INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS
|
|
|
- Joy Baldwin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 7" IC/93/57 INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS ON THE DEBYE-HUCKEL'S THEORY Ivailo M. Mladenov INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY UNITED NATIONS EDUCATIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND CULTURAL ORGANIZATION MIRAMARE-TRIESTE
2
3 IC/93/57 International Atomic Energy Agency and United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS When one studies a many particle system in which the interaction between the constituents is strong enough -, the most simple way to account for this interaction is to use the notion of mean or molecular field. This approach has been used by Debye and Huckel [i in order to find the electrostatic component of the free energy which turns out to be equivalent to the work done for charging a sphere (macroion) ON THE DEBYE-HUCKEL'S THEORY in a solution. This electrostatic component can be expressed as an integral: = J W dq (1) Ivailo M. Mladenov * International Centre for Theoretical Physics, Trieste, Italy. ABSTRACT A one-paraineter family of perturbed Debye-Huckel's models, all sharing the inherent spherical symmetry of the classical theory, is introduced and solved in a closed form. When the deformation parameter is set equal to zero one regains the Debye-Huckel's model and results. taken over all charged parts from q = 0 to its final value. It is evident that the problem of finding W, is e I simply the fundamental problem of classical electrostatics where one tries to determine the (electrostatic) potential (field) at every point in a space for a given distribution of charges. In many such situations the ambient space is modeled as a homogeneous medium in which the potential at a distance from a point charge Q is given by Coulomb's law: = QAT (2) MIRAMARE - TRIESTE March 1993 where is the dielectric constant,a quantity that indicates the extent to which the electrostatic effect of the charge is screened by the medium. In the most general form the problem covers cases where the dielectric constant can vary in the space. In the regions of uniform dielectric constant without free charges the electrostatic potential Laplace's equation at every point r : satisfies * Permanent address: Central Laboratory of Biophysics, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Acad. G. Bonchev Str., B1.21, 1113 Sofia, Bulgaria. = 0, A = (3) r
4 If there are charges present this equation is replaced by Poisson's equation: A V( r^ = - (4 n/e)p(~r > ) (4) where p (r ) is the charge density at the point r. Solving either Laplace's or Poisgon's equation where appropriate one gets local solutions depending on integration constants. The global solution is obtained by matching different solutions at common boundaries. Using continuity of ip, i.e. V, = V 2 (5) and that of its (normal) gradient: ( d y I (6) arranges the problem with the integration constants and in this way the globalization of y is achieved. When the boundary is a charged surface with surface charge density c, (6) is replaced by: (d v / (d y / d n - 4 n a (7) It should be mentioned that analytical solutions of these equations exist only for some simple geometries and more complicated cases are treated by numerical methods. Here we shall consider the Debye - Huckel model and its modification. This modification includes the Debye - Huckel model as a special case and what is also interesting, retains its explicit solvability. The classical Debye - Huckel model is shown in Fig.1. It is assumed that the macroion of which free electrostatic energy we are interested in is a low dielectric sphere medium of radius R (region I) surrounded by a solvent with an external dielectric constant c and mobile counterions. In the low dielectric region I and in the ion exclusion region II (sphere of radius R ) we can apply the Laplace's equation, while in the high dielectric region III (which supposed to be infinite) we should apply the Poisson's equation (Fig.I). Spherical geometry means spherical symmetry which can be expressed saying that y satisfies: and consequently: is )y = 0, i, j, k = 1,2,3 (8) * = = 0 (9) We recollect that as the Laplacian operator written in spherical polar coordinates (r, 6, f) looks as follows: where 0 = - L = (1/r 2 ) d/dr(r 2 dy/dr) + (10) is its angular part. Under spherical symmetry this means that in the free of movable charges regions I and II we should solve the equation: 2 2 A y = d y/dr +(2/r)(dv/dr) =0 (11) It is easily seen that the latter is equivalent to:
5 whose solution r 2 = 0 (12) y/ = C + C /r (13) Inserting (14),(15) and (18) into (5-7) and solving the resulting linear algebraic equations specifies all integration constants A, B, B, C and in this way y. Explicitly, we have: depends on two arbitrary real constants C and C. Now, as the first region contains the singular point r = 0 (of the solution) and as we are looking for y bounded, we are forced to make the restriction c = 0, i.e. V = c in region I (U) All points in region II are regular for ^ of the farm (13) and that is why y can be written there as: if - B + S../r in region II (15) 9t ( r R ) V - (q/ 2 )e 2 /(1+*R 2 )r in region III (19) V = -*r/(1 + *R 2 )]/r in region II (20) = [1 -»R 1 /(1+*R 2 )]/R 1 in region I (21) From the mathematical point of view the equations which we are dealing here are of the so-called Bessel This name refers to the second order linear equation of the form: differential with type. The situation with the third region is quite as now we must solve the equation: At/< = d v'/dr + (2/r)(dy/dr) = * V different (16) 2 ' ' ' 2 2 x y + xy + (x -v )y = 0 (22) Here v can be an arbitrary complex number and if it ' s just an integer the function: where x is the so called Debye-Huckel parameter. This equation has solutions of the form: >/' = A e /r + A e /r (1T) Again, we should pose the second constant A = 0 in order to have only bounded solutions (this time a- infinity i >co), i.e. = Z (23) is a solution of this equation. When v is not ;m integer (u+k)! in formula (23) should be exchanged for T(u+k+1) where T is the gamma function (see e.g. [2]). J (x) and J_ (x) (defined by the same formula) form in this case a basis of solutions of (22). Actually, more close to our situation is the equation: -Mr V = A e /r in region III (18) 2 ' ' ' 2 2 xy +xy -(x + y )y = 0 (24)
6 which is known as the modified Bessel equation and whose space of solutions is spanned by: and (25) For real values of i-> and positive x these functions are real.finally, the equation: 2 ' ' ' xy +xy -(Ax + y )y = 0 (26) In fact the new angular part modifies the radial component of the Laplacian operator too. The Poisson equation turns out to be: r 2 d 2 y / d r 2 + 2r / dr) - r 2 + = 0 (30) and after some analysis the bounded solution in the third region can be written as: 1/2 2,11/2 /2 (31) has a basis of solutions given by: I (Xx) and I. (Xx), V K (27) The respective bounded solutions in the regions I and II are represented by: in terms of which we shall express our results. Now, we go on to explain the modification of the Debye-Huckel's theory mentioned before. We will furnish this by a revision of the spherical symmetry of the underlying model. In analytical form this symmetry has been expressed as the properties of the momentum operators (see (9)). On the other hand these operators are connected with the Poisson brackets among canonical coordinates in the phase space. If we deform them in a smooth and explicit way as described below: (32) and (33) Placing as before these solutions into (5-7) and solving the so obtained algebraic equations we fix the integration constants A(v), B(IJ), BAV) and C(i->).In order to keep their explicit expressions transparent it seems that the following notations are useful: (x\x j } = 0, {p., x j }= 6\, (p., p.} = -(Ai/r 3 ). jk x k (28) (34) we should change also the momentum operators (see T31 for more details at this point). Fortunately, they are simply related to the old ones. -2v (35) (36) M = L + as well M 2 = L 2 + (29) (2U+1)/2 I (37)
7 With the help of the preceding the integration constants as follows: notation we can write References: B(v) = = 2q(V(v) (v) = 2q/WU') i (38) (39) (40) (41) 1. P.Debye, E.Huckel, Phys.Z. 24, 185 (1923). 2. E.Whittaker, G.Watson, Modern Analysis, Cambridge Univ. Press, I.Mladenov, Int.J.Theor.Phys. 28, 1255 (1989). 4. C.Tanford, J.Kirkwood, JACS. 79, 5333 (1957). A few remarks are in order here. First of all when we let /J -> O,i.e. v -> \/2 any of these functions goes smoothly to the value prescribed by the classical Debye-Huckel's theory. Next, besides p, a new free parameter is at our disposal in the solutions (26-28). This is the dielectric constant c which can certainly be equated to e, but our opinion is that it must be saved different in order to make the transition from low to high dielectric regions more realistic from the physical point of view. Finally,the possibility of parallel to the Tanford-Kirkwood theory 4] development of our results is obvious. We hope to report on this subject elsewhere. \ ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The author would like to thank Professor Abdus Salani, the International Atomic Energy Agency and UNESCO for hospitality at the International Centre for Theoretical Physics, Trieste. This viork was partially supported by the Bulgarian National Science Foundation Project No.K - Z02/92. Pig.l Geometry and Regions I, II, III of the Debye-Huckel Model. 10 1
8 .».»<'Aj»«i.
we1 = j+dq + = &/ET, (2)
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Europhys. Lett., 24 (S), pp. 693-698 (1993) 10 December 1993 On Debye-Huckel s Theory. I. M. MLADENOV Central Laboratory of Biophysics, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Acad. G. Bonchev
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Europhys. Lett., 24 (S), pp. 693-698 (1993) 10 December 1993 On Debye-Huckel s Theory. I. M. MLADENOV Central Laboratory of Biophysics, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Acad. G. Bonchev
Dielectrics. Lecture 20: Electromagnetic Theory. Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay
 What are dielectrics? Dielectrics Lecture 20: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay So far we have been discussing electrostatics in either vacuum or in a conductor.
What are dielectrics? Dielectrics Lecture 20: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay So far we have been discussing electrostatics in either vacuum or in a conductor.
1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian. which is given in spherical coordinates by (2)
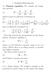 1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian operator (1) 2 = 2 x + 2 2 y + 2 2 z 2 which is given in spherical coordinates by (2) 2 = 1 ( r 2 ) + 1 r 2 r r r 2 sin θ θ and in
1. Poisson-Boltzmann 1.1. Poisson equation. We consider the Laplacian operator (1) 2 = 2 x + 2 2 y + 2 2 z 2 which is given in spherical coordinates by (2) 2 = 1 ( r 2 ) + 1 r 2 r r r 2 sin θ θ and in
Lecture 13: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay. Poisson s and Laplace s Equations
 Poisson s and Laplace s Equations Lecture 13: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay We will spend some time in looking at the mathematical foundations of electrostatics.
Poisson s and Laplace s Equations Lecture 13: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay We will spend some time in looking at the mathematical foundations of electrostatics.
d 1 µ 2 Θ = 0. (4.1) consider first the case of m = 0 where there is no azimuthal dependence on the angle φ.
 4 Legendre Functions In order to investigate the solutions of Legendre s differential equation d ( µ ) dθ ] ] + l(l + ) m dµ dµ µ Θ = 0. (4.) consider first the case of m = 0 where there is no azimuthal
4 Legendre Functions In order to investigate the solutions of Legendre s differential equation d ( µ ) dθ ] ] + l(l + ) m dµ dµ µ Θ = 0. (4.) consider first the case of m = 0 where there is no azimuthal
Solutions to Laplace s Equations- II
 Solutions to Laplace s Equations- II Lecture 15: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay Laplace s Equation in Spherical Coordinates : In spherical coordinates
Solutions to Laplace s Equations- II Lecture 15: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay Laplace s Equation in Spherical Coordinates : In spherical coordinates
Quantum Orbits. Quantum Theory for the Computer Age Unit 9. Diving orbit. Caustic. for KE/PE =R=-3/8. for KE/PE =R=-3/8. p"...
 W.G. Harter Coulomb Obits 6-1 Quantum Theory for the Computer Age Unit 9 Caustic for KE/PE =R=-3/8 F p' p g r p"... P F' F P Diving orbit T" T T' Contact Pt. for KE/PE =R=-3/8 Quantum Orbits W.G. Harter
W.G. Harter Coulomb Obits 6-1 Quantum Theory for the Computer Age Unit 9 Caustic for KE/PE =R=-3/8 F p' p g r p"... P F' F P Diving orbit T" T T' Contact Pt. for KE/PE =R=-3/8 Quantum Orbits W.G. Harter
Center for Theoretical Physics, Department of Applied Physics, Twente University, P.O. Box 217, 7500 AE Enschede, The Netherlands
 Physica A 193 (1993) 413-420 North-Holland Distribution of ions around a charged sphere P. Strating and F.W. Wiegel Center for Theoretical Physics, Department of Applied Physics, Twente University, P.O.
Physica A 193 (1993) 413-420 North-Holland Distribution of ions around a charged sphere P. Strating and F.W. Wiegel Center for Theoretical Physics, Department of Applied Physics, Twente University, P.O.
Physics 342 Lecture 23. Radial Separation. Lecture 23. Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I
 Physics 342 Lecture 23 Radial Separation Lecture 23 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, March 26th, 2010 We begin our spherical solutions with the simplest possible case zero potential. Aside from
Physics 342 Lecture 23 Radial Separation Lecture 23 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, March 26th, 2010 We begin our spherical solutions with the simplest possible case zero potential. Aside from
Summary: Curvilinear Coordinates
 Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2007, Lecture 10 1 Summary: Curvilinear Coordinates 1. Summary of Integral Theorems 2. Generalized Coordinates 3. Cartesian Coordinates: Surfaces of Constant
Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2007, Lecture 10 1 Summary: Curvilinear Coordinates 1. Summary of Integral Theorems 2. Generalized Coordinates 3. Cartesian Coordinates: Surfaces of Constant
CHAPTER 3 POTENTIALS 10/13/2016. Outlines. 1. Laplace s equation. 2. The Method of Images. 3. Separation of Variables. 4. Multipole Expansion
 CHAPTER 3 POTENTIALS Lee Chow Department of Physics University of Central Florida Orlando, FL 32816 Outlines 1. Laplace s equation 2. The Method of Images 3. Separation of Variables 4. Multipole Expansion
CHAPTER 3 POTENTIALS Lee Chow Department of Physics University of Central Florida Orlando, FL 32816 Outlines 1. Laplace s equation 2. The Method of Images 3. Separation of Variables 4. Multipole Expansion
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND RELATIVISTIC PARTICLES
 ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND RELATIVISTIC PARTICLES Emil J. Konopinski Professor of Physics Indiana University McGraw-Hill Book Company New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Hamburg Johannesburg
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS AND RELATIVISTIC PARTICLES Emil J. Konopinski Professor of Physics Indiana University McGraw-Hill Book Company New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Hamburg Johannesburg
l=0 The expansion coefficients can be determined, for example, by finding the potential on the z-axis and expanding that result in z.
 Electrodynamics I Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 15/11/6 Name Electrodynamic Score = 14 / 14 points Instructions: Use SI units. Where appropriate, define all variables or symbols you use, in words. Try
Electrodynamics I Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 15/11/6 Name Electrodynamic Score = 14 / 14 points Instructions: Use SI units. Where appropriate, define all variables or symbols you use, in words. Try
Dielectrics - III. Lecture 22: Electromagnetic Theory. Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay
 Dielectrics - III Lecture 22: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay We continue with our discussion of dielectric medium. Example : Dielectric Sphere in a uniform
Dielectrics - III Lecture 22: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay We continue with our discussion of dielectric medium. Example : Dielectric Sphere in a uniform
Two special equations: Bessel s and Legendre s equations. p Fourier-Bessel and Fourier-Legendre series. p
 LECTURE 1 Table of Contents Two special equations: Bessel s and Legendre s equations. p. 259-268. Fourier-Bessel and Fourier-Legendre series. p. 453-460. Boundary value problems in other coordinate system.
LECTURE 1 Table of Contents Two special equations: Bessel s and Legendre s equations. p. 259-268. Fourier-Bessel and Fourier-Legendre series. p. 453-460. Boundary value problems in other coordinate system.
which implies that we can take solutions which are simultaneous eigen functions of
 Module 1 : Quantum Mechanics Chapter 6 : Quantum mechanics in 3-D Quantum mechanics in 3-D For most physical systems, the dynamics is in 3-D. The solutions to the general 3-d problem are quite complicated,
Module 1 : Quantum Mechanics Chapter 6 : Quantum mechanics in 3-D Quantum mechanics in 3-D For most physical systems, the dynamics is in 3-D. The solutions to the general 3-d problem are quite complicated,
INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS
 IC/90/124.-- INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS CENTRIFUGAL FORCE IN ERNST SPACETIME A.R.Prasanna INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY UNITED NATIONS EDUCATIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND CULTURAL ORGANIZATION
IC/90/124.-- INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS CENTRIFUGAL FORCE IN ERNST SPACETIME A.R.Prasanna INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY UNITED NATIONS EDUCATIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND CULTURAL ORGANIZATION
1 Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations
 March 3, 203 6-6. Systems of Linear Equations Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations An m n matrix is an array A = a ij of the form a a n a 2 a 2n... a m a mn where each a ij is a real or complex number.
March 3, 203 6-6. Systems of Linear Equations Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations An m n matrix is an array A = a ij of the form a a n a 2 a 2n... a m a mn where each a ij is a real or complex number.
. (70.1) r r. / r. Substituting, we have the following equation for f:
 7 Spherical waves Let us consider a sound wave in which the distribution of densit velocit etc, depends only on the distance from some point, ie, is spherically symmetrical Such a wave is called a spherical
7 Spherical waves Let us consider a sound wave in which the distribution of densit velocit etc, depends only on the distance from some point, ie, is spherically symmetrical Such a wave is called a spherical
M2A2 Problem Sheet 3 - Hamiltonian Mechanics
 MA Problem Sheet 3 - Hamiltonian Mechanics. The particle in a cone. A particle slides under gravity, inside a smooth circular cone with a vertical axis, z = k x + y. Write down its Lagrangian in a) Cartesian,
MA Problem Sheet 3 - Hamiltonian Mechanics. The particle in a cone. A particle slides under gravity, inside a smooth circular cone with a vertical axis, z = k x + y. Write down its Lagrangian in a) Cartesian,
Hations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization INTERNATIONAL CEHTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS
 r ^ IC/7V6T / y REFERENCE (Limited INTERNAL distribution) REPORT t-~ : i t,.ul i-j' "! -,., \ct- \,- International Atomic Energy Agency and Hations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization INTERNATIONAL
r ^ IC/7V6T / y REFERENCE (Limited INTERNAL distribution) REPORT t-~ : i t,.ul i-j' "! -,., \ct- \,- International Atomic Energy Agency and Hations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization INTERNATIONAL
Chapter 2. Electrostatics. Introduction to Electrodynamics, 3 rd or 4 rd Edition, David J. Griffiths
 Chapter 2. Electrostatics Introduction to Electrodynamics, 3 rd or 4 rd Edition, David J. Griffiths 2.3 Electric Potential 2.3.1 Introduction to Potential E 0 We're going to reduce a vector problem (finding
Chapter 2. Electrostatics Introduction to Electrodynamics, 3 rd or 4 rd Edition, David J. Griffiths 2.3 Electric Potential 2.3.1 Introduction to Potential E 0 We're going to reduce a vector problem (finding
Average Electrostatic Potential over a Spherical Surface
 Average Electrostatic Potential over a Spherical Surface EE 141 Lecture Notes Topic 8 Professor K. E. Oughstun School of Engineering College of Engineering & Mathematical Sciences University of Vermont
Average Electrostatic Potential over a Spherical Surface EE 141 Lecture Notes Topic 8 Professor K. E. Oughstun School of Engineering College of Engineering & Mathematical Sciences University of Vermont
Curvilinear coordinates
 C Curvilinear coordinates The distance between two points Euclidean space takes the simplest form (2-4) in Cartesian coordinates. The geometry of concrete physical problems may make non-cartesian coordinates
C Curvilinear coordinates The distance between two points Euclidean space takes the simplest form (2-4) in Cartesian coordinates. The geometry of concrete physical problems may make non-cartesian coordinates
Theoretische Physik 2: Elektrodynamik (Prof. A-S. Smith) Home assignment 11
 WiSe 22..23 Prof. Dr. A-S. Smith Dipl.-Phys. Matthias Saba am Lehrstuhl für Theoretische Physik I Department für Physik Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg Problem. Theoretische Physik 2:
WiSe 22..23 Prof. Dr. A-S. Smith Dipl.-Phys. Matthias Saba am Lehrstuhl für Theoretische Physik I Department für Physik Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg Problem. Theoretische Physik 2:
Gauss s Law. Name. I. The Law: , where ɛ 0 = C 2 (N?m 2
 Name Gauss s Law I. The Law:, where ɛ 0 = 8.8510 12 C 2 (N?m 2 1. Consider a point charge q in three-dimensional space. Symmetry requires the electric field to point directly away from the charge in all
Name Gauss s Law I. The Law:, where ɛ 0 = 8.8510 12 C 2 (N?m 2 1. Consider a point charge q in three-dimensional space. Symmetry requires the electric field to point directly away from the charge in all
Schwarzschild s Metrical Model of a Liquid Sphere
 Schwarzschild s Metrical Model of a Liquid Sphere N.S. Baaklini nsbqft@aol.com Abstract We study Schwarzschild s metrical model of an incompressible (liquid) sphere of constant density and note the tremendous
Schwarzschild s Metrical Model of a Liquid Sphere N.S. Baaklini nsbqft@aol.com Abstract We study Schwarzschild s metrical model of an incompressible (liquid) sphere of constant density and note the tremendous
CS 542G: The Poisson Problem, Finite Differences
 CS 542G: The Poisson Problem, Finite Differences Robert Bridson November 10, 2008 1 The Poisson Problem At the end last time, we noticed that the gravitational potential has a zero Laplacian except at
CS 542G: The Poisson Problem, Finite Differences Robert Bridson November 10, 2008 1 The Poisson Problem At the end last time, we noticed that the gravitational potential has a zero Laplacian except at
Classical Field Theory: Electrostatics-Magnetostatics
 Classical Field Theory: Electrostatics-Magnetostatics April 27, 2010 1 1 J.D.Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd Edition, Section 1-5 Electrostatics The behavior of an electrostatic field can be described
Classical Field Theory: Electrostatics-Magnetostatics April 27, 2010 1 1 J.D.Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd Edition, Section 1-5 Electrostatics The behavior of an electrostatic field can be described
Hypersingular Integrals and Their Applications
 Hypersingular Integrals and Their Applications Stefan G. Samko Rostov State University, Russia and University ofalgarve, Portugal London and New York Contents Preface xv Notation 1 Part 1. Hypersingular
Hypersingular Integrals and Their Applications Stefan G. Samko Rostov State University, Russia and University ofalgarve, Portugal London and New York Contents Preface xv Notation 1 Part 1. Hypersingular
Lecture 3. Solving the Non-Relativistic Schroedinger Equation for a spherically symmetric potential
 Lecture 3 Last lecture we were in the middle of deriving the energies of the bound states of the Λ in the nucleus. We will continue with solving the non-relativistic Schroedinger equation for a spherically
Lecture 3 Last lecture we were in the middle of deriving the energies of the bound states of the Λ in the nucleus. We will continue with solving the non-relativistic Schroedinger equation for a spherically
Introduction. Chapter Plasma: definitions
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Plasma: definitions A plasma is a quasi-neutral gas of charged and neutral particles which exhibits collective behaviour. An equivalent, alternative definition: A plasma is a
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Plasma: definitions A plasma is a quasi-neutral gas of charged and neutral particles which exhibits collective behaviour. An equivalent, alternative definition: A plasma is a
2 Voltage Potential Due to an Arbitrary Charge Distribution
 Solution to the Static Charge Distribution on a Thin Wire Using the Method of Moments James R Nagel Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah April 2, 202
Solution to the Static Charge Distribution on a Thin Wire Using the Method of Moments James R Nagel Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah April 2, 202
Electromagnetic Field Theory (EMT)
 Electromagnetic Field Theory (EMT) Lecture # 9 1) Coulomb s Law and Field Intensity 2) Electric Fields Due to Continuous Charge Distributions Line Charge Surface Charge Volume Charge Coulomb's Law Coulomb's
Electromagnetic Field Theory (EMT) Lecture # 9 1) Coulomb s Law and Field Intensity 2) Electric Fields Due to Continuous Charge Distributions Line Charge Surface Charge Volume Charge Coulomb's Law Coulomb's
1 Differentiable manifolds and smooth maps. (Solutions)
 1 Differentiable manifolds and smooth maps Solutions Last updated: March 17 2011 Problem 1 The state of the planar pendulum is entirely defined by the position of its moving end in the plane R 2 Since
1 Differentiable manifolds and smooth maps Solutions Last updated: March 17 2011 Problem 1 The state of the planar pendulum is entirely defined by the position of its moving end in the plane R 2 Since
Duality between constraints and gauge conditions
 Duality between constraints and gauge conditions arxiv:hep-th/0504220v2 28 Apr 2005 M. Stoilov Institute of Nuclear Research and Nuclear Energy, Sofia 1784, Bulgaria E-mail: mstoilov@inrne.bas.bg 24 April
Duality between constraints and gauge conditions arxiv:hep-th/0504220v2 28 Apr 2005 M. Stoilov Institute of Nuclear Research and Nuclear Energy, Sofia 1784, Bulgaria E-mail: mstoilov@inrne.bas.bg 24 April
Exam 1 Solutions. Note that there are several variations of some problems, indicated by choices in parentheses. Problem 1
 Exam 1 Solutions Note that there are several variations of some problems, indicated by choices in parentheses. Problem 1 A rod of charge per unit length λ is surrounded by a conducting, concentric cylinder
Exam 1 Solutions Note that there are several variations of some problems, indicated by choices in parentheses. Problem 1 A rod of charge per unit length λ is surrounded by a conducting, concentric cylinder
Equations of linear stellar oscillations
 Chapter 4 Equations of linear stellar oscillations In the present chapter the equations governing small oscillations around a spherical equilibrium state are derived. The general equations were presented
Chapter 4 Equations of linear stellar oscillations In the present chapter the equations governing small oscillations around a spherical equilibrium state are derived. The general equations were presented
Distribution of induced charge
 E&M Lecture 10 Topics: (1)Distribution of induced charge on conducting plate (2)Total surface induced charge on plate (3)Point charge near grounded conducting sphere (4)Point charge near floating conducting
E&M Lecture 10 Topics: (1)Distribution of induced charge on conducting plate (2)Total surface induced charge on plate (3)Point charge near grounded conducting sphere (4)Point charge near floating conducting
Self-consistent Field
 Chapter 6 Self-consistent Field A way to solve a system of many electrons is to consider each electron under the electrostatic field generated by all other electrons. The many-body problem is thus reduced
Chapter 6 Self-consistent Field A way to solve a system of many electrons is to consider each electron under the electrostatic field generated by all other electrons. The many-body problem is thus reduced
1. Electricity and Magnetism (Fall 1995, Part 1) A metal sphere has a radius R and a charge Q.
 1. Electricity and Magnetism (Fall 1995, Part 1) A metal sphere has a radius R and a charge Q. (a) Compute the electric part of the Maxwell stress tensor T ij (r) = 1 {E i E j 12 } 4π E2 δ ij both inside
1. Electricity and Magnetism (Fall 1995, Part 1) A metal sphere has a radius R and a charge Q. (a) Compute the electric part of the Maxwell stress tensor T ij (r) = 1 {E i E j 12 } 4π E2 δ ij both inside
Physics (
 Exercises Question 2: Two charges 5 0 8 C and 3 0 8 C are located 6 cm apart At what point(s) on the line joining the two charges is the electric potential zero? Take the potential at infinity to be zero
Exercises Question 2: Two charges 5 0 8 C and 3 0 8 C are located 6 cm apart At what point(s) on the line joining the two charges is the electric potential zero? Take the potential at infinity to be zero
ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS I. CODE: 10 MAT 11 IA Marks: 25 Hrs/Week: 04 Exam Hrs: 03 PART-A
 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS I CODE: 10 MAT 11 IA Marks: 25 Hrs/Week: 04 Exam Hrs: 03 Total Hrs: 52 Exam Marks:100 PART-A Unit-I: DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS - 1 Determination of n th derivative of standard functions-illustrative
ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS I CODE: 10 MAT 11 IA Marks: 25 Hrs/Week: 04 Exam Hrs: 03 Total Hrs: 52 Exam Marks:100 PART-A Unit-I: DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS - 1 Determination of n th derivative of standard functions-illustrative
ON THE SPECTRUM OF THE GEODESIC FLOW ON SPHERES Sofia, Bulgaria,
 ON THE SPECTRUM OF THE GEODESIC FLOW ON SPHERES Ivailo M. Mladenovl and Vasil V. Tsanov2 1 Central Labora.tory of Biophysics, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Acad. G. Bonchev Str., B1.21, 1113 Sofia, Bulgaria
ON THE SPECTRUM OF THE GEODESIC FLOW ON SPHERES Ivailo M. Mladenovl and Vasil V. Tsanov2 1 Central Labora.tory of Biophysics, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Acad. G. Bonchev Str., B1.21, 1113 Sofia, Bulgaria
The 3 dimensional Schrödinger Equation
 Chapter 6 The 3 dimensional Schrödinger Equation 6.1 Angular Momentum To study how angular momentum is represented in quantum mechanics we start by reviewing the classical vector of orbital angular momentum
Chapter 6 The 3 dimensional Schrödinger Equation 6.1 Angular Momentum To study how angular momentum is represented in quantum mechanics we start by reviewing the classical vector of orbital angular momentum
1 Superfluidity and Bose Einstein Condensate
 Physics 223b Lecture 4 Caltech, 04/11/18 1 Superfluidity and Bose Einstein Condensate 1.6 Superfluid phase: topological defect Besides such smooth gapless excitations, superfluid can also support a very
Physics 223b Lecture 4 Caltech, 04/11/18 1 Superfluidity and Bose Einstein Condensate 1.6 Superfluid phase: topological defect Besides such smooth gapless excitations, superfluid can also support a very
Velocities in Quantum Mechanics
 Velocities in Quantum Mechanics Toshiki Shimbori and Tsunehiro Kobayashi Institute of Physics, University of Tsukuba Ibaraki 305-8571, Japan Department of General Education for the Hearing Impaired, Tsukuba
Velocities in Quantum Mechanics Toshiki Shimbori and Tsunehiro Kobayashi Institute of Physics, University of Tsukuba Ibaraki 305-8571, Japan Department of General Education for the Hearing Impaired, Tsukuba
Chapter 4. Electric Fields in Matter
 Chapter 4. Electric Fields in Matter 4.1.2 Induced Dipoles What happens to a neutral atom when it is placed in an electric field E? The atom now has a tiny dipole moment p, in the same direction as E.
Chapter 4. Electric Fields in Matter 4.1.2 Induced Dipoles What happens to a neutral atom when it is placed in an electric field E? The atom now has a tiny dipole moment p, in the same direction as E.
Elements of Vector Calculus : Line and Surface Integrals
 Elements of Vector Calculus : Line and Surface Integrals Lecture 2: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay In this lecture we will talk about special functions
Elements of Vector Calculus : Line and Surface Integrals Lecture 2: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay In this lecture we will talk about special functions
1 Potential due to a charged wire/sheet
 Lecture XXX Renormalization, Regularization and Electrostatics Let us calculate the potential due to an infinitely large object, e.g. a uniformly charged wire or a uniformly charged sheet. Our main interest
Lecture XXX Renormalization, Regularization and Electrostatics Let us calculate the potential due to an infinitely large object, e.g. a uniformly charged wire or a uniformly charged sheet. Our main interest
free space (vacuum) permittivity [ F/m]
![free space (vacuum) permittivity [ F/m] free space (vacuum) permittivity [ F/m]](/thumbs/79/79624275.jpg) Electrostatic Fields Electrostatic fields are static (time-invariant) electric fields produced by static (stationary) charge distributions. The mathematical definition of the electrostatic field is derived
Electrostatic Fields Electrostatic fields are static (time-invariant) electric fields produced by static (stationary) charge distributions. The mathematical definition of the electrostatic field is derived
4 Power Series Solutions: Frobenius Method
 4 Power Series Solutions: Frobenius Method Now the ODE adventure takes us to series solutions for ODEs, a technique A & W, that is often viable, valuable and informative. These can be readily applied Sec.
4 Power Series Solutions: Frobenius Method Now the ODE adventure takes us to series solutions for ODEs, a technique A & W, that is often viable, valuable and informative. These can be readily applied Sec.
Physics 606, Quantum Mechanics, Final Exam NAME ( ) ( ) + V ( x). ( ) and p( t) be the corresponding operators in ( ) and x( t) : ( ) / dt =...
 Physics 606, Quantum Mechanics, Final Exam NAME Please show all your work. (You are graded on your work, with partial credit where it is deserved.) All problems are, of course, nonrelativistic. 1. Consider
Physics 606, Quantum Mechanics, Final Exam NAME Please show all your work. (You are graded on your work, with partial credit where it is deserved.) All problems are, of course, nonrelativistic. 1. Consider
ROTATIONAL STABILITY OF A CHARGED DIELEC- TRIC RIGID BODY IN A UNIFORM MAGNETIC FIELD
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 11, 103 11, 009 ROTATIONAL STABILITY OF A CHARGED DIELEC- TRIC RIGID BODY IN A UNIFORM MAGNETIC FIELD G.-Q. Zhou Department of Physics Wuhan University
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 11, 103 11, 009 ROTATIONAL STABILITY OF A CHARGED DIELEC- TRIC RIGID BODY IN A UNIFORM MAGNETIC FIELD G.-Q. Zhou Department of Physics Wuhan University
A*'i. "i-**^ International Atomic Energy Agency and United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization
 ^ \.- / &\ ic/73/89 Slip. AUG B/3 X\ INTERNAL REPORT S \!.-'/ (Limited distribution) A*'i. "i-**^ International Atomic Energy Agency and United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization
^ \.- / &\ ic/73/89 Slip. AUG B/3 X\ INTERNAL REPORT S \!.-'/ (Limited distribution) A*'i. "i-**^ International Atomic Energy Agency and United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization
Electrostatic and other basic interactions of remote particles
 Electrostatic and other basic interactions of remote particles Elena F. Grekova elgreco@pdmi.ras.ru ing of the Russian Academy of Sciences, St. Petersburg Foreign member of the group Electrohydrodynamics
Electrostatic and other basic interactions of remote particles Elena F. Grekova elgreco@pdmi.ras.ru ing of the Russian Academy of Sciences, St. Petersburg Foreign member of the group Electrohydrodynamics
PDEs, part 1: Introduction and elliptic PDEs
 PDEs, part 1: Introduction and elliptic PDEs Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2013 Partial di erential equations The solution depends on several variables,
PDEs, part 1: Introduction and elliptic PDEs Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2013 Partial di erential equations The solution depends on several variables,
PHY752, Fall 2016, Assigned Problems
 PHY752, Fall 26, Assigned Problems For clarification or to point out a typo (or worse! please send email to curtright@miami.edu [] Find the URL for the course webpage and email it to curtright@miami.edu
PHY752, Fall 26, Assigned Problems For clarification or to point out a typo (or worse! please send email to curtright@miami.edu [] Find the URL for the course webpage and email it to curtright@miami.edu
Elastic Scattering. R = m 1r 1 + m 2 r 2 m 1 + m 2. is the center of mass which is known to move with a constant velocity (see previous lectures):
 Elastic Scattering In this section we will consider a problem of scattering of two particles obeying Newtonian mechanics. The problem of scattering can be viewed as a truncated version of dynamic problem
Elastic Scattering In this section we will consider a problem of scattering of two particles obeying Newtonian mechanics. The problem of scattering can be viewed as a truncated version of dynamic problem
Illustrating Dynamical Symmetries in Classical Mechanics: The Laplace-Runge-Lenz Vector Revisited
 Illustrating Dynamical Symmetries in Classical Mechanics: The Laplace-Runge-Lenz Vector Revisited Ross C. O Connell and Kannan Jagannathan Physics Department, Amherst College Amherst, MA 01002-5000 Abstract
Illustrating Dynamical Symmetries in Classical Mechanics: The Laplace-Runge-Lenz Vector Revisited Ross C. O Connell and Kannan Jagannathan Physics Department, Amherst College Amherst, MA 01002-5000 Abstract
Theory of Electromagnetic Fields
 Theory of Electromagnetic Fields Andrzej Wolski University of Liverpool, and the Cockcroft Institute, UK Abstract We discuss the theory of electromagnetic fields, with an emphasis on aspects relevant to
Theory of Electromagnetic Fields Andrzej Wolski University of Liverpool, and the Cockcroft Institute, UK Abstract We discuss the theory of electromagnetic fields, with an emphasis on aspects relevant to
18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. V7. Laplace's Equation and
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. V7. Laplace's Equation and
The Charged Liquid Drop Model Binding Energy and Fission
 The Charged Liquid Drop Model Binding Energy and Fission 103 This is a simple model for the binding energy of a nucleus This model is also important to understand fission and how energy is obtained from
The Charged Liquid Drop Model Binding Energy and Fission 103 This is a simple model for the binding energy of a nucleus This model is also important to understand fission and how energy is obtained from
Junior-level Electrostatics Content Review
 Junior-level Electrostatics Content Review Please fill out the following exam to the best of your ability. This will not count towards your final grade in the course. Do your best to get to all the questions
Junior-level Electrostatics Content Review Please fill out the following exam to the best of your ability. This will not count towards your final grade in the course. Do your best to get to all the questions
Potential & Potential Energy
 Potential & Potential Energy Lecture 10: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay Electrostatic Boundary Conditions : We had seen that electric field has a discontinuity
Potential & Potential Energy Lecture 10: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay Electrostatic Boundary Conditions : We had seen that electric field has a discontinuity
Chem 467 Supplement to Lecture 19 Hydrogen Atom, Atomic Orbitals
 Chem 467 Supplement to Lecture 19 Hydrogen Atom, Atomic Orbitals Pre-Quantum Atomic Structure The existence of atoms and molecules had long been theorized, but never rigorously proven until the late 19
Chem 467 Supplement to Lecture 19 Hydrogen Atom, Atomic Orbitals Pre-Quantum Atomic Structure The existence of atoms and molecules had long been theorized, but never rigorously proven until the late 19
INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS
 IC/94/195 INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS A PHASE-TRANSITION INDUCED BY THE STRUGGLE FOR LIFE IN A COMPETITIVE COEXISTENCE MODEL IN ECOLOGY Horacio S. Wio and M.N. Kuperman INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC
IC/94/195 INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS A PHASE-TRANSITION INDUCED BY THE STRUGGLE FOR LIFE IN A COMPETITIVE COEXISTENCE MODEL IN ECOLOGY Horacio S. Wio and M.N. Kuperman INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC
SIMULATION OF CORONA DISCHARGE IN CONFIGURATIONS WITH A SHARP ELECTRODE
 Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials Vol. 6, No. 3, September 004, p. 103-108 SIMULATION OF CORONA DISCHARGE IN CONFIGURATIONS WITH A SHARP ELECTRODE P Atten a*, K. Adamiak b, B. Khaddour
Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials Vol. 6, No. 3, September 004, p. 103-108 SIMULATION OF CORONA DISCHARGE IN CONFIGURATIONS WITH A SHARP ELECTRODE P Atten a*, K. Adamiak b, B. Khaddour
THE HYDROGEN ATOM ACCORDING TO WAVE MECHANICS IN CARTESIAN COORDINATES
 THE HYDROGEN ATOM ACCORDING TO WAVE MECHANICS IN CARTESIAN COORDINATES J. F. Ogilvie Centre for Experimental and Constructive Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, British
THE HYDROGEN ATOM ACCORDING TO WAVE MECHANICS IN CARTESIAN COORDINATES J. F. Ogilvie Centre for Experimental and Constructive Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, British
Magnetized Material (contd.) and Electromagnetic Induction
 Magnetized Material (contd.) and Electromagnetic Induction Lecture 28: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay In the first half of this lecture we will continue
Magnetized Material (contd.) and Electromagnetic Induction Lecture 28: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay In the first half of this lecture we will continue
Electric Field Lines
 Electric Field Lines Electric forces Electric fields: - Electric field lines emanate from positive charges - Electric field lines disappear at negative charges If you see a bunch of field lines emanating
Electric Field Lines Electric forces Electric fields: - Electric field lines emanate from positive charges - Electric field lines disappear at negative charges If you see a bunch of field lines emanating
Representation theory and quantum mechanics tutorial Spin and the hydrogen atom
 Representation theory and quantum mechanics tutorial Spin and the hydrogen atom Justin Campbell August 3, 2017 1 Representations of SU 2 and SO 3 (R) 1.1 The following observation is long overdue. Proposition
Representation theory and quantum mechanics tutorial Spin and the hydrogen atom Justin Campbell August 3, 2017 1 Representations of SU 2 and SO 3 (R) 1.1 The following observation is long overdue. Proposition
1 Assignment 1: Nonlinear dynamics (due September
 Assignment : Nonlinear dynamics (due September 4, 28). Consider the ordinary differential equation du/dt = cos(u). Sketch the equilibria and indicate by arrows the increase or decrease of the solutions.
Assignment : Nonlinear dynamics (due September 4, 28). Consider the ordinary differential equation du/dt = cos(u). Sketch the equilibria and indicate by arrows the increase or decrease of the solutions.
Linear Algebra and Eigenproblems
 Appendix A A Linear Algebra and Eigenproblems A working knowledge of linear algebra is key to understanding many of the issues raised in this work. In particular, many of the discussions of the details
Appendix A A Linear Algebra and Eigenproblems A working knowledge of linear algebra is key to understanding many of the issues raised in this work. In particular, many of the discussions of the details
Systems of Linear Equations
 LECTURE 6 Systems of Linear Equations You may recall that in Math 303, matrices were first introduced as a means of encapsulating the essential data underlying a system of linear equations; that is to
LECTURE 6 Systems of Linear Equations You may recall that in Math 303, matrices were first introduced as a means of encapsulating the essential data underlying a system of linear equations; that is to
The Basic Definition of Flux
 The Basic Definition of Flux Imagine holding a rectangular wire loop of area A in front of a fan. The volume of air flowing through the loop each second depends on the angle between the loop and the direction
The Basic Definition of Flux Imagine holding a rectangular wire loop of area A in front of a fan. The volume of air flowing through the loop each second depends on the angle between the loop and the direction
Chapter 9: Multi- Electron Atoms Ground States and X- ray Excitation
 Chapter 9: Multi- Electron Atoms Ground States and X- ray Excitation Up to now we have considered one-electron atoms. Almost all atoms are multiple-electron atoms and their description is more complicated
Chapter 9: Multi- Electron Atoms Ground States and X- ray Excitation Up to now we have considered one-electron atoms. Almost all atoms are multiple-electron atoms and their description is more complicated
QUASI-LINEAR THEORY OF THE LOSS-CONE INSTABILITY
 IC/66/92 INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS QUASI-LINEAR THEORY OF THE LOSS-CONE INSTABILITY A. A. GALEEV 1966 PIAZZA OBERDAN TRIESTE IC/66/92 International
IC/66/92 INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS QUASI-LINEAR THEORY OF THE LOSS-CONE INSTABILITY A. A. GALEEV 1966 PIAZZA OBERDAN TRIESTE IC/66/92 International
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 15: Galaxy Interactions
 ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 15: Galaxy Interactions Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 Galaxy Interactions & Transformations In this lecture we discuss galaxy interactions
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 15: Galaxy Interactions Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 Galaxy Interactions & Transformations In this lecture we discuss galaxy interactions
INTRODUCTION TO FINITE ELEMENT METHODS ON ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LONG CHEN
 INTROUCTION TO FINITE ELEMENT METHOS ON ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LONG CHEN CONTENTS 1. Poisson Equation 1 2. Outline of Topics 3 2.1. Finite ifference Method 3 2.2. Finite Element Method 3 2.3. Finite Volume
INTROUCTION TO FINITE ELEMENT METHOS ON ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LONG CHEN CONTENTS 1. Poisson Equation 1 2. Outline of Topics 3 2.1. Finite ifference Method 3 2.2. Finite Element Method 3 2.3. Finite Volume
Chapter 18. Remarks on partial differential equations
 Chapter 8. Remarks on partial differential equations If we try to analyze heat flow or vibration in a continuous system such as a building or an airplane, we arrive at a kind of infinite system of ordinary
Chapter 8. Remarks on partial differential equations If we try to analyze heat flow or vibration in a continuous system such as a building or an airplane, we arrive at a kind of infinite system of ordinary
Electrodynamics I Midterm - Part A - Closed Book KSU 2005/10/17 Electro Dynamic
 Electrodynamics I Midterm - Part A - Closed Book KSU 5//7 Name Electro Dynamic. () Write Gauss Law in differential form. E( r) =ρ( r)/ɛ, or D = ρ, E= electricfield,ρ=volume charge density, ɛ =permittivity
Electrodynamics I Midterm - Part A - Closed Book KSU 5//7 Name Electro Dynamic. () Write Gauss Law in differential form. E( r) =ρ( r)/ɛ, or D = ρ, E= electricfield,ρ=volume charge density, ɛ =permittivity
1 Differentiable manifolds and smooth maps. (Solutions)
 1 Differentiable manifolds and smooth maps Solutions Last updated: February 16 2012 Problem 1 a The projection maps a point P x y S 1 to the point P u 0 R 2 the intersection of the line NP with the x-axis
1 Differentiable manifolds and smooth maps Solutions Last updated: February 16 2012 Problem 1 a The projection maps a point P x y S 1 to the point P u 0 R 2 the intersection of the line NP with the x-axis
-RIGID SOLUTION OF THE BOHR HAMILTONIAN FOR = 30 COMPARED TO THE E(5) CRITICAL POINT SYMMETRY
 Dedicated to Acad. Aureliu Sãndulescu s 75th Anniversary -RIGID SOLUTION OF THE BOHR HAMILTONIAN FOR = 30 COMPARED TO THE E(5) CRITICAL POINT SYMMETRY DENNIS BONATSOS 1, D. LENIS 1, D. PETRELLIS 1, P.
Dedicated to Acad. Aureliu Sãndulescu s 75th Anniversary -RIGID SOLUTION OF THE BOHR HAMILTONIAN FOR = 30 COMPARED TO THE E(5) CRITICAL POINT SYMMETRY DENNIS BONATSOS 1, D. LENIS 1, D. PETRELLIS 1, P.
ON SPECTRAL FUNCTIONS SUM RULES
 IC/68/61 INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS ON SPECTRAL FUNCTIONS SUM RULES C. G. BOLLINI AND J. J. GIAMBIAGI 1968 MIRAMARE - TRIESTE IC/68/01 INTERNATIONAL
IC/68/61 INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS ON SPECTRAL FUNCTIONS SUM RULES C. G. BOLLINI AND J. J. GIAMBIAGI 1968 MIRAMARE - TRIESTE IC/68/01 INTERNATIONAL
Selected Topics in Mathematical Physics Prof. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Selected Topics in Mathematical Physics Prof. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 11 Lecture - 29 Green Function for (Del Squared plus K Squared): Nonrelativistic
Selected Topics in Mathematical Physics Prof. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 11 Lecture - 29 Green Function for (Del Squared plus K Squared): Nonrelativistic
Density Functional Theory. Martin Lüders Daresbury Laboratory
 Density Functional Theory Martin Lüders Daresbury Laboratory Ab initio Calculations Hamiltonian: (without external fields, non-relativistic) impossible to solve exactly!! Electrons Nuclei Electron-Nuclei
Density Functional Theory Martin Lüders Daresbury Laboratory Ab initio Calculations Hamiltonian: (without external fields, non-relativistic) impossible to solve exactly!! Electrons Nuclei Electron-Nuclei
Quasi-geostrophic ocean models
 Quasi-geostrophic ocean models March 19, 2002 1 Introduction The starting point for theoretical and numerical study of the three dimensional large-scale circulation of the atmosphere and ocean is a vorticity
Quasi-geostrophic ocean models March 19, 2002 1 Introduction The starting point for theoretical and numerical study of the three dimensional large-scale circulation of the atmosphere and ocean is a vorticity
3 Green s functions in 2 and 3D
 William J. Parnell: MT34032. Section 3: Green s functions in 2 and 3 57 3 Green s functions in 2 and 3 Unlike the one dimensional case where Green s functions can be found explicitly for a number of different
William J. Parnell: MT34032. Section 3: Green s functions in 2 and 3 57 3 Green s functions in 2 and 3 Unlike the one dimensional case where Green s functions can be found explicitly for a number of different
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization and International Atomic Energy Agency
 Available at: http://publications.ictp.it IC /2010/046 United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization and International Atomic Energy Agency THE ABDUS SALAM INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL
Available at: http://publications.ictp.it IC /2010/046 United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization and International Atomic Energy Agency THE ABDUS SALAM INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL
FLUX OF VECTOR FIELD INTRODUCTION
 Chapter 3 GAUSS LAW ntroduction Flux of vector field Solid angle Gauss s Law Symmetry Spherical symmetry Cylindrical symmetry Plane symmetry Superposition of symmetric geometries Motion of point charges
Chapter 3 GAUSS LAW ntroduction Flux of vector field Solid angle Gauss s Law Symmetry Spherical symmetry Cylindrical symmetry Plane symmetry Superposition of symmetric geometries Motion of point charges
2 Structure. 2.1 Coulomb interactions
 2 Structure 2.1 Coulomb interactions While the information needed for reproduction of living systems is chiefly maintained in the sequence of macromolecules, any practical use of this information must
2 Structure 2.1 Coulomb interactions While the information needed for reproduction of living systems is chiefly maintained in the sequence of macromolecules, any practical use of this information must
Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap. 2, 3, and 4, and Di Bartolo, Chap. 2. 2π nx i a. ( ) = G n.
 Chapter. Electrostatic II Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap.,, and 4, and Di Bartolo, Chap... Mathematical Considerations.. The Fourier series and the Fourier
Chapter. Electrostatic II Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap.,, and 4, and Di Bartolo, Chap... Mathematical Considerations.. The Fourier series and the Fourier
Physics 342 Lecture 22. The Hydrogen Atom. Lecture 22. Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I
 Physics 342 Lecture 22 The Hydrogen Atom Lecture 22 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, March 28th, 2008 We now begin our discussion of the Hydrogen atom. Operationally, this is just another choice
Physics 342 Lecture 22 The Hydrogen Atom Lecture 22 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, March 28th, 2008 We now begin our discussion of the Hydrogen atom. Operationally, this is just another choice
Spherical Coordinates and Legendre Functions
 Spherical Coordinates and Legendre Functions Spherical coordinates Let s adopt the notation for spherical coordinates that is standard in physics: φ = longitude or azimuth, θ = colatitude ( π 2 latitude)
Spherical Coordinates and Legendre Functions Spherical coordinates Let s adopt the notation for spherical coordinates that is standard in physics: φ = longitude or azimuth, θ = colatitude ( π 2 latitude)
the m abdus salam international centre for theoretical physics
 the m abdus salam international centre for theoretical physics K/98/211 ITERATIVE SOLUTION OF EQUATIONS INVOLVING K-p.d. OPERATORS C.E. Chidume Chika Moore Available at: http : //WV. ictp. trieste. it/-pub-
the m abdus salam international centre for theoretical physics K/98/211 ITERATIVE SOLUTION OF EQUATIONS INVOLVING K-p.d. OPERATORS C.E. Chidume Chika Moore Available at: http : //WV. ictp. trieste. it/-pub-
Motion under the Influence of a Central Force
 Copyright 004 5 Motion under the Influence of a Central Force The fundamental forces of nature depend only on the distance from the source. All the complex interactions that occur in the real world arise
Copyright 004 5 Motion under the Influence of a Central Force The fundamental forces of nature depend only on the distance from the source. All the complex interactions that occur in the real world arise
Chapter 4. Electrostatic Fields in Matter
 Chapter 4. Electrostatic Fields in Matter 4.1. Polarization 4.2. The Field of a Polarized Object 4.3. The Electric Displacement 4.4. Linear Dielectrics 4.5. Energy in dielectric systems 4.6. Forces on
Chapter 4. Electrostatic Fields in Matter 4.1. Polarization 4.2. The Field of a Polarized Object 4.3. The Electric Displacement 4.4. Linear Dielectrics 4.5. Energy in dielectric systems 4.6. Forces on
13 Spherical Coordinates
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Foundations of Wave Phenomena Library Digital Monographs 8-204 3 Spherical Coordinates Charles G. Torre Department of Physics, Utah State University, Charles.Torre@usu.edu
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Foundations of Wave Phenomena Library Digital Monographs 8-204 3 Spherical Coordinates Charles G. Torre Department of Physics, Utah State University, Charles.Torre@usu.edu
Laplace s Equation in Cylindrical Coordinates and Bessel s Equation (I)
 Laplace s Equation in Cylindrical Coordinates and Bessel s Equation I) 1 Solution by separation of variables Laplace s equation is a key equation in Mathematical Physics. Several phenomena involving scalar
Laplace s Equation in Cylindrical Coordinates and Bessel s Equation I) 1 Solution by separation of variables Laplace s equation is a key equation in Mathematical Physics. Several phenomena involving scalar
