Carleton University. Final Examination Fall DURATION: 2 HOURS No. of students: 275
|
|
|
- Rose O’Brien’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Carleton University Final Examination Fall 2017 DURATION: 2 HOURS No. of students: 275 Department Name & Course Number: Computer Science COMP 2804A Course Instructor: Michiel Smid Authorized memoranda: Calculator Students MUST count the number of pages in this examination question paper before beginning to write, and report any discrepancy to the proctor. This question paper has 13 pages (not including the cover page). This examination question paper MAY be taken from the examination room. In addition to this question paper, students require: an examination booklet: a Scantron sheet: no yes
2 COMP 2804A, FALL Instructions: 1. All questions must be answered on the scantron sheet. 2. Write your name and student number on the scantron sheet. 3. You do not have to hand in this examination paper. 4. Calculators are allowed. Marking scheme: Each of the 25 questions is worth 1 mark. ( ) n k = n!. k!(n k)! Newton: (x + y) n = n k=0 ( n k) x n k y k. For 0 < x < 1, n=0 xn = 1/(1 x). Geometric distribution: Assume an experiment has a success probability of p. We perform the experiment until it is successful for the first time. The expected number of times we perform the experiment is 1/p. Expected value: E(X) = k Pr(X = k). The sum ranges over all values k that X can take.
3 COMP 2804A, FALL You are given 20 beer bottles B 1, B 2,..., B 20 and 30 cider bottles C 1, C 2,..., C 30. Assume you arrange these 50 bottles on a horizontal line such that the leftmost 10 bottles are all beer bottles, and the rightmost 10 bottles are all cider bottles. How many such arrangements are there? (The order of the bottles matters.) (a) ( ) ( ) 30! (b) ( ) ( ! 30 10) 10! 30! (c) ( ) ( ! 30 10) 10! (d) 50! 2. Let n 2 be an even integer. A permutation a 1, a 2,..., a n of the set {1, 2,..., n} is called awesome if a 2 = 2 a 1. For example, if n = 6, then the permutation 3, 6, 4, 1, 5, 2 is awesome, whereas the permutation 3, 5, 4, 1, 6, 2 is not awesome. How many awesome permutations of the set {1, 2,..., n} are there? (a) n (n 1)! (b) n (n 2)! (c) n (n 1)! 2 (d) n (n 2)! 2 3. Consider strings consisting of characters, where each character is one of the letters a, b, and c. Such a string is called cool if or it contains exactly 8 many a s it contains exactly 7 many b s. How many cool strings are there? (a) ( ) ( ) (b) ( ) ( ) ( ( 15) 15 ) (c) ( ) ( ) ( ( 15) 15 ) 8 (d) None of the above.
4 COMP 2804A, FALL Consider strings consisting of characters, where each character is one of the letters a, b, and c. How many such strings contain at least three a s? (a) ( ) 3 (b) ( ) (c) ( ) (d) ( ) ( ) Let n 3 and m 3 be integers. What does ( ) ( ) n m + + n 3 3 count? ( ) m + m 2 ( ) n 2 (a) The number of subsets having size 3 of a set consisting of n positive numbers and m negative numbers. (b) The number of subsets having size at most 3 of a set consisting of n positive numbers and m negative numbers. (c) The number of subsets having size 2 or 3 of a set consisting of n positive numbers and m negative numbers. (d) The number of subsets having size 2 and 3 of a set consisting of n positive numbers and m negative numbers. 6. Consider a group of 100 students. In this group, 13 students like Donald Trump, 25 students like Justing Bieber, and 8 students like Donald Trump and like Justing Bieber. How many students do not like Donald Trump and do not like Justin Bieber? (a) 69 (b) 70 (c) 71 (d) 72
5 COMP 2804A, FALL How many strings can be obtained by rearranging the letters of the word (a) 2! 2! 3! (b) ( ) ( ( 2) 6 3) 3 2 (c) ( ) ( ( 2) 6 ( 3) 3 ) 2 (d) ( ) ( ( 2) 5 3) 3 2 BOOKKEEPER 8. Consider strings consisting of characters, where each character is one of the letters a, b, and c. For any integer n 1, let E n be the number of such strings of length n that contain an even number of c s, and let O n be the number of such strings of length n that contain an odd number of c s. (Remember that 0 is an even number.) Which of the following is true for any integer n 2? (a) E n = 2 E n 1 + O n 1 (b) E n = 2 E n 1 + E n 1 (c) E n = 2 O n 1 + O n 1 (d) E n = 2 O n 1 + E n 1 9. Consider bitstrings that do not contain 110. Let S n be the number of such strings having length n. Which of the following is true for any n 4? (a) S n = S n 1 + S n 2 + S n 3 (b) S n = S n 1 + S n n 2 (c) S n = S n 1 + S n n 3 (d) S n = S n 1 + S n 2 + 1
6 COMP 2804A, FALL Consider the recursive algorithm IFeelLikeSinging, which takes as input an integer n 0: Algorithm IFeelLikeSinging(n): if n = 0 or n = 1 then sing O Canada else if n is odd then IFeelLikeSinging(n + 1) else IFeelLikeSinging( n 2 ); IFeelLikeSinging( n 2 1) endif; endif If you run algorithm IFeelLikeSinging(9), how many times do you sing O Canada? (a) 6 (b) 7 (c) 8 (d) Assume you write a multiple-choice exam that has 25 questions. For each question, four options are given to you, and exactly one of these options is the correct answer. Assume that you answer each question uniformly at random, where the choices for different questions are independent of each other. What is the probability that you have exactly 17 correct answers? (a) ( ) (1/4) 17 (b) ( ) (3/4) 17 (c) ( ) 25 (1/4) 17 (3/4) 8 17 (d) ( ) (1/4)8 (3/4) 17
7 COMP 2804A, FALL A bitstring b 1 b 2... b n of length n is called a palindrome if b 1 b 2... b n 1 b n = b n b n 1... b 2 b 1, i.e., reading the string from left to right gives the same result as reading the string from right to left. Let n 2 be an even integer. You are given a uniformly random bitstring of length n. What is the probability that this bitstring is a palindrome? (a) (1/2) n (b) (1/2) n/2 (c) (1/2) 2n (d) 1/2 13. Let X = {1, 2, 3,..., 10}. Let Y be a uniformly random subset of X. Define the events What is Pr(A B)? (a) 3/16 (b) 4/16 (c) 5/16 (d) 6/16 A = Y contains at least 4 elements, B = all elements of Y are even. 14. Let n 1 be an integer. You are given two bitstrings a 1, a 2,..., a n and b 1, b 2,..., b n of length n. In both bitstrings, each bit is 0 with probability 1/2, and 1 with probability 1/2 (independent of all other bits). Consider the string a 1 + b 1, a 2 + b 2,..., a n + b n. What is the probability that each element in this string is non-zero? (a) 1 (1/4) n (b) 1 (3/4) n (c) (1/4) n (d) (3/4) n
8 COMP 2804A, FALL You flip a fair coin three times; these three flips are independent. Define the events A = the first two flips both result in heads, B = there are at least two heads in the sequence of three flips. Which of the following is true? (a) The events A and B are independent. (b) The events A and B are not independent. (c) None of the above. 16. You choose a uniformly random element, say x, from the set {1, 2, 3}, and you choose a uniformly random element, say y, from the same set {1, 2, 3}. (x and y are chosen independently of each other.) Define the events Which of the following is true? (a) The events A and B are independent. A = x is odd, B = x + y is odd. (b) The events A and B are not independent. (c) None of the above. 17. Let X = {1, 2,..., 100}. Let Y be a uniformly random 7-element subset of X. Define the event A = the set Y contains at least one even number. What is Pr(A)? (a) 1 (1/2) 7 (b) (1/2) 7 (c) 1 (50 7 ) ( ) (d) (50 7 ) ( )
9 COMP 2804A, FALL You flip a fair red coin once, and you flip a fair blue coin once, independently of each other. Define the random variables { 1 if the red coin flip resulted in heads, X = 0 if the red coin flip resulted in tails, and Y = { 1 if the blue coin flip resulted in heads, 0 if the blue coin flip resulted in tails, Z = max(x, Y ). What is the expected value E(Z) of the random variable Z? (a) 1/4 (b) 1/2 (c) 3/4 (d) Let n 2 be an integer. Consider a bitstring b 1, b 2,..., b n of length n, in which each bit b i is 0 with probability 1/2, and 1 with probability 1/2 (independent of all other bits). Define the random variable X to be the number of indices i with 1 i < n for which b i b i+1. What is the expected value E(X) of the random variable X? Hint: Use indicator random variables. (a) n 1 2 (b) n 2 (c) n+1 2 (d) None of the above
10 COMP 2804A, FALL You choose a uniformly random element, say a, from the set {1, 2,..., 100}, and you choose a uniformly random element, say b, from the same set {1, 2,..., 100}. (a and b are chosen independently of each other.) Define the random variable X to be X = max(a, b). What is the expected value E(X) of the random variable X? (a) 100 k=1 k k (b) 100 k=1 k k(k 1) (c) 100 k=1 k 2k (d) ( ) 100 k=1 k 1+2(k 1) You are given a fair red die and a fair blue die. You roll each die once, independently of each other. Let (i, j) be the outcome, where i is the result of the red die and j is the result of the blue die. Define the random variables X = i + j and Which of the following is true? Y = i j. (a) The random variables X and Y are independent. (b) The random variables X and Y are not independent. (c) None of the above.
11 COMP 2804A, FALL Alexa and May want to play the game of Monopoly. They use the following recursive algorithm to decide who goes first: Algorithm WhoGoesFirst(k): // k 1, the die is fair, and all rolls are independent Alexa rolls the die, let a be the result; May rolls the die, let m be the result; if a > m then print Alexa goes first; return k endif; if a < m then print May goes first; return k endif; if a = m then WhoGoesFirst(k + 1) endif The ladies run algorithm WhoGoesFirst(1), i.e., with k = 1. Define the random variable X to be the value of the output of this algorithm. What is the expected value E(X) of the random variable X? (a) 3/2 (b) 5/4 (c) 5/6 (d) 6/5 23. Is the following statement true or false? (a) The statement is true. (b) The statement is false. (c) None of the above. For any random variable X, E(1/X) = 1/E(X).
12 COMP 2804A, FALL Let n and k be integers such that n is even, n 2, and 1 k n. The Carleton Computer Science Society (CCSS) is having their annual Christmas Holiday Season Party, which is attended by n students. (a) k of these n students are politically correct and, thus, refuse to say Merry Christmas. Instead, they say Happy Holidays. (b) n k of these n students do not care about politicial correctness and, thus, they say Merry Christmas. Consider a uniformly random permutation of these n students. The positions in this permutation are numbered as 1, 2,..., n. Define the following random variable X: X = the number of positions i with 1 i n/2 such that both students at positions i and 2i are politically correct. What is the expected value E(X) of the random variable X? Hint: Use indicator random variables. (a) n k(k 1) n(n 1) (b) n (k 1)(k 2) n(n 1) (c) n 2 k(k 1) n(n 1) (d) n 2 (k 1)(k 2) n(n 1) 25. How do you feel about writing an exam on Friday evening? (a) I would rather sit in the pub and have a beer.
13 COMP 2804A, FALL
14 COMP 2804A, FALL
Carleton University. Final Examination Winter DURATION: 2 HOURS No. of students: 275
 Carleton University Final Examination Winter 2017 DURATION: 2 HOURS No. of students: 275 Department Name & Course Number: Computer Science COMP 2804B Course Instructor: Michiel Smid Authorized memoranda:
Carleton University Final Examination Winter 2017 DURATION: 2 HOURS No. of students: 275 Department Name & Course Number: Computer Science COMP 2804B Course Instructor: Michiel Smid Authorized memoranda:
Carleton University. Final Examination Fall DURATION: 2 HOURS No. of students: 223
 Carleton University Final Examination Fall 2016 DURATION: 2 HOURS No. of students: 223 Department Name & Course Number: Computer Science COMP 2804A Course Instructor: Michiel Smid Authorized memoranda:
Carleton University Final Examination Fall 2016 DURATION: 2 HOURS No. of students: 223 Department Name & Course Number: Computer Science COMP 2804A Course Instructor: Michiel Smid Authorized memoranda:
Carleton University. Final Examination Fall DURATION: 2 HOURS No. of students: 195
 Carleton University Final Examination Fall 15 DURATION: 2 HOURS No. of students: 195 Department Name & Course Number: Computer Science COMP 2804A Course Instructor: Michiel Smid Authorized memoranda: Calculator
Carleton University Final Examination Fall 15 DURATION: 2 HOURS No. of students: 195 Department Name & Course Number: Computer Science COMP 2804A Course Instructor: Michiel Smid Authorized memoranda: Calculator
Carleton University. Final Examination Winter DURATION: 2 HOURS No. of students: 152
 Carleton University Final Examination Winter 2014 DURATION: 2 HOURS No. of students: 152 Department Name & Course Number: Computer Science COMP 2804B Course Instructor: Michiel Smid Authorized memoranda:
Carleton University Final Examination Winter 2014 DURATION: 2 HOURS No. of students: 152 Department Name & Course Number: Computer Science COMP 2804B Course Instructor: Michiel Smid Authorized memoranda:
Midterm COMP October 19, All questions must be answered on the scantron sheet. Write your name and student number on the scantron sheet.
 Midterm COMP 80 October 19, 018 All questions must be answered on the scantron sheet. Write your name and student number on the scantron sheet. You do not have to hand in this examination paper. Calculators
Midterm COMP 80 October 19, 018 All questions must be answered on the scantron sheet. Write your name and student number on the scantron sheet. You do not have to hand in this examination paper. Calculators
COMP 2804 Assignment 4
 COMP 2804 Assignment 4 Due: Thursday April 5, before 11:55pm, through culearn. Assignment Policy: Your assignment must be submitted as one single PDF file through culearn. Late assignments will not be
COMP 2804 Assignment 4 Due: Thursday April 5, before 11:55pm, through culearn. Assignment Policy: Your assignment must be submitted as one single PDF file through culearn. Late assignments will not be
COMP 2804 Assignment 2
 COMP 804 Assignment Due: Thursday October 19, before 11:55pm (= 3:55), through culearn. Assignment Policy: Your assignment must be submitted as a PDF file through culearn. Late assignments will not be
COMP 804 Assignment Due: Thursday October 19, before 11:55pm (= 3:55), through culearn. Assignment Policy: Your assignment must be submitted as a PDF file through culearn. Late assignments will not be
EECS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2015 Walrand/Rao Final
 EECS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2015 Walrand/Rao Final PRINT Your Name:, (last) SIGN Your Name: (first) PRINT Your Student ID: CIRCLE your exam room: 220 Hearst 230 Hearst 237
EECS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2015 Walrand/Rao Final PRINT Your Name:, (last) SIGN Your Name: (first) PRINT Your Student ID: CIRCLE your exam room: 220 Hearst 230 Hearst 237
Midterm Exam 1 Solution
 EECS 126 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Fall 2015 Kannan Ramchandran September 22, 2015 Midterm Exam 1 Solution Last name First name SID Name of student on your left:
EECS 126 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Fall 2015 Kannan Ramchandran September 22, 2015 Midterm Exam 1 Solution Last name First name SID Name of student on your left:
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Summer 2014 James Cook Final Exam
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Summer 2014 James Cook Final Exam Friday August 15, 2014, 5:10pm-8:10pm. Instructions: Do not turn over this page until the proctor tells you to. Don t
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Summer 2014 James Cook Final Exam Friday August 15, 2014, 5:10pm-8:10pm. Instructions: Do not turn over this page until the proctor tells you to. Don t
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Summer 2015 Chung-Wei Lin Midterm 2
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Summer 201 Chung-Wei Lin Midterm 2 PRINT Your Name:, (last (first SIGN Your Name: PRINT Your Student ID: CIRCLE Your Exam Room: 200 VLSB 10 EVANS OTHER
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Summer 201 Chung-Wei Lin Midterm 2 PRINT Your Name:, (last (first SIGN Your Name: PRINT Your Student ID: CIRCLE Your Exam Room: 200 VLSB 10 EVANS OTHER
COMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty
 COMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty Nic Herndon and Andrew Lan University of Massachusetts at Amherst Spring 2019 Lecture 7: Counting (cont.) Summary of Counting Problems Structure Permutation k-permutation
COMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty Nic Herndon and Andrew Lan University of Massachusetts at Amherst Spring 2019 Lecture 7: Counting (cont.) Summary of Counting Problems Structure Permutation k-permutation
MA162 EXAM III SPRING 2017 APRIL 11, 2017 TEST NUMBER 01 INSTRUCTIONS:
 MA62 EXAM III SPRING 207 APRIL, 207 TEST NUMBER 0 INSTRUCTIONS:. Do not open the exam booklet until you are instructed to do so. 2. Before you open the booklet fill in the information below and use a #
MA62 EXAM III SPRING 207 APRIL, 207 TEST NUMBER 0 INSTRUCTIONS:. Do not open the exam booklet until you are instructed to do so. 2. Before you open the booklet fill in the information below and use a #
1 The Basic Counting Principles
 1 The Basic Counting Principles The Multiplication Rule If an operation consists of k steps and the first step can be performed in n 1 ways, the second step can be performed in n ways [regardless of how
1 The Basic Counting Principles The Multiplication Rule If an operation consists of k steps and the first step can be performed in n 1 ways, the second step can be performed in n ways [regardless of how
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2017 Ramchandran and Rao Midterm 2 Solutions
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2017 Ramchandran and Rao Midterm 2 Solutions PRINT Your Name: Oski Bear SIGN Your Name: OS K I PRINT Your Student ID: CIRCLE your exam room: Pimentel
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2017 Ramchandran and Rao Midterm 2 Solutions PRINT Your Name: Oski Bear SIGN Your Name: OS K I PRINT Your Student ID: CIRCLE your exam room: Pimentel
The probability of an event is viewed as a numerical measure of the chance that the event will occur.
 Chapter 5 This chapter introduces probability to quantify randomness. Section 5.1: How Can Probability Quantify Randomness? The probability of an event is viewed as a numerical measure of the chance that
Chapter 5 This chapter introduces probability to quantify randomness. Section 5.1: How Can Probability Quantify Randomness? The probability of an event is viewed as a numerical measure of the chance that
MA EXAM 3 Form A November 12, You must use a #2 pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet).
 MA 6200 EXAM 3 Form A November 2, 205 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME. You must use a #2 pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet). 2. If the cover of your question booklet is GREEN,
MA 6200 EXAM 3 Form A November 2, 205 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME. You must use a #2 pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet). 2. If the cover of your question booklet is GREEN,
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty
 CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 7: More Advanced Counting Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: February 21, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Partitions 3 More Examples 4 Clicker
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 7: More Advanced Counting Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: February 21, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Partitions 3 More Examples 4 Clicker
HW MATH425/525 Lecture Notes 1
 HW MATH425/525 Lecture Notes 1 Definition 4.1 If an experiment can be repeated under the same condition, its outcome cannot be predicted with certainty, and the collection of its every possible outcome
HW MATH425/525 Lecture Notes 1 Definition 4.1 If an experiment can be repeated under the same condition, its outcome cannot be predicted with certainty, and the collection of its every possible outcome
Introduction to Decision Sciences Lecture 11
 Introduction to Decision Sciences Lecture 11 Andrew Nobel October 24, 2017 Basics of Counting Product Rule Product Rule: Suppose that the elements of a collection S can be specified by a sequence of k
Introduction to Decision Sciences Lecture 11 Andrew Nobel October 24, 2017 Basics of Counting Product Rule Product Rule: Suppose that the elements of a collection S can be specified by a sequence of k
STA 247 Solutions to Assignment #1
 STA 247 Solutions to Assignment #1 Question 1: Suppose you throw three six-sided dice (coloured red, green, and blue) repeatedly, until the three dice all show different numbers. Assuming that these dice
STA 247 Solutions to Assignment #1 Question 1: Suppose you throw three six-sided dice (coloured red, green, and blue) repeatedly, until the three dice all show different numbers. Assuming that these dice
Senior Math Circles November 19, 2008 Probability II
 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Senior Math Circles November 9, 2008 Probability II Probability Counting There are many situations where
University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Senior Math Circles November 9, 2008 Probability II Probability Counting There are many situations where
Example 1. The sample space of an experiment where we flip a pair of coins is denoted by:
 Chapter 8 Probability 8. Preliminaries Definition (Sample Space). A Sample Space, Ω, is the set of all possible outcomes of an experiment. Such a sample space is considered discrete if Ω has finite cardinality.
Chapter 8 Probability 8. Preliminaries Definition (Sample Space). A Sample Space, Ω, is the set of all possible outcomes of an experiment. Such a sample space is considered discrete if Ω has finite cardinality.
Homework 4 Solution, due July 23
 Homework 4 Solution, due July 23 Random Variables Problem 1. Let X be the random number on a die: from 1 to. (i) What is the distribution of X? (ii) Calculate EX. (iii) Calculate EX 2. (iv) Calculate Var
Homework 4 Solution, due July 23 Random Variables Problem 1. Let X be the random number on a die: from 1 to. (i) What is the distribution of X? (ii) Calculate EX. (iii) Calculate EX 2. (iv) Calculate Var
Discrete Structures Prelim 1 Selected problems from past exams
 Discrete Structures Prelim 1 CS2800 Selected problems from past exams 1. True or false (a) { } = (b) Every set is a subset of its power set (c) A set of n events are mutually independent if all pairs of
Discrete Structures Prelim 1 CS2800 Selected problems from past exams 1. True or false (a) { } = (b) Every set is a subset of its power set (c) A set of n events are mutually independent if all pairs of
Midterm 2. Your Exam Room: Name of Person Sitting on Your Left: Name of Person Sitting on Your Right: Name of Person Sitting in Front of You:
 CS70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory, Fall 2018 Midterm 2 8:00-10:00pm, 31 October Your First Name: SIGN Your Name: Your Last Name: Your SID Number: Your Exam Room: Name of Person Sitting on
CS70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory, Fall 2018 Midterm 2 8:00-10:00pm, 31 October Your First Name: SIGN Your Name: Your Last Name: Your SID Number: Your Exam Room: Name of Person Sitting on
Math 493 Final Exam December 01
 Math 493 Final Exam December 01 NAME: ID NUMBER: Return your blue book to my office or the Math Department office by Noon on Tuesday 11 th. On all parts after the first show enough work in your exam booklet
Math 493 Final Exam December 01 NAME: ID NUMBER: Return your blue book to my office or the Math Department office by Noon on Tuesday 11 th. On all parts after the first show enough work in your exam booklet
MATH 3C: MIDTERM 1 REVIEW. 1. Counting
 MATH 3C: MIDTERM REVIEW JOE HUGHES. Counting. Imagine that a sports betting pool is run in the following way: there are 20 teams, 2 weeks, and each week you pick a team to win. However, you can t pick
MATH 3C: MIDTERM REVIEW JOE HUGHES. Counting. Imagine that a sports betting pool is run in the following way: there are 20 teams, 2 weeks, and each week you pick a team to win. However, you can t pick
ECE 302, Final 3:20-5:20pm Mon. May 1, WTHR 160 or WTHR 172.
 ECE 302, Final 3:20-5:20pm Mon. May 1, WTHR 160 or WTHR 172. 1. Enter your name, student ID number, e-mail address, and signature in the space provided on this page, NOW! 2. This is a closed book exam.
ECE 302, Final 3:20-5:20pm Mon. May 1, WTHR 160 or WTHR 172. 1. Enter your name, student ID number, e-mail address, and signature in the space provided on this page, NOW! 2. This is a closed book exam.
PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR EXAM 1
 PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR EXAM 1 Math 3160Q Spring 01 Professor Hohn Below is a list of practice questions for Exam 1. Any quiz, homework, or example problem has a chance of being on the exam. For more practice,
PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR EXAM 1 Math 3160Q Spring 01 Professor Hohn Below is a list of practice questions for Exam 1. Any quiz, homework, or example problem has a chance of being on the exam. For more practice,
UC Berkeley, CS 174: Combinatorics and Discrete Probability (Fall 2008) Midterm 1. October 7, 2008
 UC Berkeley, CS 74: Combinatorics and Discrete Probability (Fall 2008) Midterm Instructor: Prof. Yun S. Song October 7, 2008 Your Name : Student ID# : Read these instructions carefully:. This is a closed-book
UC Berkeley, CS 74: Combinatorics and Discrete Probability (Fall 2008) Midterm Instructor: Prof. Yun S. Song October 7, 2008 Your Name : Student ID# : Read these instructions carefully:. This is a closed-book
P (A) = P (B) = P (C) = P (D) =
 STAT 145 CHAPTER 12 - PROBABILITY - STUDENT VERSION The probability of a random event, is the proportion of times the event will occur in a large number of repititions. For example, when flipping a coin,
STAT 145 CHAPTER 12 - PROBABILITY - STUDENT VERSION The probability of a random event, is the proportion of times the event will occur in a large number of repititions. For example, when flipping a coin,
Math 1313 Experiments, Events and Sample Spaces
 Math 1313 Experiments, Events and Sample Spaces At the end of this recording, you should be able to define and use the basic terminology used in defining experiments. Terminology The next main topic in
Math 1313 Experiments, Events and Sample Spaces At the end of this recording, you should be able to define and use the basic terminology used in defining experiments. Terminology The next main topic in
Exam 1. Problem 1: True or false
 Exam 1 Problem 1: True or false We are told that events A and B are conditionally independent, given a third event C, and that P(B C) > 0. For each one of the following statements, decide whether the statement
Exam 1 Problem 1: True or false We are told that events A and B are conditionally independent, given a third event C, and that P(B C) > 0. For each one of the following statements, decide whether the statement
Midterm Exam 1 (Solutions)
 EECS 6 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Spring 07 Kannan Ramchandran February 3, 07 Midterm Exam (Solutions) Last name First name SID Name of student on your left: Name
EECS 6 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Spring 07 Kannan Ramchandran February 3, 07 Midterm Exam (Solutions) Last name First name SID Name of student on your left: Name
NAME (1 pt): TA (1 pt): Name of Neighbor to your left (1 pt): Name of Neighbor to your right (1 pt):
 Math 55 Final Exam May 2004 NAME ( pt): TA ( pt): Name of Neighbor to your left ( pt): Name of Neighbor to your right ( pt): Instructions: This is a closed book, closed notes, closed calculator, closed
Math 55 Final Exam May 2004 NAME ( pt): TA ( pt): Name of Neighbor to your left ( pt): Name of Neighbor to your right ( pt): Instructions: This is a closed book, closed notes, closed calculator, closed
Course: ESO-209 Home Work: 1 Instructor: Debasis Kundu
 Home Work: 1 1. Describe the sample space when a coin is tossed (a) once, (b) three times, (c) n times, (d) an infinite number of times. 2. A coin is tossed until for the first time the same result appear
Home Work: 1 1. Describe the sample space when a coin is tossed (a) once, (b) three times, (c) n times, (d) an infinite number of times. 2. A coin is tossed until for the first time the same result appear
EECS 126 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Fall 2014 Kannan Ramchandran September 23, 2014.
 EECS 126 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Fall 2014 Kannan Ramchandran September 23, 2014 Midterm Exam 1 Last name First name SID Rules. DO NOT open the exam until instructed
EECS 126 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Fall 2014 Kannan Ramchandran September 23, 2014 Midterm Exam 1 Last name First name SID Rules. DO NOT open the exam until instructed
Math 230 Final Exam, Spring 2009
 IIT Dept. Applied Mathematics, May 13, 2009 1 PRINT Last name: Signature: First name: Student ID: Math 230 Final Exam, Spring 2009 Conditions. 2 hours. No book, notes, calculator, cell phones, etc. Part
IIT Dept. Applied Mathematics, May 13, 2009 1 PRINT Last name: Signature: First name: Student ID: Math 230 Final Exam, Spring 2009 Conditions. 2 hours. No book, notes, calculator, cell phones, etc. Part
DO NOT WRITE BELOW THIS LINE Total page 1: / 20 points. Total page 2: / 20 points
 MATH M118: Finite Mathematics Sample Department Final Examination (The actual final examination will be identical to this sample in length, format, and difficulty.) Directions: Place your name and student
MATH M118: Finite Mathematics Sample Department Final Examination (The actual final examination will be identical to this sample in length, format, and difficulty.) Directions: Place your name and student
MA EXAM 3 INSTRUCTIONS VERSION 01 April 18, Section # and recitation time
 MA 16600 EXAM 3 INSTRUCTIONS VERSION 01 April 18, 2018 Your name Student ID # Your TA s name Section # and recitation time 1. You must use a #2 pencil on the scantron sheet (answer sheet). 2. Check that
MA 16600 EXAM 3 INSTRUCTIONS VERSION 01 April 18, 2018 Your name Student ID # Your TA s name Section # and recitation time 1. You must use a #2 pencil on the scantron sheet (answer sheet). 2. Check that
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty
 CMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty Lecture 5 Prof. Hanna Wallach wallach@cs.umass.edu February 7, 2012 Reminders Pick up a copy of B&T Check the course website: http://www.cs.umass.edu/ ~wallach/courses/s12/cmpsci240/
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty Lecture 5 Prof. Hanna Wallach wallach@cs.umass.edu February 7, 2012 Reminders Pick up a copy of B&T Check the course website: http://www.cs.umass.edu/ ~wallach/courses/s12/cmpsci240/
Probability: Terminology and Examples Class 2, Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom
 1 Learning Goals Probability: Terminology and Examples Class 2, 18.05 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom 1. Know the definitions of sample space, event and probability function. 2. Be able to organize a
1 Learning Goals Probability: Terminology and Examples Class 2, 18.05 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom 1. Know the definitions of sample space, event and probability function. 2. Be able to organize a
Sets. Review of basic probability. Tuples. E = {all even integers} S = {x E : x is a multiple of 3} CSE 101. I = [0, 1] = {x : 0 x 1}
![Sets. Review of basic probability. Tuples. E = {all even integers} S = {x E : x is a multiple of 3} CSE 101. I = [0, 1] = {x : 0 x 1} Sets. Review of basic probability. Tuples. E = {all even integers} S = {x E : x is a multiple of 3} CSE 101. I = [0, 1] = {x : 0 x 1}](/thumbs/85/92597043.jpg) Sets A = {a, b, c,..., z} A = 26 Review of basic probability = {0, 1} = 2 E = {all even integers} E = CSE 1 S = {x E : x is a multiple of 3} I = [0, 1] = {x : 0 x 1} In a set, the order of elements doesn
Sets A = {a, b, c,..., z} A = 26 Review of basic probability = {0, 1} = 2 E = {all even integers} E = CSE 1 S = {x E : x is a multiple of 3} I = [0, 1] = {x : 0 x 1} In a set, the order of elements doesn
Probability and random variables
 Probability and random variables Events A simple event is the outcome of an experiment. For example, the experiment of tossing a coin twice has four possible outcomes: HH, HT, TH, TT. A compound event
Probability and random variables Events A simple event is the outcome of an experiment. For example, the experiment of tossing a coin twice has four possible outcomes: HH, HT, TH, TT. A compound event
CMSC Discrete Mathematics SOLUTIONS TO FIRST MIDTERM EXAM October 18, 2005 posted Nov 2, 2005
 CMSC-37110 Discrete Mathematics SOLUTIONS TO FIRST MIDTERM EXAM October 18, 2005 posted Nov 2, 2005 Instructor: László Babai Ryerson 164 e-mail: laci@cs This exam contributes 20% to your course grade.
CMSC-37110 Discrete Mathematics SOLUTIONS TO FIRST MIDTERM EXAM October 18, 2005 posted Nov 2, 2005 Instructor: László Babai Ryerson 164 e-mail: laci@cs This exam contributes 20% to your course grade.
MAT 135B Midterm 1 Solutions
 MAT 35B Midterm Solutions Last Name (PRINT): First Name (PRINT): Student ID #: Section: Instructions:. Do not open your test until you are told to begin. 2. Use a pen to print your name in the spaces above.
MAT 35B Midterm Solutions Last Name (PRINT): First Name (PRINT): Student ID #: Section: Instructions:. Do not open your test until you are told to begin. 2. Use a pen to print your name in the spaces above.
Year 10 Mathematics Probability Practice Test 1
 Year 10 Mathematics Probability Practice Test 1 1 A letter is chosen randomly from the word TELEVISION. a How many letters are there in the word TELEVISION? b Find the probability that the letter is: i
Year 10 Mathematics Probability Practice Test 1 1 A letter is chosen randomly from the word TELEVISION. a How many letters are there in the word TELEVISION? b Find the probability that the letter is: i
MA : Introductory Probability
 MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
Math Fall Final Exam. Friday, 14 December Show all work for full credit. The problems are worth 6 points each.
 Name: Math 50 - Fall 2007 Final Exam Friday, 4 December 2007 Show all work for full credit. The problems are worth 6 points each.. Find the number of subsets of S = {, 2,... 0} that contain exactly 5 elements,
Name: Math 50 - Fall 2007 Final Exam Friday, 4 December 2007 Show all work for full credit. The problems are worth 6 points each.. Find the number of subsets of S = {, 2,... 0} that contain exactly 5 elements,
Random Variable. Pr(X = a) = Pr(s)
 Random Variable Definition A random variable X on a sample space Ω is a real-valued function on Ω; that is, X : Ω R. A discrete random variable is a random variable that takes on only a finite or countably
Random Variable Definition A random variable X on a sample space Ω is a real-valued function on Ω; that is, X : Ω R. A discrete random variable is a random variable that takes on only a finite or countably
Business Statistics PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 Business Statistics PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS CONTENTS Probability distribution functions (discrete) Characteristics of a discrete distribution Example: uniform (discrete) distribution Example: Bernoulli
Business Statistics PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS CONTENTS Probability distribution functions (discrete) Characteristics of a discrete distribution Example: uniform (discrete) distribution Example: Bernoulli
CSC 125 :: Final Exam December 15, 2010
 1-5. Complete the truth tables below: CSC 125 :: Final Exam December 15, 2010 p q p q p q p q p q p q T T F F T F T F 6-13. Fill in the missing portion of each of the rules of inference named below: 6.
1-5. Complete the truth tables below: CSC 125 :: Final Exam December 15, 2010 p q p q p q p q p q p q T T F F T F T F 6-13. Fill in the missing portion of each of the rules of inference named below: 6.
MA EXAM 3 INSTRUCTIONS VERSION 01 April 14, Section # and recitation time
 MA 16600 EXAM 3 INSTRUCTIONS VERSION 01 April 14, 2015 Your name Student ID # Your TA s name Section # and recitation time 1. You must use a #2 pencil on the scantron sheet (answer sheet). 2. Check that
MA 16600 EXAM 3 INSTRUCTIONS VERSION 01 April 14, 2015 Your name Student ID # Your TA s name Section # and recitation time 1. You must use a #2 pencil on the scantron sheet (answer sheet). 2. Check that
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis
![UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis](/thumbs/77/75937586.jpg) UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Final Exam Review Session Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Notes 140608 Review Things to Know has
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Final Exam Review Session Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Notes 140608 Review Things to Know has
Some Basic Concepts of Probability and Information Theory: Pt. 1
 Some Basic Concepts of Probability and Information Theory: Pt. 1 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University January 18, 2018 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University Some Basic Concepts of Probability and
Some Basic Concepts of Probability and Information Theory: Pt. 1 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University January 18, 2018 PHYS 476Q - Southern Illinois University Some Basic Concepts of Probability and
Theoretical Cryptography, Lecture 10
 Theoretical Cryptography, Lecture 0 Instructor: Manuel Blum Scribe: Ryan Williams Feb 20, 2006 Introduction Today we will look at: The String Equality problem, revisited What does a random permutation
Theoretical Cryptography, Lecture 0 Instructor: Manuel Blum Scribe: Ryan Williams Feb 20, 2006 Introduction Today we will look at: The String Equality problem, revisited What does a random permutation
Some Review Problems for Exam 3: Solutions
 Math 3355 Fall 018 Some Review Problems for Exam 3: Solutions I thought I d start by reviewing some counting formulas. Counting the Complement: Given a set U (the universe for the problem), if you want
Math 3355 Fall 018 Some Review Problems for Exam 3: Solutions I thought I d start by reviewing some counting formulas. Counting the Complement: Given a set U (the universe for the problem), if you want
A brief review of basics of probabilities
 brief review of basics of probabilities Milos Hauskrecht milos@pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square robability theory Studies and describes random processes and their outcomes Random processes may result in multiple
brief review of basics of probabilities Milos Hauskrecht milos@pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square robability theory Studies and describes random processes and their outcomes Random processes may result in multiple
MA EXAM 3 Form A April 16, You must use a #2 pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet).
 MA 16200 EXAM Form A April 16, 2015 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME 1. You must use a #2 pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet). 2. If the cover of your question booklet is GREEN,
MA 16200 EXAM Form A April 16, 2015 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME 1. You must use a #2 pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet). 2. If the cover of your question booklet is GREEN,
This exam contains 13 pages (including this cover page) and 10 questions. A Formulae sheet is provided with the exam.
 Probability and Statistics FS 2017 Session Exam 22.08.2017 Time Limit: 180 Minutes Name: Student ID: This exam contains 13 pages (including this cover page) and 10 questions. A Formulae sheet is provided
Probability and Statistics FS 2017 Session Exam 22.08.2017 Time Limit: 180 Minutes Name: Student ID: This exam contains 13 pages (including this cover page) and 10 questions. A Formulae sheet is provided
18440: Probability and Random variables Quiz 1 Friday, October 17th, 2014
 18440: Probability and Random variables Quiz 1 Friday, October 17th, 014 You will have 55 minutes to complete this test. Each of the problems is worth 5 % of your exam grade. No calculators, notes, or
18440: Probability and Random variables Quiz 1 Friday, October 17th, 014 You will have 55 minutes to complete this test. Each of the problems is worth 5 % of your exam grade. No calculators, notes, or
X = X X n, + X 2
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Fall 2003 Wagner Lecture 22 Variance Question: At each time step, I flip a fair coin. If it comes up Heads, I walk one step to the right; if it comes up Tails, I walk
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Fall 2003 Wagner Lecture 22 Variance Question: At each time step, I flip a fair coin. If it comes up Heads, I walk one step to the right; if it comes up Tails, I walk
3. A square has 4 sides, so S = 4. A pentagon has 5 vertices, so P = 5. Hence, S + P = 9. = = 5 3.
 JHMMC 01 Grade Solutions October 1, 01 1. By counting, there are 7 words in this question.. (, 1, ) = 1 + 1 + = 9 + 1 + =.. A square has sides, so S =. A pentagon has vertices, so P =. Hence, S + P = 9..
JHMMC 01 Grade Solutions October 1, 01 1. By counting, there are 7 words in this question.. (, 1, ) = 1 + 1 + = 9 + 1 + =.. A square has sides, so S =. A pentagon has vertices, so P =. Hence, S + P = 9..
Problem # Number of points 1 /20 2 /20 3 /20 4 /20 5 /20 6 /20 7 /20 8 /20 Total /150
 Name Student ID # Instructor: SOLUTION Sergey Kirshner STAT 516 Fall 09 Practice Midterm #1 January 31, 2010 You are not allowed to use books or notes. Non-programmable non-graphic calculators are permitted.
Name Student ID # Instructor: SOLUTION Sergey Kirshner STAT 516 Fall 09 Practice Midterm #1 January 31, 2010 You are not allowed to use books or notes. Non-programmable non-graphic calculators are permitted.
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2018 Ayazifar and Rao Final
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2018 Ayazifar and Rao Final PRINT Your Name:, (Last) (First) READ AND SIGN The Honor Code: As a member of the UC Berkeley community, I act with
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2018 Ayazifar and Rao Final PRINT Your Name:, (Last) (First) READ AND SIGN The Honor Code: As a member of the UC Berkeley community, I act with
CSC 125 :: Final Exam May 3 & 5, 2010
 CSC 125 :: Final Exam May 3 & 5, 2010 Name KEY (1 5) Complete the truth tables below: p Q p q p q p q p q p q T T T T F T T T F F T T F F F T F T T T F F F F F F T T 6-15. Match the following logical equivalences
CSC 125 :: Final Exam May 3 & 5, 2010 Name KEY (1 5) Complete the truth tables below: p Q p q p q p q p q p q T T T T F T T T F F T T F F F T F T T T F F F F F F T T 6-15. Match the following logical equivalences
k P (X = k)
 Math 224 Spring 208 Homework Drew Armstrong. Suppose that a fair coin is flipped 6 times in sequence and let X be the number of heads that show up. Draw Pascal s triangle down to the sixth row (recall
Math 224 Spring 208 Homework Drew Armstrong. Suppose that a fair coin is flipped 6 times in sequence and let X be the number of heads that show up. Draw Pascal s triangle down to the sixth row (recall
3/15/2010 ENGR 200. Counting
 ENGR 200 Counting 1 Are these events conditionally independent? Blue coin: P(H = 0.99 Red coin: P(H = 0.01 Pick a random coin, toss it twice. H1 = { 1 st toss is heads } H2 = { 2 nd toss is heads } given
ENGR 200 Counting 1 Are these events conditionally independent? Blue coin: P(H = 0.99 Red coin: P(H = 0.01 Pick a random coin, toss it twice. H1 = { 1 st toss is heads } H2 = { 2 nd toss is heads } given
Permutations and Combinations
 Permutations and Combinations Permutations Definition: Let S be a set with n elements A permutation of S is an ordered list (arrangement) of its elements For r = 1,..., n an r-permutation of S is an ordered
Permutations and Combinations Permutations Definition: Let S be a set with n elements A permutation of S is an ordered list (arrangement) of its elements For r = 1,..., n an r-permutation of S is an ordered
MA FINAL EXAM Form 01 MAY 3, 2018
 MA 16 FINAL EXAM Form 1 MAY, 18 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME 1. You must use a # pencil on the scantron. a. Write 1 in the TEST/QUIZ NUMBER boxes and darken the appropriate bubbles
MA 16 FINAL EXAM Form 1 MAY, 18 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME 1. You must use a # pencil on the scantron. a. Write 1 in the TEST/QUIZ NUMBER boxes and darken the appropriate bubbles
D I S C R E T E M AT H E M AT I C S H O M E W O R K
 D E PA R T M E N T O F C O M P U T E R S C I E N C E S C O L L E G E O F E N G I N E E R I N G F L O R I D A T E C H D I S C R E T E M AT H E M AT I C S H O M E W O R K W I L L I A M S H O A F F S P R
D E PA R T M E N T O F C O M P U T E R S C I E N C E S C O L L E G E O F E N G I N E E R I N G F L O R I D A T E C H D I S C R E T E M AT H E M AT I C S H O M E W O R K W I L L I A M S H O A F F S P R
Math 151. Rumbos Fall Solutions to Review Problems for Exam 2. Pr(X = 1) = ) = Pr(X = 2) = Pr(X = 3) = p X. (k) =
 Math 5. Rumbos Fall 07 Solutions to Review Problems for Exam. A bowl contains 5 chips of the same size and shape. Two chips are red and the other three are blue. Draw three chips from the bowl at random,
Math 5. Rumbos Fall 07 Solutions to Review Problems for Exam. A bowl contains 5 chips of the same size and shape. Two chips are red and the other three are blue. Draw three chips from the bowl at random,
MA EXAM 2 INSTRUCTIONS VERSION 01 March 9, Section # and recitation time
 MA 16600 EXAM INSTRUCTIONS VERSION 01 March 9, 016 Your name Student ID # Your TA s name Section # and recitation time 1. You must use a # pencil on the scantron sheet (answer sheet).. Check that the cover
MA 16600 EXAM INSTRUCTIONS VERSION 01 March 9, 016 Your name Student ID # Your TA s name Section # and recitation time 1. You must use a # pencil on the scantron sheet (answer sheet).. Check that the cover
Machine Learning: Homework Assignment 2 Solutions
 10-601 Machine Learning: Homework Assignment 2 Solutions Professor Tom Mitchell Carnegie Mellon University January 21, 2009 The assignment is due at 1:30pm (beginning of class) on Monday, February 2, 2009.
10-601 Machine Learning: Homework Assignment 2 Solutions Professor Tom Mitchell Carnegie Mellon University January 21, 2009 The assignment is due at 1:30pm (beginning of class) on Monday, February 2, 2009.
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Summer 2016 Dinh, Psomas, and Ye Final Exam
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Summer 2016 Dinh, Psomas, and Ye Final Exam PRINT Your Name:, (last) By signing below, I agree that (a) I will not give or receive help from others during
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Summer 2016 Dinh, Psomas, and Ye Final Exam PRINT Your Name:, (last) By signing below, I agree that (a) I will not give or receive help from others during
Great Theoretical Ideas in Computer Science
 15-251 Great Theoretical Ideas in Computer Science Probability Theory: Counting in Terms of Proportions Lecture 10 (September 27, 2007) Some Puzzles Teams A and B are equally good In any one game, each
15-251 Great Theoretical Ideas in Computer Science Probability Theory: Counting in Terms of Proportions Lecture 10 (September 27, 2007) Some Puzzles Teams A and B are equally good In any one game, each
Example. What is the sample space for flipping a fair coin? Rolling a 6-sided die? Find the event E where E = {x x has exactly one head}
 Chapter 7 Notes 1 (c) Epstein, 2013 CHAPTER 7: PROBABILITY 7.1: Experiments, Sample Spaces and Events Chapter 7 Notes 2 (c) Epstein, 2013 What is the sample space for flipping a fair coin three times?
Chapter 7 Notes 1 (c) Epstein, 2013 CHAPTER 7: PROBABILITY 7.1: Experiments, Sample Spaces and Events Chapter 7 Notes 2 (c) Epstein, 2013 What is the sample space for flipping a fair coin three times?
Combinations and Probabilities
 Combinations and Probabilities Tutor: Zhang Qi Systems Engineering and Engineering Management qzhang@se.cuhk.edu.hk November 2014 Tutor: Zhang Qi (SEEM) Tutorial 7 November 2014 1 / 16 Combination Review
Combinations and Probabilities Tutor: Zhang Qi Systems Engineering and Engineering Management qzhang@se.cuhk.edu.hk November 2014 Tutor: Zhang Qi (SEEM) Tutorial 7 November 2014 1 / 16 Combination Review
the time it takes until a radioactive substance undergoes a decay
 1 Probabilities 1.1 Experiments with randomness Wewillusethetermexperimentinaverygeneralwaytorefertosomeprocess that produces a random outcome. Examples: (Ask class for some first) Here are some discrete
1 Probabilities 1.1 Experiments with randomness Wewillusethetermexperimentinaverygeneralwaytorefertosomeprocess that produces a random outcome. Examples: (Ask class for some first) Here are some discrete
(Practice Version) Midterm Exam 2
 EECS 126 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Fall 2014 Kannan Ramchandran November 7, 2014 (Practice Version) Midterm Exam 2 Last name First name SID Rules. DO NOT open
EECS 126 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Fall 2014 Kannan Ramchandran November 7, 2014 (Practice Version) Midterm Exam 2 Last name First name SID Rules. DO NOT open
Exam 1 Solutions. Problem Points Score Total 145
 Exam Solutions Read each question carefully and answer all to the best of your ability. Show work to receive as much credit as possible. At the end of the exam, please sign the box below. Problem Points
Exam Solutions Read each question carefully and answer all to the best of your ability. Show work to receive as much credit as possible. At the end of the exam, please sign the box below. Problem Points
MA FINAL EXAM Green May 5, You must use a #2 pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet).
 MA 600 FINAL EXAM Green May 5, 06 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME. You must use a # pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet).. Be sure the paper you are looking at right now is GREEN!
MA 600 FINAL EXAM Green May 5, 06 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME. You must use a # pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet).. Be sure the paper you are looking at right now is GREEN!
Recitation 6. Randomization. 6.1 Announcements. RandomLab has been released, and is due Monday, October 2. It s worth 100 points.
 Recitation 6 Randomization 6.1 Announcements RandomLab has been released, and is due Monday, October 2. It s worth 100 points. FingerLab will be released after Exam I, which is going to be on Wednesday,
Recitation 6 Randomization 6.1 Announcements RandomLab has been released, and is due Monday, October 2. It s worth 100 points. FingerLab will be released after Exam I, which is going to be on Wednesday,
Discrete Random Variables
 Chapter 5 Discrete Random Variables Suppose that an experiment and a sample space are given. A random variable is a real-valued function of the outcome of the experiment. In other words, the random variable
Chapter 5 Discrete Random Variables Suppose that an experiment and a sample space are given. A random variable is a real-valued function of the outcome of the experiment. In other words, the random variable
Discrete Structures for Computer Science: Counting, Recursion, and Probability
 Discrete Structures for Computer Science: Counting, Recursion, and Probability Michiel Smid School of Computer Science Carleton University Ottawa, Ontario Canada michiel@scs.carleton.ca December 18, 2017
Discrete Structures for Computer Science: Counting, Recursion, and Probability Michiel Smid School of Computer Science Carleton University Ottawa, Ontario Canada michiel@scs.carleton.ca December 18, 2017
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 12th Grade Unit 9
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 9 Unit 9 COUNTING PRINCIPLES MATH 1209 COUNTING PRINCIPLES INTRODUCTION 1. PROBABILITY DEFINITIONS, SAMPLE SPACES, AND PROBABILITY ADDITION OF PROBABILITIES 11 MULTIPLICATION
MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 9 Unit 9 COUNTING PRINCIPLES MATH 1209 COUNTING PRINCIPLES INTRODUCTION 1. PROBABILITY DEFINITIONS, SAMPLE SPACES, AND PROBABILITY ADDITION OF PROBABILITIES 11 MULTIPLICATION
Probability (Devore Chapter Two)
 Probability (Devore Chapter Two) 1016-345-01: Probability and Statistics for Engineers Fall 2012 Contents 0 Administrata 2 0.1 Outline....................................... 3 1 Axiomatic Probability 3
Probability (Devore Chapter Two) 1016-345-01: Probability and Statistics for Engineers Fall 2012 Contents 0 Administrata 2 0.1 Outline....................................... 3 1 Axiomatic Probability 3
1 Basic continuous random variable problems
 Name M362K Final Here are problems concerning material from Chapters 5 and 6. To review the other chapters, look over previous practice sheets for the two exams, previous quizzes, previous homeworks and
Name M362K Final Here are problems concerning material from Chapters 5 and 6. To review the other chapters, look over previous practice sheets for the two exams, previous quizzes, previous homeworks and
CS684 Graph Algorithms
 CS684 Graph Algorithms Administration and Mathematical Background Instructor: Fei Li lifei@cs.gmu.edu with subject: CS684 Office hours: Engineering Building, Room 5326, Monday 5:00pm - 7:00pm or by appointments
CS684 Graph Algorithms Administration and Mathematical Background Instructor: Fei Li lifei@cs.gmu.edu with subject: CS684 Office hours: Engineering Building, Room 5326, Monday 5:00pm - 7:00pm or by appointments
MA Exam 1 Fall 2015 VERSION 01
 VERSION 01 Your name Student ID # Section # and recitation time 1. You must use a # pencil on the scantron sheet (answer sheet).. Check that the cover of your Question Booklet is GREEN and that it has
VERSION 01 Your name Student ID # Section # and recitation time 1. You must use a # pencil on the scantron sheet (answer sheet).. Check that the cover of your Question Booklet is GREEN and that it has
Semester 2 Final Exam Review Guide for AMS I
 Name: Semester 2 Final Exam Review Guide for AMS I Unit 4: Exponential Properties & Functions Lesson 1 Exponent Properties & Simplifying Radicals Products of Powers: when two powers with the same base
Name: Semester 2 Final Exam Review Guide for AMS I Unit 4: Exponential Properties & Functions Lesson 1 Exponent Properties & Simplifying Radicals Products of Powers: when two powers with the same base
MA FINAL EXAM Green December 16, You must use a #2 pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet).
 MA 600 FINAL EXAM Green December 6, 205 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME. You must use a #2 pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet). 2. Be sure the paper you are looking at right
MA 600 FINAL EXAM Green December 6, 205 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME. You must use a #2 pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet). 2. Be sure the paper you are looking at right
Probability Experiments, Trials, Outcomes, Sample Spaces Example 1 Example 2
 Probability Probability is the study of uncertain events or outcomes. Games of chance that involve rolling dice or dealing cards are one obvious area of application. However, probability models underlie
Probability Probability is the study of uncertain events or outcomes. Games of chance that involve rolling dice or dealing cards are one obvious area of application. However, probability models underlie
STAT Summer Exam 1
 Name: STAT 225 - Summer 2011 - Exam 1 Instructor: Class Time (Circle One): 8:40-9:40am 9:50-10:50am 11:00am-12:00pm 1:00-2:00pm Show work for full credit. Unsupported work will NOT receive full credit.
Name: STAT 225 - Summer 2011 - Exam 1 Instructor: Class Time (Circle One): 8:40-9:40am 9:50-10:50am 11:00am-12:00pm 1:00-2:00pm Show work for full credit. Unsupported work will NOT receive full credit.
MA FINAL EXAM Form A December 16, You must use a #2 pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet).
 MA 600 FINAL EXAM Form A December 6, 05 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME. You must use a # pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet).. If the cover of your question booklet is GREEN,
MA 600 FINAL EXAM Form A December 6, 05 NAME STUDENT ID # YOUR TA S NAME RECITATION TIME. You must use a # pencil on the mark sense sheet (answer sheet).. If the cover of your question booklet is GREEN,
n(1 p i ) n 1 p i = 1 3 i=1 E(X i p = p i )P(p = p i ) = 1 3 p i = n 3 (p 1 + p 2 + p 3 ). p i i=1 P(X i = 1 p = p i )P(p = p i ) = p1+p2+p3
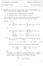 Introduction to Probability Due:August 8th, 211 Solutions of Final Exam Solve all the problems 1. (15 points) You have three coins, showing Head with probabilities p 1, p 2 and p 3. You perform two different
Introduction to Probability Due:August 8th, 211 Solutions of Final Exam Solve all the problems 1. (15 points) You have three coins, showing Head with probabilities p 1, p 2 and p 3. You perform two different
CSE 321 Solutions to Practice Problems
 CSE 321 Solutions to Practice Problems Instructions: Feel free NOT to multiply out binomial coefficients, factorials, etc, and feel free to leave answers in the form of a sum. No calculators, books or
CSE 321 Solutions to Practice Problems Instructions: Feel free NOT to multiply out binomial coefficients, factorials, etc, and feel free to leave answers in the form of a sum. No calculators, books or
Assignment 4: Solutions
 Math 340: Discrete Structures II Assignment 4: Solutions. Random Walks. Consider a random walk on an connected, non-bipartite, undirected graph G. Show that, in the long run, the walk will traverse each
Math 340: Discrete Structures II Assignment 4: Solutions. Random Walks. Consider a random walk on an connected, non-bipartite, undirected graph G. Show that, in the long run, the walk will traverse each
Entropy. Probability and Computing. Presentation 22. Probability and Computing Presentation 22 Entropy 1/39
 Entropy Probability and Computing Presentation 22 Probability and Computing Presentation 22 Entropy 1/39 Introduction Why randomness and information are related? An event that is almost certain to occur
Entropy Probability and Computing Presentation 22 Probability and Computing Presentation 22 Entropy 1/39 Introduction Why randomness and information are related? An event that is almost certain to occur
