CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition. Mathematics. 8 th Grade Unit 2: Exponents and Equations
|
|
|
- Kristin Gibson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics 8 th Grade Unit 2: Exponents and Equations These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. The contents of this guide were developed under a grant from the U. S. Department of Education. However, those contents do not necessarily represent the policy of the U. S. Department of Education, and you should not assume endorsement by the Federal Government.
2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Unit 2 EXPONENTS and EQUATIONS Overview...3 Key Standards & Related Standards...4 Enduring Understandings...5 Concepts & Skills to Maintain...6 Selected Terms and Symbols...6 Formative Assessment Lesson (FAL) Overview...8 Tasks...9 Rational or Irrational Reasoning?...9 FAL: Repeating Decimals...10 A Few Folds Alien Attack...13 Nesting Dolls...16 Exponential Exponents...17 Exploring Powers of SCT: Ponzi Pyramid Scheme...21 FAL: Estimating Length Using Scientific Notation...23 E. coli...25 SCT: Giantburgers...26 SCT: 100 People...28 FAL: Solving Linear Equations in One Variable...30 Writing for a Math Website...32 July 2013 Page 2 of 33
3 OVERVIEW In this unit student will: distinguish between rational and irrational numbers and show the relationship between the subsets of the real number system; recognize that every rational number has a decimal representation that either terminates or repeats; recognize that irrational numbers must have decimal representations that neither terminate nor repeat; understand that the value of a square root can be approximated between integers and that non perfect square roots are irrational; locate rational and irrational numbers on a number line diagram; use the properties of exponents to extend the meaning beyond counting-number exponents; recognize perfect squares and cubes, understanding that non-perfect squares and nonperfect cubes are irrational; recognize that squaring a number and taking the square root of a number are inverse operations; likewise, cubing a number and taking the cube root are inverse operations; express numbers in scientific notation; compare numbers, where one is given in scientific notation and the other is given in standard notation; compare and interpret scientific notation quantities in the context of the situation; use laws of exponents to add, subtract, multiply and divide numbers written in scientific notation; solve one-variable equations with the variables being on both sides of the equals sign, including equations with rational numbers, the distributive property, and combining like terms; and analyze and represent contextual situations with equations, identify whether there is one, none, or many solutions, and then solve to prove conjectures about the solutions. Although the units in this instructional framework emphasize key standards and big ideas at specific times of the year, routine topics such as estimation, mental computation, and basic computation facts should be addressed on an ongoing basis. Ideas related to the eight practice standards should be addressed constantly as well. To assure that this unit is taught with the appropriate emphasis, depth, and rigor, it is important that the tasks listed under Evidence of Learning be reviewed early in the planning process. A variety of resources should be utilized to supplement this unit. This unit provides much needed content information, but excellent learning activities as well. The tasks in this unit illustrate the types of learning activities that should be utilized from a variety of sources. July 2013 Page 3 of 33
4 STANDARDS ADDRESSED IN THIS UNIT Mathematical standards are interwoven and should be addressed throughout the year in as many different units and activities as possible in order to emphasize the natural connections that exist among mathematical topics. KEY STANDARDS Work with radicals and integer exponents. MCC8.EE.1 Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. For example, ( 5) = 3 ( 3) 1 = = MCC8.EE.2 Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x 2 = p and x 3 =p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that 2 is irrational. MCC8.EE.3 Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. For example, estimate the population of the United States as and the population of the world as , and determine that the world population is more than 20 times larger. MCC8.EE.4 Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology. MCC8.EE.7 Solve linear equations in one variable. a. Give examples of linear equations in one variable with one solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solutions. Show which of these possibilities is the case by successively transforming the given equation into simpler forms, until an equivalent equation of the form x = a, a = b, or a = a results (where a and b are different numbers). b. Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients, including equations whose solutions require expanding expressions using the distributive property and collecting like terms. MCC8.NS.1 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number. July 2013 Page 4 of 33
5 MCC8.NS.2 Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions (e.g., π 2 ). For example, by truncating the decimal expansion of 2 (square root of 2), show that 2 is between 1 and 2, then between 1.4 and 1.5, and explain how to continue on to get better approximations. STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL PRACTICE Refer to the Comprehensive Course Overview for more detailed information about the Standards for Mathematical Practice. 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4. Model with mathematics. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and make use of structure. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS Square roots can be rational or irrational. An irrational number is a real number that cannot be written as a ratio of two integers. Every number has a decimal expansion, for rational numbers it repeats eventually, and can be converted into a rational number. All real numbers can be plotted on a number line. Rational approximations of irrational numbers can be used to compare the size or irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line, and estimate the value of expressions. 2 is irrational. Exponents are useful for representing very large or very small numbers. Properties of integer exponents can be use to generate equivalent numerical expressions. Scientific notation can be used to estimate very large or very small quantities and to compare quantities. July 2013 Page 5 of 33
6 Linear equations in one variable can have one solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solutions. CONCEPTS/SKILLS TO MAINTAIN It is expected that students will have prior knowledge/experience related to the concepts and skills identified below. It may be necessary to pre-assess in order to determine if time needs to be spent on conceptual activities that help students develop a deeper understanding of these ideas. computation with whole numbers and decimals, including application of order of operations solving equations plotting points in four quadrant coordinate plane understanding of independent and dependent variables characteristics of a proportional relationship SELECTED TERMS AND SYMBOLS The following terms and symbols are often misunderstood. These concepts are not an inclusive list and should not be taught in isolation. However, due to evidence of frequent difficulty and misunderstanding associated with these concepts, instructors should pay particular attention to them and how their students are able to explain and apply them. The definitions below are for teacher reference only and are not to be memorized by the students. Students should explore these concepts using models and real life examples. Students should understand the concepts involved and be able to recognize and/or demonstrate them with words, models, pictures, or numbers. The websites below are interactive and include a math glossary suitable for middle school students. Note Different sources use different definitions. Please preview any website for alignment to the definitions given in the frameworks. The definitions below are from the Common Core State Standards Mathematics Glossary and/or the Common Core GPS Mathematics Glossary when available. Visit or to see additional definitions and specific examples of many terms and symbols used in grade 8 mathematics. Addition Property of Equality: For real numbers a, b, and c, if a = b, then a + c = b + c. In other words, adding the same number to each side of an equation produces an equivalent equation. July 2013 Page 6 of 33
7 Additive Inverses: Two numbers whose sum is 0 are additive inverses of one another. Example: 3/4 and 3/4 are additive inverses of one another because 3/4 + ( 3/4) = ( 3/4) + 3/4 = 0. Algebraic Expression: A mathematical phrase involving at least one variable. Expressions can contain numbers and operation symbols. Addition Property of Equality: For real numbers a, b, and c, if a = b, then a + c = b + c. In other words, adding the same number to each side of an equation produces an equivalent equation. Cube Root: If the cube root of a number b is a (i.e., 3 b = a), then a 3 = b. Decimal Expansion: The decimal expansion of a number is its representation in base 10 (i.e., the decimal system). For example, the decimal expansion of 25 2 is 625, of π is , and of 1/9 is Equation: A mathematical sentence that contains an equals sign. Evaluate an Algebraic Expression: To perform operations to obtain a single number or value. Exponent: The number of times a base is used as a factor of repeated multiplication. Exponential Notation: See Scientific Notation below. Inverse Operation: Pairs of operations that undo each other, for example, addition and subtraction are inverse operations and multiplication and division are inverse operations. Irrational: A real number whose decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating that cannot be written as the ratio of two integers. Like Terms: Monomials that have the same variable raised to the same power. Only the coefficients of like terms can be different. Linear Equation in One Variable: An equation that can be written in the form ax + b = c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a 0 Multiplication Property of Equality: For real numbers a, b, and c (c 0), if a = b, then ac = bc. In other words, multiplying both sides of an equation by the same number produces an equivalent expression. July 2013 Page 7 of 33
8 Multiplicative Inverses: Two numbers whose product is 1 are multiplicative inverses of one another. Example: 3/4 and 4/3 are multiplicative inverses of one another because 3/4 4/3 = 4/3 3/4 = 1. Perfect Square: A number that has a rational number as its square root. Radical: A symbol that is used to indicate square roots. Rational: A number that can be written as the ratio of two integers with a nonzero denominator. Scientific Notation: A representation of real numbers as the product of a number between 1 and 10 and a power of 10, used primarily for very large or very small numbers. Significant Digits: A way of describing how precisely a number is written. Solution: the value or values of a variable that make an equation a true statement Solve: Identify the value that when substituted for the variable makes the equation a true statement. Square Root: One of two equal factors of a nonnegative number. For example, 5 is a square root of 25 because 5 5 = 25. Another square root of 25 is -5 because (-5) (-5) = 25. The +5 is called the principle square root of 25 and is always assumed when the radical symbol is used. Variable: A letter or symbol used to represent a number. FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT LESSONS (FALs) Formative Assessment Lessons are intended to support teachers in formative assessment. They reveal and develop students understanding of key mathematical ideas and applications. These lessons enable teachers and students to monitor in more detail their progress towards the targets of the standards. They assess students understanding of important concepts and problem solving performance, and help teachers and their students to work effectively together to move each student s mathematical reasoning forward. More information on types of Formative Assessment Lessons may be found in the Comprehensive Course Guide. July 2013 Page 8 of 33
9 SE TASK: Rational or Irrational Reasoning? Analyze Robin s reasoning in her answer to the test question about rational or irrational numbers. Does she have a deep understanding of rational and irrational numbers? Does her reasoning make sense? If not, what misconceptions does she have about this topic? Create a study guide with explanations, examples, and graphics to help clear up any misconceptions students might have over these topics. 3 rd Block Robin Radical 1. Is 130 rational or irrational? Where would 130 be located on a number line? Explain your reasoning. 130 is a rational number because 130 is even. All rational numbers are even and irrational numbers are odd when the numbers are under the square root sign. The square root sign is the opposite of squaring a number. Squaring a number is the same as raising it to the 2 nd power. So, to find the value of a number under the square root sign, you divide it by 2. So, is 65. The answer is 65. July 2013 Page 9 of 33
10 Formative Assessment Lesson: Repeating Decimals Source: Formative Assessment Lesson Materials from Mathematics Assessment Project In this FAL, students will translate between decimal and fraction notation (particularly when the decimals are repeating), create and solve simple linear equations to find the fractional equivalent of a repeating decimal, and understand the effect of multiplying a decimal by a power of 10. STANDARDS ADDRESSED IN THIS TASK: MCC8.EE.7 Solve linear equations in one variable. a. Give examples of linear equations in one variable with one solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solutions. Show which of these possibilities is the case by successively transforming the given equation into simpler forms, until an equivalent equation of the form x = a, a = b, or a = a results (where a and b are different numbers). b. Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients, including equations whose solutions require expanding expressions using the distributive property and collecting like terms. MCC8.NS.1 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number. MCC8.NS.2 Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions (e.g., π 2 ). For example, by truncating the decimal expansion of 2 (square root of 2), show that 2 is between 1 and 2, then between 1.4 and 1.5, and explain how to continue on to get better approximations. STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL PRACTICE: This task uses all of the practices with emphasis on: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 6. Attend to precision. July 2013 Page 10 of 33
11 TASK DESCRIPTION, DEVELOPMENT AND DISCUSSION: Tasks and lessons from the Mathematics Assessment Project are specifically designed to help teachers effectively formatively assess their students. The way the tasks and lessons are designed gives the teacher a clear understanding of what the students are able to do and not do. Within the lesson, teachers will find suggestions and question prompts that will help guide students towards understanding. For more information access the MAP website: The task, Repeating Decimals, is a Formative Assessment Lesson (FAL) that can be found at the website: The FAL document provides a clear lesson design, from the opening of the lesson to the closing of the lesson. The PDF version of the task can be found at the link below: July 2013 Page 11 of 33
12 Part 1: SE TASK: A Few Folds Repeatedly fold one piece of paper in half, recording the number of folds and the resulting number of layers of paper. Assuming that you could continue the pattern, how many layers of paper would there be for 10 folds, 100 folds, n folds? How do you know? Part 2: Explain the process that is used to generate the following patterns? Cup, pint, quart, half gallon, and gallon, and so on. Penny, dime, dollar, ten dollars, one hundred dollars, and so on. July 2013 Page 12 of 33
13 Alien Attack! SE TASK: Aliens from the Outer Space Galactic Task Force have been watching the recent gains in mathematical understanding developing in human brains from Planet Earth. They have become alarmed that Planet Earth might soon develop the capabilities to discover that life exists on other planets with this increased mathematical knowledge. To slow the progress, they have organized an attack on the World Wide Web and all other forms of math textbooks. All words have been eradicated from the mathematics examples! Humans will now be forced to study the patterns of numbers and previously worked examples to rediscover the properties of mathematics! They are confident that humans will not persevere in the challenge of making sense of problems, reasoning abstractly and quantitatively, constructing viable arguments, looking for and making use of structure, and using repeated reasoning to recreate the language of mathematics. They have already declared MISSION ACCOMPLISHED! The next standard in your mathematics class requires knowledge of the properties of integer exponents. Can your team recreate and name the properties by using the Standards for Mathematical Practice to examine the examples that remain? Problem continues on next page. July 2013 Page 13 of 33
14 Problem continued from previous page = (7 7 7) (7 7) = = = (5 5 5) (5 5 5) = = = (3) ( ) = 3 5 (2 2 ) 3 = (2 2 ) (2 2 ) (2 2 ) = (2 2) (2 2) (2 2) = = 2 6 (6 4 ) 2 = (6 4 ) (6 4 ) = ( ) ( ) = = = (3 2) 5 = = (4 5) 3 = 20 3 (2 3) 6 = Problem continues on next page. July 2013 Page 14 of 33
15 Problem continued from previous page. 5 0 = = = = = = = = 55 2 = 5 3 = = 23 5 = 2 2 = = 1 4 July 2013 Page 15 of 33
16 SE TASK: Nesting Dolls The first Russian nesting dolls were made over a hundred years ago. They were brightly painted in classic Russian designs and made so that the finished doll had many similar dolls that fit one inside the other. This type of doll is called a Matroyshka which is derived from the Latin word for mother and is a common name for women in Russian villages. Suppose there are a total of eight dolls. The finished doll is n centimeters tall with seven smaller dolls that fit inside one another. Each doll is 3 2 the height of the next larger doll. a. What is the relationship of the heights of the third largest doll and the largest doll? b. What is the relationship of the smallest doll and the largest doll? As Russia has dropped the Iron Curtain and opened doors, many of their production facilities have more technology. Instead of hand carving the Matroyshka, factories use computerized robots to make them. You have been asked to develop the general statement to generalize the height of each doll regardless of the number of dolls in the finished product. July 2013 Page 16 of 33
17 SE Task: Exponential Exponents Write your numeric expression in the box in the center of the page. With your group, use the properties of integer exponents to generate expressions equivalent to your numeric expression. Each property of exponents should be represented. Write an explanation of the strategies that you used to generate the equivalent expressions. July 2013 Page 17 of 33
18 SE TASK: Exploring Powers of 10 This activity will help you to learn how to represent very large and very small numbers. Part 1: Very Small Numbers (negative exponents) Complete the following table. What patterns do you see? 10 6 = 10 5 = 10 4 = 10 3 = 10 2 = 10 1 = 10 0 = 10-1 = 10-2 = 10-3 = July 2013 Page 18 of 33
19 DIRECTIONS FOR USING THE TI-83 or TI-84: Exploring Powers of 10 It may be appropriate to use a calculator or computer when data may contain numbers that are difficult to work with using paper and pencil. Exploring very large and very small numbers can be done on the TI-83 or TI-84 graphing calculator with the following instructions. 1. Turn on the calculator ON. ^ 2. Enter the number 10, press the key, enter the number 6, and press ENTER. 3. Continue step 2 for the positive exponents and zero. 4. Enter the number 10, press the key, press the negation ( ) key, enter the number 1, and press ENTER. ^ 5. Continue step 4 for the negative exponents. July 2013 Page 19 of 33
20 Part 2: Very Large Numbers (positive exponents) Sometimes it can be cumbersome to say and write numbers in their common form (for example trying to display numbers on a calculator with limited screen space). Another option is to use exponential notation and the base-ten place-value system. Using a calculator (with exponential capabilities), complete each of the following: 1. Explore 10 N for various values of N. What patterns do you notice? 2. Enter 45 followed by a string of zeros. How many will your calculator permit? What happens when you press enter? What does 4.5E10 mean? What about 2.3E4? Can you enter this another way? 3. Try sums like ( N ) + (2 10 K ) for different values of N and K. Describe any patterns that you may notice. 4. Try products like ( N ) (2 10 K ). Describe any patterns that you may notice. 5. Try quotients like ( N ) (2 10). Describe any patterns that you may notice. July 2013 Page 20 of 33
21 Short Cycle Task: Ponzi Pyramid Scheme Source: Balanced Assessment Materials from Mathematics Assessment Project letter. In this task, students will experience a real-world application of exponents using a chain STANDARDS ADDRESSED IN THIS TASK: Work with radicals and integer exponents. MCC8.EE.1 Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. For example, ( 5) = 3 ( 3) 1 = = MCC8.EE.2 Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x 2 = p and x 3 =p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that 2 is irrational. MCC8.EE.3 Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. For example, estimate the population of the United States as and the population of the world as , and determine that the world population is more than 20 times larger. MCC8.EE.4 Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology. STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL PRACTICE: This task uses all of the practices with emphasis on: 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and make use of structure. July 2013 Page 21 of 33
22 TASK DESCRIPTION, DEVELOPMENT AND DISCUSSION: Tasks and lessons from the Mathematics Assessment Project are specifically designed to help teachers effectively formatively assess their students. The way the tasks and lessons are designed gives the teacher a clear understanding of what the students are able to do and not do. Within the lesson, teachers will find suggestions and question prompts that will help guide students towards understanding. For more information access the MAP website: The task, Ponzi Pyramid Schemes, is a Mathematics Assessment Project Assessment Task that can be found at the website: The PDF version of the task can be found at the link below: The scoring rubric can be found at the following link: July 2013 Page 22 of 33
23 Formative Assessment Lesson: Estimating Length Using Scientific Notation Source: Formative Assessment Lesson Materials from Mathematics Assessment Project Estimating lengths of everyday objects, converting between decimal and scientific notation, and making comparison of the size of numbers expressed in both decimal and scientific notation. STANDARDS ADDRESSED IN THIS TASK: MCC8.EE.3 Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. For example, estimate the population of the United States as and the population of the world as , and determine that the world population is more than 20 times larger. MCC8.EE.4 Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology. STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL PRACTICE: This task uses all of the practices with emphasis on: 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 7. Look for and make use of structure. TASK DESCRIPTION, DEVELOPMENT AND DISCUSSION Tasks and lessons from the Mathematics Assessment Project are specifically designed to help teachers effectively formatively assess their students. The way the tasks and lessons are designed gives the teacher a clear understanding of what the students are able to do and not do. Within the lesson, teachers will find suggestions and question prompts that will help guide students towards understanding. For more information access the MAP website: The task, Estimating Length Using Scientific Notation, is a Formative Assessment Lesson (FAL) that can be found at the website: The FAL document provides a clear lesson design, from the opening of the lesson to the closing of the lesson. July 2013 Page 23 of 33
24 The PDF version of the task can be found at the link below: July 2013 Page 24 of 33
25 SE TASK: E. coli The Center for Disease Control (CDC) monitors public facilities to assure that there are no health risks to the people that visit these facilities. Occasionally, Escherichia coli will be discovered, which is also known as E. coli. This is a type of bacterium that can make people very sick. The mass of each E. coli bacterium is gram. The last time that E. coli was discovered in Georgia, the number of bacteria had been increasing for 24 hours! This caused each bacterium to be replaced by a population of bacteria. a. What was the mass of the population of E. coli when it was discovered? Justify your answer. b. If the mass of a small paper clip is about 1 gram, how many times more is its mass than that of the discovered E. coli bacteria? Show how you know. Visit for more information on E. coli. July 2013 Page 25 of 33
26 Short Cycle Task: Giantburgers Source: Mathematics Assessment Project Shell Center/MARS, University of Nottingham & UC Berkeley In this task, the student will use properties of exponents and scientific notation. STANDARDS ADDRESSED IN THIS TASK: Work with radicals and integer exponents. MCC8.EE.1 Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. For example, ( 5) = 3 ( 3) 1 = = MCC8.EE.3 Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. For example, estimate the population of the United States as and the population of the world as , and determine that the world population is more than 20 times larger. MCC8.EE.4 Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology. STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL PRACTICE: This task uses all of the practices with emphasis on: 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and make use of structure. July 2013 Page 26 of 33
27 SE TASK: Giantburgers This headline appeared in a newspaper. Decide whether this headline is true using the following information. There are about Giantburger restaurants in America. Each restaurant serves about people every day. There are about Americans. Explain your reasons and show clearly how you figured it out. July 2013 Page 27 of 33
28 Short Cycle: 100 People Source: Balanced Assessment Materials from Mathematics Assessment Project In this task, students will use scientific notation in a real-world application of using population. STANDARDS ADDRESSED IN THIS TASK: Work with radicals and integer exponents. MCC8.EE.1 Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. For example, ( 5) = 3 ( 3) 1 = = MCC8.EE.2 Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x 2 = p and x 3 =p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that 2 is irrational. MCC8.EE.3 Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. For example, estimate the population of the United States as and the population of the world as , and determine that the world population is more than 20 times larger. MCC8.EE.4 Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology. STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL PRACTICE: This task uses all of the practices with emphasis on: 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and make use of structure. July 2013 Page 28 of 33
29 TASK DESCRIPTION, DEVELOPMENT AND DISCUSSION: Tasks and lessons from the Mathematics Assessment Project are specifically designed to help teachers effectively formatively assess their students. The way the tasks and lessons are designed gives the teacher a clear understanding of what the students are able to do and not do. Within the lesson, teachers will find suggestions and question prompts that will help guide students towards understanding. For more information access the MAP website: The task, 100 People, is a Mathematics Assessment Project Assessment Task that can be found at the website: The PDF version of the task can be found at the link below: The scoring rubric can be found at the following link: July 2013 Page 29 of 33
30 Formative Assessment Lesson: Solving Linear Equations in One Variable Source: Formative Assessment Lesson Materials from Mathematics Assessment Project This lesson unit is intended to help you assess how well students are able to: Solve linear equations in one variable with rational number coefficients. Collect like terms. Expand expressions using the distributive property. Categorize linear equations in one variable as having one, none, or infinitely many solutions. STANDARDS ADDRESSED IN THIS TASK: Understand the connections between proportional relationships, lines, and linear equations. MCC8.EE.5 Graph proportional relationships, interpreting the unit rate as the slope of the graph. Compare two different proportional relationships represented in different ways. MCC8.EE.6 Use similar triangles to explain why the slope m is the same between any two distinct points on a non-vertical line in the coordinate plane; derive the equation y = mx for a line through the origin and the equation y = mx + b for a line intercepting the vertical axis at b. Define, evaluate, and compare functions. MCC8.F.3 Interpret the equation y = mx + b as defining a linear function, whose graph is a straight line; give examples of functions that are not linear. STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL PRACTICE: This task uses all of the practices with emphasis on: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 7. Look for and make use of structure. July 2013 Page 30 of 33
31 TASK DESCRIPTION, DEVELOPMENT AND DISCUSSION: Tasks and lessons from the Mathematics Assessment Project are specifically designed to help teachers effectively formatively assess their students. The way the tasks and lessons are designed gives the teacher a clear understanding of what the students are able to do and not do. Within the lesson, teachers will find suggestions and question prompts that will help guide students towards understanding. For more information access the MAP website: The task, Solving Linear Equations in One Variable, is a Formative Assessment Lesson (FAL) that can be found at the website: The FAL document provides a clear lesson design, from the opening of the lesson to the closing of the lesson. The PDF version of the task can be found at the link below: July 2013 Page 31 of 33
32 SE TASK: Writing for a Math Website As a community service project your school has partnered with a national web based company to help develop a website that will provide math support to 8 th graders with the Common Core Georgia Performance Standards. Your middle school has been assigned the standards below. MCC8.EE.7 Solve linear equations in one variable. a. Give examples of linear equations in one variable with one solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solutions. Show which of these possibilities is the case by successively transforming the given equation into simpler forms, until an equivalent equation of the form x = a, a = b, or a = a results (where a and b are different numbers). b. Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients, including equations whose solutions require expanding expressions using the distributive property and collecting like terms. Your help has been requested writing the problems and providing the solutions. The new program will be interactive. It must tell the students if the answer is correct or incorrect and show the problems completely worked out along with justification for each step. 1. Create 6 equations that can be sorted into the categories in the table below (2 per category) and provide solutions to the problem. The solutions must show all steps along with written justifications for each step. Each problem created must meet the specs of the standard as listed below: linear equation in one variable include rational number coefficients require use of the distributive property variables on both sides of the equation require collecting like terms July 2013 Page 32 of 33
33 One Solution No Solution Infinitely Many Solutions 2. Provide a written explanation to help other 8 th graders understand the meaning of having one solution, no solution, or infinitely many solutions. July 2013 Page 33 of 33
CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition. Mathematics. 8 th Grade Unit 4: Functions
 CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics 8 th Grade Unit 4: Functions These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. The contents
CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics 8 th Grade Unit 4: Functions These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. The contents
CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition. Mathematics. CCGPS Analytic Geometry Unit 6: Modeling Geometry
 CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics CCGPS Analytic Geometry Unit 6: Modeling Geometry These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement.
CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics CCGPS Analytic Geometry Unit 6: Modeling Geometry These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement.
Functions MCC8.F.1 MCC8.F.2 MCC8.EE.5 MCC8.EE.6 MCC8.F.3
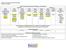 Common Core Georgia Performance Standards 8 th Grade - At a Glance Common Core Georgia Performance Standards: Curriculum Map Semester 1 Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8 Unit
Common Core Georgia Performance Standards 8 th Grade - At a Glance Common Core Georgia Performance Standards: Curriculum Map Semester 1 Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8 Unit
Mathematics. Unit 2: Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities
 CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics CCGPS Coordinate Algebra Unit 2: Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute
CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics CCGPS Coordinate Algebra Unit 2: Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute
Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics GSE Coordinate Algebra Unit 2: Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities Unit 2 Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities Table of Contents OVERVIEW...
Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics GSE Coordinate Algebra Unit 2: Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities Unit 2 Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities Table of Contents OVERVIEW...
The Number System (NS) 8.NS.1 Standards for Mathematical Practice (MP): Connections
 Domain: The Number System (NS) Cluster: Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers. Standard: 8.NS.1. Know that numbers that are not rational are called
Domain: The Number System (NS) Cluster: Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers. Standard: 8.NS.1. Know that numbers that are not rational are called
Functions MCC8.F.1 MCC8.F.2 MCC8.EE.5 MCC8.EE.6 MCC8.F.3
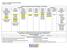 Common Core Georgia Performance Standards 8 th Grade At a Glance Common Core Georgia Performance Standards: Curriculum Map Semester 1 Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8 Unit
Common Core Georgia Performance Standards 8 th Grade At a Glance Common Core Georgia Performance Standards: Curriculum Map Semester 1 Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8 Unit
Middle School Math Solution: Course 3
 Ohio 8.MP MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES The s for Mathematical Practice describe the skills that mathematics educators should seek to develop in their students. The descriptions of the mathematical practices
Ohio 8.MP MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES The s for Mathematical Practice describe the skills that mathematics educators should seek to develop in their students. The descriptions of the mathematical practices
CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition. Mathematics. 8 th Grade Unit 4: Functions
 CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics 8 th Grade Unit 4: Functions These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. TABLE OF CONTENTS
CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics 8 th Grade Unit 4: Functions These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. TABLE OF CONTENTS
Jackson County Schools Curriculum Pacing Guide Math - Eighth Grade
 Jackson County Schools Curriculum Pacing Guide Math - Eighth Grade 1st Semester nd Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit Unit 9 Transformations, Congruence and Similarity Exponents
Jackson County Schools Curriculum Pacing Guide Math - Eighth Grade 1st Semester nd Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit Unit 9 Transformations, Congruence and Similarity Exponents
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Frameworks. Mathematics
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Frameworks Mathematics Accelerated GSE Analytic Geometry B/Advanced Algebra Unit 7: Rational and Radical Relationships These materials are for nonprofit educational
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Frameworks Mathematics Accelerated GSE Analytic Geometry B/Advanced Algebra Unit 7: Rational and Radical Relationships These materials are for nonprofit educational
Alta Loma Junior High 8 th Grade Math
 Alta Loma Junior High 8 th Grade Math Dear Parent(s): The following outline is being provided to better help you and your student to understand the current Common Core concepts of this trimester. Trimester
Alta Loma Junior High 8 th Grade Math Dear Parent(s): The following outline is being provided to better help you and your student to understand the current Common Core concepts of this trimester. Trimester
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map. Mathematics. GSE 8 th Grade
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map Mathematics GSE 8 th Grade These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. GSE Eighth Grade
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map Mathematics GSE 8 th Grade These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. GSE Eighth Grade
Mathematics. Accelerated GSE Algebra I/Geometry A. Unit 4: Modeling and Analyzing Exponential Functions
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics Accelerated GSE Algebra I/Geometry A Unit 4: Modeling and Analyzing Exponential Functions. These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes
Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics Accelerated GSE Algebra I/Geometry A Unit 4: Modeling and Analyzing Exponential Functions. These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes
Mathematics. Unit 4: Modeling and Analyzing Exponential Functions
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Frameworks Mathematics GSE Algebra I Unit 4: Modeling and Analyzing Exponential Functions. These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Frameworks Mathematics GSE Algebra I Unit 4: Modeling and Analyzing Exponential Functions. These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other
Math 8 Common Core. Mathematics Prince George s County Public Schools
 Math 8 Common Core Mathematics Prince George s County Public Schools 2014-2015 Course Code: Prerequisites: Successful completion of Math 7 Common Core This course continues the trajectory towards a more
Math 8 Common Core Mathematics Prince George s County Public Schools 2014-2015 Course Code: Prerequisites: Successful completion of Math 7 Common Core This course continues the trajectory towards a more
Sequence of Math 7 Accelerated Units Aligned with the California Standards
 Sequence of Math 7 Accelerated Units Aligned with the California Standards Year at a Glance Unit Big Ideas Math Advanced 2 Textbook Chapters Dates 1. Equations and Inequalities Ch. 1 Equations Ch. 11 Inequalities
Sequence of Math 7 Accelerated Units Aligned with the California Standards Year at a Glance Unit Big Ideas Math Advanced 2 Textbook Chapters Dates 1. Equations and Inequalities Ch. 1 Equations Ch. 11 Inequalities
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map. Mathematics. GSE 8 th Grade
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map Mathematics GSE 8 th Grade These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. GSE Eighth Grade
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map Mathematics GSE 8 th Grade These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. GSE Eighth Grade
Mathematics Curriculum
 New York State Common Core Mathematics Curriculum MODULE 1 Table of Contents 1 Relationships Between Quantities and Reasoning with Equations and... 3 Topic A: Introduction to Functions Studied this Year
New York State Common Core Mathematics Curriculum MODULE 1 Table of Contents 1 Relationships Between Quantities and Reasoning with Equations and... 3 Topic A: Introduction to Functions Studied this Year
The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course:
 Math 8 Curriculum Overview The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical Proficiency 1. Make
Math 8 Curriculum Overview The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical Proficiency 1. Make
Eighth Grade Mathematics
 Description The Appleton Area School District middle school mathematics program provides students opportunities to develop mathematical skills in thinking and applying problem-solving strategies. The framework
Description The Appleton Area School District middle school mathematics program provides students opportunities to develop mathematical skills in thinking and applying problem-solving strategies. The framework
Grade 6 PI+ Yearlong Mathematics Map
 Grade 6 PI+ Yearlong Mathematics Map Resources: Approved from Board of Education Assessments: PARCC Assessments, Performance Series, District Benchmark Assessments Common Core State Standards Standards
Grade 6 PI+ Yearlong Mathematics Map Resources: Approved from Board of Education Assessments: PARCC Assessments, Performance Series, District Benchmark Assessments Common Core State Standards Standards
April 2016 Draft. DRAFT New Louisiana Standards for Correlation to Eureka Math Page 1. eureka math.org 2016 Great Minds
 DRAFT New Louisiana Standards for 2016 2017 Correlation to Eureka Math Grade 8 April 2016 Draft DRAFT New Louisiana Standards for 2016 2017 Correlation to Eureka Math Page 1 Grade 8 Mathematics The majority
DRAFT New Louisiana Standards for 2016 2017 Correlation to Eureka Math Grade 8 April 2016 Draft DRAFT New Louisiana Standards for 2016 2017 Correlation to Eureka Math Page 1 Grade 8 Mathematics The majority
Part 2 Number and Quantity
 Part Number and Quantity Copyright Corwin 08 Number and Quantity Conceptual Category Overview Students have studied number from the beginning of their schooling. They start with counting. Kindergarten
Part Number and Quantity Copyright Corwin 08 Number and Quantity Conceptual Category Overview Students have studied number from the beginning of their schooling. They start with counting. Kindergarten
CK-12 Middle School Math Grade 8
 CK-12 Middle School Math aligned with COMMON CORE MATH STATE STANDARDS INITIATIVE Middle School Standards for Math Content Common Core Math Standards for CK-12 Middle School Math The Number System (8.NS)
CK-12 Middle School Math aligned with COMMON CORE MATH STATE STANDARDS INITIATIVE Middle School Standards for Math Content Common Core Math Standards for CK-12 Middle School Math The Number System (8.NS)
Mathematics. Accelerated GSE Geometry B/Algebra II Unit 5: Operations with Polynomials
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Frameworks Mathematics Accelerated GSE Geometry B/Algebra II Unit 5: Operations with Polynomials These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only.
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Frameworks Mathematics Accelerated GSE Geometry B/Algebra II Unit 5: Operations with Polynomials These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only.
OAKLYN PUBLIC SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM MAP EIGHTH GRADE
 OAKLYN PUBLIC SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM MAP EIGHTH GRADE STANDARD 8.NS THE NUMBER SYSTEM Big Idea: Numeric reasoning involves fluency and facility with numbers. Learning Targets: Students will know
OAKLYN PUBLIC SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM MAP EIGHTH GRADE STANDARD 8.NS THE NUMBER SYSTEM Big Idea: Numeric reasoning involves fluency and facility with numbers. Learning Targets: Students will know
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Frameworks Mathematics
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Frameworks Mathematics GSE Analytic Geometry Unit 6: Geometric and Algebraic Connections Unit 6 Geometric and Algebraic Connections Table of Contents OVERVIEW...
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Frameworks Mathematics GSE Analytic Geometry Unit 6: Geometric and Algebraic Connections Unit 6 Geometric and Algebraic Connections Table of Contents OVERVIEW...
Common Core State Standards with California Additions 1 Standards Map for a Basic Grade-Level Program. Grade Eight Mathematics
 Common Core State s with California Additions 1 s Map for a Basic Grade-Level Program Grade Eight Mathematics Publisher 8.NS 1. 8.NS 2. Language Primary Supporting THE NUMBER SYSTEM Know that there are
Common Core State s with California Additions 1 s Map for a Basic Grade-Level Program Grade Eight Mathematics Publisher 8.NS 1. 8.NS 2. Language Primary Supporting THE NUMBER SYSTEM Know that there are
PLEASANTON UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 8 Course Outline Form
 PLEASANTON UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 8 Course Outline Form Course Title: Math 8 Course Number/CBED Number: Grade Levels: Length of Course: Eighth Grade One Year Credit: 10 Meets Graduation Requirements:
PLEASANTON UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 8 Course Outline Form Course Title: Math 8 Course Number/CBED Number: Grade Levels: Length of Course: Eighth Grade One Year Credit: 10 Meets Graduation Requirements:
Mathematics Grade 8. Prepublication Version, April 2013 California Department of Education 51
 Mathematics In, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and equations, including modeling an association in bivariate data with a linear
Mathematics In, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and equations, including modeling an association in bivariate data with a linear
Overview of Structure and Content
 Introduction The Math Test Specifications provide an overview of the structure and content of Ohio s State Test. This overview includes a description of the test design as well as information on the types
Introduction The Math Test Specifications provide an overview of the structure and content of Ohio s State Test. This overview includes a description of the test design as well as information on the types
Math 8 Advanced Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Curriculum Map
 Semester 1 Standards for Mathematical Practice 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of
Semester 1 Standards for Mathematical Practice 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of
Parent Guide. Number System. Diocese of Cleveland
 Parent Guide Grade Eight Algebra Curriculum Diocese of Cleveland Below is a list of skills your child will be taught in Grade Eight Algebra. As parents, you are encouraged to support the work of your child
Parent Guide Grade Eight Algebra Curriculum Diocese of Cleveland Below is a list of skills your child will be taught in Grade Eight Algebra. As parents, you are encouraged to support the work of your child
CCGPS Frameworks Teacher Edition Mathematics
 CCGPS Frameworks Teacher Edition Mathematics 6 th Grade Unit4: One Step Equations and Inequalities Sixth Grade Mathematics Unit 4 Unit 4 One Step Equations and Inequalities TABLE OF CONTENTS Overview...3
CCGPS Frameworks Teacher Edition Mathematics 6 th Grade Unit4: One Step Equations and Inequalities Sixth Grade Mathematics Unit 4 Unit 4 One Step Equations and Inequalities TABLE OF CONTENTS Overview...3
ALGEBRA 1 CURRICULUM COMMON CORE BASED
 ALGEBRA 1 CURRICULUM COMMON CORE BASED (Supplemented with 8th grade PSSA anchors ) UPPER MERION AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT 435 CROSSFIELD ROAD KING OF PRUSSIA, PA 19406 8/20/2012 PA COMMON CORE ALIGNED MATHEMATICS
ALGEBRA 1 CURRICULUM COMMON CORE BASED (Supplemented with 8th grade PSSA anchors ) UPPER MERION AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT 435 CROSSFIELD ROAD KING OF PRUSSIA, PA 19406 8/20/2012 PA COMMON CORE ALIGNED MATHEMATICS
, Eighth Grade Mathematics, Quarter 1
 2017.18, Eighth Grade Mathematics, Quarter 1 The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical
2017.18, Eighth Grade Mathematics, Quarter 1 The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical
Accelerated Traditional Pathway: Accelerated 7 th Grade
 Accelerated Traditional Pathway: Accelerated 7 th Grade This course differs from the non-accelerated 7 th Grade course in that it contains content from 8 th grade. While coherence is retained, in that
Accelerated Traditional Pathway: Accelerated 7 th Grade This course differs from the non-accelerated 7 th Grade course in that it contains content from 8 th grade. While coherence is retained, in that
The descriptions below provide an overview of the concepts and skills that students explore throughout the 8 th grade.
 Mathematics Grade 8 The descriptions below provide an overview of the concepts and skills that students explore throughout the 8 th grade. The Number System This is the culminating area for the number
Mathematics Grade 8 The descriptions below provide an overview of the concepts and skills that students explore throughout the 8 th grade. The Number System This is the culminating area for the number
Grade 8 Yearlong Mathematics Map
 rade 8 Yearlong Mathematics Map Resources: Approved from Board of Education Assessments: PARCC Assessments, Performance Series, District Benchmark Assessments NS NS Common Core State Standards Standards
rade 8 Yearlong Mathematics Map Resources: Approved from Board of Education Assessments: PARCC Assessments, Performance Series, District Benchmark Assessments NS NS Common Core State Standards Standards
Mathematics. Accelerated GSE Algebra I/Geometry A. Unit 3: Modeling and Analyzing Quadratic Functions
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Frameworks Mathematics Accelerated GSE Algebra I/Geometry A Unit 3: Modeling and Analyzing Quadratic Functions These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Frameworks Mathematics Accelerated GSE Algebra I/Geometry A Unit 3: Modeling and Analyzing Quadratic Functions These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes
Mathematics. Algebra I (PreAP, Pt. 1, Pt. 2) Curriculum Guide. Revised 2016
 Mathematics Algebra I (PreAP, Pt. 1, Pt. ) Curriculum Guide Revised 016 Intentionally Left Blank Introduction The Mathematics Curriculum Guide serves as a guide for teachers when planning instruction and
Mathematics Algebra I (PreAP, Pt. 1, Pt. ) Curriculum Guide Revised 016 Intentionally Left Blank Introduction The Mathematics Curriculum Guide serves as a guide for teachers when planning instruction and
ALGEBRA I CCR MATH STANDARDS
 RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN QUANTITIES AND REASONING WITH EQUATIONS M.A1HS.1 M.A1HS.2 M.A1HS.3 M.A1HS.4 M.A1HS.5 M.A1HS.6 M.A1HS.7 M.A1HS.8 M.A1HS.9 M.A1HS.10 Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems.
RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN QUANTITIES AND REASONING WITH EQUATIONS M.A1HS.1 M.A1HS.2 M.A1HS.3 M.A1HS.4 M.A1HS.5 M.A1HS.6 M.A1HS.7 M.A1HS.8 M.A1HS.9 M.A1HS.10 Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems.
Lesson 1: Properties of Integer Exponents
 8 th Grade Math Instructional Guide Students should develop proficiency with Tennessee Standards for Mathematical Practice. 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly
8 th Grade Math Instructional Guide Students should develop proficiency with Tennessee Standards for Mathematical Practice. 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly
Algebra 1 Yearlong Curriculum Plan. Last modified: June 2014
 Algebra 1 Yearlong Curriculum Plan Last modified: June 2014 SUMMARY This curriculum plan is divided into four academic quarters. In Quarter 1, students first dive deeper into the real number system before
Algebra 1 Yearlong Curriculum Plan Last modified: June 2014 SUMMARY This curriculum plan is divided into four academic quarters. In Quarter 1, students first dive deeper into the real number system before
COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR
 COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR Mathematics (CCSSM) Grade 8 Mathematics Grade 8 In Grade 8, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and
COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR Mathematics (CCSSM) Grade 8 Mathematics Grade 8 In Grade 8, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Frameworks. Mathematics. GSE Algebra I. Unit 5: Comparing and Contrasting Functions
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Frameworks Mathematics GSE Algebra I Unit 5: Comparing and Contrasting Functions GSE Algebra I Unit 5 Unit 5 Comparing and Contrasting Functions Table of Contents
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Frameworks Mathematics GSE Algebra I Unit 5: Comparing and Contrasting Functions GSE Algebra I Unit 5 Unit 5 Comparing and Contrasting Functions Table of Contents
Fairfield Public Schools
 Mathematics Fairfield Public Schools Pre-Algebra 8 Pre-Algebra 8 BOE Approved 05/21/2013 1 PRE-ALGEBRA 8 Critical Areas of Focus In the Pre-Algebra 8 course, instructional time should focus on three critical
Mathematics Fairfield Public Schools Pre-Algebra 8 Pre-Algebra 8 BOE Approved 05/21/2013 1 PRE-ALGEBRA 8 Critical Areas of Focus In the Pre-Algebra 8 course, instructional time should focus on three critical
CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition. Mathematics. Accelerated CCGPS Analytic Geometry B / Advanced Algebra Unit 2: Quadratic Functions
 CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics Accelerated CCGPS Analytic Geometry B / Advanced Algebra Unit : Quadratic Functions These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use
CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics Accelerated CCGPS Analytic Geometry B / Advanced Algebra Unit : Quadratic Functions These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use
Sequence of Math 8 SDC Units Aligned with the California Standards
 Sequence of Math 8 SDC Units Aligned with the California Standards Year at a Glance Unit Big Ideas Course 3 Textbook Chapters Dates 1. Equations Ch. 1 Equations 29 days: 9/5/17 10/13/17 2. Transformational
Sequence of Math 8 SDC Units Aligned with the California Standards Year at a Glance Unit Big Ideas Course 3 Textbook Chapters Dates 1. Equations Ch. 1 Equations 29 days: 9/5/17 10/13/17 2. Transformational
Common Core State Standards for Mathematics
 A Correlation of Pearson to the for Mathematics for Mathematics Introduction This document demonstrates how Pearson s digits program meets the for Mathematics. Correlation references are to the digits
A Correlation of Pearson to the for Mathematics for Mathematics Introduction This document demonstrates how Pearson s digits program meets the for Mathematics. Correlation references are to the digits
Curriculum Summary Seventh Grade Pre-Algebra
 Curriculum Summary Seventh Grade Pre-Algebra Students should know and be able to demonstrate mastery in the following skills by the end of Seventh Grade: Ratios and Proportional Relationships Analyze proportional
Curriculum Summary Seventh Grade Pre-Algebra Students should know and be able to demonstrate mastery in the following skills by the end of Seventh Grade: Ratios and Proportional Relationships Analyze proportional
Pre-Algebra GT (Grade 6) Essential Curriculum. The Mathematical Practices
 Pre-Algebra GT (Grade 6) Essential Curriculum The Mathematical Practices The Standards for Mathematical Practice describe varieties of expertise that mathematics educators at all levels should seek to
Pre-Algebra GT (Grade 6) Essential Curriculum The Mathematical Practices The Standards for Mathematical Practice describe varieties of expertise that mathematics educators at all levels should seek to
Grade 7 Honors Yearlong Mathematics Map
 rade 7 Honors Yearlong Mathematics Map Resources: Approved from Board of Education Assessments: PARCC Assessments, Performance Series, District Benchmark Assessments NS NS Common Core State Standards Standards
rade 7 Honors Yearlong Mathematics Map Resources: Approved from Board of Education Assessments: PARCC Assessments, Performance Series, District Benchmark Assessments NS NS Common Core State Standards Standards
COLLEGE-PREP ALGEBRA I Course #042
 COLLEGE-PREP ALGEBRA I Course #042 Course of Study Findlay City Schools 2013 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Findlay City Schools Mission Statement and Beliefs 2. College-Prep Algebra I Course of Study 3. College-Prep
COLLEGE-PREP ALGEBRA I Course #042 Course of Study Findlay City Schools 2013 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Findlay City Schools Mission Statement and Beliefs 2. College-Prep Algebra I Course of Study 3. College-Prep
Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Mathematics Grade 7 Adopted 2011
 Hands On Standards 1, Deluxe Edition Grades: 7, 8, 9, 10 State: Georgia Common Core Standards Subject: Mathematics Publisher: ETA hand2mind Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Mathematics Grade 7
Hands On Standards 1, Deluxe Edition Grades: 7, 8, 9, 10 State: Georgia Common Core Standards Subject: Mathematics Publisher: ETA hand2mind Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Mathematics Grade 7
Mathematics 8 Essential Curriculum
 Mathematics 8 Essential Curriculum The Mathematical Practices The Standards for Mathematical Practice describe varieties of expertise that mathematics educators at all levels should seek to develop in
Mathematics 8 Essential Curriculum The Mathematical Practices The Standards for Mathematical Practice describe varieties of expertise that mathematics educators at all levels should seek to develop in
Standards for Mathematical Practice. Ratio and Proportional Relationships
 North Carolina Standard Course of Study Sixth Grade Mathematics 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique
North Carolina Standard Course of Study Sixth Grade Mathematics 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique
CHAPTER 7: RATIONAL AND IRRATIONAL NUMBERS (3 WEEKS)...
 Table of Contents CHAPTER 7: RATIONAL AND IRRATIONAL NUMBERS (3 WEEKS)... 20 7.0 ANCHOR PROBLEM: ZOOMING IN ON THE NUMBER LINE... 24 SECTION 7.1: REPRESENT NUMBERS GEOMETRICALLY... 26 7.1a Class Activity:
Table of Contents CHAPTER 7: RATIONAL AND IRRATIONAL NUMBERS (3 WEEKS)... 20 7.0 ANCHOR PROBLEM: ZOOMING IN ON THE NUMBER LINE... 24 SECTION 7.1: REPRESENT NUMBERS GEOMETRICALLY... 26 7.1a Class Activity:
Middle School Math Course 3. Correlation of the ALEKS course Middle School Math Course 3 to the Common Core State Standards for Grade 8 (2010)
 Middle School Math Course 3 Correlation of the ALEKS course Middle School Math Course 3 to the Common Core State Standards for Grade 8 (2010) 8.NS: The Number System 8.NS.A.1: 8.NS.A.2: = ALEKS course
Middle School Math Course 3 Correlation of the ALEKS course Middle School Math Course 3 to the Common Core State Standards for Grade 8 (2010) 8.NS: The Number System 8.NS.A.1: 8.NS.A.2: = ALEKS course
Performance Level Descriptors Grade 8 Mathematics
 Expressions and Equations Scientific Notation Grade 8 Math : Sub-Claim A The student solves problems involving the Major Content for grade/course with connections to the Standards for Mathematical Practice.
Expressions and Equations Scientific Notation Grade 8 Math : Sub-Claim A The student solves problems involving the Major Content for grade/course with connections to the Standards for Mathematical Practice.
Gary School Community Corporation Mathematics Department Unit Document. Unit Name: Polynomial Operations (Add & Sub)
 Gary School Community Corporation Mathematics Department Unit Document Unit Number: 1 Grade: Algebra 1 Unit Name: Polynomial Operations (Add & Sub) Duration of Unit: A1.RNE.7 Standards for Mathematical
Gary School Community Corporation Mathematics Department Unit Document Unit Number: 1 Grade: Algebra 1 Unit Name: Polynomial Operations (Add & Sub) Duration of Unit: A1.RNE.7 Standards for Mathematical
8th Grade The Number System and Mathematical Operations Part
 Slide 1 / 157 Slide 2 / 157 8th Grade The Number System and Mathematical Operations Part 2 2015-11-20 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 157 Table of Contents Squares of Numbers Greater than 20 Simplifying Perfect
Slide 1 / 157 Slide 2 / 157 8th Grade The Number System and Mathematical Operations Part 2 2015-11-20 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 157 Table of Contents Squares of Numbers Greater than 20 Simplifying Perfect
8th Grade. The Number System and Mathematical Operations Part 2.
 1 8th Grade The Number System and Mathematical Operations Part 2 2015 11 20 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Squares of Numbers Greater than 20 Simplifying Perfect Square Radical Expressions Approximating
1 8th Grade The Number System and Mathematical Operations Part 2 2015 11 20 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Squares of Numbers Greater than 20 Simplifying Perfect Square Radical Expressions Approximating
Standards of Learning Content Review Notes. Grade 8 Mathematics 1 st Nine Weeks,
 Standards of Learning Content Review Notes Grade 8 Mathematics 1 st Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 Revised September 2015 2 Mathematics Content Review Notes Grade 8 Mathematics: First Nine Weeks 2015-2016 -This
Standards of Learning Content Review Notes Grade 8 Mathematics 1 st Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 Revised September 2015 2 Mathematics Content Review Notes Grade 8 Mathematics: First Nine Weeks 2015-2016 -This
Algebra 1 Scope and Sequence Standards Trajectory
 Algebra 1 Scope and Sequence Standards Trajectory Course Name Algebra 1 Grade Level High School Conceptual Category Domain Clusters Number and Quantity Algebra Functions Statistics and Probability Modeling
Algebra 1 Scope and Sequence Standards Trajectory Course Name Algebra 1 Grade Level High School Conceptual Category Domain Clusters Number and Quantity Algebra Functions Statistics and Probability Modeling
Name Period Date MATHLINKS GRADE 8 STUDENT PACKET 11 EXPONENTS AND ROOTS
 Name Period Date 8-11 STUDENT PACKET MATHLINKS GRADE 8 STUDENT PACKET 11 EXPONENTS AND ROOTS 11.1 Squares and Square Roots Use numbers and pictures to understand the inverse relationship between squaring
Name Period Date 8-11 STUDENT PACKET MATHLINKS GRADE 8 STUDENT PACKET 11 EXPONENTS AND ROOTS 11.1 Squares and Square Roots Use numbers and pictures to understand the inverse relationship between squaring
Subject Area: Mathematics State-Funded Course: Mathematics/Grade 8
 FORMAT FOR CORRELATION TO THE COMMON CORE GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS (CCGPS) Subject Area: Mathematics State-Funded Course: 27.02300 Mathematics/Grade 8 Textbook Title: CCSS Mathematics Grade 8 Publisher:
FORMAT FOR CORRELATION TO THE COMMON CORE GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS (CCGPS) Subject Area: Mathematics State-Funded Course: 27.02300 Mathematics/Grade 8 Textbook Title: CCSS Mathematics Grade 8 Publisher:
GSE Fulton Eighth Grade Advanced Curriculum Map 1 st Semester 2 nd Semester
 GSE Fulton Eighth Grade Advanced Curriculum Map 1 st Semester 2 nd Semester Unit 1 Transformations, Congruence and Similarity MGSE8.G.1 MGSE8.G.2 MGSE8.G.3 MGSE8.G.4 MGSE8.G.5 Unit 2 Exponents MGSE8.EE1
GSE Fulton Eighth Grade Advanced Curriculum Map 1 st Semester 2 nd Semester Unit 1 Transformations, Congruence and Similarity MGSE8.G.1 MGSE8.G.2 MGSE8.G.3 MGSE8.G.4 MGSE8.G.5 Unit 2 Exponents MGSE8.EE1
Common Core Correlations. Mathematics Grade 8. Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions.
 Common Core Correlations Mathematics Grade 8 BENCHMARK CODE 8.EE.1.1 BENCHMARK Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. SpringBoard Page 72, 73,
Common Core Correlations Mathematics Grade 8 BENCHMARK CODE 8.EE.1.1 BENCHMARK Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. SpringBoard Page 72, 73,
Common Core State Standards for Mathematics Grade 8 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Go Math, Grade 8 Common Core Edition 2014
 Correlation to the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics Grade 8 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Go Math, Grade 8 Common Core Edition 2014 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Go Math, Grade 8 Common Core Edition
Correlation to the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics Grade 8 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Go Math, Grade 8 Common Core Edition 2014 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Go Math, Grade 8 Common Core Edition
Algebra 1. Mathematics Course Syllabus
 Mathematics Algebra 1 2017 2018 Course Syllabus Prerequisites: Successful completion of Math 8 or Foundations for Algebra Credits: 1.0 Math, Merit The fundamental purpose of this course is to formalize
Mathematics Algebra 1 2017 2018 Course Syllabus Prerequisites: Successful completion of Math 8 or Foundations for Algebra Credits: 1.0 Math, Merit The fundamental purpose of this course is to formalize
Agile Mind Mathematics 8 Scope and Sequence, Indiana Academic Standards for Mathematics
 Prior to Grade 8, students have written and interpreted expressions, solved equations and inequalities, explored quantitative relationships between dependent and independent variables, and solved problems
Prior to Grade 8, students have written and interpreted expressions, solved equations and inequalities, explored quantitative relationships between dependent and independent variables, and solved problems
8 th Grade Remediation Guide
 8 th Grade Remediation Guide Focused remediation helps target the skills students need to more quickly access and practice on-grade level content. This chart is a reference guide for teachers to help them
8 th Grade Remediation Guide Focused remediation helps target the skills students need to more quickly access and practice on-grade level content. This chart is a reference guide for teachers to help them
Connected Mathematics Project 3 (CMP3) 2014
 s Map for a Basic Grade Level Program San Diego Unified School District Connected Mathematics Project 3 (CMP3) 2014 Common Core State s with California Additions Grade 8 Mathematics Common Core State s
s Map for a Basic Grade Level Program San Diego Unified School District Connected Mathematics Project 3 (CMP3) 2014 Common Core State s with California Additions Grade 8 Mathematics Common Core State s
California Common Core State Standards for Mathematics Standards Map Algebra I
 A Correlation of Pearson CME Project Algebra 1 Common Core 2013 to the California Common Core State s for Mathematics s Map Algebra I California Common Core State s for Mathematics s Map Algebra I Indicates
A Correlation of Pearson CME Project Algebra 1 Common Core 2013 to the California Common Core State s for Mathematics s Map Algebra I California Common Core State s for Mathematics s Map Algebra I Indicates
West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Math A&E Grade 7
 West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Math A&E Grade 7 Page 1 of 24 Unit 1: Introduction to Algebra Content Area: Mathematics Course & Grade Level: A&E Mathematics, Grade 7 Summary and Rationale
West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Math A&E Grade 7 Page 1 of 24 Unit 1: Introduction to Algebra Content Area: Mathematics Course & Grade Level: A&E Mathematics, Grade 7 Summary and Rationale
Tasks for this target will require students to select or produce equivalent numerical expressions based on properties of integer exponents.
 Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. Content Domain: Expressions and Equations Target
Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. Content Domain: Expressions and Equations Target
Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks. Mathematics
 Georgia Standards of Ecellence Frameworks Mathematics Accelerated GSE Analytic Geometry B/Advanced Algebra Unit 2: Geometric and Algebraic Connections These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes
Georgia Standards of Ecellence Frameworks Mathematics Accelerated GSE Analytic Geometry B/Advanced Algebra Unit 2: Geometric and Algebraic Connections These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes
Algebra 1 Syllabus
 Algebra 1 Syllabus 2017-18 dennis_jenkins@crpusd.org Welcome to algebra, a course designed to prepare students for geometry and any other courses taken after it. Students are required by the state of California
Algebra 1 Syllabus 2017-18 dennis_jenkins@crpusd.org Welcome to algebra, a course designed to prepare students for geometry and any other courses taken after it. Students are required by the state of California
Florida State Standards for M/J Pre Algebra
 A Correlation of Pearson Grade 8, 2014 To the Florida State Standards for M/J Pre Algebra - 1205070 CORRELATION FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS CORRELATION COURSE STANDARDS/S SUBJECT:
A Correlation of Pearson Grade 8, 2014 To the Florida State Standards for M/J Pre Algebra - 1205070 CORRELATION FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS CORRELATION COURSE STANDARDS/S SUBJECT:
Granite School District Parent Guides Utah Core State Standards for Mathematics Grades K-6
 Granite School District Parent Guides Grades K-6 GSD Parents Guide for Kindergarten The addresses Standards for Mathematical Practice and Standards for Mathematical Content. The standards stress not only
Granite School District Parent Guides Grades K-6 GSD Parents Guide for Kindergarten The addresses Standards for Mathematical Practice and Standards for Mathematical Content. The standards stress not only
Common Core State Standards for Mathematics
 A Correlation of to the for Mathematics Grades 6-8 Introduction This document demonstrates how Pearson s digits 2012 meets the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics. Correlation references are to
A Correlation of to the for Mathematics Grades 6-8 Introduction This document demonstrates how Pearson s digits 2012 meets the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics. Correlation references are to
8 th Grade Intensive Math
 8 th Grade Intensive Math Ready Florida MAFS Student Edition August-September 2014 Lesson 1 Part 1: Introduction Properties of Integer Exponents Develop Skills and Strategies MAFS 8.EE.1.1 In the past,
8 th Grade Intensive Math Ready Florida MAFS Student Edition August-September 2014 Lesson 1 Part 1: Introduction Properties of Integer Exponents Develop Skills and Strategies MAFS 8.EE.1.1 In the past,
Danville District #118 Mathematics Transitional Algebra (PARCC Framework version) Curriculum and Scope and Sequence
 The eight Mathematical Practices will be incorporated throughout the course: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments
The eight Mathematical Practices will be incorporated throughout the course: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments
BPS PreAlgebra Math Planning Guide
 BPS PreAlgebra Math Planning Guide 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Mathematical Practice Standards: Vehicle for All Content 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly
BPS PreAlgebra Math Planning Guide 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Mathematical Practice Standards: Vehicle for All Content 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly
BPS Accelerated 7th Grade Math Planning Guide UNIT 7.1: THE NUMBER SYSTEM
 Mathematical Practice Standards: Vehicle for All Content Accelerated 7th Grade BPS Suggested Planning Guide BPS Accelerated 7th Grade Math Planning Guide 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving
Mathematical Practice Standards: Vehicle for All Content Accelerated 7th Grade BPS Suggested Planning Guide BPS Accelerated 7th Grade Math Planning Guide 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving
Algebra I. 60 Higher Mathematics Courses Algebra I
 The fundamental purpose of the course is to formalize and extend the mathematics that students learned in the middle grades. This course includes standards from the conceptual categories of Number and
The fundamental purpose of the course is to formalize and extend the mathematics that students learned in the middle grades. This course includes standards from the conceptual categories of Number and
Copyright Corwin 2018
 Algebra Part 3 Algebra Conceptual Category Overview The algebra conceptual category synthesizes content from previous grade levels to deepen understanding of the structure of mathematics. At the high school
Algebra Part 3 Algebra Conceptual Category Overview The algebra conceptual category synthesizes content from previous grade levels to deepen understanding of the structure of mathematics. At the high school
UNIT 1 Unit Title: The Number System Unit Description: Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers
 Milford Public Schools Curriculum Department: Mathematics Course Name: Grade 8 Math UNIT 1 Unit Title: The Number System Unit Description: Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate
Milford Public Schools Curriculum Department: Mathematics Course Name: Grade 8 Math UNIT 1 Unit Title: The Number System Unit Description: Know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate
Unit 3 Radical and Rational Functions Algebra 2
 Number of Days: 29 11/27/17 1/19/18 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: A theme of Unit 3 is that the arithmetic of rational expressions is governed by the same rules as the arithmetic of rational numbers.
Number of Days: 29 11/27/17 1/19/18 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: A theme of Unit 3 is that the arithmetic of rational expressions is governed by the same rules as the arithmetic of rational numbers.
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map. Mathematics. GSE Algebra I
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map Mathematics GSE Algebra I These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. Georgia Department
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map Mathematics GSE Algebra I These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. Georgia Department
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map. Mathematics. GSE Grade 6
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map Mathematics GSE Grade 6 These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. Georgia Department
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map Mathematics GSE Grade 6 These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. Georgia Department
New York State Testing Program Grade 8 Common Core Mathematics Test. Released Questions with Annotations
 New York State Testing Program Grade 8 Common Core Mathematics Test Released Questions with Annotations August 2013 THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT / THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK / ALBANY, NY
New York State Testing Program Grade 8 Common Core Mathematics Test Released Questions with Annotations August 2013 THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT / THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK / ALBANY, NY
Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics GSE Analytic Geometry Unit 5: Quadratic Functions Unit 5 Quadratic Functions Table of Contents OVERVIEW... 3 STANDARDS ADDRESSED IN THIS UNIT... 4
Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics GSE Analytic Geometry Unit 5: Quadratic Functions Unit 5 Quadratic Functions Table of Contents OVERVIEW... 3 STANDARDS ADDRESSED IN THIS UNIT... 4
Curriculum Guide Cover Page
 Curriculum Guide Cover Page Course Title: Pre-Algebra Grade Level: 8 th Grade Subject/Topic Area: Math Written by: Jason Hansen Revised Date: November 2013 Time Frame: One School Year (170 days) School
Curriculum Guide Cover Page Course Title: Pre-Algebra Grade Level: 8 th Grade Subject/Topic Area: Math Written by: Jason Hansen Revised Date: November 2013 Time Frame: One School Year (170 days) School
Math 6 Common Core. Mathematics Prince George s County Public Schools
 Math 6 Common Core Mathematics Prince George s County Public Schools 2014-2015 Course Code: Prerequisites: Successful completion of Math 5 Common Core This course begins the transition from the heavy emphasis
Math 6 Common Core Mathematics Prince George s County Public Schools 2014-2015 Course Code: Prerequisites: Successful completion of Math 5 Common Core This course begins the transition from the heavy emphasis
Mathematics. Accelerated GSE Algebra I/Geometry A. Unit 5: Comparing and Contrasting Functions
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics Accelerated GSE Algebra I/Geometry A Unit 5: Comparing and Contrasting Functions These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any
Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics Accelerated GSE Algebra I/Geometry A Unit 5: Comparing and Contrasting Functions These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any
River Dell Regional School District. Algebra I Curriculum
 Algebra I Curriculum 2015 Mr. Patrick Fletcher Superintendent River Dell Regional Schools Ms. Lorraine Brooks Principal River Dell High School Mr. Richard Freedman Principal River Dell Middle School Mr.
Algebra I Curriculum 2015 Mr. Patrick Fletcher Superintendent River Dell Regional Schools Ms. Lorraine Brooks Principal River Dell High School Mr. Richard Freedman Principal River Dell Middle School Mr.
8th Grade The Number System and Mathematical Operations Part
 Slide 1 / 157 Slide 2 / 157 8th Grade The Number System and Mathematical Operations Part 2 2015-11-20 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 157 Table of Contents Squares of Numbers Greater than 20 Simplifying Perfect
Slide 1 / 157 Slide 2 / 157 8th Grade The Number System and Mathematical Operations Part 2 2015-11-20 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 157 Table of Contents Squares of Numbers Greater than 20 Simplifying Perfect
