 ME E 6 Elementary Instrumentation Curve Fitting Least squares regression analysis Standard error of fit Correlation coefficient Error in static sensitivity Regression According to various Internet resources,
ME E 6 Elementary Instrumentation Curve Fitting Least squares regression analysis Standard error of fit Correlation coefficient Error in static sensitivity Regression According to various Internet resources,
Mixture Modeling. Identifying the Correct Number of Classes in a Growth Mixture Model. Davood Tofighi Craig Enders Arizona State University
 Identifying the Correct Number of Classes in a Growth Mixture Model Davood Tofighi Craig Enders Arizona State University Mixture Modeling Heterogeneity exists such that the data are comprised of two or
Identifying the Correct Number of Classes in a Growth Mixture Model Davood Tofighi Craig Enders Arizona State University Mixture Modeling Heterogeneity exists such that the data are comprised of two or
Multi Degrees of Freedom Systems
 Multi Degrees of Freedom Systems MDOF s http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano March 9, 07 Outline, a System
Multi Degrees of Freedom Systems MDOF s http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano March 9, 07 Outline, a System
Intermediate Social Statistics
 Intermediate Social Statistics Lecture 5. Factor Analysis Tom A.B. Snijders University of Oxford January, 2008 c Tom A.B. Snijders (University of Oxford) Intermediate Social Statistics January, 2008 1
Intermediate Social Statistics Lecture 5. Factor Analysis Tom A.B. Snijders University of Oxford January, 2008 c Tom A.B. Snijders (University of Oxford) Intermediate Social Statistics January, 2008 1
Lecture 3 Radioactivity
 Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following We shall begin with a general discussion on the nucleus. Learn about some characteristics of nucleons. Understand some concepts on stability of a
Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following We shall begin with a general discussion on the nucleus. Learn about some characteristics of nucleons. Understand some concepts on stability of a
Standard Practice for Heat Aging of Plastics Without Load 1
 Designation: D 3045 92 (Reapproved 2003) Standard Practice for Heat Aging of Plastics Without Load 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3045; the number immediately following the designation
Designation: D 3045 92 (Reapproved 2003) Standard Practice for Heat Aging of Plastics Without Load 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3045; the number immediately following the designation
Commentary on Basu (1956)
 Commentary on Basu (1956) Robert Serfling University of Texas at Dallas March 2010 Prepared for forthcoming Selected Works of Debabrata Basu (Anirban DasGupta, Ed.), Springer Series on Selected Works in
Commentary on Basu (1956) Robert Serfling University of Texas at Dallas March 2010 Prepared for forthcoming Selected Works of Debabrata Basu (Anirban DasGupta, Ed.), Springer Series on Selected Works in
Interpolation on lines by ridge functions
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Approximation Theory 175 (2013) 91 113 www.elsevier.com/locate/jat Full length article Interpolation on lines by ridge functions V.E.
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Approximation Theory 175 (2013) 91 113 www.elsevier.com/locate/jat Full length article Interpolation on lines by ridge functions V.E.
Dimensionality of Hierarchical
 Dimensionality of Hierarchical and Proximal Data Structures David J. Krus and Patricia H. Krus Arizona State University The coefficient of correlation is a fairly general measure which subsumes other,
Dimensionality of Hierarchical and Proximal Data Structures David J. Krus and Patricia H. Krus Arizona State University The coefficient of correlation is a fairly general measure which subsumes other,
