On the Performance of Mismatched Data Detection in Large MIMO Systems
|
|
|
- Willis Richardson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 On the Performance of Mismatched Data Detection in Large MIMO Systems Chares Jeon, Arian Maei, and Christoph Studer arxiv: v [cs.it] Jun 016 Abstract We investigate the performance of mismatched data detection in arge mutipe-input mutipe-output MIMO) systems, where the prior distribution of the transmit signa used in the data detector differs from the true prior. To minimize the performance oss caused by this prior mismatch, we incude a tuning stage into our recenty-proposed arge MIMO approximate message passing LAMA) agorithm, which aows us to deveop mismatched LAMA agorithms with optima as we as sub-optima tuning. We show that carefuy-seected priors often enabe simper and computationay more efficient agorithms compared to LAMA with the true prior whie achieving nearoptima performance. A performance anaysis of our agorithms for a Gaussian prior and a uniform prior within a hypercube covering the QAM consteation recovers cassica and recent resuts on inear and non-inear MIMO data detection, respectivey. I. INTRODUCTION Data detection in mutipe-input mutipe-output MIMO) systems deas with the recovery of the transmit data vector s 0 O MT, where O is a finite consteation e.g., QAM or PSK), from the noisy input-output reation y = Hs 0 + n. In what foows, M T and M R denotes the number of transmit and receive antennas, respectivey, y C MR is the receive vector, H C MR MT is the MIMO system matrix, and n C MR is i.i.d. circuary symmetric compex Gaussian noise. To minimize the symbo-error rate, we are interested in soving the individuay-optima IO) data detection probem [] [4] IO) s IO = arg max s O p s y, H), = 1,..., M T. Here, s IO denotes the -th IO estimate and p s y, H) is the conditiona probabiity density function of s O given the receive vector y and the channe matrix H. The probem IO) is nown to be of combinatoria nature [] [4], and the use of an exhaustive search or spheredecoding methods resuts in prohibitive compexity for systems where M T is arge [5]. In contrast, our recenty proposed agorithm referred to as arge MIMO approximate message passing LAMA) [6], achieves IO performance using a simpe iterative procedure in the arge-system imit, i.e., where we fix the system ratio β = M T /M R and et M T. For finitedimensiona systems, LAMA was shown to deiver near-io performance at ow computationa compexity [6]. Despite a these advantages, LAMA requires repeated computations of transcendenta functions that exhibit a high dynamic range. C. Jeon and C. Studer are with the Schoo of ECE at Corne University, Ithaca, NY; e-mais: jeon@cs.corne.edu, studer@corne.edu. A. Maei is with Department of Statistics at Coumbia University, New Yor City, NY; e-mai: arian@stat.coumbia.edu. The wor of CJ and CS was supported in part by Xiinx Inc. and by the US Nationa Science Foundation under grants ECCS and CCF An extended version of this paper incuding a proofs is in preparation [1]. These computations render the design of corresponding highthroughput hardware designs that rey on finite precision e.g., fixed-point) arithmetic a chaenging tas. A. Contributions We propose a mismatched version of the LAMA agorithm short M-LAMA), which enabes the design of hardwarefriendy data detectors that achieve near-io performance. We first deveop a mismatched version of the compex Bayesian approximate message passing cb-amp) agorithm [7] that incudes a tuning stage to minimize the performance oss caused by the mismatch in the signa prior. We propose the mismatched state-evoution SE) framewor to enabe a performance anaysis in the arge-system imit. We then appy our framewor to mismatched data detection in arge MIMO systems by considering two mismatched prior distributions: i) a Gaussian prior and ii) a uniform prior within a hypercube covering the QAM consteation. We anayze the performance of the resuting mismatched agorithms in the arge-system imit and demonstrate their efficacy in finite-dimensiona systems. B. Reevant prior art The performance of zero forcing ZF) and minimum meansquare error MMSE) detection, which are both we-nown instances of mismatched detection agorithms, has been investigated in [8] [10] for the arge-system imit. The use of a uniform prior within a hypercube eads to an aternative mismatched detector for antipoda e.g., BPSK) signas [11] [13]. Corresponding theoretica resuts in [14], [15] for noiseess systems reveaed that a system ratio of β < enabes perfect signa recovery. The error-rate performance for the noisy case was derived recenty in [13]. The anaysis of the mismatched agorithms presented in our paper recovers a these resuts. The proposed M-LAMA agorithm reies upon approximate message passing AMP) [16] [18], deveoped for sparse signa recovery. The case of mismatched estimation of sparse signas via AMP was studied in [19], [0], where the performance of AMP was anayzed when the true prior is unnown. This AMP agorithm incudes a tuning stage for automated, optima parameter seection that minimizes the output mean-squared error MSE). The ey differences between M-LAMA and the resuts in [19], [0] are that i) we consider MIMO data detection and ii) we now the true signa prior and intentionay seect a mismatched prior in order to design hardware-friendy data detection agorithms that enabe near-io performance. C. Notation Lowercase and uppercase bodface etters designate vectors and matrices, respectivey. We define the adjoint of matrix H as
2 H H and use to abbreviate x = 1 N N =1 x. A mutivariate compex-vaued Gaussian probabiity density function pdf) is denoted by CN m, K), where m is the mean vector and K the covariance matrix. E X [ ] and Var X [ ] denotes the mean and variance with respect to the random variabe X, respectivey. II. MISMATCHED COMPLEX BAYESIAN AMP We start by presenting a mismatched version of the compex Bayesian approximate message passing cb-amp) agorithm [7] short mcb-amp), which enabes the use a different prior distribution p s) than the true signa prior ps 0 ). A. The mismatched cb-amp mcb-amp) agorithm Given an i.i.d. prior distribution ps 0 ) = N =1 ps 0) of the true signa s 0 and a mismatched prior p s) = N =1 p s ), the proposed mcb-amp agorithm corresponds to σ t = 1 M R r t, [ 1) τ t = arg min E S0,Z F mm S 0 + σ t Z, τ) S 0 ], ) τ 0 s t+1 = F mm s t + H H r t, τ t), 3) r t+1 = y Hs t+1 + βr t F mm s t + H H r t, τ t ), which is carried out for t max iterations t = 1,..., t max. The agorithm is initiaized by s 1 = E S 0 [S 0 ] for a = 1,..., M T, where S 0 ps 0 ), r 1 = y Hs 1, and F mm is the derivative of F mm taen by its first argument. The function F mm s, τ) = E S[ S s ] = C sp s s, τ)d s, 4) is the posterior mean with respect to the mismatched prior p s ) and the variance parameter τ, p s s, τ) = 1 C ps s, τ) p s), C is a normaization constant, and ps s, τ) CN s, τ). The functions F mm s, τ) and F mm operate eement-wise on vectors and the expectation in ) is taen with respect to the true prior distribution of S 0 ps 0 ) and Z CN 0, 1). The mcb-amp agorithm differs from the origina cb-amp agorithm derived in [7] by the additiona steps 1) and ). In every iteration, step 1) estimates the so-caed decouped noise variance σt see Section II-B) and step ) tunes the variance parameter τ t based on the estimate σt. The tuning stage ) ensures that mcb-amp converges to the soution that minimizes σt for every iteration see Section II-C). B. Decouping property of AMP-based agorithms We wi frequenty use the foowing definition. Definition 1. Assume a MIMO system with M T transmit and M R receive antennas, and et the entries of H be i.i.d. CN 0, 1/M R ). We define the arge-system imit by fixing the system ratio β = M T /M R and etting M T. As shown in [7], [17], [1], AMP-based agorithms decoupe the MIMO system into parae AWGN channes in the argesystem imit, i.e., the quantity z t = s t +H H r t can be expressed equivaenty as s 0 + w t, where w t CN 0, σt I MT ) and σt is the decouped noise variance. A ey property of AMPbased agorithms is that the decouped noise variance σt can be traced exacty by the state evoution SE) framewor. We formaize the mismatched SE framewor for mcb-amp in Theorem 1. This resut is a specific instance of the SE framewor in [17] and has been adapted to mcb-amp. Theorem 1. Assume the arge-system imit and that F mm is Lipschitz continuous. Then, the decouped noise variance σ t+1 after t mcb-amp iterations is given by the couped recursion γt = arg min Ψ mm σt, γ ), 5) γ 0 σ t+1 = N 0 + βψ mm σ t, γ t ), 6) which is initiaized by σ 1 = N 0 + β Var S0 [S 0 ]. Here, S 0 ps 0 ) and the MSE function is defined by Ψ mm σ t, γ t ) = E S0,Z[ F mm S 0 + σ t Z, γ t ) S 0 ], where the expectation is taen with respect to the S 0 and Z CN 0, 1). If the true prior is identica to the mismatched prior, i.e., ps 0 ) = p s), we can show that mcb-amp deivers the same decouped noise variance as cb-amp without prior mismatch. Lemma. If ps 0 ) = p s), then the decouped noise variance σ t+1 of mcb-amp is equivaent to σ t+1 of cb-amp [7]. The proof of Lemma foows by noting that the MSE function Ψ mm σ t, γ ) in 6) is minimized by γ = σ t in 5), and reduces to the conditiona variance []. Therefore, 6) reduces to the conventiona SE recursion of cb-amp [7]. C. Optima tuning of the variance parameter τ Before we discuss the tuning stage ) in detai, we formaize what we mean by optima tuning of the variance parameter τ t. For a iterations t = 1,..., t max, our goa is to minimize the decouped noise variance σ t max+1 given by Theorem 1, as the smaest σ t max+1 minimizes the error probabiity of our agorithm. Hence, optima tuning tries to identify a sequence of variance parameters {τ 1,..., τ tmax } so that mcb-amp utimatey eads to the smaest σ t max+1; sub-optima choices of τ t either ead to a higher σ t max+1 or cause sower convergence to the smaest σ t max+1. We wi use the foowing definition [0]. Definition. Assume the arge-system imit and denote the decouped noise variance of mcb-amp obtained from the sequence {τ 1,..., τ tmax } as σt max+1τ 1,..., τ tmax ). A sequence of parameters {τ 1,..., τ tmax } is optimay tuned at iteration t max, if and ony if for a {τ 1,..., τ tmax } with τ t [0, ) we have σ t max+1τ 1,..., τ tmax ) σ t max+1τ 1,..., τ tmax ). 7) We next show that the tuning stage in ), which is carried out at every iteration of mcb-amp, achieves the smaest σ t max+1, i.e., optimay tunes the variance parameters τ t. We omit the proof detais as it foows cosey that in [0, Sec. 4.4]. Theorem 3. Suppose {τ 1,..., τ tmax } are optimay-tuned for iteration t max. Then, for any t < t max, {τ 1,..., τ } t are aso optimay-tuned for iteration t. Thus, one can obtain t max optimay-tuned variance parameters by optimizing τ 1 at t = 1, and then, proceeding iterativey by optimizing τ t unti t = t max. In genera, the exact vaue of the decouped noise variance σ t that is needed for the tuning stage in step ) to seect τ t is unnown. We therefore use the estimate ˆσ t = 1 M R r t in
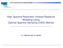
3 step 1), which was shown to converge to the true decouped noise variance σ t in the arge-system imit [18]. D. Decomposition of compex-vaued systems We now briefy discuss properties of mcb-amp in compexvaued systems that wi be necessary for our anaysis of mcb-amp in MIMO systems. In particuar, we show that for specia consteations, the compex-vaued set O can be exacty characterized by a suitaby-chosen rea-vaued set Re{O}. Definition 3. For a s O, express s as s = a + ib, where a Re{O}, b Im{O}. Then, the consteation O is separabe if ps) = pa)pb) hods for a s O and Re{O}= Im{O}. An exampe of a separabe consteation is M -QAM with equay iey transmit symbos. For such a separabe set O, the foowing emma with proof in [7]) provides the equivaence of the compex-vaued and rea-vaued SE framewor. Lemma 4. For a separabe consteation set O, the mismatched SE recursion in Theorem 1 can be expressed equivaenty by: [ F σt+1 = N 0 + β min E mm γ S0 R 0,ZR R S0 R + σ t Z R, γ ) S0 R ) ], where F mm R is posterior mean function with respect to the consteation set O R = Re{O}, S0 R O R and Z R N 0, 1/). E. Fixed-point anaysis Whie the performance of mcb-amp at every iteration can be characterized by the mismatched SE recursion equations in Theorem 1, we are interested in anayzing the performance of mcb-amp for t max. In this case, the mismatched SE in Theorem 1 converges to the foowing fixed-point equation: σ = N 0 + β min γ 0 Ψmm σ, γ ) = N 0 + βψ mm σ ). 8) Thus, as t max, σ t+1 in Theorem 1 converges to σ as given by 8). In genera, if there are mutipe fixed points, then mcb-amp converges to the argest fixed-point, which utimatey eads to a higher probabiity of error than that of the smaest fixed-point soution. To provide conditions that ensure a unique fixed-point soution to 8) see Section III), we use the foowing emma the proof is given in [7]). Lemma 5. Fix ps 0 ) and p s). The minimum recovery threshod MRT) β min for M-LAMA is defined by: β min = min σ 0 dψ mm σ ) dσ ) 1. 9) For a system ratios β < β min the fixed-point soution in 8) is unique. Furthermore, et σ = arg min dψ mm σ )/dσ ) 1. If σ 0 for any other σ σ, β min dψ mm σ )/dσ < 1, then M-LAMA aso has a unique fixed point at β = β min. III. MISMATCHED DATA DETECTION WITH TUNING We now appy the mismatched cb-amp framewor to mismatched data detection in arge MIMO systems, and refer to the agorithm as mismatched arge MIMO AMP M-LAMA). In what foows, we assume that the true prior is taen from a discrete consteation set O with equay iey symbos, i.e., ps 0 ) = 1 O a O δs 0 a), where O is the cardinaity of the set O; we aso define E S0 [ S 0 ] = E s. Note that in MIMO systems, the true signa prior is generay nown. Hence, it is natura to as why one shoud consider a mismatched prior, especiay since the LAMA agorithm [6] that uses the true prior minimizes the error probabiity. To answer this question, consider the posterior mean function 4) of LAMA [6] Fr, τ) = a O a exp 1 τ r a ) a O exp 1 τ r a ), 10) whose cacuation requires high arithmetic precision. In fact, even the use of doube-precision foating-point arithmetic becomes numericay unstabe for sma vaues of τ. Hence, the deveopment of hardware designs for LAMA that use finiteprecision arithmetic is chaenging. In contrast, suitaby-chosen mismatched priors can ead to hardware-friendy data detectors. A. Optimay-tuned data detection with a Gaussian prior We now derive an M-LAMA agorithm variant with a mismatched Gaussian prior. Without oss of generaity, we assume a standard compex Gaussian distribution for the mismatched prior, i.e., p s ) CN 0, 1) as the variance parameter τ t wi be scaed accordingy to E s in the tuning stage ). For the mismatched Gaussian prior, the posterior mean function 4) is given by F mm r, τ) = Es E s+τ r. In the arge-system imit, we can derive the foowing mismatched SE recursion given in 6) using Theorem 1: σ t+1 = N 0 + β min γ 0 E s E s+γ ) E s σ t + γ 4 ). 11) Evidenty, the mismatched SE recursion 11) ony depends on the signa energy E s and no other properties of the true prior ps 0 ). This fact aows us to optimay tune the variance parameters ony with nowedge of signa energy E s. We note that the RHS of 11) is minimized by γ = σt and thus, the mismatched SE recursion becomes: σt+1 = N 0 + β Es E s+σ σ t t. 1) By Lemma 5, M-LAMA has a unique fixed point if β 1. Interestingy, if we define signa-to-interference ratio SIR) as SIR = 1/σ and et t max, then the fixed-point soution of 1) coincides to the SIR of the inear MMSE detector in the arge-system imit [8] [10]. Hence, for a mismatched Gaussian prior, M-LAMA achieves the same performance as the inear MMSE detector. We note that the proofs given in [8] [10] use resuts from random matrix theory, whereas our anaysis uses the mismatched SE recursion in Theorem 1. Furthermore, our resut is constructive, i.e., M-LAMA is a nove, computationay efficient agorithm that impements inear MMSE detection. B. Sub-optima data detection with a Gaussian prior We can repace the optima tuning stage of τ t in ) for the M-LAMA agorithm by a fixed variance parameter choice, which eads to a sub-optima, mismatched agorithm, referred to as sub-optima M-LAMA short SM-LAMA). We now show that this approach eads to other we-nown inear data detectors. In particuar, we obtain the foowing mismatched
4 SE recursions in the arge-system imit for the foowing two choices of variance parameters γ t 0 and γ t in 5): ZF) σ t+1= N 0 + β im γ t 0 Ψ mm σ t, γ t )=N 0 + βσ t, MF) σ t+1= N 0 + β im γ t Ψ mm σ t, γ t )=N 0 + β Var S0 [S 0 ]. By Lemma 5, ZF) and MF) has a unique fixed point if β < 1 and for any finite β, respectivey. If β < 1, then the soution to the fixed-point equation of ZF) and MF) coincides exacty to the SIR given by ZF and MF detector in the argesystem imit [8] [10], respectivey. Hence, by choosing specific predefined and sub-optima variance parameters γ t, SM-LAMA can be used to perform ZF and MF data detection. C. Optimay-tuned data detection with a hypercube prior We now derive an M-LAMA agorithm variant using a mismatched uniform distribution within a hypercube around the true prior distribution of square consteations e.g., QPSK and 16-QAM). For exampe, for a QPSK system with equay iey symbos, we use a mismatched prior distributed uniformy in the interva [ 1, +1] for both the rea and imaginary part. For this mismatched prior, we use Lemma 4 to compute the posterior mean function independenty for the rea and imaginary part; the posterior mean function F mm is given by F mm s, τ) = s + τ ν s R, τ/) + iν s I, τ/)), 13) where we use s R = Re{s }, s I = Im{s }, and ν s, τ) = e 1 τ s +α) e τ 1 s α) s +α s α )), πτ Φ τ ) Φ τ with Φx)= x π e u / du. The mismatched SE recursion can be obtained from Theorem 1 and evauated numericay. There are two disadvantages of this agorithm: i) The computation of the posterior mean function 13) is not efficient from a hardware perspective as it invoves transcendenta functions. In fact, computing ν s, τ) requires simiar to that of the optima LAMA agorithm 10) excessivey high numerica precision; ii) the tuning stage ) turns out to be non-trivia and requires numerica methods to find a minimum. Hence, corresponding hardware designs are impractica. D. Sub-optima data detection with a hypercube prior Anaogousy to the ZF detector in Section III-B, we can derive a sub-optima variant of M-LAMA SM-LAMA) with the hypercube prior from Section III-C, where we repace the tuning stage in ) by the fixed choice τ t 0. This choice eads to a much simper agorithm compared to the optimay-tuned M-LAMA agorithm and enabes a detaied performance anaysis. The posterior mean function reduces to im τ 0 Fmm s, τ) = s R + sign s R ) min { α } s R, 0 + i s I + sign s I ) min { α s I, 0 }), and thus, im τ 0 F mm s, τ) and its derivative can be evauated efficienty in hardware. Furthermore, by fixing τ 0, the tuning stages in 1) and ) are no onger required. symbo error rate SER) MMSE imit) 10 3 M-LAMA-MMSE finite) M-LAMA-hypercube finite) SM-LAMA-hypercube finite) SM-LAMA-hypercube imit) LAMA finite) average SNR per receive antenna [db] Fig. 1. Symbo-error rate of M-LAMA and its variants for a arge-mimo system with 10 iterations and QPSK; finite) and imit) denote the detectors that are simuated and computed by SE in the arge-system imit), respectivey. SM-LAMA with the uniform hypercube prior performs within 1 db from LAMA [6] that achieves IO performance in the arge-system imit. We now present conditions on the system ratio β for which SM-LAMA has a unique fixed point. The foowing Lemma 6, with proof in Appendix C, shows that the MRT of SM-LAMA for M -QAM is given by β min = 1 1/M) 1. Lemma 6. Assume a M -QAM prior for S 0 with equay iey symbos. Then, the MRT for SM-LAMA is given by β min = 1 1/M) 1. Moreover, SM-LAMA has a unique fixed point at β = β min regardess of the noise variance N 0. Using Lemma 6, we obtain the same MRT for M-PAM consteations by Lemma 4. We omit the proof and refer to [7]. Coroary 7. SM-LAMA has the same MRT for M -QAM and M-PAM in a compex and rea-vaued system, respectivey. We now show that this computationay-efficient SM-LAMA variant achieves the same performance as a we-nown reaxation of the maximum ieihood data detection probem [11] [13]. The agorithm, which is nown as box reaxation BOX) detector, soves the foowing convex probem: ŝ = arg min s C M T y H s subject to s 1 14) and sices the individua entries of ŝ onto the QPSK or BSPK) consteations. The next resut shows that SM-LAMA achieves the same error rate performance as the BOX detector for β <, whie providing a simpe and computationay efficient agorithm. The proof is given in Appendix B. Lemma 8. Assume β < and the arge system imit. Then, for a compex-vaued MIMO system with QPSK or a reavaued MIMO system with BPSK), SM-LAMA achieves the same error-rate performance as the BOX agorithm in 14). IV. NUMERICAL RESULTS We now compare the error-rate performance of the M-LAMA agorithm variants proposed in this paper. Whie the mismatched
5 SE framewor in Theorem 1 enabes an exact performance anaysis in the arge-system imit, we aso carry out Monte Caro simuations in a finite-dimensiona arge MIMO system with 18 receive and 64 transmit antennas. Fig. 1 shows the symbo error-rate performance of LAMA, M-LAMA, and SM-LAMA. The optimay-tuned M-LAMA and sub-optima SM-LAMA with the uniform hypercube prior perform within 1 db of the LAMA agorithm [6], which achieves IO performance in the arge-system imit. These resuts demonstrate that carefuyseected mismatched priors enabe near-io performance in finite-dimensiona systems and in a hardware-friendy way. APPENDIX A DERIVATION OF THE MSE FUNCTION Ψ QAM σ ) We wi compute the MSE function for Ψ QAM σ ) by first computing the MSE function Ψ PAM σ ) for a rea-vaued M-PAM system with equay iey symbos and then, use Lemma 4 to express Ψ QAM σ ) for M -QAM. We start by defining F α s ) = s + signs ) min{α s, 0}. Note that for equay iey symbos, the M-PAM consteation can be expressed by ps ) = 1 M/ M = M/+1 δs 1)). Thus, by using symmetry for equay iey M-PAM symbos: Ψ PAM σ ) = M/ M =1 ΨPAM σ ), 15) where we introduced Ψ PAM σ ) that is defined by: Ψ PAM σ ) = E Z [F α 1) + σz) 1)) ] = σ + ᾱ σ )Q ᾱ ) σ + α σ )Q α ) σ σ π ᾱ e ᾱ σ σ π α e α σ, with ᾱ = α 1), α = α + 1), Z N 0, 1), and Qx) = x π e u / du. By Lemma 4, Ψ QAM can be computed by Ψ QAM σ ) = Ψ PAM σ /) with α = M 1. APPENDIX B PROOF OF LEMMA 8 We start by stating the foowing resut from [13, Thm..1] that estabishes the error-rate performance of BOX detector. Theorem 9 Theorem.1 [13]). Assume a rea-vaued BPSK system with β <. The bit-error rate in the arge-system imit converges to Q1/τ ), where τ is the unique soution to τ = arg min τ>0 gτ), where gτ) is defined by ) gτ) = τ 1 β 1 + N0 βτ + ) τ x τ π e x dx. We note that as τ is the unique, minima soution to gτ), we have g τ ) = 0. Rearranging terms in g τ ) = 0 resuts in the fixed-point equation τ = N 0 + βψτ ) with Ψτ ) = 1 τ τ π e τ τ ) + Q τ 4 τ ). 16) The function Ψτ ) in 16) is identica to 15) for a BPSK system, i.e., M = with σ = τ. This impies that the BOX-reaxed method in [13] and SM-LAMA with the uniform hypercube prior achieves the same fixed-point 8). Moreover, due to the decouping property of SM-LAMA detaied in Section II-B, the error-rate of a rea-vaued BPSK system in the arge-system imit is given by Q1/τ ). The resut of Theorem 9 can be generaized to compex-vaued QPSK systems and is equa to fixed-point soution of SM-LAMA by Lemma 4. APPENDIX C PROOF OF LEMMA 6 As shown in Appendix A, we compute dσ Ψ QAM σ ) and d observe that dσ Ψ QAM σ ) 1 1/M, where equaity is achieved ony when σ 0. Thus, β min = 1 1/M) 1. To show that M-LAMA aso has a unique fixed point when β = β min, we use Lemma 5 and observe that no other σ > 0 satisfies β min = dψσ )/dσ ) 1 at σ = σ. REFERENCES [1] C. Jeon, A. Maei, and C. Studer, Mismatched data detection in arge MIMO systems, in preparation. [] S. Verdú, Mutiuser Detection. Cambridge University Press, [3] D. Guo and S. Verdú, Mutiuser detection and statistica mechanics, in Commun., Inf. and Netw. Security. Springer, 003, pp [4], Randomy spread CDMA: Asymptotics via statistica physics, IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vo. 51, no. 6, pp , Jun [5] D. Seethaer, J. Jadén, C. Studer, and H. Böcsei, On the compexity distribution of sphere decoding, IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vo. 57, no. 9, pp , Sept [6] C. Jeon, R. Ghods, A. Maei, and C. Studer, Optimaity of arge MIMO detection via approximate message passing, in Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Inf. Theory ISIT), Jun. 015, pp [7], Optima data detection in arge MIMO, in preparation. [8] S. Verdú and S. Shamai, Spectra efficiency of CDMA with random spreading, IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vo. 45, no., pp , Mar [9] D. Tse and S. Hany, Linear mutiuser receivers: effective interference, effective bandwidth and user capacity, IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vo. 45, no., pp , Mar [10] S. Shamai and S. Verdu, The impact of frequency-fat fading on the spectra efficiency of CDMA, IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vo. 47, no. 4, pp , May 001. [11] P. H. Tan, L. K. Rasmussen, and T. J. Lim, Constrained maximumieihood detection in CDMA, IEEE Trans. Commun., vo. 49, no. 1, pp , Jan [1] A. Yener, R. D. Yates, and S. Uuus, CDMA mutiuser detection: A noninear programming approach, IEEE Trans. Commun., vo. 50, no. 6, pp , Jun. 00. [13] C. Thrampouidis, E. Abbasi, W. Xu, and B. Hassibi, BER anaysis of the box reaxation for BPSK signa recovery, IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust., Speech, Signa Process. ICASSP), 016. [14] D. L. Donoho and J. Tanner, Counting the faces of randomy-projected hypercubes and orthants, with appications, Discrete Comput. Geometry, vo. 43, no. 3, pp , Apr [15] O. Mangasarian and B. Recht, Probabiity of unique integer soution to a system of inear equations, Eur. J. Oper. Res., vo. 14, no. 1, pp. 7 30, Oct [16] D. L. Donoho, A. Maei, and A. Montanari, Message-passing agorithms for compressed sensing, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, vo. 106, no. 45, pp , Nov [17] M. Bayati and A. Montanari, The dynamics of message passing on dense graphs, with appications to compressed sensing, IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vo. 57, no., pp , Feb [18] A. Montanari, Graphica modes concepts in compressed sensing, Compressed Sensing Y.C. Edar and G. Kutynio, eds.). Cambridge University Press, 01. [19] A. Mousavi, A. Maei, and R. G. Baraniu, Parameteress Optima Approximate Message Passing, arxiv: [cs.it], Oct [0], Consistent Parameter Estimation for LASSO and Approximate Message Passing, arxiv: [math.st], Nov [1] A. Maei, Approximate message passing agorithms for compressed sensing, Ph.D. dissertation, Stanford University, Jan [] D. Guo, Y. Wu, S. Shamai, and S. Verdú, Estimation in Gaussian noise: Properties of the minimum mean-square error, IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vo. 57, no. 4, pp , Apr d
Optimality of Large MIMO Detection via Approximate Message Passing
 ptimality of Large MIM Detection via Approximate Message Passing Charles Jeon, Ramina Ghods, Arian Maleki, and Christoph Studer arxiv:5.695v [cs.it] ct 5 Abstract ptimal data detection in multiple-input
ptimality of Large MIM Detection via Approximate Message Passing Charles Jeon, Ramina Ghods, Arian Maleki, and Christoph Studer arxiv:5.695v [cs.it] ct 5 Abstract ptimal data detection in multiple-input
Maximizing Sum Rate and Minimizing MSE on Multiuser Downlink: Optimality, Fast Algorithms and Equivalence via Max-min SIR
 1 Maximizing Sum Rate and Minimizing MSE on Mutiuser Downink: Optimaity, Fast Agorithms and Equivaence via Max-min SIR Chee Wei Tan 1,2, Mung Chiang 2 and R. Srikant 3 1 Caifornia Institute of Technoogy,
1 Maximizing Sum Rate and Minimizing MSE on Mutiuser Downink: Optimaity, Fast Agorithms and Equivaence via Max-min SIR Chee Wei Tan 1,2, Mung Chiang 2 and R. Srikant 3 1 Caifornia Institute of Technoogy,
A Brief Introduction to Markov Chains and Hidden Markov Models
 A Brief Introduction to Markov Chains and Hidden Markov Modes Aen B MacKenzie Notes for December 1, 3, &8, 2015 Discrete-Time Markov Chains You may reca that when we first introduced random processes,
A Brief Introduction to Markov Chains and Hidden Markov Modes Aen B MacKenzie Notes for December 1, 3, &8, 2015 Discrete-Time Markov Chains You may reca that when we first introduced random processes,
Optimal Data Detection in Large MIMO
 1 ptimal Data Detection in Large MIM Charles Jeon, Ramina Ghods, Arian Maleki, and Christoph Studer Abstract arxiv:1811.01917v1 [cs.it] 5 Nov 018 Large multiple-input multiple-output (MIM) appears in massive
1 ptimal Data Detection in Large MIM Charles Jeon, Ramina Ghods, Arian Maleki, and Christoph Studer Abstract arxiv:1811.01917v1 [cs.it] 5 Nov 018 Large multiple-input multiple-output (MIM) appears in massive
arxiv: v1 [cs.lg] 31 Oct 2017
![arxiv: v1 [cs.lg] 31 Oct 2017 arxiv: v1 [cs.lg] 31 Oct 2017](/thumbs/86/93671836.jpg) ACCELERATED SPARSE SUBSPACE CLUSTERING Abofaz Hashemi and Haris Vikao Department of Eectrica and Computer Engineering, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA arxiv:7.26v [cs.lg] 3 Oct 27 ABSTRACT
ACCELERATED SPARSE SUBSPACE CLUSTERING Abofaz Hashemi and Haris Vikao Department of Eectrica and Computer Engineering, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA arxiv:7.26v [cs.lg] 3 Oct 27 ABSTRACT
Improved Min-Sum Decoding of LDPC Codes Using 2-Dimensional Normalization
 Improved Min-Sum Decoding of LDPC Codes sing -Dimensiona Normaization Juntan Zhang and Marc Fossorier Department of Eectrica Engineering niversity of Hawaii at Manoa Honouu, HI 968 Emai: juntan, marc@spectra.eng.hawaii.edu
Improved Min-Sum Decoding of LDPC Codes sing -Dimensiona Normaization Juntan Zhang and Marc Fossorier Department of Eectrica Engineering niversity of Hawaii at Manoa Honouu, HI 968 Emai: juntan, marc@spectra.eng.hawaii.edu
A Simple and Efficient Algorithm of 3-D Single-Source Localization with Uniform Cross Array Bing Xue 1 2 a) * Guangyou Fang 1 2 b and Yicai Ji 1 2 c)
 A Simpe Efficient Agorithm of 3-D Singe-Source Locaization with Uniform Cross Array Bing Xue a * Guangyou Fang b Yicai Ji c Key Laboratory of Eectromagnetic Radiation Sensing Technoogy, Institute of Eectronics,
A Simpe Efficient Agorithm of 3-D Singe-Source Locaization with Uniform Cross Array Bing Xue a * Guangyou Fang b Yicai Ji c Key Laboratory of Eectromagnetic Radiation Sensing Technoogy, Institute of Eectronics,
Asynchronous Control for Coupled Markov Decision Systems
 INFORMATION THEORY WORKSHOP (ITW) 22 Asynchronous Contro for Couped Marov Decision Systems Michae J. Neey University of Southern Caifornia Abstract This paper considers optima contro for a coection of
INFORMATION THEORY WORKSHOP (ITW) 22 Asynchronous Contro for Couped Marov Decision Systems Michae J. Neey University of Southern Caifornia Abstract This paper considers optima contro for a coection of
Rate-Distortion Theory of Finite Point Processes
 Rate-Distortion Theory of Finite Point Processes Günther Koiander, Dominic Schuhmacher, and Franz Hawatsch, Feow, IEEE Abstract We study the compression of data in the case where the usefu information
Rate-Distortion Theory of Finite Point Processes Günther Koiander, Dominic Schuhmacher, and Franz Hawatsch, Feow, IEEE Abstract We study the compression of data in the case where the usefu information
Source and Relay Matrices Optimization for Multiuser Multi-Hop MIMO Relay Systems
 Source and Reay Matrices Optimization for Mutiuser Muti-Hop MIMO Reay Systems Yue Rong Department of Eectrica and Computer Engineering, Curtin University, Bentey, WA 6102, Austraia Abstract In this paper,
Source and Reay Matrices Optimization for Mutiuser Muti-Hop MIMO Reay Systems Yue Rong Department of Eectrica and Computer Engineering, Curtin University, Bentey, WA 6102, Austraia Abstract In this paper,
XSAT of linear CNF formulas
 XSAT of inear CN formuas Bernd R. Schuh Dr. Bernd Schuh, D-50968 Kön, Germany; bernd.schuh@netcoogne.de eywords: compexity, XSAT, exact inear formua, -reguarity, -uniformity, NPcompeteness Abstract. Open
XSAT of inear CN formuas Bernd R. Schuh Dr. Bernd Schuh, D-50968 Kön, Germany; bernd.schuh@netcoogne.de eywords: compexity, XSAT, exact inear formua, -reguarity, -uniformity, NPcompeteness Abstract. Open
Precoding for the Sparsely Spread MC-CDMA Downlink with Discrete-Alphabet Inputs
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL.*, NO.*, MONTH 2016 1 Precoding for the Sparsey Spread MC-CDMA Downin with Discrete-Aphabet Inputs Min Li, Member, IEEE, Chunshan Liu, Member, IEEE, and Stephen
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL.*, NO.*, MONTH 2016 1 Precoding for the Sparsey Spread MC-CDMA Downin with Discrete-Aphabet Inputs Min Li, Member, IEEE, Chunshan Liu, Member, IEEE, and Stephen
Expectation-Maximization for Estimating Parameters for a Mixture of Poissons
 Expectation-Maximization for Estimating Parameters for a Mixture of Poissons Brandon Maone Department of Computer Science University of Hesini February 18, 2014 Abstract This document derives, in excrutiating
Expectation-Maximization for Estimating Parameters for a Mixture of Poissons Brandon Maone Department of Computer Science University of Hesini February 18, 2014 Abstract This document derives, in excrutiating
Iterative Decoding Performance Bounds for LDPC Codes on Noisy Channels
 Iterative Decoding Performance Bounds for LDPC Codes on Noisy Channes arxiv:cs/060700v1 [cs.it] 6 Ju 006 Chun-Hao Hsu and Achieas Anastasopouos Eectrica Engineering and Computer Science Department University
Iterative Decoding Performance Bounds for LDPC Codes on Noisy Channes arxiv:cs/060700v1 [cs.it] 6 Ju 006 Chun-Hao Hsu and Achieas Anastasopouos Eectrica Engineering and Computer Science Department University
Lecture Note 3: Stationary Iterative Methods
 MATH 5330: Computationa Methods of Linear Agebra Lecture Note 3: Stationary Iterative Methods Xianyi Zeng Department of Mathematica Sciences, UTEP Stationary Iterative Methods The Gaussian eimination (or
MATH 5330: Computationa Methods of Linear Agebra Lecture Note 3: Stationary Iterative Methods Xianyi Zeng Department of Mathematica Sciences, UTEP Stationary Iterative Methods The Gaussian eimination (or
Bayesian Unscented Kalman Filter for State Estimation of Nonlinear and Non-Gaussian Systems
 Bayesian Unscented Kaman Fiter for State Estimation of Noninear and Non-aussian Systems Zhong Liu, Shing-Chow Chan, Ho-Chun Wu and iafei Wu Department of Eectrica and Eectronic Engineering, he University
Bayesian Unscented Kaman Fiter for State Estimation of Noninear and Non-aussian Systems Zhong Liu, Shing-Chow Chan, Ho-Chun Wu and iafei Wu Department of Eectrica and Eectronic Engineering, he University
Haar Decomposition and Reconstruction Algorithms
 Jim Lambers MAT 773 Fa Semester 018-19 Lecture 15 and 16 Notes These notes correspond to Sections 4.3 and 4.4 in the text. Haar Decomposition and Reconstruction Agorithms Decomposition Suppose we approximate
Jim Lambers MAT 773 Fa Semester 018-19 Lecture 15 and 16 Notes These notes correspond to Sections 4.3 and 4.4 in the text. Haar Decomposition and Reconstruction Agorithms Decomposition Suppose we approximate
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF MULTIPLE ACCESS CHAOTIC-SEQUENCE SPREAD-SPECTRUM COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS USING PARALLEL INTERFERENCE CANCELLATION RECEIVERS
 Internationa Journa of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vo. 14, No. 10 (2004) 3633 3646 c Word Scientific Pubishing Company PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF MULTIPLE ACCESS CHAOTIC-SEQUENCE SPREAD-SPECTRUM COMMUNICATION
Internationa Journa of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vo. 14, No. 10 (2004) 3633 3646 c Word Scientific Pubishing Company PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF MULTIPLE ACCESS CHAOTIC-SEQUENCE SPREAD-SPECTRUM COMMUNICATION
Scalable Spectrum Allocation for Large Networks Based on Sparse Optimization
 Scaabe Spectrum ocation for Large Networks ased on Sparse Optimization innan Zhuang Modem R&D Lab Samsung Semiconductor, Inc. San Diego, C Dongning Guo, Ermin Wei, and Michae L. Honig Department of Eectrica
Scaabe Spectrum ocation for Large Networks ased on Sparse Optimization innan Zhuang Modem R&D Lab Samsung Semiconductor, Inc. San Diego, C Dongning Guo, Ermin Wei, and Michae L. Honig Department of Eectrica
Turbo Codes. Coding and Communication Laboratory. Dept. of Electrical Engineering, National Chung Hsing University
 Turbo Codes Coding and Communication Laboratory Dept. of Eectrica Engineering, Nationa Chung Hsing University Turbo codes 1 Chapter 12: Turbo Codes 1. Introduction 2. Turbo code encoder 3. Design of intereaver
Turbo Codes Coding and Communication Laboratory Dept. of Eectrica Engineering, Nationa Chung Hsing University Turbo codes 1 Chapter 12: Turbo Codes 1. Introduction 2. Turbo code encoder 3. Design of intereaver
NEW DEVELOPMENT OF OPTIMAL COMPUTING BUDGET ALLOCATION FOR DISCRETE EVENT SIMULATION
 NEW DEVELOPMENT OF OPTIMAL COMPUTING BUDGET ALLOCATION FOR DISCRETE EVENT SIMULATION Hsiao-Chang Chen Dept. of Systems Engineering University of Pennsyvania Phiadephia, PA 904-635, U.S.A. Chun-Hung Chen
NEW DEVELOPMENT OF OPTIMAL COMPUTING BUDGET ALLOCATION FOR DISCRETE EVENT SIMULATION Hsiao-Chang Chen Dept. of Systems Engineering University of Pennsyvania Phiadephia, PA 904-635, U.S.A. Chun-Hung Chen
LINEAR DETECTORS FOR MULTI-USER MIMO SYSTEMS WITH CORRELATED SPATIAL DIVERSITY
 LINEAR DETECTORS FOR MULTI-USER MIMO SYSTEMS WITH CORRELATED SPATIAL DIVERSITY Laura Cottateucci, Raf R. Müer, and Mérouane Debbah Ist. of Teecommunications Research Dep. of Eectronics and Teecommunications
LINEAR DETECTORS FOR MULTI-USER MIMO SYSTEMS WITH CORRELATED SPATIAL DIVERSITY Laura Cottateucci, Raf R. Müer, and Mérouane Debbah Ist. of Teecommunications Research Dep. of Eectronics and Teecommunications
A proposed nonparametric mixture density estimation using B-spline functions
 A proposed nonparametric mixture density estimation using B-spine functions Atizez Hadrich a,b, Mourad Zribi a, Afif Masmoudi b a Laboratoire d Informatique Signa et Image de a Côte d Opae (LISIC-EA 4491),
A proposed nonparametric mixture density estimation using B-spine functions Atizez Hadrich a,b, Mourad Zribi a, Afif Masmoudi b a Laboratoire d Informatique Signa et Image de a Côte d Opae (LISIC-EA 4491),
Sequential Decoding of Polar Codes with Arbitrary Binary Kernel
 Sequentia Decoding of Poar Codes with Arbitrary Binary Kerne Vera Miosavskaya, Peter Trifonov Saint-Petersburg State Poytechnic University Emai: veram,petert}@dcn.icc.spbstu.ru Abstract The probem of efficient
Sequentia Decoding of Poar Codes with Arbitrary Binary Kerne Vera Miosavskaya, Peter Trifonov Saint-Petersburg State Poytechnic University Emai: veram,petert}@dcn.icc.spbstu.ru Abstract The probem of efficient
Analysis of the problem of intervention control in the economy on the basis of solving the problem of tuning
 Anaysis of the probem of intervention contro in the economy on the basis of soving the probem of tuning arxiv:1811.10993v1 q-fin.gn] 9 Nov 2018 1 st eter Shnurov Nationa Research University Higher Schoo
Anaysis of the probem of intervention contro in the economy on the basis of soving the probem of tuning arxiv:1811.10993v1 q-fin.gn] 9 Nov 2018 1 st eter Shnurov Nationa Research University Higher Schoo
Unconditional security of differential phase shift quantum key distribution
 Unconditiona security of differentia phase shift quantum key distribution Kai Wen, Yoshihisa Yamamoto Ginzton Lab and Dept of Eectrica Engineering Stanford University Basic idea of DPS-QKD Protoco. Aice
Unconditiona security of differentia phase shift quantum key distribution Kai Wen, Yoshihisa Yamamoto Ginzton Lab and Dept of Eectrica Engineering Stanford University Basic idea of DPS-QKD Protoco. Aice
High Spectral Resolution Infrared Radiance Modeling Using Optimal Spectral Sampling (OSS) Method
 High Spectra Resoution Infrared Radiance Modeing Using Optima Spectra Samping (OSS) Method J.-L. Moncet and G. Uymin Background Optima Spectra Samping (OSS) method is a fast and accurate monochromatic
High Spectra Resoution Infrared Radiance Modeing Using Optima Spectra Samping (OSS) Method J.-L. Moncet and G. Uymin Background Optima Spectra Samping (OSS) method is a fast and accurate monochromatic
A. Distribution of the test statistic
 A. Distribution of the test statistic In the sequentia test, we first compute the test statistic from a mini-batch of size m. If a decision cannot be made with this statistic, we keep increasing the mini-batch
A. Distribution of the test statistic In the sequentia test, we first compute the test statistic from a mini-batch of size m. If a decision cannot be made with this statistic, we keep increasing the mini-batch
Limits on Support Recovery with Probabilistic Models: An Information-Theoretic Framework
 Limits on Support Recovery with Probabiistic Modes: An Information-Theoretic Framewor Jonathan Scarett and Voan Cevher arxiv:5.744v3 cs.it 3 Aug 6 Abstract The support recovery probem consists of determining
Limits on Support Recovery with Probabiistic Modes: An Information-Theoretic Framewor Jonathan Scarett and Voan Cevher arxiv:5.744v3 cs.it 3 Aug 6 Abstract The support recovery probem consists of determining
A Fundamental Storage-Communication Tradeoff in Distributed Computing with Straggling Nodes
 A Fundamenta Storage-Communication Tradeoff in Distributed Computing with Stragging odes ifa Yan, Michèe Wigger LTCI, Téécom ParisTech 75013 Paris, France Emai: {qifa.yan, michee.wigger} @teecom-paristech.fr
A Fundamenta Storage-Communication Tradeoff in Distributed Computing with Stragging odes ifa Yan, Michèe Wigger LTCI, Téécom ParisTech 75013 Paris, France Emai: {qifa.yan, michee.wigger} @teecom-paristech.fr
Centralized Coded Caching of Correlated Contents
 Centraized Coded Caching of Correated Contents Qianqian Yang and Deniz Gündüz Information Processing and Communications Lab Department of Eectrica and Eectronic Engineering Imperia Coege London arxiv:1711.03798v1
Centraized Coded Caching of Correated Contents Qianqian Yang and Deniz Gündüz Information Processing and Communications Lab Department of Eectrica and Eectronic Engineering Imperia Coege London arxiv:1711.03798v1
Power Control and Transmission Scheduling for Network Utility Maximization in Wireless Networks
 ower Contro and Transmission Scheduing for Network Utiity Maximization in Wireess Networks Min Cao, Vivek Raghunathan, Stephen Hany, Vinod Sharma and. R. Kumar Abstract We consider a joint power contro
ower Contro and Transmission Scheduing for Network Utiity Maximization in Wireess Networks Min Cao, Vivek Raghunathan, Stephen Hany, Vinod Sharma and. R. Kumar Abstract We consider a joint power contro
Theory of Generalized k-difference Operator and Its Application in Number Theory
 Internationa Journa of Mathematica Anaysis Vo. 9, 2015, no. 19, 955-964 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hiari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2015.5389 Theory of Generaized -Difference Operator and Its Appication
Internationa Journa of Mathematica Anaysis Vo. 9, 2015, no. 19, 955-964 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hiari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijma.2015.5389 Theory of Generaized -Difference Operator and Its Appication
Mismatched Estimation in Large Linear Systems
 Mismatched Estimation in Large Linear Systems Yanting Ma, Dror Baron, Ahmad Beirami Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC 7695, USA Department
Mismatched Estimation in Large Linear Systems Yanting Ma, Dror Baron, Ahmad Beirami Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC 7695, USA Department
Transmit Antenna Selection for Physical-Layer Network Coding Based on Euclidean Distance
 Transmit ntenna Seection for Physica-Layer Networ Coding ased on Eucidean Distance 1 arxiv:179.445v1 [cs.it] 13 Sep 17 Vaibhav Kumar, arry Cardiff, and Mar F. Fanagan Schoo of Eectrica and Eectronic Engineering,
Transmit ntenna Seection for Physica-Layer Networ Coding ased on Eucidean Distance 1 arxiv:179.445v1 [cs.it] 13 Sep 17 Vaibhav Kumar, arry Cardiff, and Mar F. Fanagan Schoo of Eectrica and Eectronic Engineering,
On the Achievable Rates of Decentralized Equalization in Massive MU-MIMO Systems
 On the Achievable Rates of Decentralized Equalization in Massive MU-MIMO Systems Charles Jeon, Kaipeng Li, Joseph R. Cavallaro, and Christoph Studer Abstract Massive multi-user (MU) multiple-input multipleoutput
On the Achievable Rates of Decentralized Equalization in Massive MU-MIMO Systems Charles Jeon, Kaipeng Li, Joseph R. Cavallaro, and Christoph Studer Abstract Massive multi-user (MU) multiple-input multipleoutput
An approximate method for solving the inverse scattering problem with fixed-energy data
 J. Inv. I-Posed Probems, Vo. 7, No. 6, pp. 561 571 (1999) c VSP 1999 An approximate method for soving the inverse scattering probem with fixed-energy data A. G. Ramm and W. Scheid Received May 12, 1999
J. Inv. I-Posed Probems, Vo. 7, No. 6, pp. 561 571 (1999) c VSP 1999 An approximate method for soving the inverse scattering probem with fixed-energy data A. G. Ramm and W. Scheid Received May 12, 1999
First-Order Corrections to Gutzwiller s Trace Formula for Systems with Discrete Symmetries
 c 26 Noninear Phenomena in Compex Systems First-Order Corrections to Gutzwier s Trace Formua for Systems with Discrete Symmetries Hoger Cartarius, Jörg Main, and Günter Wunner Institut für Theoretische
c 26 Noninear Phenomena in Compex Systems First-Order Corrections to Gutzwier s Trace Formua for Systems with Discrete Symmetries Hoger Cartarius, Jörg Main, and Günter Wunner Institut für Theoretische
Explicit overall risk minimization transductive bound
 1 Expicit overa risk minimization transductive bound Sergio Decherchi, Paoo Gastado, Sandro Ridea, Rodofo Zunino Dept. of Biophysica and Eectronic Engineering (DIBE), Genoa University Via Opera Pia 11a,
1 Expicit overa risk minimization transductive bound Sergio Decherchi, Paoo Gastado, Sandro Ridea, Rodofo Zunino Dept. of Biophysica and Eectronic Engineering (DIBE), Genoa University Via Opera Pia 11a,
Convergence Property of the Iri-Imai Algorithm for Some Smooth Convex Programming Problems
 Convergence Property of the Iri-Imai Agorithm for Some Smooth Convex Programming Probems S. Zhang Communicated by Z.Q. Luo Assistant Professor, Department of Econometrics, University of Groningen, Groningen,
Convergence Property of the Iri-Imai Agorithm for Some Smooth Convex Programming Probems S. Zhang Communicated by Z.Q. Luo Assistant Professor, Department of Econometrics, University of Groningen, Groningen,
A Solution to the 4-bit Parity Problem with a Single Quaternary Neuron
 Neura Information Processing - Letters and Reviews Vo. 5, No. 2, November 2004 LETTER A Soution to the 4-bit Parity Probem with a Singe Quaternary Neuron Tohru Nitta Nationa Institute of Advanced Industria
Neura Information Processing - Letters and Reviews Vo. 5, No. 2, November 2004 LETTER A Soution to the 4-bit Parity Probem with a Singe Quaternary Neuron Tohru Nitta Nationa Institute of Advanced Industria
PARSIMONIOUS VARIATIONAL-BAYES MIXTURE AGGREGATION WITH A POISSON PRIOR. Pierrick Bruneau, Marc Gelgon and Fabien Picarougne
 17th European Signa Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2009) Gasgow, Scotand, August 24-28, 2009 PARSIMONIOUS VARIATIONAL-BAYES MIXTURE AGGREGATION WITH A POISSON PRIOR Pierric Bruneau, Marc Gegon and Fabien
17th European Signa Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2009) Gasgow, Scotand, August 24-28, 2009 PARSIMONIOUS VARIATIONAL-BAYES MIXTURE AGGREGATION WITH A POISSON PRIOR Pierric Bruneau, Marc Gegon and Fabien
CS229 Lecture notes. Andrew Ng
 CS229 Lecture notes Andrew Ng Part IX The EM agorithm In the previous set of notes, we taked about the EM agorithm as appied to fitting a mixture of Gaussians. In this set of notes, we give a broader view
CS229 Lecture notes Andrew Ng Part IX The EM agorithm In the previous set of notes, we taked about the EM agorithm as appied to fitting a mixture of Gaussians. In this set of notes, we give a broader view
Maximum likelihood decoding of trellis codes in fading channels with no receiver CSI is a polynomial-complexity problem
 1 Maximum ikeihood decoding of treis codes in fading channes with no receiver CSI is a poynomia-compexity probem Chun-Hao Hsu and Achieas Anastasopouos Eectrica Engineering and Computer Science Department
1 Maximum ikeihood decoding of treis codes in fading channes with no receiver CSI is a poynomia-compexity probem Chun-Hao Hsu and Achieas Anastasopouos Eectrica Engineering and Computer Science Department
A New Algorithm for the Weighted Sum Rate Maximization in MIMO Interference Networks
 A New Agorithm for the Weighted Sum Rate Maximization in MIMO Interference Networks Xing Li, Seungi You 2, Lijun Chen, An Liu 3, Youjian Eugene Liu Abstract We propose a new agorithm to sove the non-convex
A New Agorithm for the Weighted Sum Rate Maximization in MIMO Interference Networks Xing Li, Seungi You 2, Lijun Chen, An Liu 3, Youjian Eugene Liu Abstract We propose a new agorithm to sove the non-convex
Statistical Learning Theory: A Primer
 Internationa Journa of Computer Vision 38(), 9 3, 2000 c 2000 uwer Academic Pubishers. Manufactured in The Netherands. Statistica Learning Theory: A Primer THEODOROS EVGENIOU, MASSIMILIANO PONTIL AND TOMASO
Internationa Journa of Computer Vision 38(), 9 3, 2000 c 2000 uwer Academic Pubishers. Manufactured in The Netherands. Statistica Learning Theory: A Primer THEODOROS EVGENIOU, MASSIMILIANO PONTIL AND TOMASO
MC-CDMA CDMA Systems. Introduction. Ivan Cosovic. Stefan Kaiser. IEEE Communication Theory Workshop 2005 Park City, USA, June 15, 2005
 On the Adaptivity in Down- and Upink MC- Systems Ivan Cosovic German Aerospace Center (DLR) Institute of Comm. and Navigation Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany Stefan Kaiser DoCoMo Euro-Labs Wireess Soution Laboratory
On the Adaptivity in Down- and Upink MC- Systems Ivan Cosovic German Aerospace Center (DLR) Institute of Comm. and Navigation Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany Stefan Kaiser DoCoMo Euro-Labs Wireess Soution Laboratory
DIGITAL FILTER DESIGN OF IIR FILTERS USING REAL VALUED GENETIC ALGORITHM
 DIGITAL FILTER DESIGN OF IIR FILTERS USING REAL VALUED GENETIC ALGORITHM MIKAEL NILSSON, MATTIAS DAHL AND INGVAR CLAESSON Bekinge Institute of Technoogy Department of Teecommunications and Signa Processing
DIGITAL FILTER DESIGN OF IIR FILTERS USING REAL VALUED GENETIC ALGORITHM MIKAEL NILSSON, MATTIAS DAHL AND INGVAR CLAESSON Bekinge Institute of Technoogy Department of Teecommunications and Signa Processing
Moreau-Yosida Regularization for Grouped Tree Structure Learning
 Moreau-Yosida Reguarization for Grouped Tree Structure Learning Jun Liu Computer Science and Engineering Arizona State University J.Liu@asu.edu Jieping Ye Computer Science and Engineering Arizona State
Moreau-Yosida Reguarization for Grouped Tree Structure Learning Jun Liu Computer Science and Engineering Arizona State University J.Liu@asu.edu Jieping Ye Computer Science and Engineering Arizona State
Nearly Optimal Constructions of PIR and Batch Codes
 arxiv:700706v [csit] 5 Jun 07 Neary Optima Constructions of PIR and Batch Codes Hia Asi Technion - Israe Institute of Technoogy Haifa 3000, Israe shea@cstechnionaci Abstract In this work we study two famiies
arxiv:700706v [csit] 5 Jun 07 Neary Optima Constructions of PIR and Batch Codes Hia Asi Technion - Israe Institute of Technoogy Haifa 3000, Israe shea@cstechnionaci Abstract In this work we study two famiies
FREQUENCY modulated differential chaos shift key (FM-
 Accepted in IEEE 83rd Vehicuar Technoogy Conference VTC, 16 1 SNR Estimation for FM-DCS System over Mutipath Rayeigh Fading Channes Guofa Cai, in Wang, ong ong, Georges addoum Dept. of Communication Engineering,
Accepted in IEEE 83rd Vehicuar Technoogy Conference VTC, 16 1 SNR Estimation for FM-DCS System over Mutipath Rayeigh Fading Channes Guofa Cai, in Wang, ong ong, Georges addoum Dept. of Communication Engineering,
An Algorithm for Pruning Redundant Modules in Min-Max Modular Network
 An Agorithm for Pruning Redundant Modues in Min-Max Moduar Network Hui-Cheng Lian and Bao-Liang Lu Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1954 Hua Shan Rd., Shanghai
An Agorithm for Pruning Redundant Modues in Min-Max Moduar Network Hui-Cheng Lian and Bao-Liang Lu Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1954 Hua Shan Rd., Shanghai
Fast Blind Recognition of Channel Codes
 Fast Bind Recognition of Channe Codes Reza Moosavi and Erik G. Larsson Linköping University Post Print N.B.: When citing this work, cite the origina artice. 213 IEEE. Persona use of this materia is permitted.
Fast Bind Recognition of Channe Codes Reza Moosavi and Erik G. Larsson Linköping University Post Print N.B.: When citing this work, cite the origina artice. 213 IEEE. Persona use of this materia is permitted.
Supporting Information for Suppressing Klein tunneling in graphene using a one-dimensional array of localized scatterers
 Supporting Information for Suppressing Kein tunneing in graphene using a one-dimensiona array of ocaized scatterers Jamie D Was, and Danie Hadad Department of Chemistry, University of Miami, Cora Gabes,
Supporting Information for Suppressing Kein tunneing in graphene using a one-dimensiona array of ocaized scatterers Jamie D Was, and Danie Hadad Department of Chemistry, University of Miami, Cora Gabes,
T.C. Banwell, S. Galli. {bct, Telcordia Technologies, Inc., 445 South Street, Morristown, NJ 07960, USA
 ON THE SYMMETRY OF THE POWER INE CHANNE T.C. Banwe, S. Gai {bct, sgai}@research.tecordia.com Tecordia Technoogies, Inc., 445 South Street, Morristown, NJ 07960, USA Abstract The indoor power ine network
ON THE SYMMETRY OF THE POWER INE CHANNE T.C. Banwe, S. Gai {bct, sgai}@research.tecordia.com Tecordia Technoogies, Inc., 445 South Street, Morristown, NJ 07960, USA Abstract The indoor power ine network
On the Achievable Extrinsic Information of Inner Decoders in Serial Concatenation
 On the Achievabe Extrinsic Information of Inner Decoders in Seria Concatenation Jörg Kiewer, Axe Huebner, and Danie J. Costeo, Jr. Department of Eectrica Engineering, University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame,
On the Achievabe Extrinsic Information of Inner Decoders in Seria Concatenation Jörg Kiewer, Axe Huebner, and Danie J. Costeo, Jr. Department of Eectrica Engineering, University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame,
Mode in Output Participation Factors for Linear Systems
 2010 American ontro onference Marriott Waterfront, Batimore, MD, USA June 30-Juy 02, 2010 WeB05.5 Mode in Output Participation Factors for Linear Systems Li Sheng, yad H. Abed, Munther A. Hassouneh, Huizhong
2010 American ontro onference Marriott Waterfront, Batimore, MD, USA June 30-Juy 02, 2010 WeB05.5 Mode in Output Participation Factors for Linear Systems Li Sheng, yad H. Abed, Munther A. Hassouneh, Huizhong
Uniformly Reweighted Belief Propagation: A Factor Graph Approach
 Uniformy Reweighted Beief Propagation: A Factor Graph Approach Henk Wymeersch Chamers University of Technoogy Gothenburg, Sweden henkw@chamers.se Federico Penna Poitecnico di Torino Torino, Itay federico.penna@poito.it
Uniformy Reweighted Beief Propagation: A Factor Graph Approach Henk Wymeersch Chamers University of Technoogy Gothenburg, Sweden henkw@chamers.se Federico Penna Poitecnico di Torino Torino, Itay federico.penna@poito.it
LOW-COMPLEXITY LINEAR PRECODING FOR MULTI-CELL MASSIVE MIMO SYSTEMS
 LOW-COMPLEXITY LINEAR PRECODING FOR MULTI-CELL MASSIVE MIMO SYSTEMS Aba ammoun, Axe Müer, Emi Björnson,3, and Mérouane Debbah ing Abduah University of Science and Technoogy (AUST, Saudi Arabia Acate-Lucent
LOW-COMPLEXITY LINEAR PRECODING FOR MULTI-CELL MASSIVE MIMO SYSTEMS Aba ammoun, Axe Müer, Emi Björnson,3, and Mérouane Debbah ing Abduah University of Science and Technoogy (AUST, Saudi Arabia Acate-Lucent
Nonlinear Gaussian Filtering via Radial Basis Function Approximation
 51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Contro December 10-13 01 Maui Hawaii USA Noninear Gaussian Fitering via Radia Basis Function Approximation Huazhen Fang Jia Wang and Raymond A de Caafon Abstract This
51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Contro December 10-13 01 Maui Hawaii USA Noninear Gaussian Fitering via Radia Basis Function Approximation Huazhen Fang Jia Wang and Raymond A de Caafon Abstract This
MARKOV CHAINS AND MARKOV DECISION THEORY. Contents
 MARKOV CHAINS AND MARKOV DECISION THEORY ARINDRIMA DATTA Abstract. In this paper, we begin with a forma introduction to probabiity and expain the concept of random variabes and stochastic processes. After
MARKOV CHAINS AND MARKOV DECISION THEORY ARINDRIMA DATTA Abstract. In this paper, we begin with a forma introduction to probabiity and expain the concept of random variabes and stochastic processes. After
A SIMPLIFIED DESIGN OF MULTIDIMENSIONAL TRANSFER FUNCTION MODELS
 A SIPLIFIED DESIGN OF ULTIDIENSIONAL TRANSFER FUNCTION ODELS Stefan Petrausch, Rudof Rabenstein utimedia Communications and Signa Procesg, University of Erangen-Nuremberg, Cauerstr. 7, 958 Erangen, GERANY
A SIPLIFIED DESIGN OF ULTIDIENSIONAL TRANSFER FUNCTION ODELS Stefan Petrausch, Rudof Rabenstein utimedia Communications and Signa Procesg, University of Erangen-Nuremberg, Cauerstr. 7, 958 Erangen, GERANY
The Weighted Sum Rate Maximization in MIMO Interference Networks: Minimax Lagrangian Duality and Algorithm
 1 The Weighted Sum Rate Maximization in MIMO Interference Networks: Minimax Lagrangian Duaity and Agorithm Lijun Chen Seungi You Abstract We take a new approach to the weighted sumrate maximization in
1 The Weighted Sum Rate Maximization in MIMO Interference Networks: Minimax Lagrangian Duaity and Agorithm Lijun Chen Seungi You Abstract We take a new approach to the weighted sumrate maximization in
Cryptanalysis of PKP: A New Approach
 Cryptanaysis of PKP: A New Approach Éiane Jaumes and Antoine Joux DCSSI 18, rue du Dr. Zamenhoff F-92131 Issy-es-Mx Cedex France eiane.jaumes@wanadoo.fr Antoine.Joux@ens.fr Abstract. Quite recenty, in
Cryptanaysis of PKP: A New Approach Éiane Jaumes and Antoine Joux DCSSI 18, rue du Dr. Zamenhoff F-92131 Issy-es-Mx Cedex France eiane.jaumes@wanadoo.fr Antoine.Joux@ens.fr Abstract. Quite recenty, in
Optimality of Gaussian Fronthaul Compression for Uplink MIMO Cloud Radio Access Networks
 Optimaity of Gaussian Fronthau Compression for Upink MMO Coud Radio Access etworks Yuhan Zhou, Yinfei Xu, Jun Chen, and Wei Yu Department of Eectrica and Computer Engineering, University of oronto, Canada
Optimaity of Gaussian Fronthau Compression for Upink MMO Coud Radio Access etworks Yuhan Zhou, Yinfei Xu, Jun Chen, and Wei Yu Department of Eectrica and Computer Engineering, University of oronto, Canada
STA 216 Project: Spline Approach to Discrete Survival Analysis
 : Spine Approach to Discrete Surviva Anaysis November 4, 005 1 Introduction Athough continuous surviva anaysis differs much from the discrete surviva anaysis, there is certain ink between the two modeing
: Spine Approach to Discrete Surviva Anaysis November 4, 005 1 Introduction Athough continuous surviva anaysis differs much from the discrete surviva anaysis, there is certain ink between the two modeing
A MODEL FOR ESTIMATING THE LATERAL OVERLAP PROBABILITY OF AIRCRAFT WITH RNP ALERTING CAPABILITY IN PARALLEL RNAV ROUTES
 6 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES A MODEL FOR ESTIMATING THE LATERAL OVERLAP PROBABILITY OF AIRCRAFT WITH RNP ALERTING CAPABILITY IN PARALLEL RNAV ROUTES Sakae NAGAOKA* *Eectronic
6 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES A MODEL FOR ESTIMATING THE LATERAL OVERLAP PROBABILITY OF AIRCRAFT WITH RNP ALERTING CAPABILITY IN PARALLEL RNAV ROUTES Sakae NAGAOKA* *Eectronic
Melodic contour estimation with B-spline models using a MDL criterion
 Meodic contour estimation with B-spine modes using a MDL criterion Damien Loive, Ney Barbot, Oivier Boeffard IRISA / University of Rennes 1 - ENSSAT 6 rue de Kerampont, B.P. 80518, F-305 Lannion Cedex
Meodic contour estimation with B-spine modes using a MDL criterion Damien Loive, Ney Barbot, Oivier Boeffard IRISA / University of Rennes 1 - ENSSAT 6 rue de Kerampont, B.P. 80518, F-305 Lannion Cedex
6.434J/16.391J Statistics for Engineers and Scientists May 4 MIT, Spring 2006 Handout #17. Solution 7
 6.434J/16.391J Statistics for Engineers and Scientists May 4 MIT, Spring 2006 Handout #17 Soution 7 Probem 1: Generating Random Variabes Each part of this probem requires impementation in MATLAB. For the
6.434J/16.391J Statistics for Engineers and Scientists May 4 MIT, Spring 2006 Handout #17 Soution 7 Probem 1: Generating Random Variabes Each part of this probem requires impementation in MATLAB. For the
Formulas for Angular-Momentum Barrier Factors Version II
 BNL PREPRINT BNL-QGS-06-101 brfactor1.tex Formuas for Anguar-Momentum Barrier Factors Version II S. U. Chung Physics Department, Brookhaven Nationa Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973 March 19, 2015 abstract A
BNL PREPRINT BNL-QGS-06-101 brfactor1.tex Formuas for Anguar-Momentum Barrier Factors Version II S. U. Chung Physics Department, Brookhaven Nationa Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973 March 19, 2015 abstract A
Efficiently Generating Random Bits from Finite State Markov Chains
 1 Efficienty Generating Random Bits from Finite State Markov Chains Hongchao Zhou and Jehoshua Bruck, Feow, IEEE Abstract The probem of random number generation from an uncorreated random source (of unknown
1 Efficienty Generating Random Bits from Finite State Markov Chains Hongchao Zhou and Jehoshua Bruck, Feow, IEEE Abstract The probem of random number generation from an uncorreated random source (of unknown
THE REACHABILITY CONES OF ESSENTIALLY NONNEGATIVE MATRICES
 THE REACHABILITY CONES OF ESSENTIALLY NONNEGATIVE MATRICES by Michae Neumann Department of Mathematics, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT 06269 3009 and Ronad J. Stern Department of Mathematics, Concordia
THE REACHABILITY CONES OF ESSENTIALLY NONNEGATIVE MATRICES by Michae Neumann Department of Mathematics, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT 06269 3009 and Ronad J. Stern Department of Mathematics, Concordia
Title: Crack Diagnostics via Fourier Transform: Real and Imaginary Components vs. Power Spectral Density
 Tite: rack Diagnostics via ourier Transform: ea and maginary omponents vs. Power pectra Density Authors: Leonid M. Geman Victor Giurgiutiu van V. Petrunin 3 rd nternationa Workshop on tructura Heath Monitoring
Tite: rack Diagnostics via ourier Transform: ea and maginary omponents vs. Power pectra Density Authors: Leonid M. Geman Victor Giurgiutiu van V. Petrunin 3 rd nternationa Workshop on tructura Heath Monitoring
ORTHOGONAL MULTI-WAVELETS FROM MATRIX FACTORIZATION
 J. Korean Math. Soc. 46 2009, No. 2, pp. 281 294 ORHOGONAL MLI-WAVELES FROM MARIX FACORIZAION Hongying Xiao Abstract. Accuracy of the scaing function is very crucia in waveet theory, or correspondingy,
J. Korean Math. Soc. 46 2009, No. 2, pp. 281 294 ORHOGONAL MLI-WAVELES FROM MARIX FACORIZAION Hongying Xiao Abstract. Accuracy of the scaing function is very crucia in waveet theory, or correspondingy,
Distributed average consensus: Beyond the realm of linearity
 Distributed average consensus: Beyond the ream of inearity Usman A. Khan, Soummya Kar, and José M. F. Moura Department of Eectrica and Computer Engineering Carnegie Meon University 5 Forbes Ave, Pittsburgh,
Distributed average consensus: Beyond the ream of inearity Usman A. Khan, Soummya Kar, and José M. F. Moura Department of Eectrica and Computer Engineering Carnegie Meon University 5 Forbes Ave, Pittsburgh,
Width of Percolation Transition in Complex Networks
 APS/23-QED Width of Percoation Transition in Compex Networs Tomer Kaisy, and Reuven Cohen 2 Minerva Center and Department of Physics, Bar-Ian University, 52900 Ramat-Gan, Israe 2 Department of Computer
APS/23-QED Width of Percoation Transition in Compex Networs Tomer Kaisy, and Reuven Cohen 2 Minerva Center and Department of Physics, Bar-Ian University, 52900 Ramat-Gan, Israe 2 Department of Computer
Appendix for Stochastic Gradient Monomial Gamma Sampler
 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 3 3 3 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 4 4 4 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 5 5 5 53 54 Appendix for Stochastic Gradient Monomia Gamma Samper A The Main Theorem We provide the foowing
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 3 3 3 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 4 4 4 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 5 5 5 53 54 Appendix for Stochastic Gradient Monomia Gamma Samper A The Main Theorem We provide the foowing
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Computer Science 96 (2016 )
 Avaiabe onine at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 96 (206 92 99 20th Internationa Conference on Knowedge Based and Inteigent Information and Engineering Systems Connected categorica
Avaiabe onine at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 96 (206 92 99 20th Internationa Conference on Knowedge Based and Inteigent Information and Engineering Systems Connected categorica
arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 23 Aug 2018
![arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 23 Aug 2018 arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 23 Aug 2018](/thumbs/84/89702159.jpg) An Exact Upper Bound on the L p Lebesgue Constant and The -Rényi Entropy Power Inequaity for Integer Vaued Random Variabes arxiv:808.0773v [math.fa] 3 Aug 08 Peng Xu, Mokshay Madiman, James Mebourne Abstract
An Exact Upper Bound on the L p Lebesgue Constant and The -Rényi Entropy Power Inequaity for Integer Vaued Random Variabes arxiv:808.0773v [math.fa] 3 Aug 08 Peng Xu, Mokshay Madiman, James Mebourne Abstract
Theory and implementation behind: Universal surface creation - smallest unitcell
 Teory and impementation beind: Universa surface creation - smaest unitce Bjare Brin Buus, Jaob Howat & Tomas Bigaard September 15, 218 1 Construction of surface sabs Te aim for tis part of te project is
Teory and impementation beind: Universa surface creation - smaest unitce Bjare Brin Buus, Jaob Howat & Tomas Bigaard September 15, 218 1 Construction of surface sabs Te aim for tis part of te project is
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL TO INNOVATED SCALABLE EFFICIENT ESTIMATION IN ULTRA-LARGE GAUSSIAN GRAPHICAL MODELS
 ISEE 1 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL TO INNOVATED SCALABLE EFFICIENT ESTIMATION IN ULTRA-LARGE GAUSSIAN GRAPHICAL MODELS By Yingying Fan and Jinchi Lv University of Southern Caifornia This Suppementary Materia
ISEE 1 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL TO INNOVATED SCALABLE EFFICIENT ESTIMATION IN ULTRA-LARGE GAUSSIAN GRAPHICAL MODELS By Yingying Fan and Jinchi Lv University of Southern Caifornia This Suppementary Materia
A Novel Learning Method for Elman Neural Network Using Local Search
 Neura Information Processing Letters and Reviews Vo. 11, No. 8, August 2007 LETTER A Nove Learning Method for Eman Neura Networ Using Loca Search Facuty of Engineering, Toyama University, Gofuu 3190 Toyama
Neura Information Processing Letters and Reviews Vo. 11, No. 8, August 2007 LETTER A Nove Learning Method for Eman Neura Networ Using Loca Search Facuty of Engineering, Toyama University, Gofuu 3190 Toyama
Improving the Accuracy of Boolean Tomography by Exploiting Path Congestion Degrees
 Improving the Accuracy of Booean Tomography by Expoiting Path Congestion Degrees Zhiyong Zhang, Gaoei Fei, Fucai Yu, Guangmin Hu Schoo of Communication and Information Engineering, University of Eectronic
Improving the Accuracy of Booean Tomography by Expoiting Path Congestion Degrees Zhiyong Zhang, Gaoei Fei, Fucai Yu, Guangmin Hu Schoo of Communication and Information Engineering, University of Eectronic
Bayesian Learning. You hear a which which could equally be Thanks or Tanks, which would you go with?
 Bayesian Learning A powerfu and growing approach in machine earning We use it in our own decision making a the time You hear a which which coud equay be Thanks or Tanks, which woud you go with? Combine
Bayesian Learning A powerfu and growing approach in machine earning We use it in our own decision making a the time You hear a which which coud equay be Thanks or Tanks, which woud you go with? Combine
Problem set 6 The Perron Frobenius theorem.
 Probem set 6 The Perron Frobenius theorem. Math 22a4 Oct 2 204, Due Oct.28 In a future probem set I want to discuss some criteria which aow us to concude that that the ground state of a sef-adjoint operator
Probem set 6 The Perron Frobenius theorem. Math 22a4 Oct 2 204, Due Oct.28 In a future probem set I want to discuss some criteria which aow us to concude that that the ground state of a sef-adjoint operator
Coordination and Antenna Domain Formation in Cloud-RAN systems
 Coordination and ntenna Domain Formation in Coud-RN systems Hadi Ghauch, Muhammad Mahboob Ur Rahman, Sahar Imtiaz, James Gross, Schoo of Eectrica Engineering and the CCESS Linnaeus Center, Roya Institute
Coordination and ntenna Domain Formation in Coud-RN systems Hadi Ghauch, Muhammad Mahboob Ur Rahman, Sahar Imtiaz, James Gross, Schoo of Eectrica Engineering and the CCESS Linnaeus Center, Roya Institute
II. PROBLEM. A. Description. For the space of audio signals
 CS229 - Fina Report Speech Recording based Language Recognition (Natura Language) Leopod Cambier - cambier; Matan Leibovich - matane; Cindy Orozco Bohorquez - orozcocc ABSTRACT We construct a rea time
CS229 - Fina Report Speech Recording based Language Recognition (Natura Language) Leopod Cambier - cambier; Matan Leibovich - matane; Cindy Orozco Bohorquez - orozcocc ABSTRACT We construct a rea time
arxiv:math/ v2 [math.pr] 6 Mar 2005
![arxiv:math/ v2 [math.pr] 6 Mar 2005 arxiv:math/ v2 [math.pr] 6 Mar 2005](/thumbs/92/110958410.jpg) ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOR OF RANDOM HEAPS arxiv:math/0407286v2 [math.pr] 6 Mar 2005 J. BEN HOUGH Abstract. We consider a random wa W n on the ocay free group or equivaenty a signed random heap) with m generators
ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOR OF RANDOM HEAPS arxiv:math/0407286v2 [math.pr] 6 Mar 2005 J. BEN HOUGH Abstract. We consider a random wa W n on the ocay free group or equivaenty a signed random heap) with m generators
(This is a sample cover image for this issue. The actual cover is not yet available at this time.)
 (This is a sampe cover image for this issue The actua cover is not yet avaiabe at this time) This artice appeared in a journa pubished by Esevier The attached copy is furnished to the author for interna
(This is a sampe cover image for this issue The actua cover is not yet avaiabe at this time) This artice appeared in a journa pubished by Esevier The attached copy is furnished to the author for interna
BICM Performance Improvement via Online LLR Optimization
 BICM Performance Improvement via Onine LLR Optimization Jinhong Wu, Mostafa E-Khamy, Jungwon Lee and Inyup Kang Samsung Mobie Soutions Lab San Diego, USA 92121 Emai: {Jinhong.W, Mostafa.E, Jungwon2.Lee,
BICM Performance Improvement via Onine LLR Optimization Jinhong Wu, Mostafa E-Khamy, Jungwon Lee and Inyup Kang Samsung Mobie Soutions Lab San Diego, USA 92121 Emai: {Jinhong.W, Mostafa.E, Jungwon2.Lee,
A GENERAL METHOD FOR EVALUATING OUTAGE PROBABILITIES USING PADÉ APPROXIMATIONS
 A GENERAL METHOD FOR EVALUATING OUTAGE PROBABILITIES USING PADÉ APPROXIMATIONS Jack W. Stokes, Microsoft Corporation One Microsoft Way, Redmond, WA 9852, jstokes@microsoft.com James A. Ritcey, University
A GENERAL METHOD FOR EVALUATING OUTAGE PROBABILITIES USING PADÉ APPROXIMATIONS Jack W. Stokes, Microsoft Corporation One Microsoft Way, Redmond, WA 9852, jstokes@microsoft.com James A. Ritcey, University
Optimal Control of Assembly Systems with Multiple Stages and Multiple Demand Classes 1
 Optima Contro of Assemby Systems with Mutipe Stages and Mutipe Demand Casses Saif Benjaafar Mohsen EHafsi 2 Chung-Yee Lee 3 Weihua Zhou 3 Industria & Systems Engineering, Department of Mechanica Engineering,
Optima Contro of Assemby Systems with Mutipe Stages and Mutipe Demand Casses Saif Benjaafar Mohsen EHafsi 2 Chung-Yee Lee 3 Weihua Zhou 3 Industria & Systems Engineering, Department of Mechanica Engineering,
Integrating Factor Methods as Exponential Integrators
 Integrating Factor Methods as Exponentia Integrators Borisav V. Minchev Department of Mathematica Science, NTNU, 7491 Trondheim, Norway Borko.Minchev@ii.uib.no Abstract. Recenty a ot of effort has been
Integrating Factor Methods as Exponentia Integrators Borisav V. Minchev Department of Mathematica Science, NTNU, 7491 Trondheim, Norway Borko.Minchev@ii.uib.no Abstract. Recenty a ot of effort has been
Combining reaction kinetics to the multi-phase Gibbs energy calculation
 7 th European Symposium on Computer Aided Process Engineering ESCAPE7 V. Pesu and P.S. Agachi (Editors) 2007 Esevier B.V. A rights reserved. Combining reaction inetics to the muti-phase Gibbs energy cacuation
7 th European Symposium on Computer Aided Process Engineering ESCAPE7 V. Pesu and P.S. Agachi (Editors) 2007 Esevier B.V. A rights reserved. Combining reaction inetics to the muti-phase Gibbs energy cacuation
Higher dimensional PDEs and multidimensional eigenvalue problems
 Higher dimensiona PEs and mutidimensiona eigenvaue probems 1 Probems with three independent variabes Consider the prototypica equations u t = u (iffusion) u tt = u (W ave) u zz = u (Lapace) where u = u
Higher dimensiona PEs and mutidimensiona eigenvaue probems 1 Probems with three independent variabes Consider the prototypica equations u t = u (iffusion) u tt = u (W ave) u zz = u (Lapace) where u = u
arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 13 Jun 2014
![arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 13 Jun 2014 arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 13 Jun 2014](/thumbs/90/103079172.jpg) SUBMITTED TO IEEE SIGNAL PROCESSING LETTERS, OCTOBER 8, 2018 1 Piot Signa Design for Massive MIMO Systems: A Received Signa-To-Noise-Ratio-Based Approach Jungho So, Donggun Kim, Yuni Lee, Student Members,
SUBMITTED TO IEEE SIGNAL PROCESSING LETTERS, OCTOBER 8, 2018 1 Piot Signa Design for Massive MIMO Systems: A Received Signa-To-Noise-Ratio-Based Approach Jungho So, Donggun Kim, Yuni Lee, Student Members,
Week 6 Lectures, Math 6451, Tanveer
 Fourier Series Week 6 Lectures, Math 645, Tanveer In the context of separation of variabe to find soutions of PDEs, we encountered or and in other cases f(x = f(x = a 0 + f(x = a 0 + b n sin nπx { a n
Fourier Series Week 6 Lectures, Math 645, Tanveer In the context of separation of variabe to find soutions of PDEs, we encountered or and in other cases f(x = f(x = a 0 + f(x = a 0 + b n sin nπx { a n
The EM Algorithm applied to determining new limit points of Mahler measures
 Contro and Cybernetics vo. 39 (2010) No. 4 The EM Agorithm appied to determining new imit points of Maher measures by Souad E Otmani, Georges Rhin and Jean-Marc Sac-Épée Université Pau Veraine-Metz, LMAM,
Contro and Cybernetics vo. 39 (2010) No. 4 The EM Agorithm appied to determining new imit points of Maher measures by Souad E Otmani, Georges Rhin and Jean-Marc Sac-Épée Université Pau Veraine-Metz, LMAM,
Math 124B January 31, 2012
 Math 124B January 31, 212 Viktor Grigoryan 7 Inhomogeneous boundary vaue probems Having studied the theory of Fourier series, with which we successfuy soved boundary vaue probems for the homogeneous heat
Math 124B January 31, 212 Viktor Grigoryan 7 Inhomogeneous boundary vaue probems Having studied the theory of Fourier series, with which we successfuy soved boundary vaue probems for the homogeneous heat
Appendix for Stochastic Gradient Monomial Gamma Sampler
 Appendix for Stochastic Gradient Monomia Gamma Samper A The Main Theorem We provide the foowing theorem to characterize the stationary distribution of the stochastic process with SDEs in (3) Theorem 3
Appendix for Stochastic Gradient Monomia Gamma Samper A The Main Theorem We provide the foowing theorem to characterize the stationary distribution of the stochastic process with SDEs in (3) Theorem 3
