IMAGE PROCESSING OF ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY DATA TO ESTIMATE TEXTURAL SCALES AND ANISOTROPY IN SHALES
|
|
|
- Meryl Murphy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IMAGE PROCESSING OF ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY DATA TO ESTIMATE TEXTURAL SCALES AND ANISOTROPY IN SHALES T. Mukerji 1 and M. Prasad 2 1 Stanford University and 2 Colorado School of Mines Abstract: Key words: We estimate different statistical measures for quantifying heterogeneity and textures from scanning acoustic microscope images of shale microstructures. The analyzed shales covered a range of depths, kerogen content, and maturity. We observed quantifiable and consistent patterns linking texture, shale maturity, and elastic P-wave impedance. The textural heterogeneity and P- wave impedance and velocity, and density increase with increasing maturity (decreasing kerogen content), while there is a general decrease in textural anisotropy with maturity. We also found a reasonably good match between elastic impedance estimated from SAM images and impedance computed from ultrasonic measurements. The textural anisotropy ranges from 10% to about 70% and tends to decrease with increasing depth and maturity. Kerogen shales, acoustic microscopy, Image processing, Fourier transform 1. INTRODUCTION Microgeometry plays an important role in the overall effective elastic properties of shales. Therefore characterizing and understanding the microgeometry, their textures, scales, and textural anisotropy is important for better understanding the effect of microgeometry on effective elastic properties. Microstructural characteristics of organic rich shales can give important insights on the maturation processes and on oil generation from such formations (Vernik and Nur, 1994). Optical and scanning electron
2 2 T. Mukerji1 and M. Prasad2 microscopy methods to analyze kerogen shale microstructure have been utilized in the past. However, due to the opaque nature of the kerogen and the associated pyrite, such methods are rather difficult to implement. For example, studies have shown that microgeometry, textural heterogeneity, and textural anisotropy have significant effects on the effective elastic properties of rocks. On the other hand, Prasad et al. (2002) have shown we can map textural changes with shale maturity with acoustic microscopy. 2. METHODS The acoustic images were made with an acoustic microscope and image analyses techniques are used to detect changes in texture and heterogeneity in these images. 2.1 Acoustic Microscopy We used a non-destructive technique to map the impedance microstructure of kerogen-rich shales with a Scanning Acoustic Microscope. The C-scan surface images were made at 1 GHz. With this technique we were able to map changes in elastic properties as the shales undergo maturation. The method and sample description and impedance measurement on a micrometer-scale is given in detail in Prasad et al. (2002). 2.2 Image Processing The heterogeneity was quantified by the coefficient of variation (CV, standard deviation/ mean) of the image pixel values. Textures were quantified using spatial autocorrelation functions. We used Fourier transform based autocorrelation estimation. Radial profiles of the autocorrelation function along azimuths ranging from 0 o to 180 o were computed, and the correlation length estimated at each azimuth. The texture anisotropy was quantified by the anisotropy ratio (AR) defined as the ratio between the maximum and minimum correlation lengths obtained over all azimuths. We used statistical descriptors to quantify the heterogeneity and textures observed in the images. The heterogeneity was quantified by the coefficient of variation (CV) given by the ratio of the standard deviation to the mean of the image pixel values. Spatial textures can be quantified using spatial autocorrelation functions R(m,n). As an example, Fig. 1 shows how a smoothly varying image has a broad, slowly decaying autocorrelation function. In contrast a rough salt-and-pepper image has a very narrow spiky autocorrelation function.
3 IMAGE PROCESSING OF ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY DATA TO ESTIMATE TEXTURAL SCALES AND ANISOTROPY IN SHALES 3 Figure 1. Relation between the autocorrelation function and synthetic images. We used Fourier transform based autocorrelation estimation where 1 R( m, n) F S( kx, * S( kx, I ( kx, I ( kx, I ( kx, F[ I( x, y)] In the above equations I(x,y) denotes the image intensity, while F and F -1 denote the forward and inverse Fourier transforms. The 2-d Fourier transform of the image I(x,y) is denoted by I ( kx, where kx, ky are the spatial wavenumbers in the Fourier domain. The power spectrum S(kx, is obtained by multiplying I ( kx, with its complex conjugate. Finally the 2- d ACF R(m,n) is obtained by taking the inverse Fourier transform of S. In Fig. 2, the synthetic textures image is shown on the left and its corresponding 2-d autocorrelation function (ACF) is on the right. Peak intensity is the autocorrelation at zero lag distance (maximum) and decays away on all sides with increasing lag. The rate of decay is a quantitative measure of texture. Radial profiles of the autocorrelation function along azimuths ranging from 0 to 180 degrees were computed by interpolation along the different directions, and the correlation length estimated at each azimuth. This analysis, shown in Fig. 3, allowed us to quantify the azimuthal changes in ACF due to textural anisotropy. As Fig. 3 shows, the correlation length at each azimuth is taken to be the lag value where the correlation function falls to 1/e of its maximum value at zero lag. The texture anisotropy was quantified by the anisotropy ratio (AR) defined as the ratio between the maximum and minimum correlation lengths obtained over all azimuths. All 180 ACF profiles are plotted in Fig. 3. Figure 4 and 5 show examples of actual shale SAM images and corresponding radial profiles of the ACF.
4 4 T. Mukerji1 and M. Prasad2 Figure 2. Synthetic textures and their two-dimensional ACF Figure 3. Radial profiles of the 2D autocorrelation along all azimuths from 0 o to 180 o. Figure 4. C-scan images made at 1 GHz with the Scanning Acoustic Microscope (SAM).
5 IMAGE PROCESSING OF ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY DATA TO ESTIMATE TEXTURAL SCALES AND ANISOTROPY IN SHALES 5 Figure 5. Radial profiles of the ACF from 0 to 180 for the SAM images in Figure 8. Thus, we define three parameters for textural analysis: The Coefficient of Variation (CV) that describes textural heterogeneity. A larger contrast of heterogeneity leads to high values of CV The Anisotropy Ratio (AR) that describes the textural anisotropy. Textural anisotropy leads to a directional dependence of the ACF. The Mean Correlation Length that describes textural scale in the images. Larger sized heterogeneities lead to longer correlation lengths In the following, we present analysis of all the shales. 3. RESULTS This paper shows how can we quantify textural changes and relate them to maturation and ultrasonic properties of Vp, density, and impedance. Of the dataset used in Prasad et al. (2002), we have analyzed 3 shales: Bakken, Bazhenov, and Woodford. These are organic rich shales with varying amounts of kerogen content, at different maturation stages, and from different depths. We analyzed over 280 SAM images takes at different scales ranging between ~0.1 1mm image size and ~0.2 ~2µm pixel resolution. 3.1 Image Processing Results The results of texture analyses are discussed below and shown in the following figures. The data points plotted in the figures are averages over multiple samples, with one standard deviation bars around the estimated
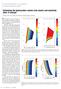
6 6 T. Mukerji1 and M. Prasad2 average. The coefficient of variation (CV) of the impedance heterogeneities ranged from about 7% to 12%. The mean correlation length ranged from 2 to 10 microns while the textural anisotropy ratio ranged from 1.1 to 1.7 (10% to 70%). We will examine the patterns between textural anisotropy and mean correlation length (Fig. 6), and between textural heterogeneity and correlation length (Fig. 7). We will also see how these patterns change with depth and maturity. Figure 6. Mean correlation length as a function of textural anisotropy (AR). Woodford shale are shown as circles; Bazhenov shale as triangles; and Bakken shale as squares. In general, textural anisotropy (AR) increases with increasing mean correlation length (Fig. 6). With depth (= maturity), textural anisotropy increase is lower while the mean correlation length increase is larger. Deeper samples have lower anisotropy but larger heterogeneities. This trend can be sub-divided further within each set. For example, in Bakken shales, the AR vs. mean correlation length trend steepens with depth; that is, textural anisotropy decreases while mean correlation length increases as we go from shallow (less mature) to deeper (more mature) shales. Increasing Maturity Figure 7. Mean correlation length as a function of textural heterogeneity (AR).
7 Coef. of variability Coef. of variability IMAGE PROCESSING OF ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY DATA TO ESTIMATE TEXTURAL SCALES AND ANISOTROPY IN SHALES 7 The textural heterogeneity and mean correlation length show a enechelon correlation pattern when we plot the Bakken samples seperated by depths (Fig. 7). For each depth we see a negative trend between heterogeneity and correlation length, but overall there is a trend of increasing heterogeneity and correlation length with increasing depth and maturity. This is consistent with the observed trend of increasing heterogeneity (CV) with decreasing kerogen content and total organic content (TOC) (Fig. 8) TOC (%) Increasing maturity Volumetric kerogen content Increasing maturity Figure 8. Coefficient of variability (textural heterogeneity) increases with decreasing kerogen content and total organic content. 3.2 Correlations with other measurements A satisfying match was obtained between P-wave impedance derived from the SAM images and the corresponding impedance from ultrasonic data on core samples (Fig. 9). Fig. 9 shows the ultrasonic impedance derived from measured V P along both the fast and the slow directions (small dots), along with the SAM impedance (large red and orange dots) for Bakken shales. Elastic impedance, density and textural heterogeneity all increase with increasing maturity (Fig. 9). 4. DISCUSSION / CONCLUSIONS Our analysis of textural parameters of SAM images from Bakken, Bazhenov, and Woodford shales showed quantifiable and consistent patterns linking texture, shale maturity process, and elastic P-wave impedance. Image derived impedances matched reasonably well with impedances estimated from ultrasonic data. The coefficient of variation, CV, (textural heterogeneity) ranges from 7% to about 12% for these samples. Textural
8 Impedance (Mrayls) 8 T. Mukerji1 and M. Prasad2 heterogeneity, elastic impedance, P-wave velocity, and density all tend to increase with increasing shale maturity. The mean spatial correlation length generally tends to increase with increasing heterogeneity. The textural anisotropy (AR) ranges from 10% to about 70% and tends to decrease with increasing depth and maturity Hydrogen Index Increasing maturity Figure 9. Consistency between P-wave impedance from SAM images (large red and orange spots) and impedance estimated from ultrasonic data (small dots). Ultrasonic data is from Vernik and Nur, 1994). Impedance shows a general increase with increasing shale maturity (from Prasad et al., 2002). ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We acknowledge the support of the sponsors of the Stanford Rock Physics Project. This work was performed under the auspices of the National Science Foundation (Grant No. EAR ) and the U. S. Department of Energy (Award No. DE-FC26-01BC15354). M.P. also acknowledges support from the sponsors of the Colorado School of Mines - University of Houston Fluids / DHI Consortium. REFERENCES Prasad, M., Reinstaedler, M., Nur, A., Arnold, W., 2002, Quantitative acoustic microscopy: Applications to petrophysical studies of reservoir rocks: Acoustical Imaging 25, Kluver Publications. Vernik L. and Nur, 1994; Ultrasonic velocity and anisotropy of hydrocarbon source rocks: Geophysics, 57, no. 5,
IMPEDANCE MICROSTRUCTURE OF KEROGEN SHALES
 IMPEDANCE MICROSTRUCTURE OF KEROGEN SHALES Manika Prasad Rock Abuse Laboratory Colorado School of Mines Presented at the 27th Oil Shale Symposium at CSM on October 17, 2007 OUTLINE Motivation Working Principles
IMPEDANCE MICROSTRUCTURE OF KEROGEN SHALES Manika Prasad Rock Abuse Laboratory Colorado School of Mines Presented at the 27th Oil Shale Symposium at CSM on October 17, 2007 OUTLINE Motivation Working Principles
THE EFFECT OF CEMENTATION ON THE SEISMIC PROPERTIES OF SANDSTONE:
 THE EFFECT OF CEMENTATION ON THE SEISMIC PROPERTIES OF SANDSTONE: Xavier Du Bernard, Manika Prasad, Michael Reinstaedtler * 1. INTRODUCTION Composition and cementation are two major parameters that control
THE EFFECT OF CEMENTATION ON THE SEISMIC PROPERTIES OF SANDSTONE: Xavier Du Bernard, Manika Prasad, Michael Reinstaedtler * 1. INTRODUCTION Composition and cementation are two major parameters that control
Summary. Simple model for kerogen maturity (Carcione, 2000)
 Malleswar Yenugu* and De-hua Han, University of Houston, USA Summary The conversion of kerogen to oil/gas will build up overpressure. Overpressure is caused by conversion of solid kerogen to fluid hydrocarbons
Malleswar Yenugu* and De-hua Han, University of Houston, USA Summary The conversion of kerogen to oil/gas will build up overpressure. Overpressure is caused by conversion of solid kerogen to fluid hydrocarbons
P314 Anisotropic Elastic Modelling for Organic Shales
 P314 Anisotropic Elastic Modelling for Organic Shales X. Wu* (British Geological Survey), M. Chapman (British Geological Survey), X.Y. Li (British Geological Survey) & H. Dai (British Geological Survey)
P314 Anisotropic Elastic Modelling for Organic Shales X. Wu* (British Geological Survey), M. Chapman (British Geological Survey), X.Y. Li (British Geological Survey) & H. Dai (British Geological Survey)
Petrophysical Study of Shale Properties in Alaska North Slope
 Petrophysical Study of Shale Properties in Alaska North Slope Minh Tran Tapan Mukerji Energy Resources Engineering Department Stanford University, CA, USA Region of Interest 1.5 miles 20 miles Stratigraphic
Petrophysical Study of Shale Properties in Alaska North Slope Minh Tran Tapan Mukerji Energy Resources Engineering Department Stanford University, CA, USA Region of Interest 1.5 miles 20 miles Stratigraphic
SPE Copyright 2009, Society of Petroleum Engineers
 SPE 123531 Maturity and Impedance Analysis of Organic-Rich Shales Manika Prasad, SPE, Kenechukwu C. Mba, SPE, T. Elizabeth McEvoy, and Michael L. Batzle, SPE, Colorado School of Mines Copyright 29, Society
SPE 123531 Maturity and Impedance Analysis of Organic-Rich Shales Manika Prasad, SPE, Kenechukwu C. Mba, SPE, T. Elizabeth McEvoy, and Michael L. Batzle, SPE, Colorado School of Mines Copyright 29, Society
Rock Physics of Shales and Source Rocks. Gary Mavko Professor of Geophysics Director, Stanford Rock Physics Project
 Rock Physics of Shales and Source Rocks Gary Mavko Professor of Geophysics Director, Stanford Rock Physics Project 1 First Question: What is Shale? Shale -- a rock composed of mud-sized particles, such
Rock Physics of Shales and Source Rocks Gary Mavko Professor of Geophysics Director, Stanford Rock Physics Project 1 First Question: What is Shale? Shale -- a rock composed of mud-sized particles, such
Rock Physics of Organic Shale and Its Implication
 Rock Physics of Organic Shale and Its Implication Lev Vernik, Marathon Oil Corporation, Houston, USA lvernik@marathonoil.com Yulia Khadeeva, Marathon Oil Corporation, Houston, USA Cris Tuttle, Marathon
Rock Physics of Organic Shale and Its Implication Lev Vernik, Marathon Oil Corporation, Houston, USA lvernik@marathonoil.com Yulia Khadeeva, Marathon Oil Corporation, Houston, USA Cris Tuttle, Marathon
Geophysical and geomechanical rock property templates for source rocks Malleswar Yenugu, Ikon Science Americas, USA
 Malleswar Yenugu, Ikon Science Americas, USA Summary Sweet spot identification for source rocks involve detection of organic rich, high porous facies combined with brittleness, which is prone for hydraulic
Malleswar Yenugu, Ikon Science Americas, USA Summary Sweet spot identification for source rocks involve detection of organic rich, high porous facies combined with brittleness, which is prone for hydraulic
Geophysical and geomechanical rock property templates for source rocks Malleswar Yenugu, Ikon Science Americas, USA
 Geophysical and geomechanical rock property templates for source rocks Malleswar Yenugu, Ikon Science Americas, USA Summary Sweet spot identification for source rocks involve detection of organic rich,
Geophysical and geomechanical rock property templates for source rocks Malleswar Yenugu, Ikon Science Americas, USA Summary Sweet spot identification for source rocks involve detection of organic rich,
Geophysical model response in a shale gas
 Geophysical model response in a shale gas Dhananjay Kumar and G. Michael Hoversten Chevron USA Inc. Abstract Shale gas is an important asset now. The production from unconventional reservoir like shale
Geophysical model response in a shale gas Dhananjay Kumar and G. Michael Hoversten Chevron USA Inc. Abstract Shale gas is an important asset now. The production from unconventional reservoir like shale
Reliability of Seismic Data for Hydrocarbon Reservoir Characterization
 Reliability of Seismic Data for Hydrocarbon Reservoir Characterization Geetartha Dutta (gdutta@stanford.edu) December 10, 2015 Abstract Seismic data helps in better characterization of hydrocarbon reservoirs.
Reliability of Seismic Data for Hydrocarbon Reservoir Characterization Geetartha Dutta (gdutta@stanford.edu) December 10, 2015 Abstract Seismic data helps in better characterization of hydrocarbon reservoirs.
Measurement of elastic properties of kerogen Fuyong Yan, De-hua Han*, Rock Physics Lab, University of Houston
 Measurement of elastic properties of kerogen Fuyong Yan, De-hua Han*, Rock Physics Lab, University of Houston Summary To have good understanding of elastic properties of organic shale, it is fundamental
Measurement of elastic properties of kerogen Fuyong Yan, De-hua Han*, Rock Physics Lab, University of Houston Summary To have good understanding of elastic properties of organic shale, it is fundamental
Workflows for Sweet Spots Identification in Shale Plays Using Seismic Inversion and Well Logs
 Workflows for Sweet Spots Identification in Shale Plays Using Seismic Inversion and Well Logs Yexin Liu*, SoftMirrors Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada yexinliu@softmirrors.com Summary Worldwide interest
Workflows for Sweet Spots Identification in Shale Plays Using Seismic Inversion and Well Logs Yexin Liu*, SoftMirrors Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada yexinliu@softmirrors.com Summary Worldwide interest
BPM37 Linking Basin Modeling with Seismic Attributes through Rock Physics
 BPM37 Linking Basin Modeling with Seismic Attributes through Rock Physics W. AlKawai* (Stanford University), T. Mukerji (Stanford University) & S. Graham (Stanford University) SUMMARY In this study, we
BPM37 Linking Basin Modeling with Seismic Attributes through Rock Physics W. AlKawai* (Stanford University), T. Mukerji (Stanford University) & S. Graham (Stanford University) SUMMARY In this study, we
Characterization of Heterogeneities in Carbonates Ravi Sharma* and Manika Prasad, Colorado School of Mines
 Characterization of Heterogeneities in Carbonates Ravi Sharma* and Manika Prasad, Colorado School of Mines Summary Heterogeneity in carbonate rock is the principal reason for its improper characterization
Characterization of Heterogeneities in Carbonates Ravi Sharma* and Manika Prasad, Colorado School of Mines Summary Heterogeneity in carbonate rock is the principal reason for its improper characterization
Seismic reservoir and source-rock analysis using inverse rock-physics modeling: A Norwegian Sea demonstration
 66 Seismic reservoir and source-rock analysis using inverse rock-physics modeling: A Norwegian Sea demonstration Kenneth Bredesen 1, Erling Hugo Jensen 1, 2, Tor Arne Johansen 1, 2, and Per Avseth 3, 4
66 Seismic reservoir and source-rock analysis using inverse rock-physics modeling: A Norwegian Sea demonstration Kenneth Bredesen 1, Erling Hugo Jensen 1, 2, Tor Arne Johansen 1, 2, and Per Avseth 3, 4
Best practices predicting unconventional reservoir quality
 Introduction Best practices predicting unconventional reservoir quality Cristian Malaver, Michel Kemper, and Jorg Herwanger 1 Unconventional reservoirs have proven challenging for quantitative interpretation
Introduction Best practices predicting unconventional reservoir quality Cristian Malaver, Michel Kemper, and Jorg Herwanger 1 Unconventional reservoirs have proven challenging for quantitative interpretation
QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF SEISMIC RESPONSE TO TOTAL-ORGANIC-CONTENT AND THERMAL MATURITY IN SHALE GAS PLAYS
 E: infoikonscience.com W: www.ikonscience.com QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF SEISMIC RESPONSE TO TOTAL-ORGANIC-CONTENT AND THERMAL MATURITY IN SHALE GAS PLAYS Ebrahim Zadeh 12, Reza Rezaee 1, Michel Kemper 2
E: infoikonscience.com W: www.ikonscience.com QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF SEISMIC RESPONSE TO TOTAL-ORGANIC-CONTENT AND THERMAL MATURITY IN SHALE GAS PLAYS Ebrahim Zadeh 12, Reza Rezaee 1, Michel Kemper 2
Estimation of shale reservoir properties based on anisotropic rock physics modelling
 Estimation of shale reservoir properties based on anisotropic rock physics modelling K. Qian* (China University of Petroleum,Beijing), F. Zhang (China University of Petroleum,Beijing), X.Y. Li (British
Estimation of shale reservoir properties based on anisotropic rock physics modelling K. Qian* (China University of Petroleum,Beijing), F. Zhang (China University of Petroleum,Beijing), X.Y. Li (British
Constraining seismic rock-property logs in organic shale reservoirs
 Constraining seismic rock-property logs in organic shale reservoirs Malleswar Yenugu 1 and Lev Vernik 2 Abstract One of the major challenges of unconventional shale reservoirs is to understand the effects
Constraining seismic rock-property logs in organic shale reservoirs Malleswar Yenugu 1 and Lev Vernik 2 Abstract One of the major challenges of unconventional shale reservoirs is to understand the effects
RP 2.7. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 1525
 Manika Prasad, Ronny Hofmann, Mike Batzle, Colorado School of Mines; M. Kopycinska-Müller, U. Rabe, and W. Arnold, Fraunhofer Institute for Nondestructive Testing, IZFP, Saarbrücken Summary Seismic wave
Manika Prasad, Ronny Hofmann, Mike Batzle, Colorado School of Mines; M. Kopycinska-Müller, U. Rabe, and W. Arnold, Fraunhofer Institute for Nondestructive Testing, IZFP, Saarbrücken Summary Seismic wave
Shaly Sand Rock Physics Analysis and Seismic Inversion Implication
 Shaly Sand Rock Physics Analysis and Seismic Inversion Implication Adi Widyantoro (IkonScience), Matthew Saul (IkonScience/UWA) Rock physics analysis of reservoir elastic properties often assumes homogeneity
Shaly Sand Rock Physics Analysis and Seismic Inversion Implication Adi Widyantoro (IkonScience), Matthew Saul (IkonScience/UWA) Rock physics analysis of reservoir elastic properties often assumes homogeneity
Oil Shale Research - 1 -
 - 1 - Organic-Rich Shale Maturity: Velocity and Impedance Study of Bakken Shale Samples Kene Mba 1.0 Executive Summary Bakken Shale core samples and log data were analyzed for variations in velocity, mineralogy
- 1 - Organic-Rich Shale Maturity: Velocity and Impedance Study of Bakken Shale Samples Kene Mba 1.0 Executive Summary Bakken Shale core samples and log data were analyzed for variations in velocity, mineralogy
Enhanced Formation Evaluation of Shales Using NMR Secular Relaxation*
 Enhanced Formation Evaluation of Shales Using NMR Secular Relaxation* Hugh Daigle 1, Andrew Johnson 1, Jameson P. Gips 1, and Mukul Sharma 1 Search and Discovery Article #41411 (2014)** Posted August 11,
Enhanced Formation Evaluation of Shales Using NMR Secular Relaxation* Hugh Daigle 1, Andrew Johnson 1, Jameson P. Gips 1, and Mukul Sharma 1 Search and Discovery Article #41411 (2014)** Posted August 11,
Lithology Evaluation of Bazhenov Formation Reservoir using Seismic and Well Log Analysis
 Lithology Evaluation of Bazhenov Formation Reservoir using Seismic and Well Log Analysis N Y Lomakina Petroleum Learning Centre Tomsk Polytechnic University Tomsk, Russia Abstract Bazhenov formation is
Lithology Evaluation of Bazhenov Formation Reservoir using Seismic and Well Log Analysis N Y Lomakina Petroleum Learning Centre Tomsk Polytechnic University Tomsk, Russia Abstract Bazhenov formation is
Ingrain has digital rock physics labs in Houston and Abu Dhabi
 SCAL in Shale Ingrain has digital rock physics labs in Houston and Abu Dhabi Ingrain Labs Ingrain Sales Offices Over 4000 rock samples processed and 125 commercial jobs have been completed in the past
SCAL in Shale Ingrain has digital rock physics labs in Houston and Abu Dhabi Ingrain Labs Ingrain Sales Offices Over 4000 rock samples processed and 125 commercial jobs have been completed in the past
A shale rock physics model for analysis of brittleness index, mineralogy, and porosity in the Barnett Shale
 1 2 A shale rock physics model for analysis of brittleness index, mineralogy, and porosity in the Barnett Shale 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Zhiqi Guo 1, Xiang-Yang Li 2,3, Cai Liu 1, Xuan Feng 1, and Ye Shen 4 1 Jilin
1 2 A shale rock physics model for analysis of brittleness index, mineralogy, and porosity in the Barnett Shale 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Zhiqi Guo 1, Xiang-Yang Li 2,3, Cai Liu 1, Xuan Feng 1, and Ye Shen 4 1 Jilin
ROCK PHYSICS DIAGNOSTICS OF NORTH SEA SANDS: LINK BETWEEN MICROSTRUCTURE AND SEISMIC PROPERTIES ABSTRACT
 ROCK PHYSICS DIAGNOSTICS OF NORTH SEA SANDS: LINK BETWEEN MICROSTRUCTURE AND SEISMIC PROPERTIES PER AVSETH, JACK DVORKIN, AND GARY MAVKO Department of Geophysics, Stanford University, CA 94305-2215, USA
ROCK PHYSICS DIAGNOSTICS OF NORTH SEA SANDS: LINK BETWEEN MICROSTRUCTURE AND SEISMIC PROPERTIES PER AVSETH, JACK DVORKIN, AND GARY MAVKO Department of Geophysics, Stanford University, CA 94305-2215, USA
We apply a rock physics analysis to well log data from the North-East Gulf of Mexico
 Rock Physics for Fluid and Porosity Mapping in NE GoM JACK DVORKIN, Stanford University and Rock Solid Images TIM FASNACHT, Anadarko Petroleum Corporation RICHARD UDEN, MAGGIE SMITH, NAUM DERZHI, AND JOEL
Rock Physics for Fluid and Porosity Mapping in NE GoM JACK DVORKIN, Stanford University and Rock Solid Images TIM FASNACHT, Anadarko Petroleum Corporation RICHARD UDEN, MAGGIE SMITH, NAUM DERZHI, AND JOEL
The Shale Spectrum: Interdisciplinary understanding across oil shale, oil-bearing shale and gas shale plays
 The Center for Oil Shale Technology & Research & The Colorado School of Mines 31sᵗOil Shale Symposium October 17-21, 2011 at the Cecil H. & Ida Green Center, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, Colorado
The Center for Oil Shale Technology & Research & The Colorado School of Mines 31sᵗOil Shale Symposium October 17-21, 2011 at the Cecil H. & Ida Green Center, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, Colorado
Uncertainties in rock pore compressibility and effects on time lapse seismic modeling An application to Norne field
 Uncertainties in rock pore compressibility and effects on time lapse seismic modeling An application to Norne field Amit Suman and Tapan Mukerji Department of Energy Resources Engineering Stanford University
Uncertainties in rock pore compressibility and effects on time lapse seismic modeling An application to Norne field Amit Suman and Tapan Mukerji Department of Energy Resources Engineering Stanford University
An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks
 An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks YONGYI LI, Paradigm Geophysical, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Clastic sediments, particularly shale, exhibit transverse isotropic
An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks YONGYI LI, Paradigm Geophysical, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Clastic sediments, particularly shale, exhibit transverse isotropic
SUMMARY INTRODUCTION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
 Frequency dependent elastic properties and attenuation in heavy-oil sands: comparison between measured and modeled data Agnibha Das, and Michael Batzle, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY We have measured
Frequency dependent elastic properties and attenuation in heavy-oil sands: comparison between measured and modeled data Agnibha Das, and Michael Batzle, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY We have measured
Calibration of the petro-elastic model (PEM) for 4D seismic studies in multi-mineral rocks Amini, Hamed; Alvarez, Erick Raciel
 Heriot-Watt University Heriot-Watt University Research Gateway Calibration of the petro-elastic model (PEM) for 4D seismic studies in multi-mineral rocks Amini, Hamed; Alvarez, Erick Raciel DOI: 10.3997/2214-4609.20132136
Heriot-Watt University Heriot-Watt University Research Gateway Calibration of the petro-elastic model (PEM) for 4D seismic studies in multi-mineral rocks Amini, Hamed; Alvarez, Erick Raciel DOI: 10.3997/2214-4609.20132136
RESEARCH PROPOSAL. Effects of scales and extracting methods on quantifying quality factor Q. Yi Shen
 RESEARCH PROPOSAL Effects of scales and extracting methods on quantifying quality factor Q Yi Shen 2:30 P.M., Wednesday, November 28th, 2012 Shen 2 Ph.D. Proposal ABSTRACT The attenuation values obtained
RESEARCH PROPOSAL Effects of scales and extracting methods on quantifying quality factor Q Yi Shen 2:30 P.M., Wednesday, November 28th, 2012 Shen 2 Ph.D. Proposal ABSTRACT The attenuation values obtained
Rock Physics Modeling in Montney Tight Gas Play
 Rock Physics Modeling in Montney Tight Gas Play Ayato Kato 1, Kunio Akihisa 1, Carl Wang 2 and Reona Masui 3 1 JOGMEC-TRC, Chiba, Japan, kato-ayato@jogmec.go.jp 2 Encana, Calgary, Alberta 3 Mitsubishi
Rock Physics Modeling in Montney Tight Gas Play Ayato Kato 1, Kunio Akihisa 1, Carl Wang 2 and Reona Masui 3 1 JOGMEC-TRC, Chiba, Japan, kato-ayato@jogmec.go.jp 2 Encana, Calgary, Alberta 3 Mitsubishi
A Study of Permeability and Velocity Anisotropy in Carbonates
 A Study of Permeability and Velocity Anisotropy in Carbonates M. Saleh 1, M. Prasad 2, S. Vega 1, and R. Sharma 2 1 The Petroleum Institute, Abu Dhabi, U.A.E. 2 Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, U.S.A.
A Study of Permeability and Velocity Anisotropy in Carbonates M. Saleh 1, M. Prasad 2, S. Vega 1, and R. Sharma 2 1 The Petroleum Institute, Abu Dhabi, U.A.E. 2 Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, U.S.A.
SEG Houston 2009 International Exposition and Annual Meeting. that the project results can correctly interpreted.
 Calibration of Pre-Stack Simultaneous Impedance Inversion using Rock Physics Scott Singleton and Rob Keirstead, Rock Solid Images Log Conditioning and Rock Physics Modeling Summary Geophysical Well Log
Calibration of Pre-Stack Simultaneous Impedance Inversion using Rock Physics Scott Singleton and Rob Keirstead, Rock Solid Images Log Conditioning and Rock Physics Modeling Summary Geophysical Well Log
23855 Rock Physics Constraints on Seismic Inversion
 23855 Rock Physics Constraints on Seismic Inversion M. Sams* (Ikon Science Ltd) & D. Saussus (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Seismic data are bandlimited, offset limited and noisy. Consequently interpretation of
23855 Rock Physics Constraints on Seismic Inversion M. Sams* (Ikon Science Ltd) & D. Saussus (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Seismic data are bandlimited, offset limited and noisy. Consequently interpretation of
AVO Attributes of a Deep Coal Seam
 AVO Attributes of a Deep Coal Seam Jinfeng Ma* State Key Laboratory of Continental Dynamics, Northwest University, China jinfengma@sohu.com Igor Morozov University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
AVO Attributes of a Deep Coal Seam Jinfeng Ma* State Key Laboratory of Continental Dynamics, Northwest University, China jinfengma@sohu.com Igor Morozov University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
Rock physics and AVO applications in gas hydrate exploration
 Rock physics and AVO applications in gas hydrate exploration ABSTRACT Yong Xu*, Satinder Chopra Core Lab Reservoir Technologies Division, 301,400-3rd Ave SW, Calgary, AB, T2P 4H2 yxu@corelab.ca Summary
Rock physics and AVO applications in gas hydrate exploration ABSTRACT Yong Xu*, Satinder Chopra Core Lab Reservoir Technologies Division, 301,400-3rd Ave SW, Calgary, AB, T2P 4H2 yxu@corelab.ca Summary
Integrating rock physics and full elastic modeling for reservoir characterization Mosab Nasser and John B. Sinton*, Maersk Oil Houston Inc.
 Integrating rock physics and full elastic modeling for reservoir characterization Mosab Nasser and John B. Sinton*, Maersk Oil Houston Inc. Summary Rock physics establishes the link between reservoir properties,
Integrating rock physics and full elastic modeling for reservoir characterization Mosab Nasser and John B. Sinton*, Maersk Oil Houston Inc. Summary Rock physics establishes the link between reservoir properties,
Rock physics of a gas hydrate reservoir. Gas hydrates are solids composed of a hydrogen-bonded ROUND TABLE
 ROUND TABLE Rock physics of a gas hydrate reservoir JACK DVORKIN and AMOS NUR, Stanford University, California, U.S. RICHARD UDEN and TURHAN TANER, Rock Solid Images, Houston, Texas, U.S. Gas hydrates
ROUND TABLE Rock physics of a gas hydrate reservoir JACK DVORKIN and AMOS NUR, Stanford University, California, U.S. RICHARD UDEN and TURHAN TANER, Rock Solid Images, Houston, Texas, U.S. Gas hydrates
Simultaneous Inversion of Clastic Zubair Reservoir: Case Study from Sabiriyah Field, North Kuwait
 Simultaneous Inversion of Clastic Zubair Reservoir: Case Study from Sabiriyah Field, North Kuwait Osman Khaled, Yousef Al-Zuabi, Hameed Shereef Summary The zone under study is Zubair formation of Cretaceous
Simultaneous Inversion of Clastic Zubair Reservoir: Case Study from Sabiriyah Field, North Kuwait Osman Khaled, Yousef Al-Zuabi, Hameed Shereef Summary The zone under study is Zubair formation of Cretaceous
QUANTITATIVE INTERPRETATION
 QUANTITATIVE INTERPRETATION THE AIM OF QUANTITATIVE INTERPRETATION (QI) IS, THROUGH THE USE OF AMPLITUDE ANALYSIS, TO PREDICT LITHOLOGY AND FLUID CONTENT AWAY FROM THE WELL BORE This process should make
QUANTITATIVE INTERPRETATION THE AIM OF QUANTITATIVE INTERPRETATION (QI) IS, THROUGH THE USE OF AMPLITUDE ANALYSIS, TO PREDICT LITHOLOGY AND FLUID CONTENT AWAY FROM THE WELL BORE This process should make
A rock physics model for the characterization of organic-rich shale from elastic properties
 Pet. Sci. (215) 12:264 272 DOI 1.17/s12182-15-29-6 ORIGINAL PAPER A rock physics model for the characterization of organic-rich shale from elastic properties Ying Li 1 Zhi-Qi Guo 2 Cai Liu 2 Xiang-Yang
Pet. Sci. (215) 12:264 272 DOI 1.17/s12182-15-29-6 ORIGINAL PAPER A rock physics model for the characterization of organic-rich shale from elastic properties Ying Li 1 Zhi-Qi Guo 2 Cai Liu 2 Xiang-Yang
The GIG consortium Geophysical Inversion to Geology Per Røe, Ragnar Hauge, Petter Abrahamsen FORCE, Stavanger
 www.nr.no The GIG consortium Geophysical Inversion to Geology Per Røe, Ragnar Hauge, Petter Abrahamsen FORCE, Stavanger 17. November 2016 Consortium goals Better estimation of reservoir parameters from
www.nr.no The GIG consortium Geophysical Inversion to Geology Per Røe, Ragnar Hauge, Petter Abrahamsen FORCE, Stavanger 17. November 2016 Consortium goals Better estimation of reservoir parameters from
SCOOP Woodford. Regional Field Study
 SCOOP Woodford Regional Field Study OVERVIEW The Woodford shale is an organic rich siliceous shale formation of late Devonian and early Mississippian age deposited throughout most of the Anadarko basin
SCOOP Woodford Regional Field Study OVERVIEW The Woodford shale is an organic rich siliceous shale formation of late Devonian and early Mississippian age deposited throughout most of the Anadarko basin
RockLab Details. Rock Physics Testing
 Rock Physics Testing Seismic velocity and electrical resistivity of rock samples are varying, as the stress/strain (and its orientation), temperature and fluid of the formation of interest are changing
Rock Physics Testing Seismic velocity and electrical resistivity of rock samples are varying, as the stress/strain (and its orientation), temperature and fluid of the formation of interest are changing
Edinburgh Anisotropy Project, British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains
 Frequency-dependent AVO attribute: theory and example Xiaoyang Wu, 1* Mark Chapman 1,2 and Xiang-Yang Li 1 1 Edinburgh Anisotropy Project, British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains Road, Edinburgh
Frequency-dependent AVO attribute: theory and example Xiaoyang Wu, 1* Mark Chapman 1,2 and Xiang-Yang Li 1 1 Edinburgh Anisotropy Project, British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains Road, Edinburgh
Seismic characterization of Montney shale formation using Passey s approach
 Seismic characterization of Montney shale formation using Passey s approach Ritesh Kumar Sharma*, Satinder Chopra and Amit Kumar Ray Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary Summary Seismic characterization of
Seismic characterization of Montney shale formation using Passey s approach Ritesh Kumar Sharma*, Satinder Chopra and Amit Kumar Ray Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary Summary Seismic characterization of
Downloaded 11/02/16 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at Summary.
 in thin sand reservoirs William Marin* and Paola Vera de Newton, Rock Solid Images, and Mario Di Luca, Pacific Exploración y Producción. Summary Rock Physics Templates (RPTs) are useful tools for well
in thin sand reservoirs William Marin* and Paola Vera de Newton, Rock Solid Images, and Mario Di Luca, Pacific Exploración y Producción. Summary Rock Physics Templates (RPTs) are useful tools for well
IDENTIFYING PATCHY SATURATION FROM WELL LOGS Short Note. / K s. + K f., G Dry. = G / ρ, (2)
 IDENTIFYING PATCHY SATURATION FROM WELL LOGS Short Note JACK DVORKIN, DAN MOOS, JAMES PACKWOOD, AND AMOS NUR DEPARTMENT OF GEOPHYSICS, STANFORD UNIVERSITY January 5, 2001 INTRODUCTION Gassmann's (1951)
IDENTIFYING PATCHY SATURATION FROM WELL LOGS Short Note JACK DVORKIN, DAN MOOS, JAMES PACKWOOD, AND AMOS NUR DEPARTMENT OF GEOPHYSICS, STANFORD UNIVERSITY January 5, 2001 INTRODUCTION Gassmann's (1951)
Elastic wavefield separation for VTI media
 CWP-598 Elastic wavefield separation for VTI media Jia Yan and Paul Sava Center for Wave Phenomena, Colorado School of Mines ABSTRACT The separation of wave modes from isotropic elastic wavefields is typically
CWP-598 Elastic wavefield separation for VTI media Jia Yan and Paul Sava Center for Wave Phenomena, Colorado School of Mines ABSTRACT The separation of wave modes from isotropic elastic wavefields is typically
BENEFITS OF HIGH-RESOLUTION CORE LOGS INTEGRATION IN CHARACTERIZING GAS SHALES CORES
 SCA2013-076 1/6 BENEFITS OF HIGH-RESOLUTION CORE LOGS INTEGRATION IN CHARACTERIZING GAS SHALES CORES B.Lalanne, L.Martinez, F.Umbhauer, F.Gélin, TOTAL E&P This paper was prepared for presentation at the
SCA2013-076 1/6 BENEFITS OF HIGH-RESOLUTION CORE LOGS INTEGRATION IN CHARACTERIZING GAS SHALES CORES B.Lalanne, L.Martinez, F.Umbhauer, F.Gélin, TOTAL E&P This paper was prepared for presentation at the
SEG Houston 2009 International Exposition and Annual Meeting
 The role of EM rock physics and seismic data in integrated 3D CSEM data analysis I. Brevik*, StatoilHydro, Pål T. Gabrielsen, Vestfonna and Jan Petter Morten, EMGS Summary An extensive 3D CSEM dataset
The role of EM rock physics and seismic data in integrated 3D CSEM data analysis I. Brevik*, StatoilHydro, Pål T. Gabrielsen, Vestfonna and Jan Petter Morten, EMGS Summary An extensive 3D CSEM dataset
Elastic wave-equation migration for laterally varying isotropic and HTI media. Richard A. Bale and Gary F. Margrave
 Elastic wave-equation migration for laterally varying isotropic and HTI media Richard A. Bale and Gary F. Margrave a Outline Introduction Theory Elastic wavefield extrapolation Extension to laterally heterogeneous
Elastic wave-equation migration for laterally varying isotropic and HTI media Richard A. Bale and Gary F. Margrave a Outline Introduction Theory Elastic wavefield extrapolation Extension to laterally heterogeneous
M. Elgmati, H. Zhang, M. Zobaa, B. Bai, and F. Oboh-Ikuenobe. June 15 th, 2011
 M. Elgmati, H. Zhang, M. Zobaa, B. Bai, and F. Oboh-Ikuenobe June 15 th, 2011 Purposes Palynofacies Analysis Kerogen Type Thermal Maturation Estimated Key Geochemical Parameters Total Organic Carbon 3D
M. Elgmati, H. Zhang, M. Zobaa, B. Bai, and F. Oboh-Ikuenobe June 15 th, 2011 Purposes Palynofacies Analysis Kerogen Type Thermal Maturation Estimated Key Geochemical Parameters Total Organic Carbon 3D
The Deconvolution of Multicomponent Trace Vectors
 The Deconvolution of Multicomponent Trace Vectors Xinxiang Li, Peter Cary and Rodney Couzens Sensor Geophysical Ltd., Calgary, Canada xinxiang_li@sensorgeo.com Summary Deconvolution of the horizontal components
The Deconvolution of Multicomponent Trace Vectors Xinxiang Li, Peter Cary and Rodney Couzens Sensor Geophysical Ltd., Calgary, Canada xinxiang_li@sensorgeo.com Summary Deconvolution of the horizontal components
Estimation of interval anisotropic attenuation from reflection data
 GEOPHYSCS, VOL. 74, NO. 6 NOVEMBER-DECEMBER 9 ; P. A69 A74, 7 FGS..9/.39733 Estimation of interval anisotropic attenuation from reflection data Jyoti Behura and lya Tsvankin ABSTRACT Knowledge of interval
GEOPHYSCS, VOL. 74, NO. 6 NOVEMBER-DECEMBER 9 ; P. A69 A74, 7 FGS..9/.39733 Estimation of interval anisotropic attenuation from reflection data Jyoti Behura and lya Tsvankin ABSTRACT Knowledge of interval
Downloaded 10/02/13 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Downloaded 10/02/13 to 129.7.247.135. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ Physical constraints on c 13 and Thomsen parameter delta for VTI rocks
Downloaded 10/02/13 to 129.7.247.135. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ Physical constraints on c 13 and Thomsen parameter delta for VTI rocks
Pre-Stack Seismic Inversion and Amplitude Versus Angle Modeling Reduces the Risk in Hydrocarbon Prospect Evaluation
 Advances in Petroleum Exploration and Development Vol. 7, No. 2, 2014, pp. 30-39 DOI:10.3968/5170 ISSN 1925-542X [Print] ISSN 1925-5438 [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org Pre-Stack Seismic Inversion
Advances in Petroleum Exploration and Development Vol. 7, No. 2, 2014, pp. 30-39 DOI:10.3968/5170 ISSN 1925-542X [Print] ISSN 1925-5438 [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org Pre-Stack Seismic Inversion
Downloaded 10/29/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Electrical anisotropy drivers in the Snøhvit region of the Barents Sea Michelle Ellis*, Lucy MacGregor, Rolf Ackermann, Paola Newton, Robert Keirstead, Alberto Rusic, Slim Bouchrara, Amanda Geck Alvarez,
Electrical anisotropy drivers in the Snøhvit region of the Barents Sea Michelle Ellis*, Lucy MacGregor, Rolf Ackermann, Paola Newton, Robert Keirstead, Alberto Rusic, Slim Bouchrara, Amanda Geck Alvarez,
Use of Seismic and EM Data for Exploration, Appraisal and Reservoir Characterization
 Use of Seismic and EM Data for Exploration, Appraisal and Reservoir Characterization Anton Ziolkowski and Folke Engelmark Petroleum Geo-Services CSEG, Calgary, 6 May 2009 Outline Exploration, appraisal,
Use of Seismic and EM Data for Exploration, Appraisal and Reservoir Characterization Anton Ziolkowski and Folke Engelmark Petroleum Geo-Services CSEG, Calgary, 6 May 2009 Outline Exploration, appraisal,
Estimating the hydrocarbon volume from elastic and resistivity data: A concept
 INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Estimating the hydrocarbon volume from elastic and resistivity data: A concept CARMEN T. GOMEZ, JACK DVORKIN, and GARY MAVKO, Stanford University,
INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Estimating the hydrocarbon volume from elastic and resistivity data: A concept CARMEN T. GOMEZ, JACK DVORKIN, and GARY MAVKO, Stanford University,
Rock Physics and Quantitative Wavelet Estimation. for Seismic Interpretation: Tertiary North Sea. R.W.Simm 1, S.Xu 2 and R.E.
 Rock Physics and Quantitative Wavelet Estimation for Seismic Interpretation: Tertiary North Sea R.W.Simm 1, S.Xu 2 and R.E.White 2 1. Enterprise Oil plc, Grand Buildings, Trafalgar Square, London WC2N
Rock Physics and Quantitative Wavelet Estimation for Seismic Interpretation: Tertiary North Sea R.W.Simm 1, S.Xu 2 and R.E.White 2 1. Enterprise Oil plc, Grand Buildings, Trafalgar Square, London WC2N
P1488 DECC Relinquishment Report OMV (U.K.) Ltd.
 1. Synopsis: P1488 DECC Relinquishment Report OMV (U.K.) Ltd. UK offshore Licence P1488 was awarded to OMV, Dana Petroleum and Rocksource in the 24 th Licence Round on the 24 th of January 2007 as a frontier
1. Synopsis: P1488 DECC Relinquishment Report OMV (U.K.) Ltd. UK offshore Licence P1488 was awarded to OMV, Dana Petroleum and Rocksource in the 24 th Licence Round on the 24 th of January 2007 as a frontier
Optimising Resource Plays An integrated GeoPrediction Approach
 Optimising Resource Plays An integrated GeoPrediction Approach Edward Hoskin, Stephen O Connor, Scott Mildren, Michel Kemper, Cristian Malaver, Jeremy Gallop and Sam Green Ikon Science Ltd. Summary A mechanical
Optimising Resource Plays An integrated GeoPrediction Approach Edward Hoskin, Stephen O Connor, Scott Mildren, Michel Kemper, Cristian Malaver, Jeremy Gallop and Sam Green Ikon Science Ltd. Summary A mechanical
Th SBT1 14 Seismic Characters of Pore Pressure Due to Smectite-to-illite Transition
 Th SBT1 14 Seismic Characters of Pore Pressure Due to Smectite-to-illite Transition X. Qin* (University of Houston) & D. Han (University of Houston) SUMMARY In this study, we strive to understand unloading
Th SBT1 14 Seismic Characters of Pore Pressure Due to Smectite-to-illite Transition X. Qin* (University of Houston) & D. Han (University of Houston) SUMMARY In this study, we strive to understand unloading
Comparison of Reservoir Quality from La Luna, Gacheta and US Shale Formations*
 Comparison of Reservoir Quality from La Luna, Gacheta and US Shale Formations* Joel Walls 1 and Elizabeth Diaz 2 Search and Discovery Article #41396 (2014) Posted July 24, 2014 *Adapted from oral presentation
Comparison of Reservoir Quality from La Luna, Gacheta and US Shale Formations* Joel Walls 1 and Elizabeth Diaz 2 Search and Discovery Article #41396 (2014) Posted July 24, 2014 *Adapted from oral presentation
11282 Rock Physics Analysis and Time-lapse Rock Imaging of Geochemical Effects Due to CO2 Injection into Reservoir Rocks
 11282 Rock Physics Analysis and Time-lapse Rock Imaging of Geochemical Effects Due to CO2 Injection into Reservoir Rocks T.V. Vanorio* (Stanford University) & E.D. Diaz (Ingrain Inc., Houston, TX) SUMMARY
11282 Rock Physics Analysis and Time-lapse Rock Imaging of Geochemical Effects Due to CO2 Injection into Reservoir Rocks T.V. Vanorio* (Stanford University) & E.D. Diaz (Ingrain Inc., Houston, TX) SUMMARY
Core Technology for Evaluating the Bakken
 Core Technology for Evaluating the Bakken Fundamentals for Reservoir Quality Assessment and Completion Analysis John Kieschnick and Roberto Suarez-Rivera TerraTek 1 Topics Covered Core Technology Changes
Core Technology for Evaluating the Bakken Fundamentals for Reservoir Quality Assessment and Completion Analysis John Kieschnick and Roberto Suarez-Rivera TerraTek 1 Topics Covered Core Technology Changes
The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe
 Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Determination of the Laminar, Structural and Disperse Shale Volumes Using a Joint Inversion of Conventional Logs*
 Determination of the Laminar, Structural and Disperse Shale Volumes Using a Joint Inversion of Conventional Logs* Ambrosio Aquino-López 1, Aleksandr Mousatov 1, Mikhail Markov 1, and Elena Kazatchenko
Determination of the Laminar, Structural and Disperse Shale Volumes Using a Joint Inversion of Conventional Logs* Ambrosio Aquino-López 1, Aleksandr Mousatov 1, Mikhail Markov 1, and Elena Kazatchenko
Borehole Acoustics and Logging Consortium. Annual Report
 Borehole Acoustics and Logging Consortium Annual Report 1994 EARTH RESOURCES LABORATORY Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Mass. 02139
Borehole Acoustics and Logging Consortium Annual Report 1994 EARTH RESOURCES LABORATORY Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Mass. 02139
SPE These in turn can be used to estimate mechanical properties.
 SPE 96112 Pressure Effects on Porosity-Log Responses Using Rock Physics Modeling: Implications on Geophysical and Engineering Models as Reservoir Pressure Decreases Michael Holmes, SPE, Digital Formation,
SPE 96112 Pressure Effects on Porosity-Log Responses Using Rock Physics Modeling: Implications on Geophysical and Engineering Models as Reservoir Pressure Decreases Michael Holmes, SPE, Digital Formation,
Modeling Optimizes Asset Performance By Chad Baillie
 MARCH 2016 The Better Business Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry Modeling Optimizes Asset Performance By Chad Baillie MISSOURI CITY, TX. As more well and completion data
MARCH 2016 The Better Business Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry Modeling Optimizes Asset Performance By Chad Baillie MISSOURI CITY, TX. As more well and completion data
THE ROCK PHYSICS HANDBOOK
 THE ROCK PHYSICS HANDBOOK TOOLS FOR SEISMIC ANALYSIS IN POROUS MEDIA Gary Mavko Tapan Mukerji Jack Dvorkin Stanford University Stanford University Stanford University CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS
THE ROCK PHYSICS HANDBOOK TOOLS FOR SEISMIC ANALYSIS IN POROUS MEDIA Gary Mavko Tapan Mukerji Jack Dvorkin Stanford University Stanford University Stanford University CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS
A model for seismic velocity and attenuation in petroleum source rocks
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 65, NO. 4 (JULY AUGUST 2000); P. 1080 1092, 15 FIGS., 1 TABLE. A model for seismic velocity and attenuation in petroleum source rocks José M. Carcione ABSTRACT Petroleum source rock is
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 65, NO. 4 (JULY AUGUST 2000); P. 1080 1092, 15 FIGS., 1 TABLE. A model for seismic velocity and attenuation in petroleum source rocks José M. Carcione ABSTRACT Petroleum source rock is
Recap and Integrated Rock Mechanics and Natural Fracture Study in the Bakken Formation, Williston Basin
 Recap and Integrated Rock Mechanics and Natural Fracture Study in the Bakken Formation, Williston Basin EERC, 2011 Cosima Theloy PhD Candidate Department of Geology and Geological Engineering Colorado
Recap and Integrated Rock Mechanics and Natural Fracture Study in the Bakken Formation, Williston Basin EERC, 2011 Cosima Theloy PhD Candidate Department of Geology and Geological Engineering Colorado
Analytic Tools for Quantitative Interpretation. Mrinal K.Sen
 Analytic Tools for Quantitative Interpretation Mrinal K.Sen Tools Modeling of fractures static, dynamic, numerical Modeling seismic wave propagation in anisotropic media Travel time an amplitude based
Analytic Tools for Quantitative Interpretation Mrinal K.Sen Tools Modeling of fractures static, dynamic, numerical Modeling seismic wave propagation in anisotropic media Travel time an amplitude based
Mixed Reservoir Wetting in Unconventional Reservoirs and Interpretation of Porosity/Resistivity Cross Plots, Derived From Triple-combo Log Data
 Mixed Reservoir Wetting in Unconventional Reservoirs and Interpretation of Porosity/Resistivity Cross Plots, Derived From Triple-combo Log Data Michael Holmes DWLS November 14, 2017 Outline Introduction
Mixed Reservoir Wetting in Unconventional Reservoirs and Interpretation of Porosity/Resistivity Cross Plots, Derived From Triple-combo Log Data Michael Holmes DWLS November 14, 2017 Outline Introduction
3D petrophysical modeling - 1-3D Petrophysical Modeling Usning Complex Seismic Attributes and Limited Well Log Data
 - 1-3D Petrophysical Modeling Usning Complex Seismic Attributes and Limited Well Log Data Mehdi Eftekhari Far, and De-Hua Han, Rock Physics Lab, University of Houston Summary A method for 3D modeling and
- 1-3D Petrophysical Modeling Usning Complex Seismic Attributes and Limited Well Log Data Mehdi Eftekhari Far, and De-Hua Han, Rock Physics Lab, University of Houston Summary A method for 3D modeling and
Ingrain Laboratories INTEGRATED ROCK ANALYSIS FOR THE OIL AND GAS INDUSTRY
 Ingrain Laboratories INTEGRATED ROCK ANALYSIS FOR THE OIL AND GAS INDUSTRY 3 INGRAIN We Help Identify and Develop the Most Productive Reservoir by Characterizing Rocks at Pore Level and Upscaling to the
Ingrain Laboratories INTEGRATED ROCK ANALYSIS FOR THE OIL AND GAS INDUSTRY 3 INGRAIN We Help Identify and Develop the Most Productive Reservoir by Characterizing Rocks at Pore Level and Upscaling to the
GRAIN SORTING, POROSITY, AND ELASTICITY. Jack Dvorkin and Mario A. Gutierrez Geophysics Department, Stanford University ABSTRACT
 GRAIN SORTING, POROSITY, AND ELASTICITY Jack Dvorkin and Mario A. Gutierrez Geophysics Department, Stanford University July 24, 2001 ABSTRACT Grain size distribution (sorting) is determined by deposition.
GRAIN SORTING, POROSITY, AND ELASTICITY Jack Dvorkin and Mario A. Gutierrez Geophysics Department, Stanford University July 24, 2001 ABSTRACT Grain size distribution (sorting) is determined by deposition.
Porosity prediction using cokriging with multiple secondary datasets
 Cokriging with Multiple Attributes Porosity prediction using cokriging with multiple secondary datasets Hong Xu, Jian Sun, Brian Russell, Kris Innanen ABSTRACT The prediction of porosity is essential for
Cokriging with Multiple Attributes Porosity prediction using cokriging with multiple secondary datasets Hong Xu, Jian Sun, Brian Russell, Kris Innanen ABSTRACT The prediction of porosity is essential for
Effects of VTI Anisotropy in Shale-Gas Reservoir Characterization
 P-014 Summary Effects of VTI Anisotropy in Shale-Gas Reservoir Characterization Niranjan Banik* and Mark Egan, WesternGeco Shale reservoirs are one of the hottest plays in the oil industry today. Our understanding
P-014 Summary Effects of VTI Anisotropy in Shale-Gas Reservoir Characterization Niranjan Banik* and Mark Egan, WesternGeco Shale reservoirs are one of the hottest plays in the oil industry today. Our understanding
The Marrying of Petrophysics with Geophysics Results in a Powerful Tool for Independents Roger A. Young, eseis, Inc.
 The Marrying of Petrophysics with Geophysics Results in a Powerful Tool for Independents Roger A. Young, eseis, Inc. While the application of new geophysical and petrophysical technology separately can
The Marrying of Petrophysics with Geophysics Results in a Powerful Tool for Independents Roger A. Young, eseis, Inc. While the application of new geophysical and petrophysical technology separately can
STACK/STACK EXTENSION MERAMEC /OSAGE/ WOODFORD STUDY
 STACK/STACK EXTENSION MERAMEC /OSAGE/ WOODFORD STUDY FIELD STUDIES OVERVIEW NUTECH has combined its expertise with the emerging interest in North American shale plays in order to develop the most detailed
STACK/STACK EXTENSION MERAMEC /OSAGE/ WOODFORD STUDY FIELD STUDIES OVERVIEW NUTECH has combined its expertise with the emerging interest in North American shale plays in order to develop the most detailed
Use of Seismic Inversion Attributes In Field Development Planning
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 6, Issue 2 Ver. II (Mar. Apr. 2018), PP 86-92 www.iosrjournals.org Use of Seismic Inversion Attributes
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 6, Issue 2 Ver. II (Mar. Apr. 2018), PP 86-92 www.iosrjournals.org Use of Seismic Inversion Attributes
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF SHALE PORE STRUCTURE ANALYSIS
 SCA2017-092 1 of 9 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF SHALE PORE STRUCTURE ANALYSIS R. Cicha-Szot, P. Budak, G. Leśniak, P. Such, Instytut Nafty i Gazu - Państwowy Instytut Badawczy, Kraków, Poland This paper was
SCA2017-092 1 of 9 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF SHALE PORE STRUCTURE ANALYSIS R. Cicha-Szot, P. Budak, G. Leśniak, P. Such, Instytut Nafty i Gazu - Państwowy Instytut Badawczy, Kraków, Poland This paper was
Relinquishment Report. for. Licences: P.1596 (Blocks 205/3, 205/4a) P.1836 (Block 205/2b) P.1837 (Block 205/5b)
 Relinquishment Report for Licences: P.1596 (Blocks 205/3, 205/4a) P.1836 (Block 205/2b) P.1837 (Block 205/5b) November 2013 1 of 9 CONTENT 1. Header 2. Synopsis 3. Exploration Activities 4. Prospectivity
Relinquishment Report for Licences: P.1596 (Blocks 205/3, 205/4a) P.1836 (Block 205/2b) P.1837 (Block 205/5b) November 2013 1 of 9 CONTENT 1. Header 2. Synopsis 3. Exploration Activities 4. Prospectivity
Quantitative Interpretation
 Quantitative Interpretation The aim of quantitative interpretation (QI) is, through the use of amplitude analysis, to predict lithology and fluid content away from the well bore. This process should make
Quantitative Interpretation The aim of quantitative interpretation (QI) is, through the use of amplitude analysis, to predict lithology and fluid content away from the well bore. This process should make
P191 Bayesian Linearized AVAZ Inversion in HTI Fractured Media
 P9 Bayesian Linearized AAZ Inversion in HI Fractured Media L. Zhao* (University of Houston), J. Geng (ongji University), D. Han (University of Houston) & M. Nasser (Maersk Oil Houston Inc.) SUMMARY A new
P9 Bayesian Linearized AAZ Inversion in HI Fractured Media L. Zhao* (University of Houston), J. Geng (ongji University), D. Han (University of Houston) & M. Nasser (Maersk Oil Houston Inc.) SUMMARY A new
OTC OTC PP. Abstract
 OTC OTC-19977-PP Using Modern Geophysical Technology to Explore for Bypassed Opportunities in the Gulf of Mexico R.A. Young/eSeis; W.G. Holt, G. Klefstad/ Fairways Offshore Exploration Copyright 2009,
OTC OTC-19977-PP Using Modern Geophysical Technology to Explore for Bypassed Opportunities in the Gulf of Mexico R.A. Young/eSeis; W.G. Holt, G. Klefstad/ Fairways Offshore Exploration Copyright 2009,
VELOCITY MODELING TO DETERMINE PORE ASPECT RATIOS OF THE HAYNESVILLE SHALE. Kwon Taek Oh
 VELOCITY MODELING TO DETERMINE PORE ASPECT RATIOS OF THE HAYNESVILLE SHALE. Kwon Taek Oh Department of Geological Sciences The University of Texas at Austin ABSTRACT This work estimates pore shapes from
VELOCITY MODELING TO DETERMINE PORE ASPECT RATIOS OF THE HAYNESVILLE SHALE. Kwon Taek Oh Department of Geological Sciences The University of Texas at Austin ABSTRACT This work estimates pore shapes from
and a contribution from Offshore Europe
 Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Calculating Total Organic Carbon (TOC) using the Passey Method
 Calculating Total Organic Carbon (TOC) using the Passey Method Chris Gent Overview 1. Passey method 2. Importance of TOC and maturity data. 3. Case Study: The Weald, UK. 1. The Passey Method A Practical
Calculating Total Organic Carbon (TOC) using the Passey Method Chris Gent Overview 1. Passey method 2. Importance of TOC and maturity data. 3. Case Study: The Weald, UK. 1. The Passey Method A Practical
AVO Crossplotting II: Examining Vp/Vs Behavior
 AVO Crossplotting II: Examining Vp/Vs Behavior Heath Pelletier* Talisman Energy, Calgary, AB hpelletier@talisman-energy.com Introduction The development of AVO crossplot analysis has been the subject of
AVO Crossplotting II: Examining Vp/Vs Behavior Heath Pelletier* Talisman Energy, Calgary, AB hpelletier@talisman-energy.com Introduction The development of AVO crossplot analysis has been the subject of
