monolayer graphene on hbn round and nearly round bubbles triangular with smooth top triangular and trapezoid with sharp ridges R (L ) (n m )
|
|
|
- Rodger Timothy Wilkinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Count a 3 monolayer graphene on hbn 2 round and nearly round bubbles triangular with smooth top triangular and trapezoid with sharp ridges 1 b R L) nm) 3 m o n o la y e r h B N o n h B N C o u n t 2 1 ro u n d a n d n e a rly ro u n d tria n g u la r w ith s m o o th to p s c R L ) n m ) m o n o la y e r M o S 2 o n M o S 2 ro u n d a n d n e a rly ro u n d C o u n t R n m ) Supplementary Figure 1. Frequency of occurrence for bubbles of dierent shapes. Shown are histograms of bubble sizes corresponding to dierent shapes. a) monolayer graphene on an hbn substrate ; data collected from an area of 12 µm 2. b) monolayer hbn on an hbn substrate, data collected from an area of 12 µm 2. c) monolayer MoS 2 on an MoS 2 substrate, data collected from an area of 4 µm 2.
2 2 a b δ R tip Supplementary Figure 2. AFM tips used in indentation experiments. a) Scanning electron microscope SEM) image of one of the AFM tips. The dashed circle emphasises its spherical shape. b) Three-dimensional image of another AFM tip obtained using the Bruker calibration procedure see Methods). The plane section indicates the maximum range of indentation depths corresponding to applicability of our numerical tting procedure.
3 3 a 5 F n N ) In d e n ta tio n b F n N ) S a p p h ire s u b s tra te firs t ru n s e c o n d ru n a fte r 3 s e c 2 4 d n m ) n m r n m ) h n m ) n m d n m ) Supplementary Figure 3. Reproducibility of force-displacement curves and denition of zero indentation. a) Two force-displacement FDC) curves taken on the same graphene bubble R =317 nm). Black line shows an FDC taken with the same AFM tip on a sapphire substrate. b) Example of an FDC obtained by full-height indentation of a graphene bubble see Methods) ; the inset shows a prole of the same bubble obtained in the scanning mode prior to indentation. Crossing dashed lines in the main panel indicate δ = zero indentation) ; the vertical part of the FDC corresponds to indentation of the substrate i.e., d reaches the height of the bubble, h max). The distance travelled by the AFM tip until it reaches the substrate, d = 34.8 nm is in excellent agreement with the measured bubble's height h max = 34.3 nm.
4 4 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1. ELASTIC ENERGY. The elastic energy of one bubble, dened by a prole h r) is µλ + µ) 1 E el = 2λ + 2µ) 4π 2 d 2 q q 2 f i,j q) i,j 2 S.1) where i, j = x, y and f ij q) = d 2 re i q r i h r) j h r) S.2) For an isotropic bubble, h r) = hr), where r = r, Supplementary Equation S.1) becomes E el = π µλ + µ) 8 λ + 2µ 2 dqq drr [J qr) J 2 qr)] r h) 2 where J u) and J 2 u) are Bessel functions. In the presence of an isotropic strain, ɛ xx = ɛ yy = ɛ/2, the bubble acquires an additional energy, ɛµλ + µ) E str = λ + 2µ lim q q 2 f i,j q) i,j S.3) S.4) where we have used the relation ɛ q) = 4π 2 ɛδ 2 q). For an isotropic height prole, hr), Supplementary Equation S.1) reduces to E str = πɛµλ + µ) 2λ + 2µ) drr [ r hr)] 2 Alternatively, for an isotropic height prole, hr), one can write the elastic energy as E el = 2π λ [ drr r u r + u r 2 r + rh) 2 ] 2 [ + 2πµ drr r u r + rh) 2 ) 2 ] + u2 r 2 2 r 2 The displacement u r can be obtained from λ + 2µ) r 2 u r + ru r u ) r r r 2 = λ + 2µ) r 2 h ) r h) + µ r rh) 2 S.7) S.5) S.6) SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 2. INFLUENCE OF TENSILE STRAINS. Tensile strains, ɛ >, modify the aspect ratio of the bubbles, as shown in Supplementary Equation S.7) in the main text. The changes signicant when the term proportional to ɛ becomes a signicant fraction of the total elastic energy. By comparing these contributions in Supplementary Equation S.7), we nd a threshold strain, ɛ th ɛ th c 1 c 2 hmax R ) 2 = c 1 πγ ) 1/2 S.8) c 2 5Y Using γ.15 ev, and the Young modulii for graphene and MoS 2 we nd, for graphene, ɛ th 1.4%, and for MoS 2, ɛ th 1.9%. For larger tensile strains,the aspect ratio tends to h max πγ R S.9) 2c 2 ɛy The bubbles become shorter in the presence of a tensile strain. The dependence of the pressure on the height of the bubble, Supplementary Equation S.18) in the main text is not signicantly modied, and we nd P πγ c V h max S.1)
5 5 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 3. INFLUENCE OF COMPRESSIVE STRAINS. In the presence of compressive strains, ɛ <, the aspect ratio h max /R, increases. A suciently high compressive strain will overcome the vdw interaction, and the graphene layer will delaminate, forming a bubble even in the absence of trapped material, or can even completely detach from the substrate. If we do not consider the internal energy of the material inside the bubble, a bubble formed spontaneously with radius R and height h max has an energy, Minimizing this expression with respect to h max, we nd E tot = c 1 Y h4 max R 2 c 2 Y ɛ h 2 max + πγr 2 S.11) The total energy of the bubble, as function of R, is h 2 max R 2 = c 2 ɛ 2c 1 S.12) E tot = Y c2 2 ɛ 2 4c 1 R 2 + πγr 2. S.13) The bubble will be stable and grow towards R if the compressive strain is such that Y c 2 2 ɛ 2 The compressive strain required for the bubble to be unstable is 4c 1 πγ ɛ Y c 2 2 4c 1 > πγ S.14) S.15) These strains are 6.2% and 8.7% for graphene and MoS 2, respectively. On the other hand, for suciently small strains, we can expand the solution of Supplementary Equation S.8) in the main text, and we obtain h max R ) 1/4 c4 γ c 2ɛ 5c 1 Y 5c 1 Y 1c 1 πγ, that is, for ɛ < compressive strain) h max /R will be greater than in the unstrained situation. S.16) SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 4. INTERACTION BETWEEN BUBBLES. Bubbles can only interact when the in plane displacements relax to the height prole. We can extend eqs.s.1) and S.3) to the case of two non overlapping proles, h 1 r) and h 2 r). Leaving out the self energy of each bubble, we obtain µλ + µ) 1 E int = 2λ + 2µ) 4π 2 d 2 qe i q R i,j q 2 fi,j q) 1 i,j q 2 fi,j q) 2 S.17) where R is the vector connecting the centers of the two bubbles, and fi,j k q) is, as before, the Fourier transform of i h k r) j h k r). E int R) = π 8 µλ + µ) λ + 2µ { dqqj qr) drr [J qr) J 2 qr)] r h 1 ) 2 drr [J qr) J 2 qr)] r h 2 ) 2 } S.18)
6 6 where R = R. A long distances R l, we obtain where E int R) απ 8 µλ + µ) λ + 2µ)R 2 drr r h 1 ) 2 drr r h 2 ) 2 α = lim r 2 dqqj qr) q S.19) S.2) The interaction between bubbles is attractive, favouring their merger into bigger bubbles, as observed experimentally.
Supplementary Figure S1. STM image of monolayer graphene grown on Rh (111). The lattice
 Supplementary Figure S1. STM image of monolayer graphene grown on Rh (111). The lattice mismatch between graphene (0.246 nm) and Rh (111) (0.269 nm) leads to hexagonal moiré superstructures with the expected
Supplementary Figure S1. STM image of monolayer graphene grown on Rh (111). The lattice mismatch between graphene (0.246 nm) and Rh (111) (0.269 nm) leads to hexagonal moiré superstructures with the expected
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Supplementary Figure S1STM images of four GNBs and their corresponding STS spectra. a-d, STM images of four GNBs are shown in the left side. The experimental STS data with respective
Supplementary information Supplementary Figure S1STM images of four GNBs and their corresponding STS spectra. a-d, STM images of four GNBs are shown in the left side. The experimental STS data with respective
Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental setup for crystal growth. Schematic drawing of the experimental setup for C 8 -BTBT crystal growth.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental setup for crystal growth. Schematic drawing of the experimental setup for C 8 -BTBT crystal growth. Supplementary Figure 2 AFM study of the C 8 -BTBT crystal growth
Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental setup for crystal growth. Schematic drawing of the experimental setup for C 8 -BTBT crystal growth. Supplementary Figure 2 AFM study of the C 8 -BTBT crystal growth
height trace of a 2L BN mechanically exfoliated on SiO 2 /Si with pre-fabricated micro-wells. Scale bar 2 µm.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Few-layer BN nanosheets. AFM image and the corresponding height trace of a 2L BN mechanically exfoliated on SiO 2 /Si with pre-fabricated micro-wells. Scale bar 2 µm. Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1. Few-layer BN nanosheets. AFM image and the corresponding height trace of a 2L BN mechanically exfoliated on SiO 2 /Si with pre-fabricated micro-wells. Scale bar 2 µm. Supplementary
Intensity (a.u.) Intensity (a.u.) Raman Shift (cm -1 ) Oxygen plasma. 6 cm. 9 cm. 1mm. Single-layer graphene sheet. 10mm. 14 cm
 Intensity (a.u.) Intensity (a.u.) a Oxygen plasma b 6 cm 1mm 10mm Single-layer graphene sheet 14 cm 9 cm Flipped Si/SiO 2 Patterned chip Plasma-cleaned glass slides c d After 1 sec normal Oxygen plasma
Intensity (a.u.) Intensity (a.u.) a Oxygen plasma b 6 cm 1mm 10mm Single-layer graphene sheet 14 cm 9 cm Flipped Si/SiO 2 Patterned chip Plasma-cleaned glass slides c d After 1 sec normal Oxygen plasma
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 1
 1 Supplementary information Effect of the viscoelasticity of substrate: In the main text, we indicated the role of the viscoelasticity of substrate. In all problems involving a coupling of a viscous medium
1 Supplementary information Effect of the viscoelasticity of substrate: In the main text, we indicated the role of the viscoelasticity of substrate. In all problems involving a coupling of a viscous medium
Large scale growth and characterization of atomic hexagonal boron. nitride layers
 Supporting on-line material Large scale growth and characterization of atomic hexagonal boron nitride layers Li Song, Lijie Ci, Hao Lu, Pavel B. Sorokin, Chuanhong Jin, Jie Ni, Alexander G. Kvashnin, Dmitry
Supporting on-line material Large scale growth and characterization of atomic hexagonal boron nitride layers Li Song, Lijie Ci, Hao Lu, Pavel B. Sorokin, Chuanhong Jin, Jie Ni, Alexander G. Kvashnin, Dmitry
Supplementary Figure 1 Simulations of the lm thickness dependence of plasmon modes on lms or disks on a 30 nm thick Si 3 N 4 substrate.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Simulations of the lm thickness dependence of plasmon modes on lms or disks on a 30 nm thick Si 3 N 4 substrate. (a) Simulated plasmon energy at k=30 µm 1 for the surface plasmon
Supplementary Figure 1 Simulations of the lm thickness dependence of plasmon modes on lms or disks on a 30 nm thick Si 3 N 4 substrate. (a) Simulated plasmon energy at k=30 µm 1 for the surface plasmon
6.5 mm. ε = 1%, r = 9.4 mm. ε = 3%, r = 3.1 mm
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Gold wires Substrate Compression holder 6.5 mm Supplementary Figure 1 Picture of the compression holder. 6.5 mm ε = 0% ε = 1%, r = 9.4 mm ε = 2%, r = 4.7
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Gold wires Substrate Compression holder 6.5 mm Supplementary Figure 1 Picture of the compression holder. 6.5 mm ε = 0% ε = 1%, r = 9.4 mm ε = 2%, r = 4.7
Supplementary Figure 1: Micromechanical cleavage of graphene on oxygen plasma treated Si/SiO2. Supplementary Figure 2: Comparison of hbn yield.
 1 2 3 4 Supplementary Figure 1: Micromechanical cleavage of graphene on oxygen plasma treated Si/SiO 2. Optical microscopy images of three examples of large single layer graphene flakes cleaved on a single
1 2 3 4 Supplementary Figure 1: Micromechanical cleavage of graphene on oxygen plasma treated Si/SiO 2. Optical microscopy images of three examples of large single layer graphene flakes cleaved on a single
Imaging Methods: Scanning Force Microscopy (SFM / AFM)
 Imaging Methods: Scanning Force Microscopy (SFM / AFM) The atomic force microscope (AFM) probes the surface of a sample with a sharp tip, a couple of microns long and often less than 100 Å in diameter.
Imaging Methods: Scanning Force Microscopy (SFM / AFM) The atomic force microscope (AFM) probes the surface of a sample with a sharp tip, a couple of microns long and often less than 100 Å in diameter.
Atomic Force Microscopy Characterization of Room- Temperature Adlayers of Small Organic Molecules through Graphene Templating
 Atomic Force icroscopy Characterization of Room- Temperature Adlayers of Small Organic olecules through Graphene Templating Peigen Cao, Ke Xu,2, Joseph O. Varghese, and James R. Heath *. Kavli Nanoscience
Atomic Force icroscopy Characterization of Room- Temperature Adlayers of Small Organic olecules through Graphene Templating Peigen Cao, Ke Xu,2, Joseph O. Varghese, and James R. Heath *. Kavli Nanoscience
Supplementary Figure 1 shows overall fabrication process and detailed illustrations are given
 Supplementary Figure 1. Pressure sensor fabrication schematics. Supplementary Figure 1 shows overall fabrication process and detailed illustrations are given in Methods section. (a) Firstly, the sacrificial
Supplementary Figure 1. Pressure sensor fabrication schematics. Supplementary Figure 1 shows overall fabrication process and detailed illustrations are given in Methods section. (a) Firstly, the sacrificial
Determining the Elastic Modulus and Hardness of an Ultrathin Film on a Substrate Using Nanoindentation
 Determining the Elastic Modulus and Hardness of an Ultrathin Film on a Substrate Using Nanoindentation The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Determining the Elastic Modulus and Hardness of an Ultrathin Film on a Substrate Using Nanoindentation The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature09450 Supplementary Table 1 Summary of kinetic parameters. Kinetic parameters were V = V / 1 K / ATP and obtained using the relationships max ( + m [ ]) V d s /( 1/ k [ ATP] + 1 k ) =,
doi:10.1038/nature09450 Supplementary Table 1 Summary of kinetic parameters. Kinetic parameters were V = V / 1 K / ATP and obtained using the relationships max ( + m [ ]) V d s /( 1/ k [ ATP] + 1 k ) =,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1. Supplementary Methods Characterization of AFM resolution We employed amplitude-modulation AFM in non-contact mode to characterize the topography of the graphene samples. The measurements were performed
1. Supplementary Methods Characterization of AFM resolution We employed amplitude-modulation AFM in non-contact mode to characterize the topography of the graphene samples. The measurements were performed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature10683 Supplementary Methods and Discussion: Possibility of Toluene Inclusion in Unit Cell: The unit cell calculations show modest, non-systematic cell volume
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature10683 Supplementary Methods and Discussion: Possibility of Toluene Inclusion in Unit Cell: The unit cell calculations show modest, non-systematic cell volume
Supporting information for. Direct imaging of kinetic pathways of atomic diffusion in. monolayer molybdenum disulfide
 Supporting information for Direct imaging of kinetic pathways of atomic diffusion in monolayer molybdenum disulfide Jinhua Hong,, Yuhao Pan,, Zhixin Hu, Danhui Lv, Chuanhong Jin, *, Wei Ji, *, Jun Yuan,,*,
Supporting information for Direct imaging of kinetic pathways of atomic diffusion in monolayer molybdenum disulfide Jinhua Hong,, Yuhao Pan,, Zhixin Hu, Danhui Lv, Chuanhong Jin, *, Wei Ji, *, Jun Yuan,,*,
The effect of plasticity in crumpling of thin sheets: Supplementary Information
 The effect of plasticity in crumpling of thin sheets: Supplementary Information T. Tallinen, J. A. Åström and J. Timonen Video S1. The video shows crumpling of an elastic sheet with a width to thickness
The effect of plasticity in crumpling of thin sheets: Supplementary Information T. Tallinen, J. A. Åström and J. Timonen Video S1. The video shows crumpling of an elastic sheet with a width to thickness
Supplementary Figure 1: Power dependence of hot-electrons reduction of 4-NTP to 4-ATP. a) SERS spectra of the hot-electron reduction reaction using
 Supplementary Figure 1: Power dependence of hot-electrons reduction of 4-NTP to 4-ATP. a) SERS spectra of the hot-electron reduction reaction using 633 nm laser excitation at different powers and b) the
Supplementary Figure 1: Power dependence of hot-electrons reduction of 4-NTP to 4-ATP. a) SERS spectra of the hot-electron reduction reaction using 633 nm laser excitation at different powers and b) the
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa.
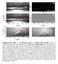 Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Electronic Kohn-Sham potential profile of a charged monolayer MoTe 2 calculated using PBE-DFT. Plotted is the averaged electronic Kohn- Sham potential
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Electronic Kohn-Sham potential profile of a charged monolayer MoTe 2 calculated using PBE-DFT. Plotted is the averaged electronic Kohn- Sham potential
Lecture #7: Basic Notions of Fracture Mechanics Ductile Fracture
 Lecture #7: Basic Notions of Fracture Mechanics Ductile Fracture by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing
Lecture #7: Basic Notions of Fracture Mechanics Ductile Fracture by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.017.65 Imaging exciton-polariton transport in MoSe waveguides F. Hu 1,, Y. Luan 1,, M. E. Scott 3, J.
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.017.65 Imaging exciton-polariton transport in MoSe waveguides F. Hu 1,, Y. Luan 1,, M. E. Scott 3, J.
Supplementary Information for Solution-Synthesized Chevron Graphene Nanoribbons Exfoliated onto H:Si(100)
 Supplementary Information for Solution-Synthesized Chevron Graphene Nanoribbons Exfoliated onto H:Si(100) Adrian Radocea,, Tao Sun,, Timothy H. Vo, Alexander Sinitskii,,# Narayana R. Aluru,, and Joseph
Supplementary Information for Solution-Synthesized Chevron Graphene Nanoribbons Exfoliated onto H:Si(100) Adrian Radocea,, Tao Sun,, Timothy H. Vo, Alexander Sinitskii,,# Narayana R. Aluru,, and Joseph
Loading σ Stress. Strain
 hapter 2 Material Non-linearity In this chapter an overview of material non-linearity with regard to solid mechanics is presented. Initially, a general description of the constitutive relationships associated
hapter 2 Material Non-linearity In this chapter an overview of material non-linearity with regard to solid mechanics is presented. Initially, a general description of the constitutive relationships associated
Mapping the mechanical stiffness of live cells with the scanning ion conductance microscope
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Mapping the mechanical stiffness of live cells with the scanning ion conductance microscope Johannes Rheinlaender and Tilman E. Schäffer Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Mapping the mechanical stiffness of live cells with the scanning ion conductance microscope Johannes Rheinlaender and Tilman E. Schäffer Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/10/eaat8797/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Single-molecule observation of nucleotide induced conformational changes in basal SecA-ATP hydrolysis Nagaraju Chada,
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/10/eaat8797/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Single-molecule observation of nucleotide induced conformational changes in basal SecA-ATP hydrolysis Nagaraju Chada,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary figure S1: Characterisation of the electron beam intensity profile. (a) A 3D plot of beam intensity (grey value) with position, (b) the beam
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary figure S1: Characterisation of the electron beam intensity profile. (a) A 3D plot of beam intensity (grey value) with position, (b) the beam
Supplementary Material
 Mangili et al. Supplementary Material 2 A. Evaluation of substrate Young modulus from AFM measurements 3 4 5 6 7 8 Using the experimental correlations between force and deformation from AFM measurements,
Mangili et al. Supplementary Material 2 A. Evaluation of substrate Young modulus from AFM measurements 3 4 5 6 7 8 Using the experimental correlations between force and deformation from AFM measurements,
Two-dimensional Phosphorus Carbide as Promising Anode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Material for Two-dimensional Phosphorus Carbide as Promising
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Material for Two-dimensional Phosphorus Carbide as Promising
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Thickness of suspended epitaxial graphene (SEG) resonators: Graphene thickness was estimated using an atomic force microscope (AFM) by going over the step edge from SiC to graphene.
Supporting Information Thickness of suspended epitaxial graphene (SEG) resonators: Graphene thickness was estimated using an atomic force microscope (AFM) by going over the step edge from SiC to graphene.
Analysis of contact deformation between a coated flat plate and a sphere and its practical application
 Computer Methods and Experimental Measurements for Surface Effects and Contact Mechanics VII 307 Analysis of contact deformation between a coated flat plate and a sphere and its practical application T.
Computer Methods and Experimental Measurements for Surface Effects and Contact Mechanics VII 307 Analysis of contact deformation between a coated flat plate and a sphere and its practical application T.
Supporting Information. Interfacial Shear Strength of Multilayer Graphene Oxide Films
 Supporting Information Interfacial Shear Strength of Multilayer Graphene Oxide Films Matthew Daly a,1, Changhong Cao b,1, Hao Sun b, Yu Sun b, *, Tobin Filleter b, *, and Chandra Veer Singh a, * a Department
Supporting Information Interfacial Shear Strength of Multilayer Graphene Oxide Films Matthew Daly a,1, Changhong Cao b,1, Hao Sun b, Yu Sun b, *, Tobin Filleter b, *, and Chandra Veer Singh a, * a Department
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Intrinsically patterned two-dimensional materials for selective adsorption of molecules and nanoclusters X. Lin 1,, J. C. Lu 1,, Y. Shao 1,, Y. Y. Zhang
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Intrinsically patterned two-dimensional materials for selective adsorption of molecules and nanoclusters X. Lin 1,, J. C. Lu 1,, Y. Shao 1,, Y. Y. Zhang
High Performance Coils and Yarns of Polymeric Piezoelectric Nanofibers
 Supplementary Information High Performance Coils and Yarns of Polymeric Piezoelectric Nanofibers Mahmoud Baniasadi 1, Jiacheng Huang 1, Zhe Xu 1, Salvador Moreno 1, Xi Yang 2, Jason Chang 3, Manuel Angel
Supplementary Information High Performance Coils and Yarns of Polymeric Piezoelectric Nanofibers Mahmoud Baniasadi 1, Jiacheng Huang 1, Zhe Xu 1, Salvador Moreno 1, Xi Yang 2, Jason Chang 3, Manuel Angel
A Nanoscale Shape Memory Oxide
 A Nanoscale Shape Memory Oxide Jinxing Zhang 1,2*, Xiaoxing Ke 3*, Gaoyang Gou 4, Jan Seidel 2,5, Bin Xiang 6,9, Pu Yu 2,7, Wen-I Liang 8, Andrew M. Minor 9,10, Ying-hao Chu 8, Gustaaf Van Tendeloo 3,
A Nanoscale Shape Memory Oxide Jinxing Zhang 1,2*, Xiaoxing Ke 3*, Gaoyang Gou 4, Jan Seidel 2,5, Bin Xiang 6,9, Pu Yu 2,7, Wen-I Liang 8, Andrew M. Minor 9,10, Ying-hao Chu 8, Gustaaf Van Tendeloo 3,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Devlin et al. 10.1073/pnas.1611740113 Optical Characterization We deposit blanket TiO films via ALD onto silicon substrates to prepare samples for spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE)
Supporting Information Devlin et al. 10.1073/pnas.1611740113 Optical Characterization We deposit blanket TiO films via ALD onto silicon substrates to prepare samples for spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE)
Supplementary material to On the rheology of pendular gels and morphological developments in paste- like ternary systems based on capillary attraction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Soft Matter. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supplementary material to On the rheology of pendular gels and morphological developments in
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Soft Matter. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supplementary material to On the rheology of pendular gels and morphological developments in
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures 8 6 Energy (ev 4 2 2 4 Γ M K Γ Supplementary Figure : Energy bands of antimonene along a high-symmetry path in the Brillouin zone, including spin-orbit coupling effects. Empty circles
Supplementary Figures 8 6 Energy (ev 4 2 2 4 Γ M K Γ Supplementary Figure : Energy bands of antimonene along a high-symmetry path in the Brillouin zone, including spin-orbit coupling effects. Empty circles
Effect of AFM Cantilever Geometry on the DPL Nanomachining process
 Int J Advanced Design and Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 9/ No. 4/ December 2016 75 Effect of AFM Cantilever Geometry on the DPL Nanomachining process A. R. Norouzi Department of New Sciences and Technologies,
Int J Advanced Design and Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 9/ No. 4/ December 2016 75 Effect of AFM Cantilever Geometry on the DPL Nanomachining process A. R. Norouzi Department of New Sciences and Technologies,
Bond-Valence Model of Ferroelectric PbTiO 3
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 5, No., pril 8, pp. 6 ond-valence Model of Ferroelectric PbTiO 3 Young-Han Shin and yeong-joo Lee Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Pohang University
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 5, No., pril 8, pp. 6 ond-valence Model of Ferroelectric PbTiO 3 Young-Han Shin and yeong-joo Lee Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Pohang University
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/3/e1701373/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Atomically thin gallium layers from solid-melt exfoliation Vidya Kochat, Atanu Samanta, Yuan Zhang, Sanjit Bhowmick,
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/3/e1701373/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Atomically thin gallium layers from solid-melt exfoliation Vidya Kochat, Atanu Samanta, Yuan Zhang, Sanjit Bhowmick,
Layer-dependent Anisotropic Frictional Behavior in Two-dimensional
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2019 Layer-dependent Anisotropic Frictional Behavior in Two-dimensional Monolayer Hybrid
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2019 Layer-dependent Anisotropic Frictional Behavior in Two-dimensional Monolayer Hybrid
Direct-writing on monolayer GO with Pt-free AFM tips in the
 Supplementary Figure S1 Direct-writing on monolayer GO with Pt-free AFM tips in the presence of hydrogen. We replaced the Pt-coated tip with a gold-coated tip or an untreated fresh silicon tip, and kept
Supplementary Figure S1 Direct-writing on monolayer GO with Pt-free AFM tips in the presence of hydrogen. We replaced the Pt-coated tip with a gold-coated tip or an untreated fresh silicon tip, and kept
AERO 214. Lab II. Measurement of elastic moduli using bending of beams and torsion of bars
 AERO 214 Lab II. Measurement of elastic moduli using bending of beams and torsion of bars BENDING EXPERIMENT Introduction Flexural properties of materials are of interest to engineers in many different
AERO 214 Lab II. Measurement of elastic moduli using bending of beams and torsion of bars BENDING EXPERIMENT Introduction Flexural properties of materials are of interest to engineers in many different
Effect of lithium-trapping on nitrogen-doped graphene as. an anchoring material for lithium-sulfur batteries: A. theoretical study
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Effect of lithium-trapping on nitrogen-doped
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Effect of lithium-trapping on nitrogen-doped
Study of oat glass as electrode for RPC
 Study of oat glass as electrode for RPC K. Raveendrababu*, P. K. Behera Physics Department, IITM, Chennai-36, INDIA. B. Satyanarayana DHEP, TIFR, Mumbai-05, INDIA. S. Mukhopadhyay, N. Majumdar ANP Division,
Study of oat glass as electrode for RPC K. Raveendrababu*, P. K. Behera Physics Department, IITM, Chennai-36, INDIA. B. Satyanarayana DHEP, TIFR, Mumbai-05, INDIA. S. Mukhopadhyay, N. Majumdar ANP Division,
Electronic Supporting Information. Microcapsule Buckling Triggered by Compression- Induced Interfacial Chase Change
 Electronic Supporting Information Microcapsule Buckling Triggered by Compression- Induced Interfacial Chase Change Andrew R Salmon, 1 Richard M Parker, 1 Alexander S Groombridge, 1 Armando Maestro, 1 Roger
Electronic Supporting Information Microcapsule Buckling Triggered by Compression- Induced Interfacial Chase Change Andrew R Salmon, 1 Richard M Parker, 1 Alexander S Groombridge, 1 Armando Maestro, 1 Roger
Determining thermal noise limiting properties of thin films
 Determining thermal noise limiting properties of thin films Courtney Linn Institute for Gravitational Research University of Glasgow Summer 2011 Abstract In order to make thermally stable mirrors to be
Determining thermal noise limiting properties of thin films Courtney Linn Institute for Gravitational Research University of Glasgow Summer 2011 Abstract In order to make thermally stable mirrors to be
Supplementary Figure 1: Reflectance at low detuning. Reflectance as a function of the pump power for a pump-polariton detuning of 0.10meV.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Reflectance at low detuning. Reflectance as a function of the pump power for a pump-polariton detuning of 0.10meV. The pillar is 6µm of diameter and the cavity detuning is δ = 5meV.
Supplementary Figure 1: Reflectance at low detuning. Reflectance as a function of the pump power for a pump-polariton detuning of 0.10meV. The pillar is 6µm of diameter and the cavity detuning is δ = 5meV.
Supplementary Figure 1 Detailed illustration on the fabrication process of templatestripped
 Supplementary Figure 1 Detailed illustration on the fabrication process of templatestripped gold substrate. (a) Spin coating of hydrogen silsesquioxane (HSQ) resist onto the silicon substrate with a thickness
Supplementary Figure 1 Detailed illustration on the fabrication process of templatestripped gold substrate. (a) Spin coating of hydrogen silsesquioxane (HSQ) resist onto the silicon substrate with a thickness
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Metal-Free Half-Metallicity in a High Energy Phase
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Metal-Free Half-Metallicity in a High Energy Phase
Appendix (Supplementary Material)
 Appendix (Supplementary Material) Appendix A. Real and Imaginary Parts of the complex modulus E*(f), and E*(f) for the Pyramidal Proe Tip The magnitude of the complex modulus, E*(f), and the phase angle,
Appendix (Supplementary Material) Appendix A. Real and Imaginary Parts of the complex modulus E*(f), and E*(f) for the Pyramidal Proe Tip The magnitude of the complex modulus, E*(f), and the phase angle,
Self-assembled and intercalated film of reduced. graphene oxide for a novel vacuum pressure sensor
 Supplementary Information for Self-assembled and intercalated film of reduced graphene oxide for a novel vacuum pressure sensor Sung Il Ahn *, Jura Jung, Yongwoo Kim, Yujin Lee, Kukjoo Kim, Seong Eui Lee
Supplementary Information for Self-assembled and intercalated film of reduced graphene oxide for a novel vacuum pressure sensor Sung Il Ahn *, Jura Jung, Yongwoo Kim, Yujin Lee, Kukjoo Kim, Seong Eui Lee
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES Supplementary Note 1: Fabrication of Scanning Thermal Microscopy Probes
 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES Supplementary Note 1: Fabrication of Scanning Thermal Microscopy Probes Fabrication of the scanning thermal microscopy (SThM) probes is summarized in Supplementary Fig. 1 and proceeds
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES Supplementary Note 1: Fabrication of Scanning Thermal Microscopy Probes Fabrication of the scanning thermal microscopy (SThM) probes is summarized in Supplementary Fig. 1 and proceeds
Mechanical Characterization of High Aspect Ratio Silicon Nanolines
 Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 1086 2008 Materials Research Society 1086-U05-07 Mechanical Characterization of High Aspect Ratio Silicon Nanolines Bin Li 1, Huai Huang 1, Qiu Zhao 1, Zhiquan Luo 1,
Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 1086 2008 Materials Research Society 1086-U05-07 Mechanical Characterization of High Aspect Ratio Silicon Nanolines Bin Li 1, Huai Huang 1, Qiu Zhao 1, Zhiquan Luo 1,
Supporting Information:
 Supporting Information: Strain Induced Optimization of Nanoelectromechanical Energy Harvesting and Nanopiezotronic Response in MoS 2 Monolayer Nanosheet Nityasagar Jena, Dimple, Shounak Dhananjay Behere,
Supporting Information: Strain Induced Optimization of Nanoelectromechanical Energy Harvesting and Nanopiezotronic Response in MoS 2 Monolayer Nanosheet Nityasagar Jena, Dimple, Shounak Dhananjay Behere,
Striped, honeycomb, and twisted moire patterns in surface adsorption systems with highly degenerate commensurate ground states
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Striped, honeycomb, and twisted moire patterns in surface adsorption systems with highly degenerate commensurate ground states This item was submitted to
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Striped, honeycomb, and twisted moire patterns in surface adsorption systems with highly degenerate commensurate ground states This item was submitted to
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2011.123 Ultra-strong Adhesion of Graphene Membranes Steven P. Koenig, Narasimha G. Boddeti, Martin L. Dunn, and J. Scott Bunch* Department of Mechanical Engineering,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2011.123 Ultra-strong Adhesion of Graphene Membranes Steven P. Koenig, Narasimha G. Boddeti, Martin L. Dunn, and J. Scott Bunch* Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Multi-color broadband visible light source via GaN hexagonal. annular structure
 Multi-color broadband visible light source via GaN hexagonal annular structure Young-Ho Ko 1[+], Jie Song 2, Benjamin Leung 2, Jung Han 2 and Yong-Hoon Cho 1* 1 Department of Physics, Korea Advanced Institute
Multi-color broadband visible light source via GaN hexagonal annular structure Young-Ho Ko 1[+], Jie Song 2, Benjamin Leung 2, Jung Han 2 and Yong-Hoon Cho 1* 1 Department of Physics, Korea Advanced Institute
Graphene Helicoid: The Distinct Properties Promote Application of Graphene Related Materials in Thermal Management
 Supporting Information Graphene Helicoid: The Distinct Properties Promote Application of Graphene Related Materials in Thermal Management Haifei Zhan 1,2, Gang Zhang 3,*, Chunhui Yang 1, and Yuantong Gu
Supporting Information Graphene Helicoid: The Distinct Properties Promote Application of Graphene Related Materials in Thermal Management Haifei Zhan 1,2, Gang Zhang 3,*, Chunhui Yang 1, and Yuantong Gu
Lecture Note October 1, 2009 Nanostructure characterization techniques
 Lecture Note October 1, 29 Nanostructure characterization techniques UT-Austin PHYS 392 T, unique # 5977 ME 397 unique # 1979 CHE 384, unique # 151 Instructor: Professor C.K. Shih Subjects: Applications
Lecture Note October 1, 29 Nanostructure characterization techniques UT-Austin PHYS 392 T, unique # 5977 ME 397 unique # 1979 CHE 384, unique # 151 Instructor: Professor C.K. Shih Subjects: Applications
Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information Self-assembled nanopatch with peptide-organic multilayers and mechanical
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information Self-assembled nanopatch with peptide-organic multilayers and mechanical
Surface stress and relaxation in metals
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12 (2000) 5541 5550. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(00)11386-4 Surface stress and relaxation in metals P M Marcus, Xianghong Qian and Wolfgang Hübner IBM Research Center, Yorktown
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12 (2000) 5541 5550. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(00)11386-4 Surface stress and relaxation in metals P M Marcus, Xianghong Qian and Wolfgang Hübner IBM Research Center, Yorktown
Supporting Information Title: The effect of preparation conditions on Raman and Photoluminescence of Monolayer WS2
 Supporting Information Title: The effect of preparation conditions on Raman and Photoluminescence of Monolayer WS2 Kathleen M. McCreary, Aubrey T. Hanbicki, Simranjeet Singh, Roland K. Kawakami, Glenn
Supporting Information Title: The effect of preparation conditions on Raman and Photoluminescence of Monolayer WS2 Kathleen M. McCreary, Aubrey T. Hanbicki, Simranjeet Singh, Roland K. Kawakami, Glenn
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Graded bandgap perovskite solar cells Onur Ergen, 1,3,4 S.Matt Gilbert 1, 3,4,,Thang Pham 1, 3,4,Sally J. Turner, 1,2,4, Mark Tian Zhi Tan 1, Marcus A. Worsley 1, 3,4 and Alex Zettl 1 Department of Physics,
Graded bandgap perovskite solar cells Onur Ergen, 1,3,4 S.Matt Gilbert 1, 3,4,,Thang Pham 1, 3,4,Sally J. Turner, 1,2,4, Mark Tian Zhi Tan 1, Marcus A. Worsley 1, 3,4 and Alex Zettl 1 Department of Physics,
Mechanical Properties of Polymer Rubber Materials Based on a New Constitutive Model
 Mechanical Properties of Polymer Rubber Materials Based on a New Constitutive Model Mechanical Properties of Polymer Rubber Materials Based on a New Constitutive Model J.B. Sang*, L.F. Sun, S.F. Xing,
Mechanical Properties of Polymer Rubber Materials Based on a New Constitutive Model Mechanical Properties of Polymer Rubber Materials Based on a New Constitutive Model J.B. Sang*, L.F. Sun, S.F. Xing,
Crystals Statics. Structural Properties. Geometry of lattices. Aug 23, 2018
 Crystals Statics. Structural Properties. Geometry of lattices Aug 23, 2018 Crystals Why (among all condensed phases - liquids, gases) look at crystals? We can take advantage of the translational symmetry,
Crystals Statics. Structural Properties. Geometry of lattices Aug 23, 2018 Crystals Why (among all condensed phases - liquids, gases) look at crystals? We can take advantage of the translational symmetry,
Crash Safety of Lithium-Ion Batteries for Electric Vehicles
 Crash Safety of Lithium-Ion Batteries for Electric Vehicles Elham Sahraei Esfahani Research Scientist, MIT Assistant Professor, GMU Vehicle Crashes and Testing Battery Packs in T Configuration Chevy Volt
Crash Safety of Lithium-Ion Batteries for Electric Vehicles Elham Sahraei Esfahani Research Scientist, MIT Assistant Professor, GMU Vehicle Crashes and Testing Battery Packs in T Configuration Chevy Volt
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Molecular structures of functional materials involved in our SGOTFT devices. Supplementary Figure 2 Capacitance measurements of a SGOTFT device. (a) Capacitance
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Molecular structures of functional materials involved in our SGOTFT devices. Supplementary Figure 2 Capacitance measurements of a SGOTFT device. (a) Capacitance
STM and graphene. W. W. Larry Pai ( 白偉武 ) Center for condensed matter sciences, National Taiwan University NTHU, 2013/05/23
 STM and graphene W. W. Larry Pai ( 白偉武 ) Center for condensed matter sciences, National Taiwan University NTHU, 2013/05/23 Why graphene is important: It is a new form of material (two dimensional, single
STM and graphene W. W. Larry Pai ( 白偉武 ) Center for condensed matter sciences, National Taiwan University NTHU, 2013/05/23 Why graphene is important: It is a new form of material (two dimensional, single
The dissertation of Bin Jiang is approved: Chair Date Date Date Date University of California at Santa Barbara 999
 Non-overlapping Domain Decomposition and Heterogeneous Modeling Used in Solving Free Boundary Problems by Bin Jiang A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of
Non-overlapping Domain Decomposition and Heterogeneous Modeling Used in Solving Free Boundary Problems by Bin Jiang A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of
Nonlinear Mechanics of Monolayer Graphene Rui Huang
 Nonlinear Mechanics of Monolayer Graphene Rui Huang Center for Mechanics of Solids, Structures and Materials Department of Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics The University of Texas at Austin
Nonlinear Mechanics of Monolayer Graphene Rui Huang Center for Mechanics of Solids, Structures and Materials Department of Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics The University of Texas at Austin
EFFECT OF PILE-UP ON THE MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF STEEL WITH DIFFERENT STRAIN HISTORY BY DEPTH SENSING INDENTATION
 EFFECT OF PILE-UP ON THE MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF STEEL WITH DIFFERENT STRAIN HISTORY BY DEPTH SENSING INDENTATION Peter BURIK 1,a, Ladislav PEŠEK 2,b, Lukáš VOLESKÝ 1,c 1 Technical University of
EFFECT OF PILE-UP ON THE MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF STEEL WITH DIFFERENT STRAIN HISTORY BY DEPTH SENSING INDENTATION Peter BURIK 1,a, Ladislav PEŠEK 2,b, Lukáš VOLESKÝ 1,c 1 Technical University of
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information An Anode Buffer Layer with Size-Controlled Ag Nanoparticles for Polymer
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information An Anode Buffer Layer with Size-Controlled Ag Nanoparticles for Polymer
One-Pot Synthesis of Core-Shell-like Pt 3 Co Nanoparticle Electrocatalyst with Pt-enriched Surface for Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Fuel Cells
 Electronic Supplementary Information for One-Pot Synthesis of Core-Shell-like 3 Co Nanoparticle Electrocatalyst with -enriched Surface for Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Fuel Cells Ji-Hoon Jang b, Juyeong
Electronic Supplementary Information for One-Pot Synthesis of Core-Shell-like 3 Co Nanoparticle Electrocatalyst with -enriched Surface for Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Fuel Cells Ji-Hoon Jang b, Juyeong
Entropic Crystal-Crystal Transitions of Brownian Squares K. Zhao, R. Bruinsma, and T.G. Mason
 Entropic Crystal-Crystal Transitions of Brownian Squares K. Zhao, R. Bruinsma, and T.G. Mason This supplementary material contains the following sections: image processing methods, measurements of Brownian
Entropic Crystal-Crystal Transitions of Brownian Squares K. Zhao, R. Bruinsma, and T.G. Mason This supplementary material contains the following sections: image processing methods, measurements of Brownian
Quantum Effects and Phase Tuning in Epitaxial 2H- and 1T -MoTe 2 Monolayers
 Supplementary Information Quantum Effects and Phase Tuning in Epitaxial 2H- and 1T -MoTe 2 Monolayers Jinglei Chen, Guanyong Wang,, ǁ Yanan Tang,, Hao Tian,,# Jinpeng Xu, Xianqi Dai,, Hu Xu, # Jinfeng
Supplementary Information Quantum Effects and Phase Tuning in Epitaxial 2H- and 1T -MoTe 2 Monolayers Jinglei Chen, Guanyong Wang,, ǁ Yanan Tang,, Hao Tian,,# Jinpeng Xu, Xianqi Dai,, Hu Xu, # Jinfeng
Accuracy and transferability of GAP models for tungsten
 Accuracy and transferability of GAP models for tungsten Wojciech J. Szlachta Albert P. Bartók Gábor Csányi Engineering Laboratory University of Cambridge 5 November 214 Motivation Number of atoms 1 1 2
Accuracy and transferability of GAP models for tungsten Wojciech J. Szlachta Albert P. Bartók Gábor Csányi Engineering Laboratory University of Cambridge 5 November 214 Motivation Number of atoms 1 1 2
Question ( ) Solution. Approximate length of an atomic bond for solid aluminum.
 Question (1450001) Approximate length of an atomic bond for solid aluminum. Spring A of stiness 10 N/m is hung vertically from a ringstand. From the lower end of this spring, a dierent spring (Spring B)
Question (1450001) Approximate length of an atomic bond for solid aluminum. Spring A of stiness 10 N/m is hung vertically from a ringstand. From the lower end of this spring, a dierent spring (Spring B)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information for Manuscript: Nanoscale wear as a stress-assisted chemical reaction Supplementary Methods For each wear increment, the diamond indenter was slid laterally relative to the silicon
Supplementary Information for Manuscript: Nanoscale wear as a stress-assisted chemical reaction Supplementary Methods For each wear increment, the diamond indenter was slid laterally relative to the silicon
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
Identifying and Visualizing the Edge Terminations of Single-Layer MoSe2 Island Epitaxially Grown on Au(111)
 Supporting Information Identifying and Visualizing the Edge Terminations of Single-Layer MoSe2 Island Epitaxially Grown on Au(111) Jianchen Lu, De-Liang Bao, Kai Qian, Shuai Zhang, Hui Chen, Xiao Lin*,
Supporting Information Identifying and Visualizing the Edge Terminations of Single-Layer MoSe2 Island Epitaxially Grown on Au(111) Jianchen Lu, De-Liang Bao, Kai Qian, Shuai Zhang, Hui Chen, Xiao Lin*,
Supplementary Information for. Origin of New Broad Raman D and G Peaks in Annealed Graphene
 Supplementary Information for Origin of New Broad Raman D and G Peaks in Annealed Graphene Jinpyo Hong, Min Kyu Park, Eun Jung Lee, DaeEung Lee, Dong Seok Hwang and Sunmin Ryu* Department of Applied Chemistry,
Supplementary Information for Origin of New Broad Raman D and G Peaks in Annealed Graphene Jinpyo Hong, Min Kyu Park, Eun Jung Lee, DaeEung Lee, Dong Seok Hwang and Sunmin Ryu* Department of Applied Chemistry,
Mechanics of Structure
 S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CE/CS/CR/CV] Mechanics of Structure Time: Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 70 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following. [1] Q.1(a) Define moment of Inertia. State MI
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CE/CS/CR/CV] Mechanics of Structure Time: Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 70 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following. [1] Q.1(a) Define moment of Inertia. State MI
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017
 Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
Bursting Drops in Solids Caused by High Voltages
 Supplementary Information for Bursting Drops in Solids Caused by High Voltages Qiming Wang 1, Zhigang Suo 2 and Xuanhe Zhao 1 * 1 Soft Active Materials Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering
Supplementary Information for Bursting Drops in Solids Caused by High Voltages Qiming Wang 1, Zhigang Suo 2 and Xuanhe Zhao 1 * 1 Soft Active Materials Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering
Math 1270 Honors ODE I Fall, 2008 Class notes # 14. x 0 = F (x; y) y 0 = G (x; y) u 0 = au + bv = cu + dv
 Math 1270 Honors ODE I Fall, 2008 Class notes # 1 We have learned how to study nonlinear systems x 0 = F (x; y) y 0 = G (x; y) (1) by linearizing around equilibrium points. If (x 0 ; y 0 ) is an equilibrium
Math 1270 Honors ODE I Fall, 2008 Class notes # 1 We have learned how to study nonlinear systems x 0 = F (x; y) y 0 = G (x; y) (1) by linearizing around equilibrium points. If (x 0 ; y 0 ) is an equilibrium
Dislocation network structures in 2D bilayer system
 Dislocation network structures in 2D bilayer system Shuyang DAI School of Mathematics and Statistics Wuhan University Joint work with: Prof. Yang XIANG, HKUST Prof. David SROLOVITZ, UPENN S. Dai IMS Workshop,
Dislocation network structures in 2D bilayer system Shuyang DAI School of Mathematics and Statistics Wuhan University Joint work with: Prof. Yang XIANG, HKUST Prof. David SROLOVITZ, UPENN S. Dai IMS Workshop,
b imaging by a double tip potential
 Supplementary Figure Measurement of the sheet conductance. Resistance as a function of probe spacing including D and 3D fits. The distance is plotted on a logarithmic scale. The inset shows corresponding
Supplementary Figure Measurement of the sheet conductance. Resistance as a function of probe spacing including D and 3D fits. The distance is plotted on a logarithmic scale. The inset shows corresponding
Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Fracture of Graphene
 Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Fracture of Graphene Dewapriya M. A. N. 1, Rajapakse R. K. N. D. 1,*, Srikantha Phani A. 2 1 School of Engineering Science, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, BC, Canada
Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Fracture of Graphene Dewapriya M. A. N. 1, Rajapakse R. K. N. D. 1,*, Srikantha Phani A. 2 1 School of Engineering Science, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, BC, Canada
Performance and Control of the Agilent Nano Indenter DCM
 Performance and Control of the Agilent Nano Indenter DCM Application Note Introduction With new materials and material applications come new test challenges. As these new challenges emerge in materials
Performance and Control of the Agilent Nano Indenter DCM Application Note Introduction With new materials and material applications come new test challenges. As these new challenges emerge in materials
Supplementary Information. for. Origami based Mechanical Metamaterials
 Supplementary Information for Origami based Mechanical Metamaterials By Cheng Lv, Deepakshyam Krishnaraju, Goran Konjevod, Hongyu Yu, and Hanqing Jiang* [*] Prof. H. Jiang, C. Lv, D. Krishnaraju, Dr. G.
Supplementary Information for Origami based Mechanical Metamaterials By Cheng Lv, Deepakshyam Krishnaraju, Goran Konjevod, Hongyu Yu, and Hanqing Jiang* [*] Prof. H. Jiang, C. Lv, D. Krishnaraju, Dr. G.
Spontaneous High Piezoelectricity in Poly (vinylidene fluoride) Nanoribbons Produced by Iterative Thermal Size Reduction Technique
 Spontaneous High Piezoelectricity in Poly (vinylidene fluoride) Nanoribbons Produced by Iterative Thermal Size Reduction Technique Mehmet Kanik 1,2, Ozan Aktas 1,3, Huseyin Sener Sen 1, Engin Durgun 1,2
Spontaneous High Piezoelectricity in Poly (vinylidene fluoride) Nanoribbons Produced by Iterative Thermal Size Reduction Technique Mehmet Kanik 1,2, Ozan Aktas 1,3, Huseyin Sener Sen 1, Engin Durgun 1,2
Supplementary Figures
 Fracture Strength (GPa) Supplementary Figures a b 10 R=0.88 mm 1 0.1 Gordon et al Zhu et al Tang et al im et al 5 7 6 4 This work 5 50 500 Si Nanowire Diameter (nm) Supplementary Figure 1: (a) TEM image
Fracture Strength (GPa) Supplementary Figures a b 10 R=0.88 mm 1 0.1 Gordon et al Zhu et al Tang et al im et al 5 7 6 4 This work 5 50 500 Si Nanowire Diameter (nm) Supplementary Figure 1: (a) TEM image
Strain-engineered artificial atom as a broad-spectrum solar energy funnel
 Supplementary Information Strain-engineered artificial atom as a broad-spectrum solar energy funnel Ji Feng 1,, Xiaofeng Qian 2,, Cheng-Wei Huang 2 and Ju Li 2,3, * 1 International Center for Quantum Materials,
Supplementary Information Strain-engineered artificial atom as a broad-spectrum solar energy funnel Ji Feng 1,, Xiaofeng Qian 2,, Cheng-Wei Huang 2 and Ju Li 2,3, * 1 International Center for Quantum Materials,
Nature Protocols: doi: /nprot Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Photographs of the 3D-MTC device and the confocal fluorescence microscopy. I: The system consists of a Leica SP8-Confocal microscope (with an option of STED), a confocal PC, a 3D-MTC
Supplementary Figure 1 Photographs of the 3D-MTC device and the confocal fluorescence microscopy. I: The system consists of a Leica SP8-Confocal microscope (with an option of STED), a confocal PC, a 3D-MTC
Colloidal Particles at Liquid Interfaces: An Introduction
 1 Colloidal Particles at Liquid Interfaces: An Introduction Bernard P. Binks and Tommy S. Horozov Surfactant and Colloid Group, Department of Chemistry, University of Hull, Hull, HU6 7RX, UK 1.1 Some Basic
1 Colloidal Particles at Liquid Interfaces: An Introduction Bernard P. Binks and Tommy S. Horozov Surfactant and Colloid Group, Department of Chemistry, University of Hull, Hull, HU6 7RX, UK 1.1 Some Basic
Supplementary Figure 1: MoS2 crystals on WSe2-EG and EG and WSe2 crystals on MoSe2-EG and EG.
 Supplementary Figure 1: MoS2 crystals on WSe2-EG and EG and WSe2 crystals on MoSe2-EG and EG. (a) The MoS2 crystals cover both of EG and WSe2/EG after the CVD growth (Scar bar: 400 nm) (b) shows TEM profiles
Supplementary Figure 1: MoS2 crystals on WSe2-EG and EG and WSe2 crystals on MoSe2-EG and EG. (a) The MoS2 crystals cover both of EG and WSe2/EG after the CVD growth (Scar bar: 400 nm) (b) shows TEM profiles
